Vaccine ingredients. Fact sheet August 2017 page 1. Continued...
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Dennis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vaccine manufacture and composition is complex and tightly regulated to maximise safety. The safety of the individual components, and of the vaccine itself, must be demonstrated before a vaccine can be approved for use in New Zealand. All vaccines contain an active component (the antigen) which generates the protective immune response. Vaccines may also contain additional components. A description of these, their function and safety is summarised in this fact sheet. Types of vaccines and vaccine antigens Vaccines can be broadly classified as live, inactivated, or subunit. s are, depending on the type of vaccine, killed or weakened forms or fragments of the disease-causing organism. The body responds to the shapes of these antigens which are very specific. Ingredients vary depending on both the manufacturing process and the nature of the antigen. Live attenuated vaccines The virus or bacteria is functional/alive but has been weakened so it can replicate in the body several times and generate an immune response without causing the disease, e.g. rotavirus, chickenpox, measles, mumps and rubella vaccine viruses. Inactivated or dead vaccines These are made from inactivated virus or killed bacteria, e.g. influenza vaccine in New Zealand. Subunit vaccines These are made using fragments such as proteins, toxoids or sugars (polysaccharides), derived from the disease-causing organism. Most vaccines on the current New Zealand National Immunisation Schedule are subunit. Vaccine additives If required, vaccines may contain the following: Adjuvant An adjuvant encourages a stronger immune response to the vaccine antigen. A substance other than the active ingredient included in the manufacturing process or contained in a finished pharmaceutical product. They include: Preservatives s s Surfactants/emulsifiers s s s Aluminium Salts Aluminium salts have been used as adjuvants for over 80 years. Most commonly these are aluminium hydroxide, aluminium phosphate and potassium aluminium sulphate (alum). Aluminium adjuvants work by helping to retain the antigen at the injection site long enough for an immune response to be generated and by inducing immune system cells and a range of inflammatory factors to the local injection site to enhance the immune response. Most current inactivated and subunit vaccines use aluminium salts which have an impressive safety record. Additionally, the use of aluminium adjuvants in vaccines generally means that less antigen is required. Some studies have found aluminium containing vaccines to be associated with local reactions and, less often, with the development of subcutaneous nodules at the injection site. This is particularly so if the injection is given too superficially. Other studies have reported fewer reactions with aluminium containing vaccines than those without, and in some cases, fewer vaccine doses were needed. An individual s exposure to aluminium from vaccines is far less than that received from a normal diet and environmental exposure. Aluminium is the eighth most abundant element on earth and the most common metallic element. It is found in the blood of all animals including humans, and we are constantly exposed to it. The average daily intake is 10 15mg. Average water has about 0.2mg of aluminium per litre, the hepatitis B vaccine has 0.25mg of aluminium. Aluminium in vaccines is absorbed into the blood and excreted via the kidneys in urine. A recent review of all the available studies of aluminiumcontaining diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis vaccines (either alone or in combination) did not find any evidence that aluminium salts in vaccines cause serious or long-term adverse events. MF59 No vaccines currently used in New Zealand contain the oil-inwater emulsion MF59. It is made using squalene (a hydrocarbon oil) which is common in foods as well as being produced in the body as precursor to cholesterol and steroid hormones. MF59 significantly enhances immune response to a variety of antigens. It is used in some influenza vaccines overseas. A recent review of safety data from five trials using MF59 adjuvanted v.s. non-adjuvanted influenza vaccines in children and adolescents, aged from 6 months to 18 years, did not identify any safety issues. However, mild to moderate injection site and systemic vaccine reactions were more common after a vaccine containing MF59 vaccine than after a non-adjuvanted vaccine. AS03 and AS04 No vaccines currently used in New Zealand contain the AS03 and AS04 adjuvants. AS03 is made with squalene, similar to MF59. It has been used in a pandemic influenza vaccine in Europe. AS04 contains aluminium hydroxide and modified molecules from the Salmonella minnesota bacterium. Theoretical concerns have been raised that these new adjuvants may cause overproduction of inflammatory factors leading to autoimmune disease. However, a large analysis of 68,000 people, some who had received AS04 adjuvanted vaccines and others who had not (controls), concluded that both vaccine recipients and controls had a low rate of autoimmune disorders. Preservatives Preservatives stop unwanted microbial contamination of vaccines. They have been used in vaccines for many years. Very few serious adverse events have been associated with the use of these preservatives. 2-phenoxyethanol The most commonly used preservative in vaccines is 2-phenoxyethanol. It is also used in cosmetics, eye and ear drops, and baby care products where it is absorbed through skin. 2-phenoxyethanol is excreted by being exhaled and in urine and faeces after being metabolised (broken down). There is little toxicity in humans and some irritation with very high doses in animals. Continued... Fact sheet August 2017 page 1
2 continued Phenol Phenol is an aromatic alcohol infrequently used as a preservative in vaccines. Thiomersal No vaccines on the New Zealand Immunisation Schedule contain thiomersal, also called thimerosal. Thiomersal is a mercury derived compound that was used as a preservative in vaccines and other health care products internationally for many years. There is no evidence that thiomersal caused any serious or long-term adverse events. s s inhibit chemical reactions and prevent components separating or sticking to the vial during transport and storage. Examples of stabilisers include sugars such as lactose and sucrose, amino acids such as glycine and monosodium glutamate (salts of amino acids), proteins such as recombinant human albumin (Recombumin ) derived from baker s yeast or fetal bovine (cow) serum and gelatin, partially hydrolysed collagen usually of porcine (pig) but can be of bovine origin. s and ionic compounds s serve to resist changes in ph, such as monopotassium phosphate and sodium borate. Ionic compounds adjust tonicity and maintain osmolarity. The most commonly used ionic compound is sodium chloride (table salt). Surfactants Surfactants are a type of emulsifier. They assist particles remain suspended in liquid, preventing settling and clumping by lowering the surface tension of the liquid. An example is polysorbate 80 (Tween 80 ), made from sorbitol (sugar alcohol) and oleic acid (omega-9 fatty acid), which is also used in foods such as ice cream. Surfactants are also used in shampoos, toothpastes, inks and fabric softeners. s A solvent is a substance that dissolves another substance, creating a solution. The most common solvent used in everyday living and vaccine manufacture is water. s s are the remaining minute quantities of substances that have been used during the manufacturing or production process of individual vaccines. s depend on the process used, which may have involved cell culture mediums, egg proteins, yeast, antibiotics such as neomycin or streptomycin, or inactivating agents such as formaldehyde. These substances are only present as traces and often measured as parts per million and parts per billion in the final vaccine formulation. s A diluent is a liquid used to dilute a vaccine to the proper concentration immediately prior to administration. This is usually sterile water. Animal derived products Some people have concerns about animal derived products such as gelatin in vaccines. This may be for faith-based reasons or concerns about the safety of animal derived products. More information on animal derived products in vaccines can be found on the Written Resources page on the Immunisation Advisory Centre web site. Allergies to vaccine ingredients Very rarely, vaccines provoke a serious allergic reaction called anaphylaxis. The risk of this occurring is between less than once to up to three times out of