Lymphoma in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
|
|
|
- Nelson King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1119 Lymphoma in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Adrian J. Greenstein, MD,* Gerard E. Mullin, MD,t James A. Strauchen, MD,$ Tomas Heimann, MD,* Henry D. Janowitz, MD, j Arthur H. Aufses Jr, MD,* and David B. Sachar, MDEj Nine patients with lymphoma occurring in association with inflammatory bowel disease were admitted to The Mount Sinai Hospital between 1960 and Five (two men and three women) occurred among 1156 patients (0.43%) with ulcerative colitis (UC) and four (men), among 1480 patients (0.27%) with Crohn's disease (CD), a strong male preponderance in the latter group. In all four of the patients with CD and in four of the five patients with UC, the lymphomas were extraintestinal. The mean age of onset of UC in these patients was late (46 years, 19 years older than in our overall series), with lymphomas occurring a mean of only 12 years later. By contrast, patients with CD had bowel disease much younger (mean age, 26 years), and their lymphomas appeared after a longer disease duration (mean, 24 years). The risk factors for the one patient with colonic lymphoma were similar to those with colitis-associated colorectal carcinoma: extensive and long-standing colitis and relatively young age when malignant disease developed. Four of the patients with lymphoma had associated colonic carcinoma; in three of them, the carcinoma appeared within the first decade of colitis, an unusual occurrence. A second malignant lesion also occurred in three patients with UC. Cancer 1992; The association of colorectal cancer with ulcerative colitis (UC) is well established.'+ Adenocarcinomas of both small and large bowel also occur more often than expected in Crohn's disease (CD).5-8 The issue of extraintestinal cancer is more controversial. Although earlier From the Departments of *Surgery, $Pathology, and Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology, Mount Sinai School of Medicine of the City University of New York, New York, New York. t Current address: Johns Hopkins University, 600 North Wolfe Street, Baltimore, MD The authors thank Jean DiCarlo and Sharon Richards for their assistance in the preparation of this report and Devaprasad Reuben for the work that made systematic collection of the data possible. Address for reprints: Adrian J. Greenstein, MD, Mount Sinai Medical Center, Department of Surgery, Box 1259, One Gustave L. Levy Place, New York, NY Accepted for publication May 31,1991. reports' including our own? found no excess of extraintestinal cancer, certain malignancies, including lymphoma, subsequently have been found to occur with increased frequency in these patients." The association of malignant lymphoma with UC was reported first in 1928 by Bargen." This association was considered to be a chance occurrence until recently. In 1977, a pathogenetic connection was suggested between CD and lymphoma; two patients were reported with this combination from the same geographic area within a 5-year period.12,13 We now report nine patients with lymphoma, five with UC and four with CD, occurring among 2636 patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). We describe their demographic features, clinical patterns, therapy, and outcome. Materials and Methods We studied, retrospectively, the case records of 2636 patients with IBD admitted to The Mount Sinai Hospital between 1960 and Only those cases that fulfilled strict diagnostic criteria for UC and CD were in- ~1uded.l~ Cases were excluded if they did not have histologic evidence of both lymphoma and IBD. The patients with IBD were subdivided into 1156 with UC and 1480 with CD (573 with regional enteritis, 638 with ileocolitis, and 269 with Crohn's colitis). In our series, there were five patients with UC and four with CD and lymphomas, only one of which was of intestinal origin. The records of these nine patients were reviewed for anatomic distribution, clinical features, and therapy of both the IBD and the lymphoma. Original histologic material was reviewed in all cases, and lymphomas were reclassified according to current conventional criteria. The outcome in each case was determined from the patient records if the patient was dead or from either the patient or the referring physician when the chart data were incomplete. Current follow-up was obtained for all patients and is recorded with other clinical data in Tables 1 and 2.
2 Table 1, Clinical Features in Five Patients With Lymphoma Occurring During the Course of Ulcerative Colitis Age at onset Age at onset Medical Patient IBD lymphoma (yr)/ Interval IBD- therapy of Surgical Type of Area of Therapy for no. Sex (yr) year of onset lymphoma (yr) Site of IBD IBD procedures lymphoma Stage involvement lymphoma Outcome U1 M 51 54/ Sigmoid to Sulfonamides None Hodgkin s disease IVA Mediastinum to Radiation Died 59 yr rectum abdomen therapy, chemotherapy U2 F 47 60/ Universal Azulfidine, Cholecystectomy Large cell IVB Sigmoid colon Cecosigmoid Died 60 yr prednisone, (carcinoma of lymphoma mesenteric bypass, Diffuse Cortenemas gallbladder) (diffuse pelvic chemotherapy lymphoma histocytic) paraaortic + CA nodes gallbladder U3 M 19 UF F 62 49/ /1979 U5 F 51 60/1962 IBD: inflammatory bowel disease. * Review diagnosis (original histologic diagnosis) t Cured for 23 vears Universal None Total colectomy Large cell IA Right inguinal Chemotherapy In remission 14 ileostomy lymphoma nodes yr revised 3 times (reticulum cell sarcoma) Sigmoid Azulfidine None Lymphocytic lymphoma colon to rectum (poorly differentiated) prednisone lvmdhoblastoma follicular lymphoma None IVA Bilateral Chemotherapy lymph nodes, retroperitoneal cervical and Died at age 70 yr skin, hip, liver, spleen, bone LA Rightinguinal Radiation Alive at 83 yrt lymph nodes therapy with metastasis h ypemephroma in 1985
3 Lymphoma in Inflammatory Bowel Disease/Greenstein et al Results The patients with UC and lymphoma included two men and three women, but all four patients with CD and lymphoma were men. The ages at appearance of lymphoma were similar for both groups (mean age, 50 and 58 years; range, 46 to 59 years and 49 to 69 years, respectively). However, the mean age at onset of CD was much younger than that at onset of UC (24 versus 46 years). Therefore, the mean duration of IBD until development of lymphoma was much longer for CD than for UC (26 versus 12 years). Although the mean age at onset of CD (24 years) in the patients with CD and lymphoma was similar to the mean age at onset for all patients with CD, the mean age at onset of 46 years in the patients with UC and lymphoma was 17 years older than in our other patients with UC. Although all four patients with CD had lymphomas in the third decade of their IBD (range, 23 to 28 years), the patients with UC had their lymphoma from 3 to 30 years after onset of UC, with three of the five occurring during the first decade of disease. Three of the four patients with CD had internal fistulae, and three of the five patients with UC had a second malignant tumor. Amyloidosis occurred in one patient with CD and renal failure in two. Two patients, one in each group of IBD, had Hodgkin's disease. Four others had lymphocytic lymphoma (two, UC; two, CD), and the rest had large cell lymphoma (one, CD; two, UC). The clinical features of the lymphomas were interesting because four patients with UC and two patients with CD were asymptomatic, with lymphadenopathy alone at the time of presentation. Constitutional symptoms, such as fever, night sweats, and weakness, were found in only three patients (one, UC; two, CD); an abdominal mass, in two (UC); hepatomegaly, in four (three, UC; one, CD); and splenomegaly in four (two, CD; two, UC). Therapy is described in Tables 1 and 2. Radiation therapy was given to four patients and chemotherapy, to seven. Two patients who were diagnosed and treated in 1961 and 1962 received radiation therapy alone; one died within 1 year, and the other is alive 23 years later. Discussion Reticuloendothelial malignant lesions occur in association with IBD and include lymphomas of both the Hodgkin's and non-hodgkin's type and leukemia. Although leukemia with IBD affects primarily the extraintestinal reticuloendothelial system?15 lymphomas with both UC and CD previously were reported more commonly in the intestinal tract itself.16
