Renal Failure and Leukocytosis Are Predictors of a Complicated Course of Clostridium difficile Infection if Measured on Day of Diagnosis
|
|
|
- Brian Dawson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Renal Failure and Leukocytosis Are Predictors of a Complicated Course of Clostridium difficile Infection if Measured on Day of Diagnosis Martijn P. Bauer, 1,a Marjolein P. M. Hensgens, 1,a Mark A. Miller, 2 Dale N. Gerding, 3,4 Mark H. Wilcox, 5,6 Adam P. Dale, 5 Warren N. Fawley, 5 Ed J. Kuijper, 1 and Sherwood L. Gorbach 7,8 1 Leiden University Medical Center, The Netherlands; 2 Division of Infectious Diseases, Jewish General Hospital, McGill University, Montreal, Quebec, Canada; 3 Hines Veterans Affairs Hospital, 4 Loyola University Chicago School of Medicine, Maywood, Illinois; 5 Department of Microbiology, The General Infirmary, Old Medical School, 6 Leeds Institute of Molecular Medicine, University of Leeds, United Kingdom; 7 Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc., San Diego, California, and 8 Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, Massachusetts Nonsevere Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) and severe CDI, which carries a higher risk than nonsevere CDI for treatment failure and CDI recurrence, are difficult to distinguish at the time of diagnosis. To investigate the prognostic value of 3 markers of severe CDI suggested by recent guidelines (fever, leukocytosis, and renal failure), we used the database of 2 randomized controlled trials, which contained information for 1105 patients with CDI. Leukocytosis (risk ratio [RR], 2.29; 95% confidence interval [CI], ) and renal failure (RR, 2.52; 95% CI, ) were associated with treatment failure. Fever, although associated with treatment failure (RR, 2.45; 95% CI, ), was rare. Renal failure was the only significant predictor of recurrence (RR, 1.45; 95% CI, ). Different timing of measurements of leukocyte count and serum creatinine level around the CDI diagnosis led to a different severity classification in many cases. In conclusion, both leukocytosis and renal failure are useful predictors, although timing of measurement is important. Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) has become an increasing problem in many hospitals in the Western world during the past decade. C. difficile causes diarrhea and colitis, with a tendency to recur after initially successful antimicrobial therapy. Furthermore, gut inflammation may be so severe that antimicrobial therapy is not effective; in such cases, complications such as hypotension, perforation, and toxic megacolon may develop. Several risk factors for CDI have been identified, of which the use of antibiotics is the most important. Predicting which patients are at risk for developing a M. P. B. and M. P. M. H. contributed equally to this work. Correspondence: E. J. Kuijper, Department of Medical Microbiology, Leiden University Medical Center, PO Box 9600, 2300 RC, Leiden, The Netherlands (E.J.Kuijper@lumc.nl). Clinical Infectious Diseases 2012;55(S2):S The Author Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please journals.permissions@oup.com. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0), which permits unrestricted noncommercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. DOI: /cid/cis340 complications or recurrences can guide the choice and duration of therapy. In 2009, a prediction rule for recurrences, incorporating age, comorbid conditions, and the necessity to continue inciting antibiotic therapy, was published [1]. This rule was derived from and was validated in 2 cohorts of 44 and 64 patients, respectively. The relatively small sample sizes challenge the credibility of this rule. Several risk factors for complications of CDI and prediction rules based on these factors have been described, but unfortunately, none of these prediction rules have been validated [2 6]. The choice of an appropriate end point for a prediction rule for complicated and/or recurrent CDI has been problematic. The clinical judgment of whether to attribute end points such as CDI-related mortality and intensive care unit admission may be highly subjective, especially for elderly patients, who are often admitted with severe illness and usually have significant comorbid conditions. End points concerning the resolution and recurrence of diarrhea need a precise definition of diarrhea and quantitative measurement of stool volume and frequency, which may be difficult to obtain. Predictors of Complicated CDI CID 2012:55 (Suppl 2) S149
2 Furthermore, the parameters included in a prediction rule should be objective, routinely measured in clinical practice, and available at the moment the rule is applied (ie, when CDI is diagnosed). A recent guideline by the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America and the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends that age, peak leukocyte count, and peak serum creatinine level be taken into account as potential indicators of a complicated course of CDI when treatment is started [7]. The European Society for Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases has issued a guidance document for the treatment of CDI that also lists qualitative and quantitative symptoms, signs, laboratory parameters, and radiological findings that may reflect more severe disease with associated higher risk for complications and recurrences [8]. Three quantitative parameters for diagnosing severe colitis were included: body temperature >38.5 C, leukocyte count > /L, and serum creatinine level >50% above baseline; however, these cutoffs have not been confirmed prospectively. In the present study, we sought to investigate the value of 3 quantitative severity criteria in predicting the failure of antimicrobial therapy and the recurrence of CDI after initially successful treatment. Furthermore, we aimed to investigate whether leukocyte count and serum creatinine level fluctuate early in the course of a CDI episode and therefore whether the timing of their measurements can influence whether severity criteria are met. For our analyses, we used the database from 2 large randomized clinical trials that used a strict objective definition of diarrhea and the database of a prospective singlecenter cohort study that recorded sequential leukocyte counts and serum creatinine levels around the date of CDI diagnosis. METHODS Databases The database from 2 randomized controlled phase III trials comparing vancomycin with fidaxomicin for the treatment of CDI was used to assess the predictive value of fever, leukocyte count, and serum creatinine level [9, 10]. Patients were recruited in the United States, Canada, and Europe (Clinical- Trials.gov registry number NCT , April 2006 July 2008, United States and Canada; and ClinicalTrials.gov registry number NCT , April 2007 November 2009, United States, Belgium, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Sweden, and United Kingdom). Patients with CDI, defined on the basis of diarrhea (>3 unformed bowel movements [UBMs] per day) and a positive stool toxin test for C. difficile, were randomly assigned to receive 125 mg of vancomycin 4 times daily or 200 mg of fidaxomicin twice daily for 10 days. The numbers and times of UBMs were recorded during treatment and for 2 days after an end-of-therapy visit. For patients with rectal collection devices, volume was converted to number of UBMs by dividing the volume by 60 ml and rounding up to the nearest whole number. At the end-oftherapy visit, an investigator assessed the success of therapy. Clinical failure was defined as the persistence of diarrhea, the need for additional therapy for CDI, or both on the basis of the opinion of the investigator [10]. Recurrence of CDI (determined by use of the same criteria as for enrollment [ie, >3 UBMs per 24 hours and a positive stool toxin test result]) was assessed during the mean follow-up duration (±SD) of 28 ± 2 days after completion of therapy. At enrollment, temperature, leukocyte count, and serum creatinine level were collected. To assess whether the timing of laboratory measurements could influence their prognostic value, we used the database of a prospective cohort study performed at Leeds Teaching Hospital in In this database, 104 consecutive adult inpatients with CDI (defined on the basis of the presence of unformed stool and a positive C. difficile toxin test result) were included. On days 3 to +3 relative to day 0 (the day the diarrheal sample was collected), leukocyte count and serum creatinine level were recorded. Data from a minimum of 2 leukocyte counts and creatinine levels on different days were required for patients to be included in the analyses. In both analyses, we defined fever as a core body temperature >38.5 C and leukocytosis as a leukocyte count > leukocytes/l. Because the pre-cdi serum creatinine level was not known for each patient, we substituted the 50% creatinine level increase with a fixed value of the creatinine level >133 μmol/l (>1.5 mg/dl). This served as a proxy for renal failure. Analyses The intention-to-treat population that received at least 1 dose of study medication was used for the analysis. Distributions of the continuous variables of temperature, leukocyte count, and creatinine level were compared for patients with and patients without clinical treatment failure and recurrence. Nonnormally distributed variables were compared with the Mann- Whitney U test. Proportions were compared with the χ 2 test. Risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were calculated for the associations of fever, leukocytosis, and renal failure with the outcome parameters. Kaplan-Meier survival curves were constructed to investigate the association of fever, leukocytosis, and renal failure with the time to resolution of diarrhea (expressed in hours from the first dose of fidaxomicin or vancomycin). The log-rank test was used to test the difference between the survival curves. Cox regression was used to calculate hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% CIs. Receiver operating characteristic curves were constructed to assess the validity of the cutoffs used to define categorical variables. Variability of leukocyte counts and serum creatinine levels were compared S150 CID 2012:55 (Suppl 2) Bauer et al
