Validation of the Xpert BCR-ABL Monitor Assay Results: King Fahd Specialist Hospital Dammam Experience. Heba N. Raslan 1 and Samir Amr 2
|
|
|
- Jonas Shelton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Validation of the Xpert BCR-ABL Monitor Assay Results: King Fahd Specialist Hospital Dammam Experience Heba N. Raslan and Samir Amr 2 Consultant Hematopathology, King Fahd Specialist Hospital-Dammam. National Cancer Institute, Cairo University 2 Consultant Histopathology, King Fahd Specialist Hospital-Dammam hebaraslan203@gmail.com Abstract: Objectives: King Fahd Specialist Hospital Dammam (KFSHD), a tertiary care hospital, has guidelines for BCR-ABL p20 quantitation using GeneXpert Real Time PCR.The assay results are automatically calculated using the Cepheid International Scale (IS), mentioned in the certificate of analysis (COA) supplied with each kit. The aim of this study was to establish an IS specific for KFSHD, instead of that supplied by the manufacturer, based on thorough validation study of the assay with Mayoclinic IS, a thing which conferred more accurate interpretation of the results. Methods: A total of 29 hemato-oncology blood, bone marrow and RNA samples were run, using the GeneXpert BCR-ABL assay and validation for all samples was carried out with Mayo clinic to compare external controls to built-in controls. We cancelled the Cepheid IS and used the Mayoclinic IS factor (2.57), which is validated by its turn with the reference method (University of Adelaide). Results: All 29 results were concordant using the acceptance criterion of +/-0.5 log 0 of the expected BCR-ABL relative quantitation. Conclusion: The Xpert BCR-ABL monitor assay provides reliable results. Replacement of the IS provided by the manufacturer with the IS calculated by our lab, and which is based upon thorough validation study, conferred more accurate results. [Heba N. Raslan. Validation of the Xpert BCR-ABL Monitor Assay Results: King Fahd Specialist Hospital Dammam Experience. J Am Sci 203;9(9):28-285]. (ISSN: ).. 37 Key words: BCR-ABL, CML, International Scale Introduction: Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) is a hematopoietic stem cell neoplasm caused by BCR- ABL fusion gene, which results in a constitutively active tyrosine kinase (). Imatinibmesylatedeveloped as a selective BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase inhibitor and became the standard first line treatment for CML patients, inducing stable minimal residual disease in the majority of patients (2).Imatinib induces complete cytogenetic response (CCR) in more than 80% of CML patients (3), of whom % to 27% have been shown to subsequently lose CCR (4). That's why disease burden in CML patients with CCR should be routinely monitored by PCR to detect 3 or more logarithmic units reduction of BCR-ABL fusion transcripts, compared to a standardized baseline, a thing which confers major molecular response (MMR) and associates with significantly lower relapse risk and prolonged progression free survival (5). Because RQ- PCR methods are not yet well standardized, relatively imprecise, have variable low-level detection limits in different laboratories, and use different techniques and various control genes, marked variation in reported BCR-ABL values is encountered (6, 7). Accordingly, alignment of BCR-ABL values became necessary to achieve comparable results for the aim of using common clinical decision values, facilitating patient monitoring between clinics that use different testing laboratories and consistent interpretation of clinical research data (8). An International Scale (IS) was designed by the Adelaide laboratory in Australia to replace the log reduction scale, with a defined value of MMR of 0.0% IS (9). Cehpheid introduced its Gene Xpert-based assay for the identification of the BCR-ABL gene fusion from blood samples, which is a self-contained automated instrument that integrates microfluidic sample preparation with RT-PCR based real time fluorescent signal detection (0). The difference in the measured BCR-ABL ct (cycle threshold) and ABL ct ; the delta ct ( ct ) is calculated by the instrument's software and interpreted as positive, negative or invalid, and represents the ratio of the two populations of mrnas, and ultimately the fraction of neoplastic cells present. 2. Patients and Methods: The GeneXpert software calculates the %BCR- ABL/ABL using the following equation: %BCR- ABL/ABL IS=E ct ( ct) X00Xconversion factor, where the ct is obtained from ABL ct minus BCR-ABL ct. A total of 29 hemato-oncology blood, bone marrow and RNA samples (27 positives and 2 negatives) were run and compared to the reference methods. All samples worked within 20 consecutive days to compare external controls to built- in controls Xpert BCR-ABL Monitor Assay A sample of 200 μl of peripheral blood, bone marrow aspirate, was lysed according to the 28
2 manufacturer's protocol. Lysates were added to GeneXpert cartridges (Cepheid) and analyzed on the GeneXpert instrument. The automated procedure is as follows: () purification of RNA using nucleic acid purification beads, (2) reverse transcription of RNA, and (3) quantitative real-time nested polymerase chain reaction of complementary DNA. Wild-type ABL transcripts served as an internal control. For patient specimens, the blood or bone marrow aspirate was lysed immediately on receipt of the sample and run on the GeneXpert instrument. Total turnaround time was less than 2.5 hours. Calculation of % BCR-ABL to ABL Transcript For positive specimens, the % BCR-ABL to ABL transcript was calculated by the following equation: % BCR-ABL/ABL = EΔ Ct ΔCt ; where Ct is the cycle threshold, EΔCt is the efficiency of the BCR-ABL to ABL RQ-PCR reaction for a given lot of reagent, and ΔCt =ABL Ct BCR-ABL Ct. For specimens that were negative for the BCR-ABL transcript, the detection limit was calculated as follows: %BCR- ABL/ABL detection limit = EΔCt ABL Ct. After thorough validation study of the assay with Mayaoclinic, which by its turn validates its results with the reference method of the University of Adelaide, King Fahd Specialist Hospital-Dammam (KFSHD) molecular diagnostic lab decided to cancel the Cepheid International Scale which is mentioned in the certificate of analysis (COA) provided with each kit and to use instead the Mayoclinic IS of We calculated our results according to the equation: X= (Y/Z)*N Where: X = KFSHD % BCR-ABL/ABL IS Y = Xpert % BCR-ABL/ABL IS Z = Cepheid COA Conversion Factor N = Mayo Clinic Conversion Factor 3. Results: Accuracy: A total of 29 hemato-oncology blood,bone marrow and RNA samples (27 positives and 2 negatives) were run and compared to the reference methods. All samples worked within 20 consecutive days to compare external controls to built- in controls. All results were concordant as shown in table (): Table : Results of 29 CML patients validated with Mayoclinic No. MR# Lab # REF. % Log Xpert% Log Log Diff Status Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid Valid 27 CAP Valid MRD-20 A 28 CAP Valid 29 CAP04 MRD-20 B Valid 282
3 All results are concordant using the acceptance criterion of +/- 0.5 log 0 of the expected BCR/ABL relative quantitation. Linearity/ Reportable range: Linearity was verified by testing prepared BCR- ABL Mbcr fusion gene serial dilutions (00%, 0%, %, 0.% and 0.0%) using MRD A 20 CAP0 Sample. All results were within the putative acceptable criteria (0.5 Log difference) and the established linearity is % BCR/ABL to ABL (Table 2). Table 2: Verification of linearity of the assay n Sample ID Target Result Acceptable Range low high 00% % % % % Precision: Precision has been validated using 00% and 0.0% CAP samples 0 and 03 respectively. 00% and 0.0% samples were run in triplicate for two consecutive days. All results were with Coefficient of variability(cv)< 5% (Table3) Table 3: Precision of results with CV < 5% n Date 00% 0.0% /04/ /04/ Limit of Detection (LOD): We achieved 0.00% LOD, by diluting the CAP06 sample (0.0) :0, and testing it in four replicates, all results were positive (Detected) as shown in table (4). Table 4: Limit of detection of the assay LOD Ratio % 0.00% Average S.D Positive/Total confidence interval % /4 >95% Recovery / Interferences: Known BCR/ABL RNA Negative (0%) samples were selected and spiked with known positive t(2;2), t(5;7) RNA samples. No interference of t(2;2) or t(5;7) RNA was detected. Clinical Performance Criteria: The clinical sensitivity and specificity of the test are 00% (Table ). The 2x2 contingency table below shows the agreement of BCR-ABL quantitative results between KFSHD and reference method showing our lab sensitivity and specificity to be 00% (table 5). Table 5: Comparison of BCR/ABL p20 detection assay at KFSHD and the reference method*: Reference * BCR ABL Quant Detected Not Detected Total KFSH-D Detected BCR-ABL Quant Not Detected Total * Reference method: Mayo Clinic Laboratories and Ipsogen results. Diagnostic Specificity = Diagnostic Sensitivity = 283
