SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Brian Barton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 METHODS Mice and rats. Behavioural experiments were performed in male and female 7 12 week old mice or in male 7 10 week old Wistar rats. Permissions for the animal experiments have been obtained from the Regierung von Mittelfranken (ref. no /03) and from the Veterinäramt des Kantons Zürich (ref. no. 121/2006 and 34/2007). In all behavioural tests, the observer was blinded to either genotype or drug treatment. Drugs. For intrathecal injection (i.t.) in mice, diazepam (dzp) was dissolved in 10% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) / 90% artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) (vehicle). Total i.t. injection volume was 2 µl (for details of the injection procedure see ref. 31). Up to a concentration of 20% i.t. DMSO had no effect on pain behaviour in mice. For i.p. injection dzp was dissolved in 0.3% tween 80, 99.7% ACSF. Morphine was dissolved in ACSF. L-838,417 synthesized by ANAWA (Wangen, Switzerland) was suspended in 0.5% methyl cellulose and 0.9% NaCl and applied to rats either p.o. or i.p. in a total volume of 200 µl. Flumazenil (10 mg/kg) and naloxone (10 mg/kg) were dissolved in DMSO (1%) and injected i.p. in a total volume of 200 µl. Formalin test 32. Formalin (20 µl, 5 % in ACSF) was injected subcutaneously into the dorsal surface of the left hindpaw. Flinches of the injected paw were counted for 60 min starting immediately after formalin injection. I.t. drugs (dzp or vehicle) were injected 10 min before formalin injection. Flumazenil (10 mg/kg) was injected i.p. 30 min prior to formalin injection. Inflammatory pain. Inflammatory pain was assessed in the zymosan A model 33. In mice, 0.06 mg zymosan A suspended in 20 µl 0.9% NaCl was injected subcutaneously into the plantar side of the left hindpaw. The model was also used in rats, but 1 mg zymosan A were used. Heat hyperalgesia was assessed 24 hours or 6 hours after induction of inflammation in mice and rats, respectively. Neuropathic pain. Dzp, L-838,417 and morphine were analyzed in the chronic constriction injury (CCI) model 34 in 7-8 week old mice or rats. Unilateral constriction injury of the left 1
2 sciatic nerve just proximal to the trifurcation was performed with three loose ligatures. In sham-operated animals the sciatic nerve was exposed and the connective tissue was freed, but no ligatures were applied. In these sham-operated animals only a minor and transient hyperalgesia occurred. Heat hyperalgesia, cold allodynia and mechanical sensitization were assessed 7-9 days after surgery. Heat hyperalgesia. Paw withdrawal latencies upon exposure to a defined radiant heat stimulus were measured using a commercially available apparatus (Plantar Test, Ugo Basile, Comerio, Italy). 4-5 measurements were taken in each animal for every time point. Measurements of paw withdrawal latencies of the inflamed or injured paw and of the contralateral paw were made alternately. Cold allodynia. The time spent lifting, shaking or licking the paw (s/min) was measured for 5 minutes following application of a drop of acetone onto the injured paw. Mechanical sensitization. Mechanical sensitivity of was assessed with electronic von-frey filaments (IITC, Woodland Hills, CA). Triple measurements of paw withdrawal thresholds (g) made for each time point and animal. Locomotor activity was tested using a commercially available microprocessor controlled activity cage (actiframe, Gerb Elektronik). Mice were placed in the apparatus 15 min before testing. Motor activity was measured min and min after i.t. and p.o. drug application, respectively. Motor impairment 35. A possible impairment of motor function was assessed in the rotarod test. Rats were trained on day zero and the maximum speed tolerated for at least 2 min was determined for each rat. On the following day, rotarod performance was determined again 30 min after treatment with L-838,417 or vehicle (p.o.). Electrophysiology. DRGs (from segments L4 L6) were removed from day old mice, dissociated and plated on poly-l-lysine coated cover slips (for details see ref. 36). GABA-induced currents were recorded from capsaicin-sensitive DRG neurones 3 30 hrs after plating. Transverse slices (250 µm thick) of the lumbar spinal cord were prepared from 2
3 14-24 day old mice. GABAergic membrane currents were recorded from superficial dorsal horn neurones (laminae I and II) as described previously 3. In both preparations, GABA (1 mm) was applied by short (10 ms) puffer applications to the soma of the recorded neuron at a frequency of 0.07 Hz. Dzp (1 µm) was applied via bath perfusion. All recordings were made in the presence of the GABA B receptor antagonist CGP-55,845 (200 µm). Immunofluorescence. The localization of GABA A receptor α subunits on primary afferent nerve terminals and intrinsic dorsal horn neurons was determined by double immunofluorescence staining on sections from perfusion-fixed adult mice 27. Antibodies were home-made subunit-specific antisera 27 and commercial antibodies against substance P (T1609, Bachem, St Helens, UK) and NK1 (S8305, Sigma, St Louis, MO). Sections processed for double immunofluorescence were digitalized by confocal laser scanning microscopy (resolution 90 nm/pixel; 2-3 images per animal; n = 3 mice) and images were processed with Imaris (Bitplane, Switzerland). Double-labeled objects (image profiles) in single confocal sections were identified by a segmentation algorithm (minimal size 0.2 µm 2 ; minimal intensity on a 256 gray-level scale). The number of single and double labeled profiles was calculated. All values are expressed as percent double-labeled profiles relative to the marker indicated. fmri methods. fmri experiments were performed in male Wistar rats weighing g. During the measurements, rats were slightly