Characterization of a Borrelia burgdorferi VlsE Invariable Region Useful in Canine Lyme Disease Serodiagnosis by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
|
|
|
- Marjorie King
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2000, p Vol. 38, No /00/$ Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Characterization of a Borrelia burgdorferi VlsE Invariable Region Useful in Canine Lyme Disease Serodiagnosis by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay FANG TING LIANG, 1 RICHARD H. JACOBSON, 2 REINHARD K. STRAUBINGER, 3 AMY GROOTERS, 4 AND MARIO T. PHILIPP 1 * Department of Parasitology, Tulane Regional Primate Research Center, Tulane University Health Sciences Center, Covington, Louisiana ; Department of Population Medicine and Diagnostic Science 2 and James A. Baker Institute for Animal Health, 3 New York State College of Veterinary Medicine, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14853; and Department of Veterinary Clinical Sciences, Louisiana State University School of Veterinary Medicine, Baton Rouge, Louisiana Received 15 June 2000/Returned for modification 23 August 2000/Accepted 30 August 2000 Sera collected from dogs experimentally infected with Borrelia burgdorferi by tick inoculation were analyzed for an antibody response to each of the six invariable regions (IRs; i.e., IR 1 to IR 6 ) of VlsE, the variable surface antigen of B. burgdorferi. Six synthetic peptides (C 1 to C 6 ), which reproduced the six IR sequences were used as peptide-based, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) antigens. Two IRs, IR 2 and IR 6, were found to be immunodominant. Studies with serially collected serum samples from experimentally infected dogs revealed that the antibody response to IR 6 appears earlier and is stronger than that to IR 2. Thus, the IR 6 sequence alone appeared to be sufficient for serodiagnosis. When C 6 alone was used as antigen, the peptide-based ELISA was positive in 7 of 23 dogs (30%) as early as 3 weeks postinfection. All dogs (n 33) became strongly positive 1 or 2 weeks later, and this response persisted for the entire study, which lasted for 69 weeks. Of 55 sera submitted by veterinarians from dogs suspected of having Lyme disease, 19 were also positive by the C 6 ELISA, compared to 20 positives detected by immunoblot analysis using cultured B. burgdorferi lysates as antigen. The sensitivity of using C 2 and C 6 together for detecting specific antibody in both experimentally infected and clinically diagnosed dogs was not better than sensitivity with C 6 alone, confirming that C 6 suffices as a diagnostic probe. Moreover, the C 6 ELISA yielded 100% specificity with serum samples collected from 70 healthy dogs, 14 dogs with infections other than B. burgdorferi, and 15 animals vaccinated with either outer surface protein A, whole-spirochete vaccines, or the common puppy-vaccines. Therefore, this C 6 ELISA was both sensitive and specific for the serodiagnosis of canine Lyme disease and could be used with vaccinated dogs. * Corresponding author. Mailing address: Tulane Regional Primate Research Center, Tulane University Health Sciences Center, Three Rivers Rd., Covington, LA Phone: (504) Fax: (504) philipp@tpc.tulane.edu. Borrelia burgdorferi, the etiologic agent of Lyme disease, can infect a variety of vertebrates, in which it causes disease or asymptomatic infections. The dog is the domestic animal at greatest risk, and it has been recommended as a sentinel animal for human Lyme disease (7, 19). Due to the lack of differential signs such as erythema migrans in infected dogs (1), laboratory methods are very important for canine Lyme disease diagnosis. We had previously analyzed the antigenicity of the six invariable regions (IRs; i.e., IR 1 to IR 6 ) located within the variable domain of VlsE (13, 15), the B. burgdorferi lipoprotein that undergoes antigenic variation (23). We determined that while in humans and nonhuman primates only IR 6 is immunodominant, in mice not only IR 6 but also IR 2 and IR 4 are antigenic, with IR 6 and IR 2 being most frequently recognized (15). We developed a peptide-based enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using as antigen a 26-mer synthetic peptide (C 6 ) based on the IR 6 sequence, and we determined that this assay is highly sensitive and specific for human Lyme disease serodiagnosis in the United States (14). We also determined that the C 6 ELISA could be used in Europe, insofar as it detected antibody in human patients that had cultureconfirmed infections with either Borrelia garinii or Borrelia afzelii, the two genospecies most prevalent in Europe (18). To identify a suitable probe for serology of canine B. burgdorferi infection, we first analyzed the antigenicity of each of the IRs of VlsE in dogs that had been experimentally infected with B. burgdorferi by tick inoculation. Like mice, dogs vigorously responded to both IR 2 and IR 6, with IR 6 stimulating a stronger and earlier antibody response than IR 2. Our further analysis ruled out the necessity of including IR 2 as a diagnostic antigen and demonstrated that IR 6 alone is enough as a probe for the serodiagnosis of canine Lyme disease. MATERIALS AND METHODS Tick collection and dog inoculation. Thirty-three 6-week-old specific-pathogen-free beagles of both sexes were infected by tick inoculation as described previously (22). Ticks were field collected in Westchester County, New York. All dogs were infected with B. burgdorferi as evidenced by skin punch biopsy culture and PCR, which were conducted at 4 weeks after tick exposure (22). Serial blood samples were collected from all of the dogs at 2- to 4-week intervals for 17 weeks beginning at day 0 of the experiment. In some dogs, blood sampling continued until week 69 postinfection. Negative control serum specimens and cutoff line. Seventy control serum specimens were collected from healthy dogs owned by students of a veterinary school in Louisiana. This panel of serum specimens was used to calibrate a cutoff line for serodiagnosis. The cutoff line was defined as the mean optical density (OD) value plus 5 standard deviations (SDs) of these 70 specimens. Lyme disease is not endemic in Louisiana, and the dogs did not have a history of travel to endemic areas. Serum specimens from vaccinated dogs or dogs with infections other than B. burgdorferi. Fourteen blood samples were collected from dogs with leptospirosis 4160
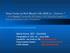
2 VOL. 38, 2000 CANINE LYME DISEASE SERODIAGNOSIS 4161 FIG. 1. VlsE structure and sequences of synthetic peptides (15, 16). VlsE consists of two invariable domains at the amino and carboxyl termini and one variable domain at the center. The variable domain contains six variable regions, VR I through VR VI, and six invariable regions, IR 1 through IR 6. The six IR sequences were obtained from one cloned variable domain of VlsE expressed by the strain IP90 of B. garinii (13). The insert (framed) shows the IR 6 sequences from IP90 of B. garinii (13) and strains 297 (11) and B31 (23) of B. burgdorferi sensu stricto. Bold letters indicate amino acids unique to each strain. The consensus sequences of the three overlapping peptides used in this study are depicted as C 6 N, C 6 M, and C 6 C. (n 5), Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF; n 2), or infection with Dirofilaria (n 5), Babesia (n 1), or Ehrlichia (n 1) spp. An additional 15 serum specimens were collected from dogs vaccinated either with the outer surface protein A (OspA; n 5), a whole fixed spirochete vaccine (n 5), or the common vaccines received by puppies (distemper, adenovirus 2, parainfluenza, parvovirus, leptospirosis, and coronavirus [DA 2 PPLCV]; n 5). These serum samples contained antibodies to OspA or other spirochetal antigenic proteins, as appropriate, as determined by immunoblotting using B. burgdorferi whole-cell extracts as antigen. Clinical serum specimens. A panel of 55 canine serum specimens was used to compare sensitivities as measured by kinetic ELISA (KELA), immunoblot analysis, and peptide-based ELISA. These samples were originally submitted for the serodiagnosis of Lyme disease and collected from dogs that were suspected of having Lyme disease. KELA and immunoblot assays were performed as previously described (22). Synthetic peptide sequences, preparation, and biotinylation. Peptides were prepared