Characterization of a non-occluded baculovirus-like agent pathogenic to penaeid shrimp
|
|
|
- Alvin Richard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Vol. 33: DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org Published July 30 Characterization of a non-occluded baculovirus-like agent pathogenic to penaeid shrimp E. Cesar B. Nadala Jr *, Lourdes M. Tapay, Philip C. Loh Department of Microbiology, University of Hawaii, Honolulu, Hawaii 96822, USA ABSTRACT: A non-occluded baculovirus-like agent recently isolated by this laboratory from moribund Penaeus japonicus shrimps obtained from China and named Chnese baculovirus (CBV) was purified and some of its properties characterized. Under the electron microscope, negatively stained virus particles were rod-shaped, enveloped, and measured 322 to 378 nm in length and 130 to 159 nm in diameter. The nucleoprotein core exhibited a unique striated structure and measured 316 to 350 nm in length and 65 to 66 nm in diameter. The striations appear to be the result of the stachng of ring-like structures. These rings consisted of 2 rows of 12 to 14 globular subunits. Each globular subunit measured approximately 10 nm in diameter. SDS-PAGE gels of purified virus preparations showed, among several, 4 prominent protein bands with approximate molecular weights of 19, 23.5, 27.5 and 75 kda. The structural viral proteins were identified by western blot analysis using polyclonal hyperlmmune serum made against purified CBV. The 19, 27.5, and 75 kda structural proteins were determined to be non-glycosylated components associated with the viral envelope. The 23.5 kda protein, also nonglycosylated, was identified with the capsid structure. Viral genornic DNA digested with Hind 111 restriction endonuclease revealed at least 29 different fragments with a conservatively estimated total size of at least 183 kb. KEY WORDS: Chinese baculovirus - Baculovirus - Penaeid shrimp INTRODUCTION A baculovirus-like agent was recently isolated by this laboratory from moribund pink shrimp Penaeus japonicus obtained from a shrimp farm in China. The isolate, labeled Chinese baculovirus (CBV), was found to cause 100% cumulative mortality 3 to 4 d postinfection in experimentally infected adult P. stylirostris (blue shrimp) and P. vannarnei (white shrimp), the 2 principal species of penaeid shrimp cultured in Hawaii and the Western Hemisphere (Tapay et al. 1997, Lu et al. 1997). Non-occluded baculovirus-like agents that closely resemble CBV have also been reported to infect P. rnonodon in Thailand (Wongteerasupaya et al. 1995), P. monodon, P. japonicus and P. penicillatus in Taiwan (Chou et al. 1995) and P. japonicus in Japan (Inouye et al. 1994, Takahashi et al. 1994, Inouye et al. 1996). These viruses have been implicated in massive disease outbreaks and mortalities among penaeid shrimp. Further characterization of the different isolates will help us to better understand these viruses and their relationships to each other. In this paper the propagation, purification, and characterization of some of the properties of CBV are described. This virus represents a potential threat to shrimp farming, particularly broodstocks in Hawaii, because of the highly lethal nature of the infection, its wide species range, and increasing geographical distribution. MATERIALS AND METHODS Virus propagation. The virus was propagated in white shrimp (50 to 60 g Penaeus vannamei) by intramuscular injection of filtrates 1200 p1 of a 4 % w/v homogenate in TNE (0.05 M Tris, 0.1 M NaC1, 1 mm EDTA), clarified at 2000 X g for 20 min, and filtered through a 0.45 pm filter] prepared from CBV-infected shrimp gill tissue. Two to four days after injection, 0 Inter-Research 1998 Resale of full article not permitted
2 222 Dis Aquat Org , 1998 hemolymph was collected from moribund specimens (by ablation of the telson and uropod), mixed with an equal volume of 20% (w/v) sodium citrate, and stored at -20 C. Virus purification. To purify the virus, various tissues were harvested from frozen infected shrimps. The tissues were suspended in TNE at 10% w/v and homogenized [Brinkmann Polytron 3000 (Kinematica AG) with 9O/Polytron PT-DA 3012/2TS] (Brinkmann Instruments Inc., NY, USA). Tissue debris was pelleted at 2500 X g for 15 min and the supernate further clarified by centrifugation at 4946 X g for 10 min. Virus was pelleted at X g for 30 min, resuspended in 30:l volume of TNE (i.e. 30 parts of original volume to 1 part of new suspension), layered on top of a 20-60% (w/v) continuous sucrese gradirct, and centrifuged at 58 20G X g for 2 h. The diffuse virus band was collected by side puncture, diluted 1:5 in TNE, and pelleted at X g for 30 min. The virus pellet was resuspended in 0.5 m1 of TNE, layered on top of a 30 to 50% (w/v) continuous CsCl gradient and centrifuged at X g for 19 h at 4 C. The bands of complete virions and nucleoprotein cores were collected, diluted 1:5 in TNE, and pelleted at X g for 15 min at 4OC. The pellets were resuspended in 0.5 m1 TNE and checked for purity under the electron microscope (EM). Electron microscopy. For EM examination, virus samples were mounted on formvar-coated, carbonstabilized copper grids (200 mesh), negatively stained with 2% (w/v) uranyl acetate, and examined under a Zeiss EMlO/A electron microscope. SDS-PAGE. The structural proteins of the virus were analyzed by 12.5 % SDS-PAGE (sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) according to the method of Laemmli (1970). Samples were electrophoresed for 40 min at 200 V and the gels stained using the silver stain plus kit (Biorad, CA, USA). Preparation of antibodies. Polyclonal hyperimmune serum against CBV was prepared in New Zealand white rabbits according to the following immunization schedule: 52 pg of CBV proteins in Freund's complete adjuvant were injected intradermally and subcutaneously on Day 0. Subsequent booster injections of CBV protein in Freund's incomplete adjuvant were given on Days 13, 27, and 41. The rabbits were exsanguinated on Day 63. Immunoglobulin G was purified from rabbit antisera using recombinant bacterial protein-g columns (Gamma-Bind G, Genex Corp., Gaithersburg, MD, USA) and adsorbed to normal shrimp hemolymph proteins to remove cross-reacting antibodies. Western blotting. For western blotting, purified CBV virions were electrophoresed on 12.5 % SDS-PAGE gel. at 200 V for 40 min and blotted onto nitrocellulose membranes (Schleicher and Schuell, NH, USA) at 100 V for 40 min. The nitrocellulose (NC) membranes were then washed with PBS (137 mm NaCl, 1 4 mm KH,PO,, 4.3 mm Na,HPO,.?H,O and 2.7 mm KCl), blocked with 5 % skim milk/pbs for 1 h, washed with PBS, and then treated with 1:1000 rabbit anti-cbv IgG diluted in 1 % skim milk/pbs for 1 h. The NC paper was washed with PBST (0.05% Tween-20/PBS) twice and once with PBS. The NC paper was then treated with 1 :2500 goat anti-rabbit HRPO (horseradish peroxidase) (Kirkegaard and Perry Laboratories, MD, USA) diluted in 1% skim milk/pbs for 1 h. The NC paper was washed 3x with PBST and then incubated with the TMB (3,3', 5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine; Kirkegaard and Perry Laboratories, MD, USA) substrate. All incubations were done at room temperature. Triion and DNAse I treatment. The locations of the different viral structural proteins were analyzed by treatment of the complete virions with 1 % Triton X- 100/TNE for 1 h at 37"C, and treatment of the nucleoprotein core with DNAse I (1 unit per log particles) for 1 h at 37 C. Triton-treated samples were centrifuged at X g for 5 min in a Beckman Airfuge (Beckman Instruments, CA, USA) to pellet the virus particles and separate it from components that were dissolved in Triton. All samples were separated by SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis and visualized by either silver staining or western blotting. Glycoprotein detection. Carbohydrate moieties of purified CBV proteins western blotted onto nitrocellulose membrane were labeled using the ECL (enhanced chemiluminescence) glycoprotein detection system (Amersham Corp., IL, USA). A parallel western blot was also done using anti-cbv IgG (1:1000 dilution) to confirm the presence of all the CBV proteins. Preparation of viral nucleic acid. The CBV DNA was purified from CsCl banded virus using the QIAamp Tissue Gt (QIAGEN Inc., CA, USA). Aliquots of the DNA (200 ng in ) were dlgested with excess (10 units) Hind 111 for 1 h at 37 C. The digest, together with undigested controls, was then electrophoresed on 0.4% agarose (TBE) at 10 V overnight or 0.7% agarose (TBE) at 60 V for 3 h. RESULTS Purification of CBV Although CBV particles were s~~ccessfully purified from gill tissues, epidermal tissues, head soft tissues, and hemolymph, the cleanest preparations (Figs. 1 & 2) were obtained from the hemolymph. Furthermore, virus purification from the hemolymph did not require the homogenization step which was necessary for all other tissues.
