Dasatinib and chemotherapy in a patient with early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and NUP214 ABL1 fusion: A case report
|
|
|
- Chrystal Green
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: , 2017 Dasatinib and chemotherapy in a patient with early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia and NUP214 ABL1 fusion: A case report YAN CHEN 1*, LI ZHANG 2*, JIANKUN HUANG 3, XIULI HONG 1, JIANGNING ZHAO 1, ZHAO WANG 1 and KEJIE ZHANG 1 1 Department of Hematology, Zhongshan Hospital, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian ; 2 Department of Hematology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, Sichuan ; 3 Central Laboratory, Zhongshan Hospital, Xiamen University, Xiamen, Fujian , P.R. China Received February 26, 2016; Accepted March 23, 2017 DOI: /etm Abstract. The present study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of dasatinib in a patient with nucleoporin 214 tyrosine protein kinase ABL1 proto oncogene 1 (NUP214 ABL1) positive early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ETP ALL), as well as that of selinexor and dasatinib for NUP214 ABL1 positive ETP ALL in vitro. ETP leukemia is a form of T cell ALL (T ALL) with poor prognosis. The NUP214 ABL1 gene is present in ~6% of T ALL cases, however the prevalence of NUP214 ABL1 gene expression in ETP ALL in particular has not yet been verified. The current study reports the rare case of a 29 year old man with ETP ALL harboring the NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene, presenting with low grade fever, stomachache and splenomegaly. The patient was successfully treated with dasatinib and vincristine, idarubicin, cyclophosphamide and prednisone (VICP) chemotherapy. The therapeutic efficacy of selinexor and dasatinib was also evaluated in vitro. Apoptosis was analyzed using Annexin V/propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry, and poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) cleavage was detected using western blot analysis. The results demonstrated that the apoptotic cell population significantly increased following selinexor or dasatinib treatment compared with the control (P<0.05). Furthermore, combined selinexor and dasatinib treatment led to a significant increase in cell apoptosis compared with either treatment alone (P<0.05). The apoptosis results Correspondence to: Dr Kejie Zhang, Department of Hematology, Zhongshan Hospital, Xiamen University, Hubinnan Road, Xiamen, Fujian , P.R. China E mail: zhangkejie0378@sina.com * Contributed equally Key words: early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia, NUP214 ABL1, dasatinib, selinexor, T cell were confirmed by PARP cleavage. Thus, NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene expression should be tested in T ALL, including ETP ALL. Dasatinib used in combination with traditional induction chemotherapy may reverse the high induction failure of ETP ALL with NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene; however, further prospective studies are required to confirm this. Therefore, selinexor with or without dasatinib may serve as a potential salvage therapy in the case of relapse and may be developed as a novel treatment for ETP ALL with the NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene. Introduction Early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ETP ALL) has been identified as a distinct biological subtype of T cell lineage ALL (T ALL), which accounts for 15% of T ALL cases (and ~2% of ALL cases). It is associated with poor clinical outcomes even following the use of current treatment regimens. Recently, the complete remission rate/complete remission with incomplete platelet recovery rate in patients with ETP ALL was indicated to be significantly lower than that of non ETP ALL patients (73 vs. 91%; P=0.03) in 2016 (1). Up to the last follow up, the median overall survival for patients with ETP ALL was 20 months vs. not yet reached for the non ETP ALL/LBL patients (P=0.008) (1). This subtype is characterized by a lack of expression of the T cell surface markers cluster of differentiation (CD) 1a and CD8, weak or absent expression of CD5, and aberrant expression of at least one of the following myeloid or hematopoietic stem cell markers: CD13, CD33, CD34, CD117, human leukocyte antigen (HLA) DR, CD11b and CD65 (2). T ALL is a genetically heterogeneous disease caused by the accumulation of multiple genetic defects in developing T cells that affect critical cellular processes, including cell differentiation, proliferation, survival and self renewal capacity (3). The presence of the nucleoporin 214 ABL proto oncogene 1 (NUP214 ABL1) fusion gene has been identified in 6% of all T ALL cases (4). NUP214, also known as CAN, is a 214 kda FG repeat containing nucleoporin located at band 9q34.1 and includes 36 exons. The
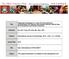
2 3980 CHEN et al: ETP ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA WITH NUP214-ABL1 FUSION encoded protein is located at the cytoplasmic side of the nuclear pore complex (NPC) (5). The NUP214 ABL1 fusion protein is a constitutively active protein tyrosine kinase. De Keersmaecker et al (6) recently identified that the sparse representation based classifier (SRC) family kinase lymphocyte specific protein tyrosine kinase (LCK) is a protein essential for the proliferation and survival of T ALL cells dependent on NUP214 ABL1 activity. These findings underscore the potential of the dual ABL1/SRC kinase inhibitor dasatinib in the treatment of NUP214 ABL1 positive T ALL. Furthermore, NUP214 serves a role in mrna export and chromosome region maintenance 1 (CRM1) mediated export of the 60S pre ribosomal subunit, and may serve a role in the transport of other proteins (7). Given that CRM1 inhibitors, such as selinexor, suppress the export of proteins associated with NUP214 (7), there is potential for their use to treat patients with T ALL that also harbor NUP214 ABL1. The NUP214 ABL1 gene is highly specific for T ALL (8), however the prevalence of NUP214 ABL1 gene expression in ETP ALL has not been verified. Zhang et al (9) reported that NUP214 ABL1 was not detected in all the 64 ETP ALL cases studied. The present case report describes a rare case of a patient with ETP ALL harboring the NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene. The present study also evaluated the therapeutic efficiency of selinexor and dasatinib to treat NUP214 ABL1 positive ETP ALL cells in vitro. ETP ALL has higher rates of relapse and remission failure following conventional chemotherapy and shorter patient survival times (1), meaning that novel therapeutic agents to treat ETP ALL are urgently required. Case report A 29 year old Han Chinese man was admitted to the Zhongshan Hospital, Xiamen University (Xiamen, China) in September 2015 with a low grade fever and stomachache, which he had experienced for 5 days. The patient had no family history of genetic or hematological disease. Ethical approval for the current case report was granted by the Medical Ethics Committee of Zhongshan Hospital, Xianmen University (Xiamen, China) and informed written consent was obtained from the patient. The patient presented with splenomegaly (spleen size, 13.2x4.3 cm) determined via abdominal ultrasonography. The patient's peripheral blood was analyzed with a hematology analyzer (Beckman Coulter, Inc., Brea, CA, USA): White blood cell count was 5.86x10 9 /l (neutrophils, 10%; lymphocytes, 66%; monocytes, 20%; reference range, white blood cell count 3.5x10 9 /l 9.5x10 9 /l; neutrophils, 50 70%; lymphocytes, 20 50%; monocytes, 3 10%), hemoglobin level (Hb) was 118 g/l (reference range, g/l) and blood platelet count (Plat) was 45x10 9 /l (reference range, 125 x10 9 /l 350 x10 9 /l). The proportion of immature cells detected in the peripheral blood was low (4%). The following blood coagulation characteristics were measured: Prothrombin time, 15.6 sec (reference range, sec); activated partial thromboplastin time, 15.2 sec (reference range, sec); fibrinogen level, 2.82 g/l (reference range, g/l) and D dimer quantification, 3,150 ng/ml (reference range, ng/ml. Lactate dehydrogenase levels were elevated (605.1 U/l; reference range, U/l), however liver and renal functions were Figure 1. Histomorphological features of leukemic blasts from bone marrow aspirates and flow cytometry analysis. (A) Blasts were large and had high nuclear/cytoplasm ratios, irregular nuclei, dispersed chromatin pattern, indistinct nucleoli and basophilic cytoplasm with pseudopods (Wright Giemsa stain, the white blood cell nucleus and cytoplasm are indicated by the characteristic blue or pink coloration; magnification, x1,000). (B) Flow cytometric immunophenotyping. normal. The patient underwent bone marrow (BM) harvesting under general anesthesia. BM was aspirated from the posterior iliac crest in a sterile operating room, and BM smears stained with Wright Giemsa stains (Electron Microscopy Sciences, Hatfield, PA, USA) were obtained and tested under an optical microscope. The white blood cell nucleus and cytoplasm were indicated by the characteristic blue or pink coloration. The 500 cell differential count from the BM aspirate on the first day of hospital admission revealed that 80% of all nucleated cells were blasts. The majority of blasts exhibited large sizes, high nuclear/cytoplasm ratios, irregularly shaped nuclei, dispersed chromatin, indistinct nucleoli and basophilic cytoplasm that occasionally formed pseudopods, but few exhibited moderate amounts of granular cytoplasm, fine nuclear chromatin and 2 3 prominent nucleoli (Fig. 1A). Cytochemical staining (10) was negative for myeloperoxidase (MPO) and ~3% positive for periodic acid Schiff staining.