using the fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl synthesis protocol (3) based on the sequences listed in Fig. 1. Synthetic peptides were covalently linked to biotin by the N-succinimidyl maleimide carboxylate method. The maleimide reagents were from Molecular Probes (Eugene, Oreg.), and the protocol suggested by the manufacturer was followed. Peptide-based ELISA. Peptide-based ELISA was conducted as described previously with minor modifications (13). Ninety-six-well ELISA plates were coated with 100 l per well of 4- g/ml streptavidin (Pierce Chemical Co., Rockford, Ill.) in coating buffer (0.1 M carbonate buffer [ph 9.2]) and incubated at 4 C overnight. The remaining steps were conducted in a rotatory shaker at room temperature. After two 3-min washes with 200 l per well of phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) Tween 20 (PBS/T, with PBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 [ph 7.4]) at 200 rpm, 200 l of5- g/ml biotinylated peptide dissolved in blocking solution (PBS/T supplemented with 5% nonfat dry milk) was applied to each well. The plate was shaken at 180 rpm for 2 h. After three washes with PBS/T, 50 l ofdog serum diluted 1:200 with blocking solution was added to each well. The plate was incubated for 1hat180rpmandthen washed three times with PBS/T. Each well then received 100 l of g/ml rabbit anti-dog immunoglobulin G conjugated to horseradish peroxidase (heavy and light chain specific; Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, Mo.), and dissolved in blocking solution. The plate was incubated for 1 h with shaking. After three washes with PBS/T, each for 3 to 4 min, the antigen-antibody reaction was probed using the TMB Microwell peroxidase substrate system (Kirkegaard & Perry Laboratories, Gaithersburg, Md.), and color was allowed to develop for 20 min. The enzyme reaction was stopped by addition of 100 l of1mh 3 PO 4. The OD was measured at 450 nm. RESULTS Canine antibody responses to IRs. To determine whether any IRs (Fig. 1) were antigenic in dogs, serum samples from eight animals that were infected with B. burgdorferi by tick inoculation were used. Blood samples were collected at 8 or 9 weeks postinoculation and analyzed for anti-ir antibody responses using peptide-based ELISAs. All of the eight dogs had a strong antibody response to IR 6 and a moderate to strong reactivity with IR 2 (Fig. 2). None of the eight dogs produced an antibody response to IR 1,IR 3,IR 4,orIR 5 except dog A96-2/2, which showed a very low level of antibody to IR 4 (data not shown). IR 6 alone may be enough as a diagnostic probe. Our analysis of the antibody response to the IRs revealed that both IR 2 and IR 6 are immunodominant in dogs. However, the serum specimens we used were obtained at one time point during infection, and they may not represent the whole spectrum of antibody responses. The level of antibody to individual epitopes may fluctuate with time. To determine whether both the IR 2 and IR 6 sequences should be included in an ELISA in order to increase assay sensitivity, an analysis of the time course of the antibody responses to these two sequences was conducted. Serial bleeds collected from nine animals between 0 and 17 weeks after they were infected with B. burgdorferi by tick inoculation were used. Sera were analyzed for antibody reactivity with both IR 2 and IR 6, using peptide-based ELISAs. The response to IR 6 in all of the animals appeared earlier and was stronger than the response to IR 2, although specific antibodies to both sequences persisted throughout the study period (Fig. 3). These results indicated that IR 6 alone is sufficient for the serodiagnosis of canine Lyme disease. C 6 cannot be significantly shortened. C 6 is a 26-mer sequence. To determine whether its size could be reduced without affecting reactivity with canine antibodies, the C 6 peptide was epitope mapped. Three 14-mer overlapping peptides, C 6 N, C 6 M, and C 6 C (Fig. 1), which reproduced the whole IR 6 sequence, were each used as ELISA antigens. Serum samples collected from eight dogs at 8 or 9 weeks after they were infected by tick inoculation were tested. Although all of the three overlapping peptides reacted with most of the bleeds, their OD values were much lower than with C 6 (Fig. 4), indicating that the C 6 length could not be shortened significantly. Sensitivity of the C 6 ELISA for diagnosing canine Lyme disease. To assess diagnostic sensitivity of the C 6 ELISA, serial bleeds were collected from 33 dogs at 0 to 17 weeks and from four of these animals up to 69 weeks after the animals were
3 4162 LIANG ET AL. J. CLIN. MICROBIOL. FIG. 2. Antigenicity of invariable regions of VlsE. Serum samples were collected from eight dogs at 0 (Pre-) and 8 or 9 weeks post (Post-)-inoculation. Animals were infected by tick inoculation. Antibody levels to the two IRs were assessed using C 2 or C 6 peptide-based ELISA. The baseline (OD 0.096) was calculated from the mean OD value plus 3 SDs of prebleeds collected from the eight dogs when the two peptide-biotin conjugates were individually used as ELISA antigen. infected with B. burgdorferi by tick bite. The bleeds were taken at 2- to 4-week intervals and assessed for antibody responses to IR 6 using C 6 alone as ELISA antigen. All of the infected animals started to show a strong antibody response at 4 or 5 weeks postinfection (Fig. 5). Although none of the animals (0 of 11) had a detectable antibody response at 2 weeks postinfection, 30% of the infected dogs (7 of 22) became positive as early as 3 weeks postinfection, indicating that this assay is capable of detecting an early infection. These responses lasted for the entire experimental period, up to 69 weeks. Thus, a chronic infection also was detectable with the C 6 ELISA. The serum specimens collected at 2 and 3 weeks postinfection were also analyzed by an ELISA in which a mixture of C 2 and C 6 was used as antigen. No additional positives were detected (data not shown). These data further confirmed that anti-ir 6 antibody alone can be used as an indicator of B. burgdorferi infection in dogs. Specificity of the C 6 ELISA. B. burgdorferi shares similar antigenic proteins, such as flagellins (2), heat shock proteins (20), and common antigens (8), with other pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria. Infections with these bacteria may cause a false positive in Lyme disease serology (21). Moreover, vaccination, especially with killed whole spirochetes, makes serology of canine Lyme disease even more complicated. To assess the specificity of the C 6 ELISA, serum specimens from 70 healthy dogs were analyzed for anti-ir 6 antibody. No significant antibody response was detected (Fig. 6). The mean ELISA OD of these sera plus 5 SDs was used as the cutoff value. None of the serum samples from 14 dogs with leptospirosis (n 5), RMSF (n 2), dirofilariasis (n 5), babesiosis (n 1), or ehrlichiosis (n 1) contained a detectable anti-ir 6 antibody titer (Fig. 6). In addition, all 15 sera were negative from dogs that were vaccinated with either the OspA vaccine (n 5), a whole-spirochete vaccine (n 5), or the DA 2 PPLCV puppy-vaccines (n 5). These data indicated that the C 6 ELISA is not only very specific to B. burgdorferi but also uniquely specific for infection with B. burgdorferi, as opposed to vaccination with fixed B. burgdorferi or its antigens or with other vaccines commonly administrated to dogs. Comparison of conventional serodiagnostic methods with the C 6 ELISA. A panel of 55 clinical sera was used to compare the sensitivity of the C 6 ELISA with those of the KELA and immunoblot assay. This panel had been originally submitted for the serodiagnosis of canine Lyme disease. The C 6 ELISA detected 19 positive samples, while the KELA and immunoblot assays each produced 20 positive results (Table 1), thus yield- FIG. 3. Antibody responses to IR 2 and IR 6 as a function of time postinfection. Serial blood samples were collected from nine dogs at 0, 3, 5, 7, 9, 13, and 17 weeks after tick exposure. Levels of antibody to the two IRs were assessed using C 2 or C 6 peptide-based ELISA. Mean OD values and standard errors are presented. The baseline (OD 0.090) was calculated from the mean OD value plus 3 SDs of prebleeds collected from the nine dogs when the two peptide-biotin conjugates were individually used as ELISA antigen.
