Pediatric Rheumatology 2007, 5:5
|
|
|
- Joella Brooks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pediatric Rheumatology This Provisional PDF corresponds to the article as it appeared upon acceptance. Copyedited and fully formatted PDF and full text (HTML) versions will be made available soon. Growing pains in children Pediatric Rheumatology 2007, 5:5 doi: / Yosef Uziel Philip J Hashkes (hashkep@ccf.org) ISSN Article type Review Submission date 3 January 2007 Acceptance date 19 April 2007 Publication date 19 April 2007 Article URL This peer-reviewed article was published immediately upon acceptance. It can be downloaded, printed and distributed freely for any purposes (see copyright notice below). Articles in Pediatric Rheumatology are listed in PubMed and archived at PubMed Central. For information about publishing your research in Pediatric Rheumatology or any BioMed Central journal, go to For information about other BioMed Central publications go to Uziel and Hashkes, licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Growing pains in children Yosef Uziel 1, Philip J. Hashkes 2* 1 Department of Pediatrics, Pediatric Rheumatology, Meir Medical Center, Kfar-Saba, Tel-Aviv University, Israel 2 Section of Pediatric Rheumatology, Dept. of Rheumatic Diseases, Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland OH, USA *Corresponding Author Philip J Hashkes, MD, MSc Section of Pediatric Rheumatology Department of Rheumatic Diseases Cleveland Clinic Cleveland, OH USA Tel: , Fax: addresses: uziely@zahav.net.il hashkep@ccf.org
3 Abstract We review the clinical manifestations of growing pains, the most common form of episodic childhood musculoskeletal pain. Physicians should be careful to adhere to clear clinical criteria as described in this review before diagnosing a child with growing pain. We expand on current theories on possible causes of growing pains and describe the management of these pains and the generally good outcome in nearly all children. 2
4 Background A 6 year-old boy is awakened at 02:00 AM, screaming of painful legs. His parents appreciate severe pain, but do not see anything wrong with his legs. They rub his legs and give him acetaminophen and he returns to sleep with pain resolution within 30 minutes. In the morning he is running about as if nothing occurred at night. The following week he has a similar episode. This causes significant anxiety in the family, and they immediately visit the primary physician. The family worries. What does he have? Is this a serious disease? A tumor? What should the family physician do? In this paper we will review the clinical presentation of this very common pain syndrome, try to understand current knowledge on the pathogenesis and natural course, what the family physician should do, especially in alleviating the family s anxiety. Extremity pain is a common presenting complaint of visits to pediatricians [1-13]. The most common cause of childhood musculoskeletal pain is termed growing pains (GP) that exemplifies a type of non-inflammatory pain syndrome. These pains are much more common than all other inflammatory rheumatic diseases. The prevalence of GP ranges from 3-37% of children. Oster found that as many as 15% of school-age children have occasional limb pain [6], and recently Evans and Scutter in a very large community study in Australia reported a prevalence of 37% in children aged 4-6 years [7]. GP mainly affects children between the ages of 3-12 years. GP has typical clinical characteristics; it is usually nonarticular, in 2/3 of children is located in the shins, calves, thighs or popliteal fossa and is almost always bilateral. The pain usually appears late in the day or is nocturnal, often awaking the child. The duration ranges from 3
5 minutes to hours. The intensity can be mild or very severe. By morning the child is almost always pain free. There are no objective signs of inflammation on physical examination. GP is episodic, with pain-free intervals from days to months. In severe cases the pain can occur daily. In our series of 44 children with GP, 43% had frequency of at least once a week [14]. Often parents can predict when the child will have pain on days of increased activity or when the child is more moody. GP is not associated with serious organic disease, and usually resolves by late childhood. However, frequent episodes may have a major impact on the child and his family s daily routine, including absences from school and work, daytime fatigue, reduced physical activity, and frequent or chronic use of pain relief medications. Pathogenesis The etiology of GP is unknown. Very few studies have been done to elucidate the etiology and pathogenesis of this common syndrome. Low pain threshold GP belong to the non-inflammatory musculoskeletal pain syndromes. Non-inflammatory pain syndromes, especially fibromyalgia, are associated with a lower pain threshold and with more characteristic tender points when measured by dolorimeter as compared to people without pain syndromes [15,16]. In fibromyalgia lower pain threshold and characteristic tender points are a dominant feature, which is found in the acute stage of the syndrome and resolves following remission [17]. Since GP is also a pain syndrome, our hypothesis was that the pain threshold in children with GP is lower compared to controls. We assessed the pain threshold by dolorimeter in 44 children with GP and indeed found that children with GP have a decreased pain threshold 4
6 compared to age and gender matched controls [14]. It was interesting to note that the pain threshold at the anterior tibia was the highest in the body, including among children with GP. This is the region most commonly reported by children with GP as painful during attacks. This indicated that GP represents a generalized pain syndrome, not only a localized disorder. Thus it is possible that GP represents the pattern of non-inflammatory pain syndromes in early childhood. Bone strength Since GP usually occurs late in the day and is often reported on days of increased activity, GP may represent a relative local overuse (stress) syndrome, and may be associated with decreased bone strength. In evaluating this theory we measured the bone speed of sound by ultrasound in 39 children with GP. We found that the bone strength density of children with GP was significantly less than values for population norms of healthy children, especially in the painful tibia region [18]. Thus GP may represent a local lower extremity overuse syndrome with bone fatigue in children with low pain thresholds. These children may experience more pain after physical activity. However while relative overuse can help explain late day pains, this theory cannot explain all features of GP such as the abrupt nocturnal episodes of pain, or pain in the upper extremity in some patients. Blood perfusion changes The sudden onset and severity of GP as well as the transience of the attacks support a hypothesis that GP has a vascular perfusion component, similar to migraines. Furthermore a higher prevalence of GP was found among children with migraine headaches [19]. 5
