Appraisal of hepatic lipase and lipoprotein lipase activities in
|
|
|
- Nora Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Appraisal of hepatic lipase and lipoprotein lipase activities in mice G.M. Dallinga-Thie 1*, A.J. Zonneveld-de Boer 2, L.C. van Vark-van der Zee 3, R. van Haperen 4, T. van Gent 4, H. Jansen 2, R. De Crom 4, A. van Tol 4 1 Department of Vascular Medicine, Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, the Netherlands; 2 Department of Clinical Chemistry, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 3 Department of Vascular Medicine, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 4 Department of Cell Biology & Genetics, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands. Corresponding author G.M. Dallinga-Thie PhD Department of Vascular Medicine, G1-113 Academic Medical Center Amsterdam PO Box DD Amsterdam the Netherlands Phone: Fax: g.m.dallinga@amc.uva.nl 1
2 Keywords: hepatic lipase, lipoprotein lipase, mice Abstract A variety of methods are currently used to analyse hepatic lipase (HL) and lipoprotein lipase (LPL) activities in mice. In search of a simple methodology we analysed mouse pre-heparin and post-heparin plasma LPL and HL activities using specific polyclonal antibodies raised in rabbit against rat HL (anti-hl) and in goat against rat LPL (anti-lpl). As an alternative, we analysed HL activity in the presence of 1 M NaCl, a condition known to inhibit LPL activity in humans. The assays were validated using plasma samples from wild type and HL-deficient C57BL/6 mice. We now show that the use of 1 M NaCl for the inhibition of plasma LPL activity in mice may generate incorrect measurements of both LPL and HL activities. Our data indicate that HL can be measured directly, without heparin injection, in pre-heparin plasma, because virtually all HL is present in an unbound form circulating in plasma. In contrast, measurable LPL activity is only present in postheparin plasma. Both HL and LPL can be measured using the same assay conditions (low salt and presence of apocii as LPL activator). Total lipase activity in postheparin plasma minus pre-heparin HL activity reflects LPL activity. Specific antibodies are not required. 2
3 Introduction Lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and hepatic lipase (HL) play an essential role in lipoprotein metabolism. Hepatic lipase is a lipolytic enzyme synthesized and secreted by hepatocytes, which binds extracellularly to parenchymal and endothelial cell surfaces in the space of Disse (1, 2). HL affects the lipid composition of all lipoprotein classes by hydrolyzing phospholipids and triglycerides. It has been demonstrated that mice have HL circulating in pre-heparin plasma (3), suggesting that the affinity between mouse HL and its cellular binding sites is low. In contrast, rat and human pre-heparin plasma do not contain any measurable HL activity (3). LPL is synthesized by parenchymal cells in a variety of tissues, including adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and heart, and is subsequently translocated to its site of action, the endothelium (4). The major target lipoproteins are the triglyceriderich apob containing VLDL and chylomicrons. LPL hydrolyzes triglycerides into free fatty acids for direct use in muscle and adipose tissue (5, 6). As a result of the action of LPL, VLDL and chylomicrons will become triglyceride-depleted, cholesterolenriched lipoprotein particles, which are potentially atherogenic. LPL may act as a bridging molecule between these atherogenic lipoproteins and hepatic receptors (7, 8). The mouse is a frequently used animal model in atherosclerosis research even though large differences exist in lipoprotein metabolism between mice and men. However, the possibilities to create specific genetic models by overexpression, deletion, specific inducible gene expression and specific tissue expression of a target gene have led to a spectacular increase in the use of transgenic mice. Recently, newly identified proteins turned out to have LPL regulating properties, e.g. 3
4 apolipoprotein AV (9), the angiopoetin-like proteins (10, 11), and the recently discovered glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored HDL-binding protein 1 (12). This further stresses the need for accurate and relatively simple assays of LPL and HL activities. In humans, LPL and HL are bound to the vascular endothelium, and their activities have been analysed in plasma obtained from blood samples collected after intravenous injection of heparin, a procedure to release LPL and HL from cellular proteoglycans. Total lipase activity is then analysed in the presence of the LPL activator apocii and at low salt concentration. LPL activity may be inhibited by high salt (1 M NaCl) in the assay mix, thereby enabling the measurement of HL activity (13). In addition, specific antibodies have been used to inhibit either LPL activity or HL activity in human post-heparin plasma (14, 15). In the present study, we compare two approaches to analyse HL and LPL activity in mouse plasma. In the first approach we use specific antibodies to inhibit either LPL or HL activity. In the second approach we tested the use of 1 M NaCl to inhibit LPL activity, thereby enabling the assay of HL activity. 4
5 Material and Methods Animals Male C57BL/6 mice were housed in a temperature-controlled room operating under a 12h:12h light/dark cycle. Animals were fed a regular chow diet and obtained water ad libitum. HL deficient mice with a C57BL/6 background were obtained from the Jackson laboratories. Pre-heparin blood was obtained by orbital puncture under isoflurane anaesthesia. Post-heparin blood was obtained 5 minutes after heparin injection (200 units/kg body weight injected into a tail vein). Plasma was isolated by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 15 minutes and frozen at C before analyzing lipase activities. Plasma LPL activity was determined in both pre-heparin and postheparin plasma obtained from three individual mice with hepatic lipase deficiency. Ten control C57BL/6 mice were used to create a pool of both pre-heparin and postheparin plasma. All animal experiments were performed in accordance with institutional and national guidelines. Antibodies Rat HL and LPL were isolated as described (16-18). Polyclonal antibodies against rat HL and LPL were generated in rabbit (anti-hl) and goat (anti-lpl). The IgG fractions of both antibodies were isolated by protein G affinity chromatography according to the manufacturer procedure. The IgG fraction were dialyzed against 5 mm (NH 4 )HCO 3 and lyophilized. The obtained pellets were resuspended in 0.15 M NaCl and stored at C (17). Total protein concentration was 18.7 g/l in anti-hl preparation and 95.3 g/l in anti-lpl preparation. 5
6 Treatment of plasma with antibodies Immuno-inhibition of HL and LPL was accomplished by mixing a mouse plasma sample with anti-lpl and anti-hl and subsequent incubation at 4 0 C for 2.5 h. As a control, plasma was incubated with a saline solution. For LPL analyses, 25 µl plasma was incubated with respectively 6.25 µl or 25 µl anti-hl in a total volume of 125 µl. For HL analyses, 25 µl plasma was incubated with 25 µl or 50 µl anti-lpl in a total volume of 125 µl. Subsequently, after the pre-incubation, 50 µl of the mixture was used in the lipase assay. Lipase assay Pre and post-heparin total lipase activity was assayed using an artificial glycerol-[1-14 C]trioleate (Sigma T-7140, USA) containing lipid emulsion (13, 19). A mixture of 20 μci [1-14 C] tri-oleylglycerol and 35 mg unlabelled tri-oleylglycerol was dried under nitrogen and emulsified by sonification in 2.5 ml 5% (w/v) gum acacia (BDH chemicals, UK) containing 1% NaHCO 3 (ph 7). The emulsion was mixed with 3 ml 10% (w/v) fat-free bovine serum albumin (Fluka BioChemika 05490), 0.5 ml 1 M Tris-HCl (ph 8.5) and 0.5 ml 2.5 M NaCl ml H 2 O (low salt assay) or 5 ml 2.5 M NaCl (high salt assay). Lipase activity was analysed in the presence of heat inactivated normolipidemic human plasma as a source of apocii (10%v/v) (20). 200 μl substrate mixture and 10 μl serum sample and 40 µl 0.9% NaCl were incubated 30 minutes at 30 0 C. The reaction was stopped by adding 3.25 ml of a mixture of chloroform, methanol, heptane (33:40:27) and 1.05 ml 0.1 M K 2 CO 3, 0.1 M H 3 BO 3 ph 10.5 and putting the tubes on ice. Free fatty acids are measured in the water 6
