Legionellosis is a relatively common cause of community-acquired
|
|
|
- Juniper Todd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Early release, published at on July 5, Subject to revision. Primer Legionellosis: Why should I test and report? Thomas J. Marrie MD, Jason R. Garay BSc BASc MHSc, Erica Weir MD MSc DOI: /cmaj Legionellosis is a relatively common cause of community-acquired and nosocomial pneumonia (Figure 1) and is identified in about 3% 5% of individuals who are admitted to hospital because of pneumonia in Canada. 1 Guidelines for the empirical treatment of these illnesses call for the use of either fluoroquinolones or macrolides. 2 Patients and physicians may feel that it is therefore not necessary to confirm the diagnosis of legionellosis in order to treat it. However, from the perspective of public health, it is important that the diagnosis be confirmed and reported so that the possibility of an outbreak and the source of exposure can be investigated. The intent of this primer is to review the organism, clinical manifestations, epidemiology, diagnosis and treatment of legionellosis. We also outline opportunities for public health interventions so that physicians may be more inclined to test and report legionellosis to their local public health units. What is special about legionellae? Legionellae are gram-negative facultative intracellular coccobacilli that measure microns in width and 2 20 microns in length. They are usually not detectable by Gram staining and require special media for growth in the laboratory. More than 50 species of legionellae, 16 different serogroups of Legionellae pneumophila and 73 serogroups overall have been identified. 3 Most patients tested for legionellosis have infections of L. pneumophila serogroup 1. Legionella spp. are found in natural and man-made water systems. They are hardy organisms and can survive in most Table 1: Features associated with Legionella compared with bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia 14 Feature Odds ratio (95% CI) Male sex 4.5 ( ) Heavy alcohol use 4.8 ( ) Previous β-lactam therapy 19.9 ( ) Axillary temperature > ( ) Myalgia 8.5 ( ) Gastrointestinal symptoms 3.5 ( ) Note: CI = confidence interval. Key points Legionellosis should be reported to public health. Under-reporting results in missed sources of exposure. All patients with severe pneumonia should be tested for legionellosis. Investigation of clusters results in identification of the likely source environments for long periods of time. They can withstand temperatures of 0 68 C and a ph range of Amoeba and other unicellular organisms in biofilms, which are aggregates of adherent microorganisms attached to a surface and embedded in a self-produced matrix of proteins and polysaccharides (e.g., slime), play a role in the proliferation, development and dissemination of potentially pathogenic Legionella species. 4 In water distribution systems, they are found in biofilms and are often resistant to biocides and chlorine. What is the pattern of outbreaks? Legionnaires disease can be acquired by the inhalation of contaminated water aerosols or the aspiration of contaminated potable water. 5 Outbreaks have been associated with exposure to various aerosol-producing devices, including showers, 6 mist machines in grocery stores, 7 cooling towers, 8 whirlpool spas, industrial plants 9 and evapourative condensers. 10 Legionnaires disease can be acquired at a distance from contaminated sources such as cooling towers or air scrubbers, where the exhaust can be carried by prevailing winds. Cases have been documented as far as 10 kmfrom such sources. 11 Some regions of Canada report more cases of legionnaires disease than others. In a study of community-acquired pneumonia requiring admission to hospital at 15 centres throughout Canada, 3.2% of the 850 patients had legionnaires disease. 1 The number of reported cases of legionellosis in the United States increased by 70% from 1310 cases in 2002 to From the Faculty of Medicine (Marrie), Dalhousie University, Halifax, NS; Infectious Diseases Control Division (Garay), Public Health Branch York Region Community and Health Services, Newmarket, Ont.; and Community Health and Epidemiology (Weir), Queen s University, Kingston, Ont DOI: /cmaj Canadian Medical Association or its licensors 1
2 2223 cases in The eastern US showed the greatest increase in age-adjusted incidence after Investigators from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention noted an association between increased rainfall in the mid-atlantic states and the increasing rate of legionnaires disease. 13 A 1-cm increase in rainfall was associated with a 2.6% increase in legionnaires disease. 13 How does legionellosis present? The incubation period of legionnaires disease is between 2 and 10 days. 3 Patients with legionnaires disease are more likely than those whose community-acquired pneumonia was caused by another agent to have myalgia, headache and diarrhea; they also have a higher mean oral temperature at the time of presentation. 1 Patients with legionnaires disease typically present to hospital sooner after the onset of symptoms. Legionella has features that are distinct from bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia (Table 1). 14 Features not usually associated with legionellosis included pleuritic chest pain, previous upper respiratory tract infection and purulent sputum. 14 There are no individual clinical features that allow physicians to make a diagnosis of legionnaires disease; however, all patients with severe pneumonia should be tested for legionnaires disease. Older people ( 65 yr) with legionnaires disease often have more comorbid illnesses than younger people, yet older people present less frequently with fever, nonrespiratory symptoms and laboratory abnormalities. This might be explained by the intracellular nature of the pathogen and altered cell-mediated immunity in elderly hosts. In a study comparing the radiographic features of legionnaires disease, pneumococcal pneumonia, mycoplasma No. of cases pneumonia and psittacosis, Macfarlane and colleagues 15 noted that progression of pneumonia following hospital admission was a particular feature of legionnaires disease, occurring in 65% (30/46) of patients, compared with 51% (14/27) of patients with bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia. Residual intrapulmonary streaky opacities remained in over a quarter of the survivors of legionnaires disease. 15 About half of the patients with legionnaires disease have unilateral pneumonic involvement throughout the course of their illness. The lower lobes are most commonly involved (Figure 2), and pleural effusions are seen in about 35% of patients. Additional laboratory findings that can accompany legionellosis are shown in Box Legionellosis may also occur as a nonpneumonic form, such as Pontiac fever. In July 1968, an illness consisting of fever, headache, myalgia and malaise with a very high attack rate (95%) occurred among employees in a new county health department building in Pontiac, Michigan. Other symptoms included dizziness, painful stiff neck, nausea, chest pain, joint pain, sore throat, sore eyes, abdominal pain, confusion, coryza, photophobia, diarrhea, poor coordination, anorexia, nose bleed, vomiting, insomnia, bizarre dreams, rash and irritability. The acute illness lasted two to five days, although many experienced weakness and fatigue afterwards. 17 The link to Legionella species is typically made by culturing legionella from water samples of likely sources and by conducting serologic and/or urine antigen testing in cases. 17 What tests can confirm the diagnosis? The Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society have developed consensus guidelines for the management of community-acquired pneumonia in Ontario cases Canada cases NA NA NA NA Canada rates NA NA NA NA Ontario rates Figure 1: Number and rate of legionellosis cases per population in Ontario and Canada. Sources: Public Health Agency of Canada Notifiable Diseases Online (extracted June 11, 2010) and the Ontario Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care, Public Health Ontario Portal (extracted June 11, 2010). NA = Data not available as of June 11, Confirmed cases per adults. 18 Almost all of the major decisions regarding management, including diagnostic and treatment issues, revolve around the initial assessment of severity. According to these guidelines, patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia should, at a minimum, have blood samples drawn for culture, urinary antigen tests for L. pneumophila and Streptococcus pneumonia and expectorated sputum samples collected for culture. The clinical diagnosis of legionnaires disease can be confirmed by the isolation of the organism from sputum, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, pleural fluid or pulmonary tissue. Detection of the antigen in the urine is a useful test for L. pneumophila serogroup 1. Respiratory specimens can also be tested for the presence of the organism using a 2