7 However when we looked for perfusion changes by comparing the ratio of blood phase of the bone scan to the static phase we did not find differences between children with GP and children who underwent bone scans for other reasons [20]. Anatomical/Mechanical Many clinicians have an impression that many children with GP are hypermobile, but this has not been assessed in a study in part due to the lack of formal criteria of hypermobility in very young children. This association, if true, may explain GP in 2 methods. GP after increased activity may be directly explained by hypermobility as part of the hypermobility syndrome. In addition children with hypermobility have an increased prevalence of fibromyalgia thus resulting in pain from a low pain threshold [21]. Other mechanical issues associated with hypermobility include flexible flat feet with hindfoot valgus. This mechanical instability might be a cause of GP in some children. In one small controlled trial shoe inserts were effective in reducing the frequency and severity of GP [22]. There is no evidence, however, that GP are actually associated with rapid growth as originally thought. The peak age of GP (about 6 years) is usually not part of the child s rapid growing phase. Family environment Naish and Apley assumed that emotional disturbances are more common in children with GP, and that recurrent abdominal pain, headaches, and limb pains are a group of pain syndromes expressing a reactive pattern to familial emotional disturbances [4,23]. Oster suggested that painful experiences during the parents childhood are a precipitating factor for development of a pain syndrome among their children [24]. In a study by Oberklaid et al, children with musculoskeletal pains (without the homogenous criteria of GP used for our studies) were often rated by their parents as having different temperamental and behavioral profiles than healthy 6
8 normal controls, suggesting a psychosocial contribution to their pain, similar to that seen with other pain syndromes [25]. In others studies, the family environment and psychological distress were also found to contribute to the development of musculoskeletal pain syndromes [26,27]. We evaluated the quality of life, depression, and anxiety levels of parents to children with GP and found that the depression levels of the parents were similar to those from other noninflammatory pain syndromes, with mothers having increased depression levels. Parents of children with GP and children without pain had similar quality of life scores, not surprising considering the episodic nature of GP [28]. Other Rarely, GP may be a manifestation of an organic disease like metabolic muscle disease (when occurring after exercise) or restless leg syndrome, especially in families with a history of this syndrome [29]. Investigations and diagnosis Currently, the diagnosis is based only on typical clinical symptoms as outlined above. There are no sensitive or specific laboratory tests, although children often undergo extensive investigations for other diseases. At least 19% of the children with GP undergo bone scans for evaluation of their pain [30]. When patients have typical clinical characteristics there is no need to do any laboratory or imaging tests. However, if the symptoms are atypical, the diagnosis of GP should not be assumed without evaluating other causes. Treatment The most important intervention is to explain the natural benign course of the GP, thus decreasing anxiety and fear. Despite the benign prognosis, GP may have an impact on the child and family, especially among children with frequent nocturnal attacks. Comforting, local 7
9 massage therapy during pain episodes or analgesics is used. Some children need to chronically use medications, especially acetaminophen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID). In our study 52% of the children used medications to relieve their pain [14]. Occasionally nighttime use of a long acting analgesic, such as naproxen, may prevent episodes and can be used on days when parents predict an episode may occur or daily in children with frequent awakenings. The calcium intake in our GP patients with lower bone strength group was relatively low [18]. It is possible that a diet enriched in calcium and vitamin D might affect bone status and pain episodes, but this theory was not investigated. We are not aware of any studies that have found an association between physical fitness and GP attacks. Our findings of lower pain thresholds in children with GP may have therapeutic implications, such as behavioral intervention to decrease pain sensitivity (including cognitive behavioral therapy), as well as physical activity programs to increase fitness, which may decrease painful episodes. Physicians should be aware of the complete family psychological environment when treating children with GP and other non-inflammatory pain syndromes. Other interventions shown to be effective in small controlled studies include in-shoe inserts such as triplane wedges or orthotics, especially in children with pronated foot posture [22], and a muscle stretching exercise program [31]. Conclusions and future studies GP is very common and easy to diagnose once the typical clinical characteristics are presented. The natural history is benign with disappearance of most attacks of pain by adolescence. However it is not clear whether some of these children develop symptoms of other non- 8
10 inflammatory pain syndromes. It would be important to progressively follow the pain thresholds of children with GP and to correlate the findings with their symptoms. Long-term outcome studies are suggested to investigate whether the children with GP who has a lower pain threshold, are prone to develop other non-inflammatory pain syndromes in the musculoskeletal or other systems later in adolescence or adulthood. If many children with GP do develop noninflammatory pain syndromes later in adolescence or adulthood, a trial of early intervention, with cognitive behavioral therapy for example, may prevent progression to other syndromes later in life. Further studies into the pathogenesis of GP should be performed. Further larger and genetically homogenous studies are required to determine whether the statistically significant findings of decreased bone SOS in our series of children with GP have clinical implication Abbreviations GP: growing pains, NSAID: non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions Both authors contributed to the collection of data and references, drafting and revising this manuscript. Both have read and approve the final manuscript. 9
11 References 1. Passo MH. Aches and limb pain. Pediatr Clin North Am 1982, 29: Bowyer SL, Hollister JR. Limb pain in childhood. Pediatr Clin North Am 1984, 34: De Inocencio J. Epidemiology of musculoskeletal pain in primary care. Arch Dis Child 2004, 89: Naish JM, Apley J. Growing pains : a clinical study of non-arthritis limb pains in children. Arch Dis Child 1951, 26: Brenning R. Growing pain. Acta Soc Med Ups 1960, 65: Oster J, Nielson A. Growing pain: a clinical investigation of a school population. Acta Paediatr Scand 1972, 61: Evans AM, Scutter SD. Prevalence of growing pains in young children. J Pediatr 2004, 145: Calabro JJ, Wachtel AE, Holgerson WB, Repice MM. Growing pains: fact or fiction? Postgrad Med 1976, 59: Weiner SR. Growing pains. Am Fam Physician 1983, 27: Peterson H. Growing pains. Pediatr Clin North Am1986, 33: Leung AKS, Robson WLM. Growing pains. Can Fam Physician 1991, 37: Manners P. Are growing pains a myth? Aust Fam Physician 1999, 28: Atar D, Lehman WB, Grant AD. Growing pains. Orthop Rev 1991, 20: Hashkes P, Friedland O, Jaber L, Cohen A, Wolach B, Uziel Y. Children with growing pains have decreased pain threshold. J Rheumatol 2004, 31:
12 15. Buskila D, Press J, Gedalia A, Klein M, Neuman L, Boehm R, Sukenik S. Assessment of nonarticular tenderness and prevalence of fibromyalgia in children. J Rheumatol 1993, 20: Yunus MB, Masi AT. Juvenile primary fibromyalgia syndrome. A clinical study of thirty-three patients and matched normal controls. Arthritis Rheum 1985, 28: Buskila D, Neuman L, Hershman E, Gedalia A, Press J, Sukenik S. Fibromyalgia syndrome in children an outcome study. J Rheumatol 1995, 22: Friedland O, Hashkes PJ, Jaber L, Cohen A, Eliakim A, Wolach B, Uziel Y: Decreased bone strength in children with growing pains as measured by quantitative ultrasound. J Rheumatol 2005, 32: Aromaa M, Sillanpaa M, Rautava P, Helenius H. Pain experience of children with headache and their families: a controlled study. Pediatrics 2000, 106: Hashkes PJ, Gorenberg M, Oren V, Friedland O, Uziel Y. Growing pains in children are not associated with changes in vascular perfusion patterns in painful regions. Clin Rheumatol 2005, 24: Gedalia A, Press J, Klein M, Buskila D. Joint hypermobility and fibromyalgia in schoolchildren. Ann Rheum Dis 1993, 52: Evans AM. Relationship between growing pains and foot posture in children: single case experimental designs in clinical practice. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 2003, 93: Apley J. Clinical canutes: A philosophy of pediatrics. Proc Royal Soc Med 1970, 63:
13 24. Oster J. Recurrent abdominal pain, headache and limb pain in children and adolescents. Pediatrics 1972, 50: Oberklaid F, Amos D, Liu C, Jarman F, Sanson A, Prior M. "Growing Pains": clinical and behavioral correlates in a community sample. J Dev Behav Pediatr 1997, 18: Sherry DD. An overview of amplified musculoskeletal pain syndromes. J Rheumatol 2000, 27 (Suppl 58): Palermo TM. Impact of recurrent and chronic pain on child and family daily functioning: a critical review of the literature. J Dev Behav Pediatr 2000, 21: Uziel Y, Friedland O, Jaber L, Press J, Buskila D, Wolach B, Hashkes PJ. Living with children with growing pains: How does it affect the parents? J Musculoskel Pain, in press. 29. Rajaram SS, Walters AS, England SJ, Mehta D, Nizam F. Some children with growing pain may actually have restless leg syndrome. Sleep 2004, 27: Macarthur C, Wright JG, Srivastava R, Rosser W, Feldman W. Variability in physicians reported ordering and perceived reassurance value of diagnostic tests in children with growing pains. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 1996, 150: Baxter MP, Dulberg C. Growing pains in childhood: a proposal for treatment. J Pediatr Orthop 1988,8:
Assessment of Growing Pain and Its Risk Factors in School Children
 American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2016; 4(5): 151-155 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajcem doi: 10.11648/j.ajcem.20160405.17 ISSN: 2330-8125 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8133 (Online)
American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2016; 4(5): 151-155 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ajcem doi: 10.11648/j.ajcem.20160405.17 ISSN: 2330-8125 (Print); ISSN: 2330-8133 (Online)
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Pediatric rheumatology. Joint hypermobility and growing pains in school children
 Pediatric rheumatology Joint hypermobility and growing pains in school children V. Viswanathan, R.P. Khubchandani Pediatric Rheumatology Clinic, Jaslok Hospital & Research Center, Gopalrao Deshmukh Marg,
Pediatric rheumatology Joint hypermobility and growing pains in school children V. Viswanathan, R.P. Khubchandani Pediatric Rheumatology Clinic, Jaslok Hospital & Research Center, Gopalrao Deshmukh Marg,
Growing Pains in Children 1.0 Contact Hour Presented by: CEU Professor
 Growing Pains in Children 1.0 Contact Hour Presented by: CEU Professor 7 www.ceuprofessoronline.com Copyright 8 2008 The Magellan Group, LLC All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these
Growing Pains in Children 1.0 Contact Hour Presented by: CEU Professor 7 www.ceuprofessoronline.com Copyright 8 2008 The Magellan Group, LLC All Rights Reserved. Reproduction and distribution of these
Written by Tricia Arndt, DC, DACCP Thursday, 01 March :00 - Last Updated Wednesday, 19 March :00
 Ouch! My legs hurt, Mommy! Have you ever had your child wake up in the middle of the night complaining of leg pains? Do you remember having them as a child? These are commonly referred to as growing pains
Ouch! My legs hurt, Mommy! Have you ever had your child wake up in the middle of the night complaining of leg pains? Do you remember having them as a child? These are commonly referred to as growing pains
In-toeing, Out-toeing, Growing Pains, Bowlegs, Knock-Knees and Flat Feet
 Jeffrey B. Neustadt, M.D. Scott W. Beck, M.D. Gregory V. Hahn, M.D. Drew E. Warnick, M.D. Paul L. Benfanti, M.D. Lee G. Phillips, M.D. Daniel C. Bland, M.D. Common Benign Orthopaedic Conditions In-toeing,
Jeffrey B. Neustadt, M.D. Scott W. Beck, M.D. Gregory V. Hahn, M.D. Drew E. Warnick, M.D. Paul L. Benfanti, M.D. Lee G. Phillips, M.D. Daniel C. Bland, M.D. Common Benign Orthopaedic Conditions In-toeing,
Growing pains: Twin family study evidence for genetic susceptibility and a genetic relationship with restless legs syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Growing pains: Twin family study evidence for genetic susceptibility and a genetic relationship with restless legs syndrome D. Champion 1,2, S. Pathirana 1,2, *, C. Flynn 1,2, *, A. Taylor
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Growing pains: Twin family study evidence for genetic susceptibility and a genetic relationship with restless legs syndrome D. Champion 1,2, S. Pathirana 1,2, *, C. Flynn 1,2, *, A. Taylor
PAIN SYNDROMES
 www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it PAIN SYNDROMES 1) Fibromyalgia Syndrome Synonyms Fibromyalgia is a diffuse idiopathic musculoskeletal pain syndrome. Fibromyalgia is a disease causing widespread musculoskeletal
www.pediatric-rheumathology.printo.it PAIN SYNDROMES 1) Fibromyalgia Syndrome Synonyms Fibromyalgia is a diffuse idiopathic musculoskeletal pain syndrome. Fibromyalgia is a disease causing widespread musculoskeletal
National Horizon Scanning Centre. Pregabalin (Lyrica) for fibromyalgia. September 2007
 Pregabalin (Lyrica) for fibromyalgia September 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to be a definitive
Pregabalin (Lyrica) for fibromyalgia September 2007 This technology summary is based on information available at the time of research and a limited literature search. It is not intended to be a definitive
What Are Sports Injuries?
 What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
What Should I Do if I Get Injured? Never try to "work through" the pain of a sports injury. Stop playing or exercising when you feel pain. Playing or exercising more only causes more harm. Some injuries
Medial Tibial Stress Syndrom
 Medial Tibial Stress Syndrom Ministry of Health:- Hong Kong January 2007 Tibial Fasciitis, Shin Splints Tibial Stress Fracture Definition Overuse, Inflammatory condition Most common cause of lower limb
Medial Tibial Stress Syndrom Ministry of Health:- Hong Kong January 2007 Tibial Fasciitis, Shin Splints Tibial Stress Fracture Definition Overuse, Inflammatory condition Most common cause of lower limb
Plantar fasciitis occurs when the strong band of tissue that supports the arch of your foot becomes irritated and inflamed.
 Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
Plantar Fasciitis and Bone Spurs Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of pain on the bottom of the heel. Approximately 2 million patients are treated for this condition every year.
Arthritis. that affects the joints.
 Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
Arthritis that affects the joints. The word arthritis literally means inflammation of the joints. Though joint inflammation is often a symptom, rather than a specific diagnosis itself, the term arthritis
This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702).
 1 of 5 17 Oct 2015 11:04 AM This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702). Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of
1 of 5 17 Oct 2015 11:04 AM This article is also available in Spanish: Fascitis plantar y protuberancias óseas (topic.cfm?topic=a00702). Plantar fasciitis (fashee-eye-tiss) is the most common cause of
Chronic Pain. For other titles published in this series, go to
 Chronic Pain For other titles published in this series, go to www.springer.com/series/7633 Dawn A. Marcus, M.D. Chronic Pain A Primary Care Guide to Practical Management Second Edition Dawn A. Marcus,
Chronic Pain For other titles published in this series, go to www.springer.com/series/7633 Dawn A. Marcus, M.D. Chronic Pain A Primary Care Guide to Practical Management Second Edition Dawn A. Marcus,
What are the symptoms of plantar fasciitis? The main symptoms of plantar fasciitis include: What causes plantar fasciitis?
 Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a condition which can cause heel pain. It happens when the strong band of tissue on the sole of your foot (fascia) becomes irritated, after repetitive use or due
Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a condition which can cause heel pain. It happens when the strong band of tissue on the sole of your foot (fascia) becomes irritated, after repetitive use or due
Make sure you have properly fitting running shoes and break these in gradually. Never wear new running shoes for a race or a long run.
 Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Common Running Injuries We are delighted that you have decided to run in the next Bath Half Marathon and very much hope that you have good running shoes, undertake a regular training programme and don
Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain
 PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
PATIENT INFORMATION Plantar Fasciitis and Heel Pain What is plantar fasciitis? Heel pain and plantar fasciitis Plantar fasciitis causes pain under your heel. It usually goes in time. Treatment may speed
HealthPartners Inspire Special Needs Basic Care Clinical Care Planning and Resource Guide CHRONIC PAIN
 The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke), Mount Sinai Beth Israel
The following evidence based guideline was used in developing this clinical care guide: National Institute of Health (NIH National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke), Mount Sinai Beth Israel
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME Description Maintain appropriate conditioning: The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the
The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database
 Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Allergic Rhinitis: Effects on Quality of Life and Co-morbid Conditions
 Disclosures : Effects on Quality of Life and Co-morbid Conditions Nycomed Pharmaceutical Sepracor Pharmaceutical Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine University of Tennessee
Disclosures : Effects on Quality of Life and Co-morbid Conditions Nycomed Pharmaceutical Sepracor Pharmaceutical Michael S. Blaiss, MD Clinical Professor of Pediatrics and Medicine University of Tennessee
Pattern of Anxiety and Depression among Secondary School. Students in Riyadh, KSA
 The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 1, No.8, DIP: C03132V3I12015 http://www.ijip.in October December, 2015 Pattern of Anxiety and Depression
The International Journal of Indian Psychology ISSN 2348-5396 (e) ISSN: 2349-3429 (p) Volume 3, Issue 1, No.8, DIP: C03132V3I12015 http://www.ijip.in October December, 2015 Pattern of Anxiety and Depression
Dr. K. Brindha, M.D PG ESI PGIMSR, K.K Nagar, Chennai
 Dr. K. Brindha, M.D PG ESI PGIMSR, K.K Nagar, Chennai Case History 9 year old boy presented with a 3 week history of: Swelling of major lower limb joints Progression was additive (right ankle followed
Dr. K. Brindha, M.D PG ESI PGIMSR, K.K Nagar, Chennai Case History 9 year old boy presented with a 3 week history of: Swelling of major lower limb joints Progression was additive (right ankle followed
Case report. Open Access. Abstract
 Open Access Case report Acute posterior neck pain in adult: a case series Yasuhiro Homma*, Akira Itoi, Tomoya Muta, Yoshio Shimamura, Kiyohito Naito, Atsuhiko Mogami, Osamu Obayashi, Colin G Murphy and
Open Access Case report Acute posterior neck pain in adult: a case series Yasuhiro Homma*, Akira Itoi, Tomoya Muta, Yoshio Shimamura, Kiyohito Naito, Atsuhiko Mogami, Osamu Obayashi, Colin G Murphy and
BACK PAIN. Spare 5 minutes to find out how to cope with back pain
 BACK PAIN Spare 5 minutes to find out how to cope with back pain You always managed your responsibilities as a wife, mother, sister, daughter, daughter in law, friend, boss, and colleague indeed managed
BACK PAIN Spare 5 minutes to find out how to cope with back pain You always managed your responsibilities as a wife, mother, sister, daughter, daughter in law, friend, boss, and colleague indeed managed
ILIOTIBIAL BAND SYNDROME
 Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Dr. S. Matthew Hollenbeck, MD Kansas Orthopaedic Center, PA 7550 West Village Circle, Wichita, KS 67205 2450 N Woodlawn, Wichita, KS 67220 Phone: (316) 838-2020 Fax: (316) 838-7574 Description ILIOTIBIAL
Up Date on TMD WHAT IS TMD? Temporomandibular Disorders (TMD)*: Donald Nixdorf DDS, MS
 Up Date on TMD Donald Nixdorf DDS, MS Associate Professor Division of TMD and Orofacial Pain WHAT IS TMD? Temporomandibular Disorders (TMD)*: MUSCLE and JOINT DISORDERS * Temporomandibular Muscle and Joint
Up Date on TMD Donald Nixdorf DDS, MS Associate Professor Division of TMD and Orofacial Pain WHAT IS TMD? Temporomandibular Disorders (TMD)*: MUSCLE and JOINT DISORDERS * Temporomandibular Muscle and Joint
Sleep History Questionnaire. Sleep Disorders Center Duke University Medical Center. General Information. Age: Sex: F M (select one)
 Sleep History Questionnaire Sleep Disorders Center Duke University Medical Center Part I: General Information Name: Address: Date: Phone: Age: Sex: F M (select one) Education (years of school): Occupation:
Sleep History Questionnaire Sleep Disorders Center Duke University Medical Center Part I: General Information Name: Address: Date: Phone: Age: Sex: F M (select one) Education (years of school): Occupation:
Understanding treatments for knee pain.
 Understanding treatments for knee pain. 2 Table of Contents Why does my knee hurt? 2 Diagnosis 4 Nonsurgical treatments 5 Surgical treatments 9 Arthroscopy Partial Knee Replacement 10 What is knee replacement?
Understanding treatments for knee pain. 2 Table of Contents Why does my knee hurt? 2 Diagnosis 4 Nonsurgical treatments 5 Surgical treatments 9 Arthroscopy Partial Knee Replacement 10 What is knee replacement?
Palindromic rheumatism
 1 What is palindromic rheumatism? The term palindromic rheumatism (also known as palindromic arthritis ) describes a form of joint pain that comes and goes in cycles or episodes, generally starting in
1 What is palindromic rheumatism? The term palindromic rheumatism (also known as palindromic arthritis ) describes a form of joint pain that comes and goes in cycles or episodes, generally starting in
A patient s guide to. Inferior Heel Pain
 A patient s guide to Inferior Heel Pain The Foot & Ankle Unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital is made up of a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of four specialist orthopaedic foot and
A patient s guide to Inferior Heel Pain The Foot & Ankle Unit at the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital is made up of a multi-disciplinary team. The team consists of four specialist orthopaedic foot and
Anterior knee pain.
 Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
Anterior knee pain What are the symptoms? Anterior knee pain is very common amongst active adolescents and athletes participating in contact sports. It is one of the most common problems/injuries seen
FIBROMYALGIA. Howard L. Feinberg, D.O. F.A.C.O.I., F.A.C.R. OPSC San Diego 2017
 FIBROMYALGIA Howard L. Feinberg, D.O. F.A.C.O.I., F.A.C.R. OPSC San Diego 2017 Sir William Osler When a patient with arthritis comes in the front door, I try to go out the back door. FEINBERG S COROLLARY
FIBROMYALGIA Howard L. Feinberg, D.O. F.A.C.O.I., F.A.C.R. OPSC San Diego 2017 Sir William Osler When a patient with arthritis comes in the front door, I try to go out the back door. FEINBERG S COROLLARY
Not Sleeping Well? Chronic physical conditions. There May Be a Medical Cause. Diabetes. Heartburn
 Not Sleeping Well? There May Be a Medical Cause People who feel they sleep perfectly well may still be troubled by excessive daytime sleepiness because of a variety of underlying medical illnesses. A sleep
Not Sleeping Well? There May Be a Medical Cause People who feel they sleep perfectly well may still be troubled by excessive daytime sleepiness because of a variety of underlying medical illnesses. A sleep
INSOMNIAS. Stephan Eisenschenk, MD Department of Neurology
 INSOMNIAS INSOMNIAS General criteria for insomnia A. Repeated difficulty with sleep initiation, duration, consolidation or quality. B. Adequate sleep opportunity, persistent sleep difficulty and associated
INSOMNIAS INSOMNIAS General criteria for insomnia A. Repeated difficulty with sleep initiation, duration, consolidation or quality. B. Adequate sleep opportunity, persistent sleep difficulty and associated
Fibromyalgia , The Patient Education Institute, Inc. id Last reviewed: 03/12/2017 1
 Fibromyalgia Introduction Fibromyalgia is a common condition that causes pain and fatigue in the muscles, joints, ligaments and tendons. Fibromyalgia affects about 3 to 6% of people worldwide. Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia Introduction Fibromyalgia is a common condition that causes pain and fatigue in the muscles, joints, ligaments and tendons. Fibromyalgia affects about 3 to 6% of people worldwide. Fibromyalgia
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis
 Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis What is polymyalgia rheumatica? Polymyalgia rheumatica is a rheumatic disorder associated with moderate-to-severe musculoskeletal pain and stiffness in the
Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis What is polymyalgia rheumatica? Polymyalgia rheumatica is a rheumatic disorder associated with moderate-to-severe musculoskeletal pain and stiffness in the
ChilDhOOD Obesity. By Brandon A. Macy, DPM, DABPO. 42 Pedorthic Footcare Association
 ChilDhOOD Obesity By Brandon A. Macy, DPM, DABPO 2 Pedorthic Footcare Association www.pedorthics.org CEP Is your patient suffering the ill effects of having been overweight as a child? Perhaps, and perhaps
ChilDhOOD Obesity By Brandon A. Macy, DPM, DABPO 2 Pedorthic Footcare Association www.pedorthics.org CEP Is your patient suffering the ill effects of having been overweight as a child? Perhaps, and perhaps
Osteoarthritis of the neck
 1 What is osteoarthritis of the neck? Osteoarthritis (OA) of the neck affects the bones at the top of the spine. It is also called cervical spondylosis. OA of the neck occurs when the springy cushioning
1 What is osteoarthritis of the neck? Osteoarthritis (OA) of the neck affects the bones at the top of the spine. It is also called cervical spondylosis. OA of the neck occurs when the springy cushioning
Periodic Fever With Apthous Pharyngitis Adenitis (PFAPA)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/za_gb/intro Periodic Fever With Apthous Pharyngitis Adenitis (PFAPA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS PFAPA 1.1 What is it? PFAPA stands for Periodic Fever Adenitis Pharyngitis
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/za_gb/intro Periodic Fever With Apthous Pharyngitis Adenitis (PFAPA) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS PFAPA 1.1 What is it? PFAPA stands for Periodic Fever Adenitis Pharyngitis
What Is Back Pain? Can Back Pain Be Prevented? When Should I See a Doctor for Pain? How Is Back Pain Diagnosed?
 What Is Back Pain? Back pain can also occur with some conditions and diseases, such as: Scoliosis Spondylolisthesis Arthritis Spinal stenosis Pregnancy Kidney stones Infections Endometriosis Fibromyalgia.
What Is Back Pain? Back pain can also occur with some conditions and diseases, such as: Scoliosis Spondylolisthesis Arthritis Spinal stenosis Pregnancy Kidney stones Infections Endometriosis Fibromyalgia.
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation.
 I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
I have no financial relationships to disclose. I will not discuss investigational use of medication in my presentation. In 1962, Bille published landmark epidemiologic survey of headache among 9,000 school
Fibromyalgia By Don L. Goldenberg
 Fibromyalgia By Don L. Goldenberg Fibromyalgia - Southern Cross NZ - Fibromyalgia is characterised by long-term muscle pain and fatigue and is most commonly diagnosed in women aged 25 to 55 years: causes,
Fibromyalgia By Don L. Goldenberg Fibromyalgia - Southern Cross NZ - Fibromyalgia is characterised by long-term muscle pain and fatigue and is most commonly diagnosed in women aged 25 to 55 years: causes,
Orthotic Management in. Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Nothing to Disclose. Objectives. JIA-Disease Types 10/29/2013. Evidence-Based References
 Orthotic Management in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis usan E. Klepper, PT, PhD Program in Physical Therapy Columbia University New York, NY Nothing to Disclose Evidence-Based References Powell M, eid M,
Orthotic Management in Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis usan E. Klepper, PT, PhD Program in Physical Therapy Columbia University New York, NY Nothing to Disclose Evidence-Based References Powell M, eid M,
Acute Low Back Pain. North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
Acute Low Back Pain North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Acute Low Back Pain? Acute low back pain (LBP) is defined as low back pain present for up to six weeks. It may be experienced
There are clues to help to decide if the bellyache is a medical problem:
 Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
Bellyaches in Children Pediatric and Adolescent Gastrointestinal Motility & Pain Program Department of Pediatrics, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center, New Orleans, Louisiana By: Paul Hyman,
Pediatric fibromyalgia
 REVIEW Reumatismo, 2012; 64 (4): 230-237 Pediatric fibromyalgia D. Buskila 1, J. Ablin 2 1 Soroka Medical Center, Beer, Sheva, Israel; 2 Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Israel summary Fibromyalgia (FM)
REVIEW Reumatismo, 2012; 64 (4): 230-237 Pediatric fibromyalgia D. Buskila 1, J. Ablin 2 1 Soroka Medical Center, Beer, Sheva, Israel; 2 Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center, Israel summary Fibromyalgia (FM)
Kids Get Chronic Pain Too
 Kids Get Chronic Pain Too DR. Kathleen Cooke Anaesthetist and pain medicine specialist, St Vincent s Hospital, Qld A holistic plan is essential, including physical, emotional and social support, to manage
Kids Get Chronic Pain Too DR. Kathleen Cooke Anaesthetist and pain medicine specialist, St Vincent s Hospital, Qld A holistic plan is essential, including physical, emotional and social support, to manage
Medically unexplained physical symptoms in children in a non-specialist paediatric setting
 Medically unexplained physical symptoms in children in a non-specialist paediatric setting H Perera 1, ASG Asiri 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2007; 36: 102-106 (Key words: somatization, medically
Medically unexplained physical symptoms in children in a non-specialist paediatric setting H Perera 1, ASG Asiri 2 Sri Lanka Journal of Child Health, 2007; 36: 102-106 (Key words: somatization, medically
Fran Pulver, MD - PM&R Laurie Bell, PT - Physical Therapy Gregg Weidner, MD - Anesthesia Steven Severyn, MD, MBA, MSS - Anesthesia
 Fran Pulver, MD - PM&R Laurie Bell, PT - Physical Therapy Gregg Weidner, MD - Anesthesia Steven Severyn, MD, MBA, MSS - Anesthesia Case Presentation-Fibromyalgia 30 year old female Chief complaint of back
Fran Pulver, MD - PM&R Laurie Bell, PT - Physical Therapy Gregg Weidner, MD - Anesthesia Steven Severyn, MD, MBA, MSS - Anesthesia Case Presentation-Fibromyalgia 30 year old female Chief complaint of back
Plantar fasciopathy (PFs)
 Plantar fasciopathy (PFs) 2016. 04. 30. Jung-Soo Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Anatomy of
Plantar fasciopathy (PFs) 2016. 04. 30. Jung-Soo Lee, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea Anatomy of
Hafizullah Azizi M.D.
 Hafizullah Azizi M.D. Eating disorders Feeding and Eating Disorders of Infancy and Early Childhood and Obesity Anorexia Nervosa Bulimia Nervosa EDNOS Binge Eating Disorder Purging Disorder Night Eating
Hafizullah Azizi M.D. Eating disorders Feeding and Eating Disorders of Infancy and Early Childhood and Obesity Anorexia Nervosa Bulimia Nervosa EDNOS Binge Eating Disorder Purging Disorder Night Eating
Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents
 A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Mental Health First Aid at a Glance
 Mental Health First Aid at a Glance Candice M. Haines, LCPC Program Supervisor Mental Health First Aid Instructor Pilsen Wellness Center chaines@pilsenmh.org Overview Address myths vs facts Warning signs
Mental Health First Aid at a Glance Candice M. Haines, LCPC Program Supervisor Mental Health First Aid Instructor Pilsen Wellness Center chaines@pilsenmh.org Overview Address myths vs facts Warning signs
Leg Posture in Children
 Leg Posture in Children Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Leg Posture in Children A guide for parents This leaflet has been produced to provide information on the normal postural variation of
Leg Posture in Children Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Leg Posture in Children A guide for parents This leaflet has been produced to provide information on the normal postural variation of
Bunion Surgery. Patient information Leaflet
 Bunion Surgery Patient information Leaflet April 2017 What is a bunion? A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot at the base of your big toe (see figure 1). This may be an isolated problem but
Bunion Surgery Patient information Leaflet April 2017 What is a bunion? A bunion is a bony lump on the side of your foot at the base of your big toe (see figure 1). This may be an isolated problem but
SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE
 SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE 02 Changes in our lives can be stressful and leaving school and moving into the
SCOTTISH MUSCLE NETWORK DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY TRANSITION SOME USEFUL THINGS TO KNOW ABOUT HEALTH AROUND ADOLESCENCE 02 Changes in our lives can be stressful and leaving school and moving into the
Participant ID: If you had no responsibilities, what time would your body tell you to go to sleep and wake up?
 What does your sleep look like on a typical week? Total Sleep Time: Bedtime:, Sleep onset latency:, Number of Awakenings:, Wake time after sleep onset:, Rise time:, Out of bed:, Naps:? Notes: Is your sleep
What does your sleep look like on a typical week? Total Sleep Time: Bedtime:, Sleep onset latency:, Number of Awakenings:, Wake time after sleep onset:, Rise time:, Out of bed:, Naps:? Notes: Is your sleep
BACK SPASM. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
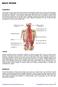 BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
BACK SPASM Explanation A back spasm occurs when the muscles of the back involuntarily contract due to injury in the musculature of the back or inflammation in the structural spine region within the discs
18 FIBROMYALGIA. What is it? What do people experience?
 18 FIBROMYALGIA What is it? Fibromyalgia is a common health problem in which individuals experience chronic, widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness. The American College of Rheumatology
18 FIBROMYALGIA What is it? Fibromyalgia is a common health problem in which individuals experience chronic, widespread musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, and tenderness. The American College of Rheumatology
What Is Back Pain? Fast Facts: An Easy-to-Read Series of Publications for the Public. Who Gets Back Pain? What Are the Causes of Back Pain?
 Back pain can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain that makes it hard to move. It can start quickly if you fall or lift something too heavy, or it can get worse slowly. Who Gets Back
Back pain can range from a dull, constant ache to a sudden, sharp pain that makes it hard to move. It can start quickly if you fall or lift something too heavy, or it can get worse slowly. Who Gets Back
Headaches in Children and Adolescents. Paul Shillito
 Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
Headaches in Children and Adolescents Paul Shillito Topics For Discussion What s different about childhood migraine Chronic daily headache (CDH) Tumours and other things to worry about Management of childhood
SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT
 C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
DEPRESSION. There are a couple of kinds, or forms. The most common are major depression and dysthymic disorder.
