BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS American Neurological Association Published by Wiley-Liss, Inc., through Wiley Subscription Services
|
|
|
- Miranda Joy Terry
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BRIEF COMMUNICATIONS Gene Transfer of Glutamic Acid Decarboxylase Reduces Neuropathic Pain Shuanglin Hao, MD, PhD, 1 Marina Mata, MD, 1 Darren Wolfe, PhD, 2 Joseph C. Glorioso, PhD, 2 and David J. Fink, MD 1 We tested whether transfer of the gene coding for glutamic acid decarboxylase to dorsal root ganglion using a herpes simplex virus vector to achieve release of GABA in dorsal horn would attenuate nociception in this condition. Subcutaneous inoculation of a replication-defective herpes simplex virus vector expressing glutamic acid decarboxylase (vector QHGAD67) 7 days after selective L5 spinal nerve ligation reversed mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia; the antiallodynic effect lasted 6 weeks and was reestablished by reinoculation. QH- GAD67 inoculation also suppressed induction of c-fos and phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 and 2 in the spinal cord. Ann Neurol 2005;57: Peripheral neuropathic pain is a common and difficult to treat concomitant of polyneuropathy or structural nerve injury. Opioids are relatively ineffective, and their use is limited by side effects. Antidepressants and anticonvulsants have demonstrated efficacy in randomized controlled trials but provide only 50% relief in less than half of patients treated. 1 Among the complex mechanisms underlying neuropathic pain, partial nerve injury results in a selective loss of GABAergic inhibitory synaptic currents in spinal cord 2 that contribute to abnormal pain sensitivity and the phenotypic features of the neuropathic pain syndrome. GABAergic agents have not been widely used in the treatment of neuropathic pain because the therapeutic window of these agents is modest and the dose is limited by side effects. Gene transfer represents a novel and useful means to target expression of peptides to focal sites within the From the 1 Department of Neurology, University of Michigan Health System and Ann Arbor VA Healthcare System, Ann Arbor, MI; and 2 Department of Molecular Genetics and Biochemistry, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA. Received Nov 30, 2004, and in revised form Mar 4 and Mar 11, Accepted for publication Mar 11, Published online May 23, 2005, in Wiley InterScience ( DOI: /ana Address correspondence to Dr Fink, Department of Neurology, University of Michigan Health System, 1500 E. Medical Center Drive, Room 1914 TC, Ann Arbor, MI djfink@umich.edu nervous system. We have shown that transduction of sensory neurons of the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) by footpad inoculation with herpes simplex virus (HSV)- based vectors can be used to achieve a regional antinociceptive effect. HSV vectors coding for proenkephalin or the glial cell derived neurotrophic factor produce an antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic effect in rodent models of inflammatory pain, neuropathic pain, and pain resulting from cancer in bone, 3 6 and an HSVvector expressing glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) provides an analgesic effect in the central neuropathic pain syndrome resulting from spinal cord injury. 7 In this study, we examined the antinociceptive effect of GAD expressed from an HSV-based vector in the spinal nerve ligation (SNL) model of neuropathic pain in the rat. Materials and Methods The nonreplicating HSV vector QHGAD67, which is defective in expression of the HSV immediate early genes ICP4, ICP22, ICP27, and ICP47 and contains the human GAD67 gene under the control of the human cytomegalovirus immediate early promoter in the U L 41 locus, has been described previously. 7 The control vector QOZHG is defective in the same HSV genes but contains the green fluorescent protein and Escherichia coli lacz reporter genes. 7 Male Sprague Dawley rats weighing 225 to 250gm underwent selective L5 SNL, as described previously, 5 with the approval of the University Committee on Use and Care of Animals. One week after SNL, 30 l of vector (either QH- GAD67 or QOZHG, plaque-forming units per milliliter) was injected subcutaneously in the plantar surface of the left hind paw, ipsilateral to the ligation. Mechanical allodynia induced by SNL was determined by assessing the response of paw withdrawal to von Frey hairs of graded tensile strength as described previously, 5,8 with a tactile stimulus producing a 50% likelihood of withdrawal determined using the up-down method. 9 Thermal hyperalgesia was determined using a Hargreaves apparatus, 10 recording the time to withdrawal from a radiant thermal stimulus positioned directly under the hind paw. Results After L5 SNL, rats displayed a significant decrease in the magnitude of the mechanical stimulus necessary to evoke a brisk withdrawal response to von Frey hair stimulation (Fig 1A) and a significant reduction in latency to withdraw from a heat stimulus (thermal hyperalgesia; see Fig 1B). Rats inoculated with QH- GAD67 showed a statistically significant increase in mechanical threshold beginning 1 week after inoculation. The antiallodynic effect of QHGAD67-mediated GABA expression was sustained and continuous, lasting 5 to 6 weeks and peaking at 2 weeks after inoculation (see Fig 1A). The peak value of mechanical threshold, 8.6gm, was close to the preoperative value. By 7 weeks after inoculation, the antiallodynic effect of American Neurological Association Published by Wiley-Liss, Inc., through Wiley Subscription Services
2 Fig 1. Antinociceptive effect of QOGAD67 in neuropathic pain. (A) L5 spinal nerve ligation (SNL) caused a significant decrease in the threshold to tactile stimulation, which persisted for more than 4 months. Subcutaneous inoculation of QHGAD67 (arrow) produced an antiallodynic effect reflected in an increase in the mechanical threshold. Reinoculation of QHGAD67 7 weeks after the initial inoculation (arrow) reestablished the antiallodynic effect. Results are expressed as mean standard error of the mean. (open circles) QHGAD67; (closed circles) QOZHG; * p 0.05; ** p 0.01; n 8 animals per group. (B) L5 SNL also caused a significant thermal hyperalgesia, which persisted for 6 weeks. Inoculation with QHGAD67 (arrow), but not QOZHG, reversed the thermal hyperalgesia induced by spinal nerve injury. * p 0.05; ** p 0.01 versus QOZHG-inoculated; n 8 animals per group. The statistical significances of the differences were determined by analysis of variance (StatView 5.2; SAS Institute, Cary, NC) corrected for the number of post hoc comparisons using Scheffé s F test. vector transduction disappeared, and the mechanical threshold of QHGAD67-injected rats was identical to that of control rats. Reinoculation into the same paw with the same dose of QHGAD67 reestablished the antiallodynic effect (see Fig 1A). SNL induced a decrease in the thermal latency from 10.7 to 6.5 seconds, which lasted 3 weeks before gradually recovery. Rats inoculated with QHGAD67 showed a statistically significant increase in thermal latency in the ipsilateral paw beginning 1 week after inoculation (see Fig 1B), an effect that was sustained and continuous, lasting 3 to 4 weeks (see Fig 1B). Shamoperated animals had no change in mechanical threshold or thermal latency (data not shown). Expression of c-fos and phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 and 2 (p-erk1/2) induced by gentle touch is one indirect biological marker of nociceptive processes. 