Neuropathic Pain. Peripheral changes Spontaneous pain. Specific Na + channel blockers. Peripheral mechanisms and spinal inputs PAG RVM.
|
|
|
- Morgan Jones
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Neuropathic Pain Fear, anxiety, sleep, punishment autonomic changes Limbic System Parabrachial PAG attention Location & intensity Cortex Thalamus VPL Descending controls allow top down processes to enhance pain-link mood, sleep and pain Dorsal Columns RVM PAG = periaqueductal gray RVM = rostroventromedial medulla VPL = thalamic nucleus ventroposterior lateralis Marie Fallon St Columba s Hospice Chair of Palliative Medicine University of Edinburgh PRC Trondheim Lamina I Spinal changes Peripheral mechanisms and spinal inputs Lamina V Motor activation/autonomic C fibres Peripheral changes Spontaneous pain A-beta fibres Ectopic discharges? Initiated by cytokine effects Spinal cord changes Amplification of response Anatomical : silent synapses Chemical: changes in receptors Electrical: central sensitisation Dorsal root ganglia Neurotransmitter changes Specific Na + channel blockers Altered Na + channel subtypes Increased afferent volley 1
2 Central sensitization Different pains, different mechanisms C fibres NMDA receptor wind up A-beta fibres Nociceptive pain Pain caused by an inflammatory or noninflammatory response to a noxious stimulus Tissue damage Neuropathic pain Pain initiated or caused by a primary lesion or disease in the peripheral or central nervous system Nerve distribution Generalized pain No tissue or nerve damage Cancer pain: extra layer, e.g. cytokines and other tumour-related factors Noradrenaline and 5HT NMDA antagonists Ion channels Na channels go K channels brakes Ca channels release of neurotransmitters Calcium channels Potassium channels Sodium channels Antidepressants Amitriptyline, Duloxetine Anticonvulsants Pregabalin, Gabapentin Opioids NMDA Antagonists Ketamine Topical Lidocaine,Capsaicin 8% patches Treatment Treatment is challenging Often limited by side effects No predictors of response, largely empirical approach Potential of linking somatosensory profile with underlying neurobiology and treatment response Finnerup et al, Pain 118 (2005) Maier et al Pain 2010, Tan et al BMJ (2010) 340,
3 BUT MOST INTENSELY PURSUED NEW STRATEGIES ARE WITH THE TRANSIENT RECEPTOR POTENTIAL (TRP) ION CHANNELS Nature Reviews 2010 Wolff TRPM8 cool analgesia? Expressed on subset of small primary afferent nerve fibres Up-regulated after nerve injury Topical application of TRPM8 agonists (icilin) in animal models Mechanism of TRPM8 analgesia Behavioural evidence of thermal and mechanical analgesia Proudfoot at al, Current Biol. 2006; 6; Fleetwood-Walker 3
4 Topical menthol: Bench to bedside An example of a novel clinical intervention using TRP channel knowledge and clinical biomarkers Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy (CIPN) is common. 60,000 patients/year in UK, receive potentially neurotoxic chemotherapy. CIPN affects up to 96% 50% require dose reduction or early cessation of treatment Platinums, taxanes, vinca alkaloids,proteosome inhibitors Mechanisms poorly understood No effective treatment available 1 year on, 35-50% patients still have symptoms Individual predictors of CIPN not currently available Significant implications for palliative care Chronic Chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy Glove and stocking distribution Predominantly Sensory Numbness Pins and needles / tingling / pain / burning Hyperalgesia (increased response to normally painful stimulus) Allodynia (pain in response to innocuous stimulus) Proprioception difficulties Functional impairment Fine motor tasks Fastening buttons / jewellery / keyboard Carrying coffee cups Walking Driving 35% still have symptoms 1 year after adjuvant chemotherapy (Storey et al, Ann. Oncol 2010;21(8): ) Proof-of-concept study: Topical menthol and neuropathic pain Aims Assess efficacy and safety of 6 weeks of topical 1% menthol for neuropathic pain (Brief Pain Inventory) Determine associations between changes in pain and Other subjective patient rated outcomes» Psychological distress» Catastrophising Objective assessments» Quantitative Sensory Testing» Physical function 4
5 Chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy patients Patients with neuropathic pain (post- treatment chemotherapy induced neuropathy subgroup) Eligible if BPI average score of 4 n=29 Median age 63 years (range 46 to 76) Female = 52% (n=15) Median 16 months since last chemo (range 2 to 35) Oxaliplatin (n=21) Cisplatin (n=3) Bortezomib (n=2) Taxanes (n=2) Carboplatin (n=1) All had CTC grade 2/3 neurosensory toxicity Approx 2/3 had tried medication for neuropathic pain Proof-of-concept study: Topical menthol and neuropathic pain Methods Open label study Applied topical menthol cream to affected areas and skin overlying corresponding dorsal root ganglia Twice daily for 6 weeks Subjective and Objective assessments Assessed at baseline, 2 and 6 weeks Questionnaire Brief Pain Inventory Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale Pain Catastrophising Scale Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs Bedside Quantitative Sensory Testing Mechanical detection threshold Mechanical pain threshold Allodynia (calibrated brush) Wind up ratio Physical function (gait and hand dexterity) Exploratory analysis METHODS - Quantitative Sensory Testing Mechanical stimuli (dorsal web space between 1 st and 2 nd digit of right hand & foot) Calibrated brush Von Frey Hairs Pin prick Dynamic allodynia Mechanical Sensation/ pain thresholds Mechanical hypo/hyperalgesia Wind up Thermal stimuli (also distal portion of arm and leg) Rolltemp Cool Warm Thermal hypo/ hyperalgesia A beta fibres A beta fibres Ad delta fibres A delta and C fibres 5
