TÉCNICA / TECHNIQUE INITIAL EXPERIENCE WITH STAPLED HEMORRHOIDOPEXY FOR TREATMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS
|
|
|
- George Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARQGA/1242 TÉCNICA / TECHNIQUE INITIAL EXPERIENCE WITH STAPLED HEMORRHOIDOPEXY FOR TREATMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS Carlos Walter SOBRADO, Guilherme Cutait de Castro COTTI, Fabricio Ferreira COELHO and Júlio Rafael Mariano da ROCHA ABSTRACT Background - Introduction of stapled hemorrhoidopexy by Longo in 1998 represented a radical change in the treatment of hemorrhoids. By avoiding multiple excisions and suture lines in the perianal region, stapled hemorrhoidopexy is intended to offer less postoperative pain than with conventional techniques. Objective - To report and analyze the intra and postoperative results gained during initial experience with stapled hemorrhoidopexy. Methods - One hundred and fifty five patients (67 males) with average age of 39.5 years (21-67 years) underwent stapled hemorrhoidopexy between June 2000 and December 2003 with symptomatic third-degree (n = 74) and fourth-degree (n = 81) hemorrhoids. Mean follow-up period was 20 months (14-60 months). Results - Preoperative symptoms were prolapse (96.7%) and anal bleeding (96.1%). Overall mean operative time was 23 minutes (16-48 minutes). We observed one case of stapler failure and one case of failure to introduce the stapler occurred in a patient with previous anal surgery. Additional sutures for hemostasis were required in 103 patients (66.5%). Resection of skin tags was performed in 45 cases (29%). Postoperatively scheduled analgesia with oral dipyrone and celecoxib was enough for pain control in 131 patients (84.5%). Rescue analgesia was necessary in 24 cases (15.5%). Five patients needed opiates for pain control. Hospital discharge took place on the first postoperative day in 140 patients (90.3%). First defecation without pain was reported by 118 patients (76.1%). Postoperative complications were anal bleeding (10.3%), severe pain (3.2%), urinary retention (3.9%), fever without any signs of perianal infection (1.9%), incontinence for flatus (1.9%), hemorrhoidal thrombosis (1.3%). Two patients presented symptoms of recurrent hemorrhoidal disease and were successfully treated by conventional hemorrhoidectomy. They were no cases of anal stenosis, permanent incontinence, chronic pain or deaths in this series. Conclusions - Hemorrhoidopexy can be considered a feasible and safe alternative technique to conventional hemorroidectomy for select patients. HEADINGS Postoperative complications. Postoperative pain. Hemorrhoids. Anorectal surgery. Surgical staplers. INTRODUCTION Despite the major advances that have occurred in the treatment of colorectal diseases, there have been few modifications in the management of hemorrhoidal disease in the last decades. Traditionally, first and second-degree hemorrhoids are treated by dietary modifications and nonoperative techniques such as rubber band ligation, infrared photocoagulation and sclerotherapy (8, 15, 22, 24, 25). Operative treatment has been reserved for advanced hemorrhoidal disease (third and fourth-grade) and comprehends excision of the hemorrhoidal tissue (8, 15, 20, 21, 25). The most frequent surgical procedures performed are the Milligan-Morgan and Ferguson techniques, both of which are associated with low complications and excellent results in terms of relief of symptoms, but severe pain may arise postoperatively due to removal of innervated anoderm below the dentate line and perianal skin (8, 9, 15, 21). Several modifications to conventional techniques have been proposed aiming to reduce postoperative pain including lateral internal sphincterotomy, anal dilatation, diathermy hemorrhoidectomy and use of anal sphincter relaxants or metronidazole (2, 16, 20, 23, 25). However, none have resulted in a significant decrease in postoperative pain to gain universal acceptance (3). Once again, in the past few years, a great debate has arisen about the surgical management of hemorrhoids, due to the introduction of a new technique for management of advanced hemorrhoidal disease called procedure for prolapse and hemorroidopexy (PPH) technique, or stapled hemorrhoidopexy. Introduced by LONGO (12) in 1998, it uses a circular stapler to excise a complete circular strip Disciplines of Digestive Surgery and Coloproctology, São Paulo University Medical School, São Paulo, SP, Brazil. Address for correspondence: Dr. Carlos Walter Sobrado - Rua Itapeva, 500 7º andar cj. B São Paulo, SP, Brasil. sobrado@iconet.com.br 238 Arq Gastroenterol v. 43 no.3 jul./set. 2006
2 of rectal mucosa above the dentate line which lifts the prolapsed hemorrhoidal tissue, removing the redundant mucosa and stapling off the end branches of the superior hemorrhoidal artery (5, 12). By avoiding multiple excisions and suture lines on the sensitive anal mucosa below the dentate line, the initial experience of several authors has shown that pain appears to be far less with PPH than with conventional techniques (8, 10, 11, 15, 24, 25). The results of stapled hemorrhoidopexy have been assessed in some randomized controlled trials (7, 10, 11, 16, 19, 24). These studies have consistently shown a decrease in postoperative pain, analgesic requirement, length of surgical procedure, short recovery time and early return to normal activities. The complications and postoperative recurrence rates are similar to those reported after excisional technique (7, 9, 11, 16). Assessment of long-term results and complications of the operation remains unknown, several studies reported chronic postoperative pain (4), recurrent prolapse (9, 16) and anal stenosis (6, 18) but findings in other studies suggest there are no significant differences between stapled hemorrhoidopexy and conventional hemorrhoidectomy in terms of quality of life and functional outcomes (1, 20). The purpose of the present study is to report the prospective data regarding our initial experience with stapled hemorrhoidopexy, comparing the results with those published in the literature. PATIENTS AND METHOD Between June 2000 and December 2003, 155 consecutive patients with symptomatic third-degree and fourth-degree hemorrhoids were included in this study (Figure 1). All patients were informed about the technique performed preoperatively. The operation was performed by a single experienced colorectal surgeon (CWS). Preoperative evaluation included a medical history, physical and proctological examinations, and routine laboratorial tests in all patients. Patients over 45 underwent cardiologic evaluation preoperatively. Colonoscopy was performed preoperatively for patients with important changes in bowel habit, a previous history of colorectal cancer or polyps and for all patients over 50. Exclusion criteria included coagulopathy and patients receiving treatment with oral anticoagulants and other associated anorectal diseases (condyloma, fistula, abscess, fissura). Operations were performed without bowel preparation and all patients were given 2 g of cefoxitin, at the time of the anesthesia. Surgery was performed either under general anesthesia (56 patients %) or spinal anesthesia (99 patients %). A chronometer measured operative time. Patients were operated in lithotomy position and the technique used in all procedures was that reported by LONGO (12). A circular anal dilatator (CAD33; Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Cincinatti, OH, USA) was introduced after manual reduction of the prolapse of the anoderm and parts of the anal mucous membrane. After removal of the obturator, the prolapsed mucous membrane falls into the lumen of the circular anal dilator. Then, a 0 polypropylene endoanal purse-string suture was placed circumferentially 4 cm above the dentate line encompassing mucosa and submucousa through the window of the anoscope (PSA33; Ethicon Endo- Surgery, Cincinatti, OH, USA). The hemorrhoidal circular stapler (HCS33; Ethicon Endo-Surgery, Cincinatti, OH, USA) was introduced through the anus, the purse-string suture tied down onto the shaft of the instrument. The instrument was closed and fired thus incorporating the mucosal tissue in the pursestring within the head of the gun. The circular knife excised the redundant tissue and the anastomosis was accomplished by a double row of titanium staples. The instrument was kept closed for 30 seconds to help achieve hemostasis. The staple line was inspected and, when necessary, additional hemostatic suture with 3-0 polyglecaprone on a 25 mm curved needle was performed. If prominent skin tags were present at the time of surgery, they FIGURE 1 Pre-operative aspect of a patient with third-degree hemorrhoids FIGURE 2 Immediate postoperative result after stapled hemorrhoidopexy of the same patient v. 43 no.3 jul./set Arq Gastroenterol 239