every million doses of a vaccine. The components more likely to cause such a reaction are gelatin, egg proteins and antibiotics, although theoretically an allergic reaction can be triggered by almost anything. There are very few occasions when vaccines should not be given. However, a person s allergy history should always be assessed prior to immunisation. A vaccine should not be given when there is a history of anaphylaxis to an ingredient in the vaccine or to a previous dose of the same vaccine. A vaccine can be given when past reactions were not anaphylaxis, for example, reactions which have only involved the skin. A person with a history of anaphylaxis after exposure to egg can usually be given MMR vaccine safely as the vaccine does not contain enough of the egg protein to cause a problem. The hydrolysed gelatin in the MMR vaccine has been recognised as a cause of anaphylaxis. Antibiotics in vaccines are only present in minute traces, usually an insufficient amount to cause a problem. An allergy to sulfonamide, beta-lactam or cephalosporin antibiotics is not a contraindication for vaccines containing traces of neomycin, streptomycin, polymyxin B or gentamicin, the antibiotics typically found in vaccines. Further advice about allergies and vaccine contraindications should be sought from a medical practitioner with expertise in vaccines or by calling 0800 IMMUNE. National Immunisation Schedule Ingredients of vaccines on the current and recent New Zealand National Immunisation Schedules are presented in tables on the following pages. A table showing the vaccine brands on the current Immunisation Schedule can be found on the Written Resources page of the Immunisation Advisory Centre website. National Immunisation Schedule vaccines are fully funded for certain age groups of children and some adults, for information about who is eligible for specific vaccines ask your doctor, nurse or 0800 IMMUNE. Specific vaccine ingredient tables are presented on the following pages: Vaccine Page Vaccine Page Act-HIB 3 IPOL 6 ADT Booster 3 M-M-R II 7 Boostrix 3 Prevenar 13 7 Gardasil 4 Priorix 7 Gardasil 9 4 Rotarix 8 HBvaxPRO 4 RotaTeq 8 Hiberix 5 Synflorix 8 Infanrix-hexa 5 Varilrix 9 Infanrix-IPV 6 Fact sheet August 2017 page 2
3 Act-HIB Vaccine against Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) disease ADT Booster Vaccine against diphtheria and tetanus diseases Diphtheria toxoid Not less than 2 IU Tetanus toxoid Not less than 20 IU Aluminium as aluminium hydroxide (hydrated) 0.5 mg Adjuvant Type: Subunit, toxoid vaccine Culture media including bovine derived materials Grow Clostridium tetani (tetanus) and Corynebacterium diphtheriae (diphtheria) Formaldehyde Inactivating agent Sodium chloride 4 mg Adjust tonicity Sodium hydroxide Boostrix Vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis diseases Type: Subunit, toxoid and inactivated protein vaccine Diphtheria toxoid, adsorbed Not less than 2.5 Lf U Tetanus toxoid, adsorbed Not less than 5 Lf U Pertussis toxoid, adsorbed 8 μg Filamentous haemagglutinin, adsorbed 8 μg Pertactin (69 kilodalton outer membrane protein) 2.5 μg Aluminium as aluminium hydroxide and aluminium phosphate 0.3 mg 0.2 mg Adjuvant Culture media including bovine derived materials Grow Clostridium tetani (tetanus), Corynebacterium diphtheriae (diphtheria) and Bordetella pertussis (pertussis) Formaldehyde, glutaraldehyde 100 μg each Inactivating agent Sodium chloride 4.5 mg Adjust tonicity Glycine Polysorbate μg Surfactant Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) polysaccharide, conjugated to tetanus toxoid 10 μg μg Carrier protein Culture media including bovine derived materials Grow Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) and Clostridium tetani (tetanus) Formaldehyde Inactivating agent Sucrose Trometamol Sodium chloride 0.4% Type: Subunit, polysaccharide conjugate vaccine Surfactant Fact sheet August 2017 page 3
4 Gardasil Vaccine against human papillomavirus disease (4-valent) r-hpv 6 & 18 L1 proteins 20 μg r-hpv 11 & 16 L1 proteins 40 μg Aluminium as amorphous aluminium hydroxyphosphate sulphate 225 µg Type: Subunit, recombinant protein vaccine Adjuvant Culture media including yeast protein Grow human papillomaviruses and yeast Sodium chloride 9.56 mg Adjust tonicity Sodium borate 35 μg L-histidine 0.78 mg Polysorbate μg Surfactant Gardasil 9 Vaccine against human papillomavirus disease (9-valent) Type: Subunit, recombinant protein vaccine r-hpv 31, 33, 45, 52 & μg r-hpv 6 L1 protein 30 μg r-hpv 11 & 18 L1 proteins 40 μg r-hpv 16 L1 protein 60 μg Aluminium as amorphous aluminium hydroxyphosphate sulphate 500 μg Adjuvant Culture media including yeast protein Grow human papillomaviruses and yeast Sodium chloride 9.56 mg Adjust tonicity Sodium borate 35 μg L-histidine 0.78 mg Polysorbate μg Surfactant HBvaxPRO Vaccine against hepatitis B disease Type: Subunit, recombinant protein vaccine Hepatitis B surface antigen 5 μg Aluminium as amorphous aluminium hydroxyphosphate sulphate 0.25 mg Adjuvant Culture media including yeast protein Grow hepatitis B viruses and yeast Formaldehyde Purify yeast protein Sodium chloride 4.5 mg Adjust tonicity Sodium borate 35 μg Fact sheet August 2017 page 4
5 Hiberix Vaccine against Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) disease Type: Subunit, polysaccharide conjugate vaccine Ingredients Quantity/dose (0.5ml) Function Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) polysaccharide, conjugated to tetanus toxoid 10 μg Approximately 25 μg Carrier protein Culture media including bovine derived material Grow Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) and Clostridium tetani (tetanus) Formaldehyde 0.5 μg Inactivating agent Lactose 12.6 mg Sodium chloride 0.9% Infanrix-hexa Vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, polio, hepatitis B, Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) diseases Type: Subunit, toxoid, inactivated protein, inactivated virus, recombinant protein and polysaccharide conjugate vaccine Diphtheria toxoid, adsorbed Not less than 30 IU (25 Lf U) Tetanus toxoid, adsorbed Not less than 40 IU (10 Lf U) Pertussis toxoid, adsorbed 25 μg Filamentous haemagglutinin, adsorbed 25 μg Pertactin, (69 kilodalton outer membrane protein) 8 μg r-hepatitis B surface antigen, adsorbed (HBsAg) 10 μg Inactivated Polio Virus Type 1 40 DU Inactivated Polio Virus Type 2 8 DU Inactivated Polio Virus Type 3 32 DU Haemophilus influenzae type b capsular polysaccharide, conjugated to tetanus toxoid Aluminium as aluminium hydroxide and aluminium phosphate Culture media including medium 199, bovine derived material 10 μg μg 0.5 mg 0.32 mg Carrier protein Adjuvant Formaldehyde Inactivating agent Potassium chloride, sodium chloride, disodium phosphate Monopotassium phosphate Glycine, lactose Polysorbate 20, polysorbate 80 Grow Clostridium tetani (tetanus), Corynebacterium diphtheriae (diphtheria), Bordetella pertussis (pertussis); stabilise polio viruses Adjust tonicity Surfactant Neomycin, polymyxin B Antibacterial Fact sheet August 2017 page 5
6 Infanrix-IPV Vaccine against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis and polio diseases Type: Subunit, toxoid, inactivated protein and inactivated virus vaccine IPOL Vaccine against polio disease Inactivated Polio virus type 1 (Mahoney) 40 DU Inactivated Polio virus type 2 (MEF-1) 8 DU Inactivated Polio virus type 3 (Saukett) 32 DU Culture media including medium 199 hanks, bovine derived material Grow polio viruses Formaldehyde 2 20 μg Inactivating agent Sodium chloride Adjust tonicity Hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide Polysorbate 80 Surfactant Neomycin, polymyxin B, streptomycin Antibacterial 2-phenoxyethanol 2 3 μl Preservative Diphtheria toxoid, adsorbed Not less than 30 IU (25 Lf U) Tetanus toxoid, adsorbed Not less than 40 IU (10 Lf U) Pertussis toxoid, adsorbed 25 μg Filamentous haemagglutinin, adsorbed 25 μg Pertactin, (69 kilodalton outer membrane protein) 8 μg Inactivated Polio Virus Type 1 40 DU Inactivated Polio Virus Type 2 8 DU Inactivated Polio Virus Type 3 32 DU Aluminium hydroxide Less than mg by assay Adjuvant Culture media including medium 199, bovine derived material Grow Clostridium tetani (tetanus), Corynebacterium diphtheriae (diphtheria), Bordetella pertussis (pertussis); stabilise polio viruses Formaldehyde Inactivating agent Potassium chloride, disodium phosphate Sodium chloride Monopotassium phosphate Adjust tonicity Glycine Polysorbate 80 Surfactant Neomycin, polymyxin B Antibacterial Type: Inactivated virus vaccine Fact sheet August 2017 page 6
7 M-M-R II Vaccine against measles, mumps and rubella diseases Prevenar 13 Vaccine against pneumococcal disease (13-valent) Pneumococcal polysaccharide serotypes 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 7F, 9V, 14, 18C,19A, 19F, 23F Type: Subunit, polysaccharide conjugate vaccine 2.2 μg Pneumococcal polysaccharide serotype 6B 4.4 μg All conjugated to diphtheria CRM μg Carrier protein Aluminium as aluminium phosphate mg Adjuvant Culture media Grow Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcal) and Corynebacterium diphtheria (diphtheria) Sodium chloride Adjust tonicity Succinic acid 295 μg Polysorbate μg Surfactant Attenuated Enders attenuated Edmonston measles virus Not less than 1,000 CCID 50 Attenuated Jeryl Lynn (B Level) mumps virus Not less than 12,500 CCID 50 Attenuated Wistar RA 27/3 rubella virus Not less than 1,000 CCID 50 Culture media including medium 199, minimum essential medium, bovine derived material Grow measles, mumps and rubella viruses Other ingredients not specified Components of growth media; buffer Sodium chloride Adjust tonicity Sodium phosphate Hydrolised gelatin, recombinant human albumin, sorbitol, sucrose 14.5 mg, 0.3 mg, 14.5 mg, 1.9 mg Neomycin Antibacterial Priorix Vaccine against measles, mumps and rubella diseases Attenuated Schwartz measles virus Not less than CCID 50 Attenuated RIT 4385 (derived from Jeryl Lynn) mumps virus Not less than CCID 50 Attenuated Wistar RA 27/3 rubella virus Not less than CCID 50 Culture media including amino acids, bovine derived material Grow measles, mumps and rubella viruses Hydrolised gelatin, lactose, mannitol, sorbitol Neomycin Antibacterial Fact sheet August 2017 page 7
8 Rotarix Vaccine against rotavirus disease Ingredients Quantity/dose (1.5mL) Function Attenuated RIX 4414 strain of human rotavirus of the G1P[8] type Culture media including dulbecco s modified eagle medium, bovine and porcine derived material CCID 50 Grow rotaviruses DNA from porcine circoviruses 1 Fragments From porcine-derived material used during manufacture Disodium adipate Sucrose RotaTeq Vaccine against rotavirus disease Live reassortant rotaviruses G1, G3 Ingredients Quantity/dose (2mL) Function 2.2 x 10 6 infectious units each Live reassortant rotavirus G2 2.8 x 10 6 infectious units Live reassortant rotavirus G4 2.0 x 10 6 infectious units Live reassortant rotavirus P1A[8] 2.3 x 10 6 infectious units Culture media including bovine and porcine derived material Grow rotaviruses DNA from porcine circoviruses 1 and 2 Fragments From porcine-derived material used during manufacture Sodium citrate, sodium hydroxide, sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate Sucrose Polysorbate 80 Synflorix Vaccine against pneumococcal disease (10-valent) Surfactant Type: Subunit, polysaccharide conjugate vaccine Pneumococcal polysaccharide serotypes 1 μg each 1, 5, 6B, 7F, 9V, 14, 23F Pneumococcal polysaccharide serotype 4 3 μg Pneumococcal polysaccharide serotype 18C 3 μg Pneumococcal polysaccharide serotype 19F 3 μg Conjugated to: Protein D (derived from non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae) 9 16 μg Carrier protein Tetanus toxoid 5 10 μg Carrier protein Diphtheria toxoid 3 6 μg Carrier protein Aluminium as aluminium phosphate 0.5 mg Adjuvant Culture media Grow streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcal), Corynebacterium diphtheria (diphtheria), Haemophilus influenzae and Clostridium tetani (tetanus) Sodium chloride 4.3 mg Adjust tonicity Fact sheet August 2017 page 8
9 Varilrix (human albumin-free) Vaccine against varicella (chickenpox) disease Ingredients Quantity/dose (0.5ml) Function Attenuated Oka strain varicella-zoster virus PFU Culture media including amino acids, fetal bovine serum Grow varicella-zoster virus Lactose, mannitol, sorbitol Neomycin Antibacterial References Black S, Della Cioppa G, Malfroot A, Nacci P, Nicolay U, Pellegrini M, et al. Safety of MF59-adjuvanted versus non-adjuvanted influenza vaccines in children and adolescents: An integrated analysis. 2010;28(45): Finn TM, Egan W. Vaccine additives and manufacturing residuals in the United States: licensed vaccines. In: Plotkin S, Orenstein W, Offit P, editors. Vaccines. 6th ed. London: W.B. Saunders; p Garçon N, Hem S, Friede M. Evolution of adjuvants across the centuries. In: Plotkin S, Orenstein W, Offit P, editors. Vaccines. 6th ed. London: W.B. Saunders; p Gomez PL, Robinson JM, Rogalewicz JA. Vaccine manufacturing. In: Plotkin S, Orenstein W, Offit P, editors. Vaccines. 6th ed. London: W.B. Saunders; p Harandi AM, Davies G, Olesen OF. Vaccine adjuvants: Scientific challenges and strategic initiatives. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2009;8(3): Jefferson T, Rudin M, Di Pietrantonj C. Adverse events after immunisation with aluminium-containing DTP vaccines: Systematic review of the evidence. Lancet Infect Dis. 2004;4(2): Medsafe, the New Zealand Medicines and Medical Devices Safety Authority. Vaccine data sheets available from: Mitkus RJ, King DB, Hess MA, Forshee RA, Walderhaug MO. Updated aluminum pharmacokinetics following infant exposures through diet and vaccination. Vaccine 2011; 29: Therapeutic Goods Administration. Vaccine product information sheets available from: U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Vaccine data sheets available from: Fact sheet August 2017 page 9
BabyJabs Vaccines. All vaccines are mercury-free We use aluminium-free vaccines wherever possible
 BabyJabs Vaccines All vaccines are mercury-free We use aluminium-free vaccines wherever possible BabyJabs is a dedicated children s immunisation service, offering a choice of single and small combination
BabyJabs Vaccines All vaccines are mercury-free We use aluminium-free vaccines wherever possible BabyJabs is a dedicated children s immunisation service, offering a choice of single and small combination
BabyJabs Vaccines. All vaccines are mercury- free We use aluminium- free vaccines wherever possible
 BabyJabs Vaccines All vaccines are mercury- free We use aluminium- free vaccines wherever possible BabyJabs is a dedicated children s immunisation service, offering a choice of single and small combination
BabyJabs Vaccines All vaccines are mercury- free We use aluminium- free vaccines wherever possible BabyJabs is a dedicated children s immunisation service, offering a choice of single and small combination
BabyJabs Vaccines. All vaccines are mercury-free We use aluminium-free vaccines wherever possible
 BabyJabs Vaccines All vaccines are mercury-free We use aluminium-free vaccines wherever possible BabyJabs is a dedicated children s immunisation service, offering a choice of single and small combination
BabyJabs Vaccines All vaccines are mercury-free We use aluminium-free vaccines wherever possible BabyJabs is a dedicated children s immunisation service, offering a choice of single and small combination
Vaccinology 101 for Fellows
 Vaccinology 101 for Fellows Meg Fisher, MD Medical Director, The Children s Hospital Monmouth Medical Center An affiliate of the Saint Barnabas Health Care System Long Branch, NJ Disclosures I have no
Vaccinology 101 for Fellows Meg Fisher, MD Medical Director, The Children s Hospital Monmouth Medical Center An affiliate of the Saint Barnabas Health Care System Long Branch, NJ Disclosures I have no
Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis-Polio- Haemophilus influenzae type b Conjugate Combined Vaccine Biological Page (DTaP-IPV-Hib)
 Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis-Polio- Haemophilus influenzae type b Conjugate Combined Vaccine Biological Page (DTaP-IPV-Hib) Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.211 Created
Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis-Polio- Haemophilus influenzae type b Conjugate Combined Vaccine Biological Page (DTaP-IPV-Hib) Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.211 Created
Vaccination-Strategies
 Vaccination-Strategies Active immunity produced by vaccine Immunity and immunologic memory similar to natural infection but without risk of disease. General Rule: The more similar a vaccine is to the disease-causing
Vaccination-Strategies Active immunity produced by vaccine Immunity and immunologic memory similar to natural infection but without risk of disease. General Rule: The more similar a vaccine is to the disease-causing
Changes to the National Immunisation Schedule
 17 December 2013 Changes to the National Immunisation Schedule PHARMAC is pleased to announce decisions related to the National Immunisation Schedule (NIS) that will take effect from 1 July 2014. This
17 December 2013 Changes to the National Immunisation Schedule PHARMAC is pleased to announce decisions related to the National Immunisation Schedule (NIS) that will take effect from 1 July 2014. This
The Ministry of Health recommends measles vaccines for all child care providers, children and parents to ensure they are protected against measles.
