The exact origin, locations, and natural habi- Ebola virus remain unknown. However, on
|
|
|
- Rhoda Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article International Ayurvedic Medical Journal ISSN: EBOLA HEMMORHAGIC FEVER- PROBABLE MULTIDIMENSIONAL AYURVEDIC CORELATION KamathNagaraj 1 Patel Yashesh 2 Kulkarni Pratibha 3 1,2 P.G.Scholar, 3 AssociateProfessorandHead, Department of ShareeraKriya, Sri DharmasthalaManjuna- theshwara College of Ayurveda& Hospital, Hassan , Karnataka, India ABSTRACT EHF is believed to occur after an Ebola virus is transmitted to an initial human by contact with an infected animal's body fluids. Human-to-human transmission can occur via direct contact with blood or bodily fluids from an infected person. The onset of illness is abrupt and is charac- swallow- terized by fever, headache, joint and muscle aches, sore throat, difficulty in breathing, ing, hiccups, and weakness, followed by diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain.more severe symptoms, such as Coagulopathywith thrombocytopenia, leading to bleeding from the nasal or oral cavities, along with hemorrhagic skin blisters.bleeding into the skin may create petechiae, purpura, ecchymoses, and hematomas. Development of renal failure leading to multisystem orapplicable in dif- gan failure and leads to death. Various concepts are dealt in Ayurveda which is ferent conditions. Among those concepts there are some of the concepts which are related to dis- NidanarthakaraRoga,Raktapitta,, EkadashaRupiRajayakshma, RaktastiviSannipataJwara, Dha- ease aspects as well. Few of the concepts relevant in this context are: SankramikaRogaNidana, tugatajwara. Ebola Hemorrhagic fever conceptually can be related tovyadhisankara. Mode of Transmission of Ebola Hemorrhagic fevercan be related tosankramikaroganidana. Mode of progress of disease can be related to dhatugatajwarain Rasa-Asthi- Rakta- ShukraGataJwarase- quence and NidanaArthakaraRoga. Considering signs and symptoms of Ebola Hemorrhagic fev- types er it can be related to acute exagerbation ofekadasharupirajayakshma, Raktapittadifferent andraktastivisannipatajwara.concept mentioned in Ayurveda- If a disease is caused due to strong or many etiological factors and the signs and symptoms are fully and severely manifested then it will lead to loss of consciousness, orientation and kill the patient can be related to severi- ty, fatality of Ebola Hemorrhagic fever. na, Lakshana, Ayurveda. Key words: Ebola, Sankraman INTRODUCTION Ebola hemorrhagic fever(ehf) is a severe, often-fatal disease in humans and nonhuman primates (monkeys, gorillas, and chimpanzees) that has appeared sporadically since its initial recognition in The disease is caused by infection with Ebola virus, named after a river in the Democratic Re- public of the Congo (formerly Zaire) in Africa, where it was first recognized. The virus is one of two members of a family of RNA viruses called the Filoviridae. There are five identified subtypess of Ebola virus. Four of the five have caused disease in hu- Ebola- mans: Ebola-Zaire, Ebola-Sudan, Ivory Coast and Ebola-Bundibugyo. The fifth, Ebola-Reston, has caused disease in nonhuman primates, but not in humans.[1] The exact origin, locations, and natural habi- reservoir") of tat (known as the "natural Ebola virus remain unknown. However, on
2 794 the basis of available evidence and the nature of similar viruses, researchers believe that the virus is zoonotic (animal-borne) with four of the five subtypes occurring in an animal host native to Africa. A similar host, most likely in the Philippines, is probably associated with the Ebola-Reston subtype, which was isolated from infected cynomolgous monkeys that were imported to the United States and Italy from the Philippines. The virus is not known to be native to other continents, such as North America.[2] Confirmed cases of Ebola hemorrhagic fever have been reported in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Gabon, Sudan, the Ivory Coast, Uganda, and the Republic of the Congo. No case of the disease in humans has ever been reported in the United States. Ebola-Reston virus caused severe illness and death in monkeys imported to research facilities in the United States and Italy from the Philippines; during these outbreaks, several research workers became infected with the virus, but did not become ill. Ebola hemorrhagic fever typically appears in sporadic outbreaks, usually spread within a healthcare setting (a situation known as amplification). It is likely that sporadic, isolated cases occur as well, but go unrecognized. Previous Ebola outbreaks have seen fatality rates as high as 90%. [3] Mode of transmission of Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever EHF is believed to occur after an Ebola virus is transmitted to an initial human by contact with an infected animal's body fluids. Human-to-human transmission can occur via direct contact with blood or bodily fluids from an infected person (including embalming of an infected dead person) or by contact with contaminated medical equipment, particularly needles and syringes.semen is infectious in survivors for up to 50 days. Transmission through oral exposure and through conjunctiva exposure is likely. Ebola virus incubates in infected humans for 2-21 days, with the majority of patients becoming symptomatic after 8-9 days. Once infected, patients can experience severe symptoms within 1-2 days.[4] Early signs and symptoms of Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever The onset of illness is abrupt and is characterized by fever, headache, joint and muscle aches, sore throat, difficulty in breathing, swallowing, hiccupsand weakness, followed by diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain.[5] Second stage signs and symptoms of Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever More severe symptoms, such as - Coagulopathy with thrombocytopenia, can develop in as soon as hours, leading to bleeding from the nasal or oral cavities, along with hemorrhagic skin blisters.bleeding into the skin may create petechiae, purpura, ecchymoses, and hematomas(especially around needle injection sites). Heavy bleeding is rare and is usually confined to the gastrointestinal tract.[6] Late stage of Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever The development of renal failure, leading to multisystem organ failure along with disseminated intravascular coagulation, can then rapidly ensue over 3-5 days, along with significant volume loss.patients who develop a fulminant course often die within 8-9 days. Those who survive beyond 2 weeks have a better prognosis for survival. In general, the development of bleeding symptoms often indicates a worse prognosis and this blood loss can result in death.all people infected show some symptoms of circulatory system involvement, including impaired blood clotting. If the infected per-
3 795 son does not recover, death due to multiple organ dysfunction syndrome occurs within 7 to 16 days (usually between days 8 and 9) after first symptoms.patients who develop a fulminant course often die within 8-9 days. Those who survive beyond 2 weeks have a better prognosis for survival.[7] Ayurveda: Ayurveda is considered as the science of life. In the history of Ayurveda it is mentioned that PunarvasuAtreyataught the knowledge of Ayurveda to his six disciples. Among them Agnivesha composed a treatise known as AgniveshaTantrawhich is later recomposed by Charakaand popularly known as CharakaSamhita. It is being told that whatever is there in this Samhita is everywhere and at the same time what is not there in this Samhitais not found elsewhere.[8] The knowledge of other Tantras is a mere waste if he has not studied SushruthaSamhita, at the same time who has not gone through CharakaSamhitacannot be a successfulvaidya(physician). It refers that- to become auttamavaidyaone should be well versed in all disciplines of Ayurveda. [9]Various concepts are dealt in Ayurveda which is applicable in different conditions. Among those concepts there are some of the concepts which are related to disease aspects as well. Few of the concepts relevant in this context are mentioned below: Many diseases may have one common manifestation; like Jwara is the common manifestation seen in many diseases. Many diseases have many manifestations; like other features than Jwara, in this example. One disease may have one manifestation like in JwaraShareeraManaTapa might be the only manifestation. One disease may have many manifestations like other Linga and Upadrava in case of Jwara. This concept of Ayurveda is considered as VyadhiSankara.