3 within patients and expressed in absolute differences. All analyses were carried out in SPSS for Windows software, version 17.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL). RESULTS There were 1105 patients with CDI in the clinical trial database. Patients treated with vancomycin (n = 566) or fidaxomicin (n = 539) had similar median values for temperature, leukocyte count, and serum creatinine level and were evenly distributed across the groups with respect to dichotomized continuous variables (data not shown). Fever was rare; only 1.2% of patients (13 of 1102) had a temperature >38.5 C. The median treatment duration was 11 days for each group. Overall, 143 patients (13%) experienced clinical treatment failure at the end of treatment. Of the 962 patients who were cured after treatment, 194 (20%) experienced recurrence a mean (±SD) of 28 ± 2 days after treatment. The median leukocyte count and creatinine level were significantly higher in patients with clinical treatment failure; temperature distributions in patients with and those without treatment failure were almost identical. In addition, dichotomous categories of fever, leukocytosis, and renal failure all showed significant correlation with treatment failure (Table 1). The median creatinine level was significantly higher in patients with recurrence, and this parameter was the only significant predictor of recurrence (Table 2). Different cutoffs for the continuous variables of temperature, leukocyte count, and creatinine level, assessed by receiver operating characteristics, did not lead to higher relative risks and therefore better performance in the prediction of clinical treatment failure or recurrent CDI. The probability of resolution of diarrhea within 10 days of treatment was slightly lower in patients with renal failure, compared with patients without renal failure (HR, 0.83; 95% CI, ; Figure 1). Neither fever (HR, 1.08; 95% CI, ) nor leukocytosis (HR, 1.02; 95% CI, ) was associated with a lower probability of resolution of diarrhea. Although creatinine level distributions were similar between patients treated with fidaxomicin and those treated with vancomycin, we repeated the analysis of renal failure as a predictor of resolution of diarrhea stratified according to treatment group and found similar results (vancomycin: HR, 0.80 [95% CI, ]; fidaxomicin: HR, 0.88 [95% CI, ]). Because recurrences occurred less often in patients treated with fidaxomicin, the CI is widest in that group. Clinical treatment failure rates were similar in the fidaxomicin and vancomycin treatment groups regardless of clinical status, using the 3 severity factors. Recurrence was significantly more frequent following vancomycin treatment, compared with fidaxomicin treatment. In patients without renal failure, 93 of 402 patients (23.1%) cured by vancomycin therapy had a recurrence, Table 1. Determinants of Clinical Treatment Failure Among Patients With Clostridium difficile Infection Variable Median Value IQR P a Continuous, outcome Temperature ( C) Failure Cure Leukocyte count ( 10 9 leukocytes/l) Failure Cure Creatinine level (μmol/l) b Failure Cure Categorical, cutoff Failure c RR d 95% CI Fever, temperature >38.5 C 4/ C 137/1089 Leukocytosis, leukocyte level > leukocytes/l 38/ leukocytes/l 90/829 Renal failure, creatinine level 133 μmol/l b 41/ <133 μmol/l b 91/896 Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; IQR, interquartile range; RR, risk ratio. a Comparison between patients with clinical treatment failure and those with clinical cure. b Creatinine conversion: 1 μmol/l is equal to mg/dl. Therefore, 133 μmol/l is equal to 1.50 mg/dl. c Data are no. of patients with failure/overall no. d For the association with failure. whereas only 56 of 403 (13.9%) experienced a recurrence after successful fidaxomicin treatment (P <.001). In patients with renal failure at baseline, fidaxomicin therapy was associated with a 60% reduction in the frequency of recurrences (8 of 54 [14.8%]) relative to vancomycin (24 of 65 [36.9%]; P =.007). Likewise, in patients categorized as having leukocytosis or severe CDI, the incidence of recurrence was more than double for patients cured with vancomycin, compared with those treated successfully with fidaxomicin (P <.01 for each comparison). Because leukocytosis and renal failure at the time of diagnosis were shown to be the strongest predictors, we investigated the stability of these parameters during a 6-day interval around diagnosis. In the population from the database of Leeds Teaching Hospital, the highest mean leukocyte count ( leukocytes/l) was found on the day of CDI diagnosis. Within the interval from 3 days before to 3 days after the diagnosis of CDI, the mean difference between the highest and lowest leukocyte counts was leukocytes/l. Twenty of 86 patients (23.3%) had a minimum to maximum leukocyte count range > leukocytes/l, and 33 (38.4%) Predictors of Complicated CDI CID 2012:55 (Suppl 2) S151
4 Table 2. Determinants of Clostridium difficile Infection Recurrence Variable Median Value IQR P a Continuous, outcome Temperature ( C) No recurrence Recurrence Leukocyte count ( 10 9 leukocytes/l) No recurrence Recurrence Creatinine level (μmol/l) b No recurrence Recurrence Categorical, cutoff Recurrence c RR d 95% CI Fever, temperature >38.5 C 1/ C 192/952 Leukocytosis, leukocyte level > leukocytes/l 22/ leukocytes/l 141/739 Renal failure, creatinine level 133 μmol/l b 32/ <133 μmol/l b 149/805 Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; IQR, interquartile range; RR, risk ratio. a Comparison between patients with recurrence and those without recurrence. b Creatinine conversion: 1 μmol/l is equal to mg/dl. Therefore, 133 μmol/l is equal to 1.50 mg/dl. c Data are no. of patients with recurrence/overall no. d For the association with recurrence. patients had a minimum to maximum leukocyte count range that included the cutoff of leukocytes/l; therefore, a difference in timing of a single blood sample around diagnosis could have led to a different severity classification. The mean serum creatinine concentration was 147 μmol/l on the day of diagnosis. The mean minimum to maximum range in serum creatinine values was 38.7 μmol/l. Nineteen of 93 patients (20.4%) had a minimum to maximum range in creatinine levels that included the cutoff of 133 μmol/l, which could have led to a different classification in the case of different timing. DISCUSSION Leukocytosis and renal failure were significant predictors of failure of CDI treatment. Only renal failure showed a trend toward longer duration of diarrhea during treatment and was correlated significantly with recurrence after successful treatment. Both leukocyte count and serum creatinine level were highly variable around diagnosis. Fever was found to be too Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier analysis of time to resolution of diarrhea for patients with and without renal failure. The hazard ratio was 0.83 (95% confidence interval, ). infrequent in our study to be a useful predictor, but its associated relative risk was significant. In previous studies, leukocytosis and renal failure were also associated with complications and recurrence of CDI [3, 11 13]. Therefore, both parameters could be suitable for evaluation in a prediction model. However, because of the variable nature of these values around the time of CDI diagnosis, a strict definition is needed before incorporating these parameters in a prediction rule. Early or late diagnosis could influence leukocyte count and serum creatinine level. Fever appeared not to be a useful predictor of failure of CDI treatment. This was also shown by a small study in 2007 [14]. Both fever and leukocytosis are thought to reflect more severe inflammation of the bowel wall. However, fever was too rare in our patient population to be of use as a predictor. Renal failure may reflect loss of effective circulating volume due either to dehydration because of diarrhea or to shock in the context of a systemic inflammatory response. Unfortunately, the predictive value of these parameters may decrease because of underlying illnesses and comorbid conditions. Renal failure was present in 14% of clinical patients and was the only significant predictor of recurrence, and it was the only parameter associated, albeit nonsignificantly, with a longer time to resolution of diarrhea. Thus, creatinine level may be a good predictor, also because of its relatively greater stability around the time of CDI diagnosis in comparison to leukocytosis. Strengths of this study are the large number of patients with CDI in the database with a well-described definition of S152 CID 2012:55 (Suppl 2) Bauer et al