4 1122 CANCER March 1,1992, Volume 69, No. 5 Since the report of non-hodgkin's lymphoma of the cecum in UC in 1928," there have been 27 complete and 5 incomplete case reports of UC with colonic lymphoma: 3 with Hodgkin's and 24 with non-hodgkin's lymph~ma.'~,'~ A review of their cases and a report of an additional case using new histochemical techniques suggested that a review of all previous cases should be done.17 In one patient previously reported to have Hodgkin's lymphoma, modem methods reclassified this tumor as a non-hodgkin's lymphoma. It has been ~uggested,'~ on the basis of five cases among 2500 patients with UC at the Lahey Clinic"*'9 and three at St. Mark's Hospital during a 16-year period,20*2' that this association is underappreciated. Our report of five patients among 1156 patients with UC supports this contention. The four patients with UC we studied with extraintestinal lymphoma seemed to differ in two respects from our one patient with UC and colonic lymphoma (and from such patients reported in the literature); they tended to be older and to have less extensive colic. The mean age at development of colonic lymphoma among the 21 previously reported patients with UC was 46 years, similar to the age of 47 years in our patient with UC and colonic lymphoma. However, the UC-associated extraintestinal lymphomas in this series appeared at an older mean age (58 years) and occurred among patients with unusually late onset. Moreover, the mean age at onset of UC (46 years) was 19 years older than the mean age at onset for our overall UC series (27 years). Our one patient UC and with colonic lymphoma was similar to all 26 previously reported such patients who had universal colitis. One reported patient had Ieft-sided By contrast, three of our four patients with UC and extraintestinal lymphomas had only proctosigmoiditis (two) or left-sided colitis (one), with normal proximal colons. Moreover, of the 26 reported patients with universal colitis, 10 had long quiescent periods, indicating that the development of lymphoma did not correlate with disease activity.16 In other words, the risk factors for colonic lymphoma in UC seemed, in three principal respects, to be similar to those of colitis-related colonic adenocarcinoma: younger age at cancer onset, universal colitis, and longstanding quiescent disease. Three patients among the 26 previously reported cases of colonic lymphoma with UC had concomitant colonic adenocarcinoma. l6 It is curious, however, that by contrast with the characteristically late development of UC-associated colorectal carcinoma, the four colonic carcinomas in patients with UC and lymphoma (three previously reported and one additional case) all appeared within the first decade of UC. An important finding among our patients was that the early diagnosis of lymphoma was difficult to make. Four of our five patients with UC and two of our four patients with CD were asymptomatic and had lymphadenopathy alone. Only one patient with UC and two with CD had the classic constitutional symptoms of lymphoma, with or without abdominal pain. The only important clinical clue among previously reported patients16 was an abrupt alteration in the clinical course or the presence of a palpable abdominal or rectal mass, which was found in approximately one half of cases. With respect to the possible association of lymphoma with CD, a review of the literature did not show a clear-cut association. The earliest reports of non- Hodgkin's lymph~ma~~-~~ gave few clinical details. Subsequent reports included patients, such as one whose long-standing CD was replaced completely by the tumor," as also occurred in several patients with adeno~arcinoma.~~*~~ An additional difficulty in assessing the association of lymphoma with CD is the radiologic similarity of the two condition^.'^ Because the radiologic features of intestinal CD also can be found in gastrointestinal lymphoma, independent histopathologic evidence of both CD and lymphoma are essential. To complicate matters further, it was shownz8 that two patients with UC and lymphoma had features of CD; three other cases of lymphoma simulated IBD and may have been superimposed on CD, obliterating evidence of the inflammatory disea~e.~~,~~ These diagnostic difficulties notwithstanding, there are at least five reports of the clear-cut association of Hodgkin's disease with CD,12*23*28*31-33 in addition to the onel7 reclassified as non-hodgkin's lymphoma. We believe the rest should be reexamined with modern histologic methods. Most of these cases involved small bowel and/or colon with or without spread to local lymph nodes, although one involved mediastinal and supraclavicular lymph nodes only?8 Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma was documented in ten patients with CD A s in UC, most of the lesions occurred in the intestinal tract, although one case" and all of ours were extraintestinal in origin. All four of our patients with CD were men, as were 12 of the 16 previously reported cases of lymphoma and CD.24,28 This strong male preponderance differs from the overall gender distribution for lymphomas in general, where the incidence figures show only a slight male prep~nderance.~~ The mean age for development of lymphoma in our four patients with CD was 50 years (mean duration from onset of disease, 26 years; range, 23 to 28 years). This is longer than the durations reported in the literature (mean, 6.6 years; range, l to 16 years). The cause of the lymphoma associated with IBD is obscure. Factors that may be suggested include primary immunologic defects associated with IBD,3"39 immunosuppressive therapy (corticosteroids or antimetabo-
5 Lymphoma in Inflammatory Bowel Disease/Greenstein et al lite~),~~ chronic inflammation as in celiac and/or frequent exposure to x-rays. Three patients had large cell lymphoma, known to occur exclusively with immunosuppression-induced lymphoma. Nevertheless, because five of the nine patients in our series had not received sulfasalazine or prednisone before diagnosis of lymphoma, these medications could not have played an essential role; furthermore, none of our patients had ever received antimetabolites. The prognosis in recent years with adequate chemotherapy and radiation therapy appears to be improving, but it still depends on the stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis. References 1. Prior P, Gyde SN, Macartney JC, Thompson H, Waterhouse JAH, Allan RN. Cancer morbidity in ulcerative colitis. Gut 1982; 23~ Greenstein AJ, Sachar DB, Smith H et al. Cancer in universal and left-sided ulcerative colitis: Factors determining risk. Gasfroenterology 1979; Edwards FC, Truelove SC. The course and prognosis of ulcerative colik: N. Carcinoma of the colon. Gut 1964; 5: Kewenter J, Ahlman H, Hulten L. Cancer risk in extensive ulcerative colitis. Ann Surg 1978; 188: Frank JD, Shorey BA. Adenocarcinoma of the smab bowel as a complication of Crohn s disease. Gut 1973; Hoffman JP, Taft DA, Wheelis RF, Walker JH. Adenocarcinoma in regional enteritis of the small intestine. Arch Surg 1977; 112~ Weedon DD, Shorter RG, nstrup DM, Huizenga KA, Taylor WF. Crohn s disease and cancer. N Engl JMed 1973; Greenstein AJ, Sachar DB, Smith H, Janowitz HD, Aufses AH Jr. A comparison of cancer risk in Crohn s disease and ulcerative colitis. Cancer 1981; 48: Gyde SN, Prior P, Macarthy JC, Thompson H, Waterhouse JAH, Man RN. Malignancy in Crohn s disease. Gut 1980; 21: Greenstein AJ, Gennuso R, Sachar DB et al. Extraintestinal cancers in inflammatory bowel disease. Cancer 1985; 56: Bargen JA. Chronic ulcerative colitis associated with malignant disease. Arch Surg 1928; Codling BW, Keighley MRB, Slaney G. Hodgkin s disease complicating Crohn s colitis. Surgery 1977; Fielding JF, Prior P, Waterhouse JA, Cooke WT. Malignancy in Crohn s disease. Scand ] Gasfroenterol 1972; Greenstein AJ, Geller SA, Drehg DA, Aufses AH Jr. Crohn s disease of the colon: N. Clinical features of Crohn s (ileo) colitis. Am J Gastroenterol 1975; 64: Fabry TL, Sachar DB, Janowitz HD. Acute myelogenous leukemia in patients with ulcerative colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 1980; 2~ Baker D, Chiprut RO, Rimer D, Lewis KL, Rosenberg MZ. Colonic lymphoma in ulcerative colitis. J Clin Gastroenterol 1985; Shepherd NA, Hall PA, Williams GT et al. Primary malignant lymphoma of the large intestine complicating chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Histopathology 1989; Nugent FW, Zuberi S, Bulan MB, Legg MA. Colonic lymphoma in ulcerative colitis: Report of four cases. Lahey Clinic Foundation Bulletin 1972; 21: Cattell RB, Boehme EJ. The importance of malignant degeneration as a complication of chronic ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology 1947; 8: Renton P, Blackshaw AJ. Colonic lymphoma complicating ulcerative colitis. Br J Surg 1976; 63: Comes JS, Smith JC, Southwood WFW. Lymphosarcoma in chronic ulcerative colitis. Br J Surg 1961; 49: Hughes RK. Reticulum cell sarcoma a case possibly originating in regional enteritis. Am SUTg 1955; 21: Wybum-Mason R. A New Protozoan: Its Relation to Malignant and Other Diseases. Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas, 1964; Collins WJ. Malignant lymphoma complicating regional enteritis. Am ] Gastroenterol 1977; 68: Papp JP, Pollard HM. Adenocarcinoma occurring in Crohn s disease of the small intestine. Am ] Gastroenterol 1971; Bersack SR, Howe JS, Rehak EM. A unique case with roentgenologic evidence of regional enteritis of long duration and histologic evidence of diffuse adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 1958; Sartoris DJ, Hare11 GS, Anderson MF, Zboralske FF. Smallbowel lymphoma and regional enteritis: Radiographic similarities. Radiology 1984; 152: Glick SN, Teplick SK, Goodman LR, Clearfield HR, Shanser JD. Development of lymphoma in patients with Crohn s disease. Radiology 1984; 153: Weir AB, Poon MC, Groarke JF, Wilkerson JA. Lymphoma simulating Crohn s colitis. Dig Dis Sci 1980; 25: Friedman HB, Silver CM, Brown CH. Lymphoma of the colon simulating ulcerative colitis: Report of four cases. Dig Dis Sci 1968; 13~ Hecker R, Sheers R, Thomas D. Hodgkin s disease as a complication of Crohn s disease. Med J Aust 1978; 2: Shaw JH, Mulvaney N. Hodgkin s lymphoma: A complication of small bowel Crohn s disease. Aust N Z J Surg 1982; 52: Morrison PD, Whitaker M. A case of Hodgkin s disease complicating Crohn s disease. Clin Oncol 1982; 8: Kwee WS, Wils JAMJ, Van Den Tweel G. Malignant lymphoma, immunoblastic with plasmacytic differentiation, complicating Crohn s disease. 1985; National Cancer Institute. Surveillance, epidemiology, end results: Incidence and mortality data Monograph 57. NCI Monogr 1981; 6:lOE-lOF. 36. Louie S, Daoust PR, Schuartz RS. Immunodeficiency and the pathogenesis of non-hodgkin s lymphoma. Semin Oncol 1980; Sachar DB, Taub RN, Brown SM, Present DH, Korelitz BI, Janowitz HD. Impaired lymphocyte responsiveness in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1973; 64: Meyburg JA, Mitcheson NA. Suppressor mechanisms in neonatally acquired tolerance to a gross virus induced lymphoma in rats. Transplantation 1976; 3: Manci EA, Heath LS, Leiibach SS, Coggin JH. Lymphoma-associated ulcerative bowel disease in the hamster (Mesocrietus auratus) induced by an unusual agent. Am J Pathol 1984; 1:l Gelb A, Zalusky R. Lymphoma in Crohn s disease occurring in a patient on 6-MP (Letter). Am J Gastroenferol 1983; 78: Penn I. The occurrence of cancer in immune deficiencies. In: Current Problems in Cancer, vol. 6. Chicago: Year Book Medical, Cleary GL, Wamke R, Sklar J. Monoclonality of lymphoproliferative lesions in cardiac-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med 1984; 310: Laughron TP, Kadin ME, Deeg JH. T-cell intestinal lymphoma associated with celiac sprue. Ann Intern Med 1986; 104:44-47.
LYMPHOMA COMPLICATING ULCERATIVE COLITIS
 LYMPHOMA COMPLICATING ULCERATIVE COLITIS Pages with reference to book, From 37 To 39 Syed Hasnain Ali Shah, Abdul Haleem Khan, Ashfaque Ahmed ( Departments of Medicine, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
LYMPHOMA COMPLICATING ULCERATIVE COLITIS Pages with reference to book, From 37 To 39 Syed Hasnain Ali Shah, Abdul Haleem Khan, Ashfaque Ahmed ( Departments of Medicine, The Aga Khan University Hospital,
Gastric Carcinoma in Patients with Crohn Disease: Report of Four Cases
 311 0361-803X/91/1 572-0311 C American Roentgen Ray Society Seth N. GIick1 Received January 1 7, 1991 ; accepted after re vision March 1 2, 1991. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Hahnemann University
311 0361-803X/91/1 572-0311 C American Roentgen Ray Society Seth N. GIick1 Received January 1 7, 1991 ; accepted after re vision March 1 2, 1991. 1 Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Hahnemann University
Page 1. Is the Risk This High? Dysplasia in the IBD Patient. Dysplasia in the Non IBD Patient. Increased Risk of CRC in Ulcerative Colitis
 Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
Screening for Colorectal Neoplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Francis A. Farraye MD, MSc Clinical Director, Section of Gastroenterology Co-Director, Center for Digestive Disorders Boston Medical Center
Ileo-rectal anastomosis for Crohn's disease of
 Ileo-rectal anastomosis for Crohn's disease of the colon W. N. W. BAKER From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London Gut, 1971, 12, 427-431 SUMMARY Twenty-six cases of Crohn's disease of the
Ileo-rectal anastomosis for Crohn's disease of the colon W. N. W. BAKER From the Research Department, St Mark's Hospital, London Gut, 1971, 12, 427-431 SUMMARY Twenty-six cases of Crohn's disease of the
GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1071-1076, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM JAMES A. NELSON,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 64: 1071-1076, 1973 Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 64, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GRANULOMATOUS COLITIS: SIGNIFICANCE OF INVOLVEMENT OF THE TERMINAL ILEUM JAMES A. NELSON,
Anergy to dinitrochlorobenzene and depression of T-lymphocytes in Crohn's disease and ulcerative
 Gut, 1976, 17, 911-915 Anergy to dinitrochlorobenzene and depression of T-lymphocytes in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis S. MEYERS, D. B. SACHAR', R. N. TAUB, AND H. D. JANOWITZ From the Divisions
Gut, 1976, 17, 911-915 Anergy to dinitrochlorobenzene and depression of T-lymphocytes in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis S. MEYERS, D. B. SACHAR', R. N. TAUB, AND H. D. JANOWITZ From the Divisions
IBD-Related Lymphoma
 IBD-Related Lymphoma Larry Burgart MD Staff Pathologist, Allina Health and Minnesota Gastroenterology Clinical Professor of Pathology, University of Minnesota College of Medicine IBD-Related Lymphoma
IBD-Related Lymphoma Larry Burgart MD Staff Pathologist, Allina Health and Minnesota Gastroenterology Clinical Professor of Pathology, University of Minnesota College of Medicine IBD-Related Lymphoma
Lymphoma (Lymphosarcoma) by Pamela A. Davol
 Lymphoma (Lymphosarcoma) by Pamela A. Davol Cells derived from the bone marrow that mature and take part in cellular immune reactions are called lymphocytes. When lymphocytes undergo transformation and
Lymphoma (Lymphosarcoma) by Pamela A. Davol Cells derived from the bone marrow that mature and take part in cellular immune reactions are called lymphocytes. When lymphocytes undergo transformation and
Colon, or Colorectal, Cancer Information
 Colon, or Colorectal, Cancer Information Definition Colon, or colorectal, cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). Other types of cancer can affect
Colon, or Colorectal, Cancer Information Definition Colon, or colorectal, cancer is cancer that starts in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum (end of the colon). Other types of cancer can affect
IBD high risk groups
 IBD high risk groups Ulcerative colitis Value (95% CI) CRC prevalence (%) 3.7 (3.2-4.2) Overall annual CRC incidence (%) 0.3 (0.2-0.4) Annual CRC incidence in first decade of UC (%) 0.2 (0.1-0.2) Annual
IBD high risk groups Ulcerative colitis Value (95% CI) CRC prevalence (%) 3.7 (3.2-4.2) Overall annual CRC incidence (%) 0.3 (0.2-0.4) Annual CRC incidence in first decade of UC (%) 0.2 (0.1-0.2) Annual
Review article: the incidence and prevalence of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease
 Aliment Pharmacol Ther 23; 18 (Suppl. 2): 1 5. Review article: the incidence and prevalence of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease P. MUNKHOLM Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Hvidovre
Aliment Pharmacol Ther 23; 18 (Suppl. 2): 1 5. Review article: the incidence and prevalence of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease P. MUNKHOLM Department of Medical Gastroenterology, Hvidovre