 Since January 1, 2014, there have been several cases of measles reported in Saskatchewan. Because measles is a highly contagious vaccine-preventable disease and there are a number of unvaccinated children
Since January 1, 2014, there have been several cases of measles reported in Saskatchewan. Because measles is a highly contagious vaccine-preventable disease and there are a number of unvaccinated children
immunisation in New Zealand
 This appendix details the history of. Section A1.1 is a brief summary of when each vaccine was introduced to the National Immunisation Schedule (the Schedule). This summary includes vaccines which were
This appendix details the history of. Section A1.1 is a brief summary of when each vaccine was introduced to the National Immunisation Schedule (the Schedule). This summary includes vaccines which were
Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis-Polio- Combined Vaccine Biological Page (DTaP-IPV)
 Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis-Polio- Combined Vaccine Biological Page (DTaP-IPV) Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.212 Created by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards
Diphtheria-Tetanus-Acellular Pertussis-Polio- Combined Vaccine Biological Page (DTaP-IPV) Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.212 Created by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards
Copyright regulations Warning
 COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright regulations 1969 Warning This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Melbourne pursuant to part VB of the Copyright
COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright regulations 1969 Warning This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the University of Melbourne pursuant to part VB of the Copyright
Use of Infanrix -IPV+Hib in the infant primary immunisation schedule
 Use of Infanrix -IPV+Hib in the infant primary immunisation schedule An update for registered healthcare practitioners July 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Acknowledgments Many thanks
Use of Infanrix -IPV+Hib in the infant primary immunisation schedule An update for registered healthcare practitioners July 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Acknowledgments Many thanks
Module 2: Vaccines and drugs: similarities and differences
 Module 2: Vaccines and drugs: similarities and differences Vaccine PV Fellowship WHO Collaborating Centre for Advocacy and Training in Pharmacovigilance Accra, Ghana 7 th 18 th September 2015 Learning
Module 2: Vaccines and drugs: similarities and differences Vaccine PV Fellowship WHO Collaborating Centre for Advocacy and Training in Pharmacovigilance Accra, Ghana 7 th 18 th September 2015 Learning
CHILDHOOD VACCINATION
 EPI (3) Age of Child How and Where is it given? CHILDHOOD VACCINATION Nicolette du Plessis Block 10 28/02/2012 10 weeks DTaP-IPV/Hib (2) Diphtheria, Tetanus, Acellular pertussis, Inactivated polio vaccine,
EPI (3) Age of Child How and Where is it given? CHILDHOOD VACCINATION Nicolette du Plessis Block 10 28/02/2012 10 weeks DTaP-IPV/Hib (2) Diphtheria, Tetanus, Acellular pertussis, Inactivated polio vaccine,
Practical Applications of Immunology. Chapter 18
 Practical Applications of Immunology Chapter 18 I. Vaccines A. Definition A suspension of organisms or fractions of organisms that is used to induce immunity (immunologic memory). The mechanism of memory
Practical Applications of Immunology Chapter 18 I. Vaccines A. Definition A suspension of organisms or fractions of organisms that is used to induce immunity (immunologic memory). The mechanism of memory
PREVENTIVE IMMUNIZATIONS. PREVENTIVE IMMUNIZATIONS These codes do not have a diagnosis code requirement for preventive benefits to apply.
 An immunization that does not fall under one of the exclusions in the Certificate of Coverage is considered covered after the following conditions are satisfied: (1) FDA approval; (2) explicit ACIP recommendation
An immunization that does not fall under one of the exclusions in the Certificate of Coverage is considered covered after the following conditions are satisfied: (1) FDA approval; (2) explicit ACIP recommendation
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Childhood and Adolescent Recommended Vaccines
 New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Childhood and Adolescent Recommended Vaccines Antigens Vaccine Approved Age Daptacel Diphtheria, Tetanus, and acellular Pertussis (DTaP)
New Jersey Department of Health Vaccine Preventable Disease Program Childhood and Adolescent Recommended Vaccines Antigens Vaccine Approved Age Daptacel Diphtheria, Tetanus, and acellular Pertussis (DTaP)
Approval / Acknowledgement Letter Ref No. / Diary no F.No.12-48/GSK/PAC- Synflorix/15-BD 25-Mar-15 2 GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals Limited.
 1 GlaxoSmithKline Deletion of a n-significant in-process test limit during the purification process of the tetanus / diphtheria toxoids used in the manufacture of GSK's PCV vaccine [brand name: Synflorix]
1 GlaxoSmithKline Deletion of a n-significant in-process test limit during the purification process of the tetanus / diphtheria toxoids used in the manufacture of GSK's PCV vaccine [brand name: Synflorix]
PREVENTIVE IMMUNIZATIONS. PREVENTIVE IMMUNIZATIONS These codes do not have a diagnosis code requirement for preventive benefits to apply.
 An immunization that does not fall under one of the exclusions in the Certificate of Coverage is considered covered after the following conditions are satisfied: (1) FDA approval; (2) explicit ACIP recommendation
An immunization that does not fall under one of the exclusions in the Certificate of Coverage is considered covered after the following conditions are satisfied: (1) FDA approval; (2) explicit ACIP recommendation
1 Principles of Vaccination Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases... 1 Classification of Vaccines... 4 Selected References...
 1 Principles of Vaccination Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases... 1 Classification of Vaccines... 4 Selected References... 7 2 General Recommendations on Immunization Timing and Spacing of Vaccines...
1 Principles of Vaccination Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases... 1 Classification of Vaccines... 4 Selected References... 7 2 General Recommendations on Immunization Timing and Spacing of Vaccines...
Overdosed Babies: Are Multiple Vaccines Safe? By Neil Z. Miller
 Overdosed Babies: Are Multiple Vaccines Safe? By Neil Z. Miller Copyright 2009 NZM. All Rights Reserved. Vaccines are Drugs! Parents need to understand that vaccines are drugs. They contain antigens, preservatives,
Overdosed Babies: Are Multiple Vaccines Safe? By Neil Z. Miller Copyright 2009 NZM. All Rights Reserved. Vaccines are Drugs! Parents need to understand that vaccines are drugs. They contain antigens, preservatives,
CyberScan Vaccine Stress Assessment
 DEMO CyberScan Vaccine Stress Assessment % imbalance is calculated from 0-100%, with 100% corresponding to increased stress. Level correlates to the aspect of the body affected. Levels 1-3 correspond to
DEMO CyberScan Vaccine Stress Assessment % imbalance is calculated from 0-100%, with 100% corresponding to increased stress. Level correlates to the aspect of the body affected. Levels 1-3 correspond to
Immunise your child on time. It s their best protection
 Immunise your child on time It s their best protection If you are a parent or caregiver, this pamphlet is for you. It tells you about the recommended ages for your baby to receive their immunisations.
Immunise your child on time It s their best protection If you are a parent or caregiver, this pamphlet is for you. It tells you about the recommended ages for your baby to receive their immunisations.
INFANRIX -penta Datasheet
 INFANRIX -penta Datasheet NAME OF THE MEDICINE INFANRIX -penta Combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B and inactivated polio vaccine. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION INFANRIX
INFANRIX -penta Datasheet NAME OF THE MEDICINE INFANRIX -penta Combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis B and inactivated polio vaccine. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION INFANRIX
Vaccines and other immunological antimicrobial therapy 1
 Vaccines and other immunological antimicrobial therapy 1 Vaccines Vaccine: a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease. Vaccine typically contains an agent that
Vaccines and other immunological antimicrobial therapy 1 Vaccines Vaccine: a biological preparation that provides active acquired immunity to a particular disease. Vaccine typically contains an agent that
PHARMAC invites proposals for the supply of various vaccines in New Zealand.
 15 February 2016 Dear Supplier REQUEST FOR PROPOSALS SUPPLY OF VARIOUS VACCINES PHARMAC invites proposals for the supply of various vaccines in New Zealand. This request for proposals (RFP) letter incorporates
15 February 2016 Dear Supplier REQUEST FOR PROPOSALS SUPPLY OF VARIOUS VACCINES PHARMAC invites proposals for the supply of various vaccines in New Zealand. This request for proposals (RFP) letter incorporates
sanofi pasteur 352 Hexaxim New Zealand Data Sheet V2.0 DATA SHEET
 DATA SHEET NAME OF THE MEDICINE HEXAXIM DTPa-hepB-IPV-Hib Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (acellular, component), hepatitis B (rdna), poliomyelitis (inactivated) and Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate
DATA SHEET NAME OF THE MEDICINE HEXAXIM DTPa-hepB-IPV-Hib Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (acellular, component), hepatitis B (rdna), poliomyelitis (inactivated) and Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate
INFANRIX hexa. Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis (DTPa), Hepatitis B, Poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine
 INFANRIX hexa Product Information 1(12) INFANRIX hexa Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis (DTPa), Hepatitis B, Poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine DESCRIPTION INFANRIX hexa
INFANRIX hexa Product Information 1(12) INFANRIX hexa Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis (DTPa), Hepatitis B, Poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine DESCRIPTION INFANRIX hexa
Polio Vaccine Biological Page
 Polio Vaccine Biological Page Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.300 Created by: Approved by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards and Quality Province-wide Immunization Program,
Polio Vaccine Biological Page Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.300 Created by: Approved by: Province-wide Immunization Program Standards and Quality Province-wide Immunization Program,
Vaccines, Not Just for Babies
 Vaccines, Not Just for Babies Meg Fisher, MD Medical Director Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products or commercial services discussed in
Vaccines, Not Just for Babies Meg Fisher, MD Medical Director Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products or commercial services discussed in
A. Children born in 1942 B. Children born in 1982 C. Children born in 2000 D. Children born in 2010
 Who do you think received the most immunologic components in vaccines? Development of which vaccine slowed after the invention of antibiotics? A. Children born in 1942 B. Children born in 1982 C. Children
Who do you think received the most immunologic components in vaccines? Development of which vaccine slowed after the invention of antibiotics? A. Children born in 1942 B. Children born in 1982 C. Children
Immunity and how vaccines work
 Immunity and how vaccines work Dr Mary O Meara National Immunisation Office Objectives of session An understanding of the following principles Overview of immunity Different types of vaccines and vaccine
Immunity and how vaccines work Dr Mary O Meara National Immunisation Office Objectives of session An understanding of the following principles Overview of immunity Different types of vaccines and vaccine
Enhanced immunisation schedule Victoria
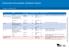 Children from March 2016 Age Disease Vaccine brand Birth Hepatitis B H-B-Vax-II Paediatric 2 months - from 6 weeks Diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis, poliomyelitis-hepatitis B- Reconstitute Site given Route
Children from March 2016 Age Disease Vaccine brand Birth Hepatitis B H-B-Vax-II Paediatric 2 months - from 6 weeks Diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis, poliomyelitis-hepatitis B- Reconstitute Site given Route
Objectives. Immunity. Childhood Immunization Risk of Non-Vaccinated Children 12/22/2015
 Childhood Immunization Risk of Non-Vaccinated Children Bertha P. Rojas, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident South Miami Hospital Objectives Understand the definition of herd immunity Identify vaccine-preventable
Childhood Immunization Risk of Non-Vaccinated Children Bertha P. Rojas, Pharm.D. PGY-1 Pharmacy Resident South Miami Hospital Objectives Understand the definition of herd immunity Identify vaccine-preventable
VACCINATION. DR.FATIMA ALKHALEDY M.B.Ch.B;F.I.C.M.S/C.M.
 VACCINATION DR.FATIMA ALKHALEDY M.B.Ch.B;F.I.C.M.S/C.M. IMMUNIZATION Immunization is defined as the procedure by which the body is prepared to fight against a specific disease. It is used to induce the
VACCINATION DR.FATIMA ALKHALEDY M.B.Ch.B;F.I.C.M.S/C.M. IMMUNIZATION Immunization is defined as the procedure by which the body is prepared to fight against a specific disease. It is used to induce the
Infanrix IPV. Copyright , MIMS Australia Page 1 of 6
 Infanrix IPV MIMS Abbreviated Prescribing Information Diphtheria toxoid; pertussis vaccine; poliomyelitis vaccine; tetanus toxoid GlaxoSmithKline Australia Section: 10(a) Vaccines - Immunology Use in pregnancy:
Infanrix IPV MIMS Abbreviated Prescribing Information Diphtheria toxoid; pertussis vaccine; poliomyelitis vaccine; tetanus toxoid GlaxoSmithKline Australia Section: 10(a) Vaccines - Immunology Use in pregnancy:
Principles of Vaccination
 Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
Immunology and Vaccine-Preventable Diseases Immunology is a complicated subject, and a detailed discussion of it is beyond the scope of this text. However, an understanding of the basic function of the
Immunizations June 5, Brenda Ormesher, MD Infectious Disease Peacehealth Medical Group Springfield, OR
 Immunizations June 5, 2015 Brenda Ormesher, MD Infectious Disease Peacehealth Medical Group Springfield, OR Disclosures None Goals Understand basic public health impact of immunization Recognize types
Immunizations June 5, 2015 Brenda Ormesher, MD Infectious Disease Peacehealth Medical Group Springfield, OR Disclosures None Goals Understand basic public health impact of immunization Recognize types
1.1 Immunity and immunisation
 1 General immunisation General immunisation It is not necessary to have an in-depth knowledge of the immune system to understand the first of vaccinology. The immune system is an extremely complex inter-connected
1 General immunisation General immunisation It is not necessary to have an in-depth knowledge of the immune system to understand the first of vaccinology. The immune system is an extremely complex inter-connected
CPT 2016 Code Changes
 CPT 2016 Code Changes Code Changes - Medicine New CPT 2016 New Codes Code Description 69209 Removal impacted cerumen using irrigation/lavage, unilateral 90620 Meningococcal recombinant protein and outer
CPT 2016 Code Changes Code Changes - Medicine New CPT 2016 New Codes Code Description 69209 Removal impacted cerumen using irrigation/lavage, unilateral 90620 Meningococcal recombinant protein and outer
Vaccine Excipients per 0.5 ml
 Vaccine Excipients per 0.5 ml Excipient Type Vaccine Name Vaccine Type Amount 2 Phenoxyethanol Stabilizer Adacel Tdap Not as a preservative 2 Phenoxyethanol Stabilizer Daptacel DTaP 3.3 mg (0.6% v/v) (not
Vaccine Excipients per 0.5 ml Excipient Type Vaccine Name Vaccine Type Amount 2 Phenoxyethanol Stabilizer Adacel Tdap Not as a preservative 2 Phenoxyethanol Stabilizer Daptacel DTaP 3.3 mg (0.6% v/v) (not
Are Vaccines SAFE? So Why Would Any Parent In Their Right Mind... Not Want To Vaccinate Their Child?
