Prevalence and clinical course of Clostridium difficile infection in a tertiary-care hospital: a retrospective analysis
|
|
|
- Samuel Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Indian J Gastroenterol (March April 2011) 30(2):89 93 DOI /s SHORT REPORT Prevalence and clinical course of Clostridium difficile infection in a tertiary-care hospital: a retrospective analysis Meghraj Ingle & Abhijit Deshmukh & Devendra Desai & Philip Abraham & Anand Joshi & Camilla Rodrigues & Ranjit Mankeshwar Received: 23 July 2010 /Accepted: 15 April 2011 /Published online: 7 May 2011 # Indian Society of Gastroenterology 2011 Abstract The spectrum of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) is changing. Apart from antibiotic use, other risk factors such as use of proton pump inhibitors (PPI) and immunosuppressive agents, intensive care unit (ICU) stay and inflammatory bowel disease are being recognized. We retrospectively analyzed data on patients whose stool samples were tested for C. difficile toxin (CDT) by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay between June 2006 and May Demographic and clinical data, and risk factors (antibiotic use, underlying malignancy, chemotherapy, use of PPI, ICU stay) were noted. The details of treatment for CDAD, response, complication and follow up were recorded. Patients whose stool samples were CDT-positive were grouped as study subjects and those with negative stool samples were included in the control group. Of the 99 patients (mean age 46.7 years; 58 men) whose stool samples were tested during this period, 17 (17%) were positive for CDT. As compared with control subjects (n=82), study subjects were more likely to have M. Ingle : A. Deshmukh : D. Desai (*) : P. Abraham : A. Joshi Division of Gastroenterology, devendracdesai@gmail.com C. Rodrigues Division of Microbiology, R. Mankeshwar Division of Research, fever, prolonged ICU stay, underlying malignancy, and exposure to immunosuppressive and chemotherapeutic agents. On multivariate analysis, exposure to immunosuppressive agents was the only risk factor associated with CDAD. Fifteen patients were treated with metronidazole and two with vancomycin. Two patients did not respond to metronidazole but responded to vancomycin. No patient developed any complication. The prevalence of C. difficile toxin in diarrheal stools sent for C. difficile toxin testing was 17%. Exposure to immunosuppressive agents was a risk factor for the infection. Metronidazole was effective in a majority of patients. Keywords Antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Immunosuppressive agents. Proton pump inhibitors Introduction Diarrhea is common in hospitalized patients, especially in those who receive antibiotics with incidence ranging from 3% to 29% [1]. Clostridium difficile is the most commonly identified organism as the causal agent for antibiotic associated diarrhea [2]. Because of the frequent use of broad-spectrum antibiotics, the incidence of C. difficileassociated diarrhea (CDAD) has risen dramatically in recent years, especially in North America and Europe [3, 4]. In addition to recognized risk factors, like old age, hospital admission, and antibiotic exposure, there have been recent reports of the occurrence of CDAD in young seemingly healthy adults and children in the community, some without antimicrobial exposure [5, 6]. Immunocompromized state is also recognized as a risk factor for CDAD [7 11]. Acid suppression, especially with proton pump inhibitors (PPI), has been reported in a number of studies to be associated with an increased risk of C. difficile infection [12]. C.
2 90 Indian J Gastroenterol (March April 2011) 30(2):89 93 difficile has been implicated as a cause of exacerbation in patients with inflammatory bowel disease [13 16]. Most studies on the prevalence and morbidity of C. difficile are from the Western countries. Data from India are limited to a few studies [17 22]. This study was done to study the profile of C. difficile infection in our tertiary-care center. Methods This was a retrospective study of all in-patients as well as outpatients attending our hospital, from June 2006 to May 2008, and whose fecal specimens were sent to the laboratory for C. difficile toxin testing. Ninety-nine such specimens from patients with diarrhea were sent. The hospital records of the corresponding patients were retrieved and clinical data were noted. Demographic and clinical data including age, sex, duration of hospitalization and ICU stay of in-patients, duration of diarrhea, clinical features, associated and/or underlying illnesses (inflammatory bowel disease, prior abdominal surgery, malignancy, prior hospitalization, immunosuppressive state), and addictions were recorded. Exposure to antibiotics, immunosuppressive agents, cancer chemotherapy, and PPI was noted. Details of any procedures done, if any, were noted. Sigmoidoscopic or colonoscopic findings and histopathology report, whenever done, were included. Data in patients with C. difficile infection (study group) were compared with those in patients without (control group). Testing for toxin A and toxin B of C. difficile was performed on the stool samples using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (Ridascreen Kit, Darmstadt, Germany) according to the manufacturer s instructions. Details of treatment given to patients with positive stool samples were recorded. The drug, duration and response, clinical course, and follow up of these patients were noted. Statistical methods Stata SE version 10.1 (StataCorp LP, Texas, USA) was used to analyze data. Student s t test for unpaired data was used for comparing means and Chi-square test or Fisher s exact test (as appropriate) for comparing proportions. To examine the relationship of each independent variable with the dependent variable, binary logistic regression was performed. Entry into the analysis was p-value of <0.1 in a univariate analysis. T- test was performed for age and duration of illness. A p-value of <0.05 was deemed statistically significant. Results Ninety-nine stool samples were tested for C. difficile toxin assay during the study period. The year-wise breakup was 2006 = 21, 2007 = 28, and 2008 = 50. Each patient s stool was tested only once. The mean age of the patients whose samples were analyzed was 46.7 years and 58 (58%) were men. Four patients were below 2 years of age. Stool positivity for C. difficile toxin assay Seventeen (17%) stool samples were positive for both C. difficile toxin assay A and B. Of these, only one positive sample belonged to a one-year-old infant. There was no difference in the age, gender distribution, and clinical features except fever, prior hospitalization, presence of inflammatory bowel disease, previous GI surgery, or antibiotic use between the two groups (Table 1). Compared with the control group, study subjects were more likely to have fever, underlying malignancy, prolonged ICU stay, and exposure to immunosuppressive and chemotherapeutic agents (Table 1). On multivariate analysis, exposure to immunosuppressive agents was the only significant associated variable (Table 2). Clinical course and treatment The median duration of diarrhea in the study patients was similar to that in the control group (5 vs. 7 days). None of the patients developed any complication and there was no mortality. Fifteen study patients were treated with metronidazole; two were given vancomycin as the first drug. The median duration of treatment was 7.5 (5 14) days and the median time taken for resolution of diarrhea was 3 (2 10) days. Two of the 15 patients treated with metronidazole did not respond and were subsequently treated with oral vancomycin, to which they responded. Discussion Most previous studies about CDAD in India have shown prevalence rates ranging from 7.1% to 26.6% [17 22]. Three prospective studies in hospitalized patients developing acute diarrhea showed prevalence rates of 11.1%, 22.6%, and 26.6% [17, 21, 22]. A recent retrospective study by Chaudhry et al. on hospitalized patients, found the prevalence over a five-year period to be 7.1% [19]. We found a prevalence rate of 17% in a combined cohort of in-patients as well as out-patients. CDAD has been reported to be more common in women and older patients [23]. The mean age of patients with CDAD in our study was 45.2 years and there were more men (64%). Studies from India have reported varying malefemale ratios [19, 24 26]. Among patients positive for C. difficile toxin, fever, cramping abdominal pain, and diarrhea have been reported to be more common [4, 27]. In our