3 Nadala et al.: Baculovirus-like agent from shrlmp Fig. 1 Electron micrographs of negatively stained CBV particles. (A) Whole virus particles partially penetrated by the stain revealing the nucleocapsid. (B) Partially degraded nucleocapsid with the globular subunits unwound. (C) Virus particle with the outer envelope almost completely removed from the nucleocapsid. (D) Whole virus particle showing a tail-like extension from the outer envelope. All scale bars = 100 nm Isopycnic centrifugation in CsCl was found to be superior to sucrose gradients for the optimal purification of CBV particles and nucleoprotein cores. The complete virions banded at 1.22 g ml-l and the nucleoprotein cores banded at 1.31 g ml-' in CsCl. Structure of CBV Electron microscopical examination of negatively stained complete CBV particles revealed a rod-shaped nucleoprotein core enclosed in a tight-fitting capsid
4 Dis Aquat Org , 1998 Flg. 2. Electron micrographs of negatively stained CBV nucleoproteln cores. (A) Lower magnification showing nng-like structures (arrowheads) peeling away from several nucleoprotein cores (scale bar = 500 nm). (B) Higher magnification shotving a close-up vlew of the nnglike structure stlll attached to the nucleoprotein core (scale bar = 100 nm) layer and a loose-fitting outer membrane (Fig. 1A. C). ited globular structures that seem to be attached to Because of the loosely fitting outer membrane, the each other like beads on a string (Fig. 1B). The total diameter of the whole virus was as large as 130 to length of the nucleoprotein core is 316 to 350 nm with 159 nm and provided an ellipsoidal shaped structure a diameter of 65 to 66 nm. (Fig. la, D) occasionally exhibiting tail-like membranous extensions (Fig. ID). Electron microscopical examination of negatively CBV structural proteins stained nucleoprotein cores revealed some 14 to 15 conspicuous vertical striations located periodically Analysis of the structural proteins of the virus by along the long axis of the rod-shaped core and about SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis of purified whole virus 22 nm apart (Fig. 1C). These striations are probably the particles revealed at least 4 prominent and consistent result of the stacking of ring-like structures making up proteins that were approximately 19, 23.5, 27.5 and the nucleoprotein core structure (Fig. 2A, B). These 75 kda in size (Fig. 4A, lane 1, asterisks). The addirings consist of 2 rows of 12 to 14 essentially globu- tional 60 kda band seen in lane 1 of Fig. 4A was not lar structures each approximately 10 nm in diameter virus-specific since it was not observed in other puri- (Fig. 3). Degraded nucleocapsids occasionally exhib- fied virus samples (data not shown). A very high mole-
5 Nadala et al Baculov~rus-l~ke agent from shnmp cular weight band (>200 kda) associated with the nucleoprotein core was also observed (Fig. 4A). Western blot analysis of complete virlons employing polyclonal antibody against CBV revealed the 4 prominent (19, 23.5, 27.5 and 75 kda) bands but not the high molecular weight band (Fig. 4B). Pre-immune rabbit serum did not react with any of these prote~n bands (data not shown). All 4 protein bands were of virus origin as confirmed by time course m vltro and In vivo virus replication experiments (Nadala et al. 1997). F+ B.9' g F?!,.:.;.W\.L.:' :F,-., -;;;G.?,,.,y&@ L...-:*;:.: c C.., ;-.F;,, i c;. 7,;:.-:..-; :,.:.V6: i. < Fig. 3. Electron micrograph of negatively stained CBV nucleoprotein cores. A computermodified image of the boxed part of the nucleocapsid illustrates the arrangement of the globular subunits. Scale bar = 100 nm Flg. 4 The structural proteins of CBV as revealed by 12.5% SDS-PAGE gel electrophores~s and western blot. Arrowheads indicate the relatlve poslt~ons of the molecular weight markers Astensks indicate the poslt~ons of the 4 promlnent structural proteins of CBV (A) Sllverstained gel Lane I: punfled whole virus, Lane 2 purlfled v~ral nucleoprotein core. (B) Western blot. Lane 1 punfied whole vlrus; Lane 2: punfled v~ral nucleoprotein core
6 Dis Aquat Org 33: , 1998 SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis A, of complete Lirions treated wlth Trlton kd, X-100 showed that the 27 5 kda protein was easlly removed from the virion when the outer lipid membrane was dl,solved (Fig 5A B) In contrast the kda protein remained with the 66 nrlcleoprotein core However, prolonged treatment with Triton X along with repeated pelleting and resuspension resulted in stripping of the 23 5 kda protein from the nucleoprotein core (Fig 4A, B) Although less 31 dlstinct (the bands arc very faint), data in Fig 5A also suggested that the 19 kna protein laras!ccated :R thc G.;:?; lipid membrane of the virus Likewise, 22 Fig 5B suggested that the 75 kda protern (barely visible in lanes 2 and 5) was also located in the outer lipid, b membrane When punfied nucleoprotein core par- * ticles were treated wlth DNAse I (Fig 6), the very high molecular weight band (lane 1, arrowhead) normally observed even in denaturing SDS-PAGE gels disappeared Howevei, no new protein bands wele detectable after DNAse digestion except for a very low molecular weight band (lane 2 arrowhead) that seemed to migrate with the dye front Glycoprotein labelling expenments showed that none of the 4 prominent viral structural proteins were glycosylated (data not shown) I I 1. l h.di Analysis of the viral nucleic acids When purified CBV DNA was digested with Hind 111 and electrophoresed in an agarose gel (0.7%), 17 bands were distinguished and reliably sized at 5500, 4361, 4150, 3700, 3400, 3000, 2900, 2450, 2027, 1557, 1350, 1050, 970, 920, 740, 610 and 530 bp (Fig. 7). When the same digest was electrophoresed on 0.4% agarose gel, 12 more bands were easily recognized and reliably sized at 22.8, 22, 15.2, 12.8, 12, 10.8, 10.2, 8.6, 8.4, 7.6, 7.4 and 6.9 kb. When combined, a total of 29 fragments were counted with a total size of about kb. Fig. 5. SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresls and western blot of untreated and Tritontreated CBV Arrowheads indicate the positions of the protein bands of interest. (A) Silver-stained gel. Lane 1. molecular weight markers; Lane 2: pellet of untreated virus; Lane 3: supernate of untreated virus; Lane 4: pellet of Triton-treated virus; Lane 5: supernate of Triton-treated virus. (B) Western blot. Lane 1: pre-stained molecular weight markers; Lane 2: pellet of untreated virus; Lane 3: supernate of untreated virus; Lane 4: pellet of Triton-treated virus; Lane 5: supernate of Triton-treated virus
