Establishment and ultrasound characteristics of atherosclerosis in rhesus monkey
|
|
|
- Solomon McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 RESEARCH Open Access Establishment and ultrasound characteristics of atherosclerosis in rhesus monkey Wen Zeng 1, Xiaorong Wen 2, Li Gong 1, Jiayu Sun 3, Jing Yang 4, Jichun Liao 3, Can Qian 1, Wei Chen 3, Bin Song 3, Fabao Gao 3* * Correspondence: gaofabao@yahoo.com 3 Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China Abstract Background: Atherosclerosis is one of the main risk factors cause acute cerebralcardio vascular diseases. It s of great significance to establish an atherosclerosis animal model that can mimic the characteristics and nature course of human patients. Therefore, a rhesus monkey model was induced by high-fat diet to monitor their lipid profile and intima-media thickness (IMT) of artery walls and study atherosclerosis progression. Methods: Fifty male rhesus monkeys were enrolled in this study. All of these monkeys were aged 7 to 14 years with BMI >30 kg/m 2. They were fed with high-fat diet containing 10% of fat for the first 48 weeks. Use ultrasound to measure the IMT at bilateral common carotid arteries and their bifurcations and aorta (AO) of the monkeys, and screen out the individuals with thickened IMT for the next phase. In the next 48 weeks, some of these monkeys (n = 4) were fed with standard diet containing 3% fat. Meanwhile the other monkeys (n = 5) were fed with high-fat diet for another 48 weeks. Their serum lipid level was monitored and arterial IMT was also determined periodically. Results: Serum lipid level of all 50 monkeys elevated after fed with high-fat diet for the first 48 weeks. IMT thickening at right common carotid bifurcation and aorta (AO) was thickened in 9 monkeys. Furthermore, 4 of these 9 monkeys were fed with standard diet and other 5 monkeys were fed with high-fat diet in the following 48 weeks. The serum lipid level of the 4 monkeys recovered and their IMT at RBIF and AO did not progress. However, the lipid level of other 5 monkeys remained high, and their IMT thickening of AO progressed, and plaques and calcification focuses were found at the anterior wall of aorta near the bifurcation of common iliac artery. Conclusions: After high-fat diet induction for 96 weeks, serum lipid levels of rhesus monkeys elevated significantly, which subsequently caused IMT thickening and plaques formation. When IMT thickening occurred, further vascular injury may be prevented by reducing diet fat content. Our study indicates that vascular injury of high-fat diet induced rhesus monkey is similar to that of human in position and progression. Introduction Cerebral-cardio vascular disease is the biggest threat to human health [1,2] and atherosclerosis is one of the main reasons that cause this critical disease. As atherosclerosis progressing, main arteries are vulnerable to form plaques. Defluxion of unstable plaques would lead to vascular thrombosis of downstream target organs, thereby causing acute cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events. Due to plaque disruption has great 2015 Zeng et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
2 Page 2 of 14 uncertainty, it is very important to establish an animal model that can adequately simulate the plaque formation like human patients, and can be used for development and research of diagnostic and therapeutic drugs. Most of the reported animal models of atherosclerosis are rodents [3]. But atherosclerotic plaque is a chronic and complex disease caused by multiple factors and there are significant differences between rodents and human in lipid metabolism, plaque components, plaque formation and position. Compared with other animal models, rhesus monkeys are more similar to human in physiology and the susceptibility of metabolic disease [4]. Because of high similarities with human in genes, histological structures, immunology, physiology and metabolism with human, rhesus monkey became the most widely used non-human primate animal in medical research [5]. Since 1950, there have been few of laboratories successfully inducing atherosclerosis in monkey. Multiple studies have indicated the influences of different contents of diet on the development of atherosclerosis in rhesus monkey, and analyzed the composition of lumens and plaques by using autopsy [6-9]. However, besides the use of highcholesterol diet would largely affect the animal s health, the lipid level of animals induced by high-cholesterol diet is not stable. Additionally, high-sugar diet is not like the normal food of patients, and using autopsy to identify the presence of atherosclerosis and plaques affects the preservation and application of models. All of these are problems existing in previous researches. Ultrasound, which can clearly picture the main arteries, particularly conditions of carotid artery walls, has been used as a non-invasive method in recent years to detect atherosclerosis at an early stage [10]. It can not only increase the predictability of cardiovascular diseases [11], but also act as an alternative maker to determine the extent of atherosclerotic progression [12]. Atherosclerotic imaging, the IMT measurement as a benchmark, has become the basic reference of the research and development of cardiovascular drugs [13]. In this study, we used non-cholesterol high-fat diet, selected non-invasive B-mode ultrasound to monitor and identify the model periodically, and compared the progression of IMT and change of serum lipid level. Hoping that our rhesus monkey model with plaques can be applied for atherosclerosis and plaque related researches. Methods Agents and apparatus Ketamine hydrochloride (10 mg/ml, Bioniche Teoranta); Electronic weighing scale (Yousheng XK3123); Electronic balance (Yousheng BS2100+); Color Doppler ultrasound apparatus (SonoSite M-turdo); Automated biochemistry analyzer Synchron CX4 PRO (Beckman Coulter, Brea, Calif) and all blood chemistry detection reagents were bought from Beckman Coulter Inc. Animals All monkeys enrolled in this study were provided by Ya an PriMed Bio-tech Co., Ltd. After examination, under the condition that other diseases were excluded, 50 middle-aged male rhesus monkeys (aged 7-14 years, and BMI > 30 kg/m 2 ) were enrolled in this study. At baseline, all monkeys had total cholesterol (TC) concentrations < 4 mmol/l, triglyceride (TG) concentrations < 1 mmol/l, and low density lipoprotein (LDL-c) concentrations < 2.5 mmol/l.
3 Page 3 of 14 Diets There are 2 kinds of diets involved in this study: high-fat diet (containing 18% protein, 58% carbohydrate, 14% water and 10% fat) and standard diet (containing 18% protein, 69% carbohydrate, 10% water and 3% fat), fat percentage of the high-fat diet used in this study is shown in Figure 1 (compared with other species in atherosclerosis modeling). Approximately 250 g feed was supplied to each animal (available ad libitum) in the mornings, and apples or vegetable with equal nutrients were provided in the afternoons. Tap water was used as drinking water, which was taken freely by monkeys via the automatic bubbler. Quarantine Animal quarantine procedures included physical examinations, intradermal skin test for mycobacterium tuberculosis, fecal examination for parasites, bacterial culture for salmonella, shigella, and serology for herpes B virus. The results of all 50 monkeys were negative. Maintenance Monkeys were raised in stainless steel pair-housing monkey cages (2 m long, 1.7 m wide, and 2 m high with swing and woods), in a feeding room with the temperature of 19 C-26 C (66 F-79 F) and humidity of 50% ± 20%. The rate of ventilation was 10 times/h and the lighting cycle was 12 (day)/12 (night) hours. The monkeys were maintained in conformity with the requirements of the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animal of the United States, and all experimental protocols were reviewed and approved by the Animal Welfare and Use Committee of Sichuan PriMed Bio-tech Co., Ltd. All the monkeys had been domesticated for at least 2 years. Before this study, there was 4-week long acclimation period in order that all monkeys could cooperate with the experimenters during the trial. Trial Arrangements As Figure 2 shows, this study lasted for approximately 2 years and was divided into 3 phases. Phase 1 is a 4-week long acclimation period. At the end of the acclimation period, the lipid parameters of all animals were measured. Meanwhile, the intima-media thickness of abdominal aorta and bilateral common carotid arteries and their Figure 1 Profile of fat content in high-fat diets for establishing atherosclerosis animal models with different species.