7 phase. Lipase activities are given in mu/ml. 1 mu represents 1 nmol of free fatty acid released from the triglyceride substrate per minute at 30 o C. Statistical analyses Mean lipase values are expressed as mean ± standard deviation and were compared using t-test statistics. 7
8 Results and discussion It is generally accepted that lipase activity in murine pre-heparin plasma represents HL activity (3), reflecting its low affinity for heparin sulfate proteoglycans. Virtually zero lipase activity was measured in pre-heparin plasma from HL deficient mice (data not shown). Subsequently we analyzed pre-heparin lipase activity in the presence of different antibodies. First, it was observed that incubation with the anti- LPL antibody does not affect lipase activity in pre-heparin plasma from wild type mice (figure 1). Hence, this antibody does not interfere with mouse HL activity, illustrating its specificity. The efficacy of the antibody directed against HL (anti-hl) to inhibit its activity was tested using the same batch of pre-heparin plasma. Figure 1 shows that the total lipase activity in pre-heparin plasma of wild type mice is 92 ± 2 mu/ml. Treatment with anti-lpl does not result in a significant change in total lipase activity (86 ± 3 mu/ml), whereas treatment with anti-hl inhibits lipase activity by 97% (remaining activity 3 ± 2 mu/ml). Different antibody dilutions were tested. These experiments illustrate the specificity of the antibody and demonstrate that virtually all lipase circulating in pre-heparin plasma in mice is indeed HL. In the experiments described above all assays were performed at low NaCl concentration. In humans, both HL and LPL activities are present in post-heparin plasma and the contribution of HL can be measured by blocking LPL activity with 1 M NaCl (21). However, in our experiments with mouse plasma, increasing the final salt concentration in the assay mix to 1 M NaCl led to a significant 61% increase in HL activity in pre-heparin mouse plasma (from 92 ± 2 mu/ml to 148 ± 3 mu/ml). Total lipase activity in post-heparin plasma of wildtype mice amounts 717 ± 10 mu/ml (figure 2). Surprisingly, in the presence of 1 M NaCl the residual lipase 8
9 activity remained 579 ± 30 mu/ml. This suggests that either most of the total lipase activity is derived from HL in post-heparin mouse plasma or that 1 M NaCl is not completely inhibiting mouse LPL. We also have to keep in mind that HL activity is increased in the presence of high salt (see above). To obtain conclusive evidence whether 1 M NaCl inhibits LPL activity in mouse plasma, we analysed total lipase activity in post-heparin plasma of the HL deficient mouse with and without 1 M NaCl. In these knock-out mice, HL is not present in post-heparin plasma. Total lipase activity was 755 ± 17 mu/ml when measured in low NaCl, whereas plasma lipase activity in 1 M NaCl was 456 ± 14 mu/ml (Figure 3). Thus 1 M NaCl only partly inhibits post-heparin plasma lipase activity in HL deficient mice, suggesting that 1 M NaCl does not completely inhibit mouse LPL. Alternatively, another lipase could contribute to total lipase activity in these animals, although no evidence for an additional lipase in mice could be found (3). Recently, endothelial lipase (EL) was described as a new member of the lipase family (22). Despite the fact that a significant degree of sequence homology exists between EL and LPL, its substrate specificity is quite different (23). In contrast to LPL, which has the capacity to hydrolyze triglycerides, EL is active as a phospholipase. Since our assay measures the capacity of the enzymes to hydrolyze triglycerides, it is unlikely that we measure EL activity. In another series of experiments we used anti-lpl and anti-hl in post-heparin mouse plasma of both wild type animals and HL deficient animals. All experiments were again performed at low salt conditions and in the presence of heat inactivated plasma as a source of apocii. Incubation of post-heparin plasma from HL deficient 9
10 mice with anti-lpl results in a 95% inhibition of lipase activity, as shown in figure 2. Total lipase activity decreased from 755 ± 17 mu/ml to 37 ± 2 mu/ml. Therefore it can be concluded that there is no alternative lipase that significantly contributes to post-heparin lipase activity other than LPL. When using plasma from wild type animals, plasma total lipase activity in post-heparin plasma after treatment with anti- LPL was inhibited from 717 ± 10 mu/ml to 110 ± 2 mu/ml. As shown in figure 2, no further inhibition can be achieved by increasing the antibody concentration. Figure 3 shows similar experiments with post-heparin plasma from wild type mice, but now after treatment with anti HL. We already showed (see figure 1) that the decrease in HL activity in pre-heparin plasma was almost complete under these conditions. In post-heparin plasma from wild type mice, treatment with anti-hl results in a decrease of the lipase activity by only about 10% (from 657 ± 10 mu/ml to 590 ± 8 mu/ml). Therefore, HL activity in post-heparin plasma amounts to 67 mu/ml. This value is similar to the pre-heparin plasma HL activity shown in figure 1. Figure 3 shows that little if any effect of anti-hl treatment is evident in post-heparin plasma from HL-deficient mice. It can be concluded that virtually all active HL is circulating in wild type mouse plasma, even before heparin injection, and that liver-bound HL is hardly present. Based on these results we therefore propose to measure LPL activity in post-heparin plasma by analyzing total lipase activity in the presence of apocii as activator and at low salt concentration. Of course this activity measured in post-heparin plasma has to be corrected for the small amount of HL activity already present in pre-heparin plasma in order to obtain the actual post-heparin LPL activity. Thus total post- 10
11 heparin plasma activity minus pre-heparin plasma activity is post-heparin plasma LPL activity. 11
12 Legends Figure 1. Effect of anti-lpl and anti-hl antibodies on lipase activity in pre-heparin plasma from wild type mice. Experiments were performed in triplicate. The indicated amounts of IgG (mg) were present in the lipase assay. Figure 2. Effect of incubation with anti-lpl antibody on lipase activity in postheparin plasma from wild type mice and HL deficient mice. Experiments were performed in triplicate. The indicated amounts of IgG (mg) were present in the lipase assay. Figure 3. Effect of incubation with anti-hl antibody on lipase activity in postheparin plasma from wild type mice HL deficient mice. Experiments were performed in triplicate. The indicated amounts of IgG (mg) were present in the lipase assay. 12
13 Figure 1 Pre-heparin plasma from wild-type mice lipase activity (mu/ml) control +1.9 mg anti-lpl in the assay mg anti-hl in the assay 13
14 Figure 2 Post-heparin plasma ± anti-lpl total lipase activity (mu/ml) Wild type HL-deficient antibody (mg) present in the assay 14
15 Figure 3 total lipase activity (mu/ml) Post-heparin plasma ± anti-hl Wild type HL-deficient Antibody (mg) present in the assay 15