3 direct fluorescent antibody technique or by polymerase chain reaction, although these are not available in many settings. Detection of the legionella antigen in urine is quick, usually with a turn around time of about one hour. In a recent meta-analysis, the pooled sensitivity of using the urine antigen test to detect legionella was 0.74 (95% confidence interval [CI] ) and specificity was 0.99 (95% CI ). 19 The rate of a positive antigen test result depends on the severity of the disease, with a positive result occurring in 40% 53% of mild cases and 88% 100% of severe cases. 20 The antigen can persist in urine for weeks to months. Antibodies to Legionella spp. can be detected in acute and convalescent serum samples by several techniques. The convalescent sample should be collected no sooner than six weeks after the acute phase. In some documented cases of legionnaires disease, seroconversion had not occurred by 12 weeks. Recent studies have shown that a previously accepted diagnostic criterion of a single antibody titer of 1:256 is not valid. 21 A four-fold rise in antibody titer between the acute and convalescent phase samples is good evidence that infection with Legionella spp. has occurred. Data from a prospective, nonrandomized study indicate that levofloxacin (and presumably other quinolones) is superior to macrolides for the treatment of severe legionnaires disease. 22 In this study, which was performed in Murcia, Spain, 3.4% of patients who received levofloxacin had complications, compared with 27.2% of those who received macrolides. The patients who received levofloxacin also had a shorter hospital stay (5.5 d v d). The addition of rifampin provided no additional benefit over levofloxacin alone. Azithromycin appears to be the best macrolide for the treatment of legionnaires disease. Box 1: Laboratory findings that may accompany legionellosis 16 Microscopic hematuria Hyponatremia Elevated liver enzymes Hypophosphatemia Elevated creatinine phosphokinase identified proximity to these types of facilities as the most likely source of exposure. Conversely, institution-based Legionella clusters are typically associated with facility-based sources of contamination, including hot and cold water systems. Environmental swabbing within these types of institutions have yielded positive Legionella cultures in shower heads, treatment or recreational water sources, respiratory therapy devices and ice machines. 24 Investigations of potential clusters of cases of legionellosis often involve mapping the locations (Figure 3) and the movement of patients over a specified period of time, along with mapping the location of possible sources of exposure. Using this technique, patterns of shared exposures between cases become evident. 24 These sources can then be sampled and tested for the presence of Legionella species. Plume modeling, which maps airborne particle dispersion under specified meterological conditions, can also aid in identifying possible sources, exposures and transmissions. Control of Legionella, whether environmentally or within institutions, is hampered by the ubiquitous nature of Why should it be reported? Legionellosis has been a nationally notifiable disease in Canada since Although reporting by health care providers and laboratories is legislated, under-reporting of the disease is common because sporadic cases are often treated without the use of empirical tests to confirm the diagnosis. 23 Individual cases of legionellosis should be fully investigated in a timely manner because they may indicate a larger pending outbreak. Risk settings for legionellosis exposure can include hot water systems, air cooling towers, spas or other publicly accessible sites; individual cases are often related to broader clusters with common exposure characteristics. 24 Geographic clusters of legionellosis have frequently been associated with water cooling towers and air conditioning systems that facilitate the transport of water molecules containing Legionella spp. into the surrounding air supply. 25 Cluster investigations have often Figure 2: Chest radiograph in a confirmed case of legionellosis with multilobar opacifications. 3
4 Figure 3: Confirmed cases of legionellosis in Ontario from June 1 to Sept. 30, Reproduced with permission from the Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care. the organism. Outbreak response to Legionella infection often involves the identification and remediation of suspect exposure sites to eliminate the source of the pathogen. Control methods include superheating, hyperchlorination, source-based ultraviolet treatment, physical cleaning of outlet points and microbial filtration. 24 However, it is generally agreed that Legionella cannot be completely eradicated Box 2: Data that physicians should provide to public health about confirmed cases of legionellosis Patient s first and last name Episode date (defined as either onset of symptoms, specimen collection date, laboratory report date) Patient s birth date Patient s address and telephone number Date and method of diagnosis Patient s symptoms Tests performed and results from water systems. Indeed, long-term control of the organism, and subsequent prevention of disease, can only be achieved through regular treatment and management of water systems following strict guidelines for the prevention of microbial growth. Robust local surveillance systems supplied with timely clinical case data will assist in the early identification of clusters and risk settings and the early application of remediation measures to limit further transmission of the disease. This is why health care providers should test for legionellosis when it is suspected and report cases (Box 2) to the local public health authorities. This article has been peer reviewed. Competing interests: None declared for Jason Garay and Erica Weir. Tom Marrie is a board member of Capital District Health Authority and an advisory board member of Wyeth. He has received speaker fees and grants from Wyeth for pneumococcal vaccines and is Dean of the Faculty of Medicine at Dalhousie University. Contributors: Each author made a substantial contribution to the conception and acquisition of data, drafting and final approval of the manuscript. 4