3 Indian J Gastroenterol (March April 2011) 30(2): Table 1 Demographic and clinical data of the patients Total (n=99) Study patients (n=17) Control group (n=82) Odds ratio (95% CI) p-value Men 58 (58) 11 (64) 47 (57.3) 0.39 Age (years) (mean [SD]) 46.7 (21.4) 45.2 (23.4) 47 (21.1) 0.76 Duration of diarrhea (days) 7(1 120) 5 (2 30) 7 (1 120) 0.22 (median [range]) Clinical features and risk factors Smoking 7 (7) 2 (11.7) 5 (6.09) 2.05 ( ) 0.35 Alcohol 6 (6) 1 (5.88) 5 (6.1) 0.96 ( ) 1.00 Fever 27 (25) 8 (47) 19 (23) 2.94 ( ) 0.07 Abdominal pain 31 (31) 7 (41.1) 24 (29.2) 1.7 ( ) 0.33 Hematochezia 9 (9.09) 3 (17.65) 6 (7.32) 2.7 ( ) 0.18 Inflammatory bowel disease 14 (14.1) 3 (17.65) 11 (13.4) 1.38 ( ) 0.70 Previous GI surgery 3 (3.03) 0 (0) 3 (3.66) 1.0 Malignancy 16 (16.1) 6 (35.29) 10 (12.2) 3.92 ( ) 0.03 Organ transplant 1 (1.01) 1 (5.88) 0 (0) 0.17 Prior hospital stay 45 (45.5) 9 (52.94) 36 (43.9) 1.43 ( ) 0.5 Intensive care stay 17 (17.2) 7 (41.18) 10 (12.2) 5.04 ( ) Antibiotic use 37 (37.4) 8 (47.06) 29 (35.4) 1.62 ( ) Immunosuppressive therapy 24 (24.2) 9 (52.94) 15 (18.3) 5.03 ( ) Proton pump inhibitors 23 (23.2) 7 (41.18) 16 (19.5) 2.88 ( ) Chemotherapy 7 (7.07) 4 (23.53) 3 (3.66) 8.10 ( ) Data are as n (%) patients, though fever was more common, there was no difference in the occurrence of abdominal pain and duration of diarrhea. C. difficile should be considered as a cause of diarrhea in high-risk patients even if the classical features not present. Fulminant colitis leading to ileus, toxic megacolon, perforation, and death have been reported in 1% to 3% of cases [28]. None of these complications was found in our study group. There was no mortality in our patients. Similar results have been shown from other studies [19, 26]. In a retrospective study over 5 years, 8 of 37 C. difficile-positive patients died, but the cause of death was not directly related to C. difficile diarrhea [19]. Similarly, Gogate et al. reported the death of two of their patients with C. difficile infection, one died from renal failure and the other was a case of hepatoblastoma [26]. Antibiotic usage is a common cause of diarrhea and these drugs have been implicated as an important risk factor for CDAD [29]. However, in our study, C. difficile positivity was not influenced by prior antibiotic use. Vaishnavi et al. reported that antibiotic usage was not different in adults with or without C. difficile toxin [30]. Studies have shown that ICU stay, underlying diseases, like malignancy and inflammatory bowel disease and exposure to chemotherapy, immunosuppressive, and PPI are additional risk factors [3, 4, 13, 14, 31, 32]. We found that underlying malignancy, ICU stay, and exposure to immunosuppressive and chemotherapeutic agents were associated with C. difficile toxin positivity on univariate analysis; however, only exposure to immunosuppressive agents was a significant risk factor on multivariate analysis. Kumar et al. reported that patients with psoriasis receiving methotrexate and/or mesalazine had increased prevalence of Table 2 Logistic regression multivariate analysis of factors associated with C. difficile infection Factors Adjusted odds ratio (95% CI) p-value Fever 4.32 ( ) Malignancy 3.65 ( ) Intensive care stay 4.04 ( ) Immunosuppressive therapy 5.38 ( ) Proton pump inhibitors 1.84 ( ) Chemotherapy 2.38 ( ) 0.462
4 92 Indian J Gastroenterol (March April 2011) 30(2):89 93 C. difficile toxin [33]. In our study, corticosteroids were responsible for all of the cases with C. difficile toxin positivity. Vancomycin has been shown to be superior to metronidazole in the treatment of severe CDAD [34, 35]. In our study, 13 of 15 patients treated with metronidazole responded; two who did not respond to metronidazole responded to vancomycin. Zar et al. found that the efficacy of metronidazole was comparable to that of vancomycin [34]. The cost difference between metronidazole and vancomycin is an important consideration. The clinical practice guidelines update by the Society of Healthcare Epidemiology of America and Infectious Diseases Society of America suggest that metronidazole be the drug of choice for the initial episode of mild to moderate C. difficile infection, and vancomycin be used for initial episode of severe C. difficile infection [36]. There is increasing evidence of increased susceptibility of patients with IBD, especially those with ulcerative colitis, to C. difficile infection [13, 14]. Balamurugan et al. found increased fecal carriage of C. difficile in patients with ulcerative colitis as compared to healthy individuals [16]. No such difference was found in our study, but the number of patients was small. Our study had several limitations. It was a retrospective analysis of data based on stool samples sent to the laboratory specifically for this test. The clinical suspicion of infection was possibly high, leading to a selection bias from among all patients with acute diarrhea. The number of patients in each risk group was small with possibility of a type 2 error. To summarize, the prevalence of C. difficile toxin in diarrheal stools sent for C. difficile toxin testing was 17%. Exposure to immunosuppressive agents was a risk factor for the infection. There was no notable feature except fever in the clinical presentation. Metronidazole was effective in a majority of patients. References 1. McFarland LV. Diarrhea acquired in the hospital. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 1993;22: Bartlett JG, Moon N, Chang TW, Taylor N, Onderdonk AB. Role of Clostridium difficile in antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis. Gastroenterology. 1978;75: Kyne L, Hamel MB, Polavaram R, Kelly CP. Health care costs and mortality associated with nosocomial diarrhea due to Clostridium difficile. Clin Infect Dis. 2002;34: Bartlett JG. Clinical practice. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 2002;346: Morinville V, McDonald J. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in 200 Canadian children. Can J Gastroenterol. 2005;19: Bauer MP, Goorhuis A, Koster T, et al. Community-onset Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea not associated with antibiotic usage two case reports with review of the changing epidemiology of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea. Neth J Med. 2008;66: Chakrabarti S, Lees A, Jones SG, Milligan DW. Clostridium difficile infection in allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients is associated with severe graft-versus-host disease and non-relapse mortality. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2000;26: Bilgrami S, Feingold JM, Dorsky D, et al. Incidence and outcome of Clostridium difficile infection following autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1999;23: Keven K, Basu A, Re L, et al. Clostridium difficile colitis in patients after kidney and pancreas-kidney transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis. 2004;6: Gorschluter M, Glasmacher A, Hahn C, et al. Clostridium difficile infection in patients with neutropenia. Clin Infect Dis. 2001;33: Pulvirenti JJ, Mehra T, Hafiz I, et al. Epidemiology and outcome of Clostridium difficile infection and diarrhea in HIV infected inpatients. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2002;44: Leonard J, Marshall JK, Moayyedi P. Systematic review of the risk of enteric infection in patients taking acid suppression. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102: quiz Rodemann JF, Dubberke ER, Reske KA, da Seo H, Stone CD. Incidence of Clostridium difficile infection in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5: Issa M, Vijayapal A, Graham MB, et al. Impact of Clostridium difficile on inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5: Kochhar R, Ayyagari A, Goenka MK, Dhali GK, Aggarwal R, Mehta SK. Role of infectious agents in exacerbations of ulcerative colitis in India. A study of Clostridium difficile. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1993;16: Balamurugan R, Balaji V, Ramakrishna BS. Estimation of faecal carriage of Clostridium difficile in patients with ulcerative colitis using real time polymerase chain reaction. Indian J Med Res. 2008;127: Niyogi SK, Bhattacharya SK, Dutta P, et al. Prevalence of Clostridium difficile in hospitalised patients with acute diarrhoea in Calcutta. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1991;9: Dhawan B, Chaudhry R, Sharma N. Incidence of Clostridium difficile infection: a prospective study in an Indian hospital. J Hosp Infect. 1999;43: Chaudhry R, Joshy L, Kumar L, Dhawan B. Changing pattern of Clostridium difficile associated diarrhoea in a tertiary care hospital: a 5 year retrospective study. Indian J Med Res. 2008;127: Katyal R, Vaishnavi C, Singh K. Faecal excretion of brush border membrane enzymes in patients with clostridium difficile diarrhoea. Indian J Med Microbiol. 2002;20: Gupta U, Yadav RN. Clostridium difficile in hospital patients. Indian J Med Res. 1985;82: Ayyagari A, Sharma P, Venkateswarlu, Mehta S, Agarwal KC. Prevalence of Clostridium difficile in pseudomembranous and antibiotic-associated colitis in north India. J Diarrhoeal Dis Res. 1986;4: Al-Eidan FA, McElnay JC, Scott MG, Kearney MP. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhoea in hospitalised patients. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2000;25: Niyogi SK. Clostridium difficile associated diarrhoeal diseases: an overview. J Indian Med Assoc. 1995;93: Vaishnavi C, Thapa BR, Thennarasu K, Singh K. Faecal lactoferrin assay as an adjunct to Clostridium difficile diarrhoea. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 2002;45: Gogate A, De A, Nanivadekar R, et al. Diagnostic role of stool culture and toxin detection in antibiotic associated diarrhoea due to Clostridium difficile in children. Indian J Med Res. 2005;122: Mylonakis E, Ryan ET, Calderwood SB. Clostridium difficileassociated diarrhea: a review. Arch Intern Med. 2001;161:
5 Indian J Gastroenterol (March April 2011) 30(2): Kelly CP, LaMont JT. Clostridium difficile infection. Annu Rev Med. 1998;49: Bignardi GE. Risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection. J Hosp Infect. 1998;40: Vaishnavi C, Bhasin D, Kochhar R, Singh K. Clostridium difficile toxin and faecal lactoferrin assays in adult patients. Microbes Infect. 2000;2: Karlstrom O, Fryklund B, Tullus K, Burman LG. A prospective nationwide study of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in Sweden. The Swedish C. difficile Study Group. Clin Infect Dis. 1998;26: Dial S, Delaney JA, Schneider V, Suissa S. Proton pump inhibitor use and risk of community-acquired Clostridium difficileassociated disease defined by prescription for oral vancomycin therapy. CMAJ. 2006;175: Kumar B, Vaishnavi C, Sandhu K, Kaur I. Clostridium difficile toxin assay in psoriatic patients. Trop Gastroenterol. 2004;25: Zar FA, Bakkanagari SR, Moorthi KM, Davis MB. A comparison of vancomycin and metronidazole for the treatment of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea, stratified by disease severity. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45: Pepin J, Valiquette L, Alary ME, et al. Clostridium difficileassociated diarrhea in a region of Quebec from 1991 to 2003: a changing pattern of disease severity. CMAJ. 2004;171: Cohen SH, Gerding DN, Johnson S, et al. Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults: 2010 update by the society for healthcare epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the infectious diseases society of America (IDSA). Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2010;31:
ABSTRACT PURPOSE METHODS
 ABSTRACT PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to characterize the CDI population at this institution according to known risk factors and to examine the effect of appropriate evidence-based treatment selection
ABSTRACT PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to characterize the CDI population at this institution according to known risk factors and to examine the effect of appropriate evidence-based treatment selection
Does Extending Clostridium Difficile Treatment In Patients Who Are Receiving Concomitant Antibiotics Reduce The Rate Of Relapse?
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases Volume 15 Number 1 Does Extending Clostridium Difficile Treatment In Patients Who Are Receiving Concomitant Antibiotics Reduce The Rate Of Relapse?
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases Volume 15 Number 1 Does Extending Clostridium Difficile Treatment In Patients Who Are Receiving Concomitant Antibiotics Reduce The Rate Of Relapse?
ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES UNIT 3 HOW TO DEAL WITH CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE
 ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES UNIT 3 HOW TO DEAL WITH CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE The diagnosis of CDI should be based on a combination of clinical and laboratory findings. A case definition for the usual
ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES UNIT 3 HOW TO DEAL WITH CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE The diagnosis of CDI should be based on a combination of clinical and laboratory findings. A case definition for the usual
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has emerged. Incidence of Clostridium difficile Infection in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:339 344 Incidence of Clostridium difficile Infection in Inflammatory Bowel Disease JOSEPH F. RODEMANN,* ERIK R. DUBBERKE, KIMBERLY A. RESKE, DA HEA SEO,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:339 344 Incidence of Clostridium difficile Infection in Inflammatory Bowel Disease JOSEPH F. RODEMANN,* ERIK R. DUBBERKE, KIMBERLY A. RESKE, DA HEA SEO,*
Stony Brook Adult Clostridium difficile Management Guidelines. Discontinue all unnecessary antibiotics
 Stony Brook Adult Clostridium difficile Management Guidelines Summary: Use of the C Diff Infection (CDI) PowerPlan (Adult) Required Patient with clinical findings suggestive of Clostridium difficile infection
Stony Brook Adult Clostridium difficile Management Guidelines Summary: Use of the C Diff Infection (CDI) PowerPlan (Adult) Required Patient with clinical findings suggestive of Clostridium difficile infection
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates April 2018 By Austin Smith, PharmD Candidate and Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD is the most common healthcare-acquired infection (HAI) in the United States. 1,2 A 2014 prevalence survey
Long-Term Care Updates April 2018 By Austin Smith, PharmD Candidate and Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD is the most common healthcare-acquired infection (HAI) in the United States. 1,2 A 2014 prevalence survey
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
Predictors of severe outcomes associated with Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
 Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics Predictors of severe outcomes associated with Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease A. N. Ananthakrishnan*,, R. Guzman-Perez,
Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics Predictors of severe outcomes associated with Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease A. N. Ananthakrishnan*,, R. Guzman-Perez,
Updated Clostridium difficile Treatment Guidelines
 Updated Clostridium difficile Treatment Guidelines Arielle Arnold, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Saint Alphonsus Regional Medical Center September 29 th, 2018 Disclosures Nothing to disclose Learning
Updated Clostridium difficile Treatment Guidelines Arielle Arnold, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Saint Alphonsus Regional Medical Center September 29 th, 2018 Disclosures Nothing to disclose Learning
Clostridium difficile Infection: Diagnosis and Management
 Clostridium difficile Infection: Diagnosis and Management Brian Viviano D.O. Case study 42 year old female with history of essential hypertension and COPD presents to ED complaining of 24 hours of intractable,
Clostridium difficile Infection: Diagnosis and Management Brian Viviano D.O. Case study 42 year old female with history of essential hypertension and COPD presents to ED complaining of 24 hours of intractable,
Predictors of Mortality and Morbidity in Clostridium Difficile Infection
 Predictors of Mortality and Morbidity in Clostridium Difficile Infection Jill Dixon, Brian F. Menezes Corresponding author: dippers82@hotmail.com Pages 23-26 ISSN 1840-4529 http://www.iomcworld.com/ijcrimph
Predictors of Mortality and Morbidity in Clostridium Difficile Infection Jill Dixon, Brian F. Menezes Corresponding author: dippers82@hotmail.com Pages 23-26 ISSN 1840-4529 http://www.iomcworld.com/ijcrimph
The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile Infection in Children: A Population-Based Study
 Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published March 5, 2013 MAJOR ARTICLE The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile Infection in Children: A Population-Based Study Sahil Khanna, 1 Larry M. Baddour,
Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published March 5, 2013 MAJOR ARTICLE The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile Infection in Children: A Population-Based Study Sahil Khanna, 1 Larry M. Baddour,
Clostridium difficile infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands
 Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2011) 30:587 593 DOI 10.1007/s10096-010-1127-4 ARTICLE Clostridium difficile infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens & A. Goorhuis & C. M.