6 METHODS Physical function assessments Gaitrite electronic walkway Slotted grooved peg board (walking velocity + cadence) (hand dexterity) Mean total pain score (BPI) Pain improved after 6 weeks of topical menthol p = BASELINE 2 WEEKS 6 WEEKS p = (6/29) dropped out after 2 weeks 2 had exacerbations of pain 3 did not like the cream 1 developed brain metastases 83% (19/23) had improved pain scores 52% (12/23) had 30% decrease in mean total BPI (clinically relevant) Pain improved after 6 weeks and also.. Subjective measures Less psychological distress (HADS 9 vs. 8.5, p= 0.042) Less catastrophising ( PCS 14.5 vs. 10, p= 0.004) No change in Leeds Assessment of Neuropathic Signs and Symptoms Scale Objective measures Faster hand dexterity ( 101 vs. 92 seconds, p=0.014) Hand numbness improved (mechanical detection thresholds decreased) (1.10 vs grammes, p=0.011) Increased walking velocity (trend only) ( 79.5 vs 89 metres/sec 0.110) Peg board time P=0.014 Abnormal sensory areas decreased and moved distally Example of one patient: abnormal sensory areas to warm stimulus (for brush, baselinewarm, cool 6 weeks stimuli) Right side assessed only Median values for all patients Arm: 70% vs. 24%, p=0.004 Leg: 90% vs. 56% p=
7 Correlations with change (decrease) in pain scores between baseline and 6 weeks Strong correlation with improved Dominant hand dexterity (Correlation Coeff = 0.636, p = 0.011) walking velocity (.... = , p = 0.009) Walking cadence (.... = , p = 0.006) Moderate correlation with improved Psychological distress (HADS) (Correlation Coeff. = 0.442, p = 0.039) Foot mech. detection threshold (.... = 0.453, p = 0.034) (less numbness) Foot mech. pain thresholds (.... = 0.453, p = 0.034) (less numbness) Wind-up ratio (.... = 0.534, p = 0.009) (got less) Menthol - the future Potentially very exciting: Subjective improvements Reduced pain Reduced psych distress Reduced catastrophising Objective improvements improved physical function Improved quantitative sensory tests Future Further work on TRP channels Cytokine blockade Linking optimum therapy with somatosensory profile, other characteristics of individual patients Understanding role of current agents THE PATIENTS University of Edinburgh TRP Research Team Dr Lesley Colvin Prof S Fleetwood-Walker Dr Rory Mitchell Dr Dawn Storey Dr Angela Scott Thanks to Edinburgh Cancer Centre Colorectal Oncology Team Dr Catriona McLean Dr Sally Clive Dr Lesley Dawson Dr Ewan Brown Dr Hamish Phillips Joyce Livingstone Anna Clarkson Susan Mckean Gillian Knowles 7
8 Acute oxaliplatin induced peripheral neuropathy Oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy = standard treatment for colorectal cancer Peripheral neuropathy = dose limiting toxicity Acute (resolves within hours or days) 94% of patients (Storey et al, Ann. Oncol 2010;21(8): ) Cold related dysaesthesia peri-oral areas Hands/ feet Pseudolaryngospasm Muscle fasciculations / myotonia / tetanic spasms affecting face and limbs Cumulative/chronic (usually resolves in months/years) Menthol did not suit everyone 6 patients dropped out after 2 weeks (6/29) 2 had worse pain Not clear why oxaliplatin neuropathy 4 months and 3 years duration 1 = heavy alcohol intake. Other neuropathy mechanism?? (other = Tea total) Different TRPM8 action in some patients?? Resolved to baseline levels within a few weeks of stopping cream 3 did not like the cream 2 female, 1 male (older men a bit more reluctant to apply cream in general) [1 = progressive disease (brain mets)] 8
9 TRP channels-the future Menthol-Potentially very exciting Topical (not another tablet) Cheap But may worsen pain in some cases?? Anti-tumour activity? TRPM8 expressed on prostate, bladder, colorectal, breast, lung carcinomas and melanoma. Interest in TRPM8 agonists for cancer treatment Unanswered questions Placebo response? Duration of response? Dose? Need randomised controlled trial Chronic oxaliplatin induced peripheral neuropathy Glove and stocking distribution Predominantly Sensory Numbness Pins and needles / tingling / pain / burning Hyperalgesia (inc response to normally painful stimulus) Allodynia (pain in response to innocuous stimulus) Proprioception difficulties Functional impairment Fine motor tasks Fastening buttons / jewellery / keyboard Carrying coffee cups Walking Driving 35% still have symptoms 1 year after adjuvant treatment (Storey et al, Ann. Oncol 2010;21(8): ) Difficult to predict whose pain scores would change Only baseline predictors were mechanical detection thresholds Hands (correl coeff. = 0.534, p= 0.027) Feet (correl coeff. = 0.511, p=0.036) But heavily influenced by 1 patient so not reliable Treatment duration Primary endpoint baseline 2 weeks 6 weeks (12 wks) (24 wks) n still on menthol n stopped menthol after this Reason for stopping Pain gone / improved and plateaued No benefit Pain worse Did not like cream Non compliant (withdrawn by investigator)
10 Chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy Common dose- limiting chemotherapy toxicity Platinums Taxanes Vinca Alkaloids Proteosome inhibitors newer drugs Can affect up to 98% of patients depending on the drug Acute (resolves within days) Chronic (resolves within months..supposedly) Prevents patients getting the life saving/prolonging treatment they need Leaves survivors with long term debilitating symptoms Complicates symptom control in advancing disease The Spinal Cord (1 st central synapse) Amino Acids Excitatory Glutamate AMPA NMDA Metabotropic p Inhibitory GABA Glycine C fibres A-beta fibres 10