 Are Vaccines SAFE? Good question huh? But there is a simple answer. NO! Now I know a lot of people give their children vaccines. I also know a lot of parents tell me that they re children are required
Are Vaccines SAFE? Good question huh? But there is a simple answer. NO! Now I know a lot of people give their children vaccines. I also know a lot of parents tell me that they re children are required
Immunity & How Vaccines Work
 Immunity & How Vaccines Work Immunisation Study Day 30 th November 2016 Talk given today by Dr. Mary Fitzgerald Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work
Immunity & How Vaccines Work Immunisation Study Day 30 th November 2016 Talk given today by Dr. Mary Fitzgerald Learning outcome To be able to describe in outline the immune system and how vaccines work
TRICARE Retail Vaccination Program Vaccine List - September 2018*
 Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids adsorbed acellular pertussis adsorbed DT DTaP Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids adsorbed Daptacel, Infanrix Tetanus and diphtheria toxoids
Diphtheria, tetanus and pertussis Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids adsorbed acellular pertussis adsorbed DT DTaP Diphtheria and tetanus toxoids adsorbed Daptacel, Infanrix Tetanus and diphtheria toxoids
Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices VACCINE ACRONYMS
 Vaccine Acronyms Page 1 of 5 Advisy Committee on Immunization Practices VACCINE ACRONYMS Vaccines Included in the Immunization Schedules f Children, Adolescents, and Adults Following is a table of standardized
Vaccine Acronyms Page 1 of 5 Advisy Committee on Immunization Practices VACCINE ACRONYMS Vaccines Included in the Immunization Schedules f Children, Adolescents, and Adults Following is a table of standardized
Boostrix polio. 3. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM Suspension for injection. 4. CLINICAL PARTICULARS
 Boostrix polio 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT boostrix polio Combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis and enhanced inactivated polio vaccine. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION boostrix
Boostrix polio 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT boostrix polio Combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis and enhanced inactivated polio vaccine. 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION boostrix
Benefit Interpretation
 Benefit Interpretation Subject: Part B vs. Part D Vaccines Issue Number: BI-039 Applies to: Medicare Advantage Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Attachments: Part B Vaccines Diagnosis Code Limits Table of Contents
Benefit Interpretation Subject: Part B vs. Part D Vaccines Issue Number: BI-039 Applies to: Medicare Advantage Effective Date: May 1, 2017 Attachments: Part B Vaccines Diagnosis Code Limits Table of Contents
INFANRIX HEXA QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 INFANRIX HEXA Combined diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, enhanced inactivated polio vaccine and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION After reconstitution,
INFANRIX HEXA Combined diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, enhanced inactivated polio vaccine and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION After reconstitution,
HOW DO VACCINES WORK?
 Official Topic from UpToDate, the clinical decision support resource accessed by 700,000+ clinicians worldwide. Available via the web and mobile devices, subscribe to UpToDate at www.uptodate.com/store.
Official Topic from UpToDate, the clinical decision support resource accessed by 700,000+ clinicians worldwide. Available via the web and mobile devices, subscribe to UpToDate at www.uptodate.com/store.
BOOSTRIX -POLIO: Diphtheria-Tetanus- Acellular Pertussis-Polio Combined Vaccine Biological Page (dtap-ipv)
 BOOSTRIX -POLIO: Diphtheria-Tetanus- Acellular Pertussis-Polio Combined Vaccine Biological Page (dtap-ipv) Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.213 Created by: Province-wide Immunization
BOOSTRIX -POLIO: Diphtheria-Tetanus- Acellular Pertussis-Polio Combined Vaccine Biological Page (dtap-ipv) Section 7: Biological Product Information Standard #: 07.213 Created by: Province-wide Immunization
Pentabio Vaccine (DTP-HB-Hib)
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS Product Name Pharmaceutical Form Strength Presentation : Pentabio : Suspension for injection : 1, 5 and 10 doses : Box of 10 vials @ 0.5 ml Box of 10 vials @ 2.5 ml Box
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS Product Name Pharmaceutical Form Strength Presentation : Pentabio : Suspension for injection : 1, 5 and 10 doses : Box of 10 vials @ 0.5 ml Box of 10 vials @ 2.5 ml Box
APEC Guidelines Immunizations
 Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
Pregnancy provides an excellent opportunity to enhance a woman s protection against disease and to provide protection to the neonate during the first 3 to 6 months of life. Women of childbearing age should
Gene Vaccine Dr. Sina Soleimani
 Gene Vaccine Dr. Sina Soleimani Human Viral Vaccines Quality Control Laboratory (HVVQC) Titles 1. A short Introduction of Vaccine History 2. First Lineage of Vaccines 3. Second Lineage of Vaccines 3. New
Gene Vaccine Dr. Sina Soleimani Human Viral Vaccines Quality Control Laboratory (HVVQC) Titles 1. A short Introduction of Vaccine History 2. First Lineage of Vaccines 3. Second Lineage of Vaccines 3. New
NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET
 1. PRODUCT NAME NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET INFANRIX HEXA Combined diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, enhanced inactivated polio vaccine and Haemophilus influenzae type b powder and suspension
1. PRODUCT NAME NEW ZEALAND DATA SHEET INFANRIX HEXA Combined diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, enhanced inactivated polio vaccine and Haemophilus influenzae type b powder and suspension
7.0 Nunavut Childhood and Adult Immunization Schedules and Catch-up Aids
 7.0 Nunavut Childhood and Adult Immunization Schedules and Catch-up Aids Contents Introduction Nunavut Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule Nunavut Routine Adult Immunization Schedule Nunavut Immunization
7.0 Nunavut Childhood and Adult Immunization Schedules and Catch-up Aids Contents Introduction Nunavut Recommended Childhood Immunization Schedule Nunavut Routine Adult Immunization Schedule Nunavut Immunization
INFANRIX HEXA QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION PHARMACEUTICAL FORM CLINICAL PARTICULARS. Indications
 INFANRIX HEXA Combined diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, enhanced inactivated polio vaccine and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION After reconstitution,
INFANRIX HEXA Combined diphtheria-tetanus-acellular pertussis, hepatitis B, enhanced inactivated polio vaccine and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION After reconstitution,
ANNEX I ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 ANNEX I ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection. Diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis
ANNEX I ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection. Diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, hepatitis
Haemophilus influenzae type B and Hib Vaccine Chapter 9
 Haemophilus influenzae type B and Hib Vaccine Chapter 9 Haemophilus influenzae Aerobic gram-negative bacteria Polysaccharide capsule Six different serotypes (a-f) of polysaccharide capsule 95% of invasive
Haemophilus influenzae type B and Hib Vaccine Chapter 9 Haemophilus influenzae Aerobic gram-negative bacteria Polysaccharide capsule Six different serotypes (a-f) of polysaccharide capsule 95% of invasive
INFANRIX hexa Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis (DTPa), Hepatitis B, Inactivated Poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type b Vaccine
 INFANRIX hexa Consumer Medicine Information 1(8) INFANRIX hexa Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis (DTPa), Hepatitis B, Inactivated Poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type b Vaccine CONSUMER
INFANRIX hexa Consumer Medicine Information 1(8) INFANRIX hexa Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis (DTPa), Hepatitis B, Inactivated Poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type b Vaccine CONSUMER
INFANRIX-IPV Product Information 1(13) INFANRIX IPV
 INFANRIX-IPV Product Information 1(13) INFANRIX IPV NAME OF THE DRUG INFANRIX IPV vaccine is a combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis (DTPa) and inactivated poliovirus vaccine. DESCRIPTION INFANRIX
INFANRIX-IPV Product Information 1(13) INFANRIX IPV NAME OF THE DRUG INFANRIX IPV vaccine is a combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis (DTPa) and inactivated poliovirus vaccine. DESCRIPTION INFANRIX
What DO the childhood immunization footnotes reveal? Questions and answers
 What DO the childhood immunization footnotes reveal? Questions and answers Stanley E. Grogg, DO, FACOP, FAAP he Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends the childhood vaccination