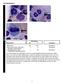
3 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: , Table I. Genetic analysis of the early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia patient. Type of analysis Gene Method Result Gene mutation FLT3 ITD RT PCR Fusion gene MLL/AF4 Multiplex nested RT PCR MLL/AF6 - MLL/AF9 - MLL/AF10 - MLL/AF17 - MLL/AF1P - MLL/AF1Q - MLL/AFX - MLL/ELL - MLL/ENL - dupmll - CBFβ/MYH11 - AML1/ETO - AML1/MDS1 - SET/CAN - DEK/CAN - PML/RARα - PLZF/RARα - NPM/RARα - NPM/ALK - TEL/AML1 - E2A/PBX1 - BCR/ABL1 - NPM/MLF1 - TEL/ABL1 - E2A/HLF - TLS/ERG SIL/TAL1 - TEL/PDGFR EVI1 HOX11 - Ph like fusion RCSD1/ABL1 Multiplex genes RT PCR ZMIZ1/ABL1 - NUP214/ABL1 + PAG/ABL2 - TNIP1/PDGFRβ - RANBP2/ABL1 - SNX2/ABL1 - RCSD1/ABL2 - SSBP2/PDGFRβ - ETV6/ABL1 - ZC3HAV1 /ABL2 ZEB2/PDGFRβ - TEL/ABL1 - SSBP2/CSF1R - EBF1/PDGFRβ - Table I. Continued. Type of analysis Gene Method Result Gene mutation FLT3 ITD RT PCR IDH1 R132 Next generation sequencing NPM1(exon12) IDH2R140 - CEBPA - IDH2R172 - DNMT3A - C kitd816 - PHF6 - TET2 (c.86c>g; p.p29r) ASXL1 (c.1954g>a; p.g652s), (c.3759t>c; p.s1253s) RT PCR, reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction; +, positive;, negative; Ph like, Philadelphia chromosome like. Figure 2. Karyotype of the abnormal clone and detection of the NUP214 ABL1 fusion transcript. (A) Karyotype of the abnormal clone. The final karyotype was 80 83<4n>,XXYY,+ mar, inc [2]/46, XY[18]. (B) NUP214 ABL1 fusion transcript detected by multiplex reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. (C) NUP214 ABL1 fusion transcript detected by DNA sequencing. NUP124 exon 32 and ABL1 exon 2 are shaded blue. NUP214 ABL1, nucleoporin 214 tyrosine protein kinase ABL1 proto oncogene 1. Flow cytometry of the BM aspirate was performed using a four color Beckman Coulter Cytomics FC 500 flow cytometer (Beckman Coulter, Inc.) as described previously (11). The results indicated that ~90% of the blasts were positive for CD45, the T cell markers ccd3, CD2 and CD7, and the myeloid/stem
4 3982 CHEN et al: ETP ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA WITH NUP214-ABL1 FUSION Figure 3. Effect of selinexor and dasatinib treatment in primary biopsy derived NUP214 ABL1 positive lymphoblast cells. Freshly isolated lymphoblast cells were treated with 10 µm selinexor and/or 10 µm dasatinib for 48 h. (A) Apoptosis was measured using Annexin V/propidium iodide staining and flow cytometry. (B) Cell extracts were analyzed by western blot analysis to determine PARP cleavage. PARP, poly ADP ribose polymerase; C, control; NUP214 ABL1, nucleoporin 214 tyrosine protein kinase ABL1 proto oncogene 1. cell markers CD34, CD38, CD13, CD33, HLA DR and CD123. However, the blasts were weak for CD5, negative for CD1a, CD8, as well as CD19, CD10, CD79a, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase, CD4, CD3, CD64, CD14, CD20, CD56, CD16, CD15, CD11b and MPO (Fig. 1B), suggesting a diagnosis of ETP ALL. Bone marrow cells were directly processed for chromosomal preparation and cytogenetic analyses were performed using the standard method and/or the G banding method (12). The result of conventional G banding chromosomal analysis of the BM cells was 80 83<4n>,XXYY,+mar,i nc[2]/46,xy[18] (Fig. 2A). The results of multiplex nested reverse transcriptionpolymerase chain reaction (RT PCR), which was performed as described previously (13), were negative for the fusion genes listed in Table I. Multiplex RT PCR was subsequently used to detect Philadelphia chromosome like fusion genes that have a gene expression profile similar to that of Ph + ALL, but lack BCR ABL1 fusion. The results demonstrated that the NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene was positive in this case (Table I; Fig. 2B), which was further confirmed by DNA sequencing (Fig. 2C). Also, gene mutation analyses (Table I) were performed. A TET2 missense mutation (c.86c>g; p.p29r), ASXL1 missense mutation (c.1954g>a; p.g652s) and ASXL1 same sense mutation (c.3759t>c; p.s1253s) were detected in this case, which were single nucleotide polymorphism variants (SNP) of TET2 and ASXL1 mutations. These SNP variants did not suggest any significant prognostic impact on leukemia. The patient received pretreatment with an intravenous drip of 10 mg/day dexamethasone (Cisen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Shandong, China). Following treatment for 7 days, stomachache and fever were attenuated and the patient's lymphocyte count decreased to <1.0x10 9 /l. The patient subsequently received induction chemotherapy with vincristine (Hangzhou Minsheng Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd., Hangzhou, China), idarubicin (Pfizer Inc., New York, NY, USA), cyclophosphamide (Baxter Oncology GmbH, Shanghai, China) and prednisone (Cisen Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.) (VICP; 2 mg vincristine on days 1, 8, 15 and 22; 10 mg idarubicinon days 1 3 and days 15 17; 1.2 g cyclophosphamide on days 1 and 15; and 60 mg prednisone on days 1 28) and dasatinib (100 mg/day, on days 8 14). On day 15, routine blood examination results were as follows: Neutrophils, 4.76x10 9 /l; lymphocytes, 1.85x10 9 /l, Hb 65 g/l and Plat 74x10 9 /l (reference range, neutrophils, 1.8x10 9 /l 6.3x10 9 /l; lymphocytes, 1.10x10 9 /l 3.2x10 9 /l, Hb g/l and Plat 125x10 9 /l 350x10 9 /l). BM aspiration revealed <5% lymphoblasts, indicating that the patient had achieved a complete hematological remission with incomplete blood count recovery. On day 30, the patient had achieved complete hematological remission (CR), which was defined as <5% marrow blasts in the bone marrow aspirate and normalization of blood counts. The patient then received consolidation chemotherapy [1.2 g cyclophosphamide on day 1; 3 g cytarabine (Pfizer Inc.) every 12 h on days 1 2; and 80 mg 6 mercaptopurine (Hangzhou Minsheng Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd.) on days 1 7] and adequate central nervous system prophylaxis with intrathecal therapy [10 mg methotrexate (Pfizer Inc.), 50 mg cytarabine and 10 mg dexamethasone] and high dose systemic chemotherapy with 5 g/m 2 methotrexate. The final date of follow up was January , at which point the patient was alive and healthy. In vitro analysis of selinexor and dasatinib treatment. Upon written informed consent, in vitro analysis was conducted on cells from the patient. A total of 2x10 6 primary lymphoblast cells were obtained from BM samples using Ficoll density gradient centrifugation (FicollPaque PLUS solution; GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Little Chalfont, UK). The protocol was as follows: 4 ml of Ficoll Histopaque was placed in a 15 ml centrifuge tube, then the bone marrow sample was gently layered on top. The tubes were centrifuged for 30 min at 100 x g at 4 C in a swing out bucket. The buffy coat that formed in the interphase between histopaque and medium was aspirated and washed (centrifuged at 100 x g for 10 min) twice with 10 ml of sterile PBS. Primary lymphoblast cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and 15% fetal calf serum (HyClone; GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Logan, UT, USA), and incubated in an atmosphere containing 5% CO 2 at 37 C. The effect of selinexor and dasatinib on apoptosis was evaluated in primary lymphoblast cells. The primary cells were treated with 10 µm selinexor (14) and/or 10 µm dasatinib (15) for 48 h at 37 C. Apoptosis was subsequently analyzed using the Annexin V/propidium iodide staining (BD PharMingen, San Diego, CA, USA) and flow cytometry was performed according to the manufacturer's protocol. Poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARP) cleavage was detected using western blot analysis (16).
5 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 14: , The results demonstrated that the apoptotic cell population significantly increased following selinexor or dasatinib treatment compared with the control (P<0.05) and combined selinexor and dasatinib treatment led to a significant increase in cell apoptosis compared with either treatment alone (P<0.05; Fig. 3A). These results were further confirmed by the detection of increased PARP cleavage by western blot analysis following selinexor or dasatinib treatment, compared with the control (Fig. 3B). Combined selinexor and dasatinib treatment induced more PARP cleavage than either treatment alone. Discussion Approximately 8% of T ALL cases harbor fusions involving the ABL1 tyrosine kinase gene (17). BCR ABL1, the prototypic ABL1 fusion kinase in chronic myeloid leukemia and subsets of B cell ALL, is rarely detected in T ALL (18). By contrast, 6% of T ALL cases express the constitutively active NUP214 ABL1 fusion kinase (5). To the best of our knowledge, there have been no studies reporting NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene expression in ETP ALL to date. The current case report describes a rare case of ETP ALL with NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene expression. ETP ALL is recognized as a form of T ALL with high induction failure (1). However, CR was achieved in the current case following 30 days induction therapy with VICP and dasatinib. Further studies are required to confirm that dasatinib used in combination with traditional induction chemotherapy is more effective than chemotherapy alone. The NUP214 ABL1 fusion protein is sensitive to tyrosine kinase inhibitors including imatinib, dasatinib and nilotinib (17); therefore, these drugs may have potential in treating this subgroup of patients with T ALL. Although NUP214 ABL1 is sensitive to ABL1 kinase inhibitors, the development of resistance to these compounds is a major clinical problem, underlining the requirement for additional drug targets in the sparsely studied NUP214 ABL1 signaling network. De Keersmaecker et al (6) identified LCK, mitotic arrest deficient like 1, structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 4 and nucleoporin 155 as proteins that NUP214 ABL1 positive T ALL tumor cells depend on for their proliferation, indicating that these proteins are potential drug targets for NUP214 ABL1 positive T ALL. Targeting LCK in NUP214 ABL1 may be possible to treat patients with T ALL that are NUP214 ABL1 positive, as dasatinib and bosutinib are able to co target ABL1 and LCK (6). The effect of dasatinib on the apoptosis of primary isolated lymphoblast cells from the patient in the present case study was evaluated. Following treatment for 48 h, apoptosis was induced, indicating that dasatinib induces a cytotoxic effect in NUP214 ABL1 positive cells. Furthermore, De Keersmaecker et al (8) reported that incorporating NUP214 ABL1 into the NPC may be critical for the activation of NUP214 ABL1 kinase. NUP214 is one component of NPC proteins. Evolutionarily conserved NPC proteins mediate the transport of molecules between the nucleoplasm and cytoplasm, which are CRM1 dependent. Mutations in nucleoporins are often linked to specific developmental defects and disease, and the resulting phenotypes are usually interpreted as the consequences of perturbed nuclear transport activity (8). The present study indicated that CRM1 inhibition with selinexor was effective against a case of NUP214 ABL1 positive T ALL in vitro. Therefore, selinexor may have a potential function as a salvage therapy at the time of relapse. In conclusion, expression of the NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene should be tested in cases of T ALL, including ETP ALL. Dasatinib in combination with traditional induction chemotherapy may reverse the high induction failure of ETP ALL with NUP214 ABL1 fusion gene, although further prospective studies are required to confirm this. Therefore, selinexor with or without dasatinib may serve as a potential salvage therapy following relapse. References 1. Jain N, Lamb AV, O'Brien S, Ravandi F, Konopleva M, Jabbour E, Zuo Z, Jorgensen J, Lin P, Pierce S, et al: Early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma (ETP ALL/LBL) in adolescents and adults: A high risk subtype. Blood 127: , Coustan Smith E, Mullighan CG, Onciu M, Behm FG, Raimondi SC, Pei D, Cheng C, Su X, Rubnitz JE, Basso G, et al: Early T cell precursor leukaemia: A subtype of very high risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Lancet Oncol 10: , De Keersmaecker K, Marynen P and Cools J: Genetic insights in the pathogenesis of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 90: , Graux C, Cools J, Melotte C, Quentmeier H, Ferrando A, Levine R, Vermeesch JR, Stul M, Dutta B, Boeckx N, et al: Fusion of NUP214 to ABL1 on amplified episomes in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Nat Genet 36: , Pante N, Bastos R, McMorrow I, Burke B and Aebi U: Interactions and three dimensional localization of a group of nuclear pore complex proteins. J Cell Biol 126: , De Keersmaecker K, Porcu M, Cox L, Girardi T, Vandepoel R, de Beeck JO, Gielen O, Mentens N, Bennett KL and Hantschel O: NUP214 ABL1 mediated cell proliferation in T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia is dependent on the LCK kinase and various interacting proteins. Haematologica 99: 85 93, Hutten S and Kehlenbach RH: Nup214 is required for CRM1 dependent nuclear protein export in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 26: , De Keersmaecker K, Rocnik JL, Bernad R, Lee BH, Leeman D, Gielen O, Verachtert H, Folens C, Munck S, Marynen P, et al: Kinase activation and transformation by NUP214 ABL1 is dependent on the context of the nuclear pore. Mol Cell 31: , Zhang J, Ding L, Holmfeldt L, Wu G, Heatley SL, Payne Turner D, Easton J, Chen X, Wang J, Rusch M, et al: The genetic basis of early T cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Nature 481: , Leinonen EA: Cytochemical studies of acute leukemias. Acta Haematol 43: , Tamul KR, Meyers DC, Bentley SA and Folds JD: Two color flow cytometric analysis of concomitant acute myeloid leukemia and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cytometry 18: 30 34, Summer AT, Evans HJ and Buckland RA: New technique for distinguishing human chromosomes. Nature 232: 31 32, Pallisgaard N, Hokland P, Riishøj DC, Pedersen B and Jørgensen P: Multiplex reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction for simultaneous screening of 29 translocations and chromosomal aberrations in acute leukemia. Blood 92: , Etchin J, Sanda T, Mansour MR, Kentsis A, Montero J, Le BT, Christie AL, McCauley D, Rodig SJ, Kauffman M, et al: KPT 330 inhibitor of CRM1 (XPO1) mediated nuclear export has selective anti leukaemic activity in preclinical models of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol 161: , 2013.
6 3984 CHEN et al: ETP ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA WITH NUP214-ABL1 FUSION 15. Quintás Cardama A, Tong W, Manshouri T, Vega F, Lennon PA, Cools J, Gilliland DG, Lee F, Cortes J, Kantarjian H, et al: Activity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors against human NUP214 ABL1 positive T cell malignancies. Leukemia 22: , Zhang YL, Guang MH, Zhuo HQ, Min XH, Yao Q, Gu AQ, Wu SH, Zhang DB, Lu JY, Chen Y, et al: Carfilzomib inhibits constitutive NF κb activation in mantle cell lymphoma B cells and leads to the induction of apoptosis. Acta Haematol 137: , De Keersmaecker K, Marynen P and Cools J: Genetic insights in the pathogenesis of T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 90: , Westbrook CA, Hooberman AL, Spino C, Dodge RK, Larson RA, Davey F, Wurster Hill DH, Sobol RE, Schiffer C and Bloomfield CD: Clinical significance of the BCR ABL fusion gene in adult acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A cancer and leukemia group B study (8762). Blood 80: , 1992.
NUP214-ABL1 Fusion: A Novel Discovery in Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia
 Case 0094 NUP214-ABL1 Fusion: A Novel Discovery in Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia Jessica Snider, MD Medical University of South Carolina Case Report - 64 year old Caucasian Male Past Medical History Osteoarthritis
Case 0094 NUP214-ABL1 Fusion: A Novel Discovery in Acute Myelomonocytic Leukemia Jessica Snider, MD Medical University of South Carolina Case Report - 64 year old Caucasian Male Past Medical History Osteoarthritis
Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation
 Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
Case Study Diagnostic challenge: Acute leukemia with biphenotypic blasts and BCR-ABL1 translocation Ling Wang 1 and Xiangdong Xu 1,2,* 1 Department of Pathology, University of California, San Diego; 2
Acute myeloid leukemia. M. Kaźmierczak 2016
 Acute myeloid leukemia M. Kaźmierczak 2016 Acute myeloid leukemia Malignant clonal disorder of immature hematopoietic cells characterized by clonal proliferation of abnormal blast cells and impaired production
Acute myeloid leukemia M. Kaźmierczak 2016 Acute myeloid leukemia Malignant clonal disorder of immature hematopoietic cells characterized by clonal proliferation of abnormal blast cells and impaired production
Case Report Blasts-more than meets the eye: evaluation of post-induction day 21 bone marrow in CBFB rearranged acute leukemia
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(7):4498-4502 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000851 Case Report Blasts-more than meets the eye: evaluation of post-induction day 21 bone marrow in CBFB rearranged acute
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(7):4498-4502 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000851 Case Report Blasts-more than meets the eye: evaluation of post-induction day 21 bone marrow in CBFB rearranged acute
Molecular Markers in Acute Leukemia. Dr Muhd Zanapiah Zakaria Hospital Ampang
 Molecular Markers in Acute Leukemia Dr Muhd Zanapiah Zakaria Hospital Ampang Molecular Markers Useful at diagnosis Classify groups and prognosis Development of more specific therapies Application of risk-adjusted
Molecular Markers in Acute Leukemia Dr Muhd Zanapiah Zakaria Hospital Ampang Molecular Markers Useful at diagnosis Classify groups and prognosis Development of more specific therapies Application of risk-adjusted
Relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Lymphoma Tumor Board. July 21, 2017
 Relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia Lymphoma Tumor Board July 21, 2017 Diagnosis - Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Symptoms/signs include: Fever Increased risk of infection (especially bacterial
Relapsed acute lymphoblastic leukemia Lymphoma Tumor Board July 21, 2017 Diagnosis - Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) Symptoms/signs include: Fever Increased risk of infection (especially bacterial
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
 Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Terri Boyer 17 th October 2006 Overview Disease information: Aetiology of ALL proposed theory, contributing factors Symptoms Complications Diagnostic approaches - morphology
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Terri Boyer 17 th October 2006 Overview Disease information: Aetiology of ALL proposed theory, contributing factors Symptoms Complications Diagnostic approaches - morphology
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias
 Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias CHEN GAO; AMY M. SANDS; JIANLAN SUN NORTH AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE APR 2012 VOL 5 NO.2 INTRODUCTION Most cases of acute leukemia can be classified based
Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemias CHEN GAO; AMY M. SANDS; JIANLAN SUN NORTH AMERICAN JOURNAL OF MEDICINE AND SCIENCE APR 2012 VOL 5 NO.2 INTRODUCTION Most cases of acute leukemia can be classified based
ETP - Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia
 ETP - Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Dr Sally Campbell - Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne 24 February 2017 T-ALL 12-15% of all newly diagnosed ALL cases in pediatrics are T-ALL T-ALL behaves differently
ETP - Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia Dr Sally Campbell - Royal Children s Hospital Melbourne 24 February 2017 T-ALL 12-15% of all newly diagnosed ALL cases in pediatrics are T-ALL T-ALL behaves differently
Case 1. Sa A.Wang, MD UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX
 Case 1 Sa A.Wang, MD UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of all CME
Case 1 Sa A.Wang, MD UT MD Anderson Cancer Center Houston, TX Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships The USCAP requires that anyone in a position to influence or control the content of all CME
Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology
 Qian Jiang, M.D. Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology No. 11 Xizhimen South Street, Beijing, 100044, China. Phone number: 86-10-66583802 Mobile: 86-13611115100
Qian Jiang, M.D. Peking University People's Hospital, Peking University Institute of Hematology No. 11 Xizhimen South Street, Beijing, 100044, China. Phone number: 86-10-66583802 Mobile: 86-13611115100
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Introduction. Case Reports
 CASE REPORT Two Elderly Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia Who Were Successfully Treated with Dasatinib and Prednisolone Hiroyuki Takata 1, Taichi Ikebe 1, Hitohiro
CASE REPORT Two Elderly Patients with Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia Who Were Successfully Treated with Dasatinib and Prednisolone Hiroyuki Takata 1, Taichi Ikebe 1, Hitohiro
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and
 Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
Group of malignant disorders of the hematopoietic tissues characteristically associated with increased numbers of white cells in the bone marrow and / or peripheral blood Classified based on cell type
Concomitant WT1 mutations predicted poor prognosis in CEBPA double-mutated acute myeloid leukemia
 Concomitant WT1 mutations predicted poor prognosis in CEBPA double-mutated acute myeloid leukemia Feng-Ming Tien, Hsin-An Hou, Jih-Luh Tang, Yuan-Yeh Kuo, Chien-Yuan Chen, Cheng-Hong Tsai, Ming Yao, Chi-Cheng
Concomitant WT1 mutations predicted poor prognosis in CEBPA double-mutated acute myeloid leukemia Feng-Ming Tien, Hsin-An Hou, Jih-Luh Tang, Yuan-Yeh Kuo, Chien-Yuan Chen, Cheng-Hong Tsai, Ming Yao, Chi-Cheng
ADx Bone Marrow Report. Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information
 ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
ADx Bone Marrow Report Patient Information Referring Physician Specimen Information Patient Name: Specimen: Bone Marrow Site: Left iliac Physician: Accession #: ID#: Reported: 08/19/2014 - CHRONIC MYELOGENOUS
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED
 Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
Done By : WESSEN ADNAN BUTHAINAH AL-MASAEED Acute Myeloid Leukemia Firstly we ll start with this introduction then enter the title of the lecture, so be ready and let s begin by the name of Allah : We
JAK2 V617F analysis. Indication: monitoring of therapy
 JAK2 V617F analysis BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
JAK2 V617F analysis BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Elderly Patients The Philadelphia Chromosome May Not Be a Significant Adverse Prognostic Factor
 Hematopathology / ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA IN ELDERLY PATIENTS Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Elderly Patients The Philadelphia Chromosome May Not Be a Significant Adverse Prognostic Factor Mihaela
Hematopathology / ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA IN ELDERLY PATIENTS Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia in Elderly Patients The Philadelphia Chromosome May Not Be a Significant Adverse Prognostic Factor Mihaela
WBCs Disorders 1. Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD
 WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
WBCs Disorders 1 Dr. Nabila Hamdi MD, PhD ILOs Compare and contrast ALL, AML, CLL, CML in terms of age distribution, cytogenetics, morphology, immunophenotyping, laboratory diagnosis clinical features
MPL W515L K mutation
 MPL W515L K mutation BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
MPL W515L K mutation BCR-ABL genotyping The exact chromosomal defect in Philadelphia chromosome is a translocation. Parts of two chromosomes, 9 and 22, switch places. The result is a fusion gene, created
Jordi Esteve Hospital Clínic (Barcelona) Acute Leukemia Working Party. The European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation
 36th EBMT & 9th Data Management Group Annual Meeting Vienna, 23 March 2010 Jordi Esteve Hospital Clínic (Barcelona) Acute Leukemia Working Party The European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation
36th EBMT & 9th Data Management Group Annual Meeting Vienna, 23 March 2010 Jordi Esteve Hospital Clínic (Barcelona) Acute Leukemia Working Party The European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML
 Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
Personalized Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Patrick Stiff MD Loyola University Medical Center
 Personalized Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patrick Stiff MD Loyola University Medical Center 708-327-3216 Major groups of Mutations in AML Targets for AML: Is this Achievable? Chronic Myeloid Leukemia:
Personalized Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patrick Stiff MD Loyola University Medical Center 708-327-3216 Major groups of Mutations in AML Targets for AML: Is this Achievable? Chronic Myeloid Leukemia:
Role of FISH in Hematological Cancers
 Role of FISH in Hematological Cancers Thomas S.K. Wan PhD,FRCPath,FFSc(RCPA) Honorary Professor, Department of Pathology & Clinical Biochemistry, Queen Mary Hospital, University of Hong Kong. e-mail: wantsk@hku.hk
Role of FISH in Hematological Cancers Thomas S.K. Wan PhD,FRCPath,FFSc(RCPA) Honorary Professor, Department of Pathology & Clinical Biochemistry, Queen Mary Hospital, University of Hong Kong. e-mail: wantsk@hku.hk
PAX5-JAK2 fusion in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Dr Andrew Baldi Royal Children s Hospital 24 February 2017 Melbourne
 PAX5-JAK2 fusion in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia Dr Andrew Baldi Royal Children s Hospital 24 February 2017 Melbourne Case 12-year-old girl Diagnosed with BCP ALL in November 2015 Presenting WCC 35x10
PAX5-JAK2 fusion in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia Dr Andrew Baldi Royal Children s Hospital 24 February 2017 Melbourne Case 12-year-old girl Diagnosed with BCP ALL in November 2015 Presenting WCC 35x10
Case 3. Ann T. Moriarty,MD
 Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Case 3 Ann T. Moriarty,MD Case 3 59 year old male with asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy. These images are from a fine needle biopsy of a left cervical lymph node. Image 1 Papanicolaou Stained smear,100x.