16 References 1. Jansen, H., A. J. Verhoeven, and E. J. Sijbrands Hepatic lipase: a pro- or anti-atherogenic protein? J Lipid Res 43, Olivecrona, T., and G. Bengtsson-Olivecrona Lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 4, Peterson, J., G. Bengtsson-Olivecrona, and T. Olivecrona Mouse preheparin plasma contains high levels of hepatic lipase with low affinity for heparin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 878, Mead, J. R., S. A. Irvine, and D. P. Ramji Lipoprotein lipase: structure, function, regulation, and role in disease. J. Mol. Med. 80, Eckel, R. H lipoprotein lipase: a multifactorial enzyme relevant to common metabolic disease. N. Engl. J. Med Goldberg, I. J Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: Central roles in lipoprotein metabolismand atherogenesis. J Lipid Res 37, Beisiegel, U., W. Weber, and G. Bengtsson Olivecrona Lipoprotein lipase enhances the binding of chylomicrons to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88,
17 8. Heeren, J., A. Niemeier, M. Merkel, and U. Beisiegel Endothelialderived lipoprotein lipase is bound to postprandial triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and mediates their hepatic clearance in vivo. J. Mol. Med. 80, Merkel, M., B. Loeffler, M. Kluger, N. Fabig, G. Geppert, L. A. Pennacchio, A. Laatsch, and J. Heeren Apolipoprotein AV accelerates plasma hydrolysis of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins by interaction with proteoglycanbound lipoprotein lipase. J. Biol. Chem. 280, Koster, A., Y. B. Chao, M. Mosior, A. Ford, P. A. Gonzalez-DeWhitt, J. E. Hale, D. Li, Y. Qiu, C. C. Fraser, D. D. Yang, J. G. Heuer, S. R. Jaskunas, and P. Eacho Transgenic angiopoietin-like (angptl)4 overexpression and targeted disruption of angptl4 and angptl3: regulation of triglyceride metabolism. Endocrinology 146, Shimizugawa, T., M. Ono, M. Shimamura, K. Yoshida, Y. Ando, R. Koishi, K. Ueda, T. Inaba, H. Minekura, T. Kohama, and H. Furukawa ANGPTL3 decreases very low density lipoprotein triglyceride clearance by inhibition of lipoprotein lipase. J. Biol. Chem. 277, Beigneux, A. P., B. S. Davies, P. Gin, M. M. Weinstein, E. Farber, X. Qiao, F. Peale, S. Bunting, R. L. Walzem, J. S. Wong, W. S. Blaner, Z. M. Ding, K. Melford, N. Wongsiriroj, X. Shu, S. F. de, R. O. Ryan, L. G. Fong, A. Bensadoun, and S. G. Young Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-Anchored 17
18 High-Density Lipoprotein-Binding Protein 1 Plays a Critical Role in the Lipolytic Processing of Chylomicrons. Cell Metab 5, Huttunen, J. K., C. Ehnholm, P. K. Kinnunen, and E. A. Nikkila An immunochemical method for the selective measurements of two triglyceride lipases in human postheparin plasma. Clin Chim. Acta 63, Greten, H., V. Laible, G. Zipperle, and J. Augustin Comparison of assay methods for selective measurement of plasma lipase. The effect of clofibrate on hepatic and lipoprotein lipase in normals and patients with hypertriglyceridemia. Atherosclerosis 26, Olivecrona, T., and Olivecrona, G. (1997) Determination and clinical significance of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic lipase. In Handbook of lipoprotein testing (Rifai, N., Warnick, G. R., and Dominiczak, M. H., eds) pp , AACC press, Washington. 16. Persoon, N. L., W. C. Hulsmann, and H. Jansen Localization of the salt-resistant heparin-releasable lipase in the rat liver, adrenal and ovary. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 41, Vieira-van Bruggen, D., I. Kalkman, T. van Gent, A. van Tol, and H. Jansen Induction of adrenal scavenger receptor BI and increased high density lipoprotein-cholesteryl ether uptake by in vivo inhibition of hepatic lipase. J. Biol. Chem. 273,
19 18. Persoon, N. L., W. C. Hulsmann, and H. Jansen Structural modulation of salt-resistant rat-liver lipase alters the relative phospholipase and triacylglycerol hydrolase activities. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 917, Jansen, H., W. Hop, A. v. Tol, A. V. G. Bruschke, and J. C. Birkenhäger Hepatic lipase and lipoprotein lipase are not major determinants of the low density lipoprotein subclass pattern in human subjects with coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis 107, Bengtsson, G., and T. Olivecrona Activation of lipoprotein lipase by apolipoprotein CII. Demonstration of an effect of the activator on the binding of the enzyme to milk-fat globules. FEBS Lett. 147, Bensadoun, A Lipoprotein lipase. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 11, Jaye, M., K. J. Lynch, T. Krawiec, D. Marchadier, C. Maugeais, K. Doan, V. South, D. Amin, M. Perrone, and D. J. Rader A novel endothelialderived lipase that modulates HDL metabolism. Nature Genet. 21, Griffon, N., E. C. Budreck, C. J. Long, U. C. Broedl, D. H. Marchadier, J. M. Glick, and D. J. Rader Substrate specificity of lipoprotein lipase and endothelial lipase: studies of lid chimeras. J. Lipid Res. 47,
Inhibition of endothelial lipase causes increased HDL cholesterol levels in vivo
 Inhibition of endothelial lipase causes increased HDL cholesterol levels in vivo See the related Commentary beginning on page 318. Weijun Jin, John S. Millar, Uli Broedl, Jane M. Glick, and Daniel J. Rader
Inhibition of endothelial lipase causes increased HDL cholesterol levels in vivo See the related Commentary beginning on page 318. Weijun Jin, John S. Millar, Uli Broedl, Jane M. Glick, and Daniel J. Rader
Lipoprotein Lipase Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 Lipoprotein Lipase Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA4538 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
Lipoprotein Lipase Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number KA4538 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Lipoprotein Metabolism
 ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Lipoprotein Metabolism I. Chylomicrons (exogenous pathway) A. 83% triacylglycerol, 2% protein, 8% cholesterol plus cholesterol esters, 7% phospholipid (esp. phosphatidylcholine)
ANSC/NUTR 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Lipoprotein Metabolism I. Chylomicrons (exogenous pathway) A. 83% triacylglycerol, 2% protein, 8% cholesterol plus cholesterol esters, 7% phospholipid (esp. phosphatidylcholine)
ModifiedHeparin-SepharoseProcedurefor Determinationof Plasma LipolyticActivitiesof Normotipidemicand HyperlipidemicSubjectsafter Injectionof Heparin
 CLIN. CHEM. 27/5, 663-668 (1981) ModifiedHeparin-SepharoseProcedurefor Determinationof Plasma LipolyticActivitiesof Normotipidemicand HyperlipidemicSubjectsafter Injectionof Heparin ChI-Sun Wang, Helen
CLIN. CHEM. 27/5, 663-668 (1981) ModifiedHeparin-SepharoseProcedurefor Determinationof Plasma LipolyticActivitiesof Normotipidemicand HyperlipidemicSubjectsafter Injectionof Heparin ChI-Sun Wang, Helen
Summary and concluding remarks
 Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Characterization of the lipolytic activity of endothelial lipase
 Characterization of the lipolytic activity of endothelial lipase Mary G. McCoy, Gwo-Shing Sun, Dawn Marchadier, Cyrille Maugeais, Jane M. Glick, 1 and Daniel J. Rader Department of Medicine, University
Characterization of the lipolytic activity of endothelial lipase Mary G. McCoy, Gwo-Shing Sun, Dawn Marchadier, Cyrille Maugeais, Jane M. Glick, 1 and Daniel J. Rader Department of Medicine, University
High density lipoprotein metabolism
 High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
Lipoproteins Metabolism
 Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
Lipid Metabolism Prof. Dr. rer physiol. Dr.h.c. Ulrike Beisiegel
 Lipid Metabolism Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology II Medical Center Hamburg-ppendorf 1 Lipids. visceral fat. nutritional lipids 0 1.5 3 4.5 9 h. serum lipids. lipid accumulation in the
Lipid Metabolism Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology II Medical Center Hamburg-ppendorf 1 Lipids. visceral fat. nutritional lipids 0 1.5 3 4.5 9 h. serum lipids. lipid accumulation in the
Lipoprotein lipase secretion by human monocyte-derived macrophages.