4 Page 4 of 14 Figure 2 Trial flow chart. bifurcations were measured. Phase 2 is a high-fat diet induction period which lasted for 48 weeks. In phase 2, all 50 animals were fed with high-fat diet, and at the end of this period the lipid profile and IMT were measured in order to acquaint the influence of this composition of high-fat diet on serum lipid and screen out the individuals with thickened IMT. Only individuals with thickened IMT were enrolled in phase 3. Phase 3 lasted for another 48 weeks, in this period, monkeys with thickened IMT were divided into 2 groups randomly. Monkeys in one group were fed with high-fat diet while the other group were fed with standard diet instead. Similarly, lipid profile and artery IMT were measured at the end of phase 3. Lipid levels measurement Blood samples were collected at cephalic veins after fasting for 16 hours after fasting. TC, TG and LDL-c levels were measured by enzymatic methods using an automated biochemistry analyzer. Ultrasound examination After fasting for 8 hours, monkeys were sedated by an intramuscular injection of 10% ketamine hydrochloride and ultrasound examinations were performed with the use of an 8-MHz ultrasonic probe by a single trained sonographer who was kept unaware of the trial information. Monkeys were examined in the supine position with their heads slightly extended. With this technique, 2 parallel echogenic lines separated by an anechoic space can be visualized at levels of the artery wall. It was previously proved that these lines were generated by the blood-intima and media adventitia interfaces [14]. We define the IMT value as the distance from the adventitia-media boundary of the near wall to the lumen-intima and media adventitia interfaces of the far wall following the typical double line pattern (Figure 3) [15]. IMT values of 3 different projections: anterior, lateral, and the bifurcation, were averaged to obtain the mean IMT. An atherosclerotic plaque was defined as a distinct area where the intima-media encroached into the vessel lumen and where its thickness was at least 50% greater than that of the adjacent sites. When an atherosclerotic plaque was present, it was included in the measurements of IMT [16]. Carotid artery When determining one side of carotid arteries, adjust the head of the monkey 45 to the opposite side. Longitudinally view the common carotid artery and bifurcation with
5 Page 5 of 14 Figure 3 A typical double line pattern ultrasound image of a normal abdominal aortic artery wall of a monkey. The distance between the centers of the two crosses represents the distance between the inner and the outer echogenic lines and corresponds to the ultrasound image of intima-media thickness. a superficial probe, freeze and amplify the image when it shows clearly the intima of anterior and posterior wall of artery so that IMT values could be determined. Abdominal aorta About 1.0 cm left to the medioventral line, longitudinally view the whole aorta (from diaphragm to the bifurcation of iliac artery). Observe from multi-section and multiangle if the monkey is obese or filled with gas in the abdominal cavity. Statistical analysis All data were expressed as mean±sd. Differences among groups were compared by analysis of variance. Difference before and after treatment were compared by paired t- test. All statistical analysis were performed using SPSS statistics 19.0 software and a P value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results Phase 1 To acquire the baseline, we assayed the serum lipid related parameters of all 50 monkeys. IMT of different positions were measured by ultrasound. The mean values of lipid parameters are as below: TC = 3.12 ± 0.64 mmol/l, TG = 0.57 ± 0.17 mmol/l, LDL-C = 1.31 ± 0.24 mmol/l (n = 50). The mean values of IMT determined at different artery positions are as below: IMT (RCCA) = 0.36 ± 0.08, IMT (RBIF) = 0.40 ± 0.05, IMT (LCCA) = 0.34 ± 0.06, IMT (LBIF) = 0.40 ± 0.01, IMT (AO) = 0.42 ± 0.09 (Figure 4 shows normal IMT value measured at different positions). Phase 2 After induced by high-fat diet for 48 weeks, levels of lipid related parameters of these 50 monkeys all elevated significantly: TC = 5.2 ± 0.79 mmol/l, TG = 1.1 ± 0.31 mmol/l, LDL-C = 2.5 ± 0.81 mmol/l (n = 50, p < 0.05). Among these monkeys, 9 monkeys showed thickened IMT at common carotid artery bifurcation and abdominal aorta: IMT-RBIF =0.58 ± 0.21, IMT-AO = 0.68 ± 0.29 (n = 9, p < 0.05). The IMT profile and serum lipid profile of these 9 monkeys are shown in table 1 and table 2. Other 41 monkeys were dropped out from the trial. Phase 3 At the beginning of phase 3, we divided those 9 monkeys into 2 groups: 4 monkeys in group1and5monkeysingroup2.group1wereinducedbystandarddietinthe
6 Page 6 of 14 Figure 4 Typical ultrasound images of normal carotid arteries and aortas of different rhesus monkeys. A, B and C show images of normal intima plus medial thickness measurement of RBIF, LBIF and AO, respectively. The values of IMT in picture A, B and C are 0.3 mm, 0.4 mm and 0.3 mm respectively.
7 Page 7 of 14 Table 1 IMT profile of 2 groups of rhesus monkeys at the end of each phase IMT (mm) high-fat diet for 1 year & standard diet for 1 year (n = 4) high-fat diet for 2 years (n = 5) phase 1 phase 2 phase 3 phase 1 phase 2 phase 3 RCCA 0.33 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.04 RBIF 0.38 ± ± 0.10* 0.58 ± 0.10* 0.41 ± ± 0.06* 0.60 ± 0.12# LCCA 0.33 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.04 LBIF 0.40 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.05 AO 0.34 ± ± 0.06* 0.55 ± 0.06* 0.48 ± ± 0.11* 1.12 ± 0.23# *p < 0.05, compared with phase 1 #p < 0.05, compared with phase 2 following 46 weeks, while group 2 were sequentially fed with high-fat diets. Similarly, lipid related parameters and IMT of those 9 monkeys were determined at the end of phase 3 (See Figure 5, table 1 and table 2). All serum lipid parameters of animals in group 1 decreased to normal range, while the parameters of animals in group 2 remained at a high level. Moreover, IMT values of animals in group 1 measured at all positions did not show further changes. Nonetheless, in animals of group 2, abdominal aorta IMT thickening and RBIF IMT thickening progressed (Figure 6, Figure 7) and plaques as well as calcification focuses were found at the anterior wall of aorta near the bifurcation of common iliac artery (Figure 8). Shown from the results of this trial, long-term high-fat diet causes elevation of serum lipid levels of rhesus monkeys, furthermore, impels IMT thickening and plaque formation. The most severe position affected by this damage is the aorta, especially position near the bifurcation of common iliac artery, then the carotid bifurcations (Table 3). After adjusting the ingredients of the diets, standard diet with relatively low fat content could ameliorate high blood lipid level, while intake of high-fat diet sequentially could not only keep the serum lipid at a high level but also impel IMT thickening progressing. Discussion To establish atherosclerosis animal models, researchers have studied the effects of different lipid content diets on different species. Diets were added with certain amount of cholesterol in most of the modeling studies (Figure 1). High cholesterol diets elevate animal serum lipid levels rapidly. Atherosclerosis model established by high-cholesterol diets cannot completely mimic the nature course of human atherosclerosis. Moreover, the use of high-cholesterol diet would largely affect the animal s health, and the lipid level of animals induced by high-cholesterol diet is not stable. The high-fat diet used in this experiment was free from cholesterol and contained only 10% fat. This ingredient is relatively mild in establishing atherosclerosis in rhesus monkeys, while a diet Table 2 Serum lipid profile at the end of each phase serum lipid parameters (mmol/l) high-fat diet for 1 year & standard diet high-fat diet for 2 years (n = 5) for 1 year (n = 4) phase 1 phase 2 phase 3 phase 1 phase 2 phase 3 TC 3.42 ± ± 0.87* 3.12 ± 0.64# 3.08 ± ± 0.60* 4.91 ± 0.14* TG 0.66 ± ± 0.35* 0.71 ± 0.15# 0.55 ± ± 0.28* 1.37 ± 0.25* LDL-C 1.41 ± ± 0.88* 1.58 ± 0.64# 1.28 ± ± 0.76* 2.17 ± 0.26* *p < 0.05, compared with phase 1 #p < 0.05, compared with phase 2
8 Page 8 of 14 Figure 5 Lipid and IMT profiles of the 9 monkeys with thickened IMT throughout the trial. Picture A and B show the lipid profile. Picture C and D show the IMT profile. * p < 0.05.