5 REFERENCES 1. Marrie TJ, de Carolis E, Yu VL et al.; Canadian community-acquired pneumonia investigators. Legionnaires Disease results of a multicentre Canadian study. Can J Infect Dis 2003;14: Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement. Health care guideline: communityacquired pneumonia in adults. Bloomington (MN): Institute for Clinical Systems Improvement; Available: /community-acquired_pneumonia_2.html (accessed 2009 Mar. 23). 3. Luck PC. Diagnostics and clinical disease treatment. In: Heuner K, Swanson M, editors. Legionella molecular microbiology. Norfolk (UK): Caister Academic Press; p Lau h, Ashbolt NJ. The role of biofilms and protozoa in legionella pathogenesis: implications for drinking water. J Appl Microbiol 2009;107: Hanrahan JP, Morse DL, Scharf VB, et al. A community hospital outbreak of Legionellosis: transmission by potable hot water. Am J Epidemiol 1987;125: Delia S, Lagana P, Minutoli E. Occurrence of legionella in beach shower facilities. J Prev Med Hyg 2007;48: Mahoney FJ, Hoge CW, Farley TA, et al. Community-wide outbreak of Legionnaires disease associated with a grocery store mist machine. J Infect Dis 1992; 165: Dondero TJ Jr, Rendtorff RC, Mallison GF, et al. An outbreak of Legionnaires disease associated with a contaminated air-conditioning cooling tower. N Engl J Med 1980;302: Borgen K, Aaberge I, Werner-Johansen O, et al. A cluster of Legionnaire disease linked to an Industrial plant in southeast Norway, June July Euro Surveill 2008;13:pii: Cordes LG, Fraser DW, Skaliy P, et al. Legionnaires disease outbreak at an Atlanta, Georgia, country club: Evidence for spread from an evaporative condenser. Am J Epidemiol 1980;111: Nygard K, Werner-Johansen O, Ronsen S, et al. An outbreak of Legionnaires disease caused by long distance spread from an industrial air scrubber in Sarpsborg, Norway. Clin Infect Dis 2008;46: Neil K, Berkelman R. Increasing incidence of Legionellosis in the United States, Clin Infect Dis 2008;47: Hicks LA, Rose CE Jr, Fields BS, et al. Increased rainfall is associated with increased risk for Legionellosis. Epidemiol Infect 2007;135: Fernandez-Sabe N, Reson B, Carratala J, et al. Clinical diagnosis of Legionella pneumonia revisited: Evaluation of the community-based pneumonia incidence study group scoring system. Clin Infect Dis 2003;37: Macfarlane JT, Miller AC, Smith WHR, et al. Comparative radiographic features of community acquired legionnaires disease, pneumococcal pneumonia, mycoplasma pneumonia, and psittacosis. Thorax 1984;39: Meyer RD. Legionella infections: A review of five years of research. Rev Infect Dis 1983;5: Modi A, Gardner J, Lighton L, Pontiac fever outbreak associated with a spa-pool, United Kingdom, April Euro Surveill. 2008;13:pii: Mandell l, Wunderink R, Anzueto A, et al. Infectious disease society of America/American thoracic society consensus guidelines on the management of community-acquired pneumonia in adults. Clin Infect Dis 2007;44:S Shimada T, Noguchi Y, Jackson JL, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis: urinary tests for Legionellosis. Chest 2009;136: Waterer GW, Baselski VS, Wunderink RG. Legionella and community-acquired pneumonia: A review of current diagnostic tests from a clinician s viewpoint. Am J Med 2001;110: Plouffe JF, File TM Jr, Breiman RF, et al. Reevaluation of the definition of Legionnaires disease: use of the urinary antigen assay. Community Based Pneumonia Incidence Study Group. Clin Infect Dis 1995;20: Blazquez Garrido RM, Parra FJE, Frances LA, et al. Antimicrobial chemotherapy for Legionnaires disease; Levofloxacin versus macrolides. Clin Infect Dis 2005;40: Edelstein PH, Ciancioto NP. Legionnella. In: Mandell, Douglas and Bennett s principles and practice of infectious diseases, 6 th edition. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier; p Guideline on Management of Legionella Incidents. Outbreaks and Clusters in the Community. Health Protection Network Scottish Guidance 2. Glasgow (Scotland): Health Protection Scotland; Moore Matthew R, Fields Barry S. Legionellosis. In: Maxcy-Rosenau-Last public health and preventive medicine, 15th edition. New York (NY): McGraw Hill Medical; p Correspondence to: Dr. Erica Weir, Community Health and Epidemiology, Queen s University, Kingston ON; erica.weir@york.ca Resources Infectious Diseases Society of America/American Thoracic Society Consensus Guidelines on the Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults European Guidelines for Control and Prevention of Travel Associated Legionnaires Disease guidelines_jan05.pdf Centre for Disease Control and prevention legionellosis resource site /references.htm Primer articles are brief narrative reviews on interesting, important and timely clinical topics. The articles emphasize clinical application and are based on the best evidence available. Author instructions are available at cmaj.ca. Submit Primers (maximum 1800 words and up to 20 references) to or to discuss ideas. 5
Preventing Legionella Transmission An Environmental Health View
 Preventing Legionella Transmission An Environmental Health View April 25, 2013 Erin Reinsborough Environmental Health Specialist Mission Statement Together with the Halton community, the Health Department
Preventing Legionella Transmission An Environmental Health View April 25, 2013 Erin Reinsborough Environmental Health Specialist Mission Statement Together with the Halton community, the Health Department
What is Legionnaires' disease?
 Understanding Legionnaires disease: A Fact Sheet For Workers Organization(s): New York Committee for Occupational Safety and Health Other languages: Spanish Summary Statement: This NYCOSH fact sheet is
Understanding Legionnaires disease: A Fact Sheet For Workers Organization(s): New York Committee for Occupational Safety and Health Other languages: Spanish Summary Statement: This NYCOSH fact sheet is
Legionnella. You can t t see it but you can catch it. Dr Charmaine Gauci MD, MSc, PhD Head of Disease Surveillance Unit
 Legionnella You can t t see it but you can catch it Dr Charmaine Gauci MD, MSc, PhD Head of Disease Surveillance Unit Legionella infections First documented outbreak name from 221 cases of pneumonia occurred
Legionnella You can t t see it but you can catch it Dr Charmaine Gauci MD, MSc, PhD Head of Disease Surveillance Unit Legionella infections First documented outbreak name from 221 cases of pneumonia occurred
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia. Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali
 Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
Microbiology of Atypical Pneumonia Dr. Mohamed Medhat Ali Pneumonia P n e u m o n i a i s a n infection of the lungs that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, and fungi. Atypical! Pneumonia Symptoms. X-ray
Legionellosis Water Management and Investigation Case Study
 Legionellosis Water Management and Investigation Case Study Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Bryce Spiker, MPH Legionellosis Epidemiologist Mike Wesenberg Environmental Health Specialist
Legionellosis Water Management and Investigation Case Study Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Bryce Spiker, MPH Legionellosis Epidemiologist Mike Wesenberg Environmental Health Specialist
Outbreak of travel-associated Legionnaires' disease Palmanova, Mallorca (Spain), September October Main conclusions and options for response
 RAPID RISK ASSESSMENT Outbreak of travel-associated Legionnaires' disease Palmanova, Mallorca (Spain), September October 2017 23 October 2017 Main conclusions and options for response An increase in Legionnaires
RAPID RISK ASSESSMENT Outbreak of travel-associated Legionnaires' disease Palmanova, Mallorca (Spain), September October 2017 23 October 2017 Main conclusions and options for response An increase in Legionnaires
Legionnaires Disease: Epidemiology and Outbreak Investigation
 Legionnaires Disease: Epidemiology and Outbreak Investigation Ellen Laine, JD, MPH Emerging Infections Unit Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention and Control Division History of Legionnaires Disease
Legionnaires Disease: Epidemiology and Outbreak Investigation Ellen Laine, JD, MPH Emerging Infections Unit Infectious Disease Epidemiology, Prevention and Control Division History of Legionnaires Disease
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT
 THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
THIS IS AN OFFICIAL NH DHHS HEALTH ALERT Distributed by the NH Health Alert Network Health.Alert@nh.gov August 25, 2018 0800 EDT NH-HAN 20180825 Cluster of Legionella pneumophila Pneumonia (Legionnaire
Cases in employees. Cases. Day of onset (July)
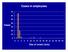 Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Cases in employees 70 60 50 Cases 40 30 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24 26 28 30 Day of onset (July) 70 60 50 40 Cases 30 Cases in employees and visitors Employees Visitors 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 8
Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics
 Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics Nicole Wolter Centre for Respiratory Diseases and Meningitis (CRDM) National Institute for Communicable Diseases nicolew@nicd.ac.za 7 th FIDSSA Conference, Cape