How do I choose amongst medicines for inflammatory bowel disease. Maria T. Abreu, MD
 How do I choose amongst medicines for inflammatory bowel disease Maria T. Abreu, MD Overview of IBD Pathogenesis Bacterial Products Moderately Acutely Inflamed Chronic Inflammation = IBD Normal Gut Mildly
How do I choose amongst medicines for inflammatory bowel disease Maria T. Abreu, MD Overview of IBD Pathogenesis Bacterial Products Moderately Acutely Inflamed Chronic Inflammation = IBD Normal Gut Mildly
Burkitt s Lymphoma of the Abdomen: The Northern California Kaiser Permanente Experience
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 18 Number 2 Burkitt s Lymphoma of the Abdomen: The Northern California Kaiser Permanente Experience J McClenathan Citation J McClenathan. Burkitt s Lymphoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 18 Number 2 Burkitt s Lymphoma of the Abdomen: The Northern California Kaiser Permanente Experience J McClenathan Citation J McClenathan. Burkitt s Lymphoma
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know. Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC
 Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
Lymphoma: What You Need to Know Richard van der Jagt MD, FRCPC Overview Concepts, classification, biology Epidemiology Clinical presentation Diagnosis Staging Three important types of lymphoma Conceptualizing
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE. Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic
 INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic WHAT IS INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)? Chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract Two related
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Jean-Paul Achkar, MD Center for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Cleveland Clinic WHAT IS INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE (IBD)? Chronic inflammation of the intestinal tract Two related
2009 USCAP Gyn Pathology Evening Session Case #3. Richard J. Zaino, MD Hershey Medical Center Penn State University Hershey, PA
 2009 USCAP Gyn Pathology Evening Session Case #3 Richard J. Zaino, MD Hershey Medical Center Penn State University Hershey, PA rzaino@psu.edu Clinical history Middle aged woman with an exophytic mass of
2009 USCAP Gyn Pathology Evening Session Case #3 Richard J. Zaino, MD Hershey Medical Center Penn State University Hershey, PA rzaino@psu.edu Clinical history Middle aged woman with an exophytic mass of
Positioning Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis
 Positioning Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS Acting Chief, Gastrointestinal Unit Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Sequential Therapies
Positioning Biologics in Ulcerative Colitis Bruce E. Sands, MD, MS Acting Chief, Gastrointestinal Unit Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Sequential Therapies
St Mark's Hospital from 1953 to 1968
 Gut, 1970, 11, 235-239 The results of ileorectal anastomosis at St Mark's Hospital from 1953 to 1968 W. N. W. BAKER From St Mark's Hospital, London SUMMARY The popular view of ileorectal anastomosis for
Gut, 1970, 11, 235-239 The results of ileorectal anastomosis at St Mark's Hospital from 1953 to 1968 W. N. W. BAKER From St Mark's Hospital, London SUMMARY The popular view of ileorectal anastomosis for
GASTROENTEROLOGY. Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association. CoPYRIGHT 1975 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS Co.
 GASTROENTEROLOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association CoPYRIGHT 1975 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS Co. Vol68 April 1975 Number 4 ALIMENTARY TRACT CLINICAL PATTERNS IN CROHN'S DISEASE:
GASTROENTEROLOGY Official Publication of the American Gastroenterological Association CoPYRIGHT 1975 THE WILLIAMS & WILKINS Co. Vol68 April 1975 Number 4 ALIMENTARY TRACT CLINICAL PATTERNS IN CROHN'S DISEASE:
GASTROINTESTINAL MANIFESTATIONS OF MALIGNANT
 GASTROENTEROLOGY CopYright 1968 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 54, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GASTROINTESTINAL MANIFESTATIONS OF MALIGNANT L Y M P H O ~ I A ALVIN N. EHRLICH, M.D., GEORGE STALDER, M.D.,
GASTROENTEROLOGY CopYright 1968 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 54, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. GASTROINTESTINAL MANIFESTATIONS OF MALIGNANT L Y M P H O ~ I A ALVIN N. EHRLICH, M.D., GEORGE STALDER, M.D.,
Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous
 Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
Available online at www.worldscientificnews.com WSN 90 (2017) 265-270 EISSN 2392-2192 SHORT COMMUNICATION Lymphoma co existing with Tuberculosis granulomatous Madeeha Subhan 1, *, Waleed Sadiq 2 1 Ayub
Mantle Cell Lymphoma
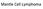 Mantle Cell Lymphoma Clinical Case A 56 year-old woman complains of pain and fullness in the left superior abdominal quadrant for the last 8 months. She has lost 25 kg, and lately has had night sweats.
Mantle Cell Lymphoma Clinical Case A 56 year-old woman complains of pain and fullness in the left superior abdominal quadrant for the last 8 months. She has lost 25 kg, and lately has had night sweats.
Ulcerative Colitis after Multidisciplinary Treatment for Colorectal Cancer with Multiple Liver Metastases : A Case Report
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 315 319, September 2017 Case Report Ulcerative Colitis after Multidisciplinary Treatment for Colorectal Cancer with Multiple Liver Metastases : A Case Report Kodai TOMIOKA 1
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 315 319, September 2017 Case Report Ulcerative Colitis after Multidisciplinary Treatment for Colorectal Cancer with Multiple Liver Metastases : A Case Report Kodai TOMIOKA 1
Pediatric PSC A children s tale
 Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
Pediatric PSC A children s tale September 8 th PSC Partners seeking a cure Tamir Miloh Assistant Professor Pediatric Hepatology Mount Sinai Hospital, NY Incidence Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) ;
Abstracting Hematopoietic Neoplasms
 CASE 1: LYMPHOMA PHYSICAL EXAMINATION 43yo male with a history of lower gastrointestinal bleeding and melena undergoing colonoscopy and biopsy to rule out neoplasm versus inflammation. Patient had no other
CASE 1: LYMPHOMA PHYSICAL EXAMINATION 43yo male with a history of lower gastrointestinal bleeding and melena undergoing colonoscopy and biopsy to rule out neoplasm versus inflammation. Patient had no other
COLORECTAL CANCER FAISALGHANISIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOETHICS; MCPS-HPE
 COLORECTAL CANCER FAISALGHANISIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y faisal.siddiqui@jsmu.edu.pk
COLORECTAL CANCER FAISALGHANISIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y faisal.siddiqui@jsmu.edu.pk
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Surgery for Ulcerative Colitis in Elderly Persons. Changes in Indications for Surgery and Outcome Over Time
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgery for Ulcerative Colitis in Elderly Persons Changes in Indications for Surgery and Outcome Over Time Gidon Almogy, MD; David B. Sachar, MD; Carol A. Bodian, DrPH; Adrian J. Greenstein,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgery for Ulcerative Colitis in Elderly Persons Changes in Indications for Surgery and Outcome Over Time Gidon Almogy, MD; David B. Sachar, MD; Carol A. Bodian, DrPH; Adrian J. Greenstein,
LEUKAEMIA and LYMPHOMA. Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University
 LEUKAEMIA and LYMPHOMA Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES Identify etiology and epidemiology for leukemia and lymphoma. Discuss common types of leukemia. Distinguish
LEUKAEMIA and LYMPHOMA Dr Mubarak Abdelrahman Assistant Professor Jazan University OBJECTIVES Identify etiology and epidemiology for leukemia and lymphoma. Discuss common types of leukemia. Distinguish
Indium-111 Zevalin Imaging
 Indium-111 Zevalin Imaging Background: Most B lymphocytes (beyond the stem cell stage) contain a surface antigen called CD20. It is possible to kill these lymphocytes by injecting an antibody to CD20.
Indium-111 Zevalin Imaging Background: Most B lymphocytes (beyond the stem cell stage) contain a surface antigen called CD20. It is possible to kill these lymphocytes by injecting an antibody to CD20.