4 VOL. 38, 2000 CANINE LYME DISEASE SERODIAGNOSIS 4163 FIG. 4. Epitope mapping of IR 6. Serum samples were collected from eight dogs at 8 or 9 weeks after tick inoculation. Levels of antibody to C 6 and each of the overlapping 14-mers were assessed using peptide-based ELISA. The baseline (OD 0.091) was calculated from the mean OD value plus 3 SDs of the eight prebleeds reacted individually with each of the overlapping peptides and C 6. ing similar sensitivities. This serum panel also was analyzed by a peptide-based ELISA in which combined C 2 and C 6 were used as antigen. No enhanced sensitivity was achieved, confirming once again that C 2 is not required for the serodiagnosis of dog Lyme disease (data not shown). DISCUSSION B. burgdorferi sensu lato is able to infect a variety of vertebrate hosts. Lameness is the key clinical sign of Lyme disease in dogs. Unfortunately, lameness is not a pathognomonic sign, and therefore reliable serology is important in canine Lyme disease diagnosis. Blood samples collected from experimentally infected dogs were analyzed for antibody responses to all of the six IRs of VlsE. Unlike humans and monkeys but as with mice (15), all dogs responded to both IR 2 and IR 6, and one animal also responded weakly to IR 4 (Fig. 2). The evaluation of the levels of antibody to IR 2 and IR 6 in serial bleeds confirmed that at no time during the course of infection did the anti-ir 2 antibody level surpass that of the anti-ir 6 antibody (Fig. 3). Moreover, the anti-ir 6 response appeared earlier than the response to FIG. 5. Sensitivity of the C 6 ELISA for detection of early and late infection. Thirty-three dogs were infected by tick inoculation. Serial blood samples were collected from 11 dogs (group I) at 0, 2, 4, and 8 weeks and from the remaining animals (group II) at 0, 3, 5, 7, and 9 weeks postinoculation. From 13 dogs of group II, serum sampling continued at 17 weeks, and sampling from 4 dogs continued until week 69 postinoculation. Levels of antibody to C 6 were assessed using the C 6 ELISA. The cutoff line (OD 0.376) was defined as the mean OD value plus 5 SDs of serum samples collected from 70 healthy dogs from an area where Lyme disease is not endemic.
5 4164 LIANG ET AL. J. CLIN. MICROBIOL. FIG. 6. Specificity of the C 6 ELISA. Seventy negative control sera (healthy control) were collected from dogs in an area where Lyme disease is not endemic. Fourteen serum specimens (other infections) were collected from dogs with leptospirosis or RMSF or infected with Dirofilaria, Babesia, orehrlichia spp. Fifteen serum specimens (Vaccinated) were collected from dogs that had been vaccinated with the OspA vaccine (n 5), a whole-spirochete vaccine (n 5), or the DA 2 PPLCV vaccines (n 5). Antibody levels were assessed using the C 6 ELISA. The cutoff line (OD 0.376) was defined as the mean OD value plus 5 SDs of the 70 healthy controls. IR 2, and the two peptides, when combined in an ELISA, yielded no enhanced sensitivity when compared to C 6 used alone. Taken together, these results demonstrated that C 6 alone is sufficient as a diagnostic probe. Our antigenic analysis of the IRs, using dog serum, echoes our previous finding that IR 2,IR 4, and IR 6 are antigenic in mice (15). These results also are in agreement with the conclusion drawn from our previous studies, namely, that these three IRs are exposed at the surface of the VlsE molecule (13, 17). Features of protein domains such as surface accessibility, hydrophilicity, flexibility, and proximity to a site recognized by helper T cells are all important in positively determining domain antigenicity (5). Unlike T-cell epitopes, all B-cell epitopes are presumably exposed at the antigen s surface (4). The full length of the C 6 peptide is probably required for optimal antigenicity, as none of the 14-mers examined was as antigenic as the C 6 26-mer (Fig. 4). In monkeys (n 10), neither of the 14-mers examined was antigenic, except for C 6 C, which yielded a low OD value with the serum of one animal (16). In humans (n 10), only C 6 M was antigenic and only in four patients, whereas in mice (n 10), all of these 14-mers were antigenic or strongly antigenic in several animals (16). The C 6 epitopes recognized by dogs resemble those discerned by the antibody response of primate hosts, in that in most animals, C 6 M was antigenic, albeit less than C 6 itself. The antigenicity of the whole VlsE molecule has been investigated by Lawrenz and colleagues (12). These authors used a whole recombinant VlsE protein cloned from B. burgdorferi sensu stricto strain B31 as the ELISA antigen. Their study indicated that the recombinant VlsE ELISA could be a sensitive and specific method for the serodiagnosis of Lyme disease (12). Our previous antigenic analysis has revealed that IR 6 is the only immunodominant IR in humans (13, 14). Since VlsE is a variable antigen, its six variable regions (13, 23) (Fig. 1), regardless of their antigenicity, should be of no value for serodiagnosis. VlsE also contains two invariable domains at the amino and carboxyl termini, which collectively comprise one half of the entire VlsE molecule length (13, 23). It is unknown whether these two invariable domains are antigenic or have any diagnostic value. Recent data, however, indicate that these two invariable domains may not be conserved even among strains within the genospecies B. burgdorferi sensu stricto (9), although they remain unchanged during antigenic variation (23). Their role in serodiagnosis remains to be investigated. Our previous survey of a large number of human serum specimens collected from both U.S. and European Lyme disease patients demonstrated that IR 6 (C 6 ) alone can serve as a probe for the universal serodiagnosis of human Lyme disease (14, 17). The results presented herein strongly support the conclusion that the single probe IR 6 (C 6 ) is sufficient for canine Lyme disease serodiagnosis. When a single peptide sequence is used as a diagnostic probe, its antigenic conservation and antigenicity must be considered. The IR 6 sequence remains unchanged during antigenic variation (23), and it is both structurally and antigenically conserved among pathogenic B. burgdorferi strains and genospecies (13). It is so immunodominant that all experimentally infected animals, including mice and monkeys in previous studies (13, 14) and dogs in this study, produce an early, persistent, and strong antibody response to this sequence. Its antigenicity was also underscored by surveys of a large number of human samples. When this sequence was used in ELISA, diagnostic sensitivities of 80% for early Lyme disease and nearly 100% for late Lyme disease were achieved (14, 18). Previous and current antigenic analyses indicate that mice and dogs respond to IR 6 as well as or better than monkeys and humans do (13 15, 18). Within 6 weeks, all experimentally infected monkeys produced a detectable antibody response to C 6 (14), although 5 weeks were required for all of the infected dogs to show a high titer of antibody to this peptide. Similarly, the sensitivities of the C 6 ELISA were 42, 72, 80, 83, and 90% with human samples collected at 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 to 8 weeks, respectively, after the disease onset (14). The C 6 ELISA was able to detect both early and chronic infections. Although we can offer no proof that the dogs remained infected, we have preliminary evidence that the C 6
