Tzu-Yung Chen, MD. Original Article
|
|
|
- Melissa Mathews
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article 81 Efficacy of Topical Microfibrillar Collagen Mixed with Steroid Hormone and Morphine for Postoperative Pain Control during Lumbar Laminectomy: A Preliminary Report Tzu-Yung Chen, MD Background: Current inpatient management of postoperative pain in lumbar surgery includes the use of intramuscular opioid analgesics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or patient-controlled analgesia; however, all types of medications are associated with side effects that can limit their usefulness in the inpatient setting. Methods: In a well-conducted non-randomized prospective trial, 80 consecutive patients who underwent elective multilevel lumbar laminectomy surgery were identified. Two types of trials with different doses of steroids were used. Patients' preoperative medical records, pain scores, narcotics consumption, costs for the regimen, hospital stay, unwanted complications, and Results: walking ability were evaluated postoperatively. Pain in patients after lumbar surgery can be dramatically controlled postoperatively. Seventy-eight patients (97.5%) were able to walk without support on the first postoperative day. Major side effects were found in 5 patients (6.2%). Conclusions: This experience indicates that pain-control agents with epidural sustainedreleased preparation seem to be beneficial in early mobilization, are cost effective, and require lower analgesic consumption by patients. Similar pain control can be obtained with lower doses of methylprednisolone. In spite of its clinical attractiveness, improvements in the side effects of complications from epidural morphine and the combination of steroids and microfibrillar collagen have yet to be realized. (Chang Gung Med J 2002;25:81-8) Key words: epidural morphine, methylprednisolone, laminectomy, pain. Pain after spinal surgery can be difficult to control. Patients often fear postoperative pain more than the risks of the operation itself. (1) Ineffective pain therapy in inpatients has been commonly reported. (2,3) Until recently, laminectomy was performed as a common surgical procedure for multilevel lumbar spinal stenosis. Management of postoperative discomfort remains the critical issue in clinical practice. The popularity of patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) in use after lumbar surgery is based on the assumption that postoperative pain control is better with self-administration of opioids using small, repetitive, From the Department of Neurosurgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taipei. Received: Jul. 19, 2000; Accepted: Sep. 26, 2001 Address for reprints: Dr. Tzu-Yung Chen, Department of Neurosurgery, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital. 5, Fu-Shin Street, Kweishan, Taoyuan, 333, Taiwan, R.O.C. Tel.: ext. 2219; Fax: ; yun0710@cgmh.org.tw
2 82 concentration- maintained, on-demand intravenous doses than with timed (around-the-clock) or demanded intramuscular or oral application of an analgesic. However, the negative effects from PCA turned our focus to finding a more efficient method to try to minimize the pain from operations and the adverse effects from narcotics. (4) Since the report of Gibbons et al. (5) in 1995, many investigators (6-9) have demonstrated the efficacy of epidural use of morphine and steroids associated with local anesthesia during a lumbar operation for postoperative pain control. The purposes of this study were to thoroughly evaluate the effectiveness for postoperative wound pain control using an epidural pain-control regimen containing low doses of morphine and methylprednisolone, and to analyze the duration of pain subsidence, the cost, and the unwanted complications from the paincontrol agents. METHODS This study prospectively examined 80 patients who underwent lumbar laminectomy procedures performed by 1 physician from March 1998 to January All patients were admitted to Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taoyuan, Taiwan, to undergo operations for benign conditions of the lumbar spine, and informed consent was obtained from each. Exclusive criteria were sequestered disc herniation, biomechanically unstable spine, or previous surgery at the treated level. Preoperative variables including age, sex, duration of symptoms, historical use of herbal drugs or acupuncture, and major diseases were thoroughly assessed. Pain scores (on a 4-point pain scale), narcotics consumption, costs for the regimen, hospital stay, unwanted complications, and walking ability of patients were evaluated postoperatively. Accordingly, we collected the subjects with major unwanted complications, and tried to evaluate the relationship between past history and adverse effects. There were two separate trials in this study. After adjustment for baseline differences from the methylprednisolone used, 37 patients were enrolled in group A, and 43 patients were enrolled in group B (Table 1). Based on the 16% infection rate during the first trial, we adjusted the dose of methylprednisolone beginning in December In the first trial (Group A) of the study, absorbable microfibrillar collagen (Avitene, Davol Inc., Cranston, RI) was soaked in 80 mg of methylprednisolone (Solumedrol, Upjohn Co., Kalamazoo, MI) and 3 mg of preservative-free morphine with a thickness of about 0.5 cm on the dura surface to allow maximum absorption. During wound closure, the paravertebral muscles and subcutaneous tissues were injected with 20 ml 0.25% bupivacaine (Abbott Lab., North Chicago, IL) combined with 40 mg methylprednisolone. The second Table 1. Clinical Information on 80 Patients with Epidural Pain-Controlled Regimen Application Variable Group A Group B p (N = 37) (N = 43) Regimen constituent Epidural Avitene (microfibrillar collagen) Avitene 80 mg methylprednisolone 40 mg methylprednisolone 3 mg morphine 3 mg morphine Subcutaneous 20 cc, 0.25% bupivacaine 20 cc,0.25% bupivacaine 40 mg methylprednisolone Age (year) Gender (M:F) 16:21 18:25 >0.950 Major disease NA Herb/Ampuncture 9 13 NA Walking without support (hr) (mean SD) First voiding (hr) (mean SD) LOS (day) (mean SD) NA: non-applicable; Major disease: diabetes, hypertension, renal disease, heart failure,coagulapthy or lung disease; Herb/accupuncture: a history of treatment with herbal drugs and/or accupuncture; First voiding, duration to first self voiding after intraurethral catheter removed; LOS, length of stay.
3 83 Table 2. Frequency of Self-administered Narcotics (50 mg Meperidine Hydrochloride) Use in 63 Patients Group Frequency Post-operative periods Total patient's no. 0-1 hr 1-8 hrs 8-24 hrs 1-3 days >3 days A 2 0 a,b,c,d, d a,c, b* 4 > 3 0 e e e (2),f (2) e*(3), f*(2) B 2 0 g,h (2) g > i i* (3) 1 a - e, represents individual patient; (n), frequency of narcotics injection during specific time periods; *: deeply infected patients. Table 3. Patient Number with Side Effects in Groups A and B Side effect Post-operative periods 3-8 hrs (A/B) 8-24 hrs (A/B) over 24 hrs (A/B) Respiration depression 2 (2/0) 0 0 Nausea 13 (4/9) 6 (2/4) 1*(0/1) Vomiting 2 (1/1) 1* (0/1) 0 Ileus 4 (1/3) 1* (0/1) 0 Constipation NA NA 8 (3/5) Urinary retention NA 2 (1/1) 1* (0/1) Wound dehiscence/swelling (3/0) Wound infection (superficial) (3/0) Wound infection (deep) (3/1) Skin itchiness 0 4 (1/3) 2* (0/2) Clonus convulsion 1 (1/0) 1* (1/0) 0 A/B, number of patients in groups A and B; *: patients with residual symptoms from previous time period. trial (Group B) of the study used epidural microfibrillar collagen soaked with 40 mg methylprednisolone and 3 mg of preservative-free morphine associated with subcutaneous 20 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine for postoperative pain control. All patients underwent a standard clinical evaluation, including history of systemic disease (history of hypertension, diabetes, cardiopulmonary disease, renal failure, and coagulation disease), physical examination, planar radiographic study, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) performed under general anesthesia. Anesthesia was induced in all patients with midazolem (up to 2 mg), propofol ( mg/kg), and muscle relaxant. The patients' tracheas were intubated, and anesthesia was maintained with N2O/O2 70%/30% (nitrous oxide/oxygen), 3 ug/kg fentanyl, and isoflurane (at up to 1.5% end-tidal concentration). After induction of general anesthesia, patients were placed in the knee-chest position on a laminectomy seat. A 10- to 12-cm midline skin incision was made under intraoperative fluoroscope localization. Subperiosteal dissection along the spinous process and laminar was made. Rongeurs and kerrisson were then used to remove the 2 to 3 levels of spinous process, laminar, hypertrophic facets, and ligamentum flavum. After the dura sac, exiting roots, and hemostasis were confirmed, microfibrillar collagen was contoured to loosely pack the laminectomy defect. Microfibrillar collagen was soaked in 80 mg (Group 1) or 40 mg (Group 2) of methylprednisolone (Solumedrol) and 3 mg of preservative-free morphine with a thickness of about 0.5 cm on the dura surface to allow maximum absorption. During wound closure, the paravertebral muscles and subcutaneous tissues were injected with 20 ml of 0.25% bupivacaine alone in patients of Group B or com-