4 4. Discussion: During imatinibmesylate therapy, more than 70% of patients achieve CCR (). A major molecular response exceeding 3 logs of BCR-ABL transcript reduction from the reference baseline in RT-PCR studies associates with excellent progression-free survival (2,3). However, a minority of such patients relapse (4). The predominant mechanism of imatinib resistance is point mutations in the BCR-ABL kinase domain, which impair optimal imatinib binding to its target (5-7).Thus sensitive monitoring of minimal residual disease is of major importance and early recognition of patients at higher risk of relapse could trigger more intense follow up and help expedite necessary changes to therapeutic strategies, including dose modification or shifting to second line kinase inhibitors (8,9). RT-PCR is by far the most sensitive technique for monitoring CML patient response, in addition to the feasibility of being performed on peripheral blood samples, being therefore less invasive than techniques that require bone marrow aspirate (20). Increasing levels of BCR-ABL transcripts may indicate loss of response to imatinib or relapse after transplantation (2, 22). There was a clear need for standardization of measurement of BCR-ABL transcripts by RT-PCR by different laboratories. The IRIS trial established a standard baseline for measurement (00% BCR-ABL on the international scale) and a major molecular response (MMR, good response to therapy) was defined as a 3 log reduction in the amount of BCR- ABL (0.% BCR-ABL on the international scale). Laboratories wishing to align their results with the international scale could do so by exchanging samples with the Adelaide laboratory, Australia, and by this process, conversion factors are established for different laboratories (8). GeneXpert introduced by Cepheid identifies leukemia cells harboring the BCR-ABL gene fusion through a self-contained automated instrument which integrates microfluidic sample preparation with RT- PCR based real time fluorescent signal detection (0). KFSHD uses the Cepheid GeneXpert BCR-ABL fusion detection system as an alternative to current clinical diagnostic tools for CML patients monitoring for minimal residual disease. To align the results of any laboratory using the GeneXpert system, the system automatically calculates the BCR-ABL copies and multiplies them by the Cepheid international scale, which is stated in the certificate of analysis provided with each kit. Our experience in KFSHD, which was gained after thorough validation studies of our results with Mayoclinic, revealed that better validation of the our results were obtained when we cancelled the Cepheid international scale and multiplied the results by the Mayoclinic factor, which is equal to It is noteworthy that Mayoclinic validates its results with the reference laboratory, which is Adelaide laboratory in Australia. Conclusion: Standardization of RT-PCR results of BCR-ABL copies detected by various laboratories throughout the world is of utmost importance for the alignment of the results. Comparable results are mandatory for facilitating patient monitoring between clinics that use different testing laboratories and consistent interpretation of clinical research data. KFSHD experience with the Cepheid fully automated BCR- ABL detection system revealed better alignment of results after cancelling the Cepheid international scale and applying our own calculated one. References:. Daley GQ, Van Etten RA, Baltimore D. Induction of chronic myelogenous leukemia in mice by the p20bcr/abl gene of the Philadelphia chromosome. Science 990;247: Baccarani M., Saglio G., Goldman J, Hochhaus A, Simonsson B, Applebaum F. Evolving concepts in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: recommendations from an expert panel on behalf of the European leukemianet. Blood 2006;08: Drucker BJ, Guilhot F, O'Brien SG, Gathman I, Kantarjan H, Gatterman N, Deininger M, Silver R, Goldman J, Stone R, Cervantes S, Hochhaus A, Powel B. Five year follow up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl j Med 2006;355: Iacobucci I, Saglio G, Rosti G, Testoni N, Pane F, Amabile M, Poerio A, Soverini S, Bassi S, Cilloni D, Bassan R, Breccia M, Lauria F, Izzo B, Merante S, Frassoni F, Paolini S, Montefusco E, Baccarani M, Martinelli G; GIMEMA Working Party on Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Achieving a major molecular response at the time of a complete cytogenetic response (CCgR) predicts a better duration of CCgR in imatinib treated chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Clin Cancer Res 2006;2: Ludan T, Juvonen V, Mueller M, Mustjoki S, Lakkala T, Kairisto V, Hochhaus A, Knuutila S, Porkka k. Comparison of bone marrow high mitotic index metaphase fluorescence in situ hybridization to peripheral blood and bone marrow real time quantitative polymerase chain reaction on the International Scale for detecting residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia. Hematologica 2008; 93(2): Jobbagy Z, van Atta R, Murphy K, Eshleman J, Gocke C. Evaluation of the Cepheid GeneXpert BCR-ABL assay. J MolDiag 2007; 9(2): Zhang T, Greiner S, Nwachukwu B, Wei C, Lipton J, Kamel-Reid S. Inter-laboratory comparison of 284
5 chronic myeloid leukemia minimal residual disease moinitoring: summary and recommendations. J MolDiag 2007;9: Branford S, Cross N, Hochhaus A, Radich j, Saglio G, Kaeda j, Goldman j, Hughes T. Rationale for the recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2006;20: Branford S, Fletcher L, Cross N, Muller M, Hochhaus A, Kim D, Radich J, Saglio G, Pane F, Kamel-Reid S, Wang Y, Press R, Lynch K, Rudzki Z, Goldman J, Hughes T. Desirable performance for BCR-ABL measurement on an international reporting scale to allow consistent interpretation of individual patient response and comparison of response rates between clinical trials. Blood 2008; 2: Raja S, Ching J, Hughes S, Chang R, Wong W, McMillan W, Gooding W, McCarty K, Chestney M, Luketich J, Godfrey T. Technology for automated, rapid and quantitative PCR or reverse transcription- PCR clinical testing. ClinChem 2005;5P O'Brien S, Guilhot E, Larsons R, Gathman I, Baccarani M, Cervantes F, Cornelissen J, Fischer T, Hochhaus J, Hughes T, Lechner k. Imatinib compared with interferon and low-dose cytarabine for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003;348: Hughes T, Kaeda J, Branford S, Rudzki Z, Hochhaus A, Hensley M,Gathmann I, Bolton A, van Hoomissen I, Goklman J, Radich j. Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferonalfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: Wang L, Knight K, Lucas C, Clark R. The role of serial BCR-ABL transcript monitoring in predicting the emergence of BCR-ABL kinase mutations in imatinib-treated patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2003;7: Press RD, Galderisi C, Yang R, Rempfer C, Willis SG, Mauro MJ, Druker BJ, Deininger M.A half-log increase in BCR-ABL RNA predicts relapse in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia with an imatinib-induced complete cytogenetic response. Clin Cancer Res 2007;3: Roy L, Guilhot J, Krahnke T,Guerci-Bresler A, Druker BJ, Larson RA, O'Brien S, So C, Massimini G, Guilhot F. Survival advantage from imatinib compared to the combination interferon-α plus cytarabine in chronic phase CML: historical comparison between two phase III trials. Blood 2006;08: Marin D, Kaeda J, Szydlo R, Saunders S, Fleming A, Howard J, Andreasson C, Bua M, Olavarria E, Rahemtulla A, Dazzi F, Kanfer E, Goldman J, Apperley J. Monitoring patients in complete cytogenetic remission after treatment of CML in chronic phase with imatinib: patterns of residual leukemia and prognostic factors for cytogenetic relapse. Leukemia 2005;9: Kantarjan H, Cortes J, O'Brien S, Luthra R, Giles F, Verstovsek S, Faderl S, Thomas D, Garcia-Manero G, Rios MB, Shan J, Jones D, Talpaz M. Long-term survival benefit and improved complete cytogenetic and molecular response rates withjimatinibmesylate in Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia after failure of interferonα. Blood 2004;04: Kantarjan H, Giles F, Wunderle L, Bhalla K, O'Brien S, Wassmann B, Tanaka C, Manley P, Rae P, Mietlowski W, Bochinski K, Hochhaus A, Griffin J, Hoelzer D, Albitar M, Dugan M, Cortes J, Alland L, Ottmann O. Nilotinib in imatinib-resistant CML and Philadelphia chromosome-positive ALL. N Engl J Med 2006;354: Talpaz M, Shah N, Kantarjian H, Donato N, Nicoll J, Paquette R, Cortes J, O'Brien S, Nicaise C, Bleickardt E, Blackwood-Chirchir A, Iyer V, Chen T, Huang F, Decillis A, Sawyers C. Dasatinib in imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemias. N Engl J Med 2006; 354: Metcalfe P, Gray E, Hawkins R, Rigsby P, A proposed st WHO international genetic reference panel for the quantitation of BCR-ABL translocation by RQ-PCR, NIBSC code 09/38. Expert committee on biological standardization. Geneva Olavarria E, Kanfer E, Szydlo R, Kaeda J, Rezvani K, Cwynarski K, Pocock C, Dazzi F, Craddock C, Apperley JF, Cross NC, Goldman J.Early detection of BCR-ABL transcripts by quantitative reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction predicts outcome after allogenic stem cell transplantation for chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 200;97: Kanatrjaian H,Talpaz M, Cortes J, O'Brien S, Faderl S, Thomas D, Giles F, Rios MB, Shan J, Arlinghaus R. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction monitoring of BCR-ABL during therapy with imatinibmesylate (ST57; gleevec) in chronic-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2003;9: //
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia
 Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Molecular Response: What is really important? Jeff Szer The Royal Melbourne Hospital PROBABILITY, % PROBABILITY OF SURVIVAL AFTER MYELOABLATIVE TRANSPLANTS FOR CML IN CHRONIC
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia Molecular Response: What is really important? Jeff Szer The Royal Melbourne Hospital PROBABILITY, % PROBABILITY OF SURVIVAL AFTER MYELOABLATIVE TRANSPLANTS FOR CML IN CHRONIC
The significance of major and stable molecular responses in chronic myeloid leukemia in the tyrosine kinase inhibitor era
 Review Article The significance of major and stable molecular responses in chronic myeloid leukemia in the tyrosine kinase inhibitor era Ilana Zalcberg Renault 1 Vanesa Scholl 1 Rocio Hassan 1 Paola Capelleti
Review Article The significance of major and stable molecular responses in chronic myeloid leukemia in the tyrosine kinase inhibitor era Ilana Zalcberg Renault 1 Vanesa Scholl 1 Rocio Hassan 1 Paola Capelleti
MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1)
 MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1) Moleculaire Biologie en Cytometrie cursus Barbara Denys LAbo Hematologie UZ Gent 6 mei 2011 2008 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 1 Myeloproliferative Neoplasms o WHO classification 2008:
MRD in CML (BCR-ABL1) Moleculaire Biologie en Cytometrie cursus Barbara Denys LAbo Hematologie UZ Gent 6 mei 2011 2008 Universitair Ziekenhuis Gent 1 Myeloproliferative Neoplasms o WHO classification 2008:
Talpaz M. et al. Dasatinib in Imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosomepositive leukemias. N Engl J Med (2006) 354;24:
 References Sprycel Talpaz M. et al. Dasatinib in Imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosomepositive leukemias. N Engl J Med (2006) 354;24:2531-2541. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical Practice
References Sprycel Talpaz M. et al. Dasatinib in Imatinib-resistant Philadelphia chromosomepositive leukemias. N Engl J Med (2006) 354;24:2531-2541. National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical Practice
CML CML CML. tyrosine kinase inhibitor CML. 22 t(9;22)(q34;q11) chronic myeloid leukemia CML ABL. BCR-ABL c- imatinib mesylate CML CML BCR-ABL
 1 Key Wordschronic myeloid leukemiaimatinib mesylate tyrosine kinase inhibitor chronic myeloid leukemia CML imatinib mesylate CML CML CML CML Ph 10 1 30 50 3 5 CML α IFNα Ph Ph cytogenetic response CRmajor
1 Key Wordschronic myeloid leukemiaimatinib mesylate tyrosine kinase inhibitor chronic myeloid leukemia CML imatinib mesylate CML CML CML CML Ph 10 1 30 50 3 5 CML α IFNα Ph Ph cytogenetic response CRmajor
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML
 Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
Molecular Detection of BCR/ABL1 for the Diagnosis and Monitoring of CML Imran Mirza, MD, MS, FRCPC Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Institute Sheikh Khalifa Medical City, Abu Dhabi, UAE. imirza@skmc.ae
The BCR-ABL1 fusion. Epidemiology. At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine
 At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia Robert E. Richard MD PhD rrichard@uw.edu robert.richard@va.gov Philadelphia chromosome
At the center of advances in hematology and molecular medicine Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia Robert E. Richard MD PhD rrichard@uw.edu robert.richard@va.gov Philadelphia chromosome
How I monitor residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia
 CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS How I treat How I monitor residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia Jerald P. Radich 1 1 Clinical Research Division, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle,
CLINICAL TRIALS AND OBSERVATIONS How I treat How I monitor residual disease in chronic myeloid leukemia Jerald P. Radich 1 1 Clinical Research Division, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle,
"Molecular Monitoring Strategies to Track Response to BCR-ABL Kinase Inhibitors in CML"
 Association of Molecular Pathology USCAP Companion Meeting Sunday, February 12, 2006 7:00 PM Dan Jones, MD, PhD Associate Professor Medical Director, Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory Division of Pathology
Association of Molecular Pathology USCAP Companion Meeting Sunday, February 12, 2006 7:00 PM Dan Jones, MD, PhD Associate Professor Medical Director, Molecular Diagnostic Laboratory Division of Pathology
35 Current Trends in the
 35 Current Trends in the Management of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Abstract: CML is a hematopoietic stem cell disease which is characterized by the presence of Philadelphia chromosome (Ph-chromosome)
35 Current Trends in the Management of Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Abstract: CML is a hematopoietic stem cell disease which is characterized by the presence of Philadelphia chromosome (Ph-chromosome)
Radowan Elnair 1 and Ahmed Galal 2*
 Elnair and Galal BMC Cancer (2018) 18:1097 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5004-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Finding the right BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor: a case report of successful treatment
Elnair and Galal BMC Cancer (2018) 18:1097 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5004-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Finding the right BCR-ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor: a case report of successful treatment
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Introduction. Methods Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
 BCR/ABL level at 6 months identifies good risk CML subgroup after failing early molecular response at 3 months following imatinib therapy for CML in chronic phase AJH Dennis (Dong Hwan) Kim, 1 * Nada Hamad,