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2011) 30:587 593 DOI 10.1007/s10096-010-1127-4 ARTICLE Clostridium difficile infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens & A. Goorhuis & C. M.
Atypical Presentation of Clostridium Difficille Infection (CDI).
 Article ID: WMC004648 ISSN 2046-1690 Atypical Presentation of Clostridium Difficille Infection (CDI). Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Syed A Gardezi, CT1, Medicine,NevillHall Hospital
Article ID: WMC004648 ISSN 2046-1690 Atypical Presentation of Clostridium Difficille Infection (CDI). Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Syed A Gardezi, CT1, Medicine,NevillHall Hospital
Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published December 7, 2012
 Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published December 7, 2012 1 Physician Attitudes Towards the Use of Fecal Transplantation for Recurrent Clostridium Difficile Infection in a Large Metropolitan
Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published December 7, 2012 1 Physician Attitudes Towards the Use of Fecal Transplantation for Recurrent Clostridium Difficile Infection in a Large Metropolitan
-2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine. -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency
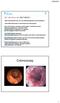 SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
RESEARCH. The Clostridium difficile problem: A South African tertiary institution s prospective perspective
 The Clostridium difficile problem: A South African tertiary institution s prospective perspective N Rajabally, M Pentecost, G Pretorius, A Whitelaw, M Mendelson, G Watermeyer Division of Gastroenterology,
The Clostridium difficile problem: A South African tertiary institution s prospective perspective N Rajabally, M Pentecost, G Pretorius, A Whitelaw, M Mendelson, G Watermeyer Division of Gastroenterology,
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates April 2017 Bezlotoxumab to Prevent Recurrent Infection By Amy Wilson, PharmD and Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction The Gram-positive bacteria is a common cause
Long-Term Care Updates April 2017 Bezlotoxumab to Prevent Recurrent Infection By Amy Wilson, PharmD and Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction The Gram-positive bacteria is a common cause
Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Review
 Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Review October 18, 2010 James Kahn and Carolyn Kenney, MSIV Overview Burden of disease associated
Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Review October 18, 2010 James Kahn and Carolyn Kenney, MSIV Overview Burden of disease associated
March 3, To: Hospitals, Long Term Care Facilities, and Local Health Departments
 March 3, 2010 To: Hospitals, Long Term Care Facilities, and Local Health Departments From: NYSDOH Bureau of Healthcare Associated Infections HEALTH ADVISORY: GUIDANCE FOR PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF HEALTHCARE
March 3, 2010 To: Hospitals, Long Term Care Facilities, and Local Health Departments From: NYSDOH Bureau of Healthcare Associated Infections HEALTH ADVISORY: GUIDANCE FOR PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF HEALTHCARE
Antibiotic treatment comparison in patients with diarrhea
 Original Research Article Antibiotic treatment comparison in patients with diarrhea Deva Lal Kast * Senior Consultant Physician, Department of General Medicine, Krishna Hospital, Ex senior Specialist and
Original Research Article Antibiotic treatment comparison in patients with diarrhea Deva Lal Kast * Senior Consultant Physician, Department of General Medicine, Krishna Hospital, Ex senior Specialist and
MAJOR ARTICLE. Clostridium difficile infection; vancomycin; metronidazole; mortality; sepsis.
 MAJOR ARTICLE The Addition of Intravenous Metronidazole to Oral Vancomycin is Associated With Improved Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Clostridium difficile Infection Kristina E. E. Rokas, 1
MAJOR ARTICLE The Addition of Intravenous Metronidazole to Oral Vancomycin is Associated With Improved Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Clostridium difficile Infection Kristina E. E. Rokas, 1
Antibiotic use, gastroenteritis and respiratory illness in South Australian children
 Epidemiol. Infect. (2002), 129, 507 513. f 2002 Cambridge University Press DOI: 10.1017/S0950268802007628 Printed in the United Kingdom Antibiotic use, gastroenteritis and respiratory illness in South
Epidemiol. Infect. (2002), 129, 507 513. f 2002 Cambridge University Press DOI: 10.1017/S0950268802007628 Printed in the United Kingdom Antibiotic use, gastroenteritis and respiratory illness in South
Learning Objectives. A Critical Analysis of Recent Fidaxomicin & Nesiritide Trials. Fidaxomicin vs. Vancomycin. Outline 1/3/2012
 Learning Objectives A Critical Analysis of Recent Fidaxomicin & Nesiritide Trials Amy E. Lodolce, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Director, Drug Information Group UIC College of Pharmacy Describe the methods and
Learning Objectives A Critical Analysis of Recent Fidaxomicin & Nesiritide Trials Amy E. Lodolce, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Director, Drug Information Group UIC College of Pharmacy Describe the methods and
Identification of Factors Impacting Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection and Development of a Risk Evaluation Tool
 Identification of Factors Impacting Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection and Development of a Risk Evaluation Tool Bethanne P Carpenter 1, Erin K Hennessey 2,3, Alex M Bryant 3, Jad A Khoury 3, Andrew
Identification of Factors Impacting Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection and Development of a Risk Evaluation Tool Bethanne P Carpenter 1, Erin K Hennessey 2,3, Alex M Bryant 3, Jad A Khoury 3, Andrew
Factors Affecting Mortality and Length of Stay Following Clostridium Difficile Associated Diarrhoea: Validating A Consistent Scoring System
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Archives of Clinical Microbiology DOI: 10.4172/1989-8436.100046 Factors Affecting Mortality and Length of Stay Following Clostridium Difficile
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Archives of Clinical Microbiology DOI: 10.4172/1989-8436.100046 Factors Affecting Mortality and Length of Stay Following Clostridium Difficile
Division of GIM Lecture Series Case Presentation David A. Erickson, M.D October 9th, 2013
 Division of GIM Lecture Series Case Presentation David A. Erickson, M.D October 9th, 2013 Financial Disclosures No financial disclosures Objectives Review a case of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection
Division of GIM Lecture Series Case Presentation David A. Erickson, M.D October 9th, 2013 Financial Disclosures No financial disclosures Objectives Review a case of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Management Guideline
 Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Management Guideline Do not test all patients with loose or watery stools for CDI o CDI is responsible for
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Management Guideline Do not test all patients with loose or watery stools for CDI o CDI is responsible for
Epidemiology of CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE infection among active duty United States military personnel ( )
 Gutiérrez et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2013, 13:609 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Epidemiology of CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE infection among active duty United States military personnel (1998-2010) Ramiro
Gutiérrez et al. BMC Infectious Diseases 2013, 13:609 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Epidemiology of CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE infection among active duty United States military personnel (1998-2010) Ramiro
Modern approach to Clostridium Difficile Infection
 Modern approach to Clostridium Difficile Infection Pseudomembranous Colitis: Principles for diagnosis and treatment Aggelos Stefos Internist, Infectious diseases Specialist Department of Medicine and Research
Modern approach to Clostridium Difficile Infection Pseudomembranous Colitis: Principles for diagnosis and treatment Aggelos Stefos Internist, Infectious diseases Specialist Department of Medicine and Research
Clostridium difficile CRISTINA BAKER, MD, MPH INFECTIOUS DISEASE PARK NICOLLET/HEALTH PARTNERS 11/9/2018