anaesthetized with isoflurane (1-2%) to maintain a respiration rate of about 60 cycles / min and constant blood pco 2 levels. Measurements were made using a 4.7 T BRUKER Biospec scanner with a free bore of 40 cm, equipped with an actively RF-decoupled coil system. A whole-body birdcage resonator enabled homogenous excitation and a 3 cm quadrature surface coil, which served as a receiver, was located directly above the head of the animal to maximize the signal-to-noiseratio. Constant positioning of the rat s head within the scanner was verified by rapid MR measurements. A functional series of 1470 sets (4 s each, total of 96 min) of 22 axial images (slice thickness 1 mm, field of view 25 x 25 mm, 5.20 mm to mm from the bregma 37 ) were acquired using the Echo Planar Imaging Technique (EPI: matrix 64 x 64, TR = 4000 ms, TEef = 23.4 ms, 2 acquisitions). Anatomical scans with a high spatial resolution were 3
4 obtained with RARE 38 (slice thickness 1 mm, field of view 25 x 25 mm, matrix 256 x 256, TR = 400 ms, TE = 18 ms, NEX = 8). Noxious heat stimulation was performed by applying temperature ramps (34 C to 52 C [noxious stimulation] or to 42 C [innocuous stimulation] with 15 s rise and fall times and a 5 s plateau phase) through two Peltier elements tightly attached to both hind paws (in awake rats this stimulation paradigm yielded paw withdrawal latencies similar to those obtained in the behavioural tests with radiant heat). Thermal stimuli were applied to the left and right hindpaw alternately at 2 min intervals. After 32 min of recording, L-838,417 (1 mg/kg) or vehicle was injected via an i.p. catheter without changing the position of the animal in the scanner. After drug injection recording was continued for 64 min using the same stimulation paradigm. Data were analysed with Brainvoyager QX after appropriate pre-processing (motion correction, mean intensity adjustment, spatial smoothing 0.6 mm FWHM, temporal Gaussian smoothing: 12 s and temporal high pass filtering of 9 cycles) with a GLM approach with 4 predictors: inflamed (left) / non-inflamed (right) paw before and after drug injection and Bonferroni correction. Z-score maps of the individual rats were group analysed using custommade analysis software (MagnAn 39 running under IDL ). Anatomical and functional images were transferred into the register by an affine transformation scheme with only 6 degrees of freedom derived from the individual brain masks. The registered anatomical data and z-score maps were averaged over all animals. Contrast specific mean z-score maps were calculated using a threshold of 3.0. Significantly activated voxels were labelled automatically using a digital standard rat brain atlas 37. For each rat, brain structure and stimulation condition, we then first calculated the activation intensity as the stimulus-induced relative change in the BOLD signal (F). To quantify the effect of L-838,417 on the stimulus-induced BOLD signal changes we calculated ΔF/F = (F postdrug F predrug ) / F predrug. Statistical analysis was performed using the paired Student t-test. False colour images of stimulus-induced changes in BOLD signals were obtained by mapping the calculated mean BOLD signal change of each voxel onto all significantly activated voxels. Note that the different colours in Fig. 4 encode F (signal amplitude), not statistical coefficients. 4
5 31. Depner, U. B., Reinscheid, R. K., Takeshima, H., Brune, K. & Zeilhofer, H. U. Normal sensitivity to acute pain, but increased inflammatory hyperalgesia in mice lacking the nociceptin precursor polypeptide or the nociceptin receptor. Eur J Neurosci 17, (2003). 32. Dubuisson, D. & Dennis, S. G. The formalin test: a quantitative study of the analgesic effects of morphine, meperidine, and brain stem stimulation in rats and cats. Pain 4, (1977). 33. Hargreaves, K., Dubner, R., Brown, F., Flores, C. & Joris, J. A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32, (1988). 34. Bennett, G. J. & Xie, Y. K. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 33, (1988). 35. Bonetti, E.P. et al. Ro : partial inverse agonism at the BZR and interaction with ethanol. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 31, (1988). 36. Zeilhofer, H.U., Kress, M. & Swandulla, D. Fractional Ca 2+ currents through capsaicinand proton-activated ion channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurones. J Physiol 503, (1997). 37. Paxinos G. & Watson C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates. 4th edition (Academic Press, San Diego, 1998). 38. Hennig, J., Nauerth, A. & Friedburg, H. RARE imaging: a fast imaging method for clinical MR. Magn Reson Med 3, (1986). 39. Hess, A., Sergejeva, M., Budinsky, L., Zeilhofer, H.U. & Brune K. Imaging of hyperalgesia in rats by functional MRI. Eur J Pain 11, (2007). 5
6 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary figure 1 Antinociceptive effects of diazepam (dzp) in the mouse formalin test. a, number of flinches (mean ± SEM, n = 5) versus time in wild-type (wt) mice treated with dzp 0.09 mg/kg i.t. and/or flumazenil (flu, 10 mg/kg, i.p.). b, maximum possible analgesia (number flinches in dzp-treated mice / number flinches in vehicle-treated mice x 100%) (mean ± SEM) obtained with different doses of i.t. dzp. **, statistically significant against vehicle with P 0.01; ***, P (analysis of variance [ANOVA] followed by Bonferroni post hoc test). c, total number of flinches (mean ± SEM). ***, statistically significant against all other groups (P 0.001, ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post-hoc test). 6
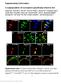
7 Supplemantary figure 2 Laminar distribution of GABA A receptor α subunits and of substance P (SP) and NK1 receptor immunoreactivity. Single immunofluorescence staining for the GABA A receptor α1, α2, α3, α5 subunits, SP, and NK1 receptors in lamina I and II of mouse lumbar spinal dorsal horn. a d, distinct laminar distribution of GABA A receptor α subunits, illustrating the high relative abundance of α2 and α3 subunits. e, f, distribution of SP-positive primary afferent nerve fibers and NK1 receptor-positive neurons in the dorsal horn. Scale bar: 100 µm. Supplementary table 1: Quantitative assessment of GABA A receptor subunit colocalization with substance P (SP) and NK1 receptors markers α2-sp/α2 α3-sp/α3 α2-nk1/α2 α3-nk1/α3 α2α-sp/sp α3-sp/sp α2-nk1/nk1 α3-nk1/nk1 co-localization 37±8% 19±5% 9±3% 21±4% 47±13% 24±5% 27±6% 47±9% 7
8 Supplementary figure 3 Antihyperalgesic effects of intrathecal diazepam (dzp) in the rat. Inflammatory hyperalgesia was induced by subcutaneous injection of 1 mg zymosan A into the left hindpaw. Dzp (0.09 mg/kg) was injected i.t. and paw withdrawal latencies (mean ± sem, n = 5 / group) were measured. The maximum analgesia achieved in rats was similar to that obtained mice, but shorter lasting. 8
9 Supplementary table 2: Changes in heat-induced brain activation measured by rat fmri after injection of vehicle. Stimulation of inflamed paw with noxious heat Stimulation of non-inflamed paw with noxious heat Stimulation of non-inflamed paw with innocuous temperature Area ΔF/F (mean±sem) Sign. vs. ΔF/F (mean±sem) Sign. vs. ΔF/F (mean±sem) Sign. vs. Incidence* predrug Incidence* predrug Incidence* predrug (P) + (P) + (P) + MTh 0.26±0.09 8/ ±0.07 8/ ±0.10 5/ S1c -0.04± ± ±0.24 6/ Cg -0.07± ± ±0.30 7/ FAC -0.19± ± ±0.39 6/ LS 0.09± ± ± MTh, medial thalamus; S1c, primary somatosensory cortex contralateral; Cg, cingulate cortex; FAC, frontal association cortex; LS, limbic system (including amygdala, entorhinal cortex and hippocampus). * Number of rats, in which a significant noxious heat-induced activation of the respective area occurred / total number of rats studied + Paired Student t-test 9
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch
 Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
 University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
University of Kentucky From the SelectedWorks of Renee R. Donahue 2001 Enhanced formalin nociceptive responses following L5 nerve ligation in the rat reveals neuropathy-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice.
 Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
Rapamycin Suppresses Astrocytic and Microglial Activation and Reduced Development of Neuropathic Pain after Spinal Cord Injury in Mice. Satoshi Tateda, M.D., Haruo Kanno, M.D., Ph.D., Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D.,
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis
 Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Supplementary Information Methods Subjects The study was comprised of 84 chronic pain patients with either chronic back pain (CBP) or osteoarthritis (OA). All subjects provided informed consent to procedures
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007)
 Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat
 Physiol. Res. 3: 31-3, GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat M. FRANĚK, Š. VACULÍN, R. ROKYTA Department of Normal, Pathological
Physiol. Res. 3: 31-3, GABA B Receptor Agonist Baclofen Has Non-Specific Antinociceptive Effect in the Model of Peripheral Neuropathy in the Rat M. FRANĚK, Š. VACULÍN, R. ROKYTA Department of Normal, Pathological
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy
 Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Supporting Online Material for
 www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/325/5941/760/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Spinal Endocannabinoids and CB 1 Receptors Mediate C-Fiber Induced Heterosynaptic Pain Sensitization Alejandro J. Pernía-Andrade,
www.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/325/5941/760/dc1 Supporting Online Material for Spinal Endocannabinoids and CB 1 Receptors Mediate C-Fiber Induced Heterosynaptic Pain Sensitization Alejandro J. Pernía-Andrade,
Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods
 Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods Subjects The experiment included twelve subjects: ten sighted subjects and two blind. Five of the ten sighted subjects were expert users of a visual-to-auditory
Supplementary information Detailed Materials and Methods Subjects The experiment included twelve subjects: ten sighted subjects and two blind. Five of the ten sighted subjects were expert users of a visual-to-auditory
Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA
 Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
Contribution of Calcium Channel α 2 δ Binding Sites to the Pharmacology of Gabapentin and Pregabalin Charlie Taylor, PhD CpTaylor Consulting Chelsea, MI, USA Disclosure Information Charlie Taylor, PhD
PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus. MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive
 PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome 10 in rodent model of neuropathic pain
 Huang et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015) 12:59 DOI 10.1186/s12974-015-0280-1 JOURNAL OF NEUROINFLAMMATION RESEARCH Open Access Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome
Huang et al. Journal of Neuroinflammation (2015) 12:59 DOI 10.1186/s12974-015-0280-1 JOURNAL OF NEUROINFLAMMATION RESEARCH Open Access Involvement of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome
San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001
 PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Tohoku University Graduate School of Medicine, Sendai, Japan, 2
 Low-energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Promotes VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis and Improve Locomotor and Sensory Functions after spinal cord injury Kenichiro Yahata 1, Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D.