What DO the childhood immunization footnotes reveal? Questions and answers Stanley E. Grogg, DO, FACOP, FAAP he Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends the childhood vaccination
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection. Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular, component)
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Infanrix hexa, Powder and suspension for suspension for injection. Diphtheria (D), tetanus (T), pertussis (acellular, component)
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. Medicinal product no longer authorised
 ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT HEXAVAC suspension for injection in pre-filled syringe Diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, inactivated poliomyelitis,
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT HEXAVAC suspension for injection in pre-filled syringe Diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis, inactivated poliomyelitis,
Infanrix Hexa. Copyright , MIMS Australia Page 1 of 5
 Infanrix Hexa MIMS Abbreviated Prescribing Information Diphtheria toxoid; haemophilus influenzae vaccine; hepatitis B vaccine; pertussis vaccine; poliomyelitis vaccine; tetanus toxoid GlaxoSmithKline Australia
Infanrix Hexa MIMS Abbreviated Prescribing Information Diphtheria toxoid; haemophilus influenzae vaccine; hepatitis B vaccine; pertussis vaccine; poliomyelitis vaccine; tetanus toxoid GlaxoSmithKline Australia
Immunisation Policy. Country Children s Early Learning Ph: M:
 Immunisation Policy Published June 2018 Review Date December 2019 Sources Education and Care Services National Regulations, October 2017 Guide to the Education and Care Services National Law and the Education
Immunisation Policy Published June 2018 Review Date December 2019 Sources Education and Care Services National Regulations, October 2017 Guide to the Education and Care Services National Law and the Education
A Review of the Pediatric Immunization Schedule
 A Review of the Pediatric Immunization Schedule Michaela Christian PGY-1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Mercy Hospital, A Campus of Plantation General Hospital Michaela.Christian@Hcahealthcare.com Objectives
A Review of the Pediatric Immunization Schedule Michaela Christian PGY-1 Pharmacy Practice Resident Mercy Hospital, A Campus of Plantation General Hospital Michaela.Christian@Hcahealthcare.com Objectives
Appendix An Assessment Tool to Determine the Validity of Vaccine Doses
 Appendix 4.4 - An Assessment Tool to Determine the Validity of Vaccine Doses Note: Refer to the Canadian Immunization Guide and New Brunswick (NB) immunization program directives for recommendations for
Appendix 4.4 - An Assessment Tool to Determine the Validity of Vaccine Doses Note: Refer to the Canadian Immunization Guide and New Brunswick (NB) immunization program directives for recommendations for
3 rd dose. 3 rd or 4 th dose, see footnote 5. see footnote 13. for certain high-risk groups
 Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
Vaccination and Immunity
 Vaccination and Immunity Eric A. Utt, PhD Director, Worldwide Science Policy Pfizer Inc California Immunization Coalition Summit 2012 Completing the Circle: Ensuring Adult & Adolescent Vaccination for
Vaccination and Immunity Eric A. Utt, PhD Director, Worldwide Science Policy Pfizer Inc California Immunization Coalition Summit 2012 Completing the Circle: Ensuring Adult & Adolescent Vaccination for
ROTAVIRUS VACCINES. Virology
 ROTAVIRUS VACCINES Virology Rotavirus is a triple-layers viral particle belonging to the Reoviridae family. It contains 11 segments of double-stranded RNA, of which 6 are structural and 5 are non-structural
ROTAVIRUS VACCINES Virology Rotavirus is a triple-layers viral particle belonging to the Reoviridae family. It contains 11 segments of double-stranded RNA, of which 6 are structural and 5 are non-structural
Immunisation Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 28 October 2015
 Immunisation Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 28 October 2015 (minutes for web publishing) Immunisation Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology
Immunisation Subcommittee of PTAC Meeting held 28 October 2015 (minutes for web publishing) Immunisation Subcommittee minutes are published in accordance with the Terms of Reference for the Pharmacology
Rotavirus. Factsheet for parents. Immunisation for babies up to a year old
 Rotavirus Factsheet for parents This factsheet describes the rotavirus infection and the vaccine that protects against it. It also provides the background to the development and introduction of the vaccination
Rotavirus Factsheet for parents This factsheet describes the rotavirus infection and the vaccine that protects against it. It also provides the background to the development and introduction of the vaccination
NOTE: The above recommendations must be read along with the footnotes of this schedule.
 Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
Figure 1. Recommended immunization schedule for persons aged 0 through 18 years 2013. (FOR THOSE WHO FALL BEHIND OR START LATE, SEE THE CATCH-UP SCHEDULE [FIGURE 2]). These recommendations must be read
IMPORTANT: PLEASE READ
 PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION combined hepatitis A (inactivated) and hepatitis B (recombinant) vaccine This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when was approved for sale
PART III: CONSUMER INFORMATION combined hepatitis A (inactivated) and hepatitis B (recombinant) vaccine This leaflet is part III of a three-part "Product Monograph" published when was approved for sale
BCHOOSE TO VACCINATED. Ask your doctor about the MenB * vaccine.
 BCHOOSE TO VACCINATED Vaccinate against meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis group B strains (MenB) with BEXSERO BEXSERO multicomponent meningococcal B vaccine (recombinant, adsorbed)
BCHOOSE TO VACCINATED Vaccinate against meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis group B strains (MenB) with BEXSERO BEXSERO multicomponent meningococcal B vaccine (recombinant, adsorbed)
INFANRIX IPV PRODUCT INFORMATION
 INFANRIX IPV PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE INFANRIX IPV vaccine is a combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis (DTPa) and inactivated poliovirus vaccine. DESCRIPTION INFANRIX IPV vaccine
INFANRIX IPV PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE INFANRIX IPV vaccine is a combined diphtheria, tetanus, acellular pertussis (DTPa) and inactivated poliovirus vaccine. DESCRIPTION INFANRIX IPV vaccine
Healthy People 2020 objectives were released in 2010, with a 10-year horizon to achieve the goals by 2020.
 Appendix 1: Healthy People 2020 Immunization-related Objectives Healthy People provides science-based, 10-year national objectives for improving the health of all Americans. For three decades, Healthy
Appendix 1: Healthy People 2020 Immunization-related Objectives Healthy People provides science-based, 10-year national objectives for improving the health of all Americans. For three decades, Healthy
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory
 For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory INFANRIX HEXA Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (acellular component), hepatitis B (rdna), poliomyelitis (inactivated) and
For the use only of Registered Medical Practitioners or a Hospital or a Laboratory INFANRIX HEXA Diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis (acellular component), hepatitis B (rdna), poliomyelitis (inactivated) and
46825 (260) $UPONT
 Be wise. Immunize. Keeping track of the shots your children receive can be confusing. This is an important responsibility that is shared by you and your immunization providers. This booklet contains the
Be wise. Immunize. Keeping track of the shots your children receive can be confusing. This is an important responsibility that is shared by you and your immunization providers. This booklet contains the
INFANRIX hexa. Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis (DTPa), Hepatitis B, Poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine
 INFANRIX hexa Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis (DTPa), Hepatitis B, Poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine NAME OF THE MEDICINE INFANRIX hexa Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular
INFANRIX hexa Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular Pertussis (DTPa), Hepatitis B, Poliovirus and Haemophilus influenzae type b vaccine NAME OF THE MEDICINE INFANRIX hexa Combined Diphtheria-Tetanus-acellular
Vaccina&on in childhood. Agnieszka Wegner MD, PhD Department of Pediatric Neurology Medical University of Warsaw
 Vaccina&on in childhood Agnieszka Wegner MD, PhD Department of Pediatric Neurology Medical University of Warsaw Vaccina&on 1. VaccinaCon - accve immunizacon, synthecc, consiscng of the insercon into the
Vaccina&on in childhood Agnieszka Wegner MD, PhD Department of Pediatric Neurology Medical University of Warsaw Vaccina&on 1. VaccinaCon - accve immunizacon, synthecc, consiscng of the insercon into the