7 Nadala et al.: Baculovirus-like agent from shrimp 227 DISCUSSION Fig. 6. SDS-PAGE gel electrophoresis of DNAse 1 treated viral nucleoprotein cores. Silver-stained gel of purified nucleoprotein cores showing the high molecular weight band (arrowhead) in lane 1, DNAse 1 treated nucleoprotein cores showing the new low molecular weight band (arrowhead) in lane 2, DNAse I alone in lane 3, and prestained molecular we~ght markers in lane 4 The results above suggest that the complete CBV particle consists of a nucleoprotein core, covered with capsid protein, and enveloped in a lipid membrane. The nucleoprotein core is arranged as a serles of 14 or 15 stacked rings. It apparently contains the viral DNA and a closely associated low molecular weight protein. The nucleoprotein core has a relatively complex structure and it is likely that there are other proteins that are part of it but have not been clearly demonstrated in our SDS-PAGE gels. These, along with the low molecular weight protein, need to be further characterized. The nucleoprotein core is covered with a capsid protein of approximately 23.5 kda. The nucleocapsid in turn is enveloped in a lipid membrane containing at least 3 major structural proteins (19, 27.5, and 75 kda). Based on comparisons between silver-stained gels and their corresponding western blots, the 27.5 and 75 kda outer membrane proteins seem to be the most immunogenic. However, neither protein was glycosylated. A proposed schematic cutaway diagram of CBV, indicating the tentative locations of the various viral structural proteins and the nucleoprotein core, is shown in Fig. 8. The protein profile of CBV is unlike that of any known baculovirus. Instead of the 12 to 30 polypeptide species usually seen in SDS-PAGE analyses of baculoviruses (both occluded and non-occluded) (Bilimoria 1986), CBV has 4 prominent structural proteins plus an unknown number of. polypeptides.. - present at much lower concentration. This, plus the unique structure of its nucleocapsid, distinguishes CBV from present members of the Baculoviridae family. Although similar to the baculoviruses in size, general structure, and genome composition, CBV along with the former members of the Nudibaculovirinae subfamily await reassignment by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (Murphy et al. 1995). Lipid Envelope 19 kda 27.5 kda 75 kda Capsid 23.5 kda Nucleoprotein core Fig. 7. Agarose gel electrophoresis of purified CBV DNA digested with Hind 111. Lane 1: uncut CBV genomic DNA; Lane 2: the CBV genomic DNA digested with Hind 111; Lane 3: lambda DNA digested with Hind I11 Fig. 8. Proposed schematic cutaway diagram of CBV indicat~ng the tentative locations of the various viral structural proteins
8 Dis Aquat Org 33: , 1998 The CBV isolate in the present study is one of several non-occluded baculovirus-like agents which have been recently reported to infect several species of penaeid shrimp and cause high mortalities in Asia and SE Asia (Inouye et al. 1994, Takahashi et al. 1994, Arimoto et al. 1995, Wang et al. 1995, Wongsteerasupaya et al. 1995). The present isolate shares a unique nucleocapsid morphology (striated structure) with the white spot baculovirus (WSBV) described by Wang et al. (1995), the Penaeus monodon non-occluded baculovirus I1 (PmNOBII) described by Wongteerasupaya et al. (1995), and the penaeid rod-shaped DNA virus (PRDV) described by Inouye et al. (1996). The estimated total size of the Hind 111-digested fragments of CBV-DNA seemed to be larger than that reported for WSRV ( kb versus 150t kb) by Wang et al. (1995). However, this is probably due to the fact that Wang et al. counted only 22 fragments versus our 29. At least 2 of the higher molecular weight fragments migrated very closely with other fragments and could have been easily missed. In addition, 5 smaller fragments (530, 610, 740, 920, and 970 bp) were not included. Despite the slight differences in our estimates of the sizes of individual Hind 111 fragments, the profile is virtually identical. This suggests that the WSBV isolate of Wang et al. (1995) is probably identical to our CBV. The sizes estimated for PRDV DNA by Inouye et al. (1996) and for PmNOBII DNA by Wongteerasupaya et al. (1995) were and 168 kb respectively. The lower estimate for DNA size compared to CBV-DNA could again be due to these authors' conservative counting of the restriction fragments. Because Wongteerasupaya et al. (1995) did not report the individual sizes of their fragments, it was not possible to make direct comparisons. However, if one compares the profile of the EcoR I restriction fragments of PRDV (Inouye et al. 1996) with that of PmNOBII (Wongteerasupaya et al. 1995), it is apparent that they are also nearly identical. Inouye et al. noted a difference only because Wongteerasupaya et al. had inadvertently transposed the names of the restriction enzymes in their figure (Lo et al. 1996). More recent data reported by Lo et al. (1996) indicate that WSBV EcoR I and BamH I restriction profiles were similar to those of PmNOBII. Since we already have some evidence that WSBV is identical to CBV, this means that PRDV and PmNOBII may be the same virus as well. More restriction endonuclease analyses using a battery of enzymes are needed to confirm this close relatedness or identity among the different isolates. The size dimensions of the virus particles appeared to vary among the different isolates. However, it is difficult to compare virus dimensions of even negativelystained purified virus samples prepared in different laboratories. A difference was noted between CBV and the other isolates (PRDV, WSBV, PmNOBII) in the characteristic pathological response of cultured penaeid shrimp, such as Penaeus monodon, P. japonicus, and P. penicillatus when infected with these viruses. Observed in such infected shrimp were a general reddish coloration and the production of conspicuous white spots on the carapace, appendages and inside surface of the body. In contrast, CBV infection of the 2 commercial species, P, stylirostris and P. vannarnei cultured in Hawaii, does not result in the appearance of white spots. Also, the general reddish coloration is seen only occasionally and primarily in the extremities of the infected shrimp. These differences in responses however, may reflect a difference in the penaeid species invoived and/or the fact that CBV was inoculated into the shrimps by injection at a high dosage while the other isolates underwent a natural infection. Lastly it should be noted that the CBV was originally isolated from Penaeus japonicus obtained from a farm in the People's Republic of China. The virus was found to be highly pathogenic for the penaeid species cultured here in Hawaii (Tapay et al. 1997, Lu et al. 1997). Available data indicate that the CBV isolate is probably closely related if not identical to the other isolates associated with the white spot syndrome disease. A recent report employing an in situ DNA hybridization procedure has presented evidence to strongly suggest that these isolates may be closely related variants (Wongteerasupaya et al. 1996). However, a definitive comparison awaits further characterization of these viruses, especially protein profiles, more RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) studies, nucleic acid sequencing, and serologic testing. Acknowledgements. This study was supported by grants from the University of Hawaii Sea Grant and College Program, Institutional Grant No. NA36RG0507, UNIHI-SEAGRANT- JC-98-03, and the Aquaculture Development Program, Department of Land and Natural Resources. State of Hawaii Contract No LITERATURE CITED Arimoto M, Yamazaki T, Mizuta Y, Furusawa 1 (1995) Characterization and partial clon~ng of the genomic DNA of a baculovirus from Penaeus japonicus (PjNOB=BMNV). Aquaculture (Amsterdam) 132: Bilimoria SL (1986) Taxonomy and identification of baculoviruses. In: Granados RR. Federici BA (eds) The biology of baculoviruses, 1st edn, Vol 1 Biological properties and molecular biology. CRC Press, Boca Raton, p Chou HY, Huang CY, Wang CH, Lo CF (1995) Pathogenicity of a baculovirus infection causing white spot syndrome in cultured penaeid shrimp in Taiwan. Dis Aquat Org 23:
9 Nadala et al.: Baculovirus-like agent from shrimp 229 Inouye K, Miwa S, Oseko N. Nakano H, Kimwa T, Momoyama K. Hiraoka M (1994) Mass mortalities of cultured kuruma shrimp, Penaeus japonicus, in Japan in 1993: electron microscopic evldence of the causative virus. Fish Path01 29: lnouye K, Yamano K, Ikeda N. Kimwa T. Nakano H, Momoyama K, Kobayashi J, Miyajima S (1996) The penaeid rodshaped DNA vlrus (PRDV), which causes penaeid acute viremia (PAV). F~sh Path Laemmll UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteln during the ashembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: Lo CF, Ho CH, Peng SE, Chen CH, Hsu HC, Chiu YL, Chang CF, Liu KF, Su MS, Wang CH, Kou GH (1996) White spot syndrome baculovirus (WSBV) detected In cultured and captured shrimp, crabs and other arthropods. Dis Aquat Org 27: Lu Y, Tapay LM, Loh PC, Gose RB, Brock JA (1997) The pathogenicity of a baculo-like virus isolated from diseased penaeid shrimp obtained from China for cultured penaeld species in Hawaii. Aquacult Int 5: Murphy FA. Fauquet CM, Bishop DHL, Ghabrial SA, Jarvis AW, Martelli GP, Mayo MA. Summers MD (1995) Virus taxonomy. ArchIves of virology Springer-Verlag, Vienna Nadala ECB Jr, Tapay LM, Cao S, Loh PC (1997) Detection of yellowhead vlrus and Chinese baculov~rus In penaeld shrimp by the western blot technique. J Virol Meth 69: Editorial responsibility- Larry Va ughan, Dubhn, Ireland Takahashi Y, Itami T. Kondo M, Maeda M. Fujii R, Tomonaga S. Supamattaya K, Boonyaratpalin S (1994) Electron m~croscopic evidence of bacilliform virus infection In k~lri~ma shrimp (Penaeus japonicus). Flsh Pathol 29: Tapay LM, Lu Y, Gose RB, Brock JA, Loh PC (1997) lnfection of wh~tc-spot baculovirus-like virus (WSBV) in two species of penaricl shr~mp, Penaeus stylirostns (Stimpson) and P. vanndmei (Boone). In: Flegel TLV, h4acrae IH (eds) Disedses In Asian aquaculture 111 Flsh Health Section, Asian Fisheries Socicty, Manila, p Wang CH. Lo CF, Leu JH, Chou CM, Yeh PY, Chou HY, Tung MC, Chang CF, Su MS, Kou GH (1995) Purification and genomic analysis of baculovirus associated with whlte spot syndrome (WSBV) of Penaeus monodon. Dis Aquat Org 23: Wongteerasupaya C, Vickers JE, Sriurairatana S. Nash GL, Akarajamorn A, Boonsaeng V, Panyim S, Tassanakajon A, Wlthyachumnarnkul B, Flegel TW (1995) A non-occluded, systemic baculov~rus that occurs in cells of ectodermal and mesodermal origin and causes high mortality In the black tiger prawn Penaeus monodon. Dis Aquat Org 21:69-77 Wongteerasupaya C, Wongwisansri S, Boonsaeng V, Panyim S, Pratanpipat P, Nash G, Withyachumnarnkul B, Flegel TW (1996) DNA fragment of Penaeus monodon baculov~rus PmNOBll glves positive in situ hybridnation with white-spot viral infections in six penaeid shrimp species. Aquaculture (Amsterdam) 143:23-32 Submitted. September 27, 1997; Accepted: Apr~l 15, 1998 Proofs I-eceived from autllor(s): June 6, 1998
Tissue distribution of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in shrimp and crabs
 Tissue distribution of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in shrimp and crabs *Guang-Hsiung Kou, Shao-En Peng, Ya-Lin Chiu, Chu-Fang Lo Department of Zoology, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan,
Tissue distribution of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in shrimp and crabs *Guang-Hsiung Kou, Shao-En Peng, Ya-Lin Chiu, Chu-Fang Lo Department of Zoology, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan,
Electron Microscopic Evidence of Bacilliform Virus Infection in Kuruma Shrimp (Penaeus japonicus)
 Electron Microscopic Evidence Bacilliform Virus Infection in Kuruma Shrimp (Penaeus japonicus) Yukinori Takahashi*1, Toshiaki Itami*1, Masakazu Kondo*2, Minoru Maeda*1, Reiko Fujii*3, Susumu Tomonaga3,
Electron Microscopic Evidence Bacilliform Virus Infection in Kuruma Shrimp (Penaeus japonicus) Yukinori Takahashi*1, Toshiaki Itami*1, Masakazu Kondo*2, Minoru Maeda*1, Reiko Fujii*3, Susumu Tomonaga3,
Examination for Viral Inactivation of WSSV (White Spot Syndrome Virus) Isolated in Malaysia Using Black Tiger Prawn (Penaeus monodon)
 JARQ 4 (1), 93 97 (26) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp Examination for Viral Inactivation of WSSV (White Spot Syndrome Virus) Isolated in Malaysia Using Black Tiger Prawn (Penaeus monodon) Norihisa OSEKO
JARQ 4 (1), 93 97 (26) http://www.jircas.affrc.go.jp Examination for Viral Inactivation of WSSV (White Spot Syndrome Virus) Isolated in Malaysia Using Black Tiger Prawn (Penaeus monodon) Norihisa OSEKO
Model of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) epidemics in Litopenaeus vannamei
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 50: 199 209, 2002 Published July 29 Dis Aquat Org Model of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) epidemics in Litopenaeus vannamei Jeffrey M. Lotz*, M. Andres Soto** Department
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 50: 199 209, 2002 Published July 29 Dis Aquat Org Model of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) epidemics in Litopenaeus vannamei Jeffrey M. Lotz*, M. Andres Soto** Department
Identification of the Nucleocapsid, Tegument, and Envelope Proteins of the Shrimp White Spot Syndrome Virus Virion
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2006, p. 3021 3029 Vol. 80, No. 6 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.80.6.3021 3029.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Identification
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 2006, p. 3021 3029 Vol. 80, No. 6 0022-538X/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jvi.80.6.3021 3029.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Identification
A White Spot Disease - like syndrome in the Pacific Blue Shrimp (Litopenaeus stylirostris) as a form of bacterial shell disease
 Aquaculture MARCH 2000; 183 (1-2) : 25-30 http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00284-7 @ 2004 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved Archimer http://www.ifremer.fr/docelec/ Archive Institutionnelle de l
Aquaculture MARCH 2000; 183 (1-2) : 25-30 http://dx.doi.org/ 10.1016/S0044-8486(99)00284-7 @ 2004 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved Archimer http://www.ifremer.fr/docelec/ Archive Institutionnelle de l
Effects of shrimp density on transmission of penaeid acute viremia in Penaeus japonicus by cannibalism and the waterborne route
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 47: 129 135, 2001 Published November 8 Dis Aquat Org Effects of shrimp density on transmission of penaeid acute viremia in Penaeus japonicus by cannibalism and the waterborne
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 47: 129 135, 2001 Published November 8 Dis Aquat Org Effects of shrimp density on transmission of penaeid acute viremia in Penaeus japonicus by cannibalism and the waterborne
INTRODUCTION. KEY WORDS: Viral transmission. White spot syndrome virus. Penaeus monodon. Crab. Krill. DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org
 Vol. 32: 79-85,1998 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org l Published March 5 Experimental transmission of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) from black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon to the sand crab
Vol. 32: 79-85,1998 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org l Published March 5 Experimental transmission of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) from black tiger shrimp Penaeus monodon to the sand crab
bacterial shell disease
 Ž. Aquaculture 183 2000 25 30 www.elsevier.nlrlocateraqua-online A white spot disease-like syndrome in the Pacific blue shrimp ž Litopenaeus stylirostris/ as a form of bacterial shell disease Cyrille Goarant
Ž. Aquaculture 183 2000 25 30 www.elsevier.nlrlocateraqua-online A white spot disease-like syndrome in the Pacific blue shrimp ž Litopenaeus stylirostris/ as a form of bacterial shell disease Cyrille Goarant
The Viability of Taura Syndrome Virus in Low-salinity Water