 Clostridium difficile CRISTINA BAKER, MD, MPH INFECTIOUS DISEASE PARK NICOLLET/HEALTH PARTNERS 11/9/2018 Disclosures None Objectives Highlight important changes in the management of Clostridium difficile
Clostridium difficile CRISTINA BAKER, MD, MPH INFECTIOUS DISEASE PARK NICOLLET/HEALTH PARTNERS 11/9/2018 Disclosures None Objectives Highlight important changes in the management of Clostridium difficile
Updates to pharmacological management in the prevention of recurrent Clostridium difficile
 Updates to pharmacological management in the prevention of recurrent Clostridium difficile Julia Shlensky, PharmD PGY2 Internal Medicine Resident September 12, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 Clinical Impact Increasing
Updates to pharmacological management in the prevention of recurrent Clostridium difficile Julia Shlensky, PharmD PGY2 Internal Medicine Resident September 12, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 Clinical Impact Increasing
Predictors of serious complications due to Clostridium difficile infection
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Predictors of serious complications due to Clostridium difficile infection D. GUJJA* & F. K. FRIEDENBERG *Department of Medicine, Abington Memorial Hospital, Abington,
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Predictors of serious complications due to Clostridium difficile infection D. GUJJA* & F. K. FRIEDENBERG *Department of Medicine, Abington Memorial Hospital, Abington,
The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in hospitals, longterm care and the community. J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM
 The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in hospitals, longterm care and the community J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM C. difficile Gram positive anaerobic sporeforming bacterium first
The epidemiology of Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in hospitals, longterm care and the community J Scott Weese DVM DVSc DipACVIM C. difficile Gram positive anaerobic sporeforming bacterium first
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ANTIBIOTIC- ASSOCIATED DIARRHOEA IN ADULTS
 GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ANTIBIOTIC- ASSOCIATED DIARRHOEA IN ADULTS Version 3.0 Date ratified May 2008 Review date May 2010 Ratified by NUH Antibiotic Guidelines Committee NUH Drugs and Therapeutics
GUIDELINE FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF ANTIBIOTIC- ASSOCIATED DIARRHOEA IN ADULTS Version 3.0 Date ratified May 2008 Review date May 2010 Ratified by NUH Antibiotic Guidelines Committee NUH Drugs and Therapeutics
CDI The Impact. Disclosures. Acknowledgments. Objectives and Agenda. What s in the Name? 11/14/2012. Lets Talk Numbers
 Disclosures No conflict of interest to declare Acknowledgments Objectives and Agenda Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Guidelines
Disclosures No conflict of interest to declare Acknowledgments Objectives and Agenda Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA) Guidelines
! Macrolide antibacterial. Fidaxomicin (Dificid ) package labeling. Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. May 2011.
 Disclosure! I have no conflicts of interest related to this presentation Nina Naeger Murphy, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Infectious Diseases MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives!
Disclosure! I have no conflicts of interest related to this presentation Nina Naeger Murphy, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Infectious Diseases MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives!
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in C. diff. colitis Benefits and Limitations
 January 27th 2017, 8th Gastro Foundation Weekend for Fellows; Spier Hotel & Conference Centre, Stellenbosch Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in C. diff. colitis Benefits and Limitations Gerhard Rogler,
January 27th 2017, 8th Gastro Foundation Weekend for Fellows; Spier Hotel & Conference Centre, Stellenbosch Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in C. diff. colitis Benefits and Limitations Gerhard Rogler,
Revisiting Clostridium Difficile Infection
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE Revisiting Clostridium Difficile Infection Michael A. Pfeffer, M.D., Ruby Shandilya, M.D., and Jeffrey Hsu, M.Eng. Clostridium difficile infection is commonly seen in patients in the
CLINICAL VIGNETTE Revisiting Clostridium Difficile Infection Michael A. Pfeffer, M.D., Ruby Shandilya, M.D., and Jeffrey Hsu, M.Eng. Clostridium difficile infection is commonly seen in patients in the
EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale
 Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Public Health Theses School of Public Health January 2013 Comparisons Of Patients With Recurrent Vs. Incident-Only Clostridium
Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Public Health Theses School of Public Health January 2013 Comparisons Of Patients With Recurrent Vs. Incident-Only Clostridium
Learning Goals. Clostridium difficile. Historical Context. Historical Context 6/27/2012
 Learning Goals Clostridium difficile Justin L. Sewell, MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital Understand the epidemiology,
Learning Goals Clostridium difficile Justin L. Sewell, MD, MPH Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco San Francisco General Hospital Understand the epidemiology,
C.Difficile Associated Diarrhea Overview & Management. Sajal Chopra Pharm D. Candidate
 C.Difficile Associated Diarrhea Overview & Management Sajal Chopra Pharm D. Candidate Learning Objectives 1. Recognize the increasing incidence of C.difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) and its risk factors
C.Difficile Associated Diarrhea Overview & Management Sajal Chopra Pharm D. Candidate Learning Objectives 1. Recognize the increasing incidence of C.difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) and its risk factors
Prevalence and clinical features of Clostridium difficileassociated diarrhea in a tertiary hospital in northern Taiwan
 C. J Microbiol difficile-associated Immunol Infect diarrhea 2006;39:242-248 Prevalence and clinical features of Clostridium difficileassociated diarrhea in a tertiary hospital in northern Taiwan Meng-Shiuan
C. J Microbiol difficile-associated Immunol Infect diarrhea 2006;39:242-248 Prevalence and clinical features of Clostridium difficileassociated diarrhea in a tertiary hospital in northern Taiwan Meng-Shiuan
Antimicrobial Use and Risk for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Antimicrobial Use and Risk for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection Dimitri M. Drekonja, MD, MS, a,b William H. Amundson, BA, c Douglas D. DeCarolis, PharmD, a,d Michael A.
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Antimicrobial Use and Risk for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection Dimitri M. Drekonja, MD, MS, a,b William H. Amundson, BA, c Douglas D. DeCarolis, PharmD, a,d Michael A.
The Bristol Stool Scale and Its Relationship to Clostridium difficile Infection
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 July 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01303-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 The Bristol Stool Scale
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 July 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01303-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 The Bristol Stool Scale
SUMMARY. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 2015, 40, doi: /jcpt.12329
 Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 2015, 40, 655 660 doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12329 Evaluation of a Clostridium difficile infection management policy with clinical pharmacy and medical microbiology
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 2015, 40, 655 660 doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12329 Evaluation of a Clostridium difficile infection management policy with clinical pharmacy and medical microbiology
Long-Term Clinical Outcome of Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized Patients: A Single Center Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.4.299 Intest Res 2014;12(4):299-305 Long-Term Clinical Outcome of Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.4.299 Intest Res 2014;12(4):299-305 Long-Term Clinical Outcome of Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized
Case 1. Which of the following would be next appropriate investigation/s regarding the pts diarrhoea?