BCR/ABL level at 6 months identifies good risk CML subgroup after failing early molecular response at 3 months following imatinib therapy for CML in chronic phase AJH Dennis (Dong Hwan) Kim, 1 * Nada Hamad,
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Session Chair: Armand Keating, MD Speakers: Timothy Hughes, MD, MBBS; Michael J. Mauro, MD; and Jane F. Apperley, MBChB ABL Kinase Inhibitor Therapy for CML: Baseline Assessments
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Session Chair: Armand Keating, MD Speakers: Timothy Hughes, MD, MBBS; Michael J. Mauro, MD; and Jane F. Apperley, MBChB ABL Kinase Inhibitor Therapy for CML: Baseline Assessments
When to change therapy? Andreas Hochhaus Universitätsklinikum Jena, Germany
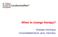 When to change therapy? Andreas Hochhaus Universitätsklinikum Jena, Germany Chromosome 22 Chromosome 9 e1 1b m-bcr M-bcr e1 e2 b1 b5 5 3 BCR ABL 5 3 1a a2 a3 μ -bcr e19 a11 e1a2 b2a2 b3a2 e19a2 p190 bcr-abl
When to change therapy? Andreas Hochhaus Universitätsklinikum Jena, Germany Chromosome 22 Chromosome 9 e1 1b m-bcr M-bcr e1 e2 b1 b5 5 3 BCR ABL 5 3 1a a2 a3 μ -bcr e19 a11 e1a2 b2a2 b3a2 e19a2 p190 bcr-abl
Response to treatment with imatinib mesylate in previously treated chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients in a hospital in Brazil
 Response to treatment with imatinib mesylate in previously treated chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients in a hospital in Brazil C.A.P. Silveira 1, M.B. Daldegan 1 and I. Ferrari 2 1 Núcleo de
Response to treatment with imatinib mesylate in previously treated chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients in a hospital in Brazil C.A.P. Silveira 1, M.B. Daldegan 1 and I. Ferrari 2 1 Núcleo de
Imatinib Mesylate in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Local Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imatinib Mesylate in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Local Experience PC Bee, MMed*, G G Gan, MRCP*, A Teh, FRCP**, A R Haris, MRCP* *Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imatinib Mesylate in the Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: A Local Experience PC Bee, MMed*, G G Gan, MRCP*, A Teh, FRCP**, A R Haris, MRCP* *Department of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine,
Kinetics of BCR-ABL Transcripts in Imatinib Mesylate treated Chronic Phase CML (CPCML), A Predictor of Response and Progression Free Survival
 International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kinetics of BCR-ABL Transcripts in Imatinib Mesylate treated Chronic Phase CML (CPCML), A Predictor of Response and Progression Free Survival
International journal of Biomedical science ORIGINAL ARTICLE Kinetics of BCR-ABL Transcripts in Imatinib Mesylate treated Chronic Phase CML (CPCML), A Predictor of Response and Progression Free Survival
EUROPEAN LEUKEMIANET RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA
 EUROPEAN LEUKEMIANET RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA SAN DIEGO, 11 DECEMBER 2011 AMSTERDAM, 14 JUNE 2012 BALTIMORE, 20 SEPTEMBER 2012 ATLANTA, 6 DECEMBER 2012 ELN, CML Panel Jane Apperley
EUROPEAN LEUKEMIANET RECOMMENDATIONS FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA SAN DIEGO, 11 DECEMBER 2011 AMSTERDAM, 14 JUNE 2012 BALTIMORE, 20 SEPTEMBER 2012 ATLANTA, 6 DECEMBER 2012 ELN, CML Panel Jane Apperley
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2018 Related Policies: None BCR-ABL1 Testing in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Description In the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome positive leukemias,
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2018 Related Policies: None BCR-ABL1 Testing in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Description In the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome positive leukemias,
An update on imatinib mesylate therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients in a teaching hospital in Malaysia
 Singapore Med J 2012; 53(1) : 57 An update on imatinib mesylate therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients in a teaching hospital in Malaysia Bee PC 1, MD, MMed, Gan GG 1, MBBS, FRCP, Tai YT 1, MBBS,
Singapore Med J 2012; 53(1) : 57 An update on imatinib mesylate therapy in chronic myeloid leukaemia patients in a teaching hospital in Malaysia Bee PC 1, MD, MMed, Gan GG 1, MBBS, FRCP, Tai YT 1, MBBS,
Cancer Biology 2017;7(3)
 Retrospective preliminary study on the magnitude of q-rt-pcr for BCR-ABL over FISH BCR-ABL in follow up of CML patient receiving First Line TKI Therapy Mohammed Al-Sayegh 1, 2, Hani Al Hashmi 1, Omar Abduljali
Retrospective preliminary study on the magnitude of q-rt-pcr for BCR-ABL over FISH BCR-ABL in follow up of CML patient receiving First Line TKI Therapy Mohammed Al-Sayegh 1, 2, Hani Al Hashmi 1, Omar Abduljali
KEY WORDS Chronic myelogenous leukemia Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Relapse Imatinib mesylate Minimal residual disease
 Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 10:718-725 (2004) 2004 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/04/1010-0007$30.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2004.06.033 Early Prediction of
Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation 10:718-725 (2004) 2004 American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation 1083-8791/04/1010-0007$30.00/0 doi:10.1016/j.bbmt.2004.06.033 Early Prediction of
Monitor TM assay: comparison with traditional RT-qPCR methods
 Preliminary evaluation of the GeneXpert Dx System for CML patients monitoring through the Xpert BCR-ABL Monitor TM assay: comparison with traditional RT-qPCR methods Silvia Calatroni Division of Hematology
Preliminary evaluation of the GeneXpert Dx System for CML patients monitoring through the Xpert BCR-ABL Monitor TM assay: comparison with traditional RT-qPCR methods Silvia Calatroni Division of Hematology
Review Article. Introduction
 Review Article Importance of monitoring and early switch to second generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the prognosis of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia with imatinib resistance or intolerance
Review Article Importance of monitoring and early switch to second generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the prognosis of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia with imatinib resistance or intolerance
Blast Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
 Blast Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Benjamin Powers, MD; and Suman Kambhampati, MD The dramatic improvement in survival with tyrosine kinase inhibitors has not been demonstrated in the advanced blast
Blast Phase Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Benjamin Powers, MD; and Suman Kambhampati, MD The dramatic improvement in survival with tyrosine kinase inhibitors has not been demonstrated in the advanced blast
MP BCR-ABL1 Testing in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
 Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.85 Last Review: 10/18/2018 Effective Date: 10/18/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 8.01.30 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Medical Policy BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.85 Last Review: 10/18/2018 Effective Date: 10/18/2018 Section: Medicine Related Policies 8.01.30 Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
Analytical and economic evaluation of the fully automated Xpert BCR-ABL assay from Cepheid
 Analytical and economic evaluation of the fully automated Xpert BCR-ABL assay from Cepheid Jean-Michel Cayuela Saint-Louis hospital Paris July 5, 2012 Talk outline Chronic myeloid leukemia > Genetic bases,
Analytical and economic evaluation of the fully automated Xpert BCR-ABL assay from Cepheid Jean-Michel Cayuela Saint-Louis hospital Paris July 5, 2012 Talk outline Chronic myeloid leukemia > Genetic bases,
Adecade ago imatinib mesylate, the first tyrosine
 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA: AFTER A DECADE OF IMATIINIB Monitoring disease response to tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in CML Timothy P. Hughes 1 and Susan Branford 1 1 Centre for Cancer Biology, Departments