9 Page 9 of 14 Figure 6 Progress of IMT thickening at AO of one monkey with the No. 4353#. A, B and C represent results measured at the end of phase 1,2,3 respectively, and the values of IMT in picture A, B and C are 0.5 mm, 0.6 mm and 0.8 mm respectively. consisting of 26% lipids, 22% proteins, and 52% carbohydrates were considered as lowfat diet in human [12]. Formation of human atherosclerotic plaque is a chronic long-term process in contrast with establishing animal models such as rodents, swine, etc., which costs only a
10 Page 10 of 14 Figure 7 Progress of IMT thickening at RBIF of one monkey with the No. 4353#. Picture A, B and C represent results measured at the end of phase 1, 2, 3 respectively, and the values of IMT of picture A, B and C are 0.4 mm, 0.5 mm and 0.6 mm respectively. few months. We have noticed that the IMT progression rate of our rhesus monkeys was slower than other animal species in atherogenic modeling. While in human atherosclerosis study, in patients with type 2 diabetes, an average annual increase of IMT 0.02 mm/year has been reported [17,18]. However, Jagdip et al. reported the common
11 Page 11 of 14 Figure 8 Ultrasound images of calcification focuses found at different positions of monkey arteries. A: a calcification focus at AO, near the bifurcation of common iliac artery. B: a calcification focus at LBIF. C: a calcification focus at RBIF. carotid artery IMT progression in coronary artery disease human patients were mm/48 weeks [19]. The average annual progression rates of IMT at different locations of monkeys in this study is similar to human patients (table 4). It is a chronic modeling process that we induced rhesus monkeys with mild high-fat diet for 2 years. During the induction period, we can monitor vascular changes dynamically. And the rhesus monkey model we established is more similar to patients, which might be more suitable for biomedical research. Table 3 Record of plaques at different positions at the end of this trial position RCCA RBIF LCCA LBIF AO plaque 2 1 5
12 Page 12 of 14 Table 4 Average annual progression rates of IMT at different positions of monkey arteries location IMT progression rate (mm/year) RCCA RBIF LCCA 0.02 LBIF 0.03 AO 0.32 Early stage atherosclerosis is only characterized by the thickening of artery wall. Researchers compared the ultrasound and pathological methods, and found that ultrasound could accurately measure the arterial IMT, and the results obtained via ultrasound correspond well with pathological determination. The changes of IMT during atherosclerosis appeared earlier than the formation of plaques [11,20]. Among 50 rhesusmonkeysenrolledinthisstudy, 9 individuals showed IMT thickening, 5 formed plaques in different positions of arteries. The IMT of all animals formed plaques were thickened at certain degree, which accords with clinical features of human patients. Meanwhile, the sites of plaques mostly occurred at the bifurcation of bilateral common carotid arteries and the bifurcation of aorta close to common iliac artery, which highly resemble the clinical situation of patients (See Figure 8). There were many studies focused on identifying risk factors contributing to atherosclerosis and coronary heart diseases (CHD). The Framingham Study developed a risk score that includes major risk factors, such as age, blood pressure, cigarette smoking, total cholesterol and diabetes status [21]. A similar score was developed that demonstrates the ability of traditional risk factors to predict CHD in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study [22]. Other than TC and age, monkeys in this trial were free from other atherogenic risk factors. Monkeys in this study were middle-aged, which may be one of the reasons why the monkeys with preserved IMT were not so susceptible to high-fat diet. However, genetic polymorphism contributing to atherosclerosis and cardiovascular incidence is another type of emerging risk factor [23]. Similarly, family studies have demonstrated both mean and maximum measurements of CCA IMT are heritable [24]. The Northern Manhattan Family Study also indicated that the heritability for total carotid IMT, CCA and carotid bifurcation IMT were significant [25]. All 50 monkeys in this study showed elevated lipid level, but only 9 monkeys showed increased IMT after 48 weeks high-fat diet induction. This phenomenon indicates there may be heritability for CCA IMT, carotid bifurcation IMT and aorta IMT in rhesus monkeys. Conclusion In rhesus monkey, levels of serum lipid-related parameters such as TC, TG and LDL-c may significantly elevate after being induced by high-fat diet which contents 10% of fat for 48 weeks. Part of these monkeys with elevated lipid levels show significantly thickened IMT at right common carotid bifurcation and aorta, which can be determined by ultrasound accurately. Continue to feed standard diet which contents 3% of fat to part of these monkeys with thickened IMT for another 48 weeks may neither ameliorate IMT thickening nor deteriorate, while serum lipid profile was benefited. However, for the rest of them fed with high-fat diet for the following 48 weeks sequentially, the
13 Page 13 of 14 IMT thickening at abdominal aorta progressed, meanwhile, their serum lipid remained at a high level. Since IMT at different positions could be determined by ultrasound which is a non-invasive method, and IMT act as an alternative maker to determine the extent of atherosclerotic progression, we can not only validate our atherosclerosis rhesus monkey model easily, but also apply it on new drug evaluation. Ethics statement The protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Sichuan PriMed Bio-tech Co., Ltd. Competing interests Other than the grants listed in the acknowledgement section, the authors declare that they have no other competing interest. Authors contributions W Zeng, F Gao and L Gong were responsible for designing the experiment and overall investigation. F Gao, X Wen, J Sun, J Liao and W Chen were responsible for coordinate the ultrasound measurement. X Wen was responsible for Doppler ultrasound measurement. J Yang was responsible for anesthesia. X Wen, L Gong and C Qian were responsible for data collection and image analysis. All authors have given final approval of the version to be published. Each author has participated sufficiently in the work to take public responsibility for appropriate portions of the content. Authors information Zeng s group has been studying human disease monkey models for many years. For more information, please visit PriMed website: The Sichuan University group consists of sonographers, radiologists and an anesthetist from the Imaging Center of West China Hospital, Sichuan University. They all have been doing research in cardiovascular disease. See website: Acknowledgements This study was supported by China s Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period (2012BAI23B08) and the Natural Science Foundation of China ( ). Declarations Publication charges for this article have been funded by China s Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-year Plan Period (2012BAI23B08). This article has been published as part of BioMedical Engineering OnLine Volume 14 Supplement 1, 2015: Cardiovascular Disease and Vulnerable Plaque Biomechanics. The full contents of the supplement are available online at Authors details 1 Sichuan PriMed Bio-tech Co., Ltd. Chengdu, China. 2 Department of Ultrasonography, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China. 3 Department of Radiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China. 4 Department of Anesthesiology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China. Published: 9 January 2015 References 1. Laslett LJ, Alagona P, Clark BA, et al: The Worldwide Environment of Cardiovascular Disease: Prevalence, Diagnosis, Therapy, and Policy IssuesA Report From the American College of Cardiology. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2012, 60(25_S):S1-S Mirzaei M, Truswell AS, Arnett K, Page A, Taylor R, Leeder SR: Cerebrovascular disease in 48 countries: secular trends in mortality Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 2012, 83(2): Moghadasian MH: Experimental atherosclerosis: a historical overview. Life sciences 2002, 70(8): Gibbs RA, Rogers J, Katze MG, et al: Evolutionary and biomedical insights from the rhesus macaque genome. Science 2007, 316(5822): Bremer AA, Stanhope KL, Graham JL, et al: Fructose-fed rhesus monkeys: a nonhuman primate model of insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes. Clinical and translational science 2011, 4(4): , Aug. 6. Vesselinovitch D, Getz G, Hughes R, Wissler R: Atherosclerosis in the rhesus monkey fed three food fats. Atherosclerosis 1974, 20(2): Pal Mohan A, Chakravarti R: Serum and aortic lipid profiles in spontaneous and cholesterol-induced atherosclerosis in rhesus monkeys. Atherosclerosis 1975, 22(1): Vesselinovitch D, Wissler RW, Schaffner TJ, Borensztajn J: The effect of various diets on atherogenesis in rhesus monkeys. Atherosclerosis 1980, 35(2): Armstrong ML, Megan MB, Cheng FH, Warner ED: Dietary disaccharides in experimental atherosclerosis in rhesus monkeys. Experimental and molecular pathology 1976, 24(3):