 Case 1 21 yr old HIV +ve, Cd4-100 HAART naïve Profuse diarrhoea for 3/52. Stool MC&S ve Which of the following would be next appropriate investigation/s regarding the pts diarrhoea? Repeat stool MC&S Stool
Case 1 21 yr old HIV +ve, Cd4-100 HAART naïve Profuse diarrhoea for 3/52. Stool MC&S ve Which of the following would be next appropriate investigation/s regarding the pts diarrhoea? Repeat stool MC&S Stool
Management of Clostridium Difficile: Total Colectomy versus Colon Sparing Surgery
 Management of Clostridium Difficile: Total Colectomy versus Colon Sparing Surgery Rahul Narang, MD Colon and Rectal Surgery Assistant Professor of Surgery No Disclosure Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Treatments,
Management of Clostridium Difficile: Total Colectomy versus Colon Sparing Surgery Rahul Narang, MD Colon and Rectal Surgery Assistant Professor of Surgery No Disclosure Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Treatments,
Le infezioni da Clostridium difficile, gravi, ricorrenti e complicate Nicola Petrosillo
 Le infezioni da Clostridium difficile, gravi, ricorrenti e complicate Nicola Petrosillo Istituto Nazionale per le Malattie Infettive «lazzaro Spallanzani», IRCCS-Roma The infectious cycle of transmission
Le infezioni da Clostridium difficile, gravi, ricorrenti e complicate Nicola Petrosillo Istituto Nazionale per le Malattie Infettive «lazzaro Spallanzani», IRCCS-Roma The infectious cycle of transmission
Probiotics for Primary Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infection
 Probiotics for Primary Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infection Objectives Review risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Describe guideline recommendations for CDI prevention Discuss
Probiotics for Primary Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infection Objectives Review risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Describe guideline recommendations for CDI prevention Discuss
Clostridium Difficile Infection: Applying New Treatment Guidelines and Strategies to Reduce Recurrence Rate
 Clostridium Difficile Infection: Applying New Treatment Guidelines and Strategies to Reduce Recurrence Rate Objectives Summarize the changing epidemiology and demographics of patients at risk for Clostridium
Clostridium Difficile Infection: Applying New Treatment Guidelines and Strategies to Reduce Recurrence Rate Objectives Summarize the changing epidemiology and demographics of patients at risk for Clostridium
ADJUVANT TIGECYCLINE FOR SEVERE CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA
 ADJUVANT TIGECYCLINE FOR SEVERE CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Candace Marr, DO Catholic Health System University at Buffalo, NY Kevin Shiley, MD Catholic Health System Buffalo, NY FINANCIAL
ADJUVANT TIGECYCLINE FOR SEVERE CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Candace Marr, DO Catholic Health System University at Buffalo, NY Kevin Shiley, MD Catholic Health System Buffalo, NY FINANCIAL
International Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatal Health
 Research Article International Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatal Health Open Access Clostridium difficile Infection in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients in the Era of Molecular Diagnostics
Research Article International Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatal Health Open Access Clostridium difficile Infection in Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients in the Era of Molecular Diagnostics
CLOSTRIDIUM DIFICILE. Negin N Blattman Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare System
 CLOSTRIDIUM DIFICILE Negin N Blattman Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare System ANTIBIOTIC ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA 1978: C diff first identified 1989-1992: Four large outbreaks in the US caused by J
CLOSTRIDIUM DIFICILE Negin N Blattman Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare System ANTIBIOTIC ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA 1978: C diff first identified 1989-1992: Four large outbreaks in the US caused by J
Literature Scan: Antibiotics for Clostridium difficile Infection. Month/Year of Review: May 2015 Date of Last Review: April 2012
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
 Review paper Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease Jacek Czepiel 1, Grażyna Biesiada 1, William Perucki 2, Tomasz Mach 1 1 Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology
Review paper Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease Jacek Czepiel 1, Grażyna Biesiada 1, William Perucki 2, Tomasz Mach 1 1 Department of Gastroenterology, Hepatology
Treatment of Clostridium Difficile Infection in Community Teaching Hospital: A Retrospective Study
 International Journal of Infectious Diseases and Therapy 2018; 3(3): 52-61 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijidt doi: 10.11648/j.ijidt.20180303.12 ISSN: 2578-9651 (Print); ISSN: 2578-966X (Online)
International Journal of Infectious Diseases and Therapy 2018; 3(3): 52-61 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijidt doi: 10.11648/j.ijidt.20180303.12 ISSN: 2578-9651 (Print); ISSN: 2578-966X (Online)
DETECTION OF TOXIGENIC CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE
 CLINICAL GUIDELINES For use with the UnitedHealthcare Laboratory Benefit Management Program, administered by BeaconLBS DETECTION OF TOXIGENIC CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE Policy Number: PDS 021 Effective Date:
CLINICAL GUIDELINES For use with the UnitedHealthcare Laboratory Benefit Management Program, administered by BeaconLBS DETECTION OF TOXIGENIC CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE Policy Number: PDS 021 Effective Date:
Fecal microbiota transplantation: Breaking the chain of recurrent C. difficile infection
 Fecal microbiota transplantation: Breaking the chain of recurrent C. difficile infection Issue Date: June 2013 Vol. 8 No. 6 Author: Amy Marinski, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNL More than 3 million new cases of Clostridium
Fecal microbiota transplantation: Breaking the chain of recurrent C. difficile infection Issue Date: June 2013 Vol. 8 No. 6 Author: Amy Marinski, MSN, RN, CCRN, CNL More than 3 million new cases of Clostridium
In recent years, Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) has
 BRIEF REPORTS Poor Functional Status as a Risk Factor for Severe Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized Older Adults Krishna Rao, MD,* Dejan Micic, MD,* Elizabeth Chenoweth, MD, Lili Deng, MD,
BRIEF REPORTS Poor Functional Status as a Risk Factor for Severe Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized Older Adults Krishna Rao, MD,* Dejan Micic, MD,* Elizabeth Chenoweth, MD, Lili Deng, MD,
Clostridium difficile infection: clinical spectrum and approach to management
 Indian J Gastroenterol (November December 2011) 30(6):245 254 DOI 10.1007/s12664-011-0148-y REVIEW ARTICLE Clostridium difficile infection: clinical spectrum and approach to management Chetana Vaishnavi
Indian J Gastroenterol (November December 2011) 30(6):245 254 DOI 10.1007/s12664-011-0148-y REVIEW ARTICLE Clostridium difficile infection: clinical spectrum and approach to management Chetana Vaishnavi
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Fecal Bacteriotherapy
 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Fecal Bacteriotherapy Number: 0844 Policy Aetna considers fecal bacteriotherapy medically necessary for persons with Clostridium difficile infection, with infection confirmed
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Fecal Bacteriotherapy Number: 0844 Policy Aetna considers fecal bacteriotherapy medically necessary for persons with Clostridium difficile infection, with infection confirmed
International Journal of Food and Allied Sciences
 International Journal of Food and Allied Sciences ISSN: 2415-0290 (Print) ISSN: 2413-2543 (Online) DOI:10.21620/ijfaas.2017120-26 Research Article History The Role of Saccharomyces boulardii in the Treatment
International Journal of Food and Allied Sciences ISSN: 2415-0290 (Print) ISSN: 2413-2543 (Online) DOI:10.21620/ijfaas.2017120-26 Research Article History The Role of Saccharomyces boulardii in the Treatment
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Guideline
 Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Guideline Site Applicability All VCH PHC acute care and residential sites. Practice Level Physicians basic skill Pharmacists basic skill Nurses (RN, LPN, RPN) basic
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Guideline Site Applicability All VCH PHC acute care and residential sites. Practice Level Physicians basic skill Pharmacists basic skill Nurses (RN, LPN, RPN) basic
Prospective Derivation and Validation of a Clinical Prediction Rule for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:1206 1214 Prospective Derivation and Validation of a Clinical Prediction Rule for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection MARY Y. HU,* KIANOOSH KATCHAR,* LORRAINE KYNE, SEEMA
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:1206 1214 Prospective Derivation and Validation of a Clinical Prediction Rule for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection MARY Y. HU,* KIANOOSH KATCHAR,* LORRAINE KYNE, SEEMA
New approaches to treating Clostridium difficile Infection
 7:45 8:45 am New Approaches to Treating C. difficile Infection SPEAKER Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Fred A. Lopez,
7:45 8:45 am New Approaches to Treating C. difficile Infection SPEAKER Fred A. Lopez, MD, MACP Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Fred A. Lopez,
Bezlotoxumab (Zinplava) as Adjunct Treatment for Clostridium difficile. Janel Liane Cala, RPh Medical Center Hospital
 Bezlotoxumab (Zinplava) as Adjunct Treatment for Clostridium difficile Janel Liane Cala, RPh Medical Center Hospital Objectives Review pathophysiology, risk factors, prevention, and treatment options of
Bezlotoxumab (Zinplava) as Adjunct Treatment for Clostridium difficile Janel Liane Cala, RPh Medical Center Hospital Objectives Review pathophysiology, risk factors, prevention, and treatment options of
Impact of Clostridium difficile infection in patients with ulcerative colitis
 Journal of Crohn's and Colitis (2011) 5, 34 40 available at www.sciencedirect.com Impact of Clostridium difficile infection in patients with ulcerative colitis Revital Kariv, Udayakumar Navaneethan, Preethi
Journal of Crohn's and Colitis (2011) 5, 34 40 available at www.sciencedirect.com Impact of Clostridium difficile infection in patients with ulcerative colitis Revital Kariv, Udayakumar Navaneethan, Preethi
Which is the Safest Strategy to Treat Moderate to Severe IBD?