 Lipoprotein lipase secretion by human monocyte-derived macrophages. A Chait,, P H Iverius, J D Brunzell J Clin Invest. 1982;69(2):490-493. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci110473. Research Article Human monocyte-derived
Lipoprotein lipase secretion by human monocyte-derived macrophages. A Chait,, P H Iverius, J D Brunzell J Clin Invest. 1982;69(2):490-493. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci110473. Research Article Human monocyte-derived
review Remnant lipoprotein metabolism: key pathways involving cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans and apolipoprotein E
 review Remnant lipoprotein metabolism: key pathways involving cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans and apolipoprotein E Robert W. Mahley 1, *, and Zhong-Sheng Ji* Gladstone Institute of Cardiovascular
review Remnant lipoprotein metabolism: key pathways involving cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans and apolipoprotein E Robert W. Mahley 1, *, and Zhong-Sheng Ji* Gladstone Institute of Cardiovascular
Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats
 J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 2, June 1987, pp. 137 142. Printed in India. Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats P. VALSALA and P. A. KURUP Department
J. Biosci., Vol. 12, Number 2, June 1987, pp. 137 142. Printed in India. Investigations on the mechanism of hypercholesterolemia observed in copper deficiency in rats P. VALSALA and P. A. KURUP Department
Lipids digestion and absorption, Biochemistry II
 Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui
 Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by. Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam
 Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-616 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol is a lipid sterol
Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) ELISA Kit Catalog Number STA-616 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol is a lipid sterol
Fig. S1. REGN1500 reduces plasma levels of cholesterol, TG and NEFA in WT and Ldlr -/- mice. (A) WT
 Figure Legends for Supplementary Figures. Fig. S1. REGN15 reduces plasma levels of cholesterol, TG and NEF in WT and Ldlr -/- mice. () WT and Ldlr -/- mice were injected with control IgG or REGN15 (1 mg/kg)
Figure Legends for Supplementary Figures. Fig. S1. REGN15 reduces plasma levels of cholesterol, TG and NEF in WT and Ldlr -/- mice. () WT and Ldlr -/- mice were injected with control IgG or REGN15 (1 mg/kg)
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Plasma apolipoprotein AV levels in mice are positively associated with plasma triglyceride levels
 Plasma apolipoprotein AV levels in mice are positively associated with plasma triglyceride levels S. F. C. Vaessen,* G. M. Dallinga-Thie,* C. J. D. Ross, L. J. Splint,* L. W. Castellani, P. C. N. Rensen,**
Plasma apolipoprotein AV levels in mice are positively associated with plasma triglyceride levels S. F. C. Vaessen,* G. M. Dallinga-Thie,* C. J. D. Ross, L. J. Splint,* L. W. Castellani, P. C. N. Rensen,**
PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS AND LIPIDS DETERMINATION OF PLASMA CHOLESTEROL AND TRIGLICERIDE LEVEL
 PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS AND LIPIDS DETERMINATION OF PLASMA CHOLESTEROL AND TRIGLICERIDE LEVEL Lipids are characterized by low polarity and limited solubility in water. Their plasma concentration is about 500-600
PLASMA LIPOPROTEINS AND LIPIDS DETERMINATION OF PLASMA CHOLESTEROL AND TRIGLICERIDE LEVEL Lipids are characterized by low polarity and limited solubility in water. Their plasma concentration is about 500-600
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3561
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE AND ENDOTHELIAL LIPASE: STUDIES OF LID CHIMERAS
 SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE AND ENDOTHELIAL LIPASE: STUDIES OF LID CHIMERAS Nathalie Griffon*, Elaine C. Budreck*, Christopher J. Long*, Uli C. Broedl*, Dawn H.L. Marchadier*, Jane M. Glick,
SUBSTRATE SPECIFICITY OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE AND ENDOTHELIAL LIPASE: STUDIES OF LID CHIMERAS Nathalie Griffon*, Elaine C. Budreck*, Christopher J. Long*, Uli C. Broedl*, Dawn H.L. Marchadier*, Jane M. Glick,
Kinetics of an Intravenously Injected Fat Emulsion Reflect Postheparin Plasma Lipoprotein Lipase Mass and Activity
 J. Clin. Biochem. Nut:, 31, 37-43, 2002 Kinetics of an Intravenously Injected Fat Emulsion Reflect Postheparin Plasma Lipoprotein Lipase Mass and Activity Nagahiko SAKUMA,* Reiko IKEUCHI, Takeshi HIBINO,
J. Clin. Biochem. Nut:, 31, 37-43, 2002 Kinetics of an Intravenously Injected Fat Emulsion Reflect Postheparin Plasma Lipoprotein Lipase Mass and Activity Nagahiko SAKUMA,* Reiko IKEUCHI, Takeshi HIBINO,
Lipoprotein lipase mediates an increase in the selective uptake of high density lipoprotein-associated cholesteryl esters by hepatic cells in culture
 Lipoprotein lipase mediates an increase in the selective uptake of high density lipoprotein-associated cholesteryl esters by hepatic cells in culture Franz Rinninger, 1 Tatjana Kaiser, W. Alexander Mann,
Lipoprotein lipase mediates an increase in the selective uptake of high density lipoprotein-associated cholesteryl esters by hepatic cells in culture Franz Rinninger, 1 Tatjana Kaiser, W. Alexander Mann,
Byung Hong Chung 1, * and Nassrin Dashti
 Lipolytic remnants of human VLDL produced in vitro: effect of HDL levels in the lipolysis mixtures on the apocs to apoe ratio and metabolic properties of VLDL core remnants Byung Hong Chung 1, * and Nassrin
Lipolytic remnants of human VLDL produced in vitro: effect of HDL levels in the lipolysis mixtures on the apocs to apoe ratio and metabolic properties of VLDL core remnants Byung Hong Chung 1, * and Nassrin
Synopsis. Received March 2, adrenaline. Mosinger and Kujalova (1964) reported that adrenaline-induced lipolysis
 Studies on Reduction of Lipolysis in Adipose Tissue on Freezing and Thawing YASUSHI SAITO1, NoBUO MATSUOKA1, AKIRA KUMAGAI1, HIROMICHI OKUDA2, AND SETSURO FUJII3 Chiba University, Chiba 280, Japan, 2Department
Studies on Reduction of Lipolysis in Adipose Tissue on Freezing and Thawing YASUSHI SAITO1, NoBUO MATSUOKA1, AKIRA KUMAGAI1, HIROMICHI OKUDA2, AND SETSURO FUJII3 Chiba University, Chiba 280, Japan, 2Department
Lipoprotein lipase expression level influences tissue clearance of chylomicron retinyl ester
 Lipoprotein lipase expression level influences tissue clearance of chylomicron retinyl ester Arlette M. van Bennekum,* Yuko Kako, Peter H. Weinstock, Earl H. Harrison,** Richard J. Deckelbaum,* Ira J.
Lipoprotein lipase expression level influences tissue clearance of chylomicron retinyl ester Arlette M. van Bennekum,* Yuko Kako, Peter H. Weinstock, Earl H. Harrison,** Richard J. Deckelbaum,* Ira J.