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 39 : 406-410 (2005) The Viability of Taura Syndrome Virus in Low-salinity Water Niti Chuchird and Chalor Limsuwan ABSTRACT Taura syndrome virus (TSV) could survive up to 10 days
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 39 : 406-410 (2005) The Viability of Taura Syndrome Virus in Low-salinity Water Niti Chuchird and Chalor Limsuwan ABSTRACT Taura syndrome virus (TSV) could survive up to 10 days
Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x
 J. gen. Virol. (1972), I6, 215-22I Printed in Great Britain 2I 5 Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x By JUDY BRUCE, R. N. GOURLAY, AND D. J. GARWES R. HULL* Agricultural Research Council,
J. gen. Virol. (1972), I6, 215-22I Printed in Great Britain 2I 5 Ultrastructure of Mycoplasmatales Virus laidlawii x By JUDY BRUCE, R. N. GOURLAY, AND D. J. GARWES R. HULL* Agricultural Research Council,
Effect of dietary P-1,3-glucan on resistance to white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in postlarval and juvenile Penaeus monodon
 Vol. 36: 163-168.1999 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org l Published May 31 Effect of dietary P-1,3-glucan on resistance to white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in postlarval and juvenile Penaeus
Vol. 36: 163-168.1999 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org l Published May 31 Effect of dietary P-1,3-glucan on resistance to white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in postlarval and juvenile Penaeus
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 67-73) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 113-117), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 119), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 75-77).
PRODUCTION OF RECOMBINANT BACULOVIRUS EXPRESSING WSSV VP28 AND EGFP IN SF-9 INSECT CELL
 PRODUCTION OF RECOMBINANT BACULOVIRUS EXPRESSING WSSV VP28 AND EGFP IN SF-9 INSECT CELL Kittipong Thanasaksiri 1, Triwit Rattanarojpong 2 and Kanokwan Poomputsa 3 Abstract White spot syndrome virus (WSSV)
PRODUCTION OF RECOMBINANT BACULOVIRUS EXPRESSING WSSV VP28 AND EGFP IN SF-9 INSECT CELL Kittipong Thanasaksiri 1, Triwit Rattanarojpong 2 and Kanokwan Poomputsa 3 Abstract White spot syndrome virus (WSSV)
CpSBV, a systemic virus of the edible crab, Cancer pagurus (L.)
 Short communication CpSBV, a systemic virus of the edible crab, Cancer pagurus (L.) V Corbel, F Coste and J-R Bonami UMR5098, DRIM, CNRS/IFREMER/UM2, cc080, Université de Montpellier 2, Montpellier, France
Short communication CpSBV, a systemic virus of the edible crab, Cancer pagurus (L.) V Corbel, F Coste and J-R Bonami UMR5098, DRIM, CNRS/IFREMER/UM2, cc080, Université de Montpellier 2, Montpellier, France
However, 31.2% showed resistance to cotrimaxasole, 91.6% to sulphafurazole and 65.8% to sulphadiazine (Otta, 1997).
 416 I. Karunasagar, S. K. Otta et al. (1994) reported mass mortality of P. monodon larvae due to chloramphenicol resistant strains of V. harveyi. Later studies showed that V harveyi is capable of forming
416 I. Karunasagar, S. K. Otta et al. (1994) reported mass mortality of P. monodon larvae due to chloramphenicol resistant strains of V. harveyi. Later studies showed that V harveyi is capable of forming
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual)
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases
 Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
Lab Tuesday: Virus Diseases Quiz for Bacterial Pathogens lab (pp 69-75) and Biocontrol of Crown Gall (p. 115-119), Observation of Viral Movement in Plants (p. 121), and Intro section for Viruses (pp. 77-79).
Taura Syndrome Virus Disease in Farm-Reared Penaeus monodon in Thailand
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 41 : 319-323 (2007) Taura Syndrome Virus Disease in Farm-Reared Penaeus monodon in Thailand Chalor Limsuwan and Niti Chuchird* ABSTRACT Taura syndrome virus (TSV) has caused major
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 41 : 319-323 (2007) Taura Syndrome Virus Disease in Farm-Reared Penaeus monodon in Thailand Chalor Limsuwan and Niti Chuchird* ABSTRACT Taura syndrome virus (TSV) has caused major
Differences in susceptibility of palaemonid shrimp species to yellow head virus (YHV) infection
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 64: 5 12, 2005 Published April 6 Dis Aquat Org Differences in susceptibility of palaemonid shrimp species to yellow head virus (YHV) infection Siwaporn Longyant 1, Paisarn
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 64: 5 12, 2005 Published April 6 Dis Aquat Org Differences in susceptibility of palaemonid shrimp species to yellow head virus (YHV) infection Siwaporn Longyant 1, Paisarn
Protein Expression and Microscopic Evidence of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in Tiger prawns Penaeus monodon
 Protein Expression and Microscopic Evidence of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in Tiger prawns Penaeus monodon Bhatt, S.S. a*, Chavda, D. V. a and Sreepada, R. A. b a B.R. Doshi School of Biosciences,
Protein Expression and Microscopic Evidence of White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in Tiger prawns Penaeus monodon Bhatt, S.S. a*, Chavda, D. V. a and Sreepada, R. A. b a B.R. Doshi School of Biosciences,
Compound eye as a target organ of white spot baculovirus (WSBV) in Penaeus indicus H. Milne Edwards
 Indian J. Fish., 48(3): 243-248, Jul.-Sep., 2001 Compound eye as a target organ of white spot baculovirus (WSBV) in Penaeus indicus H. Milne Edwards JASMIN K. JOSE AND MARY K. MANISSERI Central Marine
Indian J. Fish., 48(3): 243-248, Jul.-Sep., 2001 Compound eye as a target organ of white spot baculovirus (WSBV) in Penaeus indicus H. Milne Edwards JASMIN K. JOSE AND MARY K. MANISSERI Central Marine
The Special Danger of Viral Pathogens in Shrimp Translocated for Aquaculture
 doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2006.32.215 ScienceAsia 32 (2006): 215-221 The Special Danger of Viral Pathogens in Shrimp Translocated for Aquaculture Timothy W. Flegel * Centex Shrimp and National
doi: 10.2306/scienceasia1513-1874.2006.32.215 ScienceAsia 32 (2006): 215-221 The Special Danger of Viral Pathogens in Shrimp Translocated for Aquaculture Timothy W. Flegel * Centex Shrimp and National
Identification of Stressors that Affect White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) Infection and Outbreak in Pond Cultured Penaeus monodon
 The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture - Bamidgeh, IIC:63.2011.616, 7 pages The IJA appears exclusively as a peer-reviewed on-line open access journal at http://www.siamb.org.il Sale of IJA papers is strictly
The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture - Bamidgeh, IIC:63.2011.616, 7 pages The IJA appears exclusively as a peer-reviewed on-line open access journal at http://www.siamb.org.il Sale of IJA papers is strictly
Journal of Advanced Scientific Research
 Debnath P. P. et al, J Adv Sci Res, 212, 3(3): 58-63 58 Journal of Advanced Scientific Research Available online through http://www.sciensage.info/jasr ISSN 976-9595 Research Article Prevalence of White
Debnath P. P. et al, J Adv Sci Res, 212, 3(3): 58-63 58 Journal of Advanced Scientific Research Available online through http://www.sciensage.info/jasr ISSN 976-9595 Research Article Prevalence of White
A yellow-head-like virus from Penaeus monodon cultured in Australia
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org Published December 30 A yellowheadlike virus from Penaeus monodon cultured in Australia 'Department of Parasitology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane 4072.