 Which is the Safest Strategy to Treat Moderate to Severe IBD? David G. Binion, M.D. Co-Director, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Director, Translational Inflammatory Bowel Disease Research Visiting Professor
Which is the Safest Strategy to Treat Moderate to Severe IBD? David G. Binion, M.D. Co-Director, Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center Director, Translational Inflammatory Bowel Disease Research Visiting Professor
Advanced chronic kidney disease: a strong risk factor for Clostridium difficile infection
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2016;31:125-133 Advanced chronic kidney disease: a strong risk factor for Clostridium difficile infection Sun Chul Kim, Min Young Seo, Jun Yong Lee, Ki Tae Kim, Eunjung
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Korean J Intern Med 2016;31:125-133 Advanced chronic kidney disease: a strong risk factor for Clostridium difficile infection Sun Chul Kim, Min Young Seo, Jun Yong Lee, Ki Tae Kim, Eunjung
infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands
 infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis, C. M. J. Kinschot, M. J. T. Crobach, C. Harmanus, E. J. Kuijper To cite this version: M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis,
infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis, C. M. J. Kinschot, M. J. T. Crobach, C. Harmanus, E. J. Kuijper To cite this version: M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis,
Renal Failure and Leukocytosis Are Predictors of a Complicated Course of Clostridium difficile Infection if Measured on Day of Diagnosis
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Renal Failure and Leukocytosis Are Predictors of a Complicated Course of Clostridium difficile Infection if Measured on Day of Diagnosis Martijn P. Bauer, 1,a Marjolein P. M. Hensgens,
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Renal Failure and Leukocytosis Are Predictors of a Complicated Course of Clostridium difficile Infection if Measured on Day of Diagnosis Martijn P. Bauer, 1,a Marjolein P. M. Hensgens,
Sherwood L. Gorbach, MD Professor of Public Health, Medicine, and Microbiology Tufts University School of Medicine
 Sherwood L. Gorbach, MD Professor of Public Health, Medicine, and Microbiology Tufts University School of Medicine Chief Scientific Officer, Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Conflicts: Chief Scientific Officer,
Sherwood L. Gorbach, MD Professor of Public Health, Medicine, and Microbiology Tufts University School of Medicine Chief Scientific Officer, Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Conflicts: Chief Scientific Officer,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.15 Rapid Diagnosis of Toxigenic Clostridium
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.15 Rapid Diagnosis of Toxigenic Clostridium
HEALTHCARE- ASSOCIATED CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTIONS IN CANADIAN ACUTE- CARE HOSPITALS
 HEALTHCARE- ASSOCIATED CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTIONS IN CANADIAN ACUTE- CARE HOSPITALS SURVEILLANCE REPORT JANUARY 1 st, 2007 TO DECEMBER 31 st, 2012 TO PROMOTE AND PROTECT THE HEALTH OF CANADIANS THROUGH
HEALTHCARE- ASSOCIATED CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE INFECTIONS IN CANADIAN ACUTE- CARE HOSPITALS SURVEILLANCE REPORT JANUARY 1 st, 2007 TO DECEMBER 31 st, 2012 TO PROMOTE AND PROTECT THE HEALTH OF CANADIANS THROUGH
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22997 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wilden, Gwendolyn M. van der Title: The value of surgical treatment in abdominal
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22997 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wilden, Gwendolyn M. van der Title: The value of surgical treatment in abdominal
Consequences of Clostridium difficile infection: understanding the healthcare burden
 REVIEW 10.1111/1469-0691.12064 Consequences of Clostridium difficile infection: understanding the healthcare burden E. Bouza 1,2 1) Department of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Hospital General
REVIEW 10.1111/1469-0691.12064 Consequences of Clostridium difficile infection: understanding the healthcare burden E. Bouza 1,2 1) Department of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Hospital General
Factors associated with prolonged symptoms and severe disease due to Clostridium difficile
 Age and Ageing 1999; 28: 107 113 Factors associated with prolonged symptoms and severe disease due to Clostridium difficile LORRAINE KYNE, CONCEPTA MERRY 2,BRIAN O CONNELL 2,ALAN KELLY 3,CONOR KEANE 2,
Age and Ageing 1999; 28: 107 113 Factors associated with prolonged symptoms and severe disease due to Clostridium difficile LORRAINE KYNE, CONCEPTA MERRY 2,BRIAN O CONNELL 2,ALAN KELLY 3,CONOR KEANE 2,
Study on Incidence of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhoea in General Paediatric Ward
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2002;7:33-38 Study on Incidence of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhoea in General Paediatric Ward CM HUI, K TSE Abstract Objective: To estimate the incidence rate and risk factors
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2002;7:33-38 Study on Incidence of Antibiotic Associated Diarrhoea in General Paediatric Ward CM HUI, K TSE Abstract Objective: To estimate the incidence rate and risk factors
Prevention of Cdiff recurrence: Evidence from a Cdiff Antitoxin
 Prevention of Cdiff recurrence: Evidence from a Cdiff Antitoxin Prof. Emilio Bouza Departament of Medicine. Hospital Gregorio Marañon and Complutense University. Madrid. Spain Disclosures Last year Participation
Prevention of Cdiff recurrence: Evidence from a Cdiff Antitoxin Prof. Emilio Bouza Departament of Medicine. Hospital Gregorio Marañon and Complutense University. Madrid. Spain Disclosures Last year Participation
OCTOBER 7-10 PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA
 OMED 17 OCTOBER 7-10 PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA 29.5 Category 1-A CME credits anticipated ACOFP / AOA s 122 nd Annual Osteopathic Medical Conference & Exposition Joint Session with ACOFP and Cleveland
OMED 17 OCTOBER 7-10 PHILADELPHIA, PENNSYLVANIA 29.5 Category 1-A CME credits anticipated ACOFP / AOA s 122 nd Annual Osteopathic Medical Conference & Exposition Joint Session with ACOFP and Cleveland
A Comparison of Vancomycin and Metronidazole for the Treatment of Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea, Stratified by Disease Severity
 MAJOR ARTICLE A Comparison of Vancomycin and Metronidazole for the Treatment of Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea, Stratified by Disease Severity Fred A. Zar, 1 Srinivasa R. Bakkanagari, 2 K. M.
MAJOR ARTICLE A Comparison of Vancomycin and Metronidazole for the Treatment of Clostridium difficile Associated Diarrhea, Stratified by Disease Severity Fred A. Zar, 1 Srinivasa R. Bakkanagari, 2 K. M.
Clostridium difficile in Children: To Treat or Not to Treat?
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2014.17.2.80 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2014 June 17(2):80-84 Review Article PGHN Clostridium difficile in Children: To Treat or
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2014.17.2.80 Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 2014 June 17(2):80-84 Review Article PGHN Clostridium difficile in Children: To Treat or
Presenter Disclosure Information
 10:45 11:45am New Approaches to Treating C. Difficile Infection SPEAKER Kalpana Gupta, MD, MPH Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Kalpana Gupta,
10:45 11:45am New Approaches to Treating C. Difficile Infection SPEAKER Kalpana Gupta, MD, MPH Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Kalpana Gupta,
New approaches to treating
 9:45 10:45am New Approaches to Treating C Difficile Infection SPEAKER Kalpana Gupta, MD, MPH Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Kalpana Gupta,
9:45 10:45am New Approaches to Treating C Difficile Infection SPEAKER Kalpana Gupta, MD, MPH Presenter Disclosure Information The following relationships exist related to this presentation: Kalpana Gupta,
AN OUTBREAK OF TOXIN A NEGATIVE, TOXIN B POSITIVE CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE -ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA IN A CANADIAN TERTIARY-CARE HOSPITAL
 Vol. 25-7 Date of publication: 1 April 1999 Contained in this FAX issue: (No. of pages: 6) Official page numbers: AN OUTBREAK OF TOXIN A NEGATIVE, TOXIN B POSITIVE CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA
Vol. 25-7 Date of publication: 1 April 1999 Contained in this FAX issue: (No. of pages: 6) Official page numbers: AN OUTBREAK OF TOXIN A NEGATIVE, TOXIN B POSITIVE CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA
Predictors of Death after Clostridium difficile Infection: A Report on 128 Strain-Typed Cases from a Teaching Hospital in the United Kingdom
 BRIEF REPORT Predictors of Death after Clostridium difficile Infection: A Report on 128 Strain-Typed Cases from a Teaching Hospital in the United Kingdom Vhairi Wilson, 1 Liz Cheek, 2 Giovanni Satta, 1
BRIEF REPORT Predictors of Death after Clostridium difficile Infection: A Report on 128 Strain-Typed Cases from a Teaching Hospital in the United Kingdom Vhairi Wilson, 1 Liz Cheek, 2 Giovanni Satta, 1
Incidence of and risk factors for communityassociated Clostridium difficile infection
 University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 2010 Incidence of and risk factors for communityassociated Clostridium difficile infection Jennifer Lee Kuntz University of Iowa Copyright
University of Iowa Iowa Research Online Theses and Dissertations 2010 Incidence of and risk factors for communityassociated Clostridium difficile infection Jennifer Lee Kuntz University of Iowa Copyright
Clostridium Difficile Infection in Adults Treatment and Prevention
 Clostridium Difficile Infection in Adults Treatment and Prevention Definition: Clostridium Difficile colonizes the human intestinal tract after the normal gut flora has been altered by antibiotic therapy
Clostridium Difficile Infection in Adults Treatment and Prevention Definition: Clostridium Difficile colonizes the human intestinal tract after the normal gut flora has been altered by antibiotic therapy
Differentiation Between Ileocecal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease using a Combination of Clinical, Endoscopic and Histological Characteristics
 38 Original Article Differentiation Between Ileocecal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease using a Combination of Clinical, Endoscopic and Histological Characteristics Anuchapreeda S Leelakusolvong S Charatcharoenwitthaya
38 Original Article Differentiation Between Ileocecal Tuberculosis and Crohn s Disease using a Combination of Clinical, Endoscopic and Histological Characteristics Anuchapreeda S Leelakusolvong S Charatcharoenwitthaya
HEALTHCARE- ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS: A FOCUS ON Clostridium difficile
 OBJECTIVES HEALTHCARE- ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS: A FOCUS ON Clostridium difficile Identify and describe the pathophysiology of C. diff. Identify and describe current therapies in treatment of C. diff Identify
OBJECTIVES HEALTHCARE- ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS: A FOCUS ON Clostridium difficile Identify and describe the pathophysiology of C. diff. Identify and describe current therapies in treatment of C. diff Identify
complicating inflammatory bowel disease
 Gut, 1982, 23, 410-414 Clostridium difficile toxin in acute diarrhoea complicating inflammatory bowel disease M R B KEIGHLEY*, DENISE YOUNGS, MARGARET JOHNSON, R N ALLAN, and D W BURDON From The General
Gut, 1982, 23, 410-414 Clostridium difficile toxin in acute diarrhoea complicating inflammatory bowel disease M R B KEIGHLEY*, DENISE YOUNGS, MARGARET JOHNSON, R N ALLAN, and D W BURDON From The General
9/18/2018. Clostridium Difficile: Updates on Diagnosis and Treatment. Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI)
 Clostridium Difficile: Updates on Diagnosis and Treatment Elizabeth Hudson, DO, MPH 9/25/18 Antibiotic-associated diarrhea and colitis were well established soon after widespread use of antibiotics In
Clostridium Difficile: Updates on Diagnosis and Treatment Elizabeth Hudson, DO, MPH 9/25/18 Antibiotic-associated diarrhea and colitis were well established soon after widespread use of antibiotics In
Labeled Uses: Treatment of Clostiridum Difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD)
 Brand Name: Dificid Generic Name: fidaxomicin Manufacturer 1,2,3,4,5 : Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Drug Class 1,2,3,4,5 : Macrolide Antibiotic Uses 1,2,3,4,5 : Labeled Uses: Treatment of Clostiridum
Brand Name: Dificid Generic Name: fidaxomicin Manufacturer 1,2,3,4,5 : Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Drug Class 1,2,3,4,5 : Macrolide Antibiotic Uses 1,2,3,4,5 : Labeled Uses: Treatment of Clostiridum
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infections
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infections Christina M. Surawicz, MD 1, Lawrence J. Brandt, MD 2, David G. Binion, MD 3, Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infections Christina M. Surawicz, MD 1, Lawrence J. Brandt, MD 2, David G. Binion, MD 3, Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan,
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Week 52 (Ending 30/12/2017)
 Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Week 52 (Ending 30/12/2017) What is Clostridium difficile? Clostridium difficile is a Gram-positive anaerobic spore forming bacillus. It is ubiquitous in nature and
Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Week 52 (Ending 30/12/2017) What is Clostridium difficile? Clostridium difficile is a Gram-positive anaerobic spore forming bacillus. It is ubiquitous in nature and
Clostridium difficile
 Clostridium difficile Care Homes IPC Study Day Sue Barber Infection Prevention & Control Lead AV & Chiltern CCG s Clostridium difficile A spore forming Bacterium. Difficult to grow in the laboratory hence
Clostridium difficile Care Homes IPC Study Day Sue Barber Infection Prevention & Control Lead AV & Chiltern CCG s Clostridium difficile A spore forming Bacterium. Difficult to grow in the laboratory hence
Hospital-acquired diarrhoea in elderly patients: epidemiology and staff awareness
 Age and Ageing 1998; 27: 339-343 Hospital-acquired diarrhoea in elderly patients: epidemiology and staff awareness LORRAINE KYNE, AIDEEN MORAN, CONOR KEANE 1, DESMOND O'NEILL Age-Related Health Cane, Meath
Age and Ageing 1998; 27: 339-343 Hospital-acquired diarrhoea in elderly patients: epidemiology and staff awareness LORRAINE KYNE, AIDEEN MORAN, CONOR KEANE 1, DESMOND O'NEILL Age-Related Health Cane, Meath
Safety of Saccharomyces boulardii (Florastor) in Solid Organ Transplant Patients
 Butler University Digital Commons @ Butler University Undergraduate Honors Thesis Collection Undergraduate Scholarship 5-12-2012 Safety of Saccharomyces boulardii (Florastor) in Solid Organ Transplant
Butler University Digital Commons @ Butler University Undergraduate Honors Thesis Collection Undergraduate Scholarship 5-12-2012 Safety of Saccharomyces boulardii (Florastor) in Solid Organ Transplant