Colitis ulcerosa complicated by malignant lymphoma: case report and analysis of published works
 306 Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology R Lenzen H Lubke G Strohmeyer Department of Pathology, Heinrich- Heine-University, Dusseldorf, Germany F Borchard Correspondence to: Dr R Lenzen,
306 Department of Medicine, Division of Gastroenterology R Lenzen H Lubke G Strohmeyer Department of Pathology, Heinrich- Heine-University, Dusseldorf, Germany F Borchard Correspondence to: Dr R Lenzen,
Frequency of Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer with Double Contrast Barium Enema
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.3, September 2002 Frequency of Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer with Double Contrast Barium Enema Najeeb S Jamsheer, MD, FRCR* Neelam. Malik, MD, MNAMS** Objective: To
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.3, September 2002 Frequency of Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer with Double Contrast Barium Enema Najeeb S Jamsheer, MD, FRCR* Neelam. Malik, MD, MNAMS** Objective: To
Disclosure of Affiliations. The Way We Hope It Goes. Medicines and Surgery for IBD. None. Cases: Sweet and Not So Sweet
 Immunomodulators and Complications of Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Disclosure of Affiliations None Thomas E. Read, MD, FACS, FASCRS Professor of Surgery Tufts University School of Medicine Senior
Immunomodulators and Complications of Surgery for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Disclosure of Affiliations None Thomas E. Read, MD, FACS, FASCRS Professor of Surgery Tufts University School of Medicine Senior
PEDIATRIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
 PEDIATRIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Alexis Rodriguez, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Advocate Children s Hospital Disclosers Abbott Nutrition - Speaker Inflammatory Bowel Disease Chronic inflammatory disease
PEDIATRIC INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE Alexis Rodriguez, MD Pediatric Gastroenterology Advocate Children s Hospital Disclosers Abbott Nutrition - Speaker Inflammatory Bowel Disease Chronic inflammatory disease
Lugano classification: Role of PET-CT in lymphoma follow-up
 CAR Educational Exhibit: ID 084 Lugano classification: Role of PET-CT in lymphoma follow-up Charles Nhan 4 Kevin Lian MD Charlotte J. Yong-Hing MD FRCPC Pete Tonseth 3 MD FRCPC Department of Diagnostic
CAR Educational Exhibit: ID 084 Lugano classification: Role of PET-CT in lymphoma follow-up Charles Nhan 4 Kevin Lian MD Charlotte J. Yong-Hing MD FRCPC Pete Tonseth 3 MD FRCPC Department of Diagnostic
How to differentiate Segmental Colitis Associated with Diverticulosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases?
 How to differentiate Segmental Colitis Associated with Diverticulosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases? Alessandro Armuzzi Lead IBD Unit Complesso Integrato Columbus Fondazione Policlinico Gemelli Università
How to differentiate Segmental Colitis Associated with Diverticulosis and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases? Alessandro Armuzzi Lead IBD Unit Complesso Integrato Columbus Fondazione Policlinico Gemelli Università
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center
 LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
LYMPHOMA Joginder Singh, MD Medical Oncologist, Mercy Cancer Center Lymphoma is cancer of the lymphatic system. The lymphatic system is made up of organs all over the body that make up and store cells
11/13/11. Biologics for CD and CUC: The Impact on Surgical Outcomes. Principles of Successful Intestinal Surgery
 Biologics for CD and CUC: The Impact on Surgical Outcomes Robert R. Cima, M.D., M.A. Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery Overview Antibody based medications (biologics)
Biologics for CD and CUC: The Impact on Surgical Outcomes Robert R. Cima, M.D., M.A. Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery Overview Antibody based medications (biologics)
MULTIPLE CARCINOMAS OF THE LARGE INTESTINE- CASE REPORT AND A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 MULTIPLE CARCINOMAS OF THE LARGE INTESTINE- CASE REPORT AND A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 147 To 149 Masood Hameed, Mushtaq Ahmed ( Surgical Unit I, Civil Hospital,
MULTIPLE CARCINOMAS OF THE LARGE INTESTINE- CASE REPORT AND A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 147 To 149 Masood Hameed, Mushtaq Ahmed ( Surgical Unit I, Civil Hospital,
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
 Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Approaches to Dysplasia in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases Parakkal Deepak, M.B.B.S., M.S. Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Gastroenterology John T. Milliken Department
Cancer Risk with IBD Therapies How to Discuss with your Patients?
 Cancer Risk with IBD Therapies How to Discuss with your Patients? Douglas L Nguyen, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California, Irvine Medical Center H.H. Chao Comprehensive Digestive
Cancer Risk with IBD Therapies How to Discuss with your Patients? Douglas L Nguyen, MD Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California, Irvine Medical Center H.H. Chao Comprehensive Digestive
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is associated with an increased risk of colorectal
 854 Cancer Risk in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease A Population-Based Study Charles N. Bernstein, M.D. 1,2 James F. Blanchard, M.D., Ph.D. 2,3,4 Erich Kliewer, Ph.D. 4,5 Andre Wajda, M.S. 4 1
854 Cancer Risk in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease A Population-Based Study Charles N. Bernstein, M.D. 1,2 James F. Blanchard, M.D., Ph.D. 2,3,4 Erich Kliewer, Ph.D. 4,5 Andre Wajda, M.S. 4 1
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 4 2013 Article 3 Sigmoidorectal Intussusception Presenting as Prolapse Per Anus in an Adult Venugopal Hg Hasmukh B. Vora Mahendra S. Bhavsar SMT.NHL
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 4 2013 Article 3 Sigmoidorectal Intussusception Presenting as Prolapse Per Anus in an Adult Venugopal Hg Hasmukh B. Vora Mahendra S. Bhavsar SMT.NHL
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies
 Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Staging and Treatment Update for Gynecologic Malignancies Bunja Rungruang, MD Medical College of Georgia No disclosures 4 th most common new cases of cancer in women 5 th and 6 th leading cancer deaths
Management of Perforated Colon Cancers
 Management of Perforated Colon Cancers Introduction Colon and rectal cancers are the most common gastrointestinal cancers. They are 3 rd most common and 2 nd most common causes of cancer deaths among men
Management of Perforated Colon Cancers Introduction Colon and rectal cancers are the most common gastrointestinal cancers. They are 3 rd most common and 2 nd most common causes of cancer deaths among men
Clinical Study Small Bowel Tumors: Clinical Presentation, Prognosis, and Outcomein33PatientsinaTertiaryCareCenter
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Oncology Volume 2008, Article ID 212067, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2008/212067 Clinical Study Small Bowel Tumors: Clinical Presentation, Prognosis, and Outcomein33PatientsinaTertiaryCareCenter
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Oncology Volume 2008, Article ID 212067, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2008/212067 Clinical Study Small Bowel Tumors: Clinical Presentation, Prognosis, and Outcomein33PatientsinaTertiaryCareCenter
L hyperfixation dans le suivi des lymphomes représente-t-elle toujours une maladie active?
 L hyperfixation dans le suivi des lymphomes représente-t-elle toujours une maladie active? Thierry Vander Borght UCL Mont-Godinne, Belgique FDG-PET in Lymphoma: Mont-Godinne Experience 03/2000 10/2002:
L hyperfixation dans le suivi des lymphomes représente-t-elle toujours une maladie active? Thierry Vander Borght UCL Mont-Godinne, Belgique FDG-PET in Lymphoma: Mont-Godinne Experience 03/2000 10/2002:
Infliximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody directed CASE REPORTS. The Relationship Between Infliximab Treatment and Lymphoma in Crohn s Disease
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 1999;117:1433 1437 CASE REPORTS The Relationship Between Infliximab Treatment and Lymphoma in Crohn s Disease STEPHEN J. BICKSTON,* GARY R. LICHTENSTEIN, KRISTEN O. ARSENEAU,* ROGER B.