14 Page 14 of Salonen J, Salonen R: Ultrasound B-mode imaging in observational studies of atherosclerotic progression. Circulation 1993, 87(3 Suppl):II Pignoli P, Tremoli E, Poli A, Oreste P, Paoletti R: Intimal plus medial thickness of the arterial wall: a direct measurement with ultrasound imaging. Circulation 1986, 74(6): Baldassarre D, Amato M, Bondioli A, Sirtori CR, Tremoli E: Carotid artery intima-media thickness measured by ultrasonography in normal clinical practice correlates well with atherosclerosis risk factors. Stroke 2000, 31(10): O Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr: Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. New England Journal of Medicine 1999, 340(1): Baldassarre D, Hamsten A, Veglia F, et al: Measurements of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and of Interadventitia Common Carotid Diameter Improve Prediction of Cardiovascular Events: Results of the IMPROVE (Carotid Intima Media Thickness [IMT] and IMT-Progression as Predictors of Vascular Events in a High Risk European Population) Study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 60(16): , 10/16/ De Groot E, Hovingh GK, Wiegman A, et al: Measurement of arterial wall thickness as a surrogate marker for atherosclerosis. Circulation 2004, 109(23 suppl 1):III-33-III Duivenvoorden R, Nederveen AJ, De Groot E, Kastelein JJ: Atherosclerosis imaging as a benchmark in the development of novel cardiovasular drugs. Current opinion in lipidology 2007, 18(6): Lonn EM, Yusuf S, Dzavik V, et al: Effects of ramipril and vitamin E on atherosclerosis the study to evaluate carotid ultrasound changes in patients treated with ramipril and vitamin E (SECURE). Circulation 2001, 103(7): Hosomi N, Mizushige K, Ohyama H, et al: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition with enalapril slows progressive intima-media thickening of the common carotid artery in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Stroke 2001, 32(7): Sidhu JS, Kaposzta Z, Markus HS, Kaski JC: Effect of rosiglitazone on common carotid intima-media thickness progression in coronary artery disease patients without diabetes mellitus. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology 2004, 24(5): Wong M, Edelstein J, Wollman J, Bond MG: Ultrasonic-pathological comparison of the human arterial wall. Verification of intima-media thickness. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 1993, 13(4): Morrison AC, Bare LA, Chambless LE, et al: Prediction of coronary heart disease risk using a genetic risk score: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. American journal of epidemiology 2007, 166(1): Chambless LE, Heiss G, Folsom AR, et al: Association of coronary heart disease incidence with carotid arterial wall thickness and major risk factors: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study, American journal of epidemiology 1997, 146(6): Stephens J, Humphries S: The molecular genetics of cardiovascular disease: clinical implications. Journal of internal medicine 2003, 253(2): Fox CS, Polak JF, Chazaro I, et al: Genetic and environmental contributions to atherosclerosis phenotypes in men and women heritability of carotid intima-media thickness in the Framingham Heart Study. Stroke 2003, 34(2): Juo S-HH, Lin H-F, Rundek T, et al: Genetic and environmental contributions to carotid intima-media thickness and obesity phenotypes in the Northern Manhattan Family Study. Stroke 2004, 35(10): doi: / x-14-s1-s13 Cite this article as: Zeng et al.: Establishment and ultrasound characteristics of atherosclerosis in rhesus monkey. BioMedical Engineering OnLine (Suppl 1):S13. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Asian J. Exp. Sci., Vol. 27, No. 1, 2013; 67-72
 Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
Carotid Intima-media Thickness as a Surrogate Marker of Atherosclerosis and its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors and Angiographic Severity of Coronary Artery Disease. 1 2 Rajeev Gupta and Rajendra
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
Corporate Medical Policy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: carotid_intimal_medial_thickness 12/2006 10/2016 10/2018 10/2017 Description of Procedure or Service Ultrasonographic
ABSTRACT ORIGINAL ARTICLE INTRODUCTION. e-issn: p-issn: doi: /apjhs G. Vikas Naik 1 *, K. P.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE e-issn: 2349-0659 p-issn: 2350-0964 doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2018.5.1.21 Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of atherosclerosis in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects - A study from
ORIGINAL ARTICLE e-issn: 2349-0659 p-issn: 2350-0964 doi: 10.21276/apjhs.2018.5.1.21 Carotid intima-media thickness as a predictor of atherosclerosis in diabetic and non-diabetic subjects - A study from
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1
 ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
ASSOCIATION BETWEEN COMMON CAROTID INTIMA-MEDIA THICKNESS (CAROTID IMT) AND CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE Srinivasa Rao Malladi 1 HOWTOCITETHISARTICLE: Srinivasa Rao Malladi. Association between Common Carotid
Individuals of African and African Caribbean descent living
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.D. Mackinnon P. Jerrard-Dunne L. Porteous H.S. Markus Carotid Intima-Media Thickness is Greater but Carotid Plaque Prevalence is Lower in Black Compared with White Subjects BACKGROUND
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A.D. Mackinnon P. Jerrard-Dunne L. Porteous H.S. Markus Carotid Intima-Media Thickness is Greater but Carotid Plaque Prevalence is Lower in Black Compared with White Subjects BACKGROUND
Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients With Coronary Atherosclerosis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DOI 10.4070 / kcj.2009.39.8.317 Print ISSN 1738-5520 / On-line ISSN 1738-5555 Copyright c 2009 The Korean Society of Cardiology Prevalence and Significance of Carotid Plaques in Patients
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 10 Page October 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.82 Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Can
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i10.82 Carotid Intima Media Thickness and Can
Measurements of carotid intima media thickness in non-invasive high-frequency ultrasound images: the effect of dynamic range setting
 Gaarder and Seierstad Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2015, 13:5 CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND RESEARCH Open Access Measurements of carotid intima media thickness in non-invasive high-frequency ultrasound images:
Gaarder and Seierstad Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2015, 13:5 CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND RESEARCH Open Access Measurements of carotid intima media thickness in non-invasive high-frequency ultrasound images:
Evaluation of carotid intima-medial thickness as a marker of atherosclerosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
 43 Research Article Evaluation of carotid intima-medial thickness as a marker of atherosclerosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Authors : Dr. G.S Kejriwal MD 1, Dr. M. Jyothirmayee
43 Research Article Evaluation of carotid intima-medial thickness as a marker of atherosclerosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Authors : Dr. G.S Kejriwal MD 1, Dr. M. Jyothirmayee
Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness. The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study
 Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study Andrew D. Mackinnon, MRCP; Paula Jerrard-Dunne, MRCPI; Matthias
Rates and Determinants of Site-Specific Progression of Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness The Carotid Atherosclerosis Progression Study Andrew D. Mackinnon, MRCP; Paula Jerrard-Dunne, MRCPI; Matthias
Carotid intima media thickness as an usefull tool in predicting cerebrovaskular events
 Carotid intima media thickness as an usefull tool in predicting cerebrovaskular events Poster No.: C-0005 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Rahimic - Catic; Sarajevo/BA
Carotid intima media thickness as an usefull tool in predicting cerebrovaskular events Poster No.: C-0005 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit A. Rahimic - Catic; Sarajevo/BA
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration. EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006
 Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006 Vascular Imaging Technologies Carotid Ultrasound-IMT IVUS-PAV QCA-% stenosis 2 ICH E
Imaging Biomarkers: utilisation for the purposes of registration EMEA-EFPIA Workshop on Biomarkers 15 December 2006 Vascular Imaging Technologies Carotid Ultrasound-IMT IVUS-PAV QCA-% stenosis 2 ICH E
Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease
 Original Article Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease Yuba Raj Limbu, Rajib Rajbhandari, Ranjit
Original Article Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and carotid plaques in young Nepalese patients with angiographically documented coronary artery disease Yuba Raj Limbu, Rajib Rajbhandari, Ranjit
Intima-Media Thickness
 European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
European Society of Cardiology Stockholm, 30th August 2010 Intima-Media Thickness Integration of arterial assessment into clinical practice Prof Arno Schmidt-Trucksäss, MD Institute of Exercise and Health
Clinical Investigation and Reports. Predictive Value of Noninvasive Measures of Atherosclerosis for Incident Myocardial Infarction
 Clinical Investigation and Reports Predictive Value of Noninvasive Measures of Atherosclerosis for Incident Myocardial Infarction The Rotterdam Study Irene M. van der Meer, MD, PhD; Michiel L. Bots, MD,
Clinical Investigation and Reports Predictive Value of Noninvasive Measures of Atherosclerosis for Incident Myocardial Infarction The Rotterdam Study Irene M. van der Meer, MD, PhD; Michiel L. Bots, MD,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein
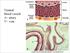 Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Normal blood vessels A= artery V= vein Artery (A) versus vein (V) ARTERIOSCLEROSIS Arteriosclerosis ="hardening of the arteries" arterial wall thickening and loss of elasticity. Three patterns are recognized,
Sonographic Assessment of Intima Media Thickness of Common Carotid Artery in Normotensive and Hypertensive Individuals
 Sonographic Assessment of Intima Media Thickness of Common Carotid Artery in Normotensive and Hypertensive Individuals Rana Muhammad Athar Azeem Shams, Ahmed Naeem, Muhammad Yousaf, Hasham Hafeez Hanjra,
Sonographic Assessment of Intima Media Thickness of Common Carotid Artery in Normotensive and Hypertensive Individuals Rana Muhammad Athar Azeem Shams, Ahmed Naeem, Muhammad Yousaf, Hasham Hafeez Hanjra,
How would you manage Ms. Gold
 How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
How would you manage Ms. Gold 32 yo Asian woman with dyslipidemia Current medications: Simvastatin 20mg QD Most recent lipid profile: TC = 246, TG = 100, LDL = 176, HDL = 50 What about Mr. Williams? 56
REAGENTS. RANDOX sdldl CHOLESTEROL (sdldl-c) SIZE MATTERS: THE TRUE WEIGHT OF RISK IN LIPID PROFILING
 REAGENTS RANDOX sdldl CHOLESTEROL (sdldl-c) SIZE MATTERS: THE TRUE WEIGHT OF RISK IN LIPID PROFILING Randox sdldl Cholesterol (sdldl-c) Size Matters: The True Wight of Risk in Lipid Profiling 1. BACKGROUND
REAGENTS RANDOX sdldl CHOLESTEROL (sdldl-c) SIZE MATTERS: THE TRUE WEIGHT OF RISK IN LIPID PROFILING Randox sdldl Cholesterol (sdldl-c) Size Matters: The True Wight of Risk in Lipid Profiling 1. BACKGROUND
ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233. PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority:
 ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233 PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: Subclinical atherosclerosis precedes type 2 diabetes in the ARIC study cohort
ARIC Manuscript Proposal #1233 PC Reviewed: 4_/_10/07 Status: _A Priority: 2_ SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: Subclinical atherosclerosis precedes type 2 diabetes in the ARIC study cohort
CardioHealth Station. powered by. Healthcare CardioHealth
 CardioHealth Station FDA cleared, in-office ultrasound imaging that helps you directly identify atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) allowing you to make a more informed decision about your patients
CardioHealth Station FDA cleared, in-office ultrasound imaging that helps you directly identify atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) allowing you to make a more informed decision about your patients
A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetis Mellitus
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/21 A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Bingi Srinivas
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/21 A Study to Show Postprandial Hypertriglyceridemia as a Risk Factor for Macrovascular Complications in Bingi Srinivas
Chapter 18. Diet and Health
 Chapter 18 Diet and Health Risk Factors and Chronic Diseases Interrelationships among Chronic Diseases Chronic Disease Heart Disease and Stroke Hypertension Cancer Diabetes The Formation of Plaques in
Chapter 18 Diet and Health Risk Factors and Chronic Diseases Interrelationships among Chronic Diseases Chronic Disease Heart Disease and Stroke Hypertension Cancer Diabetes The Formation of Plaques in
Objective Calcium score carotid IMT hs-crp
 P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
P3952 Role of coronary calcium score, carotid intima-media thickness and C-reactive protein in predicting extent of coronary artery disease in young patients. Bedside Poster P3952 Role of coronary calcium
Observe the effects of atherosclerosis on the coronary artery lumen
 Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Clumps and Bumps: A Look at Atherosclerosis Activity 4B Activity Description This activity features actual photomicrographs of coronary artery disease in young people aged 18 24 years. Students will observe
Report For Center Created Gender D.O.B Page 1 Sean Breen HeartSmart IMT plus 3/29/2012 Male 11/26/1973 B C D E
 Report For Center Created Gender D.O.B Page 1 Carotid Assessment A B C D E Good Satisfactory Concern Serious Highest Risk Intima-Media Thickness Additional Findings Plaque Character Percent Stenosis Comments:
Report For Center Created Gender D.O.B Page 1 Carotid Assessment A B C D E Good Satisfactory Concern Serious Highest Risk Intima-Media Thickness Additional Findings Plaque Character Percent Stenosis Comments:
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Carotid artery intima-media thickness is a marker for coronary artery disease
 Scientific Journal of Medical Science (2013) 2(8) 145-150 ISSN 2322-5025 doi: 10.14196/sjms.v2.i8.894 Contents lists available at Sjournals Journal homepage: www.sjournals.com Original article Carotid
Scientific Journal of Medical Science (2013) 2(8) 145-150 ISSN 2322-5025 doi: 10.14196/sjms.v2.i8.894 Contents lists available at Sjournals Journal homepage: www.sjournals.com Original article Carotid
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 06 Page June 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.69 Role of Aging, Hypertension and Dyslipidaemia
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i6.69 Role of Aging, Hypertension and Dyslipidaemia
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE MINOR RESEARCH PROJECT Submitted to UNIVERSITY GRANTS COMMISSION
 1 A STUDY ON THE EFFECT OF DIET & LIFE STYLE ON THE INCIDENCE OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE IN MODERATELY DRINKING EX MILITARY MEN IN PATHANAMTHITTA DISTRICT. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE MINOR RESEARCH PROJECT
1 A STUDY ON THE EFFECT OF DIET & LIFE STYLE ON THE INCIDENCE OF CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE IN MODERATELY DRINKING EX MILITARY MEN IN PATHANAMTHITTA DISTRICT. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY OF THE MINOR RESEARCH PROJECT
CVD Risk Assessment. Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic
 CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
CVD Risk Assessment Michal Vrablík Charles University, Prague Czech Republic What is Risk? A cumulative probability of an event, usually expressed as percentage e.g.: 5 CV events in 00 pts = 5% risk This
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both
 Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Low-density lipoprotein as the key factor in atherogenesis too high, too long, or both Lluís Masana Vascular Medicine and Metabolism Unit. Sant Joan University Hospital. IISPV. CIBERDEM Rovira i Virgili
Carotid-Wall Intima Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Events
 original article Carotid-Wall Intima Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Events Joseph F. Polak, M.D., M.P.H., Michael J. Pencina, Ph.D., Karol M. Pencina, Ph.D., Christopher J. O Donnell, M.D., M.P.H.,
original article Carotid-Wall Intima Media Thickness and Cardiovascular Events Joseph F. Polak, M.D., M.P.H., Michael J. Pencina, Ph.D., Karol M. Pencina, Ph.D., Christopher J. O Donnell, M.D., M.P.H.,
Citation for published version (APA): Terpstra, W. F. (2003). Beyond blood pressure monitoring Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Beyond blood pressure monitoring Terpstra, Willem Fopke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Beyond blood pressure monitoring Terpstra, Willem Fopke IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
cubital tunnel syndrome CTS 19 ~ ± cm 1. 1 CSA / CSA CSA CSA CSA 1. 3 SPSS 11.