4 84 bined with 40 mg methylpredisolone in patients of Group A. The patient was then awakened and extubated. During the postoperative period, patients were prescribed oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and 50 mg meperidine hydrochloride intramuscularly every 6 hours as needed. The pain scores and nausea assessment were conducted by nursing staff or residents upon the patient's arrival in the post anesthesia care unit and at 30 minutes, 1 hour, and every 8 hours thereafter. For patients who were discharged, we assessed the wound condition at an average of 7.52 postoperative days in the outpatient clinic. To assure the effectiveness of the epidural paincontrol regimen, pain evaluation focused on the area of the wound. In other words, during evaluation, complaints from the hip or leg pain were ignored, and to exclude possible effects from the anesthesia, side effects from the pain-control regimen were thoroughly evaluated 3 hours after surgery. Time of first ambulation and first voiding were documented, as was narcotics consumption. The intraurethral catheter was routinely removed the next morning. Patients were encouraged to stand and walk when they were comfortable doing so. After surgery, the baseline pain score was assessed with the aid of the standard pain scale as follows: 0=no pain, 1=minimal or occasional pain not requiring medication, 2=mild pain controlled with non-narcotic analgesics, 3=moderate pain controlled with occasional narcotic analgesics, and 4=severe constant pain requiring regular narcotic analgesics. (10) In pain scale, intramuscular narcotics consumption, respiratory patterns, nausea, itching, and ability to control voiding were evaluated. The cost of the pain-control regimen and length of stay were assessed. Independent t-test and chi-squared test were used to compare the effectiveness and unwanted side effects of the 2 trials. All results were considered statistically significant at p < RESULT Demographic data and clinical characteristics obtained from the 80 patients are summarized in Table 1, and total intramuscular narcotics consumption was noted in 63 patients (78.7%) as summarized in Table 2. The age at surgery ranged from 48 to 81 years (mean SD, years), and was slightly female dominant. After the intraurethral catheter was removed the next morning, most patients had the ability to control voiding during 2.6-hour periods (1-22 hours). The average time for controlled voiding was hours in group A and hours in group B ( t = 0.567, p = 0.573). Seventyeight patients (97.5%) were able to walk without support at least for a short distance on the first postoperative day. The average time for encouraged ambulatory walking was 17.6 hours in group A and 17.2 hours in group B ( t = 0.383, p = 0.703). There was no statistically significant difference in length of stay of the 2 groups ( days) in group A and days in group B, p = 0.261). Twelve subjects in group A and 18 subjects in group B had a history of health problems with severe medical diseases; 22 patients (9 in group A and 13 in group B) reported a history of using herbal drugs and/or acupuncture treatment. Twenty-one patients (26.2%) in group A and 33 patients (41.2%) in group B received 50 mg of meperidine hydrochloride once and most (50/54) within 8 hours (Table 2). Seven patients needed narcotics after 24 hours postoperatively (patients a, b, c, e, f, I, and 1 patient in group A). Among them, 4 (patients b, e, f, and i) were found to have deep infections (57.1%). The pain scale records of the 2 groups are illustrated in Fig. 1. Data were collected 1 hour, 8 hours, 24 hours, 3 days, and 7 days postoperatively. Average scores in group A were , , , , and , while in group B, scores were , , , and at the respective individual times. Although group A showed a better pain response, there were no statistical differences in postoperative 1-hour and 3-day time periods. Sixty-eight patients (85%) were essentially pain-free or with minimal wound pain under regular oral analgesics with no need for narcotics after 8 hours postoperatively. Seventy-three 73 patients (91.2%) still felt the wound was painless at 7 days postoperatively, excluding the 3 patients with superficial and the 4 with deep infected wounds (Table 2). Possible adverse events from the epidural and subcutaneous regimen are shown in Table 3. Nausea and vomiting occurred in 15 patients within 8 hours which decreased to 7 patients (8.7%) at 24 hours.
5 85 Only 1 patient complained of the nausea after 24 hours postoperatively. Urinary retention was a complaint of 2 patients who had delayed voiding 12 hours postoperatively, after the intraurethral catheter was removed. Respiratory depression was noticed in 2 patients within 8 hours postoperatively, and they were treated successfully with oxygen support. Abdominal disturbance (ileus) with poor peristalsis was noted in 4 patients (1 patient in group A and 3 in group B) within 24 hours, and constipation was recorded after 24 hours in 8 patients (10%). Skin itchiness was a complaint of 4 patients. All minor side effects were treated uneventfully and were resolved within 3 days postoperatively. Major adverse effects occurred in 5 patients (1 with clonic convulsion and 4 with deep wound infections). One patient in group A suffered from back tightness and severe restlessness 3 hours postoperatively, then proceeded to clonic convulsions and respiratory failure at the neurosurgical ward, and was treated by emergent endotracheal tube insertion and medication. The incidence of infection was 16.2% (6 patients) in group A and 2.3% (1 patient) in group B. These consisted of superficial wound infections in 3 (3 in group A and none in group B) and deep infections in 4 (3 in group A and 1 in group B). These lesions were noted days (3 to 7 days) postoperatively. The pain was severe enough to reuse intramuscular narcotics 24 hours after surgery in all 4 deep infection cases (Table 2). The pathogen was Staphylococcus aureus in all 4 patients. The prognosis was uneventful after the patients were treated with surgical debridement and 14 days of parenteral antibiotics. Tracing the past history of 5 patients with major complications, 3 deep infection subjects (cases b, e, and i) reported herbal drug/acupuncture treatment within 3 months before surgery. The patient who suffered from postoperative clonic convulsions had a history of an allergic reaction to narcotic injections 3 years previous when she had undergone surgery for a hysterectomy. The average costs of the epidural pain-control regimen and subcutaneous injection was about NT$2,800 in group A (approximately US$85) and about NT$2,500 in group B. DISCUSSION The pain model used in these 2 trials was based on draft documents issued by several basic scientific studies reported in the anesthesia and surgical literature. (7,11-15) The objective of our research was not only to study the short-term effects of epidural regimens, but also to accurately assess the risk of this combination and the economic effect in our patients. Use of an epidural sustained-release pain-control regimen, containing morphine and methylprednisolone, may effectively reduce the postoperative wound pain in most patients, as reported by most studies in the relevant literature. (6,8,16) Yates compared the response of injections of anesthetics to injections of anesthetics combined with steroids and found better outcomes in the latter group. (17) Combinations of the various constituents applied epidurally are also being adopted as tools in the surgeon's armamentarium to enhance successful treatment of postoperative pain in lumbar surgery. (3,5,6,12,14) Because so many solutions are available for the same surgical problem, it is our belief that the gold standard is still far from being selected. The most difficult challenge posed by sustainedreleased regimens is maintaining a low concentration in cerebral-spinal fluid (CSF) and decreasing the infection rate. To address these issues, some authors have pointed out theoretical reasons why complication rates or failure rates of those with previous surgeries may be so high. (16,18,19) Despite these arguments for and against the use of epidural sustained-released regimens, increasing experimental work has been reported to support either method for pain control after lumbar surgery, as well as the use of this compound as opposed to a epidural catheter to reduce infection morbidity. (6,17,20,21) Opiate drugs are known to exert only not a direct anti-nociceptive influence on the spinal cord, but also a direct endogenous inhibitory effect according to the drug' s concentration in the CSF. The pharmacokinetics of epidurally administered narcotics appears to be due to passage of these agents across the dura, where it acts on opiate receptors both in the spinal cord and in the supraspinal structure. (15,20,22) Epidural steroids may effectively decrease the inflammation reaction induced by tissue damage and surgical manipulation. (14,18) Our review shows that lowering the dose of epidural steroids (as in group B) may reduce the infection rate and achieve similar pain control as does a higher steroid dose. Using this compound, binding of the drug at low spinal levels and the slow