[10] The same concept can be applied in case of etiological factors. Many etiological factors can cause one disease or can cause many diseases; one etiological factor may cause one disease or may cause many diseases. This concept of Ayurvedais considered as Hetusankara.[11] Sexual Intercouse, close body contact, via breathe, via various bodily secretions, by using clothings, utilization of siiting, sleeping place of diseased person all these are the etiological factors for SankramikaRoga like Kusta, Jwara, Sosha, Netrabhishyanda.[12]The concept of Janapadodwamsa also should be considered via Jala, Desha, Kala factors. The concept of NidanaArthakarRogais a unique concept of Ayurveda. For example- Jwara will lead to the disease Raktapitta, Raktapittamay lead to Jwara and it may lead to Sosha and finally death.[13] In RasagataJwara features like pyrexia, Myalgia, excessive yawning may be present.in AsthidhatugataJwara there will be body pain, restlessness, breathing difficulty. In RaktadhatugataJwara features like petechie, excessive thirst, hemoptysis, burning sensation, discolouration, impaired orientation and conciousness etc are seen.[14] Raktapitta is a disease in which blood will be coming from external orifices. In case of UrdwagaRaktapitta blood comes out from mouth, eyes etc. In AdhogaRaktapittablood comes out through Guda, Mutramarga. In TiryagataRaktapittablood tends to come out of Romakupa.[15] The features of EkadashaRupiRajayakshma features are heaviness in head, soar throat, cough, breathing difficulty, diarrhea, backpain, myalgia, tastelessness, sputum, hemoptysis.[16]
4 796 In RaktaStiviSannipaJwara features like blood coming out of mouth fever, vomiting, excessive thirst, confusion, pain, loosemotion, hiccup, distention of abdomen, giddiness, burning sensation in eyes, breathing difficulty, unconsciousness, blackish red discoloration of tongue with petechie.[17] If a disease is caused due to strong or many etiological factors and the signs and symptoms are fully and severely manifested then it will lead to loss of consciousness, orientation and kill the patient.[18] If the DoshicJwara is being manifested with all its features as mentioned then it will kill the individual in seven, ten, twelve days in case of Vataja, Pittaja, KaphajaJwara respectively and the major features observed will be inappropriate talking, giddiness, breathing difficulty respectively.[19] AIMS & OBJECTIVES To critically analyze the concepts of Ayurveda in relation to ebola hemorrhagic fever. MATERIALS & METHODS The Ebola hemorrhagic fever was studied from modern medical text books and from internet sources. Later the BruhatTrayiand other classical text books ofayurvedawere scrutinised regarding the references for the various disease conditions and various concepts regarding disease. Later, supportive correlation was done between Ayurvedic and modern views to build valid and reliable hypothesis regarding the concepts of Ayurvedain relation to ebola hemorrhagic fever. one manifestation like in Jwara- Shareera,ManaTapa might be the only manifestation. One disease may have many manifestations like other Linga and Upadrava in case of Jwara. Mode of Transmission: Human-to-human transmission can occur via direct contact with blood or bodily fluids from an infected person (including embalming of an infected dead person) or by contact with contaminated medical equipment, particularly needles and syringes. This can be related to SankramikaRogaNidana - Sexual Intercouse, close body contact, via breathe, via various bodily secretions, by using clothings, utilization of siiting, sleeping place of diseased person all these are the etiological factors for SankramikaRoga like Kusta, Jwara, Sosha, Netrabhishyanda. Mode of Progress of disease: The onset of illness is abrupt and is characterized by fever, headache, joint and muscle aches, sore throat, difficulty in breathing, swallowing, hiccups,and weakness, followed by diarrhea, vomiting, and stomach pain.more severe symptoms, such as - Coagulopathy with thrombocytopenia, can develop in as soon as hours, leading to bleeding from the nasal or oral cavities, along with hemorrhagic skin blisters.bleeding into the skin may create petechiae, purpura, ecchymoses, and hematomas. Development of renal failure leading to multisystem organ failure and leads to death. The first stage signs and symptoms can be related to RasagataJwaraand AsthigataJwaraLakshana. The second stage signs and symptoms can be related to RaktagataJwaraLakshana. Last stage where death occurs can be related to ShukragataJwaraLakshana. The other concept which can be related to mode of progress of Ebola hemorrhagic fev- DISCUSSION Conceptual: In Ebola hemorrhagic fever initially there will be symptoms of fever followed by coagulopathy, later will cause superseded bacterial etc infections multiple organ failure and death. Conceptually this can be related to the concept of Vyadhisankara of Ayurveda. One disease may have
5 er is the concept of NidanaArthakaraRoga. Considering the progress of the disease it can be related to NidanaRogaKaratva of Rakta-Pitta to Jwara or viceversa leading to Sosha and then Marana. Signs and symptoms of disease: Even though if a disease is chronic in nature, if the Hetu(etiological factor) is Balavan then VyadhiBala will be Balavan leading to acute exagerbation of features rather than chronic; Yakshma is considered as Rogasamuha(group of diseases). Considering all the signs and symptoms of the Ebola hemorrhagic fever and the above two aspects it can be considered as the state of EkadashaRupi- Rajayakshma with acute exacerbation. Considering one of the major sign i.e. bleeding from orifices and petechie it can be related to Ubhayaga and TiryagaRaktapitta as per the condition. It can be also related toraktastivisannipajwara - features like blood coming out of mouth fever, vomiting, excessive thirst, confusion, pain, loosemotion, hiccup, distention of abdomen, giddiness, burning sensation in eyes, breathing difficulty, unconsciousness, blackish red discoloration of tongue with petechie will be present and the same features are even seen in Ebola hemorrhagic fever. Fatality-Prognosis: Ebola hemorrhagic fever outbreaks are having the fatality rates of 90%. Those who survive beyond 2 weeks have a better prognosis for survival. This two aspects of Ebola hemorrhagic fever can be related to following concept mentioned in Ayurveda- If a disease is caused due to strong or many etiological factors and the signs and symptoms are fully and severely manifested then it will lead to loss of consciousness, orientation and kill the patient. The concept of Janapadodwamsa also should be considered via Jala, Desha, Kala factors CONCLUSION Ayurveda is considered as the science of life.it is being told that whatever is there in this Samhita is everywhere and at the same time what is not there in this Samhitais not found elsewhere. Various concepts are dealt in Ayurveda which is applicable in different conditions. Among those concepts there are some of the concepts which are related to disease aspects as well. Few of the concepts relevant in this context are: SankramikaRogaNidana, NidanarthakaraRoga,Raktapitta, EkadashaRupiRajayakshma, RaktastiviSannipataJwara, DhatugataJwara. Ebola Hemorrhagic fever conceptually can be related tovyadhisankara. Mode of Transmission of Ebola Hemorrhagic fevercan be related tosankramikaroganidana. Mode of progress of disease can be related to dhatugatajwarain Rasa-Asthi- Rakta- ShukraGataJwarasequence and NidanaArthakaraRoga. Considering signs and symptoms of Ebola Hemorrhagic fever it can be related to acute exagerbation ofekadasha- RupiRajayakshma, Raktapittadifferent types andraktastivisannipatajwara.concept mentioned in Ayurveda- If a disease is caused due to strong or many etiological factors and the signs and symptoms are fully and severely manifested then it will lead to loss of consciousness, orientation and kill the patient can be related to severity, fatality of Ebola Hemorrhagic fever. Even the concept of Janapadodwamsa can be considered in this context REFERENCES 1. Bwaka, M.A., Bonnet, M.J.,Calain, P.et,al.Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever in Kikwit, Democratic Republic of the Congo (formerly Zaire): Clinical Obser- 797