Current and Emerging Legionella Diagnostics Nicole Wolter Centre for Respiratory Diseases and Meningitis (CRDM) National Institute for Communicable Diseases nicolew@nicd.ac.za 7 th FIDSSA Conference, Cape
Community acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in a tertiary care hospital
 101 Research article Community acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in a tertiary care hospital Abstract BN Dissanayake 1,, DE Jayawardena 2, CG Senevirathna 1, TM Gamage 1 Sri Lankan Journal
101 Research article Community acquired pneumonia due to Legionella pneumophila in a tertiary care hospital Abstract BN Dissanayake 1,, DE Jayawardena 2, CG Senevirathna 1, TM Gamage 1 Sri Lankan Journal
Guideline on the management of Legionella cases, incidents, outbreaks and clusters in the community Quick Reference Guide
 2 2014 Edition Guideline on the management of Legionella cases, incidents, outbreaks and clusters in the community Quick Reference Guide Health Protection Network Scottish Guidance November 2014 Initial
2 2014 Edition Guideline on the management of Legionella cases, incidents, outbreaks and clusters in the community Quick Reference Guide Health Protection Network Scottish Guidance November 2014 Initial
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia
 Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Antimicrobial Stewardship in Community Acquired Pneumonia Medicine Review Course 2018 Dr Lee Tau Hong Consultant Department of Infectious Diseases National Centre for Infectious Diseases Scope 1. Diagnosis
Legionnaires Disease Q&A (General) (Source: OSHA) (4/29/10)
 Legionnaires Disease Q&A (General) (Source: OSHA) (4/29/10) Q. What is Legionnaires Disease? A. Legionnaires disease is a common name for one of the several illnesses caused by Legionella bacteria. Legionnaires
Legionnaires Disease Q&A (General) (Source: OSHA) (4/29/10) Q. What is Legionnaires Disease? A. Legionnaires disease is a common name for one of the several illnesses caused by Legionella bacteria. Legionnaires
Show me the evidence! Water can cause infection and illness if hospital water systems are not properly engineered and managed 6/29/2017
 Key Takeaways can May 5, 2017 HEALTHCARE PLUMBING SYSTEMS: PUBLIC HEALTH RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH LEGIONNAIRES DISEASE AND OTHER HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS JOHN HANLIN AND IAN EISNER NALCO WATER A DIVISION
Key Takeaways can May 5, 2017 HEALTHCARE PLUMBING SYSTEMS: PUBLIC HEALTH RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH LEGIONNAIRES DISEASE AND OTHER HEALTHCARE-ASSOCIATED INFECTIONS JOHN HANLIN AND IAN EISNER NALCO WATER A DIVISION
Respiratory Infections
 Respiratory Infections NISHANT PRASAD, MD THE DR. JAMES J. RAHAL, JR. DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN QUEENS Disclosures Stockholder: Contrafect Corp., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co Research
Respiratory Infections NISHANT PRASAD, MD THE DR. JAMES J. RAHAL, JR. DIVISION OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES NEWYORK-PRESBYTERIAN QUEENS Disclosures Stockholder: Contrafect Corp., Bristol-Myers Squibb Co Research
Legionnaires Disease Outbreak at the Rio All-Suites Hotel and Casino, 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada
 Legionnaires Disease Outbreak at the Rio All-Suites Hotel and Casino, 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada PUBLIC HEALTH INVESTIGATION FINAL REPORT Southern Nevada Health District OFFICE OF EPIDEMIOLOGY AND DISEASE
Legionnaires Disease Outbreak at the Rio All-Suites Hotel and Casino, 2017 Las Vegas, Nevada PUBLIC HEALTH INVESTIGATION FINAL REPORT Southern Nevada Health District OFFICE OF EPIDEMIOLOGY AND DISEASE
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
ANSI/ASHRAE Standard Legionellosis: Risk Management for Building Water Systems
 ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 188-2015 Legionellosis: Risk Management for Building Water Systems Published June 26, 2015 Patricia T. Graef, P.E. Member SSPC-188 January, 2018 PURPOSE: Establish minimum legionellosis
ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 188-2015 Legionellosis: Risk Management for Building Water Systems Published June 26, 2015 Patricia T. Graef, P.E. Member SSPC-188 January, 2018 PURPOSE: Establish minimum legionellosis
Making the Right Call With. Pneumonia. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a. Community-Acquired. What exactly is CAP?
 Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Ontario Novel H1N1 Influenza A Virus Epidemiologic Summary June 4, 2009 As of 8:30am, June 4, 2009
 Ontario Novel H1N1 Influenza A Virus Epidemiologic Summary June 4, 29 As of 8:3am, June 4, 29 Background On April 2, 29, the Public Health Agency of Canada alerted the Ministry of Health and Long-Term
Ontario Novel H1N1 Influenza A Virus Epidemiologic Summary June 4, 29 As of 8:3am, June 4, 29 Background On April 2, 29, the Public Health Agency of Canada alerted the Ministry of Health and Long-Term
A community outbreak of Legionnaires disease linked to hospital cooling towers: an epidemiological method to calculate dose of exposure
 International Epidemiological Association 1999 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 1999;28:353 359 A community outbreak of Legionnaires disease linked to hospital cooling towers:
International Epidemiological Association 1999 Printed in Great Britain International Journal of Epidemiology 1999;28:353 359 A community outbreak of Legionnaires disease linked to hospital cooling towers:
National Legionnaires Disease Surveillance, Outbreak Detection, and Response
 National Center for Immunization & Respiratory Diseases National Legionnaires Disease Surveillance, Outbreak Detection, and Response Ally Binder, MS Surveillance Epidemiologist Respiratory Diseases Branch
National Center for Immunization & Respiratory Diseases National Legionnaires Disease Surveillance, Outbreak Detection, and Response Ally Binder, MS Surveillance Epidemiologist Respiratory Diseases Branch
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
Unit II Problem 2 Microbiology Lab: Pneumonia - What are the steps needed to obtain a proper sputum specimen? You need the following: A wide-mouth labeled container. Gloves. Water. Mouth wash + tissues.
CMS REQUIREMENTS TO REDUCE LEGIONELLA: RISK IN HEALTHCARE FACILITY WATER SYSTEMS. May 21, 2018
 CMS REQUIREMENTS TO REDUCE LEGIONELLA: RISK IN HEALTHCARE FACILITY WATER SYSTEMS May 21, 2018 LEGIONELLOSIS AND PUBLIC HEALTH Rebecca Greeley, MPH Infectious Disease Team Lead Communicable Disease Service
CMS REQUIREMENTS TO REDUCE LEGIONELLA: RISK IN HEALTHCARE FACILITY WATER SYSTEMS May 21, 2018 LEGIONELLOSIS AND PUBLIC HEALTH Rebecca Greeley, MPH Infectious Disease Team Lead Communicable Disease Service
Fact Sheet: Legionellosis March 2017
 Fact Sheet Fact Sheet: Legionellosis March 2017 Brought to you by the APSP Recreational Water Quality Committee (RWQC) I. INTRODUCTION Legionellosis is an infection caused by the bacterium Legionella.
Fact Sheet Fact Sheet: Legionellosis March 2017 Brought to you by the APSP Recreational Water Quality Committee (RWQC) I. INTRODUCTION Legionellosis is an infection caused by the bacterium Legionella.
Trends in Legionnaires Disease, : Declining Mortality and New Patterns of Diagnosis
 MAJOR ARTICLE Trends in Legionnaires Disease, 1980 1998: Declining Mortality and New Patterns of Diagnosis Andrea L. Benin, a Robert F. Benson, and Richard E. Besser Respiratory Diseases Branch, Division
MAJOR ARTICLE Trends in Legionnaires Disease, 1980 1998: Declining Mortality and New Patterns of Diagnosis Andrea L. Benin, a Robert F. Benson, and Richard E. Besser Respiratory Diseases Branch, Division
Presented. April 22nd 1986
 J. LEGIONNAIRES' DISEASE Presented at ALBERTA Public Works, Supply and Services Property Management Division Water Treatment Coordinators' Meeting Edmonton, Alberta April 22nd 1986 by G.F. Yuzwa, P.Eng.
J. LEGIONNAIRES' DISEASE Presented at ALBERTA Public Works, Supply and Services Property Management Division Water Treatment Coordinators' Meeting Edmonton, Alberta April 22nd 1986 by G.F. Yuzwa, P.Eng.