Bumps on the Neck and Groin of a 2-Year-Old Male. Laboratory Findings: Table 1, Table 2; Figure 1; Image 1, Image 2, Image 3
 Bumps on the Neck and Groin of a 2-Year-Old Male 1 Erikakelly Strand, BS* Clinical History Patient: 2-year-old white male. Chief Complaint: Bumps on neck and groin. History of Present Illness: A 2-year-old
Bumps on the Neck and Groin of a 2-Year-Old Male 1 Erikakelly Strand, BS* Clinical History Patient: 2-year-old white male. Chief Complaint: Bumps on neck and groin. History of Present Illness: A 2-year-old
Acute myeloid leukemia: prognosis and treatment. Dimitri A. Breems, MD, PhD Internist-Hematoloog Ziekenhuis Netwerk Antwerpen Campus Stuivenberg
 Acute myeloid leukemia: prognosis and treatment Dimitri A. Breems, MD, PhD Internist-Hematoloog Ziekenhuis Netwerk Antwerpen Campus Stuivenberg Patient Female, 39 years History: hypothyroidism Present:
Acute myeloid leukemia: prognosis and treatment Dimitri A. Breems, MD, PhD Internist-Hematoloog Ziekenhuis Netwerk Antwerpen Campus Stuivenberg Patient Female, 39 years History: hypothyroidism Present:
Corporate Medical Policy. Policy Effective February 23, 2018
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for FLT3, NPM1 and CEBPA Mutations in Acute File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_flt3_npm1_and_cebpa_mutations_in_acute_myeloid_leukemia
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for FLT3, NPM1 and CEBPA Mutations in Acute File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_flt3_npm1_and_cebpa_mutations_in_acute_myeloid_leukemia
Evolving Targeted Management of Acute Myeloid Leukemia
 Evolving Targeted Management of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Jessica Altman, MD Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University Learning Objectives Identify which mutations should be assessed
Evolving Targeted Management of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Jessica Altman, MD Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University Learning Objectives Identify which mutations should be assessed
The BCR-ABL1 fusion. Epidemiology. At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine
 At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia Robert E. Richard MD PhD rrichard@uw.edu robert.richard@va.gov Philadelphia chromosome
At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia Robert E. Richard MD PhD rrichard@uw.edu robert.richard@va.gov Philadelphia chromosome
Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material
 Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Objectives Hematology Unit Lab 2 Review Material - 2018 Laboratory Instructors: 1. Assist students during lab session Students: 1. Review the introductory material 2. Study the case histories provided
Elisabeth Koller 3rd Medical Dept., Center for Hematology and Oncology, Hanusch Hospital, Vienna, Austria
 Elisabeth Koller 3rd Medical Dept., Center for Hematology and Oncology, Hanusch Hospital, Vienna, Austria Incidence Diagnosis Prognostic factors Treatment Induction therapy - HSCT Indications for HSCT
Elisabeth Koller 3rd Medical Dept., Center for Hematology and Oncology, Hanusch Hospital, Vienna, Austria Incidence Diagnosis Prognostic factors Treatment Induction therapy - HSCT Indications for HSCT
AML: WHO classification, biology and prognosis. Dimitri Breems, MD, PhD Internist-Hematoloog Ziekenhuis Netwerk Antwerpen
 AML: WHO classification, biology and prognosis Dimitri Breems, MD, PhD Internist-Hematoloog Ziekenhuis Netwerk Antwerpen Acute myeloid leukemia Clonal expansion of undifferentiated myeloid precursors Impaired
AML: WHO classification, biology and prognosis Dimitri Breems, MD, PhD Internist-Hematoloog Ziekenhuis Netwerk Antwerpen Acute myeloid leukemia Clonal expansion of undifferentiated myeloid precursors Impaired
MP BCR-ABL1 Testing in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.85 Last Review: 10/18/2018 Effective Date: 10/18/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 8.01.30 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.85 Last Review: 10/18/2018 Effective Date: 10/18/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 8.01.30 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Hematopathology Case Study
 Hematopathology Case Study AMP Outreach Course 2009 AMP Annual Meeting John Greg Howe Ph.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale University School of Medicine November 19, 2009 HISTORY Case History An
Hematopathology Case Study AMP Outreach Course 2009 AMP Annual Meeting John Greg Howe Ph.D. Department of Laboratory Medicine Yale University School of Medicine November 19, 2009 HISTORY Case History An
HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES BIOLOGY
 HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES BIOLOGY Failure of terminal differentiation Failure of differentiated cells to undergo apoptosis Failure to control growth Neoplastic stem cell FAILURE OF TERMINAL DIFFERENTIATION
HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES BIOLOGY Failure of terminal differentiation Failure of differentiated cells to undergo apoptosis Failure to control growth Neoplastic stem cell FAILURE OF TERMINAL DIFFERENTIATION
Adult T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Lymphoma Tumor Board. September 8, 2017
 Adult T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma Lymphoma Tumor Board September 8, 2017 Diagnosis of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma Lymphoblastic lymphoma (LBL) is rare Sub-type of lymphoma that is
Adult T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma Lymphoma Tumor Board September 8, 2017 Diagnosis of T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma Lymphoblastic lymphoma (LBL) is rare Sub-type of lymphoma that is
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal 1 0.
 Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
Cell Identification Mitotic figure 212 99.5 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal BMD-02 The arrowed cell is a mitotic figure. It was correctly identified by 99.5% of the participants. A cell containing
SWOG ONCOLOGY RESEARCH PROFESSIONAL (ORP) MANUAL LEUKEMIA FORMS CHAPTER 16A REVISED: DECEMBER 2017
 LEUKEMIA FORMS The guidelines and figures below are specific to Leukemia studies. The information in this manual does NOT represent a complete set of required forms for any leukemia study. Please refer
LEUKEMIA FORMS The guidelines and figures below are specific to Leukemia studies. The information in this manual does NOT represent a complete set of required forms for any leukemia study. Please refer
Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities
 Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities Acute Myeloid Leukemia with recurrent cytogenetic Abnormalities -t(8;21)(q22;q22)(aml/eto) -inv(16) or t(16;16) -t(15;17) -11q23 Acute Myeloid
Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Recurrent Cytogenetic Abnormalities Acute Myeloid Leukemia with recurrent cytogenetic Abnormalities -t(8;21)(q22;q22)(aml/eto) -inv(16) or t(16;16) -t(15;17) -11q23 Acute Myeloid
TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION. 14 February 2007
 The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 14 February 2007 GLIVEC 100 mg, capsule B/120 capsules (CIP: 358 493-5) GLIVEC 100 mg, capsule B/180 capsules (CIP:
The legally binding text is the original French version TRANSPARENCY COMMITTEE OPINION 14 February 2007 GLIVEC 100 mg, capsule B/120 capsules (CIP: 358 493-5) GLIVEC 100 mg, capsule B/180 capsules (CIP:
Selinexor: Novel Anti-Cancer Agent: Restores Tumor Suppressors & Reduces Oncoproteins
 PHASE I STUDY OF SELINEXOR, A SELECTIVE INHIBITOR OF NUCLEAR EXPORT, IN COMBINATION WITH FLUDARABINE AND CYTARABINE IN CHILDREN WITH RELAPSED OR REFRACTORY LEUKEMIA Thomas B Alexander 1, Norman J Lacayo
PHASE I STUDY OF SELINEXOR, A SELECTIVE INHIBITOR OF NUCLEAR EXPORT, IN COMBINATION WITH FLUDARABINE AND CYTARABINE IN CHILDREN WITH RELAPSED OR REFRACTORY LEUKEMIA Thomas B Alexander 1, Norman J Lacayo
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval. Positive
 LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091533 Age 28 Years Gender Male 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 105415AM 4/9/2017 23858M Ref By Final LEUKEMIA DIAGNOSTIC COMREHENSIVE ROFILE, ANY 6 MARKERS t (1;19) (q23
LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091533 Age 28 Years Gender Male 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 105415AM 4/9/2017 23858M Ref By Final LEUKEMIA DIAGNOSTIC COMREHENSIVE ROFILE, ANY 6 MARKERS t (1;19) (q23