6 798 vations in 103 Patients. J Infect Dis. 1999; 179 (suppl 1): S1 - S7. 2. Centers for Disease Control. Outbreak of Ebola viral hemorrhagic fever--zaire, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 1995; 44(19): Centers for Disease Control. Update: Outbreak of Ebola viral hemorrhagic fever Zaire, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 1995; 44(19): Centers for Disease Control. Ebola- Reston virus infection among quarantined non-human primates. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 1996; 45: Centers for Disease Control. Management of patients with suspected viral hemorrhagic fever. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 1998; 37 (suppl 3): Dalgard, D., J.Y. Baumgardner, C.W. Armstrong, S.R. Jenkins, C.D. Woolard, G.B. Miller, Jr., P.B. Jahrling, T.G. Ksiazek, E.D. Johnson, and C.J. Peters. Ebola virus infection in imported primates, Virginia, Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report. 1989; 38(48): Dalgard, D.W., R.J. Hardy, S.L. Pearson, G.J. Pucak, R.V. Quander, P.M. Zack, C.J. Peters, and P.B. Jahrling. Combined simian hemorrhagic fever and Ebola virus infection in cynomolgus monkeys. Lab. Anim. Sci. 1992; Apr:42(2): Leela k. VaidyakeeyaSubhashita sahitya.3 rd edition.mysore(india): Vidyut Prakashana;2004.p Leela k. VaidyakeeyaSubhashita sahitya.3 rd edition.mysore(india): Vidyut Prakashana;2004.p Acharya JT. CharakaSamhita with Acharya JT. CharakaSamhita with Acharya JT. SusruthaSamhita with Nibandhasangraha commentary of Dalhana. Chaukambha Sanskrit Sansthan; p Acharya JT. CharakaSamhita with Acharya JT. CharakaSamhita with Acharya JT. CharakaSamhita with Acharya JT. CharakaSamhita with Sharma Krishna(ed). Yogaratnakara.1 st edition.nirnayasagar press;1908.p Acharya JT. CharakaSamhita with Acharya JT. CharakaSamhita with 403. CORRESPONDING AUTHOR Dr Kamath Nagaraj P.G.Scholar,Department of ShareeraKriya, Sri DharmasthalaManjunatheshwara College of Ayurveda& Hospital, Hassan , Karnata nagaraj.kamath1989@gmail.com
UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October EMS TB Ebola Virus Disease (EVD)
 UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October 2014 EMS TB 14-006 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Purpose: 1. To inform & provide management recommendations to UTSW/BioTel EMS System EMS Providers about Ebola Virus
UTSW/BioTel EMS TRAINING BULLETIN October 2014 EMS TB 14-006 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Purpose: 1. To inform & provide management recommendations to UTSW/BioTel EMS System EMS Providers about Ebola Virus
Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Essential information
 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Essential information Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Origins The Ebola virus is named after the Ebola River in what was Zaire (now Democratic Republic of Congo) where the first outbreak
Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Essential information Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Origins The Ebola virus is named after the Ebola River in what was Zaire (now Democratic Republic of Congo) where the first outbreak
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers
 Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs) http://www.ncrr.nih.gov/publications/ncrr_reporter/summer-fall2009/images/essential_2.jpg Definition Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) refer to a group of illnesses that are
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers (VHFs) http://www.ncrr.nih.gov/publications/ncrr_reporter/summer-fall2009/images/essential_2.jpg Definition Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) refer to a group of illnesses that are
Ebola Virus Patient Advisory
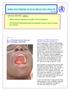
 22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
22 September 2014 Ebola Virus Patient Advisory Introduction Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly
Ebola Virus Introduction
 Ebola Ebola Virus Introduction First appeared in Africa 1976 African Hemorrhagic Fever acute, mostly fatal disease causes blood vessel bursting systemic (all organs/tissues) humans and nonhuman primates
Ebola Ebola Virus Introduction First appeared in Africa 1976 African Hemorrhagic Fever acute, mostly fatal disease causes blood vessel bursting systemic (all organs/tissues) humans and nonhuman primates
Ebola Virus Disease. Global Epidemiology and Surveillance in Hong Kong. as of 13 August 2014
 Ebola Virus Disease Global Epidemiology and Surveillance in Hong Kong as of 13 August 2014 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Ebola virus disease (EVD), (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe,
Ebola Virus Disease Global Epidemiology and Surveillance in Hong Kong as of 13 August 2014 Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) Ebola virus disease (EVD), (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe,
An Outbreak of Hemorrhagic Fever in Africa
 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Case Studies in Applied Epidemiology No. 812-N10 An Outbreak of Hemorrhagic Fever in Africa Student s Guide Learning Objectives After completing this case study,
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Case Studies in Applied Epidemiology No. 812-N10 An Outbreak of Hemorrhagic Fever in Africa Student s Guide Learning Objectives After completing this case study,
VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVER (VHF)
 VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVER (VHF) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive laboratory result to the local public health department where
VIRAL HEMORRHAGIC FEVER (VHF) REPORTING INFORMATION Class A: Report immediately via telephone the case or suspected case and/or a positive laboratory result to the local public health department where
The Ebola Virus. By Emilio Saavedra
 The Ebola Virus By Emilio Saavedra Etiological Agents: Ebolavirus is the etiologic agent. [1] There are four main families of viruses that are agents of Ebola (hemorrhagic fever). [1] These four families
The Ebola Virus By Emilio Saavedra Etiological Agents: Ebolavirus is the etiologic agent. [1] There are four main families of viruses that are agents of Ebola (hemorrhagic fever). [1] These four families
WHO SOUTHERN SUDAN HEALTH UPDATE May 2004
 WHO SOUTHERN SUDAN HEALTH UPDATE SPECIAL EDITION: EBOLA Ebola outbreak confirmed in Yambio, Western Equatoria World Health Organization leads international response team to contain the outbreak Photo by:
WHO SOUTHERN SUDAN HEALTH UPDATE SPECIAL EDITION: EBOLA Ebola outbreak confirmed in Yambio, Western Equatoria World Health Organization leads international response team to contain the outbreak Photo by:
Media centre Ebola virus disease
 1 of 6 10/15/2014 10:59 AM Media centre Ebola virus disease Fact sheet N 103 Updated September 2014 Key facts Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal
1 of 6 10/15/2014 10:59 AM Media centre Ebola virus disease Fact sheet N 103 Updated September 2014 Key facts Ebola virus disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever, is a severe, often fatal
Summary of current outbreak in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone
 ALERT TO HEALTHCARE WORKERS: EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE OUTBREAK IN GUINEA, LIBERIA AND SIERRA LEONE, WEST AFRICA 04 April 2014 Summary of current outbreak in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone In this update and
ALERT TO HEALTHCARE WORKERS: EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE OUTBREAK IN GUINEA, LIBERIA AND SIERRA LEONE, WEST AFRICA 04 April 2014 Summary of current outbreak in Guinea, Liberia and Sierra Leone In this update and
saipem Ebola virus diseases EVD August 2014
 Ebola virus diseases EVD August 2014 Why Ebola generates such fear? Ebola is one of the world's most deadly diseases. It can kill up to 90% of people who developed Ebola virus disease. There is not treatment
Ebola virus diseases EVD August 2014 Why Ebola generates such fear? Ebola is one of the world's most deadly diseases. It can kill up to 90% of people who developed Ebola virus disease. There is not treatment
12 June The average EVD case fatality rate has been around 50 per cent.
 12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
12 June 2015 Ebola virus was first identified in Sudan and Zaire in 1976. It belongs to the family of Filoviridae. It causes Ebola Virus Disease (EVD), formerly known as Ebola Hemorrhagic Fever. EVD is
EBOLA. Harford County Health Department October 22, 2014
 EBOLA Harford County Health Department October 22, 2014 Zaire ebolvirus The 2014 Ebola outbreak concerns the most deadly of the five Ebola viruses, Zaire ebolvirus, which has killed 79 percent of the people
EBOLA Harford County Health Department October 22, 2014 Zaire ebolvirus The 2014 Ebola outbreak concerns the most deadly of the five Ebola viruses, Zaire ebolvirus, which has killed 79 percent of the people
Ebola Virus Disease: the Facts, Response & the Way Forward. Dr. Abraham Idokoko Ebola Emergency Operations Centre (EEOC), Lagos.