6 VOL. 38, 2000 CANINE LYME DISEASE SERODIAGNOSIS 4165 Serum ID a TABLE 1. Comparison of KELA, immunoblot assay, and C 6 ELISA results Results of KELA (U) b Immunoblot c C 6 ELISA (OD) d a These sera were originally received for serology of Lyme disease by a diagnostic laboratory. b KELA was conducted as described previously (22). KELA values of 100 U were defined as positive. c Immunoblotting diagnosis was performed as described previously (22). d The C 6 ELISA was performed as described in Materials and Methods. The cutoff line (OD 0.376) was defined as described in the legend to Fig. 5. antibody level diminishes significantly within a 12-week period following treatment of dogs with antibiotics (Liang et al., unpublished data). In contrast, all of the four (untreated) dogs tested herein maintained a strong anti-ir 6 response for at least 69 weeks postinfection (Fig. 5). Serology of Lyme disease may be complicated by the low specificity of the conventional assays, in which whole-cell lysates of cultured spirochetes are used as antigen. Low specificity may be caused by cross-reactive antigens shared between B. burgdorferi and other pathogenic and nonpathogenic bacteria. Examples of such antigens are bacterial heat shock proteins (20), flagellin (2), and other common antigens (8). Unrelated bacterial infections may thus elicit antibodies that react with B. burgdorferi antigens, causing false positive results. In contrast to the existing diagnostic techniques, the C 6 ELISA is expected to be highly specific. None of the blood samples collected from 14 dogs with leptospirosis or RMSF or infected with Babesia, Ehrlichia,orDirofilaria spp. contained detectable antibody to C 6. In fact, except for VlsE, which is expressed solely by B. burgdorferi, no other protein sequences homologous to IR 6 could be identified by BLAST searches in the National Center for Biotechnology Information database (13). More importantly, vaccination with the recombinant OspA or whole-spirochete vaccines did not induce an antibody response cross-reactive with C 6 (Fig. 6). In contrast, bacterin immunization resulted in multiple strong bands on B. burgdorferi immunoblots (6). These limited data suggest that the C 6 ELISA is not only specific but also usable in the current vaccination era. It was possible to establish cutoffs in the C 6 ELISA that yielded 100% sensitivity and 100% specificity when the assay was evaluated using experimentally infected beagles (Fig. 5). The assay did not give false positive results when testing dogs that were known to be uninfected with B. burgdorferi or dogs infected with other organisms. As already mentioned above, it was of considerable interest that the assay did not react with sera from dogs that had been vaccinated with either the wholecell or recombinant OspA commercial vaccine for Lyme disease or the common puppy shots (Fig. 6). This makes the assay more valuable in detecting infected animals despite their vaccinal status. However, when the assay was applied to 55 serum samples submitted to a diagnostic laboratory by veterinarians who requested Lyme serology, 5 samples were misclassified by the C 6 ELISA (Table 1) if immunoblot or KELA was used as the gold standard (10). This discrepancy may be explained by the fact that these 55 samples were not collected from welldefined clinical cases. It will be necessary to further assess these assays using a larger number of serum specimens from dogs with clinically well-defined Lyme disease. Unfortunately, the clinical diagnosis of Lyme disease is much more difficult in dogs than in humans, and such clinical samples are not easily available in large numbers. Experimental infection may be the best alternative to examine the potential of new serologic assays for canine Lyme disease, as we have done in this paper. ACKNOWLEDGMENT This work was supported in part by NCRR-NIH grant RR REFERENCES 1. Appel, M. J. G., S. Allan, R. H. Jacobson, T. L. Lauderdale, Y. F. Chang, S. J. Shin, J. W. Thomford, R. J. Todhunter, and B. A. Summers Experimental Lyme disease in dogs produces arthritis and persistent infection. J. Infect. Dis. 167: Barbour, A. G., S. F. Hayes, R. A. Heiland, and M. E. Schrumpf A Borrelia genus-specific monoclonal antibody binds to a flagellar epitope. Infect. Immun. 52: Barony, G., and R. B. Merrifield The peptides: analysis, synthesis, & biology. Academic Press, Inc., New York, N.Y. 4. Benjamin, D. C B-cell epitopes: fact and fiction, p In L. M. Aledort et al. (ed.), Inhibitors to coagulation factors. Plenum Press, New York, N.Y.
7 4166 LIANG ET AL. J. CLIN. MICROBIOL. 5. Berzofsky, J. A., and I. J. Berkower Immunogenicity and antigen structure, p In W. E. Paul (ed.), Fundamental immunology. Raven Press, New York, N.Y. 6. Chu, H. J., L. G. Chavez, B. M. Blumer, R. W. Sebring, T. L. Wasmoen, and W. M. Acree Immunogenicity and efficacy study of a commercial Borrelia burgdorferi bacterin. J. Am. Vet. Med. Assoc. 201: Eng, T. R., M. L. Wilson, A. Spielman, and C. C. Lastavica Greater risk of Borrelia burgdorferi infection in dogs than in people. J. Infect. Dis. 158: Hansen, K., J. M. Bangsborg, H. Fjordvang, N. S. Pedersen, and P. Hindersson Immunochemical characterization of and isolation of the gene for a Borrelia burgdorferi immunodominant 60-kilodalton antigen common to a wide range of bacteria. Infect. Immun. 56: Iyer, R., J. M. Hardham, G. P. Wormser, I. Schwartz, and S. J. Norris Conservation and heterogeneity of vlse among human and tick isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect. Immun. 68: Jacobson, R. H Validation of serological assays for diagnosis of infectious diseases. Rev. Sci. Tech. 17: Kawabata, H., F. Myouga, Y. Inagaki, N. Murai, and H. Watanabe Genetic and immunological analyses of Vls (VMP-like sequences) of Borrelia burgdorferi. Microb. Pathog. 24: Lawrenz, M. B., J. M. Hardham, R. T. Owens, J. Nowakowski, A. C. Steere, G. P. Wormser, and S. J. Norris Human antibody responses to VlsE antigenic variable protein of Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37: Liang, F. T., A. L. Alvarez, Y. Gu, J. M. Nowling, R. Ramamoorthy, and M. T. Philipp An immunodominant conserved region within the variable domain of VlsE, the variable surface antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Immunol. 163: Liang, F. T., A. C. Steere, A. R. Marques, B. J. B. Johnson, J. N. Miller, and M. T. Philipp Sensitive and specific serodiagnosis of Lyme disease by ELISA with a peptide based on an immunodominant conserved region of Borrelia burgdorferi VlsE. J. Clin. Microbiol. 37: Liang, F. T., and M. T. Philipp Analysis of antibody response to invariable regions of VlsE, the variable surface antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect. Immun. 67: Liang, F. T., and M. T. Philipp Epitope mapping of the immunodominant invariable region of VlsE, the variable surface antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect. Immun. 68: Liang, F. T., J. M. Nowling, and M. T. Philipp Cryptic and exposed invariable regions of VlsE, the variable surface antigen of Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Bacteriol. 182: Liang, F. T., E. Aberer, M. Cinco, L. Gern, C. M. Hu, Y. N. Lobet, M. Ruscio, P. E. Voet, Jr., V. E. Weynants, and M. T. Philipp. Antigenic conservation of an immunodominant invariable region of the VlsE lipoprotein among European pathogenic genospecies of Borrelia burgdorferi s1. J. Infect. Dis., in press. 19. Lindenmayer, J. M., D. Marshall, and A. B. Onderdonk Dogs as sentinels for Lyme disease in Massachusetts. Am. J. Public Health 81: Luft, B. J., P. D. Gorevic, W. Jiang, P. Munoz, and R. J. Dattwyler Immunologic and structural characterization of the dominant 66- to 73-kDa antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi. J. Immunol. 146: Shin, S. J., Y. F. Chang, R. H. Jacobson, E. Shaw, T. L. Lauderdale, M. J. G. Appel, and D. H. Lein Cross-reactivity between Borrelia burgdorferi and other spirochetes affects specificity of serotests for detection of antibodies to the Lyme disease agent in dogs. Vet. Microbiol. 36: Straubinger, R. K., A. F. Straubinger, B. A. Summers, and R. H. Jacobson Status of Borrelia burgdorferi infection after antibiotic treatment and the effects of corticosteroids: an experimental study. J. Infect. Dis. 181: Zhang, J. R., J. M. Hardham, A. G. Barbour, and S. J. Norris Antigenic variation in Lyme disease Borreliae by promiscuous recombination of VMP-like sequence cassettes. Cell 89: Downloaded from on September 28, 2018 by guest
Received 16 September 2003/Returned for modification 14 November 2003/Accepted 16 February 2004
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, May 2004, p. 458 462 Vol. 11, No. 3 1071-412X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.11.3.458 462.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, May 2004, p. 458 462 Vol. 11, No. 3 1071-412X/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.11.3.458 462.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1999, p Vol. 37, No. 12. Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1999, p. 3990 3996 Vol. 37, 12 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Sensitive and Specific Serodiagnosis
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Dec. 1999, p. 3990 3996 Vol. 37, 12 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Sensitive and Specific Serodiagnosis
Antibody Response to IR, a Conserved Immunodominant Region of the VlsE
 870 Antibody Response to IR 6, a Conserved Immunodominant Region of the VlsE Lipoprotein, Wanes Rapidly after Antibiotic Treatment of Borrelia burgdorferi Infection in Experimental Animals and in Humans
