Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 and Vitamin D Receptor Genetic Polymorphisms, and Their Interactions with Occupational Exposure in Lumbar Disc Degeneration
|
|
|
- Annis Anthony
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 J Occup Health 2010; 52: Journal of Occupational Health Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 and Vitamin D Receptor Genetic Polymorphisms, and Their Interactions with Occupational Exposure in Lumbar Disc Degeneration Han-Yan YUAN 1, 2, Ying TANG 1, You-Xin LIANG 1, Ling LEI 1, Guo-Bing XIAO 3, Sheng WANG 4 and Zhao-Lin XIA 1 1 Department of Occupational Health, School of Public Health, Fudan University, 2 Center for Disease Control and Prevention & Women and Children s Health Care of Gongshu District in Hangzhou, 3 Ningbo Municipal Institute of Public Health Inspection and 4 Department of Occupational Health, School of Public Health, Beijing University, China Abstract: Matrix Metalloproteinase-3 and Vitamin D Receptor Genetic Polymorphisms, and Their Interactions with Occupational Exposure in Lumbar Disc Degeneration: Han-Yan YUAN, et al. Department of Occupational Health, School of Public Health, Fudan University, China Objectives: To investigate the occupational and genetic risk factors inducing lumbar disc degeneration in a Chinese population, and to explore their synergistic interactions. Methods: A case-control study involving 178 low back pain patients with lumbar disc degeneration and 284 controls was carried out. Five types of work-related factors were investigated using questionnaires. Polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragments length polymorphism was used to detect the polymorphisms of MMP-3 (matrix metalloproteinase-3)(rs731236), VDR-Taq (vitamin D receptor-taq) and VDR-Apa (vitamin D receptor-apa)(rs ). Rothman s synergy index was used to measure the synergistic interactions between gene polymorphisms and occupational risk factors. Results: Family history of lumbar disc diseases, back injury history, whole-body vibration, bending/twisting, heavy physical workload, age, mutation alleles 5A of MMP-3 and A of VDR-Apa were significantly associated with lumbar disc degeneration (OR=12.70, 11.79, 8.96, 5.46, 1.05, 1.96 and 1.70, respectively, p<0.05). Synergistic interactions existed between the mutation allele 5A of MMP-3 and wholebody vibration exposure, the mutation allele 5A of MMP- 3 and bending/twisting, and the mutation allele A of Received Oct 20, 2008; Accepted Oct 28, 2009 Published online in J-STAGE Dec 16, 2009 Correspondence to: Z.-L. Xia, Department of Occupational Health, School of Public Health, Fudan University, 138 Yixueyuan Road, Xuhui District, Shanghai , China ( zlxia@shmu.edu.cn) VDR-Apa and bending/twisting (SI=13.27, 2.91, 2.35, respectively, p<0.05). Conclusions: The results of this study suggest that gene-occupation interaction might play a certain role in exaggerating lumbar disc degeneration. There is a possibility that subjects who carry mutation alleles 5A of MMP-3 and/or A of VDR- Apa are more vulnerable to lumbar disc degeneration when they are exposed to whole-body vibration and/or bending/twisting under ergonomic loads. (J Occup Health 2010; 52: 23 30) Key words: Gene polymorphism, Lumbar disc degeneration, Occupational risk factors It is estimated that 15% to 20% of adults have back pain during a single year, and 50% to 80% experience at least one episode of back pain during their lifetime 1). Jin 2) reported that the incidence of low-back pain (LBP) was as high as 50% in an investigation of one population of Chinese workers. Lumbar disc degeneration is considered to be a primary cause of LBP 3, 4). The pathogenesis of lumbar disc degeneration includes radial fissures, rim tears in the annulus, and loss of water content in the nucleus pulpous and annulus. These changes are suspected of underlying many back pain symptoms. The etiology of lumbar disc degeneration is complex, and recent research on the causes of disc degeneration have shed light upon a better understanding of the risk factors contributing to disc degeneration. Magora 5) suggested that occupational factors contributing to the acceleration of spinal degeneration included heavy physical loads, manual materials handling consisting of lifting, bending and twisting, prolonged sitting, sustained non-neutral work postures, and vehicle driving. Videman 6) confirmed that occupational exposures are viewed as the primary source of the mechanical factors
2 24 J Occup Health, Vol. 52, 2010 damaging the spine. This finding was supported by Frymoyer 7), who found that age, gender, occupation, cigarette smoking, and exposure to vehicular vibration are all associated with the occurrence of LBP. Thus the occupational risk factors mentioned above have remained the focus of recent epidemiologic studies on lumbar disc degeneration. In contrast, Ala-Kokko s recent studies among families and twins concluded that sciatica, disc herniation, and disc degeneration may be explained to a large degree by genetic factors. As such, the effects of environmental and constitutional risk factors could be relatively minor 8). Other relevant studies have supported the idea that degenerative disc disorders may be genetically determined 9 12). The first gene mutations associated with intervertebral disc degeneration in humans were reported in ). That study showed that low MRI signal intensity of thoracic and lumbar discs was associated with TaqI tt genotypes of the vitamin D receptor gene, and a similar MRI pattern was observed for bulging and disc height in both TaqI and FokI genotypes. Subsequent research revealed that a number of genes are associated with disc degeneration in human beings, including an aggrecan gene with shorter numbers of tandem repeat lengths; mutation genes coding for collagen IX (COL 9 A2 and COL 9 A3), and the matrix metalloproteinase-3 gene 14 17). Solovieva 18) presented evidence suggesting that the effect of obesity on lumbar disc degeneration is modified by COL9A3 gene polymorphisms in Finnish men. These findings indicated that genetic risk factors may interact with environmental factors in exaggerating the development of disc degeneration. The current study attempted to identify the occupational exposure and genetic risk factors inducing lumbar disc degeneration, and to evaluate their possible synergistic interactions on lumbar disc degeneration in a Chinese population. Methods Subjects Using a case-control design, all LBP patients diagnosed as having lumbar disc degeneration were recruited from the outpatient clinics of two local hospitals in one community of Ningbo City, Zhejiang Province between June 2005 and February The total number of diagnosed lumbar disc degeneration cases was 201, and 178 participated in the current research. During the same enrollment period, 294 controls with no medical history of LBP or lumbar disc degenerative disorders were randomly selected from residents in this community and from among those who visited the same hospitals for a regular medical examination and were diagnosed with no lumbar disc degeneration. Of these 284 controls completed the questionnaire investigation. All cases had disc degeneration confirmed by undergoing CT (Computed Tomography) examination of the lumbar spine. The degrees of degeneration were evaluated from the CT images by two independent radiologists and an orthopedic spine surgeon, who were not informed about this research. According to a fourpoint scale 19), degeneration was graded as 0 (no signal change), 1 (slight decrease in signal intensity in nucleus pulposus), 2 (distinct decrease in signal intensity in nucleus pulposus with normal disc height), and 3 (severe decrease in signal intensity in nucleus pulposus with disc space narrowing). This scale resulted in a classification of degenerative disorders as non-existent, mild, moderate, and severe, respectively. In the 284 controls, 80.82% (230) were healthy with no disease, 12.68% (36) were diagnosed as having normal cardiovascular diseases and 6.50% (18) were diagnosed as having normal digestive system diseases, which were confirmed to be unconnected with intervertebral disease. The study was approved by the City Ethics Committee. Informed consent was received from all subjects concerned. Occupational exposure evaluation Data regarding individual characteristics were collected by a questionnaire instrument that included items on anthropometric measures. The Body Mass Index (BMI= weight [kg] per height squared [m 2 ]) was calculated for each subject. Smoking habits, family history of lumbar disc diseases and medical history of back injury were recorded. A separate questionnaire, developed by the Stockholm Musculoskeletal Intervention Center for assessing manual materials handling, was modified and applied to the assessment of physical and postural loads at work 20). Questionnaires were implemented via face-to-face interviews conducted by trained interviewers. Subjects were asked to recall in detail their work history, including descriptions of past jobs, along with the intensity, frequency, and duration of engaging in risk factors that their line of work required. Five potential risk factors for degeneration agreed by US-NIOSH (USA-National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health) prolonged sitting, whole body vibration, bending/twisting, lifting, and heavy workload were identified 21). Subjects were asked to estimate the number of hours spent per day working under each of the five risk factors. Risk factors were classified into three levels by considering the exposure frequency and employment years: low, moderate and high (Table 1). Determination of genotypes Blood samples were collected intravenously from the 178 cases and 284 controls. Genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) was extracted from white blood cells according to the procedures of the genomic DNA extraction kit.