 DEPRESSION OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1.list and describe several kinds of depression, 2.discuss the signs of depression, and 3.relate the treatment of depression. INTRODUCTION
DEPRESSION OBJECTIVES: At the end of this class, you will be able to: 1.list and describe several kinds of depression, 2.discuss the signs of depression, and 3.relate the treatment of depression. INTRODUCTION
9/2/2010. Welcome. Nationwide Children s Hospital. Follow the Journey of Children with Chronic Pain. ASPMN Conference September 25, 2010
 Follow the Journey of Children with Chronic Pain Sharon Wrona RN-BC, MS, PNP ASPMN Conference September 25, 2010 Welcome Nationwide Children s Hospital 1 Chronic Pain in Children Chronic pain affects approximately
Follow the Journey of Children with Chronic Pain Sharon Wrona RN-BC, MS, PNP ASPMN Conference September 25, 2010 Welcome Nationwide Children s Hospital 1 Chronic Pain in Children Chronic pain affects approximately
16 year old with Disabling Chest Wall Pain after Thoracoscopic Talc Pleurodesis for Treatment of Recurrent Spontaneous Pneumothoraces
 16 year old with Disabling Chest Wall Pain after Thoracoscopic Talc Pleurodesis for Treatment of Recurrent Spontaneous Pneumothoraces Moderators: Kendra Grim, MD, Robert T. Wilder, MD, PhD Institution:
16 year old with Disabling Chest Wall Pain after Thoracoscopic Talc Pleurodesis for Treatment of Recurrent Spontaneous Pneumothoraces Moderators: Kendra Grim, MD, Robert T. Wilder, MD, PhD Institution:
Sleep and epilepsy. Light sleep - your eye movements stop, your heart rate slows, and your body cools down.
 Sleep and epilepsy This information looks at the connection between epilepsy, seizures and medicines and sleep. It also gives hints and tips for better sleep and better seizure control if seizures are
Sleep and epilepsy This information looks at the connection between epilepsy, seizures and medicines and sleep. It also gives hints and tips for better sleep and better seizure control if seizures are
Brisbin Family Chiropractic
 Information reviewed with patient: Dr. Initials Today s Date Brisbin Family Chiropractic Name: Sex: Male Female Address: City: Postal Code: Home Ph# Work# Ext# Cell# Preferred number (circle one) Home
Information reviewed with patient: Dr. Initials Today s Date Brisbin Family Chiropractic Name: Sex: Male Female Address: City: Postal Code: Home Ph# Work# Ext# Cell# Preferred number (circle one) Home
Will ibuprofen help leg cramps
 Will ibuprofen help leg cramps Search 28-2-2018 When suffering from a severe muscle cramp, ibuprofen helps ease the discomfort, according to Healthline. A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory such as Advil or.
Will ibuprofen help leg cramps Search 28-2-2018 When suffering from a severe muscle cramp, ibuprofen helps ease the discomfort, according to Healthline. A nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory such as Advil or.
Impact of Chronic Pain
 BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Pain Healthcare costs 6 Sleep disturbances 2 Depression 2 Presenteeism and absenteeism 4,5 Chronic pain 1 Anxiety 2 Disability 4 Decreased quality of life 3
BURDEN OF ILLNESS Overview Impact of Chronic Pain Healthcare costs 6 Sleep disturbances 2 Depression 2 Presenteeism and absenteeism 4,5 Chronic pain 1 Anxiety 2 Disability 4 Decreased quality of life 3
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints)
 MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
MEDIAL TIBIAL STRESS SYNDROME (Shin Splints) Description Expected Outcome Shin splints is a term broadly used to describe pain in the lower extremity brought on by exercise or athletic activity. Most commonly
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline. Guideline for the child with possible arthritis (joint swelling/pain, loss of function)
 Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Guideline for the child with possible arthritis (joint swelling/pain, loss of function) Definition: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is defined as arthritis
Department of Paediatrics Clinical Guideline Guideline for the child with possible arthritis (joint swelling/pain, loss of function) Definition: Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is defined as arthritis
JUVENILE PRIMARY FIBROMYALGIA SYNDROME
 138 JUVENILE PRIMARY FIBROMYALGIA SYNDROME A Clinical Study of Thirty-Three Patients and Matched Normal Controls MUHAMMAD B. YUNUS and ALFONSE T. MAS1 Primary fibromyalgia syndrome (PFS) is a common and
138 JUVENILE PRIMARY FIBROMYALGIA SYNDROME A Clinical Study of Thirty-Three Patients and Matched Normal Controls MUHAMMAD B. YUNUS and ALFONSE T. MAS1 Primary fibromyalgia syndrome (PFS) is a common and
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome
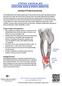 Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
Iliotibial (IT) Band Syndrome The iliotibial band is the tendon attachment of hip muscles into the upper leg (tibia) just below the knee to the outer side of the front of the leg. Where the tendon passes
A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts
 A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts 1436 Exchange Street Middlebury, VT 05753 Phone: 802-388-3194 Fax: 802-388-4881 cvo@champlainvalleyortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A new website is underconstruction with the latesest updated information. Please us ethe below as a general guide only.