3 were resected. Figure 2 illustrates the immediate postoperative result after the stapled hemorrhoidopexy. The excised tissue was sent for histopathological examination in all cases. During hospital stay, a dietician evaluated all patients to ensure they received mg of additional fiber supplements (administered as Psyllium) and at least 2 liters of water/day postoperatively. Dimethicone was also administered for the first 5 postoperative days. Postoperative analgesia consisted of dipyrone (1 g/orally four times daily) and celecoxib (200 mg/orally twice a day). Analgesia was suspended on the third to fifth postoperative days, or when the patient referred defecation without pain. When necessary, intramuscular cetoprofen (100 mg twice a day) or oral oxycodone 20 mg was administered as rescue analgesia. Patients were discharge from the hospital on the first postoperative day or later if rescue analgesia was necessary. Clinical evaluations, including complete proctological examination, were routinely repeated at postoperative days 5 to 7, 3 weeks and 6 months after surgery. Preoperative data included demographic characteristics, symptoms of hemorrhoidal disease and anal continence. Operative data evaluated were type of anesthesia, patient position, operative time, distance from the stapling to the dentate line, need for complementary hemostasis, associated procedures and any unexpected events. Postoperative outcomes included postoperative pain, frequency of rescue analgesia, characteristics of the first defecation, control of hemorrhoidal symptoms, frequency of hemorrhoid recurrence, fecal incontinence, resume of normal activities, and all kinds of complications. RESULTS A total of 155 patients operated between June 2000 and December 2003 with symptomatic third-degree (n = 74) and fourth-degree (n = 81) hemorrhoids were included in this study, with 67 males and 88 females. Average age was 39.5 years (range years). Mean follow-up period was 20 months (range 14 to 60 months). Demographic data are show in Table 1. Preoperative symptoms were prolapse (n = %), anal bleeding (n = %), anal discomfort (n = 99 64%) and anal itching (n = 70 45%). Associated skin tags were detected in 45 patients (29%). All patients were operated in lithotomy position and surgery was performed under general anesthesia in 56 patients (36.1%) and spinal anesthesia in 99 (63.9%). TABLE 1 Baseline characteristics of patients Characteristic Number (n) % Male Female Degree of hemorrhoids Third Fourth Mean age (range) years 39.5 (21-67) - Total of patients Mean operative time was 23 minutes (16 to 48 minutes). The suture line was performed 4.0 cm above the dentate line. One case of stapler failure resulted, due to an interruption in the posterior titanium staples. A manual suture with 0 polyglecaprone successfully corrected it. Failure to introduce the stapler occurred in a patient with previous anal surgery. Additional sutures for hemostasis were required in 103 patients (66.5%). Resection of skin tags while undergoing PPH was performed in 45 cases (29%). Small residual prolapsed mucosa were detected below the suture line in 18 patients (11,6%) and were treated with an additional 3.0 polyglecaprone manual suture. Postoperatively scheduled analgesia with oral dipyrone and celecoxib was enough for pain control in 131 patients (84.5%). Rescue analgesia was necessary in 24 cases (15.5%). Five patients (3.2%) needed opiates for pain control. Analgesic usage decreased over time and by the fifth postoperative day, almost all patients were not requiring analgesics. Hospital discharge took place on the first postoperative day in 140 patients. First defecation occurred during hospital stay in 125 patients (80.6%). First defecation without pain was reported by 118 of these patients (76.1%). Resume of normal activities and/or return to work took place after 3 to 14 days (mean 5.9 days). Postoperative complications are illustrated in Table 2. Six patients (3.9%), with urinary retention required catheterization. Pain was referred by 37 patients (23.8%), and was controlled by standard analgesia in all cases. No cases of chronic pain were detected after 12 weeks. Fever (>37.8ºC) was observed in three patients (1.9%), without any signs of perianal infection but patients were medicated with ciprofloxacin (1 g/day for 5 days). No additional therapy was necessary. After the procedure, three patients referred incontinence for flatus (1.9%) and no patients referred incontinence for feces. Mucous prolapse occurred in five cases (3.2%) and treated by rubber band ligation, with satisfactory result. Hemorrhoidal TABLE 2 Postoperative complications Complication Number (n) % Bleeding Tenesmus Fecal impactation Urgency Severe pain (needs opiates) Urinary retention Fever Partial incontinence Mucous prolapse Failure of circular stapler Introduction failure of PPH Hemorrhoidal thrombosis Recurrence Arq Gastroenterol v. 43 no.3 jul./set. 2006
4 thrombosis was observed in two cases (1.3%) that required surgical excision. After the stapled hemorrhoidopexy, two patients (1.3%) presented symptoms of recurrent hemorrhoidal disease and were successfully treated by conventional hemorrhoidectomy. Sixteen patients (10.3%) referred anal bleeding in the first follow-up visit at postoperative days 5 to 7. All of these cases were submitted rectosigmoidoscopy. No alterations were detected in 15 patients. Oozing from the anastomosis was observed in one patient and was successfully managed by infiltration of xylocaine with epinephrine and local compression. None of these sixteen subjects required a new surgery or blood transfusion. There were no cases of anal stenosis, permanent incontinence or deaths in this series. DISCUSSION Pain control after hemorrhoidectomy has always been a major concern for surgeons and represents one of the most feared conditions associated with the surgical treatment of hemorrhoidal disease. A great number of alternative measures have been proposed to reduce postoperative pain without satisfactory results. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy, as proposed by LONGO (12) in 1998, represented a great modification in the treatment of advanced hemorrhoid disease. Its main advantage would be a lower incidence of postoperative pain since the sensitive anal mucosa is not traumatized during the procedure as compared with standard surgical techniques (8, 9, 15, 24). Several randomized trials comparing stapled hemorrhoidopexy with traditional hemorrhoidectomy were developed to test the feasibility and efficacy of the technique (7, 9, 10, 11, 16, 24). A systematic review conducted by SUTHERLAND et al. (24) that included seven prospective randomized trials comparing stapled hemorrhoidopexy with conventional hemorrhoidectomy, found strong evidence in favor of the stapled procedure considering length of surgical procedure, anal bleeding during the first 2 weeks and postoperative pain, analgesic consumption, healing and return to normal activities. These results are in agreement with a multicenter study (7) that found a significant reduction in period of hospitalization (mean 1 day vs. 2 days). In this study, 90.3% of patients were discharged on the first postoperative day. Other interesting finding was that resume of normal activities and return to work took place after 3 to 14 days, with a mean period of 6 days. A reduction of postoperative pain and need for analgesics are one of the most attractive features of the stapling technique highlighted by many authors (8, 9, 11, 13, 15, 24). In our series, analgesia has been accomplished with oral medications in 84.5% that were usually interrupted during the third to fifth postoperative days. This lower incidence of postoperative pain would be a consequence of less surgical trauma to the anal region and a faster healing of surgical wound (4-7 weeks for the conventional technique vs. 1-2 weeks for the stapling technique) (19, 24). HETZER et al. (9) found no difference in the occurrence of recurrent hemorrhoidal disease when comparing the stapled and conventional procedures. However, other authors reported a higher recurrence with the stapled technique specially with fourth degree hemorrhoidal disease (16). We had two cases of recurrence (1.3%) an originally grade IV hemorrhoid - successfully managed with conventional hemorrhoidectomy. There are reports of perianal infections and sepsis after the stapling technique that have led some authors to propose the use of prophylactic antibiotics (14, 16, 24). Despite the absence of strong evidence in favor of such measures, all our patients received antibiotic prophylaxis with cefoxitin during anesthetic induction. Three (1.9%) patients developed fever in the postoperative period and received ciprofloxacin (1 g/day) despite any evidence of systemic or surgical site infection. After analysis of the early postoperative results, evaluation of functional results focused on several studies (7, 11, 16, 19, 20). Some authors found no difference regarding fecal incontinence when comparing conventional hemorrhoidectomy and stapled hemorrhoidopexy. GANIO et al. (7) observed no difference regarding rest pressure and squeeze pressure in the pre and postoperative period in both groups. SHALABY and DESOKY (19) obtained the same results in the PPH group; however, they found lower rest and squeeze pressures in the postoperative period in the group submitted to conventional hemorrhoidectomy. In our series, we observed three cases of incontinence to gas and no incontinence for solids after at least 14 months of follow-up. Some surgeons are still afraid of a higher risk of stenosis with PPH. Nevertheless, there is no evidence in the literature to support this statement. In fact, SHALABY and DESOKY (19) reported a stenosis frequency of 2% in the PPH group and of 5% in the conventional hemorrhoidectomy group. Similarly to other series (8, 9), no cases of anal stenosis were verified during our follow up. Long-term evaluation of results and complications of hemorrhoidopexy are still lacking in the literature (17, 20). SMYTH et al. (20) published a series of patients submitted to PPH with a mean follow-up of 37 months and found no significant differences in terms of quality of life, functional outcomes and recurrence (no cases in both groups). In our series, there were six cases of tenesmus, urgency was found in two cases and fecal impactation in another two cases that improved with conservative measures. The fact that the present study is a prospective non-randomized trial could impose some limitations to our results interpretations. However, as stated above, these results are in agreement to other large prospective randomized and non-randomized trials already published that validate the benefits and restrictions observed with this new technique in the management of advanced hemorrhoids. CONCLUSION In summary and in agreement with other published series, hemorrhoidopexy can be considered an alternative technique with good outcomes for management of advanced hemorrhoid disease for selected patients. In these patients, PPH may be considered a feasible and safe procedure associated with lower postoperative pain, earlier return to normal activity and complication rates similar to the conventional technique. v. 43 no.3 jul./set Arq Gastroenterol 241