6 86 rostral circulation of cerebrospinal fluid may limit respiratory depression with epidural administration of narcotics. Postoperative infiltration of surgical wounds with 0.25% bupivacaine may theoretically result in significant reduction in pain, both at rest and during mobilization. (14,22,23) However, considering the time of using opioid analgesics, early consumption of narcotics (less than 8 hours) was seen in 58 postoperative patients (72.5%), and the rate would increase to 85.7% if only the 63 patients who needed the narcotics were assessed. We were unable to demonstrate the benefits of paravertebral wound infiltration with bupivacaine in the present study. The value of high-dose local anesthesia in this situation may be questioned. The adverse effects of morphine, subcutaneous fluid collection and foreign epidural masses from blood and solvents are always a problem and limit the effects of sustained-released agents. The prolonged necessity for narcotics consumption in deeply infected patients attracted our early attention to the complicated adverse events. Of the 4 patients with complications of deep infections, only one had a history of renal disease, and there seems to be no contraindication of this application for patients associated with preoperative major health problems. Three patients who suffered from deep infections, however, had histories of herbal drug/acupuncture treatment (3 in 22 patients), compared to 1 in 58 patients who had no experience with herbal drug/acupuncture treatment. Although the frequency of use of herbal drugs or acupuncture in our patients may predispose a patient to infection in our analysis, no conclusion can be made from this data due to the unknown constituents of the herbal drugs. After excluding the possibility that general anesthesia was the cause, the postoperative convulsions seen in 1 patient may be attributable to an allergic reaction to bupivacaine, a devastating response to this local anesthetic. (23) Cost is a significant concern in today's medical environment, and patients undergoing the pain control procedure may significantly reduce the need for narcotics consumption and their length of stay. Although the study is limited by the use of welldesigned comparative clinical groups rather than a double-blind placebo-controlled group, this study may be the first such review in our country, and the results must be considered preliminary. Sensory or motor loss, urinary retention, or itching did appear in some patients after epidural morphine, but the side effects were minor and appeared to fade within a few hours to 3 days. When recovery time and surgical morbidity are both decreased, an epidural pain regimen can be considered extremely effective. Careful patient selection, decreasing the dose of methylprednisolone and adjusting bupivacaine may be more likely to decrease the major adverse effects of pain-control therapy. Based on these findings, we believe that total pain relief and safety in lumbar decompressive surgery can be obtained with relatively low doses of morphine and methylpredisolone soaked in epidural microfibrillary collagen. Despite the clinical attractiveness, it has yet to be proven whether this method should be advocated in instrumentation surgery or cervical procedures. Acknowledgments The author would like to thank Ms. Shu Yun for assistance with the preparation of the manuscript and Ms. Chen Fu Ru for help with statistical analysis. REFERENCES 1. Cronin M, Redfern PA, Utting JE. Psychiatry and postoperative complaints in surgical patients. Br J Anaesth 1973;45: Kehlet H. Surgical stress-the role of pain and analgesia. Br J Anaesth 1989;63: Mack PF, Hass D, Lavyne MH, Snow RB, Lien CA. Postoperative narcotic requirement after microscopic lumbar discectomy in not affected by intraoperative ketorolac or bupivacaine. Spine 2001;26: Baubillier E, Leppert C, Delaunay L, Bonnet F. Patientcontrolled analgesia: Effect of adding continuous infusion of morphine. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim 1992;11: Gibbons JB, Barth AP, Ahuja A, Budny JL, Hopkins LN. Lumbar discectomy: Use of an epidural morphine sponge for post-operative pain control. Neurosurgery 1995;36: Hurlbert RH, Theodore N, Drabier JB, Magwood AM, Sonntag VK. A prospective randomized double-blind controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of an analgesic epidural paste following lumbar decompressive surgery. J Neurosurg (Spine 2) 1999;90: Needham CW. Painless lumbar surgery: morphine nerve paste. Conn Med 1996;60: Rechtine GR, Reinert CM, Bohlman HH. The use of epidural morphine to decrease postoperative pain in
7 87 patients undergoing lumbar laminectomy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1984;66: Schmidek HH, Cutler SG. Epidural morphine for control of pain after spinal surgery: A preliminary report. Neurosurgery 1983;13; McAfee PC, Zdeblick TA. Tumors of the thoracic and lumbar spine: surgical treatment via the anterior approach. J Spinal Disord 1989;2: Bromage PR, Camporesi EM, Durant PA. Rostral spread of epidural morphine. Anesthesiology 1982;56: Chadduck JB, Sneyd JR, Pobereskin LH. The role of bupivacaine in early postoperative pain control after lumbar decompression. J Neurosurg (Spine 1) 1999;90: Dierking GW, Ostergaard E, Ostergaard HT, Dahl JB. The effects of wound infiltration with bupivacaine versus saline on postoperative pain and opioid requirements after herniorraphy. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1994;38: Glasser RS, Knego RS, Delashaw JB. The perioperative use of corticosteroids and bupivacaine in the management of lumbar disc disease. J Neurosurg 1993;78: Sjostrom S, Pharm PH, Pharm PP, Tamsen A. Pharmacokinetics of epidural morphine and meperidine in humans. Anaesthesia 1987;67: McNeill TW, Andersson GBJ, Schell B, Sinkora G, Nelson J, Lavender SA. Epidural administration of methylprednisolone and morphine for pain after a spinal operation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77A: Yates DW. A comparison of the types of epidural injection commonly used in the treatment of low back pain and sciatica. Rhematol Rehabil 1978;17: Knight CL, Burnell JC. Systemic side effects of extradural steroids. Anaesthesia 1980;35: Reiz S, Westberg M. Side effects of epidural morphine. Lancet 1980;2: Nelson DA. Intraspinal therapy using methylprednisolone acetate. Twenty-three years of clinical controversy. Spine 1993;18: Weller R, Rosenblum M, Conard P, Gross JB. Comparison of epidural and patient-controlled intravenous morphine following joint replacement surgery. Can J Anaesth 1991;38: Milligan KR, Macafee AL, Fogarty DJ, Wallace RGH, Ramsey P. Intraoperative bupivacaine diminishes pain after lumbar discectomy. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993; 75B: Teddy PJ, Fabinyi GC, Kerr JH. Bupivacaine infiltrtion after lumbar laminectomy pain. Anaesthesia 1981;36:380-3.
8 (97.5%) 5 (6.2%) ( 2002;25:81-8) ł' ' x _ ˇ fl«g ~ G Ø ` G ` Œ 90ƒ~7 º19 Ø F Z G ` Œ 90ƒ~9 º28 Ø C fl` œ' ƒl» B G fl l«i fiv A ł' ' fl«g ~ G Cfi Ø 333 t s m _ 5 C Tel.: (03) ; Fax: (03) ; yun0710@cgmh.org.tw
Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia Community Nurses Competency Test
 Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia Community Nurses Competency Test 1 Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia for Community Nurses Competency Test 1) Name the two major classifications of pain. i. ii. 2) Neuropathic
Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia Community Nurses Competency Test 1 Intraspinal (Neuraxial) Analgesia for Community Nurses Competency Test 1) Name the two major classifications of pain. i. ii. 2) Neuropathic
A prospective randomized double-blind controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of an analgesic epidural paste following lumbar decompressive surgery
 J Neurosurg (Spine 2) 90:191 197, 1999 A prospective randomized double-blind controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of an analgesic epidural paste following lumbar decompressive surgery R. JOHN HURLBERT,
J Neurosurg (Spine 2) 90:191 197, 1999 A prospective randomized double-blind controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy of an analgesic epidural paste following lumbar decompressive surgery R. JOHN HURLBERT,
Show Me the Evidence: Epidurals, PVBs, TAP Blocks Christopher L. Wu, MD Professor of Anesthesiology The Johns Hopkins Hospital
 Show Me the Evidence: Epidurals, PVBs, TAP Blocks Christopher L. Wu, MD Professor of Anesthesiology The Johns Hopkins Hospital Overview Review overall (ERAS and non-eras) data for EA, PVB, TAP Examine
Show Me the Evidence: Epidurals, PVBs, TAP Blocks Christopher L. Wu, MD Professor of Anesthesiology The Johns Hopkins Hospital Overview Review overall (ERAS and non-eras) data for EA, PVB, TAP Examine
Balanced Analgesia With NSAIDS and Coxibs. Raymond S. Sinatra MD, Ph.D
 Balanced Analgesia With NSAIDS and Coxibs Raymond S. Sinatra MD, Ph.D Prostaglandins and Pain The primary noxious mediator released from damaged tissue is prostaglandin (PG) PG is responsible for nociceptor
Balanced Analgesia With NSAIDS and Coxibs Raymond S. Sinatra MD, Ph.D Prostaglandins and Pain The primary noxious mediator released from damaged tissue is prostaglandin (PG) PG is responsible for nociceptor
Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government
 Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government Introduction Brief update Two main topics Use of Gabapentin Local Infiltration Analgesia
Mr David A McDonald Service Improvement Manager Whole System patient Flow Improvement Programme Scottish Government Introduction Brief update Two main topics Use of Gabapentin Local Infiltration Analgesia
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 29 / No. 3 / July - September
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 29 / No. 3 / July - September 2014 67-72 Original Article Comparison of Epidural Morphine Soaked Gel Foam and Continuous Intravenous Morphine Using PCA in the Management
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 29 / No. 3 / July - September 2014 67-72 Original Article Comparison of Epidural Morphine Soaked Gel Foam and Continuous Intravenous Morphine Using PCA in the Management
EFFECTS OF INTRAOPERATIVE-INTRATHECAL SUFENTANIL INJECTION ON POSTOPERATIVE PAIN MANAGEMENT AFTER SINGLE LEVEL LUMBAR DISCECTOMY
 EFFECTS OF INTRAOPERATIVE-INTRATHECAL SUFENTANIL INJECTION ON POSTOPERATIVE PAIN MANAGEMENT AFTER SINGLE LEVEL LUMBAR DISCECTOMY Saeid Abrishamkar *, Mohammadhossein Karimi **, Mohammadreza Safavi ***,
EFFECTS OF INTRAOPERATIVE-INTRATHECAL SUFENTANIL INJECTION ON POSTOPERATIVE PAIN MANAGEMENT AFTER SINGLE LEVEL LUMBAR DISCECTOMY Saeid Abrishamkar *, Mohammadhossein Karimi **, Mohammadreza Safavi ***,
Intravenous lidocaine infusions. Dr Ian McConachie FRCA FRCPC
 Intravenous lidocaine infusions Dr Ian McConachie FRCA FRCPC Thank the organisers for inviting me. No conflicts or disclosures Lidocaine 1 st amide local anesthetic Synthesized in 1943 by Lofgren in Sweden.
