Phospholipid-assisted formation and dispersion of aqueous nano-c 60
|
|
|
- Nelson Cross
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Phospholipid-assisted formation and dispersion of aqueous nano-c 60 Yanjing Chen and Geoffrey D. Bothun* Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Rhode Island, Kingston, RI, USA Introduction Water-soluble carbon fullerenes have been widely explored as candidates in the areas of medicine, materials and cosmetics [1, 2]. Despite of their potential application, their instability in aqueous solution has limited their application [3, 4]. Recent efforts have attempted to overcome this. For example, Deguchi stabilized nano-c 60 by protein adsorption [5] and Govindaraj used cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) to prepare nano-c 60 dispersion Water-soluble nano-c 60 is commonly prepared based on the method of Deguchi et al. [6]. This method is laborious, solvent intensive, and time consuming. In our study, DPPC vesicle assemblies were used to aid in the rapid formation of aqueous nano-c 60. Dipalmityolphosphatidylcholine (DPPC, 734 MW) lipid dispersions form bilayer vesicles, or liposomes, spontaneously in aqueous solution because of their hydrophilic choline headgroups and their hydrophobic dual hexadecane (C 16 ) tails. DPPC is a main component of mammalian cell membranes and a primary lung surfactant. In addition to their use as drug delivery vehicles, DPPC liposomes have been used as nanoscale reactors and templating agents for synthesizing inorganic materials. In the area of lipid-c 60 complexes, Ikeda et al. [3] used a C 60 fullerene exchange method to prepare lipid membrane-incorporated C 60 fullerenes and Szymanska [7] utilized fullerene-modified supported lipid membranes as sensors. These reports suggest that C 60 fullerenes are able to partition into liposome bilayers and enhance electron flow across the bilayer [8, 9]. However, the effect of C 60 and nano-c 60 aggregate on the stability of the bilayer, and how bilayer stability relates to the degree of dispersion, is unknown. In this study, we examine the extent as which C 60 nanoparticles can be adsorbed or entrapped in the DPPC liposome bilayers, and if DPPC liposomes can assist in the formation and dispersion of aqueous nano-c 60. In this study, DPPC/C 60 vesicle assemblies were prepared by the reverse phase evaporation (REV) method [10]. We attempted to elucidate (i) the preference of molecular C 60 to partition into the vesicle bilayer or form nano-c 60 in solution, (ii) the formation of small nano-c 60 in the bilayer due to aggregation, and (iii) the ability to back extract the lipids and isolate nano-c 60 as a function of the DPPC/C 60 molar ratio and presence of magnesium perchlorate (Mg(ClO 4 ) 2 ). Effects of nanoparticle-lipid interactions on bilayer phase behavior investigated were by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC). Structure and morphology of the liposomes and nano-c 60 were imaged by cryogenic transmission electron microscopy (cryo-tem). In addition to aiding the formation of small, potentially water-soluble nano-c 60, this work also provides insight into the ability of C 60 to partition into biological membranes and its effect on membrane structure.
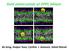
2 Experimental A modified reverse phase evaporation (REV) method for liposome formation was used to prepare the DPPC/C 60 assemblies. A set of samples were prepared at DPPC concentrations of 20 mm with DPPC/C 60 molar ratios of 500:1, 200:1, and 100:1. DPPC dissolved in chloroform and C 60 dissolved in carbon disulfide where placed in round-bottom flask. Deionized water was then added to form an emulsion. The solvents were removed rotary evaporation at 50 (above the DPPC melting temperature of ~42 o C) and 300 mbar for 15 minutes, at which point the pressure was reduced to 100 mbar for 10 minutes. The procedure is described in Figure 1, from A to C. To observe the morphologies and sizes of DPPC/C 60 assemblies, artifact-free images were taken by cryo-tem. Samples were vitrified from room temperature in liquid ethane. Lipid bilayer phase behavior in the DPPC/C 60 assemblies was analyzed by differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) where the samples were equilibrated at 25 and sequential heat/cool cycles were performed from o C at scan rate of 1 o C min -1. The Folch Method was used to extract DPPC from the DPPC/C 60 assemblies and recover the nano-c 60. We added a chloroform-methanol (2:1 by volume) mixture into C to extract the lipids. The bottom phase was composed of chloroform-methanol- water at 86:14:1 (by volume) and contained virtually all of the lipids, while the top phase was composed of chloroform-methanol-water at 3:48:47. Nano-C 60 in the top phase (aqueous) was dried and imaged by TEM. Figure 1. Schematic illustration for preparation of C 60 /DPPC assembly and extraction of lipids from DPPC/C 60 assemblies. Results and Discussion The size, morphology, and location of nano-c 60, relative to DPPC vesicles, that were formed during the REV process were observed by cryo-tem. In Figures 2A-C, the C 60 nanoparticles are observed in DPPC/C 60 assemblies. From the observation, the size of C 60 nanoparticles ranges from approximately 20 to 80 nm, which is similar to the average size of C 60 nanoparticles reported previously (50 nm) in aqueous solution [8]. Moreover, the images show the location of nano-c 60 that some C 60 nanoparticles existed within liposomes, and others existed outside liposomes.
3 Figure 2. Cryo-TEM images of the DPPC vesicle control (A,no C60) and samples at a DPPC/C60 ratio of 200:1 containing DPPC vesicles and nano-c60 (B and C). TEM images of the aqueous phase after extracting lipids from DPPC/C60 at a ratio of 200:1 (D-F; F is a magnification of the selected region in E). Figure 2 D-F shows TEM images of C60 nanoparticles and nano-c60 aggregates that remained in the top aqueous phase after extracting the lipids. In Figure 2F, we observe large nano-c60 aggregates (ca nm) composed of small individual C60 nanoparticles (ca. 5 nm). The small C60 nanoparticles have diameters similar to that of
4 the thickness of a lipid bilayer (4-5 nm), which suggest that these small nanoparticles may have formed within the bilayer. Based on cryo-tem, the presence of lipid assisted in the rapid formation of aqueous nano-c 60 during liposome formation; however, C 60 is hydrophobic and has also been shown to partition into the acyl region of lipid bilayers. This may occur as molecular C 60 or, as suggested by back-extraction studies, small nano-c 60. To detect the presence of C 60 within the bilayers, we have examined the effects of C 60 on the lipid bilayer phase behavior using DSC. Figure 3 shows the DSC transition curves of the samples at different DPPC/C 60 molar ratios. The presence of C 60 broadened the temperature range of main phase transition (i.e. bilayer melting) and lowered the melting (T m ). Meanwhile, the pre-transition of DPPC/C 60 liposome assemblies is eliminated. This suggests that nano-c 60 can be incorporated in lipid bilayers. Figure 3. DSC transition curves of DPPC liposome and DPPC/C 60 assemblies. Conclusion In this study, C 60 nanoparticles were form in aqueous solution assisted with DPPC liposomes, which improved the stability of C 60 and increased the rate of formation. From the cryo-tem results, two kinds of C 60 nanoparticles were observed: (i) large aqueous nano-c 60 existing outside or encapsulated within the vesicles and (ii) small nano-c 60 trapped within the bilayer. DSC results suggest that small nano-c 60, and likely molecular C 60, trapped within the bilayer disrupted the bilayer, decreasing the melting temperature and broadening the phase transition range. We propose that the DPPC/C 60 assemblies provide a convenient means of rapidly forming nano-c 60 in aqueous solution.