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org Published December 30 A yellowheadlike virus from Penaeus monodon cultured in Australia 'Department of Parasitology, The University of Queensland, Brisbane 4072.
Astrovirus-associated gastroenteritis in children
 Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 939-943 Astrovirus-associated gastroenteritis in children C. R. ASHLEY, E. 0. CAUL, AND W. K. PAVER1 From the Public Health Laboratory, Myrtle Road, Bristol BS2
Journal of Clinical Pathology, 1978, 31, 939-943 Astrovirus-associated gastroenteritis in children C. R. ASHLEY, E. 0. CAUL, AND W. K. PAVER1 From the Public Health Laboratory, Myrtle Road, Bristol BS2
Study on the Pathogenesis of the White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) on Juvenile Penaeus monodon in Vietnam
 248 The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture Bamidgeh 61(3), 2009 Study on the Pathogenesis of the White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) on Juvenile Penaeus monodon in Vietnam Cuong Van Doan, Anh Thi Tuyet Pham,
248 The Israeli Journal of Aquaculture Bamidgeh 61(3), 2009 Study on the Pathogenesis of the White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) on Juvenile Penaeus monodon in Vietnam Cuong Van Doan, Anh Thi Tuyet Pham,
The study of binding between VP28 of WSSV and Rab7 of
 The study of binding between VP28 of WSSV and Rab7 of giant tiger prawn Penaeus monodon Yi-Cheng Huang, Hong Sun, Yu-San Han Institute of Fisheries Science, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan Abstract:
The study of binding between VP28 of WSSV and Rab7 of giant tiger prawn Penaeus monodon Yi-Cheng Huang, Hong Sun, Yu-San Han Institute of Fisheries Science, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan Abstract:
HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit
 HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI009 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5/20 Duration of Experiment: ~ 2 days Day 1: 6-8 hours (SDS- PAGE and Electroblotting) Day 2: 3 hours
HiPer Western Blotting Teaching Kit Product Code: HTI009 Number of experiments that can be performed: 5/20 Duration of Experiment: ~ 2 days Day 1: 6-8 hours (SDS- PAGE and Electroblotting) Day 2: 3 hours
ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS
 Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Onderstepoort]. vet. Res. 40 (2), 53-58 (1973) ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON EQUINE ENCEPHALOSIS VIRUS G. LECATSAS, B. J. ERASMUS and H. J. ELS, Veterinary Research Institute, Onderstepoort ABSTRACT
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Transcriptional Analysis for Oral Vaccination of Recombinant Viral Proteins against White Spot Syndrome Virus (WSSV) in Litopenaeus vannamei
 J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2011), 21(2), 170 175 doi: 10.4014/jmb.1005.05036 First published online 26 November 2010 Transcriptional Analysis for Oral Vaccination of Recombinant Viral Proteins against
J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. (2011), 21(2), 170 175 doi: 10.4014/jmb.1005.05036 First published online 26 November 2010 Transcriptional Analysis for Oral Vaccination of Recombinant Viral Proteins against
TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet
 Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Website: thermofisher.com Customer Service (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 1 Technical Support (US): 1 800 955 6288 ext. 441 TSH Receptor Monoclonal Antibody (49) Catalog Number MA3-218 Product data sheet Details
Sampling and evaluation of white spot syndrome virus in commercially important Atlantic penaeid shrimp stocks
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 59: 179 185, 2004 Published June 11 Dis Aquat Org Sampling and evaluation of white spot syndrome virus in commercially important Atlantic penaeid shrimp stocks Robert
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Vol. 59: 179 185, 2004 Published June 11 Dis Aquat Org Sampling and evaluation of white spot syndrome virus in commercially important Atlantic penaeid shrimp stocks Robert
Cellular targets and pathways of yellow head virus infection in lymphoid organ of Penaeus monodon as studied by transmission electron microscopy
 Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 33 (2), 121-127, Mar. - Apr. 2011 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Cellular targets and pathways of yellow head virus infection in lymphoid organ of Penaeus monodon
Songklanakarin J. Sci. Technol. 33 (2), 121-127, Mar. - Apr. 2011 http://www.sjst.psu.ac.th Original Article Cellular targets and pathways of yellow head virus infection in lymphoid organ of Penaeus monodon
Virology. *Viruses can be only observed by electron microscope never by light microscope. The size of the virus: nm in diameter.
 Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody
 Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12
 Diagnostic Microbiology Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12 Electron Microscopy 106 virus particles per ml required for visualization, 50,000-60,000 magnification normally used. Viruses may be detected
Diagnostic Microbiology Identification of Microbes Lecture: 12 Electron Microscopy 106 virus particles per ml required for visualization, 50,000-60,000 magnification normally used. Viruses may be detected
Structural vs. nonstructural proteins
 Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
A Reo-like virus associated with high mortality rates in cultured mud crab, Scylla serrata, in East China
 Diseases in Asian Aquaculture VII A Reo-like virus associated with high mortality rates in cultured mud crab, Scylla serrata, in East China JI-GANG CHEN, JI-FANG YANG, DAN LOU, XIONG JUAN and SONG-YAN
Diseases in Asian Aquaculture VII A Reo-like virus associated with high mortality rates in cultured mud crab, Scylla serrata, in East China JI-GANG CHEN, JI-FANG YANG, DAN LOU, XIONG JUAN and SONG-YAN
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary. y Antigens A. antibodies
 Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(1), 115-119 NOTE Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary y Antigens A ntibodies SHIGEKI YABE, MASAMI MURAKAMI*, KAYOKO MARUYAMA, HIDEKO MIWA,
Endocrine Journal 1995, 42(1), 115-119 NOTE Western Blot Analysis of Rat Pituitar Recognized by Human Antipituitary y Antigens A ntibodies SHIGEKI YABE, MASAMI MURAKAMI*, KAYOKO MARUYAMA, HIDEKO MIWA,
Synthesis of Proteins in Cells Infected with Herpesvirus,
 Proceedings of the National Academy of Science8 Vol. 66, No. 3, pp. 799-806, July 1970 Synthesis of Proteins in Cells Infected with Herpesvirus, VI. Characterization of the Proteins of the Viral Membrane*
Proceedings of the National Academy of Science8 Vol. 66, No. 3, pp. 799-806, July 1970 Synthesis of Proteins in Cells Infected with Herpesvirus, VI. Characterization of the Proteins of the Viral Membrane*
psittaci by Silver-Methenamine Staining and
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 267-271 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 111, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Location of Polysaccharide on Chlamydia psittaci by Silver-Methenamine
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, July 1972, p. 267-271 Copyright 1972 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 111, No. 1 Printed in U.S.A. Location of Polysaccharide on Chlamydia psittaci by Silver-Methenamine
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A
 MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A Specifications and performance P.1 Comparison of the conventional method P.2 Operation methods and composition P.4 Amount of starting sample P.5 Analysis after exosomes
MagCapture Exosome Isolation Kit PS Q&A Specifications and performance P.1 Comparison of the conventional method P.2 Operation methods and composition P.4 Amount of starting sample P.5 Analysis after exosomes
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range
 Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Human HBcAb IgM ELISA kit
 Human HBcAb IgM ELISA kit Catalog number: NR-R10163 (96 wells) The kit is designed to qualitatively detect HBcAb IgM in human serum or plasma. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC PURPOSES
Human HBcAb IgM ELISA kit Catalog number: NR-R10163 (96 wells) The kit is designed to qualitatively detect HBcAb IgM in human serum or plasma. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC PURPOSES
ab Glycated Protein Detection Kit
 Version 1 Last updated 27 July 2017 ab219802 Glycated Protein Detection Kit For the detection of glycated proteins (AGEs) using a simple polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis-based method. This product is
Version 1 Last updated 27 July 2017 ab219802 Glycated Protein Detection Kit For the detection of glycated proteins (AGEs) using a simple polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis-based method. This product is
Immunological Cross-Reactivities of Woodchuck and Hepatitis
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Feb. 1982, p. 752-757 0019-9567/82/020752-06$02.00/0 Vol. 35, No. 2 Immunological Cross-Reactivities of Woodchuck and Hepatitis B Viral Antigens IRVING MILLMAN,* THERESA HALBHERR,
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Feb. 1982, p. 752-757 0019-9567/82/020752-06$02.00/0 Vol. 35, No. 2 Immunological Cross-Reactivities of Woodchuck and Hepatitis B Viral Antigens IRVING MILLMAN,* THERESA HALBHERR,
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
SUPPORTING MATREALS. Methods and Materials
 SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
SUPPORTING MATREALS Methods and Materials Cell Culture MC3T3-E1 (subclone 4) cells were maintained in -MEM with 10% FBS, 1% Pen/Strep at 37ºC in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2. MC3T3 cell differentiation
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Antigenic Analysis of Isolated Polypeptides from Visna Virus
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 1976, p. 1728-1732 Copyright 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 6 Printed in USA. Antigenic Analysis of Isolated Polypeptides from Visna Virus P. D. MEHTA,*
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, June 1976, p. 1728-1732 Copyright 1976 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 13, No. 6 Printed in USA. Antigenic Analysis of Isolated Polypeptides from Visna Virus P. D. MEHTA,*
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
Plasma Membrane Protein Extraction Kit
 ab65400 Plasma Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and sensitive extraction and purification of Plasma Membrane proteins from cultured cells and tissue samples. This product
ab65400 Plasma Membrane Protein Extraction Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and sensitive extraction and purification of Plasma Membrane proteins from cultured cells and tissue samples. This product
Overview of virus life cycle
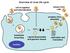 Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
The Structure of Viruses of the Newcastle Disease- Mumps-Influenza (Myxovirus) Group
 680 * VALENTINE, R. C. & ISAACS, A. (1957). J. gen. Microbiol. 16, 680-685 The Structure of Viruses of the Newcastle Disease- Mumps-Influenza (Myxovirus) Group BY R. C. VALENTINE AND A. IsAAcS National
680 * VALENTINE, R. C. & ISAACS, A. (1957). J. gen. Microbiol. 16, 680-685 The Structure of Viruses of the Newcastle Disease- Mumps-Influenza (Myxovirus) Group BY R. C. VALENTINE AND A. IsAAcS National
WSSD. Fenneropenaeus indicus. FAO Food and Agriculture Organization. Aquaculture Alliance. * پست الکترونيک نويسندهي مسؤول:
 * Fenneropenaeus indicus WSSD FAO Food and Agriculture Organization Fenneropenaeus indicus Global GAA Aquaculture Alliance * پست الکترونيک نويسندهي مسؤول: msmohamadi@yahoo.com GAA. japonicus 25 18'59.5"N
* Fenneropenaeus indicus WSSD FAO Food and Agriculture Organization Fenneropenaeus indicus Global GAA Aquaculture Alliance * پست الکترونيک نويسندهي مسؤول: msmohamadi@yahoo.com GAA. japonicus 25 18'59.5"N
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology
 علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
Abstract: During the June until September 2005 two hundred shrimp Penaeus. Delvar and Mond) along the coast of Bushehr province.
 Prevalence of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in the cultured shrimp Penaeus indicus along the coast of Bushehr Province M.afsharnasab 1, A, dashtyannasab 2 and V, yeganeh 2 Email:mafsharnasab@yahoo.com
Prevalence of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) in the cultured shrimp Penaeus indicus along the coast of Bushehr Province M.afsharnasab 1, A, dashtyannasab 2 and V, yeganeh 2 Email:mafsharnasab@yahoo.com
- (SDS-PAGE) (Western blot), TQ93
 42 6 Vol.42, No.6 2011 11 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA Nov., 2011 * ( 361021) - (SDS-PAGE) (Western blot), (Tropomyosin, TM) (Parvalbumin, PV), / ph (SGF), TM, TM, / 10/1, ; ph 5, TM PV (0.33U / g,
42 6 Vol.42, No.6 2011 11 OCEANOLOGIA ET LIMNOLOGIA SINICA Nov., 2011 * ( 361021) - (SDS-PAGE) (Western blot), (Tropomyosin, TM) (Parvalbumin, PV), / ph (SGF), TM, TM, / 10/1, ; ph 5, TM PV (0.33U / g,
ACTG Laboratory Technologist Committee Revised Version 2.0 ACTG Lab Man Coulter HIV-1 p24 ELISA May 21, 2004
 Coulter HIV p24 1. PRINCIPLE The Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) is recognized as the etiologic agent of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). The virus is transmitted by sexual contact,
Coulter HIV p24 1. PRINCIPLE The Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 (HIV-1) is recognized as the etiologic agent of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). The virus is transmitted by sexual contact,
Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy uridine in Human Lymphoblastoid Cells F ro m a Rhabdom yosarcom a*
 A n n a ls o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, No. 6 Copyright 1973, Institute for Clinical Science Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy
A n n a ls o f C l i n i c a l L a b o r a t o r y S c i e n c e, Vol. 3, No. 6 Copyright 1973, Institute for Clinical Science Epstein-Barr Virus: Stimulation By 5 '-Iododeoxy uridine or 5 '-Brom odeoxy
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto, Canada *For correspondence:
 Zymogram Assay for the Detection of Peptidoglycan Hydrolases in Streptococcus mutans Delphine Dufour and Céline M. Lévesque * Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Zymogram Assay for the Detection of Peptidoglycan Hydrolases in Streptococcus mutans Delphine Dufour and Céline M. Lévesque * Dental Research Institute, Faculty of Dentistry, University of Toronto, Toronto,
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES
 STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
H5N1 ( Avian Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA Pair Set
 H5N1 ( Avian Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK002 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
H5N1 ( Avian Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK002 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Short communication. C W Tung, C S Wang and S N Chen
 Short communication Histological and electron microscopic study on Macrobrachium muscle virus (MMV) infection in the giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man), cultured in Taiwan C W Tung,
Short communication Histological and electron microscopic study on Macrobrachium muscle virus (MMV) infection in the giant freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium rosenbergii (de Man), cultured in Taiwan C W Tung,
Experimental challenge of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) From Polychaete Pereneris cultifera To Peppermint shrimp Lysmata wurdemanni in captivity
 Experimental challenge of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) From Polychaete Pereneris cultifera To Peppermint shrimp Lysmata wurdemanni in captivity M.Nirosh Banu 1, Centre of Advanced Study in Marine Biology,
Experimental challenge of white spot syndrome virus (WSSV) From Polychaete Pereneris cultifera To Peppermint shrimp Lysmata wurdemanni in captivity M.Nirosh Banu 1, Centre of Advanced Study in Marine Biology,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Nair S, Branagan AR, Liu J, Boddupalli CS, Mistry PK, Dhodapkar
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Nair S, Branagan AR, Liu J, Boddupalli CS, Mistry PK, Dhodapkar
Influenza or flu is a
 Clinical and Research Area Infectious Diseases Influenza Virus Types A and B Influenza or flu is a respiratory illness that is caused by influenza viruses. Influenza viruses type A and type B cause seasonal
Clinical and Research Area Infectious Diseases Influenza Virus Types A and B Influenza or flu is a respiratory illness that is caused by influenza viruses. Influenza viruses type A and type B cause seasonal
Genomic Alterations Associated with Persistent Infections by Equine Infectious Anaemia Virus, a Retrovirus
 J. gen. Virol. (1984), 65, 1395-1399. Printed in Great Britain 1395 Key words: EIA V/retrovirus persistence~antigenic variation/oligonucleotide mapping Genomic Alterations Associated with Persistent Infections
J. gen. Virol. (1984), 65, 1395-1399. Printed in Great Britain 1395 Key words: EIA V/retrovirus persistence~antigenic variation/oligonucleotide mapping Genomic Alterations Associated with Persistent Infections
Purification and Fluorescent Labeling of Exosomes Asuka Nanbo 1*, Eri Kawanishi 2, Ryuji Yoshida 2 and Hironori Yoshiyama 3
 Purification and Fluorescent Labeling of Exosomes Asuka Nanbo 1*, Eri Kawanishi 2, Ryuji Yoshida 2 and Hironori Yoshiyama 3 1 Graduate School of Medicine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan; 2 Graduate
Purification and Fluorescent Labeling of Exosomes Asuka Nanbo 1*, Eri Kawanishi 2, Ryuji Yoshida 2 and Hironori Yoshiyama 3 1 Graduate School of Medicine, Hokkaido University, Sapporo, Japan; 2 Graduate
Shotgun Identification of Structural Proteome of Shrimp White Spot Syndrome. Virus and itraq Differentiation of Envelope and Nucleocapsid Subproteomes
 MCP Papers in Press. Published on June 2, 2007 as Manuscript M600327-MCP200 Shotgun Identification of Structural Proteome of Shrimp White Spot Syndrome Virus and itraq Differentiation of Envelope and Nucleocapsid
MCP Papers in Press. Published on June 2, 2007 as Manuscript M600327-MCP200 Shotgun Identification of Structural Proteome of Shrimp White Spot Syndrome Virus and itraq Differentiation of Envelope and Nucleocapsid
Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus
 244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
244 STOKER, M. G. P., SMITH, K. M. & Ross, R. W. (1958). J. gen. Microbiol. 19,244-249 Electron Microscope Studies of HeLa Cells Infected with Herpes Virus BY M: G. P. STOKER, K. M. SMITH AND R. W. ROSS
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL Purification and biochemical properties of SDS-stable low molecular weight alkaline serine protease from Citrullus Colocynthis Muhammad Bashir Khan, 1,3 Hidayatullah khan, 2 Muhammad
Anthrax protective antigen IgG ELISA Kit
 Anthrax protective antigen IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0953 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3
Anthrax protective antigen IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0953 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 16207 Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 3 ARTICLE NUMBER: 16207 Clay nanosheets for topical delivery of RNAi for sustained protection against plant viruses
Mengovirus Virions. growth (48-h cultures) were infected with a. cell at a density of 107 cells per ml of ABM42-
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 1977, p. 1256-1261 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 21, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Factors Affecting Composition and Thermostability of Mengovirus Virions CLIFFORD
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, Mar. 1977, p. 1256-1261 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 21, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Factors Affecting Composition and Thermostability of Mengovirus Virions CLIFFORD
Viruses. Picture from:
 Viruses Understand the structure of bacteriophages & human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Appreciate that viruses replicate in host cells (thereby destroying them) Picture from: http://eands.caltech.edu/articles/lxvii1/viruses.html
Viruses Understand the structure of bacteriophages & human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Appreciate that viruses replicate in host cells (thereby destroying them) Picture from: http://eands.caltech.edu/articles/lxvii1/viruses.html
PEG Virus Precipitation Kit
 ab102538 PEG Virus Precipitation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate purification of viruses in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for
ab102538 PEG Virus Precipitation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate purification of viruses in various samples This product is for research use only and is not intended for
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates
 HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
HIV-1 Virus-like Particle Budding Assay Nathan H Vande Burgt, Luis J Cocka * and Paul Bates Department of Microbiology, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, USA
Summary and Conclusions
 s The present investigation has been designed to identify the various endemic diseases and their control measure prevailing in selected cultured shrimps, L. vannamei.and P. monodon. The study has envisaged
s The present investigation has been designed to identify the various endemic diseases and their control measure prevailing in selected cultured shrimps, L. vannamei.and P. monodon. The study has envisaged
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set
 Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
White Spot Disease in Mozambique
 White Spot Disease in Mozambique Experiences and lessons learned A.P. BALOI (1), M. LE GROUMELLEC (2) (1) Ministry of Fisheries, National Institute for Fish Inspection, Mozambique. (2) OIE Consultant on
White Spot Disease in Mozambique Experiences and lessons learned A.P. BALOI (1), M. LE GROUMELLEC (2) (1) Ministry of Fisheries, National Institute for Fish Inspection, Mozambique. (2) OIE Consultant on
Norovirus Report. Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report
 Norovirus Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Introduction Norovirus is the leading cause of non-bacterial
Norovirus Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Can copper and silver ionisation kill norovirus? A Study Report Introduction Norovirus is the leading cause of non-bacterial
Monodon baculovirus from Australia: ultrastructural observations
 DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org Published February 9 Monodon baculovirus from Australia: ultrastructural observations 'Department of Microbiology, 'Department of Parasitology and 3Centre for
DISEASES OF AQUATIC ORGANISMS Dis Aquat Org Published February 9 Monodon baculovirus from Australia: ultrastructural observations 'Department of Microbiology, 'Department of Parasitology and 3Centre for
DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL
 DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL Background and Introduction SPERM HY-LITER is the first immunofluorescent
DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL Background and Introduction SPERM HY-LITER is the first immunofluorescent