Intravenous lidocaine infusions Dr Ian McConachie FRCA FRCPC Thank the organisers for inviting me. No conflicts or disclosures Lidocaine 1 st amide local anesthetic Synthesized in 1943 by Lofgren in Sweden.
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia
 The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
Fast Track Surgery and Surgical Carepath in Optimising Colorectal Surgery. R Sim Centre for Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery, TTSH
 Fast Track Surgery and Surgical Carepath in Optimising Colorectal Surgery R Sim Centre for Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery, TTSH Conventional Surgery Postop care Nasogastric tube Enteral feeds when ileus
Fast Track Surgery and Surgical Carepath in Optimising Colorectal Surgery R Sim Centre for Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery, TTSH Conventional Surgery Postop care Nasogastric tube Enteral feeds when ileus
Comparison of Bolus Bupivacaine, Fentanyl, and Mixture of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Thoracic Epidural Analgesia for Upper Abdominal Surgery
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/156 Comparison of Bolus Bupivacaine, Fentanyl, and Mixture of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Thoracic Epidural Analgesia for Upper Abdominal Surgery Sachin Gajbhiye
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/156 Comparison of Bolus Bupivacaine, Fentanyl, and Mixture of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Thoracic Epidural Analgesia for Upper Abdominal Surgery Sachin Gajbhiye
META-ANALYSIS OF INTRATHECAL MORPHINE FOR LUMBAR SPINE SURGERY
 META-ANALYSIS OF INTRATHECAL MORPHINE FOR LUMBAR SPINE SURGERY RESIDENT RESEARCH EXCHANGE DAY MAY 30 TH, 2014 SUPERVISOR: DR. JAMES PAUL SUSAN JO PGY4 SUZANNE LAMBERT PGY4 ADA HINDLE PGY4 INTRODUCTION
META-ANALYSIS OF INTRATHECAL MORPHINE FOR LUMBAR SPINE SURGERY RESIDENT RESEARCH EXCHANGE DAY MAY 30 TH, 2014 SUPERVISOR: DR. JAMES PAUL SUSAN JO PGY4 SUZANNE LAMBERT PGY4 ADA HINDLE PGY4 INTRODUCTION
Senior Visceral Surgery Fast-Track in Colorectal Surgery The anesthetist s point of view
 Senior Visceral Surgery Fast-Track in Colorectal Surgery The anesthetist s point of view 1st Geneva International SCIENTIFIC DAY February 3 rd 2010 E. Schiffer Dept APSI, HUG 1 Fast-Track in colorectal
Senior Visceral Surgery Fast-Track in Colorectal Surgery The anesthetist s point of view 1st Geneva International SCIENTIFIC DAY February 3 rd 2010 E. Schiffer Dept APSI, HUG 1 Fast-Track in colorectal
North American Spine Society Public Education Series
 Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Herniated Lumbar Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The disc is a combination of strong
Current evidence in acute pain management. Jeremy Cashman
 Current evidence in acute pain management Jeremy Cashman Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side effects Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side
Current evidence in acute pain management Jeremy Cashman Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side effects Optimal analgesia Best possible pain relief Lowest incidence of side
The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
DORIS DUKE MEDICAL STUDENTS JOURNAL Volume V,
 Continuous Femoral Perineural Infusion (CFPI) Using Ropivacaine after Total Knee Arthroplasty and its Effect on Postoperative Pain and Early Functional Outcomes Eric Lloyd Scientific abstract Total Knee
Continuous Femoral Perineural Infusion (CFPI) Using Ropivacaine after Total Knee Arthroplasty and its Effect on Postoperative Pain and Early Functional Outcomes Eric Lloyd Scientific abstract Total Knee
A randomised controlled study of epidural fentanyl analgesia following lumbar laminectomy
 A randomised controlled study of epidural fentanyl analgesia following lumbar laminectomy Mr. S Thomson 1 Mr. P Mitchell 3 Mr. PT van Hille 2 Dr. B Gregson 3 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Cambridge University
A randomised controlled study of epidural fentanyl analgesia following lumbar laminectomy Mr. S Thomson 1 Mr. P Mitchell 3 Mr. PT van Hille 2 Dr. B Gregson 3 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Cambridge University
Controlled Trial of Wound Infiltration with Bupivacaine for Post Operative Pain Relief after Caesarean Section
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.23, No.2, June 2001 Controlled Trial of Wound Infiltration with Bupivacaine for Post Operative Pain Relief after Caesarean Section Omar Momani, MD, MBBS, JBA* Objective: The
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.23, No.2, June 2001 Controlled Trial of Wound Infiltration with Bupivacaine for Post Operative Pain Relief after Caesarean Section Omar Momani, MD, MBBS, JBA* Objective: The
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Radiculopathy or Cervical Myelopathy (ACDF)
 Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Radiculopathy or Cervical Myelopathy (ACDF) About your condition The pressure from your bulging disc(s) might be causing your pain, numbness or weakness.
Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion for Cervical Radiculopathy or Cervical Myelopathy (ACDF) About your condition The pressure from your bulging disc(s) might be causing your pain, numbness or weakness.
Enhanced Recovery after Surgery - A Colorectal Perspective. R Sim Centre for Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery, TTSH
 Enhanced Recovery after Surgery - A Colorectal Perspective R Sim Centre for Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery, TTSH Conventional Surgery Postop care Nasogastric tube Enteral feeds when ileus resolves Opioid
Enhanced Recovery after Surgery - A Colorectal Perspective R Sim Centre for Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery, TTSH Conventional Surgery Postop care Nasogastric tube Enteral feeds when ileus resolves Opioid
Setting The setting was a hospital (tertiary care). The economic study was carried out in Ankara, Turkey.
 Inhalation versus total intravenous anesthesia for lumbar disc herniation: comparison of hemodynamic effects, recovery characteristics, and cost Ozkose Z, Ercan B, Unal Y, Yardim S, Kaymaz M, Dogulu F,
Inhalation versus total intravenous anesthesia for lumbar disc herniation: comparison of hemodynamic effects, recovery characteristics, and cost Ozkose Z, Ercan B, Unal Y, Yardim S, Kaymaz M, Dogulu F,
Gabapentin Does Not Improve Analgesia Outcomes For Total Joint Replacement. Manyat Nantha-Aree, MD
 Gabapentin Does Not Improve Analgesia Outcomes For Total Joint Replacement Manyat Nantha-Aree, MD Objective n Preliminary results of MOBILE study in total hip and knee arthroplasty Background n Gabapentin=
Gabapentin Does Not Improve Analgesia Outcomes For Total Joint Replacement Manyat Nantha-Aree, MD Objective n Preliminary results of MOBILE study in total hip and knee arthroplasty Background n Gabapentin=
LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION / DISCECTOMY SURGERY INFORMATION
 LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION / DISCECTOMY SURGERY INFORMATION WHAT IS LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION / DISCECTOMY SURGERY? During lumbar decompression/ discectomy back surgery, a small portion of the bone over the nerve
LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION / DISCECTOMY SURGERY INFORMATION WHAT IS LUMBAR DECOMPRESSION / DISCECTOMY SURGERY? During lumbar decompression/ discectomy back surgery, a small portion of the bone over the nerve
Nerve Blocks & Long Acting Analgesia for Plastic Surgeons. Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS
 Nerve Blocks & Long Acting Analgesia for Plastic Surgeons Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures None related to this topic Why is Non-Opioid Analgesia Important Opioid epidemic Less opioid use Less PONV
Nerve Blocks & Long Acting Analgesia for Plastic Surgeons Karol A Gutowski, MD, FACS Disclosures None related to this topic Why is Non-Opioid Analgesia Important Opioid epidemic Less opioid use Less PONV
Objectives 9/7/2012. Optimizing Analgesia to Enhance the Recovery After Surgery CME FACULTY DISCLOSURE
 Optimizing Analgesia to Enhance the Recovery After Surgery Francesco Carli, M.D.. McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada. ASPMN, Baltimore, 2012 CME FACULTY DISCLOSURE Francesco Carli has no affiliation
Optimizing Analgesia to Enhance the Recovery After Surgery Francesco Carli, M.D.. McGill University, Montreal, QC, Canada. ASPMN, Baltimore, 2012 CME FACULTY DISCLOSURE Francesco Carli has no affiliation
Type of intervention Anaesthesia. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Comparison of the costs and recovery profiles of three anesthetic techniques for ambulatory anorectal surgery Li S T, Coloma M, White P F, Watcha M F, Chiu J W, Li H, Huber P J Record Status This is a
Comparison of the costs and recovery profiles of three anesthetic techniques for ambulatory anorectal surgery Li S T, Coloma M, White P F, Watcha M F, Chiu J W, Li H, Huber P J Record Status This is a
Remifentanil. Addressing the challenges of ambulatory orthopedic procedures 1-3
 Remifentanil Addressing the challenges of ambulatory orthopedic procedures 1-3 INDICATIONS AND IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION INDICATIONS ULTIVA (remifentanil HCl) for Injection is indicated for intravenous
Remifentanil Addressing the challenges of ambulatory orthopedic procedures 1-3 INDICATIONS AND IMPORTANT RISK INFORMATION INDICATIONS ULTIVA (remifentanil HCl) for Injection is indicated for intravenous
Anaesthesia and Pain Management for Endo Exo Femoral Prosthesis (EEFP) Bridging the Gap from Surgery to Rehabilitation
 Anaesthesia and Pain Management for Endo Exo Femoral Prosthesis (EEFP) Bridging the Gap from Surgery to Rehabilitation Dr Ajay Kumar Senior Lecturer Macquarie and Melbourne University Introduction Amputee
Anaesthesia and Pain Management for Endo Exo Femoral Prosthesis (EEFP) Bridging the Gap from Surgery to Rehabilitation Dr Ajay Kumar Senior Lecturer Macquarie and Melbourne University Introduction Amputee
Pain relief after major surgery
 Page 1 of 6 Pain relief after major surgery Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to tell you about the main pain relief options available after major surgery. You will probably only need this for the
Page 1 of 6 Pain relief after major surgery Introduction The aim of this leaflet is to tell you about the main pain relief options available after major surgery. You will probably only need this for the
Analgesia for ERAS programs. Dr Igor Lemech VMO Anaesthetist Wagga Wagga Base Hospital
 Analgesia for ERAS programs Dr Igor Lemech VMO Anaesthetist Wagga Wagga Base Hospital Disclosure I have received honoraria from Mundipharma and MSD The new Wagga Wagga Rural Referral Centre Scope Analgesic
Analgesia for ERAS programs Dr Igor Lemech VMO Anaesthetist Wagga Wagga Base Hospital Disclosure I have received honoraria from Mundipharma and MSD The new Wagga Wagga Rural Referral Centre Scope Analgesic
Anesthetic Techniques in Endoscopic Sinus and Skull Base Surgery
 Anesthetic Techniques in Endoscopic Sinus and Skull Base Surgery Martha Cordoba Amorocho, MD Iuliu Fat, MD Supplement to Cordoba Amorocho M, Fat I. Anesthetic techniques in endoscopic sinus and skull base
Anesthetic Techniques in Endoscopic Sinus and Skull Base Surgery Martha Cordoba Amorocho, MD Iuliu Fat, MD Supplement to Cordoba Amorocho M, Fat I. Anesthetic techniques in endoscopic sinus and skull base
SURGICAL REMOVAL OF A LOOPED AND KNOTTED EPIDURAL CATHETER IN A POSTPARTUM PATIENT
 SURGICAL REMOVAL OF A LOOPED AND KNOTTED EPIDURAL CATHETER IN A POSTPARTUM PATIENT - A Case Report - O. AL-KAYED *, F. AL-BOUTI **, AND M.O. ABABNEH *** Summary We report a case of unsuccessful removal
SURGICAL REMOVAL OF A LOOPED AND KNOTTED EPIDURAL CATHETER IN A POSTPARTUM PATIENT - A Case Report - O. AL-KAYED *, F. AL-BOUTI **, AND M.O. ABABNEH *** Summary We report a case of unsuccessful removal
Setting The setting was tertiary care. The economic study appears to have been performed in Heidelberg, Germany.
 Comparative analysis of costs of total intravenous anaesthesia with propofol and remifentanil vs. balanced anaesthesia with isoflurane and fentanyl Epple J, Kubitz J, Schmidt H, Motsch J, Bottiger B W,
Comparative analysis of costs of total intravenous anaesthesia with propofol and remifentanil vs. balanced anaesthesia with isoflurane and fentanyl Epple J, Kubitz J, Schmidt H, Motsch J, Bottiger B W,
Continuous Wound Infusion and Postoperative Pain Current status?
 Continuous Wound Infusion and Postoperative Pain Current status? Pr Patricia Lavand homme Department of Anesthesiology St Luc Hospital University Catholic of Louvain Medical School Brussels, Belgium Severe
Continuous Wound Infusion and Postoperative Pain Current status? Pr Patricia Lavand homme Department of Anesthesiology St Luc Hospital University Catholic of Louvain Medical School Brussels, Belgium Severe
Role and safety of epidural analgesia
 Anaesthesia for Liver Resection Surgery The Association of Anaesthetists Seminars 21 Portland Place, London Thursday 15 th December 2005 Role and safety of epidural analgesia Lennart Christiansson MD,
Anaesthesia for Liver Resection Surgery The Association of Anaesthetists Seminars 21 Portland Place, London Thursday 15 th December 2005 Role and safety of epidural analgesia Lennart Christiansson MD,
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia
 Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: epidural_steroid_injections_for_back_pain 2/2016 4/2017 4/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Epidural Steroid Injections for Back Pain File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: epidural_steroid_injections_for_back_pain 2/2016 4/2017 4/2018
5 Steps to a More Prosperous ASC June 12, Greg Poulter, MD, Vail Summit Orthopaedics
 Greg Poulter, MD, Vail Summit Orthopaedics 1 Complex Spine Surgery Complex Spine Surgery Capital intensive Challenging setup Technically difficult Minimally invasive Little pain May be outpatient 2 Concerns
Greg Poulter, MD, Vail Summit Orthopaedics 1 Complex Spine Surgery Complex Spine Surgery Capital intensive Challenging setup Technically difficult Minimally invasive Little pain May be outpatient 2 Concerns
Perioperative Pain Management
 Perioperative Pain Management Overview and Update As defined by the Anesthesiologist's Task Force on Acute Pain Management are from the practice guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists
Perioperative Pain Management Overview and Update As defined by the Anesthesiologist's Task Force on Acute Pain Management are from the practice guidelines from the American Society of Anesthesiologists
Lumbar Disc Prolapse. Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan. Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon
 Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Lumbar Disc Prolapse By Dr. Ahmed Salah Eldin Hassan Professor of Neurosurgery & Consultant spinal surgeon 1-What are the Functions of the Spine Structural support for upright posture Protection of Spinal
Effective pain management begins with OFIRMEV (acetaminophen) injection FIRST Proven efficacy with rapid reduction in pain 1