 Important Note A new website is underconstruction with the latesest updated information. Please us ethe below as a general guide only. The Below has become of historical interest only. Reproduced verbatim
Important Note A new website is underconstruction with the latesest updated information. Please us ethe below as a general guide only. The Below has become of historical interest only. Reproduced verbatim
Club Feet, Flat Feet, Bow Legs, and Knock-Knees
 Club Feet, Flat Feet, Bow Legs, and Knock-Knees CHAPTER 11 113 WHAT IS A DEFORMITY AND WHAT IS? Sometimes parents worry because they think a part of their child s body is abnormal or deformed. But in small
Club Feet, Flat Feet, Bow Legs, and Knock-Knees CHAPTER 11 113 WHAT IS A DEFORMITY AND WHAT IS? Sometimes parents worry because they think a part of their child s body is abnormal or deformed. But in small
STRESS KUON? AUR KAISE KARE MANAGE? Dr. NAYNA KADAM (Dept. Of Engg. Mathematics)
 STRESS KUON? AUR KAISE KARE MANAGE? Dr. NAYNA KADAM (Dept. Of Engg. Mathematics) Outline What is Stress? Causes of Stress Check your anxiety level Symptoms of stress Stress Management What is Stress? Stress
STRESS KUON? AUR KAISE KARE MANAGE? Dr. NAYNA KADAM (Dept. Of Engg. Mathematics) Outline What is Stress? Causes of Stress Check your anxiety level Symptoms of stress Stress Management What is Stress? Stress
Is Sodium Oxybate a Safe and Effective Treatment for Patients with Fibromyalgia
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2012 Is Sodium Oxybate a Safe and Effective
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2012 Is Sodium Oxybate a Safe and Effective
The role of benign joint hypermobility in the pain experience in Juvenile Fibromyalgia: an observational study
 Ting et al. Pediatric Rheumatology 2012, 10:16 RESEARCH Open Access The role of benign joint hypermobility in the pain experience in Juvenile Fibromyalgia: an observational study Tracy V Ting 1*, Philip
Ting et al. Pediatric Rheumatology 2012, 10:16 RESEARCH Open Access The role of benign joint hypermobility in the pain experience in Juvenile Fibromyalgia: an observational study Tracy V Ting 1*, Philip
CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT PLANS
 CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT PLANS C H A P T E R 2 EXPERIENCES OF CLIENT AND CLINICIAN PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDER: EXPERIENCES OF CLIENT AND CLINICIAN Psychologist: Healthcare professional offering psychological
CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT PLANS C H A P T E R 2 EXPERIENCES OF CLIENT AND CLINICIAN PSYCHOLOGICAL DISORDER: EXPERIENCES OF CLIENT AND CLINICIAN Psychologist: Healthcare professional offering psychological
Fibromyalgia: Current Trends and Concepts
 Fibromyalgia: Current Trends and Concepts Dr. Brian Kahan Fellow American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Diplomat American Academy of Pain Medicine American College of Rheumatology (ACR)
Fibromyalgia: Current Trends and Concepts Dr. Brian Kahan Fellow American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation Diplomat American Academy of Pain Medicine American College of Rheumatology (ACR)
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis
 Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Overcoming joint pain and arthritis The 9 things you need to know to get moving again This guide provides an overview about managing joint pain, stiffness and swelling without sacrificing your quality
Pain Control After Surgery. Patient Information
 Pain Control After Surgery Patient Information What is Pain? Pain is an uncomfortable feeling that tells you something may be wrong in your body. Pain is your body s way of sending a warning to your brain.
Pain Control After Surgery Patient Information What is Pain? Pain is an uncomfortable feeling that tells you something may be wrong in your body. Pain is your body s way of sending a warning to your brain.
Why am I so Tired? Cancer Related Fatigue. Rose Bell, PhD, ARNP, AOCNP Northwest Medical Specialties
 Why am I so Tired? Cancer Related Fatigue Rose Bell, PhD, ARNP, AOCNP Northwest Medical Specialties Cancer Related Fatigue (CRF) Significantly different in quality and severity Unrelieved by sleep or rest
Why am I so Tired? Cancer Related Fatigue Rose Bell, PhD, ARNP, AOCNP Northwest Medical Specialties Cancer Related Fatigue (CRF) Significantly different in quality and severity Unrelieved by sleep or rest
Coach on Call. Thank you for your interest in How to Prevent and Treat Aches and Pains. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful.
 It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
It was great to talk with you. Thank you for your interest in. I hope you find this tip sheet helpful. Please give me a call if you have more questions about this or other topics. As your UPMC Health Plan
1 of 5 1/8/2017 8:06 PM
 Four s: Recognizing Plantar Fasciitis Symptoms Understanding the Causes of Plantar Fasciitis Getting a Diagnosis Treating Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a common heel inflammatory disorder that
Four s: Recognizing Plantar Fasciitis Symptoms Understanding the Causes of Plantar Fasciitis Getting a Diagnosis Treating Plantar Fasciitis Plantar fasciitis is a common heel inflammatory disorder that
The Effects of Sodium Oxybate on Clinical Symptoms and Sleep Patterns in Patients with Fibromyalgia
 2002-683-1 The Effects of Sodium Oxybate on Clinical Symptoms and Sleep Patterns in Patients with Fibromyalgia MARTIN B. SCHARF, MARGARET BAUMANN, and DAVID V. BERKOWITZ ABSTRACT. Objective. Fibromyalgia
2002-683-1 The Effects of Sodium Oxybate on Clinical Symptoms and Sleep Patterns in Patients with Fibromyalgia MARTIN B. SCHARF, MARGARET BAUMANN, and DAVID V. BERKOWITZ ABSTRACT. Objective. Fibromyalgia
Chronic non-bacterial Osteomyelitis/Osteitis (or CRMO)
 www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Chronic non-bacterial Osteomyelitis/Osteitis (or CRMO) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS CRMO 1.1 What is it? Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis (CRMO) is
www.printo.it/pediatric-rheumatology/gb/intro Chronic non-bacterial Osteomyelitis/Osteitis (or CRMO) Version of 2016 1. WHAT IS CRMO 1.1 What is it? Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis (CRMO) is
Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet
 Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder About your shoulder The shoulder is a ball and socket joint formed by a
Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder Orthopaedic Department Patient Information Leaflet Page 1 Subacromial Impingement of Shoulder About your shoulder The shoulder is a ball and socket joint formed by a
Recurrent Abdominal Pain (RAP) in Children
 Providing care together in York, Scarborough, Bridlington, Malton, Selby and Easingwold Communities Recurrent Abdominal Pain (RAP) in Children Information for parents, relatives and carers For more information,
Providing care together in York, Scarborough, Bridlington, Malton, Selby and Easingwold Communities Recurrent Abdominal Pain (RAP) in Children Information for parents, relatives and carers For more information,
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN. Explanation. Causes. Symptoms
 ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
ANTERIOR KNEE PAIN Explanation Anterior knee pain is most commonly caused by irritation and inflammation of the patellofemoral joint of the knee (where the patella/kneecap connects to the femur/thigh bone).
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
P T Carl Marino, PT. Physical Therapy Asheville, NC 28803
 P T Carl Marino, PT Physical Therapy Asheville, NC 28803 Dear MedMassager Customer, I developed these Techniques specifically with the home consumer in mind. Your pain management professional may have
P T Carl Marino, PT Physical Therapy Asheville, NC 28803 Dear MedMassager Customer, I developed these Techniques specifically with the home consumer in mind. Your pain management professional may have
A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts
 A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Popliteal Cysts Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
Lower back pain. Calderdale and Huddersfield. Understanding the lower back. What is lower back pain? What is the cause of non-specific low back pain?
 Calderdale and Huddersfield Emergency Department Advice Sheet Lower Back Pain Lower back pain Understanding the lower back The lower back is also called the 'lumbosacral area' of the back. It is the part
Calderdale and Huddersfield Emergency Department Advice Sheet Lower Back Pain Lower back pain Understanding the lower back The lower back is also called the 'lumbosacral area' of the back. It is the part
Treating your leg ulcer
 Page 1 of 7 Treating your leg ulcer Introduction The information in this leaflet will answer many questions you may have about your leg ulcer. If you have any further questions about your condition or
Page 1 of 7 Treating your leg ulcer Introduction The information in this leaflet will answer many questions you may have about your leg ulcer. If you have any further questions about your condition or