2.5% of all deaths globally each year. 7th leading cause of death by % of people with diabetes live in low and middle income countries
 Lipid Disorders in Diabetes (Diabetic Dyslipidemia) Khosrow Adeli PhD, FCACB, DABCC Head and Professor, Clinical Biochemistry, The Hospital for Sick Children, University it of Toronto Diabetes A Global
Lipid Disorders in Diabetes (Diabetic Dyslipidemia) Khosrow Adeli PhD, FCACB, DABCC Head and Professor, Clinical Biochemistry, The Hospital for Sick Children, University it of Toronto Diabetes A Global
N-3 Fatty Acids Non-HDL-Cand LDL-C Thomas Dayspring MD, FACP
 Omega or N-3 Fatty Acids (FA) significantly reduce TG synthesis and significantly deplete the TG content of VLDL particles indicated by significantly reduced V. FA are the substrate for TG synthesis. N3-FA
Omega or N-3 Fatty Acids (FA) significantly reduce TG synthesis and significantly deplete the TG content of VLDL particles indicated by significantly reduced V. FA are the substrate for TG synthesis. N3-FA
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL
 Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Hypertriglyceridemia: Why, When, and How to Treat. Gregory Cohn, MD, FNLA, FASPC
 Hypertriglyceridemia: Why, When, and How to Treat Gregory Cohn, MD, FNLA, FASPC DISCLOSURES Consultant to Akcea Therapeutics (in the past 12 months). OUTLINE I. Lipoproteins II. Non-HDL-C III. Causes and
Hypertriglyceridemia: Why, When, and How to Treat Gregory Cohn, MD, FNLA, FASPC DISCLOSURES Consultant to Akcea Therapeutics (in the past 12 months). OUTLINE I. Lipoproteins II. Non-HDL-C III. Causes and
Change of plasma lipoproteins by heparin-released lipoprotein lipase
 EXPERIMENTAL and MOLECULAR MEDICINE, Vol. 31, No 2, 60-64, June 1999 Change of plasma lipoproteins by heparin-released lipoprotein lipase Jeong-Yeh Yang 1, Tae-Keun Kim 1, Bon-Sun Koo 1, Byung-Hyun Park
EXPERIMENTAL and MOLECULAR MEDICINE, Vol. 31, No 2, 60-64, June 1999 Change of plasma lipoproteins by heparin-released lipoprotein lipase Jeong-Yeh Yang 1, Tae-Keun Kim 1, Bon-Sun Koo 1, Byung-Hyun Park
Measurement of the Phospholipase Activity of Endothelial Lipase in Mouse Plasma. Running title: Mouse Plasma Endothelial Phospholipase Activity
 Measurement of the Phospholipase Activity of Endothelial Lipase in Mouse Plasma Debapriya Basu 1, Xia Lei 1, Joby Josekutty 1, M. Mahmood Hussain 1, Weijun Jin 1 1 Department of Cell Biology, State University
Measurement of the Phospholipase Activity of Endothelial Lipase in Mouse Plasma Debapriya Basu 1, Xia Lei 1, Joby Josekutty 1, M. Mahmood Hussain 1, Weijun Jin 1 1 Department of Cell Biology, State University
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored HDL-binding protein stabilizes lipoprotein lipase
 Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored HDL-binding protein stabilizes lipoprotein lipase and prevents its inhibition by angiopoietin-like 3 and angiopoietin-like 4 William K. Sonnenburg,1,2, Daiguan Yu,2,
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored HDL-binding protein stabilizes lipoprotein lipase and prevents its inhibition by angiopoietin-like 3 and angiopoietin-like 4 William K. Sonnenburg,1,2, Daiguan Yu,2,
Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis
 Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis Ira J. Goldberg Department of Medicine, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, 630 West 168th
Lipoprotein lipase and lipolysis: central roles in lipoprotein metabolism and atherogenesis Ira J. Goldberg Department of Medicine, Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons, 630 West 168th
Plasma apolipoprotein AV levels in mice are positively associated with plasma triglyceride levels
 Plasma apolipoprotein AV levels in mice are positively associated with plasma triglyceride levels S.F.C. Vaessen 1, G.M. Dallinga-Thie 1, C.J.D. Ross 3, L.J. Splint 1, L.W. Castellani 4, P.C.N. Rensen
Plasma apolipoprotein AV levels in mice are positively associated with plasma triglyceride levels S.F.C. Vaessen 1, G.M. Dallinga-Thie 1, C.J.D. Ross 3, L.J. Splint 1, L.W. Castellani 4, P.C.N. Rensen
Plasma concentrations of high-density lipoprotein (HDL)
 Angiopoietin-Like Protein3 Regulates Plasma HDL Cholesterol Through Suppression of Endothelial Lipase Mitsuru Shimamura, Morihiro Matsuda, Hiroaki Yasumo, Mitsuyo Okazaki, Kazunori Fujimoto, Keita Kono,
Angiopoietin-Like Protein3 Regulates Plasma HDL Cholesterol Through Suppression of Endothelial Lipase Mitsuru Shimamura, Morihiro Matsuda, Hiroaki Yasumo, Mitsuyo Okazaki, Kazunori Fujimoto, Keita Kono,
The Role of Apolipoprotein CIII in Coronary Artery Disease. Disclosures
 Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute Cardiovascular Disease Prevention 15th Annual Symposium February 16, 2017 Nobu Eden Roc Hotel, Miami Beach, Florida. The Role of Apolipoprotein CIII in Coronary Artery
Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute Cardiovascular Disease Prevention 15th Annual Symposium February 16, 2017 Nobu Eden Roc Hotel, Miami Beach, Florida. The Role of Apolipoprotein CIII in Coronary Artery
Lipase Activity Assay Kit
 Lipase Activity Assay Kit Item. 700640 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials
Lipase Activity Assay Kit Item. 700640 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials
BIOL2171 ANU TCA CYCLE
 TCA CYCLE IMPORTANCE: Oxidation of 2C Acetyl Co-A 2CO 2 + 3NADH + FADH 2 (8e-s donated to O 2 in the ETC) + GTP (energy) + Heat OVERVIEW: Occurs In the mitochondrion matrix. 1. the acetyl portion of acetyl-coa
TCA CYCLE IMPORTANCE: Oxidation of 2C Acetyl Co-A 2CO 2 + 3NADH + FADH 2 (8e-s donated to O 2 in the ETC) + GTP (energy) + Heat OVERVIEW: Occurs In the mitochondrion matrix. 1. the acetyl portion of acetyl-coa
Plasma concentrations of HDL cholesterol (HDL-C) and
 Dose-Dependent Acceleration of High-Density Lipoprotein Catabolism by Endothelial Lipase Cyrille Maugeais, PhD; Uwe J.F. Tietge, MD; Uli C. Broedl, MD; Dawn Marchadier, MS; William Cain, PhD; Mary G. McCoy,
Dose-Dependent Acceleration of High-Density Lipoprotein Catabolism by Endothelial Lipase Cyrille Maugeais, PhD; Uwe J.F. Tietge, MD; Uli C. Broedl, MD; Dawn Marchadier, MS; William Cain, PhD; Mary G. McCoy,
Role of N-linked glycosylation in the secretion and activity of endothelial lipase
 Role of N-linked glycosylation in the secretion and activity of endothelial lipase Gwen C. Miller, 1, * Christopher J. Long, 1, * Ekaterina D. Bojilova,* Dawn Marchadier,* Karen O. Badellino,* Nadine Blanchard,*
Role of N-linked glycosylation in the secretion and activity of endothelial lipase Gwen C. Miller, 1, * Christopher J. Long, 1, * Ekaterina D. Bojilova,* Dawn Marchadier,* Karen O. Badellino,* Nadine Blanchard,*
Human LDL ELISA Kit. Innovative Research, Inc.
 Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Human LDL ELISA Kit Catalog No: IRKTAH2582 Lot No: SAMPLE INTRODUCTION Human low-density lipoprotein (LDL) transports cholesterol from the liver to tissues where it is incorporated into cell membranes.
Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL
 Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Palermo, Italy & Affiliate Associate Professor of Internal
Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Palermo, Italy & Affiliate Associate Professor of Internal
Turnover of chylomicrons in the rat
 UMEÅ UNIVERSITY MEDICAL DISSERTATIONS New Series No 424 From the Department o f Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Umeå Universitet, Umeå, Sweden Turnover of chylomicrons in the rat AKADEMISK AVHANDLING
UMEÅ UNIVERSITY MEDICAL DISSERTATIONS New Series No 424 From the Department o f Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics Umeå Universitet, Umeå, Sweden Turnover of chylomicrons in the rat AKADEMISK AVHANDLING
Chylomicronemia can be caused by a deficiency of
 Chylomicronemia With a Mutant GPIHBP1 (Q115P) That Cannot Bind Lipoprotein Lipase Anne P. Beigneux, Remco Franssen, André Bensadoun, Peter Gin, Kristan Melford, Jorge Peter, Rosemary L. Walzem, Michael
Chylomicronemia With a Mutant GPIHBP1 (Q115P) That Cannot Bind Lipoprotein Lipase Anne P. Beigneux, Remco Franssen, André Bensadoun, Peter Gin, Kristan Melford, Jorge Peter, Rosemary L. Walzem, Michael
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants
 Hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants Allen D. Cooper Research Institute, Palo Alto Medical Foundation, 860 Bryant Street, Palo Alto, CA 94301, and Department of Medicine, Stanford University, Stanford,
Hepatic uptake of chylomicron remnants Allen D. Cooper Research Institute, Palo Alto Medical Foundation, 860 Bryant Street, Palo Alto, CA 94301, and Department of Medicine, Stanford University, Stanford,
DAG (Diacylglycerol) Assay Kit
 Product Manual DAG (Diacylglycerol) Assay Kit Catalog Number MET-5028 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Diacylglycerols (DAG) are key intermediates in the
Product Manual DAG (Diacylglycerol) Assay Kit Catalog Number MET-5028 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Diacylglycerols (DAG) are key intermediates in the
Hepatic lipase mediates an increase in selective uptake of HDL-associated cholesteryl esters by cells in culture independent from SR-BI
 Hepatic lipase mediates an increase in selective uptake of HDL-associated cholesteryl esters by cells in culture independent from SR-BI May Brundert,* Joerg Heeren, Heiner Greten,* and Franz Rinninger
Hepatic lipase mediates an increase in selective uptake of HDL-associated cholesteryl esters by cells in culture independent from SR-BI May Brundert,* Joerg Heeren, Heiner Greten,* and Franz Rinninger
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
The effect of phosphatidyl choline on the degradation of phosphatidyl ethanolamine by the phospholipase of post-heparin plasma or snake venom
 The effect of phosphatidyl choline on the degradation of phosphatidyl ethanolamine by the phospholipase of post-heparin plasma or snake venom WILLIAM C. VOGEL, J. L. KOPPEL, and J. H. OLWIN Coagulation
The effect of phosphatidyl choline on the degradation of phosphatidyl ethanolamine by the phospholipase of post-heparin plasma or snake venom WILLIAM C. VOGEL, J. L. KOPPEL, and J. H. OLWIN Coagulation
Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number STA-615 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol
Product Manual Lecithin Cholesterol Acyltransferase (LCAT) Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Catalog Number STA-615 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cholesterol
The lipoprotein lipase of cow s milk
 J. Lipid Research, April, 1962 Volume 3. Number 2 The lipoprotein lipase of cow s milk EDWARD D. KORN Laboratory of Cellular Physiology and Metabolism, National Heart stitute, Bethesda 14, Maryland [Itcceived
J. Lipid Research, April, 1962 Volume 3. Number 2 The lipoprotein lipase of cow s milk EDWARD D. KORN Laboratory of Cellular Physiology and Metabolism, National Heart stitute, Bethesda 14, Maryland [Itcceived
Role of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and hepatic lipase in determining the particle size and composition of high density lipoproteins
 Role of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and hepatic lipase in determining the particle size and composition of high density lipoproteins Garry J. Hopkins' and Philip J. Barter Department of Biochemistry,
Role of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and hepatic lipase in determining the particle size and composition of high density lipoproteins Garry J. Hopkins' and Philip J. Barter Department of Biochemistry,
A Simplified Intravenous Fat Emulsion. Nagahiko SAKUMA,1,* Yasuhiro HASEGAWA,2 Reiko IKEUCHI,1 Rin CUI,1 Takayoshi ICHIKAWA,1 and Takao FUJINAMII
 J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr., 3, 251-256, 1987 A Simplified Intravenous Fat Emulsion Tolerance Test Nagahiko SAKUMA,1,* Yasuhiro HASEGAWA,2 Reiko IKEUCHI,1 Rin CUI,1 Takayoshi ICHIKAWA,1 and Takao FUJINAMII
J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr., 3, 251-256, 1987 A Simplified Intravenous Fat Emulsion Tolerance Test Nagahiko SAKUMA,1,* Yasuhiro HASEGAWA,2 Reiko IKEUCHI,1 Rin CUI,1 Takayoshi ICHIKAWA,1 and Takao FUJINAMII
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Endothelial Lipase Is Synthesized by Hepatic and Aorta Endothelial Cells and Its Expression Is Altered in apoe Deficient Mice
 Endothelial Lipase Is Synthesized by Hepatic and Aorta Endothelial Cells and Its Expression Is Altered in apoe Deficient Mice Kenneth C-W. Yu, Christopher David, Sujata Kadambi, Andreas Stahl, Ken-Ichi
Endothelial Lipase Is Synthesized by Hepatic and Aorta Endothelial Cells and Its Expression Is Altered in apoe Deficient Mice Kenneth C-W. Yu, Christopher David, Sujata Kadambi, Andreas Stahl, Ken-Ichi
Relevance of hepatic lipase to the metabolism of triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins
 1070 Biochemical Society Transactions (2003) Volume 31, part 5 Relevance of hepatic lipase to the metabolism of triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins A. Zambon 1,S.Bertocco, N. Vitturi, V. Polentarutti, D.
1070 Biochemical Society Transactions (2003) Volume 31, part 5 Relevance of hepatic lipase to the metabolism of triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins A. Zambon 1,S.Bertocco, N. Vitturi, V. Polentarutti, D.