 Ebola Virus Disease: the Facts, Response & the Way Forward. Dr. Abraham Idokoko Ebola Emergency Operations Centre (EEOC), Lagos. 2 Yearly trend of Emergence of New Infectious Diseases Globally, an average
Ebola Virus Disease: the Facts, Response & the Way Forward. Dr. Abraham Idokoko Ebola Emergency Operations Centre (EEOC), Lagos. 2 Yearly trend of Emergence of New Infectious Diseases Globally, an average
Ebola Virus Disease(EVD)
 Yemeni International Congress of Infectious Diseases 16-18 December 2014 University of Science & Technology Hospital Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences Ebola Virus Disease(EVD) Presented by: Dr Ahmed
Yemeni International Congress of Infectious Diseases 16-18 December 2014 University of Science & Technology Hospital Faculty of Medicine & Health Sciences Ebola Virus Disease(EVD) Presented by: Dr Ahmed
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES WITH GLOBAL IMPACT
 Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education on
Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE credits click on Earn CE Credits under Continuing Education on
EBOLA VIRUS AWARENESS
 EBOLA VIRUS AWARENESS Yvonne S. Butler, MD Assistant Professor; Obstetrics and Gynecology Global Women s Health Program Liberia Chevron-Liberia / BIPAI Partnership Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children
EBOLA VIRUS AWARENESS Yvonne S. Butler, MD Assistant Professor; Obstetrics and Gynecology Global Women s Health Program Liberia Chevron-Liberia / BIPAI Partnership Baylor College of Medicine Texas Children
CE Unit. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
Genus Ebolavirus is 1 of 3 members of the Filoviridae family (filovirus), along with genus Marburgvirus and genus Cuevavirus.
 EBOLA VIRUS Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a severe, often fatal illness, with a case fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most virulent diseases.the infection is transmitted by direct contact
EBOLA VIRUS Ebola virus disease (EVD) is a severe, often fatal illness, with a case fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most virulent diseases.the infection is transmitted by direct contact
Ebola Virus Transmission
 Ebola Virus Zoonotic virus bats the most likely reservoir, although species unknown Spillover event from infected wild animals (e.g., fruit bats, monkey, duiker) to humans, followed by human-human transmission
Ebola Virus Zoonotic virus bats the most likely reservoir, although species unknown Spillover event from infected wild animals (e.g., fruit bats, monkey, duiker) to humans, followed by human-human transmission
Making Sense Of The Ebola Virus
 Fodder for young minds Making Sense Of The Ebola Virus By Meera Dolasia on September 29, 2014 CCSS NAS-6 Grades: 5-8 Word Search Every few years, a new pandemic hits the globe and sends shivers down everyone's
Fodder for young minds Making Sense Of The Ebola Virus By Meera Dolasia on September 29, 2014 CCSS NAS-6 Grades: 5-8 Word Search Every few years, a new pandemic hits the globe and sends shivers down everyone's
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens. Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM
 Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Viruses: Select Agents and Emerging Pathogens Patricia Bolívar MS., CLS, PHM Objectives Review Select Agent Viruses. Key features to recognize Smallpox virus Update on emerging Viruses of possible pandemic
Questions and Answers on Ebola
 Updated: August 26, 2014 The 2014 Ebola outbreak is the largest Ebola outbreak in history and the first in West Africa. The current outbreak is affecting four countries in West Africa: Guinea, Liberia,
Updated: August 26, 2014 The 2014 Ebola outbreak is the largest Ebola outbreak in history and the first in West Africa. The current outbreak is affecting four countries in West Africa: Guinea, Liberia,
Key Points Ebola Virus Disease, West Africa Newly updated information is indicated in red
 Key Points Ebola Virus Disease, West Africa Newly updated information is indicated in red In this document: Summary Key Messages Ebola Cases and Deaths (West Africa) Ebola in U.S. Health Workers (in Liberia)
Key Points Ebola Virus Disease, West Africa Newly updated information is indicated in red In this document: Summary Key Messages Ebola Cases and Deaths (West Africa) Ebola in U.S. Health Workers (in Liberia)
EBOLA INFORMATION KIT 20 to 26 October 2014 MEMBERS NEWS HUNTING SERVICES FUND LEGISLATION CALENDAR GENERAL SHOP POPULAR ARTICLES
 HOME ABOUT PHASA MEMBERS NEWS HUNTING SERVICES FUND LEGISLATION CALENDAR GENERAL SHOP DOWNLOAD: PROFESSIONAL HUNTER STATUS SECTION 16A (click to download) DOWNLOADS NEWSLETTERS F.A.Q TWITTER FACEBOOK Home
HOME ABOUT PHASA MEMBERS NEWS HUNTING SERVICES FUND LEGISLATION CALENDAR GENERAL SHOP DOWNLOAD: PROFESSIONAL HUNTER STATUS SECTION 16A (click to download) DOWNLOADS NEWSLETTERS F.A.Q TWITTER FACEBOOK Home
U.S. and British troops head to West Africa to help fight Ebola virus
 U.S. and British troops head to West Africa to help fight Ebola virus By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff - Sept. 09, 2014 1 2 3 4 To slow down the spread of the deadly virus Ebola, the United
U.S. and British troops head to West Africa to help fight Ebola virus By Los Angeles Times, adapted by Newsela staff - Sept. 09, 2014 1 2 3 4 To slow down the spread of the deadly virus Ebola, the United
Modeling the Effects of Policy Changes on the Spread of Ebola New Mexico Final Report April 5, 2016 Team#: 112 Saturday Science and Math Academy Team
 Modeling the Effects of Policy Changes on the Spread of Ebola New Mexico Final Report April 5, 2016 Team#: 112 Saturday Science and Math Academy Team Members: Joaquín Madrid Larrañaga Malcolm Tatum Teachers:
Modeling the Effects of Policy Changes on the Spread of Ebola New Mexico Final Report April 5, 2016 Team#: 112 Saturday Science and Math Academy Team Members: Joaquín Madrid Larrañaga Malcolm Tatum Teachers:
Acute respiratory illness This is a disease that typically affects the airways in the nose and throat (the upper respiratory tract).
 Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
CE Unit 7. Viruses and Vaccines
 CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
CE Unit 7 Viruses and Vaccines DO NOT WRITE What is a virus? Have you ever had a virus? What is a vaccine? How is a virus different from bacteria? What are the deadliest viruses? 10. Dengue fever 50 million
EBOLA FACTS. During this outbreak, most of the disease has spread through human-to-human transmission.