Department of Leukemia, The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas; 2 Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc, South San Francisco
 Phase I/II Study of Vosaroxin and Decitabine in Newly Diagnosed Older Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and High Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) Naval Daver 1, Hagop Kantarjian 1, Guillermo
Phase I/II Study of Vosaroxin and Decitabine in Newly Diagnosed Older Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and High Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) Naval Daver 1, Hagop Kantarjian 1, Guillermo
MS.4/ Acute Leukemia: AML. Abdallah Al Abbadi.MD.FRCP.FRCPath Feras Fararjeh MD
 MS.4/ 27.02.2019 Acute Leukemia: AML Abdallah Al Abbadi.MD.FRCP.FRCPath Feras Fararjeh MD Case 9: Acute Leukemia 29 yr old lady complains of fever and painful gums for 1 week. She developed easy bruising
MS.4/ 27.02.2019 Acute Leukemia: AML Abdallah Al Abbadi.MD.FRCP.FRCPath Feras Fararjeh MD Case 9: Acute Leukemia 29 yr old lady complains of fever and painful gums for 1 week. She developed easy bruising
Aberrant Expression of CD7 in Myeloblasts Is Highly Associated With De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemias With FLT3/ITD Mutation
 Hematopathology / CD7 Expression and FLT3/ITD Mutation in AML Aberrant Expression of CD7 in Myeloblasts Is Highly Associated With De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemias With FLT3/ITD Mutation Veronica Rausei-Mills,
Hematopathology / CD7 Expression and FLT3/ITD Mutation in AML Aberrant Expression of CD7 in Myeloblasts Is Highly Associated With De Novo Acute Myeloid Leukemias With FLT3/ITD Mutation Veronica Rausei-Mills,
Citation International Journal of Hematology, 2013, v. 98 n. 4, p The original publication is available at
 Title Diagnostic challenges in a case of B cell lymphoma unclassifiable with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma Author(s) So, JCC; Yung, KH; Chu, ML; Wan,
Title Diagnostic challenges in a case of B cell lymphoma unclassifiable with features intermediate between diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and Burkitt lymphoma Author(s) So, JCC; Yung, KH; Chu, ML; Wan,
Pathology. #11 Acute Leukemias. Farah Banyhany. Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16
 35 Pathology #11 Acute Leukemias Farah Banyhany Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16 1 Salam First of all, this tafreegh is NOT as long as you may think. If you just focus while studying this, everything will
35 Pathology #11 Acute Leukemias Farah Banyhany Dr. Sohaib Al- Khatib 23/2/16 1 Salam First of all, this tafreegh is NOT as long as you may think. If you just focus while studying this, everything will
Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MDS/MPN) Post-HCT Data
 Instructions for Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MDS/MPN) Post-HCT Data (Form 2114) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative
Instructions for Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MDS/MPN) Post-HCT Data (Form 2114) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the Myelodysplasia/Myeloproliferative
Results of treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemias in adults by the modified program "M-Hyper-CVAD-L-Asp-HD-Mtx-HD-Ara-C"
 Journal of research in health science 2018 ¹ 1 (3), May-August www.journalofresearch.org; info@journalofresearch.org DOI 10.26739/2523-1243 ISSN Print: 2523-1243; ISSN Online: 2523-1251 Results of treatment
Journal of research in health science 2018 ¹ 1 (3), May-August www.journalofresearch.org; info@journalofresearch.org DOI 10.26739/2523-1243 ISSN Print: 2523-1243; ISSN Online: 2523-1251 Results of treatment
Participants Identification No. % Evaluation. Mitotic figure Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/
 Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Cell Identification BMD-09 Participants Identification No. % Evaluation Mitotic figure 233 96.7 Educational Erythrocyte precursor, abnormal/ 4 1.7 Educational dysplastic nuclear features Erythrocyte precursor
Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study
 Original Research Article Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study Priyanka Poonam 1*, N.K. Bariar 2 1 Tutor, Department of Pathology, Patna Medical
Original Research Article Bone marrow aspiration as the initial diagnostic tool in the diagnosis of leukemia - A case study Priyanka Poonam 1*, N.K. Bariar 2 1 Tutor, Department of Pathology, Patna Medical
Therapy-related MDS/AML with KMT2A (MLL) Rearrangement Following Therapy for APL Case 0328
 Therapy-related MDS/AML with KMT2A (MLL) Rearrangement Following Therapy for APL Case 0328 Kenneth N. Holder, Leslie J. Greebon, Gopalrao Velagaleti, Hongxin Fan, Russell A. Higgins Initial Case: Clinical
Therapy-related MDS/AML with KMT2A (MLL) Rearrangement Following Therapy for APL Case 0328 Kenneth N. Holder, Leslie J. Greebon, Gopalrao Velagaleti, Hongxin Fan, Russell A. Higgins Initial Case: Clinical
Case #16: Diagnosis. T-Lymphoblastic lymphoma. But wait, there s more... A few weeks later the cytogenetics came back...
 Case #16: Diagnosis T-Lymphoblastic lymphoma But wait, there s more... A few weeks later the cytogenetics came back... 46,XY t(8;13)(p12;q12)[12] Image courtesy of Dr. Xinyan Lu Further Studies RT-PCR
Case #16: Diagnosis T-Lymphoblastic lymphoma But wait, there s more... A few weeks later the cytogenetics came back... 46,XY t(8;13)(p12;q12)[12] Image courtesy of Dr. Xinyan Lu Further Studies RT-PCR
CHALLENGING CASES PRESENTATION
 CHALLENGING CASES PRESENTATION Michael C. Wiemann, MD, FACP Program Co-Chair and Vice President Indy Hematology Education President, Clinical St. John Providence Physician Network Detroit, Michigan 36
CHALLENGING CASES PRESENTATION Michael C. Wiemann, MD, FACP Program Co-Chair and Vice President Indy Hematology Education President, Clinical St. John Providence Physician Network Detroit, Michigan 36
MS.4/ 1.Nov/2015. Acute Leukemia: AML. Abdallah Abbadi
 MS.4/ 1.Nov/2015. Acute Leukemia: AML Abdallah Abbadi Case 9: Acute Leukemia 29 yr old lady complains of fever and painful gums for 1 week. She developed easy bruising and hemorrhagic spots on her trunk
MS.4/ 1.Nov/2015. Acute Leukemia: AML Abdallah Abbadi Case 9: Acute Leukemia 29 yr old lady complains of fever and painful gums for 1 week. She developed easy bruising and hemorrhagic spots on her trunk
ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43
 ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43 IN A PATIENT WITH THERAPY-RELATED ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA AND A HISTORY OF MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Yen-Chuan Hsieh, 1 Chien-Liang Lin, 2 Chao-Jung Tsao, 2 Pin-Pen Hsieh,
ABERRANT EXPRESSION OF CD19 AND CD43 IN A PATIENT WITH THERAPY-RELATED ACUTE MYELOID LEUKEMIA AND A HISTORY OF MANTLE CELL LYMPHOMA Yen-Chuan Hsieh, 1 Chien-Liang Lin, 2 Chao-Jung Tsao, 2 Pin-Pen Hsieh,
Objectives. Morphology and IHC. Flow and Cyto FISH. Testing for Heme Malignancies 3/20/2013
 Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
Molecular Markers in Hematologic Malignancy: Ways to locate the needle in the haystack. Objectives Review the types of testing for hematologic malignancies Understand rationale for molecular testing Marcie
Myeloproliferative Disorders - D Savage - 9 Jan 2002
 Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Disease Usual phenotype acute leukemia precursor chronic leukemia low grade lymphoma myeloma differentiated Total WBC > 60 leukemoid reaction acute leukemia Blast Pro Myel Meta Band Seg Lymph 0 0 0 2
Summary. Olga Zając, Katarzyna Derwich, Katarzyna Stefankiewicz, Jacek Wachowiak. Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2007; 12(5):
 Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2007; 12(5): 283-288 Preliminary Communication Received: 2007.03.27 Accepted: 2007.07.24 Published: 2007.10.18 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical
Rep Pract Oncol Radiother, 2007; 12(5): 283-288 Preliminary Communication Received: 2007.03.27 Accepted: 2007.07.24 Published: 2007.10.18 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical
Treatments and Current Research in Leukemia. Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago
 Treatments and Current Research in Leukemia Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago 2 Acute (rapid progression) Myeloid Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) Lymphoid Acute