GASTROENTEROLOGY 1999;117:1433 1437 CASE REPORTS The Relationship Between Infliximab Treatment and Lymphoma in Crohn s Disease STEPHEN J. BICKSTON,* GARY R. LICHTENSTEIN, KRISTEN O. ARSENEAU,* ROGER B.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Experience and Controversy A Teaching Seminar on Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sponsored by (New York) and the American College of Gastroenterology Edited by BURTON I. KORELITZ,
Inflammatory Bowel Disease Experience and Controversy A Teaching Seminar on Inflammatory Bowel Disease Sponsored by (New York) and the American College of Gastroenterology Edited by BURTON I. KORELITZ,
Cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease
 SURGICAL ISSUES IN IBD Cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease ANDERS M EKBOM MD PHD AM EKBOM. Cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease. Can J Gastroenterol 1995;9(1):23-26. There is an increased risk
SURGICAL ISSUES IN IBD Cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease ANDERS M EKBOM MD PHD AM EKBOM. Cancer risk in inflammatory bowel disease. Can J Gastroenterol 1995;9(1):23-26. There is an increased risk
MULTIPLE PRIMARY CANCERS: PRIMARY MALIGNANT LYMPHOMAS AND CARCINOMAS OF THE INTESTINAL TRACT IN THE SAME PATIENT
 J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 483. MULTIPLE PRIMARY CANCERS: PRIMARY MALIGNANT LYMPHOMAS AND CARCINOMAS OF THE INTESTINAL TRACT IN THE SAME PATIENT BY JOHN S. CORNES From the Vincent Square Laboratories,
J. clin. Path. (1960), 13, 483. MULTIPLE PRIMARY CANCERS: PRIMARY MALIGNANT LYMPHOMAS AND CARCINOMAS OF THE INTESTINAL TRACT IN THE SAME PATIENT BY JOHN S. CORNES From the Vincent Square Laboratories,
Can We Predict the Natural History of Ulcerative Colitis? Edward V Loftus, Jr, MD Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota, USA
 Can We Predict the Natural History of Ulcerative Colitis? Edward V Loftus, Jr, MD Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota, USA Endpoints Overview Hospitalization Surgery Colorectal cancer
Can We Predict the Natural History of Ulcerative Colitis? Edward V Loftus, Jr, MD Professor of Medicine Mayo Clinic Rochester, Minnesota, USA Endpoints Overview Hospitalization Surgery Colorectal cancer
HODGKIN LYMPHOMA DR. ALEJANDRA ZARATE OSORNO HOSPITAL ESPAÑOL DE MEXICO
 HODGKIN LYMPHOMA DR. ALEJANDRA ZARATE OSORNO HOSPITAL ESPAÑOL DE MEXICO HODGKIN LYMPHOMA CLASSIFICATION Lukes & Butler Rye WHO-2016 Linphocytic and/or histiocytic Nodular & diffuse Nodular Sclerosis Lymphocyte
HODGKIN LYMPHOMA DR. ALEJANDRA ZARATE OSORNO HOSPITAL ESPAÑOL DE MEXICO HODGKIN LYMPHOMA CLASSIFICATION Lukes & Butler Rye WHO-2016 Linphocytic and/or histiocytic Nodular & diffuse Nodular Sclerosis Lymphocyte
WHAT ARE PAEDIATRIC CANCERS
 WHAT ARE PAEDIATRIC CANCERS INTRODUCTION Childhood cancers are RARE 0.5% of all cancers in the West Overall risk that a child will develop cancer during first 15 years of life is 1 in 450 and 1 in 600
WHAT ARE PAEDIATRIC CANCERS INTRODUCTION Childhood cancers are RARE 0.5% of all cancers in the West Overall risk that a child will develop cancer during first 15 years of life is 1 in 450 and 1 in 600
Moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis
 Adalimumab in the Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Ulcerative Colitis: ULTRA 2 Trial Results Sandborn WJ, van Assche G, Reinisch W, et al. Adalimumab induces and maintains clinical remission in patients
Adalimumab in the Treatment of Moderate-to-Severe Ulcerative Colitis: ULTRA 2 Trial Results Sandborn WJ, van Assche G, Reinisch W, et al. Adalimumab induces and maintains clinical remission in patients
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Michael Weiss MD, FACG
 Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Michael Weiss MD, FACG What is IBD? IBD is an immune-mediated chronic intestinal disorder, characterized by chronic or relapsing inflammation within the GI tract.
Treatment of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Michael Weiss MD, FACG What is IBD? IBD is an immune-mediated chronic intestinal disorder, characterized by chronic or relapsing inflammation within the GI tract.
IBD Understanding Your Medications. Thomas V. Aguirre, MD Santa Barbara GI Consultants
 IBD Understanding Your Medications Thomas V. Aguirre, MD Santa Barbara GI Consultants IBD Understanding Your Medications (& Your Doctor) Thomas V. Aguirre, MD Santa Barbara GI Consultants Disclosure I
IBD Understanding Your Medications Thomas V. Aguirre, MD Santa Barbara GI Consultants IBD Understanding Your Medications (& Your Doctor) Thomas V. Aguirre, MD Santa Barbara GI Consultants Disclosure I
colorectal cancer Colorectal cancer hereditary sporadic Familial 1/12/2018
 colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
colorectal cancer Adenocarcinoma of the colon and rectum is the third most common site of new cancer cases and deaths in men (following prostate and lung or bronchus cancer) and women (following breast
Persistence of mucosal abnormality in ulcerative colitis
 Gut, 966, 7, 55 Persistence of mucosal abnormality in ulcerative colitis A. P. DICK, L. P. HOLT', AND E. R. DALTON rom Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, and the Department of Human Ecology, University
Gut, 966, 7, 55 Persistence of mucosal abnormality in ulcerative colitis A. P. DICK, L. P. HOLT', AND E. R. DALTON rom Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, and the Department of Human Ecology, University
It is well established that patients with long-standing. Screening and Surveillance Colonoscopy in Chronic Crohn s Colitis. Materials and Methods
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2001;120:820 826 Screening and Surveillance Colonoscopy in Chronic Crohn s Colitis SONIA FRIEDMAN,* PETER H. RUBIN, CAROL BODIAN, ERIC GOLDSTEIN, NOAM HARPAZ, and DANIEL H. PRESENT *Division
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2001;120:820 826 Screening and Surveillance Colonoscopy in Chronic Crohn s Colitis SONIA FRIEDMAN,* PETER H. RUBIN, CAROL BODIAN, ERIC GOLDSTEIN, NOAM HARPAZ, and DANIEL H. PRESENT *Division
Predicting the natural history of IBD. Séverine Vermeire, MD, PhD Department of Gastroenterology University Hospital Leuven Belgium
 Predicting the natural history of IBD Séverine Vermeire, MD, PhD Department of Gastroenterology University Hospital Leuven Belgium Patient 1 Patient 2 Age 22 Frequent cramps and diarrhea for 6 months Weight
Predicting the natural history of IBD Séverine Vermeire, MD, PhD Department of Gastroenterology University Hospital Leuven Belgium Patient 1 Patient 2 Age 22 Frequent cramps and diarrhea for 6 months Weight
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) Clinical aspects Nitsan Maharshak M.D., IBD Center, Department of Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases Tel Aviv Soura
 Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) Clinical aspects Nitsan Maharshak M.D., IBD Center, Department of Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center Tel Aviv, Israel IBD- clinical features
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD) Clinical aspects Nitsan Maharshak M.D., IBD Center, Department of Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center Tel Aviv, Israel IBD- clinical features
Incidence of Neoplasms in Patients Who Develop Sustained Leukopenia During or After Treatment With 6-Mercaptopurine for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1025 1029 Incidence of Neoplasms in Patients Who Develop Sustained Leukopenia During or After Treatment With 6-Mercaptopurine for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2006;4:1025 1029 Incidence of Neoplasms in Patients Who Develop Sustained Leukopenia During or After Treatment With 6-Mercaptopurine for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
NON INVASIVE MONITORING OF MUCOSAL HEALING IN IBD. THE ROLE OF BOWEL ULTRASOUND. Fabrizio Parente
 NON INVASIVE MONITORING OF MUCOSAL HEALING IN IBD. THE ROLE OF BOWEL ULTRASOUND Fabrizio Parente Gastrointestinal Unit, A.Manzoni Hospital, Lecco & L.Sacco School of Medicine,University of Milan - Italy
NON INVASIVE MONITORING OF MUCOSAL HEALING IN IBD. THE ROLE OF BOWEL ULTRASOUND Fabrizio Parente Gastrointestinal Unit, A.Manzoni Hospital, Lecco & L.Sacco School of Medicine,University of Milan - Italy
Surgical Management of IBD. Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003
 Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer
 Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Anatomic Pathology / PERITONEAL INVOLVEMENT IN STAGE II COLON CANCER Peritoneal Involvement in Stage II Colon Cancer A.M. Lennon, MB, MRCPI, H.E. Mulcahy, MD, MRCPI, J.M.P. Hyland, MCh, FRCS, FRCSI, C.
Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD):
 Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD): What Every Patient Needs to Know William H Holderman, MD Digestive Health Specialists Tacoma, WA Today s Objectives Define IBD, its potential causes and
Understanding Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD): What Every Patient Needs to Know William H Holderman, MD Digestive Health Specialists Tacoma, WA Today s Objectives Define IBD, its potential causes and
Differentiation Between Ileocecal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease using a Combination of Clinical, Endoscopic and Histological Characteristics
 38 Original Article Differentiation Between Ileocecal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease using a Combination of Clinical, Endoscopic and Histological Characteristics Anuchapreeda S Leelakusolvong S Charatcharoenwitthaya
38 Original Article Differentiation Between Ileocecal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease using a Combination of Clinical, Endoscopic and Histological Characteristics Anuchapreeda S Leelakusolvong S Charatcharoenwitthaya
Primary Results Citation 2
 Table S1. Adalimumab clinical trials 1 ClinicalTrials.gov Rheumatoid Arthritis 3 NCT00195663 Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical
Table S1. Adalimumab clinical trials 1 ClinicalTrials.gov Rheumatoid Arthritis 3 NCT00195663 Breedveld FC, Weisman MH, Kavanaugh AF, et al. The PREMIER study. A multicenter, randomized, double-blind clinical
Surgical resection improves survival in pancreatic cancer patients without vascular invasion- a population based study
 Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 346-352 Surgical resection improves survival in pancreatic cancer patients without vascular invasion- a population based study Subhankar Chakraborty
Original article Annals of Gastroenterology (2013) 26, 346-352 Surgical resection improves survival in pancreatic cancer patients without vascular invasion- a population based study Subhankar Chakraborty
Gastrointestinal Diverticulosis A Retrospective Analysis
 Abstract Gastrointestinal Diverticulosis A Retrospective Analysis Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 19 Huma Qureshi, Sarwar J. Zuberi ( PMRC Research Centre, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Abstract Gastrointestinal Diverticulosis A Retrospective Analysis Pages with reference to book, From 14 To 19 Huma Qureshi, Sarwar J. Zuberi ( PMRC Research Centre, Jinnah Postgraduate Medical Centre,
Azathioprine for Induction and Maintenance of Remission in Crohn s Disease
 Azathioprine for Induction and Maintenance of Remission in Crohn s Disease William J. Sandborn, MD Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Director, UCSD IBD Center Objectives Azathioprine as induction and
Azathioprine for Induction and Maintenance of Remission in Crohn s Disease William J. Sandborn, MD Chief, Division of Gastroenterology Director, UCSD IBD Center Objectives Azathioprine as induction and
155.2 Malignant neoplasm of liver not specified as primary or secondary. C22.9 Malignant neoplasm of liver, not specified as primary or secondary
 ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
ICD-9 TO ICD-10 Reference ICD-9 150.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus unspecified site C15.9 Malignant neoplasm of esophagus, unspecified 151.9 Malignant neoplasm of stomach unspecified site C16.9 Malignant
Surgical Management of IBD in the Age of Biologics
 Surgical Management of IBD in the Age of Biologics Lisa S. Poritz, M.D Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery Objectives Discuss surgical management of IBD When to operate
Surgical Management of IBD in the Age of Biologics Lisa S. Poritz, M.D Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery Objectives Discuss surgical management of IBD When to operate
Carcinoma and DNA aneuploidy in Crohn's colitis -
 9 Gut, 99,32,9-94 The Gastroenterology Units, Huddinge University Hospital, Huddinge and South Hospital, Stockholm and Departments of Pathology and Medical Radiobiology, Karolinska Institute and Hospital,
9 Gut, 99,32,9-94 The Gastroenterology Units, Huddinge University Hospital, Huddinge and South Hospital, Stockholm and Departments of Pathology and Medical Radiobiology, Karolinska Institute and Hospital,
To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint prevented this external picture from being automatically downloaded. To download and display this picture,
 To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint prevented this external picture from being automatically downloaded. To download and display this picture, click Options in the Message Bar, and then click Enable
To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint prevented this external picture from being automatically downloaded. To download and display this picture, click Options in the Message Bar, and then click Enable
21/07/2017. Lymphoproliferations in immunodeficiency. IBD and EBV associated LPD in GIT Han van Krieken. Inflammatory bowel disease and cancer
 IBD and EBV associated LPD in GIT Han van Krieken Lymphoproliferations in immunodeficiency Primary immunodeficiencies Large variation in conditions and lesions Acquired immunodeficiencies HIV: changes
IBD and EBV associated LPD in GIT Han van Krieken Lymphoproliferations in immunodeficiency Primary immunodeficiencies Large variation in conditions and lesions Acquired immunodeficiencies HIV: changes
HLA TYPING AND EXPRESSION: POTENTIAL MARKER FOR IDENTIFYING EARLY DYSPLASIA AND STRATIFYING THE RISK FOR IBD-CANCER
 HLA TYPING AND EXPRESSION: POTENTIAL MARKER FOR IDENTIFYING EARLY DYSPLASIA AND STRATIFYING THE RISK FOR IBD-CANCER Megan Garrity, S. Breanndan Moore, M.D., William Sandborn, M.D., Vernon Pankratz, Ph.D.,
HLA TYPING AND EXPRESSION: POTENTIAL MARKER FOR IDENTIFYING EARLY DYSPLASIA AND STRATIFYING THE RISK FOR IBD-CANCER Megan Garrity, S. Breanndan Moore, M.D., William Sandborn, M.D., Vernon Pankratz, Ph.D.,
Doppler ultrasound of the abdomen and pelvis, and color Doppler
 - - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
- - - - - - - - - - - - - Testicular tumors are rare in children. They account for only 1% of all pediatric solid tumors and 3% of all testicular tumors [1,2]. The annual incidence of testicular tumors
A superficial radiotherapy B single pass curettage C excision with 2 mm margins D excision with 5 mm margins E Mohs micrographic surgery.