 EBOLA FACTS Ebola virus disease (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe and often fatal illness, with a fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most dreaded diseases. However,
EBOLA FACTS Ebola virus disease (formerly known as Ebola haemorrhagic fever) is a severe and often fatal illness, with a fatality rate of up to 90%. It is one of the world s most dreaded diseases. However,
Marburg virus disease
 Marburg virus disease Fact sheet available at http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs_marburg/en/ Updated 20 October 2017 Key facts Marburg virus disease (MVD), formerly known as Marburg haemorrhagic
Marburg virus disease Fact sheet available at http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs_marburg/en/ Updated 20 October 2017 Key facts Marburg virus disease (MVD), formerly known as Marburg haemorrhagic
Ebola. Wessex CPD Event 14/11/14. Dr Ishani Kar-Purkayastha, CCDC, Wessex PHE Centre Tel:
 Ebola Wessex CPD Event 14/11/14 Dr Ishani Kar-Purkayastha, CCDC, Wessex PHE Centre wessex@phe.gov.uk Tel: 0345 055 2022 Outline Background About the current outbreak Situation in the UK Clinical management
Ebola Wessex CPD Event 14/11/14 Dr Ishani Kar-Purkayastha, CCDC, Wessex PHE Centre wessex@phe.gov.uk Tel: 0345 055 2022 Outline Background About the current outbreak Situation in the UK Clinical management
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) By : Assis. Prof Nader Alaridah MD, PhD
 Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) By : Assis. Prof Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Overview Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a group of illnesses caused by four families of viruses. Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae,
Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) By : Assis. Prof Nader Alaridah MD, PhD Overview Viral hemorrhagic fevers (VHFs) are a group of illnesses caused by four families of viruses. Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae,
PUBLIC HEALTH SIGNIFICANCE SEASONAL INFLUENZA AVIAN INFLUENZA SWINE INFLUENZA
 INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
INFLUENZA DEFINITION Influenza is an acute highly infectious viral disease characterized by fever, general and respiratory tract catarrhal manifestations. Influenza has 3 Types Seasonal Influenza Avian
Ebola Virus Diseases
 CDC/Dr F A Murphy Frequently Asked Questions on Ebola Virus Diseases Frequently asked questions on Ebola virus disease World Health Organization 2014 All rights reserved. Requests for publications, or
CDC/Dr F A Murphy Frequently Asked Questions on Ebola Virus Diseases Frequently asked questions on Ebola virus disease World Health Organization 2014 All rights reserved. Requests for publications, or
Epidemic Ebola Virus Disease Understanding, demystifying and controlling a frightening disease Republic of Guinea, 2014
 Epidemic Ebola Virus Disease Understanding, demystifying and controlling a frightening disease Republic of Guinea, 2014 James A. Zingeser, DVM, MPH Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN Rome, Italy
Epidemic Ebola Virus Disease Understanding, demystifying and controlling a frightening disease Republic of Guinea, 2014 James A. Zingeser, DVM, MPH Food and Agriculture Organization of the UN Rome, Italy
Case study: Epidemic modelling in real life
 Case study: Epidemic modelling in real life Epidemic modelling, simulation and statistical analysis Stockholm 2015. Sharon Kühlmann-Berenzon 2015-11-09 Outline for the day 1.Epidemic modelling: what is
Case study: Epidemic modelling in real life Epidemic modelling, simulation and statistical analysis Stockholm 2015. Sharon Kühlmann-Berenzon 2015-11-09 Outline for the day 1.Epidemic modelling: what is
OUR COMMUNITY: OUR WORLD: ONE HEALTH. Ebola : Geomedicine Conference
 OUR COMMUNITY: OUR WORLD: ONE HEALTH Ebola 2013-14: Geomedicine Conference Early Geomedicine East Africa, El Nino 1997 RVF: A One Health Response Ecological prediction models Animal vaccination Human
OUR COMMUNITY: OUR WORLD: ONE HEALTH Ebola 2013-14: Geomedicine Conference Early Geomedicine East Africa, El Nino 1997 RVF: A One Health Response Ecological prediction models Animal vaccination Human
The Struggle with Infectious Disease. Lecture 5
 The Struggle with Infectious Disease Lecture 5 Tropical Diseases Life and infectious disease began in the rift valley/rain forest of Eastern Africa Peoples migrated North to temperate regions Tropical
The Struggle with Infectious Disease Lecture 5 Tropical Diseases Life and infectious disease began in the rift valley/rain forest of Eastern Africa Peoples migrated North to temperate regions Tropical
Ebola Outbreak deadly infectious diseases as a potential major threat. Dilys Morgan
 Ebola Outbreak deadly infectious diseases as a potential major threat Dilys Morgan Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) 1976: First documented outbreak in Zaïre (now: the Democratic Republic of Congo) The incubation
Ebola Outbreak deadly infectious diseases as a potential major threat Dilys Morgan Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) 1976: First documented outbreak in Zaïre (now: the Democratic Republic of Congo) The incubation
SHARE SELECTION. Click here to print. Thursday, Nov 6th AM 46 F 10AM 44 F 5 Day Forecast. By Associated Press
 SHARE SELECTION Click here to print Thursday, Nov 6th 2014 7AM 46 F 10AM 44 F 5 Day Forecast The day Ebola was almost released on U.S. soil: Doctor recalls 1990 race to stop epidemic after infected monkey
SHARE SELECTION Click here to print Thursday, Nov 6th 2014 7AM 46 F 10AM 44 F 5 Day Forecast The day Ebola was almost released on U.S. soil: Doctor recalls 1990 race to stop epidemic after infected monkey
Ebola Virus Disease. What the physician needs to know. (Overview, Transmission and Clinical Features)
 Ebola Virus Disease What the physician needs to know (Overview, Transmission and Clinical Features) Sources: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines (www.cdc.gov) and WHO guidelines
Ebola Virus Disease What the physician needs to know (Overview, Transmission and Clinical Features) Sources: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines (www.cdc.gov) and WHO guidelines
Viral Hemorrhagic Fevers CDC, AFIP
 CDC, AFIP Diverse group of illnesses caused by RNA viruses from 4 families: Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, Flaviridae Differ by geographic occurrence and vector/reservoir Share certain clinical
CDC, AFIP Diverse group of illnesses caused by RNA viruses from 4 families: Arenaviridae, Bunyaviridae, Filoviridae, Flaviridae Differ by geographic occurrence and vector/reservoir Share certain clinical
Virology and clinical aspects of EVD. ID and PH Forum 13 Aug 2014
 Virology and clinical aspects of EVD ID and PH Forum 13 Aug 2014 Virology Filoviruses First recognized in 1967 Non-segmented, negative-sense, singlestranded RNA viruses 5 different species (the Zaire,
Virology and clinical aspects of EVD ID and PH Forum 13 Aug 2014 Virology Filoviruses First recognized in 1967 Non-segmented, negative-sense, singlestranded RNA viruses 5 different species (the Zaire,
Confronting Ebola. Keeping NY patients and healthcare workers safe and healthy
 Confronting Ebola Keeping NY patients and healthcare workers safe and healthy All materials provided by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. October 16, 2014 What You Need to Know about Ebola The
Confronting Ebola Keeping NY patients and healthcare workers safe and healthy All materials provided by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. October 16, 2014 What You Need to Know about Ebola The
This also applies to all travellers transiting through countries with risk of transmission of yellow fever.