Treatments and Current Research in Leukemia Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago 2 Acute (rapid progression) Myeloid Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) Lymphoid Acute
New treatment strategies in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia van der Helm, Lidia Henrieke
 University of Groningen New treatment strategies in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia van der Helm, Lidia Henrieke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
University of Groningen New treatment strategies in myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid leukemia van der Helm, Lidia Henrieke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version
Case 089: Therapy Related t(8;21)(q22;q22) AML and
 Case 089: Therapy Related t(8;21)(q22;q22) AML and SM-AHNMD ST Pullarkat 1, V Pullarkat 2, SH Kroft 3, CS Wilson 4, M Thein 5, WW Grody 1, and RK Brynes 5 1 UCLA, 2 City of Hope National Med Ctr, 3 Med
Case 089: Therapy Related t(8;21)(q22;q22) AML and SM-AHNMD ST Pullarkat 1, V Pullarkat 2, SH Kroft 3, CS Wilson 4, M Thein 5, WW Grody 1, and RK Brynes 5 1 UCLA, 2 City of Hope National Med Ctr, 3 Med
CME/SAM. Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia
 AJCP / Original Article Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia A Study of 61 Cases Using World Health Organization and European Group for the Immunological Classification of Leukaemias Criteria Olga K. Weinberg,
AJCP / Original Article Mixed Phenotype Acute Leukemia A Study of 61 Cases Using World Health Organization and European Group for the Immunological Classification of Leukaemias Criteria Olga K. Weinberg,
CML TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 CML TREATMENT GUIDELINES INITIAL INVESTIGATION Propose enrolment in the CML Registry of the CML-MPN Quebec Research Group. Medical history : Question for cardio-respiratory disorders, diabetes, pancreatitis,
CML TREATMENT GUIDELINES INITIAL INVESTIGATION Propose enrolment in the CML Registry of the CML-MPN Quebec Research Group. Medical history : Question for cardio-respiratory disorders, diabetes, pancreatitis,
Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm with DNMT3A and TET2 mutations (SH )
 Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm with DNMT3A and TET2 mutations (SH2017-0314) Habibe Kurt, Joseph D. Khoury, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, Jeffrey L. Jorgensen, Guilin Tang, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, and
Blastic Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cell Neoplasm with DNMT3A and TET2 mutations (SH2017-0314) Habibe Kurt, Joseph D. Khoury, Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, Jeffrey L. Jorgensen, Guilin Tang, L. Jeffrey Medeiros, and
Extramedullary precursor T-lymphoblastic transformation of CML at presentation
 Extramedullary precursor T-lymphoblastic transformation of CML at presentation Neerja Vajpayee, Constance Stein, Bernard Poeisz & Robert E. Hutchison Clinical History 30 year old man presented to the emergency
Extramedullary precursor T-lymphoblastic transformation of CML at presentation Neerja Vajpayee, Constance Stein, Bernard Poeisz & Robert E. Hutchison Clinical History 30 year old man presented to the emergency
A 34-year old women came because of abdominal discomfort. Vital sign was stable. Spleen tip was palpable.
 1 Case 1 A 34-year old women came because of abdominal discomfort. Vital sign was stable. Spleen tip was palpable. CBC and bone marrow aspiration and biopsy were done. Chromosome study showed she had t(9;22)
1 Case 1 A 34-year old women came because of abdominal discomfort. Vital sign was stable. Spleen tip was palpable. CBC and bone marrow aspiration and biopsy were done. Chromosome study showed she had t(9;22)
2011: ALL Pre-HCT. Subsequent Transplant
 2011: ALL Pre-HCT The Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pre-HCT Data Form is one of the Comprehensive Report Forms. This form captures ALL-specific pre-hct data such as: the recipient s hematologic and cytogenetic
2011: ALL Pre-HCT The Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pre-HCT Data Form is one of the Comprehensive Report Forms. This form captures ALL-specific pre-hct data such as: the recipient s hematologic and cytogenetic
Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia Pre-HCT Data
 Instructions for Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia Pre-HCT Data (Form 2015) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the JMML Pre-HCT Form. E-mail
Instructions for Juvenile Myelomonocytic Leukemia Pre-HCT Data (Form 2015) This section of the CIBMTR Forms Instruction Manual is intended to be a resource for completing the JMML Pre-HCT Form. E-mail
Blood Cell Identification Graded
 BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
BCP-21 Blood Cell Identification Graded Case History The patient is a 37-year-old female with a history of multiple sickle cell crises. She now presents with avascular necrosis of the left hip. Laboratory
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Information S1 Frequency of DNMT3A mutations in hematologic disorders and their associated clinical phenotypes. Disease Patient population Frequency (%) Associated Clinical Characteristics
Supplementary Information S1 Frequency of DNMT3A mutations in hematologic disorders and their associated clinical phenotypes. Disease Patient population Frequency (%) Associated Clinical Characteristics
Department of Leukemia, The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, Texas; 2 Sunesis Pharmaceuticals, Inc, South San Francisco
 Phase I/II Study of Vosaroxin and Decitabine in Newly Diagnosed Older Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and High Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) Naval Daver 1, Hagop Kantarjian 1, Guillermo
Phase I/II Study of Vosaroxin and Decitabine in Newly Diagnosed Older Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and High Risk Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) Naval Daver 1, Hagop Kantarjian 1, Guillermo
Granular lymphoblast in a case of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A rare morphology
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Granular lymphoblast in a case of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A rare morphology Shehab Fareed Mohamed, Dina Sameh Soliman, Firyal Ibrahim
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Granular lymphoblast in a case of acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A rare morphology Shehab Fareed Mohamed, Dina Sameh Soliman, Firyal Ibrahim
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Reporting cytogenetics Can it make sense? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota
 Reporting cytogenetics Can it make sense? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Reporting cytogenetics What is it? Terminology Clinical value What details are important Diagnostic Tools for Leukemia
Reporting cytogenetics Can it make sense? Daniel Weisdorf MD University of Minnesota Reporting cytogenetics What is it? Terminology Clinical value What details are important Diagnostic Tools for Leukemia
Case #1. 65 yo man with no prior history presented with leukocytosis and circulating blasts: Bone marrow biopsy was performed
 Case #1 65 yo man with no prior history presented with leukocytosis and circulating blasts: WBC 187.4K/uL ; Hgb 10.0gm/dL; Platelet 68K/uL Neutrophil % 25.0% Lymphocyte % 38.0% Monocyte % 12.0% Metamyelocyte
Case #1 65 yo man with no prior history presented with leukocytosis and circulating blasts: WBC 187.4K/uL ; Hgb 10.0gm/dL; Platelet 68K/uL Neutrophil % 25.0% Lymphocyte % 38.0% Monocyte % 12.0% Metamyelocyte
Mast Cell Disease Case 054 Session 7
 Mast Cell Disease Case 054 Session 7 Rodney R. Miles, M.D., Ph.D. Lauren B. Smith, M.D. Cem Akin, M.D. Diane Roulston,, Ph.D. Charles W. Ross, M.D. Departments of Pathology and Internal Medicine University
Mast Cell Disease Case 054 Session 7 Rodney R. Miles, M.D., Ph.D. Lauren B. Smith, M.D. Cem Akin, M.D. Diane Roulston,, Ph.D. Charles W. Ross, M.D. Departments of Pathology and Internal Medicine University
Risk Stratification in Childhood Leukemia
 Risk Stratification in Childhood Leukemia Why is risk stratification important? Toxicities Deepa Bhojwani, MD May 11, 2018 To determine intensity of therapy - When to intensify therapy - When to de-intensify
Risk Stratification in Childhood Leukemia Why is risk stratification important? Toxicities Deepa Bhojwani, MD May 11, 2018 To determine intensity of therapy - When to intensify therapy - When to de-intensify