 1- A 63-year-old woman presents with a non-healing lesion on her right temple that has been present for over two years. On examination there is a 6 mm well defined lesion with central ulceration, telangiectasia
1- A 63-year-old woman presents with a non-healing lesion on her right temple that has been present for over two years. On examination there is a 6 mm well defined lesion with central ulceration, telangiectasia
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS
 SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS Cary B. Aarons, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon & Rectal Surgery University of Pennsylvania AGENDA Background Diagnosis/Work-up Medical Management
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ULCERATIVE COLITIS Cary B. Aarons, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Division of Colon & Rectal Surgery University of Pennsylvania AGENDA Background Diagnosis/Work-up Medical Management
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL)
 Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Hodgkin lymphoma )HL) Lymphoid Neoplasms: 1- non-hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) 2- Hodgkin lymphoma 3- plasma cell neoplasms Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma
Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Closer Look at the Characteristics of These Diverse Tumors
 Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Closer Look at the Characteristics of These Diverse Tumors Jaume Capdevila, MD, PhD Vall d'hebron University Hospital Vall d'hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO)
Gastrointestinal Neuroendocrine Tumors: A Closer Look at the Characteristics of These Diverse Tumors Jaume Capdevila, MD, PhD Vall d'hebron University Hospital Vall d'hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO)
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a. The Patient with Newly Diagnosed Ulcerative Colitis: Anticipating the Questions and Individualizing the Answers
 The Patient with Newly Diagnosed Ulcerative Colitis: Anticipating the Questions and Individualizing the Answers James Gregor, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, The University of Western Ontario, London,
The Patient with Newly Diagnosed Ulcerative Colitis: Anticipating the Questions and Individualizing the Answers James Gregor, MD, Division of Gastroenterology, The University of Western Ontario, London,
Diagnosing and Managing IBS in IBD Patients. September 2012
 Diagnosing and Managing IBS in IBD Patients September 2012 Professor David S Sanders Consultant Gastroenterologist Royal Hallamshire Hospital & University of Sheffield Patient Comes to see you with GI
Diagnosing and Managing IBS in IBD Patients September 2012 Professor David S Sanders Consultant Gastroenterologist Royal Hallamshire Hospital & University of Sheffield Patient Comes to see you with GI
Ali Keshavarzian MD Rush University Medical Center
 Treatment: Step Up or Top Down? Ali Keshavarzian MD Rush University Medical Center Questions What medication should IBD be treated with? Can we predict which patients with IBD are high risk? Is starting
Treatment: Step Up or Top Down? Ali Keshavarzian MD Rush University Medical Center Questions What medication should IBD be treated with? Can we predict which patients with IBD are high risk? Is starting
What is a hematological malignancy? Hematology and Hematologic Malignancies. Etiology of hematological malignancies. Leukemias
 Hematology and Hematologic Malignancies Cancer of the formed elements of the blood What is a hematological malignancy? A hematologic malignancy is a malignancy (or cancer) of any of the formed elements
Hematology and Hematologic Malignancies Cancer of the formed elements of the blood What is a hematological malignancy? A hematologic malignancy is a malignancy (or cancer) of any of the formed elements
The role of Surgery and Stomas in IBD
 The role of Surgery and Stomas in IBD When do I need it? Can I avoid it? How do I live with it? Kyle G. Cologne, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery USC Division of Colorectal Surgery Topics Surgical Differences
The role of Surgery and Stomas in IBD When do I need it? Can I avoid it? How do I live with it? Kyle G. Cologne, MD Assistant Professor of Surgery USC Division of Colorectal Surgery Topics Surgical Differences
Colorectal cancer surveillance in inflammatory bowel diseases
 Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.2, 2004 55 Colorectal cancer surveillance in inflammatory bowel diseases MURAT TÖRÜNER Ankara University Medical School, Department of Gastroenterology, Ankara-Turkey
Turkish Journal of Cancer Volume 34, No.2, 2004 55 Colorectal cancer surveillance in inflammatory bowel diseases MURAT TÖRÜNER Ankara University Medical School, Department of Gastroenterology, Ankara-Turkey
HIPEC Controversies in the Indications and Application of Regional Chemotherapy for Peritoneal Surface Malignancies
 HIPEC Controversies in the Indications and Application of Regional Chemotherapy for Peritoneal Surface Malignancies Crescent City Cancer Update: GI and HPB Saturday September 24, 2016 George M. Fuhrman,
HIPEC Controversies in the Indications and Application of Regional Chemotherapy for Peritoneal Surface Malignancies Crescent City Cancer Update: GI and HPB Saturday September 24, 2016 George M. Fuhrman,
disease Aim of surgical treatment of Crohn's Leading article 32-75%), but there was less agreement concerning low incidence after
 Gut, 1984, 25, 217-222 Leading article Aim of surgical treatment of Crohn's disease The study published in this issue' once again emphasises a topic which has dogged the management of Crohn's disease since
Gut, 1984, 25, 217-222 Leading article Aim of surgical treatment of Crohn's disease The study published in this issue' once again emphasises a topic which has dogged the management of Crohn's disease since
Patient underwent hemicolectomy: 7 x 4.5 cm intusscepted segment of ileum in colon - mucosal
 Extranodal Lymphomas Rena Buckstein Odette Cancer Center Case: JT 69 yo male COO software company PMHx: basal cell back, cholesterol Presents to ER with severe abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea x 2d In ER
Extranodal Lymphomas Rena Buckstein Odette Cancer Center Case: JT 69 yo male COO software company PMHx: basal cell back, cholesterol Presents to ER with severe abdominal pain, bloody diarrhea x 2d In ER
Lancashire and South Cumbria Haematology NSSG Guidelines for Follicular Lymphoma:
 1 Lancashire and South Cumbria Haematology NSSG Guidelines for Follicular Lymphoma: 2018-19 1.1 Pretreatment evaluation The following tests should be performed: FBC, U&Es, creat, LFTs, calcium, LDH, Igs/serum
1 Lancashire and South Cumbria Haematology NSSG Guidelines for Follicular Lymphoma: 2018-19 1.1 Pretreatment evaluation The following tests should be performed: FBC, U&Es, creat, LFTs, calcium, LDH, Igs/serum
TREATMENT OF INPATIENTS WITH ACUTE SEVERE ULCERATIVE COLITIS
 TREATMENT OF INPATIENTS WITH ACUTE SEVERE ULCERATIVE COLITIS Target Audience: Physicians, Physician Assistants, Nurse Practitioners and Nurses impacted by the protocol. Scope/Patient Population: All adult
TREATMENT OF INPATIENTS WITH ACUTE SEVERE ULCERATIVE COLITIS Target Audience: Physicians, Physician Assistants, Nurse Practitioners and Nurses impacted by the protocol. Scope/Patient Population: All adult
Pediatric Oncology. Vlad Radulescu, MD
 Pediatric Oncology Vlad Radulescu, MD Objectives Review the epidemiology of childhood cancer Discuss the presenting signs and symptoms, general treatment principles and overall prognosis of the most common
Pediatric Oncology Vlad Radulescu, MD Objectives Review the epidemiology of childhood cancer Discuss the presenting signs and symptoms, general treatment principles and overall prognosis of the most common
Short and longterm outcomes after endoscopic resection of malignant polyps.
 Short and longterm outcomes after endoscopic resection of malignant polyps. Short and longterm outcomes High risk features Lymph node metastasis Lymph node metastases sm1 sm2 sm3 Son 2008 3.1 % 14.9% 25.0
Short and longterm outcomes after endoscopic resection of malignant polyps. Short and longterm outcomes High risk features Lymph node metastasis Lymph node metastases sm1 sm2 sm3 Son 2008 3.1 % 14.9% 25.0
An Investigation into the Validity of the Present Classification of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 54, No. 214,pp. 183 190, February 1985 An Investigation into the Validity of the Present Classification of Inflammatory Bowel Disease G. HOLDSTOCK, D. SAVAGE,
Quarterly Journal of Medicine, New Series 54, No. 214,pp. 183 190, February 1985 An Investigation into the Validity of the Present Classification of Inflammatory Bowel Disease G. HOLDSTOCK, D. SAVAGE,
-2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine. -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency
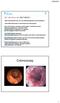 SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
8. The polyp in the illustration can be described as (circle all that apply) a. Exophytic b. Pedunculated c. Sessile d. Frank
 Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Quiz 1 Overview 1. Beginning with the cecum, which is the correct sequence of colon subsites? a. Cecum, ascending, splenic flexure, transverse, hepatic flexure, descending, sigmoid. b. Cecum, ascending,
Prognostic factors in squamous cell anal cancers
 Prognostic factors in squamous cell anal cancers Zainul Abedin Kapacee Year 4-5 Intercalating Medical Student, University of Manchester Dr. Shabbir Susnerwala, Mr. Nigel Scott Dr. Falalu Danwata, Dr. Marcus
Prognostic factors in squamous cell anal cancers Zainul Abedin Kapacee Year 4-5 Intercalating Medical Student, University of Manchester Dr. Shabbir Susnerwala, Mr. Nigel Scott Dr. Falalu Danwata, Dr. Marcus