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA: AFTER A DECADE OF IMATIINIB Monitoring disease response to tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy in CML Timothy P. Hughes 1 and Susan Branford 1 1 Centre for Cancer Biology, Departments
Measuring Response to BCR-ABL Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 Review Article Measuring Response to BCR-ABL Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Jerald P. Radich, MD In patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), the hallmark Philadelphia chromosome is the marker
Review Article Measuring Response to BCR-ABL Inhibitors in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Jerald P. Radich, MD In patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), the hallmark Philadelphia chromosome is the marker
NEW DRUGS IN HEMATOLOGY
 NEW DRUGS IN HEMATOLOGY BOLOGNA, 15-17 April 2013 TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITORS IN CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA MICHELE BACCARANI michele.baccarani@unibo.it Historic Development of CML Therapy Palliative Therapy
NEW DRUGS IN HEMATOLOGY BOLOGNA, 15-17 April 2013 TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITORS IN CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA MICHELE BACCARANI michele.baccarani@unibo.it Historic Development of CML Therapy Palliative Therapy
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+)
 Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
Template for Reporting Results of Monitoring Tests for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (BCR-ABL1+) Version: CMLBiomarkers 1.0.0.2 Protocol Posting Date: June 2017 This biomarker template is
Milestones and Monitoring
 Curr Hematol Malig Rep (2015) 10:167 172 DOI 10.1007/s11899-015-0258-1 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIAS (E JABBOUR, SECTION EDITOR) Milestones and Monitoring Alessandro Morotti 1 & Carmen Fava 1 & Giuseppe Saglio
Curr Hematol Malig Rep (2015) 10:167 172 DOI 10.1007/s11899-015-0258-1 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIAS (E JABBOUR, SECTION EDITOR) Milestones and Monitoring Alessandro Morotti 1 & Carmen Fava 1 & Giuseppe Saglio
Imatinib Mesylate (Glivec) in Pediatric Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imatinib Mesylate (Glivec) in Pediatric Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Bahoush Gr, 1 Alebouyeh M, 2 Vossough P 1 1 Pediatric Hematology-Oncology Department, Ali-Asghar Children's Hospital,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Imatinib Mesylate (Glivec) in Pediatric Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Bahoush Gr, 1 Alebouyeh M, 2 Vossough P 1 1 Pediatric Hematology-Oncology Department, Ali-Asghar Children's Hospital,
Managing Relapse of CML Using Therapeutic Imatinib Plasma Level
 H&0 CLINICAL CASE STUDIES Managing Relapse of CML Using Therapeutic Imatinib Plasma Level Adedayo A. Onitilo, MD, MSCR, FACP 1 Jessica M. Engel, MSN, FNP-BC 2 Department of Hematology/Oncology, 1 Marshfield
H&0 CLINICAL CASE STUDIES Managing Relapse of CML Using Therapeutic Imatinib Plasma Level Adedayo A. Onitilo, MD, MSCR, FACP 1 Jessica M. Engel, MSN, FNP-BC 2 Department of Hematology/Oncology, 1 Marshfield
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Disease of Young at Heart but Not of Body
 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Disease of Young at Heart but Not of Body Jeffrey H Lipton, PhD MD FRCPC Staff Physician, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Professor of Medicine University of Toronto POGO November,
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia A Disease of Young at Heart but Not of Body Jeffrey H Lipton, PhD MD FRCPC Staff Physician, Princess Margaret Cancer Centre Professor of Medicine University of Toronto POGO November,
Chronic myeloid leukemia (CML)
 Bioscientia Int. Support Services Dept. Konrad-Adenauer-Strasse 17 55218 Ingelheim Germany Phone 49(0)6132-781-203 49(0)6132-781-224 49(0)6132-781-165 Fax 49(0)6132-781-236 int.support@bioscientia.com
Bioscientia Int. Support Services Dept. Konrad-Adenauer-Strasse 17 55218 Ingelheim Germany Phone 49(0)6132-781-203 49(0)6132-781-224 49(0)6132-781-165 Fax 49(0)6132-781-236 int.support@bioscientia.com
Persistent splenomegaly during imatinib therapy and the definition of complete hematological response in chronic myelogenous leukemia
 Persistent splenomegaly during imatinib therapy and the definition of complete hematological response in chronic myelogenous leukemia Zdenek Racil, Hana Klamova, Jaroslava Voglova, Edgar Faber, Filip Razga,
Persistent splenomegaly during imatinib therapy and the definition of complete hematological response in chronic myelogenous leukemia Zdenek Racil, Hana Klamova, Jaroslava Voglova, Edgar Faber, Filip Razga,
Clinical Significance of ABL Kinase Domain Mutation in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia under Imatinib Therapy.
 Clinical Significance of ABL Kinase Domain Mutation in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia under Imatinib Therapy 1 Amr A.Ghannam, Abdou S. M. 2 and Mona Hatata 2 1 Department of Clinical Oncology, Tanta university
Clinical Significance of ABL Kinase Domain Mutation in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia under Imatinib Therapy 1 Amr A.Ghannam, Abdou S. M. 2 and Mona Hatata 2 1 Department of Clinical Oncology, Tanta university
CML EHA: what s new? Novità dall EHA >> [ Leucemia mieloide cronica ] Relatore: G. MARTINELLI. Borgo S. Luigi Monteriggioni (Siena) ottobre 2008
![CML EHA: what s new? Novità dall EHA >> [ Leucemia mieloide cronica ] Relatore: G. MARTINELLI. Borgo S. Luigi Monteriggioni (Siena) ottobre 2008 CML EHA: what s new? Novità dall EHA >> [ Leucemia mieloide cronica ] Relatore: G. MARTINELLI. Borgo S. Luigi Monteriggioni (Siena) ottobre 2008](/thumbs/75/71485931.jpg) Novità dall EHA >> [ Leucemia mieloide cronica ] CML EHA: what s new? Relatore: G. MARTINELLI 27-28 ottobre 2008 Borgo S. Luigi Monteriggioni (Siena) Leucemia mieloide cronica - Copyright FSE 1 CML EHA:
Novità dall EHA >> [ Leucemia mieloide cronica ] CML EHA: what s new? Relatore: G. MARTINELLI 27-28 ottobre 2008 Borgo S. Luigi Monteriggioni (Siena) Leucemia mieloide cronica - Copyright FSE 1 CML EHA:
Recent advances in the path toward the cure for chronic myeloid leukemia
 VOLUME 46 ㆍ NUMBER 3 ㆍ September 2011 THE KOREAN JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY REVIEW ARTICLE Recent advances in the path toward the cure for chronic myeloid leukemia Dong-Wook Kim Department of Hematology, Seoul
VOLUME 46 ㆍ NUMBER 3 ㆍ September 2011 THE KOREAN JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY REVIEW ARTICLE Recent advances in the path toward the cure for chronic myeloid leukemia Dong-Wook Kim Department of Hematology, Seoul
Patient With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Complete Cytogenetic Response: What Does It Mean, and What Does One Do Next?
 VOLUME 32 NUMBER 5 FEBRUARY 10 2014 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY ONCOLOGY GRAND ROUNDS Patient With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Complete Cytogenetic Response: What Does It Mean, and What Does One Do Next?
VOLUME 32 NUMBER 5 FEBRUARY 10 2014 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY ONCOLOGY GRAND ROUNDS Patient With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in Complete Cytogenetic Response: What Does It Mean, and What Does One Do Next?
Greater Manchester and Cheshire Cancer Network Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia v3 2012
 Greater Manchester and Cheshire Cancer Network Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia v3 2012 Dr Simon Watt Dr Shiva Natarajan 1.0 Introduction The landscape in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) has changed dramatically
Greater Manchester and Cheshire Cancer Network Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia v3 2012 Dr Simon Watt Dr Shiva Natarajan 1.0 Introduction The landscape in chronic myeloid leukaemia (CML) has changed dramatically
A 34-year old women came because of abdominal discomfort. Vital sign was stable. Spleen tip was palpable.