3 Han-Yan YUAN, et al.: MMP-3 and VDR Polymorphisms Interactions with Occupational Exposure in Lumbar Disc Degeneration 25 Table 1. Three-level scaled occupational risk factors Risk factors Level Description Prolonged sitting Low 4 h/day and <1 yr Bending/twisting Moderate 4 h/day and 1 10 yr OR >4 h/day and 5 yr High 4 h/day and >10 yr OR >4 h/day and >5 yr Whole body vibration Low 4 h/day and 1 yr Lifting Moderate 4 h/day and 1 5 yr OR >4 h/day and 2.5yr Heavy physical workload High 4 h/day and >5 yr OR >4 h/day and >2.5 yr Polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) methods were applied to detect the polymorphisms of MMP-3 (rs731236) 17, 22), VDR-Taq, and VDR-Apa (rs ) 13, 23). The primers of MMP-3 were designed as: 5 - GGT TCT CCA TTC CTT TGA TGG GGG GAA AGA -3 and 5 - CTT CCT GGA ATT CAC ATC ACT GCC ACC ACT -3 ; and the primers of VDR were designed as: 5 -CAG AGC ATG GAC AGG GAG CAA G-3 and 5 -GCA ACT CCT CAT GGC TGA GGT CTC A-3. The fragments of MMP-3 digested by the restriction enzyme Tth111Iwere: 6A6A (130 bp), 6A5A (130, 100, 30 bp), and 5A5A (100, 30 bp); 5A was the mutation allele. There were two mutated allele sites in the PCR products of VDR, which were recognized and digested by restriction enzymes TaqI and ApaI. The fragments in different sizes of VDR-Taq included TT (495, 245 bp), Tt (495, 245, 290, 205 bp) and tt (245, 290, 205 bp); t was the mutation allele. The genotypes of VDR-Apa were AA (740 bp), Aa (740, 520, 220 bp) and aa (520, 220 bp); A was the mutation allele. All blood samples were successfully genotyped. The frequency distribution of gene polymorphisms conformed to the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. Statistical analysis The odds ratios (OR) of occupational and genetic risk factors, as estimators of relative risk, and their 95% confidence intervals (CI) were computed using nonconditional logistic regression. The Chi-squared goodness of fit test was used to check for any deviations from the Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium. Interaction between a gene polymorphism (G) and an environmental factor (E) was evaluated using an additive model 24). The synergism for the additive scale was measured with a synergy index (SI), which can be calculated by the mathematical formula: SI= (OR GE 1) / (OR G E + OR G E 2). The OR GE is a joint effect of factors G and E, in which the OR G E is the main effect caused by factor E only; and OR G E is the main effect by factor G only. The SI will be 1.0 when there is no interaction between factors G and E, while a SI value over 1.0 indicates the presence of synergistic interaction, meaning that the joint effect of factors G and E is stronger than the additivity of the single effect. The higher the SI value, the stronger the joint effect will be. A two-tailed U test 25) was used to examine the statistical significance of SI, and values of p 0.05 were considered to be statistically significant. Results Characteristics of subjects The characteristics of cases and controls, including age, gender, BMI, smoking, back injury history and family history of disc degeneration, are shown in Table 2. Environmental risk factors In non-conditional logistic analyses, we found that family history of lumbar disc diseases, back injury history, whole-body vibration, bending/twisting, heavy physical workload, and age were associated with lumbar disc degeneration, with statistically significant differences between the case and control groups. The OR value of whole-body vibration reached 8.96 (95% CI= ), indicating that people exposed to whole-body vibration at high levels were more likely to develop lumbar disc degeneration than those without exposure. A family history of disc degenerative disease and back injury showed a high risk of lumbar disc degeneration, as demonstrated by the OR values of 9.19 (95% CI= ) and (95% CI= ), respectively. Exercise may be a protective factor for a functioning lumbar spine (OR=0.43, [95% CI= ]) (Table 3). Effect of MMP-3 and VDR gene polymorphisms on lumbar disc degeneration The frequencies of mutation genotypes MMP-3 and VDR-Apa in lumbar disc degeneration cases were significantly higher than those in controls (OR=1.96 [95% CI= ] and 1.70 [95% CI= ], respectively), while no significant difference was observed for the distribution of VDR-Taq variant genotypes (Table 4). Synergistic interactions between polymorphisms and occupational exposure The joint effects of mutation genotypes and
4 26 J Occup Health, Vol. 52, 2010 Table 2. Caracteristics of subjects Variables Cases (178) Controls (284) p Age (mean ± SD) 48.5 ± ± 15.8 <0.05 Gender Male (%) 84 (47.8) 96 (32.7) <0.05 Femal (%) 94 (52.2) 188 (67.4) BMI (mean ± SD) 22.8 ± ± 3.3 >0.05 Smoking Yes (%) 66 (37.3) 57 (20.1) <0.05 No (%) 112 (62.7) 127 (79.9) Back injury history Yes (%) 48 (26.9) 6 (2.0) <0.05 No (%) 130 (73.1) 278 (98.0) Family history of disc Yes (%) 14 (18.4) 7 (2.7) <0.05 degeneration No (%) 164 (71.6) 277 (97.3) 6A6A (%) 59 (33.15) 140 (49.30) <0.05 MMP3 6A5A (%) 107 (60.11) 126 (44.37) <0.05 5A5A (%) 12 (6.74) 18 (6.34) VDR-Taq TT (%) 156 (87.64) 256 (90.14) >0.05 Tt (%) 22 (12.36) 28 (9.86) VDR-Apa AA (%) 20 (11.24) 27 (9.51) <0.05 Aa (%) 100 (56.18) 129 (45.42) aa (%) 58 (32.58) 128 (45.07) Table 3. Non-conditional logistic analyses for risk factors of lumbar disc degeneration Factors OR (95% CI) p Age 1.05 ( ) <0.001 Family history 9.19 ( ) <0.001 Injury history ( ) <0.001 Exercise 0.43 ( ) <0.001 Moderate bending/twisting 3.54 ( ) <0.001 High bending/twisting 4.06 ( ) <0.001 Moderate whole-body vibration 2.71 ( ) 0.04 High whole-body vibration 8.96 ( ) <0.001 High heavy physical workload 5.46 ( ) <0.001 OR=odds ratio, 95%CI=95% confidence intervals. Table 4. The association between polymorphisms and lumbar disc degeneration Genotypes Controls Cases OR (95%CI) n % n % MMP-3 6A6A ( ) 6A5A/5A5A VDR-Taq TT ( ) Tt VDR-Apa aa ( ) AA /Aa Adjusted for gender, age, BMI, smoking, family history of disc degeneration and back injury history.
5 Han-Yan YUAN, et al.: MMP-3 and VDR Polymorphisms Interactions with Occupational Exposure in Lumbar Disc Degeneration 27 Table 5. The interaction between gene polymorphisms and occupational exposure (OR, 95% CI)* Occupational risk MMP-3 genotypes VDR-Apa genotypes VDR-Taq genotypes factors 6A6A 6A5A/5A5A aa Aa/AA TT Tt lifting Low level ( ) ( ) ( ) Moderate/High level ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) SI=1.28, AP=0.30 SI=2.01, AP=0.41 SI=0.70 u=1.2706, p>0.05 u=1.6390, p>0.05 u= , p>0.05 Bending/twisting Low level ( ) ( ) ( ) Moderate/High level ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) SI=2.91, AP=0.59 SI=2.35, AP=0.50 SI=1.78, AP=0.38 u=2.3313, p<0.05 u=2.0022, p<0.05 u=0.6065, p>0.05 Heavy physical workload Low level ( ) ( ) ( ) Moderate/High level ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) SI=1.35, AP # =0.27 SI=1.58, AP=0.32 SI=2.32, AP=0.51 u=0.6746, p>0.05 u=1.3033, p>0.05 u=0.8317, p>0.05 Whole-body vibration Low level ( ) ( ) ( ) Moderate/High level ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) SI=13.27, AP=0.72 SI=1.67, AP=0.30 SI=1.57, AP=0.27 u=1.9735, p<0.05 u=0.9988, p>0.05 u=0.4932, p>0.05 *: Adjusted for gender, age, BMI, smoking, family history of disc degeneration and back injury history. # : Attributable Proportion (AP) is the proportion that the synergistic effect could explain. occupational exposure on lumbar disc degeneration are presented in Table 5. Two mutation alleles (5A of MMP- 3 and A of VDR-Apa) and bending/twisting acted synergistically to increase the risk of lumbar disc degeneration (SI=2.91 and 2.35, respectively, p<0.05). Additionally, the synergistic interaction between mutation allele 5A of MMP-3 and whole-body vibration made the risk of lumbar disc degeneration much higher than each factor acting alone (SI=13.27, p<0.05). The synergistic interactions between mutation genotypes were also analyzed, but there were not statistically significant (not shown in Table 5). Discussion The OR value associated with age was 1.05 (p<0.05) by non-conditional logistic analyses, suggesting an increased tendency to develop disc degeneration with age. A previous study showed an increased prevalence of disc degeneration from 16% at age 20 to about 98% at age 70, based on macroscopic disc degeneration grades of 600 autopsy specimens 26). Some researchers have pointed out that lumbar disc degeneration may start from the age of 20, and the flexibility of the lumbar disc reduces as age increases 27, 28). Early degenerative changes in the mature disc are characterized by loss of water content in the nucleus pulpous and annular tears, which are commonly associated with disc space narrowing. The degeneration develops with increasing age, and the stability of the motion segment may be compromised eventually.
