BRCA population screening for predicting breast cancer: for or against?
|
|
|
- Candace Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
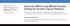
1 Perspective Page 1 of 5 BRCA population screening for predicting breast cancer: for or against? Giuseppe Lippi 1, Camilla Mattiuzzi 2, Martina Montagnana 1 1 Section of Clinical Biochemistry, University of Verona, Verona, Italy; 2 Service of Clinical Governance, Provincial Agency for Sanitary Services, Trento, Italy Correspondence to: Prof. Giuseppe Lippi. Section of Clinical Biochemistry, University Hospital of Verona, Piazzale LA Scuro, Verona 37100, Italy. giuseppe.lippi@univr.it or ulippi@tin.it. Abstract: The pathogenesis of breast cancer, the most frequent female malignancy, entails both genetic and acquired risk factors. Among the various oncogenetic mutations, those involving the BReast Cancer 1 (BRCA1) and BReast Cancer 2 (BRCA2) genes are associated with an extremely high risk of developing breast cancer, with a penetration approximating 70% in women with a positive family history for this malignancy. This important evidence elicits some pragmatic considerations, such as the clinical effectiveness of screening for the most penetrant BRCA mutations in women with or without a positive familial history, but also raises important issues related to the most appropriate clinical management of these patients. Despite it seems now almost certain that BRCA testing should be offered to women with a positive familial history for breast cancer, the balance between advantages and limitations of a population screening remains largely debated. Whatever conclusion can be reach at this point in time must be accurately weighed against at least four different perspectives, which include the low prevalence of these mutations in the general population, the relatively lower risk of developing breast cancer in women without a familial history for this malignancy, the direct and indirect cost of genetic testing and, last but not least, the many potential psychological and clinical consequences in patients receiving a positive test result. Many of these still unresolved issues will be tentatively discussed in this article. Keywords: Breast cancer; BRCA; BReast Cancer 1 (BRCA1); BReast Cancer 2 (BRCA2); screening Submitted Jun 20, Accepted for publication Jun 25, doi: /atm View this article at: Breast cancer Breast cancer is the most frequent female malignancy, with estimated 1,384,155 new cases and approximately 459,000 related deaths around the world (1). According to these figures it can be predicted that one every eight women will develop breast cancer during her lifespan (1). As for many other malignancies, the pathogenesis of breast cancer is clearly multifactorial, thus involving both environmental and genetic risk factors. The former class of risk factors includes different forms of ionizing radiations (e.g., environmental, occupational or diagnostic-therapeutic), synthetic chemicals such as organochlorines (e.g., pesticides, industrial chemicals and dioxins), oral contraceptives (OCs), hormone replacement therapy (HRT), pregnancy and menstrual history. Regarding genetics, dominant gene mutations seem to occur in a minority of breast cancers, and the most common among these are those affecting the BReast Cancer 1 (BRCA1) and BReast Cancer 2 (BRCA2) genes (1) (Figure 1). Both these genes are conventionally known to act as tumor suppressors, since they are actively involved in cell-cycle regulation and double-strand DNA breaks repair by means of homologous recombination (2). In patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations associated with impaired gene function (e.g., 5' to c.2281, c.2282 to c.4071, c.4072 to 3', c.68_69delag, c.5266dupc for BRCA1, and 5' to c.3846, c.3847 to c.6275 and c.6276 to 3' for BRCA2, respectively), double strand DNA breaks cannot
2 Page 2 of 5 Lippi et al. BRCA population screening Notably, the risk of breast cancer was found to be further increased to 84% in Ashkenazi Jewish carriers of the c.68_69delag BRCA1 polymorphism, irrespective of the familial history (5). Population screening? Figure 1 Pathogenesis of breast cancer. be efficiently repaired, so that chromosomal rearrangements gradually accumulate during cell division, some of which may engender the development of cell lineages with potency of autonomous cell replication or carcinogenic and metastatic potential (3). BRCA mutations and breast cancer It has been convincingly demonstrated that the overall prevalence of BRCA1 or BRCA2 oncogenic mutations may differ widely according to the study populations. In particular, the prevalence is usually found to be very low in the general population (i.e., between %), is enhanced to approximately 3% in all breast cancer carriers, further increases to 6% in those with breast cancer development before the age of 40, but can be as high as 20% in women with a positive familial history of breast cancer (4). Despite the overall prevalence in the general population is definitely low, reliable evidence attests that the penetrance (i.e., the risk of developing breast cancer in carriers of BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations) may be high, especially in women with affected relatives. This concept has been recently emphasized by data published by Kuchenbaecker et al. (5), who carried out a prospective cohort study including 6,036 BRCA1 and 3,820 BRCA2 female carriers, 4,810 of whom with breast or ovarian cancer and 5,046 without. The 5-year prospective follow-up allowed to demonstrate that the overall risk of developing breast cancer was 73% in women with a positive familial history for this malignancy and carrying BRCA1 oncogenic mutations, and as high as 65% in women with positive familial history for breast cancer and bearing BRCA2 oncogenic mutations. These important findings elicit some pragmatic considerations about the cost-effectiveness of widespread population screening for identifying subjects carrying oncogenic BRCA mutations. The recent case of the famous actress Angelina Jolie has added more fuel to the fire of the ongoing debate developing between those in favor or against BRCA (population) screening. Briefly, Angelina Jolie decided to undergo preventive double mastectomy because she was found to be carrier of a BRCA1 mutation, but she had previously lost her mother, grandmother and aunt for cancer while bearing the same polymorphism (6). This paradigmatic case has then contributed to generate the socalled Angelina Jolie effect, with the number of BRCA tests in the US increasing from 0.71:100,000 to 1.13:100,000 women (i.e., +60%) immediately after the media gave wide and unfiltered airtime to the event. Along with the broad diffusion in the social media, Jolie s decision also attracted a large number of negative and positive opinions about the clinical efficacy and consequences of BRCA testing in unaffected women or in those with no risk factors (7). According to the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, BRCA testing may be offered to women with family members affected by breast, ovarian, fallopian tube or peritoneal cancer, along to those who may have a family history suggestive for the presence of BRCA mutations (4). This recommendation is hence fully confirmed by the data recently published by Kuchenbaecker et al. (5), since the overall risk of developing breast cancer was shown to increase from 53% to 73% in women carrying a BRCA1 oncogenic mutation and having a positive familial history for this type of cancer, and from 39% to 65% in women carrying a BRCA2 oncogenic mutation and having a positive familial history for breast cancer. Yet, a major question remains unanswered. What should be recommended to women without a positive familial history? Inevitably, whatever conclusion can be reached at this point in time must be accurately weighed against at least four different perspectives, which include the low prevalence of these mutations in the general population, the relatively lower risk of developing breast cancer in women without a family history for this malignancy, the direct and indirect
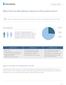
3 Annals of Translational Medicine, Vol 5, No 13 July 2017 Page 3 of 5 Cancer prevention Early diagnosis Target treatment Figure 2 Main advantages and limitations of BRCA population screening. Low prevalence of BRCA mutations the general population Relatively lower penetrance Direct and indirect cost of testing Potential psy chological and clinical consequences cost of genetic testing and, last but not least, the many potential psychological and clinical consequences (Figure 2). The first two aspects (i.e., the low prevalence and lower penetrance of BRCA mutations in the general population) have already been argued, but should be further analyzed according to an economic projection. Consistent with a financial and organizational perspective, genetic testing in clinical laboratories is not like screening for cholesterol, glucose or prostate specific antigen (PSA). We may all agree that the cost of measuring cholesterol, regardless of established criteria of appropriates (8), may produce a relatively modest impact on healthcare economics (i.e., the cost of a cholesterol test is approximately US$ in the local laboratory). Unlike cholesterol, the cost of BRCA testing currently ranges between 300 and 5,000 US$, depending on the analytical technique and the number or type of mutations being assessed. Therefore, given for granted that none of us would not much complain about performing population screening for hypercholesterolemia, the actual impact of widespread