Acute Lymphoblastic and Myeloid Leukemia
 Acute Lymphoblastic and Myeloid Leukemia Pre- and Post-Disease Form Acute Lympoblastic Leukemia Mary Eapen MD, MS Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia SEER Age-adjusted incidence rate 1.6 per 100,000 men and women
Acute Lymphoblastic and Myeloid Leukemia Pre- and Post-Disease Form Acute Lympoblastic Leukemia Mary Eapen MD, MS Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia SEER Age-adjusted incidence rate 1.6 per 100,000 men and women
Fluorescence in-situ Hybridization (FISH) ETO(RUNX1T1)/AML1(RUNX1) or t(8;21)(q21.3;q22)
 PML/RARA t(15;17) Translocation Assay Result : nuc ish(pml 2)(RARA 2)[200] : 200/200(100%) interphase nuclei show normal 2O 2G signals for PML/RARA : is Negative for t(15;17)(q22;q21.1) 2 Orange 2 Green
PML/RARA t(15;17) Translocation Assay Result : nuc ish(pml 2)(RARA 2)[200] : 200/200(100%) interphase nuclei show normal 2O 2G signals for PML/RARA : is Negative for t(15;17)(q22;q21.1) 2 Orange 2 Green
SH A CASE OF PERSISTANT NEUTROPHILIA: BCR-ABL
 SH2017-0124 A CASE OF PERSISTANT NEUTROPHILIA: BCR-ABL NEGATIVE John R Goodlad 1, Pedro Martin-Cabrera 2, Catherine Cargo 2 1. Department of Pathology, NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde, QEUH, Glasgow 2. Haematological
SH2017-0124 A CASE OF PERSISTANT NEUTROPHILIA: BCR-ABL NEGATIVE John R Goodlad 1, Pedro Martin-Cabrera 2, Catherine Cargo 2 1. Department of Pathology, NHS Greater Glasgow & Clyde, QEUH, Glasgow 2. Haematological
ONE STEP MULTIPLEX RT-PCR FOR BCRlABL GENE IN MALAY PATIENTS DIAGNOSED AS LEUKAEMIA
 ONE STEP MULTIPLEX RT-PCR FOR BCRlABL GENE IN MALAY PATIENTS DIAGNOSED AS LEUKAEMIA 1Rosline H, 1Majdan R, 1Wan Zaidah A, 1Rapiaah M, 1Selamah G, 2A A Baba, 3D M Donald 1Department of Haematology, 2Department
ONE STEP MULTIPLEX RT-PCR FOR BCRlABL GENE IN MALAY PATIENTS DIAGNOSED AS LEUKAEMIA 1Rosline H, 1Majdan R, 1Wan Zaidah A, 1Rapiaah M, 1Selamah G, 2A A Baba, 3D M Donald 1Department of Haematology, 2Department
N Engl J Med Volume 373(12): September 17, 2015
 Review Article Acute Myeloid Leukemia Hartmut Döhner, M.D., Daniel J. Weisdorf, M.D., and Clara D. Bloomfield, M.D. N Engl J Med Volume 373(12):1136-1152 September 17, 2015 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Most
Review Article Acute Myeloid Leukemia Hartmut Döhner, M.D., Daniel J. Weisdorf, M.D., and Clara D. Bloomfield, M.D. N Engl J Med Volume 373(12):1136-1152 September 17, 2015 Acute Myeloid Leukemia Most
Beyond the CBC Report: Extended Laboratory Testing in the Evaluation for Hematologic Neoplasia Disclosure
 Beyond the CBC Report: Extended Laboratory Testing in the Evaluation for Hematologic Neoplasia Disclosure I am receiving an honorarium from Sysmex for today s presentation. 1 Determining the Etiology for
Beyond the CBC Report: Extended Laboratory Testing in the Evaluation for Hematologic Neoplasia Disclosure I am receiving an honorarium from Sysmex for today s presentation. 1 Determining the Etiology for
Test Name Results Units Bio. Ref. Interval. Positive
 LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091534 Age 36 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 105316AM 2/9/2017 104147AM Ref By Final LEUKEMIA GENETIC ROFILE ANY SIX MARKERS, CR QUALITATIVE AML ETO
LL - LL-ROHINI (NATIONAL REFERENCE 135091534 Age 36 Years Gender Female 1/9/2017 120000AM 1/9/2017 105316AM 2/9/2017 104147AM Ref By Final LEUKEMIA GENETIC ROFILE ANY SIX MARKERS, CR QUALITATIVE AML ETO
Minimal residual disease (MRD) in AML; coming of age. Dr. Mehmet Yılmaz Gaziantep University Medical School Sahinbey Education and Research hospital
 Minimal residual disease (MRD) in AML; coming of age Dr. Mehmet Yılmaz Gaziantep University Medical School Sahinbey Education and Research hospital 1. The logistics of MRD assessment in AML 2. The clinical
Minimal residual disease (MRD) in AML; coming of age Dr. Mehmet Yılmaz Gaziantep University Medical School Sahinbey Education and Research hospital 1. The logistics of MRD assessment in AML 2. The clinical
Cost-Effective Strategies in the Workup of Hematologic Neoplasm. Karl S. Theil, Claudiu V. Cotta Cleveland Clinic
 Cost-Effective Strategies in the Workup of Hematologic Neoplasm Karl S. Theil, Claudiu V. Cotta Cleveland Clinic In the past 12 months, we have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
Cost-Effective Strategies in the Workup of Hematologic Neoplasm Karl S. Theil, Claudiu V. Cotta Cleveland Clinic In the past 12 months, we have not had a significant financial interest or other relationship
Leukemias. Prof. Mutti Ullah Khan Head of Department Medical Unit-II Holy Family Hospital Rawalpindi Medical College
 Leukemias Prof. Mutti Ullah Khan Head of Department Medical Unit-II Holy Family Hospital Rawalpindi Medical College Introduction Leukaemias are malignant disorders of the haematopoietic stem cell compartment,
Leukemias Prof. Mutti Ullah Khan Head of Department Medical Unit-II Holy Family Hospital Rawalpindi Medical College Introduction Leukaemias are malignant disorders of the haematopoietic stem cell compartment,
Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood
 Review article DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2011.54.3.106 Korean J Pediatr 2011;54(3):106-110 Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood Hong Hoe Koo, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics,
Review article DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2011.54.3.106 Korean J Pediatr 2011;54(3):106-110 Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia in childhood Hong Hoe Koo, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics,
HEMATOPATHOLOGY SUMMARY REPORT RL;MMR;
 HEMATOPATHOLOGY SUMMARY REPORT RL;MMR; Page 1 of 1 05/15/20XX HP000000-20XX 05/21/20XX (212) 123-457 (51) 32-3455 (51) 123-457 Age: 78 DOB: 0/05/19XX SS#: 45-45-45 Clinical Information: 78 y/o female with
HEMATOPATHOLOGY SUMMARY REPORT RL;MMR; Page 1 of 1 05/15/20XX HP000000-20XX 05/21/20XX (212) 123-457 (51) 32-3455 (51) 123-457 Age: 78 DOB: 0/05/19XX SS#: 45-45-45 Clinical Information: 78 y/o female with
2402: Pre-TED Disease Classification
 2402: Pre-TED Disease Classification The Pre-TED Form is now required for all transplants, including subsequent transplants on * the comprehensive report form track. All transplant centers participating
2402: Pre-TED Disease Classification The Pre-TED Form is now required for all transplants, including subsequent transplants on * the comprehensive report form track. All transplant centers participating
Molecular Markers. Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC
 Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Molecular Markers Marcie Riches, MD, MS Associate Professor University of North Carolina Scientific Director, Infection and Immune Reconstitution WC Overview Testing methods Rationale for molecular testing
Hematologic and cytogenetic responses of Imatinib Mesylate and significance of Sokal score in chronic myeloid leukemia patients
 ORIGINAL ALBANIAN MEDICAL RESEARCH JOURNAL Hematologic and cytogenetic responses of Imatinib Mesylate and significance of Sokal score in chronic myeloid leukemia patients Dorina Roko 1, Anila Babameto-Laku
ORIGINAL ALBANIAN MEDICAL RESEARCH JOURNAL Hematologic and cytogenetic responses of Imatinib Mesylate and significance of Sokal score in chronic myeloid leukemia patients Dorina Roko 1, Anila Babameto-Laku
screening procedures Disease resistant to full-dose imatinib ( 600 mg/day) or intolerant to any dose of imatinib
 Table S1. Study inclusion and exclusion criteria Inclusion criteria Aged 18 years Signed and dated informed consent form prior to protocol-specific screening procedures Cytogenetic- or PCR-based diagnosis
Table S1. Study inclusion and exclusion criteria Inclusion criteria Aged 18 years Signed and dated informed consent form prior to protocol-specific screening procedures Cytogenetic- or PCR-based diagnosis
JPMA ( Journal Of Pakistan Medical Association) Vol 53, No.9,Sep Original Articles
 JPMA ( Journal Of Pakistan Medical Association) Vol 53, No.9,Sep. 2003 Original Articles Outcome of Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: a Single Center Experience M. Usman, I. Burney*, A. Nasim*, S. N.
JPMA ( Journal Of Pakistan Medical Association) Vol 53, No.9,Sep. 2003 Original Articles Outcome of Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia: a Single Center Experience M. Usman, I. Burney*, A. Nasim*, S. N.