Revisions to Communicable Disease Control Manual: Chapter 2 Immunization Program
 January 5, 2010 ATTN: Medical Health Officers and Branch Offices Public Health Nursing Administrators and Assistant Administrators Holders of Communicable Disease Control Manuals Re: Revisions to Communicable
January 5, 2010 ATTN: Medical Health Officers and Branch Offices Public Health Nursing Administrators and Assistant Administrators Holders of Communicable Disease Control Manuals Re: Revisions to Communicable
9/10/2018. Principles of Vaccination. Immunity. Antigen. September 2018
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Principles of Vaccination September 2018 Chapter 1 September 2018 Photographs and images included in
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases Principles of Vaccination September 2018 Chapter 1 September 2018 Photographs and images included in
Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices VACCINE ACRONYMS
 May 1, 2015 Vaccine Acronyms Page 1 of 5 Advisy Committee on Immunization Practices VACCINE ACRONYMS Vaccines Included in the Immunization Schedules f Children, Adolescents, and Adults Following is a table
May 1, 2015 Vaccine Acronyms Page 1 of 5 Advisy Committee on Immunization Practices VACCINE ACRONYMS Vaccines Included in the Immunization Schedules f Children, Adolescents, and Adults Following is a table
1. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 INFANRIX 1. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION contains diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, and three purified pertussis antigens [pertussis toxoid (PT), filamentous haemagglutinin (FHA) and 69 kilodalton
INFANRIX 1. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION contains diphtheria toxoid, tetanus toxoid, and three purified pertussis antigens [pertussis toxoid (PT), filamentous haemagglutinin (FHA) and 69 kilodalton
National Immunisation News
 National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office July 2016 Changes to the Primary Childhood Immunisation Programme The National Immunisation Advisory Committee (NIAC) has
National Immunisation News The newsletter of the HSE National Immunisation Office July 2016 Changes to the Primary Childhood Immunisation Programme The National Immunisation Advisory Committee (NIAC) has
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB combination vaccine
 The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB combination vaccine Greenwich Practice Nurse Forum Oct 17 th 2017 Introduction of a hexavalent infant vaccine From autumn 2017, all babies born on or after 1 August 2017
The hexavalent DTaP/IPV/Hib/ HepB combination vaccine Greenwich Practice Nurse Forum Oct 17 th 2017 Introduction of a hexavalent infant vaccine From autumn 2017, all babies born on or after 1 August 2017
The Science of Vaccines:
 The Science of Vaccines: Addressing Common Concerns Paul A. Offit Division of Infectious Diseases Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine The University of Pennsylvania Are vaccines
The Science of Vaccines: Addressing Common Concerns Paul A. Offit Division of Infectious Diseases Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Perelman School of Medicine The University of Pennsylvania Are vaccines
GENERAL IMMUNIZATION GUIDE FOR CHILDCARE PROVIDERS August 2018 **CHILD VACCINES** DIPHTHERIA, TETANUS, PERTUSSIS VACCINES
 GENERAL IMMUNIZATION GUIDE FOR CHILDCARE PROVIDERS August 2018 **CHILD VACCINES** DIPHTHERIA, TETANUS, PERTUSSIS VACCINES DTaP: Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis Vaccine Infanrix Licensed in 1997
GENERAL IMMUNIZATION GUIDE FOR CHILDCARE PROVIDERS August 2018 **CHILD VACCINES** DIPHTHERIA, TETANUS, PERTUSSIS VACCINES DTaP: Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis Vaccine Infanrix Licensed in 1997
Early Learning Centre Immunisation Policy Legislation ACT Public Health Regulations (2000)
 Early Learning Centre Immunisation Policy Legislation ACT Public Health Regulations (2000) National Quality Standard / Education and Care Services National Regulations Standard 2.1 Each child s health
Early Learning Centre Immunisation Policy Legislation ACT Public Health Regulations (2000) National Quality Standard / Education and Care Services National Regulations Standard 2.1 Each child s health
Syrian Programme Refugees Advice on assessment of immunisation status and recommendations for additional immunisation
 Syrian Programme Refugees Advice on assessment of immunisation status and recommendations for additional immunisation Background Information Immunisation services in Syria Syria had good immunisation services,
Syrian Programme Refugees Advice on assessment of immunisation status and recommendations for additional immunisation Background Information Immunisation services in Syria Syria had good immunisation services,
IPOL. Inactivated Poliomyelitis Vaccine. Consumer Medicine Information
 IPOL Inactivated Poliomyelitis Vaccine What is in this leaflet Consumer Medicine Information This leaflet answers some common questions about IPOL vaccine. It does not contain all the available information.
IPOL Inactivated Poliomyelitis Vaccine What is in this leaflet Consumer Medicine Information This leaflet answers some common questions about IPOL vaccine. It does not contain all the available information.
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for midwives. August 2014
 Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for midwives August 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Key Message There is a lot
Vaccination against pertussis (whooping cough) - the replacement of Repevax with Boostrix -IPV an update for midwives August 2014 Quality Education for a Healthier Scotland 1 Key Message There is a lot
IMMUNISATION OF CHILDREN DURING and AFTER CANCER THERAPY
 NATIONAL GUIDELINES PAEDIATRIC ONCOLOGY AND HAEMATOLOGY For the Care of Childhood Cancer in Specialist Child Cancer and Shared Care Centres. IMMUNISATION OF CHILDREN DURING and AFTER CANCER THERAPY Date
NATIONAL GUIDELINES PAEDIATRIC ONCOLOGY AND HAEMATOLOGY For the Care of Childhood Cancer in Specialist Child Cancer and Shared Care Centres. IMMUNISATION OF CHILDREN DURING and AFTER CANCER THERAPY Date
Coverage of Vaccines Medicaid and Child Health Plus Members
 Coverage of Vaccines Medicaid and Child Health Plus Members For children between the ages 0-18, routine recommended vaccinations are covered through Vaccines for Children program [VFC]. Fidelis Care will
Coverage of Vaccines Medicaid and Child Health Plus Members For children between the ages 0-18, routine recommended vaccinations are covered through Vaccines for Children program [VFC]. Fidelis Care will
Trends in vaccinology
 Trends in vaccinology Mathieu Peeters, MD Joint Conference of European Human Pharmacological Societies and Joint Conference of European Human Pharmacological Societies and 20th Anniversary of AGAH March
Trends in vaccinology Mathieu Peeters, MD Joint Conference of European Human Pharmacological Societies and Joint Conference of European Human Pharmacological Societies and 20th Anniversary of AGAH March
A. Vaccines B. Breast milk C. Soy-based formulas D. Regular formula. A. Measles B. Smallpox C. Polio D. Influenza
 Vaccines Safety Infants are exposed to the greatest amount of aluminum from what? In 1916, rumors circulated that candy was the cause of what infectious disease? A. Vaccines B. Breast milk C. Soy-based
Vaccines Safety Infants are exposed to the greatest amount of aluminum from what? In 1916, rumors circulated that candy was the cause of what infectious disease? A. Vaccines B. Breast milk C. Soy-based
EUROPEAN MEDICINES AGENCY DECISION. of 31 March 2009
 European Medicines Agency Doc. Ref. EMEA/160106/2009 P/64/2009 EUROPEAN MEDICINES AGENCY DECISION of 31 March 2009 on the acceptance of a modification of an agreed Paediatric Investigation Plan for Purified
European Medicines Agency Doc. Ref. EMEA/160106/2009 P/64/2009 EUROPEAN MEDICINES AGENCY DECISION of 31 March 2009 on the acceptance of a modification of an agreed Paediatric Investigation Plan for Purified
If you have any concerns about being given this vaccine, ask your doctor.
 NEW ZEALAND CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION VARIVAX Varicella Virus Vaccine Live (Oka/Merck) Single dose vial What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about VARIVAX. It does not
NEW ZEALAND CONSUMER MEDICINE INFORMATION VARIVAX Varicella Virus Vaccine Live (Oka/Merck) Single dose vial What is in this leaflet This leaflet answers some common questions about VARIVAX. It does not
A Review of Pediatric Vaccines Gary Overturf, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics, Inf. Dis. University of New Mexico
 Review of Pediatric and Adolescent Vaccines 2012 Idaho Society of Health- System Pharmacists Boise, ID April 28 th 2012 A Review of Pediatric Vaccines - 2012 Gary Overturf, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics,
Review of Pediatric and Adolescent Vaccines 2012 Idaho Society of Health- System Pharmacists Boise, ID April 28 th 2012 A Review of Pediatric Vaccines - 2012 Gary Overturf, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics,