5 References 1. Innocenzi, P.; Brusatin, G., Fullerene-Based Organic-Inorganic Nanocomposites and Their Applications Chemical Materials 2001, 13, (10), Colvin, V. L., The potential environmental impact of engineered nanomaterials. Nat Biotechnol 2003, 21, (10), Ikeda, A.; Sato, T.; Kitamura, K.; Nishiguchi, K.; Sasaki, Y.; Kikuchi, J.; Ogawa, T.; Yogo, K.; Takeya, T., Efficient photocleavage of DNA utilising water-soluble lipid membrane-incorporated [60]fullerenes prepared using a [60]fullerene exchange method. Org Biomol Chem 2005, 3, (16), Chen, K. L.; Elimelech, M., Aggregation and deposition kinetics of fullerene (C60) nanoparticles. Langmuir 2006, 22, (26), Deguchi, S.; Yamazaki, T.; Mukai, S.-a.; Usami, R.; Horikoshi, K., Stabilization of C60 Nanoparticles by Protein Adsorption and Its Implications for Toxicity Studies Chem. Res. Toxicol 2006, 20, (6), Fortner, J. D.; Lyon, D. Y.; Sayes, C. M.; Boyd, A. M.; Falkner, J. C.; Hotze, E. M.; Alemany, L. B.; Tao, Y. J.; Guo, W.; Ausman, K. D.; Colvin, V. L.; Hughes, J. B., C60 in water: nanocrystal formation and microbial response. Environ Sci Technol 2005, 39, (11), Szymanska, I.; Radecka, H.; Radecki, J.; Kikut-Ligaj, D., Fullerene modified supported lipid membrane as sensitive element of sensor for odorants. Biosens Bioelectron 2001, 16, (9-12), Sayes, C. M.; Gobin, A. M.; Ausman, K. D.; Mendez, J.; West, J. L.; Colvin, V. L., Nano-C60 cytotoxicity is due to lipid peroxidation. Biomaterials 2005, 26, (36), Braun, M.; Hirsch, A., Fullerene derivatives in bilayer membranes: an overview Carbon 2000, 38, (11-12), Gregoriadis, G., Liposome Technology. New York : Informa Healthcare 2007, 1,
Interaction of Functionalized C 60 Nanoparticles with Lipid Membranes
 Interaction of Functionalized C 60 Nanoparticles with Lipid Membranes Kevin Gasperich Advisor: Dmitry Kopelevich ABSTRACT The recent rapid development of applications for fullerenes has led to an increase
Interaction of Functionalized C 60 Nanoparticles with Lipid Membranes Kevin Gasperich Advisor: Dmitry Kopelevich ABSTRACT The recent rapid development of applications for fullerenes has led to an increase
PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF NABUMETONE LIPOSOMES
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 K L Senthilkumar et al., 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol.1, Issue. 1, January 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 K L Senthilkumar et al., 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol.1, Issue. 1, January 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved PREPARATION AND CHARACTERIZATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE e-issn:
 Available online at www.ijtpls.com International Journal of Trends in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Vol. 1, Issue: 5, 2015: 587-592 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF LIPOSOMES CONTAINING ZIDOVUDINE CH.B.V.V.L.S.Latha,KVR.
Available online at www.ijtpls.com International Journal of Trends in Pharmacy and Life Sciences Vol. 1, Issue: 5, 2015: 587-592 PREPARATION AND EVALUATION OF LIPOSOMES CONTAINING ZIDOVUDINE CH.B.V.V.L.S.Latha,KVR.
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF PENTOXIFYLLINE LIPOSOME FORMULATION
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 4, No. 4, December 2009, p. 857 862 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF PENTOXIFYLLINE LIPOSOME FORMULATION U. D. SHIVHARE *, D.U. AMBULKAR, V. B. MATHUR,
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 4, No. 4, December 2009, p. 857 862 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF PENTOXIFYLLINE LIPOSOME FORMULATION U. D. SHIVHARE *, D.U. AMBULKAR, V. B. MATHUR,
Dispersants and Related Oil Spill Technologies at the Nanoscale!
 vj@tulane.edu Dispersants and Related Oil Spill Technologies at the Nanoscale! Vijay T. John Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Tulane University Funding: Gulf of Mexico Research Initiative
vj@tulane.edu Dispersants and Related Oil Spill Technologies at the Nanoscale! Vijay T. John Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Tulane University Funding: Gulf of Mexico Research Initiative
Self-Assembly. Lecture 3 Lecture 3 Surfactants Self-Assembly
 Self-Assembly Lecture 3 Lecture 3 Surfactants Self-Assembly Anionic surfactants unsaturated omega-3 3 fatty acids rd carbon from the metyl end has double bond saturated Non-ionic surfactants Cationic surfactants
Self-Assembly Lecture 3 Lecture 3 Surfactants Self-Assembly Anionic surfactants unsaturated omega-3 3 fatty acids rd carbon from the metyl end has double bond saturated Non-ionic surfactants Cationic surfactants
Supporting Information for
 Supporting Information for Rupture of Lipid Membranes Induced by Amphiphilic Janus Nanoparticles Kwahun Lee, Liuyang Zhang, Yi Yi, Xianqiao Wang, Yan Yu* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University, Bloomington,
Supporting Information for Rupture of Lipid Membranes Induced by Amphiphilic Janus Nanoparticles Kwahun Lee, Liuyang Zhang, Yi Yi, Xianqiao Wang, Yan Yu* Department of Chemistry, Indiana University, Bloomington,
Xianren Zhang ( 张现仁 )
 The interaction between nanoparticles and membranes: from cytotoxicity to drug delivery Xianren Zhang ( 张现仁 ) zhangxr@mail.buct.edu.cn State Key Laboratory of Organic-Inorganic Composites, Beijing University
The interaction between nanoparticles and membranes: from cytotoxicity to drug delivery Xianren Zhang ( 张现仁 ) zhangxr@mail.buct.edu.cn State Key Laboratory of Organic-Inorganic Composites, Beijing University
LIPOSOME STABILITY VERIFICATION BY ATOMIC FORCE MICROSCOPY
 34 Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. 5 (2003) 34-40 E. F. de Souza and O. Teschke LIPOSOME STABILITY VERIFICATION BY ATOMIC FORCE MICROSCOPY E. F. de Souza 1 and O. Teschke 2 1 Faculdade de Química, CEATEC/PUC-Campinas,
34 Rev.Adv.Mater.Sci. 5 (2003) 34-40 E. F. de Souza and O. Teschke LIPOSOME STABILITY VERIFICATION BY ATOMIC FORCE MICROSCOPY E. F. de Souza 1 and O. Teschke 2 1 Faculdade de Química, CEATEC/PUC-Campinas,
Appendix A: Mesoporous Silica Particles in Biological Applications
 Appendix A: Mesoporous Silica Particles in Biological Applications Klimisch Criteria Figure 1. Klimisch criteria in the ToxRTool for the reliability assessment of in vivo toxicity studies. 118 The Klimisch
Appendix A: Mesoporous Silica Particles in Biological Applications Klimisch Criteria Figure 1. Klimisch criteria in the ToxRTool for the reliability assessment of in vivo toxicity studies. 118 The Klimisch
Enhanced delivery methods for greater efficacy
 On-Line Formulation Training - Anywhere In The World - Enhanced delivery methods for greater efficacy Belinda Carli Director, Institute of Personal Care Science Image showing absorbance in the outer stratum
On-Line Formulation Training - Anywhere In The World - Enhanced delivery methods for greater efficacy Belinda Carli Director, Institute of Personal Care Science Image showing absorbance in the outer stratum
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF MIXED LIPID BILAYER WITH DPPC AND MPPC: EFFECT OF CONFIGURATIONS IN GEL-PHASE
 MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF MIXED LIPID BILAYER WITH DPPC AND MPPC: EFFECT OF CONFIGURATIONS IN GEL-PHASE A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Young Kyoung Kim In Partial Fulfillment of the
MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION OF MIXED LIPID BILAYER WITH DPPC AND MPPC: EFFECT OF CONFIGURATIONS IN GEL-PHASE A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Young Kyoung Kim In Partial Fulfillment of the
Protein directed assembly of lipids
 Protein directed assembly of lipids D. Nordin, O. Yarkoni, L. Donlon, N. Savinykh, and D.J. Frankel SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Supported bilayer preparation 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
Protein directed assembly of lipids D. Nordin, O. Yarkoni, L. Donlon, N. Savinykh, and D.J. Frankel SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Materials and Methods Supported bilayer preparation 1,2-dioleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine
OXIDATIVE STRESS STUDIES ON LIPID MODEL MEMBRANES
 OXIDATIVE STRESS STUDIES ON LIPID MODEL MEMBRANES MARCELA ELISABETA BARBINTA-PATRASCU *, LAURA TUGULEA * * Faculty of Physics, University of Bucharest, Romania Received December 21, 2004 The liposomes
OXIDATIVE STRESS STUDIES ON LIPID MODEL MEMBRANES MARCELA ELISABETA BARBINTA-PATRASCU *, LAURA TUGULEA * * Faculty of Physics, University of Bucharest, Romania Received December 21, 2004 The liposomes
Light and X-ray triggered liposomal gene/drug delivery system for cancer therapy
 Light and X-ray triggered liposomal gene/drug delivery system for cancer therapy Wei Deng, 1 Wenjie Chen, 2 Sandhya Clement, 1 Anna Guller, 1 Alexander Engel, 3 Ewa Goldys 1 1 The Graduate School of Biomedical
Light and X-ray triggered liposomal gene/drug delivery system for cancer therapy Wei Deng, 1 Wenjie Chen, 2 Sandhya Clement, 1 Anna Guller, 1 Alexander Engel, 3 Ewa Goldys 1 1 The Graduate School of Biomedical
3.1.3 Lipids. Source: AQA Spec
 alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
Preparation of Nonionic Vesicles Using the Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Reverse Phase Evaporation Method and Analysis of Their Solution Properties
 Journal of Oleo Science Copyright 2016 by Japan Oil Chemists Society J-STAGE Advance Publication date : December 11, 2015 doi : 10.5650/jos.ess15192 Preparation of Nonionic Vesicles Using the Supercritical
Journal of Oleo Science Copyright 2016 by Japan Oil Chemists Society J-STAGE Advance Publication date : December 11, 2015 doi : 10.5650/jos.ess15192 Preparation of Nonionic Vesicles Using the Supercritical
Gold nanocrystals at DPPC bilayer. Bo Song, Huajun Yuan, Cynthia J. Jameson, Sohail Murad
 Gold nanocrystals at DPPC bilayer Bo Song, Huajun Yuan, Cynthia J. Jameson, Sohail Murad Coarse-grained mapping strategy of a DPPC lipid molecule. The structure of gold nanocrystals (bare gold nanoparticles)
Gold nanocrystals at DPPC bilayer Bo Song, Huajun Yuan, Cynthia J. Jameson, Sohail Murad Coarse-grained mapping strategy of a DPPC lipid molecule. The structure of gold nanocrystals (bare gold nanoparticles)
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138,
 J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11568 11574 Madhuri Jash 17/09/2016 1 INTRODUCTION: The catalytic activity of nanocrystalline catalysts used to have singleinterface length scale, where the atomic arrangements
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11568 11574 Madhuri Jash 17/09/2016 1 INTRODUCTION: The catalytic activity of nanocrystalline catalysts used to have singleinterface length scale, where the atomic arrangements
3.1 Background. Preformulation Studies
 Preformulation Studies 3.1 Background Delivery of any drug requires a suitable dosage form to get optimum therapeutic effects. The development of such dosage forms fundamental properties of the drug molecule
Preformulation Studies 3.1 Background Delivery of any drug requires a suitable dosage form to get optimum therapeutic effects. The development of such dosage forms fundamental properties of the drug molecule
Physical Cell Biology Lecture 10: membranes elasticity and geometry. Hydrophobicity as an entropic effect
 Physical Cell Biology Lecture 10: membranes elasticity and geometry Phillips: Chapter 5, Chapter 11 and Pollard Chapter 13 Hydrophobicity as an entropic effect 1 Self-Assembly of Lipid Structures Lipid
Physical Cell Biology Lecture 10: membranes elasticity and geometry Phillips: Chapter 5, Chapter 11 and Pollard Chapter 13 Hydrophobicity as an entropic effect 1 Self-Assembly of Lipid Structures Lipid
Self-assembled nanostructures soft and hard matter
 Hands-On Nano-Technology course Nano-Science Center University of Copenhagen Self-assembled nanostructures soft and hard matter One-day workshop, August 12, 2004 Division of Physical Chemistry 1, Center
Hands-On Nano-Technology course Nano-Science Center University of Copenhagen Self-assembled nanostructures soft and hard matter One-day workshop, August 12, 2004 Division of Physical Chemistry 1, Center
Protection of DPPC phospholipid liposomal membrane against radiation oxidative damage by antioxidants
 Protection of DPPC phospholipid liposomal membrane against radiation oxidative damage by antioxidants D. L. Marathe, B. N. Pandey and K. P. Mishra Radiation Biology Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre,
Protection of DPPC phospholipid liposomal membrane against radiation oxidative damage by antioxidants D. L. Marathe, B. N. Pandey and K. P. Mishra Radiation Biology Division, Bhabha Atomic Research Centre,
General and Facile Surface Functionalization of Hydrophobic Nanocrystals with Poly(amino acid) for Cell Luminescence Imaging
 General and Facile Surface Functionalization of Hydrophobic Nanocrystals with Poly(amino acid) for Cell Luminescence Imaging Sheng Huang, Min Bai, Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
General and Facile Surface Functionalization of Hydrophobic Nanocrystals with Poly(amino acid) for Cell Luminescence Imaging Sheng Huang, Min Bai, Leyu Wang* State Key Laboratory of Chemical Resource Engineering,
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Supporting Information Modulating Interactions between Ligand-Coated Nanoparticles and Phase-Separated
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Supporting Information Modulating Interactions between Ligand-Coated Nanoparticles and Phase-Separated
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
Chapter 1 Membrane Structure and Function Architecture of Membranes Subcellular fractionation techniques can partially separate and purify several important biological membranes, including the plasma and
Colloid Chemistry. Lecture #2 Association colloid
 Colloid Chemistry Lecture #2 Association colloid 1 https://ilustracionmedica.wordpress.com/2014/08/27/fisicos-haciendo-medicina-john-tyndall/ Solution Classical vs. Colloid solution Tyndall effect Increased
Colloid Chemistry Lecture #2 Association colloid 1 https://ilustracionmedica.wordpress.com/2014/08/27/fisicos-haciendo-medicina-john-tyndall/ Solution Classical vs. Colloid solution Tyndall effect Increased
Modeling of Nanostructures : Bionanosystems, Polymers, and Surfaces
 2008 Alberta Nanotech Showcase November 20, 2008 Maria Stepanova Research Officer Principal Investigator NINT Modeling of Nanostructures : Bionanosystems, Polymers, and Surfaces We develop numeric tools
2008 Alberta Nanotech Showcase November 20, 2008 Maria Stepanova Research Officer Principal Investigator NINT Modeling of Nanostructures : Bionanosystems, Polymers, and Surfaces We develop numeric tools
STUDY OF MIXED LIPID BILAYER SYSTEM USING MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION
 STUDY OF MIXED LIPID BILAYER SYSTEM USING MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by JaeHyung Choi In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Bachelor of
STUDY OF MIXED LIPID BILAYER SYSTEM USING MOLECULAR DYNAMICS SIMULATION A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by JaeHyung Choi In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Bachelor of
Chapter 3. Need for Present Study
 Need for Present Study Chapter 3 Chemotherapy, the use of cytotoxic drugs to kill cancerous cells remains the most common approach for cancer therapy. In conventional chemotherapy most of the anticancer
Need for Present Study Chapter 3 Chemotherapy, the use of cytotoxic drugs to kill cancerous cells remains the most common approach for cancer therapy. In conventional chemotherapy most of the anticancer
Raman spectroscopy methods for detecting and imaging supported lipid bilayers
 Spectroscopy 24 (2010) 113 117 113 DOI 10.3233/SPE-2010-0426 IOS Press Raman spectroscopy methods for detecting and imaging supported lipid bilayers Claire S. Sweetenham and Ioan Notingher Nanoscience
Spectroscopy 24 (2010) 113 117 113 DOI 10.3233/SPE-2010-0426 IOS Press Raman spectroscopy methods for detecting and imaging supported lipid bilayers Claire S. Sweetenham and Ioan Notingher Nanoscience
MıCELLES AS NANOSıZED CARRıERS FOR SKıN DELıVERY OF DRUGS. Sevgi Güngör
 MıCELLES AS NANOSıZED CARRıERS FOR SKıN DELıVERY OF DRUGS Sevgi Güngör Istanbul University, Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology 4 th International Conference on Nanotek&Expo,01-03
MıCELLES AS NANOSıZED CARRıERS FOR SKıN DELıVERY OF DRUGS Sevgi Güngör Istanbul University, Faculty of Pharmacy, Department of Pharmaceutical Technology 4 th International Conference on Nanotek&Expo,01-03
International Journal of Chemical Sciences
 International Journal of Chemical Sciences Research Vol 15 Iss 4 Simple Method for the Demonstration of Drug-Loaded Nano-Liposomes Riam Abu-Much *, Naim Najami, Saba Hugerat and Muhamad Hugerat The Academic
International Journal of Chemical Sciences Research Vol 15 Iss 4 Simple Method for the Demonstration of Drug-Loaded Nano-Liposomes Riam Abu-Much *, Naim Najami, Saba Hugerat and Muhamad Hugerat The Academic
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Formulation and evaluation of sustained released niosomes containing pregabalin P. Aravinth Kumar *, Ranjit Singh, K. Karthick and K.S.G. Arulkumaran KMCH
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Formulation and evaluation of sustained released niosomes containing pregabalin P. Aravinth Kumar *, Ranjit Singh, K. Karthick and K.S.G. Arulkumaran KMCH
Self-assembly and phase behavior
 Self-assembly and phase behavior Amphiphiles and surface tension Lyotropic phases Micelles Key parameters for micellisation Critical packing parameter Other lyotropic phases Special lyotropic phases: vesicles
Self-assembly and phase behavior Amphiphiles and surface tension Lyotropic phases Micelles Key parameters for micellisation Critical packing parameter Other lyotropic phases Special lyotropic phases: vesicles
Preparation and Characterization of Candesartan Cilexetil Solid Lipid Nanoparticulate Capsules
 Research Article Preparation and Characterization of Candesartan Cilexetil Solid Lipid Nanoparticulate Capsules *Surya Kiran Vuddisa, Subramanian S., Sindhu Raavi Department of Pharmaceutics, PSG College
Research Article Preparation and Characterization of Candesartan Cilexetil Solid Lipid Nanoparticulate Capsules *Surya Kiran Vuddisa, Subramanian S., Sindhu Raavi Department of Pharmaceutics, PSG College
Willem J.M. Mulder, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Assistant Professor of Gene and Cell Medicine Director Nanomedicine Laboratory
 Willem J.M. Mulder, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Assistant Professor of Gene and Cell Medicine Director Nanomedicine Laboratory Noordwijkerhout, The Netherlands 17-18 March 2011 Nanometer (10-9
Willem J.M. Mulder, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Radiology Assistant Professor of Gene and Cell Medicine Director Nanomedicine Laboratory Noordwijkerhout, The Netherlands 17-18 March 2011 Nanometer (10-9
Supplementary Figure 1. Sample preparation schematic. First (Stage I), square islands of MoO 3 are prepared by either photolithography followed by
 Supplementary Figure 1. Sample preparation schematic. First (Stage I), square islands of MoO 3 are prepared by either photolithography followed by thermal evaporation and liftoff or by a process where
Supplementary Figure 1. Sample preparation schematic. First (Stage I), square islands of MoO 3 are prepared by either photolithography followed by thermal evaporation and liftoff or by a process where
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 22: Aggregates of lipids: micelles, liposomes and their applications OBJECTIVE
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 22: Aggregates of lipids: micelles, liposomes and their applications OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students to the types
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 22: Aggregates of lipids: micelles, liposomes and their applications OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module is to introduce the students to the types
The Effects of Buckminster Fullerenes on Mitochondrial Function
 Science Honors Research Proposal: Abstract Form Project title: The Effects of Buckminster Fullerenes on Mitochondrial Function Abstract (not to exceed 150 words): Since the discovery of Buckminster Fullerenes
Science Honors Research Proposal: Abstract Form Project title: The Effects of Buckminster Fullerenes on Mitochondrial Function Abstract (not to exceed 150 words): Since the discovery of Buckminster Fullerenes
Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry)
 051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
051117 Quiz 8 Introduction to Polymers (Chemistry) (Figures from Heimenz Colloid Sci.) 1) Surfactants are amphiphilic molecules (molecules having one end hydrophobic and the other hydrophilic) and are
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Contents. xiv xv xvi. About the authors Preface Acknowledgments
 About the authors Preface Acknowledgments 1 Introduction to spray drying 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Stage 1: Atomization 2 1.2.1 Principle of atomization 3 1.2.2 Classification of atomizers 4 1.2.2.1 Rotary