 558 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 33 6 2011 6 1674-6309 2011 06-0558 - 04 1 2 3 3 1. 750004 2. 750004 3. 750004 39 CTS 40 20 40 CSA P < 0. 05 CSA MNCV r = - 0. 933 P < 0. 01 R445. 1 A cubital tunnel
558 Journal of Ningxia Medical University 33 6 2011 6 1674-6309 2011 06-0558 - 04 1 2 3 3 1. 750004 2. 750004 3. 750004 39 CTS 40 20 40 CSA P < 0. 05 CSA MNCV r = - 0. 933 P < 0. 01 R445. 1 A cubital tunnel
Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults?
 Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults? Rachael A. Wyman, MD; Jon G. Keevil, MD; Kjersten L. Busse, RN, MSN; Susan E. Aeschlimann,
Is the Ankle-Brachial Index a Useful Screening Test for Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic, Middle-Aged Adults? Rachael A. Wyman, MD; Jon G. Keevil, MD; Kjersten L. Busse, RN, MSN; Susan E. Aeschlimann,
Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
 Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease ROXANA BUZAŞ, CORINA ŞERBAN, IOANA SUCEAVA, DANIEL LIGHEZAN University
Association between Plasma Homocysteine Concentrations and Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease ROXANA BUZAŞ, CORINA ŞERBAN, IOANA SUCEAVA, DANIEL LIGHEZAN University
Familial hypercholesterolemia in childhood: diagnostics, therapeutical options and risk stratification Rodenburg, J.
 UvADARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia in childhood: diagnostics, therapeutical options and risk stratification Rodenburg, J. Link to publication Citation for published version
UvADARE (Digital Academic Repository) Familial hypercholesterolemia in childhood: diagnostics, therapeutical options and risk stratification Rodenburg, J. Link to publication Citation for published version
Detection of carotid plaque neovascularization with Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging
 Detection of carotid plaque neovascularization with Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging Yong Qiang Professor Ultrasonic Department, Beijing An-Zhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, China 1. Background Conventional
Detection of carotid plaque neovascularization with Superb Micro-Vascular Imaging Yong Qiang Professor Ultrasonic Department, Beijing An-Zhen Hospital, Capital Medical University, China 1. Background Conventional
ARIC Manuscript Proposal # 1036r. PC Reviewed: _07/26/05 Status: D Priority: SC Reviewed: Status: Priority:
 ARIC Manuscript Proposal # 1036r PC Reviewed: _07/26/05 Status: D Priority: SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: The Association between Isolated vs Combined Large and Small Artery Disease with
ARIC Manuscript Proposal # 1036r PC Reviewed: _07/26/05 Status: D Priority: SC Reviewed: Status: Priority: 1.a. Full Title: The Association between Isolated vs Combined Large and Small Artery Disease with
A study of brachial artery flow mediated dilatation and carotid intima media thickness in subjects having risk factors for coronary artery disease
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20171037 A study of brachial
International Journal of Advances in Medicine http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20171037 A study of brachial
Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY
 MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
MCC-006 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN CLINICAL CARDIOLOGY (PGDCC) 00269 Term-End Examination December, 2009 MCC-006 : CARDIOVASCULAR EPIDEMIOLOGY Time : 2 hours Maximum Marks : 60 Note : There will be multiple
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis
 Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
Intermediate Methods in Epidemiology 2008 Exercise No. 4 - Passive smoking and atherosclerosis The purpose of this exercise is to allow students to recapitulate issues discussed throughout the course which
Calcium is a chemical element that is essential for living organisms.
 1 of 8 9/28/2015 9:04 AM Home About me Health and Nutrition Diet General Health Heart Disease August 19, 2014 By Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 259 Comments Like Share 82 Calcium is a chemical element that is essential
1 of 8 9/28/2015 9:04 AM Home About me Health and Nutrition Diet General Health Heart Disease August 19, 2014 By Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 259 Comments Like Share 82 Calcium is a chemical element that is essential
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders
 Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Pathophysiology of Lipid Disorders Henry Ginsberg, M.D. Division of Preventive Medicine and Nutrition CHD in the United States CHD is the single largest killer of men and women 12 million have history
Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment
 207 Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment Yong-Hui Lee and Shoou-Jeng Yeh Abstract- Background and Purpose: Atherosclerosis
207 Correlation of Common Carotid Artery Intima Media Thickness, Intracranial Arterial Stenosis and Post-stroke Cognitive Impairment Yong-Hui Lee and Shoou-Jeng Yeh Abstract- Background and Purpose: Atherosclerosis
Practical challenges in CV risk management: When to start intervening in CVD?
 The National Research Center for Preventive Medicine Ministry of Healthcare, Russian Federation Practical challenges in CV risk management: When to start intervening in CVD? Prof. Drapkina O.M., Eliashevich
The National Research Center for Preventive Medicine Ministry of Healthcare, Russian Federation Practical challenges in CV risk management: When to start intervening in CVD? Prof. Drapkina O.M., Eliashevich
INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX
 INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX Diagnostic Partners provides a range of onsite, in-office cardiac and vascular diagnostic testing services. From Resting Echocardiograms to Abdominal Aorta scans, each study is performed
INTRODUCTORY TEXT BOX Diagnostic Partners provides a range of onsite, in-office cardiac and vascular diagnostic testing services. From Resting Echocardiograms to Abdominal Aorta scans, each study is performed
Original Research Article
 A STUDY TO ESTIMATE SUBCLINICAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS BY MEASURING THE CAROTID INTIMAL MEDIAL THICKNESS Natarajan Kandasamy 1, Rajan Ganesan 2, Thilakavathi Rajendiran
A STUDY TO ESTIMATE SUBCLINICAL ATHEROSCLEROSIS IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS BY MEASURING THE CAROTID INTIMAL MEDIAL THICKNESS Natarajan Kandasamy 1, Rajan Ganesan 2, Thilakavathi Rajendiran
The clinical significance of carotid intima-media thickness in cardiovascular diseases: a survey in Beijing
 (2008) 22, 259 265 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE The clinical significance of carotid intima-media thickness in cardiovascular
(2008) 22, 259 265 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE The clinical significance of carotid intima-media thickness in cardiovascular
ATHEROSCLEROSIS; ASSOCIATION OF ADIPONECTIN/LEPTIN RATIO TO INTIMA MEDIA THICKNESS IN LOCAL POPULATION
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/17.4044 ORIGINAL PROF-4044 ATHEROSCLEROSIS; ASSOCIATION OF ADIPONECTIN/LEPTIN RATIO TO INTIMA MEDIA THICKNESS IN LOCAL POPULATION 1. MBBS, M. Phil (Physiology)
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/17.4044 ORIGINAL PROF-4044 ATHEROSCLEROSIS; ASSOCIATION OF ADIPONECTIN/LEPTIN RATIO TO INTIMA MEDIA THICKNESS IN LOCAL POPULATION 1. MBBS, M. Phil (Physiology)
Glycemic and blood pressure control in older patients with hypertension and diabetes: association with carotid atherosclerosis
 Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2011) 8: 24 30 2011 IGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Articles Open Access Glycemic and blood pressure control in older patients with hypertension and diabetes:
Journal of Geriatric Cardiology (2011) 8: 24 30 2011 IGC All rights reserved; www.jgc301.com Research Articles Open Access Glycemic and blood pressure control in older patients with hypertension and diabetes:
PATIENTS AND METHODS:
 BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
BACKGROUND: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic systemic inflammatory disease characterized by erosive synovitis that involves peripheral joints and implicates an important influence in the quality
Intima Media Thickness Variability (IMTV) and its association with cerebrovascular events: a novel marker of carotid therosclerosis?
 Original Article Intima Media Thickness Variability (IMTV) and its association with cerebrovascular events: a novel marker of carotid therosclerosis? Luca Saba 1, Giorgio Mallarini 1, Roberto Sanfilippo
Original Article Intima Media Thickness Variability (IMTV) and its association with cerebrovascular events: a novel marker of carotid therosclerosis? Luca Saba 1, Giorgio Mallarini 1, Roberto Sanfilippo
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings?
 Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
Which CVS risk reduction strategy fits better to carotid US findings? Dougalis A, Soulaidopoulos S, Cholongitas E, Chalevas P, Vettas Ch, Doumtsis P, Vaitsi K, Diavasti M, Mandala E, Garyfallos A 4th Department
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 12 Page December 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.115 Evaluation of Carotid Intima
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i12.115 Evaluation of Carotid Intima
Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure
 801 Original Article Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure Akira YAMASHINA, Hirofumi TOMIYAMA, Tomio ARAI, Yutaka KOJI, Minoru YAMBE, Hiroaki MOTOBE, Zydem
801 Original Article Nomogram of the Relation of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity with Blood Pressure Akira YAMASHINA, Hirofumi TOMIYAMA, Tomio ARAI, Yutaka KOJI, Minoru YAMBE, Hiroaki MOTOBE, Zydem
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension.
 2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
2003 World Health Organization (WHO) / International Society of Hypertension (ISH) Statement on Management of Hypertension Writing Group: Background Hypertension worldwide causes 7.1 million premature
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism
 Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Aneurysms & a Brief Discussion on Embolism Aneurysms, overview = congenital or acquired dilations of blood vessels or the heart True aneurysms -involve all three layers of the artery (intima, media, and
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA
 Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA John M. Violanti, PhD* a ; LuendaE. Charles, PhD, MPH b ; JaK. Gu, MSPH b ; Cecil M. Burchfiel, PhD, MPH b ; Michael E. Andrew, PhD
Society for Behavioral Medicine 33 rd Annual Meeting New Orleans, LA John M. Violanti, PhD* a ; LuendaE. Charles, PhD, MPH b ; JaK. Gu, MSPH b ; Cecil M. Burchfiel, PhD, MPH b ; Michael E. Andrew, PhD
Data Alert. Vascular Biology Working Group. Blunting the atherosclerotic process in patients with coronary artery disease.
 1994--4 Vascular Biology Working Group www.vbwg.org c/o Medical Education Consultants, LLC 25 Sylvan Road South, Westport, CT 688 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Eminent Scholar American Heart Association
1994--4 Vascular Biology Working Group www.vbwg.org c/o Medical Education Consultants, LLC 25 Sylvan Road South, Westport, CT 688 Chairman: Carl J. Pepine, MD Eminent Scholar American Heart Association
Categorical Course: Update of Doppler US 8 : 00 8 : 20
 159 Categorical Course: Update of Doppler US 8 : 00 8 : 20 160 161 Table 1.Comparison of Recommended Values from Data in the Published Literature* S t u d y Lesion PSV E D V VICA/VCCA S e v e r i t y (
159 Categorical Course: Update of Doppler US 8 : 00 8 : 20 160 161 Table 1.Comparison of Recommended Values from Data in the Published Literature* S t u d y Lesion PSV E D V VICA/VCCA S e v e r i t y (
Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD
 Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD 1 Preclinical? No symptoms No physical findings No diagnostic ECG findings No chest X-ray X findings No diagnostic events 2
Preclinical Detection of CAD: Is it worth the effort? Michael H. Crawford, MD 1 Preclinical? No symptoms No physical findings No diagnostic ECG findings No chest X-ray X findings No diagnostic events 2
Influence of Atorvastatin/Probucol Combination on Blood Lipid and Serum C-Reactive Protein Levels in Patients with Cerebral Infarction
 Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research December 2015; 14 (12): 2313-2317 ISSN: 1596-5996 (print); 1596-9827 (electronic) Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City,
Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research December 2015; 14 (12): 2313-2317 ISSN: 1596-5996 (print); 1596-9827 (electronic) Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City,
Relationship between incident types and impact on patients in drug name errors: a correlational study
 Tsuji et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2015) 1:11 DOI 10.1186/s40780-015-0011-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between incident types and impact on patients in drug
Tsuji et al. Journal of Pharmaceutical Health Care and Sciences (2015) 1:11 DOI 10.1186/s40780-015-0011-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Relationship between incident types and impact on patients in drug
Cardiometabolics in Children or Lipidology for Kids. Stanley J Goldberg MD Diplomate: American Board of Clinical Lipidology Tucson, Az
 Cardiometabolics in Children or Lipidology for Kids Stanley J Goldberg MD Diplomate: American Board of Clinical Lipidology Tucson, Az No disclosures for this Presentation Death Risk Approximately 40% of
Cardiometabolics in Children or Lipidology for Kids Stanley J Goldberg MD Diplomate: American Board of Clinical Lipidology Tucson, Az No disclosures for this Presentation Death Risk Approximately 40% of
Coronary Artery Calcium Score
 Coronary Artery Calcium Score August 19, 2014 by Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 174 Comments essential for living organisms. Calcium is a chemical element that is Most of the calcium within the human body is found
Coronary Artery Calcium Score August 19, 2014 by Axel F. Sigurdsson MD 174 Comments essential for living organisms. Calcium is a chemical element that is Most of the calcium within the human body is found
Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system
 1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
1 Health and Disease of the Cardiovascular system DR CHRIS MOORE Instructions 2 USE THE ARROWS TO NAVIGATE, OR TAP OUTLINE AT THE TOP TO BRING DOWN A SLIDE MENU Click these where you see them to zoom or
The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011
 DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
DOI 10.1186/s40880-015-0042-6 REVIEW Open Access The updated incidences and mortalities of major cancers in China, 2011 Wanqing Chen *, Rongshou Zheng, Hongmei Zeng and Siwei Zhang Abstract Introduction:
Clinical Correlates of Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in African Americans: Ethnic and Geographic Disparities
 Clinical Correlates of Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in African Americans: Ethnic and Geographic Disparities By Meisam Moghbelli A Master s Paper submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina
Clinical Correlates of Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in African Americans: Ethnic and Geographic Disparities By Meisam Moghbelli A Master s Paper submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina
Omics and coronary atherosclerosis
 Omics and coronary atherosclerosis Dr.ssa Rosalinda Madonna Centro Scienze dell Invecchiamento e Medicina Traslazionale CESI-Met Università G. d Annunzio Chieti Geographic Distribution of Relative Mortality
Omics and coronary atherosclerosis Dr.ssa Rosalinda Madonna Centro Scienze dell Invecchiamento e Medicina Traslazionale CESI-Met Università G. d Annunzio Chieti Geographic Distribution of Relative Mortality
Arterial Wall Thickness in Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Ultrasound Measurement of Intima-Media Thickness in the Common Carotid Artery
 70 Arterial Wall Thickness in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Ultrasound Measurement of Intima-Media Thickness in the Common Carotid Artery Inger Wendelhag, Olov Wiklund, and John Wikstrand B-mode ultrasound
70 Arterial Wall Thickness in Familial Hypercholesterolemia Ultrasound Measurement of Intima-Media Thickness in the Common Carotid Artery Inger Wendelhag, Olov Wiklund, and John Wikstrand B-mode ultrasound
Risk Factors for Heart Disease
 Risk Factors for Heart Disease Risk Factors we cannot change (Age, Gender, Family History) Risk Factors we can change (modifiable) Smoking Blood pressure Cholesterol Diabetes Inactivity Overweight Stress
Risk Factors for Heart Disease Risk Factors we cannot change (Age, Gender, Family History) Risk Factors we can change (modifiable) Smoking Blood pressure Cholesterol Diabetes Inactivity Overweight Stress
Carotid Intimomedial Thickness in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors
 Original Article# Carotid Intimomedial Thickness in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors AK Agarwal*, PK Gupta**, S Singla***, U Garg+, A Prasad++, R Yadav+++ Abstract
Original Article# Carotid Intimomedial Thickness in Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Its Correlation with Coronary Risk Factors AK Agarwal*, PK Gupta**, S Singla***, U Garg+, A Prasad++, R Yadav+++ Abstract
Atherosclerosis Regression An Overview of Recent Findings & Issues
 Atherosclerosis Regression An Overview of Recent Findings & Issues 13th Angioplasty Summit 2008 Cheol Whan Lee, MD University of Ulsan, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea CardioVascular Research Foundation
Atherosclerosis Regression An Overview of Recent Findings & Issues 13th Angioplasty Summit 2008 Cheol Whan Lee, MD University of Ulsan, Asan Medical Center, Seoul, Korea CardioVascular Research Foundation
Prognostic Value of Brachial Artery Endothelial Function and Wall Thickness
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 6, 2005 2005 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/05/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.05.070