testing for BRCA, even performed once in a lifetime, would be nothing but meaningless. According to the United States Census Bureau, the current US population averages million people, million of whom are women (9). Therefore, by estimating an optimistic cost of around 1,000 US$ for detecting the most penetrant BRCA mutations, once in a lifetime genetic testing would cost approximately 165,800 million US$ compared to a 325 million US$ (i.e., ~0.20%) expenditure for annual cholesterol screening in all US women in the age range between years (Figure 3). This estimation would actually make it unfeasible to even imagine public coverage for this type of genetic testing in a world with limited resources, just now recovering from an unprecedented economic crisis. Yet, someone may then argue that BRCA testing might be ultimately cost-effective, since cancer prevention by prophylactic double mastectomy will contribute to lower the overall expenditure for treating breast cancer patients. According to reliable statistics, the cost of treating breast cancer approximated 16.5 billion US$ in the United States in the year 2010 (10). Considering that the prevalence of BRCA mutations is approximately 3% in all breast cancer carriers (4), population screening would theoretically produce a 495 US$ million saving due to prevention of cancer development in carriers of BRCA mutations, but this sum is just 0.30% of the overall predicted expenditure of once in a lifetime BRCA testing (Figure 3). Despite we would all agree that each patient can chose to pay out of pocket for a given test, thus including genetic analyses and BRCA screening (11), the possible consequences on the healthcare system of a positive test results cannot be discounted. Beside simple surveillance or using chemoprevention, preventive bilateral mastectomy, even with no public health insurance option, may be associated with severe health consequences. Surgery carries a number of immediate risks (e.g., bleeding, infections, lymphedema), but also many long-term complications such as onset of chronic symptoms (i.e., pain, tingling or tightness sensations), fatigue, loss of mobility and the need for cosmetic surgery (12), some of which may ultimately lead the patients to seek publicly funded care, so indirectly raising the economic burden of genetic testing. Indeed, strict surveillance in BRCA-positive women is virtually unavoidable, even though the efficiency of mammography for early cancer detection remains unproven, especially for carriers of BRCA1 oncogenic mutations.
4 Page 4 of 5 Lippi et al. BRCA population screening Annual cholesterol screening Once in lifetime BRCA testing Savings for preventing cancer in carriers of BRCA mutations been convincingly associated with BRCA status (5). How these women should be managed or treated, especially if they are underage females? Should oophorectomy be considered, despite the risk of developing ovarian cancer in women with negative familial history for this malignancy is only comprised between 16 41% (5)? No definitive answers to these crucial questions have been provided so far, to the best of our knowledge. Figure 3 Estimated costs of once in lifetime BRCA testing, expenditure for annual cholesterol screening and potential economic savings for preventing cancer in carriers of BRCA mutations. Overuse Negative familial history BRCA testing Figure 4 Over- and under-use of BRCA testing. Positive familial history Underuse The psychological implication of a positive BRCA test in patients with no familial history for this type of cancer is the last, but not meaningless, issue. As earlier discussed, the penetrance of BRCA mutations is comprised between 39 53% in women with negative familial history (5), so meaning that the probability of developing breast cancer may involve, at worst, one every two women. Some women may hence feel empowered by knowing their BRCA status, but others may suffer this condition as an unsurmountable psychological burden. As for other types of genetic analyses, a positive BRCA testing may disclose unpredictable scenarios, being possibly associated with increased anxiety, distress, persuasion of undergoing emotionally-driven but unnecessary preventive surgery, up to possible cases of suicides especially involving psychologically fragile women (13). Then, although prophylactic bilateral mastectomy seems to reduce the future risk of breast cancer by % in women with highly penetrant BRCA mutations (14), this type of surgery does not have any impact on the future risk of ovarian cancer, which has also Conclusions Genetic testing, which allows identifying a kaleidoscope of polymorphisms and penetrant mutations with high accuracy and at an affordable cost for many, has completely revolutionized the history of science and medicine (15), thus becoming the ideal bridge connecting laboratory testing and personalized medicine (16). Nevertheless, although a number of extraordinary technological progresses have allowed to increase the quality of in vitro diagnostics and care, some notable threats are also emerging. Widespread genetic testing, without qualified medical advice and guidance, should probably be seen as a risk rather than an opportunity. In particular, the clinical interpretation of genetic cancer testing is already challenging for geneticists and physicians, but it may become awkward or even deceptive for the patients. The screening for BRCA is not an exception to this rule, since the boundaries between overand under-use are not clearly defined (Figure 4), and the potential risks due to the generation of false-positive results (i.e., unwarranted further testing and unnecessary surgery) have been scarcely explored as well as false-negative findings (i.e., analytical errors, incomplete panels of mutations) (17). Considering that no universal consensus has been reached about the clinical management of patients with oncogenic mutations but no familial history of breast cancer (4,18), being in favor or against a population screening remains a genuine individual opinion. In this still unclear scenario, transparent and patient-oriented genetic counselling becomes imperative. The patient should be clearly informed about the potential clinical advantages and the possible consequences of positive and negative results of BRCA testing, along with the clinical efficacy and the inherent risks of narrow clinical monitoring or management, especially regarding prophylactic mastectomy. Waiting for Godot (i.e., the publication of collective evidence about the clinical efficacy and sustainability of a population BRCA screening), we believe that women at low risk of breast cancer should be allowed to take a medically-driven but autonomous
5 Annals of Translational Medicine, Vol 5, No 13 July 2017 Page 5 of 5 decision about undergoing or declining BRCA testing. Acknowledgements None. Footnote Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. References 1. Tao Z, Shi A, Lu C, et al. Breast Cancer: Epidemiology and Etiology. Cell Biochem Biophys 2015;72: Narod SA, Salmena L. BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations and breast cancer. Discov Med 2011;12: Narod SA, Foulkes WD. BRCA1 and BRCA2: 1994 and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 2004;4: Nelson HD, Fu R, Goddard K, et al. Risk Assessment, Genetic Counseling, and Genetic Testing for BRCA- Related Cancer: Systematic Review to Update the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation. Rockville (MD): Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (US); 2013 Dec. Report No.: EF Kuchenbaecker KB, Hopper JL, Barnes DR, et al. Risks of Breast, Ovarian, and Contralateral Breast Cancer for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers. JAMA 2017;317: McCarthy AM, Armstrong K. The role of testing for BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations in cancer prevention. JAMA Intern Med 2014;174: Spruill L. Benign mimickers of malignant breast lesions. Semin Diagn Pathol 2016;33: Lippi G, Bovo C, Ciaccio M. Inappropriateness in laboratory medicine: an elephant in the room? Ann Transl Med 2017;5: United States Census Bureau. Available online: Last access: 21 June, Costs of Care. The Costs of Breast Cancer in the U.S. Available online: Last access: 21 June, Plebani M, Lippi G. Direct-to-consumer genomewide profiling. N Engl J Med 2011;364: Bodai BI, Tuso P. Breast cancer survivorship: a comprehensive review of long-term medical issues and lifestyle recommendations. Perm J 2015;19: Lippi G, Favaloro EJ, Plebani M. Direct-to-consumer testing: more risks than opportunities. Int J Clin Pract 2011;65: Meijers-Heijboer H, van Geel B, van Putten WL, et al. Breast cancer after prophylactic bilateral mastectomy in women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation. N Engl J Med 2001;345: Katsanis SH, Katsanis N. Molecular genetic testing and the future of clinical genomics. Nat Rev Genet 2013;14: Lippi G, Bassi A, Bovo C. The future of laboratory medicine in the era of precision medicine. J Lab Prec Med 2016;1: Nelson HD, Pappas M, Zakher B, et al. Risk assessment, genetic counseling, and genetic testing for BRCA-related cancer in women: a systematic review to update the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force recommendation. Ann Intern Med 2014;160: Lancaster JM, Powell CB, Kauff ND, et al. Society of Gynecologic Oncologists Education Committee statement on risk assessment for inherited gynecologic cancer predispositions. Gynecol Oncol 2007;107: Cite this article as: Lippi G, Mattiuzzi C, Montagnana M. BRCA population screening for predicting breast cancer: for or against?. doi: / atm
Does Cancer Run in Your Family?