About the authors Preface Acknowledgments 1 Introduction to spray drying 1 1.1 Introduction 1 1.2 Stage 1: Atomization 2 1.2.1 Principle of atomization 3 1.2.2 Classification of atomizers 4 1.2.2.1 Rotary
Chapter 12: Membranes. Voet & Voet: Pages
 Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
Chapter 12: Membranes Voet & Voet: Pages 390-415 Slide 1 Membranes Essential components of all living cells (define boundry of cells) exclude toxic ions and compounds; accumulation of nutrients energy
Penetration of Gold Nanoparticle through Human Skin: Unraveling Its Mechanisms at the Molecular Scale
 Penetration of Gold Nanoparticle through Human Skin: Unraveling Its Mechanisms at the Molecular Scale Rakesh Gupta and Beena Rai* TATA Research Development & Design Centre, TCS Innovation labs, Pune India,
Penetration of Gold Nanoparticle through Human Skin: Unraveling Its Mechanisms at the Molecular Scale Rakesh Gupta and Beena Rai* TATA Research Development & Design Centre, TCS Innovation labs, Pune India,
Supporting Information. Maximizing the Supported Bilayer Phenomenon: LCP Liposomes Comprised Exclusively
 S-1 Supporting Information Maximizing the Supported Bilayer Phenomenon: LCP Liposomes Comprised Exclusively of PEGylated Phospholipids for Enhanced Systemic and Lymphatic Delivery Matthew T. Haynes and
S-1 Supporting Information Maximizing the Supported Bilayer Phenomenon: LCP Liposomes Comprised Exclusively of PEGylated Phospholipids for Enhanced Systemic and Lymphatic Delivery Matthew T. Haynes and
LIPOSOMES CONTAINING UNDOPED AND Au + / Ag + DOPED TITANIUM DIOXIDE NANOPARTICLES
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 5, No 4, October-December 2010, p. 919-925 LIPOSOMES CONTAINING UNDOPED AND Au + / Ag + DOPED TITANIUM DIOXIDE NANOPARTICLES D. I. HĂDĂRUGĂ a, N.
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 5, No 4, October-December 2010, p. 919-925 LIPOSOMES CONTAINING UNDOPED AND Au + / Ag + DOPED TITANIUM DIOXIDE NANOPARTICLES D. I. HĂDĂRUGĂ a, N.
EFFECT OF COMPRESSED CO 2 ON THE PROPERTIES OF AOT IN ISOOCTANE REVERSE MICELLAR SOLUTION AND ITS APPLICATION TO RECOVER NANOPARTICLES
 EFFECT OF COMPRESSED CO 2 ON THE PROPERTIES OF AOT IN ISOOCTANE REVERSE MICELLAR SOLUTION AND ITS APPLICATION TO RECOVER NANOPARTICLES Dongxia Liu, Jianling Zhang, Tiancheng Mu, Jing Chen, Weize Wu, Jun
EFFECT OF COMPRESSED CO 2 ON THE PROPERTIES OF AOT IN ISOOCTANE REVERSE MICELLAR SOLUTION AND ITS APPLICATION TO RECOVER NANOPARTICLES Dongxia Liu, Jianling Zhang, Tiancheng Mu, Jing Chen, Weize Wu, Jun
CHARACTERIZATION OF NANO CARRIERS FOR DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS: THE LIPIDOTS NanoSafe 2016 Amandine Arnould 07-11/11/2016
 CHARACTERIZATION OF NANO CARRIERS FOR DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS: THE LIPIDOTS NanoSafe 2016 Amandine Arnould 07-11/11/2016 CONTEXT : NANOPARTICLES IN SENSITIVE MEDIA Nano-safety issue Environment Medicine
CHARACTERIZATION OF NANO CARRIERS FOR DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS: THE LIPIDOTS NanoSafe 2016 Amandine Arnould 07-11/11/2016 CONTEXT : NANOPARTICLES IN SENSITIVE MEDIA Nano-safety issue Environment Medicine
Kobe Pharmaceutical University, Motoyama-kitamachi, Higashinada-ku, Kobe , Japan. Received June 29, 1999; accepted October 1, 1999
 48 Chem. Pharm. Bull. 48(1) 48 52 (2000) Vol. 48, No. 1 Interactions of Cyclodextrins with Dipalmitoyl, Distearoyl, and Dimyristoyl Phosphatidyl Choline Liposomes. A Study by Leakage of Carboxyfluorescein
48 Chem. Pharm. Bull. 48(1) 48 52 (2000) Vol. 48, No. 1 Interactions of Cyclodextrins with Dipalmitoyl, Distearoyl, and Dimyristoyl Phosphatidyl Choline Liposomes. A Study by Leakage of Carboxyfluorescein
Chem Lecture 8 Lipids and Cell Membranes
 Chem 452 - Lecture 8 Lipids and Cell Membranes 111114 Like carbohydrates, lipids are one of the four major classes of biomolecules, which also include the proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids. Lipids
Chem 452 - Lecture 8 Lipids and Cell Membranes 111114 Like carbohydrates, lipids are one of the four major classes of biomolecules, which also include the proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids. Lipids
DEVELOPMENT OF SOLID LIPID NANOPARTICLES OF A WATER SOLUBLE DRUG
 Page4813 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2016 ISSN NO: 2231-6876 DEVELOPMENT OF SOLID LIPID NANOPARTICLES OF A WATER SOLUBLE DRUG Akkshata Parab*, Amrita Bajaj Department of Pharmaceutics,
Page4813 Indo American Journal of Pharmaceutical Research, 2016 ISSN NO: 2231-6876 DEVELOPMENT OF SOLID LIPID NANOPARTICLES OF A WATER SOLUBLE DRUG Akkshata Parab*, Amrita Bajaj Department of Pharmaceutics,
Encapsulation techniques
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Encapsulation techniques This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: VLADISAVLJEVIC, G.T.,
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Encapsulation techniques This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: VLADISAVLJEVIC, G.T.,
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI)
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) One-Step Encapsulation and Triggered Release Based on
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) One-Step Encapsulation and Triggered Release Based on
Chemical Surface Transformation 1
 Chemical Surface Transformation 1 Chemical reactions at Si H surfaces (inorganic and organic) can generate very thin films (sub nm thickness up to µm): inorganic layer formation by: thermal conversion:
Chemical Surface Transformation 1 Chemical reactions at Si H surfaces (inorganic and organic) can generate very thin films (sub nm thickness up to µm): inorganic layer formation by: thermal conversion:
A Facile Method for Enhancing the Sensing Performance of Zinc Oxide. Nanofibers Gas Sensors
 Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI): A Facile Method for Enhancing the Sensing Performance of Zinc Oxide Nanofibers Gas Sensors Pei-Pei Wang a, Qi Qi a, Rui-Fei Xuan a,b, Jun Zhao a, Li-Jing Zhou
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI): A Facile Method for Enhancing the Sensing Performance of Zinc Oxide Nanofibers Gas Sensors Pei-Pei Wang a, Qi Qi a, Rui-Fei Xuan a,b, Jun Zhao a, Li-Jing Zhou
Supporting Information. Self-assembly in a drying nanofluid droplet: Spontaneous formation of 3D fibre network structures
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Self-assembly in a drying nanofluid droplet: Spontaneous formation of
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Soft Matter. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Supporting Information Self-assembly in a drying nanofluid droplet: Spontaneous formation of
ERC TeleSeminar Series Steven O. Nielsen The University of Texas at Dallas February 7, 2013
 ERC TeleSeminar Series Steven O. Nielsen The University of Texas at Dallas February 7, 2013 SRC/SEMATECH Engineering Research Center for Environmentally Benign Semiconductor Manufacturing 1 Outline 1.