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 46, No. 6, 2005 2005 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/05/$30.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2005.05.070
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS
 UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS UNDERSTANDING ATHEROSCLEROSIS ARTERIES Arteries are blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood to all the organs of the body. Arteries are made up of three important layers:
Name of Policy: Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness as an Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis
 Name of Policy: Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness as an Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis Policy #: 245 Latest Review Date: July 2014 Category: Medicine Policy Grade:
Name of Policy: Ultrasonographic Measurement of Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness as an Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis Policy #: 245 Latest Review Date: July 2014 Category: Medicine Policy Grade:
Primary results of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening in the at-risk residents in middle China
 Li et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2018) 18:60 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-018-0793-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Primary results of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening in the at-risk residents
Li et al. BMC Cardiovascular Disorders (2018) 18:60 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-018-0793-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Primary results of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening in the at-risk residents
Predictors of progression and relationship with incident coronary heart disease. Diabetes Care 23: , 2000
 Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Japanese Type 2 Diabetic Subjects Predictors of progression and relationship with incident
Epidemiology/Health Services/Psychosocial Research O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Carotid Intima-Media Thickness in Japanese Type 2 Diabetic Subjects Predictors of progression and relationship with incident
Dehiscence of detached internal limiting membrane in eyes with myopic traction maculopathy with spontaneous resolution
 Hirota et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2014, 14:39 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dehiscence of detached internal limiting membrane in eyes with myopic traction maculopathy with spontaneous resolution Kazunari
Hirota et al. BMC Ophthalmology 2014, 14:39 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Dehiscence of detached internal limiting membrane in eyes with myopic traction maculopathy with spontaneous resolution Kazunari
Ezetimibe and SimvastatiN in Hypercholesterolemia EnhANces AtherosClerosis REgression (ENHANCE)
 Ezetimibe and SimvastatiN in Hypercholesterolemia EnhANces AtherosClerosis REgression (ENHANCE) Thomas Dayspring, MD, FACP Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Medicine and Dentistry
Ezetimibe and SimvastatiN in Hypercholesterolemia EnhANces AtherosClerosis REgression (ENHANCE) Thomas Dayspring, MD, FACP Clinical Assistant Professor of Medicine University of Medicine and Dentistry
Small dense low-density lipoprotein is a risk for coronary artery disease in an urban Japanese cohort: The Suita study
 Small dense low-density lipoprotein is a risk for coronary artery disease in an urban Japanese cohort: The Suita study Hidenori Arai 1, Yoshihiro Kokubo 2, Makoto Watanabe 2, Tatsuya Sawamura 3, Tomonori
Small dense low-density lipoprotein is a risk for coronary artery disease in an urban Japanese cohort: The Suita study Hidenori Arai 1, Yoshihiro Kokubo 2, Makoto Watanabe 2, Tatsuya Sawamura 3, Tomonori
Rehabilitation and Research Training Center on Secondary Conditions in Individuals with SCI. James S. Krause, PhD
 Disclosure The contents of this presentation were developed with support from educational grants from the Department of Education, NIDRR grant numbers H133B090005, H133B970011 and H133G010160. However,
Disclosure The contents of this presentation were developed with support from educational grants from the Department of Education, NIDRR grant numbers H133B090005, H133B970011 and H133G010160. However,
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors
 Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Autonomic nervous system, inflammation and preclinical carotid atherosclerosis in depressed subjects with coronary risk factors Carmine Pizzi 1 ; Lamberto Manzoli 2, Stefano Mancini 3 ; Gigliola Bedetti
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease. Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
 Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Vascular disease. Structural evaluation of vascular disease Goo-Yeong Cho, MD, PhD Seoul National University Bundang Hospital resistance vessels : arteries
Journal of American Science 2014;10(8)
 Role of Doppler Ultrasound and Peripheral Angiography (as a Diagnostic Modality of Atherosclerosis) in Combination with Conventional Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Coronary Artery Disease Prediction Hussein
Role of Doppler Ultrasound and Peripheral Angiography (as a Diagnostic Modality of Atherosclerosis) in Combination with Conventional Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Coronary Artery Disease Prediction Hussein
SUMMARY. Introduction. Study design. Summary
 SUMMARY Introduction The global prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing rapidly and nowadays affects almost 250 million people. Cardiovascular disease is the most prevalent complication of type 2 diabetes,
SUMMARY Introduction The global prevalence of type 2 diabetes is increasing rapidly and nowadays affects almost 250 million people. Cardiovascular disease is the most prevalent complication of type 2 diabetes,
Associations of blood pressure with carotid intima-media thickness in elderly Finns with diabetes mellitus or impaired glucose tolerance
 (2003) 17, 705 711 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Associations of blood pressure with carotid intima-media thickness in elderly
(2003) 17, 705 711 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Associations of blood pressure with carotid intima-media thickness in elderly
Correlations between measures of atherosclerosis change using carotid ultrasonography and coronary angiography
 Atherosclerosis 150 (2000) 371 379 www.elsevier.com/locate/atherosclerosis Correlations between measures of atherosclerosis change using carotid ultrasonography and coronary angiography Wendy J. Mack a,b,
Atherosclerosis 150 (2000) 371 379 www.elsevier.com/locate/atherosclerosis Correlations between measures of atherosclerosis change using carotid ultrasonography and coronary angiography Wendy J. Mack a,b,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005
 VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
VA/DoD Clinical Practice Guideline for the Diagnosis and Management of Hypertension - Pocket Guide Update 2004 Revision July 2005 1 Any adult in the health care system 2 Obtain blood pressure (BP) (Reliable,
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Heart Disease. Signs and Symptoms
 Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
Heart Disease The term "heart disease" refers to several types of heart conditions. The most common type is coronary artery disease, which can cause heart attack, angina, heart failure, and arrhythmias.
(Department of Radiology, Beylikdüzü State Hospital, İstanbul, Turkey) Corresponding Author: Dr. Mete Özdikici
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 5~ Issue 6 (2018) pp: 61-65 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Quantitative Measurements
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 5~ Issue 6 (2018) pp: 61-65 ISSN(Online) : 2394-076X ISSN (Print):2394-0751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Quantitative Measurements
Is Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Useful in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment? The Rotterdam Study
 Is Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Useful in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment? The Rotterdam Study Antonio Iglesias del Sol, MD; Karel G.M. Moons, MD, PhD; Monika Hollander, MD; Albert Hofman, MD,
Is Carotid Intima-Media Thickness Useful in Cardiovascular Disease Risk Assessment? The Rotterdam Study Antonio Iglesias del Sol, MD; Karel G.M. Moons, MD, PhD; Monika Hollander, MD; Albert Hofman, MD,
Understanding Cholesterol
 Understanding Cholesterol Dr Mike Laker Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute for personal
Understanding Cholesterol Dr Mike Laker Published by Family Doctor Publications Limited in association with the British Medical Association IMPORTANT This book is intended not as a substitute for personal
Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD INTRODUCTION
 2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
2 Hyperlipidemia Andrew Cohen, MD and Neil S. Skolnik, MD CONTENTS INTRODUCTION RISK CATEGORIES AND TARGET LDL-CHOLESTEROL TREATMENT OF LDL-CHOLESTEROL SPECIAL CONSIDERATIONS OLDER AND YOUNGER ADULTS ADDITIONAL
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