 JAMAICA YELLOW FEVER ENTRY REQUIREMENTS 29 MAY 2016 Vaccination against yellow fever is required to prevent the importation of yellow fever virus into Jamaica where the disease does not occur but where
JAMAICA YELLOW FEVER ENTRY REQUIREMENTS 29 MAY 2016 Vaccination against yellow fever is required to prevent the importation of yellow fever virus into Jamaica where the disease does not occur but where
Grace Kubin, Ph.D. 10 th Annual Alabama Laboratory Meeting 2015
 Grace Kubin, Ph.D. 10 th Annual Alabama Laboratory Meeting 2015 Viral hemorrhagic fever Member of Filoviridae family Ebolavirus genera: Zaire 50-90% fatality rate Sudan 50% fatality rate Bundibugyo 30%
Grace Kubin, Ph.D. 10 th Annual Alabama Laboratory Meeting 2015 Viral hemorrhagic fever Member of Filoviridae family Ebolavirus genera: Zaire 50-90% fatality rate Sudan 50% fatality rate Bundibugyo 30%
Peterborough County-City Health Unit Pandemic Influenza Plan Section 1: Background
 1. Background Every expert on influenza agrees that the ability of the influenza virus to re-assort genes means that another influenza pandemic not only can happen, it almost certainly will happen Influenza
1. Background Every expert on influenza agrees that the ability of the influenza virus to re-assort genes means that another influenza pandemic not only can happen, it almost certainly will happen Influenza
Communicable diseases. Gastrointestinal track infection. Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology
 Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Communicable diseases Gastrointestinal track infection Sarkhell Araz MSc. Public health/epidemiology Communicable diseases : Refer to diseases that can be transmitted and make people ill. They are caused
Safety Tips from the WorkSafe People
 Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
Blood Borne Pathogens Training HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B Determining Exposure Protecting Yourself Preventing Exposure during an Emergency HIV/AIDS Definition: AIDS stands for Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome.
EBOLA & OTHER VIRUSES IN THE NEWS EBOLA VIRUS, CHIKUNGUNYA VIRUS, & ENTEROVIRUS D68
 EBOLA & OTHER VIRUSES IN THE NEWS EBOLA VIRUS, CHIKUNGUNYA VIRUS, & ENTEROVIRUS D68 PRESENTERS Patricia Quinlisk, MD, MPH, Medical Director /State Epidemiologist Samir Koirala, MBBS, MSc Epidemic Intelligence
EBOLA & OTHER VIRUSES IN THE NEWS EBOLA VIRUS, CHIKUNGUNYA VIRUS, & ENTEROVIRUS D68 PRESENTERS Patricia Quinlisk, MD, MPH, Medical Director /State Epidemiologist Samir Koirala, MBBS, MSc Epidemic Intelligence
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3 EBOLA 2014 WEST AFRICA CENTRAL AND EAST AFRICA. Hosted by: Bhagavatula Ramakrishna, M.D.
 Slide 1 EBOLA 2014 WEST AFRICA Hosted by: Bhagavatula Ramakrishna, M.D. Slide 2 CENTRAL AND EAST AFRICA Slide 3 Slide 4 EBOLA IN WEST AFRICA 2014 Slide 5 It is a disease of poverty and neglect of health
Slide 1 EBOLA 2014 WEST AFRICA Hosted by: Bhagavatula Ramakrishna, M.D. Slide 2 CENTRAL AND EAST AFRICA Slide 3 Slide 4 EBOLA IN WEST AFRICA 2014 Slide 5 It is a disease of poverty and neglect of health
CIRCULAR LETTER No
 CIRCULAR LETTER No 06-204 0.0.203 To: MASTER CREW MEMBERS 07 th August, 204 URGENT Due to the serious nature of the outbreak of the Ebola virus in West Africa, the following 5 safe precautions to be strictly
CIRCULAR LETTER No 06-204 0.0.203 To: MASTER CREW MEMBERS 07 th August, 204 URGENT Due to the serious nature of the outbreak of the Ebola virus in West Africa, the following 5 safe precautions to be strictly
GOAL. Disclosure. Objectives 11/12/2014. Epi 101: Basic Epidemiological Definitions and Principles for Non-Epidemiologists
 Epi 101: Basic Epidemiological Definitions and Principles for Non-Epidemiologists Anil T. Mangla., MS., PhD., PHD., FRIPH Assistant Director, San Antonio Metro Health Associate Adjunct Professor University
Epi 101: Basic Epidemiological Definitions and Principles for Non-Epidemiologists Anil T. Mangla., MS., PhD., PHD., FRIPH Assistant Director, San Antonio Metro Health Associate Adjunct Professor University
Ebola Virus Disease: Occupational Safety and Health
 Ebola Virus Disease: Occupational Safety and Health Joint WHO/ILO Briefing Note for Workers and Employers 25 August 2014 (update 5 September 2014) This briefing note is based on the existing WHO and ILO
Ebola Virus Disease: Occupational Safety and Health Joint WHO/ILO Briefing Note for Workers and Employers 25 August 2014 (update 5 September 2014) This briefing note is based on the existing WHO and ILO
Information for Primary Care: Managing patients who require assessment for Ebola virus disease Updated 17 Oct 2014
 Information for Primary Care: Managing patients who require assessment for Ebola virus This guidance is aimed at clinical staff undertaking direct patient care in primary care, including GP surgeries,
Information for Primary Care: Managing patients who require assessment for Ebola virus This guidance is aimed at clinical staff undertaking direct patient care in primary care, including GP surgeries,
EBOLA 101. Update for EMS System Stakeholders. Eric M. Rudnick, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Medical Director Nor Cal EMS Version 10/25/2014
 EBOLA 101 Update for EMS System Stakeholders Eric M. Rudnick, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Medical Director Nor Cal EMS Version 10/25/2014 Conference 1 Version #1 Date 10/25/14 Content good for current situation 10/25/14
EBOLA 101 Update for EMS System Stakeholders Eric M. Rudnick, MD, FACEP, FAAEM Medical Director Nor Cal EMS Version 10/25/2014 Conference 1 Version #1 Date 10/25/14 Content good for current situation 10/25/14
Emerging Infectious Disease (2): Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever
 S47 Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever Emerging Infectious Disease (2): Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever Yung-Cheng Su, MD; Yuh-Jeng Yang, MD; Tzong-Luen Wang, MD, PhD Abstract Since its first identification in 1967,
S47 Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever Emerging Infectious Disease (2): Marburg Hemorrhagic Fever Yung-Cheng Su, MD; Yuh-Jeng Yang, MD; Tzong-Luen Wang, MD, PhD Abstract Since its first identification in 1967,
Palliative Care in Ebola
 Palliative Care in Ebola CHALLENGES IN DELIVERY AND EXPERIENCES FROM THE CURRENT OUTBREAK Background Ebola: filovirus from the family filoviridae Named after the Ebola River in DRC (then Zaire) where first
Palliative Care in Ebola CHALLENGES IN DELIVERY AND EXPERIENCES FROM THE CURRENT OUTBREAK Background Ebola: filovirus from the family filoviridae Named after the Ebola River in DRC (then Zaire) where first
Health care workers (HCWs) caring for suspected (clinically diagnosed) or confirmed cases of. Influenza A(H1N1)v FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
 Health care workers (HCWs) caring for suspected (clinically diagnosed) or confirmed cases of Questions found here: FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS What is pandemic flu? What is the difference between seasonal
Health care workers (HCWs) caring for suspected (clinically diagnosed) or confirmed cases of Questions found here: FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS What is pandemic flu? What is the difference between seasonal
Cholera. Ebola. Symptoms of Ebola include. Fever. Severe headache. Muscle pain. Weakness. Fatigue. Diarrhea. Vomiting. Abdominal (stomach) pain
 Cholera Cholera is caused by a bacterial infection of the intestine. In many cases the infection is mild sometimes producing no symptoms at all. But approximately one in 20 people infected with cholera
Cholera Cholera is caused by a bacterial infection of the intestine. In many cases the infection is mild sometimes producing no symptoms at all. But approximately one in 20 people infected with cholera
A BSL-1 lab houses activities that require only standard microbial practices. These include:
 BSL-1 A BSL-1 lab houses activities that require only standard microbial practices. These include: Work should be performed on an open lab bench or table Spills must be decontaminated immediately Infectious
BSL-1 A BSL-1 lab houses activities that require only standard microbial practices. These include: Work should be performed on an open lab bench or table Spills must be decontaminated immediately Infectious
Epidemiology of Lassa Fever
 Epidemiology of Lassa Fever Njideka E. Kanu Department of Community Medicine, University of Medical Sciences, Ondo A lecture delivered at the Academic Seminar of University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, 14
Epidemiology of Lassa Fever Njideka E. Kanu Department of Community Medicine, University of Medical Sciences, Ondo A lecture delivered at the Academic Seminar of University of Medical Sciences, Ondo, 14
Buy The Complete Version of This Book at Booklocker.com:
 Amazing breakthrough remedy for swine flu from mother nature. How to Beat Swine Flu Naturally Buy The Complete Version of This Book at Booklocker.com: http://www.booklocker.com/p/books/4341.html?s=pdf
Amazing breakthrough remedy for swine flu from mother nature. How to Beat Swine Flu Naturally Buy The Complete Version of This Book at Booklocker.com: http://www.booklocker.com/p/books/4341.html?s=pdf
Ebola: 22,000 cases, 8700 deaths. Enterovirus D68: 1100 cases, 14 deaths. Chikungunya virus: almost a million cases in the Western Hemisphere
 Sally Williams MD Ebola: 22,000 cases, 8700 deaths Enterovirus D68: 1100 cases, 14 deaths Chikungunya virus: almost a million cases in the Western Hemisphere } A nonpolio enterovirus identified in 1962,
Sally Williams MD Ebola: 22,000 cases, 8700 deaths Enterovirus D68: 1100 cases, 14 deaths Chikungunya virus: almost a million cases in the Western Hemisphere } A nonpolio enterovirus identified in 1962,
2. According to the information provided by the WHO, there is no justification at this stage for restrictions on travel or trade.
 Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
Outbreak of Plague in Madagascar The following information is being disseminated by both the International Chamber of Shipping and The International Transport Workers Federation to draw attention to the
Norovirus in Healthcare Settings
 ST. JAMES HEALTHCARE DECEMBER 2012 INFECTION PREVENTION NEWSLETTER INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Norovirus in Healthcare Settings The Impacts of Unsafe Medical Injections in the U.S. Preparing Your Skin Before Surgery:
ST. JAMES HEALTHCARE DECEMBER 2012 INFECTION PREVENTION NEWSLETTER INSIDE THIS ISSUE: Norovirus in Healthcare Settings The Impacts of Unsafe Medical Injections in the U.S. Preparing Your Skin Before Surgery:
EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES EMERGING NONE
 EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES NONE EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES New, re-emerging, or drug-resistant infections whose incidence: threatens to increase in humans has increased within the past
EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES DISCLOSURES NONE EMERGING INFECTIOUS DISEASES New, re-emerging, or drug-resistant infections whose incidence: threatens to increase in humans has increased within the past
Yellow fever. Key facts
 From: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/yellow-fever WHO/E. Soteras Jalil Yellow fever 14 March 2018 Key facts Yellow fever is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected
From: http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/yellow-fever WHO/E. Soteras Jalil Yellow fever 14 March 2018 Key facts Yellow fever is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected
Influenza B viruses are not divided into subtypes, but can be further broken down into different strains.
 Influenza General Information Influenza (the flu) is a highly transmissible respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild to severe illness, and may lead to death. Older people, young
Influenza General Information Influenza (the flu) is a highly transmissible respiratory illness caused by influenza viruses. It can cause mild to severe illness, and may lead to death. Older people, young
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences A STUDY OF CLINCAL PROFILE IN DENGUE CASES ABSTRACT
 Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A STUDY OF CLINCAL PROFILE IN DENGUE CASES DHANDAPANI E.* 1 AND SUDHA M 2 1 Formerly Professor of Medicine,
Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 A STUDY OF CLINCAL PROFILE IN DENGUE CASES DHANDAPANI E.* 1 AND SUDHA M 2 1 Formerly Professor of Medicine,
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority
 HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
HIBA ABDALRAHIM Capsca Focal Point Public Health Authority Introduction Definition Symptom Transmission Global situation Local situation Control Content Introduction Yellow fever (YF) is a mosquito-borne
Influenza. Gwen Clutario, Terry Chhour, Karen Lee
 Influenza Gwen Clutario, Terry Chhour, Karen Lee Overview Commonly referred to as the flu Defined as a highly contagious viral infection where it starts at the upper respiratory tract and attacks the nose,
Influenza Gwen Clutario, Terry Chhour, Karen Lee Overview Commonly referred to as the flu Defined as a highly contagious viral infection where it starts at the upper respiratory tract and attacks the nose,
Epidemiology Update Hepatitis A
 December 2011 Epidemiology Update Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Key Points Between 2000 and 2010, 209 cases of hepatitis A were reported in Hennepin County residents. This represents 30% of the cases reported
December 2011 Epidemiology Update Hepatitis A Hepatitis A Key Points Between 2000 and 2010, 209 cases of hepatitis A were reported in Hennepin County residents. This represents 30% of the cases reported
Fever virus going around 2017
 Fever virus going around 2017 Bad cough that won't quit part of winter virus going around. by LIZ BONIS, WKRC. Monday, December 25th 2017. June 9, 2017. Every time May and June roll around these viruses
Fever virus going around 2017 Bad cough that won't quit part of winter virus going around. by LIZ BONIS, WKRC. Monday, December 25th 2017. June 9, 2017. Every time May and June roll around these viruses
(and what you can do about them)
 (and what you can do about them) What s an outbreak? In general, more cases than expected (baseline) More cases clustered in a specific unit or facility than you d expect at a particular time of year Some
(and what you can do about them) What s an outbreak? In general, more cases than expected (baseline) More cases clustered in a specific unit or facility than you d expect at a particular time of year Some
SJCEMSC EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE RESPONSE GUIDELINE
 SJCEMSC EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE RESPONSE GUIDELINE KEY POINTS Ebola Facts: Ebola hemorrhagic fever is a disease caused by one of five different Ebola viruses. Four of the strains can cause severe illness in
SJCEMSC EBOLA VIRUS DISEASE RESPONSE GUIDELINE KEY POINTS Ebola Facts: Ebola hemorrhagic fever is a disease caused by one of five different Ebola viruses. Four of the strains can cause severe illness in
Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? 19 October 2017
 19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
19 October 2017 Advisory on Plague WHAT IS PLAGUE? Plague is an infectious disease caused by the zoonotic bacteria, Yersinia pestis. This bacteria often infects small rodents (like rats, mice, and squirrels)
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 7-1. Identify the common types of hepatitis.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Hepatitis. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-11. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 7-1. Identify the common types of hepatitis.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 7 Hepatitis. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 7-1 through 7-11. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 7-1. Identify the common types of hepatitis.