5 diarrhea and a consistent measure of UBMs. One limitation is that other potential predictors of severe CDI, such as age, serum albumin level, or use of concomitant antibiotics, were not included in this analysis. Therefore, we were not able to develop a complete risk score. Another limitation is the absence of a baseline creatinine level for each patient, precluding us from distinguishing between chronic and acute renal failure. The results of our study suggest that both leukocytosis and renal failure predict clinical treatment failure, whereas only renal failure is a predictor of recurrence after therapy. However, these predictors are highly dependent on the timing of their determination, hampering their use in clinical practice. We need better and more closely defined predictors to construct a reliable prediction score for complicated and recurrent CDI that is applicable in clinical practice. Notes Acknowledgments. Yin Kean provided statistical support. Supplement sponsorship. This article was published as part of a supplement entitled Fidaxomicin and the Evolving Approach to the Treatment of Clostridium difficile Infection," sponsored by Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Potential conflicts of interest. S. L. G. is a part-time employee of Optimer Pharmaceuticals, receiving honoraria from and owning stock options in Cempra. M. M. is a consultant for Optimer Pharmaceuticals. D. N. G. holds patents licensed to ViroPharma for the treatment and prevention of CDI; is a consultant for ViroPharma, Optimer, Cubist, Merck, Pfizer, TheraDoc, Astellas, BioRelix, and Actelion; and holds research grants from GOJO, Merck, Optimer, Sanofi Pasteur, Eurofins Medinet, and ViroPharma. M. H. W. has received honoraria for consultancy work, financial support to attend meetings, and research funding from Astellas, Astra-Zeneca, Bayer, biomerieux, Cerexa, Cubist, Nabriva, Novacta, Pfizer, Sanofi-Pasteur, Summit, The Medicines Company, and Viropharma. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed. References 1. Hu MY, Katchar K, Kyne L, et al. Prospective derivation and validation of a clinical prediction rule for recurrent Clostridium difficile infection. Gastroenterology 2009; 136: Fujitani S, George WL, Murthy AR. Comparison of clinical severity score indices for Clostridium difficile infection. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2011; 32: Henrich TJ, Krakower D, Bitton A, Yokoe DS. Clinical risk factors for severe Clostridium difficile-associated disease. Emerg Infect Dis 2009; 15: Hubert B, Loo VG, Bourgault AM, et al. A portrait of the geographic dissemination of the Clostridium difficile North American pulsed-field type 1 strain and the epidemiology of C. difficile-associated disease in Québec. Clin Infect Dis 2007; 44: Miller M, Gravel D, Mulvey M, et al. Health care-associated Clostridium difficile infection in Canada: patient age and infecting strain type are highly predictive of severe outcome and mortality. Clin Infect Dis 2010; 50: Pépin J, Valiquette L, Alary ME, et al. Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea in a region of Quebec from 1991 to 2003: a changing pattern of disease severity. CMAJ 2004; 171: Cohen SH, Gerding DN, Johnson S, et al. Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America; Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clinical practice guidelines for Clostridium difficile infection in adults: 2010 update by the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) and the Infectious Diseases Society of America (IDSA). Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 2010; 31: Bauer MP, Kuijper EJ, van Dissel JT. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases. European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID): treatment guidance document for Clostridium difficile infection (CDI). Clin Microbiol Infect 2009; 15: Crook D, Peto T, Miller M, et al. Efficacy and safety of fidaxomicin (FDX) vs vancomycin (VAN) in Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in 2 randomized controlled trials (RCT) with 1105 patients [abstract 1417]. Presented at: Infectious Diseases Society of America 48th Annual Meeting, October 2010, Vancouver, Canada. 10. Louie TJ, Miller MA, Mullane KM, et al. OPT Clinical Study Group. Fidaxomicin versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile infection. N Engl J Med 2011; 364: Moshkowitz M, Ben-Baruch E, Kline Z, Shimoni Z, Niven M, Konikoff F. Risk factors for severity and relapse of pseudomembranous colitis in an elderly population. Colorectal Dis 2007; 9: Pepin J, Alary ME, Valiquette L, et al. Increasing risk of relapse after treatment of Clostridium difficile colitis in Quebec, Canada. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: Sailhamer EA, Carson K, Chang Y, et al. Fulminant Clostridium difficile colitis: patterns of care and predictors of mortality. Arch Surg 2009; 144:433 9; discussion Belmares J, Gerding DN, Parada JP, Miskevics S, Weaver F, Johnson S. Outcome of metronidazole therapy for Clostridium difficile disease and correlation with a scoring system. J Infect 2007; 55: Predictors of Complicated CDI CID 2012:55 (Suppl 2) S153
Sustained Clinical Response as an Endpoint in Treatment Trials of. Clostridium difficile-associated Diarrhea
 AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 May 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00605-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Sustained Clinical
AAC Accepts, published online ahead of print on 21 May 2012 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.00605-12 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Sustained Clinical
Updated Clostridium difficile Treatment Guidelines
 Updated Clostridium difficile Treatment Guidelines Arielle Arnold, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Saint Alphonsus Regional Medical Center September 29 th, 2018 Disclosures Nothing to disclose Learning
Updated Clostridium difficile Treatment Guidelines Arielle Arnold, PharmD, BCPS Clinical Pharmacist Saint Alphonsus Regional Medical Center September 29 th, 2018 Disclosures Nothing to disclose Learning
Learning Objectives. A Critical Analysis of Recent Fidaxomicin & Nesiritide Trials. Fidaxomicin vs. Vancomycin. Outline 1/3/2012
 Learning Objectives A Critical Analysis of Recent Fidaxomicin & Nesiritide Trials Amy E. Lodolce, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Director, Drug Information Group UIC College of Pharmacy Describe the methods and
Learning Objectives A Critical Analysis of Recent Fidaxomicin & Nesiritide Trials Amy E. Lodolce, PharmD, BCPS Assistant Director, Drug Information Group UIC College of Pharmacy Describe the methods and
ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES UNIT 3 HOW TO DEAL WITH CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE
 ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES UNIT 3 HOW TO DEAL WITH CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE The diagnosis of CDI should be based on a combination of clinical and laboratory findings. A case definition for the usual
ENGLISH FOR PROFESSIONAL PURPOSES UNIT 3 HOW TO DEAL WITH CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE The diagnosis of CDI should be based on a combination of clinical and laboratory findings. A case definition for the usual
Does Extending Clostridium Difficile Treatment In Patients Who Are Receiving Concomitant Antibiotics Reduce The Rate Of Relapse?
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases Volume 15 Number 1 Does Extending Clostridium Difficile Treatment In Patients Who Are Receiving Concomitant Antibiotics Reduce The Rate Of Relapse?
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Infectious Diseases Volume 15 Number 1 Does Extending Clostridium Difficile Treatment In Patients Who Are Receiving Concomitant Antibiotics Reduce The Rate Of Relapse?
Predictors of Death after Clostridium difficile Infection: A Report on 128 Strain-Typed Cases from a Teaching Hospital in the United Kingdom
 BRIEF REPORT Predictors of Death after Clostridium difficile Infection: A Report on 128 Strain-Typed Cases from a Teaching Hospital in the United Kingdom Vhairi Wilson, 1 Liz Cheek, 2 Giovanni Satta, 1
BRIEF REPORT Predictors of Death after Clostridium difficile Infection: A Report on 128 Strain-Typed Cases from a Teaching Hospital in the United Kingdom Vhairi Wilson, 1 Liz Cheek, 2 Giovanni Satta, 1
Clostridium Difficile Infection: Applying New Treatment Guidelines and Strategies to Reduce Recurrence Rate
 Clostridium Difficile Infection: Applying New Treatment Guidelines and Strategies to Reduce Recurrence Rate Objectives Summarize the changing epidemiology and demographics of patients at risk for Clostridium
Clostridium Difficile Infection: Applying New Treatment Guidelines and Strategies to Reduce Recurrence Rate Objectives Summarize the changing epidemiology and demographics of patients at risk for Clostridium
! Macrolide antibacterial. Fidaxomicin (Dificid ) package labeling. Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. May 2011.
 Disclosure! I have no conflicts of interest related to this presentation Nina Naeger Murphy, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Infectious Diseases MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives!
Disclosure! I have no conflicts of interest related to this presentation Nina Naeger Murphy, Pharm.D., BCPS Clinical Pharmacy Specialist Infectious Diseases MetroHealth Medical Center Learning Objectives!