Low-energy Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy Promotes VEGF Expression and Angiogenesis and Improve Locomotor and Sensory Functions after spinal cord injury Kenichiro Yahata 1, Hiroshi Ozawa, M.D., Ph.D.
Diabetic Complications Consortium
 Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: Cathepsin S inhibition and diabetic neuropathy Principal Investigator: Nigel A Calcutt 1. Project Accomplishments: We investigated the efficacy of cathepsin
Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: Cathepsin S inhibition and diabetic neuropathy Principal Investigator: Nigel A Calcutt 1. Project Accomplishments: We investigated the efficacy of cathepsin
NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions as Related to Analgesia and Tolerance
 Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Vol. 19 No. 1(Suppl.) January 2000 Journal of Pain and Symptom Management S7 Proceedings Supplement NDMA-Receptor Antagonists: Evolving Role in Analgesia NMDA-Receptor Antagonists and Opioid Receptor Interactions
Twelve right-handed subjects between the ages of 22 and 30 were recruited from the
 Supplementary Methods Materials & Methods Subjects Twelve right-handed subjects between the ages of 22 and 30 were recruited from the Dartmouth community. All subjects were native speakers of English,
Supplementary Methods Materials & Methods Subjects Twelve right-handed subjects between the ages of 22 and 30 were recruited from the Dartmouth community. All subjects were native speakers of English,
Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice.
 Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice. Satoshi Tateda, MD, Haruo Kanno, MD, PhD, Hiroshi Ozawa, MD, PhD,
Rapamycin suppresses astrocytic and microglial activation and reduces development of neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in mice. Satoshi Tateda, MD, Haruo Kanno, MD, PhD, Hiroshi Ozawa, MD, PhD,
Evaluation of Gabapentin and S-( )-3-Isobutylgaba in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/97/2823-1242$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 282, No. 3 Copyright 1997 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT
 PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain
 Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Keyur S Patel *, Punam D Sachdeva Department of Pharmacology, A.R.College
Centrally Mediated Anti-Hyperalgesic and Anti-Allodynic Effect of Tolperisone in Spared Nerve Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Keyur S Patel *, Punam D Sachdeva Department of Pharmacology, A.R.College
Hallucinations and conscious access to visual inputs in Parkinson s disease
 Supplemental informations Hallucinations and conscious access to visual inputs in Parkinson s disease Stéphanie Lefebvre, PhD^1,2, Guillaume Baille, MD^4, Renaud Jardri MD, PhD 1,2 Lucie Plomhause, PhD
Supplemental informations Hallucinations and conscious access to visual inputs in Parkinson s disease Stéphanie Lefebvre, PhD^1,2, Guillaume Baille, MD^4, Renaud Jardri MD, PhD 1,2 Lucie Plomhause, PhD
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and. widespread hyperalgesia
 Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Repeated intra-articular injections of acidic saline produce long-lasting joint pain and widespread hyperalgesia N. Sugimura 1, M. Ikeuchi 1 *, M. Izumi 1, T. Kawano 2, K. Aso 1, T. Kato 1, T. Ushida 3,
Curcumin Attenuates Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constrictive Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain
 Pain Ther (2014) 3:59 69 DOI 10.1007/s40122-014-0024-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Curcumin Attenuates Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constrictive Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Yu Xiang Di Cao
Pain Ther (2014) 3:59 69 DOI 10.1007/s40122-014-0024-4 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Curcumin Attenuates Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Chronic Constrictive Injury Model of Neuropathic Pain Yu Xiang Di Cao
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Supplementary Online Content Gregg NM, Kim AE, Gurol ME, et al. Incidental cerebral microbleeds and cerebral blood flow in elderly individuals. JAMA Neurol. Published online July 13, 2015. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2015.1359.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
QUANTIFYING CEREBRAL CONTRIBUTIONS TO PAIN 1
 QUANTIFYING CEREBRAL CONTRIBUTIONS TO PAIN 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Overview of the SIIPS1 development. The development of the SIIPS1 consisted of individual- and group-level analysis steps. 1) Individual-person
QUANTIFYING CEREBRAL CONTRIBUTIONS TO PAIN 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Overview of the SIIPS1 development. The development of the SIIPS1 consisted of individual- and group-level analysis steps. 1) Individual-person
Original Article FEMALE CASTRATED RATS WITH NEUROPATHIC PAIN: BEHAVIOURAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL CORRELATES. Summary. Slavina K.
 J Biomed Clin Res Volume 2 Number 2, 2009 Original Article FEMALE CASTRATED RATS WITH NEUROPATHIC PAIN: BEHAVIOURAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL CORRELATES Slavina K. Surcheva, 2 Milka A. Nashar, 1 Lachezar K. Surchev,
J Biomed Clin Res Volume 2 Number 2, 2009 Original Article FEMALE CASTRATED RATS WITH NEUROPATHIC PAIN: BEHAVIOURAL AND MORPHOLOGICAL CORRELATES Slavina K. Surcheva, 2 Milka A. Nashar, 1 Lachezar K. Surchev,
Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse
 nature methods Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse Dale J Langford 1, Andrea L Bailey 1, Mona Lisa Chanda 1, Sarah E Clarke 1, Tanya E Drummond 1, Stephanie Echols 2, Sarah Glick
nature methods Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse Dale J Langford 1, Andrea L Bailey 1, Mona Lisa Chanda 1, Sarah E Clarke 1, Tanya E Drummond 1, Stephanie Echols 2, Sarah Glick
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
ABSTRACT ABBREVIATIONS: 804
 0022-3565/03/3062-804 814$7.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 306, No. 2 Copyright 2003 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 50039/1082433
0022-3565/03/3062-804 814$7.00 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 306, No. 2 Copyright 2003 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 50039/1082433
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Green SA, Hernandez L, Tottenham N, Krasileva K, Bookheimer SY, Dapretto M. The neurobiology of sensory overresponsivity in youth with autism spectrum disorders. Published
Supplementary Online Content Green SA, Hernandez L, Tottenham N, Krasileva K, Bookheimer SY, Dapretto M. The neurobiology of sensory overresponsivity in youth with autism spectrum disorders. Published
Preclinical evaluation of pain in endometriosis
 receptor antagonism reduces peripheral and central hyperalgesia in a preclinical mouse model of endometriosis Erin Greaves, Andrew W Horne, Helen Jerina, arta ikolajczak, Lisa Hilferty, Rory itchell, Sue
receptor antagonism reduces peripheral and central hyperalgesia in a preclinical mouse model of endometriosis Erin Greaves, Andrew W Horne, Helen Jerina, arta ikolajczak, Lisa Hilferty, Rory itchell, Sue
Outline. Biological Psychology: Research Methods. Dr. Katherine Mickley Steinmetz
 Biological Psychology: Research Methods Dr. Katherine Mickley Steinmetz Outline Neuroscience Methods Histology Electrophysiological Recordings Lesion Neuroimaging Neuroanatomy Histology: Brain structure
Biological Psychology: Research Methods Dr. Katherine Mickley Steinmetz Outline Neuroscience Methods Histology Electrophysiological Recordings Lesion Neuroimaging Neuroanatomy Histology: Brain structure
WHAT DOES THE BRAIN TELL US ABOUT TRUST AND DISTRUST? EVIDENCE FROM A FUNCTIONAL NEUROIMAGING STUDY 1
 SPECIAL ISSUE WHAT DOES THE BRAIN TE US ABOUT AND DIS? EVIDENCE FROM A FUNCTIONAL NEUROIMAGING STUDY 1 By: Angelika Dimoka Fox School of Business Temple University 1801 Liacouras Walk Philadelphia, PA
SPECIAL ISSUE WHAT DOES THE BRAIN TE US ABOUT AND DIS? EVIDENCE FROM A FUNCTIONAL NEUROIMAGING STUDY 1 By: Angelika Dimoka Fox School of Business Temple University 1801 Liacouras Walk Philadelphia, PA
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Sensory Assessment of Regional Analgesia in Humans
 REVIEW ARTICLE Dennis M. Fisher, M.D., Editor-in-Chief Anesthesiology 2000; 93:1517 30 2000 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sensory Assessment of Regional
REVIEW ARTICLE Dennis M. Fisher, M.D., Editor-in-Chief Anesthesiology 2000; 93:1517 30 2000 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sensory Assessment of Regional
To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
Supplementary Materials and Methods Gene Expression Analysis To compare the relative amount of of selected gene expression between sham and mice given renal ischemia-reperfusion injury (IRI), ncounter
Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix
 Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix Partap S. Khalsa, D.C., Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Engineering The Neuromatrix From: Melzack R (1999) Pain Suppl 6:S121-6. NIOSH STAR Symposium May
Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix Partap S. Khalsa, D.C., Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Engineering The Neuromatrix From: Melzack R (1999) Pain Suppl 6:S121-6. NIOSH STAR Symposium May
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Pathophysiology of Pain. Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC
 Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor
 Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
EVALUATION OF ANTI-NOCICEPTIVE EFFECT OF TOLPERISONE BY COMPARING ITS EFFECT WITH TRAMADOL IN NEUROPATHIC PAIN
 Journal of Pharmaceutical Biology www.jpbjournal.com e-issn - 2249-7560 Print ISSN - 2249-7579 EVALUATION OF ANTI-NOCICEPTIVE EFFECT OF TOLPERISONE BY COMPARING ITS EFFECT WITH TRAMADOL IN NEUROPATHIC
Journal of Pharmaceutical Biology www.jpbjournal.com e-issn - 2249-7560 Print ISSN - 2249-7579 EVALUATION OF ANTI-NOCICEPTIVE EFFECT OF TOLPERISONE BY COMPARING ITS EFFECT WITH TRAMADOL IN NEUROPATHIC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat. Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The Calcium-activated Chloride Channel Anoctamin 1 acts as a Heat Sensor in Nociceptive Neurons Hawon Cho, Young Duk Yang, Jesun Lee, Byeongjoon Lee, Tahnbee Kim Yongwoo Jang,
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(9):5916-5921 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001263 Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats Guojun Wang 1,2*, Dawei Dai
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(9):5916-5921 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0001263 Original Article Upregulation of neuregulin-1 reverses signs of neuropathic pain in rats Guojun Wang 1,2*, Dawei Dai
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses
 Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Somatosensory System There are three parts Cutaneous senses - perception of touch and pain from stimulation of the skin Proprioception - ability to sense position of the
Chapter 14: The Cutaneous Senses Somatosensory System There are three parts Cutaneous senses - perception of touch and pain from stimulation of the skin Proprioception - ability to sense position of the
Analgesia Mediated by the TRPM8 Cold Receptor in Chronic Neuropathic Pain
 Current Biology 16, 1591 1605, August 22, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2006.07.061 Analgesia Mediated by the TRPM8 Cold Receptor in Chronic Neuropathic Pain Article Clare
Current Biology 16, 1591 1605, August 22, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Ltd All rights reserved DOI 10.1016/j.cub.2006.07.061 Analgesia Mediated by the TRPM8 Cold Receptor in Chronic Neuropathic Pain Article Clare
Group-Wise FMRI Activation Detection on Corresponding Cortical Landmarks
 Group-Wise FMRI Activation Detection on Corresponding Cortical Landmarks Jinglei Lv 1,2, Dajiang Zhu 2, Xintao Hu 1, Xin Zhang 1,2, Tuo Zhang 1,2, Junwei Han 1, Lei Guo 1,2, and Tianming Liu 2 1 School
Group-Wise FMRI Activation Detection on Corresponding Cortical Landmarks Jinglei Lv 1,2, Dajiang Zhu 2, Xintao Hu 1, Xin Zhang 1,2, Tuo Zhang 1,2, Junwei Han 1, Lei Guo 1,2, and Tianming Liu 2 1 School
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/1/10/e1500775/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Structural-functional connectivity deficits of neocortical circuits in the Fmr1 /y mouse model of autism Matthias
Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist BD1047 Reduces Allodynia and Spinal ERK Phosphorylation Following Chronic Compression of Dorsal Root Ganglion in Rats
 Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Vol 14: 359-364, December, 2010 DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.6.359 Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist BD1047 Reduces Allodynia and Spinal ERK Phosphorylation Following Chronic Compression
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol Vol 14: 359-364, December, 2010 DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.6.359 Sigma-1 Receptor Antagonist BD1047 Reduces Allodynia and Spinal ERK Phosphorylation Following Chronic Compression
modulator NS11394 with diazepam, zolpidem, bretazenil and gaboxadol in rat
 JPET Fast This Forward. article has not Published been copyedited on and September formatted. The 12, final 2008 version as may DOI:10.1124/jpet.108.144568 differ from this version. Comparison of the novel
JPET Fast This Forward. article has not Published been copyedited on and September formatted. The 12, final 2008 version as may DOI:10.1124/jpet.108.144568 differ from this version. Comparison of the novel
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Role of CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors in the development of joint pain. induced by monosodium iodoacetate
 *Manuscript 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Role of CB1 and CB cannabinoid receptors in the development of joint pain induced by monosodium iodoacetate Carmen La Porta 1*, Simona Andreea Bura 1*, Auxiliadora Aracil-Fernández,
*Manuscript 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Role of CB1 and CB cannabinoid receptors in the development of joint pain induced by monosodium iodoacetate Carmen La Porta 1*, Simona Andreea Bura 1*, Auxiliadora Aracil-Fernández,
Comparison of the Effects of Zonisamide, Ethosuximide and Pregabalin in the Chronic Constriction Injury Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats
 Original Article Comparison of the Effects of Zonisamide, Ethosuximide and Pregabalin in the Chronic Constriction Injury Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats Goyal S, Singla S, Kumar D, Menaria G Department
Original Article Comparison of the Effects of Zonisamide, Ethosuximide and Pregabalin in the Chronic Constriction Injury Induced Neuropathic Pain in Rats Goyal S, Singla S, Kumar D, Menaria G Department
Investigations in Resting State Connectivity. Overview
 Investigations in Resting State Connectivity Scott FMRI Laboratory Overview Introduction Functional connectivity explorations Dynamic change (motor fatigue) Neurological change (Asperger s Disorder, depression)
Investigations in Resting State Connectivity Scott FMRI Laboratory Overview Introduction Functional connectivity explorations Dynamic change (motor fatigue) Neurological change (Asperger s Disorder, depression)
The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced by Spinal Nerve Ligation
 J Korean Med Sci 2002; 17: 225-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced
J Korean Med Sci 2002; 17: 225-9 ISSN 1011-8934 Copyright The Korean Academy of Medical Sciences The Effect of Intrathecal Gabapentin on Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Neuropathic Rats Induced
Human pain experiments as an alternative to animal models
 Human pain experiments as an alternative to animal models Asbjørn Mohr Drewes Dept. of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Aalborg University Hospital Aalborg, Denmark Visceral specific changes? Visceral pain
Human pain experiments as an alternative to animal models Asbjørn Mohr Drewes Dept. of Gastroenterology & Hepatology Aalborg University Hospital Aalborg, Denmark Visceral specific changes? Visceral pain
Materials and Methods
 Anesthesiology 2004; 101:753 8 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. The Spinal Antinociceptive Effect of Nocistatin in Neuropathic Rats Is Blocked by D-Serine
Anesthesiology 2004; 101:753 8 2004 American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. The Spinal Antinociceptive Effect of Nocistatin in Neuropathic Rats Is Blocked by D-Serine
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical Allodynia in a Rat Model of Postoperative Pain
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
Original Article Korean J Pain 2013 April; Vol. 26, No. 2: 125-129 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.2.125 Effects of Palonosetron, a 5-HT3 Receptor Antagonist, on Mechanical
TRP modulators based on glycine and mono-, bicyclic terpenoids synthesis and pharmacological properties
 TRP modulators based on glycine and mono-, bicyclic terpenoids synthesis and pharmacological properties Mariia Nesterkina*and Iryna Kravchenko I.I. Mechnikov dessa National University, 2 Dvorjanskaya st.,
TRP modulators based on glycine and mono-, bicyclic terpenoids synthesis and pharmacological properties Mariia Nesterkina*and Iryna Kravchenko I.I. Mechnikov dessa National University, 2 Dvorjanskaya st.,
Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in the rat
 Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
Cheppudira et al. BMC Anesthesiology (2016) 16:73 DOI 10.1186/s12871-016-0242-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Anti-nerve growth factor antibody attenuates chronic morphine treatmentinduced tolerance in
MOLECULAR PAIN. Josée Guindon 1,3*, Liting Deng 1,2,3, Baochang Fan 1, Jim Wager-Miller 1 and Andrea G Hohmann 1,2,3*
 Guindon et al. Molecular Pain 2014, 10:56 MOLECULAR PAIN RESEARCH Open Access Optimization of a cisplatin model of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy in mice: use of vitamin C and sodium bicarbonate
Guindon et al. Molecular Pain 2014, 10:56 MOLECULAR PAIN RESEARCH Open Access Optimization of a cisplatin model of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy in mice: use of vitamin C and sodium bicarbonate
Evaluation of Selective NK 1 Receptor Antagonist CI-1021 in Animal Models of Inflammatory and Neuropathic Pain
 0022-3565/00/2942-0444$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 294, No. 2 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
0022-3565/00/2942-0444$03.00/0 THE JOURNAL OF PHARMACOLOGY AND EXPERIMENTAL THERAPEUTICS Vol. 294, No. 2 Copyright 2000 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics Printed in
By the end of this lecture the students will be able to:
 UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
UNIT VII: PAIN Objectives: By the end of this lecture the students will be able to: Review the concept of somatosensory pathway. Describe the function of Nociceptors in response to pain information. Describe
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS. Subjects and Confederates. We investigated a total of 32 healthy adult volunteers, 16
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Subjects and Confederates. We investigated a total of 32 healthy adult volunteers, 16 women and 16 men. One female had to be excluded from brain data analyses because of strong movement
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Subjects and Confederates. We investigated a total of 32 healthy adult volunteers, 16 women and 16 men. One female had to be excluded from brain data analyses because of strong movement
Charles University in Prague, Third Faculty of Medicine, Dpt. of Normal, Pathological and
 TITLE: Baclofen reversed thermal place preference in rats with chronic constriction injury Kim Salte, Gunnar Lea, Miloslav Franek, Simon Vaculin Charles University in Prague, Third Faculty of Medicine,
TITLE: Baclofen reversed thermal place preference in rats with chronic constriction injury Kim Salte, Gunnar Lea, Miloslav Franek, Simon Vaculin Charles University in Prague, Third Faculty of Medicine,
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation
 Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Differentiating Thermal Allodynia and Hyperalgesia Using Dynamic Hot and Cold Plate in Rodents
 The Journal of Pain, Vol 10, No 7 (July), 2009: pp 767-773 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Differentiating Thermal Allodynia and Hyperalgesia Using Dynamic Hot and Cold Plate in Rodents Ipek
The Journal of Pain, Vol 10, No 7 (July), 2009: pp 767-773 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Differentiating Thermal Allodynia and Hyperalgesia Using Dynamic Hot and Cold Plate in Rodents Ipek
1604 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 62, NO. 6, JUNE 2015
 1604 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 62, NO. 6, JUNE 2015 Burst and Tonic Spinal Cord Stimulation Differentially Activate GABAergic Mechanisms to Attenuate Pain in a Rat Model of Cervical
1604 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING, VOL. 62, NO. 6, JUNE 2015 Burst and Tonic Spinal Cord Stimulation Differentially Activate GABAergic Mechanisms to Attenuate Pain in a Rat Model of Cervical
The Kv4.2 Potassium Channel Subunit Is Required for Pain Plasticity
 Neuron 50, 89 100, April 6, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.03.010 The Kv4.2 Potassium Channel Subunit Is Required for Pain Plasticity Hui-Juan Hu, 1 Yarimar Carrasquillo, 1 Farzana
Neuron 50, 89 100, April 6, 2006 ª2006 Elsevier Inc. DOI 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.03.010 The Kv4.2 Potassium Channel Subunit Is Required for Pain Plasticity Hui-Juan Hu, 1 Yarimar Carrasquillo, 1 Farzana
Functional MRI Mapping Cognition
 Outline Functional MRI Mapping Cognition Michael A. Yassa, B.A. Division of Psychiatric Neuro-imaging Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Why fmri? fmri - How it works Research
Outline Functional MRI Mapping Cognition Michael A. Yassa, B.A. Division of Psychiatric Neuro-imaging Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Why fmri? fmri - How it works Research
Somatosensory modalities!
 Somatosensory modalities! The somatosensory system codes five major sensory modalities:! 1. Discriminative touch! 2. Proprioception (body position and motion)! 3. Nociception (pain and itch)! 4. Temperature!
Somatosensory modalities! The somatosensory system codes five major sensory modalities:! 1. Discriminative touch! 2. Proprioception (body position and motion)! 3. Nociception (pain and itch)! 4. Temperature!
Reproducibility of Visual Activation During Checkerboard Stimulation in Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 4 Tesla
 Reproducibility of Visual Activation During Checkerboard Stimulation in Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 4 Tesla Atsushi Miki*, Grant T. Liu*, Sarah A. Englander, Jonathan Raz, Theo G. M. van Erp,
Reproducibility of Visual Activation During Checkerboard Stimulation in Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 4 Tesla Atsushi Miki*, Grant T. Liu*, Sarah A. Englander, Jonathan Raz, Theo G. M. van Erp,
Somatosensation. Recording somatosensory responses. Receptive field response to pressure
 Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Opioid Receptor Trafficking in Pain States
 Encyclopedia of Pain Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2007 10.1007/978-3-540-29805-2_2962 Robert F. Schmidt and William D. Willis Opioid Receptor Trafficking in Pain States Catherine M. Cahill 3, Anne
Encyclopedia of Pain Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2007 10.1007/978-3-540-29805-2_2962 Robert F. Schmidt and William D. Willis Opioid Receptor Trafficking in Pain States Catherine M. Cahill 3, Anne
Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09511 Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke Pre Post 7-days Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature09511 Supplementary Table I Blood pressure and heart rate measurements pre- and post-stroke Pre Post 7-days Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic Diastolic BPM Systolic
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Local GABAergic signaling within sensory ganglia controls peripheral nociceptive transmission
 Local GABAergic signaling within sensory ganglia controls peripheral nociceptive transmission Xiaona Du, 1 Han Hao, 1 Yuehui Yang, 1 Sha Huang, 1 Caixue Wang, 1 Sylvain Gigout, 2 Rosmaliza Ramli, 2,3 Xinmeng
Local GABAergic signaling within sensory ganglia controls peripheral nociceptive transmission Xiaona Du, 1 Han Hao, 1 Yuehui Yang, 1 Sha Huang, 1 Caixue Wang, 1 Sylvain Gigout, 2 Rosmaliza Ramli, 2,3 Xinmeng
Paclitaxel induces acute pain via directly activating toll like receptor 4
 Yan et al. Molecular Pain (2015) 11:10 DOI 10.1186/s12990-015-0005-6 MOLECULAR PAIN RESEARCH Paclitaxel induces acute pain via directly activating toll like receptor 4 Open Access Xisheng Yan 1,2, Dylan
Yan et al. Molecular Pain (2015) 11:10 DOI 10.1186/s12990-015-0005-6 MOLECULAR PAIN RESEARCH Paclitaxel induces acute pain via directly activating toll like receptor 4 Open Access Xisheng Yan 1,2, Dylan
Somatic Sensory System I. Background
 Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Possible Involvement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Analgesic Effects of 4-Methylcatechol on Neuropathic Pain
 49 Bull Yamaguchi Med School 57 3-4 :49-56, 2010 Possible Involvement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Analgesic Effects of 4-Methylcatechol on Neuropathic Pain Kozo Ishikawa 2 Department of Emergency
49 Bull Yamaguchi Med School 57 3-4 :49-56, 2010 Possible Involvement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in Analgesic Effects of 4-Methylcatechol on Neuropathic Pain Kozo Ishikawa 2 Department of Emergency
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress REDUCING THE PAIN FACTOR AN UPDATE ON PERI-OPERATIVE ANALGESIA Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of Veterinary,
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress REDUCING THE PAIN FACTOR AN UPDATE ON PERI-OPERATIVE ANALGESIA Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of Veterinary,
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
enhances nociceptive responses in rats
 Brazilian Chronic intrathecal Journal of Medical cannulation and Biological Research (2000) 33: 949-956 ISSN 0100-879X 949 Chronic intrathecal cannulation enhances nociceptive responses in rats F.R.C.
Brazilian Chronic intrathecal Journal of Medical cannulation and Biological Research (2000) 33: 949-956 ISSN 0100-879X 949 Chronic intrathecal cannulation enhances nociceptive responses in rats F.R.C.
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience
 Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Simon Musall NNA47695 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 6 # Supplementary Figures: 14 # Supplementary Tables:
Corresponding Author: Manuscript Number: Manuscript Type: Simon Musall NNA47695 Article Reporting Checklist for Nature Neuroscience # Main Figures: 6 # Supplementary Figures: 14 # Supplementary Tables:
