NORTH CAROLINA STATE HEALTH PLAN FOR TEACHERS AND STATE EMPLOYEES
|
|
|
- Ruby May
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 NORTH CAROLINA STATE HEALTH PLAN FOR TEACHERS AND STATE EMPLOYEES Using Clinical Risk Groups to Focus Board Strategic Initiatives July 26, 2013 Copyright 2013 by The Segal Group, Inc., parent of The Segal Company. All rights reserved. 0 0
2 Agenda Review of SHPNC mission and strategic opportunities Define the financial opportunities for managing the health of SHPNC population Discuss aspects of behavioral economics that drive health care costs Review the findings of the Clinical Risk Group analysis of SHPNC Next Steps for using findings to focus SHPNC s strategy and measure the impact of the strategy 1
3 Background Mission for the SHPNC Our mission is to improve the health and healthcare of North Carolina teachers, state employees, retirees, and their dependents, in a financially sustainable manner, thereby serving as a model to the people of North Carolina for improving their health and wellbeing. 2
4 Background SHPNC Strategic Opportunities Increase the SHPNC participants awareness of their health status and to available support resources Improve the health of the SHPNC participants through focused programs Improve medication adherence and treatment compliance of SHPNC participants with chronic conditions Impact positive trends in utilization management to reduce medical trend 3
5 Study Shows Avoidable Medical Care Services Contribute to Costs Behavioral $493 billion (18.9%*) Clinical $312 billion (11.9%*) Operational $134 billion (5.1%*) Total $939 billion * NOTE: Percentage of total health dollars spent in 2012 in the United States In 2012, $939 billion of the $2.6 trillion spent on medical care in the United States was avoidable due to factors related to patient behaviors, clinical ineffectiveness, and operational inefficiency in the delivery of health care Source: PricewaterhouseCoopers Health Research Institute 2012 study 4
6 Unhealthy Behaviors Factor into Avoidable Medical Cost Obesity/Overweight: $200 billion Smoking: $191 billion *Non-adherence to drug regimens: $100-$290 billion Alcohol abuse: $2 billion Over 50% of avoidable healthcare is attributable to preventable risk factors linked to behavior. Example overweight diabetic not controlling blood sugar level * New England Healthcare Institute 2012 study of medication non-adherence - $290 billion. Pricewaterhouse Coopers Health Research Institute 2012 study of waste in the health care system - $100 billion 5
7 Clinical Care Practices Factor into Avoidable Medical Cost Defensive medicine: $210 billion Preventable hospital visits: $25 billion Poorly managed diabetes: $22 billion Medical errors: $17 billion Unnecessary ER visits: $14 billion Treatment variations: $10 billion Hospital acquired infections: $3 billion Over-prescribing of antibiotics: $1 billion Those providing or paying for care often don t have the best information on the right thing to do or don t utilize information available to them. Example patient getting back surgery when physical therapy was sufficient to resolve medical problem. * New England Healthcare Institute 2012 study of medication non-adherence - $290 billion. Pricewaterhouse Coopers Health Research Institute 2012 study of waste in the health care system - $100 billion 6
8 Operational Complexities Factor into Avoidable Medical Cost Claims processing: $21-$210 billion Ineffective use of IT: $81-$88 billion Staffing turnover: $21 billion Paper prescriptions: $4 billion Administrative complexities and redundancies fuel expenses in scheduling, registration, financial clearance, coding, claims processing, credentialing, and utilization management. Example hospital needing to accommodate 700 billing systems for plans New England Healthcare Institute 2012 study of medication non-adherence - $290 billion. Pricewaterhouse Coopers Health Research Institute 2012 study of waste in the health care system - $100 billion 7
9 Opportunity Cost of Patient Behavior, Clinic Effectiveness, and Operational Complexity of Health Care Delivery for SHPNC State Health Plan NC 2013 Projected Medical Costs $ 1,859,949, Projected Drug Costs - $ 678,096,922 Total $ 2,537,190,620 Applying the results of the study reported on the previous pages to the SHPNC s overall costs, there is the potential to achieve savings such as the following: Potentially Avoidable Medical Cost Savings from Behavior Modifications - $ 479,529,027 (18.9%*) Savings from Clinical Efficiencies - $ 301,925,684 (11.9%*) Savings from Operational Efficiencies - $ 129,396,722 ( 5.1%*) Total $ 910,851,433 (35.9%*) * Source: SHPNC March 5, 2013 FY projected costs SHPNC has initiatives in place focused on improving participant behaviors that contribute to avoidable claims expenditures. 8
10 What are the Participant Behaviors that are Worth Managing? Poor Diet Physical Inactivity Excess Alcohol Consumption Smoking Poor Standard-of- Care Compliance 8 Behaviors and Risks Poor Stress Management Insufficient Sleep Lack of Health Screening Diabetes CAD Hypertension Top 15 Most Costly Conditions Back Pain Obesity Cancer Asthma Arthritis Allergies Sinusitis Depression CHF COPD CKD High Cholesterol Avoidable and modifiable human behaviors contribute to 80% of the cost associated with the chronic conditions listed above Source: 2010 World Economic Forum 9
11 The Success of Health Management Programs Depends On Active Engagement of Participants that Leads to Behavior Change Case Management Highly complex patients Disease Management High-risk patients Wellness & Health Promotion Healthy and at-risk patients Initiatives are in place to support the wide range of SHPNC population needs. The challenge is to get participants to engage in the various initiatives and modify unhealthy behaviors. 10
12 Monitoring the Health Risk Profile of the SHPNC Clinical Risk Grouping as a Tool Clinical Risk Grouper (CRG) A starting point The purpose of performing a detailed study is to: To identify the prevalent health risks within the plan s population and predict the financial impact of those risks. Uncover opportunities for the plan to better control plan cost and improve the health of the covered population. Long-term objectives can include the following: Quantify health status and underlying drivers of trend Proactively identify aberrant utilization patterns Improve financial evaluation of program/vendor performance Evaluate the ROI saving of case management and disease management programs that are true savings and not simply a regression to the mean Target high risk groups for preventive interventions Measure provider performance 11
13 Definitions for Clinical Risk Groups (CRG) Descriptors and severity-of-illness subclasses In the 3M CRG system, an individual is assigned two descriptors: Base CRG Each individual is assigned to a single base CRG that reflects the full range of diagnoses for that individual Severity-of-illness subclass for the base CRG The subclass addresses individual differences relating to severity of illness and take into account: Recency of occurrence (e.g., last 90 days) Site of occurrence (e.g., hospital, ambulance) Recurrence or persistency over time Combination of diagnoses in individual s history Severity level describes the extent and progression of disease and range from minor (1) to extreme (6). (See next page for levels of severity by CRG health status) All individuals are assigned to a single, mutually exclusive group, which is in one of nine health statuses, ranging from catastrophic (e.g., history of a heart transplant) to healthy (e.g., no chronic health problems or other indication of risk). 12
14 Definitions for Clinical Risk Groups (CRG) See Appendix for Examples of Each Category CRG 1 Healthy CRG health status category Description/Example of base 3M CRG Healthy (no chronic health problems) Severity levels None 2 History of significant acute disease Chest pains None 3 Single minor chronic disease Migraine 2 4 Minor chronic diseases in multiple organ systems Migraine and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) 5 Significant chronic disease Diabetes mellitus Significant chronic diseases in multiple organ systems Dominant chronic disease in 3 or more organ systems Diabetes mellitus and CHF 6 Diabetes mellitus, congestive heart failure (CHF) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) 8 Dominant/Metastatic malignancy Metastatic colon malignancy 4 9 Catastrophic History of major organ transplant
15 CRG Population Profiles by Cost and Risk Available for SHPNC Non-Medicare Actives Retirees Groups, systems, departments This presentation of CRGs is limited to the non-medicare population. Full report is available to Board 14
16 Monitoring the Health Risk Profile of the SHPNC Population - Total Non-Medicare Member Profile The following is a distribution of membership and claims for Fiscal Year 2012 Members % Total Claims % Total PMPY CRG Health Status Category 1. Healthy 230, % $235,721, % $ 1, Significant Acute 28, % $95,336, % $ 3, Single Minor Chronic 57, % $200,340, % $ 3, Multiple Minor Chronic 20, % $117,227, % $ 5, Single Dominant or Moderate Chronic 108, % $580,175, % $ 5, Pairs - Multiple Dominant and / or Moderate Chronic 90, % $1,125,714, % $ 12, Triples - Multiple Dominant Chronic 2, % $115,596, % $ 40, Malignancies - Metastatic, Compound or Dominant 2, % $199,364, % $ 83, Catastrophic 1, % $83,501, % $ 53,869 Total 542, % $2,752,977, % $ 5,077 Healthy/Acute - risk category 1 and 2 259, % $331,058, % $ 1,277 Chronic risk category 3 through 7 279, % $2,139,053, % $ 7,664 Catastrophic/Malignancy risk category 8 and 9 3, % $282,866, % $ 71,862 19% of healthy members (45,647 members) did not have a claim in
17 Monitoring the Health Risk Profile of the SHPNC Population - Total Non - Medicare Member Profile Complex Case Management and Wellness Programs Effective with These Populations Healthy/Acute includes participants with no claims, moderate claims and Acute conditions 47.8% of the total population are considered to be Healthy/Acute $331 million or 12.0% of total claims were from Healthy/Acute members Healthy/Acute members cost an average of $1,277 Catastrophic/Malignancy includes Malignancies and Catastrophic 0.7% of the total population are considered to be Catastrophic/Malignancy $282 million or 10.3% of all claims were from Catastrophic/Malignancy members Catastrophic/Malignant members cost an average of $71,862 Disease Management, Complex Case Management, and Wellness Program Effective with these Populations Chronic includes participants with single and multiple conditions 51.5% of the total population are considered to be Chronic $2.1 billion or 77.7% of total claims were from Chronic members Chronic members cost an average of $7,664 (over 6 times that of a Healthy/Acute member) 16
18 Monitoring the Health Risk Profile of the SHPNC Population - Severity Analysis (Total Non-Medicare) Membership by Level of Severity Level 0 Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Total CRG Health Status Category 1. Healthy 230, , Significant Acute 28, , Single Minor Chronic 0 42,748 15, , Multiple Minor Chronic 0 8,073 1,169 7,687 3, , Single Dominant or Moderate Chronic 0 84,225 19,021 3, , Pairs - Multiple Dominant and / or Moderate Chronic 0 58,219 17,346 9,220 4,075 1, , Triples - Multiple Dominant Chronic 0 1, , Malignancies - Metastatic, Compound or Dominant , Catastrophic ,550 Total 259, ,697 55,035 22,704 8,446 1, ,198 Per Member per Year Cost by Level of Severity Level 0 Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Total CRG Health Status Category 1. Healthy $1,022 $1, Significant Acute $3,339 $3, Single Minor Chronic $2,998 $4,763 $3, Multiple Minor Chronic $4,641 $6,271 $6,076 $8,376 $5, Single Dominant or Moderate Chronic $3,953 $8,525 $15,604 $27,036 $21,825 $47,955 $5, Pairs - Multiple Dominant and / or Moderate Chronic $7,706 $14,807 $21,992 $32,518 $54,364 $98,185 $12, Triples - Multiple Dominant Chronic $16,948 $27,542 $45,355 $83,525 $116,524 $189,019 $40, Malignancies - Metastatic, Compound or Dominant $25,073 $57,642 $87,593 $143,538 $212,193 $83, Catastrophic $12,641 $25,294 $50,885 $103,535 $162,859 $231,607 $53,869 Total $1,277 $4,996 $10,705 $18,836 $31,154 $67,186 $128,378 $5,077 Risk Factor
19 Monitoring the Health Risk Profile of the SHPNC Population Risk Factor Analysis by Health Status and Severity Level Active - Risk Factors Severity Level CRG Health Status Category Level 0 Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Total 1. Healthy Significant Acute Single Minor Chronic Multiple Minor Chronic Single Dominant or Moderate Chronic Pairs - Multiple Dominant and / or Moderate Chronic Triples - Multiple Dominant Chronic Malignancies - Metastatic, Compound or Dominant Catastrophic Total Retiree Non-Medicare - Risk Factors CRG Health Status Category Level 0 Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Level 4 Level 5 Level 6 Total 1. Healthy Significant Acute Single Minor Chronic Multiple Minor Chronic Single Dominant or Moderate Chronic Pairs - Multiple Dominant and / or Moderate Chronic Triples - Multiple Dominant Chronic Malignancies - Metastatic, Compound or Dominant Catastrophic Total Risk factors are normalized averages often called relative weights or norms There are expected relative differences for a measure of utilization between subgroups within a population The average measure of utilization used to calculate CRG weights was PMPY 18
20 Primary Disease Profile (Total Non-Medicare) Annual Membership CRGs were mapped into a primary disease through the hierarchy below FY2010 FY2011 FY2012 Code Description Members % Total Members % Total Members % Total 1 AIDS/HIV 725 0% 760 0% 767 0% 2 Oncology 10,443 2% 10,680 2% 9,803 2% 3 End Stage Renal Disease-Kidney 1,242 0% 1,316 0% 1,278 0% 4 Sickle Cell Anemia 54 0% 60 0% 69 0% 5 CP - Cerebral Palsy % 19 0% 6 CF - Cystic Fibrosis N/A N/A N/A N/A 7 0% 7 Diabetes 39,294 7% 40,911 7% 39,381 7% 8 CAD - Coronary Artery Disease 14,117 3% 13,540 2% 13,022 2% 9 CHF - Congestive Heart Failure 756 0% 725 0% 730 0% 10 COPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 1,064 0% 959 0% 1,002 0% 11 Asthma 13,148 2% 12,638 2% 12,169 2% 12 Hypertension 54,660 10% 53,094 10% 53,918 10% 13 Epilepsy 1,851 0% 1,804 0% 1,899 0% 14 Osteoporosis 3,063 1% 2,437 0% 1,729 0% 15 Premature Birth 13 0% 23 0% 19 0% 16 Drug Abuse Related Diagnoses 1,258 0% 1,375 0% 1,414 0% 17 Alcohol Related 6 0% 8 0% 5 0% 18 Mental Health 28,786 5% 28,973 5% 30,777 6% 19 Joint and Musculoskeletal Related 11,799 2% 11,298 2% 10,965 2% 20 Respiratory 948 0% 930 0% 823 0% 21 Dermatology 3,036 1% 2,706 0% 2,653 0% 22 Dominant Chronic 7,381 1% 7,365 1% 7,387 1% 23 Moderate Chronic 50,098 9% 52,802 10% 47,996 9% 24 Minor Chronic 44,189 8% 45,452 8% 44,493 8% 25 Acute 27,347 5% 26,999 5% 28,566 5% 26 Catastrophic 683 0% 698 0% 703 0% 27 Healthy 233,041 42% 229,061 42% 230,601 43% Total 549, % 546, % 542, % 48% of the members had no particular health risk in 2012, which is slightly higher than 47% in FY2010. Mental Health had the highest net member increase, 1,991, from 2010 to
21 CRG Health Status 5 & 6 Breakout by Primary Disease Profile Total Non-Medicare Membership & Allowed Claims FY 2012 CRGs were mapped into a primary disease through the hierarchy below Health Status 5 Health Status 6 Code Description Members % Total Claims % Total Members % Total Claims % Total 1 AIDS/HIV 0 0% $0 0% 0 0% $0 0% 2 Oncology 2,135 2% $35 6% 3,848 4% $93 8% 3 End Stage Renal Disease-Kidney 183 0% $4 1% 679 1% $29 3% 4 Sickle Cell Anemia 69 0% $1 0% 0 0% $0 0% 5 CP - Cerebral Palsy 19 0% $0 0% 0 0% $0 0% 6 CF - Cystic Fibrosis 0 0% $0 0% 0 0% $0 0% 7 Diabetes 7,642 7% $43 7% 29,346 33% $315 28% 8 CAD - Coronary Artery Disease 1,727 2% $25 4% 1,670 2% $43 4% 9 CHF - Congestive Heart Failure 282 0% $4 1% 415 0% $14 1% 10 COPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 239 0% $2 0% 736 1% $15 1% 11 Asthma 6,694 6% $28 5% 5,458 6% $56 5% 12 Hypertension 53,916 50% $195 34% 0 0% $0 0% 13 Epilepsy 1,899 2% $10 2% 0 0% $0 0% 14 Osteoporosis 1,729 2% $7 1% 0 0% $0 0% 15 Premature Birth 0 0% $0 0% 0 0% $0 0% 16 Drug Abuse Related Diagnoses 696 1% $5 1% 714 1% $12 1% 17 Alcohol Related 5 0% $0 0% 0 0% $0 0% 18 Mental Health 6,260 6% $36 6% 6,667 7% $95 8% 19 Joint and Musculoskeletal Related 4,703 4% $52 9% 8 0% $0 0% 20 Respiratory 46 0% $1 0% 0 0% $0 0% 21 Dermatology 133 0% $1 0% 656 1% $13 1% 22 Dominant Chronic 1,083 1% $17 3% 6,190 7% $150 13% 23 Moderate Chronic 14,091 13% $94 16% 33,883 38% $290 26% 24 Minor Chronic 4,319 4% $17 3% 0 0% $0 0% 25 Acute 0 0% $0 0% 0 0% $0 0% 26 Catastrophic 190 0% $3 1% 0 0% $0 0% 27 Healthy 0 0% $0 0% 0 0% $0 0% Total 108, % $ % 90, % $1, % 20
22 Monitoring the Health Risk Profile of the SHPNC Population - Cost and Risk by Population Segments Summary of Fiscal Year 2012 by Group Members & Claims for Fiscal Year 2012 Members Claims PMPY Relative Cost Risk Factor 1. Community College System 23,325 $117,207,662 $ 5, Department of Corrections 26,346 $137,912,602 $ 5, Department of Health and Human Services 24,224 $126,763,853 $ 5, Department of Transportation 17,722 $80,011,318 $ 4, North Carolina Public Schools 258,201 $1,146,714,186 $ 4, University of North Carolina Healthcare & NC System 80,830 $361,210,293 $ 4, All Other Groups 46,290 $227,198,846 $ 4, Active Total 476,937 $2,197,018,761 $ 4, Retirees (Non-Medicare) 65,260 $555,958,909 $ 8, Total 542,198 $2,752,977,670 $ 5, Reviewing risk factors by department may provide specific opportunities using health promotion efforts boost participation in wellness programs offered through departments or by adding health improvement competitions between departments. 21
23 Advancement of Health Risk In the SHPNC Population 10-Year Projection (Total Non-Medicare) If there is no further action to improve the health risk profile of the covered SHPNC population, there is a natural decline in the health risk that can be expected to happen: CRG Health Status Category FY2012 Projected FY2022 Members % Total Members % Total Movement 1. Healthy 230, % 219, % (10,906) 2. Significant Acute 28, % 24, % (4,066) 3. Single Minor Chronic 57, % 54, % (3,406) 4. Multiple Minor Chronic 20, % 20, % Single Dominant or Moderate Chronic 108, % 111, % 3, Pairs - Multiple Dominant and / or Moderate Chronic 90, % 103, % 12, Triples - Multiple Dominant Chronic 2, % 3, % Malignancies - Metastatic, Compound or Dominant 2, % 2, % Catastrophic 1, % 1, % 43 Total 542, % 542, % Healthy/Acute 1 and 2 259, % 244, % Chronic 3 through 7 279, % 293, % Catastrophic/Malignancy 8 and 9 3, % 4, % Relative Risk Score The percentage of Healthy/Acute members is projected to decrease 2.8% Overall risk factor for the SHP population will increase from 1.00 to
24 Primary Disease Advancement of Risk 5 & 10 Year Projection (Total Non-Medicare) FY2012 FY2017 FY to 2022 Code Description Members % Total Members % Total Members % Total Movement 1 AIDS/HIV % 865 0% 914 0% Oncology 9, % 11,154 2% 11,213 2% 1,410 3 End Stage Renal Disease-Kidney 1, % 1,527 0% 1,592 0% Sickle Cell Anemia % 63 0% 63 0% -6 5 CP - Cerebral Palsy % 9 0% 9 0% CF - Cystic Fibrosis 7 N/A 3 N/A 1 N/A N/A 7 Diabetes 39, % 45,473 8% 47,801 9% 8,420 8 CAD - Coronary Artery Disease 13, % 13,185 2% 13,178 2% CHF - Congestive Heart Failure % 732 0% 738 0% 8 10 COPD - Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 1, % 925 0% 925 0% Asthma 12, % 11,833 2% 11,781 2% Hypertension 53, % 52,535 10% 52,673 10% -1, Epilepsy 1, % 1,720 0% 1,711 0% Osteoporosis 1, % 2,004 0% 2,009 0% Premature Birth % 17 0% 17 0% Drug Abuse Related Diagnoses 1, % 1,485 0% 1,481 0% Alcohol Related 5 0.0% 9 0% 9 0% 5 18 Mental Health 30, % 29,035 5% 28,873 5% -1, Joint and Musculoskeletal Related 10, % 10,866 2% 10,801 2% Respiratory % 907 0% 901 0% Dermatology 2, % 2,572 0% 2,556 0% Dominant Chronic 7, % 7,508 1% 7,535 1% Moderate Chronic 47, % 54,421 10% 54,497 10% 6, Minor Chronic 44, % 45,328 8% 45,126 8% Acute 28, % 24,807 5% 24,608 5% -3, Catastrophic % 729 0% 734 0% Healthy 230, % 222,483 41% 220,450 41% -10,151 Total 542, % 542, % 542, % Diabetes (8,420) and oncology (1,410) will have the highest net member increases for specific primary diseases 23
25 Next Steps for Strategy Application of CRG Information Focus the health management & wellness strategy on the health risk profile of the SHPNC population Define the metrics that the SHPNC will use to measure improvements in the health risk profile of the SHPNC population Set targets for each metric and monitor progress Link metrics to the performance of partners (e.g. BCBSNC, Active Health, Community Care Network, others) supporting the strategy Use Dashboard metrics as indicators of the effectiveness of the strategy 24
26 Questions 25
27 Appendix CRG Characteristics CRG Characteristics Assigns members to a single, mutually exclusive risk group based on clinical information/experience Clinically meaningful categorization provides a refined assessment of health status and risk adjusted trends Degree of severity leveling improves financial analysis, performance measurement and plan/program design Transparent methodology established a foundation for actionable and defendable intervention strategies Enhanced ability to measure and monitor vendor performance with statistically matched cohorts 26
28 Appendix 4 Definitions: CRG assignment occurs in four phases Phase 1: Creates a profile of the individual s past medical history Phase 2: Identifies the individual s most significant chronic diseases (if any) and the relative severity of the most significant chronic diseases Phase 3: Assigns the individual s risk group and severity level (i.e., the CRG) Phase 4: Assigns the individual to aggregated risk groups (ACGR3s) 27
29 Appendix Categorization of ACGR3s Statuses Status 9 Catastrophic Conditions Catastrophic conditions include long term dependency on a medical technology (e.g. dialysis and respirator) and life-defining chronic diseases or conditions that dominate the medical care required (e.g., persistent vegetative state, cystic fibrosis, AIDS, and history of heart transplant). The severity level for Status 9, Catastrophic,is based on the presence of specific Episode Disease Categories (EDCs) or Episode Procedure Categories (EPCs) that meet explicit conditions. Status 8 Dominant, Metastatic and Complicated Malignancies A malignancy that dominates the medical care required (e.g., brain malignancy) or a non-dominant malignancy (e.g., prostate malignancy) that is metastatic or complicated (e.g., requiring a bone marrow transplant). The severity level for Status 8, Dominant Metastatic and Complicated Malignancies, is set in three steps. The first step, setting the initial level, is designed to reflect the total burden of illness including both malignancy and non-malignancy related illnesses. The initial severity level is the higher of the two levels, with one based on the presence of non-malignancy Primary Chronic Diseases (PCDs) and the other based on specified malignancy related complications and metastases. The next step adjusts the initial severity level if specific EDCs or EPCs are present and meet explicit conditions. The final step converts the interim severity level to the final severity level based on malignancy related conditions and metastases. 28
30 Appendix Categorization of ACGR3s Statuses Status 7 Dominant Chronic Disease in Three or More Organ Systems Dominant chronic disease in three or more organ systems is identified by the presence of three or more dominant chronic PCDs or two dominant chronic PCDs with a selected moderate chronic PCD The severity level for Status 7, Dominant Chronic Disease in Three or more Organ Systems, is determined by establishing an initial severity level based on the severity levels of the three PCDs which form the base CRG. The initial severity is adjusted to determine a final severity level if specific EDCs or EPCs are present and meet explicit conditions (rules). Status 6 Significant Chronic Disease in Multiple Organ Systems Significant chronic diseases in multiple organ systems are identified by the presence of two or more PCDs, of which at least one is a Dominant or Moderate Chronic PCD. PCDs that are a severity level 1 minor chronic disease are not considered a significant chronic disease, and are not used to identify the presence of significant chronic disease in multiple organ systems. Minor Chronic PCDs that are severity level 2 minor chronic diseases are used. The severity level for Status 6, Significant Chronic Disease in Multiple Organ Systems, is determined by using the severity level of the two PCDs which form the basis of the base CRG to assign an initial severity level. The initial level takes into account the possibility that the two PCDs are of disparate importance. The initial severity is adjusted to determine a final severity level if specified EDCs or EPCs are present and meet explicit conditions (rules). 29
31 Appendix Categorization of ACGR3 Statuses Status 5 Single Dominant or Moderate Chronic Disease Single dominant chronic disease is identified by the presence of a single dominant or moderate PCD. If a Minor Chronic PCD with a level of 1 is present, it is ignored. The severity level for Status 5, Single Dominant or Moderate Chronic Disease is the PCD severity level. Status 4 Minor Chronic Disease in Multiple Organ Systems Minor chronic disease in multiple organ systems is identified by the presence of two or more Minor Chronic PCDs. The severity level for Status 4, Minor Chronic Disease in Multiple Organ Systems, is based on the number of Minor Chronic PCDs and their severity levels. Status 3 Single Minor Chronic Disease A single minor chronic disease is identified by the presence of a single Minor Chronic PCD. The severity level for Status 3, Single Minor Chronic Disease, is the PCD severity level. Status 2 History of Significant Acute Disease A history of significant Acute disease is identified by the presence within the most recent six month period of one or more Significant Acute EDCs or one of a set of Significant Acute EPCs with no PCDs (i.e., identifiable chronic conditions) present. Status 1 Healthy A Healthy status is identified by the absence of any PCDs or Significant Acute EDCs or EPCs. There are no severity levels. 30
32 Appendix CRG Assignment CRG Assignment CLAIM Claim No: Date: 01/01/01 Name: Sam Smith Hospital: Healthy Diagnosis: URI Atopic Dermatitis 31
33 Appendix CRG Assignment continued CRG Assignment CLAIM Claim No: Date: 01/01/01 Name: Sam Smith Hospital: Healthy Diagnosis: URI Atopic Dermatitis Chest Pain Office Visit 32
34 Appendix CRG Assignment continued CRG Assignment CLAIM Claim No: Date: 01/01/01 Name: Sam Smith Hospital: Diagnosis: URI Atopic Dermatitis Chest Pain Office Visit Chest Pain Hospital Admission 33
35 Appendix CRG Assignment continued CRG Assignment CLAIM Claim No: Date: 01/01/01 Name: Sam Smith Hospital: Diagnosis: URI Atopic Dermatitis Chest Pain Office Visit Chest Pain Hospital Admission Cholesterol (220) 34
36 Appendix CRG Assignment continued CRG Assignment CLAIM Claim No: Date: 01/01/01 Name: Sam Smith Hospital: Diagnosis: URI Atopic Dermatitis Chest Pain Office Visit Chest Pain Hospital Admission Cholesterol (220) Diabetes (weight gain 50lbs) One Significant Chronic Disease 35
37 Appendix CRG Assignment continued CRG Assignment CLAIM Claim No: Date: 01/01/01 Name: Sam Smith Hospital: Diagnosis: URI Atopic Dermatitis Chest Pain Office Visit Chest Pain Hospital Admission Cholesterol (220) Diabetes (weight gain 50lbs) Angina Two Significant Chronic Diseases 36
38 Appendix CRG Assignment continued CRG Assignment CLAIM Claim No: Date: 01/01/01 Name: Sam Smith Hospital: Diagnosis: URI Atopic Dermatitis Chest Pain Office Visit Chest Pain Hospital Admission Cholesterol (220) Diabetes (weight gain 50lbs) Angina End Stage Renal Disease Dialysis Catastrophic Conditions 37
Making a Business Case for Wellness. Diane Andrea, RD, LD Wellness Consultant
 Making a Business Case for Wellness Diane Andrea, RD, LD Wellness Consultant Overview of Presentation 1 Cost of unhealthy behaviors 2 Return on Investment 3 Biggest bang for your wellness buck What is
Making a Business Case for Wellness Diane Andrea, RD, LD Wellness Consultant Overview of Presentation 1 Cost of unhealthy behaviors 2 Return on Investment 3 Biggest bang for your wellness buck What is
Performance Analysis:
 Performance Analysis: Healthcare Utilization of CCNC- Population 2007-2010 Prepared by Treo Solutions JUNE 2012 Table of Contents SECTION ONE: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 4-5 SECTION TWO: REPORT DETAILS 6 Inpatient
Performance Analysis: Healthcare Utilization of CCNC- Population 2007-2010 Prepared by Treo Solutions JUNE 2012 Table of Contents SECTION ONE: EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 4-5 SECTION TWO: REPORT DETAILS 6 Inpatient
Risk Adjustment and Hierarchical Condition Category Coding
 Risk Adjustment 101 Agenda Risk Adjustment Model Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCC) Patient Example Documentation MEAT Documentation Guidance Chronic Conditions Risk Score Calculations Steps for Physician
Risk Adjustment 101 Agenda Risk Adjustment Model Hierarchical Condition Categories (HCC) Patient Example Documentation MEAT Documentation Guidance Chronic Conditions Risk Score Calculations Steps for Physician
ACOFP 55th Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars. How Complicated is Your Panel? Effective Risk Coding in Primary Care. Alison Mancuso, DO, FACOFP
 8 ACOFP 55th Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars How Complicated is Your Panel? Effective Risk Coding in Primary Care Alison Mancuso, DO, FACOFP How Complicated is Your Panel?: Effective Risk Coding
8 ACOFP 55th Annual Convention & Scientific Seminars How Complicated is Your Panel? Effective Risk Coding in Primary Care Alison Mancuso, DO, FACOFP How Complicated is Your Panel?: Effective Risk Coding
Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for CKD
 Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for CKD Introduction Determining the economic impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) on the health care system is challenging on several levels. There is, for instance,
Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for CKD Introduction Determining the economic impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) on the health care system is challenging on several levels. There is, for instance,
Information Management. A System We Can Count On. Chronic Conditions. in the Central East LHIN
 Information Management A System We Can Count On Chronic Conditions in the Central East LHIN Health System Intelligence Project October 2007 Table of Contents About HSIP..................................ii
Information Management A System We Can Count On Chronic Conditions in the Central East LHIN Health System Intelligence Project October 2007 Table of Contents About HSIP..................................ii
Do OurHealth primary care clinics improve health & reduce healthcare costs? OurHealth Patient Engagement Analysis June 2018
 Question: Do OurHealth primary care clinics improve health & reduce healthcare costs? OurHealth Patient Engagement Analysis June 2018 An examination of health improvements, utilization & cost of care for
Question: Do OurHealth primary care clinics improve health & reduce healthcare costs? OurHealth Patient Engagement Analysis June 2018 An examination of health improvements, utilization & cost of care for
PREVENTION FOR A HEALTHIER AMERICA: Investments in Disease Prevention Yield Significant Savings, Stronger Communities
 PREVENTION FOR A HEALTHIER AMERICA: Investments in Disease Prevention Yield Significant Savings, Stronger Communities Jeffrey Levi, PhD Executive Director, Trust for America s Health Barbara A. Ormond,
PREVENTION FOR A HEALTHIER AMERICA: Investments in Disease Prevention Yield Significant Savings, Stronger Communities Jeffrey Levi, PhD Executive Director, Trust for America s Health Barbara A. Ormond,
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for Persons With CKD Medicare spending for patients with CKD aged 65 and older exceeded $50 billion in 2013, representing 20% of all
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 6: Medicare Expenditures for Persons With CKD Medicare spending for patients with CKD aged 65 and older exceeded $50 billion in 2013, representing 20% of all
Care Facilitation Quality Improvement Report
 Disease Management Program Clinical Outcomes for Reporting Period: 2006 Diabetes 100.0% 90.0% % of participants with diabetes 80.0% 70.0% 60.0% 50.0% 40.0% 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% % participants with at
Disease Management Program Clinical Outcomes for Reporting Period: 2006 Diabetes 100.0% 90.0% % of participants with diabetes 80.0% 70.0% 60.0% 50.0% 40.0% 30.0% 20.0% 10.0% 0.0% % participants with at
HealtheCNY Indicator List by Data Source
 American Community Survey 23 Adults with Health Insurance Children Living Below Poverty Level Children with Health Insurance Families Living Below Poverty Level Homeowner Vacancy Rate Homeownership Households
American Community Survey 23 Adults with Health Insurance Children Living Below Poverty Level Children with Health Insurance Families Living Below Poverty Level Homeowner Vacancy Rate Homeownership Households
State of Wellness: The Goods, the Bads & What s Next for Creighton
 Creighton University Organizational Health Report State of Wellness: The Goods, the Bads & What s Next for Creighton Presented by: Dawn Obermiller, MA Date: May 8, 2014 Presentation Overview 2012-13 Wellness
Creighton University Organizational Health Report State of Wellness: The Goods, the Bads & What s Next for Creighton Presented by: Dawn Obermiller, MA Date: May 8, 2014 Presentation Overview 2012-13 Wellness
Manitoba Primary Care Quality Indicators Full Guide Version 3.0 Quick Reference Summary
 PREVENTION 2.01 Cervical Cancer 2.02 Colon Cancer 2.03 Breast Cancer 2.04 Dyslipidemia for Women 2.05 Dyslipidemia for Men Female 21-69 PAP 36 Percentage of female enrolled patients 21 to 69 years of age
PREVENTION 2.01 Cervical Cancer 2.02 Colon Cancer 2.03 Breast Cancer 2.04 Dyslipidemia for Women 2.05 Dyslipidemia for Men Female 21-69 PAP 36 Percentage of female enrolled patients 21 to 69 years of age
A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment
 A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment Michigan Society for Respiratory Care 2015 Fall Conference K. James Ehlen, MD October 6, 2015 Objectives Describe patients who will
A Place For Airway Clearance Therapy In Today s Healthcare Environment Michigan Society for Respiratory Care 2015 Fall Conference K. James Ehlen, MD October 6, 2015 Objectives Describe patients who will
Health Care in Appalachia. Foundations of Modern Health Care, Lecture 12 Anya K. Cope, DO
 Health Care in Appalachia Foundations of Modern Health Care, Lecture 12 Anya K. Cope, DO Learning Objectives: At the completion of this exercise, learners should be able to: Discuss the mortality rates
Health Care in Appalachia Foundations of Modern Health Care, Lecture 12 Anya K. Cope, DO Learning Objectives: At the completion of this exercise, learners should be able to: Discuss the mortality rates
Tennessee Department of Health in collaboration with Tennessee State University and University of Tennessee Health Science Center
 Tennessee Department of Health in collaboration with Tennessee State University and University of Tennessee Health Science Center 2006 Tennessee Department of Health 2006 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS CONTRIBUTING
Tennessee Department of Health in collaboration with Tennessee State University and University of Tennessee Health Science Center 2006 Tennessee Department of Health 2006 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS CONTRIBUTING
Christine A. Bono, PhD Program Associate. Elizabeth Shenkman, PhD Principal Investigator. October 24, 2003
 COMPARING HEALTH CARE OUTCOMES FOR CHILDREN ENROLLED IN THE FLORIDA HEALTHY KIDS PROGRAM AND CARED FOR BY PEDIATRICIANS VS. FAMILY PRACTITIONERS A REPORT PREPARED FOR THE HEALTHY KIDS BOARD OF DIRECTORS
COMPARING HEALTH CARE OUTCOMES FOR CHILDREN ENROLLED IN THE FLORIDA HEALTHY KIDS PROGRAM AND CARED FOR BY PEDIATRICIANS VS. FAMILY PRACTITIONERS A REPORT PREPARED FOR THE HEALTHY KIDS BOARD OF DIRECTORS
DISEASE MANAGEMENT: A CASE FOR COST EFFECTIVENESS AND QUALITY. Presented by Rob Parke Lalit Baveja
 DISEASE MANAGEMENT: A CASE FOR COST EFFECTIVENESS AND QUALITY CARE Presented by Rob Parke Lalit Baveja Jaiwardhan Vij February 12-13, 13 2009 Agenda India s s Chronic Disease Burden Overview of Disease
DISEASE MANAGEMENT: A CASE FOR COST EFFECTIVENESS AND QUALITY CARE Presented by Rob Parke Lalit Baveja Jaiwardhan Vij February 12-13, 13 2009 Agenda India s s Chronic Disease Burden Overview of Disease
The clinical and economic benefits of better treatment of adult Medicaid beneficiaries with diabetes
 The clinical and economic benefits of better treatment of adult Medicaid beneficiaries with diabetes September, 2017 White paper Life Sciences IHS Markit Introduction Diabetes is one of the most prevalent
The clinical and economic benefits of better treatment of adult Medicaid beneficiaries with diabetes September, 2017 White paper Life Sciences IHS Markit Introduction Diabetes is one of the most prevalent
Welcome to the Healthplex!
 Welcome to the Healthplex! Program Please check program that applies to you. If unsure, please ask our staff. Aftercare Employee Health Pulmonary Rehab Lung Gym Cardiac Rehab Health Improvement Prenatal/Post-Partum
Welcome to the Healthplex! Program Please check program that applies to you. If unsure, please ask our staff. Aftercare Employee Health Pulmonary Rehab Lung Gym Cardiac Rehab Health Improvement Prenatal/Post-Partum
Dana L. Gilbert Chief Operating Officer Sharon Rudnick Vice President Outpatient Care Management
 Ambulatory Sensitive Admissions Dana L. Gilbert Chief Operating Officer Sharon Rudnick Vice President Outpatient Care Management 1 Sites Of Care Advocate Health Care 12 Hospitals 10 acute care hospitals
Ambulatory Sensitive Admissions Dana L. Gilbert Chief Operating Officer Sharon Rudnick Vice President Outpatient Care Management 1 Sites Of Care Advocate Health Care 12 Hospitals 10 acute care hospitals
Texas Chronic Disease Burden Report. April Publication #E
 Texas Chronic Disease Burden Report April 2010 Publication #E81-11194 Direction and Support Lauri Kalanges, MD, MPH Medical Director Health Promotion and Chronic Disease Prevention Section, Texas Department
Texas Chronic Disease Burden Report April 2010 Publication #E81-11194 Direction and Support Lauri Kalanges, MD, MPH Medical Director Health Promotion and Chronic Disease Prevention Section, Texas Department
Unmanaged Behavioral Health Puts Your Company At Risk. Presented by: Dr. Sam Mayhugh Integrated Behavioral Health
 Unmanaged Behavioral Health Puts Your Company At Risk Presented by: Dr. Sam Mayhugh Integrated Behavioral Health Behavioral Health Management Webinar Overview History of BH management Prevalence of behavioral
Unmanaged Behavioral Health Puts Your Company At Risk Presented by: Dr. Sam Mayhugh Integrated Behavioral Health Behavioral Health Management Webinar Overview History of BH management Prevalence of behavioral
Combining Risk Adjustment and HEDIS to Improve Quality of Care. Colleen Gianatasio, CPC, CPC-P, CPMA, CPC-I, CRC
 Combining Risk Adjustment and HEDIS to Improve Quality of Care Colleen Gianatasio, CPC, CPC-P, CPMA, CPC-I, CRC Agenda Improving primary care in today s health care environment Risk adjustment basics (using
Combining Risk Adjustment and HEDIS to Improve Quality of Care Colleen Gianatasio, CPC, CPC-P, CPMA, CPC-I, CRC Agenda Improving primary care in today s health care environment Risk adjustment basics (using
Affordability AMGA - MIPS Webinar
 Affordability AMGA - MIPS Webinar Beth Averbeck, MD Senior Medical Director Primary Care, HealthPartners Consumer-governed, non-profit HealthPartners Medical Group Primary Care: 500,000 patients 29 locations
Affordability AMGA - MIPS Webinar Beth Averbeck, MD Senior Medical Director Primary Care, HealthPartners Consumer-governed, non-profit HealthPartners Medical Group Primary Care: 500,000 patients 29 locations
Value Based Pay for Performance Results & Highlights Measurement Year September 2017
 Value Based Pay for Performance Results & Highlights Measurement Year 2016 September 2017 IHA s Value Based Pay for Performance (VBP4P) ~200 Medical Groups & IPAs 9 Health Plans Common Measurement Public
Value Based Pay for Performance Results & Highlights Measurement Year 2016 September 2017 IHA s Value Based Pay for Performance (VBP4P) ~200 Medical Groups & IPAs 9 Health Plans Common Measurement Public
The ALS Association Mid-America Chapter 87 people in Nebraska have ALS. Every 90 minutes, someone is diagnosed with or passes away from ALS.
 HEALTH FACTS The ALS Association Mid-America Chapter 87 people in Nebraska have ALS. Every 90 minutes, someone is diagnosed with or passes away from ALS. Alzheimer s Association Nebraska Chapter 5.5 million
HEALTH FACTS The ALS Association Mid-America Chapter 87 people in Nebraska have ALS. Every 90 minutes, someone is diagnosed with or passes away from ALS. Alzheimer s Association Nebraska Chapter 5.5 million
Community Health Needs Assessment Centra Southside Medical Center
 Community Health Needs Assessment Centra Southside Medical Center 2017-2019 Healthy People 2020 Healthy People provides a framework for prevention for communities in the U.S. Healthy People 2020 is a comprehensive
Community Health Needs Assessment Centra Southside Medical Center 2017-2019 Healthy People 2020 Healthy People provides a framework for prevention for communities in the U.S. Healthy People 2020 is a comprehensive
TENNCARE Bundled Payment Initiative: Description of Bundle Risk Adjustment for Wave 2 Episodes
 TENNCARE Bundled Payment Initiative: Description of Bundle Risk Adjustment for Wave 2 Episodes Acute COPD exacerbation (COPD); Screening and surveillance colonoscopy (COL); and Outpatient and non-acute
TENNCARE Bundled Payment Initiative: Description of Bundle Risk Adjustment for Wave 2 Episodes Acute COPD exacerbation (COPD); Screening and surveillance colonoscopy (COL); and Outpatient and non-acute
In your own words, please write the reason you are here. Please be specific, putting in dates as necessary. Use the back of the form if needed.
 Name: SS# In your own words, please write the reason you are here. Please be specific, putting in dates as necessary. Use the back of the form if needed. Patient Medical, Surgical and Family History Review
Name: SS# In your own words, please write the reason you are here. Please be specific, putting in dates as necessary. Use the back of the form if needed. Patient Medical, Surgical and Family History Review
County of Sacramento. Review of Population Health through Kaiser Permanente Data
 County of Sacramento Review of Population Health through Kaiser Permanente Data Dr. Diane Dailey, M.D., Chief of Business Health Engagement Eileen Peterson, MPH, RD, TPMG Business Health Consultant, Public
County of Sacramento Review of Population Health through Kaiser Permanente Data Dr. Diane Dailey, M.D., Chief of Business Health Engagement Eileen Peterson, MPH, RD, TPMG Business Health Consultant, Public
A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health
 2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health live for life duke Institute for genome sciences & policy Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes
2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health live for life duke Institute for genome sciences & policy Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes
Expenditure Share United States, 2003
 Expenditure Share United States, 2003 Source: MEPS Chronic Disease Share of MEPS Expenditure ( Percent ) Share of Health Care Expenditure Breast Cancer 0.5 0.3 Colon Cancer 0.8 0.5 Lung Cancer 0.6 0.3
Expenditure Share United States, 2003 Source: MEPS Chronic Disease Share of MEPS Expenditure ( Percent ) Share of Health Care Expenditure Breast Cancer 0.5 0.3 Colon Cancer 0.8 0.5 Lung Cancer 0.6 0.3
A Prospective Comparison of Two Commercially Available Hospital Admission Risk Scores
 A Prospective Comparison of Two Commercially Available Hospital Admission Risk Scores Dale Eric Green, MD MHA FCCP: Chief Medical Information Officer, Cornerstone Health Care AMGA April, 2014 Disclosure
A Prospective Comparison of Two Commercially Available Hospital Admission Risk Scores Dale Eric Green, MD MHA FCCP: Chief Medical Information Officer, Cornerstone Health Care AMGA April, 2014 Disclosure
LECOM Health Ophthalmology
 Patient Name: Date of Birth: New Patient Questionnaire Your answers will be used by your healthcare provider get an accurate history of your medical conditions and ocular concerns. If you are uncomfortable
Patient Name: Date of Birth: New Patient Questionnaire Your answers will be used by your healthcare provider get an accurate history of your medical conditions and ocular concerns. If you are uncomfortable
Table of Contents. Page 2 of 20
 Page 1 of 20 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 NMHCTOD Participants... 3 Introduction... 4 Methodology... 5 Types of Data Available... 5 Diabetes in New Mexico... 7 HEDIS Quality Indicators for
Page 1 of 20 Table of Contents Table of Contents... 2 NMHCTOD Participants... 3 Introduction... 4 Methodology... 5 Types of Data Available... 5 Diabetes in New Mexico... 7 HEDIS Quality Indicators for
Summary of Strategic Competitive Analysis and Publication Planning
 Summary of Strategic Competitive Analysis and Publication Planning Carole Alison Chrvala, PhD 919.545.2149 (Work) 919.951.5230 (Mobile) cchrvala@centurylink.net www.healthmattersmedwriting.com 1 Briefing
Summary of Strategic Competitive Analysis and Publication Planning Carole Alison Chrvala, PhD 919.545.2149 (Work) 919.951.5230 (Mobile) cchrvala@centurylink.net www.healthmattersmedwriting.com 1 Briefing
JUSTUS WARREN TASK FORCE MEETING DECEMBER 05, 2012
 SAMUEL TCHWENKO, MD, MPH Epidemiologist, Heart Disease & Stroke Prevention Branch Chronic Disease & Injury Section; Division of Public Health NC Department of Health & Human Services JUSTUS WARREN TASK
SAMUEL TCHWENKO, MD, MPH Epidemiologist, Heart Disease & Stroke Prevention Branch Chronic Disease & Injury Section; Division of Public Health NC Department of Health & Human Services JUSTUS WARREN TASK
National health-care expenditures are projected to rise to $5.2 trillion by 2023
 National health-care expenditures are projected to rise to $5.2 trillion by 2023 US$ trillions 6 5 4 3 2.3 2.5 2.7 2.9 3.2 3.6 4.0 4.6 5.2 2 1 0 2007 2011 2015* 2019* 2023* * Projected. Source: Centers
National health-care expenditures are projected to rise to $5.2 trillion by 2023 US$ trillions 6 5 4 3 2.3 2.5 2.7 2.9 3.2 3.6 4.0 4.6 5.2 2 1 0 2007 2011 2015* 2019* 2023* * Projected. Source: Centers
Progress Tracker. Photo - https://www.healthypeople.gov/
 Progress Tracker Healthy People provides a framework for prevention for communities in the U.S. Healthy People 2020 is a comprehensive set of key disease prevention and health promotion objectives. The
Progress Tracker Healthy People provides a framework for prevention for communities in the U.S. Healthy People 2020 is a comprehensive set of key disease prevention and health promotion objectives. The
Hu J, Gonsahn MD, Nerenz DR. Socioeconomic status and readmissions: evidence from an urban teaching hospital. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33(5).
 Appendix Definitions of Index Admission and Readmission Definitions of index admission and readmission follow CMS hospital-wide all-cause unplanned readmission (HWR) measure as far as data are available.
Appendix Definitions of Index Admission and Readmission Definitions of index admission and readmission follow CMS hospital-wide all-cause unplanned readmission (HWR) measure as far as data are available.
Participation - Demographics. Age Ranges*
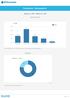 Participation - Demographics January 1, 2017 - March 31, 2017 Age Ranges* 50% n = 139 42.4% Total 38% 25% 20.9% 20.1% 13% 12.9% 3.6% 0% 18-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60+ * Age ranges
Participation - Demographics January 1, 2017 - March 31, 2017 Age Ranges* 50% n = 139 42.4% Total 38% 25% 20.9% 20.1% 13% 12.9% 3.6% 0% 18-29 years 30-39 years 40-49 years 50-59 years 60+ * Age ranges
2013: The Year of the ACO (Franciscan Northwest Physicians Health Network, LLC)
 2013: The Year of the ACO (Franciscan Northwest Physicians Health Network, LLC) Scott Kronlund, MD, MS Northwest Physicians Network Institute of Medicine Value Incentives Learning Collaborative November
2013: The Year of the ACO (Franciscan Northwest Physicians Health Network, LLC) Scott Kronlund, MD, MS Northwest Physicians Network Institute of Medicine Value Incentives Learning Collaborative November
Your Partnership in Health Report: Chronic Conditions ABC Company and Kaiser Permanente
 Your Partnership in Health Report: s ABC Company and Kaiser Permanente Measurement Period: JUL-01-2012 through JUN-30-2013 Report Date: DEC-31-2013 Commercial All Members Partnership in Health (PIH) reports:
Your Partnership in Health Report: s ABC Company and Kaiser Permanente Measurement Period: JUL-01-2012 through JUN-30-2013 Report Date: DEC-31-2013 Commercial All Members Partnership in Health (PIH) reports:
MArch The 2014 Drug Trend Report Highlights
 MArch 2015 The 2014 Drug Report Highlights Highest Increase in U.S. Drug Spend Over Past Decade In 2014, the pharmacy landscape underwent a seismic change, and the budgetary impact to healthcare payers
MArch 2015 The 2014 Drug Report Highlights Highest Increase in U.S. Drug Spend Over Past Decade In 2014, the pharmacy landscape underwent a seismic change, and the budgetary impact to healthcare payers
Working Paper Distribution and types of multiple chronic conditions in Korea. Young-Ho Jung, Sukja Ko
 Working Paper 2014-09 Distribution and types of multiple chronic conditions in Korea Young-Ho Jung, Sukja Ko Distribution and types of multiple chronic conditions in Korea Young-Ho Jung, Research Fellow
Working Paper 2014-09 Distribution and types of multiple chronic conditions in Korea Young-Ho Jung, Sukja Ko Distribution and types of multiple chronic conditions in Korea Young-Ho Jung, Research Fellow
Healthcare Transformation: Translating Aspiration into Action. Charlotte Yeh, MD Chief Medical Officer, AARP Services, Inc.
 Healthcare Transformation: Translating Aspiration into Action Charlotte Yeh, MD Chief Medical Officer, AARP Services, Inc. The Healthcare Transformation Mission: Deliver on the promise of quality care
Healthcare Transformation: Translating Aspiration into Action Charlotte Yeh, MD Chief Medical Officer, AARP Services, Inc. The Healthcare Transformation Mission: Deliver on the promise of quality care
Chapter 6: Healthcare Expenditures for Persons with CKD
 Chapter 6: Healthcare Expenditures for Persons with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR), we introduce information from the Optum Clinformatics DataMart for persons with Medicare Advantage and commercial
Chapter 6: Healthcare Expenditures for Persons with CKD In this 2017 Annual Data Report (ADR), we introduce information from the Optum Clinformatics DataMart for persons with Medicare Advantage and commercial
Risk Adjustment Documentation & Coding Improvement Reference Information for 2017
 Risk Adjustment Documentation & Coding Improvement Reference Information for 2017 In today s quality and patient-centered health care environment, the importance of accurate, specific and thorough medical
Risk Adjustment Documentation & Coding Improvement Reference Information for 2017 In today s quality and patient-centered health care environment, the importance of accurate, specific and thorough medical
Continua Health Alliance Industry Statistics
 Continua Health Alliance Industry Statistics Health and Wellness statistics and insights Global statistics: Worldwide obesity has more than doubled since 1980 (WHO Fact Sheet, 2008) In 2008, 1.5 billion
Continua Health Alliance Industry Statistics Health and Wellness statistics and insights Global statistics: Worldwide obesity has more than doubled since 1980 (WHO Fact Sheet, 2008) In 2008, 1.5 billion
SENIOR PDHPE HEALTH PRIORITIES IN AUSTRALIA INTRODUCTORY NOTES NAME SCHOOL / ORGANISATION DATE
 SENIOR PDHPE HEALTH PRIORITIES IN AUSTRALIA NAME SCHOOL / ORGANISATION DATE INTRODUCTORY NOTES AUSTRALIA S HEALTH PRIORITIES The current AIHW report, Australia s Health, identifies nine major categories
SENIOR PDHPE HEALTH PRIORITIES IN AUSTRALIA NAME SCHOOL / ORGANISATION DATE INTRODUCTORY NOTES AUSTRALIA S HEALTH PRIORITIES The current AIHW report, Australia s Health, identifies nine major categories
Screening and Referral. Unit: Programming Pilates Matwork
 Screening and Referral Unit: Programming Pilates Matwork Learning outcomes & assessment criteria Learning outcome: The learner will: LO2: Understand how to screen clients prior to a Pilates matwork programme
Screening and Referral Unit: Programming Pilates Matwork Learning outcomes & assessment criteria Learning outcome: The learner will: LO2: Understand how to screen clients prior to a Pilates matwork programme
ASN s Legislative Priorities for 2010
 ASN s Legislative Priorities for 2010 3 Address Profound Health Care Disparities Congress should fund more research to address inequities in treatment of Americans with kidney disease. Only 7% of US physicians
ASN s Legislative Priorities for 2010 3 Address Profound Health Care Disparities Congress should fund more research to address inequities in treatment of Americans with kidney disease. Only 7% of US physicians
Member-centered cancer care In Georgia
 Quality health plans & benefits Healthier living Financial well-being Intelligent solutions Member-centered cancer care In Georgia Ira Klein, MD, MBA, FACP GASCO Annual Meeting September 5, 2015 > One
Quality health plans & benefits Healthier living Financial well-being Intelligent solutions Member-centered cancer care In Georgia Ira Klein, MD, MBA, FACP GASCO Annual Meeting September 5, 2015 > One
Marc Moss, MD President, American Thoracic Society (202) th St, N.W. #300 Washington, DC 20036
 Marc Moss, MD President, American Thoracic Society Nmoore@thoracic.org; (202) 296. 9770 1150 18 th St, N.W. #300 Washington, DC 20036 STATEMENT OF THE AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY SUBMITTED TO THE HOUSE LABOR,
Marc Moss, MD President, American Thoracic Society Nmoore@thoracic.org; (202) 296. 9770 1150 18 th St, N.W. #300 Washington, DC 20036 STATEMENT OF THE AMERICAN THORACIC SOCIETY SUBMITTED TO THE HOUSE LABOR,
This presentation was current at the time it was published or uploaded onto the web. Medicare and commercial payers change their policies frequently.
 Cost, The Forgotten Component of the Medicare Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) for National Society of Certified Healthcare Business Consultants Presented By Maxine Lewis, CMM, CPC, CPC-I, CCS-P,
Cost, The Forgotten Component of the Medicare Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) for National Society of Certified Healthcare Business Consultants Presented By Maxine Lewis, CMM, CPC, CPC-I, CCS-P,
Patient-Centered Cancer Treatment Planning: Improving the Quality of Oncology Care
 Patient-Centered Cancer Treatment Planning: Improving the Quality of Oncology Care Carolyn M. Clancy, MD Director Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality IOM National Cancer Policy Forum and the National
Patient-Centered Cancer Treatment Planning: Improving the Quality of Oncology Care Carolyn M. Clancy, MD Director Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality IOM National Cancer Policy Forum and the National
Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims:
 Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims: Implications for Non- Medical Switching August 2017 THE MORAN COMPANY 1 Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims: Implications for Non-Medical
Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims: Implications for Non- Medical Switching August 2017 THE MORAN COMPANY 1 Cost-Motivated Treatment Changes in Commercial Claims: Implications for Non-Medical
Chronicity and Aging: The Geriatric Imperative
 Chronicity and Aging: The Geriatric Imperative Steven L. Phillips, MD Medical Director Sanford Center for Aging Professor, Clinical Internal Medicine University of Nevada, Reno School of Medicine dhs.unr.edu/aging
Chronicity and Aging: The Geriatric Imperative Steven L. Phillips, MD Medical Director Sanford Center for Aging Professor, Clinical Internal Medicine University of Nevada, Reno School of Medicine dhs.unr.edu/aging
An Unhealthy America: The Economic Burden of Chronic Disease Charting a New Course to Save Lives and Increase Productivity and Economic Growth
 An Unhealthy America: The Economic Burden of Chronic Disease Charting a New Course to Save Lives and Increase Productivity and Economic Growth Kevin Klowden Managing Economist Milken Institute (310) 570
An Unhealthy America: The Economic Burden of Chronic Disease Charting a New Course to Save Lives and Increase Productivity and Economic Growth Kevin Klowden Managing Economist Milken Institute (310) 570
Advanced Concepts of Personal Training Study Guide Answer Key
 Advanced Concepts of Personal Training Study Guide Answer Key Lesson 22 Working with Special Populations LESSON TWENTY TWO Lesson Twenty Two Working with Special Populations WORKING WITH SPECIAL POPULATIONS
Advanced Concepts of Personal Training Study Guide Answer Key Lesson 22 Working with Special Populations LESSON TWENTY TWO Lesson Twenty Two Working with Special Populations WORKING WITH SPECIAL POPULATIONS
PHYSICIAN PROXY PANEL. Dr. Sample report Sample report PCN
 PHYSICIAN PROXY PANEL Dr. Sample report Sample report PCN The Health Quality Council of Alberta is a provincial agency that pursues opportunities to improve patient safety and health service quality for
PHYSICIAN PROXY PANEL Dr. Sample report Sample report PCN The Health Quality Council of Alberta is a provincial agency that pursues opportunities to improve patient safety and health service quality for
Easing the Burden of Noncommunicable Disease
 09 Easing the Burden of Noncommunicable Disease Situation According to the World Health Organization (WHO), of 57 million global deaths in 2008, 36 million, or 63 percent, were due to noncommunicable diseases
09 Easing the Burden of Noncommunicable Disease Situation According to the World Health Organization (WHO), of 57 million global deaths in 2008, 36 million, or 63 percent, were due to noncommunicable diseases
Methodological Issues
 Methodological Issues Presentation by Ian Brownwood for the meeting of Health Promotion, Prevention and Primary Care Subgroup 22 October, 2009, Paris The Indicators Asthma* Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
Methodological Issues Presentation by Ian Brownwood for the meeting of Health Promotion, Prevention and Primary Care Subgroup 22 October, 2009, Paris The Indicators Asthma* Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary
ACE Prevention Media launch 8 September Prof Theo Vos Prof Rob Carter for ACE Prevention research team
 ACE Prevention Media launch 8 September 2010 Prof Theo Vos Prof Rob Carter for ACE Prevention research team Australia ranks second world wide in life expectancy Large improvements in health in last 40
ACE Prevention Media launch 8 September 2010 Prof Theo Vos Prof Rob Carter for ACE Prevention research team Australia ranks second world wide in life expectancy Large improvements in health in last 40
Magellan Rx. A smarter approach to pharmacy benefits management
 Magellan Rx A smarter approach to pharmacy benefits management Presented by: Cheri Caruso, VP of Sales, Magellan Rx Management Bryce Canfield, VP, Client Development, GoodRx A unique vision of care We
Magellan Rx A smarter approach to pharmacy benefits management Presented by: Cheri Caruso, VP of Sales, Magellan Rx Management Bryce Canfield, VP, Client Development, GoodRx A unique vision of care We
Population Health 2.0 through Personalized Medicine
 DISCOVERING WHAT WORKS. AND FOR WHOM. Population Health 2.0 through Personalized Medicine Colin Hill CEO and Co-Founder "Fifty-five percent of drugs used in America don't work for the patients they are
DISCOVERING WHAT WORKS. AND FOR WHOM. Population Health 2.0 through Personalized Medicine Colin Hill CEO and Co-Founder "Fifty-five percent of drugs used in America don't work for the patients they are
Appendix 1: Supplementary tables [posted as supplied by author]
![Appendix 1: Supplementary tables [posted as supplied by author] Appendix 1: Supplementary tables [posted as supplied by author]](/thumbs/81/83505567.jpg) Appendix 1: Supplementary tables [posted as supplied by author] Table A. International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification Codes Used to Define Heart Failure, Acute Myocardial
Appendix 1: Supplementary tables [posted as supplied by author] Table A. International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Clinical Modification Codes Used to Define Heart Failure, Acute Myocardial
Executive Summary Report Sample Executive Report Page 1
 Sample Executive Report Page 1 Introduction This report summarizes the primary health findings for those individuals who completed the Personal Wellness Profile (PWP) health assessment. Group health needs
Sample Executive Report Page 1 Introduction This report summarizes the primary health findings for those individuals who completed the Personal Wellness Profile (PWP) health assessment. Group health needs
A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health
 2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health INTERMOUNTAIN HEALTHCARE Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique? 2 Tell me more about
2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health INTERMOUNTAIN HEALTHCARE Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique? 2 Tell me more about
A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health
 2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health National Council of La Raza Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique? 2 Tell me more about
2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health National Council of La Raza Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique? 2 Tell me more about
Leveraging Analytics and Artificial Intelligence to Predict Health Risk
 Leveraging Analytics and Artificial Intelligence to Predict Health Risk A case study on using machine learning to boost atrial fibrillation identification and anticoagulant drug use Arthur L. Forni, MD,
Leveraging Analytics and Artificial Intelligence to Predict Health Risk A case study on using machine learning to boost atrial fibrillation identification and anticoagulant drug use Arthur L. Forni, MD,
Economics of Reducing Out-of-Pocket Costs for Cardiovascular Preventive Services for Patients with High Blood Pressure and High Cholesterol
 s of Reducing Out-of-Pocket Costs for Cardiovascular Preventive Services for Patients with High Blood Pressure and High Cholesterol Summary Evidence Tables Study Author (Year) Bunting (2008) Prepost Incomplete
s of Reducing Out-of-Pocket Costs for Cardiovascular Preventive Services for Patients with High Blood Pressure and High Cholesterol Summary Evidence Tables Study Author (Year) Bunting (2008) Prepost Incomplete
Kaiser Permanente Complete Care. Michael H. Kanter, MD Medical Director of Quality and Clinical Analysis
 Kaiser Permanente Complete Care Michael H. Kanter, MD Medical Director of Quality and Clinical Analysis Joint Commission Journal on Quality & Patient Safety November 2013; 39(11):484-494 HEDIS Results
Kaiser Permanente Complete Care Michael H. Kanter, MD Medical Director of Quality and Clinical Analysis Joint Commission Journal on Quality & Patient Safety November 2013; 39(11):484-494 HEDIS Results
ICD-9-CM CODING FUNDAMENTALS CODING EXERCISES
 Steps to Accurate Coding Underline the main term, then locate code: Stenosis of Carotid Artery Transient Ischemic Attack Gastrointestinal hemorrhage Degenerative Joint Disease Coronary Artery Disease Alcoholic
Steps to Accurate Coding Underline the main term, then locate code: Stenosis of Carotid Artery Transient Ischemic Attack Gastrointestinal hemorrhage Degenerative Joint Disease Coronary Artery Disease Alcoholic
BTS Guideline for Home Oxygen use in adults Appendix 9 (online only) Key Questions - PICO 10 December 2012
 BTS Guideline for Home Oxygen use in adults Appendix 9 (online only) Key Questions - PICO 10 December 2012 Evidence base for Home Oxygen therapy in COPD, non-copd respiratory disease and nonrespiratory
BTS Guideline for Home Oxygen use in adults Appendix 9 (online only) Key Questions - PICO 10 December 2012 Evidence base for Home Oxygen therapy in COPD, non-copd respiratory disease and nonrespiratory
LCD L B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) Assays
 LCD L30559 - B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) Assays Contractor Information Contractor Name: Novitas Solutions, Inc. Contractor Number(s): 12501, 12502, 12101, 12102, 12201, 12202, 12301, 12302, 12401,
LCD L30559 - B-type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) Assays Contractor Information Contractor Name: Novitas Solutions, Inc. Contractor Number(s): 12501, 12502, 12101, 12102, 12201, 12202, 12301, 12302, 12401,
LIST OF CLINICAL PRIVILEGES DIETITIAN
 LIST OF CLINICAL PRIVILEGES DIETITIAN AUTHORITY: Title 10, U.S.C. Chapter 55, Sections 1094 and 1102. PRINCIPAL PURPOSE: To define the scope and limits of practice for individual providers. Privileges
LIST OF CLINICAL PRIVILEGES DIETITIAN AUTHORITY: Title 10, U.S.C. Chapter 55, Sections 1094 and 1102. PRINCIPAL PURPOSE: To define the scope and limits of practice for individual providers. Privileges
Opportunities for Dental Disease Management Programs in Managed Care
 Opportunities for Dental Disease Management Programs in Managed Care Jay Feldstein, DO, FACPM Keystone Mercy Health Plan Lawrence Paul, DDS QualDent David Williams, PhD QualDent Goal of Dental Disease
Opportunities for Dental Disease Management Programs in Managed Care Jay Feldstein, DO, FACPM Keystone Mercy Health Plan Lawrence Paul, DDS QualDent David Williams, PhD QualDent Goal of Dental Disease
Physiological disorders
 Physiological disorders Overview of major causes and signs and symptoms Learning Aim A: Tuesday 7 th February 2017 Grading Criteria Causative factors in physiological disorders Aetiology is the medical
Physiological disorders Overview of major causes and signs and symptoms Learning Aim A: Tuesday 7 th February 2017 Grading Criteria Causative factors in physiological disorders Aetiology is the medical
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Dharmarajan K, Wang Y, Lin Z, et al. Association of changing hospital readmission rates with mortality rates after hospital discharge. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.8444 etable
Supplementary Online Content Dharmarajan K, Wang Y, Lin Z, et al. Association of changing hospital readmission rates with mortality rates after hospital discharge. JAMA. doi:10.1001/jama.2017.8444 etable
Episodes of Care Risk Adjustment
 Episodes of Care Risk Adjustment Episode Types Wave 1 Asthma Acute Exacerbation Perinatal Total Joint Replacement Wave 2 Acute Percutaneous Coronary Intervention COPD Acute Exacerbation Non-acute Percutaneous
Episodes of Care Risk Adjustment Episode Types Wave 1 Asthma Acute Exacerbation Perinatal Total Joint Replacement Wave 2 Acute Percutaneous Coronary Intervention COPD Acute Exacerbation Non-acute Percutaneous
Medical Declaration Form. Important information to read before completing the form:
 Administered by Medical Declaration Form Important information to read before completing the form: Pre-Existing Medical conditions Travel insurance only provides cover for emergency medical events that
Administered by Medical Declaration Form Important information to read before completing the form: Pre-Existing Medical conditions Travel insurance only provides cover for emergency medical events that
PQRS 2015Applicable Measure Group Codes ICD-9 and ICD-10 diagnosis codes and CPT encounter and surgical codes
 PQRS 2015Applicable Measure Group Codes ICD-9 and and CPT encounter and surgical codes Acute Otisis Externa (AOE) Measures Group Page 1 Asthma Measures Group Page 2 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
PQRS 2015Applicable Measure Group Codes ICD-9 and and CPT encounter and surgical codes Acute Otisis Externa (AOE) Measures Group Page 1 Asthma Measures Group Page 2 Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG)
The 465 medicines in development include: 142 for diabetes, which affects 10.9 million Americans age 65 and older;
 Medicines in Development Older Americans The Medicare Population and Leading Chronic Diseases presented by america s biopharmaceutical research companies Overview 2013 REPORT Biopharmaceutical Research
Medicines in Development Older Americans The Medicare Population and Leading Chronic Diseases presented by america s biopharmaceutical research companies Overview 2013 REPORT Biopharmaceutical Research
A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health
 2 D o e s i t Ru n i n t h e Fa m i ly? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health Institute for Cultural Partnerships Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique?
2 D o e s i t Ru n i n t h e Fa m i ly? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health Institute for Cultural Partnerships Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique?
UNITED NATIONS HIGH-LEVEL MEETING ON NCDs A CALL TO ACTION ON KIDNEY DISEASE. Advancing Nephrology Around the World
 2018 UNITED NATIONS HIGH-LEVEL MEETING ON NCDs A CALL TO ACTION ON KIDNEY DISEASE Advancing Nephrology Around the World Introduction The 2018 United Nations High-Level Meeting on Non-Communicable Diseases
2018 UNITED NATIONS HIGH-LEVEL MEETING ON NCDs A CALL TO ACTION ON KIDNEY DISEASE Advancing Nephrology Around the World Introduction The 2018 United Nations High-Level Meeting on Non-Communicable Diseases
An Unhealthy America: The Economic Burden of Chronic Disease Charting a New Course to Save Lives and Increase Productivity and Economic Growth
 An Unhealthy America: The Economic Burden of Chronic Disease Charting a New Course to Save Lives and Increase Productivity and Economic Growth Ross DeVol Director, Center for Health Economics Director,
An Unhealthy America: The Economic Burden of Chronic Disease Charting a New Course to Save Lives and Increase Productivity and Economic Growth Ross DeVol Director, Center for Health Economics Director,
Shallotte Vision Care J. Mark Saunders, OD PA 4637 Main Street Shallotte NC Patient Demographic Information
 Shallotte Vision Care J. Mark Saunders, OD PA 4637 Main Street Shallotte NC 28470 Patient Demographic Information Account # Last Name: SSN: / / First: Middle: Marital Status: Single Married Separated Nickname:
Shallotte Vision Care J. Mark Saunders, OD PA 4637 Main Street Shallotte NC 28470 Patient Demographic Information Account # Last Name: SSN: / / First: Middle: Marital Status: Single Married Separated Nickname:
OBSERVATIONAL MEDICAL OUTCOMES PARTNERSHIP
 OBSERVATIONAL Patient-centered observational analytics: New directions toward studying the effects of medical products Patrick Ryan on behalf of OMOP Research Team May 22, 2012 Observational Medical Outcomes
OBSERVATIONAL Patient-centered observational analytics: New directions toward studying the effects of medical products Patrick Ryan on behalf of OMOP Research Team May 22, 2012 Observational Medical Outcomes
Quality measures a for measurement year 2016
 Quality measures a for measurement year 2016 Measure Description Eligible members Childhood immunizations b Adolescent immunizations b Children who turned 2 during the measurement and who were identified
Quality measures a for measurement year 2016 Measure Description Eligible members Childhood immunizations b Adolescent immunizations b Children who turned 2 during the measurement and who were identified
2018 MIPS Reporting Family Medicine
 2018 MIPS Reporting Family Medicine Quality Reporting Requirements: Report on 6 quality measures or a specialty measure set Include at least ONE outcome or high-priority measure Report on patients of All-Payers
2018 MIPS Reporting Family Medicine Quality Reporting Requirements: Report on 6 quality measures or a specialty measure set Include at least ONE outcome or high-priority measure Report on patients of All-Payers
A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health
 2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health brookdale hospital and medical center Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique? 2 Tell me
2 Does it Run in the Family? A Guide for Understanding Genetics and Health brookdale hospital and medical center Contents Why is genetics important to my family and me? 1 What makes me unique? 2 Tell me
Heart Disease and Stroke in New Mexico. Facts and Figures: At-A-Glance
 Heart Disease and Stroke in New Mexico Facts and Figures: At-A-Glance December H e a r t D i s e a s e a n d S t r o k e Heart disease and stroke are the two most common conditions that fall under the
Heart Disease and Stroke in New Mexico Facts and Figures: At-A-Glance December H e a r t D i s e a s e a n d S t r o k e Heart disease and stroke are the two most common conditions that fall under the
Your Medical Details and Treatment Tracker. About You
 This document is intended to help you keep a record of important details that you may need to share with healthcare professionals throughout your Living with Neuroendocrine Tumours (NETs) journey. Take
This document is intended to help you keep a record of important details that you may need to share with healthcare professionals throughout your Living with Neuroendocrine Tumours (NETs) journey. Take
Predictive Diagnosis. Clustering to Better Predict Heart Attacks x The Analytics Edge
 Predictive Diagnosis Clustering to Better Predict Heart Attacks 15.071x The Analytics Edge Heart Attacks Heart attack is a common complication of coronary heart disease resulting from the interruption
Predictive Diagnosis Clustering to Better Predict Heart Attacks 15.071x The Analytics Edge Heart Attacks Heart attack is a common complication of coronary heart disease resulting from the interruption
Obesity: Trends, Impact, Complexity
 Obesity: Trends, Impact, Complexity Ross A. Hammond, Ph.D. Director, Center on Social Dynamics & Policy Senior Fellow, Economic Studies Program The Brookings Institution Attorneys General Education Program
Obesity: Trends, Impact, Complexity Ross A. Hammond, Ph.D. Director, Center on Social Dynamics & Policy Senior Fellow, Economic Studies Program The Brookings Institution Attorneys General Education Program
Pharmacy Prep. Qualifying Pharmacy Review
 Pharmacy Prep 2014 Misbah Biabani, Ph.D Director, Tips Review Centres 5460 Yonge St. Suites 209 & 210 Toronto ON M2N 6K7, Canada Luay Petros, R.Ph Pharmacy Manager, Wal-Mart, Canada 1 Disclaimer Your use
Pharmacy Prep 2014 Misbah Biabani, Ph.D Director, Tips Review Centres 5460 Yonge St. Suites 209 & 210 Toronto ON M2N 6K7, Canada Luay Petros, R.Ph Pharmacy Manager, Wal-Mart, Canada 1 Disclaimer Your use