23/08/2015. What are we going to discuss here today? Legionella. Can dust and water harm you? Legionella Aspergillus
 Can dust and water harm you? Carol Robinson CNM3 Infection Prevention and Control SIVUH What are we going to discuss here today? Legionella Aspergillus Some bacteria not covered are Pseudomonas spp, Cryptosporidiosis,
Can dust and water harm you? Carol Robinson CNM3 Infection Prevention and Control SIVUH What are we going to discuss here today? Legionella Aspergillus Some bacteria not covered are Pseudomonas spp, Cryptosporidiosis,
Legionnaire s disease
 Legionnaire s disease Connecticut Environmental Health Association Meeting April 9, 2019 Paul Gacek MPH, CPH Legionellosis Surveillance Coordinator & Waterborne Disease Coordinator Epidemiology and Emerging
Legionnaire s disease Connecticut Environmental Health Association Meeting April 9, 2019 Paul Gacek MPH, CPH Legionellosis Surveillance Coordinator & Waterborne Disease Coordinator Epidemiology and Emerging
 Reducing Legionella Risk What is Legionella? Legionella Species Biofilm stable structures and breeding grounds Where does Legionella live? Non-potable Water Shower Aerosol Cooling Tower Aerosol Infectivity
Reducing Legionella Risk What is Legionella? Legionella Species Biofilm stable structures and breeding grounds Where does Legionella live? Non-potable Water Shower Aerosol Cooling Tower Aerosol Infectivity
Increasing Incidence of Legionellosis in the United States, : Changing Epidemiologic Trends
 MAJOR ARTICLE Increasing Incidence of Legionellosis in the United States, 1990 2005: Changing Epidemiologic Trends Karen Neil and Ruth Berkelman Department of Epidemiology, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia
MAJOR ARTICLE Increasing Incidence of Legionellosis in the United States, 1990 2005: Changing Epidemiologic Trends Karen Neil and Ruth Berkelman Department of Epidemiology, Emory University, Atlanta, Georgia
Legionellosis Outbreak-Genesee County, June, 2014 March, Summary Analysis
 Legionellosis Outbreak-Genesee County, June, 2014 March, 2015 Summary Analysis Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Genesee County Health Department (This report was edited on January 15, 2016
Legionellosis Outbreak-Genesee County, June, 2014 March, 2015 Summary Analysis Michigan Department of Health and Human Services Genesee County Health Department (This report was edited on January 15, 2016
Streptococcus Pneumoniae
 Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Invasive Pneumococcal Disease) DISEASE REPORTABLE WITHIN 24 HOURS OF DIAGNOSIS Per N.J.A.C. 8:57, healthcare providers and administrators shall report by mail or by electronic
Investigation and Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Frequently Asked Questions
 Investigation and Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Frequently Asked Questions 1. Why was this algorithm developed? Emergency department physicians were seeking guidance about best antimicrobial
Investigation and Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Frequently Asked Questions 1. Why was this algorithm developed? Emergency department physicians were seeking guidance about best antimicrobial
Legionnaire s disease is a febrile illness with pneumonia. The Radiologic Manifestations of Legionnaire s Disease*
 The Radiologic Manifestations of Legionnaire s Disease* Michael J. Tan, MD; James S. Tan, MD, FCCP; Robert H. Hamor, MD; Thomas M. File, Jr., MD, FCCP; Robert F. Breiman, MD; and the Ohio Community-Based
The Radiologic Manifestations of Legionnaire s Disease* Michael J. Tan, MD; James S. Tan, MD, FCCP; Robert H. Hamor, MD; Thomas M. File, Jr., MD, FCCP; Robert F. Breiman, MD; and the Ohio Community-Based
EPIDEMIOLOGY SURVEILLANCE REPORT Northeast Region. Namitha Reddy Regional Coordinator North/Central West Region
 EPIDEMIOLOGY SURVEILLANCE REPORT Northeast Region Namitha Reddy Regional Coordinator North/Central West Region 1 This report is for use by Public Health Officials only and not for public distribution.
EPIDEMIOLOGY SURVEILLANCE REPORT Northeast Region Namitha Reddy Regional Coordinator North/Central West Region 1 This report is for use by Public Health Officials only and not for public distribution.
Clinical Outcomes for Hospitalized Patients with Legionella Pneumonia in the Antigenuria Era: The Influence of Levofloxacin Therapy
 MAJOR ARTICLE Clinical Outcomes for Hospitalized Patients with Legionella Pneumonia in the Antigenuria Era: The Influence of Levofloxacin Therapy Analía Mykietiuk, 1 Jordi Carratalà, 1 Núria Fernández-Sabé,
MAJOR ARTICLE Clinical Outcomes for Hospitalized Patients with Legionella Pneumonia in the Antigenuria Era: The Influence of Levofloxacin Therapy Analía Mykietiuk, 1 Jordi Carratalà, 1 Núria Fernández-Sabé,
Appendix A: Disease-Specific Chapters
 Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix A: Disease-Specific Chapters Chapter: Haemophilus influenzae disease, all types, invasive Effective: May 2018 Haemophilus influenzae,
Ministry of Health and Long-Term Care Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix A: Disease-Specific Chapters Chapter: Haemophilus influenzae disease, all types, invasive Effective: May 2018 Haemophilus influenzae,
Influenza-Associated Pediatric Mortality rev Jan 2018
 rev Jan 2018 Infectious Agent Influenza A, B or C virus BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission Transmission occurs via droplet spread. After a person infected with influenza coughs, sneezes, or talks, influenza
rev Jan 2018 Infectious Agent Influenza A, B or C virus BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Transmission Transmission occurs via droplet spread. After a person infected with influenza coughs, sneezes, or talks, influenza
Importance of Atypical Pathogens of Community-Acquired Pneumonia
 S35 Importance of Atypical Pathogens of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Joseph F. Plouffe Departments of Internal Medicine and Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Ohio State University College of Medicine,
S35 Importance of Atypical Pathogens of Community-Acquired Pneumonia Joseph F. Plouffe Departments of Internal Medicine and Medical Microbiology and Immunology, Ohio State University College of Medicine,
Epidemiology and Etiology of Community-Acquired Pneumonia 761 Lionel A. Mandell
 LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS Preface Thomas M. File, Jr xiii Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Pathophysiology and Host Factors with Focus on Possible New Approaches to Management of Lower Respiratory
LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS Preface Thomas M. File, Jr xiii Community-Acquired Pneumonia: Pathophysiology and Host Factors with Focus on Possible New Approaches to Management of Lower Respiratory
Evaluation of the Oxoid Xpect Legionella test kit for Detection of Legionella
 JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 May 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00397-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
JCM Accepts, published online ahead of print on 6 May 2009 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.00397-09 Copyright 2009, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases)
 INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
INFLUENZA (Outbreaks; hospitalized or fatal pediatric cases) 1. Agent: Influenza viruses A, B, and C. Only influenza A and B are of public health concern since they are responsible for epidemics. 2. Identification:
BC MHOs, PHNLs, ICPs, ERDOCs, IDSPEC, MEDMICRO, AMBULANCE, BCCDC Internal Groups, National Surveillance Network Partners
 To: Subject: Purpose: Action required: Recommendations: BC MHOs, PHNLs, ICPs, ERDOCs, IDSPEC, MEDMICRO, AMBULANCE, BCCDC Internal Groups, National Surveillance Network Partners November 1, 2013 Emerging
To: Subject: Purpose: Action required: Recommendations: BC MHOs, PHNLs, ICPs, ERDOCs, IDSPEC, MEDMICRO, AMBULANCE, BCCDC Internal Groups, National Surveillance Network Partners November 1, 2013 Emerging
Legionella Bacteria and Microorganisms in Data Center HVAC Systems
 Legionella Bacteria and Microorganisms in Data Center HVAC Systems Rob Rottersman, MS, CIH Principal Ramboll #DATACENTERWORLD #CPEXPO CHANNELPARTNERSCONFERENCE.COM DATACENTERWORLD.COM Data Center World
Legionella Bacteria and Microorganisms in Data Center HVAC Systems Rob Rottersman, MS, CIH Principal Ramboll #DATACENTERWORLD #CPEXPO CHANNELPARTNERSCONFERENCE.COM DATACENTERWORLD.COM Data Center World
JCP Online First, published on June 17, 2013 as /jclinpath Original article
 JCP Online First, published on June 17, 2013 as 10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201209 Original article Diagnostic, therapeutic and economic consequences of a positive urinary antigen test for Legionella spp. in
JCP Online First, published on June 17, 2013 as 10.1136/jclinpath-2012-201209 Original article Diagnostic, therapeutic and economic consequences of a positive urinary antigen test for Legionella spp. in
Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics)
 Page 1 of 8 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2014 UpToDate Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics) Authors Thomas J Marrie, MD Thomas M File, Jr, MD Section Editor John
Page 1 of 8 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2014 UpToDate Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics) Authors Thomas J Marrie, MD Thomas M File, Jr, MD Section Editor John
Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated
 Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated Edwin Yu Clin Infect Dis 2007;44(S2):27-72 Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171:388-416 IDSA / ATS Guidelines Microbiology Principles and Practice of Infectious
Pneumonia Community-Acquired Healthcare-Associated Edwin Yu Clin Infect Dis 2007;44(S2):27-72 Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005; 171:388-416 IDSA / ATS Guidelines Microbiology Principles and Practice of Infectious
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Effective Methods for Implementing Water Management. Programs (WMPs) to Reduce Growth of Transmission of
 This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 08/18/2017 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2017-17491, and on FDsys.gov BILLING CODE 4163-18-P DEPARTMENT OF
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 08/18/2017 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2017-17491, and on FDsys.gov BILLING CODE 4163-18-P DEPARTMENT OF
Legionella. A detailed insight from our specialists. Overview Lifecycle How it manifests Strains and species Facts and statistics
 Legionella. A detailed insight from our specialists Overview Lifecycle How it manifests Strains and species Facts and statistics Laboratory process Sampling and analysis Illness and symptoms Interpreting
Legionella. A detailed insight from our specialists Overview Lifecycle How it manifests Strains and species Facts and statistics Laboratory process Sampling and analysis Illness and symptoms Interpreting
Community-Acquired Pneumonia OBSOLETE 2
 Community-Acquired Pneumonia OBSOLETE 2 Clinical practice guidelines serve as an educational reference, and do not supersede the clinical judgment of the treating physician with respect to appropriate
Community-Acquired Pneumonia OBSOLETE 2 Clinical practice guidelines serve as an educational reference, and do not supersede the clinical judgment of the treating physician with respect to appropriate
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Disease Under Surveillance Management Guidelines March 2011
 March 2011 Histoplasmosis Case Definition Confirmed Case Clinical illness [1] with laboratory confirmation of infection: Isolation of Histoplasma capsulatum from an appropriate clinical specimen (tissue
March 2011 Histoplasmosis Case Definition Confirmed Case Clinical illness [1] with laboratory confirmation of infection: Isolation of Histoplasma capsulatum from an appropriate clinical specimen (tissue
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA
 KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Methodology: Expert opinion Issue Date: 8-97 Champion: Pulmonary Medicine Most Recent Update: 6-08, 7-10, 7-12 Key Stakeholders: Pulmonary Medicine,
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Methodology: Expert opinion Issue Date: 8-97 Champion: Pulmonary Medicine Most Recent Update: 6-08, 7-10, 7-12 Key Stakeholders: Pulmonary Medicine,
Epidemiology of Legionnaires' Disease in Genesee County, Michigan, CHART BOOK MAY 2018
 Epidemiology of Legionnaires' Disease in Genesee County, Michigan, 2014-2017 CHART BOOK MAY 2018 1 Table of Contents Page Content 4 Purpose 6 Legionella Background 8 Legionella Background -2 10 National
Epidemiology of Legionnaires' Disease in Genesee County, Michigan, 2014-2017 CHART BOOK MAY 2018 1 Table of Contents Page Content 4 Purpose 6 Legionella Background 8 Legionella Background -2 10 National
Antimicrobial Chemotherapy for Legionnaires Disease: Levofloxacin versus Macrolides
 MAJOR ARTICLE Antimicrobial Chemotherapy for Legionnaires Disease: Levofloxacin versus Macrolides Rosa Mª Blázquez Garrido, 1 Francisco Javier Espinosa Parra, 1 Loreto Alemany Francés, 2 Rosa Mª Ramos
MAJOR ARTICLE Antimicrobial Chemotherapy for Legionnaires Disease: Levofloxacin versus Macrolides Rosa Mª Blázquez Garrido, 1 Francisco Javier Espinosa Parra, 1 Loreto Alemany Francés, 2 Rosa Mª Ramos
Sporadic and epidemic community legionellosis: two faces of the same illness
 Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 138 142 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00077206 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Sporadic and epidemic community legionellosis: two faces of the same illness N. Sopena*, L. Force #, M.L. Pedro-Botet*,
Eur Respir J 2007; 29: 138 142 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00077206 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2007 Sporadic and epidemic community legionellosis: two faces of the same illness N. Sopena*, L. Force #, M.L. Pedro-Botet*,
Influence of Social Media on an Acute Respiratory Outbreak at a High Profile Party Venue Los Angeles, February 2011
 Influence of Social Media on an Acute Respiratory Outbreak at a High Profile Party Venue Los Angeles, February 2011 Dawn Terashita, MD, MPH Acute Communicable Disease Control Los Angeles County Department
Influence of Social Media on an Acute Respiratory Outbreak at a High Profile Party Venue Los Angeles, February 2011 Dawn Terashita, MD, MPH Acute Communicable Disease Control Los Angeles County Department
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL. Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 47: Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae Authors E-B Kruse, MD H. Wisplinghoff, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH) Topic Outline Key Issue Known
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER 47: Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae Authors E-B Kruse, MD H. Wisplinghoff, MD Chapter Editor Michelle Doll, MD, MPH) Topic Outline Key Issue Known
Human infection with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus: updated interim WHO guidance on global surveillance
 Human infection with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus: updated interim WHO guidance on global surveillance 10 July 2009 Background This document updates the interim WHO guidance on global surveillance of pandemic
Human infection with pandemic (H1N1) 2009 virus: updated interim WHO guidance on global surveillance 10 July 2009 Background This document updates the interim WHO guidance on global surveillance of pandemic
Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases
 Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: Influenza Revised December 2014 Influenza 1.0 Provincial Reporting Confirmed cases of disease 2.0 Type
Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: Influenza Revised December 2014 Influenza 1.0 Provincial Reporting Confirmed cases of disease 2.0 Type
Peterborough County-City Health Unit Pandemic Influenza Plan Section 1: Background
 1. Background Every expert on influenza agrees that the ability of the influenza virus to re-assort genes means that another influenza pandemic not only can happen, it almost certainly will happen Influenza
1. Background Every expert on influenza agrees that the ability of the influenza virus to re-assort genes means that another influenza pandemic not only can happen, it almost certainly will happen Influenza
SECTION 10.4 LEGIONELLA
 SECTION 10.4 LEGIONELLA Introduction Legionella in Healthcare Settings Legionnaires Disease Appendix 10.4.1 Management of Nebulisers Developed by Patricia Coughlan, Maire Flynn, Liz Forde, Niamh Mc Donnell
SECTION 10.4 LEGIONELLA Introduction Legionella in Healthcare Settings Legionnaires Disease Appendix 10.4.1 Management of Nebulisers Developed by Patricia Coughlan, Maire Flynn, Liz Forde, Niamh Mc Donnell
GROUP A STREPTOCOCCUS (GAS) INVASIVE
 GROUP A STREPTOCOCCUS (GAS) INVASIVE Case definition CONFIRMED CASE Laboratory confirmation of infection with or without clinical evidence of invasive disease: isolation of group A streptococcus (Streptococcus
GROUP A STREPTOCOCCUS (GAS) INVASIVE Case definition CONFIRMED CASE Laboratory confirmation of infection with or without clinical evidence of invasive disease: isolation of group A streptococcus (Streptococcus
Received 3 August 2005/Returned for modification 13 September 2005/Accepted 13 January 2006
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Mar. 2006, p. 361 364 Vol. 13, No. 3 1556-6811/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.13.3.361 364.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evaluation
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Mar. 2006, p. 361 364 Vol. 13, No. 3 1556-6811/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.13.3.361 364.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evaluation
Human Infection with Novel Influenza A Virus Case Report Form
 Human Infection with Novel Influenza A Virus Case Report Form Form Approved OMB No. 0920-0004 Exp. Date 6/30/2013 Reporter Information State: Date reported to state/local health department: / / (MM/DD/YYYY)
Human Infection with Novel Influenza A Virus Case Report Form Form Approved OMB No. 0920-0004 Exp. Date 6/30/2013 Reporter Information State: Date reported to state/local health department: / / (MM/DD/YYYY)
PROCEDURE FOR DEALING WITH MENINGITIS AND MENINGOCOCCAL DISEASE
 PROCEDURE FOR DEALING WITH MENINGITIS AND MENINGOCOCCAL DISEASE 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Purpose of Procedure To ensure that the University has clear guidelines on preventing or managing cases of meningitis
PROCEDURE FOR DEALING WITH MENINGITIS AND MENINGOCOCCAL DISEASE 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Purpose of Procedure To ensure that the University has clear guidelines on preventing or managing cases of meningitis
Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association
 Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association The County Health Department held a briefing on Monday, April 27thto outline the issues surrounding the Swine Flu and its migration
Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association The County Health Department held a briefing on Monday, April 27thto outline the issues surrounding the Swine Flu and its migration
Pneumonia. Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine
 Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
Acute respiratory illness This is a disease that typically affects the airways in the nose and throat (the upper respiratory tract).
 Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Early mortality in patients with communityacquired pneumonia: causes and risk factors
 Eur Respir J 2008; 32: 733 739 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00128107 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2008 Early mortality in patients with communityacquired : causes and risk factors C. Garcia-Vidal*, N. Fernández-Sabé*,
Eur Respir J 2008; 32: 733 739 DOI: 10.1183/09031936.00128107 CopyrightßERS Journals Ltd 2008 Early mortality in patients with communityacquired : causes and risk factors C. Garcia-Vidal*, N. Fernández-Sabé*,
Health Board Logo. Post SARS Outbreak Surveillance. Report of possible or probable cases (Form version 1) February 11 th 2004
 Post SARS Outbreak Surveillance Report of possible or probable cases (Form version 1) February 11 th 2004 This form is to be used for persons who fit the surveillance case definition of possible or probable
Post SARS Outbreak Surveillance Report of possible or probable cases (Form version 1) February 11 th 2004 This form is to be used for persons who fit the surveillance case definition of possible or probable
WORKSHOP. The Multiple Facets of CAP. Community acquired pneumonia (CAP) continues. Jennifer s Situation
 Practical Pointers pointers For for Your your Practice practice The Multiple Facets of CAP Dr. George Fox, MD, MSc, FRCPC, FCCP Community acquired pneumonia (CAP) continues to be a significant health burden
Practical Pointers pointers For for Your your Practice practice The Multiple Facets of CAP Dr. George Fox, MD, MSc, FRCPC, FCCP Community acquired pneumonia (CAP) continues to be a significant health burden
SPICe Briefing Frequently Asked Questions: Legionnaires disease
 The Scottish Parliament and Scottish Parliament Infor mation C entre l ogos. SPICe Briefing Frequently Asked Questions: Legionnaires disease Suzi Macpherson 12 June 2012 12/39 The recent outbreak of Legionnaires
The Scottish Parliament and Scottish Parliament Infor mation C entre l ogos. SPICe Briefing Frequently Asked Questions: Legionnaires disease Suzi Macpherson 12 June 2012 12/39 The recent outbreak of Legionnaires
Annual Epidemiological Report
 July 2018 Annual Epidemiological Report 1 Legionellosis in Ireland, 2017 Key Facts There were 25 cases of Legionnaires disease notified in Ireland in 2017 The rate per million population increased from
July 2018 Annual Epidemiological Report 1 Legionellosis in Ireland, 2017 Key Facts There were 25 cases of Legionnaires disease notified in Ireland in 2017 The rate per million population increased from
A Newborn withdomestically Acquired Legionnaires Disease Confirmed by Molecular Typing
 MAJOR ARTICLE A Newborn withdomestically Acquired Legionnaires Disease Confirmed by Molecular Typing Kirsi Skogberg, 1,4 J. Pekka Nuorti, 1 Harri Saxen, 5 Jaana Kusnetsov, 2 Silja Mentula, 3 Vineta Fellman,
MAJOR ARTICLE A Newborn withdomestically Acquired Legionnaires Disease Confirmed by Molecular Typing Kirsi Skogberg, 1,4 J. Pekka Nuorti, 1 Harri Saxen, 5 Jaana Kusnetsov, 2 Silja Mentula, 3 Vineta Fellman,
Chapter. Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Outbreak in a University Hospital in Hong Kong. Epidemiology-University Hospital Experience
 content Chapter Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Outbreak in a University Hospital in Hong Kong 3 Nelson Lee, Joseph JY Sung Epidemiology-University Hospital Experience Diagnosis of SARS Clinical
content Chapter Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (SARS) Outbreak in a University Hospital in Hong Kong 3 Nelson Lee, Joseph JY Sung Epidemiology-University Hospital Experience Diagnosis of SARS Clinical
Preventing Legionellosis
 The following article was published in ASHRAE Journal, October 2007. Copyright 2007 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. It is presented for educational purposes
The following article was published in ASHRAE Journal, October 2007. Copyright 2007 American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers, Inc. It is presented for educational purposes
Legionnaire s Disease: Overview and Treatment
 Legionnaire s Disease: Overview and Treatment Sarah Newman, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Nicklaus Children s Hospital Disclosures Authors of this presentation have the following to disclose concerning
Legionnaire s Disease: Overview and Treatment Sarah Newman, PharmD PGY1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Nicklaus Children s Hospital Disclosures Authors of this presentation have the following to disclose concerning
Infection control in Aged Residential Care Facilities. Dr Sally Roberts Clinical Advisor for IP&C Service, ADHB
 Infection control in Aged Residential Care Facilities Dr Sally Roberts Clinical Advisor for IP&C Service, ADHB Background Endemic infections Epidemic infections Managing outbreaks Administrative measures
Infection control in Aged Residential Care Facilities Dr Sally Roberts Clinical Advisor for IP&C Service, ADHB Background Endemic infections Epidemic infections Managing outbreaks Administrative measures
PPHSN Reporting Form Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) outbreak
 ANNEX 2 PPHSN Reporting Form Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) outbreak (updated 09.05.2003) PPHSN Reporting Form Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) outbreak Report of suspected or probable
ANNEX 2 PPHSN Reporting Form Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) outbreak (updated 09.05.2003) PPHSN Reporting Form Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) outbreak Report of suspected or probable
West Nile Virus in the Region of Peel 2002
 HUMAN CASE SURVEILLANCE Introduction Human illness caused by mosquito-borne WNV acquired in Peel occurred for the first time in 2002. In 1999, a Peel resident who had traveled to New York City acquired
HUMAN CASE SURVEILLANCE Introduction Human illness caused by mosquito-borne WNV acquired in Peel occurred for the first time in 2002. In 1999, a Peel resident who had traveled to New York City acquired
12/12/2011. Atypical Pneumonia. Objectives. Causative Agents of Acute Pneumonia Bacteria. Causative Agents of Acute Pneumonia Other Agents
 Objectives Atypical Pneumonia K. Sue Kehl, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Associate Professor, Pathology Medical College of Wisconsin Associate Director of Clinical Pathology & Technical Director of Microbiology, Children's
Objectives Atypical Pneumonia K. Sue Kehl, Ph.D., D(ABMM) Associate Professor, Pathology Medical College of Wisconsin Associate Director of Clinical Pathology & Technical Director of Microbiology, Children's
MEASLES HEALTH ALERT/ADVISORY. Date: February 5, Dear Colleague:
 MEASLES HEALTH ALERT/ADVISORY Date: February 5, 2019 Dear Colleague: Details of situation: Five measles cases, four between the ages of 12 to 21 months, have been reported in three different counties within
MEASLES HEALTH ALERT/ADVISORY Date: February 5, 2019 Dear Colleague: Details of situation: Five measles cases, four between the ages of 12 to 21 months, have been reported in three different counties within