870 Antibody Response to IR 6, a Conserved Immunodominant Region of the VlsE Lipoprotein, Wanes Rapidly after Antibiotic Treatment of Borrelia burgdorferi Infection in Experimental Animals and in Humans
Animal Health Diagnostic Center. Lyme Disease Multiplex Testing for Dogs. Background on Lyme disease and Lyme diagnostics in dogs
 Animal Health Diagnostic Center Lyme Disease Multiplex Testing for Dogs Background on Lyme disease and Lyme diagnostics in dogs Lyme disease is induced by the spirochete B. burgdorferi. Spirochetes are
Animal Health Diagnostic Center Lyme Disease Multiplex Testing for Dogs Background on Lyme disease and Lyme diagnostics in dogs Lyme disease is induced by the spirochete B. burgdorferi. Spirochetes are
C 6 Test as an Indicator of Therapy Outcome for Patients with Localized or Disseminated Lyme Borreliosis
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2003, p. 4955 4960 Vol. 41, No. 11 0095-1137/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.11.4955 4960.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 2003, p. 4955 4960 Vol. 41, No. 11 0095-1137/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.41.11.4955 4960.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Evidence That the Variable Regions of the Central Domain of VlsE Are Antigenic during Infection with Lyme Disease Spirochetes
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2002, p. 4196 4203 Vol. 70, No. 8 0019-9567/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4196 4203.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evidence
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Aug. 2002, p. 4196 4203 Vol. 70, No. 8 0019-9567/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.70.8.4196 4203.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Evidence
LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University
 LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in European journal of clinical microbiology & infectious diseases: official publication
LU:research Institutional Repository of Lund University This is an author produced version of a paper published in European journal of clinical microbiology & infectious diseases: official publication
1 of 12 23/11/ :25
 1 of 12 23/11/2008 09:25 And The Bands Played On - Western blot serological test for Lyme disease http://www.geocities.com/hotsprings/oasis/6455/western-blot.txt ************************************************************************
1 of 12 23/11/2008 09:25 And The Bands Played On - Western blot serological test for Lyme disease http://www.geocities.com/hotsprings/oasis/6455/western-blot.txt ************************************************************************
Department of Medical Microbiology, University Hospital Maastricht, Maastricht, The Netherlands
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01448.x Comparison of five different immunoassays for the detection of Borrelia burgdorferi IgM and IgG antibodies A. Smismans, V. J. Goossens, E. Nulens and C.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2006.01448.x Comparison of five different immunoassays for the detection of Borrelia burgdorferi IgM and IgG antibodies A. Smismans, V. J. Goossens, E. Nulens and C.
Received 7 March 2002/Returned for modification 21 June 2002/Accepted 10 July 2002
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Nov. 2002, p. 1348 1355 Vol. 9, No. 6 1071-412X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.9.6.1348 1355.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Nov. 2002, p. 1348 1355 Vol. 9, No. 6 1071-412X/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CDLI.9.6.1348 1355.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights
Persistence of Immunoglobulin M or Immunoglobulin G Antibody Responses to Borrelia burgdorferi Years after Active Lyme Disease
 MAJOR ARTICLE Persistence of Immunoglobulin M or Immunoglobulin G Antibody Responses to Borrelia burgdorferi 10 20 Years after Active Lyme Disease Robert A. Kalish, 1 Gail McHugh, 1 John Granquist, 1 Barry
MAJOR ARTICLE Persistence of Immunoglobulin M or Immunoglobulin G Antibody Responses to Borrelia burgdorferi 10 20 Years after Active Lyme Disease Robert A. Kalish, 1 Gail McHugh, 1 John Granquist, 1 Barry
Anti-Borrelia burgdorferi Antibody Profile in Post-Lyme Disease Syndrome
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, May 2011, p. 767 771 Vol. 18, No. 5 1556-6811/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.00002-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Anti-Borrelia burgdorferi
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, May 2011, p. 767 771 Vol. 18, No. 5 1556-6811/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.00002-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Anti-Borrelia burgdorferi
BlueBLOT-LINE Borrelia. Test Characteristics. Antibody Response
 BlueDiver Instrument IMMUNOBLOT KITS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF LYME BORRELIOSIS INFECTIOUS SEROLOGY IN NEW AUTOMATED SYSTEM FOR THE ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION OF IMMUNOBLOTS BlueDiver Instrument, Immunoblot Software
BlueDiver Instrument IMMUNOBLOT KITS FOR DIAGNOSIS OF LYME BORRELIOSIS INFECTIOUS SEROLOGY IN NEW AUTOMATED SYSTEM FOR THE ANALYSIS AND EVALUATION OF IMMUNOBLOTS BlueDiver Instrument, Immunoblot Software
MAJOR ARTICLE. John A. Branda, 1 Katy Linskey, 1 Yeowon A. Kim, 1 Allen C. Steere, 2 and Mary Jane Ferraro 1,2
 MAJOR ARTICLE Two-Tiered Antibody Testing for Lyme Disease With Use of 2 Enzyme Immunoassays, a Whole-Cell Sonicate Enzyme Immunoassay Followed by a VlsE C6 Peptide Enzyme Immunoassay John A. Branda, 1
MAJOR ARTICLE Two-Tiered Antibody Testing for Lyme Disease With Use of 2 Enzyme Immunoassays, a Whole-Cell Sonicate Enzyme Immunoassay Followed by a VlsE C6 Peptide Enzyme Immunoassay John A. Branda, 1
Quantitative Approach for the Serodiagnosis of Canine Lyme Disease by the Immunoblot Procedure
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 2000, p. 2628 2632 Vol. 38, No. 7 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Quantitative Approach for the Serodiagnosis
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 2000, p. 2628 2632 Vol. 38, No. 7 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Quantitative Approach for the Serodiagnosis
E. Histolytica IgG (Amebiasis)
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Microfluidics-based point-of-care test for serodiagnosis of Lyme Disease
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Microfluidics-based point-of-care test for serodiagnosis of Lyme Disease Samiksha Nayak 1, Archana Sridhara 1, Rita Melo 2, Luciana Richer 3, Natalie H. Chee 1, Jiyoon Kim 1,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Microfluidics-based point-of-care test for serodiagnosis of Lyme Disease Samiksha Nayak 1, Archana Sridhara 1, Rita Melo 2, Luciana Richer 3, Natalie H. Chee 1, Jiyoon Kim 1,
Fatigue, persistence after Lyme borreliosis 196, 197 Francisella tularensis, see Tularemia
 Subject Index Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (ACA) antibiotic therapy 121, 122 Borrelia induction 13 clinical characteristics 64, 65, 82 diagnosis 65, 66 differential diagnosis 66 etiology 62 frequency
Subject Index Acrodermatitis chronica atrophicans (ACA) antibiotic therapy 121, 122 Borrelia induction 13 clinical characteristics 64, 65, 82 diagnosis 65, 66 differential diagnosis 66 etiology 62 frequency
Western immunoblot analysis for distinguishing vaccination and infection status with Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease) in dogs
 J Vet Diagn Invest 11:259 265 (1999) Western immunoblot analysis for distinguishing vaccination and infection status with Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease) in dogs David T. Gauthier, Linda S. Mansfield
J Vet Diagn Invest 11:259 265 (1999) Western immunoblot analysis for distinguishing vaccination and infection status with Borrelia burgdorferi (Lyme disease) in dogs David T. Gauthier, Linda S. Mansfield
Antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi OspA, OspC, OspF and C6 antigens as markers for early
 CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 15 February 2012 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.05653-11 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Antibodies to
CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 15 February 2012 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.05653-11 Copyright 2012, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Antibodies to
Immunoblot Interpretation Criteria for Serodiagnosis of Early Lyme Disease
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1995, p. 419 427 Vol. 33, No. 2 0095-1137/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Immunoblot Interpretation Criteria for Serodiagnosis of Early
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Feb. 1995, p. 419 427 Vol. 33, No. 2 0095-1137/95/$04.00 0 Copyright 1995, American Society for Microbiology Immunoblot Interpretation Criteria for Serodiagnosis of Early
STATEMENT FOR MANAGING LYME DISEASE IN NOVA SCOTIA
 INFECTIOUS DISEASES EXPERT GROUP (IDEG) DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND WELLNESS STATEMENT FOR MANAGING LYME DISEASE IN NOVA SCOTIA Executive Summary: In 2016, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) modified
INFECTIOUS DISEASES EXPERT GROUP (IDEG) DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH AND WELLNESS STATEMENT FOR MANAGING LYME DISEASE IN NOVA SCOTIA Executive Summary: In 2016, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) modified
Serodiagnosis of Lyme Borreliosis by Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Stricto, B. garinii, and B. afzelii Western Blots (Immunoblots)
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1996, p. 1732 1738 Vol. 34, No. 7 0095-1137/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Serodiagnosis of Lyme Borreliosis by Borrelia burgdorferi
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1996, p. 1732 1738 Vol. 34, No. 7 0095-1137/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Serodiagnosis of Lyme Borreliosis by Borrelia burgdorferi
Detection of Multiple Reactive Protein Species by Immunoblotting after Recombinant Outer Surface Protein A Lyme Disease Vaccination
 42 Detection of Multiple Reactive Protein Species by Immunoblotting after Recombinant Outer Surface Protein A Lyme Disease Vaccination Philip J. Molloy, 1,2 Victor P. Berardi, 2 David H. Persing, 2,3,a
42 Detection of Multiple Reactive Protein Species by Immunoblotting after Recombinant Outer Surface Protein A Lyme Disease Vaccination Philip J. Molloy, 1,2 Victor P. Berardi, 2 David H. Persing, 2,3,a
Infectious Diseases Expert Group (IDEG) Department of Health and Wellness. Statement for Managing Lyme Disease in Nova Scotia
 Infectious Diseases Expert Group (IDEG) Department of Health and Wellness Statement for Managing Lyme Disease in Nova Scotia 2018 Executive Summary: In 2016, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) modified
Infectious Diseases Expert Group (IDEG) Department of Health and Wellness Statement for Managing Lyme Disease in Nova Scotia 2018 Executive Summary: In 2016, the Public Health Agency of Canada (PHAC) modified
HIV-1 p24 Antigen ELISA Catalog Number:
 INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK HIV-1 p24 Antigen ELISA is supplied for research purposes only. It is not intended for use in the diagnosis or prognosis of disease, or for screening and may not be used as a
INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK HIV-1 p24 Antigen ELISA is supplied for research purposes only. It is not intended for use in the diagnosis or prognosis of disease, or for screening and may not be used as a
Taenia solium IgG ELISA Kit
 Taenia solium IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3191 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Taenia solium IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3191 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Interpretation Criteria for Standardized Western Blots for Three European Species of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1997, p. 1433 1444 Vol. 35, No. 6 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Interpretation Criteria for Standardized Western Blots for
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 1997, p. 1433 1444 Vol. 35, No. 6 0095-1137/97/$04.00 0 Copyright 1997, American Society for Microbiology Interpretation Criteria for Standardized Western Blots for
Antibody Profiling of Borrelia burgdorferi Infection in Horses
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2011, p. 1562 1567 Vol. 18, No. 9 1556-6811/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.05123-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antibody Profiling
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2011, p. 1562 1567 Vol. 18, No. 9 1556-6811/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.05123-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Antibody Profiling
CONTENTS. STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1
 CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
Technical Bulletin No. 121
 CPAL Central Pennsylvania Alliance Laboratory Technical Bulletin No. 121 January 31, 2014 Lyme Blot, IgG and IgM - Now Performed at CPAL Contact: J. Matthew Groeller, 717.851.1416 Operations Manager, Clinical
CPAL Central Pennsylvania Alliance Laboratory Technical Bulletin No. 121 January 31, 2014 Lyme Blot, IgG and IgM - Now Performed at CPAL Contact: J. Matthew Groeller, 717.851.1416 Operations Manager, Clinical
E. Histolytica IgG ELISA Kit
 E. Histolytica IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3193 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
E. Histolytica IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3193 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Toxocara. Cat # Toxocara ELISA. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay. ELISA-Indirect; Antigen Coated Plate
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite D/E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Prospective Study of Serologic Tests for Lyme Disease
 MAJOR ARTICLE Prospective Study of Serologic Tests for Lyme Disease Allen C. Steere, Gail McHugh, Nitin Damle, and Vijay K. Sikand Center for Immunology and Inflammatory Diseases, Division of Rheumatology,
MAJOR ARTICLE Prospective Study of Serologic Tests for Lyme Disease Allen C. Steere, Gail McHugh, Nitin Damle, and Vijay K. Sikand Center for Immunology and Inflammatory Diseases, Division of Rheumatology,
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit
 Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
Mouse Anti-OVA IgM Antibody Assay Kit Catalog # 3017 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Ovalbumin (OVA) is a widely used antigen for inducing allergic reactions in experimental
A Study of the Technique of Western Blot for Diagnosis of Lyme Disease caused by Borrelia afzelii in China *
 190 Biomed Environ Sci, 2013; 26(3): 190 200 Original Article A Study of the Technique of Western Blot for Diagnosis of Lyme Disease caused by Borrelia afzelii in China * LIU Zhi Yun 1,2,3,+, HAO Qin 1,+,
190 Biomed Environ Sci, 2013; 26(3): 190 200 Original Article A Study of the Technique of Western Blot for Diagnosis of Lyme Disease caused by Borrelia afzelii in China * LIU Zhi Yun 1,2,3,+, HAO Qin 1,+,
IVD. DRG Toxocara canis ELISA (EIA-3518) Revised 12 Feb rm (Vers. 6.1)
 Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. Intended Use For the qualitative screening of serum IgG antibodies to Toxocara using an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. Intended Use For the qualitative screening of serum IgG antibodies to Toxocara using an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Panel # Panel CPT Code Price 2010 AUTOIMMUNE PROFILE - BASIC 99.00
 2010 AUTOIMMUNE PROFILE - BASIC 99.00 Anti-Nuclear Antibody (ANA) 86038 33.00 Rheumatoid Factor 86431 33.00 C1Q Immune Complex 86332 33.00 2011 AUTOIMMUNE PROFILE (COMPREHENSIVE) 210.00 Anti-Nuclear Antibody
2010 AUTOIMMUNE PROFILE - BASIC 99.00 Anti-Nuclear Antibody (ANA) 86038 33.00 Rheumatoid Factor 86431 33.00 C1Q Immune Complex 86332 33.00 2011 AUTOIMMUNE PROFILE (COMPREHENSIVE) 210.00 Anti-Nuclear Antibody
Received 12 January 2005/Returned for modification 9 May 2005/Accepted 15 June 2005
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2005, p. 1036 1040 Vol. 12, No. 9 1071-412X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cdli.12.9.1036 1040.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, Sept. 2005, p. 1036 1040 Vol. 12, No. 9 1071-412X/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cdli.12.9.1036 1040.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All
ELISA Range. VIROTECH Diagnostics GmbH. Lot independent. Reagent. System. IgG-Conjugate. Substrate. IgM-Conjugate. Washing Solution.