11 TRP family of ion channels Thermal sensation TRPV1-4 TRPA1 TRPM8: cooling sensation Temp ( C ) Mint Menthol and related compounds TRPM8 cool analgesia? Expressed on subset of small primary afferents Up-regulated after nerve injury Topical application of TRPM8 agonists Behavioural evidence of thermal and mechanical analgesia Proudfoot at al, 2006 Cooling analgesia Menthol (mint) and related products used in traditional medicines as analgesics Mechanism previously not known TRP family of ion channels (found in sensory neurons) Transient Receptor Potential (TRP) ion channels (transducers) transform stimuli into action potentials Revolutionised understanding of cutaneous temperature detection TRPV1, TRPA1 (noxious heat and cold (<5 C ).etc TRPM8: moderate cooling sensation Temp (18-24 C ) Activated by menthol (mint) and related compounds Noxious stimulus Dynamic system Modulation at each level Pain pathway Dorsal root ganglia Neurotransmitter changes Increased afferent volley Peripheral Spinal cord Brain Further amplification 11
12 Peripheral afferent changes: chemical Thermal sensation: TRPV1 TRPA1 TRPM8 Thermal Mechanical Chemical Retrograde transport blocked/ altered Primary afferent phenotype changes Growth factors Cytokines Peptides Proudfoot,C. Current Biology (2006), Brief Pain Inventory Effects of topical menthol QST: Rapid improvement esp in mechanical responses HADs: reduced from 22 to 14 at 2 weeks Subsequently able to tolerate further chemotherapy Least pain Average pain Worst pain General activity Colvin,Johnstone,Mitchell,Fleetwood-Walker,Fallon (JCO, Sept 2008) 12
Pain Pathways. Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH
 Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Pain Pathways Dr Sameer Gupta Consultant in Anaesthesia and Pain Management, NGH Objective To give you a simplistic and basic concepts of pain pathways to help understand the complex issue of pain Pain
Neuropathic Pain in Palliative Care
 Neuropathic Pain in Palliative Care Neuropathic Pain in Advanced Cancer Affects 40% of patients Multiple concurrent pains are common Often complex pathophysiology with mixed components Nocioceptive Neuropathic
Neuropathic Pain in Palliative Care Neuropathic Pain in Advanced Cancer Affects 40% of patients Multiple concurrent pains are common Often complex pathophysiology with mixed components Nocioceptive Neuropathic
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation
 Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Pharmacology of Pain Transmission and Modulation 2 Jürg Schliessbach and Konrad Maurer Nociceptive Nerve Fibers Pain is transmitted to the central nervous system via thinly myelinated Aδ and unmyelinated
Spinal Cord Injury Pain. Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018
 Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Spinal Cord Injury Pain Michael Massey, DO CentraCare Health St Cloud, MN 11/07/2018 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, participants should be able to: 1. Understand the difference between nociceptive
Cancer-induced bone pain
 Cancer-induced bone pain Common Prevalent in particular cancers: breast (73%), prostate (68%), thyroid (42%), lung (36%), renal (35%), colon (5%) Correlates with an increased morbidity Reduced performance
Cancer-induced bone pain Common Prevalent in particular cancers: breast (73%), prostate (68%), thyroid (42%), lung (36%), renal (35%), colon (5%) Correlates with an increased morbidity Reduced performance
San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001
 PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
PAIN San Francisco Chronicle, June 2001 CONGENITAL INSENSITIVITY TO PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional)
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me. Agenda. What We Know About Pain 9/7/2012
 Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Receptors and Neurotransmitters: It Sounds Greek to Me Cathy Carlson, PhD, RN Northern Illinois University Agenda We will be going through this lecture on basic pain physiology using analogies, mnemonics,
Pathophysiology of Pain. Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC
 Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Pathophysiology of Pain Ramon Go MD Assistant Professor Anesthesiology and Pain medicine NYP-CUMC Learning Objectives Anatomic pathway of nociception Discuss the multiple target sites of pharmacological
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor
 Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Introduction to some interesting research questions: Molecular biology of the primary afferent nociceptor NOCICEPTORS ARE NOT IDENTICAL PEPTIDE SubP/CGRP Trk A NON-PEPTIDE IB4 P2X 3 c-ret Snider and McMahon
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D.
 Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
Somatosensory Physiology (Pain And Temperature) Richard M. Costanzo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture the student should be familiar with: 1. The relationship between nociception
Pain teaching. Muhammad Laklouk
 Pain teaching Muhammad Laklouk Definition Pain An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage. Sensory (discriminatiory)
Pain teaching Muhammad Laklouk Definition Pain An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage or described in terms of such damage. Sensory (discriminatiory)
Pathophysiology of Pain
 Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Pathophysiology of Pain Wound Inflammatory response Chemical mediators Activity in Pain Path PAIN http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter08.html Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Assessment of animal pain and mechanism-based strategies for its reversal Citation for published version: Fleetwood-Walker, S, Sun, L, Jerina, H & Mitchell, R 2012, 'Assessment
Edinburgh Research Explorer Assessment of animal pain and mechanism-based strategies for its reversal Citation for published version: Fleetwood-Walker, S, Sun, L, Jerina, H & Mitchell, R 2012, 'Assessment
What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. Pain is always subjective
 Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
Pain & Acupuncture What is Pain? An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage. NOCICEPTION( the neural processes of encoding and processing noxious stimuli.)
PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus. MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive
 PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
PAIN PAIN IS A SUBJECTIVE EXPERIENCE: It is not a stimulus MAJOR FEATURES OF THE PAIN EXPERIENCE: Sensory discriminative Affective (emotional) Cognitive MEASUREMENT OF PAIN: A BIG PROBLEM Worst pain ever
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD
 Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Brian Kahan, D.O. FAAPMR, DABPM, DAOCRM, FIPP Center for Pain Medicine and Physiatric Rehabilitation 2002 Medical Parkway Suite 150 Annapolis, MD 1630 Main Street Suite 215 Chester, MD 410-571-9000 www.4-no-pain.com
Tony Dickenson, Neuroscience, Physiology and Pharmacology University College London PAIN - WHAT DOES IT DO TO US, AND WHAT CAN WE DO ABOUT IT?
 Tony Dickenson, Neuroscience, Physiology and Pharmacology University College London PAIN - WHAT DOES IT DO TO US, AND WHAT CAN WE DO ABOUT IT? Cortex - where and how much pain Limbic areas - unpleasantness
Tony Dickenson, Neuroscience, Physiology and Pharmacology University College London PAIN - WHAT DOES IT DO TO US, AND WHAT CAN WE DO ABOUT IT? Cortex - where and how much pain Limbic areas - unpleasantness
Refractory Central Neurogenic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury. Case Presentation
 Refractory Central Neurogenic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury Case Presentation Edwin B. George, MD, PhD Wayne State University John D. Dingell VAMC 2012 Disclosures This continuing education activity is managed
Refractory Central Neurogenic Pain in Spinal Cord Injury Case Presentation Edwin B. George, MD, PhD Wayne State University John D. Dingell VAMC 2012 Disclosures This continuing education activity is managed
The anatomy and physiology of pain
 The anatomy and physiology of pain Charlotte E Steeds Abstract Pain is an unpleasant experience that results from both physical and psychological responses to injury. A complex set of pathways transmits
The anatomy and physiology of pain Charlotte E Steeds Abstract Pain is an unpleasant experience that results from both physical and psychological responses to injury. A complex set of pathways transmits
Sensory coding and somatosensory system
 Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Sensory coding and somatosensory system Sensation and perception Perception is the internal construction of sensation. Perception depends on the individual experience. Three common steps in all senses
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress REDUCING THE PAIN FACTOR AN UPDATE ON PERI-OPERATIVE ANALGESIA Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of Veterinary,
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress REDUCING THE PAIN FACTOR AN UPDATE ON PERI-OPERATIVE ANALGESIA Sandra Forysth, BVSc DipACVA Institute of Veterinary,
Pain Mechanisms. Prof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong. The Somatosensory System
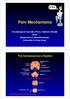 ain Mechanisms rof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong The Somatosensory System Frontal cortex Descending pathway eriaqueductal gray matter
ain Mechanisms rof Michael G Irwin MD, FRCA, FANZCA FHKAM Head Department of Anaesthesiology University of Hong Kong The Somatosensory System Frontal cortex Descending pathway eriaqueductal gray matter
THE ROLE OF HIGH FREQUENCY ELECTRICAL STIMULATION IN THE CHEMOTHERAPY INDUCED PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY POPULATION: A CASE SERIES
 THE ROLE OF HIGH FREQUENCY ELECTRICAL STIMULATION IN THE CHEMOTHERAPY INDUCED PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY POPULATION: A CASE SERIES Kathleen Fortier, PT, DPT, MBA Background Chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy
THE ROLE OF HIGH FREQUENCY ELECTRICAL STIMULATION IN THE CHEMOTHERAPY INDUCED PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY POPULATION: A CASE SERIES Kathleen Fortier, PT, DPT, MBA Background Chemotherapy induced peripheral neuropathy
Basic Neuroscience. Sally Curtis
 The Physiology of Pain Basic Neuroscience Sally Curtis sac3@soton.ac.uk The behaviour of humans is a result of the actions of nerves. Nerves form the basis of Thoughts, sensations and actions both reflex
The Physiology of Pain Basic Neuroscience Sally Curtis sac3@soton.ac.uk The behaviour of humans is a result of the actions of nerves. Nerves form the basis of Thoughts, sensations and actions both reflex
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
Pain classifications slow and fast
 Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
Pain classifications slow and fast Fast Pain Slow Pain Sharp, pricking (Aδ) fiber Short latency Well localized Short duration Dull, burning (C) fiber Slower onset Diffuse Long duration Less emotional Emotional,
1/21/14. Barriers to Assessment and Management of Chemotherapy- Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Conflicts of Interest. Learning Objective
 Barriers to Assessment and Management of Chemotherapy- Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Connie Visovsky, PhD, RN, ACNP-BC Associate Dean University of South Florida College of Nursing Conflicts of Interest
Barriers to Assessment and Management of Chemotherapy- Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Connie Visovsky, PhD, RN, ACNP-BC Associate Dean University of South Florida College of Nursing Conflicts of Interest
What it Takes to be a Pain
 What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
What it Takes to be a Pain Pain Pathways and the Neurophysiology of pain Dennis S. Pacl, MD, FACP, FAChPM Austin Palliative Care/ Hospice Austin A Definition of Pain complex constellation of unpleasant
What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle.
 What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle. Nociception The detection of tissue damage or impending tissue damage, but There can be tissue damage without
What is pain?: An unpleasant sensation. What is an unpleasant sensation?: Pain. - Aristotle. Nociception The detection of tissue damage or impending tissue damage, but There can be tissue damage without
Neuropathic Pain. Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC
 Neuropathic Pain Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC Pain is our friend "An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described
Neuropathic Pain Scott Magnuson, MD Pain Management of North Idaho, PLLC Pain is our friend "An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described
Psychophysical laws. Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 )
 Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
Psychophysical laws Legge di Weber: ΔS=K*S Legge di Fechner: I=K*log(S/S 0 ) Sensory receptors Vision Smell Taste Touch Thermal senses Pain Hearing Balance Proprioception Sensory receptors Table 21-1 Classification
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN A 21 year old man presented with a stab wound of the right side of the neck (Panel A). Neurological examination revealed right hemiplegia and complete right-sided loss of
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS AND PAIN A 21 year old man presented with a stab wound of the right side of the neck (Panel A). Neurological examination revealed right hemiplegia and complete right-sided loss of
Seizure: the clinical manifestation of an abnormal and excessive excitation and synchronization of a population of cortical
 Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Are There Sharing Mechanisms of Epilepsy, Migraine and Neuropathic Pain? Chin-Wei Huang, MD, PhD Department of Neurology, NCKUH Basic mechanisms underlying seizures and epilepsy Seizure: the clinical manifestation
Complicated pain. Dr Stephanie Lippett
 Complicated pain Dr Stephanie Lippett UK incidence & prevalence of cancer pain 1% of UK population are living with cancer at present 70% of cancer patients experience pain 70-90% of patients with advanced
Complicated pain Dr Stephanie Lippett UK incidence & prevalence of cancer pain 1% of UK population are living with cancer at present 70% of cancer patients experience pain 70-90% of patients with advanced
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT
 PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
PAIN MANAGEMENT in the CANINE PATIENT Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT Part 1: Laurie Edge-Hughes, BScPT, MAnimSt (Animal Physio), CAFCI, CCRT 1 Pain is the most common reason
Neurobiology of Pain Adjuvant analgesia
 Neurobiology of Pain Adjuvant analgesia Jason Brooks Consultant Anaesthesia and Pain Management BCH March 2017 The Brief A broad overview of the abnormal and normal anatomy and physiology of pain pathways
Neurobiology of Pain Adjuvant analgesia Jason Brooks Consultant Anaesthesia and Pain Management BCH March 2017 The Brief A broad overview of the abnormal and normal anatomy and physiology of pain pathways
Common Side Effects. Fatigue Neuropathy Hot flashes
 Common Side Effects Fatigue Neuropathy Hot flashes Fatigue According to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2017), cancer related fatigue is defined as a distressing, persistent, subjective sense
Common Side Effects Fatigue Neuropathy Hot flashes Fatigue According to the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (2017), cancer related fatigue is defined as a distressing, persistent, subjective sense
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014
 UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY NEUROPHYSIOLOGY (MEDICAL), SPRING 2014 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition 2011 Eman Al-Khateeb,
Preventing and managing neurotoxicity by oncologists and neurologists
 Preventing and managing neurotoxicity by oncologists and neurologists Thomas Hundsberger Department of Neurology and Department of Haematology/Oncology Cantonal hospital St. Gallen Switzerland Long-term
Preventing and managing neurotoxicity by oncologists and neurologists Thomas Hundsberger Department of Neurology and Department of Haematology/Oncology Cantonal hospital St. Gallen Switzerland Long-term
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007)
 Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
Somatic Sensation (MCB160 Lecture by Mu-ming Poo, Friday March 9, 2007) Introduction Adrian s work on sensory coding Spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia Four somatic sense modalities Touch Mechanoreceptors
211MDS Pain theories
 211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
211MDS Pain theories Definition In 1986, the International Association for the Study of Pain (IASP) defined pain as a sensory and emotional experience associated with real or potential injuries, or described
1 The Physiology of Pain
 1 The Physiology of Pain Rohit Juneja and Siân Jaggar Introduction Definitions Key Messages Pain is still underdiagnosed and undertreated. Pain is a subjective experience and may even be present in the
1 The Physiology of Pain Rohit Juneja and Siân Jaggar Introduction Definitions Key Messages Pain is still underdiagnosed and undertreated. Pain is a subjective experience and may even be present in the
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
PAIN TERMINOLOGY TABLE
 PAIN TERMINOLOGY TABLE TERM DEFINITION HOW TO USE CLINICALLY Acute Pain Pain that is usually temporary and results from something specific, such as a surgery, an injury, or an infection Addiction A chronic
PAIN TERMINOLOGY TABLE TERM DEFINITION HOW TO USE CLINICALLY Acute Pain Pain that is usually temporary and results from something specific, such as a surgery, an injury, or an infection Addiction A chronic
The Somatosensory System
 The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
The Somatosensory System Reading: BCP Chapter 12 cerebrovortex.com Divisions of the Somatosensory System Somatosensory System Exteroceptive External stimuli Proprioceptive Body position Interoceptive Body
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways.
 Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
Last time we talked about the descending pathways of pain and the ALS. Today we will continue talking about these descending pathways. Each higher level will control the level under It. In controlling
Transition from acute to chronic pain
 A Feizerfan FRCA G Sheh BHB MBChB FAFRM(RACP) FFPMANZCA Matrix reference 3E00 Key points Physiology of pain involves activation and complex interactions of autonomic, peripheral and central nervous systems,
A Feizerfan FRCA G Sheh BHB MBChB FAFRM(RACP) FFPMANZCA Matrix reference 3E00 Key points Physiology of pain involves activation and complex interactions of autonomic, peripheral and central nervous systems,
Somatic Sensory System I. Background
 Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Somatic Sensory System I. Background A. Differences between somatic senses and other senses 1. Receptors are distributed throughout the body as opposed to being concentrated at small, specialized locations
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT
 Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
Acute Pain NETP: SEPTEMBER 2013 COHORT Pain & Suffering an unpleasant sensory & emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage International
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
CHAPTER 10 THE SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEM 10.1. SOMATOSENSORY MODALITIES "Somatosensory" is really a catch-all term to designate senses other than vision, hearing, balance, taste and smell. Receptors that could
PAIN MANAGEMENT IN CHILDREN
 SIOP PODC Supportive Care Education (ICON 2016) Presentation Date: 23 rd January 2016 PAIN MANAGEMENT IN CHILDREN Aziza Shad, MD Ellen Wasserman Chair of Pediatrics Chief, Division of Pediatric Hematology
SIOP PODC Supportive Care Education (ICON 2016) Presentation Date: 23 rd January 2016 PAIN MANAGEMENT IN CHILDREN Aziza Shad, MD Ellen Wasserman Chair of Pediatrics Chief, Division of Pediatric Hematology
ANAT2010. Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018
 ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
ANAT2010 Concepts of Neuroanatomy (II) S2 2018 Table of Contents Lecture 13: Pain and perception... 3 Lecture 14: Sensory systems and visual pathways... 11 Lecture 15: Techniques in Neuroanatomy I in vivo
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sat, 03 Nov 2018 09:24:50 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 10/06/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Sat, 03 Nov 2018 09:24:50 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 10/06/2013 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Pain and Temperature Objectives
 Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Various Types of Pain Defined
 Various Types of Pain Defined Pain: The International Association for the Study of Pain describes pain as, An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage,
Various Types of Pain Defined Pain: The International Association for the Study of Pain describes pain as, An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage,
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
Chronic pain: We should not underestimate the contribution of neural plasticity. *Gwyn N Lewis 1, David A Rice 1,2
 Chronic pain: We should not underestimate the contribution of neural plasticity *Gwyn N Lewis 1, David A Rice 1,2 1 Health and Rehabilitation Research Institute, AUT University, Auckland, New Zealand 2
Chronic pain: We should not underestimate the contribution of neural plasticity *Gwyn N Lewis 1, David A Rice 1,2 1 Health and Rehabilitation Research Institute, AUT University, Auckland, New Zealand 2
Neuropathic Pain Treatment Guidelines
 Neuropathic Pain Treatment Guidelines Background Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience that can have a significant impact on a person s quality of life, general health, psychological health,
Neuropathic Pain Treatment Guidelines Background Pain is an unpleasant sensory and emotional experience that can have a significant impact on a person s quality of life, general health, psychological health,
All questions below pertain to mandatory material: all slides, and mandatory homework (if any).
 ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
ECOL 182 Spring 2008 Dr. Ferriere s lectures Lecture 6: Nervous system and brain Quiz Book reference: LIFE-The Science of Biology, 8 th Edition. http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire8e/ All questions below
Peripheral neuropathy
 Peripheral neuropathy This Infosheet explains what the peripheral nervous system is, what peripheral neuropathy is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, its symptoms and treatments and tips for self-management.
Peripheral neuropathy This Infosheet explains what the peripheral nervous system is, what peripheral neuropathy is, what causes it in AL amyloidosis patients, its symptoms and treatments and tips for self-management.
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense
 The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
The Physiology of the Senses Chapter 8 - Muscle Sense www.tutis.ca/senses/ Contents Objectives... 1 Introduction... 2 Muscle Spindles and Golgi Tendon Organs... 3 Gamma Drive... 5 Three Spinal Reflexes...
Gabapentin and pregabalin
 Pain CONCERN Medicines for long-term pain Gabapentin and pregabalin This leaflet is about gabapentin and pregabalin, two drugs which are part of a group sometimes called gabapentinoids. The leaflet will
Pain CONCERN Medicines for long-term pain Gabapentin and pregabalin This leaflet is about gabapentin and pregabalin, two drugs which are part of a group sometimes called gabapentinoids. The leaflet will
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT
 CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
CHAPTER 4 PAIN AND ITS MANAGEMENT Pain Definition: An unpleasant sensory and emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Types of Pain
Name Biology 125 Midterm #2 ( ) Total Pages: 9
 Name - 1 - Biology 125 Midterm #2 (11-15-07) Part 1: (30 pts) Part 2: (40 pts) Part 3: (6 pts) Part 4: (12 pts) Part 5: (12 pts) Total Pages: 9 Total Score: (100 pts) 1 Name - 2 - Part 1: True or False.
Name - 1 - Biology 125 Midterm #2 (11-15-07) Part 1: (30 pts) Part 2: (40 pts) Part 3: (6 pts) Part 4: (12 pts) Part 5: (12 pts) Total Pages: 9 Total Score: (100 pts) 1 Name - 2 - Part 1: True or False.
SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE
 Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
Dental Neuroanatomy Thursday, February 3, 2011 Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD SOMATIC SENSATION PART I: ALS ANTEROLATERAL SYSTEM (or SPINOTHALAMIC SYSTEM) FOR PAIN AND TEMPERATURE Reading: Waxman 26 th ed, :
UCSF Pediatric Hospital Medicine Boot Camp Pain Session 6/21/14. Cynthia Kim and Stephen Wilson
 UCSF Pediatric Hospital Medicine Boot Camp Pain Session 6/21/14 Cynthia Kim and Stephen Wilson Rules Buzz first and player answers If answer correct, then the player asks teammates if they want to keep
UCSF Pediatric Hospital Medicine Boot Camp Pain Session 6/21/14 Cynthia Kim and Stephen Wilson Rules Buzz first and player answers If answer correct, then the player asks teammates if they want to keep
Pain and impulse conduction
 1 Pain and impulse conduction L.H.D.J. Booij According to the World Health Organisation pain is defined as an unpleasant sensation that occurs from imminent tissue damage. From a physiological perspective,
1 Pain and impulse conduction L.H.D.J. Booij According to the World Health Organisation pain is defined as an unpleasant sensation that occurs from imminent tissue damage. From a physiological perspective,
Intracellular signalling cascades associated with TRP channels
 Gerald Thiel Intracellular signalling cascades associated with TRP channels Current state of investigations and potential applications Saarland University, Germany Campus Saarbrücken Department of Medical
Gerald Thiel Intracellular signalling cascades associated with TRP channels Current state of investigations and potential applications Saarland University, Germany Campus Saarbrücken Department of Medical
Management of Neuropathic pain
 Management of Neuropathic pain Ravi Parekodi Consultant in Anaesthetics and Pain Management 08/04/2014 Ref: BJA July2013, Map of Medicine2013, Pain Physician 2007, IASP 2012, Nice guideline 2013 Aims Highlight
Management of Neuropathic pain Ravi Parekodi Consultant in Anaesthetics and Pain Management 08/04/2014 Ref: BJA July2013, Map of Medicine2013, Pain Physician 2007, IASP 2012, Nice guideline 2013 Aims Highlight
Infosheet. Peripheral neuropathy. What is peripheral neuropathy? The peripheral nervous system
 Infosheet Peripheral neuropathy What is peripheral neuropathy? Peripheral neuropathy is the term used to describe damage to the nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system. In myeloma the nerves
Infosheet Peripheral neuropathy What is peripheral neuropathy? Peripheral neuropathy is the term used to describe damage to the nerves that make up the peripheral nervous system. In myeloma the nerves
The Nervous System. Chapter 4. Neuron 3/9/ Components of the Nervous System
 Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
Chapter 4 The Nervous System 1. Components of the Nervous System a. Nerve cells (neurons) Analyze and transmit information Over 100 billion neurons in system Four defined regions Cell body Dendrites Axon
High-dose 8% capsaicin patch in treatment of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy: single-center experience
 Med Oncol (2017) 34:162 DOI 10.1007/s12032-017-1015-1 ORIGINAL PAPER High-dose 8% capsaicin patch in treatment of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy: single-center experience Iwona Filipczak-Bryniarska
Med Oncol (2017) 34:162 DOI 10.1007/s12032-017-1015-1 ORIGINAL PAPER High-dose 8% capsaicin patch in treatment of chemotherapyinduced peripheral neuropathy: single-center experience Iwona Filipczak-Bryniarska
Lesson 14. The Nervous System. Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1
 Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Lesson 14 The Nervous System Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Structures and Functions of Nerve Cells The nervous system has two principal cell types: Neurons (nerve cells) Glia The functions
Overview of Neuropathic pain
 Overview of Neuropathic pain Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn,M.D. Neurology division Thammasat University 1 Contents Overview of pain New concepts and mechanism Treatment options New data in management 2 3 Breaking
Overview of Neuropathic pain Kongkiat Kulkantrakorn,M.D. Neurology division Thammasat University 1 Contents Overview of pain New concepts and mechanism Treatment options New data in management 2 3 Breaking
Pain. Types of Pain. Types of Pain 8/21/2013
 Pain 1 Types of Pain Acute Pain Complex combination of sensory, perceptual, & emotional experiences as a result of a noxious stimulus Mediated by rapidly conducting nerve pathways & associated with increased
Pain 1 Types of Pain Acute Pain Complex combination of sensory, perceptual, & emotional experiences as a result of a noxious stimulus Mediated by rapidly conducting nerve pathways & associated with increased
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00
 Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Shift 1, 8 July 2018, 09:30-13:00 CNS patterning A001-A014 Stem cells: basic biology and postnatal neurogenesis - part I Development of neural systems: Molecular and genetic characterisationa Epigenetic
Peripheral neuropathy (PN)
 Peripheral neuropathy (PN) damage or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health, depending on the type of nerve affected o chronic:
Peripheral neuropathy (PN) damage or disease affecting nerves, which may impair sensation, movement, gland or organ function, or other aspects of health, depending on the type of nerve affected o chronic:
Managing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
 Managing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain Juzar Hooker Consulting Neurologist, Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi juzar.hooker@aku.edu Disclosure Eli lilly (have not driven, reviewed or controlled
Managing Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain Juzar Hooker Consulting Neurologist, Aga Khan University Hospital, Nairobi juzar.hooker@aku.edu Disclosure Eli lilly (have not driven, reviewed or controlled
Management of Pain related to Spinal Cord Lesion
 Management of Pain related to Spinal Cord Lesion A Neurologist s Perspective Vincent Mok, MD Associate Professor Division of Neurology Department of Medicine and Therapeutics The Chinese University of
Management of Pain related to Spinal Cord Lesion A Neurologist s Perspective Vincent Mok, MD Associate Professor Division of Neurology Department of Medicine and Therapeutics The Chinese University of
NEUROFIX S MISSION & VISION
 NEUROFIX S MISSION & VISION MISSION Neurofix aims to discover and develop innovative therapies for the treatment of neurological disorders. Our main focus now is Spinal Cord Injury. VISION Spinal Cord
NEUROFIX S MISSION & VISION MISSION Neurofix aims to discover and develop innovative therapies for the treatment of neurological disorders. Our main focus now is Spinal Cord Injury. VISION Spinal Cord
INTERACTIVE QUESTIONS
 INTERACTIVE QUESTIONS Pathophysiology What is pain? Pathophysiology Does everyone feel pain the same way? Pathophysiology From a practical point of view, how do you classify pain? Pathophysiology What