 Effective pain management begins with OFIRMEV (acetaminophen) injection FIRST Proven efficacy with rapid reduction in pain 1 Fast onset of pain relief with 7% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) scores
Effective pain management begins with OFIRMEV (acetaminophen) injection FIRST Proven efficacy with rapid reduction in pain 1 Fast onset of pain relief with 7% reduction in visual analog scale (VAS) scores
Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression and Fusion
 Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Egyptian Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 9 / No. 4 / October - December 014 51-56 Original Article Management of Single Level Lumbar Degenerative Spondylolisthesis: Decompression Alone or Decompression
Effect of low-dose intravenous dexamethasone on post-lumbar discectomy pain: Randomized and Double blind study
 Effect of low-dose intravenous dexamethasone on post-lumbar discectomy pain: Randomized and Double blind study Firooz Salehpoor 1, Ali Meshkini 1, Amirhossein Haghir 2, Peyman Vahedi 3, Asghar Ashrafi
Effect of low-dose intravenous dexamethasone on post-lumbar discectomy pain: Randomized and Double blind study Firooz Salehpoor 1, Ali Meshkini 1, Amirhossein Haghir 2, Peyman Vahedi 3, Asghar Ashrafi
Post Tonsillectomy Pain Presented by: Dr.Z.Sarafraz Otolaryngologist
 Post Tonsillectomy Pain Presented by: Dr.Z.Sarafraz Otolaryngologist Tonsillectomy is a common surgery in children Post tonsillectomy pain is an important concern. Duration &severity of pain depend on:
Post Tonsillectomy Pain Presented by: Dr.Z.Sarafraz Otolaryngologist Tonsillectomy is a common surgery in children Post tonsillectomy pain is an important concern. Duration &severity of pain depend on:
Epidural analgesia technique
 Epidural analgesia technique Martin Pearson School of Veterinary Science University of Queensland, Gatton 0254601834 Peter Best Greencross South Tamworth Animal Hospital 88Duri Road, Tamworth 02 6765 4244
Epidural analgesia technique Martin Pearson School of Veterinary Science University of Queensland, Gatton 0254601834 Peter Best Greencross South Tamworth Animal Hospital 88Duri Road, Tamworth 02 6765 4244
J Med Assoc Thai 2014; 97 (Suppl. 9): S62-S67 Full text. e-journal:
 The Effect of Epidural Low-Dose Morphine-Soaked Microfibrillar Collagen Sponge in Postoperative Pain Control after Laminectomy and Instrumented Fusion: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study
The Effect of Epidural Low-Dose Morphine-Soaked Microfibrillar Collagen Sponge in Postoperative Pain Control after Laminectomy and Instrumented Fusion: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Study
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adverse drug events, polypharmacy and perioperative considerations in elderly patients, 377 389 Age, and risk of postoperative urinary retention,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adverse drug events, polypharmacy and perioperative considerations in elderly patients, 377 389 Age, and risk of postoperative urinary retention,
Thoracic epidural versus patient-controlled analgesia in elective bowel resections Paulsen E K, Porter M G, Helmer S D, Linhardt P W, Kliewer M L
 Thoracic epidural versus patient-controlled analgesia in elective bowel resections Paulsen E K, Porter M G, Helmer S D, Linhardt P W, Kliewer M L Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
Thoracic epidural versus patient-controlled analgesia in elective bowel resections Paulsen E K, Porter M G, Helmer S D, Linhardt P W, Kliewer M L Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic
PREMIER SPINE CARE. Adrian P. Jackson, MD (Cervical Spine Specialist) Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF)
 PREMIER SPINE CARE Adrian P. Jackson, MD (Cervical Spine Specialist) Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) After your physical examination and a review of your films, you have been recommended
PREMIER SPINE CARE Adrian P. Jackson, MD (Cervical Spine Specialist) Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) After your physical examination and a review of your films, you have been recommended
Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries
 Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Alessandro Di Filippo Manuela Magherini Peggy Ruggiano Antonio Ciardullo Silvia Falsini
 DOI 10.1007/s40520-014-0272-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Postoperative analgesia in patients older than 75 years undergoing intervention for per-trochanteric hip fracture: a single centre retrospective cohort study
DOI 10.1007/s40520-014-0272-5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Postoperative analgesia in patients older than 75 years undergoing intervention for per-trochanteric hip fracture: a single centre retrospective cohort study
Problem Based Learning. Problem. Based Learning
 Problem 2013 Based Learning Problem Based Learning Your teacher presents you with a problem in anesthesia, our learning becomes active in the sense that you discover and work with content that you determine
Problem 2013 Based Learning Problem Based Learning Your teacher presents you with a problem in anesthesia, our learning becomes active in the sense that you discover and work with content that you determine
North American Spine Society Public Education Series
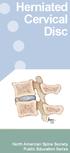 Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Herniated Cervical Disc North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is a Herniated Disc? The backbone, or spine, is composed of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. The vertebrae
Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
 Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. In about
Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis North American Spine Society Public Education Series What Is Adult Isthmic Spondylolisthesis? The spine is made up of a series of connected bones called vertebrae. In about
Digital RIC. Rhode Island College. Linda M. Green Rhode Island College
 Rhode Island College Digital Commons @ RIC Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers Overview Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers 1-1-2013 The Relationship
Rhode Island College Digital Commons @ RIC Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers Overview Master's Theses, Dissertations, Graduate Research and Major Papers 1-1-2013 The Relationship
Multimodal Approach for Managing Postoperative Ileus: Role of Health- System Pharmacists (ACPE program H01P)
 1. In the normal gastrointestinal tract, what percent of nutrient absorption occurs in the jejunum? a. 20%. b. 40%. c. 70%. d. 90%. 2. According to Dr. Erstad, the four components of gastrointestinal control
1. In the normal gastrointestinal tract, what percent of nutrient absorption occurs in the jejunum? a. 20%. b. 40%. c. 70%. d. 90%. 2. According to Dr. Erstad, the four components of gastrointestinal control
Minimally Invasive Discectomy/ Decompression
 Minimally Invasive Discectomy/ Decompression What Is A Minimally Invasive Lumbar Discectomy? A lumbar discectomy is a surgical procedure that involves relieving the pressure placed on nerve roots and/or
Minimally Invasive Discectomy/ Decompression What Is A Minimally Invasive Lumbar Discectomy? A lumbar discectomy is a surgical procedure that involves relieving the pressure placed on nerve roots and/or
JSLS. Analgesia Following Major Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery - PCA versus Intermittent Intramuscular Injection
 Analgesia Following Major Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery - PCA versus Intermittent Intramuscular Injection David M. B. Rosen, Alan M. Lam, Mark A. Carlton, Gregory M. Cario, Lindsay McBride 3 JSLS
Analgesia Following Major Gynecological Laparoscopic Surgery - PCA versus Intermittent Intramuscular Injection David M. B. Rosen, Alan M. Lam, Mark A. Carlton, Gregory M. Cario, Lindsay McBride 3 JSLS
Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent Option For Day Care Surgeries
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 2 Ver. III. (Feb. 2014), PP 09-13 Hyperbaric 2% Lignocaine In Spinal Anaesthesia An Excellent
SUPRAPUBIC PUNCTURE IN THE TREATMENT OF NEUROGENIC BLADDER
 SUPRAPUBIC PUNCTURE IN THE TREATMENT OF NEUROGENIC BLADDER CHARLES C. HIGGINS, M.D. W. JAMES GARDNER, M.D. WM. A. NOSIK, M.D. The treatment of "cord bladder", a disturbance of bladder function from disease
SUPRAPUBIC PUNCTURE IN THE TREATMENT OF NEUROGENIC BLADDER CHARLES C. HIGGINS, M.D. W. JAMES GARDNER, M.D. WM. A. NOSIK, M.D. The treatment of "cord bladder", a disturbance of bladder function from disease
Disclosure. Thoracolumbar Tumors. Intraspinal Tumor Removal Options 6/4/2011. Minimally Invasive Approaches for Spinal Tumors
 Minimally Invasive Approaches for Spinal Tumors Praveen V. Mummaneni, M.D. Disclosure Medtronic (Consultant, Grants) DePuy (Consultant, Other Financial Support) Associate Professor Dept. of Neurosurgery
Minimally Invasive Approaches for Spinal Tumors Praveen V. Mummaneni, M.D. Disclosure Medtronic (Consultant, Grants) DePuy (Consultant, Other Financial Support) Associate Professor Dept. of Neurosurgery
Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
 Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Typical approach Describe anesthesia technique Rather Describe issues with THA and TKA How anesthesia can modify Issues Total Hip Total Knee Blood Loss ++
Anesthesia for Total Hip and Knee Arthroplasty Typical approach Describe anesthesia technique Rather Describe issues with THA and TKA How anesthesia can modify Issues Total Hip Total Knee Blood Loss ++
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis
 Lumbar Spinal Stenosis This article is also available in Spanish: Estenosis de la columna lumbar (topic.cfm?topic=a00701). A common cause of low back and leg pain is lumbar spinal stenosis. As we age,
Lumbar Spinal Stenosis This article is also available in Spanish: Estenosis de la columna lumbar (topic.cfm?topic=a00701). A common cause of low back and leg pain is lumbar spinal stenosis. As we age,
Intro Who should read this document 2 Key practice points 2 What is new in this version 3 Background 3 Guideline Subsection headings
 Enhanced Recovery for Major Urology and Gynaecological Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Dr Dominic O Connor Additional author(s): Jane Kingham Authors Division: Anaesthesia Unique ID: DDCAna3(12)
Enhanced Recovery for Major Urology and Gynaecological Classification: Clinical Guideline Lead Author: Dr Dominic O Connor Additional author(s): Jane Kingham Authors Division: Anaesthesia Unique ID: DDCAna3(12)
NORLAND AVENUE PHARMACY PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING FOR PAIN MANAGEMENT
 NOVEMBER 2011 NORLAND AVENUE PHARMACY PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING N ORLANDA VENUEP HARMACY. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Sciatic Pain
NOVEMBER 2011 NORLAND AVENUE PHARMACY PRESCRIPTION COMPOUNDING N ORLANDA VENUEP HARMACY. COM We customize individual prescriptions for the specific needs of our patients. INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Sciatic Pain
Satisfactory Analgesia Minimal Emesis in Day Surgeries. (SAME-Day study) A Randomized Control Trial Comparing Morphine and Hydromorphone
 Satisfactory Analgesia Minimal Emesis in Day Surgeries (SAME-Day study) A Randomized Control Trial Comparing Morphine and Hydromorphone HARSHA SHANTHANNA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ANESTHESIOLOGY MCMASTER UNIVERSITY
Satisfactory Analgesia Minimal Emesis in Day Surgeries (SAME-Day study) A Randomized Control Trial Comparing Morphine and Hydromorphone HARSHA SHANTHANNA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ANESTHESIOLOGY MCMASTER UNIVERSITY
ANESTHESIA EXAM (four week rotation)
 SPARROW HEALTH SYSTEM ANESTHESIA SERVICES ANESTHESIA EXAM (four week rotation) Circle the best answer 1. During spontaneous breathing, volatile anesthetics A. Increase tidal volume and decrease respiratory
SPARROW HEALTH SYSTEM ANESTHESIA SERVICES ANESTHESIA EXAM (four week rotation) Circle the best answer 1. During spontaneous breathing, volatile anesthetics A. Increase tidal volume and decrease respiratory
POST-OESOPHAGECTOMY ANALGESIC REGIMES: A 15-YEAR REVIEW OF 90 CASES AT UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 40 1\,1 March 1985 POST-OESOPHAGECTOMY ANALGESIC REGIMES: A 15-YEAR REVIEW OF 90 CASES AT UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR A. E. DELILKAN R. VIJAYAN SANNASI SUMMARY 24-48 hour IPPV
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 40 1\,1 March 1985 POST-OESOPHAGECTOMY ANALGESIC REGIMES: A 15-YEAR REVIEW OF 90 CASES AT UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL, KUALA LUMPUR A. E. DELILKAN R. VIJAYAN SANNASI SUMMARY 24-48 hour IPPV
Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan, BA a James Capon, BS, MS a Hayden Smith, BA a Alexandra Napoli, BS a Patrick Gaspar, MD b
 Pre-operative Lumbar Plexus Block Provides Superior Post-operative Analgesia when compared with Fascia Iliaca Block or General Anesthesia alone in Hip Arthroscopy Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan,
Pre-operative Lumbar Plexus Block Provides Superior Post-operative Analgesia when compared with Fascia Iliaca Block or General Anesthesia alone in Hip Arthroscopy Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan,
Urinary Retention in Elective Total Hip and Knee Replacement Surgery
 British Journal of Medical Practitioners, Dec. 8, Volume, Number BJMP 8:() 8-3 Article Post-Operative Urinary Retention in Elective Total Hip and Knee Replacement Surgery Sumit Dutta Introduction: Post-operative
British Journal of Medical Practitioners, Dec. 8, Volume, Number BJMP 8:() 8-3 Article Post-Operative Urinary Retention in Elective Total Hip and Knee Replacement Surgery Sumit Dutta Introduction: Post-operative
I. Chien, I.C. Lu, F.Y. Wang, et al airway management [9]. An examination of a patient s back for spinal landmarks was reported to be a better predict
![I. Chien, I.C. Lu, F.Y. Wang, et al airway management [9]. An examination of a patient s back for spinal landmarks was reported to be a better predict I. Chien, I.C. Lu, F.Y. Wang, et al airway management [9]. An examination of a patient s back for spinal landmarks was reported to be a better predict](/thumbs/92/108339438.jpg) SPINAL PROCESS LANDMARK AS A PREDICTING FACTOR FOR DIFFICULT EPIDURAL BLOCK: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY IN TAIWANESE PATIENTS I Chien, I-Chen Lu, Fu-Yuan Wang, Lee-Ying Soo, Kwong-Leung Yu, and Chao-Shun Tang
SPINAL PROCESS LANDMARK AS A PREDICTING FACTOR FOR DIFFICULT EPIDURAL BLOCK: A PROSPECTIVE STUDY IN TAIWANESE PATIENTS I Chien, I-Chen Lu, Fu-Yuan Wang, Lee-Ying Soo, Kwong-Leung Yu, and Chao-Shun Tang
Assistant Professor, Anaesthesia Department, Govt. General Hospital / Guntur Medical College, Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of 0.25% Ropivacaine
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. I (August. 2016), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of 0.25% Ropivacaine
Tripler Army Medical Center Obstetric Anesthesia Service - FAQs
 Tripler Army Medical Center Obstetric Anesthesia Service - FAQs What is a labor epidural? A labor epidural is a thin tube (called an epidural catheter) placed in a woman s lower back by an anesthesia provider.
Tripler Army Medical Center Obstetric Anesthesia Service - FAQs What is a labor epidural? A labor epidural is a thin tube (called an epidural catheter) placed in a woman s lower back by an anesthesia provider.
As laparoscopic surgeries are gaining popularity, Original Article. Maharjan SK 1, Shrestha S 2 1. Introduction
 , Vol. 1, No. 1, Issue 1, Jul.-Sep., 2012 Original Article Maharjan SK 1, Shrestha S 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Kathmandu Medical College,
, Vol. 1, No. 1, Issue 1, Jul.-Sep., 2012 Original Article Maharjan SK 1, Shrestha S 2 1 Associate Professor, 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Kathmandu Medical College,
Intraperitoneal and Intravenous Routes for Pain Relief in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Intraperitoneal and Intravenous Routes for Pain Relief in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Samar I. Jabbour-Khoury, MD, Aliya S. Dabbous, MD, Frederic J. Gerges, MD, Mireille S. Azar, MD,
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Intraperitoneal and Intravenous Routes for Pain Relief in Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy Samar I. Jabbour-Khoury, MD, Aliya S. Dabbous, MD, Frederic J. Gerges, MD, Mireille S. Azar, MD,
FENTANYL BY CONSTANT RATE I.V. INFUSION FOR POSTOPERATIVE ANALGESIA
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1985), 5, 250-254 FENTANYL BY CONSTANT RATE I.V. INFUSION FOR POSTOPERATIVE ANALGESIA W. S. NIMMO AND J. G. TODD is a synthetic opioid analgesic 50 times more potent than morphine, with
Br. J. Anaesth. (1985), 5, 250-254 FENTANYL BY CONSTANT RATE I.V. INFUSION FOR POSTOPERATIVE ANALGESIA W. S. NIMMO AND J. G. TODD is a synthetic opioid analgesic 50 times more potent than morphine, with
Multi-Modal Pain Management
 Multi-Modal Pain Management July 14th, 2017 Todd Edmiston, MD Disclosures None Fellowship training in Sports and Adult Reconstruction Director of Orthopaedic Center, South Baldwin Regional Medical Center,
Multi-Modal Pain Management July 14th, 2017 Todd Edmiston, MD Disclosures None Fellowship training in Sports and Adult Reconstruction Director of Orthopaedic Center, South Baldwin Regional Medical Center,
Anesthesia for OutPatient Spine Surgery. Michael A. Kellams, D.O.
 Anesthesia for OutPatient Spine Surgery Michael A. Kellams, D.O. DISCLOSURE None! Hot Topics 2017 -Multimodal Analgesia/ERAS -TAP block -Inpatient procedures outpatient (Fusions) Multimodal Analgesia -Using
Anesthesia for OutPatient Spine Surgery Michael A. Kellams, D.O. DISCLOSURE None! Hot Topics 2017 -Multimodal Analgesia/ERAS -TAP block -Inpatient procedures outpatient (Fusions) Multimodal Analgesia -Using
WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML)
 , 49, 2013, 3 63 (5 MG/ML) (5 MG/ML).,.,.,..,..,, SPINAL ANESTHESIA: COMPARISON OF ISOBARIC ROPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) D. Tzoneva, Vl. Miladinov, Al. Todorov, M. P. Atanasova,
, 49, 2013, 3 63 (5 MG/ML) (5 MG/ML).,.,.,..,..,, SPINAL ANESTHESIA: COMPARISON OF ISOBARIC ROPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) WITH ISOBARIC BUPIVACAINE (5 MG/ML) D. Tzoneva, Vl. Miladinov, Al. Todorov, M. P. Atanasova,
WORRIED ABOUT PAIN AFTER ORAL SURGERY?
 WORRIED ABOUT PAIN AFTER ORAL SURGERY? OPIOIDS ARE NOT THE ONLY WAY TO MANAGE PAIN Ask your doctor about opioid-free EXPAREL EXPAREL is indicated for single-dose infiltration in adults to produce postsurgical
WORRIED ABOUT PAIN AFTER ORAL SURGERY? OPIOIDS ARE NOT THE ONLY WAY TO MANAGE PAIN Ask your doctor about opioid-free EXPAREL EXPAREL is indicated for single-dose infiltration in adults to produce postsurgical
Combined Subfascial and Subcutaneous Bupivacaine Instillation for Inguinal Hernia Wounds
 Original Article Combined Subfascial and Subcutaneous Bupivacaine Instillation for Inguinal Hernia Wounds Khaled Mohammed El-Radaideh, Mohammed Ahmed Al-Ghazo 1 and Kamal Eddin Bani-Hani, 2 Departments
Original Article Combined Subfascial and Subcutaneous Bupivacaine Instillation for Inguinal Hernia Wounds Khaled Mohammed El-Radaideh, Mohammed Ahmed Al-Ghazo 1 and Kamal Eddin Bani-Hani, 2 Departments
Influence of Intrapleural Infusion of Marcaine on Post Thoracotomy Pain
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tanaffos (2007) 6(1), 47-51 2007 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran Influence of Intrapleural Infusion of Marcaine on Post Thoracotomy Pain Hamid
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tanaffos (2007) 6(1), 47-51 2007 NRITLD, National Research Institute of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease, Iran Influence of Intrapleural Infusion of Marcaine on Post Thoracotomy Pain Hamid
Efficacy of postoperative epidural analgesia Block B M, Liu S S, Rowlingson A J, Cowan A R, Cowan J A, Wu C L
 Efficacy of postoperative epidural analgesia Block B M, Liu S S, Rowlingson A J, Cowan A R, Cowan J A, Wu C L CRD summary This review evaluated the efficacy of post-operative epidural analgesia. The authors
Efficacy of postoperative epidural analgesia Block B M, Liu S S, Rowlingson A J, Cowan A R, Cowan J A, Wu C L CRD summary This review evaluated the efficacy of post-operative epidural analgesia. The authors
Postoperative epidural analgesia using local anesthetic
 REGIONAL ANESTHESIA SECTION EDITOR DENISE J. WEDEL A Comparison of 0.1% and 0.2% Ropivacaine and Bupivacaine Combined with Morphine for Postoperative Patient-Controlled Epidural Analgesia After Major Abdominal
REGIONAL ANESTHESIA SECTION EDITOR DENISE J. WEDEL A Comparison of 0.1% and 0.2% Ropivacaine and Bupivacaine Combined with Morphine for Postoperative Patient-Controlled Epidural Analgesia After Major Abdominal
Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy
 Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy Department of Anaesthesia University Children s Hospital Zurich Switzerland Epidemiology Herniotomy needed in
Awake regional versus general anesthesia in preterms and ex-preterm infants for herniotomy Department of Anaesthesia University Children s Hospital Zurich Switzerland Epidemiology Herniotomy needed in
Local anesthetic infiltration is not effective in decreasing post- Cesarean section skin pain severity. Iman Fayez Anees
 Rawal Medical Journal An official publication of Pakistan Medical Association Rawalpindi Islamabad branch Established 1975 Volume 36 Number 2 March- June 2011 Original Article Local anesthetic infiltration
Rawal Medical Journal An official publication of Pakistan Medical Association Rawalpindi Islamabad branch Established 1975 Volume 36 Number 2 March- June 2011 Original Article Local anesthetic infiltration
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Comparison of Spinal vs General Anesthesia via Laryngeal Mask Airway in Inguinal Hernia Repair
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Spinal vs General Anesthesia via Laryngeal Mask Airway in Inguinal Hernia Repair Richard E. Burney, MD; Mythili A. Prabhu, MD; Mary Lou V. H. Greenfield, MPH, MS; Amy Shanks,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Spinal vs General Anesthesia via Laryngeal Mask Airway in Inguinal Hernia Repair Richard E. Burney, MD; Mythili A. Prabhu, MD; Mary Lou V. H. Greenfield, MPH, MS; Amy Shanks,
Post-operative nausea and vomiting after gynecologic laparoscopic surgery: comparison between propofol and sevoflurane
 Clinical Research Article Korean J Anesthesiol 2011 January 60(1): 36-40 DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2011.60.1.36 Post-operative nausea and vomiting after gynecologic laparoscopic surgery: comparison between propofol
Clinical Research Article Korean J Anesthesiol 2011 January 60(1): 36-40 DOI: 10.4097/kjae.2011.60.1.36 Post-operative nausea and vomiting after gynecologic laparoscopic surgery: comparison between propofol
Thank you for choosing Saint Joseph s Hospital Health Center for your spine surgery. Updated Jan 2017
 Thank you for choosing Saint Joseph s Hospital Health Center for your spine surgery Updated Jan 2017 This class is designed to give you some basic, important information about spine surgery We will cover
Thank you for choosing Saint Joseph s Hospital Health Center for your spine surgery Updated Jan 2017 This class is designed to give you some basic, important information about spine surgery We will cover
Recurrent Lumbar Disk Herniation With or Without Posterolateral Fusion. Ahmed Zaater, MD, Alaa Azzazi, MD, Sameh Sakr, MD, and Ahmed Elsayed, MD
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Recurrent Lumbar Disk Herniation With or Without Posterolateral Fusion Ahmed Zaater, MD, Alaa Azzazi, MD, Sameh Sakr, MD, and Ahmed Elsayed, MD Study Design: A prospective study assessing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Recurrent Lumbar Disk Herniation With or Without Posterolateral Fusion Ahmed Zaater, MD, Alaa Azzazi, MD, Sameh Sakr, MD, and Ahmed Elsayed, MD Study Design: A prospective study assessing
Nerve root blocks in the treatment of lumbar radicular pain: A minimum five-year follow-up
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 8-1-2006 Nerve root blocks in the treatment of lumbar radicular pain: A minimum five-year follow-up K. Daniel Riew
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 8-1-2006 Nerve root blocks in the treatment of lumbar radicular pain: A minimum five-year follow-up K. Daniel Riew
E to be the analgesic method of choice for painful
 Thoracic Versus Lumbar Epidural Fentanyl for Postthoracotomy Pain Corey W. T. Sawchuk, MD, Bill Ong, MD, Helmut W. Unruh, MD, Thomas A. Horan, MD, and Roy Greengrass, MD Departments of Anesthesia and Surgery,
Thoracic Versus Lumbar Epidural Fentanyl for Postthoracotomy Pain Corey W. T. Sawchuk, MD, Bill Ong, MD, Helmut W. Unruh, MD, Thomas A. Horan, MD, and Roy Greengrass, MD Departments of Anesthesia and Surgery,
ESCOME Pre-Course Outline (v1.09)
 ESCOME Pre-Course Outline (v1.09) 1. Basics of Spinal Disorders Introduction to Spinal Surgery Spinal Anatomy Introduction to Vertebral Anatomical Concepts Anatomy and Function of Joints and Ligaments
ESCOME Pre-Course Outline (v1.09) 1. Basics of Spinal Disorders Introduction to Spinal Surgery Spinal Anatomy Introduction to Vertebral Anatomical Concepts Anatomy and Function of Joints and Ligaments
Anesthesia Processing Guidelines
 Anesthesia Processing Guidelines Policy Number: 10.01.511 Last Review: 5/2014 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 5/2015 Policy The following guidelines are utilized in processing anesthesia claims: 1) Anesthesia
Anesthesia Processing Guidelines Policy Number: 10.01.511 Last Review: 5/2014 Origination: 10/1988 Next Review: 5/2015 Policy The following guidelines are utilized in processing anesthesia claims: 1) Anesthesia
ERAS: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery. Christopher L. Wu, M.D. Professor of Anesthesiology The Johns Hopkins University; Baltimore, Maryland
 ERAS: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Christopher L. Wu, M.D. Professor of Anesthesiology The Johns Hopkins University; Baltimore, Maryland Overview History and basic principles of ERAS Review published
ERAS: Enhanced Recovery After Surgery Christopher L. Wu, M.D. Professor of Anesthesiology The Johns Hopkins University; Baltimore, Maryland Overview History and basic principles of ERAS Review published
Pain Relief Options for Labor. Providing you with quality care, information and support
 Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing you with quality care, information and support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery suite at Lucile Packard Children
Pain Relief Options for Labor Providing you with quality care, information and support What can I expect during my labor and delivery? As a patient in the Labor and Delivery suite at Lucile Packard Children
COMPARISON OF EPIDURAL BUTORPHANOL VERSUS EPIDURAL MORPHINE IN POSTOPERATIVE PAIN RELIEF
 COMPARISON OF EPIDURAL BUTORPHANOL VERSUS EPIDURAL MORPHINE IN POSTOPERATIVE PAIN RELIEF Geeta P. Parikh *, Shah Veena R **, Kalpana Vora ***, Beena Parikh *** and Anish Joshi **** Abstract Introduction:
COMPARISON OF EPIDURAL BUTORPHANOL VERSUS EPIDURAL MORPHINE IN POSTOPERATIVE PAIN RELIEF Geeta P. Parikh *, Shah Veena R **, Kalpana Vora ***, Beena Parikh *** and Anish Joshi **** Abstract Introduction:
