Patient comfort and surgeon satisfaction during cataract surgery using topical anesthesia with or without dexmedetomidine sedation
|
|
|
- Thomas Rice
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Erdurmus:Shoja :33 Pagina 361 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 3, 2008 / pp Patient comfort and surgeon satisfaction during cataract surgery using topical anesthesia with or without dexmedetomidine sedation M. ERDURMUS 1, B. AYD N 1, B. USTA 2, R. YAĞC 1, M. GOZDEM R 2, Y. TOTAN 1 1 Department of Ophthalmology 2 Department of Anesthesia and Critical Care, Fatih University Medical School, Ankara - Turkey PURPOSE. To determine the safety and efficacy of perioperative dexmedetomidine (Dex) sedation on patient comfort and surgeon satisfaction during cataract surgery under topical anesthesia. METHODS. Forty-four patients having routine clear corneal phacoemulsification surgery under topical anesthesia were included in the study. Patients were randomly divided into two groups: Dex group (n=22) and control group (n=22). Patients in the Dex group were to receive intravenous Dex using an infusion pump and those in the control group were to receive 0.9% saline infusion. Primary outcome measures were patient comfort, surgeon satisfaction, and patient pain perception. RESULTS. There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of baseline characteristics including age, sex, eye side, pupil diameter, and vital signs (p>0.05 for all). Patient comfort and surgeon satisfaction in Dex group was better than in control group (p=0.042 and p=0.003, respectively). The mean pain perception score was lesser in the Dex group (1.23±1.72) than control group (3.64±1.43), (p<0.001). The mean surgical time and intraoperative complications were similar in both groups (p>0.05). There was no significant effect of the Dex sedation on vital signs perioperatively (p>0.05 for all). CONCLUSIONS. Dex sedation improved patient and surgeon satisfaction and decreased patients pain perception while undergoing cataract surgery under topical anesthesia. It appears to be a safe and suitable choice of sedation for cataract surgery. (Eur J Ophthalmol 2008; 18: 361-7) KEY WORDS. Cataract surgery, Dexmedetomidine sedation, Patient comfort, Surgeon satisfaction Accepted: November 27, 2007 INTRODUCTION For many years, retrobulbar and peribulbar anesthesia were the standard for cataract surgery; however, many serious adverse effects have been reported (1, 2). With the introduction of modern phacoemulsification cataract surgery, topical anesthesia without retrobulbar or periocular injections has become a well-established, minimally invasive technique (3). The addition of intracameral lidocaine to topical anesthesia has been shown to reduce intraocular sensation during phacoemulsification safely and effectively (4), thus addressing an important perceived disadvantage of the topical anesthetic option. However, ideal anesthesia should allow patients to relax in the hands of a skilled surgeon, give the surgeon the opportunity to concentrate exclusively on the primary goals of cataract surgery, and eliminate surgical discomfort from awareness, pressure, and pain. Nielsen and Allerod (5) found that topical anesthesia without sedation has an incomplete intraocular anesthetic effect. The use of complementary intravenous (IV) sedation is thought to increase patients comfort and satisfaction during surgery (6). Presented as a poster at the XXV ESCRS Congress; Stockholm; September 8-12, 2007 Wichtig Editore, /361-07$25.00/0
2 Erdurmus:Shoja :33 Pagina 362 Dexmedetomidine sedation and cataract surgery Several techniques of IV sedation have been advocated, with varying success (6, 7). Nowadays, several drugs have been used for sedation during cataract surgery, including propofol, benzodiazepines, and opioids (8-10). However, propofol may cause oversedation and disorientation (8), benzodiazepines may result in confusion, particularly when administered to elderly patients (11), and opioids are associated with increased risk of respiratory depression and oxygen desaturation (10). All of these untoward effects may hamper patients cooperation during surgery (7), and would make these agents less than ideal for the intraoperative management of sedation. In contrast, dexmedetomidine (Dex) is a highly selective α2- adrenoceptor agonist with both sedative and analgesic properties and is devoid of respiratory depressant effect (12). Dex has been used mainly in the intensive care unit as a sedative agent with some analgesic properties; however, its efficacy outside the critical care environment has also been documented without adverse effects (13, 14), and patients typically remain cooperative while sedated (14, 15). The aim of this study was to ascertain whether IV sedation using Dex minimizes pain and increases patient and surgeon satisfaction in routine phacoemulsification cataract extraction with foldable intraocular lens (IOL) implantation using topical anesthesia. METHODS A prospective randomized double-blind trial was performed after local ethics committee approval. Forty-four patients having routine elective clear corneal phacoemulsification surgery under topical anesthesia were included in the study. All patients received written details of the study and signed an informed consent form before participating. Patients were excluded according to the following criteria: mature cataract, previous ocular surgery, inflammation or injury, pharmacologic mydriasis less than 5 mm, shallow anterior chamber, nystagmus, muscle spasm around the eye, orthopnea, breakdown in communication or cooperation such as deafness, senile dementia, and claustrophobia, sensitivity to study drugs, uncontrolled hypertension, and history of hepatic disease. All patients received diclofenac sodium 0.1%, two drops every 20 minutes two times; phenylephrine hydrochloride 2.5%, one drop every 5 minutes two times; and cyclopentolate 1%, one drop every 5 minutes three times beginning 45 minutes before the procedure for pharmacologic mydriasis. On arrival to the anesthesia room, patients were randomized to one of two groups. All patients had an IV cannula inserted by an experienced anesthetist. Anesthesia and sedation techniques Patients arrived in the operating room un-premedicated. Baseline vital signs including heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and O 2 saturation were taken. A 20 gauge cannula was inserted into one of the two nasal prongs of an oxygen nasal cannula. Other standard monitors including electrocardiogram, noninvasive arterial pressure, and pulse oximeter were also applied, and oxygen was administered at 2 liter/min in all patients. Patients in the sedation group were to receive IV dexmedetomidine 1 µg/kg over 10 min using an infusion pump and this was followed by a continuous infusion of Dex µg/kg titrated to Ramsey sedation score of 3 (16). The control group received 0.9% saline infusion. Both surgeon and patient were masked as to whether IV sedation was administered perioperatively. The nurse assessing the patients pain score, patient satisfaction, surgeon satisfaction, and other outcome measures was also masked to the randomization schedule. This schedule was kept by the anesthetist until the end of the study. The anesthetist was not involved in outcomes evaluation or data analysis. Topical anesthesia comprised proparacaine 0.5% drops administered into the conjunctival sac three or four times in the 10 minutes preceding surgery. A protocol was established for supplemental anesthesia for breakthrough pain during the surgery. If a patient reported pain, two additional drops of topical anesthetic were placed in the eye. If pain persisted, the anterior chamber was irrigated with lidocaine 1% solution. Surgical technique All surgical procedures began 10 to 15 minutes after randomization. After standard aseptic preparation, a wire speculum was inserted and the operating microscope was swung into position and turned on. Phacoemulsification was performed with a Sovereign phacoemulsifier through a superior temporal or nasal, two-plane, 3.2 mm clear corneal incision, two side-port paracentesis; a mm continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis; hydrodissection with balanced salt solution (BSS); and 362
3 Erdurmus:Shoja :33 Pagina 363 Erdurmus et al cataract extraction by the stop and chop technique in all patients. The clear corneal incision was enlarged to a maximum of 3.5 to 4.0 mm. Sodium hyaluronate was injected into the capsular bag in all patients and a singlepiece foldable hydrophilic acrylic IOL was implanted. After the ophthalmic viscoelastic substance was removed, the wound was sealed by corneal stromal hydration. All surgical procedures were performed by one experienced ophthalmic surgeon (M.E.). Primary outcome measures Patient satisfaction. The patients were asked to rate their satisfaction with the operative experience on a five-point satisfaction scale: 0 = extremely dissatisfied; 1 = dissatisfied; 2 = neither satisfied nor dissatisfied; 3 = satisfied; 4 = extremely satisfied. Patients were also asked whether they would choose the same anesthesia method if they had surgery in the fellow eye. Surgeon satisfaction. The surgeon was asked to rate satisfaction and patient cooperation during surgery (4 = excellent; 3 = good; 2 = fair; 1 = poor; 0 = extremely poor). Patient s pain perception. Immediately after the conclusion of surgery, patients were asked to assess pain they experienced during surgery using the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) (17): 0 = none, 1 = slight discomfort, 2 = slight to light 3 = light, 4 = light to moderate, 5 = moderate, 6 = moderate to severe, 7 = severe, 8 = very severe, 9 = excruciating, 10 = worst pain imaginable. Secondary outcome measures Pupil diameter. Because of the inhibitory effects of Dex on pupilloconstrictor nucleus, we measured the effect of this agent on the duration of pupil size during surgery (18). The horizontal pupil diameter was measured using Castroviejo surgical caliper at the beginning of surgery, after nucleus delivery, and after IOL implantation. All measurements were obtained after the viscoelastic material was removed. Intraoperative complications. Complications such as squeezing of eyelids, inadvertent eye or head movement, posterior capsule rupture, and vitreous loss were reported immediately after the surgery. Mean surgical time. Immediately after the conclusion of surgery, the total time spent between creating corneal incisions and corneal stromal hydration was documented. Vital signs. Heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressures, and arterial oxygen saturation were taken before the drug infusion, at the beginning of the surgery and every 10 minutes during surgery, and at the end of the surgery. Statistical analysis Data analysis was performed by using SPSS statistical software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) version 11.5 for Windows. Data were shown as mean ± standard deviation for continuous variables, median (minimum maximum) for ordinal ones, and frequency with percent for categorical ones. Means were compared using Student t or Mann-Whitney U test, where appropriate. Difference among vital signs and pupil diameters were evaluated by repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) or Friedman test. When the p value from the ANOVA and Friedman test statistics are statistically significant, Bonferroni and Friedman multiple comparison tests were used to know which measurements differ from which others. Categorical comparisons were made by using chi-square or Fisher exact test, where appropriate. A p value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS This study comprised 44 eyes of 44 patients, with 22 eyes having topical anesthesia under Dex sedation and 22 having topical anesthesia only for surgery. Table I shows the baseline characteristics of the patients in both groups. There was no difference between the groups in terms of baseline characteristics (p>0.05 for all). The mean pain perception score was less in the Dex group than control group, 1.23±1.72 (range 0 to 5) and 3.64±1.43 (range 0 to 6), respectively. Patients in Dex group reported better satisfaction scores and this was statistically significant (p=0.042). The mean surgeon satisfaction score was higher in the Dex group than control group, 3.41±0.80 (range 2 to 4) and 2.36±1.26 (range 0 to 4), respectively. Surgeon satisfaction in Dex group was also better than in control group (p=0.003). Patients pain perception scores according to the VAS 363
4 Erdurmus:Shoja :33 Pagina 364 Dexmedetomidine sedation and cataract surgery TABLE I - BASELINE PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS Dex group Control group Number of patients Age, yr 67.41±9.83 (44 80) 69.46±9.99 (52 85) Sex (male/female) 7/15 8/14 Eye (right/left) 12/10 11/11 Preoperative Systolic arterial pressure (mmhg) ±28.07 ( ) ±17.64 ( ) Diastolic arterial pressure (mmhg) 85.45±13.57 (61 118) 91.13±14.70 (60 123) Heart rate (beats per min) 76.46±11.67 (54 107) 78.55±12.74 (57 100) Oxygen saturation (%) 97.45±1.65 (92 100) 96.82±2.28 (90 99) Pupil diameter (mm) 8.31±0.55 ( ) 7.91±0.97 ( ) Data presented as mean ± standard deviation (range) or absolute numbers. Dex = Dexmedetomidine TABLE II - PATIENTS PAIN PERCEPTION SCORES AC- CORDING TO THE 10-POINT SCALE DUR- ING CATARACT SURGERY IN THE GROUPS Pain perception score Dex Control None (0) 13 (59.1) 1 (4.5) Slight discomfort (1) 2 (9.1) 1 (4.5) Slight to light (2) 1 (4.5) Light (3) 4 (18.2) 6 (27.3) Light to moderate (4) 2 (9.1) 8 (36.4) Moderate (5) 1 (4.5) 3 (13.6) Moderate to severe (6) 2 (9.1) Severe (7) Very severe (8) Excruciating (9) Worst pain imaginable (10) Values are n (%) of eyes. The mean pain perception score was less in the Dex group tahn control group, 1.23±1.72 (range 0 to 5) and 3.64±1.43 (range 0 to 6), respectively. Dex = Dexmedetomidine during cataract surgery in Dex and control groups are summarized in Table II. The mean pain perception score was less in the Dex group than control group, 1.23±1.72 (range 0 to 5) and 3.64±1.43 (range 0 to 8), respectively. The difference of pain perception between the groups was statistically significant (p<0.001). The question Would you choose the same anesthesia method if you had surgery in the fellow eye? was answered Yes by all of the Dex group and 18 patients (81.8%) in the control group. This difference was not statistically significant (p=0.108). The mean horizontal pupil diameter at baseline was 8.31±0.55 mm in Dex group and 7.92±0.97 mm in control group, after nucleus removal was 6.20±1.41 mm in Dex group and 5.82±1.18 mm in control group, and after IOL implantation was 5.25±1.21 mm in Dex group and 4.61±1.07 mm in control group. Although the horizontal pupil was higher in Dex group at all the timepoints, there was no statistically significant difference between the groups (p>0.05 for all). The mean surgical time in Dex group was 25.41±6.05 minutes (median 24.5 minutes, range 15 to 35 minutes) and control group was 23.18±3.97 minutes (median 23.5 minutes, range 15 to 32 minutes). There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of mean surgical time (p=0.158). Differences in systolic and diastolic pressures and heart rate during surgery are shown in Figures 1 and 2, respectively. There was no difference in oxygen saturation during surgery in Dex or control groups and between the groups (p>0.05 for all). Table III summarizes the intraoperative surgical complications and additional anesthesia requirement within the groups. Surgical complications and additional anesthesia requirement were relatively higher in the control group, but it was not statistically significant (p=0.24). In three patients, uncontrolled head movements occurred in Dex group. All of these patients were over 75 years of age. DISCUSSION This randomized, double-blind study demonstrated that sedation with Dex was more comfortable for patients and 364
5 Erdurmus:Shoja :33 Pagina 365 Erdurmus et al Fig. 1 - Perioperative systolic and diastolic arterial blood pressure changes in the groups. In control group, there was no difference in systolic and diastolic blood pressures perioperatively (p>0.05 for both). In addition, in Dex group, there was no difference in diastolic blood pressure, perioperatively. However, systolic blood pressure has a tendency to decrease during surgery in this group. But this was not statistically significant. Systolic or diastolic blood pressures in both groups did not differ at all time points (p>0.05 for all). P = Pressure. Fig. 2 - Perioperative heart rate changes in the groups. Initial, baseline, and intraoperative heart rate of the groups were not different (p=0.40). There was a tendency to decreased heart rate in Dex group after initiation of the sedation and this effect lasted at the end of surgery. In control group, heart rate was stable perioperatively. TABLE III - SURGICAL COMPLICATIONS AND ADDITIONAL ANESTHESIA REQUIREMENT Surgical complication Dex Control Inadvertent eye movement 1 (4.6) 3 (13.6) Inadvertent head movement 3 (13.6) Posterior capsule rupture Squeezing of eyelid 2 (9.1) Suturation 1 (4.6) Additional anesthesia requirement 2 (9.1) 6 (27.3) Values are n (%) of eyes. Dex = Dexmedetomidine the surgeon than without sedation in cataract surgery under topical anesthesia. Dex sedation did not significantly affect the hemodynamic parameters or pupil diameter perioperatively. A wide variety of local anesthesia options is available for cataract surgery. As cataract removal has become faster, safer, and less traumatic, the need for akinesia and anesthesia has declined significantly. In today s environment, akinesia is not the issue once it was and there is increasing concern to reduce the need for regional anesthesia and the morbidity associated with needle injections. Topical anesthesia effectively eliminates the risk of complications associated with regional blocks. Moreover, phacoemulsification using topical anesthesia has comparable pain levels as with sub-tenon (19) and peribulbar techniques (20) and offers a safe and effective alternative in the hands of experienced surgeons. Topical anesthesia without sedation, however, may have some disadvantages in terms of patient and surgeon satisfaction. Kallio et al (21) reported that patients having topical anesthesia needed additional sedation during surgery significantly more often than patients having a retrobulbar or peribulbar block. Still, about 4% of patients having topical anesthesia report being dissatisfied and having some discomfort during surgery in Uusitalo et al s study (22) In the present study, 13.6% (3 of 22) of the patients undergoing cataract surgery under topical anesthesia were dissatisfied while Dex group reported no dissatisfaction related with surgery. In light of our results, we suggest that Dex sedation increases patient satisfaction for routine elective cataract surgery under topical anesthesia. It is previously reported that Dex sedation was equally effective to midazolam in patients undergoing cataract surgery under peribulbar anesthesia (15). In addition, slightly better subjective patient satisfaction was reported compared with the midazolam in this study. These results are in keeping with those reported by Virkkila et al (23), who have demonstrated that a single dose of IM Dex administered 45 min before operation provides sedation comparable with that produced by IM midazolam. Sedative and analgesic properties along with its relatively short elimination half-life of 2 hours make Dex an attractive agent for sedation during monitored 365
6 Erdurmus:Shoja :33 Pagina 366 Dexmedetomidine sedation and cataract surgery anesthesia care for cataract surgery. Dex has several advantages for use as a sedative because it does not cause respiratory depression (12, 24). It is easy to arouse the treated patients and they can be calm and cooperative (25). However, with the need for fiscal responsibility, researchers have begun to question whether IV sedation and monitored anesthesia care during cataract surgery is necessary (26). The prolonged recovery associated with sedation and the costs associated with the presence of an anesthesiologist throughout surgery are disadvantages of IV Dex for clear corneal phacoemulsification surgery. Surgeon comfort is another important point for cataract surgery under topical anesthesia and it is directly related to patients cooperation. Communication with the patient is crucial to the success of topical anesthesia. The full range of eye movements under voluntary control may be advantageous to the surgeon during superior cortical cleanup and for better access to IOL implantation by instructing the patient to look up or look down. Most of the common sedatives for cataract surgery unlike Dex provide good sedation but not cooperation. Therefore, voluntary control of the eye movements, which is one of the fundamental aims of the topical anesthesia, may be troublesome. However, Dex provides good patient cooperation along with sedation and analgesia (25). The dose of Dex we used was chosen for similarities to a previous study (15). In the present study, three patients in Dex group exhibited unwanted head movement because of excessive sedation. We think that this event was the most important disadvantage of the drug. All of these patients were over 75 years of age. Lowering the dose of the drug or head fixation may be helpful for older patients (especially >75 years) before Dex-assisted cataract surgery. Although the pain induced by phacoemulsification with topical anesthesia is more difficult to characterize qualitatively (27), because of the patient s past cognitive experiences, cultural background and degree of anxiety affect this process (28). Dex sedation decreased the patient s pain perception versus that of control subjects in our study. This could be explained in part by the additional analgesic activity of Dex that could have contributed to improved patient pain perception. In conclusion, Dex in the studied dose provides satisfactory sedation during cataract surgery under topical anesthesia. Its characteristic conscious sedation enables good cooperation and potentially better operating conditions than that of topical anesthesia alone. However, head fixation seems to be necessary to control unwanted head movements, especially in older patients during cataract surgery with IV Dex sedation. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors thank Salih Ergocen, Ankara, Turkey, for statistical assistance. None of the authors has any competing financial interests in this study. Reprint requests to: Mesut Erdurmus, MD Department of Ophthalmology Fatih University Medical School Alparslan Turkes Cad No: Emek, Ankara, Turkey merdurmus@yahoo.com REFERENCES 1. Haider SA. Survey of complications associated with current practice of cataract surgery under local anaesthesia [letter]. Br J Ophthalmol 1994; 78: Gillow JT, Aggarwal RK, Kirkby GR. A survey of ocular perforation during ophthalmic local anaesthesia in the United Kingdom. Eye 1996; 10: Fichman RA. Use of topical anesthesia alone in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 1996; 22: Gills JP, Cherchio M, Raanan MG. Unpreserved lidocaine to control discomfort during cataract surgery using topical anesthesia. J Cataract Refract Surg 1997; 23: Nielsen PJ, Allerod CW. Evaluation of local anesthesia techniques for small incision cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 1998; 24: Wine NA. Sedation with neuroleptanalgesia in cataract surgery. Am J Ophthalmol 1966; 61: Salmon JF, Mets B, James MF, Murray AD. Intravenous sedation for ocular surgery under local anaesthesia. Br J Ophthalmol 1992; 76: Janzen PR, Christys A, Vucevic M. Patient-controlled sedation using propofol in elderly patients in day-case cataract surgery. Br J Anaesth 1999; 82: Aydin ON, Kir E, Ozkan SB, Gursoy F. Patient-controlled analgesia and sedation with fentanyl in phacoemulsi- 366
7 Erdurmus:Shoja :33 Pagina 367 Erdurmus et al fication under topical anesthesia. J Cataract Refract Surg 2002; 28: Wong DH, Merrick PM. Intravenous sedation prior to peribulbar anaesthesia for cataract surgery in elderly patients. Can J Anaesth 1996; 43: Weinbroum AA, Szold O, Ogorek D, Flaishon R. The midazolam-induced paradox phenomenon is reversible by flumazenil. Epidemiology, patient characteristics and review of the literature. Eur J Anaesthesiol 2001; 18: Hall JE, Uhrich TD, Barney JA, Arain SR, Ebert TJ. Sedative, amnesic, and analgesic properties of small-dose dexmedetomidine infusions. Anesth Analg 2000; 90: Aantaa R, Jaakola ML, Kallio A, Kanto J, Scheinin M, Vuorinen J. A comparison of dexmedetomidine, and alpha 2-adrenoceptor agonist, and midazolam as i.m. premedication for minor gynaecological surgery. Br J Anaesth 1991; 67: Alhashemi JA, Kaki AM. Dexmedetomidine in combination with morphine PCA provides superior analgesia for shockwave lithotripsy. Can J Anaesth 2004; 51: Alhashemi JA. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for monitored anaesthesia care during cataract surgery. Br J Anaesth 2006; 96: Ramsay MA, Savege TM, Simpson BR, Goodwin R. Controlled sedation with alphaxalone-alphadolone. Br Med J 1974; 2: Stevens JD. A new local anaesthesia technique for cataract extraction by one quadrant sub-tenon s infiltration. Br J Ophthalmol 1992; 76: Larson MD, Talke PO. Effect of dexmedetomidine, an alpha2-adrenoceptor agonist, on human pupillary reflexes during general anaesthesia. Br J Clin Pharmacol 2001; 51: Manners TD, Burton RL. Randomised trial of topical versus sub-tenon s local anaesthesia for small-incision cataract surgery. Eye 1996; 10: Zehetmayer M, Radax U, Skorpik C, et al. Topical versus peribulbar anesthesia in clear corneal cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 1996; 22: Kallio H, Uusitalo RJ, Maunuksela EL. Topical anesthesia with or without propofol sedation versus retrobulbar/peribulbar anesthesia for cataract extraction: prospective randomized trial. J Cataract Refract Surg 2001; 27: Uusitalo RJ, Maunuksela E-L, Paloheimo M, Kallio H, Laatikainen L. Converting to topical anesthesia in cataract surgery. J Cataract Refract Surg 1999; 25: Virkkila M, Ali-Melkkila T, Kanto J, Turunen J, Scheinin H. Dexmedetomidine as intramuscular premedication for day-case cataract surgery. A comparative study of dexmedetomidine, midazolam and placebo. Anaesthesia 1994; 49: Bhana N, Goa KL, McClellan KJ. Dexmedetomidine. Drugs 2000; 59: Ayoglu H, Altunkaya H, Ozer Y, et al. Dexmedetomidine sedation during cataract surgery under regional anaesthesia. Br J Anaesth 2007; 99: Rosenfeld SI, Litinsky SM, Snyder DA, et al. Effectiveness of monitored anesthesia care in cataract surgery. Ophthalmology 1999; 106: Coelho RP, Weissheimer J, Romao E, Velasco e Cruz AA. Pain induced by phacoemulsification without sedation using topical or peribulbar anesthesia. J Cataract Refract Surg 2005; 31: Melzack R. Psychological aspects of pain: implications for neural blockade. In: Cousins MJ, Bridenbaugh PO, eds. Clinical Anesthesia and Management of Pain, 3rd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott, 1998;
An Evaluation of Topical and Local Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification
 An Evaluation of Topical and Local Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification Z. Rizvi,T. Rehman,S. Malik,A. Qureshi,L. Paul,K. Qureshi,S. Memon,S Rafi,A. Ali ( Final Year Medical Students and Department of Ophthalmology*,
An Evaluation of Topical and Local Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification Z. Rizvi,T. Rehman,S. Malik,A. Qureshi,L. Paul,K. Qureshi,S. Memon,S Rafi,A. Ali ( Final Year Medical Students and Department of Ophthalmology*,
ISSN: (Paper) eissn: (Online) JOURNAL OF ADVANCED ACADEMIC RESEARCH (JAAR) April 2017
 Topical proparacaine vs combined topical-intracameral lidocaine anesthesia in phacoemulsification surgery with preoperative counseling about intraoperative visual fear Kiran Shakya 1, Sangita Shakya 2,
Topical proparacaine vs combined topical-intracameral lidocaine anesthesia in phacoemulsification surgery with preoperative counseling about intraoperative visual fear Kiran Shakya 1, Sangita Shakya 2,
Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery
 (Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2008, 59, 27-32) Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery O. YALCIN COK (*), A. ERTAN (**) and M. BAHADIR (**) Abstract : We compared the effect
(Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2008, 59, 27-32) Comparison of midazolam sedation with or without fentanyl in cataract surgery O. YALCIN COK (*), A. ERTAN (**) and M. BAHADIR (**) Abstract : We compared the effect
Type of intervention Anaesthesia. Economic study type Cost-effectiveness analysis.
 Comparison of the costs and recovery profiles of three anesthetic techniques for ambulatory anorectal surgery Li S T, Coloma M, White P F, Watcha M F, Chiu J W, Li H, Huber P J Record Status This is a
Comparison of the costs and recovery profiles of three anesthetic techniques for ambulatory anorectal surgery Li S T, Coloma M, White P F, Watcha M F, Chiu J W, Li H, Huber P J Record Status This is a
Penetrating keratoplsty (PKP) is traditionally performed under
 CLINICAL SCIENCES Combined Topical and Intracameral Anesthesia in Penetrating Keratoplasty Fani Segev, MD,* Aristotle N. Voineskos,* Gladwin Hui,* Michael S. H. Law, MD,* Robert Paul, MD,* Frances Chung,
CLINICAL SCIENCES Combined Topical and Intracameral Anesthesia in Penetrating Keratoplasty Fani Segev, MD,* Aristotle N. Voineskos,* Gladwin Hui,* Michael S. H. Law, MD,* Robert Paul, MD,* Frances Chung,
Comparison of topical versus peribulbar anaesthesia for manual small incision cataract surgery with intraocular lens implantation
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Joseph B et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Nov;4(11):4862-4866 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20163781
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Joseph B et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Nov;4(11):4862-4866 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20163781
IJBCP International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology
 Print ISSN 2319-2003 Online ISSN 2279-0780 IJBCP International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology doi: 10.5455/2319-2003.ijbcp20141220 Research Article Comparison of two different doses of dexmedetomidine
Print ISSN 2319-2003 Online ISSN 2279-0780 IJBCP International Journal of Basic & Clinical Pharmacology doi: 10.5455/2319-2003.ijbcp20141220 Research Article Comparison of two different doses of dexmedetomidine
Keywords: Dexmedetomidine, fentanyl, tympanoplasty, monitored anaesthesia care. INTRODUCTION:
 13 Original article A COMPARATIVE OBSERVATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN DEXMEDETOMIDINE V/S COMBINATION OF MIDAZOLAM- FENTANYL FOR TYMPANOPLASTY SURGERY UNDER MONITORED ANESTHESIA CARE Dr. Parul Pachotiya (Professor
13 Original article A COMPARATIVE OBSERVATIONAL STUDY BETWEEN DEXMEDETOMIDINE V/S COMBINATION OF MIDAZOLAM- FENTANYL FOR TYMPANOPLASTY SURGERY UNDER MONITORED ANESTHESIA CARE Dr. Parul Pachotiya (Professor
Visual perception during phacoemulsification cataract surgery under subtenons anaesthesia
 (23) 17, 51 55 & 23 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 95-222X/3 $25. www.nature.com/eye Visual perception during phacoemulsification cataract surgery under subtenons anaesthesia SS Wickremasinghe,
(23) 17, 51 55 & 23 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 95-222X/3 $25. www.nature.com/eye Visual perception during phacoemulsification cataract surgery under subtenons anaesthesia SS Wickremasinghe,
Sub-Tenon Versus Peribulbar Anaesthesia for Cataract Surgery
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No.3, September 2003 Sub-Tenon Versus Peribulbar Anaesthesia for Cataract Surgery Nada Al-Yousuf, FRCSEd * Purpose: The aim of this study is to compare the efficacy of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No.3, September 2003 Sub-Tenon Versus Peribulbar Anaesthesia for Cataract Surgery Nada Al-Yousuf, FRCSEd * Purpose: The aim of this study is to compare the efficacy of
Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical Trial
 J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
J Arch Mil Med. 1 August; (3): e1977. Published online 1 August 3. DOI: 1.81/jamm.1977 Research Article Comparison of Bier's Block and Systemic Analgesia for Upper Extremity Procedures: A Randomized Clinical
Clinical Study Perceived Pain during Cataract Surgery with Topical Anesthesia: A Comparison between First-Eye and Second-Eye Surgery
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2015, Article ID 383456, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/383456 Clinical Study Perceived Pain during Cataract Surgery with Topical
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Journal of Ophthalmology Volume 2015, Article ID 383456, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/383456 Clinical Study Perceived Pain during Cataract Surgery with Topical
Phacoemulsification with topical anesthesia: Resident experience
 J CATARACT REFRACT SURG - VOL 32, AUGUST 2006 Phacoemulsification with topical anesthesia: Resident experience Mustafa Ünal, MD, _Iclal Yücel, MD, Ahmet Sarıcı, MD, Özgür Artunay, MD, Kazım Devranoğlu,
J CATARACT REFRACT SURG - VOL 32, AUGUST 2006 Phacoemulsification with topical anesthesia: Resident experience Mustafa Ünal, MD, _Iclal Yücel, MD, Ahmet Sarıcı, MD, Özgür Artunay, MD, Kazım Devranoğlu,
They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest version of this NICE Pathway see:
 bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
bring together everything NICE says on a topic in an interactive flowchart. are interactive and designed to be used online. They are updated regularly as new NICE guidance is published. To view the latest
REVIEW ARTICLE. Ophthalmologic Procedures and Local/Regional Anesthetic Techniques
 REVIEW ARTICLE David C. Warltier, M.D., Ph.D., Editor Anesthesiology 2007; 107:502 8 Copyright 2007, the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sedation and Anesthesia
REVIEW ARTICLE David C. Warltier, M.D., Ph.D., Editor Anesthesiology 2007; 107:502 8 Copyright 2007, the American Society of Anesthesiologists, Inc. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Sedation and Anesthesia
Intraoperative visual experience and preoperative counselling during phacoemulsification under topical anaesthesia
 Journal of Kathmandu Medical College, Vol. 4, No. 2, Issue 12, Apr.-Jun., 2015 Original Article Intraoperative visual experience and preoperative counselling during phacoemulsification under topical anaesthesia
Journal of Kathmandu Medical College, Vol. 4, No. 2, Issue 12, Apr.-Jun., 2015 Original Article Intraoperative visual experience and preoperative counselling during phacoemulsification under topical anaesthesia
Single Injection versus Double Injection Peribulbar Anaesthesia in Eye Camp Surgery: a Comparative evaluation of Akinesia and Anaesthesia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 18 Number 2 Single Injection versus Double Injection Peribulbar Anaesthesia in Eye Camp Surgery: a Comparative P Singh, A Jadon, B Singh Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 18 Number 2 Single Injection versus Double Injection Peribulbar Anaesthesia in Eye Camp Surgery: a Comparative P Singh, A Jadon, B Singh Citation
Controlled Trial of Wound Infiltration with Bupivacaine for Post Operative Pain Relief after Caesarean Section
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.23, No.2, June 2001 Controlled Trial of Wound Infiltration with Bupivacaine for Post Operative Pain Relief after Caesarean Section Omar Momani, MD, MBBS, JBA* Objective: The
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.23, No.2, June 2001 Controlled Trial of Wound Infiltration with Bupivacaine for Post Operative Pain Relief after Caesarean Section Omar Momani, MD, MBBS, JBA* Objective: The
Outcomes of manual small incision cataract surgery under topical anesthesia with lignocaine 2% jelly
 Original articles Outcomes of manual small incision cataract surgery under topical anesthesia with lignocaine 2% jelly Mithal C, Agarwal P, Mithal N Upgraded Department of Ophthalmology LLRM Medical College
Original articles Outcomes of manual small incision cataract surgery under topical anesthesia with lignocaine 2% jelly Mithal C, Agarwal P, Mithal N Upgraded Department of Ophthalmology LLRM Medical College
CLINICAL SCIENCES. A Comparative Study of Topical vs Retrobulbar Anesthesia in Complicated Cataract Surgery
 CLINICAL SCIENCES A Comparative Study of Topical vs Retrobulbar Anesthesia in Complicated Cataract Surgery Philipp C. Jacobi, MD; Thomas S. Dietlein, MD; Felix K. Jacobi, MD Objectives: To evaluate and
CLINICAL SCIENCES A Comparative Study of Topical vs Retrobulbar Anesthesia in Complicated Cataract Surgery Philipp C. Jacobi, MD; Thomas S. Dietlein, MD; Felix K. Jacobi, MD Objectives: To evaluate and
Randomized Comparative Study of Drug Regimens: Fentanyl with Propofol and Fentanyl with Midazolam as Sedating Agents in Day Care Oral Surgery
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/467 Randomized Comparative Study of Drug Regimens: Fentanyl with Propofol and Fentanyl with Midazolam as Sedating Agents
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/467 Randomized Comparative Study of Drug Regimens: Fentanyl with Propofol and Fentanyl with Midazolam as Sedating Agents
Incidence, clinical findings and management of intraoperative floppy iris syndrome associated with tamsulosin
 Incidence, clinical findings and management of intraoperative floppy iris syndrome associated with tamsulosin Ugur Keklikci, 1 Kenan Isen, 2 Kaan Unlu, 1 Yusuf Celik 3 and Mine Karahan 1 1 Department of
Incidence, clinical findings and management of intraoperative floppy iris syndrome associated with tamsulosin Ugur Keklikci, 1 Kenan Isen, 2 Kaan Unlu, 1 Yusuf Celik 3 and Mine Karahan 1 1 Department of
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences
 Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Research and Reviews: Journal of Medical and Health Sciences Evaluation of Epidural Clonidine for Postoperative Pain Relief. Mukesh I Shukla, Ajay Rathod, Swathi N*, Jayesh Kamat, Pramod Sarwa, and Vishal
Intravenous magnesium-fentanyl sedation versus midazolam-fentanyl sedation before local anesthesia for eye surgery: a comparative study
 Hussien and Ibrahim Ain-Shams Journal of Anesthesiology (2018) 10:5 https://doi.org/10.1186/s42077-018-0009-3 Ain-Shams Journal of Anesthesiology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Intravenous magnesium-fentanyl
Hussien and Ibrahim Ain-Shams Journal of Anesthesiology (2018) 10:5 https://doi.org/10.1186/s42077-018-0009-3 Ain-Shams Journal of Anesthesiology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Intravenous magnesium-fentanyl
Optimal sedation and management of anxiety in patients undergoing endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS)
 Optimal sedation and management of anxiety in patients undergoing endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) Georgios Dadoudis Anesthesiologist ICU DIRECTOR INTERBALKAN MEDICAL CENTER Optimal performance requires:
Optimal sedation and management of anxiety in patients undergoing endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) Georgios Dadoudis Anesthesiologist ICU DIRECTOR INTERBALKAN MEDICAL CENTER Optimal performance requires:
Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone and Diclofenac Sodium Eye Drops in Phacoemulsification
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone and Diclofenac Sodium Eye Drops in Phacoemulsification Muhammad Waseem and Sadia Humayun ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the effectiveness
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Dexamethasone and Diclofenac Sodium Eye Drops in Phacoemulsification Muhammad Waseem and Sadia Humayun ABSTRACT Objective: To compare the effectiveness
Vanderbilt Eye Institute
 Vanderbilt Eye Institute Joshua Ki Hu Vanderbilt Eye Institute Ophthalmology, PGY-4 DATE 05.30.08 Introduction Cataract surgery is one of the most commonly performed surgeries in the world, with over 1
Vanderbilt Eye Institute Joshua Ki Hu Vanderbilt Eye Institute Ophthalmology, PGY-4 DATE 05.30.08 Introduction Cataract surgery is one of the most commonly performed surgeries in the world, with over 1
The Visual Outcome between Foldable and Rigid Intraocular Lens Implantation in Phacoemulsification A Hospital Based Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. XIII (Oct. 2017), PP 74-80 www.iosrjournals.org The Visual Outcome between Foldable
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. XIII (Oct. 2017), PP 74-80 www.iosrjournals.org The Visual Outcome between Foldable
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. HIGH VOLUME CAMP SURGERIES A CLINICAL STUDY D. N. Prakash, K, Sathish, Sankalp Singh Sharma, Soujanya. K, Savitha Patil.
 HIGH VOLUME CAMP SURGERIES A CLINICAL STUDY D. N. Prakash, K, Sathish, Sankalp Singh Sharma, Soujanya. K, Savitha Patil. 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Ophthalmology, MMC & RI, Mysore, 2. Associate
HIGH VOLUME CAMP SURGERIES A CLINICAL STUDY D. N. Prakash, K, Sathish, Sankalp Singh Sharma, Soujanya. K, Savitha Patil. 1. Assistant Professor. Department of Ophthalmology, MMC & RI, Mysore, 2. Associate
Clinical Evaluation of the BunnyLens IOL
 Clinical Evaluation of the BunnyLens IOL Introduction: BunnyLens is a foldable Hydrophlic Acrylic IOL with four ear shaped haptic design. The lens design offers many advantages in terms of: 1. Centration
Clinical Evaluation of the BunnyLens IOL Introduction: BunnyLens is a foldable Hydrophlic Acrylic IOL with four ear shaped haptic design. The lens design offers many advantages in terms of: 1. Centration
A Comparative Study of Topical Versus Peribulbar Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification and Implantation of Foldable Intraocular Lens in Cataract Surgery
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Ophthalmology and Visual Science Volume 2 Number 1 A Comparative Study of Topical Versus Peribulbar Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification and Implantation of K Said, M Hassan,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Ophthalmology and Visual Science Volume 2 Number 1 A Comparative Study of Topical Versus Peribulbar Anesthesia in Phacoemulsification and Implantation of K Said, M Hassan,
Series 2 dexmedetomidine, tramadol, fentanyl, intellectually disabled patients:
 Series 2 dexmedetomidine, tramadol, fentanyl, intellectually disabled patients: Read the following published scientific articles and answer the questions at the end: Abstract We get a substantial number
Series 2 dexmedetomidine, tramadol, fentanyl, intellectually disabled patients: Read the following published scientific articles and answer the questions at the end: Abstract We get a substantial number
Cataract Surgery Management in Eyes with Extensive Iridoschisis
 Cataract Surgery Management in Eyes with Extensive Iridoschisis Hassan Hashemi, MD 1,2 Golshan Latifi, MD 3 Sasan Moghimi, MD 4 S-Farzad Mohammadi, MD 5 Abstract Purpose: To demonstrate an approach to
Cataract Surgery Management in Eyes with Extensive Iridoschisis Hassan Hashemi, MD 1,2 Golshan Latifi, MD 3 Sasan Moghimi, MD 4 S-Farzad Mohammadi, MD 5 Abstract Purpose: To demonstrate an approach to
Dexmedetomidine for Sedation During Ambulatory Colonoscopy in Older Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, September: 741-745, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Dexmedetomidine for Sedation During Ambulatory Colonoscopy in Older Patients MOHAMED ABD EL MONEIM
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 81, No. 1, September: 741-745, 2013 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Dexmedetomidine for Sedation During Ambulatory Colonoscopy in Older Patients MOHAMED ABD EL MONEIM
Engineered. Simplicity. for. VISTHESIA : The unique combination of OVD and ancillary anesthesia.
 Supplement to July/August 2010 Engineered for Simplicity VISTHESIA : The unique combination of OVD and ancillary anesthesia. Sponsored by an educational grant from Carl Zeiss Meditec VISTHESIA The unique
Supplement to July/August 2010 Engineered for Simplicity VISTHESIA : The unique combination of OVD and ancillary anesthesia. Sponsored by an educational grant from Carl Zeiss Meditec VISTHESIA The unique
Surgically Induced Astigmatism Comparison between Forceps and Injector Delivery System for Foldable IOL in Phacoemulsification
 Original Article Surgically Induced Astigmatism Comparison between Forceps and Injector Delivery System for Foldable IOL in Phacoemulsification Nasrullah Khan, Atif Mansoor Ahmed, Khalid Waheed, Tahir
Original Article Surgically Induced Astigmatism Comparison between Forceps and Injector Delivery System for Foldable IOL in Phacoemulsification Nasrullah Khan, Atif Mansoor Ahmed, Khalid Waheed, Tahir
Research Article. Shital S. Ahire 1 *, Shweta Mhambrey 1, Sambharana Nayak 2. Received: 22 July 2016 Accepted: 08 August 2016
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ahire SS et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Sep;4(9):3838-3844 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20162824
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Ahire SS et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016 Sep;4(9):3838-3844 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20162824
A clinical study of corneal complications of manual small incision cataract surgery
 Original Research Article Anitha S. Maiya 1,*, Akshatha M. Dharmesh 2, R. Jayaram 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Senior Resident, 3 Professor, Dept. of Ophthalmology, Adichunchanagiri Institute of Medical
Original Research Article Anitha S. Maiya 1,*, Akshatha M. Dharmesh 2, R. Jayaram 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 Senior Resident, 3 Professor, Dept. of Ophthalmology, Adichunchanagiri Institute of Medical
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation
 Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
Transient Intraocular Pressure Elevation after Trabeculotomy and its Occurrence with Phacoemulsification and Intraocular Lens Implantation Masaru Inatani*, Hidenobu Tanihara, Takahito Muto*, Megumi Honjo*,
International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubric (ICO-OSCAR)
 International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubric (ICO-OSCAR) The International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubrics
International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubric (ICO-OSCAR) The International Council of Ophthalmology s Ophthalmology Surgical Competency Assessment Rubrics
Comparison of Surgically Induced Astigmatisms after Clear Corneal Incisions of Different Sizes
 Comparison of Surgically Induced Astigmatisms after Clear Corneal Incisions of Different Sizes Sung Chur Moon, MD, PhD, Tarek Mohamed, MD, I. Howard Fine, MD Oregon Eye Institute, Eugene, Oregon, USA Purpose:
Comparison of Surgically Induced Astigmatisms after Clear Corneal Incisions of Different Sizes Sung Chur Moon, MD, PhD, Tarek Mohamed, MD, I. Howard Fine, MD Oregon Eye Institute, Eugene, Oregon, USA Purpose:
COURSE DESCRIPTION BASIC FUNDAMENTALS
 TACKLING POSTERIOR CAPSULE RUPTURE AND IOL IMPLANTATION: A VIDEO BASED COURSE TUESDAY - 29 th APRIL, 2014: 1.00 PM-2.30 PM, BCEC, ROOM 258 A ; SESSION 29-308 COURSE DESCRIPTION BASIC FUNDAMENTALS Early
TACKLING POSTERIOR CAPSULE RUPTURE AND IOL IMPLANTATION: A VIDEO BASED COURSE TUESDAY - 29 th APRIL, 2014: 1.00 PM-2.30 PM, BCEC, ROOM 258 A ; SESSION 29-308 COURSE DESCRIPTION BASIC FUNDAMENTALS Early
Intraoperative biometry for intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation at silicone oil removal
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 622-626 Intraoperative biometry for intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation at silicone oil removal S.M. EL-BAHA, A. EI-SAMADONI, H.F. IDRIS,
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 13 no. 7, 2003 / pp. 622-626 Intraoperative biometry for intraocular lens (IOL) power calculation at silicone oil removal S.M. EL-BAHA, A. EI-SAMADONI, H.F. IDRIS,
Intracameral Mydriasis: The New Standard Route for Cataract Surgery
 Supplement February 2016 Intracameral Mydriasis: The New Standard Route for Cataract Surgery Laboratoires Théa Satellite Symposium XXXIII Congress of the ESCRS 6 September 2015 Barcelona, Spain Chairperson
Supplement February 2016 Intracameral Mydriasis: The New Standard Route for Cataract Surgery Laboratoires Théa Satellite Symposium XXXIII Congress of the ESCRS 6 September 2015 Barcelona, Spain Chairperson
Comparison of Bolus Bupivacaine, Fentanyl, and Mixture of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Thoracic Epidural Analgesia for Upper Abdominal Surgery
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/156 Comparison of Bolus Bupivacaine, Fentanyl, and Mixture of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Thoracic Epidural Analgesia for Upper Abdominal Surgery Sachin Gajbhiye
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/156 Comparison of Bolus Bupivacaine, Fentanyl, and Mixture of Bupivacaine with Fentanyl in Thoracic Epidural Analgesia for Upper Abdominal Surgery Sachin Gajbhiye
Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5% Bupivacaine Plus Buprenorphine in Brachial Plexus Block
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. 2016), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5%
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. VIII (Jan. 2016), PP 01-08 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison Of 0.5%Bupivacaine And 0.5%
Clonidine in Cineangiocardiography: Sedative Effects on Blood Pressure and Heart Rate
 in Cineangiocardiography: Sedative Effects on Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Jedson dos Santos Nascimento, Norma Sueli Pinheiro Módolo, Heitor Ghissoni de Carvalho, Edilma Maria Lima Dórea, Kleber Pimentel
in Cineangiocardiography: Sedative Effects on Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Jedson dos Santos Nascimento, Norma Sueli Pinheiro Módolo, Heitor Ghissoni de Carvalho, Edilma Maria Lima Dórea, Kleber Pimentel
Richard M H Lee 1, John R Thompson 2, Tom Eke 3. 1 Department of Ocular Biology and Therapeutics, Institute of Ophthalmology, London
 Severe adverse events associated with local anaesthesia in cataract surgery: one year national survey of practice and complications in the United Kingdom. Richard M H Lee 1, John R Thompson 2, Tom Eke
Severe adverse events associated with local anaesthesia in cataract surgery: one year national survey of practice and complications in the United Kingdom. Richard M H Lee 1, John R Thompson 2, Tom Eke
Ruba Alobaidy Jia Y Ng Sathish Srinivasan
 Ruba Alobaidy Jia Y Ng Sathish Srinivasan Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital Ayr, Ayr, Scotland The authors have no financial interests to declare. Continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis (CCC)
Ruba Alobaidy Jia Y Ng Sathish Srinivasan Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital Ayr, Ayr, Scotland The authors have no financial interests to declare. Continuous curvilinear capsulorhexis (CCC)
The Effect of Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation on Intraocular Pressure and Anterior Chamber Depth
 The Effect of Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation on Intraocular Pressure and Anterior Chamber Depth Mohammad Javad Mohamadi, MD 1 Reza Soltani Moghadam, MD 1 Hasan
The Effect of Phacoemulsification with Posterior Chamber Intraocular Lens Implantation on Intraocular Pressure and Anterior Chamber Depth Mohammad Javad Mohamadi, MD 1 Reza Soltani Moghadam, MD 1 Hasan
Original Article Capsular tension ring implantation after lens extraction for management of subluxated cataracts
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(7):3733-3738 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000754 Original Article Capsular tension ring implantation after lens extraction for management of subluxated cataracts Xiao
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7(7):3733-3738 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0000754 Original Article Capsular tension ring implantation after lens extraction for management of subluxated cataracts Xiao
Phacoemulsification: Complications in First 300 Cases
 Original Article Phacoemulsification: Complications in First 300 Cases Abrar Ali, Tabassum Ahmed, Tahir Ahmed Pak J Ophthalmol 2007, Vol. 23 No. 2.................................................................................................
Original Article Phacoemulsification: Complications in First 300 Cases Abrar Ali, Tabassum Ahmed, Tahir Ahmed Pak J Ophthalmol 2007, Vol. 23 No. 2.................................................................................................
Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries
 Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Original Research Article Comparison of fentanyl versus fentanyl plus magnesium as post-operative epidural analgesia in orthopedic hip surgeries P V Praveen Kumar 1*, Sreemanth 2 1 Associate Professor,
Optometric Postoperative Cataract Surgery Management
 Financial Disclosures Optometric Postoperative Cataract Surgery Management David Dinh, OD Oak Cliff Eye Clinic Dallas Eye Consultants March 10, 2015 Comanagement Joint cooperation between two or more specialists
Financial Disclosures Optometric Postoperative Cataract Surgery Management David Dinh, OD Oak Cliff Eye Clinic Dallas Eye Consultants March 10, 2015 Comanagement Joint cooperation between two or more specialists
Satisfactory Analgesia Minimal Emesis in Day Surgeries. (SAME-Day study) A Randomized Control Trial Comparing Morphine and Hydromorphone
 Satisfactory Analgesia Minimal Emesis in Day Surgeries (SAME-Day study) A Randomized Control Trial Comparing Morphine and Hydromorphone HARSHA SHANTHANNA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ANESTHESIOLOGY MCMASTER UNIVERSITY
Satisfactory Analgesia Minimal Emesis in Day Surgeries (SAME-Day study) A Randomized Control Trial Comparing Morphine and Hydromorphone HARSHA SHANTHANNA ASSISTANT PROFESSOR ANESTHESIOLOGY MCMASTER UNIVERSITY
Eye (2008) 22, & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved X/08 $30.00
 (2008) 22, 425 429 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye Comparative clinical trial of topical anaesthetic agents for cataract surgery with phacoemulsification:
(2008) 22, 425 429 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye Comparative clinical trial of topical anaesthetic agents for cataract surgery with phacoemulsification:
DOCTORAL DISSERTATION
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL DOCTORAL DISSERTATION - Summary - METHODS OF ANALGESIA AND SEDATION IN THE POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD PhD SUPERVISER: PH. D. PROFESSOR : VALENTIN C#RLIG
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA DOCTORAL SCHOOL DOCTORAL DISSERTATION - Summary - METHODS OF ANALGESIA AND SEDATION IN THE POSTOPERATIVE PERIOD PhD SUPERVISER: PH. D. PROFESSOR : VALENTIN C#RLIG
Evaluation of Oral Midazolam as Pre-Medication in Day Care Surgery in Adult Pakistani Patients
 Evaluation of Oral Midazolam as Pre-Medication in Day Care Surgery in Adult Pakistani Patients Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 239 To 241 Nauman Ahmed, Fauzia A. Khan ( Department of Anaesthesia,
Evaluation of Oral Midazolam as Pre-Medication in Day Care Surgery in Adult Pakistani Patients Abstract Pages with reference to book, From 239 To 241 Nauman Ahmed, Fauzia A. Khan ( Department of Anaesthesia,
84 Year Old with Rosacea
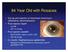 84 Year Old with Rosacea S/p tap and injection of intravitreal vancomycin, ceftazidime, dexamethasone Post-injection day#1 Va HM IOP 14 mmhg Post-injection week#3 BCVA 20/20-3 (plano +0.50 x 180) IOP 23
84 Year Old with Rosacea S/p tap and injection of intravitreal vancomycin, ceftazidime, dexamethasone Post-injection day#1 Va HM IOP 14 mmhg Post-injection week#3 BCVA 20/20-3 (plano +0.50 x 180) IOP 23
Disorders of the. blood-aqueous barrier after. phacoemulsification in diabetic patients CLINICAL STUDY. Y Liu, L Luo, M He and X Liu
 (2004) 18, 900 904 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Disorders of the blood-aqueous barrier after phacoemulsification in diabetic
(2004) 18, 900 904 & 2004 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-222X/04 $30.00 www.nature.com/eye CLINICAL STUDY Disorders of the blood-aqueous barrier after phacoemulsification in diabetic
Original contribution. Department of Anesthesiology, Sapporo Medical University, School of Medicine, Sapporo, Hokkaido, Japan
 Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2007) 19, 25 29 Original contribution A comparison of spinal anesthesia with small-dose lidocaine and general anesthesia with fentanyl and propofol for ambulatory prostate
Journal of Clinical Anesthesia (2007) 19, 25 29 Original contribution A comparison of spinal anesthesia with small-dose lidocaine and general anesthesia with fentanyl and propofol for ambulatory prostate
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures
 Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
Oral Midazolam for Premedication in Children Undergoing Various Elective Surgical procedures E-mail gauripanjabi@yahoo.co.in 1 st Author:. Dr Panjabi Gauri M., M.D., D.A., Senior Assistant professor. 2
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia
 The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated with the amount of morphine needed for postoperative analgesia This study has been published: The intensity of preoperative pain is directly correlated
Tracheal intubation in children after induction of anesthesia with propofol and remifentanil without a muscle relaxant
 Original Article Tracheal intubation in children after induction of anesthesia with propofol and remifentanil without a muscle relaxant Mirmohammad Taghi Mortazavi, 1 Masood Parish, 1 Naghi Abedini, 2
Original Article Tracheal intubation in children after induction of anesthesia with propofol and remifentanil without a muscle relaxant Mirmohammad Taghi Mortazavi, 1 Masood Parish, 1 Naghi Abedini, 2
Microincisional cataract surgery (MICS) with pulse and burst modes
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 16 no. 6, 2006 / pp. 804-808 Microincisional cataract surgery (MICS) with pulse and burst modes M. BAYKARA 1, I.. ERCAN 2, H. OZCETIN 1 1 Department of Ophthalmology
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 16 no. 6, 2006 / pp. 804-808 Microincisional cataract surgery (MICS) with pulse and burst modes M. BAYKARA 1, I.. ERCAN 2, H. OZCETIN 1 1 Department of Ophthalmology
Inadvertent trypan blue staining of posterior capsule during cataract surgery associated with "Argentinian flag" event
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 Inadvertent trypan blue staining of posterior capsule during cataract surgery associated with "Argentinian
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2016 Inadvertent trypan blue staining of posterior capsule during cataract surgery associated with "Argentinian
A comparison of different proportions of a ketaminepropofol mixture administered in a single injection for patients undergoing colonoscopy
 Clinical research A comparison of different proportions of a ketaminepropofol mixture administered in a single injection for patients undergoing colonoscopy Meltem Türkay Aydogmus, Hacer Sebnem Türk, Sibel
Clinical research A comparison of different proportions of a ketaminepropofol mixture administered in a single injection for patients undergoing colonoscopy Meltem Türkay Aydogmus, Hacer Sebnem Türk, Sibel
Effects of intraoperative i.v. acetaminophen vs i.m. meperidine on post-tonsillectomy pain in children
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 96 (6): 790 5 (2006) doi:10.1093/bja/ael084 Advance Access publication April 13, 2006 Effects of intraoperative i.v. acetaminophen vs i.m. meperidine on post-tonsillectomy
British Journal of Anaesthesia 96 (6): 790 5 (2006) doi:10.1093/bja/ael084 Advance Access publication April 13, 2006 Effects of intraoperative i.v. acetaminophen vs i.m. meperidine on post-tonsillectomy
ACETYLCHOLINE IN CATARACT SURGERY*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 429 ACETYLCHOLINE IN CATARACT SURGERY* BY Atlantic City, New Jersey ALTHOUGH the use of acetylcholine as a miotic agent in ophthalmic surgery is not new, it has not been widely
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 429 ACETYLCHOLINE IN CATARACT SURGERY* BY Atlantic City, New Jersey ALTHOUGH the use of acetylcholine as a miotic agent in ophthalmic surgery is not new, it has not been widely
(For National Authority Use Only) Name of Study Drug: to Part of Dossier:
 2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: (For National Authority Use Only) Name of Study Drug: Volume: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Page: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen
2.0 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: (For National Authority Use Only) Name of Study Drug: Volume: Vicodin CR Name of Active Ingredient: Page: Hydrocodone/Acetaminophen
Phacoemulsification with hydrodelineation and OVD-assisted hydrodissection in posterior polar cataract
 Hua et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:165 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0845-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Phacoemulsification with hydrodelineation and OVD-assisted hydrodissection in posterior
Hua et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2018) 18:165 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-018-0845-8 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Phacoemulsification with hydrodelineation and OVD-assisted hydrodissection in posterior
DORIS DUKE MEDICAL STUDENTS JOURNAL Volume V,
 Continuous Femoral Perineural Infusion (CFPI) Using Ropivacaine after Total Knee Arthroplasty and its Effect on Postoperative Pain and Early Functional Outcomes Eric Lloyd Scientific abstract Total Knee
Continuous Femoral Perineural Infusion (CFPI) Using Ropivacaine after Total Knee Arthroplasty and its Effect on Postoperative Pain and Early Functional Outcomes Eric Lloyd Scientific abstract Total Knee
Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation. Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital
 Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital Briefly review ketamine s history, mechanism of action, and unique properties
Results of a one-year, retrospective medication use evaluation Joseph Ladd, PharmD PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident BHSF Homestead Hospital Briefly review ketamine s history, mechanism of action, and unique properties
Relevant and Reliable Systematic Review Mapped to this Section. Relevance of Review to other sections of AAO PPP- 2011
 Table 1. American Academy for Ophthalmology s (AAO) Preferred Practice Patterns (PPP) Nonsurgical Hodge, 2005 Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2005 Jul;(117):1-6. Effects of omega- 3 fatty acids on eye
Table 1. American Academy for Ophthalmology s (AAO) Preferred Practice Patterns (PPP) Nonsurgical Hodge, 2005 Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2005 Jul;(117):1-6. Effects of omega- 3 fatty acids on eye
Informed Consent For Cataract Surgery. And/Or Implantation of an Intraocular Lens INTRODUCTION
 Informed Consent For Cataract Surgery And/Or Implantation of an Intraocular Lens INTRODUCTION This information is given to you so that you can make an informed decision about having eye surgery. Take as
Informed Consent For Cataract Surgery And/Or Implantation of an Intraocular Lens INTRODUCTION This information is given to you so that you can make an informed decision about having eye surgery. Take as
The bispectral index (BIS) monitor was developed
 Validation of the Bispectral Index Monitor During Conscious and Deep Sedation in Children Nicole Brown McDermott, MD, Tamitha VanSickle, MD, Dominika Motas, MD, and Robert H. Friesen, MD Department of
Validation of the Bispectral Index Monitor During Conscious and Deep Sedation in Children Nicole Brown McDermott, MD, Tamitha VanSickle, MD, Dominika Motas, MD, and Robert H. Friesen, MD Department of
Comparison of ropivacaine 0.75% and bupivacaine 0.5% in peribulbar block for cataract surgery.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 23 Number 2 Comparison of ropivacaine 0.75% and bupivacaine 0.5% in peribulbar block for cataract surgery. L Trivedi, H Trivedi, D Tripathi, P Jha,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 23 Number 2 Comparison of ropivacaine 0.75% and bupivacaine 0.5% in peribulbar block for cataract surgery. L Trivedi, H Trivedi, D Tripathi, P Jha,
Beta Blockers for ENT Surgery
 Beta Blockers for ENT Surgery Dr. Giuliano Michelagnoli U.O. Anestesia e Rianimazione Nuovo Ospedale di Prato Perioperative Beta-Blockade 1. Reduction of perioperative cardiovascular risk 2. Multimodal
Beta Blockers for ENT Surgery Dr. Giuliano Michelagnoli U.O. Anestesia e Rianimazione Nuovo Ospedale di Prato Perioperative Beta-Blockade 1. Reduction of perioperative cardiovascular risk 2. Multimodal
Every week, the John A. Moran Eye Center at the
 Analyzing Explanted IOLs A review of the pathological processes that affect pseudophakic patients postoperative vision. BY LILIANA WERNER, MD, PHD Every week, the John A. Moran Eye Center at the University
Analyzing Explanted IOLs A review of the pathological processes that affect pseudophakic patients postoperative vision. BY LILIANA WERNER, MD, PHD Every week, the John A. Moran Eye Center at the University
Clinical Study Air Bubble Technique for Fundus Visualization during Vitrectomy in Aphakia
 Hindawi Ophthalmology Volume 2017, Article ID 4721540, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4721540 Clinical Study Air Bubble Technique for Fundus Visualization during Vitrectomy in Aphakia Mahmoud Mohamed
Hindawi Ophthalmology Volume 2017, Article ID 4721540, 5 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4721540 Clinical Study Air Bubble Technique for Fundus Visualization during Vitrectomy in Aphakia Mahmoud Mohamed
A Nationwide Survey on the Knowledge and Attitudes of Malaysian Optometry Students on Patients Visual Experiences During Cataract Surgery
 72 Original Article A Nationwide Survey on the Knowledge and Attitudes of Malaysian Optometry Students on Patients Visual Experiences During Cataract Surgery Colin SH Tan, 1 MBBS, M Med (Ophth), MRCS (Edin),
72 Original Article A Nationwide Survey on the Knowledge and Attitudes of Malaysian Optometry Students on Patients Visual Experiences During Cataract Surgery Colin SH Tan, 1 MBBS, M Med (Ophth), MRCS (Edin),
Comparison of local anesthetic effects of Tramadol and Lidocaine used subcutaneously in minor surgeries with local anesthesia
 Comparison of local anesthetic effects of Tramadol and Lidocaine used subcutaneously in minor surgeries with local anesthesia S. Vahabi **, M. Heidari **, M. Ahmadinejad ***, J. Akhlaghi **** and M. Birjandi
Comparison of local anesthetic effects of Tramadol and Lidocaine used subcutaneously in minor surgeries with local anesthesia S. Vahabi **, M. Heidari **, M. Ahmadinejad ***, J. Akhlaghi **** and M. Birjandi
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia
 Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Subspecialty Rotation: Anesthesia Faculty: John Heaton, M.D. GOAL: Maintenance of Airway Patency and Oxygenation. Recognize and manage upper airway obstruction and desaturation. Recognize and manage upper
Long-term Outcomes of Vitreous Floaters Management with 23-Gauge Transconjunctival Sutureless Vitrectomy
 Long-term Outcomes of Vitreous Floaters Management with 23-Gauge Transconjunctival Sutureless Vitrectomy Malhar 1Consultant 1 Soni, Minas G 2 Georgopoulos, Adriana 2 Kovakova Vitreo-Retinal Surgeon, London,
Long-term Outcomes of Vitreous Floaters Management with 23-Gauge Transconjunctival Sutureless Vitrectomy Malhar 1Consultant 1 Soni, Minas G 2 Georgopoulos, Adriana 2 Kovakova Vitreo-Retinal Surgeon, London,
COMPARISON OF FENTANYL AND MORPHINE IN INTRAVENOUS PATIENT-CONTROLLED ANALGESIA AFTER OPEN GASTRECTOMY SURGERY
 COMPARISON OF FENTANYL AND MORPHINE IN INTRAVENOUS PATIENT-CONTROLLED ANALGESIA AFTER OPEN GASTRECTOMY SURGERY Nguyen Toan Thang, Nguyen Huu Tu Department of Anesthesia Critical Care, Hanoi Medical University
COMPARISON OF FENTANYL AND MORPHINE IN INTRAVENOUS PATIENT-CONTROLLED ANALGESIA AFTER OPEN GASTRECTOMY SURGERY Nguyen Toan Thang, Nguyen Huu Tu Department of Anesthesia Critical Care, Hanoi Medical University
Pre-operative Care For Surgery of Forearm Fracture. WONG Mei Chee OT (CMC)
 Pre-operative Care For Surgery of Forearm Fracture WONG Mei Chee OT (CMC) Pre-operative Nursing Considerations for Surgery of Forearm Fracture 1. Patient s problems - Diagnosis: Clinical features, x-ray
Pre-operative Care For Surgery of Forearm Fracture WONG Mei Chee OT (CMC) Pre-operative Nursing Considerations for Surgery of Forearm Fracture 1. Patient s problems - Diagnosis: Clinical features, x-ray
VISUAL OUTCOME AFTER MICROCOAXIAL PHACOEMULSIFICATION WITH MICRIOL PLUS LENS IMPLANTATION. of Corresponding Author:
 VISUAL OUTCOME AFTER MICROCOAXIAL PHACOEMULSIFICATION WITH MICRIOL PLUS IJCRR Vol 04 issue 23 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 12/10/12 Revised on: 06/11/12 Accepted on: 27/11/12 Mohd
VISUAL OUTCOME AFTER MICROCOAXIAL PHACOEMULSIFICATION WITH MICRIOL PLUS IJCRR Vol 04 issue 23 Section: Healthcare Category: Research Received on: 12/10/12 Revised on: 06/11/12 Accepted on: 27/11/12 Mohd
SEEING KETAMINE IN A NEW LIGHT
 SEEING KETAMINE IN A NEW LIGHT BobbieJean Sweitzer, M.D., FACP Professor of Anesthesiology Director of Perioperative Medicine Northwestern University Bobbie.Sweitzer@northwestern.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES
SEEING KETAMINE IN A NEW LIGHT BobbieJean Sweitzer, M.D., FACP Professor of Anesthesiology Director of Perioperative Medicine Northwestern University Bobbie.Sweitzer@northwestern.edu LEARNING OBJECTIVES
Original Article Influence of butorphanol on the postoperative remifentanil hyperalgesia
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4685-4689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017991 Original Article Influence of butorphanol on the postoperative remifentanil hyperalgesia Chen Lv, Hui Zheng, Mingyang Wei,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):4685-4689 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017991 Original Article Influence of butorphanol on the postoperative remifentanil hyperalgesia Chen Lv, Hui Zheng, Mingyang Wei,
Intrascleral-fixated intraocular lenses for aphakic correction in the absence of capsular support
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 5, 2007 / pp. 714-719 Intrascleral-fixated intraocular lenses for aphakic correction in the absence of capsular support R.A. AZNABAYEV, I.S. ZAIDULLIN, M.S.H.
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 17 no. 5, 2007 / pp. 714-719 Intrascleral-fixated intraocular lenses for aphakic correction in the absence of capsular support R.A. AZNABAYEV, I.S. ZAIDULLIN, M.S.H.
Capsule fixation device for cataract surgery
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 19 no. 1, 2009 / pp. 143-146 SHORT COMMUNICATIONS & CASE REPORTS Capsule fixation device for cataract surgery N.M. SERGIENKO 1, Y.N. KONDRATENKO 1, A.K. YAKIMOV
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 19 no. 1, 2009 / pp. 143-146 SHORT COMMUNICATIONS & CASE REPORTS Capsule fixation device for cataract surgery N.M. SERGIENKO 1, Y.N. KONDRATENKO 1, A.K. YAKIMOV
Conjunctival displacement to the corneal side for oblique-parallel insertion in 25-gauge vitrectomy
 European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 5, 2008 / pp. 848-851 SHORT COMMUNICATIONS & CASE REPORTS Conjunctival displacement to the corneal side for oblique-parallel insertion in 25-gauge vitrectomy
European Journal of Ophthalmology / Vol. 18 no. 5, 2008 / pp. 848-851 SHORT COMMUNICATIONS & CASE REPORTS Conjunctival displacement to the corneal side for oblique-parallel insertion in 25-gauge vitrectomy
Management. of the Small Pupil. for Cataract Surgery. Chapter 3. Alan S. Crandall. Core Messages. 3.2 Surgical Management. of the Small Pupil
 Chapter Management of the Small Pupil for Cataract Surgery Alan S. Crandall Core Messages While there are various causes of small pupils, adequate pupil size is imperative for safe cataract removal. Instruments
Chapter Management of the Small Pupil for Cataract Surgery Alan S. Crandall Core Messages While there are various causes of small pupils, adequate pupil size is imperative for safe cataract removal. Instruments
PDF of Trial CTRI Website URL -
 Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Tue, 09 Oct 2018 14:20:31 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 23/07/2012 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
Clinical Trial Details (PDF Generation Date :- Tue, 09 Oct 2018 14:20:31 GMT) CTRI Number Last Modified On 23/07/2012 Post Graduate Thesis Type of Trial Type of Study Study Design Public Title of Study
The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study
 Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Kasr El Aini Journal of Surgery VOL., 10, NO 3 September 2009 97 The use of Pudendal Nerve Block in Hemorrhoidectomy Operations: A Prospective Double Blind Placebo Control Study Sherif Adly and Mohamed
Sedation in Children
 CHILDREN S SERVICES Sedation in Children See text for full explanation and drug doses Patient for Sedation Appropriate staffing Resuscitation equipment available Monitoring equipment Patient suitability
CHILDREN S SERVICES Sedation in Children See text for full explanation and drug doses Patient for Sedation Appropriate staffing Resuscitation equipment available Monitoring equipment Patient suitability
The Effect of Preemptive Analgesia in Postoperative Pain Relief A Prospective Double-Blind Randomized Study
 PAIN MEDICINE Volume 10 Number 1 2009 The Effect of Preemptive Analgesia in Postoperative Pain Relief A Prospective Double-Blind Randomized Study Seetharaman Hariharan, MD, Harley Moseley, FFARCS, Areti
PAIN MEDICINE Volume 10 Number 1 2009 The Effect of Preemptive Analgesia in Postoperative Pain Relief A Prospective Double-Blind Randomized Study Seetharaman Hariharan, MD, Harley Moseley, FFARCS, Areti
Propofol (PRO) is an intravenous anesthetic
 RESEARCH Intravenous Sedation for Implant Surgery: Midazolam, Butorphanol, and Dexmedetomidine Versus Midazolam, Butorphanol, and Propofol Hiroyoshi Kawaai, DDS, PhD 1 * Shu Tomita, DDS 1 Yoshihiro Nakaike,
RESEARCH Intravenous Sedation for Implant Surgery: Midazolam, Butorphanol, and Dexmedetomidine Versus Midazolam, Butorphanol, and Propofol Hiroyoshi Kawaai, DDS, PhD 1 * Shu Tomita, DDS 1 Yoshihiro Nakaike,