 1 Case 1 A 34-year old women came because of abdominal discomfort. Vital sign was stable. Spleen tip was palpable. CBC and bone marrow aspiration and biopsy were done. Chromosome study showed she had t(9;22)
1 Case 1 A 34-year old women came because of abdominal discomfort. Vital sign was stable. Spleen tip was palpable. CBC and bone marrow aspiration and biopsy were done. Chromosome study showed she had t(9;22)
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML): resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors
 17 (Supplement 10): x274 x279, 2006 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdl273 Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML): resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors A. Hochhaus III Medizinische Klinik, Medizinische Fakultät Mannheim
17 (Supplement 10): x274 x279, 2006 doi:10.1093/annonc/mdl273 Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML): resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors A. Hochhaus III Medizinische Klinik, Medizinische Fakultät Mannheim
Laboratory Tools for Diagnosis and Monitoring Response in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
 in chromosome Laboratory Tools for Diagnosis and Monitoring Response in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Tali Tohami PhD 1, Arnon Nagler MD 2,3 and Ninette Amariglio PhD 1 1 Hematology Laboratory
in chromosome Laboratory Tools for Diagnosis and Monitoring Response in Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Tali Tohami PhD 1, Arnon Nagler MD 2,3 and Ninette Amariglio PhD 1 1 Hematology Laboratory
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) is a slowprogressing
 At a Glance Practical Implications p e148 Author Information p e151 Full text and PDF Web exclusive Patterns of Specific Testing for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Original Research Allison
At a Glance Practical Implications p e148 Author Information p e151 Full text and PDF Web exclusive Patterns of Specific Testing for Patients With Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Original Research Allison
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Research Paper
 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Research Paper The impact of the combination of baseline risk group and cytogenetic response on the survival of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with interferon-α
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Research Paper The impact of the combination of baseline risk group and cytogenetic response on the survival of patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with interferon-α
Dynamics of chronic myeloid leukemia response to dasatinib, nilotinib, and high-dose imatinib
 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Dynamics of chronic myeloid leukemia response to dasatinib, nilotinib, and high-dose imatinib ARTICLES Adam Olshen, * Min Tang, * Jorge Cortes, Mithat Gonen, Timothy Hughes, Susan
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Dynamics of chronic myeloid leukemia response to dasatinib, nilotinib, and high-dose imatinib ARTICLES Adam Olshen, * Min Tang, * Jorge Cortes, Mithat Gonen, Timothy Hughes, Susan
Chronic myeloid leukemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up
 clinical practice guidelines Annals of Oncology 23 (Supplement 7): vii72 vii77, 2012 doi:10.1093/annonc/mds228 Chronic myeloid leukemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up
clinical practice guidelines Annals of Oncology 23 (Supplement 7): vii72 vii77, 2012 doi:10.1093/annonc/mds228 Chronic myeloid leukemia: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up
Molecular monitoring of CML patients
 EHA, Education Session, CML Stockholm, 14 June 2013 Molecular monitoring of CML patients Martin C. Müller Medical Faculty Mannheim Ruprecht-Karls-University Heidelberg Mannheim, Germany Disclosures Research
EHA, Education Session, CML Stockholm, 14 June 2013 Molecular monitoring of CML patients Martin C. Müller Medical Faculty Mannheim Ruprecht-Karls-University Heidelberg Mannheim, Germany Disclosures Research
Starting & stopping therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What more is needed? Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago March 2019
 Starting & stopping therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What more is needed? Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago March 2019 Disclosures Richard A. Larson, MD Research funding to the University
Starting & stopping therapy in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What more is needed? Richard A. Larson, MD University of Chicago March 2019 Disclosures Richard A. Larson, MD Research funding to the University
Molecular Monitoring of Residual Disease in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia by Genomic DNA Compared with Conventional mrna Analysis
 Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, Vol. 11, No. 5, September 2009 Copyright American Society for Investigative Pathology and the Association for Molecular Pathology DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2009.080150 Molecular
Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, Vol. 11, No. 5, September 2009 Copyright American Society for Investigative Pathology and the Association for Molecular Pathology DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2009.080150 Molecular
Cancer Biology 2016;6(1) Imatinib Mesylate Effectiveness in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia patients in Upper Egypt. Mervat M.
 Imatinib Mesylate Effectiveness in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia patients in Upper Egypt Mervat M. Omar Department of Oncology, Assuit University Hospital, Assuit, Egypt drmervatomar@yahoo.com Abstract: Background
Imatinib Mesylate Effectiveness in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia patients in Upper Egypt Mervat M. Omar Department of Oncology, Assuit University Hospital, Assuit, Egypt drmervatomar@yahoo.com Abstract: Background
Guidelines and real World: Management of CML in chronic and advanced phases. Carolina Pavlovsky. FUNDALEU May 2017 Frankfurt
 Guidelines and real World: Management of CML in chronic and advanced phases Carolina Pavlovsky. FUNDALEU 26-28 May 217 Frankfurt Some Issues in CML 217 First Line treatment: Imatinib vs 2nd generation
Guidelines and real World: Management of CML in chronic and advanced phases Carolina Pavlovsky. FUNDALEU 26-28 May 217 Frankfurt Some Issues in CML 217 First Line treatment: Imatinib vs 2nd generation
Suboptimal Response to or Failure of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What Is the Optimal Strategy?
 REVIEW IMATINIB TREATMENT FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Suboptimal Response to or Failure of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What Is the Optimal Strategy? ELIAS JABBOUR, MD; JORGE E. CORTES,
REVIEW IMATINIB TREATMENT FOR CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Suboptimal Response to or Failure of Imatinib Treatment for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: What Is the Optimal Strategy? ELIAS JABBOUR, MD; JORGE E. CORTES,
Stopping TKI s in CML- Are we There Yet? Joseph O. Moore, MD Duke Cancer Institute
 Stopping TKI s in CML- Are we There Yet? Joseph O. Moore, MD Duke Cancer Institute Natural History of CML Accumulation of immature myeloid cells New cytogenetic changes Chronic Phase Accelerated Phase
Stopping TKI s in CML- Are we There Yet? Joseph O. Moore, MD Duke Cancer Institute Natural History of CML Accumulation of immature myeloid cells New cytogenetic changes Chronic Phase Accelerated Phase
Implementation of Management Guidelines
 Implementation of Management Guidelines For Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Perspectives in the United States David Rizzieri, MD; and Joseph O. Moore, MD ABSTRACT Clinical practice guidelines are developed to
Implementation of Management Guidelines For Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Perspectives in the United States David Rizzieri, MD; and Joseph O. Moore, MD ABSTRACT Clinical practice guidelines are developed to
Dynamics of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Supplementary Online Material
 Dynamics of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Supplementary Online Material Franziska Michor, Timothy P. Hughes, Yoh Iwasa, Susan Branford, Neil P. Shah, Charles L. Sawyers & Martin A. Nowak The basic model. Our
Dynamics of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Supplementary Online Material Franziska Michor, Timothy P. Hughes, Yoh Iwasa, Susan Branford, Neil P. Shah, Charles L. Sawyers & Martin A. Nowak The basic model. Our
Loss of Response to Imatinib: Mechanisms and Management
 Loss of Response to Imatinib: Mechanisms and Management Neil P. Shah The treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has been revolutionized by the small molecule BCR-ABLselective kinase inhibitor imatinib.
Loss of Response to Imatinib: Mechanisms and Management Neil P. Shah The treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) has been revolutionized by the small molecule BCR-ABLselective kinase inhibitor imatinib.
FEP Medical Policy Manual
 FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2019 Related Policies: None BCR-ABL1 Testing in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Acute Description In the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome positive
FEP Medical Policy Manual Effective Date: January 15, 2019 Related Policies: None BCR-ABL1 Testing in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia and Acute Description In the treatment of Philadelphia chromosome positive
Research Article The Hasford Score May Predict Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients: A Single Institution Experience
 Disease Markers Volume 216, Article ID 7531472, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/7531472 Research Article The Hasford Score May Predict Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients: A Single
Disease Markers Volume 216, Article ID 7531472, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/216/7531472 Research Article The Hasford Score May Predict Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients: A Single
Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/12 Next Review Date: 03/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 03/10, 03/11, 03/12
 Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous (80130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/12 Next Review Date: 03/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 03/10, 03/11,
Hematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myelogenous (80130) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/12 Next Review Date: 03/13 Preauthorization* Yes Review Dates: 04/07, 05/08, 03/10, 03/11,
Abstract and Introduction
 Tomado con permiso de www.medscape.com From Cancer Control: Journal of the Moffitt Cancer Center Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia:
Tomado con permiso de www.medscape.com From Cancer Control: Journal of the Moffitt Cancer Center Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for Chronic Myeloid Leukemia:
Introduction NEOPLASIA
 NEOPLASIA Desirable performance characteristics for BCR-ABL measurement on an international reporting scale to allow consistent interpretation of individual patient response and comparison of response
NEOPLASIA Desirable performance characteristics for BCR-ABL measurement on an international reporting scale to allow consistent interpretation of individual patient response and comparison of response
C Longer follow up on IRIS data
 hronic Myeloid Leukemia Drs. Rena Buckstein, Mervat Mahrous & Eugenia Piliotis with input from Dr. J. Lipton (PMH) Updated August 2008* Updates: C Longer follow up on IRIS data Guidelines for monitoring
hronic Myeloid Leukemia Drs. Rena Buckstein, Mervat Mahrous & Eugenia Piliotis with input from Dr. J. Lipton (PMH) Updated August 2008* Updates: C Longer follow up on IRIS data Guidelines for monitoring
Journal of Molecular Biology Research Vol. 1, No. 1; December 2011
 Evaluation of Molecular Response to Imatinib in Iraqi Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Using Real Time Reveres Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-RT-PCR) Taqman Assay Maysaa Abdul Razzaq Dhahii
Evaluation of Molecular Response to Imatinib in Iraqi Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Patients Using Real Time Reveres Transcriptase-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-RT-PCR) Taqman Assay Maysaa Abdul Razzaq Dhahii
Molecular monitoring in CML and the prospects for treatment-free remissions
 MANAGING TYPICAL AND ATYPICAL CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Molecular monitoring in CML and the prospects for treatment-free remissions Michael W. Deininger 1,2 1 Huntsman Cancer Institute, The University of
MANAGING TYPICAL AND ATYPICAL CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Molecular monitoring in CML and the prospects for treatment-free remissions Michael W. Deininger 1,2 1 Huntsman Cancer Institute, The University of
Studying First Line Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) in a Real-world Setting (SIMPLICITY)
 A service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health Studying First Line Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) in a Real-world Setting (SIMPLICITY) This study is currently recruiting participants.