Bacterial Meningitis Concerns in Collegiate Athletics.5 hr. CEU
 Bacterial Meningitis Concerns in Collegiate Athletics.5 hr. CEU This unit is designed to increase your understanding of a highly dangerous infection, and help you protect your student athletes from its
Bacterial Meningitis Concerns in Collegiate Athletics.5 hr. CEU This unit is designed to increase your understanding of a highly dangerous infection, and help you protect your student athletes from its
Cooling Towers Received 1 May 1981/Accepted 24 August were not infected to have stayed in rooms that
 APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1982, p. 24-244 0099-2240/82/010240-05$02.00/0 Vol. 43, No. 1 Failure of Legionella pneumophila Sensitivities to Predict Culture Results from Disinfectant-Treated
APPLIED AND ENVIRONMENTAL MICROBIOLOGY, Jan. 1982, p. 24-244 0099-2240/82/010240-05$02.00/0 Vol. 43, No. 1 Failure of Legionella pneumophila Sensitivities to Predict Culture Results from Disinfectant-Treated
Complete the Distinguished Lecturer Event Summary Critique
 This ASHRAE Distinguished Lecturer is brought to you by the Society Chapter Technology Transfer Committee Complete the Distinguished Lecturer Event Summary Critique CTTC needs your feedback to continue
This ASHRAE Distinguished Lecturer is brought to you by the Society Chapter Technology Transfer Committee Complete the Distinguished Lecturer Event Summary Critique CTTC needs your feedback to continue
Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR (1167)
 From the Japanese Association of Medical Sciences The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR
From the Japanese Association of Medical Sciences The Japanese Association for Infectious Diseases Simultaneous and Rapid Detection of Causative Pathogens in Community-acquired Pneumonia by Real-time PCR
PCR Is Not Always the Answer
 PCR Is Not Always the Answer Nicholas M. Moore, PhD(c), MS, MLS(ASCP) CM Assistant Director, Division of Clinical Microbiology Assistant Professor Rush University Medical Center Disclosures Contracted
PCR Is Not Always the Answer Nicholas M. Moore, PhD(c), MS, MLS(ASCP) CM Assistant Director, Division of Clinical Microbiology Assistant Professor Rush University Medical Center Disclosures Contracted
Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
 Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Robin Jump, MD, PhD Cleveland Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center Case Western Reserve University
Upper...and Lower Respiratory Tract Infections Robin Jump, MD, PhD Cleveland Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center Case Western Reserve University
Legionnaires disease in Europe: all quiet on the eastern front?
 EDITORIAL LEGIONNAIRES DISEASE IN EUROPE Legionnaires disease in Europe: all quiet on the eastern front? Julien Beauté, Emmanuel Robesyn and Birgitta de Jong, on behalf of the European Legionnaires Disease
EDITORIAL LEGIONNAIRES DISEASE IN EUROPE Legionnaires disease in Europe: all quiet on the eastern front? Julien Beauté, Emmanuel Robesyn and Birgitta de Jong, on behalf of the European Legionnaires Disease
BCCDC Measles, Mumps and Rubella Enhanced Surveillance Case Report Form
 A. PERSON REPTING Disease: Measles Mumps Rubella INSTRUCTIONS Report cases of Measles, Mumps and/or Rubella to your MHO that meet suspect, probable/clinical or confirmed case definitions. Enter cases into
A. PERSON REPTING Disease: Measles Mumps Rubella INSTRUCTIONS Report cases of Measles, Mumps and/or Rubella to your MHO that meet suspect, probable/clinical or confirmed case definitions. Enter cases into
WHO Technical Consultation on the severity of disease caused by the new influenza A (H1N1) virus infections
 WHO Technical Consultation on the severity of disease caused by the new influenza A (H1N1) virus infections Original short summary posted 6 May 2009. Revised full report posted May 9 2009. On 5 May 2009
WHO Technical Consultation on the severity of disease caused by the new influenza A (H1N1) virus infections Original short summary posted 6 May 2009. Revised full report posted May 9 2009. On 5 May 2009
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani
 RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Zeina Alkudmani Lower Respiratory Tract Upper Respiratory Tract Anatomy of the Respiratory System Nasopharynx Oropharynx Respiratory Tract Infections
Community Acquired Pneumonia. Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP
 Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
CHAMPIONS for LUNG Health. Learn About Pertussis PERTUSSIS
 CHAMPIONS for LUNG Health PERTUSSIS Learn About Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is an extremely contagious respiratory infection caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria. It can be especially
CHAMPIONS for LUNG Health PERTUSSIS Learn About Pertussis Pertussis, also known as whooping cough, is an extremely contagious respiratory infection caused by Bordetella pertussis bacteria. It can be especially
Influenza. Dr Bhakti Vasant Public Health Physician Metro South Public Health Unit. Metro South Public Health Unit
 Metro South Public Health Unit Influenza Dr Bhakti Vasant Public Health Physician Metro South Public Health Unit Source of image: CDC. Influenza images. Available from URL: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/images/h1
Metro South Public Health Unit Influenza Dr Bhakti Vasant Public Health Physician Metro South Public Health Unit Source of image: CDC. Influenza images. Available from URL: https://www.cdc.gov/flu/images/h1
- Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP): important respiratory pathogen in children that cause many upper and lower respiratory tract diseases, including
 KHOA DICH VU HO HAP - Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP): important respiratory pathogen in children that cause many upper and lower respiratory tract diseases, including wheezing, coryza, bronchopneumonia. -
KHOA DICH VU HO HAP - Mycoplasma pneumoniae (MP): important respiratory pathogen in children that cause many upper and lower respiratory tract diseases, including wheezing, coryza, bronchopneumonia. -
Objectives 3/3/2017. Disease Reporting in Georgia: The School Nurse s Role. Georgia Department of Public Health
 Disease Reporting in Georgia: The School Nurse s Role Presentation to: Georgia s School Nurses Presented by: Ebony S. Thomas, MPH Date: Friday, March 10, 2017 Objectives Describe the school nurse s role
Disease Reporting in Georgia: The School Nurse s Role Presentation to: Georgia s School Nurses Presented by: Ebony S. Thomas, MPH Date: Friday, March 10, 2017 Objectives Describe the school nurse s role
Communicable Diseases Report, NSW, March and April 2012
 Communicable Diseases Report,, March and April 2 Communicable Diseases Branch Department of Health For updated information, including data and facts on specific diseases, visit www.health.nsw.gov.au and
Communicable Diseases Report,, March and April 2 Communicable Diseases Branch Department of Health For updated information, including data and facts on specific diseases, visit www.health.nsw.gov.au and