 Does Cancer Run in Your Family? A Patient s Guide to Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome What is Hereditary Cancer? Most cancers occur in people who do not have a strong family history of that
Does Cancer Run in Your Family? A Patient s Guide to Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome What is Hereditary Cancer? Most cancers occur in people who do not have a strong family history of that
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations MARCH 2015 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is a complex disease thought to be caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer
HBOC Syndrome A review of BRCA 1/2 testing, Cancer Risk Assessment, Counseling and Beyond.
 HBOC Syndrome A review of BRCA 1/2 testing, Cancer Risk Assessment, Counseling and Beyond. Conni Murphy, ARNP Cancer Risk Assessment and Genetics Program Jupiter Medical Center Learning Objectives Identify
HBOC Syndrome A review of BRCA 1/2 testing, Cancer Risk Assessment, Counseling and Beyond. Conni Murphy, ARNP Cancer Risk Assessment and Genetics Program Jupiter Medical Center Learning Objectives Identify
Precision Medicine and Genetic Counseling : Is Yes always the correct answer?
 Precision Medicine and Genetic Counseling : Is Yes always the correct answer? Beverly M. Yashar, MS, PhD, CGC Director, Graduate Program in Genetic Counseling Professor, Department of Human Genetics. (yashar@umich.edu)
Precision Medicine and Genetic Counseling : Is Yes always the correct answer? Beverly M. Yashar, MS, PhD, CGC Director, Graduate Program in Genetic Counseling Professor, Department of Human Genetics. (yashar@umich.edu)
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for individuals and families
 Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for individuals and families What is Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC)? Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer is a genetic condition which
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Information for individuals and families What is Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC)? Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer is a genetic condition which
BRCA genes and inherited breast and ovarian cancer. Information for patients
 BRCA genes and inherited breast and ovarian cancer Information for patients This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could be
BRCA genes and inherited breast and ovarian cancer Information for patients This booklet has been written for people who have a personal or family history of breast and/or ovarian cancer that could be
Prophylactic mastectomy, a look at the problem
 www.clinicaloncology.com.ua 1 Prophylactic mastectomy, a look at the problem I.I.Smolanka, S.Y.Skliar, A.D.Loboda The National Cancer Institute, Kiev Summary: The question of the bilateral prophylactic
www.clinicaloncology.com.ua 1 Prophylactic mastectomy, a look at the problem I.I.Smolanka, S.Y.Skliar, A.D.Loboda The National Cancer Institute, Kiev Summary: The question of the bilateral prophylactic
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Rebecca Sutphen, MD, FACMG
 Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer 2015 Rebecca Sutphen, MD, FACMG Among a consecutive series of 11,159 women requesting BRCA testing over one year, 3874 responded to a mailed survey. Most respondents
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer 2015 Rebecca Sutphen, MD, FACMG Among a consecutive series of 11,159 women requesting BRCA testing over one year, 3874 responded to a mailed survey. Most respondents
Management of BRCA Positive Breast Cancer. Archana Ganaraj, MD February 17, 2018 UPDATE ON WOMEN S HEALTH
 Management of BRCA Positive Breast Cancer Archana Ganaraj, MD February 17, 2018 UPDATE ON WOMEN S HEALTH The number of American women who have lost their lives to breast cancer outstrips the total number
Management of BRCA Positive Breast Cancer Archana Ganaraj, MD February 17, 2018 UPDATE ON WOMEN S HEALTH The number of American women who have lost their lives to breast cancer outstrips the total number
HEREDITY & CANCER: Breast cancer as a model
 HEREDITY & CANCER: Breast cancer as a model Pierre O. Chappuis, MD Divisions of Oncology and Medical Genetics University Hospitals of Geneva, Switzerland Genetics, Cancer and Heredity Cancers are genetic
HEREDITY & CANCER: Breast cancer as a model Pierre O. Chappuis, MD Divisions of Oncology and Medical Genetics University Hospitals of Geneva, Switzerland Genetics, Cancer and Heredity Cancers are genetic
The Genetics of Breast and Ovarian Cancer Prof. Piri L. Welcsh
 The Genetics of Breast Piri L. Welcsh, PhD Research Assistant Professor University of Washington School of Medicine Division of Medical Genetics 1 Genetics of cancer All cancers arise from genetic and
The Genetics of Breast Piri L. Welcsh, PhD Research Assistant Professor University of Washington School of Medicine Division of Medical Genetics 1 Genetics of cancer All cancers arise from genetic and
FAQ-Protocol 3. BRCA mutation carrier guidelines Frequently asked questions
 ULast updated: 09/02/2015 Protocol 3 BRCA mutation carrier guidelines Frequently asked questions UQ: How accurate are the remaining lifetime and 5 year breast cancer risks in the table? These figures are
ULast updated: 09/02/2015 Protocol 3 BRCA mutation carrier guidelines Frequently asked questions UQ: How accurate are the remaining lifetime and 5 year breast cancer risks in the table? These figures are
Utilization of BRCA Testing. Breast and Ovarian Cancer in Texas
 Utilization of BRCA Testing in Older Ode Women with Breast and Ovarian Cancer in Texas Ana M. Rodriguez, MD Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Texas Medical Branch
Utilization of BRCA Testing in Older Ode Women with Breast and Ovarian Cancer in Texas Ana M. Rodriguez, MD Assistant Professor Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Texas Medical Branch
Jill Stopfer, MS, CGC Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania
 Jill Stopfer, MS, CGC Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Aging Family history Early menarche Late menopause Nulliparity Estrogen / Progesterone use after menopause More than two alcoholic
Jill Stopfer, MS, CGC Abramson Cancer Center University of Pennsylvania Aging Family history Early menarche Late menopause Nulliparity Estrogen / Progesterone use after menopause More than two alcoholic
patient education Fact Sheet
 patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations OCTOBER 2017 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer run in families. These types are
patient education Fact Sheet PFS007: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations OCTOBER 2017 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutations Cancer is caused by several different factors. A few types of cancer run in families. These types are
Cancer Conversations
 Cancer Conversations Announcer: Welcome to Cancer Conversations, a podcast series from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. In this Episode from July 2014, Dr. Huma Rana, Clinical Director of Dana-Farber s Center
Cancer Conversations Announcer: Welcome to Cancer Conversations, a podcast series from Dana-Farber Cancer Institute. In this Episode from July 2014, Dr. Huma Rana, Clinical Director of Dana-Farber s Center
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Breast and Ovarian Cancer
 Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Breast and Ovarian Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_breast_and_ovarian_cancer 8/1997 8/2017
Corporate Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Breast and Ovarian Cancer File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: genetic_testing_for_breast_and_ovarian_cancer 8/1997 8/2017
INTRODUCTION BREAST CANCER CARE
 INTRODUCTION Breast Cancer Care welcomes the HFEA s consultation on embryo selection for inherited cancer. This is an extremely important and complex issue. Because of this, Breast Cancer Care has encouraged
INTRODUCTION Breast Cancer Care welcomes the HFEA s consultation on embryo selection for inherited cancer. This is an extremely important and complex issue. Because of this, Breast Cancer Care has encouraged
Genetics of Oncology. Ryan Allen Roy MD July 8, 2004 University of Tennessee
 Genetics of Oncology Ryan Allen Roy MD July 8, 2004 University of Tennessee CREOG Objectives Describe the clinical relevance of viral oncogenes Describe the role of aneuploidy in the pathogenesis of neoplasia
Genetics of Oncology Ryan Allen Roy MD July 8, 2004 University of Tennessee CREOG Objectives Describe the clinical relevance of viral oncogenes Describe the role of aneuploidy in the pathogenesis of neoplasia
This information explains the advice about familial breast cancer (breast cancer in the family) that is set out in NICE guideline CG164.
 Familial breast cancer (breast cancer in the family) Information for the public Published: 1 June 2013 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on the care and support that should
Familial breast cancer (breast cancer in the family) Information for the public Published: 1 June 2013 nice.org.uk About this information NICE guidelines provide advice on the care and support that should
GeneHealth BRCA 1&2_ qxp_Layout 1 21/02/ :44 Page 3 BRCA1 & BRCA2 GeneHealth UK
 GeneHealth BRCA 1&2_8.2.17.qxp_Layout 1 21/02/2017 16:44 Page 3 BRCA1 & BRCA2 GeneHealth UK GeneHealth BRCA 1&2_8.2.17.qxp_Layout 1 21/02/2017 16:44 Page 4 BRCA1 & BRCA2 What is hereditary breast cancer?
GeneHealth BRCA 1&2_8.2.17.qxp_Layout 1 21/02/2017 16:44 Page 3 BRCA1 & BRCA2 GeneHealth UK GeneHealth BRCA 1&2_8.2.17.qxp_Layout 1 21/02/2017 16:44 Page 4 BRCA1 & BRCA2 What is hereditary breast cancer?
BRCA Precertification Information Request Form
 BRCA Precertification Information Request Form Failure to complete this form in its entirety may result in the delay of review. Fax to: BRCA Precertification Department Fax number: 1-860-975-9126 Section
BRCA Precertification Information Request Form Failure to complete this form in its entirety may result in the delay of review. Fax to: BRCA Precertification Department Fax number: 1-860-975-9126 Section
Inherited Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis and Prevention
 Inherited Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis and Prevention Dr. Jacob Korach - Deputy director Gynecologic Oncology (past chair - Israeli Society of Gynecologic Oncology) Prof. Eitan Friedman - Head, Oncogenetics
Inherited Ovarian Cancer Diagnosis and Prevention Dr. Jacob Korach - Deputy director Gynecologic Oncology (past chair - Israeli Society of Gynecologic Oncology) Prof. Eitan Friedman - Head, Oncogenetics
Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer 15 Years of Progress
 Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer 15 Years of Progress Bethan Powell, M. D. Kaiser Permanente UCSF Gynecologic Cancer Risk Program Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer Syndromes BRCA 1 and 2: ovarian Lynch: ovarian/endometrial
Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer 15 Years of Progress Bethan Powell, M. D. Kaiser Permanente UCSF Gynecologic Cancer Risk Program Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer Syndromes BRCA 1 and 2: ovarian Lynch: ovarian/endometrial
Outline. Identifying your risk for hereditary breast or ovarian cancer. Genetics 101. What causes cancer? Genetics
 Identifying your risk for hereditary breast or ovarian cancer David Andorsky, MD Breanna Roscow, MS, CGC 303-993-0161 Outline Genetics and biology of hereditary cancer syndromes BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genetic
Identifying your risk for hereditary breast or ovarian cancer David Andorsky, MD Breanna Roscow, MS, CGC 303-993-0161 Outline Genetics and biology of hereditary cancer syndromes BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genetic
Policy Specific Section: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental. October 15, 1997 October 9, 2013
 Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Breast and/or Ovarian Cancer Type: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section: Laboratory/Pathology Original Policy Date:
Medical Policy Genetic Testing for Hereditary Breast and/or Ovarian Cancer Type: Medical Necessity and Investigational / Experimental Policy Specific Section: Laboratory/Pathology Original Policy Date:
BRCA1 & BRCA2 GeneHealth UK
 BRCA1 & BRCA2 GeneHealth UK BRCA1 & BRCA2 What is hereditary breast cancer? Cancer is unfortunately very common, with 1 in 2 people developing cancer at some point in their lifetime. Breast cancer occurs
BRCA1 & BRCA2 GeneHealth UK BRCA1 & BRCA2 What is hereditary breast cancer? Cancer is unfortunately very common, with 1 in 2 people developing cancer at some point in their lifetime. Breast cancer occurs
From laboratory instrumentation to physician s brain calibration: the next frontier for improving diagnostic accuracy?
 Perspective Page 1 of 5 From laboratory instrumentation to physician s brain calibration: the next frontier for improving diagnostic accuracy? Giuseppe Lippi 1, Gianfranco Cervellin 2 1 Section of Clinical
Perspective Page 1 of 5 From laboratory instrumentation to physician s brain calibration: the next frontier for improving diagnostic accuracy? Giuseppe Lippi 1, Gianfranco Cervellin 2 1 Section of Clinical
Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes
 Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes Jason M. Goldman, MD, FACP FAU School of Medicine Syndromes Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
Primary Care Approach to Genetic Cancer Syndromes Jason M. Goldman, MD, FACP FAU School of Medicine Syndromes Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC)
Sporadic Cancer - Cancer which occurs by chance. People with sporadic cancer typically do not have relatives with the same type of cancer.
 to risk assessment Hereditary Cancer Testing: Is it Right for You? This workbook is designed to help you decide if hereditary cancer testing is right for you and should be reviewed with a trained healthcare
to risk assessment Hereditary Cancer Testing: Is it Right for You? This workbook is designed to help you decide if hereditary cancer testing is right for you and should be reviewed with a trained healthcare
6/8/17. Genetics 101. Professor, College of Medicine. President & Chief Medical Officer. Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer 2017
 Genetics 101 Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer 2017 Rebecca Sutphen, MD, FACMG Professor, College of Medicine President & Chief Medical Officer INVASIVE CANCER GENETICALLY ALTERED CELL HYPERPLASIA DYSPLASIA
Genetics 101 Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer 2017 Rebecca Sutphen, MD, FACMG Professor, College of Medicine President & Chief Medical Officer INVASIVE CANCER GENETICALLY ALTERED CELL HYPERPLASIA DYSPLASIA
Approximately 5% to 10% of breast cancer (BC) is hereditary in nature. Since. By Dawna Gilchrist, MD, FRCPC, FCCMG
 By Dawna Gilchrist, MD, FRCPC, FCCMG Approximately 5% to 10% of breast cancer (BC) is hereditary in nature. Since the discovery of the genes BRCA 1 and 2 in the early 1990s, genetic counselling and testing
By Dawna Gilchrist, MD, FRCPC, FCCMG Approximately 5% to 10% of breast cancer (BC) is hereditary in nature. Since the discovery of the genes BRCA 1 and 2 in the early 1990s, genetic counselling and testing
GENETIC MANAGEMENT OF A FAMILY HISTORY OF BREAST AND / OR OVARIAN CANCER. Dr Abhijit Dixit. Family Health Clinical Genetics
 GENETIC MANAGEMENT OF A FAMILY HISTORY OF BREAST AND / OR OVARIAN CANCER Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review
GENETIC MANAGEMENT OF A FAMILY HISTORY OF BREAST AND / OR OVARIAN CANCER Full Title of Guideline: Author (include email and role): Division & Speciality: Scope (Target audience, state if Trust wide): Review
The New World of Genomics
 The New World of Genomics Amy Sturm, LCGC Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Learning Objectives To define genomic medicine To review early
The New World of Genomics Amy Sturm, LCGC Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Learning Objectives To define genomic medicine To review early
The New World of Genomics
 The New World of Genomics Amy Sturm, LCGC Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Learning Objectives To define genomic medicine To review early
The New World of Genomics Amy Sturm, LCGC Associate Professor Department of Internal Medicine The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center Learning Objectives To define genomic medicine To review early
Medical Policy Manual. Topic: Genetic Testing for Hereditary Breast and/or Ovarian Cancer. Date of Origin: January 27, 2011
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Genetic Testing for Hereditary Breast and/or Ovarian Cancer Date of Origin: January 27, 2011 Section: Genetic Testing Last Reviewed Date: July 2014 Policy No: 02 Effective
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Genetic Testing for Hereditary Breast and/or Ovarian Cancer Date of Origin: January 27, 2011 Section: Genetic Testing Last Reviewed Date: July 2014 Policy No: 02 Effective
GeneticsNow TM. A Guide to Testing Hereditary Conditions in Women & Men. Patient & Physician Information
 GeneticsNow TM A Guide to Testing Hereditary Conditions in Women & Men Patient & Physician Information How can BRCA status affect your health? Everyone has BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. However, sometimes the
GeneticsNow TM A Guide to Testing Hereditary Conditions in Women & Men Patient & Physician Information How can BRCA status affect your health? Everyone has BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes. However, sometimes the
BRCAnowTM It s Your Decision
 Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer BRCAnowTM It s Your Decision Patient & Physician Information What is BRCA? The breast cancer genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 are found within an individual s normal genetic makeup;
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer BRCAnowTM It s Your Decision Patient & Physician Information What is BRCA? The breast cancer genes BRCA1 and BRCA2 are found within an individual s normal genetic makeup;
So, Who are the appropriate individuals that should consider genetic counseling and genetic testing?
 Hello, I m Banu Arun, Professor of Breast Medical Oncology and Co-Director of Clinical Cancer Genetics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Today I will be discussing with you Hereditary
Hello, I m Banu Arun, Professor of Breast Medical Oncology and Co-Director of Clinical Cancer Genetics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Today I will be discussing with you Hereditary
Cancer Genomics 101. BCCCP 2015 Annual Meeting
 Cancer Genomics 101 BCCCP 2015 Annual Meeting Objectives Identify red flags in a person s personal and family medical history that indicate a potential inherited susceptibility to cancer Develop a systematic
Cancer Genomics 101 BCCCP 2015 Annual Meeting Objectives Identify red flags in a person s personal and family medical history that indicate a potential inherited susceptibility to cancer Develop a systematic
Information leaflet for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer. Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC)
 Information leaflet for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) What is Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC)? Hereditary Breast
Information leaflet for women with an increased lifetime risk of breast and ovarian cancer Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC) What is Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer (HBOC)? Hereditary Breast
A Patient s Guide to. Hereditary Ovarian Cancer: Is Hereditary Cancer Testing Right for You?
 A Patient s Guide to Hereditary Ovarian Cancer: Is Hereditary Cancer Testing Right for You? What is Hereditary Cancer? Most cancers occur in people who do not have a strong family history of that cancer.
A Patient s Guide to Hereditary Ovarian Cancer: Is Hereditary Cancer Testing Right for You? What is Hereditary Cancer? Most cancers occur in people who do not have a strong family history of that cancer.
Enhanced Surveillance vs. Risk Reducing Mastectomy for BRCA+ Patients with Advanced Ovarian Cancer: Surgical Futility or Valuable Prevention?
 Enhanced Surveillance vs. Risk Reducing Mastectomy for BRCA+ Patients with Advanced Ovarian Cancer: Surgical Futility or Valuable Prevention? Gina Westhoff, MD LMG Gynecologic Oncologist gwestho@lhs.org
Enhanced Surveillance vs. Risk Reducing Mastectomy for BRCA+ Patients with Advanced Ovarian Cancer: Surgical Futility or Valuable Prevention? Gina Westhoff, MD LMG Gynecologic Oncologist gwestho@lhs.org
Introduction to Genetics
 Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
Introduction to Genetics Table of contents Chromosome DNA Protein synthesis Mutation Genetic disorder Relationship between genes and cancer Genetic testing Technical concern 2 All living organisms consist
PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES
 PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES BRCA GENETIC TESTING The purpose of this document is to assist providers enrolled in the Connecticut Medical Assistance Program (CMAP) with the information needed to support
PROVIDER POLICIES & PROCEDURES BRCA GENETIC TESTING The purpose of this document is to assist providers enrolled in the Connecticut Medical Assistance Program (CMAP) with the information needed to support
BSO, HRT, and ERT. No relevant financial disclosures
 BSO, HRT, and ERT Jubilee Brown, MD Professor & Associate Director, Gynecologic Oncology Levine Cancer Institute at the Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte, North Carolina No relevant financial disclosures
BSO, HRT, and ERT Jubilee Brown, MD Professor & Associate Director, Gynecologic Oncology Levine Cancer Institute at the Carolinas HealthCare System Charlotte, North Carolina No relevant financial disclosures
Understanding Your Genetic Test Result. Positive for a Deleterious Mutation or Suspected Deleterious
 Understanding Your Genetic Test Result Positive for a Deleterious Mutation or Suspected Deleterious This workbook is designed to help you understand the results of your genetic test and is best reviewed
Understanding Your Genetic Test Result Positive for a Deleterious Mutation or Suspected Deleterious This workbook is designed to help you understand the results of your genetic test and is best reviewed
Genetics of Breast and Ovarian Cancer: Risk Assessment, Screening, and Risk Reduction
 Genetics of Breast and Ovarian Cancer: Risk Assessment, Screening, and Risk Reduction Forum INCA-ASCO sobre Cancer Hereditario e Predisposicao Genetica ao Cancer Jeffrey N. Weitzel, M.D. Professor of Oncology
Genetics of Breast and Ovarian Cancer: Risk Assessment, Screening, and Risk Reduction Forum INCA-ASCO sobre Cancer Hereditario e Predisposicao Genetica ao Cancer Jeffrey N. Weitzel, M.D. Professor of Oncology
So, now, that we have reviewed some basics of cancer genetics I will provide an overview of some common syndromes.
 Hello. My name is Maureen Mork and I m a Certified Genetic Counselor in the Clinical Cancer Genetics Program at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I ll be lecturing today on the Cancer
Hello. My name is Maureen Mork and I m a Certified Genetic Counselor in the Clinical Cancer Genetics Program at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I ll be lecturing today on the Cancer
What Are Genes And Chromosomes?
 Clinical Genetics Predictive testing for a Breast Cancer 2(BRCA2) Gene alteration Information for families where an altered cancer gene has been found and who are considering undergoing predictive testing
Clinical Genetics Predictive testing for a Breast Cancer 2(BRCA2) Gene alteration Information for families where an altered cancer gene has been found and who are considering undergoing predictive testing
Genetic Testing: who, what, why?
 Genetic Testing: who, what, why? Gina Westhoff MD LMG Gynecologic Oncology March 16, 2019 Disclosures Speaker for Merck (unrelated to today s topic) Objectives Determine who should undergo genetic risk
Genetic Testing: who, what, why? Gina Westhoff MD LMG Gynecologic Oncology March 16, 2019 Disclosures Speaker for Merck (unrelated to today s topic) Objectives Determine who should undergo genetic risk
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention
 Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
Ovarian Cancer Causes, Risk Factors, and Prevention Risk Factors A risk factor is anything that affects your chance of getting a disease such as cancer. Learn more about the risk factors for ovarian cancer.
Universal BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genetic Testing for Ovarian Cancer Patients
 Universal BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genetic Testing for Ovarian Cancer Patients An initiative to improve genetic counseling and genetic testing rates among patients with high grade, non-mucinous epithelial ovarian
Universal BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genetic Testing for Ovarian Cancer Patients An initiative to improve genetic counseling and genetic testing rates among patients with high grade, non-mucinous epithelial ovarian
Progress Update June 2017 Lay Summary Funding: $6,000,000 Grant Funded: July 2015 Dream Team Members Dream Team Leader:
 SU2C -Ovarian Cancer Research Fund Alliance-National Ovarian Cancer Coalition Dream Team Translational Research Grant: DNA Repair Therapies for Ovarian Cancer AND SU2C Catalyst Merck-Supported Supplemental
SU2C -Ovarian Cancer Research Fund Alliance-National Ovarian Cancer Coalition Dream Team Translational Research Grant: DNA Repair Therapies for Ovarian Cancer AND SU2C Catalyst Merck-Supported Supplemental
LESSON 5.2 WORKBOOK. What do cancer screens really tell us? Workbook Lesson 5.2
 Mortality rate The rate at which people die from a specific cancer. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 5.2 WORKBOOK What do cancer screens really tell us? Treating cancer successfully
Mortality rate The rate at which people die from a specific cancer. For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. LESSON 5.2 WORKBOOK What do cancer screens really tell us? Treating cancer successfully
Information for You and Your Family
 Information for You and Your Family What is Prevention? Cancer prevention is action taken to lower the chance of getting cancer. In 2017, more than 1.6 million people will be diagnosed with cancer in the
Information for You and Your Family What is Prevention? Cancer prevention is action taken to lower the chance of getting cancer. In 2017, more than 1.6 million people will be diagnosed with cancer in the
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer
 What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
What You Need to Know About Ovarian Cancer About Us The Rhode Island Ovarian Cancer Alliance (RIOCA) was formed in honor and memory of Jessica Morris. Jessica was diagnosed with Stage IIIC Ovarian Cancer
GRANT SUBMISSION Northern Sunrise County. Submitted to: Peter Thomas, CAO
 GRANT SUBMISSION Northern Sunrise County Submitted to: Peter Thomas, CAO January 2016 Contents 1. PROJECT OVERVIEW... 1 2. ABOUT THE CAUSE... 1 2.1. What is HBOC syndrome?... 1 2.1. What can be done?...
GRANT SUBMISSION Northern Sunrise County Submitted to: Peter Thomas, CAO January 2016 Contents 1. PROJECT OVERVIEW... 1 2. ABOUT THE CAUSE... 1 2.1. What is HBOC syndrome?... 1 2.1. What can be done?...
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Testing Page 1 of 33 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Testing Pre-Determination of Services IS REQUIRED by the Member
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Testing Page 1 of 33 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Testing Pre-Determination of Services IS REQUIRED by the Member
GeneHealth BreastGene_New qxp_Layout 1 21/02/ :42 Page 3 BreastGene GeneHealth UK
 GeneHealth BreastGene_New 8.2.17.qxp_Layout 1 21/02/2017 16:42 Page 3 BreastGene GeneHealth UK BreastGene What is hereditary breast cancer? Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Unfortunately
GeneHealth BreastGene_New 8.2.17.qxp_Layout 1 21/02/2017 16:42 Page 3 BreastGene GeneHealth UK BreastGene What is hereditary breast cancer? Breast cancer is the most common cancer in the UK. Unfortunately
The assessment of genetic risk of breast cancer: a set of GP guidelines
 Family Practice Vol. 16, No. 1 Oxford University Press 1999 Printed in Great Britain The assessment of genetic risk of breast cancer: a set of GP guidelines GH de Bock, a,b TPM Vliet Vlieland, b GCHA Hageman,
Family Practice Vol. 16, No. 1 Oxford University Press 1999 Printed in Great Britain The assessment of genetic risk of breast cancer: a set of GP guidelines GH de Bock, a,b TPM Vliet Vlieland, b GCHA Hageman,
Predictive and Diagnostic Testing for Cancer in Women. Aparna Rajadhyaksha MD
 Predictive and Diagnostic Testing for Cancer in Women Aparna Rajadhyaksha MD Hereditary Cancer s in Women BRCA1 &2 Other Breast Cancer Genes Li Fraumeni PTEN CHEK2 BRCA1&2 t BRCA1 is part of a complex
Predictive and Diagnostic Testing for Cancer in Women Aparna Rajadhyaksha MD Hereditary Cancer s in Women BRCA1 &2 Other Breast Cancer Genes Li Fraumeni PTEN CHEK2 BRCA1&2 t BRCA1 is part of a complex
Genomic/Genetic Services: Barriers to Access. Sue Friedman, DVM National Academies of Science Roundtable 06/26/18
 Genomic/Genetic Services: Barriers to Access Sue Friedman, DVM National Academies of Science Roundtable 06/26/18 No conflicts to disclose Disclosure Overview Awareness and knowledge Insurance coverage
Genomic/Genetic Services: Barriers to Access Sue Friedman, DVM National Academies of Science Roundtable 06/26/18 No conflicts to disclose Disclosure Overview Awareness and knowledge Insurance coverage
MP Genetic Testing for BRCA1 or BRCA2 for Hereditary Breast/Ovarian Cancer Syndrome and Other High-Risk Cancers
 Medical Policy MP 2.04.02 Genetic Testing for BRCA1 or BRCA2 for Hereditary Breast/Ovarian Cancer Syndrome and Other High-Risk BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.02 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 02/15/2019
Medical Policy MP 2.04.02 Genetic Testing for BRCA1 or BRCA2 for Hereditary Breast/Ovarian Cancer Syndrome and Other High-Risk BCBSA Ref. Policy: 2.04.02 Last Review: 11/15/2018 Effective Date: 02/15/2019
Cancer Survivorship Symposium Cancer and Heredity January 16, Jeanne P. Homer, MS Licensed Certified Genetic Counselor
 Cancer Survivorship Symposium Cancer and Heredity January 16, 2017 Jeanne P. Homer, MS Licensed Certified Genetic Counselor Outline Cancer and Heredity Hereditary Cancer Risk Assessment & Genetic testing
Cancer Survivorship Symposium Cancer and Heredity January 16, 2017 Jeanne P. Homer, MS Licensed Certified Genetic Counselor Outline Cancer and Heredity Hereditary Cancer Risk Assessment & Genetic testing
ProstateGene What is hereditary prostate cancer? What are genes?
 ProstateGene ProstateGene What is hereditary prostate cancer? Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men in the UK. Unfortunately, 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer, with 75% being
ProstateGene ProstateGene What is hereditary prostate cancer? Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men in the UK. Unfortunately, 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer, with 75% being
Key Recommendations. Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer
 Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program Lead, Kaiser Permanente Northern California
Gynecologic management of women with inherited risk of gynecologic cancer C. Bethan Powell MD Kaiser Permanente Northern California Gynecologic Oncology Program Lead, Kaiser Permanente Northern California
Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer. Information for Women at Increased Risk
 Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer Information for Women at Increased Risk Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health 2017 The Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health Level 5 2C Herbert St St
Surgery to Reduce the Risk of Ovarian Cancer Information for Women at Increased Risk Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health 2017 The Centre for Genetics Education NSW Health Level 5 2C Herbert St St
Eligibility criteria for prophylactic treatment allowance
 Eligibility criteria for prophylactic treatment allowance Southern Cross will only pay the prophylactic treatment allowance for the following healthcare services when the applicable eligibility criteria
Eligibility criteria for prophylactic treatment allowance Southern Cross will only pay the prophylactic treatment allowance for the following healthcare services when the applicable eligibility criteria
AllinaHealthSystems 1
 Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
Overview Biology and Introduction to the Genetics of Cancer Denise Jones, MS, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Virginia Piper Cancer Service Line I. Our understanding of cancer the historical perspective
So how much of breast and ovarian cancer is hereditary? A). 5 to 10 percent. B). 20 to 30 percent. C). 50 percent. Or D). 65 to 70 percent.
 Welcome. My name is Amanda Brandt. I am one of the Cancer Genetic Counselors at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Today, we are going to be discussing how to identify patients at high
Welcome. My name is Amanda Brandt. I am one of the Cancer Genetic Counselors at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. Today, we are going to be discussing how to identify patients at high
Management of BRCA mutation carriers
 Management of BRCA mutation carriers Clinical Case Presentation Shani Paluch-Shimon, MBBS, MSc Head, Breast Cancer Service for Young Women Oncology Institute Sheba Medical Center, Israel esmo.org DISCLOSURES
Management of BRCA mutation carriers Clinical Case Presentation Shani Paluch-Shimon, MBBS, MSc Head, Breast Cancer Service for Young Women Oncology Institute Sheba Medical Center, Israel esmo.org DISCLOSURES
What is the gynecologist s role in the care of BRCA previvors?
 What is the gynecologist s role in the care of BRCA previvors? Here, your patient s options for surgery and your best options for her follow-up care and ongoing surveillance OBG Manag. Sept 2013;25(9):10-14.
What is the gynecologist s role in the care of BRCA previvors? Here, your patient s options for surgery and your best options for her follow-up care and ongoing surveillance OBG Manag. Sept 2013;25(9):10-14.
Applies to: All Aetna plans, except Traditional Choice plans. All Innovation Health plans, except indemnity plans
 BRCA Precertification Information Request Form Applies to: All Aetna plans, except Traditional Choice plans All Innovation Health plans, except indemnity plans All Health benefits and health insurance
BRCA Precertification Information Request Form Applies to: All Aetna plans, except Traditional Choice plans All Innovation Health plans, except indemnity plans All Health benefits and health insurance
The impact of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC) syndrome testing on patient management and your practice
 The impact of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC) syndrome testing on patient management and your practice Use BRACAnalysis as a guide in your medical and surgical management BRACAnalysis testing
The impact of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC) syndrome testing on patient management and your practice Use BRACAnalysis as a guide in your medical and surgical management BRACAnalysis testing
BRCA Testing in Ovarian cancer Arabic Approach
 BRCA Testing in Ovarian cancer Arabic Approach Khalid El Khalfaoui Departement of Gynecology and Gyn Oncology Wermelskirchen Hospital 25.04.2018 Krankenhaus Wermelskirchen GmbH I 1 Development of cancer
BRCA Testing in Ovarian cancer Arabic Approach Khalid El Khalfaoui Departement of Gynecology and Gyn Oncology Wermelskirchen Hospital 25.04.2018 Krankenhaus Wermelskirchen GmbH I 1 Development of cancer
Hereditary breast cancer who to refer to a cancer genetics clinic and how to counsel patients with
 Hereditary breast cancer who to refer to a cancer genetics clinic and how to counsel patients with positive and negative results? SAMO Workshop Luzern 3./4.10.2014 Dr. med. Barbara Bolliger TumorTumor-
Hereditary breast cancer who to refer to a cancer genetics clinic and how to counsel patients with positive and negative results? SAMO Workshop Luzern 3./4.10.2014 Dr. med. Barbara Bolliger TumorTumor-
Why Test for Hereditary Cancer in Preventive Care?
 Why Test for Hereditary Cancer in Preventive Care? Millions of people are sidelined by cancer. Wouldn't it be worth it for your patients to know their risk? background HEREDITARY (5-10%) More than 1 in
Why Test for Hereditary Cancer in Preventive Care? Millions of people are sidelined by cancer. Wouldn't it be worth it for your patients to know their risk? background HEREDITARY (5-10%) More than 1 in
Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer
 CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
CHAPTER 19 THE ORGANIZATION AND CONTROL OF EUKARYOTIC GENOMES Section D: The Molecular Biology of Cancer 1. Cancer results from genetic changes that affect the cell cycle 2. Oncogene proteins and faulty
Assessment and Management of Genetic Predisposition to Breast Cancer. Dr Munaza Ahmed Consultant Clinical Geneticist 2/7/18
 Assessment and Management of Genetic Predisposition to Breast Cancer Dr Munaza Ahmed Consultant Clinical Geneticist 2/7/18 Overview The role of the Cancer Genetics team NICE guidelines for Familial Breast
Assessment and Management of Genetic Predisposition to Breast Cancer Dr Munaza Ahmed Consultant Clinical Geneticist 2/7/18 Overview The role of the Cancer Genetics team NICE guidelines for Familial Breast
Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers
 Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers The term cancer applies to a group of diseases in which cells grow abnormally and form a malignant tumor. It is a long term multistage genetic process. The first
Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers The term cancer applies to a group of diseases in which cells grow abnormally and form a malignant tumor. It is a long term multistage genetic process. The first
WELCOME. Taking Care of Your Health. April 30, 8 am to noon
 WELCOME Taking Care of Your Health April 30, 8 am to noon Cancer: Know Your Risk Emily Kuchinsky, MS, CGC, Certified Genetic Counselor Sporadic Cancer Lifetime Probability- Women Family Cluster Risk factors
WELCOME Taking Care of Your Health April 30, 8 am to noon Cancer: Know Your Risk Emily Kuchinsky, MS, CGC, Certified Genetic Counselor Sporadic Cancer Lifetime Probability- Women Family Cluster Risk factors
1. Collaborative Group on Epidemiological Studies of Ovarian Cancer. Ovarian cancer and oral contraceptives: collaborative reanalysis of data from 45
 1 2 3 1. Collaborative Group on Epidemiological Studies of Ovarian Cancer. Ovarian cancer and oral contraceptives: collaborative reanalysis of data from 45 epidemiological studies including 23,257 women
1 2 3 1. Collaborative Group on Epidemiological Studies of Ovarian Cancer. Ovarian cancer and oral contraceptives: collaborative reanalysis of data from 45 epidemiological studies including 23,257 women
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Screening & Genetic Counseling
 Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Screening & Genetic Counseling Cecelia Bellcross, PhD, MS, CGC Emory University School of Medicine Department of Human Genetics The First Line of Defense February 21,
Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer Screening & Genetic Counseling Cecelia Bellcross, PhD, MS, CGC Emory University School of Medicine Department of Human Genetics The First Line of Defense February 21,
Understanding Your Genetic Test Result. Positive for a Deleterious Mutation or Suspected Deleterious
 Understanding Your Genetic Test Result Positive for a Deleterious Mutation or Suspected Deleterious This workbook is designed to help you understand the results of your genetic test and is best reviewed
Understanding Your Genetic Test Result Positive for a Deleterious Mutation or Suspected Deleterious This workbook is designed to help you understand the results of your genetic test and is best reviewed
Information leaflet for for men from families with a known alteration in the BRCA1/2 gene. BRCA1 and BRCA2 for men
 Information leaflet for for men from families with a known alteration in the BRCA1/2 gene BRCA1 and BRCA2 for men Introduction BRCA1 and BRCA2 are two genes which can sometimes be linked to breast, ovarian
Information leaflet for for men from families with a known alteration in the BRCA1/2 gene BRCA1 and BRCA2 for men Introduction BRCA1 and BRCA2 are two genes which can sometimes be linked to breast, ovarian
--- or not, and do we need to come up with newer strategies for ovarian cancer screening.
 My name is Dr. Karen Lu and I am a Professor of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I also serve as Co-Medical Director for Clinical Cancer Genetics. I m going to
My name is Dr. Karen Lu and I am a Professor of Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. I also serve as Co-Medical Director for Clinical Cancer Genetics. I m going to
Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer: 20 Years of Progress and Future Directions
 Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer: 20 Years of Progress and Future Directions Noah D. Kauff, MD, FACOG Director, Clinical Cancer Genetics Duke Cancer Institute / Duke University Health System Disclosures
Inherited Breast and Ovarian Cancer: 20 Years of Progress and Future Directions Noah D. Kauff, MD, FACOG Director, Clinical Cancer Genetics Duke Cancer Institute / Duke University Health System Disclosures
LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK. How do normal cells become cancer cells? Workbook Lesson 3.2
 For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. Transformation the process by which a cell acquires characteristics of a tumor cell. LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do normal cells become cancer cells?
For a complete list of defined terms, see the Glossary. Transformation the process by which a cell acquires characteristics of a tumor cell. LESSON 3.2 WORKBOOK How do normal cells become cancer cells?
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 BRCA1 and BRCA2 Testing Page 1 of 26 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Testing Pre-Determination of Services IS REQUIRED by the Member
BRCA1 and BRCA2 Testing Page 1 of 26 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: BRCA1 and BRCA2 Testing Pre-Determination of Services IS REQUIRED by the Member
Lynch Syndrome. Angie Strang, PGY2
 Lynch Syndrome Angie Strang, PGY2 Background Previously hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer Autosomal dominant inherited cancer susceptibility syndrome Caused by defects in the mismatch repair system
Lynch Syndrome Angie Strang, PGY2 Background Previously hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer Autosomal dominant inherited cancer susceptibility syndrome Caused by defects in the mismatch repair system
CANCER GENETICS PROVIDER SURVEY
 Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Dear Participant, Previously you agreed to participate in an evaluation of an education program we developed for primary care providers on the topic of cancer genetics. This is an IRB-approved, CDCfunded
Identification of patients suggestive of hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome that warrants further professional evaluation.
 Allina Breast Program Committee Consensus Guidelines These guidelines apply to clinical interventions that have well-documented outcomes, but whose outcomes are not clearly desirable to all patients Identification
Allina Breast Program Committee Consensus Guidelines These guidelines apply to clinical interventions that have well-documented outcomes, but whose outcomes are not clearly desirable to all patients Identification
Risk Reduction management for Ovarian Cancer in Women with BRCA1/2 Mutation
 Risk Reduction management for Ovarian Cancer in Women with BRCA1/2 Mutation Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 2018. 4. 6 (Fri) Songdo, Incheon, Korea Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer Clinic Precision Medicine
Risk Reduction management for Ovarian Cancer in Women with BRCA1/2 Mutation Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 2018. 4. 6 (Fri) Songdo, Incheon, Korea Hereditary Gynecologic Cancer Clinic Precision Medicine
GENETIC TESTING FOR HEREDITARY BREAST AND OVARIAN CANCER BRCA1 BRCA2
 GENETIC TESTING FOR HEREDITARY BREAST AND OVARIAN CANCER BRCA1 BRCA2 Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
GENETIC TESTING FOR HEREDITARY BREAST AND OVARIAN CANCER BRCA1 BRCA2 Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific
Presymptomatic diagnosis of hereditary breast cancer
 Presymptomatic diagnosis of hereditary breast cancer Published Oct 5, 2000 Version 1 Findings by SBU Alert The discovery that mutations in two specific genes increase the risk for breast cancer and ovarian
Presymptomatic diagnosis of hereditary breast cancer Published Oct 5, 2000 Version 1 Findings by SBU Alert The discovery that mutations in two specific genes increase the risk for breast cancer and ovarian
Does Cancer Run in Your Family?
 Does Cancer Run in Your Family? Nancie Petrucelli, MS, CGC Clinical Assistant Professor Certified Genetic Counselor/Coordinator Cancer Genetic Counseling Service Karmanos Cancer Institute Wayne State University
Does Cancer Run in Your Family? Nancie Petrucelli, MS, CGC Clinical Assistant Professor Certified Genetic Counselor/Coordinator Cancer Genetic Counseling Service Karmanos Cancer Institute Wayne State University
ProstateGene GeneHealth UK
 ProstateGene GeneHealth UK ProstateGene What is hereditary Prostate cancer? Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men in the UK. Unfortunately, 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer,
ProstateGene GeneHealth UK ProstateGene What is hereditary Prostate cancer? Prostate cancer is the most common cancer among men in the UK. Unfortunately, 1 in 8 men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer,
HBOC. Jessica M. Salamone, ScM, CGC
 HBOC Jessica M. Salamone, ScM, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Director of the Cancer Risk Assessment & Genetic Counseling Program Elizabeth Wende Breast Care, LLC Elizabeth Wende Breast Care Internationally
HBOC Jessica M. Salamone, ScM, CGC Certified Genetic Counselor Director of the Cancer Risk Assessment & Genetic Counseling Program Elizabeth Wende Breast Care, LLC Elizabeth Wende Breast Care Internationally
HOW COVERAGE EXCLUSIONS IN MARKETPLACE PLANS COMPROMISE WOMEN S HEALTH AND ECONOMIC SECURITY
 HOW COVERAGE EXCLUSIONS IN MARKETPLACE PLANS COMPROMISE WOMEN S HEALTH AND ECONOMIC SECURITY Dania Palanker, Georgetown University Sue Friedman, FORCE Tim Clement, Parity Track Janel George, National Women
HOW COVERAGE EXCLUSIONS IN MARKETPLACE PLANS COMPROMISE WOMEN S HEALTH AND ECONOMIC SECURITY Dania Palanker, Georgetown University Sue Friedman, FORCE Tim Clement, Parity Track Janel George, National Women