A service of the U.S. National Institutes of Health Studying First Line Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) in a Real-world Setting (SIMPLICITY) This study is currently recruiting participants.
Tomonaga, Masao; Miyazaki, Yasushi. available at
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Successful treatment of a chronic-p myelogenous leukemia patient with a interferon-alfa Itonaga, Hidehiro; Tsushima, Hideki Imanishi, Daisuke;
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Citation Successful treatment of a chronic-p myelogenous leukemia patient with a interferon-alfa Itonaga, Hidehiro; Tsushima, Hideki Imanishi, Daisuke;
Molecular monitoring in chronic myeloid leukemia how low can you go?
 CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Molecular monitoring in chronic myeloid leukemia how low can you go? Susan Branford Department of Genetics and Molecular Pathology, Centre for Cancer Biology, SA Pathology, Adelaide,
CHRONIC MYELOID LEUKEMIA Molecular monitoring in chronic myeloid leukemia how low can you go? Susan Branford Department of Genetics and Molecular Pathology, Centre for Cancer Biology, SA Pathology, Adelaide,
In this issue of the journal two articles deal with different
 EDITORIALS & PERSPECTIVES Monitoring treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia Michele Baccarani, 1 Fabrizio Pane, 2 and Giuseppe Saglio 3 1 Department of Hematology-Oncology "L. and A. Seràgnoli" University
EDITORIALS & PERSPECTIVES Monitoring treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia Michele Baccarani, 1 Fabrizio Pane, 2 and Giuseppe Saglio 3 1 Department of Hematology-Oncology "L. and A. Seràgnoli" University
Research Article The Use of Imatinib Mesylate as a Lifesaving Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Relapse after Bone Marrow Transplantation
 Transplantation Volume 2009, Article ID 357093, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/357093 Research Article The Use of Imatinib Mesylate as a Lifesaving Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Relapse after Bone Marrow
Transplantation Volume 2009, Article ID 357093, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2009/357093 Research Article The Use of Imatinib Mesylate as a Lifesaving Treatment of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Relapse after Bone Marrow
CML and Future Perspective. Hani Al-Hashmi, MD
 CML and Future Perspective Hani Al-Hashmi, MD Objectives Learning from CML history Outcome of interest to clinician Patient and community interest!! Learning from CML history Survival Probability (All
CML and Future Perspective Hani Al-Hashmi, MD Objectives Learning from CML history Outcome of interest to clinician Patient and community interest!! Learning from CML history Survival Probability (All
Special Article. A Report of the Association for Molecular Pathology
 JMD CME Program Special Article Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, Vol. 11, No. 1, January 2009 Copyright American Society for Investigative Pathology and the Association for Molecular Pathology DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2009.080095
JMD CME Program Special Article Journal of Molecular Diagnostics, Vol. 11, No. 1, January 2009 Copyright American Society for Investigative Pathology and the Association for Molecular Pathology DOI: 10.2353/jmoldx.2009.080095
IN PHILADELPHIA CHROMOSOME positive (Ph )
 Targeted Therapies in the Treatment of Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Dieter Hoelzer, Nicola Gökbuget, and Oliver G. Ottmann Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec, Novartis Pharmaceuticals
Targeted Therapies in the Treatment of Philadelphia Chromosome Positive Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Dieter Hoelzer, Nicola Gökbuget, and Oliver G. Ottmann Imatinib mesylate (Gleevec, Novartis Pharmaceuticals
Nilotinib in Imatinib-Resistant CML and Philadelphia Chromosome Positive ALL
 The new england journal of medicine original article Nilotinib in Imatinib-Resistant CML and Philadelphia Chromosome Positive ALL Hagop Kantarjian, M.D., Francis Giles, M.D., Lydia Wunderle, M.D., Kapil
The new england journal of medicine original article Nilotinib in Imatinib-Resistant CML and Philadelphia Chromosome Positive ALL Hagop Kantarjian, M.D., Francis Giles, M.D., Lydia Wunderle, M.D., Kapil
Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Research Paper
 [haematologica] 2004;89:49-57 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Research Paper Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction should not replace conventional cytogenetics for monitoring patients with
[haematologica] 2004;89:49-57 Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Research Paper Quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction should not replace conventional cytogenetics for monitoring patients with
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) By DEISSEROTH READ ONLINE
 Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) By DEISSEROTH READ ONLINE If searched for the ebook by DEISSEROTH Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) in pdf format, in that case you come on to correct
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) By DEISSEROTH READ ONLINE If searched for the ebook by DEISSEROTH Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (Hematology) in pdf format, in that case you come on to correct
10 YEARS EXPERIENCE OF TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR THERAPY FOR CML IN OXFORD
 10 YEARS EXPERIENCE OF TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR THERAPY FOR CML IN OXFORD Dalia Khan 1, Noemi Roy 1, Vasha Bari 1, Grant Vallance 1, Helene Dreau 1, Timothy Littlewood 1, Andrew Peniket 1, Paresh Vyas
10 YEARS EXPERIENCE OF TYROSINE KINASE INHIBITOR THERAPY FOR CML IN OXFORD Dalia Khan 1, Noemi Roy 1, Vasha Bari 1, Grant Vallance 1, Helene Dreau 1, Timothy Littlewood 1, Andrew Peniket 1, Paresh Vyas
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Efficacy of escalated imatinib combined with cytarabine in newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukemia Deenik, W.; Janssen, J.J.W.M.; van der Holt, B.;
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Efficacy of escalated imatinib combined with cytarabine in newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukemia Deenik, W.; Janssen, J.J.W.M.; van der Holt, B.;
Should nilotinib replace imatinib as first line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP)?