ABSTRACT PURPOSE METHODS
 ABSTRACT PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to characterize the CDI population at this institution according to known risk factors and to examine the effect of appropriate evidence-based treatment selection
ABSTRACT PURPOSE The purpose of this study was to characterize the CDI population at this institution according to known risk factors and to examine the effect of appropriate evidence-based treatment selection
Stony Brook Adult Clostridium difficile Management Guidelines. Discontinue all unnecessary antibiotics
 Stony Brook Adult Clostridium difficile Management Guidelines Summary: Use of the C Diff Infection (CDI) PowerPlan (Adult) Required Patient with clinical findings suggestive of Clostridium difficile infection
Stony Brook Adult Clostridium difficile Management Guidelines Summary: Use of the C Diff Infection (CDI) PowerPlan (Adult) Required Patient with clinical findings suggestive of Clostridium difficile infection
Labeled Uses: Treatment of Clostiridum Difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD)
 Brand Name: Dificid Generic Name: fidaxomicin Manufacturer 1,2,3,4,5 : Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Drug Class 1,2,3,4,5 : Macrolide Antibiotic Uses 1,2,3,4,5 : Labeled Uses: Treatment of Clostiridum
Brand Name: Dificid Generic Name: fidaxomicin Manufacturer 1,2,3,4,5 : Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Drug Class 1,2,3,4,5 : Macrolide Antibiotic Uses 1,2,3,4,5 : Labeled Uses: Treatment of Clostiridum
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates April 2017 Bezlotoxumab to Prevent Recurrent Infection By Amy Wilson, PharmD and Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction The Gram-positive bacteria is a common cause
Long-Term Care Updates April 2017 Bezlotoxumab to Prevent Recurrent Infection By Amy Wilson, PharmD and Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction The Gram-positive bacteria is a common cause
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE. Pamela Sears, 1 Derrick W. Crook, 2,3 Thomas J. Louie, 4,5 Mark A. Miller, 6 and Karl Weiss 7
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Fidaxomicin Attains High Fecal Concentrations With Minimal Plasma Concentrations Following Oral Administration in Patients With Clostridium difficile Infection Pamela Sears, 1 Derrick
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Fidaxomicin Attains High Fecal Concentrations With Minimal Plasma Concentrations Following Oral Administration in Patients With Clostridium difficile Infection Pamela Sears, 1 Derrick
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates April 2018 By Austin Smith, PharmD Candidate and Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD is the most common healthcare-acquired infection (HAI) in the United States. 1,2 A 2014 prevalence survey
Long-Term Care Updates April 2018 By Austin Smith, PharmD Candidate and Lindsay Slowiczek, PharmD is the most common healthcare-acquired infection (HAI) in the United States. 1,2 A 2014 prevalence survey
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE UPDATE Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click
ADJUVANT TIGECYCLINE FOR SEVERE CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA
 ADJUVANT TIGECYCLINE FOR SEVERE CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Candace Marr, DO Catholic Health System University at Buffalo, NY Kevin Shiley, MD Catholic Health System Buffalo, NY FINANCIAL
ADJUVANT TIGECYCLINE FOR SEVERE CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE-ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA Candace Marr, DO Catholic Health System University at Buffalo, NY Kevin Shiley, MD Catholic Health System Buffalo, NY FINANCIAL
Clostridium Difficile Infection in Adults Treatment and Prevention
 Clostridium Difficile Infection in Adults Treatment and Prevention Definition: Clostridium Difficile colonizes the human intestinal tract after the normal gut flora has been altered by antibiotic therapy
Clostridium Difficile Infection in Adults Treatment and Prevention Definition: Clostridium Difficile colonizes the human intestinal tract after the normal gut flora has been altered by antibiotic therapy
Prevention of Cdiff recurrence: Evidence from a Cdiff Antitoxin
 Prevention of Cdiff recurrence: Evidence from a Cdiff Antitoxin Prof. Emilio Bouza Departament of Medicine. Hospital Gregorio Marañon and Complutense University. Madrid. Spain Disclosures Last year Participation
Prevention of Cdiff recurrence: Evidence from a Cdiff Antitoxin Prof. Emilio Bouza Departament of Medicine. Hospital Gregorio Marañon and Complutense University. Madrid. Spain Disclosures Last year Participation
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Management Guideline
 Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Management Guideline Do not test all patients with loose or watery stools for CDI o CDI is responsible for
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Management Guideline Do not test all patients with loose or watery stools for CDI o CDI is responsible for
March 3, To: Hospitals, Long Term Care Facilities, and Local Health Departments
 March 3, 2010 To: Hospitals, Long Term Care Facilities, and Local Health Departments From: NYSDOH Bureau of Healthcare Associated Infections HEALTH ADVISORY: GUIDANCE FOR PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF HEALTHCARE
March 3, 2010 To: Hospitals, Long Term Care Facilities, and Local Health Departments From: NYSDOH Bureau of Healthcare Associated Infections HEALTH ADVISORY: GUIDANCE FOR PREVENTION AND CONTROL OF HEALTHCARE
Clostridium difficile infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands
 Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2011) 30:587 593 DOI 10.1007/s10096-010-1127-4 ARTICLE Clostridium difficile infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens & A. Goorhuis & C. M.
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2011) 30:587 593 DOI 10.1007/s10096-010-1127-4 ARTICLE Clostridium difficile infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens & A. Goorhuis & C. M.
500,000 29,000. New 2015 Data. Lessa et al, N Eng J Med 2015: 34.2% of CDI cases were considered community-acquired
 Cost-effective Treatment of Clostridium difficile Infection in the ICU Kevin W. Garey, PharmD, MS. Professor and Chair University of Houston College of Pharmacy New 2015 Data 500,000 29,000 Lessa et al,
Cost-effective Treatment of Clostridium difficile Infection in the ICU Kevin W. Garey, PharmD, MS. Professor and Chair University of Houston College of Pharmacy New 2015 Data 500,000 29,000 Lessa et al,
Clostridium difficile (C difficile)
 Patient Knowledge and Attitudes About for Clostridium difficile Infection Colin Goodman, MD; Nicholas O Rourke, PharmD; Carla Amundson, MA; and Dimitri Drekonja, MD, MS In a survey of patients with Clostridium
Patient Knowledge and Attitudes About for Clostridium difficile Infection Colin Goodman, MD; Nicholas O Rourke, PharmD; Carla Amundson, MA; and Dimitri Drekonja, MD, MS In a survey of patients with Clostridium
Serious MRSA infection: anything new?
 Serious MRSA infection: anything new? Professor Mark H. Wilcox Leeds Teaching Hospitals & University of Leeds, UK Public Health England & NHS Improvement Potential Conflicts of Interest I have received:
Serious MRSA infection: anything new? Professor Mark H. Wilcox Leeds Teaching Hospitals & University of Leeds, UK Public Health England & NHS Improvement Potential Conflicts of Interest I have received:
Literature Scan: Antibiotics for Clostridium difficile Infection. Month/Year of Review: May 2015 Date of Last Review: April 2012
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Division of GIM Lecture Series Case Presentation David A. Erickson, M.D October 9th, 2013
 Division of GIM Lecture Series Case Presentation David A. Erickson, M.D October 9th, 2013 Financial Disclosures No financial disclosures Objectives Review a case of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection
Division of GIM Lecture Series Case Presentation David A. Erickson, M.D October 9th, 2013 Financial Disclosures No financial disclosures Objectives Review a case of recurrent Clostridium difficile infection
L infezione da Clostridium difficile (CDI) Quadri clinici e nuovi approcci terapeutici
 L infezione da Clostridium difficile (CDI) Quadri clinici e nuovi approcci terapeutici Roberto Luzzati SC Malattie Infettive, AOU Trieste Presidente :Prof. Enzo Raise Clinical presentation of infection
L infezione da Clostridium difficile (CDI) Quadri clinici e nuovi approcci terapeutici Roberto Luzzati SC Malattie Infettive, AOU Trieste Presidente :Prof. Enzo Raise Clinical presentation of infection
The Bristol Stool Scale and Its Relationship to Clostridium difficile Infection
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 July 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01303-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 The Bristol Stool Scale
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 July 2014 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01303-14 Copyright 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 The Bristol Stool Scale
Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2016) 35:251 259 DOI 10.1007/s10096-015-2538-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE The impact of the introduction of fidaxomicin on the management of Clostridium difficile infection in seven
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2016) 35:251 259 DOI 10.1007/s10096-015-2538-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE The impact of the introduction of fidaxomicin on the management of Clostridium difficile infection in seven
Does Empirical Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Therapy Result in False-Negative CDI Diagnostic Test Results?
 MAJOR ARTICLE Does Empirical Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Therapy Result in False-Negative CDI Diagnostic Test Results? Venkata C. K. Sunkesula, 1 Sirisha Kundrapu, 1 Christine Muganda, 3 Ajay
MAJOR ARTICLE Does Empirical Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Therapy Result in False-Negative CDI Diagnostic Test Results? Venkata C. K. Sunkesula, 1 Sirisha Kundrapu, 1 Christine Muganda, 3 Ajay
Sherwood L. Gorbach, MD Professor of Public Health, Medicine, and Microbiology Tufts University School of Medicine
 Sherwood L. Gorbach, MD Professor of Public Health, Medicine, and Microbiology Tufts University School of Medicine Chief Scientific Officer, Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Conflicts: Chief Scientific Officer,
Sherwood L. Gorbach, MD Professor of Public Health, Medicine, and Microbiology Tufts University School of Medicine Chief Scientific Officer, Optimer Pharmaceuticals, Inc. Conflicts: Chief Scientific Officer,
Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Review
 Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Review October 18, 2010 James Kahn and Carolyn Kenney, MSIV Overview Burden of disease associated
Diagnosis, Management, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile infection in Long-Term Care Facilities: A Review October 18, 2010 James Kahn and Carolyn Kenney, MSIV Overview Burden of disease associated
Atypical Presentation of Clostridium Difficille Infection (CDI).
 Article ID: WMC004648 ISSN 2046-1690 Atypical Presentation of Clostridium Difficille Infection (CDI). Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Syed A Gardezi, CT1, Medicine,NevillHall Hospital
Article ID: WMC004648 ISSN 2046-1690 Atypical Presentation of Clostridium Difficille Infection (CDI). Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Syed A Gardezi, CT1, Medicine,NevillHall Hospital
MAJOR ARTICLE. Clostridium difficile infection; vancomycin; metronidazole; mortality; sepsis.
 MAJOR ARTICLE The Addition of Intravenous Metronidazole to Oral Vancomycin is Associated With Improved Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Clostridium difficile Infection Kristina E. E. Rokas, 1
MAJOR ARTICLE The Addition of Intravenous Metronidazole to Oral Vancomycin is Associated With Improved Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Clostridium difficile Infection Kristina E. E. Rokas, 1
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Guideline
 Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Guideline Site Applicability All VCH PHC acute care and residential sites. Practice Level Physicians basic skill Pharmacists basic skill Nurses (RN, LPN, RPN) basic
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Guideline Site Applicability All VCH PHC acute care and residential sites. Practice Level Physicians basic skill Pharmacists basic skill Nurses (RN, LPN, RPN) basic
Clostridium difficile Infec&on (CDI): Discovering the need for new treatment algorithms and care pathways APRIL 4, 2013
 Clostridium difficile Infec&on (CDI): Discovering the need for new treatment algorithms and care pathways APRIL 4, 2013 Overview of Poten&al Treatment Op&ons for CDI APRIL 4, 2013 Overview of Poten&al Treatment
Clostridium difficile Infec&on (CDI): Discovering the need for new treatment algorithms and care pathways APRIL 4, 2013 Overview of Poten&al Treatment Op&ons for CDI APRIL 4, 2013 Overview of Poten&al Treatment
Prospective Derivation and Validation of a Clinical Prediction Rule for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:1206 1214 Prospective Derivation and Validation of a Clinical Prediction Rule for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection MARY Y. HU,* KIANOOSH KATCHAR,* LORRAINE KYNE, SEEMA
GASTROENTEROLOGY 2009;136:1206 1214 Prospective Derivation and Validation of a Clinical Prediction Rule for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection MARY Y. HU,* KIANOOSH KATCHAR,* LORRAINE KYNE, SEEMA
Le infezioni da Clostridium difficile, gravi, ricorrenti e complicate Nicola Petrosillo
 Le infezioni da Clostridium difficile, gravi, ricorrenti e complicate Nicola Petrosillo Istituto Nazionale per le Malattie Infettive «lazzaro Spallanzani», IRCCS-Roma The infectious cycle of transmission
Le infezioni da Clostridium difficile, gravi, ricorrenti e complicate Nicola Petrosillo Istituto Nazionale per le Malattie Infettive «lazzaro Spallanzani», IRCCS-Roma The infectious cycle of transmission
Ongoing Developments in Management of Clostridium difficile Infection
 Ongoing Developments in Management of Clostridium difficile Infection Infectious Diseases Spring Symposium Creighton University School of Medicine April 28, 2018, Omaha, NB Stuart Johnson, MD Loyola U.
Ongoing Developments in Management of Clostridium difficile Infection Infectious Diseases Spring Symposium Creighton University School of Medicine April 28, 2018, Omaha, NB Stuart Johnson, MD Loyola U.
The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile Infection in Children: A Population-Based Study
 Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published March 5, 2013 MAJOR ARTICLE The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile Infection in Children: A Population-Based Study Sahil Khanna, 1 Larry M. Baddour,
Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published March 5, 2013 MAJOR ARTICLE The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile Infection in Children: A Population-Based Study Sahil Khanna, 1 Larry M. Baddour,
Factors Affecting Mortality and Length of Stay Following Clostridium Difficile Associated Diarrhoea: Validating A Consistent Scoring System
 Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Archives of Clinical Microbiology DOI: 10.4172/1989-8436.100046 Factors Affecting Mortality and Length of Stay Following Clostridium Difficile
Research Article imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com/ Archives of Clinical Microbiology DOI: 10.4172/1989-8436.100046 Factors Affecting Mortality and Length of Stay Following Clostridium Difficile
Clostridium difficile Infection: Diagnosis and Management
 Clostridium difficile Infection: Diagnosis and Management Brian Viviano D.O. Case study 42 year old female with history of essential hypertension and COPD presents to ED complaining of 24 hours of intractable,
Clostridium difficile Infection: Diagnosis and Management Brian Viviano D.O. Case study 42 year old female with history of essential hypertension and COPD presents to ED complaining of 24 hours of intractable,
Surotomycin versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile infection: Phase 2, randomized, controlled, double-blind, non-inferiority, multicentre trial
 J Antimicrob Chemother 2016; 71: 2964 2971 doi:10.1093/jac/dkw246 Advance Access publication 17 July 2016 Surotomycin versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile infection: Phase 2, randomized, controlled,
J Antimicrob Chemother 2016; 71: 2964 2971 doi:10.1093/jac/dkw246 Advance Access publication 17 July 2016 Surotomycin versus vancomycin for Clostridium difficile infection: Phase 2, randomized, controlled,
Antibiotic treatment comparison in patients with diarrhea
 Original Research Article Antibiotic treatment comparison in patients with diarrhea Deva Lal Kast * Senior Consultant Physician, Department of General Medicine, Krishna Hospital, Ex senior Specialist and
Original Research Article Antibiotic treatment comparison in patients with diarrhea Deva Lal Kast * Senior Consultant Physician, Department of General Medicine, Krishna Hospital, Ex senior Specialist and
Modern approach to Clostridium Difficile Infection
 Modern approach to Clostridium Difficile Infection Pseudomembranous Colitis: Principles for diagnosis and treatment Aggelos Stefos Internist, Infectious diseases Specialist Department of Medicine and Research
Modern approach to Clostridium Difficile Infection Pseudomembranous Colitis: Principles for diagnosis and treatment Aggelos Stefos Internist, Infectious diseases Specialist Department of Medicine and Research
Treatment of Clostridium Difficile Infection in Community Teaching Hospital: A Retrospective Study
 International Journal of Infectious Diseases and Therapy 2018; 3(3): 52-61 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijidt doi: 10.11648/j.ijidt.20180303.12 ISSN: 2578-9651 (Print); ISSN: 2578-966X (Online)
International Journal of Infectious Diseases and Therapy 2018; 3(3): 52-61 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijidt doi: 10.11648/j.ijidt.20180303.12 ISSN: 2578-9651 (Print); ISSN: 2578-966X (Online)
A Pharmacist Perspective
 Leveraging Technology to Reduce CDI A Pharmacist Perspective Ed Eiland, Pharm.D., MBA, BCPS (AQ-ID) Clinical Practice and Business Supervisor Huntsville Hospital System Huntsville Hospital 881 licensed
Leveraging Technology to Reduce CDI A Pharmacist Perspective Ed Eiland, Pharm.D., MBA, BCPS (AQ-ID) Clinical Practice and Business Supervisor Huntsville Hospital System Huntsville Hospital 881 licensed
Clostridium difficile CRISTINA BAKER, MD, MPH INFECTIOUS DISEASE PARK NICOLLET/HEALTH PARTNERS 11/9/2018
 Clostridium difficile CRISTINA BAKER, MD, MPH INFECTIOUS DISEASE PARK NICOLLET/HEALTH PARTNERS 11/9/2018 Disclosures None Objectives Highlight important changes in the management of Clostridium difficile
Clostridium difficile CRISTINA BAKER, MD, MPH INFECTIOUS DISEASE PARK NICOLLET/HEALTH PARTNERS 11/9/2018 Disclosures None Objectives Highlight important changes in the management of Clostridium difficile
Predictors of severe outcomes associated with Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease
 Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics Predictors of severe outcomes associated with Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease A. N. Ananthakrishnan*,, R. Guzman-Perez,
Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics Predictors of severe outcomes associated with Clostridium difficile infection in patients with inflammatory bowel disease A. N. Ananthakrishnan*,, R. Guzman-Perez,
White Rose Research Online URL for this paper:
 This is an author produced version of Efficacy of vancomycin extended dosing regimens for treatment of simulated Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) within an in vitro human gut model. White Rose Research
This is an author produced version of Efficacy of vancomycin extended dosing regimens for treatment of simulated Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) within an in vitro human gut model. White Rose Research
Management of Clostridium Difficile: Total Colectomy versus Colon Sparing Surgery
 Management of Clostridium Difficile: Total Colectomy versus Colon Sparing Surgery Rahul Narang, MD Colon and Rectal Surgery Assistant Professor of Surgery No Disclosure Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Treatments,
Management of Clostridium Difficile: Total Colectomy versus Colon Sparing Surgery Rahul Narang, MD Colon and Rectal Surgery Assistant Professor of Surgery No Disclosure Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Treatments,
Clostridium difficile Strain NAP-1 Is Not Associated With Severe Disease in a Nonepidemic Setting
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:868 873 Clostridium difficile Strain NAP-1 Is Not Associated With Severe Disease in a Nonepidemic Setting JEFFREY CLOUD,* LAURA NODDIN, AMANDA PRESSMAN,
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2009;7:868 873 Clostridium difficile Strain NAP-1 Is Not Associated With Severe Disease in a Nonepidemic Setting JEFFREY CLOUD,* LAURA NODDIN, AMANDA PRESSMAN,
Clostridium Difficile colitismore
 Clostridium Difficile colitismore virulent than ever ECHO- February 18, 2016 Charles Krasner, M.D. UNR School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Hospital Growing problem of pseudomembranous colitis
Clostridium Difficile colitismore virulent than ever ECHO- February 18, 2016 Charles Krasner, M.D. UNR School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Hospital Growing problem of pseudomembranous colitis
Clostridium difficile: Can you smell the new updates?
 Clostridium difficile: Can you smell the new updates? Sunish Shah, Pharm.D. PGY-2 Infectious Disease Pharmacy Resident Yale-New Haven Hospital sshah1741@mail.usciences.edu Learning objectives Recognize
Clostridium difficile: Can you smell the new updates? Sunish Shah, Pharm.D. PGY-2 Infectious Disease Pharmacy Resident Yale-New Haven Hospital sshah1741@mail.usciences.edu Learning objectives Recognize
Summary of Results for Laypersons
 What was the Study Called? Summary of Results for Laypersons A Phase IIIb/IV Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Parallel Group Study to Compare the Efficacy of Vancomycin Therapy to Extended Duration
What was the Study Called? Summary of Results for Laypersons A Phase IIIb/IV Randomized, Controlled, Open-Label, Parallel Group Study to Compare the Efficacy of Vancomycin Therapy to Extended Duration
Predictors of serious complications due to Clostridium difficile infection
 Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Predictors of serious complications due to Clostridium difficile infection D. GUJJA* & F. K. FRIEDENBERG *Department of Medicine, Abington Memorial Hospital, Abington,
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics Predictors of serious complications due to Clostridium difficile infection D. GUJJA* & F. K. FRIEDENBERG *Department of Medicine, Abington Memorial Hospital, Abington,
Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published December 7, 2012
 Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published December 7, 2012 1 Physician Attitudes Towards the Use of Fecal Transplantation for Recurrent Clostridium Difficile Infection in a Large Metropolitan
Clinical Infectious Diseases Advance Access published December 7, 2012 1 Physician Attitudes Towards the Use of Fecal Transplantation for Recurrent Clostridium Difficile Infection in a Large Metropolitan
C.Difficile Associated Diarrhea Overview & Management. Sajal Chopra Pharm D. Candidate
 C.Difficile Associated Diarrhea Overview & Management Sajal Chopra Pharm D. Candidate Learning Objectives 1. Recognize the increasing incidence of C.difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) and its risk factors
C.Difficile Associated Diarrhea Overview & Management Sajal Chopra Pharm D. Candidate Learning Objectives 1. Recognize the increasing incidence of C.difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) and its risk factors
Bezlotoxumab (Zinplava) as Adjunct Treatment for Clostridium difficile. Janel Liane Cala, RPh Medical Center Hospital
 Bezlotoxumab (Zinplava) as Adjunct Treatment for Clostridium difficile Janel Liane Cala, RPh Medical Center Hospital Objectives Review pathophysiology, risk factors, prevention, and treatment options of
Bezlotoxumab (Zinplava) as Adjunct Treatment for Clostridium difficile Janel Liane Cala, RPh Medical Center Hospital Objectives Review pathophysiology, risk factors, prevention, and treatment options of
infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands
 infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis, C. M. J. Kinschot, M. J. T. Crobach, C. Harmanus, E. J. Kuijper To cite this version: M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis,
infection in an endemic setting in the Netherlands M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis, C. M. J. Kinschot, M. J. T. Crobach, C. Harmanus, E. J. Kuijper To cite this version: M. P. M. Hensgens, A. Goorhuis,
Terapia dell infezione da Clostridium difficile. Massimo Coen I Div Mal Inf AO L Sacco
 Terapia dell infezione da Clostridium difficile Massimo Coen I Div Mal Inf AO L Sacco Disease Severity Mild CDI 3 5 BM/day WBC 15,000/mm 3 Defining CDI Disease Severity Mild abdominal pain due to CDI Moderate
Terapia dell infezione da Clostridium difficile Massimo Coen I Div Mal Inf AO L Sacco Disease Severity Mild CDI 3 5 BM/day WBC 15,000/mm 3 Defining CDI Disease Severity Mild abdominal pain due to CDI Moderate
Updates to pharmacological management in the prevention of recurrent Clostridium difficile
 Updates to pharmacological management in the prevention of recurrent Clostridium difficile Julia Shlensky, PharmD PGY2 Internal Medicine Resident September 12, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 Clinical Impact Increasing
Updates to pharmacological management in the prevention of recurrent Clostridium difficile Julia Shlensky, PharmD PGY2 Internal Medicine Resident September 12, 2017 2017 MFMER slide-1 Clinical Impact Increasing
9/18/2018. Clostridium Difficile: Updates on Diagnosis and Treatment. Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI)
 Clostridium Difficile: Updates on Diagnosis and Treatment Elizabeth Hudson, DO, MPH 9/25/18 Antibiotic-associated diarrhea and colitis were well established soon after widespread use of antibiotics In
Clostridium Difficile: Updates on Diagnosis and Treatment Elizabeth Hudson, DO, MPH 9/25/18 Antibiotic-associated diarrhea and colitis were well established soon after widespread use of antibiotics In
SUMMARY. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 2015, 40, doi: /jcpt.12329
 Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 2015, 40, 655 660 doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12329 Evaluation of a Clostridium difficile infection management policy with clinical pharmacy and medical microbiology
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 2015, 40, 655 660 doi: 10.1111/jcpt.12329 Evaluation of a Clostridium difficile infection management policy with clinical pharmacy and medical microbiology
Overcoming barriers to effective recognition and diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection
 REVIEW 10.1111/1469-0691.12057 Overcoming barriers to effective recognition and diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection M. H. Wilcox Department of Microbiology, Old Medical School, Leeds Teaching
REVIEW 10.1111/1469-0691.12057 Overcoming barriers to effective recognition and diagnosis of Clostridium difficile infection M. H. Wilcox Department of Microbiology, Old Medical School, Leeds Teaching
All POOPed out: fecal microbiota transplant in C. difficile
 All POOPed out: fecal microbiota transplant in C. difficile SUSAN M. KELLIE, MD, MPH PROFESSOR OF INTERNAL MEDICINE DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO SCHOOL OF MEDICINE HOSPITAL
All POOPed out: fecal microbiota transplant in C. difficile SUSAN M. KELLIE, MD, MPH PROFESSOR OF INTERNAL MEDICINE DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES UNIVERSITY OF NEW MEXICO SCHOOL OF MEDICINE HOSPITAL
Zinplava. (bezlotoxumab) New Product Slideshow
 Zinplava (bezlotoxumab) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Zinplava Generic name: Bezlotoxumab Pharmacological class: Human IgG1 monoclonal antibody Strength and Formulation: 25mg/mL; solution
Zinplava (bezlotoxumab) New Product Slideshow Introduction Brand name: Zinplava Generic name: Bezlotoxumab Pharmacological class: Human IgG1 monoclonal antibody Strength and Formulation: 25mg/mL; solution
Fidaxomicin versus Vancomycin for Clostridium difficile Infection
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e original article Fidaxomicin versus Vancomycin for Clostridium difficile Infection Thomas J. Louie, M.D., Mark A. Miller, M.D., Kathleen M. Mullane,
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e original article Fidaxomicin versus Vancomycin for Clostridium difficile Infection Thomas J. Louie, M.D., Mark A. Miller, M.D., Kathleen M. Mullane,
In recent years, Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) has
 BRIEF REPORTS Poor Functional Status as a Risk Factor for Severe Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized Older Adults Krishna Rao, MD,* Dejan Micic, MD,* Elizabeth Chenoweth, MD, Lili Deng, MD,
BRIEF REPORTS Poor Functional Status as a Risk Factor for Severe Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized Older Adults Krishna Rao, MD,* Dejan Micic, MD,* Elizabeth Chenoweth, MD, Lili Deng, MD,
CLOSTRIDIUM DIFICILE. Negin N Blattman Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare System
 CLOSTRIDIUM DIFICILE Negin N Blattman Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare System ANTIBIOTIC ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA 1978: C diff first identified 1989-1992: Four large outbreaks in the US caused by J
CLOSTRIDIUM DIFICILE Negin N Blattman Infectious Diseases Phoenix VA Healthcare System ANTIBIOTIC ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA 1978: C diff first identified 1989-1992: Four large outbreaks in the US caused by J
Long-Term Clinical Outcome of Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized Patients: A Single Center Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.4.299 Intest Res 2014;12(4):299-305 Long-Term Clinical Outcome of Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ISSN 1598-9100(Print) ISSN 2288-1956(Online) http://dx.doi.org/10.5217/ir.2014.12.4.299 Intest Res 2014;12(4):299-305 Long-Term Clinical Outcome of Clostridium difficile Infection in Hospitalized
Incidence, case fatality and genotypes causing Clostridium difficile infections, Finland, 2008*
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EPIDEMIOLOGY Incidence, case fatality and genotypes causing Clostridium difficile infections, Finland, 2008* S. M. Kotila 1, A. Virolainen 1, M. Snellman 1, S. Ibrahem 1, J. Jalava 2 and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EPIDEMIOLOGY Incidence, case fatality and genotypes causing Clostridium difficile infections, Finland, 2008* S. M. Kotila 1, A. Virolainen 1, M. Snellman 1, S. Ibrahem 1, J. Jalava 2 and
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infections
 ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infections Christina M. Surawicz, MD 1, Lawrence J. Brandt, MD 2, David G. Binion, MD 3, Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan,
ACG Clinical Guideline: Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Clostridium difficile Infections Christina M. Surawicz, MD 1, Lawrence J. Brandt, MD 2, David G. Binion, MD 3, Ashwin N. Ananthakrishnan,
Nicola Petrosillo Istituto Nazionale per le Malattie Infettive Lazzaro Spallanzani, IRCCS Roma. L infezione da C difficile grave o complicata
 Nicola Petrosillo Istituto Nazionale per le Malattie Infettive Lazzaro Spallanzani, IRCCS Roma L infezione da C difficile grave o complicata Bagdasarian N et al. JAMA 2015; 313: 398-408 European Society
Nicola Petrosillo Istituto Nazionale per le Malattie Infettive Lazzaro Spallanzani, IRCCS Roma L infezione da C difficile grave o complicata Bagdasarian N et al. JAMA 2015; 313: 398-408 European Society
Pros and Cons of Alternative Diagnostic Testing Strategies for C. difficile Infection
 Pros and Cons of Alternative Diagnostic Testing Strategies for C. difficile Infection Christopher R. Polage, MD, MAS Associate Professor of Pathology and Infectious Diseases UC Davis Disclosures Test materials
Pros and Cons of Alternative Diagnostic Testing Strategies for C. difficile Infection Christopher R. Polage, MD, MAS Associate Professor of Pathology and Infectious Diseases UC Davis Disclosures Test materials
-2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine. -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency
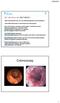 SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
SD, male 40 yrs. old. (680718M467.) -2002: Rectal blood loss, UC? (no definite diagnosis) rectal mesalazine -June 2008: Recurrence of rectal blood loss and urgency Total colonoscopy: ulcerative rectitis,
Case 1. Which of the following would be next appropriate investigation/s regarding the pts diarrhoea?
 Case 1 21 yr old HIV +ve, Cd4-100 HAART naïve Profuse diarrhoea for 3/52. Stool MC&S ve Which of the following would be next appropriate investigation/s regarding the pts diarrhoea? Repeat stool MC&S Stool
Case 1 21 yr old HIV +ve, Cd4-100 HAART naïve Profuse diarrhoea for 3/52. Stool MC&S ve Which of the following would be next appropriate investigation/s regarding the pts diarrhoea? Repeat stool MC&S Stool
DISCLAIMER: ECHO Nevada emphasizes patient privacy and asks participants to not share ANY Protected Health Information during ECHO clinics.
 DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
DISCLAIMER: Video will be taken at this clinic and potentially used in Project ECHO promotional materials. By attending this clinic, you consent to have your photo taken and allow Project ECHO to use this
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Guideline Update:
 Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Guideline Update: Understanding the Data Behind the Recommendations Erik R. Dubberke, MD, MSPH A Webinar for HealthTrust Members Professor of Medicine September 24,
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) Guideline Update: Understanding the Data Behind the Recommendations Erik R. Dubberke, MD, MSPH A Webinar for HealthTrust Members Professor of Medicine September 24,
MAJOR ARTICLE. (See the editorial commentary by Bouza on pages 577 9)
 MAJOR ARTICLE Health Care Associated Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults Admitted to Acute Care Hospitals in Canada: A Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program Study Denise Gravel, 1 Mark
MAJOR ARTICLE Health Care Associated Clostridium difficile Infection in Adults Admitted to Acute Care Hospitals in Canada: A Canadian Nosocomial Infection Surveillance Program Study Denise Gravel, 1 Mark
SMT19969: A Selective Therapy for C. difficile Infection
 SMT19969: A Selective Therapy for C. difficile Infection One Bug, One Drug 25 th September 2012 SMT19969: A Selective Therapy for CDI SMT19969 is a novel antibiotic for the specific treatment of Clostridium
SMT19969: A Selective Therapy for C. difficile Infection One Bug, One Drug 25 th September 2012 SMT19969: A Selective Therapy for CDI SMT19969 is a novel antibiotic for the specific treatment of Clostridium
Los Angeles County Department of Public Health: Your Partner in CDI Prevention
 Los Angeles County Department of Public Health: Your Partner in CDI Prevention Dawn Terashita, MD, MPH Acute Communicable Disease Control Los Angeles County Department of Public Health dterashita@ph.lacounty.gov
Los Angeles County Department of Public Health: Your Partner in CDI Prevention Dawn Terashita, MD, MPH Acute Communicable Disease Control Los Angeles County Department of Public Health dterashita@ph.lacounty.gov
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Fecal Bacteriotherapy
 Clinical Policy Bulletin: Fecal Bacteriotherapy Number: 0844 Policy Aetna considers fecal bacteriotherapy medically necessary for persons with Clostridium difficile infection, with infection confirmed
Clinical Policy Bulletin: Fecal Bacteriotherapy Number: 0844 Policy Aetna considers fecal bacteriotherapy medically necessary for persons with Clostridium difficile infection, with infection confirmed
declara&ons Clostridium difficile infec&on. Time to wake up and smell the..., um, nevermind. OK, next slide please. Bruce Dalton, BScPhm. PharmD.
 Clostridium difficile infec&on. Time to wake up and smell the..., um, nevermind. OK, next slide please. Bruce Dalton, BScPhm. PharmD. declara&ons No financial disclosures Personal acquaintance, co- worker,
Clostridium difficile infec&on. Time to wake up and smell the..., um, nevermind. OK, next slide please. Bruce Dalton, BScPhm. PharmD. declara&ons No financial disclosures Personal acquaintance, co- worker,
What s New for Clostridium difficile John Lynch MD MPH Harborview Medical Center University of Washington
 What s New for Clostridium difficile 2013 John Lynch MD MPH Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Pathogenic Mechanisms of Diarrhea Toxins: Preformed: S aureus, C perfringens, B cereus Formed
What s New for Clostridium difficile 2013 John Lynch MD MPH Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Pathogenic Mechanisms of Diarrhea Toxins: Preformed: S aureus, C perfringens, B cereus Formed
Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI)
 18.09.10 월요집담회 Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) R4 송주혜 Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Anaerobic gram (+), spore-forming, toxin(tcda&tcdb)-producing bacillus Transmitted among humans through
18.09.10 월요집담회 Clostridium difficile Infection (CDI) R4 송주혜 Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) Anaerobic gram (+), spore-forming, toxin(tcda&tcdb)-producing bacillus Transmitted among humans through
Corporate Medical Policy Fecal Microbiota Transplantation
 Corporate Medical Policy Fecal Microbiota Transplantation File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: Fecal_microbiota_transplantation 7/2014 11/2017 11/2018 11/2017 Description
Corporate Medical Policy Fecal Microbiota Transplantation File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: Fecal_microbiota_transplantation 7/2014 11/2017 11/2018 11/2017 Description
Current State of Clostridium difficile Treatment Options
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Current State of Clostridium difficile Treatment Options Anilrudh A. Venugopal 1 and Stuart Johnson 2,3 1 St John Hospital and Medical Center and Wayne State University School of Medicine,
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Current State of Clostridium difficile Treatment Options Anilrudh A. Venugopal 1 and Stuart Johnson 2,3 1 St John Hospital and Medical Center and Wayne State University School of Medicine,
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22997 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wilden, Gwendolyn M. van der Title: The value of surgical treatment in abdominal
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/22997 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Wilden, Gwendolyn M. van der Title: The value of surgical treatment in abdominal
The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile DANIEL SAMAN, DRPH, MPH RESEARCH SCIENTIST ESSENTIA INSTITUTE OF RURAL HEALTH
 The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile DANIEL SAMAN, DRPH, MPH RESEARCH SCIENTIST ESSENTIA INSTITUTE OF RURAL HEALTH Some history first Clostridium difficile, a spore-forming gram-positive (i.e., thick
The Epidemiology of Clostridium difficile DANIEL SAMAN, DRPH, MPH RESEARCH SCIENTIST ESSENTIA INSTITUTE OF RURAL HEALTH Some history first Clostridium difficile, a spore-forming gram-positive (i.e., thick
Drug Class Update with New Drug Evaluation: Medications for Clostridium difficile Infection
 Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Copyright 2012 Oregon State University. All Rights Reserved Drug Use Research & Management Program Oregon State University, 500 Summer Street NE, E35 Salem, Oregon 97301-1079 Phone 503-947-5220 Fax 503-947-1119
Clinical characteristics of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea among patients in a tertiary care center in China
 Open Access Original Article Clinical characteristics of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea among patients in a tertiary care center in China Yongqiang Li 1, Yi Huang 2, Yuyuan Li 3, Yuqiang Nie
Open Access Original Article Clinical characteristics of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea among patients in a tertiary care center in China Yongqiang Li 1, Yi Huang 2, Yuyuan Li 3, Yuqiang Nie
Research Article Predictive Factors for Medical Consultation for Sore Throat in Adults with Recurrent Pharyngotonsillitis
 International Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 6095689, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6095689 Research Article Predictive Factors for Medical Consultation for Sore Throat in Adults with
International Otolaryngology Volume 2016, Article ID 6095689, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6095689 Research Article Predictive Factors for Medical Consultation for Sore Throat in Adults with
Journey to Decreasing Clostridium Difficile and the Unexpected Twist. Jackie Morton, Infection Prevention Cortney Swiggart, Medication Safety Officer
 Journey to Decreasing Clostridium Difficile and the Unexpected Twist Jackie Morton, Infection Prevention Cortney Swiggart, Medication Safety Officer 4/13/2018 Objectives Discuss the organism and clinical
Journey to Decreasing Clostridium Difficile and the Unexpected Twist Jackie Morton, Infection Prevention Cortney Swiggart, Medication Safety Officer 4/13/2018 Objectives Discuss the organism and clinical
Consequences of Clostridium difficile infection: understanding the healthcare burden
 REVIEW 10.1111/1469-0691.12064 Consequences of Clostridium difficile infection: understanding the healthcare burden E. Bouza 1,2 1) Department of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Hospital General
REVIEW 10.1111/1469-0691.12064 Consequences of Clostridium difficile infection: understanding the healthcare burden E. Bouza 1,2 1) Department of Microbiology and Infectious Diseases, Hospital General
Antimicrobial Use and Risk for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection
 CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Antimicrobial Use and Risk for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection Dimitri M. Drekonja, MD, MS, a,b William H. Amundson, BA, c Douglas D. DeCarolis, PharmD, a,d Michael A.
CLINICAL RESEARCH STUDY Antimicrobial Use and Risk for Recurrent Clostridium difficile Infection Dimitri M. Drekonja, MD, MS, a,b William H. Amundson, BA, c Douglas D. DeCarolis, PharmD, a,d Michael A.
NHS Suffolk Drug & Therapeutics Committee New Medicine Report (Adopted by the CCG until review and further notice)
 NHS Suffolk Drug & Therapeutics Committee New Medicine Report (Adopted by the CCG until review and further notice) This drug has been reviewed because it is a product that may be prescribed in primary
NHS Suffolk Drug & Therapeutics Committee New Medicine Report (Adopted by the CCG until review and further notice) This drug has been reviewed because it is a product that may be prescribed in primary
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has emerged. Incidence of Clostridium difficile Infection in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:339 344 Incidence of Clostridium difficile Infection in Inflammatory Bowel Disease JOSEPH F. RODEMANN,* ERIK R. DUBBERKE, KIMBERLY A. RESKE, DA HEA SEO,*
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:339 344 Incidence of Clostridium difficile Infection in Inflammatory Bowel Disease JOSEPH F. RODEMANN,* ERIK R. DUBBERKE, KIMBERLY A. RESKE, DA HEA SEO,*
Primary Endpoint The primary endpoint is overall survival, measured as the time in weeks from randomization to date of death due to any cause.
 CASE STUDY Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial of NES-822 plus AMO-1002 vs. AMO-1002 alone as first-line therapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer This is a multicenter, randomized Phase
CASE STUDY Randomized, Double-Blind, Phase III Trial of NES-822 plus AMO-1002 vs. AMO-1002 alone as first-line therapy in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer This is a multicenter, randomized Phase
Development and Validation of a Recurrent Clostridium difficile Risk-Prediction Model
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Development and Validation of a Recurrent Clostridium difficile Risk-Prediction Model Marya D. Zilberberg, MD, MPH 1,2 *, Kimberly Reske, MPH 3, Margaret Olsen, PhD, MPH 3, Yan Yan, MD,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Development and Validation of a Recurrent Clostridium difficile Risk-Prediction Model Marya D. Zilberberg, MD, MPH 1,2 *, Kimberly Reske, MPH 3, Margaret Olsen, PhD, MPH 3, Yan Yan, MD,