Ebola haemorrhagic fever among hospitalised children and adolescents in nothern Uganda : Epidemiologic and clinical observations
 Ebola haemorrhagic fever among hospitalised children and adolescents in nothern Uganda : Epidemiologic and clinical observations 1 Mupere E, 2 Kaducu O.F and 2 Yoti Z 1 Gulu Regional Referral Hospital
Ebola haemorrhagic fever among hospitalised children and adolescents in nothern Uganda : Epidemiologic and clinical observations 1 Mupere E, 2 Kaducu O.F and 2 Yoti Z 1 Gulu Regional Referral Hospital
RISK OF INFECTIONN CENTRAL AND MIDDLE AFRICA
 16 may 2012 16 may 2012 RISK OF INFECTIONN CENTRAL AND MIDDLE AFRICA RECENT OUTBREAKS OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Country Burundi Central African Republic Chad Congo Rwanda Disease Date of Outbreak Cholera
16 may 2012 16 may 2012 RISK OF INFECTIONN CENTRAL AND MIDDLE AFRICA RECENT OUTBREAKS OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Country Burundi Central African Republic Chad Congo Rwanda Disease Date of Outbreak Cholera
General Description. Significance
 General Description The Zika virus is a member of the Flavivirus family, and is a small, enveloped virus (easy to kill with a hospital disinfectant). Zika virus is an emerging mosquito-borne virus that
General Description The Zika virus is a member of the Flavivirus family, and is a small, enveloped virus (easy to kill with a hospital disinfectant). Zika virus is an emerging mosquito-borne virus that
Information About H3N2v
 Information About H3N2v James R. Ginder, MS, NREMT,PI,CHES,NCEE Health Education Specialist Hamilton County Health Department www.hamiltoncounty.in.gov Mary Jo Skinner, RN, BSN, MBA Public Health Nurse
Information About H3N2v James R. Ginder, MS, NREMT,PI,CHES,NCEE Health Education Specialist Hamilton County Health Department www.hamiltoncounty.in.gov Mary Jo Skinner, RN, BSN, MBA Public Health Nurse
CDC Ebola Response Team
 Ebola Preparations from the Healthcare Epidemiologists Perspective August 25th, 2014 CDC Ebola Response Team Barbara Knust, DVM, MPH Epidemiology Team Lead Tim Uyeki, MD Clinical Team Lead Nancy Cornish,
Ebola Preparations from the Healthcare Epidemiologists Perspective August 25th, 2014 CDC Ebola Response Team Barbara Knust, DVM, MPH Epidemiology Team Lead Tim Uyeki, MD Clinical Team Lead Nancy Cornish,
Influenza Update for Iowa Long-Term Care Facilities. Iowa Department of Public Health Center for Acute Disease Epidemiology
 Influenza Update for Iowa Long-Term Care Facilities Iowa Department of Public Health Center for Acute Disease Epidemiology Webinar Information All participants will be muted during the presentation. Questions
Influenza Update for Iowa Long-Term Care Facilities Iowa Department of Public Health Center for Acute Disease Epidemiology Webinar Information All participants will be muted during the presentation. Questions
Smallpox. Houston Academy of Medicine - Texas Medical Center Library. From the SelectedWorks of Richard N Bradley
 Houston Academy of Medicine - Texas Medical Center Library From the SelectedWorks of Richard N Bradley September, 2007 Smallpox Richard N Bradley, The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston
Houston Academy of Medicine - Texas Medical Center Library From the SelectedWorks of Richard N Bradley September, 2007 Smallpox Richard N Bradley, The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston
What is hepatitis? What is hepatitis A? How is it spread? What are the symptoms? How soon do symptoms appear? How is hepatitis A diagnosed?
 Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
Hepatitis A Massachusetts Department of Public Health, 305 South Street, Jamaica Plain, MA 02130 What is hepatitis? Hepatitis is any kind of inflammation (a reaction which can include swelling and pain)
A Virus is a very small organism which can only be viewed under the electron microscope.
 Pandemic Influenza Fact Sheet What is a Virus? A Virus is a very small organism which can only be viewed under the electron microscope. Properties of viruses Although they are very small, they are live
Pandemic Influenza Fact Sheet What is a Virus? A Virus is a very small organism which can only be viewed under the electron microscope. Properties of viruses Although they are very small, they are live
Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association
 Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association The County Health Department held a briefing on Monday, April 27thto outline the issues surrounding the Swine Flu and its migration
Swine Flu Information Provided by Santa Barbara Human Resources Association The County Health Department held a briefing on Monday, April 27thto outline the issues surrounding the Swine Flu and its migration
TRAVEL ADVISORY TO PREVENT THE IMPORTATION OF EBOLA INTO SOUTH AFRICA
 TRAVEL ADVISORY TO PREVENT THE IMPORTATION OF EBOLA INTO SOUTH AFRICA The purpose of this advisory is to notify travellers about the Ebola disease outbreak and inform them about preventative measures they
TRAVEL ADVISORY TO PREVENT THE IMPORTATION OF EBOLA INTO SOUTH AFRICA The purpose of this advisory is to notify travellers about the Ebola disease outbreak and inform them about preventative measures they
Khaled Ali Abu Ali. BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. -Nursing. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer
 Khaled Ali Abu Ali BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer -Nursing Khaled_abuali@yahoo.com Communicable Disease Surveillance during Gaza War, 214. Introduction Public Health
Khaled Ali Abu Ali BSN. MPH. Ph.D. cand. Director of Epidemiology Department UCAS Lecturer -Nursing Khaled_abuali@yahoo.com Communicable Disease Surveillance during Gaza War, 214. Introduction Public Health
Fact sheet. Yellow fever
 Fact sheet Key facts is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes. The yellow in the name refers to the jaundice that affects some patients. Up to 50% of severely affected
Fact sheet Key facts is an acute viral haemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes. The yellow in the name refers to the jaundice that affects some patients. Up to 50% of severely affected
Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN
 Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of
Breaking the Chain of Infection Designated Officer Education Day September 3, 2014 Jodi-Marie Black RN BScN PHN Topics Covered in Presentation The Chain of infection and how to break the chain Role of
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
 Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) By Jennifer Osita Disease The disease I am studying is AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) which is when the immune system is too weak to fight off many
Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome (AIDS) By Jennifer Osita Disease The disease I am studying is AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome) which is when the immune system is too weak to fight off many
INFECTION PREVENTION NEWS & UPDATES
 CONTACT + DROPLET EBOLA INFECTION While the Ebola outbreak from the Democratic Republic of the Congo from earlier this year is over, a new outbreak of Ebola has been identified that has infected at least
CONTACT + DROPLET EBOLA INFECTION While the Ebola outbreak from the Democratic Republic of the Congo from earlier this year is over, a new outbreak of Ebola has been identified that has infected at least
Hepatitis B is a virus that attacks the liver. It is highly infectious. Hepatitis B is transmitted primarily
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGENS TRAINING FOR SCHOOL STAFF Blood Borne Pathogen (BBP): A blood borne pathogen is defined as an organism found in human blood or other infected body fluids that may cause disease in
Mathematical Modelling of Effectiveness of H1N1
 ISSN: 2455-2631 April 216 IJSDR Volume 1, Issue 4 Mathematical Modelling of Effectiveness of H1N1 1 Fenny J. Narsingani, 2 Dr. M.B.Prajapati 1 Assistant Professor, L.D.College of Engineering, Ahmedabad,
ISSN: 2455-2631 April 216 IJSDR Volume 1, Issue 4 Mathematical Modelling of Effectiveness of H1N1 1 Fenny J. Narsingani, 2 Dr. M.B.Prajapati 1 Assistant Professor, L.D.College of Engineering, Ahmedabad,
Distribution: As Appendix 1 Dr Ruth Hussey, Chief Medical Officer, Welsh Government Date: 10 October Ongoing Ebola outbreak in West Africa
 Public Health Link From the Chief Medical Officer for Wales Distribution: As Appendix 1 From: Dr Ruth Hussey, Chief Medical Officer, Welsh Government Date: 10 October 2014 Reference: Category: Title: What
Public Health Link From the Chief Medical Officer for Wales Distribution: As Appendix 1 From: Dr Ruth Hussey, Chief Medical Officer, Welsh Government Date: 10 October 2014 Reference: Category: Title: What