INTERACTIVE QUESTIONS Pathophysiology What is pain? Pathophysiology Does everyone feel pain the same way? Pathophysiology From a practical point of view, how do you classify pain? Pathophysiology What
BEYOND OPIOIDS: ADJUNCTS FOR TREATING PAIN
 BEYOND OPIOIDS: ADJUNCTS FOR TREATING PAIN Ronald Januchowski, D.O. 2017 Objectives By the end of the presentation, the learner should be able to: Summarize the risks of opiates when used for non-cancer
BEYOND OPIOIDS: ADJUNCTS FOR TREATING PAIN Ronald Januchowski, D.O. 2017 Objectives By the end of the presentation, the learner should be able to: Summarize the risks of opiates when used for non-cancer
CHEMOTHERAPY-INDUCED PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY
 CHEMOTHERAPY-INDUCED PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY LONG-TERM OUTCOMES OF PACLITAXEL- INDUCED PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY FOR CANCER SURVIVORS Hannah Timmins Faculty Disclosure x No, nothing to disclose Yes, please specify:
CHEMOTHERAPY-INDUCED PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY LONG-TERM OUTCOMES OF PACLITAXEL- INDUCED PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY FOR CANCER SURVIVORS Hannah Timmins Faculty Disclosure x No, nothing to disclose Yes, please specify:
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8
 NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
NERVOUS SYSTEM C H A P T E R 2 8 CAN AN INJURED SPINAL CORD BE FIXED? Injuries to the spinal cord disrupt communication between the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the rest of the body
Painful Diabetic Neuropathy Effective Management. Ketan Dhatariya Consultant in Diabetes NNUH
 Painful Diabetic Neuropathy Effective Management Ketan Dhatariya Consultant in Diabetes NNUH Neuropathic Pain Prevalence varies between 10 and 90% depending on classification Accounts for 50-75% of non-traumatic
Painful Diabetic Neuropathy Effective Management Ketan Dhatariya Consultant in Diabetes NNUH Neuropathic Pain Prevalence varies between 10 and 90% depending on classification Accounts for 50-75% of non-traumatic
Chapter 7. Objectives
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Chapter 7 The Nervous System: Structure and Control of Movement Objectives Discuss the general organization of the nervous system Describe the structure & function of a nerve Draw and label the pathways
Other classical forms of neuropathic pain include diabetic peripheral neuropathy, trigeminal neuralgia and postherpetic
 Guideline Name: Neuropathic Pain Neuropathic pain is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain, Neuropathic Special Interest group as pain arising as a direct consequence of a lesion
Guideline Name: Neuropathic Pain Neuropathic pain is defined by the International Association for the Study of Pain, Neuropathic Special Interest group as pain arising as a direct consequence of a lesion
PAIN MODULATION. numerical value. adjectives. DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH
 PAIN MODULATION numerical value adjectives DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe:
PAIN MODULATION numerical value adjectives DR SYED SHAHID HABIB Professor & Consultant Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture you should be able to describe:
Peripheral neuropathy
 Peripheral neuropathy This Infosheet explains what peripheral neuropathy is, what causes it in myeloma patients, how it is treated and some tips for selfmanagement. What is peripheral neuropathy? Peripheral
Peripheral neuropathy This Infosheet explains what peripheral neuropathy is, what causes it in myeloma patients, how it is treated and some tips for selfmanagement. What is peripheral neuropathy? Peripheral
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015
 EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
EE 791 Lecture 2 Jan 19, 2015 Action Potential Conduction And Neural Organization EE 791-Lecture 2 1 Core-conductor model: In the core-conductor model we approximate an axon or a segment of a dendrite
Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix
 Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix Partap S. Khalsa, D.C., Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Engineering The Neuromatrix From: Melzack R (1999) Pain Suppl 6:S121-6. NIOSH STAR Symposium May
Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix Partap S. Khalsa, D.C., Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Engineering The Neuromatrix From: Melzack R (1999) Pain Suppl 6:S121-6. NIOSH STAR Symposium May
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
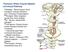 Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Peripheral neuropathy
 Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphoma-action.org.uk www.lymphoma-action.org.uk Peripheral neuropathy Peripheral neuropathy is damage to the nerves of your peripheral nervous system (network
Freephone helpline 0808 808 5555 information@lymphoma-action.org.uk www.lymphoma-action.org.uk Peripheral neuropathy Peripheral neuropathy is damage to the nerves of your peripheral nervous system (network
Neurons Chapter 7 2/19/2016. Learning Objectives. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System. Cells of the Nervous System
 Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Learning Objectives Neurons Chapter 7 Identify and describe the functions of the two main divisions of the nervous system. Differentiate between a neuron and neuroglial cells in terms of structure and
Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 22: A little Neurobiology http://compbio.uchsc.edu/hunter/bio5099 Larry.Hunter@uchsc.edu Nervous system development Part of the ectoderm
Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN) Measurement Approaches
 Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN) Measurement Approaches Ellen Lavoie Smith PhD, APRN, AOCN, FAAN Associate Professor PhD Program Director University of Michigan School of Nursing Faculty
Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy (CIPN) Measurement Approaches Ellen Lavoie Smith PhD, APRN, AOCN, FAAN Associate Professor PhD Program Director University of Michigan School of Nursing Faculty
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation
 Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Anatomical Substrates of Somatic Sensation John H. Martin, Ph.D. Center for Neurobiology & Behavior Columbia University CPS The 2 principal somatic sensory systems: 1) Dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
Peripheral Neuropathy Caused by Chemotherapy
 Peripheral Neuropathy Caused by Chemotherapy Some chemotherapy drugs can cause peripheral neuropathy, a set of symptoms caused by damage to nerves that control the sensations and movements of our arms
Peripheral Neuropathy Caused by Chemotherapy Some chemotherapy drugs can cause peripheral neuropathy, a set of symptoms caused by damage to nerves that control the sensations and movements of our arms