ERC TeleSeminar Series Steven O. Nielsen The University of Texas at Dallas February 7, 2013 SRC/SEMATECH Engineering Research Center for Environmentally Benign Semiconductor Manufacturing 1 Outline 1.
Investigating Lipids
 Investigating Lipids In today s culture, there is a stigma associated with the word fat. While it is true that too much fat can lead to health problems, fats (or lipids) play very important roles in biology.
Investigating Lipids In today s culture, there is a stigma associated with the word fat. While it is true that too much fat can lead to health problems, fats (or lipids) play very important roles in biology.
Methods and Materials
 a division of Halcyonics GmbH Anna-Vandenhoeck-Ring 5 37081 Göttingen, Germany Application Note Micostructured lipid bilayers ANDREAS JANSHOFF 1), MAJA GEDIG, AND SIMON FAISS Fig.1: Thickness map of microstructured
a division of Halcyonics GmbH Anna-Vandenhoeck-Ring 5 37081 Göttingen, Germany Application Note Micostructured lipid bilayers ANDREAS JANSHOFF 1), MAJA GEDIG, AND SIMON FAISS Fig.1: Thickness map of microstructured
: Application of Nanotechnology to Cosmetics and Foods
 LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP : Application of Nanotechnology to Cosmetics and Foods Robert L. Bronaugh, Ph.D. Director, Cosmetics Staff Office of Cosmetics and Colors Tuesday, November 24,
LIVE INTERACTIVE LEARNING @ YOUR DESKTOP : Application of Nanotechnology to Cosmetics and Foods Robert L. Bronaugh, Ph.D. Director, Cosmetics Staff Office of Cosmetics and Colors Tuesday, November 24,
9/11/18. Cell Function & Chemistry. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell
 Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
The Assembly and Use of Tethered Bilayer Lipid Membranes (tblms)
 The Assembly and Use of Tethered Bilayer Lipid Membranes (tblms) Charles Cranfield 1,2,4, Sonia Carne 3, Boris Martinac 1,2 and Bruce Cornell 3 1 Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute, Darlinghurst,
The Assembly and Use of Tethered Bilayer Lipid Membranes (tblms) Charles Cranfield 1,2,4, Sonia Carne 3, Boris Martinac 1,2 and Bruce Cornell 3 1 Victor Chang Cardiac Research Institute, Darlinghurst,
Development of lysolipid-based thermosensitive liposomes for delivery of high. molecular weight proteins
 Development of lysolipid-based thermosensitive liposomes for delivery of high molecular weight proteins Xin Zhang a, Paul F. Luckham* a, Alun D. Hughes b, Simon Thom b, and Xiao Yun Xu a a Department of
Development of lysolipid-based thermosensitive liposomes for delivery of high molecular weight proteins Xin Zhang a, Paul F. Luckham* a, Alun D. Hughes b, Simon Thom b, and Xiao Yun Xu a a Department of
Formulation and Evaluation of Acyclovir Liposomes
 Krishna Mohan Chinnala and Rabinarayan Panigrahy., 217/ Formulation and evaluation of acyclovir RESEARCH ARTICLE International Research Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biosciences Pri -ISSN: 2394-5826 http://www.irjpbs.com
Krishna Mohan Chinnala and Rabinarayan Panigrahy., 217/ Formulation and evaluation of acyclovir RESEARCH ARTICLE International Research Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biosciences Pri -ISSN: 2394-5826 http://www.irjpbs.com
Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid Jun Gong, Xin Lu, Xueqin An*
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Fluorescent Carbon Dots as Off-On Nanosensor for Ascorbic Acid Jun Gong, Xin Lu, Xueqin An*
TA Instruments Applications Note. Thermodynamics of Micelle Formation
 Thermodynamics of Micelle Formation Angélica Román Guerrero 1, E. Jaime Vernon Carter 1 and Neil A. Demarse 2 1 DIPH and DBT, Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana Iztapalapa, San Rafael Atlixco #186, Col.
Thermodynamics of Micelle Formation Angélica Román Guerrero 1, E. Jaime Vernon Carter 1 and Neil A. Demarse 2 1 DIPH and DBT, Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana Iztapalapa, San Rafael Atlixco #186, Col.
Model for measurement of water layer thickness under lipid bilayers by surface plasmon resonance
 Model for measurement of water layer thickness under lipid bilayers by surface plasmon resonance Koyo Watanabe Unit of Measurement Technology, CEMIS-OULU, University of Oulu, PO Box 51, 87101 Kajaani,
Model for measurement of water layer thickness under lipid bilayers by surface plasmon resonance Koyo Watanabe Unit of Measurement Technology, CEMIS-OULU, University of Oulu, PO Box 51, 87101 Kajaani,
B. semisolid materials consisting of hydrophilic and hydrophobic portions
 CHEM 470 Understanding Emulsions I. Definitions A. Any heterogeneous system which has at least one immiscible or barely miscible liquid dispersed in another liquid in the form of tiny droplets. A. Becher,
CHEM 470 Understanding Emulsions I. Definitions A. Any heterogeneous system which has at least one immiscible or barely miscible liquid dispersed in another liquid in the form of tiny droplets. A. Becher,
8 Influence of permeation modulators on the behaviour of a SC lipid model mixture
 8 Influence of permeation modulators on the behaviour of a SC lipid model mixture 8.1 Introduction In the foregoing parts of this thesis, a model membrane system of SC lipids has been developed and characterized.
8 Influence of permeation modulators on the behaviour of a SC lipid model mixture 8.1 Introduction In the foregoing parts of this thesis, a model membrane system of SC lipids has been developed and characterized.
Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology
 Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology Instability of Lipid Membrane Benxin Jing a, Marie Hutin c, Erin Connor a, Leroy Cronin c,* and Yingxi Zhu a,b,* a Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Polyoxometalate Macroion Induced Phase and Morphology Instability of Lipid Membrane Benxin Jing a, Marie Hutin c, Erin Connor a, Leroy Cronin c,* and Yingxi Zhu a,b,* a Department of Chemical and Biomolecular
Formation of Nano-carriers by the Depressurization of Expanded Solution into an Aqueous Media (DESAM)
 Formation of Nano-carriers by the Depressurization of Expanded Solution into an Aqueous Media (DESAM) Chau Chun Beh, Raffaella Mammucari, Neil Russell Foster* School of Chemical Engineering, University
Formation of Nano-carriers by the Depressurization of Expanded Solution into an Aqueous Media (DESAM) Chau Chun Beh, Raffaella Mammucari, Neil Russell Foster* School of Chemical Engineering, University
Effect of number of extrusion passes on liposome nanoparticle size
 CENG 176B, Spring 2016 Drews, Zhang, Yang, Xu, and Fenning Section B01 (W/F), Team 07: Double-O Seven, Lab 5: Effect of number of extrusion passes on liposome nanoparticle size Part I: Part II: Part III:
CENG 176B, Spring 2016 Drews, Zhang, Yang, Xu, and Fenning Section B01 (W/F), Team 07: Double-O Seven, Lab 5: Effect of number of extrusion passes on liposome nanoparticle size Part I: Part II: Part III:
Modifying the Release Properties of Liposomes Toward Personalized Medicine
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology Modifying the Release Properties of Liposomes Toward Personalized Medicine DAVID CIPOLLA, 1,2 HUIYING WU, 2 IGOR GONDA, 2 SIMON EASTMAN, 3 TOM REDELMEIER,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Pharmaceutical Nanotechnology Modifying the Release Properties of Liposomes Toward Personalized Medicine DAVID CIPOLLA, 1,2 HUIYING WU, 2 IGOR GONDA, 2 SIMON EASTMAN, 3 TOM REDELMEIER,
A quantitative study of chemical kinetics for the synthesis of. doped oxide nanocrystals using FTIR spectroscopy
 Supporting information A quantitative study of chemical kinetics for the synthesis of doped oxide nanocrystals using FTIR spectroscopy Na Zhang, 1,2 Xin Wang, 1 Zhizhen Ye 1 and Yizheng Jin, 1,3* 1 State
Supporting information A quantitative study of chemical kinetics for the synthesis of doped oxide nanocrystals using FTIR spectroscopy Na Zhang, 1,2 Xin Wang, 1 Zhizhen Ye 1 and Yizheng Jin, 1,3* 1 State
Studies concerning the entrapment of Anethum graveolens essential oil in liposomes
 Roumanian Biotechnological Letters Vol. 14, No. 3, 2009, pp. 4411-4417 Copyright 2008 Bucharest University Printed in Romania. All rights reserved Roumanian Society of Biological Sciences ORIGINAL PAPER
Roumanian Biotechnological Letters Vol. 14, No. 3, 2009, pp. 4411-4417 Copyright 2008 Bucharest University Printed in Romania. All rights reserved Roumanian Society of Biological Sciences ORIGINAL PAPER
Neutron reflectivity in biology and medicine. Jayne Lawrence
 Neutron reflectivity in biology and medicine Jayne Lawrence Why neutron reflectivity studies? build up a detailed picture of the structure of a surface in the z direction n e u tro n s in n e u tro n s
Neutron reflectivity in biology and medicine Jayne Lawrence Why neutron reflectivity studies? build up a detailed picture of the structure of a surface in the z direction n e u tro n s in n e u tro n s
Novel drug delivery system. Nanos-in-Micros
 Novel drug delivery system Nanos-in-Micros Janne Raula The annual symposium of the Finnish Society of Physical Pharmacy February 9 th, 2012 Medicinal treatment Indications -Neurosurgery -General surgery
Novel drug delivery system Nanos-in-Micros Janne Raula The annual symposium of the Finnish Society of Physical Pharmacy February 9 th, 2012 Medicinal treatment Indications -Neurosurgery -General surgery
Liposomes in polymer matrix. Stability of liposomes in PEG 400 and PEG 8000 solutions.
 Liposomes in polymer matrix. Stability of liposomes in PEG 400 and PEG 8000 solutions. Magdalena Bajgrowicz 1,2, Jerzy Detyna 2, Marek Langner 1 1 Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Instrumentation,
Liposomes in polymer matrix. Stability of liposomes in PEG 400 and PEG 8000 solutions. Magdalena Bajgrowicz 1,2, Jerzy Detyna 2, Marek Langner 1 1 Institute of Biomedical Engineering and Instrumentation,
PHOSPHOLIPID SURFACE BILAYERS AT THE AIR-WATER INTERFACE
 PHOSPHOLIPID SURFACE BILAYERS AT THE AIR-WATER INTERFACE III. Relation Between Surface Bilayer Formation and Lipid Bilayer Assembly in Cell Membranes NORMAN L. GERSHFELD Laboratory ofbiochemical Pharmacology,
PHOSPHOLIPID SURFACE BILAYERS AT THE AIR-WATER INTERFACE III. Relation Between Surface Bilayer Formation and Lipid Bilayer Assembly in Cell Membranes NORMAN L. GERSHFELD Laboratory ofbiochemical Pharmacology,
Hybrid polymer/lipid vesicles: fine control of the lipid and polymer distribution in the binary membrane
 SUPPORTING INFORMATIONS FOR Hybrid polymer/lipid vesicles: fine control of the lipid and polymer distribution in the binary membrane Maud Chemin, a,b Pierre-Marie Brun, a,b Sébastien Lecommandoux, a,b
SUPPORTING INFORMATIONS FOR Hybrid polymer/lipid vesicles: fine control of the lipid and polymer distribution in the binary membrane Maud Chemin, a,b Pierre-Marie Brun, a,b Sébastien Lecommandoux, a,b
Cell membrane & Transport. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Development, Characterization and In-Vitro Evaluation of Azithromycin Niosomes
 Human Journals Research Article October 2018 Vol.:13, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Senthil S.P et al. Development, Characterization and In-Vitro Evaluation of Azithromycin Niosomes Keywords: Azithromycin,
Human Journals Research Article October 2018 Vol.:13, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Senthil S.P et al. Development, Characterization and In-Vitro Evaluation of Azithromycin Niosomes Keywords: Azithromycin,
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Lecture 15 The Lipid Bilayer: A Dynamic Self- Assembled Structure of Multiple Lipid Classes
 Lecture 15 The Lipid Bilayer: A Dynamic Self- Assembled Structure of Multiple Lipid Classes LIPIDS-Biological molecules with low solubility in water and high solubility in non-polar solvents -Lipids form
Lecture 15 The Lipid Bilayer: A Dynamic Self- Assembled Structure of Multiple Lipid Classes LIPIDS-Biological molecules with low solubility in water and high solubility in non-polar solvents -Lipids form
Physical Pharmacy. Interfacial phenomena. Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department
 Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information The Effects of Spacer Length and Composition on Aptamer-Mediated Cell-Specific Targeting with Nanoscale PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin Hang Xing +, [a] Ji Li +, [a] Weidong Xu,
Supporting Information The Effects of Spacer Length and Composition on Aptamer-Mediated Cell-Specific Targeting with Nanoscale PEGylated Liposomal Doxorubicin Hang Xing +, [a] Ji Li +, [a] Weidong Xu,
AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes
 University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
University of Wollongong Research Online Faculty of Science - Papers (Archive) Faculty of Science, Medicine and Health 2006 AFM In Liquid: A High Sensitivity Study On Biological Membranes Michael J. Higgins
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
 Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport Particles like atoms, molecules and ions are always moving Movement increases with temperature (affects phases of matter - solid, liquid, gas) Solids - atoms, molecules
Dental Materials Journal 10(2): ,
 Dental Materials Journal 10(2): 121-127, 1991 121 Changes in 1H-NMR Chemical Shifts of Bis-GMA and Its Related Methacrylates Induced by Their Interaction with Phosphatidylcholine/Cholesterol Liposomes
Dental Materials Journal 10(2): 121-127, 1991 121 Changes in 1H-NMR Chemical Shifts of Bis-GMA and Its Related Methacrylates Induced by Their Interaction with Phosphatidylcholine/Cholesterol Liposomes
Focused ultrasound a novel tool for liposome formulation
 Focused ultrasound a novel tool for liposome formulation Introduction Liposomes are excellent carriers of active pharmaceutical ingredients and cosmetic agents. Their vesicular structure, housed by lipid
Focused ultrasound a novel tool for liposome formulation Introduction Liposomes are excellent carriers of active pharmaceutical ingredients and cosmetic agents. Their vesicular structure, housed by lipid
Surfactants. The Basic Theory. Surfactants (or surface active agents ): are organic compounds with at least one lyophilic. Paints and Adhesives
 Surfactants Surfactants (or surface active agents ): are organic compounds with at least one lyophilic ( solvent-loving ) group and one lyophobic ( solvent-fearing ) group in the molecule. In the simplest
Surfactants Surfactants (or surface active agents ): are organic compounds with at least one lyophilic ( solvent-loving ) group and one lyophobic ( solvent-fearing ) group in the molecule. In the simplest
Endocytosis of Nanoparticles
 Endocytosis of Nanoparticles Reinhard Lipowsky Theory & Bio-Systems, MPI-CI, Potsdam Motivation: Cellular Uptake of NPs Dissecting Endocytosis into Adhesion + Engulfment + Fission Quantitative Relationships
Endocytosis of Nanoparticles Reinhard Lipowsky Theory & Bio-Systems, MPI-CI, Potsdam Motivation: Cellular Uptake of NPs Dissecting Endocytosis into Adhesion + Engulfment + Fission Quantitative Relationships
9 2 ll 93'72 i III '!lli lll 11 10M
 AD-A266 505 ENCAPSULATION OF HEMOGLOBIN IN NON-PHOSPHtOLIPID VESI CLES Vandegriff, K.D.1' 2, Wallach, D.F.H. 3, and Winslow, R.M.1 'Blood Cells, Inc., La Jolla, CA and ' Microvesicular Systems, Nashua,
AD-A266 505 ENCAPSULATION OF HEMOGLOBIN IN NON-PHOSPHtOLIPID VESI CLES Vandegriff, K.D.1' 2, Wallach, D.F.H. 3, and Winslow, R.M.1 'Blood Cells, Inc., La Jolla, CA and ' Microvesicular Systems, Nashua,
Effects of DNA Adsorption on the Phase Cycling of a Supported Mixed Phospholipid Bilayer
 Effects of DNA Adsorption on the Phase Cycling of a Supported Mixed Phospholipid Bilayer NANO LETTERS 2002 Vol. 2, No. 4 305-309 Zoya Leonenko and David Cramb* Department of Chemistry, UniVersity of Calgary,
Effects of DNA Adsorption on the Phase Cycling of a Supported Mixed Phospholipid Bilayer NANO LETTERS 2002 Vol. 2, No. 4 305-309 Zoya Leonenko and David Cramb* Department of Chemistry, UniVersity of Calgary,
Biology 4410 First Examination Version B
 Biology 4410 Spring 2006 Name First Examination Version B This examination consists of two parts, a multiple-choice section and an essay section. Be sure to put your name on both the mark-sense sheet and
Biology 4410 Spring 2006 Name First Examination Version B This examination consists of two parts, a multiple-choice section and an essay section. Be sure to put your name on both the mark-sense sheet and
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/12/e1601838/dc1 Supplementary Materials for General and programmable synthesis of hybrid liposome/metal nanoparticles Jin-Ho Lee, Yonghee Shin, Wooju Lee, Keumrai
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/2/12/e1601838/dc1 Supplementary Materials for General and programmable synthesis of hybrid liposome/metal nanoparticles Jin-Ho Lee, Yonghee Shin, Wooju Lee, Keumrai
TUTORIAL IN SMALL ANGLE X-RAY SCATTERING ANALYSIS
 TUTORIAL IN SMALL ANGLE X-RAY SCATTERING ANALYSIS at the Abdus Salam International Center of Theoretical Physics (ICTP) Heinz Amenitsch Sigrid Bernstorff Michael Rappolt Trieste, 15. May 2006 (14:30-17:15)
TUTORIAL IN SMALL ANGLE X-RAY SCATTERING ANALYSIS at the Abdus Salam International Center of Theoretical Physics (ICTP) Heinz Amenitsch Sigrid Bernstorff Michael Rappolt Trieste, 15. May 2006 (14:30-17:15)
Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography.
 Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography. Representative low-magnification scanning electron micrographs of a) Black silicon (bsi) and b) Diplacodes bipunctata dragonfly
Supplementary Figure S1 Black silicon and dragonfly wing nanotopography. Representative low-magnification scanning electron micrographs of a) Black silicon (bsi) and b) Diplacodes bipunctata dragonfly
Ethosomes: A Novel approach in the design of transdermal drug delivery system
 International Journal of MediPharm Research ISSN:2395-423X www.medipharmsai.com Vol.02, No.01, pp 17-22, 2015 Ethosomes: A Novel approach in the design of transdermal drug delivery system Syeda Shabana
International Journal of MediPharm Research ISSN:2395-423X www.medipharmsai.com Vol.02, No.01, pp 17-22, 2015 Ethosomes: A Novel approach in the design of transdermal drug delivery system Syeda Shabana
NANO LIPOSOMAL PRODUCTS NANO PRODUCTS
 NANO LIPOSOMAL PRODUCTS Liposomes are most often composed of phospholipids, especially phosphatidylcholine, but may also include other lipids, such as eggphosphatidylethanolamine, so long as they are compatible
NANO LIPOSOMAL PRODUCTS Liposomes are most often composed of phospholipids, especially phosphatidylcholine, but may also include other lipids, such as eggphosphatidylethanolamine, so long as they are compatible