6 28 J Occup Health, Vol. 52, 2010 The OR of back injury history in the present research was 11.79, showing a strong association with disc degeneration. This finding may in part be interpreted by the theory of accident-related trauma, which posits that structural lesions of the disc will lead to degenerative changes. Subjects with family history of lumbar disc diseases demonstrated an increased risk of suffering from lumbar disc degeneration. This indicates that familial susceptibility is a contributing factor to degeneration, and that lumbar disc degeneration may be genetically determined. The three work-related risk factors of whole-body vibration, bending/twisting, and heavy physical workload were associated with lumbar disc degeneration. Individuals exposed to high levels of whole-body vibration were approximately eight times more likely to suffer from lumbar disc degeneration, compared to those who were unexposed. Prolonged sitting and lifting, however, were not significantly associated with disc degeneration. This result is similar to Lawrence s findings, in which lumbar disc degeneration was more common in male workers with physically demanding tasks than those who were more sedentary 29). Furthermore, Farfan 30) suggested that bending/twisting was the main cause of disc damage. Thus, the effects of occupational factors seem to depend on the combination of their frequency, intensity, and duration. As the occupational factor becomes stronger, it is likely to damage the structure of the lumbar disc by narrowing the disc space and breaking annular fibrosis, and by gradually destroying the function of the musculoskeletal system. Earlier experiments have indicated that vibration may affect the metabolism of the disc cell matrix and nutrition supply, exacerbating the lumbar disc pressure, energy consumption, and water loss from nucleus pulposus and annular tears 31). For genetic risk factors, the results of this study showed a significantly higher frequency of VDR and MMP-3 mutation genotypes in lumbar disc degeneration patients relative to controls. Mutation genotype tt of VDR-Taq was the first genetic risk factor associated with intervertebral disc degeneration in humans 13). However, tt genotype was found in this study, and there was no significant difference for the distribution of VDR-Taq variant genotypes between cases and controls. The most likely explanation for this finding may lie in the fact that the tt genotype seldom exists in Chinese populations. In one study involving 804 subjects in China, for example, only one single subject carried the tt genotype 32). In contrast, AA and Aa genotypes of VDR-Apa showed a significant effect on disc degeneration (OR=1.70), indicating that the VDR-Apa gene polymorphism is one of the genetic risk factors involved in lumbar disc degeneration. A possible mechanism for the action of this polymorphism may depend on the role of the vitamin D receptor within chondrocytes. The vitamin D receptor binds to the active form of vitamin D and helps to control the calcium balance, and may additionally act in the differentiation, proliferation, and maturation of chondrocytes. It has been confirmed that chondrocytes play a role in influencing the proteoglycan synthesis in vitro and moreover, that there is a rich presence of chondrocytes and proteoglycans in the lumbar disc 33). As a result, vitamin D receptor polymorphism may be involved in lumbar disc degeneration indirectly, through its function within the chondrocyte. The exact mechanism of action, however, requires further investigation. It is evident that matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) regulate the equilibrium of extracellular matrix degradation. Stromelysin (MMP-3) can degrade collagens and also break down other structural components such as proteoglycan and fibronectin 33). The expression of MMP-3 is primarily regulated at the level of its transcription. There is a common variant in the promoter sequence of the MMP-3 gene, in which one allele has six adenosines (6A) while the other has only five (5A). Compared with other genotypes, individuals homozygous for the 6A allele will have lower MMP3 levels in their tissues because of reduced gene transcription, and the 5A5A and 5A6A genotypes of MMP-3 were associated with more degenerative findings in the elderly than the 6A6A genotype 17). A similar phenomenon was observed in the present study. The frequencies of 5A5A and 5A6A genotypes of MMP-3 in lumbar disc degeneration cases were significantly higher than those in the controls. The fact that MMP-3 has the ability to degrade various connective matrix components, and activate other MMPs, shows that the mutation of MMP-3 may disturb the extracellular matrix balance in the lumbar disc and promote its degeneration. Soloviea 18) found that people carrying the trp3 allele of COL9A3 were at greater risk of disc degeneration if they were persistently obese. In our study, obesity did not appear to be a risk factor, because the distribution of BMI was the same in the case and control groups. However, we observed a synergistic interaction between the mutation allele 5A of MMP-3 and whole-body vibration exposure, the mutation allele 5A of MMP-3 and bending/twisting, and the mutation allele A of VDR-Apa and whole-body vibration exposure. Simultaneous presence of mutation alleles 5A of MMP-3 and/or A of VDR-Apa and whole-body vibration and/or bending/ twisting exposure increased the risk of lumbar disc degeneration about three to five times. This finding assumes that mechanical stress coupled with metabolic imbalance mediated by gene polymorphisms accelerates the disc structural damage leading to disc degeneration. The exact mechanism for this action, however, needs to be further researched.
7 Han-Yan YUAN, et al.: MMP-3 and VDR Polymorphisms Interactions with Occupational Exposure in Lumbar Disc Degeneration 29 In the current research, we focused on synergistic interactions between gene polymorphisms and occupational risk factors affecting lumbar disc degeneration, which may be a more reasonable interpretation of the causes of lumbar disc degeneration in Chinese people. The size of the study sample was not large enough to predict the synergic effect of geneenvironment interaction with conclusive accuracy. Follow-up studies with larger sample sizes need to be conducted. Also, we will continue to investigate other gene polymorphisms (COL 9 A2, COL 9 A3 and aggrecan gene) to look for the potential causes of disc degeneration. In the multiple comparisons applied to the measure of synergistic interactions, there may have been some statistically bias which will need to be reduced in our future research. Conclusion The results of the present study provide some evidence of gene-environmental interaction on lumbar disc degeneration in Chinese people. Our findings suggest the possibility that subjects carrying mutation alleles 5A of MMP-3 and/or A of VDR-Apa are more vulnerable to lumbar disc degeneration when exposed to whole-body vibration and/or bending/twisting. Workers carrying mutation alleles 5A of MMP-3 and/or A of VDR-Apa should avoid work involving whole-body vibration exposure and/or bending/twisting ergonomic loads in order to reduce the risk of suffering from lumbar disc degeneration. Acknowledgment: This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC ), project 2006BAI06B08 from Ministry of Science and Technology, and grants 08GWD12, 08GWZX0402 from the Shanghai Bureau of Public Health. References 1) Rubin DI. Epidemiology and risk factors for spine pain. Neurol Clin 2007; 25: ) Jin K, Sorock GS, Courtney TK. Prevalence of low back pain in three occupational groups in Shanghai, People s Republic of China. J Safety Res 2004; 35: ) Luoma K, Riihimaki H, Luukkonen R, et al. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine 2000; 25: ) Borenstein DG. Epidemiology, etiology, diagnostic evaluation, and treatment of low back pain. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2001; 13: ) Magora A. Investigation of the relation between low back pain and occupation: IV. Physical requirements: Bending, rotation, reaching, and sudden maximal effort. Scand J Rehabil Med 1973; 5: ) Videman T, Battie MC. Spine update: The influence of occupation on lumbar degeneration. Spine 1999; 24: ) Frymoyer JW. Lumbar disk disease: Epidemiology. Instr Course Lect 1992; 41: ) Ala-Kokko L. Genetic risk factors for lumbar disc disease. Ann Med 2002; 34: ) Gunzburg R, Fraiser RD, Fraser GA. Lumbar intervertebral disc prolapse in teenage twins: A case report and review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surgery UK 1990; 180: ) Varlotta GP, Brown MD, Kelsey JL, et al. Familial predisposition for herniation of a lumbar disc in patients who are less than twenty-one years old. J Bone Joint Surg USA 1991; 73: ) Simmons Jr ED, Guntupalli M, Kowalski JM, et al. Familial predisposition for degenerative disc disease: A case-control study. Spine 1996; 21: ) Richardson JK, Chung T, Schultz JS, et al. A familial predisposition toward lumbar disc injury. Spine 1997; 22: ) Videman T, Leppavuori J, Kaprio J, et al. Intragenic polymorphisms of the vitamin D receptor gene associated with intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine 1998; 23: ) Kawaguchi Y, Osada R, Kanamori M, et al. Association between an aggrecan gene polymorphism and lumbar disc degeneration. Spine 1999; 24: ) Annune S, Paassilta P, Lohivina J, et al. An allele of COL9A2 associated with intervertebral disc disease. Science 1999; 285: ) Perala M, Raina SS, Karppinen J, et al. Identification of a novel common genetic risk factor for lumbar disk disease. JAMA 2001; 14: ) Takahashi M, Haro H, Wakabayashi Y, et al. The association of degeneration of the intervertebral disc with 5a/6a polymorphism in the promoter of the human matrixmetalloproteinase-3 gene. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2001; 83: ) Solovieva S, Lohiniva J, Leino-Arjas P, et al. COL9A3 gene polymorphism and obesity in intervertebral disc degeneration of the lumbar spine: Evidence of geneenvironment interaction. Spine 2002; 27: ) Kettler A, Rohlmann F, Neidlinger Wilke C, et al. Validity and interobserver agreement of a new radiographic grading system for intervertebral disc degeneration: Part II. Cervical spine. Eur Spine J 2006; 15: ) Wiktorin C, Hjelm EW, Winkel J, et al. Reproducibility of a questionnaire for assessment of physical load during work and leisure time. Stockholm MUSIC I Study Group. MUSculoskeletal Intervention Center. J Occup Environ Med 1996; 38: ) NIOSH. National occupational research agenda for musculoskeletal disorders, DHHS (NIOSH) Publication No Cincinnati: DHHS, NIOSH; ) Fang SM, Jin X, Li Y, et al. Correlation of matrix metalloproteinase-3 polymorphism to genetic susceptibility and lymph node metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer. Chinese J Cancer 2005; 24:
8 30 J Occup Health, Vol. 52, ) Wang S, Liu J, Hu S, et al. Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms with calcium oxalate calculus disease. J Huazhong University of Science and Technology Med Sci 2003; 23: ) Rothman KJ, Greenland S. Modern Epidemiology, 2nd ed[m]. New York: Lippincott-Raven Publishers; p ) Rongsheng L. Principle and Method of Epidemiology. Chengdu: Publishing House of Sichuang University; 2005 (in Chinese). 26) Miller JA, Schmatz C, Schultz AB. Lumbar disc degeneration: correlation with prospective study. Br J Sports Med 1989; 3: ) Adams MA, Dolan P, et al. Stress distributions inside interverterbral discs. The effects of age and degeneration. J Bone Joint Br 1996; 78: ) Buckwalter JA. Aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc. Spine 1995; 20: ) Lawrence JS. Rheumatism in miners: III. Occupational factors. Br J Industr Med 1955; 12: ) Hf F. Mechanical disorders of the low back. In: Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger. London: Henry Kimpton Publishers; ) Holm S, Nachemson A, et al. Nutrition of the intervertebral disc: Effects induced by vibration. Orthop Transact 1985; 9: ) Cheung KM, Chan D, Karppine J, et al. Association of the Taq I allele in vitamin D receptor with degenerative disc disease and disc bulge in a Chinese population. Spine 2006; 31: ) Yupigu H. Hernia of intervertebral discs. Beijing: People s Medical Publishing House; 2004 (in Chinese).
Identification of a Novel Common Genetic Risk Factor for Lumbar Disk Disease Original Contribution JAMA, Vol. 285 No. 14: , April 11, 2001
 1 Identification of a Novel Common Genetic Risk Factor for Lumbar Disk Disease Original Contribution JAMA, Vol. 285 No. 14:1843-1849, April 11, 2001 Petteri Paassilta; Jaana Lohiniva; Harald H. H. Göring;
1 Identification of a Novel Common Genetic Risk Factor for Lumbar Disk Disease Original Contribution JAMA, Vol. 285 No. 14:1843-1849, April 11, 2001 Petteri Paassilta; Jaana Lohiniva; Harald H. H. Göring;
Incomplete cauda equina syndrome in adult monozygotic twins
 Incomplete cauda equina syndrome in adult monozygotic twins J. Mohar, R. Kramar, N. Hero, R. J. Cirman Department of Spine Surgery and Paediatric Orthopaedics, Orthopaedic Hospital Valdoltra, Ankaran,
Incomplete cauda equina syndrome in adult monozygotic twins J. Mohar, R. Kramar, N. Hero, R. J. Cirman Department of Spine Surgery and Paediatric Orthopaedics, Orthopaedic Hospital Valdoltra, Ankaran,
Perspective. Lumbar degenerative disc disease: all in the genes? William Ryan Spiker 1 & Alpesh A Patel 1
 Perspective Lumbar degenerative disc disease: all in the genes? Lumbar degenerative disc disease is a common ailment that causes patients significant pain, disability and psychologic distress, in addition
Perspective Lumbar degenerative disc disease: all in the genes? Lumbar degenerative disc disease is a common ailment that causes patients significant pain, disability and psychologic distress, in addition
c Tuj1(-) apoptotic live 1 DIV 2 DIV 1 DIV 2 DIV Tuj1(+) Tuj1/GFP/DAPI Tuj1 DAPI GFP
 Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
Supplementary Figure 1 Establishment of the gain- and loss-of-function experiments and cell survival assays. a Relative expression of mature mir-484 30 20 10 0 **** **** NCP mir- 484P NCP mir- 484P b Relative
The Foundation of a New Paradigm of Disc Degeneration: The Twin Spine Study
 The Foundation of a New Paradigm of Disc Degeneration: The Twin Spine Study Submitted for Consideration for the Kappa Delta Award Michele C. Battié, PhD 1,2, Tapio Videman, MD, PhD 1,2, Jaakko Kaprio,
The Foundation of a New Paradigm of Disc Degeneration: The Twin Spine Study Submitted for Consideration for the Kappa Delta Award Michele C. Battié, PhD 1,2, Tapio Videman, MD, PhD 1,2, Jaakko Kaprio,
Supplementary Table 3. 3 UTR primer sequences. Primer sequences used to amplify and clone the 3 UTR of each indicated gene are listed.
 Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
Supplemental Figure 1. DLKI-DIO3 mirna/mrna complementarity. Complementarity between the indicated DLK1-DIO3 cluster mirnas and the UTR of SOX2, SOX9, HIF1A, ZEB1, ZEB2, STAT3 and CDH1with mirsvr and PhastCons
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sherman SI, Wirth LJ, Droz J-P, et al. Motesanib diphosphate
Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. (2012) /tpc YFP N
 MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
MYC YFP N PIF5 YFP C N-TIC TIC Supplemental Data. Shin et al. Plant Cell. ()..5/tpc..95 Supplemental Figure. TIC interacts with MYC in the nucleus. Bimolecular fluorescence complementation assay using
Supplementary Document
 Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Supplementary Document 1. Supplementary Table legends 2. Supplementary Figure legends 3. Supplementary Tables 4. Supplementary Figures 5. Supplementary References 1. Supplementary Table legends Suppl.
Abbreviations: P- paraffin-embedded section; C, cryosection; Bio-SA, biotin-streptavidin-conjugated fluorescein amplification.
 Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Supplementary Table 1. Sequence of primers for real time PCR. Gene Forward primer Reverse primer S25 5 -GTG GTC CAC ACT ACT CTC TGA GTT TC-3 5 - GAC TTT CCG GCA TCC TTC TTC-3 Mafa cds 5 -CTT CAG CAA GGA
Myoglobin A79G polymorphism association with exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage
 Myoglobin A79G polymorphism association with exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage T. Cui and M.S. Jiang College of Physical Education, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Ji nan, Shandong,
Myoglobin A79G polymorphism association with exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage T. Cui and M.S. Jiang College of Physical Education, Shandong University of Finance and Economics, Ji nan, Shandong,
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards
 Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
Toluidin-Staining of mast cells Ear tissue was fixed with Carnoy (60% ethanol, 30% chloroform, 10% acetic acid) overnight at 4 C, afterwards incubated in 100 % ethanol overnight at 4 C and embedded in
a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Supplementary Figure 1. Induction of p53 LOH by MADM. a) Primary cultures derived from the pancreas of an 11-week-old Pdx1-Cre; K-MADM-p53 mouse revealed increased p53 KO/KO (green,
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
696 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(9):
 696 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(9): 696-700 Letter to the Editor Fluoride Exposure, Follicle Stimulating Hormone Receptor Gene Polymorphism and Hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian Axis Hormones in Chinese
696 Biomed Environ Sci, 2015; 28(9): 696-700 Letter to the Editor Fluoride Exposure, Follicle Stimulating Hormone Receptor Gene Polymorphism and Hypothalamus-pituitary-ovarian Axis Hormones in Chinese
IL10 rs polymorphism is associated with liver cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis B
 IL10 rs1800896 polymorphism is associated with liver cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis B L.N. Cao 1, S.L. Cheng 2 and W. Liu 3 1 Kidney Disease Department of Internal Medicine, Xianyang Central Hospital,
IL10 rs1800896 polymorphism is associated with liver cirrhosis and chronic hepatitis B L.N. Cao 1, S.L. Cheng 2 and W. Liu 3 1 Kidney Disease Department of Internal Medicine, Xianyang Central Hospital,
3 脊椎変形の相互関係とリスク分析の今後の方向
 Reprint request: DEGENERATIVE SPINE AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN ELDERLY PEOPLE Toshitaka NAKAMURA Department of Orthopedics, University of Occupational and Environmental Health School of Medicine Vertebral osteophytes,
Reprint request: DEGENERATIVE SPINE AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN ELDERLY PEOPLE Toshitaka NAKAMURA Department of Orthopedics, University of Occupational and Environmental Health School of Medicine Vertebral osteophytes,
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most
 Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1 MicroRNA expression in human synovial fibroblasts from different locations. MicroRNA, which were identified by RNAseq as most differentially expressed between human synovial fibroblasts
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at
 Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Supplementary Figure 1. ROS induces rapid Sod1 nuclear localization in a dosagedependent manner. WT yeast cells (SZy1051) were treated with 4NQO at different concentrations for 30 min and analyzed for
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back
 Herniated Disk in the Lower Back This article is also available in Spanish: Hernia de disco en la columna lumbar (topic.cfm?topic=a00730). Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk
Herniated Disk in the Lower Back This article is also available in Spanish: Hernia de disco en la columna lumbar (topic.cfm?topic=a00730). Sometimes called a slipped or ruptured disk, a herniated disk
Association between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism (TaqI) and obesity in Chinese population
 c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH NOTE Association between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism (TaqI) and obesity in Chinese population HUI-RU FAN, LI-QUN LIN, HAO MA, YING LI and CHANG-HAO SUN National
c Indian Academy of Sciences RESEARCH NOTE Association between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism (TaqI) and obesity in Chinese population HUI-RU FAN, LI-QUN LIN, HAO MA, YING LI and CHANG-HAO SUN National
What causes new vertebral endplate signal changes (modic changes)?
 What causes new vertebral endplate signal changes (modic changes)? Poster No.: C-2417 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: T. S. Jensen 1, P. Kjaer 2, L. Korsholm
What causes new vertebral endplate signal changes (modic changes)? Poster No.: C-2417 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Musculoskeletal Authors: T. S. Jensen 1, P. Kjaer 2, L. Korsholm
Relationship between alterations of the lumbar spine, visualized with magnetic resonance imaging, and occupational variables
 Eur Spine J (2007) 16: 255 266 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0036-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Massimo Mariconda Olimpio Galasso Luigi Imbimbo Giovanni Lotti Carlo Milano Relationship between alterations of the lumbar
Eur Spine J (2007) 16: 255 266 DOI 10.1007/s00586-005-0036-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Massimo Mariconda Olimpio Galasso Luigi Imbimbo Giovanni Lotti Carlo Milano Relationship between alterations of the lumbar
Supplementary Table 2. Conserved regulatory elements in the promoters of CD36.
 Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
Supplementary Table 1. RT-qPCR primers for CD3, PPARg and CEBP. Assay Forward Primer Reverse Primer 1A CAT TTG TGG CCT TGT GCT CTT TGA TGA GTC ACA GAA AGA ATC AAT TC 1B AGG AAA TGA ACT GAT GAG TCA CAG
Associations between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and osteoarthritis: an updated meta-analysis
 RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2014;53:998 1008 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ket418 Advance Access publication 4 February 2014 Meta-analysis Associations between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and osteoarthritis:
RHEUMATOLOGY Rheumatology 2014;53:998 1008 doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ket418 Advance Access publication 4 February 2014 Meta-analysis Associations between vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms and osteoarthritis:
Common Thoraco- Lumbar Problems in the Mature Athlete
 Common Thoraco- Lumbar Problems in the Mature Athlete Diana Heiman, MD Associate Professor, Family Medicine Residency Director East Tennessee State University Objectives Review the pathophysiology of the
Common Thoraco- Lumbar Problems in the Mature Athlete Diana Heiman, MD Associate Professor, Family Medicine Residency Director East Tennessee State University Objectives Review the pathophysiology of the
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Supplementary Figure 1 U1 inhibition causes a shift of RNA-seq reads from exons to introns. (a) Evidence for the high purity of 4-shU-labeled RNAs used for RNA-seq. HeLa cells transfected with control
Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and cdna sequences of the targeted regions in WT-KI and
 Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and sequences of the targeted regions in and indicated mutant KI cells, with WT and corresponding mutant sequences underlined. (A) cells; (B) K21E-KI cells; (C) D33A-KI cells;
Figure S1. Analysis of genomic and sequences of the targeted regions in and indicated mutant KI cells, with WT and corresponding mutant sequences underlined. (A) cells; (B) K21E-KI cells; (C) D33A-KI cells;
Citation for published version (APA): Oosterveer, M. H. (2009). Control of metabolic flux by nutrient sensors Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Control of metabolic flux by nutrient sensors Oosterveer, Maaike IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Control of metabolic flux by nutrient sensors Oosterveer, Maaike IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Table S1. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION 2 3 Table S. Oligonucleotides used for the in-house RT-PCR assays targeting the M, H7 or N9 genes. Assay (s) Target Name Sequence (5 3 ) Comments CDC M InfA Forward (NS), CDC M
Relationship of the APOA5/A4/C3/A1 gene cluster and APOB gene polymorphisms with dyslipidemia
 elationship of the APOA5/A4/C3/A1 gene cluster and APOB gene polymorphisms with dyslipidemia H.J. Ou 1, G. Huang 2, W. Liu 3, X.L. Ma 2, Y. Wei 4, T. Zhou 5 and Z.M. Pan 3 1 Department of Neurology, The
elationship of the APOA5/A4/C3/A1 gene cluster and APOB gene polymorphisms with dyslipidemia H.J. Ou 1, G. Huang 2, W. Liu 3, X.L. Ma 2, Y. Wei 4, T. Zhou 5 and Z.M. Pan 3 1 Department of Neurology, The
BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks
 Name: Date: Block: BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks INTRODUCTION: In this simulation activity, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on
Name: Date: Block: BIOLOGY 621 Identification of the Snorks INTRODUCTION: In this simulation activity, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism - the Snork. Snorks were discovered on
Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients
 Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients Shuichi OTABE, Karine CLEMENT, Séverine DUBOIS, Frederic LEPRETRE, Veronique PELLOUX,
Mutation Screening and Association Studies of the Human UCP 3 Gene in Normoglycemic and NIDDM Morbidly Obese Patients Shuichi OTABE, Karine CLEMENT, Séverine DUBOIS, Frederic LEPRETRE, Veronique PELLOUX,
Associations between matrix metalloproteinase gene polymorphisms and the development of cerebral infarction
 Associations between matrix metalloproteinase gene polymorphisms and the development of cerebral infarction J.H. Zhao 1,2, Y.M. Xu 1, H.X. Xing 2, L.L. Su 2, S.B. Tao 2, X.J. Tian 2, H.Q. Yan 2 and S.B.
Associations between matrix metalloproteinase gene polymorphisms and the development of cerebral infarction J.H. Zhao 1,2, Y.M. Xu 1, H.X. Xing 2, L.L. Su 2, S.B. Tao 2, X.J. Tian 2, H.Q. Yan 2 and S.B.
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk in a Chinese Han population
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(12):5832-5836 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0002117 Original Article The programmed death-1 gene polymorphism (PD-1.5 C/T) is associated with non-small cell lung cancer risk
Lumbar osteoarthritis encompasses a series of diseases
 SPINE Volume 39, Number 16, pp 1301-1310 2014, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins EPIDEMIOLOGY The High Prevalence of Symptomatic Degenerative Lumbar Osteoarthritis in Chinese Adults A Population-Based Study
SPINE Volume 39, Number 16, pp 1301-1310 2014, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins EPIDEMIOLOGY The High Prevalence of Symptomatic Degenerative Lumbar Osteoarthritis in Chinese Adults A Population-Based Study
Supplementary Information. Bamboo shoot fiber prevents obesity in mice by. modulating the gut microbiota
 Supplementary Information Bamboo shoot fiber prevents obesity in mice by modulating the gut microbiota Xiufen Li 1,2, Juan Guo 1, Kailong Ji 1,2, and Ping Zhang 1,* 1 Key Laboratory of Tropical Plant Resources
Supplementary Information Bamboo shoot fiber prevents obesity in mice by modulating the gut microbiota Xiufen Li 1,2, Juan Guo 1, Kailong Ji 1,2, and Ping Zhang 1,* 1 Key Laboratory of Tropical Plant Resources
Low-back pain and early retirement among Danish semiskilled construction workers
 Scand j work environ health 8 (1982): suppl 1, 100-104 Low-back pain and early retirement among Danish semiskilled construction by Marianne Damlund, MD, Steffen G0th, PhD, Peter Has/e, MSc, Karen Munk
Scand j work environ health 8 (1982): suppl 1, 100-104 Low-back pain and early retirement among Danish semiskilled construction by Marianne Damlund, MD, Steffen G0th, PhD, Peter Has/e, MSc, Karen Munk
Lack of association between ERCC5 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population
 Lack of association between ERCC5 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population J.J. Lu, H.Q. Zhang, P. Mai, X. Ma, X. Chen, Y.X. Yang and L.P. Zhang Gansu Provincial Hospital, Donggang
Lack of association between ERCC5 gene polymorphisms and gastric cancer risk in a Chinese population J.J. Lu, H.Q. Zhang, P. Mai, X. Ma, X. Chen, Y.X. Yang and L.P. Zhang Gansu Provincial Hospital, Donggang
A preliminary association study of fat mass and obesity associated gene polymorphisms and degenerative disc disease in a Chinese Han population
 Research Note A preliminary association study of fat mass and obesity associated gene polymorphisms and degenerative disc disease in a Chinese Han population Journal of International Medical Research 2014,
Research Note A preliminary association study of fat mass and obesity associated gene polymorphisms and degenerative disc disease in a Chinese Han population Journal of International Medical Research 2014,
Flexion and Rotation of the Trunk and Lifting at Work Are Risk Factors for Low Back Pain
 Flexion and Rotation of the Trunk and Lifting at Work Are Risk Factors for Low Back Pain Results of a Prospective Cohort Study Wilhelmina E. Hoogendoorn, MSc,* Paulien M. Bongers, PhD,* Henrica C.W. de
Flexion and Rotation of the Trunk and Lifting at Work Are Risk Factors for Low Back Pain Results of a Prospective Cohort Study Wilhelmina E. Hoogendoorn, MSc,* Paulien M. Bongers, PhD,* Henrica C.W. de
Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk in a Chinese population
 Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk in a Chinese population R. Zhao and M.F. Ying Department of Pharmacy, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University,
Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 polymorphisms and breast cancer risk in a Chinese population R. Zhao and M.F. Ying Department of Pharmacy, Sir Run Run Shaw Hospital, School of Medicine, Zhejiang University,
Association of interleukin 1 gene polymorphism with. intervertebral disc degeneration risk in a Chinese Han
 Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
Bioscience Reports: this is an Accepted Manuscript, not the final Version of Record. You are encouraged to use the Version of Record that, when published, will replace this version. The most up-to-date
BACK PROBLEMS AMONG CAR DRIVERS: A SUMMARY OF STUDIES DURING THE LAST 30 YEARS
 BACK PROBLEMS AMONG CAR DRIVERS: A SUMMARY OF STUDIES DURING THE LAST 30 YEARS Lenka Justinova Human Factors Research Unit Institute of Sound and Vibration University of Southampton Southampton SO17 1BJ
BACK PROBLEMS AMONG CAR DRIVERS: A SUMMARY OF STUDIES DURING THE LAST 30 YEARS Lenka Justinova Human Factors Research Unit Institute of Sound and Vibration University of Southampton Southampton SO17 1BJ
Prospective study of MTHFR genetic polymorphisms as a possible etiology of male infertility
 Prospective study of MTHFR genetic polymorphisms as a possible etiology of male infertility S.-S. Li 1, J. Li 1, Z. Xiao 2, A.-G. Ren 3 and L. Jin 3 1 Beijing Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, Capital
Prospective study of MTHFR genetic polymorphisms as a possible etiology of male infertility S.-S. Li 1, J. Li 1, Z. Xiao 2, A.-G. Ren 3 and L. Jin 3 1 Beijing Obstetrics and Gynecology Hospital, Capital
Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to pancreatic cancer
 Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to pancreatic cancer M.G. He, K. Zheng, D. Tan and Z.X. Wang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Nuclear Industry 215 Hospital
Association between ERCC1 and ERCC2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to pancreatic cancer M.G. He, K. Zheng, D. Tan and Z.X. Wang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery, Nuclear Industry 215 Hospital
Financial Disclosure
 Financial Disclosure I do not have any affiliation (financial or otherwise) with a commercial organization that may have a direct or indirect connection to the content of my presentation(s). REFERENCES
Financial Disclosure I do not have any affiliation (financial or otherwise) with a commercial organization that may have a direct or indirect connection to the content of my presentation(s). REFERENCES
ASJ. Prevalence, Patterns, and Genetic Association Analysis of Modic Vertebral Endplate Changes. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 Asian Spine Journal 594 Rishi Mugesh Clinical Kanna Study et al. https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.4.594 Prevalence, Patterns, and Genetic Association Analysis of Modic Vertebral Endplate Changes Rishi
Asian Spine Journal 594 Rishi Mugesh Clinical Kanna Study et al. https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2017.11.4.594 Prevalence, Patterns, and Genetic Association Analysis of Modic Vertebral Endplate Changes Rishi
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
Supplementary Figure 1 3 3 3 1 1 Bregma -1.6mm 3 : Bregma Ref) Http://www.mbl.org/atlas165/atlas165_start.html Bregma -.18mm Supplementary Figure 1 Schematic representation of the utilized brain slice
The association between TCM syndromes and SCAP polymorphisms in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
 The association between TCM syndromes and SCAP polymorphisms in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Shanshan Sun, Tao Wu, Miao Wang, Wei Li, Lin Wang, Songhua He, Huafeng Wei, Haiyan Song,
The association between TCM syndromes and SCAP polymorphisms in subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Shanshan Sun, Tao Wu, Miao Wang, Wei Li, Lin Wang, Songhua He, Huafeng Wei, Haiyan Song,
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. H3F3B expression in lung cancer. a. Comparison of H3F3B expression in relapsed and non-relapsed lung cancer patients. b. Prognosis of two groups of lung cancer
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. H3F3B expression in lung cancer. a. Comparison of H3F3B expression in relapsed and non-relapsed lung cancer patients. b. Prognosis of two groups of lung cancer
S pinal stenosis (MIM ) is defined as a narrowing
 1208 EXTENDED REPORT Sequence variations in the collagen IX and XI genes are associated with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis N Noponen-Hietala, E Kyllönen, M Männikkö, E Ilkko, J Karppinen, J Ott,
1208 EXTENDED REPORT Sequence variations in the collagen IX and XI genes are associated with degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis N Noponen-Hietala, E Kyllönen, M Männikkö, E Ilkko, J Karppinen, J Ott,
Artificial intervertebral disc
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Artificial intervertebral disc Vikas Ghai Medical University of Ohio Follow this and additional works
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Artificial intervertebral disc Vikas Ghai Medical University of Ohio Follow this and additional works
HERNIATED DISCS AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO HERNIATED S This booklet provides general information on herniated discs. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
AN INTRODUCTION TO HERNIATED S This booklet provides general information on herniated discs. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician or other
Association between matrix metalloproteinase-9 rs polymorphism and development of coronary artery disease in a Chinese population
 Association between matrix metalloproteinase-9 rs3918242 polymorphism and development of coronary artery disease in a Chinese population L.M. Qin 1, G.M. Qin 2, X.H. Shi 1, A.L. Wang 1 and H. Zuo 1 1 The
Association between matrix metalloproteinase-9 rs3918242 polymorphism and development of coronary artery disease in a Chinese population L.M. Qin 1, G.M. Qin 2, X.H. Shi 1, A.L. Wang 1 and H. Zuo 1 1 The
Investigation on ERCC5 genetic polymorphisms and the development of gastric cancer in a Chinese population
 Investigation on ERCC5 genetic polymorphisms and the development of gastric cancer in a Chinese population L.Q. Yang 1, Y. Zhang 2 and H.F. Sun 3 1 Department of Gastroenterology, The Second Affiliated
Investigation on ERCC5 genetic polymorphisms and the development of gastric cancer in a Chinese population L.Q. Yang 1, Y. Zhang 2 and H.F. Sun 3 1 Department of Gastroenterology, The Second Affiliated
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3836
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recombinant LIGHT-VTP induces pericyte contractility and endothelial cell activation. (a) Western blot showing purification steps for full length murine LIGHT-VTP (CGKRK) protein:
Supplementary Figure 1 Recombinant LIGHT-VTP induces pericyte contractility and endothelial cell activation. (a) Western blot showing purification steps for full length murine LIGHT-VTP (CGKRK) protein:
Original Article Genetic risk factors of disc degeneration among year-old Danish children: a population study
 Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet 2010;1(2):158-165 www.ijmeg.org /IJMEG912002 Original Article Genetic risk factors of disc degeneration among 12-14- year-old Danish children: a population study Pasi J Eskola
Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet 2010;1(2):158-165 www.ijmeg.org /IJMEG912002 Original Article Genetic risk factors of disc degeneration among 12-14- year-old Danish children: a population study Pasi J Eskola
High-Intensity Zone on L-spine MRI: Clinical Relevance and Association with Trauma History
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 1, No. 1, pp 38~42, 2007 High-Intensity Zone on L-spine MRI: Clinical Relevance and Association with Trauma History Kun-Woo Park*, Kwang-Sup Song, Jae Yoon Chung*, Jin-Man Choi*,
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 1, No. 1, pp 38~42, 2007 High-Intensity Zone on L-spine MRI: Clinical Relevance and Association with Trauma History Kun-Woo Park*, Kwang-Sup Song, Jae Yoon Chung*, Jin-Man Choi*,
Reliability of change in lumbar MRI findings
 Reliability of change in lumbar MRI findings Poster No.: C-0539 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Berg 1, O. Gjertsen 2, C. Hellum 2, G. F. Neckelmann 1, L. G. Johnsen 3, G. E. Eide
Reliability of change in lumbar MRI findings Poster No.: C-0539 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Berg 1, O. Gjertsen 2, C. Hellum 2, G. F. Neckelmann 1, L. G. Johnsen 3, G. E. Eide
 www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Protein Synthesis - Sentence Activity Summary: Students will simulate transcription and translation by building a sentence/polypeptide from words/amino acids. Goals & Objectives:
www.lessonplansinc.com Topic: Protein Synthesis - Sentence Activity Summary: Students will simulate transcription and translation by building a sentence/polypeptide from words/amino acids. Goals & Objectives:
Influence of interleukin-17 gene polymorphisms on the development of pulmonary tuberculosis
 Influence of interleukin-17 gene polymorphisms on the development of pulmonary tuberculosis G.-C. Shi and L.-G. Zhang Department of Tuberculosis, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University,
Influence of interleukin-17 gene polymorphisms on the development of pulmonary tuberculosis G.-C. Shi and L.-G. Zhang Department of Tuberculosis, The First Affiliated Hospital of Xinxiang Medical University,
LOW BACK PAIN EPIDEMIOLOGY:
 LOW BACK PAIN OBJECTIVES: Discuss epidemiology of low back pain Summarize diagnosis/ special tests Review Red Flags Discuss treatment and referral guidelines Discuss light duty guidelines EPIDEMIOLOGY:
LOW BACK PAIN OBJECTIVES: Discuss epidemiology of low back pain Summarize diagnosis/ special tests Review Red Flags Discuss treatment and referral guidelines Discuss light duty guidelines EPIDEMIOLOGY:
Genetic background of degenerative disc disease in the lumbar spine
 REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Genetic background of degenerative disc disease in the lumbar spine Yoshiharu Kawaguchi Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Toyama, Toyama,
REVIEW ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Genetic background of degenerative disc disease in the lumbar spine Yoshiharu Kawaguchi Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, University of Toyama, Toyama,
290 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(4):
 290 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(4): 290-294 Letter to the Editor Prevalence and Predictors of Hypertension in the Labor Force Population in China: Results from a Cross-sectional Survey in Xinjiang Uygur
290 Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(4): 290-294 Letter to the Editor Prevalence and Predictors of Hypertension in the Labor Force Population in China: Results from a Cross-sectional Survey in Xinjiang Uygur
THE PREVALENCE OF CHRONIC
 THE PREVALENCE OF CHRONIC LOW BACK PAIN IN OFFICE WORKERS OF LAHORE MEDICAL AND DENTAL COLLEGE AND GHURKI TRUST TEACHING HOSPITAL, LAHORE Authors: Hafiz Muhammad Asim, Muhammad Shahid Ismail Abstract Objective:
THE PREVALENCE OF CHRONIC LOW BACK PAIN IN OFFICE WORKERS OF LAHORE MEDICAL AND DENTAL COLLEGE AND GHURKI TRUST TEACHING HOSPITAL, LAHORE Authors: Hafiz Muhammad Asim, Muhammad Shahid Ismail Abstract Objective:
Culture Density (OD600) 0.1. Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600) Culture Density (OD600)
 A. B. C. D. E. PA JSRI JSRI 2 PA DSAM DSAM 2 DSAM 3 PA LNAP LNAP 2 LNAP 3 PAO Fcor Fcor 2 Fcor 3 PAO Wtho Wtho 2 Wtho 3 Wtho 4 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB
A. B. C. D. E. PA JSRI JSRI 2 PA DSAM DSAM 2 DSAM 3 PA LNAP LNAP 2 LNAP 3 PAO Fcor Fcor 2 Fcor 3 PAO Wtho Wtho 2 Wtho 3 Wtho 4 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB Low Iron 2 4 6 8 2 4 6 8 2 22 DTSB
CYP19 gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility to breast cancer in Xinjiang Uigur women
 CYP19 gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility to breast cancer in Xinjiang Uigur women L. Yang, X.Y. Wang, Y.T. Li, H.L. Wang, T. Wu, B. Wang, Q. Zhao, D. Jinsihan and L.P. Zhu The Department of Mammary
CYP19 gene polymorphisms and the susceptibility to breast cancer in Xinjiang Uigur women L. Yang, X.Y. Wang, Y.T. Li, H.L. Wang, T. Wu, B. Wang, Q. Zhao, D. Jinsihan and L.P. Zhu The Department of Mammary
Can a bulging disc cause ear pain
 Can a bulging disc cause ear pain that can be attributed to their nonotogenic ear pain: 37, cervical spine degenerative disease (eg, disc changes and herniation, osteophytes, spinal/ foramen. Surgeon says
Can a bulging disc cause ear pain that can be attributed to their nonotogenic ear pain: 37, cervical spine degenerative disease (eg, disc changes and herniation, osteophytes, spinal/ foramen. Surgeon says
NECK AND BACK PAIN AN INTRODUCTION TO
 AN INTRODUCTION TO NECK AND BACK PAIN This booklet provides general information on neck and back pain. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician
AN INTRODUCTION TO NECK AND BACK PAIN This booklet provides general information on neck and back pain. It is not meant to replace any personal conversations that you might wish to have with your physician
A smart acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive. live cell mrna imaging by the target-triggered intracellular self-assembly
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A smart ZnO@polydopamine-nucleic acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive live cell mrna imaging
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Chemical Science. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 A smart ZnO@polydopamine-nucleic acid nanosystem for ultrasensitive live cell mrna imaging
Studies of high or moderate quality used for results and conclusions in the present report
 Studies of high or moderate quality used for results and conclusions in the present report 1 First author Pub. Year Reference Country Allen et al 2010 [1] USA Design Time to follow-up Setting Performed
Studies of high or moderate quality used for results and conclusions in the present report 1 First author Pub. Year Reference Country Allen et al 2010 [1] USA Design Time to follow-up Setting Performed
CD31 5'-AGA GAC GGT CTT GTC GCA GT-3' 5 ' -TAC TGG GCT TCG AGA GCA GT-3'
 Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
Table S1. The primer sets used for real-time RT-PCR analysis. Gene Forward Reverse VEGF PDGFB TGF-β MCP-1 5'-GTT GCA GCA TGA ATC TGA GG-3' 5'-GGA GAC TCT TCG AGG AGC ACT T-3' 5'-GAA TCA GGC ATC GAG AGA
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1: Cryopreservation alters CD62L expression by CD4 T cells. Freshly isolated (left) or cryopreserved PBMCs (right) were stained with the mix of antibodies described
Lumbar Disc Prolapse: Management and Outcome Analysis of 96 Surgically treated Patients
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse: Management and Outcome Analysis of 96 Surgically treated Patients A. Akbar ( Department of Neurosurgery, Chandka Medical College, Larkana. ) A. Mahar ( Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
Lumbar Disc Prolapse: Management and Outcome Analysis of 96 Surgically treated Patients A. Akbar ( Department of Neurosurgery, Chandka Medical College, Larkana. ) A. Mahar ( Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Introduction to Bioinformatics
 Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Beta Thalassemia Case Study Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University San José, California, USA sami.khuri@sjsu.edu www.cs.sjsu.edu/faculty/khuri Outline v Hemoglobin v Alpha
Influence of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms on acute pancreatitis susceptibility in a Chinese population
 Influence of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms on acute pancreatitis susceptibility in a Chinese population H.B. Gui 1, X.G. Du 2, Z.H. Fu 3 and X.M. Chen 1 1 Department of Emergency, The First Affiliated
Influence of interleukin-18 gene polymorphisms on acute pancreatitis susceptibility in a Chinese population H.B. Gui 1, X.G. Du 2, Z.H. Fu 3 and X.M. Chen 1 1 Department of Emergency, The First Affiliated
2016 OPAM Mid-Year Educational Conference, sponsored by AOCOPM Thursday, March 10, 2016 C-1
 Long-term Outcomes of Lumbar Fusion Among Workers Compensation Subjects : An Historical Cohort Study Trang Nguyen M.D., Ph.D. David C. Randolph M.D, M.P.H. James Talmage MD Paul Succop PhD Russell Travis
Long-term Outcomes of Lumbar Fusion Among Workers Compensation Subjects : An Historical Cohort Study Trang Nguyen M.D., Ph.D. David C. Randolph M.D, M.P.H. James Talmage MD Paul Succop PhD Russell Travis
Introduction. Castellvi Spine Are We Closer to Finding the True Lumbar Pain Generator? DISCLOSURE 5/27/2016. Dom Coric, M.D.
 Castellvi Spine Are We Closer to Finding the True Lumbar Pain Generator? Dom Coric, M.D. Carolina Neurosurgery and Spine Associates Chief, Department of Neurosurgery, CMC Charlotte, NC 5/20/16 DISCLOSURE
Castellvi Spine Are We Closer to Finding the True Lumbar Pain Generator? Dom Coric, M.D. Carolina Neurosurgery and Spine Associates Chief, Department of Neurosurgery, CMC Charlotte, NC 5/20/16 DISCLOSURE
SAFE LIFTING Protecting Your Back. Dwayne Fuchs Reg. Kinesiologist Ergonomist
 SAFE LIFTING Protecting Your Back Dwayne Fuchs Reg. Kinesiologist Ergonomist Back Injury 60 % of all adults experience back pain Most frequent cause of activity limitation in individuals under 45 years
SAFE LIFTING Protecting Your Back Dwayne Fuchs Reg. Kinesiologist Ergonomist Back Injury 60 % of all adults experience back pain Most frequent cause of activity limitation in individuals under 45 years
Non-Operative Management of Low Back Pain in the Elderly
 www.4-no-pain.com Non-Operative Management of Low Back Pain in the Elderly Brian Kahan, D.O., FAAPMR Low Back Pain Outline Etiologies Initial Assessment Physical examination and Diagnostic work-up Clinical
www.4-no-pain.com Non-Operative Management of Low Back Pain in the Elderly Brian Kahan, D.O., FAAPMR Low Back Pain Outline Etiologies Initial Assessment Physical examination and Diagnostic work-up Clinical
Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain
 Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Patient Information ACDF. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion
 Patient Information ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Table of Contents Anatomy of the Spine...2-3 General Conditions of the Cervical Spine...4 5 What is an ACDF?...6 How is an ACDF performed?...7
Patient Information ACDF Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Table of Contents Anatomy of the Spine...2-3 General Conditions of the Cervical Spine...4 5 What is an ACDF?...6 How is an ACDF performed?...7
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis
 Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
Human leukocyte antigen-b27 alleles in Xinjiang Uygur patients with ankylosing spondylitis H.-Y. Zou, W.-Z. Yu, Z. Wang, J. He and M. Jiao Institute of Clinical Medicine, Urumqi General Hospital, Lanzhou
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05883 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Figure 1 Prostaglandin agonists and antagonists alter runx1/cmyb expression. a-e, Embryos were exposed to (b) PGE2 and (c) PGI2 (20μM) and
doi: 10.1038/nature05883 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Figure 1 Prostaglandin agonists and antagonists alter runx1/cmyb expression. a-e, Embryos were exposed to (b) PGE2 and (c) PGI2 (20μM) and
Influence of lifestyle characteristics and VDR polymorphisms as risk factors for intervertebral disc degeneration: a case control study
 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-018-0309-x European Journal of Medical Research RESEARCH Open Access Influence of lifestyle characteristics and VDR polymorphisms as risk factors for intervertebral disc
https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-018-0309-x European Journal of Medical Research RESEARCH Open Access Influence of lifestyle characteristics and VDR polymorphisms as risk factors for intervertebral disc
Definition. Ergonomics is a science of fitting workplace conditions & job demands to the capabilities of the working population - OSHA
 Office Ergonomics Definition Ergonomics is a science of fitting workplace conditions & job demands to the capabilities of the working population - OSHA Why talk about Ergonomics? Poor ergonomics invariably
Office Ergonomics Definition Ergonomics is a science of fitting workplace conditions & job demands to the capabilities of the working population - OSHA Why talk about Ergonomics? Poor ergonomics invariably
Genetic Markers of a Predisposition to Lumbar Disc Degeneration in Young Adults. Travis Fulton
 Genetic Markers of a Predisposition to Lumbar Disc Degeneration in Young Adults by Travis Fulton A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science Approved
Genetic Markers of a Predisposition to Lumbar Disc Degeneration in Young Adults by Travis Fulton A Thesis Presented in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science Approved
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1269/12
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1269/12 BEFORE: S. Peckover: Vice-Chair HEARING: June 18, 2012 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: June 28, 2012 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2012 ONWSIAT
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 1269/12 BEFORE: S. Peckover: Vice-Chair HEARING: June 18, 2012 at Toronto Written DATE OF DECISION: June 28, 2012 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2012 ONWSIAT
Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects identifies susceptibility loci at PLCE1 and C20orf54
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Genet. 42, 759 763 (2010); published online 22 August 2010; corrected online 27 August 2014 Genome-wide association study of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Chinese subjects
Supplemental Information. Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal. Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based. Model of Parkinson's Disease
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based Model of Parkinson's Disease Annika Sommer, Franz Maxreiter, Florian Krach, Tanja Fadler,
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 23 Supplemental Information Th17 Lymphocytes Induce Neuronal Cell Death in a Human ipsc-based Model of Parkinson's Disease Annika Sommer, Franz Maxreiter, Florian Krach, Tanja Fadler,
Spine Conditions and Treatments. Your Guide to Common
 Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
Association between IL-17A and IL-17F gene polymorphisms and risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population
 Association between IL-17A and IL-17F gene polymorphisms and risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population W.M. Zhao 1, P. Shayimu 1, L. Liu 1, F. Fang 1 and X.L. Huang 2 1 Department of Gastrointestinal
Association between IL-17A and IL-17F gene polymorphisms and risk of gastric cancer in a Chinese population W.M. Zhao 1, P. Shayimu 1, L. Liu 1, F. Fang 1 and X.L. Huang 2 1 Department of Gastrointestinal
Investigating the role of polymorphisms in mir-146a, -149, and -196a2 in the development of gastric cancer
 Investigating the role of polymorphisms in mir-146a, -149, and -196a2 in the development of gastric cancer Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong
Investigating the role of polymorphisms in mir-146a, -149, and -196a2 in the development of gastric cancer Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Ren Ji Hospital, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong
Common Low Back Injuries in Dancers
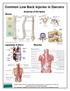 Common Low Back Injuries in Dancers Bones Anatomy of the Spine Ligaments & Discs Muscles Quadratus Lumborum (QL) Muscle Strain or Trigger Point The QL originates from the posterior iliac crest and inserts
Common Low Back Injuries in Dancers Bones Anatomy of the Spine Ligaments & Discs Muscles Quadratus Lumborum (QL) Muscle Strain or Trigger Point The QL originates from the posterior iliac crest and inserts
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, Osteoarthritis Research Society /95/ $08.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 399/15
 WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 399/15 BEFORE: J. Josefo: Vice-Chair HEARING: February 24, 2015 at Sudbury Oral DATE OF DECISION: March 16, 2015 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2015 ONWSIAT
WORKPLACE SAFETY AND INSURANCE APPEALS TRIBUNAL DECISION NO. 399/15 BEFORE: J. Josefo: Vice-Chair HEARING: February 24, 2015 at Sudbury Oral DATE OF DECISION: March 16, 2015 NEUTRAL CITATION: 2015 ONWSIAT
Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Spring 2015
 Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development SMPD 287 Three Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Hemoglobin Outline Anatomy of a gene Hemoglobinopathies
Bioinformatics in Medical Product Development SMPD 287 Three Beta Thalassemia Sami Khuri Department of Computer Science San José State University Hemoglobin Outline Anatomy of a gene Hemoglobinopathies
Association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of pri-mir-34b/c and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma
 Association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of pri-mir-34b/c and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma L.L. Chen 1,2, Y. Shen 3, J.B. Zhang 4, S. Wang 5, T. Jiang 6, M.Q. Zheng 6, Z.J. Zheng 7
Association between polymorphisms in the promoter region of pri-mir-34b/c and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma L.L. Chen 1,2, Y. Shen 3, J.B. Zhang 4, S. Wang 5, T. Jiang 6, M.Q. Zheng 6, Z.J. Zheng 7