 Should nilotinib replace imatinib as first line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP)? http://test.metromomsblog.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/tortoise-and-the-hare.jpg D. Van
Should nilotinib replace imatinib as first line treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP)? http://test.metromomsblog.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/02/tortoise-and-the-hare.jpg D. Van
BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia
 T h e n e w e ng l a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical therapeutics BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Charles A. Schiffer, M.D. This Journal feature begins with
T h e n e w e ng l a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e clinical therapeutics BCR-ABL Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia Charles A. Schiffer, M.D. This Journal feature begins with
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) was first described
 Imatinib Resistance Obstacles and Opportunities Mark R. Litzow, MD Objective. To review the current status of resistance to imatinib mesylate (IM) in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia, and the
Imatinib Resistance Obstacles and Opportunities Mark R. Litzow, MD Objective. To review the current status of resistance to imatinib mesylate (IM) in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia, and the
A novel isothermal amplification approach for rapid identification of BCR-ABL fusion genes at onset:
 A novel isothermal amplification approach for rapid identification of BCR-ABL fusion genes at onset: Josh Glason: Sales Manager, DiaSorin Australia Pty Ltd September 6, 2014 This product is not currently
A novel isothermal amplification approach for rapid identification of BCR-ABL fusion genes at onset: Josh Glason: Sales Manager, DiaSorin Australia Pty Ltd September 6, 2014 This product is not currently
Deposited on: 24 November 2011
 Iqbal, Z., Elliott, M., Watson, D.G., Holyoake, T.L. and Jorgensen, H.G. (2011) Analysis of imatinib in bone marrow and plasma samples of chronic myeloid leukaemia patients using solid phase extraction
Iqbal, Z., Elliott, M., Watson, D.G., Holyoake, T.L. and Jorgensen, H.G. (2011) Analysis of imatinib in bone marrow and plasma samples of chronic myeloid leukaemia patients using solid phase extraction
Original Study. Abstract
 Original Study The Effectiveness of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Molecular Monitoring Patterns in Newly Diagnosed Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in the Community Setting Nicholas J. Di Bella,
Original Study The Effectiveness of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors and Molecular Monitoring Patterns in Newly Diagnosed Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in the Community Setting Nicholas J. Di Bella,
Ponatinib Withdrawal Update
 Hello. This is Dr. Stuart Goldberg from the Leukemia Division at the John Theurer Cancer Center at Hackensack University Medical Center in Hackensack, New Jersey. I am speaking on behalf of ManagingCML.com
Hello. This is Dr. Stuart Goldberg from the Leukemia Division at the John Theurer Cancer Center at Hackensack University Medical Center in Hackensack, New Jersey. I am speaking on behalf of ManagingCML.com
Achieving deeper molecular response is associated with a better clinical outcome in chronic myeloid leukemia patients on imatinib frontline therapy
 Published Ahead of Print on December 20, 2013, as doi:10.3324/haematol.2013.095158. Copyright 2013 Ferrata Storti Foundation. Achieving deeper molecular response is associated with a better clinical outcome
Published Ahead of Print on December 20, 2013, as doi:10.3324/haematol.2013.095158. Copyright 2013 Ferrata Storti Foundation. Achieving deeper molecular response is associated with a better clinical outcome
HOW I TREAT CML. 4. KONGRES HEMATOLOGOV IN TRANSFUZIOLOGOV SLOVENIJE Z MEDNARODNO UDELEŽBO Terme Olimia, Podčetrtek,
 HOW I TREAT CML 4. KONGRES HEMATOLOGOV IN TRANSFUZIOLOGOV SLOVENIJE Z MEDNARODNO UDELEŽBO Terme Olimia, Podčetrtek, 12. - 14. april, 2012 Gianantonio Rosti Dpt of Hematology and Oncological Sciences S.
HOW I TREAT CML 4. KONGRES HEMATOLOGOV IN TRANSFUZIOLOGOV SLOVENIJE Z MEDNARODNO UDELEŽBO Terme Olimia, Podčetrtek, 12. - 14. april, 2012 Gianantonio Rosti Dpt of Hematology and Oncological Sciences S.
MUTATION ANALYSIS OF THE KINASE DOMAIN OF THE BCR-ABL FUSION PROTEIN (REFERENCE )
 MUTATION ANALYSIS OF THE KINASE DOMAIN OF THE BCR-ABL FUSION PROTEIN (REFERENCE 2014.02.002) Notice of Assessment December 2014 DISCLAIMER: This document was originally drafted in French by the Institut
MUTATION ANALYSIS OF THE KINASE DOMAIN OF THE BCR-ABL FUSION PROTEIN (REFERENCE 2014.02.002) Notice of Assessment December 2014 DISCLAIMER: This document was originally drafted in French by the Institut
Venice Meeting Highlights: Key lessons. Conclusions Michele Baccarani Rüdiger Hehlmann
 Venice Meeting Highlights: Key lessons Conclusions Michele Baccarani Rüdiger Hehlmann CML therapy in the imatinib era CML prognosis has improved dramatically Cellular and molecular biology studies help
Venice Meeting Highlights: Key lessons Conclusions Michele Baccarani Rüdiger Hehlmann CML therapy in the imatinib era CML prognosis has improved dramatically Cellular and molecular biology studies help
Molecular testing for the BCR-ABL1 fusion gene by
 Conversion, Correction, and International Scale Standardization Results From a Multicenter External Quality Assessment Study for BCR-ABL1 Testing Michael Griffiths, BSc; Simon J. Patton, PhD; Alberto Grossi,
Conversion, Correction, and International Scale Standardization Results From a Multicenter External Quality Assessment Study for BCR-ABL1 Testing Michael Griffiths, BSc; Simon J. Patton, PhD; Alberto Grossi,
Colombia Médica ISSN: Universidad del Valle Colombia
 Colombia Médica ISSN: 0120-8322 colombiamedica@correounivalle.edu.co Universidad del Valle Colombia Guevara, Gonzalo Follow-up of the tumor load in patients with de novo chronic myeloid leukemia and in
Colombia Médica ISSN: 0120-8322 colombiamedica@correounivalle.edu.co Universidad del Valle Colombia Guevara, Gonzalo Follow-up of the tumor load in patients with de novo chronic myeloid leukemia and in
Profiles in CML: Case-Based Approaches to Managing Resistance and Improving Outcomes. A CME/CE On-Demand Webcast
 Peer Review Directed by: SM Medical Education Activities for Clinicians Since 1980 University of California Irvine, School of Medicine Peer Review Directed by Offices of CME at: Education Initiative in
Peer Review Directed by: SM Medical Education Activities for Clinicians Since 1980 University of California Irvine, School of Medicine Peer Review Directed by Offices of CME at: Education Initiative in
Oxford Style Debate on STOPPING Treatment.
 Oxford Style Debate on STOPPING Treatment. This house believes that there are good reasons NOT to stop CML treatment. It should be done within clinical trials, OR only in expert centers where frequent,
Oxford Style Debate on STOPPING Treatment. This house believes that there are good reasons NOT to stop CML treatment. It should be done within clinical trials, OR only in expert centers where frequent,
Managing the Patient with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Through and After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation
 Managing the Patient with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Through and After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Jane F. Apperley Although the only curative therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia remains allogeneic
Managing the Patient with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Through and After Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation Jane F. Apperley Although the only curative therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia remains allogeneic
Peripheral Blood Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia During Treatment With Imatinib, Second-Line Agents, and Beyond
 Peripheral Blood Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia During Treatment With Imatinib, Second-Line Agents, and Beyond Lisa Lima, MS 1 ; Leon Bernal-Mizrachi, MD 1 ; Debra Saxe, PhD 2 ; Karen P. Mann,
Peripheral Blood Monitoring of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia During Treatment With Imatinib, Second-Line Agents, and Beyond Lisa Lima, MS 1 ; Leon Bernal-Mizrachi, MD 1 ; Debra Saxe, PhD 2 ; Karen P. Mann,
Major molecular response to imatinib in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia expressing a novel form of e8a2 BCR-ABL transcript.
 Major molecular response to imatinib in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia expressing a novel form of e8a2 BCR-ABL transcript. Andrei Tchirkov, Jean-Louis Couderc, Bernard Périssel, Carole Goumy,
Major molecular response to imatinib in a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia expressing a novel form of e8a2 BCR-ABL transcript. Andrei Tchirkov, Jean-Louis Couderc, Bernard Périssel, Carole Goumy,
Extending the duration of response in chronic myelogenous leukemia: targeted therapy with sequential tyrosine kinase inhibitors
 Oncol Rev (2009) 3:59 70 DOI 10.1007/s12156-009-0004-9 REVIEW Extending the duration of response in chronic myelogenous leukemia: targeted therapy with sequential tyrosine kinase inhibitors Michael G.
Oncol Rev (2009) 3:59 70 DOI 10.1007/s12156-009-0004-9 REVIEW Extending the duration of response in chronic myelogenous leukemia: targeted therapy with sequential tyrosine kinase inhibitors Michael G.
Bosulif. Bosulif (bosutinib) Description
 Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.22 Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1,2018 Subject: Bosulif Page: 1 of 5 Last Review
Federal Employee Program 1310 G Street, N.W. Washington, D.C. 20005 202.942.1000 Fax 202.942.1125 5.21.22 Section: Prescription Drugs Effective Date: April 1,2018 Subject: Bosulif Page: 1 of 5 Last Review