5 Sobrado CW, Cotti GCC, Coelho FF, Rocha JRM. Experiência inicial com o tratamento da doença hemorroidária pela técnica de grampeamento circular. Arq Gastroenterol. 2006;43(3): RESUMO Racional - A introdução por Longo em 1998, da hemorroidopexia pela técnica de grampeamento circular representou uma mudança radical no tratamento cirúrgico da doença hemorroidária, ao passo que propõe o reposicionamento da mucosa anorretal prolapsada, sem excisão do mamilo hemorroidário, cursando assim com menor dor e menor tempo de recuperação pós-operatórios. Objetivo - Apresentar e analisar os resultados intra e pós-operatórios obtidos durante a experiência inicial com a técnica de grampeamento circular. Pacientes e método - Foram incluídos 155 pacientes (67 homens) com média de idade de 39,5 anos (21-67 anos) e doença hemorroidária sintomática grau III (n = 74) e IV (n = 81), operados consecutivamente pelo método do grampeamento circular entre junho de 2000 e dezembro de Resultados e complicações pós-operatórias foram aferidos num tempo de seguimento médio de 20 meses (14 60 meses). Resultados - Os principais sintomas pré-operatórios foram prolapso (96,7%) e sangramento (96,1%). O tempo operatório médio foi de 23 minutos (16-48 minutos). Houve um caso de falha do equipamento e um de impossibilidade de introdução do mesmo (paciente com cirurgia anal prévia). Hemostasia adicional com sutura foi necessária em 103 pacientes (66,5%) e a ressecção de plicomas foi realizada concomitantemente ao procedimento em 45 pacientes (29%). A analgesia pós-operatória via oral com dipirona e celecoxib foi eficiente no controle da dor em 131 pacientes (84,5%), 24 (15,5%) necessitaram de analgesia complementar, sendo que 5 pacientes receberam opióides devido a dor intensa. A maioria dos pacientes (140-90,3%) teve alta no primeiro dia de pós-operatório e 118 (76,1%) referiram a primeira evacuação sem dor. As complicações pós-operatórias observadas foram: sangramento (10,3%), tenesmo (3,9%), retenção urinária (3,9%), febre sem sinais infecciosos (1,9%), incontinência transitória para flatos (1,9%) e trombose hemorroidária (1,3%). Ocorreram duas recurrências sintomáticas, tratadas com sucesso por hemorroidectomia convencional. Na presente casuística não foram observados casos de estenose, dor crônica, incontinência permanente ou óbito. Conclusões - O grampeamento circular para o tratamento da doença hemorroidária é técnica segura e factível, representando uma alternativa à hemorroidectomia convencional, para casos selecionados. DESCRITORES Complicações pós-operatórias. Cirurgia anorretal. Hemorróidas. Técnicas de sutura. Grampeamento cirúrgico. REFERENCES 1. Altomare DF, Rinaldi M, Sallustio PL, Martino P, De Fazio M, Memeo V. Long-term effects of stapled haemorrhoidectomy on internal anal function and sensitivity. Br J Surg. 2001;88: Borba MR, Sobrado CW, Sokol S. Hemorroidectomia pela técnica fechada (técnica de Sokol). Análise de 322 doentes. Rev Bras Coloproctol. 1997;17: Carapeti EA, Kamm MA, McDonald PJ, Phillips RK. Double-blind randomized controlled trial of effect of metronidazole on pain after day-case haemorrhoidectomy. Lancet. 1998;351: Cheetam MJ, Mortensen NJ, Nystron PO, Kamm MA, Phillips RK. Persistent pain and faecal urgency after stapled haemorrhoidectomy. Lancet. 2000;356: Corman ML, Gravie JF, Hager T, Loudon MA, Mascagni D, Nystrom PO, Seow-Choen F, Abcarian H, Marcello P, Weiss E, Longo A. Stapled hemorrhoidopexy: a consensus position paper by an international working party indications, contra-indications and technique. Colorectal Dis. 2003;5: Fazio VW. Early promise of stapling technique for haemorrhoidectomy. Lancet. 2000;355: Ganio E, Altomare DF, Gabrielli F, Milito G, Canuti S. Prospective randomized multicentre trial comparing stapled with open hemorrhoidectomy. Br J Surg. 2001;88: Habr-Gama A, Silva-e-Sousa Jr AH, Rovelo JMC, Souza JS, Benício F, Regadas FSP, Wainstein C, Cunha TMR, Marques CFS, Bonardi RA, Ramos JR, Pandini LC, Kiss DR. Stapled hemorrhoidectomy: initial experience of a Latin American group. J Gastrointest Surg. 2003;7: Hetzer FH, Demartines N, Handschin AE, Clavien PA. Stapled vs excision hemorrhoidectomy long-term results of a prospective randomized trial. Arch Surg. 2002;137: Ho YH, Seow-Choen F, Tsang C, Eu KW. Randomized trial assessing sphincter injuries after stapled hemorrhoidectomy. Br J Surg. 2001;88: Khalil KH, O Bichere A, Sellu D. Randomized clinical trial of sutured versus stapled closed hemorrhoidectomy. Br J Surg. 2000;87: Longo A. Treatment of hemorrhoidal disease by reduction of mucosa and hemorrhoidal prolapse with a circular-suturing device: a new procedure. In: Proceedings of the 6 th World Congress of Endoscopic. Rome, Italy: Surgery; Mehigan BJ, Monson JR, Hartley JE. Stapling procedure for haemorrhoids versus Milligan- Morgan haemorrhoidectomy: randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2000;355: Molloy RG, Kingsmore D. Life threatening pelvic sepsis after stapled haemorrhoidectomy. Lancet. 2000;355: Nahas SC, Borba MR, Brochado MCT, Marques CFS, Nahas CSR, Miott-Neto B. Stapled hemorrhoidectomy for the treatment of hemorrhoids. Arq Gastroenterol. 2003;40: Ortiz H, Marzo J, Armendariz P. Randomized clinical trial of stapled hemorrhoidopexy versus conventional diathermy hemorrhoidectomy. Br J Surg. 2002;89: Pernice LM, Bartalucci B, Bencini L, Borri A, Catarzi S, Kröning K. Early and late (ten years) experience with circular stapled hemorrhoidectomy. Dis Colon Rectum. 2001;44: Ravo B, Amato A, Bianco V, Boccasanta P, Bottini C, Carriero A, Milito G, Dodi G, Mascagni D, Orsini S, Pietroletti R, Ripetti V, Tagariello GB. Complications after stapled hemorrhoidectomy: can they be prevent? Tech Coloproctol. 2002;6: Shalaby R, Desoky A. Randomized clinical trial of stapled versus Milligan-Morgan hemorrhoidectomy. Br J Surg. 2001;88: Smyth EF, Baker RP, Wilken BJ, Hartley JE, White TJ, Monson JR. Stapled versus excision haemorrhoidectomy: long-term follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2003;361: Sobrado CW, Bringel RWA, Nahas SC. Tratamento cirúrgico da doença hemorroidária. In: Cruz GMG, editor. Coloproctologia terapêutica. Rio de Janeiro: Revinter; v.3, p Sobrado CW. Doença hemorroidária. In: Silva JH, editor. Manual de coloproctologia. São Paulo: Zeppelini; p Sobrado CW. Tratamento cirúrgico da doença hemorroidária. In: Silva JH, editor. Manual de coloproctologia. São Paulo: Zeppelini; p Sutherland LM, Burchard AK, Matsuda K, Sweeney JL, Bokey EL, Childs PA, Roberts AK, Waxman BP, Maddern GJ. A systematic review of stapled hemorrhoidectomy. Arch Surg. 2002;137: Wexner SD. The quest for painless surgical treatment of hemorrhoids continues. J Am Coll Surg. 2001;193: Recebido em 9/11/2005. Aprovado em 16/12/ Arq Gastroenterol v. 43 no.3 jul./set. 2006
STAPLED HEMORRHOIDECTOMY VERSUS TRADITIONAL HEMORRHOIDECTOMY FOR THE TREATMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS
 Egyptian Journal of Surgery Vol. 29, No. 2, April, 2010 ORIGINAL ARTICLE STAPLED HEMORRHOIDECTOMY VERSUS TRADITIONAL HEMORRHOIDECTOMY FOR THE TREATMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS Gouda El-labban Department of General
Egyptian Journal of Surgery Vol. 29, No. 2, April, 2010 ORIGINAL ARTICLE STAPLED HEMORRHOIDECTOMY VERSUS TRADITIONAL HEMORRHOIDECTOMY FOR THE TREATMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS Gouda El-labban Department of General
Impact of stapled haemorrhoidopexy on stool continence and anorectal function long-term follow-up of 242 patients
 Langenbecks Arch Surg (2008) 393:501 505 DOI 10.1007/s00423-007-0257-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of stapled haemorrhoidopexy on stool continence and anorectal function long-term follow-up of 242 patients
Langenbecks Arch Surg (2008) 393:501 505 DOI 10.1007/s00423-007-0257-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Impact of stapled haemorrhoidopexy on stool continence and anorectal function long-term follow-up of 242 patients
Stapled haemorrhoidectomy in Chinese patients: a prospective randomised control study!"#$%&'()*+,-./
 Key words: Hemorrhoids; Pain, postoperative; Surgical stapling; Manometry!!"#!" PYY Lau WCS Meng AWC Yip Hong Kong Med J 2004;10:373-7 Department of Surgery, Kwong Wah Hospital, 25 Waterloo Road, Kowloon,
Key words: Hemorrhoids; Pain, postoperative; Surgical stapling; Manometry!!"#!" PYY Lau WCS Meng AWC Yip Hong Kong Med J 2004;10:373-7 Department of Surgery, Kwong Wah Hospital, 25 Waterloo Road, Kowloon,
Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: The Mayo Hospital Experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: The Mayo Hospital Experience MUHAMMAD RAFAIH IQBAL, YASEEN RAFI, SAAD JAVED, KHALID JAVED ABID ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate clinical outcome after Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: The Mayo Hospital Experience MUHAMMAD RAFAIH IQBAL, YASEEN RAFI, SAAD JAVED, KHALID JAVED ABID ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate clinical outcome after Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy.
J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) June 2007
 J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) June 2007 Case Analysis Staple Hemorrhoidectomy A Modified Low Transection Technique of PPH Shih-Chang Chang 1 Henry Hsin-Chung Lee 1,2 1 Division of Colorectal Surgery,
J Soc Colon Rectal Surgeon (Taiwan) June 2007 Case Analysis Staple Hemorrhoidectomy A Modified Low Transection Technique of PPH Shih-Chang Chang 1 Henry Hsin-Chung Lee 1,2 1 Division of Colorectal Surgery,
Hemorrhoids represent one of the most common
 THE JOURNAL OF FAMILY PRACTICE S U P P L E M E N T A new treatment option for grades III and IV hemorrhoids Glenn S. Parker, MD, FACS, FASCRS Chief, Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery, and Director,
THE JOURNAL OF FAMILY PRACTICE S U P P L E M E N T A new treatment option for grades III and IV hemorrhoids Glenn S. Parker, MD, FACS, FASCRS Chief, Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery, and Director,
Hemorrhoidal disease affects millions of people
 DOI: 10.1590/0100-69912017003010 Original Article Partial stapled hemorrhoidopexy: clinical aspects and impact on anorectal physiology Hemorroidopexia por grampeamento parcial: aspectos clínicos e impacto
DOI: 10.1590/0100-69912017003010 Original Article Partial stapled hemorrhoidopexy: clinical aspects and impact on anorectal physiology Hemorroidopexia por grampeamento parcial: aspectos clínicos e impacto
PPH AND BIOLOGICAL GLUE IN PATIENTS WITH HIGH RISK OF BLEEDING IN STAPLED HEMORRHOIDOPEXY
 PPH AND BIOLOGICAL GLUE IN PATIENTS WITH HIGH RISK OF BLEEDING IN STAPLED HEMORRHOIDOPEXY The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
PPH AND BIOLOGICAL GLUE IN PATIENTS WITH HIGH RISK OF BLEEDING IN STAPLED HEMORRHOIDOPEXY The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 haemorrhoids. Haemorrhoidectomy is indicated in third and fourth degree haemorrhoids. The Milligan-Morgan open haemorrhoidectomy is the most widely practiced surgical technique used for the management
haemorrhoids. Haemorrhoidectomy is indicated in third and fourth degree haemorrhoids. The Milligan-Morgan open haemorrhoidectomy is the most widely practiced surgical technique used for the management
Stapler hemorrhoidectomy versus open hemorrhoidectomy
 International Surgery Journal Baliga K et al. Int Surg J. 2016 Nov;3(4):1901-1905 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20163120
International Surgery Journal Baliga K et al. Int Surg J. 2016 Nov;3(4):1901-1905 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20163120
New Hyde Park, New York 5 Department of Colon and Rectal Surgery, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, California
 A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Multicenter Trial Comparing Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy and Ferguson Hemorrhoidectomy: Perioperative and One-Year Results A. J. Senagore, M.D., M.S., 1,8 M. Singer, M.D.,
A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled Multicenter Trial Comparing Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy and Ferguson Hemorrhoidectomy: Perioperative and One-Year Results A. J. Senagore, M.D., M.S., 1,8 M. Singer, M.D.,
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.88 Comparative Study of Stapled and Open
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.88 Comparative Study of Stapled and Open
Haemorrhoidal disorders -What is the optimal treatment?
 Haemorrhoidal disorders -What is the optimal treatment? Per-Olof Nyström, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Surgery Karolinska Institutet and Karolinska University Hospital Huddinge Stockholm, Sweden The methods
Haemorrhoidal disorders -What is the optimal treatment? Per-Olof Nyström, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Surgery Karolinska Institutet and Karolinska University Hospital Huddinge Stockholm, Sweden The methods
Treatment of Hemorrhoids with Circular Stapler, a New Alternative to Conventional Methods: A Prospective Study of 140 Patients
 Treatment of Hemorrhoids with Circular Stapler, a New Alternative to Conventional Methods: A Prospective Study of 140 Patients Jean-Pierre Arnaud, MD, Patrick Pessaux, MD, Noel Huten, MD, Nicolo De Manzini,
Treatment of Hemorrhoids with Circular Stapler, a New Alternative to Conventional Methods: A Prospective Study of 140 Patients Jean-Pierre Arnaud, MD, Patrick Pessaux, MD, Noel Huten, MD, Nicolo De Manzini,
Stapler Haemorrhoidopexy As Compared To Conventional Haemorrhoidectomy: A Short-Term Prospective Randomised Controlled Study
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 16 Number 1 Stapler Haemorrhoidopexy As Compared To Conventional Haemorrhoidectomy: A Short-Term Prospective Randomised Controlled Study H Aggarwal, R Bansod,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 16 Number 1 Stapler Haemorrhoidopexy As Compared To Conventional Haemorrhoidectomy: A Short-Term Prospective Randomised Controlled Study H Aggarwal, R Bansod,
Hemorrhoids. Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery
 Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Hemorrhoids Carlos R. Alvarez-Allende PGY-III Colorectal Surgery Overview Anatomy Classification Etiology Incidence Symptoms Differential Diagnosis Medical Management Surgical Management Anatomy Anal canal
Internationally Indexed Journal
 Internationally Indexed Journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services(USA),Index Coppernicus,Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals,Google scholar,cabi,doaj,psoar, EBSCO,SCOPUS, EMBASE etc. Rapid Publishing
Internationally Indexed Journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services(USA),Index Coppernicus,Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals,Google scholar,cabi,doaj,psoar, EBSCO,SCOPUS, EMBASE etc. Rapid Publishing
Comparison of Electrotherapy, Rubber Band Ligation and Hemorrhoidectomy in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids: A Clinical and Manometric Study
 Original Article 9 Comparison of Electrotherapy, Rubber Band Ligation and Hemorrhoidectomy in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids: A Clinical and Manometric Study A Izadpanah 1*, SV Hosseini 2, M Mahjoob 1 1.
Original Article 9 Comparison of Electrotherapy, Rubber Band Ligation and Hemorrhoidectomy in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids: A Clinical and Manometric Study A Izadpanah 1*, SV Hosseini 2, M Mahjoob 1 1.
STAPLED HEMORRHOIDECTOMY; IS IT REALLY SUPERIOR TO CONVENTIONAL HEMORRHOIDECTOMY? A LONG- TERM ANALYSIS
 The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/16.3643 ORIGINAL PROF-3643 STAPLED HEMORRHOIDECTOMY; IS IT REALLY SUPERIOR TO CONVENTIONAL HEMORRHOIDECTOMY? A LONG- TERM ANALYSIS twaseem@gmail.com
The Professional Medical Journal DOI: 10.17957/TPMJ/16.3643 ORIGINAL PROF-3643 STAPLED HEMORRHOIDECTOMY; IS IT REALLY SUPERIOR TO CONVENTIONAL HEMORRHOIDECTOMY? A LONG- TERM ANALYSIS twaseem@gmail.com
Stapled Versus Open Haemorrhoidectomy- Evaluation of Short Term Results
 Surgery Section DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2016/19403:2142 Original Article Stapled Versus Open Haemorrhoidectomy- Evaluation of Short Term Results Srikanth Kulkarni, Manohar Shivamalavaiah, Rajkumar Janvikulam
Surgery Section DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2016/19403:2142 Original Article Stapled Versus Open Haemorrhoidectomy- Evaluation of Short Term Results Srikanth Kulkarni, Manohar Shivamalavaiah, Rajkumar Janvikulam
Stapled Haemorrhoidopexy NICE review. 1 Executive Summary
 1 Executive Summary In the United Kingdom, the most common surgical procedure for the treatment of haemorrhoids is the Milligan-Morgan haemorrhoidectomy. This technique has been subject to numerous modifications
1 Executive Summary In the United Kingdom, the most common surgical procedure for the treatment of haemorrhoids is the Milligan-Morgan haemorrhoidectomy. This technique has been subject to numerous modifications
A Comparative Study of Open Haemorrhoidectomy with Minimally Invasive Procedure For Haemorrhoids (M.I.P.H)
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (January. 2017), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of Open Haemorrhoidectomy
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (January. 2017), PP 51-56 www.iosrjournals.org A Comparative Study of Open Haemorrhoidectomy
Piotr Walega, *Piotr Krokowicz, Michal Romaniszyn, Jakub Kenig, Jerzy Sałówka, Michał Nowakowski, Roman M Herman, Wojciech Nowak
 Received 8 Feb 2009; Accepted 30 March 2009 Doppler Guided Haemorrhoidal Arterial Ligation with recto-anal-repair (RAR)for the treatment of advanced haemorrhoidal disease. Piotr Walega, *Piotr Krokowicz,
Received 8 Feb 2009; Accepted 30 March 2009 Doppler Guided Haemorrhoidal Arterial Ligation with recto-anal-repair (RAR)for the treatment of advanced haemorrhoidal disease. Piotr Walega, *Piotr Krokowicz,
Stapled hemorrhoidopexy was introduced in 1998 as a
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Long-term Results After Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: A Prospective Study With a 6-Year Follow-up A. Ommer, M.D. 1 Jakob Hinrichs, M.D. 1 Horst Möllenberg, M.D. 1 Babji Marla, M.D. 2 Martin
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Long-term Results After Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: A Prospective Study With a 6-Year Follow-up A. Ommer, M.D. 1 Jakob Hinrichs, M.D. 1 Horst Möllenberg, M.D. 1 Babji Marla, M.D. 2 Martin
Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy Versus Classical Hemorrhoidectomy A Prospective Comparative Study with 3 Years Follow-up
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 ICV: 71.54 Research Article Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy Versus Classical Hemorrhoidectomy A Prospective Comparative Study with 3 Years Follow-up Kasibhatla
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 ICV: 71.54 Research Article Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy Versus Classical Hemorrhoidectomy A Prospective Comparative Study with 3 Years Follow-up Kasibhatla
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 1 Article 3 Starr Surgery In ODS: A Case Series Of 500 ODS Patients Operated At India s Largest Proctology Clinic Ashwin Dhanarajji Porwal Paresh Manilal
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 6, Issue 1 Article 3 Starr Surgery In ODS: A Case Series Of 500 ODS Patients Operated At India s Largest Proctology Clinic Ashwin Dhanarajji Porwal Paresh Manilal
INCONTINENCE & DEFAECATORY DISORDERS AFTER HAEMORRHOIDECTOMY - MINIMISING THE RISK
 INCONTINENCE & DEFAECATORY DISORDERS AFTER HAEMORRHOIDECTOMY - MINIMISING THE RISK SURGICAL CONTROVERSIES SYMPOSIUM OCTOBER 2015 Stephen Grobler Bloemfontein Haemorrhoidal Disease One of the most common
INCONTINENCE & DEFAECATORY DISORDERS AFTER HAEMORRHOIDECTOMY - MINIMISING THE RISK SURGICAL CONTROVERSIES SYMPOSIUM OCTOBER 2015 Stephen Grobler Bloemfontein Haemorrhoidal Disease One of the most common
Treatment of haemorrhoids. Mr Rowan Collinson FRACS Colorectal and General Surgeon Auckland
 Treatment of haemorrhoids Mr Rowan Collinson FRACS Colorectal and General Surgeon Auckland Much overlap of haemorrhoidal symptoms with other conditions Is it just the haemorrhoids? what type of haemorrhoidal
Treatment of haemorrhoids Mr Rowan Collinson FRACS Colorectal and General Surgeon Auckland Much overlap of haemorrhoidal symptoms with other conditions Is it just the haemorrhoids? what type of haemorrhoidal
To inject, to band or to excise? These were the alternatives for a colorectal surgeon
 CHAPTER 2 Hemorrhoids To inject, to band or to excise? These were the alternatives for a colorectal surgeon some 50 years ago, when sclerosant injection, rubber band ligation and hemorrhoidectomy were
CHAPTER 2 Hemorrhoids To inject, to band or to excise? These were the alternatives for a colorectal surgeon some 50 years ago, when sclerosant injection, rubber band ligation and hemorrhoidectomy were
Prospective, Randomized Study: Proximate PPH Stapler vs. LigaSure for Hemorrhoidal Surgery
 Prospective, Randomized Study: Proximate PPH vs. LigaSure for Hemorrhoidal Surgery Matthias Kraemer, M.D., 1 Tengis Parulava, M.D., 2 Michael Roblick, M.D., 1 Lothar Duschka, M.D., 2 Heinrich Müller-Lobeck,
Prospective, Randomized Study: Proximate PPH vs. LigaSure for Hemorrhoidal Surgery Matthias Kraemer, M.D., 1 Tengis Parulava, M.D., 2 Michael Roblick, M.D., 1 Lothar Duschka, M.D., 2 Heinrich Müller-Lobeck,
Safety of surgical treatment of hemorrhoids in elderly patients
 Journal of Health Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Safety of surgical treatment of hemorrhoids in elderly patients Mustafa Cellalettin Haksal 1 *, Murat Burc Yazicioğlu 2, Cagri Tiryaki 2, Ali Ciftci
Journal of Health Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Safety of surgical treatment of hemorrhoids in elderly patients Mustafa Cellalettin Haksal 1 *, Murat Burc Yazicioğlu 2, Cagri Tiryaki 2, Ali Ciftci
Maurizio Gentile, Michele De Rosa, Gabriele Carbone, Vincenzo Pilone, Francesca Mosella, and Pietro Forestieri. 1. Introduction
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Gastroenterology Volume 2011, Article ID 467258, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2011/467258 Clinical Study Haemorrhoidectomy versus Conventional for IV-Degree Haemorrhoids:
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Gastroenterology Volume 2011, Article ID 467258, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2011/467258 Clinical Study Haemorrhoidectomy versus Conventional for IV-Degree Haemorrhoids:
Hesham M. Hasan 1 and Hani M. Hasan Introduction
 International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 652345, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2012/652345 Clinical Study Stapled Transanal Rectal Resection for the Surgical Treatment of Obstructed
International Scholarly Research Network ISRN Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 652345, 6 pages doi:10.5402/2012/652345 Clinical Study Stapled Transanal Rectal Resection for the Surgical Treatment of Obstructed
J COLOPROCTOL. 2013;33(3): Journal of. Coloproctology.
 J COLOPROCTOL. 2013;33(3):151 156 Journal of Coloproctology www.jcol.org.br Original articles High macro rubber band ligature José A. Reis Neto a,c, *, José A. Reis Junior b, Odorino H. Kagohara b, Joaquim
J COLOPROCTOL. 2013;33(3):151 156 Journal of Coloproctology www.jcol.org.br Original articles High macro rubber band ligature José A. Reis Neto a,c, *, José A. Reis Junior b, Odorino H. Kagohara b, Joaquim
REVIEW ARTICLE. Long-term Outcomes of Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy vs Conventional Hemorrhoidectomy
 REVIEW ARTICLE Long-term Outcomes of Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy vs Conventional Hemorrhoidectomy A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Pasquale Giordano, MD, FRCSEd, FRCS; Gianpiero Gravante, MD;
REVIEW ARTICLE Long-term Outcomes of Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy vs Conventional Hemorrhoidectomy A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials Pasquale Giordano, MD, FRCSEd, FRCS; Gianpiero Gravante, MD;
SAS Journal of Surgery ISSN SAS J. Surg., Volume-2; Issue-1 (Jan-Feb, 2016); p Available online at
 SAS Journal of Surgery ISSN 2454-5104 SAS J. Surg., Volume-2; Issue-1 (Jan-Feb, 2016); p-34-39 Available online at http://sassociety.com/sasjs/ Case Report A comparative study of Barron s banding versus
SAS Journal of Surgery ISSN 2454-5104 SAS J. Surg., Volume-2; Issue-1 (Jan-Feb, 2016); p-34-39 Available online at http://sassociety.com/sasjs/ Case Report A comparative study of Barron s banding versus
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 2 2013 Article 7 Delayed Bleeding Following LigaSure Hemorrhoidectomy Alexander Becker, MD Yakov Khromov, MD Joel Sayfan,MD, FACS Department of Surgery
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 2 2013 Article 7 Delayed Bleeding Following LigaSure Hemorrhoidectomy Alexander Becker, MD Yakov Khromov, MD Joel Sayfan,MD, FACS Department of Surgery
One Year Follow-up Result of Doppler-guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and Recto-Anal Repair in 97 Consecutive Patients
 Original Article Journal of the Korean Society of http://dx.doi.org/10.3393/jksc.2011.27.6.298 pissn 2093-7822 eissn 2093-7830 One Year Follow-up Result of Doppler-guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and
Original Article Journal of the Korean Society of http://dx.doi.org/10.3393/jksc.2011.27.6.298 pissn 2093-7822 eissn 2093-7830 One Year Follow-up Result of Doppler-guided Hemorrhoidal Artery Ligation and
50 ISSN East Cent. Afr. J. surg
 50 ISSN 03-9990 East Cent. Afr. J. surg Post-operative Complications of stapled versus Ferguson Hemorrhoidectomy at Mulago Hospital. A Randomized Comparative Study. J. Yiga, A Wesonga, S Kirunda, E Elobu,
50 ISSN 03-9990 East Cent. Afr. J. surg Post-operative Complications of stapled versus Ferguson Hemorrhoidectomy at Mulago Hospital. A Randomized Comparative Study. J. Yiga, A Wesonga, S Kirunda, E Elobu,
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS: A CRITICAL APPRAISAL OF THE CURRENT OPTIONS
 ABCDDV/1002 ABCD Arq Bras Cir Dig 2014;27(1):66-70 Review Article SURGICAL TREATMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS: A CRITICAL APPRAISAL OF THE CURRENT OPTIONS Tratamento cirúrgico das hemorroidas: uma análise crítica
ABCDDV/1002 ABCD Arq Bras Cir Dig 2014;27(1):66-70 Review Article SURGICAL TREATMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS: A CRITICAL APPRAISAL OF THE CURRENT OPTIONS Tratamento cirúrgico das hemorroidas: uma análise crítica
The American Journal of Surgery 182 (2001) Manuscript received July 26, 2000; revised manuscript February 14, 2001
 The American Journal of Surgery 182 (2001) 64 68 Randomised controlled trial between stapled circumferential mucosectomy and conventional circular hemorrhoidectomy in advanced hemorrhoids with external
The American Journal of Surgery 182 (2001) 64 68 Randomised controlled trial between stapled circumferential mucosectomy and conventional circular hemorrhoidectomy in advanced hemorrhoids with external
Office Management of Anorectal Disease. Waqar Qureshi, MD, FRCP, FACG, FASGE Professor Baylor College of Medicine Houston Texas
 Office Management of Anorectal Disease Waqar Qureshi, MD, FRCP, FACG, FASGE Professor Baylor College of Medicine Houston Texas Commonly seen Anorectal Disease Hemorrhoids Anal fissures Pruritus Abscesses
Office Management of Anorectal Disease Waqar Qureshi, MD, FRCP, FACG, FASGE Professor Baylor College of Medicine Houston Texas Commonly seen Anorectal Disease Hemorrhoids Anal fissures Pruritus Abscesses
Clinical Study Quality of Life after Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: A Prospective Observational Study
 BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 903271, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/903271 Clinical Study Quality of Life after Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: A Prospective Observational Study
BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 903271, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/903271 Clinical Study Quality of Life after Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy: A Prospective Observational Study
The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Anterior anal fissure is much more common in women and may arise following vaginal delivery.
 ANAL FISSURE Definition An anal fissure (synonym: fissure-in-ano) is a longitudinal split in the anoderm of the distal anal canal which extends from the anal verge proximally towards, but not beyond, the
ANAL FISSURE Definition An anal fissure (synonym: fissure-in-ano) is a longitudinal split in the anoderm of the distal anal canal which extends from the anal verge proximally towards, but not beyond, the
Outcome of Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy Versus Milligan Morgan s Haemorrhoidectomy
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy Versus Milligan Morgan s Haemorrhoidectomy Nawaid Farooque Khan, Syed Sagheer Hussain Shah, Shahid Rasul, Iram Bokhari, Samreen Mahboob*, Mansoor Akhtar
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Outcome of Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy Versus Milligan Morgan s Haemorrhoidectomy Nawaid Farooque Khan, Syed Sagheer Hussain Shah, Shahid Rasul, Iram Bokhari, Samreen Mahboob*, Mansoor Akhtar
Comparison of Open Hemorrhoidectomy under Local and Spinal Anesthesia and its Practical Feasibility at a Tertiary Care Institute
 DOI: 10.17354/SUR/2016/18 Original Article Comparison of Open Hemorrhoidectomy under Local and Spinal Anesthesia and its Practical Feasibility at a Tertiary Care Institute Praveen Singh Baghel 1, Maneesh
DOI: 10.17354/SUR/2016/18 Original Article Comparison of Open Hemorrhoidectomy under Local and Spinal Anesthesia and its Practical Feasibility at a Tertiary Care Institute Praveen Singh Baghel 1, Maneesh
Tailored excisional treatment for high-grade haemorrhoidal disease
 Updates Surg (2014) 66:283 287 DOI 10.1007/s13304-014-0269-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tailored excisional treatment for high-grade haemorrhoidal disease C. Elbetti I. Giani F. M. Consiglio E. Novelli A. Santini
Updates Surg (2014) 66:283 287 DOI 10.1007/s13304-014-0269-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Tailored excisional treatment for high-grade haemorrhoidal disease C. Elbetti I. Giani F. M. Consiglio E. Novelli A. Santini
Introduction. L. Trenti 1,2 S. Biondo. E. Kreisler 1,2
 Tech Coloproctol (2017) 21:337 344 DOI 10.1007/s10151-017-1620-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distal Doppler-guided transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization with mucopexy versus conventional hemorrhoidectomy for grade
Tech Coloproctol (2017) 21:337 344 DOI 10.1007/s10151-017-1620-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Distal Doppler-guided transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization with mucopexy versus conventional hemorrhoidectomy for grade
Haemorrhoidectomy: a Comparative Study of Open & Closed Methods MMJ 2009; 8:23 26
 Haemorrhoidectomy: a Comparative Study of Open & Methods MMJ 2009; 8:23 26 Hamid I. Jasim*, Mohammed H. Al Alwan** FIBS, Department of Surgery, Al Yarmouk Teaching Hospital FRCS, Professor, Department
Haemorrhoidectomy: a Comparative Study of Open & Methods MMJ 2009; 8:23 26 Hamid I. Jasim*, Mohammed H. Al Alwan** FIBS, Department of Surgery, Al Yarmouk Teaching Hospital FRCS, Professor, Department
Hemorrhoidal Disease: A Comprehensive Review
 COLLECTIVE REVIEWS Hemorrhoidal Disease: A Comprehensive Review Orit Kaidar-Person, MD, Benjamin Person, MD, Steven D Wexner, MD, FACS, FRCS, FRCS (Ed) Hemorrhoids are one of the most common conditions
COLLECTIVE REVIEWS Hemorrhoidal Disease: A Comprehensive Review Orit Kaidar-Person, MD, Benjamin Person, MD, Steven D Wexner, MD, FACS, FRCS, FRCS (Ed) Hemorrhoids are one of the most common conditions
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. a randomized study
 Int J Colorectal Dis (2004) 19:176 180 DOI 10.1007/s00384-003-0517-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Attila Bursics Krisztina Morvay Péter Kupcsulik Lajos Flautner Comparison of early and 1-year follow-up results of
Int J Colorectal Dis (2004) 19:176 180 DOI 10.1007/s00384-003-0517-9 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Attila Bursics Krisztina Morvay Péter Kupcsulik Lajos Flautner Comparison of early and 1-year follow-up results of
Haemorrhoidal artery ligation
 Haemorrhoidal artery ligation Issued: May 2010 NICE interventional procedure guidance 342 www.nice.org.uk/ipg342 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme
Haemorrhoidal artery ligation Issued: May 2010 NICE interventional procedure guidance 342 www.nice.org.uk/ipg342 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme
Perineale Rektumprolapsoperation: Gute Resultate bei geringem Aufwand! F.H. Hetzer
 Perineale Rektumprolapsoperation: Gute Resultate bei geringem Aufwand! F.H. Hetzer STARR: Wunderwaffe beim Obstructed Defecation Syndrom (ODS) F.H. Hetzer Stapled TransAnal Rectal Resection STARR PPH 01
Perineale Rektumprolapsoperation: Gute Resultate bei geringem Aufwand! F.H. Hetzer STARR: Wunderwaffe beim Obstructed Defecation Syndrom (ODS) F.H. Hetzer Stapled TransAnal Rectal Resection STARR PPH 01
A Novel Therapy for Haemorrhoids: Hand-sewn Haemorrhoidopexy using a Modified Anoscope
 A Novel Therapy for Haemorrhoids: Hand-sewn Haemorrhoidopexy using a Modified Anoscope J-H Wang, R-S Fei, Z Wang, J-J Lin, J-H Xu, W-B Chen ABSTRACT Purpose: Grades III and IV haemorrhoids have been preferentially
A Novel Therapy for Haemorrhoids: Hand-sewn Haemorrhoidopexy using a Modified Anoscope J-H Wang, R-S Fei, Z Wang, J-J Lin, J-H Xu, W-B Chen ABSTRACT Purpose: Grades III and IV haemorrhoids have been preferentially
Internationally Indexed Journal
 Internationally Indexed Journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services(USA),Index Coppernicus,Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals,Google scholar,cabi,doaj,psoar, EBSCO,SCOPUS, EMBASE etc. Rapid Publishing
Internationally Indexed Journal Indexed in Chemical Abstract Services(USA),Index Coppernicus,Ulrichs Directory of Periodicals,Google scholar,cabi,doaj,psoar, EBSCO,SCOPUS, EMBASE etc. Rapid Publishing
Dr Stephanie Ulmer General Surgeon Middlemore Hospital Auckland
 Dr Stephanie Ulmer General Surgeon Middlemore Hospital Auckland 16:30-17:25 WS #168: Modern Treatment of Haemorrhoids 17:35-18:30 WS #180: Modern Treatment of Haemorrhoids (Repeated) BOTTOMS Science and
Dr Stephanie Ulmer General Surgeon Middlemore Hospital Auckland 16:30-17:25 WS #168: Modern Treatment of Haemorrhoids 17:35-18:30 WS #180: Modern Treatment of Haemorrhoids (Repeated) BOTTOMS Science and
The Use of Glyceryl Tri-Nitrate Ointment in Treatment of Chronic Fissure in Ano
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 4, December 2006 The Use of Glyceryl Tri-Nitrate Ointment in Treatment of Chronic Fissure in Ano Suhair Al-Saad, MBChB,FRCS I,CABS,* Hamdi Al- Shenawi, MBBS, FRCS
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 28, No. 4, December 2006 The Use of Glyceryl Tri-Nitrate Ointment in Treatment of Chronic Fissure in Ano Suhair Al-Saad, MBChB,FRCS I,CABS,* Hamdi Al- Shenawi, MBBS, FRCS
Routine Internal Sphincterotomy with Hemorrhoidectomy: A Prospective Study
 Original Article DOI:./ijss// Routine Internal Hemorrhoidectomy: A Prospective Study S Harish, R Raxith Sringeri, G Ajay Associate Professor, Department of Surgery, JSS University, Mysore, Karnataka, India,
Original Article DOI:./ijss// Routine Internal Hemorrhoidectomy: A Prospective Study S Harish, R Raxith Sringeri, G Ajay Associate Professor, Department of Surgery, JSS University, Mysore, Karnataka, India,
Closed Versus Open Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy in Treatment of Chronic Anal Fissure: A Comparative Study
 Original Article Archives of Clinical Experimental Surgery Closed Versus Open Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy in Treatment of Chronic Anal Fissure: A Comparative Study Hamid H. Sarhan Abstract Background:
Original Article Archives of Clinical Experimental Surgery Closed Versus Open Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy in Treatment of Chronic Anal Fissure: A Comparative Study Hamid H. Sarhan Abstract Background:
Local Glyceryl Trinitrate Versus Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy In Management Of Anal Fissure
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 22 Number 2 Local Glyceryl Trinitrate Versus Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy In Management Of Anal Fissure G El-Labban, G El-Gazzaz, E Hokamam Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 22 Number 2 Local Glyceryl Trinitrate Versus Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy In Management Of Anal Fissure G El-Labban, G El-Gazzaz, E Hokamam Citation
Randomized controlled study: radiofrequency coagulation and plication versus ligation and excision technique for rectal mucosal prolapse
 The American Journal of Surgery 19 (6) 155 16 Clinical surgery International Randomized controlled study: radiofrequency coagulation and plication versus ligation and excision technique for rectal mucosal
The American Journal of Surgery 19 (6) 155 16 Clinical surgery International Randomized controlled study: radiofrequency coagulation and plication versus ligation and excision technique for rectal mucosal
Benign anorectal diseases
 Benign anorectal diseases Symptoms Bleeding Pruritus Discharge Fecal incontinence Diarrhea Constipation False need to defecate Examinations Clinical exam Anuscopy Rectosigmoidoscopy Endosonography MRI
Benign anorectal diseases Symptoms Bleeding Pruritus Discharge Fecal incontinence Diarrhea Constipation False need to defecate Examinations Clinical exam Anuscopy Rectosigmoidoscopy Endosonography MRI
Case Presentation and Discussion on GI Bleeding Nolan Ortega Aludino, M.D.
 Case Presentation and Discussion on GI Bleeding Nolan Ortega Aludino, M.D. General Data R.L. R.L. 4343 years old MaleMale PacoPaco Manila Chief Complaint Anal Anal bleeding History of Present Illness 3
Case Presentation and Discussion on GI Bleeding Nolan Ortega Aludino, M.D. General Data R.L. R.L. 4343 years old MaleMale PacoPaco Manila Chief Complaint Anal Anal bleeding History of Present Illness 3
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 3 2013 Article 5 Closed Versus Open Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy Technique in Treatment of Anal Fissure Seyed Reza Mousavi Jr Shohada Medical Center,
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 3, Issue 3 2013 Article 5 Closed Versus Open Lateral Internal Sphincterotomy Technique in Treatment of Anal Fissure Seyed Reza Mousavi Jr Shohada Medical Center,
Landmarks in the History of Haemorrhoids
 Landmarks in the History of Haemorrhoids Charles V. Mann Date Comments c.2250 BC 1700 BC 1552 BC 460-375 BC Old Testament, Samuel 5:9 Old Testament Samuel 5:12 25 BC-AD 50 AD 130-200 Sometime between the
Landmarks in the History of Haemorrhoids Charles V. Mann Date Comments c.2250 BC 1700 BC 1552 BC 460-375 BC Old Testament, Samuel 5:9 Old Testament Samuel 5:12 25 BC-AD 50 AD 130-200 Sometime between the
Stapled haemorrhoidopexy for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a review of our experience
 Original paper Videosurgery Stapled haemorrhoidopexy for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a review of our experience Wiesław Pesta 1, Adam Wirkowski 2, Krzysztof Leksowski 3,4 1Clinical Department of General
Original paper Videosurgery Stapled haemorrhoidopexy for the treatment of haemorrhoids: a review of our experience Wiesław Pesta 1, Adam Wirkowski 2, Krzysztof Leksowski 3,4 1Clinical Department of General
Common Office Anorectal Problems
 Common Office Anorectal Problems Sandra J. Beck, M.D., FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Colon and Rectal Surgery University of Kentucky Medical Center l None Disclosures Benign Anal Rectal Disease l
Common Office Anorectal Problems Sandra J. Beck, M.D., FACS, FASCRS Associate Professor of Colon and Rectal Surgery University of Kentucky Medical Center l None Disclosures Benign Anal Rectal Disease l
Recent trends in management of haemorrhoids
 International Surgery Journal Ali SA et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Apr;4(4):1276-1280 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20171127
International Surgery Journal Ali SA et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Apr;4(4):1276-1280 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20171127
P. Giordano P. Nastro A. Davies G. Gravante
 Tech Coloproctol (2011) 15:67 73 DOI 10.1007/s10151-010-0667-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prospective evaluation of stapled haemorrhoidopexy versus transanal haemorrhoidal dearterialisation for stage II and III
Tech Coloproctol (2011) 15:67 73 DOI 10.1007/s10151-010-0667-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prospective evaluation of stapled haemorrhoidopexy versus transanal haemorrhoidal dearterialisation for stage II and III
K Tirumala Prasad 1*, R V Apparao 2. Original Research Article. Abstract
 Original Research Article Stapler hemorrhoidectomy versus Milligan Morgan hemorrhoidectomy in hemorrhoids in terms of post-operative pain and hospital stay - A prospective randomized control trial K Tirumala
Original Research Article Stapler hemorrhoidectomy versus Milligan Morgan hemorrhoidectomy in hemorrhoids in terms of post-operative pain and hospital stay - A prospective randomized control trial K Tirumala
A Comparative Study of Different Treatments of Hemorrhoids
 From the Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah. Adnan M. R. Jamjoom, MD; Yasir S. Jamal, MD Address reprint requests and correspondence to Dr. Jamjoom: Department of Surgery, King Abdulaziz
From the Faculty of Medicine, King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah. Adnan M. R. Jamjoom, MD; Yasir S. Jamal, MD Address reprint requests and correspondence to Dr. Jamjoom: Department of Surgery, King Abdulaziz
THE RATIONAL TREATMENT OF INTERNAL HEMORRHOID BASED ON ITS PATHOGENESIS
 THE RATIONAL TREATMENT OF INTERNAL HEMORRHOID BASED ON ITS PATHOGENESIS Ignatius Riwanto Dept. of Surgery, Digestive div. Diponegoro Medical Faculty ACUTE CARE SURGERY BANDUNG FEBRUARY 2018 HEMORRHOID
THE RATIONAL TREATMENT OF INTERNAL HEMORRHOID BASED ON ITS PATHOGENESIS Ignatius Riwanto Dept. of Surgery, Digestive div. Diponegoro Medical Faculty ACUTE CARE SURGERY BANDUNG FEBRUARY 2018 HEMORRHOID
ORIGINAL ARTICLES. Day-clinic. Orifice surgery, cost-benefit analysis.
 MAY/JUNE REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 54 (3): 75-80, 1999 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ORIFICE DISEASES PROJECT - EXPERIENCE OF THE HOSPITAL DAS CLÍNICAS UNIVERSITY OF SÃO PAULO MEDICAL CENTER IN DAY-HOSPITAL
MAY/JUNE REV. HOSP. CLÍN. FAC. MED. S. PAULO 54 (3): 75-80, 1999 ORIGINAL ARTICLES ORIFICE DISEASES PROJECT - EXPERIENCE OF THE HOSPITAL DAS CLÍNICAS UNIVERSITY OF SÃO PAULO MEDICAL CENTER IN DAY-HOSPITAL
Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy (Haemorrhoidopexy) for the Treatment of Haemorrhoids
 Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy (Haemorrhoidopexy) for the Treatment of Haemorrhoids Produced by: CRD/CHE Technology Assessment Group (Centre for Reviews and Dissemination/Centre for Health Economics), University
Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy (Haemorrhoidopexy) for the Treatment of Haemorrhoids Produced by: CRD/CHE Technology Assessment Group (Centre for Reviews and Dissemination/Centre for Health Economics), University
A study of surgical profile of patients undergoing hemorrhoidectomy
 International Surgery Journal Pande PK et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):2947-2951 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173613
International Surgery Journal Pande PK et al. Int Surg J. 2017 Sep;4(9):2947-2951 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20173613
A Randomized Trial of Transanal Hemorrhoidal Dearterialization With Anopexy Compared With Open Hemorrhoidectomy in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION A Randomized Trial of Transanal Hemorrhoidal Dearterialization With Anopexy Compared With Open Hemorrhoidectomy in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids Solveig E. Elmér, M.D. Jonas O. Nygren,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION A Randomized Trial of Transanal Hemorrhoidal Dearterialization With Anopexy Compared With Open Hemorrhoidectomy in the Treatment of Hemorrhoids Solveig E. Elmér, M.D. Jonas O. Nygren,
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed defaecation syndrome
 Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
Stapled transanal rectal resection for obstructed Issued: June 2010 www.nice.org.uk/ipg351 NHS Evidence has accredited the process used by the NICE Interventional Procedures Programme to produce interventional
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences Available online at: Original Article
 International Journal of Research in Health Sciences Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Original Article A Comparative Study of Hemorrhoidectomy using Ligasure v/s Conventional Open Method Rahul
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Original Article A Comparative Study of Hemorrhoidectomy using Ligasure v/s Conventional Open Method Rahul
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery
 World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 2, Issue 1 10 Article 12 LOCAL GLYCERYL TRINITRATE VERSUS LATERAL INTERNAL SPHINCTEROTOMY IN MANAGEMENT OF ANAL FISSURE gouda m. ellabban galal elkazaz emad hokam
World Journal of Colorectal Surgery Volume 2, Issue 1 10 Article 12 LOCAL GLYCERYL TRINITRATE VERSUS LATERAL INTERNAL SPHINCTEROTOMY IN MANAGEMENT OF ANAL FISSURE gouda m. ellabban galal elkazaz emad hokam
Original Article Clinical observation on treatment of mixed hemorrhoids with milligan morgan hemorrhoidectomy combined with purse-string suture
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(11):12555-12562 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0080094 Original Article Clinical observation on treatment of mixed hemorrhoids with milligan morgan hemorrhoidectomy combined
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(11):12555-12562 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0080094 Original Article Clinical observation on treatment of mixed hemorrhoids with milligan morgan hemorrhoidectomy combined
Letters to the Editor
 Letters to the Editor Evidence-Based Guidelines? To the Editor In a recent issue of Diseases of the Colon & Rectum, The Standards Practice Task Force of The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons
Letters to the Editor Evidence-Based Guidelines? To the Editor In a recent issue of Diseases of the Colon & Rectum, The Standards Practice Task Force of The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons
19th Annual International Colorectal Disease Symposium An International Exchange of Medical and Surgical Concepts
 Wednesday, February 13, 2008 7-9:00p Early Check-In / Registration (Grand Ballroom Foyer) Thursday, February 14, 2008 6:45 AM Breakfast (Caribbean Ballroom and Foyer) 7:00 AM Registration (Grand Ballroom
Wednesday, February 13, 2008 7-9:00p Early Check-In / Registration (Grand Ballroom Foyer) Thursday, February 14, 2008 6:45 AM Breakfast (Caribbean Ballroom and Foyer) 7:00 AM Registration (Grand Ballroom
RAR) FOR TREATMENT HEMORRHOID III-IV IV GRADE : A NEW MINI-INVASIVE INVASIVE TECHNOLOLOGY
 TRANSANAL DOPPLER-GUIDED HEMORRHOIDAL ARTERY LIGATION / RECTO ANAL REPAIR (HAL-RAR RAR) FOR TREATMENT HEMORRHOID III-IV IV GRADE : A NEW MINI-INVASIVE INVASIVE TECHNOLOLOGY Author: : Zagryadskiy Eugeny
TRANSANAL DOPPLER-GUIDED HEMORRHOIDAL ARTERY LIGATION / RECTO ANAL REPAIR (HAL-RAR RAR) FOR TREATMENT HEMORRHOID III-IV IV GRADE : A NEW MINI-INVASIVE INVASIVE TECHNOLOLOGY Author: : Zagryadskiy Eugeny
Documented Complications of Staple Hemorrhoidopexy: A Systematic Review
 Int Surg 2015;100:44 57 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00173.1 Documented Complications of Staple Hemorrhoidopexy: A Systematic Review Liesel J. Porrett, Jemma K. Porrett, Yik-Hong Ho Townsville Hospital, Queensland,
Int Surg 2015;100:44 57 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-13-00173.1 Documented Complications of Staple Hemorrhoidopexy: A Systematic Review Liesel J. Porrett, Jemma K. Porrett, Yik-Hong Ho Townsville Hospital, Queensland,
2015 General Surgery Survival Guide
 2015 General Surgery Survival Guide Chapter 9: Hemorrhoids New codes in the block: 45350 & 45398 45350: Sigmoidoscopy, flexible; with band ligation(s) (eg, hemorrhoids) 45398: Colonoscopy, flexible; with
2015 General Surgery Survival Guide Chapter 9: Hemorrhoids New codes in the block: 45350 & 45398 45350: Sigmoidoscopy, flexible; with band ligation(s) (eg, hemorrhoids) 45398: Colonoscopy, flexible; with
International Journal of Surgery
 International Journal of Surgery 8 (21) 243 247 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Scalpel Ò compared with bipolar electro-cautery
International Journal of Surgery 8 (21) 243 247 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Scalpel Ò compared with bipolar electro-cautery
Surgical Treatment Of Hemorrhoids READ ONLINE
 Surgical Treatment Of Hemorrhoids READ ONLINE If you are searching for a book Surgical Treatment of Hemorrhoids in pdf format, then you've come to the right site. We present full variation of this book
Surgical Treatment Of Hemorrhoids READ ONLINE If you are searching for a book Surgical Treatment of Hemorrhoids in pdf format, then you've come to the right site. We present full variation of this book
Correspondence should be addressed to Michal Romaniszyn,
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2012, Article ID 324040, 6 pages doi:10.1100/2012/324040 The cientificworldjournal Clinical Study Doppler-Guided Hemorrhoid Artery Ligation with Recto-Anal-Repair Modification:
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2012, Article ID 324040, 6 pages doi:10.1100/2012/324040 The cientificworldjournal Clinical Study Doppler-Guided Hemorrhoid Artery Ligation with Recto-Anal-Repair Modification:
DISEASES OF THE COLON, RECTUM, & ANUS
 DISEASES OF THE COLON, RECTUM, & ANUS Rocco Ricciardi, MD, MPH Chief, Section of Colon & Rectal Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Surgery Harvard Medical School CASE 1 Hemorrhoid
DISEASES OF THE COLON, RECTUM, & ANUS Rocco Ricciardi, MD, MPH Chief, Section of Colon & Rectal Surgery Massachusetts General Hospital Associate Professor of Surgery Harvard Medical School CASE 1 Hemorrhoid
Life Science Journal 2018;15(4)
 LigaSure hemorrhoidectomy compared with stapled hemorrhoidopexy for management of grade III and IV hemorrhoids: A prospective randomized study. Islam M. Ibrahim MD, Abd Elrahman Metwalli MD, Ashraf Goda
LigaSure hemorrhoidectomy compared with stapled hemorrhoidopexy for management of grade III and IV hemorrhoids: A prospective randomized study. Islam M. Ibrahim MD, Abd Elrahman Metwalli MD, Ashraf Goda
Combined Colonoscopy and Three-Quadrant Hemorrhoidal Ligation: 500 Consecutive Cases
 Combined Colonoscopy and Three-Quadrant Hemorrhoidal Ligation: 500 Consecutive Cases Kurt G. Davis, M.D., Arie E. Pelta, M.D., David N. Armstrong, M.D., F.R.C.S. Georgia Colon & Rectal Surgical Clinic,
Combined Colonoscopy and Three-Quadrant Hemorrhoidal Ligation: 500 Consecutive Cases Kurt G. Davis, M.D., Arie E. Pelta, M.D., David N. Armstrong, M.D., F.R.C.S. Georgia Colon & Rectal Surgical Clinic,
, may spread caudally to present as a perianal abscess, laterally across the external sphincter to form an ischiorectal abscess or, rarely,
 ANORECTAL ABSCESSES , may spread caudally to present as a perianal abscess, laterally across the external sphincter to form an ischiorectal abscess or, rarely, superiorly above the anorectal junction
ANORECTAL ABSCESSES , may spread caudally to present as a perianal abscess, laterally across the external sphincter to form an ischiorectal abscess or, rarely, superiorly above the anorectal junction
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Research SJIF Impact Factor 5.990
 SJIF Impact Factor 5.990 Volume 4, Issue 9, 608-613. Review Article ISSN 2277 7105 AYURVEDIC MANAGEMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS *Dr Sunil Kumar Pandey Lecturer, Deptt. of Shalya Tantra, A & U Tibbia College & Hospital,
SJIF Impact Factor 5.990 Volume 4, Issue 9, 608-613. Review Article ISSN 2277 7105 AYURVEDIC MANAGEMENT OF HEMORRHOIDS *Dr Sunil Kumar Pandey Lecturer, Deptt. of Shalya Tantra, A & U Tibbia College & Hospital,
Evaluation of transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization: a single surgeon experience
 Tech Coloproctol (2015) 19:153 157 DOI 10.1007/s10151-015-1269-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization: a single surgeon experience G. D. LaBella W. P. L. Main L. R. Hussain
Tech Coloproctol (2015) 19:153 157 DOI 10.1007/s10151-015-1269-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization: a single surgeon experience G. D. LaBella W. P. L. Main L. R. Hussain
Although disparate topics, these two different pathologic
 34 H E M O R R H O I D S A N D R E C T A L P R O L A P S E CHARLES N. HEADRICK MICHAEL J. STAMOS Although disparate topics, these two different pathologic entities are commonly misdiagnosed by both layperson
34 H E M O R R H O I D S A N D R E C T A L P R O L A P S E CHARLES N. HEADRICK MICHAEL J. STAMOS Although disparate topics, these two different pathologic entities are commonly misdiagnosed by both layperson
The third generation of HAL-RAR equipment combines all the advantages of these procedures with the world s first wireless technology for
 The third generation of HAL-RAR equipment combines all the advantages of these procedures with the world s first wireless technology for Doppler-guided treatment of haemorrhoids. Comfort and convenience
The third generation of HAL-RAR equipment combines all the advantages of these procedures with the world s first wireless technology for Doppler-guided treatment of haemorrhoids. Comfort and convenience
DG-RAR for the treatment of symptomatic grade III and grade IV haemorrhoids: a 12-month multi-centre, prospective observational study
 Eur Surg (2013) 45:26 30 DOI 10.1007/s10353-012-0182-8 DG-RAR for the treatment of symptomatic grade III and grade IV haemorrhoids: a 12-month multi-centre, prospective observational study S. Roka, D.
Eur Surg (2013) 45:26 30 DOI 10.1007/s10353-012-0182-8 DG-RAR for the treatment of symptomatic grade III and grade IV haemorrhoids: a 12-month multi-centre, prospective observational study S. Roka, D.
Motility Disorders. Pelvic Floor. Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 701) January 2010 November 2011
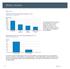 Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
Motility Disorders Pelvic Floor Colorectal Center for Functional Bowel Disorders (N = 71) January 21 November 211 New Patients 35 3 25 2 15 1 5 Constipation Fecal Incontinence Rectal Prolapse Digestive-Genital
Hyung Kyu Yang. Hemorrhoids
 Hyung Kyu Yang Hemorrhoids 123 Hemorrhoids Hyung Kyu Yang Hemorrhoids Hyung Kyu Yang Yang Hospital Seoul Republic of Korea Videos to this book can be accessed at http://www.springerimages.com/videos/978-3-642-41797-9
Hyung Kyu Yang Hemorrhoids 123 Hemorrhoids Hyung Kyu Yang Hemorrhoids Hyung Kyu Yang Yang Hospital Seoul Republic of Korea Videos to this book can be accessed at http://www.springerimages.com/videos/978-3-642-41797-9