11 Three weeks after SNL, gentle touch was applied once every 4 seconds for 10 minutes, with the flat surface of the experimenter s thumb to the rat s paw, and the number of immunoreactive cells (anti c-fos or anti p-erk1/2 antibodies; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) detected avidinbiotin horseradish peroxidase followed by nickelenhanced diaminobenzidine (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA). 12 The number of Fos-LI positive neurons was substantially increased ipsilateral to SNL compared with sham-operated control rats (Fig 2), and inoculation of vector QHGAD67 significantly reduced the number Fos-LI positive neurons in laminae I VI (see Fig 2). p-erk1/2 expression in laminae I and II was also increased in rats after gentle touch stimulation with SNL, and that increase was blocked in animals inoculated with QHGAD67 (Fig 3). Discussion These results demonstrate that subcutaneous inoculation of an HSV vector expressing GAD to transduce DRG in vivo attenuated the behavioral manifestations of mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia in a model of peripheral neuropathic pain; the effect on behavior was confirmed by histological measures showing a block in the induction of expression of c-fos and p-erk1/2 in the ipsilateral spinal dorsal horn. We have demonstrated previously that transduction of primary sensory neurons with QHGAD67 results in the release of GABA from those cells in vitro and from sensory nerve terminals in spinal cord in vivo. 7 Subcutaneous inoculation of the vector results in transduction of both large and small neurons in the DRG, as determined by immunocytochemical detection of GAD expression. 7 GABA release from transduced cells is constitutive and is mediated by the GABA transporter type 1 (GAT-1). In the spinal cord hemisection model of central neuropathic pain, transduction of DRG by subcutaneous inoculation of QHGAD67 in both hind paws reduces below-level mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia. 7 This study is the first application of this vector to peripheral neuropathic pain. In the spinal cord, GABA is found primarily in in- Hao et al: GAD Gene Transfer 915
3 Fig 2. Effect of QHGAD67 on Fos-LI in dorsal horn. (A) Fos-LI in dorsal horn induced by 10 minutes of gentle tactile stimulation was markedly increased in rats inoculated with QOZHG 1 week after spinal nerve ligation (SNL) and tested 2 weeks later (3 weeks after SNL). (B) This increase was blocked in rats with SNL that had been inoculated with QHGAD67 1 week after SNL and tested 2 weeks later (3 weeks after SNL), and it was found in laminae I VI of dorsal horn. Results are expressed as mean standard error of the mean. ** p 0.01; n 5 animals per group. The difference between sham-operated and SNL animals inoculated with QOZHG was also statistically significant (p 0.01). terneurons of the superficial dorsal horn predominantly in laminae II and III that form axoaxonic synapses on primary afferent terminals and axodendritic synapses on projection neurons. Tonic GABAergic inhibition plays an important role in normal sensory processing, as indicated by increased behavior responsiveness 13 and electrophysiological activity in spinal nociceptive neurons 14 after spinal administration of the GABA A antagonist bicuculline to normal animals and by the development of mechanical allodynia after spinal administration of the GABA B receptor antagonist CGP The mechanical allodynia that results from selective SNL can be reversed by the GABA B agonist baclofen 16 or the GABA A agonist muscimol, 17 and both mechanical allodynia and thermal hyperalgesia after spinal nerve injury are reversed by the GABA A agonist 4,5,6,7-tetrahydroisoxazolo [5,4-c] pyridin-3-ol (isoguvacine) and baclofen. 18 These findings are consistent with observations of loss of GABA activity in dorsal horn after chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve, 19 a decrease in GABA A receptor mediated inhibitory postsynaptic potentials, reduction of GAD65, and evidence of apoptosis in dorsal horn in both the chronic constriction and spared nerve injury models of neuropathic pain. 2 Transgene-mediated GABA released in the dorsal horn acts at both GABA A and GABA B receptors. As we have demonstrated previously, the antinociceptive effect produced by QHGAD67-mediated GABA release can be partially blocked by the GABA A antagonist bicuculline or by the GABA B antagonist phaclofen. 7 GABAergic therapy for neuropathic pain has had limited success. Gene transfer offers the possibility of targeted alteration in the neurotransmitter phenotype to produce the local release of selected neurotransmitters. Among the many viral and nonviral vectors that may be used for gene transfer, HSV, because of its natural neurotropism and high-affinity retrograde transport in sensory neurons, is uniquely suited for modifying neurotransmitter release in dorsal horn after subcutaneous inoculation. 20 We have found previously 916 Annals of Neurology Vol 57 No 6 June 2005
4 Fig 3. Effect of QHGAD67 on the phosphorylated extracellular signal regulated kinase 1 and 2 (p-erk1/2) expression in dorsal horn. p-erk is not induced by 10 minutes of gentle tactile stimulation in sham-operated animals (A), but it is substantially induced after spinal nerve ligation (SNL) in animals inoculated with QOZHG (B). Touch-induced expression of p-erk1/2 was suppressed in animals inoculated with QHGAD67 (C), confirmed by counts of p-erk1/2 positive neurons in the dorsal horn (D). Results are expressed as mean standard error of the mean. ** p 0.01; *** p 0.001; n 5 animals per group. that HSV-mediated transfer of proenkephalin produces a sustained antiallodynic effect in the SNL model of neuropathic pain, 5 and that similar results can be achieved with a vector expressing glial cell derived neurotrophic factor. 6 The magnitude of the antiallodynic effect achieved with the GAD67-expressing vector is substantially greater than that produced by either the proenkephalin- or glial cell derived neurotrophic factor expressing vectors. We propose that this differential effect reflects the role of reduced spinal GABAergic tone in the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain and the selective ability of QHGAD67 to correct that deficit locally. The results suggest that this novel approach may prove useful in the treatment of neuropathic pain. This study was supported by grants from the NIH (National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, NS44507, NS38850, D.J.F., NS43247, M.M.) and the Department of Veterans Affairs (M.M., D.J.F.). We thank V. Thakur and S. Liu for their excellent technical assistance. References 1. Sindrup SH, Jensen TS. Efficacy of pharmacological treatments of neuropathic pain: an update and effect related to mechanism of drug action. Pain 1999;83: Moore KA, Kohno T, Karchewski LA, et al. Partial peripheral nerve injury promotes a selective loss of GABAergic inhibition in the superficial dorsal horn of the spinal cord. J Neurosci 2002;22: Wilson SP, Yeomans DC, Bender MA, et al. Antihyperalgesic effects of infection with a preproenkephalin-encoding herpes virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999;96: Braz J, Beaufour C, Coutaux A, et al. Therapeutic efficacy in experimental polyarthritis of viral-driven enkephalin overproduction in sensory neurons. J Neurosci 2001;21: Hao S, Mata M, Goins W, et al. Transgene-mediated enkephalin release enhances the effect of morphine and evades tolerance to produce a sustained antiallodynic effect. Pain 2003;102: Hao S, Mata M, Wolfe D, et al. HSV-mediated gene transfer of the glial cell derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) provides an anti-allodynic effect in neuropathic pain. Mol Ther 2003;8: Liu J, Wolfe D, Hao S, et al. Peripherally delivered glutamic acid decarboxylase gene therapy for spinal cord injury pain. Mol Ther 2004;10: Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, et al. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 1994;53: Dixon WJ. Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 1980;20: Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, et al. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 1988;32: Catheline G, Le Guen S, Besson JM. Intravenous morphine does not modify dorsal horn touch-evoked allodynia in the mononeuropathic rat: a Fos study. Pain 2001;92: Hao S, Takahata O, Mamiya K, Iwasaki H. Sevoflurane suppresses noxious stimulus-evoked expression of Fos-like immunoreactivity in the rat spinal cord via activation of endogenous opioid systems. Life Sci 2002;71: Yaksh TL. Behavioral and autonomic correlates of the tactile evoked allodynia produced by spinal glycine inhibition: effects of modulatory receptor systems and excitatory amino acid antagonists. Pain 1989;37: Sorkin LS, Puig S, Jones DL. Spinal bicuculline produces hypersensitivity of dorsal horn neurons: effects of excitatory amino acid antagonists. Pain 1998;77: Hao et al: GAD Gene Transfer 917
5 15. Hao JX, Xu XJ, Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z. Intrathecal gammaaminobutyric acidb (GABAB) receptor antagonist CGP induces hypersensitivity to mechanical stimuli in the rat. Neurosci Lett 1994;182: Smith GD, Harrison SM, Birch PJ, et al. Increased sensitivity to the antinociceptive activity of ( / )-baclofen in an animal model of chronic neuropathic, but not chronic inflammatory hyperalgesia. Neuropharmacology 1994;33: Hwang JH, Yaksh TL. The effect of spinal GABA receptor agonists on tactile allodynia in a surgically-induced neuropathic pain model in the rat. Pain 1997;70: Malan TP, Mata HP, Porreca F. Spinal GABA(A) and GABA(B) receptor pharmacology in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Anesthesiology 2002;96: Ibuki T, Hama AT, Wang XT, et al. Loss of GABAimmunoreactivity in the spinal dorsal horn of rats with peripheral nerve injury and promotion of recovery by adrenal medullary grafts. Neuroscience 1997;76: Glorioso JC, Fink DJ. Herpes vector-mediated gene transfer in treatment of diseases of the nervous system. Annu Rev Microbiol 2004;58: An LRRK2 Mutation as a Cause for the Parkinsonism in the Original PARK8 Family Manabu Funayama, PhD, 1 Kazuko Hasegawa, MD, PhD, 2 Etsuro Ohta, MMSci, 1 Noriko Kawashima, MD, 3 Masaru Komiyama, BS, 1 Hisayuki Kowa, MD, PhD, 4 Shoji Tsuji, MD, PhD, 5 and Fumiya Obata, PhD 1 We detected a missense mutation in the kinase domain of the LRRK2 gene in members with autosomal dominant Parkinson s disease of the Japanese family (the Sagamihara family) who served as the basis for the original defining of the PARK8 Parkinson s disease locus. The results of the Sagamihara family, in combination with the unique pathological features characterized by pure nigral degeneration without Lewy bodies, provided us with valuable information for elucidating the protein structure pathogenesis relationship for the gene product of LRRK2. We did not detect this mutation or other known mutations of the LRRK2 gene in Japanese patients with sporadic Parkinson s disease. Ann Neurol 2005;57: Parkinson s disease (PD) [MIM ] is one of the most common neurological disorders and is characterized by rigidity, bradykinesia, tremor, and postural instability. Although PD is a sporadic disease in most cases, various hereditary forms presenting clinical phenotypes similar to those of sporadic PD have been recognized. Molecular genetic studies on these familial forms of parkinsonism have substantially advanced our understanding of the molecular pathogenesis of this disease. 1 6 In a previous study, we identified a new locus for PD, PARK8 (12p11.2-q13.1), by genome-wide linkage From the 1 Division of Clinical Immunology, Kitasato University Graduate School of Medical Sciences; 2 Department of Neurology, National Hospital Organization, Sagamihara National Hospital, Sagamihara; 3 Kawashima Neurological Clinic, Fujisawa; 4 Kitasato University, Sagamihara; and 5 Department of Neurology, Tokyo University, Tokyo, Japan. Received Dec 27, 2004, and in revised form Mar 11, Accepted for publication Mar 11, Current address for Dr Funayama: Research Institute for Diseases of Old Ages, School of Medicine, Juntendo University, Tokyo, Japan. Published online May 4, 2005 in Wiley InterScience ( DOI: /ana Address correspondence to Dr Obata, Department of Immunology, Kitasato University School of Allied Health Sciences, Kitasato, Sagamihara, Kanagawa , Japan. obata@ahs.kitasato-u.ac.jp American Neurological Association Published by Wiley-Liss, Inc., through Wiley Subscription Services
A Clinical Trial of Gene Therapy for Chronic Painpme_720
 1325..1330 PAIN MEDICINE Volume 10 Number 7 2009 A Clinical Trial of Gene Therapy for Chronic Painpme_720 Darren Wolfe, PhD,* James Wechuck, PhD,* David Krisky, MD, PhD,* Marina Mata, MD, and David J.
1325..1330 PAIN MEDICINE Volume 10 Number 7 2009 A Clinical Trial of Gene Therapy for Chronic Painpme_720 Darren Wolfe, PhD,* James Wechuck, PhD,* David Krisky, MD, PhD,* Marina Mata, MD, and David J.
GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat
 Physiol. Res. 3: 31-3, GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat M. FRANĚK, Š. VACULÍN, R. ROKYTA Department of Normal, Pathological
Physiol. Res. 3: 31-3, GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat M. FRANĚK, Š. VACULÍN, R. ROKYTA Department of Normal, Pathological
NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions as Related to Analgesia and Tolerance
 Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy
 Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Yan-Ping Chen, Shao-Rui Chen, and Hui-Lin Pan
 0022-3565/05/3152-696 703$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 315, No. 2 Copyright 2005 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 91314/3054541
0022-3565/05/3152-696 703$20.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 315, No. 2 Copyright 2005 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 91314/3054541
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
Evaluation of Gabapentin and S-( )-3-Isobutylgaba in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
What Does the Mechanism of Spinal Cord Stimulation Tell Us about Complex Regional Pain Syndrome?pme_
 Pain Medicine 2010; 11: 1278 1283 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. What Does the Mechanism of Spinal Cord Stimulation Tell Us about Complex Regional Pain Syndrome?pme_915 1278..1283 Joshua P. Prager, MD, MS Center
Pain Medicine 2010; 11: 1278 1283 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. What Does the Mechanism of Spinal Cord Stimulation Tell Us about Complex Regional Pain Syndrome?pme_915 1278..1283 Joshua P. Prager, MD, MS Center
Special Issue on Pain and Itch
 Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
Special Issue on Pain and Itch Title: Recent Progress in Understanding the Mechanisms of Pain and Itch Guest Editor of the Special Issue: Ru-Rong Ji, PhD Chronic pain is a major health problem world-wide.
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice.
 Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
Changes in long2term syna ptic plasticity in the spinal dorsal horn of neuropathic pa in rats
 226 ( ) JOURNAL OF PEKIN G UNIVERSITY( HEAL TH SCIENCES) Vol. 35 No. 3 J une 2003,,, (, 100083) [ ] / ; ; ; / [ ] :, (central sensitization) :Sprague2Dawley 5/ 6 (L5/ L6), C2, C2 L TP : (1), ( 100 Hz,
226 ( ) JOURNAL OF PEKIN G UNIVERSITY( HEAL TH SCIENCES) Vol. 35 No. 3 J une 2003,,, (, 100083) [ ] / ; ; ; / [ ] :, (central sensitization) :Sprague2Dawley 5/ 6 (L5/ L6), C2, C2 L TP : (1), ( 100 Hz,
Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA
 Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD
 Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 275-279, 2013 Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling YA-JING GUO 1, XU-DAN SHI 2, DI FU
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 275-279, 2013 Analgesic effects of the COX-2 inhibitor parecoxib on surgical pain through suppression of spinal ERK signaling YA-JING GUO 1, XU-DAN SHI 2, DI FU
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Anesthesiology, V 100, No 4, Apr American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc.
 Anesthesiology 2004; 100:912 21 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Nerve Injury Induces a Tonic Bilateral -Opioid Receptor mediated Inhibitory Effect on
Anesthesiology 2004; 100:912 21 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Nerve Injury Induces a Tonic Bilateral -Opioid Receptor mediated Inhibitory Effect on
A role for uninjured afferents in neuropathic pain
 Acta Physiologica Sinica, October 25, 2008, 60 (5): 605-609 http://www.actaps.com.cn 605 Review A role for uninjured afferents in neuropathic pain Richard A. Meyer 1,2,3,*, Matthias Ringkamp 1 Departments
Acta Physiologica Sinica, October 25, 2008, 60 (5): 605-609 http://www.actaps.com.cn 605 Review A role for uninjured afferents in neuropathic pain Richard A. Meyer 1,2,3,*, Matthias Ringkamp 1 Departments
Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
 University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
enhances nociceptive responses in rats
 Brazilian Chronic intrathecal Journal of Medical cannulation and Biological Research (2000) 33: 949-956 ISSN 0100-879X 949 Chronic intrathecal cannulation enhances nociceptive responses in rats F.R.C.
Brazilian Chronic intrathecal Journal of Medical cannulation and Biological Research (2000) 33: 949-956 ISSN 0100-879X 949 Chronic intrathecal cannulation enhances nociceptive responses in rats F.R.C.
Materials and Methods
 Anesthesiology 2004; 100:1258 62 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Spinal Adenosine Receptor Activation Reduces Hypersensitivity after Surgery by a Different
Anesthesiology 2004; 100:1258 62 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Spinal Adenosine Receptor Activation Reduces Hypersensitivity after Surgery by a Different
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced by Spinal Nerve Ligation
 J Korean Med Sci 2002; 17: 225-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced
J Korean Med Sci 2002; 17: 225-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced
HIGH-FREQUENCY ELECTRIC nerve stimulation (HFS)
 1575 ARTICLES The Relationship Between Dorsal Horn Neurotransmitter Content and Allodynia in Neuropathic Rats Treated With High-Frequency Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation David L. Somers, PhD,
1575 ARTICLES The Relationship Between Dorsal Horn Neurotransmitter Content and Allodynia in Neuropathic Rats Treated With High-Frequency Transcutaneous Electric Nerve Stimulation David L. Somers, PhD,
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor
 Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Opioid Receptor Trafficking in Pain States
 Encyclopedia of Pain Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2007 10.1007/978-3-540-29805-2_2962 Robert F. Schmidt and William D. Willis Opioid Receptor Trafficking in Pain States Catherine M. Cahill 3, Anne
Encyclopedia of Pain Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2007 10.1007/978-3-540-29805-2_2962 Robert F. Schmidt and William D. Willis Opioid Receptor Trafficking in Pain States Catherine M. Cahill 3, Anne
Lidocaine inhibits neurite growth in mouse dorsal root ganglion cells in culture
 Lidocaine inhibits neurite growth in mouse dorsal root ganglion cells in culture 3 Hiromi ~iruma', Hiroshi ~ aru~ama~, Zyun'ici B. Simada, Takashi Katakural, Sumio ~ oka~, Toshifumi ~akenaka~ and Tadashi
Lidocaine inhibits neurite growth in mouse dorsal root ganglion cells in culture 3 Hiromi ~iruma', Hiroshi ~ aru~ama~, Zyun'ici B. Simada, Takashi Katakural, Sumio ~ oka~, Toshifumi ~akenaka~ and Tadashi
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Synthesis and Evaluation of Antiallodynic and Anticonvulsant Activity of Novel Amide and Urea Derivatives of Valproic Acid Analogues Dan Kaufmann, Meir Bialer, $, Jakob Avi Shimshoni,
Supporting Information Synthesis and Evaluation of Antiallodynic and Anticonvulsant Activity of Novel Amide and Urea Derivatives of Valproic Acid Analogues Dan Kaufmann, Meir Bialer, $, Jakob Avi Shimshoni,
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) Analgesic Contrast of Diverse Administrations of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoTN/A) Using Rat Neuropathic Pain Model Qiong-Fang YANG1,3,
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) Analgesic Contrast of Diverse Administrations of Botulinum Neurotoxin A (BoTN/A) Using Rat Neuropathic Pain Model Qiong-Fang YANG1,3,
Novel Compounds for Anxiety, Epilepsy, and Neuropathic Pain
 ovel Compounds for Anxiety, Epilepsy, and europathic Pain (OTT ID 1268) Inventors: James Cook, Ph.D. (Lead Inventor and PI) Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry UW-Milwaukee For further information
ovel Compounds for Anxiety, Epilepsy, and europathic Pain (OTT ID 1268) Inventors: James Cook, Ph.D. (Lead Inventor and PI) Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry UW-Milwaukee For further information
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and. widespread hyperalgesia
 Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Gabapentin Antinociception in Mice with Acute Herpetic Pain Induced by Herpes Simplex Virus Infection
 0022-3565/01/2962-270 275$3.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 296, No. 2 Copyright 2001 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 3229/880565
0022-3565/01/2962-270 275$3.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 296, No. 2 Copyright 2001 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 3229/880565
Exercise 1: (5pts) Exercise 2: (5pts) Observe the following diagram and answer the questions below.
 S.E. Biology Exercise 1: (5pts) Observe the following diagram and answer the questions below. 1. Give a suitable title for the given schematic drawing. 2. Indicate the type of the stimulus, the conductor,
S.E. Biology Exercise 1: (5pts) Observe the following diagram and answer the questions below. 1. Give a suitable title for the given schematic drawing. 2. Indicate the type of the stimulus, the conductor,
Virtually everyone has experienced pain in one
 Transfer of Advances in Sciences into Dental Education Recent Insights into Brainstem Mechanisms Underlying Craniofacial Pain Barry J. Sessle, B.D.S., M.D.S., B.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.S.C., D.Sc. (honorary) Abstract:
Transfer of Advances in Sciences into Dental Education Recent Insights into Brainstem Mechanisms Underlying Craniofacial Pain Barry J. Sessle, B.D.S., M.D.S., B.Sc., Ph.D., F.R.S.C., D.Sc. (honorary) Abstract:
Dissecting out mechanisms responsible for peripheral neuropathic pain: Implications for diagnosis and therapy
 Life Sciences 74 (2004) 2605 2610 www.elsevier.com/locate/lifescie Dissecting out mechanisms responsible for peripheral neuropathic pain: Implications for diagnosis and therapy Clifford J. Woolf* Neural
Life Sciences 74 (2004) 2605 2610 www.elsevier.com/locate/lifescie Dissecting out mechanisms responsible for peripheral neuropathic pain: Implications for diagnosis and therapy Clifford J. Woolf* Neural
Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix
 Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix Partap S. Khalsa, D.C., Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Engineering The Neuromatrix From: Melzack R (1999) Pain Suppl 6:S121-6. NIOSH STAR Symposium May
Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix Partap S. Khalsa, D.C., Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Engineering The Neuromatrix From: Melzack R (1999) Pain Suppl 6:S121-6. NIOSH STAR Symposium May
9.98 Neuropharmacology January (IAP) 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.98 Neuropharmacology January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Neuropharmacology: The
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 9.98 Neuropharmacology January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Neuropharmacology: The
1604 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 62, NO. 6, JUNE 2015
 1604 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 62, NO. 6, JUNE 2015 Burst and Tonic Spinal Cord Stimulation Differentially Activate GABAergic Mechanisms to Attenuate Pain in a Rat Model of Cervical
1604 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 62, NO. 6, JUNE 2015 Burst and Tonic Spinal Cord Stimulation Differentially Activate GABAergic Mechanisms to Attenuate Pain in a Rat Model of Cervical
Materials and Methods
 Anesthesiology 2003; 98:203 8 2003 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Intrathecal Lidocaine Reverses Tactile Allodynia Caused by Nerve Injuries and Potentiates
Anesthesiology 2003; 98:203 8 2003 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Intrathecal Lidocaine Reverses Tactile Allodynia Caused by Nerve Injuries and Potentiates
Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice.
 Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice. Satoshi Tateda, MD, Haruo Kanno, MD, PhD, Hiroshi Ozawa, MD, PhD,
Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice. Satoshi Tateda, MD, Haruo Kanno, MD, PhD, Hiroshi Ozawa, MD, PhD,
Pain Mechanisms. Prof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong. The Somatosensory System
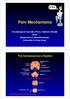 ain Mechanisms rof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong The Somatosensory System Frontal cortex Descending pathway eriaqueductal gray matter
ain Mechanisms rof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong The Somatosensory System Frontal cortex Descending pathway eriaqueductal gray matter
Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain
 Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Keyur S Patel *, Punam D Sachdeva Department of Pharmacology, A.R.College
Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Keyur S Patel *, Punam D Sachdeva Department of Pharmacology, A.R.College
European Society of Anaesthesiologists NITROUS OXIDE (N2O)-INDUCED ANALGESIA
 European Society of Anaesthesiologists NITROUS OXIDE (N2O)-INDUCED ANALGESIA 14RC2 MERVYN MAZE Sir Ivan Magill Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care, Imperial College, London, UK Saturday June
European Society of Anaesthesiologists NITROUS OXIDE (N2O)-INDUCED ANALGESIA 14RC2 MERVYN MAZE Sir Ivan Magill Department of Anaesthetics and Intensive Care, Imperial College, London, UK Saturday June
Neuropathic Pain Activates the Endogenous Opioid System in Mouse Spinal Cord and Induces Opioid Receptor Tolerance
 4576 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 12, 2004 24(19):4576 4584 Development/Plasticity/Repair Neuropathic Pain Activates the Endogenous Opioid System in Mouse Spinal Cord and Induces Opioid Receptor Tolerance
4576 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 12, 2004 24(19):4576 4584 Development/Plasticity/Repair Neuropathic Pain Activates the Endogenous Opioid System in Mouse Spinal Cord and Induces Opioid Receptor Tolerance
Pathophysiology of Pain
 Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
Local GABAergic signaling within sensory ganglia controls peripheral nociceptive transmission
 Local GABAergic signaling within sensory ganglia controls peripheral nociceptive transmission Xiaona Du, 1 Han Hao, 1 Yuehui Yang, 1 Sha Huang, 1 Caixue Wang, 1 Sylvain Gigout, 2 Rosmaliza Ramli, 2,3 Xinmeng
Local GABAergic signaling within sensory ganglia controls peripheral nociceptive transmission Xiaona Du, 1 Han Hao, 1 Yuehui Yang, 1 Sha Huang, 1 Caixue Wang, 1 Sylvain Gigout, 2 Rosmaliza Ramli, 2,3 Xinmeng
Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(9):5916-5921 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001263 Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats Guojun Wang 1,2*, Dawei Dai
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(9):5916-5921 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001263 Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats Guojun Wang 1,2*, Dawei Dai
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in the rat
 Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist BD1047 Reduces Allodynia and Spinal ERK Phosphorylation Following Chronic Compression of Dorsal Root Ganglion in Rats
 Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Vol 14: 359-364, December, 2010 DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.6.359 Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist BD1047 Reduces Allodynia and Spinal ERK Phosphorylation Following Chronic Compression
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Vol 14: 359-364, December, 2010 DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.6.359 Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist BD1047 Reduces Allodynia and Spinal ERK Phosphorylation Following Chronic Compression
Glycine-gated ion channels Converging mechanism and therapeutic potentials
 Glycine-gated ion channels Converging mechanism and therapeutic potentials Li Zhang Laboratory for Integrative Neuroscience, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institutes of Health,
Glycine-gated ion channels Converging mechanism and therapeutic potentials Li Zhang Laboratory for Integrative Neuroscience, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institutes of Health,
Comparison of the Effects of Zonisamide, Ethosuximide and Pregabalin in the Chronic Constriction Injury Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats
 Original Article Comparison of the Effects of Zonisamide, Ethosuximide and Pregabalin in the Chronic Constriction Injury Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats Goyal S, Singla S, Kumar D, Menaria G Department
Original Article Comparison of the Effects of Zonisamide, Ethosuximide and Pregabalin in the Chronic Constriction Injury Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats Goyal S, Singla S, Kumar D, Menaria G Department
Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer
 Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Name Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Period Chapter 48: Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling Concept 48.1 Neuron organization and structure reflect function in information transfer 1. What is
Curcumin Attenuates Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constrictive Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain
 Pain Ther (2014) 3:59 69 DOI 10.1007/s40122-014-0024-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Curcumin Attenuates Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constrictive Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Yu Xiang Di Cao
Pain Ther (2014) 3:59 69 DOI 10.1007/s40122-014-0024-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Curcumin Attenuates Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constrictive Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Yu Xiang Di Cao
Neurodegenerative Disease. April 12, Cunningham. Department of Neurosciences
 Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Neurodegenerative Disease April 12, 2017 Cunningham Department of Neurosciences NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASE Any of a group of hereditary and sporadic conditions characterized by progressive dysfunction,
Received 26 April 2004; revised 21 August 2004; accepted 20 September 2004 Available online 19 November 2004
 Experimental Neurology 191 (2005) 128 136 www.elsevier.com/locate/yexnr Ectopic discharges from injured nerve fibers are highly correlated with tactile allodynia only in early, but not late, stage in rats
Experimental Neurology 191 (2005) 128 136 www.elsevier.com/locate/yexnr Ectopic discharges from injured nerve fibers are highly correlated with tactile allodynia only in early, but not late, stage in rats
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sat, 03 Nov 2018 09:24:50 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 10/06/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sat, 03 Nov 2018 09:24:50 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 10/06/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Enhanced Evoked Excitatory Transmitter Release in Experimental Neuropathy Requires Descending Facilitation
 8370 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 10, 2003 23(23):8370 8379 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Enhanced Evoked Excitatory Transmitter Release in Experimental Neuropathy Requires Descending Facilitation
8370 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 10, 2003 23(23):8370 8379 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Enhanced Evoked Excitatory Transmitter Release in Experimental Neuropathy Requires Descending Facilitation
Byeol-Rim Kang and Chang-Beohm Ahn Department of Acupuncture and Moxibustion, College of Oriental Medicine Dong-Eui University, Busan , Korea
 The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, Vol. 35, No. 6, 987 993 2007 World Scientific Publishing Company Institute for Advanced Research in Asian Science and Medicine N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Antagonist
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, Vol. 35, No. 6, 987 993 2007 World Scientific Publishing Company Institute for Advanced Research in Asian Science and Medicine N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Antagonist
The Nervous System Mark Stanford, Ph.D.
 The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System Functional Neuroanatomy and How Neurons Communicate Mark Stanford, Ph.D. Santa Clara Valley Health & Hospital System Addiction Medicine and Therapy Services The Nervous System In response
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 METHODS Mice and rats. Behavioural experiments were performed in male and female 7 12 week old mice or in male 7 10 week old Wistar rats. Permissions for the animal experiments have been obtained from
METHODS Mice and rats. Behavioural experiments were performed in male and female 7 12 week old mice or in male 7 10 week old Wistar rats. Permissions for the animal experiments have been obtained from
Reflexes. Handout on The Basic Reflex Arc and Stretch and Tendon Reflexes. -55 mv -70 mv EPSP. By Noel Ways
 Reflexes Handout on The Basic Reflex Arc and Stretch and Tendon Reflexes By Noel Ways Basic Reflex Arch 2. : s are always unipolar and will conduct and impulse to a control center. In this case the control
Reflexes Handout on The Basic Reflex Arc and Stretch and Tendon Reflexes By Noel Ways Basic Reflex Arch 2. : s are always unipolar and will conduct and impulse to a control center. In this case the control
Analgesic Drugs PHL-358-PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS-I. Mr.D.Raju,M.pharm, Lecturer
 Analgesic Drugs PHL-358-PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS-I Mr.D.Raju,M.pharm, Lecturer Mechanisms of Pain and Nociception Nociception is the mechanism whereby noxious peripheral stimuli are transmitted to
Analgesic Drugs PHL-358-PHARMACOLOGY AND THERAPEUTICS-I Mr.D.Raju,M.pharm, Lecturer Mechanisms of Pain and Nociception Nociception is the mechanism whereby noxious peripheral stimuli are transmitted to
Research Article Effects of Electroacupuncture Treatment on Bone Cancer Pain Model with Morphine Tolerance
 Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8028474, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8028474 Research Article Effects of Electroacupuncture Treatment on Bone Cancer
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 8028474, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8028474 Research Article Effects of Electroacupuncture Treatment on Bone Cancer
What it Takes to be a Pain
 What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
Mechanical sensitization of cutaneous sensory fibers in the spared nerve injury mouse model
 Smith et al. Molecular Pain 2013, 9:61 MOLECULAR PAIN SHORT REPORT Open Access Mechanical sensitization of cutaneous sensory fibers in the spared nerve injury mouse model Amanda K Smith, Crystal L O Hara
Smith et al. Molecular Pain 2013, 9:61 MOLECULAR PAIN SHORT REPORT Open Access Mechanical sensitization of cutaneous sensory fibers in the spared nerve injury mouse model Amanda K Smith, Crystal L O Hara
Opiates distinguish spinal excitation from inhibition evoked by noxious heat stimuli in the rat: relevance to theories of analgesia
 Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 94, 185-191 Opiates distinguish spinal excitation from inhibition evoked by noxious heat stimuli in the rat: relevance to theories of analgesia 1N.C. Harris & 2R.W. Ryall Department
Br. J. Pharmacol. (1988), 94, 185-191 Opiates distinguish spinal excitation from inhibition evoked by noxious heat stimuli in the rat: relevance to theories of analgesia 1N.C. Harris & 2R.W. Ryall Department
Possible Involvement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Analgesic Effects of 4-Methylcatechol on Neuropathic Pain
 49 Bull Yamaguchi Med School 57 3-4 :49-56, 2010 Possible Involvement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Analgesic Effects of 4-Methylcatechol on Neuropathic Pain Kozo Ishikawa 2 Department of Emergency
49 Bull Yamaguchi Med School 57 3-4 :49-56, 2010 Possible Involvement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Analgesic Effects of 4-Methylcatechol on Neuropathic Pain Kozo Ishikawa 2 Department of Emergency
Tlx3 and Tlx1 are post-mitotic selector genes determining glutamatergic over GABAergic cell fates
 Tlx3 and Tlx1 are post-mitotic selector genes determining glutamatergic over GABAergic cell fates L. Cheng, A. Arata, R. Mizuguchi, Y. Qian, A. Karunaratne, P.A. Gray, S. Arata, S. Shirasawa, M. Bouchard,
Tlx3 and Tlx1 are post-mitotic selector genes determining glutamatergic over GABAergic cell fates L. Cheng, A. Arata, R. Mizuguchi, Y. Qian, A. Karunaratne, P.A. Gray, S. Arata, S. Shirasawa, M. Bouchard,
Hong Jiang 1, Dong Fang 1, Ling-Yu Kong 1, Zi-Run Jin 1, Jie Cai 1, Xue-Jing Kang 1, You Wan 2,3* and Guo-Gang Xing 1,2,3*
 Jiang et al. Molecular Brain 2014, 7:72 RESEARCH Open Access Sensitization of neurons in the central nucleus of the amygdala via the decreased GABAergic inhibition contributes to the development of neuropathic
Jiang et al. Molecular Brain 2014, 7:72 RESEARCH Open Access Sensitization of neurons in the central nucleus of the amygdala via the decreased GABAergic inhibition contributes to the development of neuropathic
EFFECTS OF Pueraria mirifica ON NEUROPATHIC PAIN IN RATS
 EFFECTS OF Pueraria mirifica ON NEUROPATHIC PAIN IN RATS Kamolchanok Tanchotikul 1, Quankamon Dejativongse Na Ayudhya 1*, Orawan Piyaboon 1 and Supin Chompoopong 2 1 Department of Biology, Mahidol Wittayanusorn
EFFECTS OF Pueraria mirifica ON NEUROPATHIC PAIN IN RATS Kamolchanok Tanchotikul 1, Quankamon Dejativongse Na Ayudhya 1*, Orawan Piyaboon 1 and Supin Chompoopong 2 1 Department of Biology, Mahidol Wittayanusorn
Analgesics, pain and tolerance: The St John s discussion
 EDITORIAL Analgesics, pain and tolerance: The St John s discussion Four of the articles in the present issue of Pain Research & Management discuss preclinical issues relevant to understanding the changes
EDITORIAL Analgesics, pain and tolerance: The St John s discussion Four of the articles in the present issue of Pain Research & Management discuss preclinical issues relevant to understanding the changes
Functional Plasticity of Group II Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in. Regulating Spinal Excitatory and Inhibitory Synaptic Input in Neuropathic Pain
 JPET Fast This article Forward. has not been Published copyedited on and October formatted. The 5, 2010 final version as DOI:10.1124/jpet.110.173112 may differ from this version. JPET #173112 1 Functional
JPET Fast This article Forward. has not been Published copyedited on and October formatted. The 5, 2010 final version as DOI:10.1124/jpet.110.173112 may differ from this version. JPET #173112 1 Functional
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Yanbing He 1, 2, Shiyuan Xu 1, Junjie Huang 2, Qingjuan Gong 2. NEURAL REGENERATION RESEARCH May 2014,Volume 9,Issue 10
 NEURAL REGENERATION RESEARCH May 14,Volume 9,Issue 1 www.nrronline.org Analgesic effect of intrathecal bumetanide is accompanied by changes in spinal sodium-potassium-chloride co-transporter 1 and potassium-chloride
NEURAL REGENERATION RESEARCH May 14,Volume 9,Issue 1 www.nrronline.org Analgesic effect of intrathecal bumetanide is accompanied by changes in spinal sodium-potassium-chloride co-transporter 1 and potassium-chloride
THE EFFECT OF VOLUNATARY EXERCISE ON NEUROPATHIC PAIN. Kevin L. Farmer
 THE EFFECT OF VOLUNATARY EXERCISE ON NEUROPATHIC PAIN BY Kevin L. Farmer Submitted to the graduate degree program in Rehabilitation Science and the Graduate Faculty of the University of Kansas Medical
THE EFFECT OF VOLUNATARY EXERCISE ON NEUROPATHIC PAIN BY Kevin L. Farmer Submitted to the graduate degree program in Rehabilitation Science and the Graduate Faculty of the University of Kansas Medical
San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001
 PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
Applied physiology: neuropathic pain
 1 Applied physiology: neuropathic pain VICTORIA CJ WALLACE AND ANDREW SC RICE Introduction 3 Animal models of neuropathic pain 4 Mechanisms of neuropathic hypersensitivity 7 Conclusions 16 References 16
1 Applied physiology: neuropathic pain VICTORIA CJ WALLACE AND ANDREW SC RICE Introduction 3 Animal models of neuropathic pain 4 Mechanisms of neuropathic hypersensitivity 7 Conclusions 16 References 16
A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch
 Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Descending modulation in persistent pain: an update
 Pain 100 (2002) 1 6 Topical review Descending modulation in persistent pain: an update Ke Ren, Ronald Dubner* www.elsevier.com/locate/pain Department of Oral and Craniofacial Biological Sciences, Program
Pain 100 (2002) 1 6 Topical review Descending modulation in persistent pain: an update Ke Ren, Ronald Dubner* www.elsevier.com/locate/pain Department of Oral and Craniofacial Biological Sciences, Program
TRANSLATIONAL AND CLINICAL RESEARCH
 TRANSLATIONAL AND CLINICAL RESEARCH Transplantation of GABAergic Neurons from ESCs Attenuates Tactile Hypersensitivity Following Spinal Cord Injury DAE-SUNG KIM, a SE JUNG JUNG, a TAICK SANG NAM, a,b YOUNG
TRANSLATIONAL AND CLINICAL RESEARCH Transplantation of GABAergic Neurons from ESCs Attenuates Tactile Hypersensitivity Following Spinal Cord Injury DAE-SUNG KIM, a SE JUNG JUNG, a TAICK SANG NAM, a,b YOUNG
Pathophysiological Classification of Pain
 PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Overview Pathophysiological Classification of Pain Central sensitization/ dysfunctional pain Nociceptive pain - Somatic - Visceral Multiple pain mechanisms may coexist (mixed pain) Neuropathic
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Overview Pathophysiological Classification of Pain Central sensitization/ dysfunctional pain Nociceptive pain - Somatic - Visceral Multiple pain mechanisms may coexist (mixed pain) Neuropathic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue. Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1
 Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Chapter 12 Nervous Tissue Copyright 2009 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1 Terms to Know CNS PNS Afferent division Efferent division Somatic nervous system Autonomic nervous system Sympathetic nervous system Parasympathetic
Calcitonin gene-related peptide is involved in inflammatory pain but not in postoperative pain.
 Calcitonin gene-related peptide is involved in inflammatory pain but not in postoperative pain. Kumiko Ishida, M.D.,* Tomoyuki Kawamata, M.D.,* Satoshi Tanaka M.D.,* Takayuki Shindo, M.D., Mikito Kawamata,
Calcitonin gene-related peptide is involved in inflammatory pain but not in postoperative pain. Kumiko Ishida, M.D.,* Tomoyuki Kawamata, M.D.,* Satoshi Tanaka M.D.,* Takayuki Shindo, M.D., Mikito Kawamata,
What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle.
 What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle. Nociception The detection of tissue damage or impending tissue damage, but There can be tissue damage without
What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle. Nociception The detection of tissue damage or impending tissue damage, but There can be tissue damage without
Title proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago. Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Olopatadine hydrochloride inhibits proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago Yoshizaki, Ayumi; Sato, Shinichi Citation Journal of dermatological science, Issue
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Olopatadine hydrochloride inhibits proteinase-activated receptor 2 ago Yoshizaki, Ayumi; Sato, Shinichi Citation Journal of dermatological science, Issue
Somatosensation. Recording somatosensory responses. Receptive field response to pressure
 Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Cancer-induced bone pain
 Cancer-induced bone pain Common Prevalent in particular cancers: breast (73%), prostate (68%), thyroid (42%), lung (36%), renal (35%), colon (5%) Correlates with an increased morbidity Reduced performance
Cancer-induced bone pain Common Prevalent in particular cancers: breast (73%), prostate (68%), thyroid (42%), lung (36%), renal (35%), colon (5%) Correlates with an increased morbidity Reduced performance
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress REDUCING THE PAIN FACTOR AN UPDATE ON PERI-OPERATIVE ANALGESIA Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of Veterinary,
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress REDUCING THE PAIN FACTOR AN UPDATE ON PERI-OPERATIVE ANALGESIA Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of Veterinary,
Analgesia Mediated by the TRPM8 Cold Receptor in Chronic Neuropathic Pain
 Current Biology 16, 1591 1605, August 22, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2006.07.061 Analgesia Mediated by the TRPM8 Cold Receptor in Chronic Neuropathic Pain Article Clare
Current Biology 16, 1591 1605, August 22, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2006.07.061 Analgesia Mediated by the TRPM8 Cold Receptor in Chronic Neuropathic Pain Article Clare
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT
 Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics
 279 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics Available online at Print ISSN: 2278 2648 Online ISSN: 2278-2656 IJRPP Volume 2 Issue 1 2013 Research article Protective effect
279 International Journal of Research in Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapeutics Available online at Print ISSN: 2278 2648 Online ISSN: 2278-2656 IJRPP Volume 2 Issue 1 2013 Research article Protective effect