Supplemental Material. Results
 Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
GPIHBP1 stabilizes lipoprotein lipase and prevents its inhibition by angiopoietin-like 3 and angiopoietin-like 4
 GPIHBP1 stabilizes lipoprotein lipase and prevents its inhibition by angiopoietin-like 3 and angiopoietin-like 4 William K. Sonnenburg, 1,3, * Daiguan Yu, 1, * E-Chiang Lee, * Wei Xiong, * Gennady Gololobov,
GPIHBP1 stabilizes lipoprotein lipase and prevents its inhibition by angiopoietin-like 3 and angiopoietin-like 4 William K. Sonnenburg, 1,3, * Daiguan Yu, 1, * E-Chiang Lee, * Wei Xiong, * Gennady Gololobov,
Fluorogenic substrates for high-throughput measurements of endothelial. lipase activity
 Fluorogenic substrates for high-throughput measurements of endothelial lipase activity Lyndon J. Mitnaul 1, Jenny Tian 1, Charlotte Burton 1, My-Hanh Lam 1, Yuping Zhu, Steve H. Olson. 2, Jonathan E. Schneeweis
Fluorogenic substrates for high-throughput measurements of endothelial lipase activity Lyndon J. Mitnaul 1, Jenny Tian 1, Charlotte Burton 1, My-Hanh Lam 1, Yuping Zhu, Steve H. Olson. 2, Jonathan E. Schneeweis
Reduction in Serum Lecithin:Cholesterol Acyltransferase Activity Prior to the Occurrence of Ketosis and Milk Fever in Cows
 FULL PAPER Biochemistry Reduction in Serum Lecithin:Cholesterol Acyltransferase Activity Prior to the Occurrence of Ketosis and Milk Fever in Cows Hisami NAKAGAWA-UETA 1) and Norio KATOH 2) * 1) Ishikawa
FULL PAPER Biochemistry Reduction in Serum Lecithin:Cholesterol Acyltransferase Activity Prior to the Occurrence of Ketosis and Milk Fever in Cows Hisami NAKAGAWA-UETA 1) and Norio KATOH 2) * 1) Ishikawa
ab Lipoprotein Lipase Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric)
 ab204721 Lipoprotein Lipase Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for use: For quantitative measurement of Lipoprotein Lipase activity in a variety of biological samples. This product is for research
ab204721 Lipoprotein Lipase Activity Assay Kit (Fluorometric) Instructions for use: For quantitative measurement of Lipoprotein Lipase activity in a variety of biological samples. This product is for research
Effect of phosphatidylcholine molecular species on the uptake of HDL triglycerides and cholesteryl esters by the liver
 Effect of phosphatidylcholine molecular species on the uptake of HDL triglycerides and cholesteryl esters by the liver Hiroko Kadowaki,' George M. Patton and Sander J. Robins Division of Lipid Metabolism,
Effect of phosphatidylcholine molecular species on the uptake of HDL triglycerides and cholesteryl esters by the liver Hiroko Kadowaki,' George M. Patton and Sander J. Robins Division of Lipid Metabolism,
CHM333 LECTURE 34: 11/30 12/2/09 FALL 2009 Professor Christine Hrycyna
 Lipid Metabolism β-oxidation FA Acetyl-CoA Triacylglycerols (TAGs) and glycogen are the two major forms of stored energy in vertebrates Glycogen can supply ATP for muscle contraction for less than an hour
Lipid Metabolism β-oxidation FA Acetyl-CoA Triacylglycerols (TAGs) and glycogen are the two major forms of stored energy in vertebrates Glycogen can supply ATP for muscle contraction for less than an hour
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid Metabolism in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol
 Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol The aim of this chapter is to summarize the different etiological factors mainly the role of life-style and different disease conditions contributing to the
Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol The aim of this chapter is to summarize the different etiological factors mainly the role of life-style and different disease conditions contributing to the
Hydrolysis of rat chylomicron acylglycerols: a kinetic model
 Hydrolysis of rat chylomicron acylglycerols: a kinetic model D. M. Foster and M. Berman Laboratory of Theoretical Biology, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20205 Abstract
Hydrolysis of rat chylomicron acylglycerols: a kinetic model D. M. Foster and M. Berman Laboratory of Theoretical Biology, National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20205 Abstract
Digestion and transport of TAG by plasma lipoproteins
 Digestion and transport of TAG by plasma lipoproteins Lipoproteins are multimolecular complexes of lipids and proteins, they are not macromolecules They transport lipids in the plasma because lipids are
Digestion and transport of TAG by plasma lipoproteins Lipoproteins are multimolecular complexes of lipids and proteins, they are not macromolecules They transport lipids in the plasma because lipids are
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins
 Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Suppression of Hepatic Lipogenesis by Pectin and Galacturonic Acid Orally-Fed at the Separate Timing from Digestion-Absorption of Nutrients in Rat
 J, Nutr. Sci, Vitaminol., 29, 553-562, 1983 Suppression of Hepatic Lipogenesis by Pectin and Galacturonic Acid Orally-Fed at the Separate Timing from Digestion-Absorption of Nutrients in Rat Masashige
J, Nutr. Sci, Vitaminol., 29, 553-562, 1983 Suppression of Hepatic Lipogenesis by Pectin and Galacturonic Acid Orally-Fed at the Separate Timing from Digestion-Absorption of Nutrients in Rat Masashige
Numerous epidemiological studies have established a
 Differential Additive Effects of Endothelial Lipase and Scavenger Receptor-Class B Type I on High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism in Knockout Mouse Models Ke Ma, Trudy Forte, James D. Otvos, Lawrence Chan
Differential Additive Effects of Endothelial Lipase and Scavenger Receptor-Class B Type I on High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism in Knockout Mouse Models Ke Ma, Trudy Forte, James D. Otvos, Lawrence Chan
Lipoprotein lipase-like activity in the liver of mice with Sarcoma 180
 Lipoprotein lipase-like activity in the liver of mice with Sarcoma 180 Hiroshi Masuno,**' Takahiro Tsujita,* Hayao Nakanishi,**** Aichi Yoshida,** Ryo Fukunishi,** and Hiromichi Okuda* Departments of Medical
Lipoprotein lipase-like activity in the liver of mice with Sarcoma 180 Hiroshi Masuno,**' Takahiro Tsujita,* Hayao Nakanishi,**** Aichi Yoshida,** Ryo Fukunishi,** and Hiromichi Okuda* Departments of Medical
CHAPTER FORTY FIVE ENDOGENOUS LIPID TRANSPORT PATHWAY: VLDL AND IDL
 CHAPTER FORTY FIVE ENDOGENOUS LIPID TRANSPORT PATHWAY: VLDL AND IDL You will notice that the endogenous pathway is very similar to the exogenous pathway What is the average daily amount of triacylglycerol
CHAPTER FORTY FIVE ENDOGENOUS LIPID TRANSPORT PATHWAY: VLDL AND IDL You will notice that the endogenous pathway is very similar to the exogenous pathway What is the average daily amount of triacylglycerol
ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA. Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD
 ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD Plasma lipids consist mostly of lipoproteins Spherical complexes of lipids and specific proteins (apolipoproteins). The clinically important lipoproteins, listed
ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIA Darmawan,dr.,M.Kes,Sp.PD Plasma lipids consist mostly of lipoproteins Spherical complexes of lipids and specific proteins (apolipoproteins). The clinically important lipoproteins, listed
Niacin Metabolism: Effects on Cholesterol
 Niacin Metabolism: Effects on Cholesterol By Julianne R. Edwards For Dr. William R. Proulx, PhD, RD Associate Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics In partial fulfillments for the requirements of NUTR342
Niacin Metabolism: Effects on Cholesterol By Julianne R. Edwards For Dr. William R. Proulx, PhD, RD Associate Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics In partial fulfillments for the requirements of NUTR342
Lipoprotein lipase activity and interactions studied in human plasma by isothermal titration
 Lipoprotein lipase activity and interactions studied in human plasma by isothermal titration calorimetry Mart Reimund 1, Oleg Kovrov 1,2, Gunilla Olivecrona 2, and Aivar Lookene 1 1 Department of Chemistry,
Lipoprotein lipase activity and interactions studied in human plasma by isothermal titration calorimetry Mart Reimund 1, Oleg Kovrov 1,2, Gunilla Olivecrona 2, and Aivar Lookene 1 1 Department of Chemistry,
Mendelian disorders refer to diseases caused by mutations. Review. Mendelian Disorders of High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism
 Review This Review is part of a thematic series on High-Density Lipoprotein, which includes the following articles: Mendelian Disorders of HDL Metabolism Regulation of High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism
Review This Review is part of a thematic series on High-Density Lipoprotein, which includes the following articles: Mendelian Disorders of HDL Metabolism Regulation of High-Density Lipoprotein Metabolism
Free Glycerol Assay Kit (Colorimetric)
 Product Manual Free Glycerol Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-398 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Glycerol is the backbone of Triglycerides
Product Manual Free Glycerol Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Catalog Number STA-398 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Glycerol is the backbone of Triglycerides
The enzyme lipoprotein lipase (LPL) plays a pivotal role
 Angptl4 Upregulates Cholesterol Synthesis in Liver via Inhibition of LPL- and HL-Dependent Hepatic Cholesterol Uptake Laeticia Lichtenstein, Jimmy F.P. Berbée, Susan J. van Dijk, Ko Willems van Dijk, André
Angptl4 Upregulates Cholesterol Synthesis in Liver via Inhibition of LPL- and HL-Dependent Hepatic Cholesterol Uptake Laeticia Lichtenstein, Jimmy F.P. Berbée, Susan J. van Dijk, Ko Willems van Dijk, André
Moh Tarek + Suhayb. Tamara Al-Azzeh + Asmaa Aljeelani ... Faisal
 28 Moh Tarek + Suhayb Tamara Al-Azzeh + Asmaa Aljeelani... Faisal Digestion of dietary lipids Lipid digestion and absorption are complex processes. They involve soluble enzymes, substrates with different
28 Moh Tarek + Suhayb Tamara Al-Azzeh + Asmaa Aljeelani... Faisal Digestion of dietary lipids Lipid digestion and absorption are complex processes. They involve soluble enzymes, substrates with different
Separation of HDL Particles by Immunoprecipitation
 Sun Diagnostics, LLC Separation of HDL Particles by Immunoprecipitation Rae-Anne Nguyen and John H. Contois 13 Introduction We all know that HDL cholesterol concentration is inversely associated with coronary
Sun Diagnostics, LLC Separation of HDL Particles by Immunoprecipitation Rae-Anne Nguyen and John H. Contois 13 Introduction We all know that HDL cholesterol concentration is inversely associated with coronary
ASP stimulates glucose transport in cultured human adipocytes
 International Journal of Obesity (1997) 21, 261±266 ß 1997 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/97 $12.00 in cultured human adipocytes M Maslowska 1, AD Sniderman 1, R Germinario 2 and K Cian one
International Journal of Obesity (1997) 21, 261±266 ß 1997 Stockton Press All rights reserved 0307±0565/97 $12.00 in cultured human adipocytes M Maslowska 1, AD Sniderman 1, R Germinario 2 and K Cian one
Cholesterol metabolism. Function Biosynthesis Transport in the organism Hypercholesterolemia
 Cholesterol metabolism Function Biosynthesis Transport in the organism Hypercholesterolemia - component of all cell membranes - precursor of bile acids steroid hormones vitamin D Cholesterol Sources: dietary
Cholesterol metabolism Function Biosynthesis Transport in the organism Hypercholesterolemia - component of all cell membranes - precursor of bile acids steroid hormones vitamin D Cholesterol Sources: dietary
Metabolism of lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B in hepatic lipase-deficient mice
 Metabolism of lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B in hepatic lipase-deficient mice Shiqiang Qiu,* Nathalie Bergeron,* Leila Kotite,* Ronald M. Krauss, Andre Bensadoun, and Richard J. Havel 1, * Cardiovascular
Metabolism of lipoproteins containing apolipoprotein B in hepatic lipase-deficient mice Shiqiang Qiu,* Nathalie Bergeron,* Leila Kotite,* Ronald M. Krauss, Andre Bensadoun, and Richard J. Havel 1, * Cardiovascular
OxiSelect Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (OxPL-LDL Quantitation)
 Product Manual OxiSelect Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (OxPL-LDL Quantitation) Catalog Number STA-358 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
Product Manual OxiSelect Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (OxPL-LDL Quantitation) Catalog Number STA-358 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
Devastating Metabolic Consequences of a Life of Plenty: Focus on the Dyslipidemia of Overnutrition
 2013 CSCI DISTINGUISHED SCIENTIST AWARD LECTURE Gary F. Lewis, MD Departments of Medicine and Physiology and the Banting and Best Diabetes Centre, University of Toronto Devastating Metabolic Consequences
2013 CSCI DISTINGUISHED SCIENTIST AWARD LECTURE Gary F. Lewis, MD Departments of Medicine and Physiology and the Banting and Best Diabetes Centre, University of Toronto Devastating Metabolic Consequences
Control 7 d cold 7 d CL
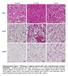 Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
LIPID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; Tel.: ; Fax:
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184-6223; doi:10.3390/ijms15046184 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications:
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184-6223; doi:10.3390/ijms15046184 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications:
Evidence for separate monoglyceride hydrolase and triglyceride lipase in post-heparin human plasma
 Evidence for separate monoglyceride hydrolase and triglyceride lipase in post-heparin human plasma HEINER GRETEN,* ROBERT I. LEVY, and DONALD S. FREDRICKSON Molecular Disease Branch, National Heart Institute,
Evidence for separate monoglyceride hydrolase and triglyceride lipase in post-heparin human plasma HEINER GRETEN,* ROBERT I. LEVY, and DONALD S. FREDRICKSON Molecular Disease Branch, National Heart Institute,
ASSUMPTIONS AND DETAILS OF CALCULATIONS FOR FATTY ACID KINETICS
 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 ASSUMPTIONS AND DETAILS OF CALCULATIONS FOR FATTY ACID KINETICS Our hypothesis was that many sources of palmitate (NEFA, lipogenesis, diet) could contribute to newly-synthesized VLDL-TG
1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 ASSUMPTIONS AND DETAILS OF CALCULATIONS FOR FATTY ACID KINETICS Our hypothesis was that many sources of palmitate (NEFA, lipogenesis, diet) could contribute to newly-synthesized VLDL-TG
Glycosaminoglycans are important macromolecular components. surface of cell membranes and also membranes of subcellular
 Chapter VII EFFECT OF GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS ON THE SYNTHESIS AND SECRETION OF APOLIPOPROTEIN B BY RAT HEPATOCYTES IN CULTURE Glycosaminoglycans are important macromolecular components of intercellular matrix
Chapter VII EFFECT OF GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS ON THE SYNTHESIS AND SECRETION OF APOLIPOPROTEIN B BY RAT HEPATOCYTES IN CULTURE Glycosaminoglycans are important macromolecular components of intercellular matrix
lipoprotein receptor (low density lipoprotein-related protein/receptor-associated protein/cholesteryl esters)
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 92, pp. 4611-4615, May 1995 Medical Sciences Initial hepatic removal of chylomicron remnants is unaffected but endocytosis is delayed in mice lacking the low density lipoprotein
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 92, pp. 4611-4615, May 1995 Medical Sciences Initial hepatic removal of chylomicron remnants is unaffected but endocytosis is delayed in mice lacking the low density lipoprotein
ENZYME HISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN THE LIVER AND ADRENAL GLANDS IN CLINICALLY HEALTHY RABBITS
 Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2011), 14, No 3, 137 141 ENZYME HISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN THE LIVER AND ADRENAL GLANDS IN CLINICALLY HEALTHY RABBITS Summary P. Y. YONKOVA
Bulgarian Journal of Veterinary Medicine (2011), 14, No 3, 137 141 ENZYME HISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF LIPOPROTEIN LIPASE IN THE LIVER AND ADRENAL GLANDS IN CLINICALLY HEALTHY RABBITS Summary P. Y. YONKOVA