 Quelle: www.fotolia.com ELISA Range IgG-Conjugate IgM-Conjugate IgA-Conjugate Lot independent Reagent System Stop Solution Substrate Washing Solution Serum Dilution Dilution Buffer Incubation Time Cerebrospinal
Quelle: www.fotolia.com ELISA Range IgG-Conjugate IgM-Conjugate IgA-Conjugate Lot independent Reagent System Stop Solution Substrate Washing Solution Serum Dilution Dilution Buffer Incubation Time Cerebrospinal
guidelines types Why change? This is a disturbing trend.
 Canine Vaccination Protocols Richard B. Ford, DVM, MS, Dipl ACVIM Professor of Medicine, North Carolina State University North Carolina, USA Richard_Ford@ncsu.edu 18288593 The rapid proliferation of companion
Canine Vaccination Protocols Richard B. Ford, DVM, MS, Dipl ACVIM Professor of Medicine, North Carolina State University North Carolina, USA Richard_Ford@ncsu.edu 18288593 The rapid proliferation of companion
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Serodiagnosis of Canine Babesiosis
 Serodiagnosis of Canine Babesiosis Xuenan XUAN, DVM, PhD National Research Center for Protozoan Diseases Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine Obihiro, Hokkaido 080-8555, Japan Tel.:+81-155-495648;
Serodiagnosis of Canine Babesiosis Xuenan XUAN, DVM, PhD National Research Center for Protozoan Diseases Obihiro University of Agriculture and Veterinary Medicine Obihiro, Hokkaido 080-8555, Japan Tel.:+81-155-495648;
Diagnostic and Biological Significance of Anti-p41 IgM Antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi
 Scand. J. Immunol. 53, 416±421, 2001 Diagnostic and Biological Significance of Anti-p41 IgM Antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi E. ULVESTAD,* A. KANESTRéM,* L. J. SéNSTEBY,* R. JUREEN,* T. OMLAND,*
Scand. J. Immunol. 53, 416±421, 2001 Diagnostic and Biological Significance of Anti-p41 IgM Antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi E. ULVESTAD,* A. KANESTRéM,* L. J. SéNSTEBY,* R. JUREEN,* T. OMLAND,*
Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit.
 Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. Intended Use For the qualitative screening of serum IgG antibodies to Trichinella using an Enzyme Linked Immunoabsorbant Assay
Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. Intended Use For the qualitative screening of serum IgG antibodies to Trichinella using an Enzyme Linked Immunoabsorbant Assay
PRICE LIST Effective Date: October 16, 2017
 Effective October 16, 2017 we are offering our new tests for Lyme IGXSpot, Lyme Borreliosis, and Tick-borne Relapsing Fever Borreliosis The new ImmunoBlot tests have replaced the original Western Blot
Effective October 16, 2017 we are offering our new tests for Lyme IGXSpot, Lyme Borreliosis, and Tick-borne Relapsing Fever Borreliosis The new ImmunoBlot tests have replaced the original Western Blot
False-negative serology in patients with neuroborreliosis and the value of employing of different borrelial strains in serological assays
 J. Med. Microbiol. Ð Vol. 49 2000), 911±915 # 2000 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland ISSN 0022-2615 IMMUNOLOGICAL RESPONSE TO INFECTION False-negative serology in patients with neuroborreliosis
J. Med. Microbiol. Ð Vol. 49 2000), 911±915 # 2000 The Pathological Society of Great Britain and Ireland ISSN 0022-2615 IMMUNOLOGICAL RESPONSE TO INFECTION False-negative serology in patients with neuroborreliosis
Cross-Reactivity to Field Isolates of Canine Influenza Virus by a Killed Canine Influenza Virus (H3N8, Iowa05) Vaccine
 Cross-Reactivity to Field Isolates of Canine Influenza Virus by a Killed Canine Influenza Virus (H3N8, Iowa05) Vaccine Nancee Oien, B.S., M.S. a Sally Mattern, B.S a Jaime Brozowski, B.S., M.S. b Janet
Cross-Reactivity to Field Isolates of Canine Influenza Virus by a Killed Canine Influenza Virus (H3N8, Iowa05) Vaccine Nancee Oien, B.S., M.S. a Sally Mattern, B.S a Jaime Brozowski, B.S., M.S. b Janet
Beyond the next generation: data mining and T cells. Amanda Semper, Scientific Programmes Manager, PHE Rare and Imported Pathogens Laboratory
 Beyond the next generation: data mining and T cells Amanda Semper, Scientific Programmes Manager, PHE Rare and Imported Pathogens Laboratory Overview Data mining Getting the most from diagnostic data The
Beyond the next generation: data mining and T cells Amanda Semper, Scientific Programmes Manager, PHE Rare and Imported Pathogens Laboratory Overview Data mining Getting the most from diagnostic data The
ENZYME IMMUNOASSAYS AND AGGLUTINATION FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF PERTUSSIS AND PARAPERTUSSIS
 INFECTIOUS SEROLOGY Bacteriology ENZYME IMMUNOASSAYS AND AGGLUTINATION FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF PERTUSSIS AND PARAPERTUSSIS Bordetella pertussis Bordetella parapertussis ELISA and IMMUNOBLOT kits are optimized
INFECTIOUS SEROLOGY Bacteriology ENZYME IMMUNOASSAYS AND AGGLUTINATION FOR THE DIAGNOSIS OF PERTUSSIS AND PARAPERTUSSIS Bordetella pertussis Bordetella parapertussis ELISA and IMMUNOBLOT kits are optimized
Q fever. Lyme disease LDA Conference Anja Garritsen 1. Lyme Disease Diagnostics. Today s presentation
 Today s presentation Lyme Disease Diagnostics What can we use now What do we need for the future? Anja Garritsen, Innatoss Laboratories, NL Innatoss Diagnostics for Lyme Disease The present Diagnostic
Today s presentation Lyme Disease Diagnostics What can we use now What do we need for the future? Anja Garritsen, Innatoss Laboratories, NL Innatoss Diagnostics for Lyme Disease The present Diagnostic
Anti-HIV I(0), II/p24 (Human) ELISA Kit
 Anti-HIV I(0), II/p24 (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3985 96 assays Version: 3.1 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3
Anti-HIV I(0), II/p24 (Human) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA3985 96 assays Version: 3.1 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3
Human HBcAb IgM ELISA kit
 Human HBcAb IgM ELISA kit Catalog number: NR-R10163 (96 wells) The kit is designed to qualitatively detect HBcAb IgM in human serum or plasma. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC PURPOSES
Human HBcAb IgM ELISA kit Catalog number: NR-R10163 (96 wells) The kit is designed to qualitatively detect HBcAb IgM in human serum or plasma. FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY. NOT FOR DIAGNOSTIC OR THERAPEUTIC PURPOSES
Humoral Immune Responses in Patients with Lyme Neuroborreliosis
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Apr. 2010, p. 645 650 Vol. 17, No. 4 1556-6811/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.00341-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Humoral Immune
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Apr. 2010, p. 645 650 Vol. 17, No. 4 1556-6811/10/$12.00 doi:10.1128/cvi.00341-09 Copyright 2010, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Humoral Immune
Trichinella Cat #
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
Panel & Test Price List Effective Date: October 16, 2017
 -New tests now available: Bartonella IGXSpot, Bartonella Western Blot IgG & IgM -Tests Now available for New York residents: Lyme ImmunoBlots IgG & IgM *IGXSP IGXSpot Panel $442.50 Lyme IGXSpot 86352 Bartonella
-New tests now available: Bartonella IGXSpot, Bartonella Western Blot IgG & IgM -Tests Now available for New York residents: Lyme ImmunoBlots IgG & IgM *IGXSP IGXSpot Panel $442.50 Lyme IGXSpot 86352 Bartonella
Lyme Disease. By Farrah Jangda
 Lyme Disease By Farrah Jangda Disease Name: Lyme Disease Lyme disease is a common tick-borne bacterial infection transmitted from the bite of a tick in United States and Europe (2). It is caused by the
Lyme Disease By Farrah Jangda Disease Name: Lyme Disease Lyme disease is a common tick-borne bacterial infection transmitted from the bite of a tick in United States and Europe (2). It is caused by the
Vaccination Recommendations Practice and Shelter-Housed Dogs
 Vaccination Recommendations Practice and Shelter-Housed Dogs 1. MIXING VACCINES. Can different types of vaccines be mixed in the same syringe? No. Unless specifically stated on the product label (package
Vaccination Recommendations Practice and Shelter-Housed Dogs 1. MIXING VACCINES. Can different types of vaccines be mixed in the same syringe? No. Unless specifically stated on the product label (package
Instructions for Use. Borrelia Veterinary plus OspA LINE
 Instructions for Use Borrelia Veterinary plus OspA LINE IgG Line Immunoblot To determine IgG antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in dog and horse sera Order No.: DE226G32 IgG Line Immunoblot
Instructions for Use Borrelia Veterinary plus OspA LINE IgG Line Immunoblot To determine IgG antibodies to Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato in dog and horse sera Order No.: DE226G32 IgG Line Immunoblot
[1]. Therefore, determination of antibody titers is currently the best laboratory
![[1]. Therefore, determination of antibody titers is currently the best laboratory [1]. Therefore, determination of antibody titers is currently the best laboratory](/thumbs/75/71961750.jpg) THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 57 (1984), 561-565 The Antibody Response in Lyme Disease JOSEPH E. CRAFT, M.D., ROBERT L. GRODZICKI, M.S., MAHESH SHRESTHA, B.A., DUNCAN K. FISCHER, M.Phil., MARIANO
THE YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 57 (1984), 561-565 The Antibody Response in Lyme Disease JOSEPH E. CRAFT, M.D., ROBERT L. GRODZICKI, M.S., MAHESH SHRESTHA, B.A., DUNCAN K. FISCHER, M.Phil., MARIANO
Vaccines for Dogs. "Immunity has memory."
 Vaccines for Dogs What is a vaccine? The word vaccine comes from the Latin word "vacca", which means cow. An English country doctor, Dr. Edward Jenner, discovered that people given a preparation or vaccine
Vaccines for Dogs What is a vaccine? The word vaccine comes from the Latin word "vacca", which means cow. An English country doctor, Dr. Edward Jenner, discovered that people given a preparation or vaccine
Evaluation of two commercially available rapid diagnostic tests for Lyme borreliosis
 DOI 10.1007/s10096-014-2217-5 ARTICLE Evaluation of two commercially available rapid diagnostic tests for Lyme borreliosis P. W. Smit & S. Kurkela & M. Kuusi & O. Vapalahti Received: 26 June 2014 /Accepted:
DOI 10.1007/s10096-014-2217-5 ARTICLE Evaluation of two commercially available rapid diagnostic tests for Lyme borreliosis P. W. Smit & S. Kurkela & M. Kuusi & O. Vapalahti Received: 26 June 2014 /Accepted:
Performance of a Recombinant LipL32 Based Rapid In-clinic ELISA (SNAP Lepto) for the Detection of Antibodies Against Leptospira in Dogs
 Performance of a Recombinant LipL32 Based Rapid In-clinic ELISA (SNAP Lepto) for the Detection of Antibodies Against Leptospira in Dogs Curtis, KM 1 Foster, PC 1 Smith, PS 1 Monn, MP Stillman, BA 1 Chandrashekar
Performance of a Recombinant LipL32 Based Rapid In-clinic ELISA (SNAP Lepto) for the Detection of Antibodies Against Leptospira in Dogs Curtis, KM 1 Foster, PC 1 Smith, PS 1 Monn, MP Stillman, BA 1 Chandrashekar
NOTES. Received 4 November 2005/Returned for modification 30 December 2005/Accepted 2 February 2006
 CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Apr. 2006, p. 525 529 Vol. 13, No. 4 1556-6811/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.13.4.525 529.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES
CLINICAL AND VACCINE IMMUNOLOGY, Apr. 2006, p. 525 529 Vol. 13, No. 4 1556-6811/06/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cvi.13.4.525 529.2006 Copyright 2006, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES
Anthrax protective antigen IgG ELISA Kit
 Anthrax protective antigen IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0953 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3
Anthrax protective antigen IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0953 96 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set
 Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Ring Forms in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Babesia? from Danish Chronically Ill Patients, All Clinically Suspect of Having Persistent Active Borreliosis!
 Ring Forms in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Babesia? from Danish Chronically Ill Patients, All Clinically Suspect of Having Persistent Active Borreliosis! Marie Kroun, MD Denmark Presentation in York, UK June
Ring Forms in Red Blood Cells (RBCs) Babesia? from Danish Chronically Ill Patients, All Clinically Suspect of Having Persistent Active Borreliosis! Marie Kroun, MD Denmark Presentation in York, UK June
Comparison of Different Strains of Borrelia burgdorferi Sensu Lato Used as Antigens in Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assays
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1994, p. 1154-1158 Vol. 32, No. 5 0095-1 137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright C) 1994, American Society for Microbiology Comparison of Different Strains of Borrelia burgdorferi
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, May 1994, p. 1154-1158 Vol. 32, No. 5 0095-1 137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright C) 1994, American Society for Microbiology Comparison of Different Strains of Borrelia burgdorferi
Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2017) 36:2137 2146 DOI 10.1007/s10096-017-3037-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Disagreement between the results from three commercial tests for the detection of Borrelia-specific serum
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis (2017) 36:2137 2146 DOI 10.1007/s10096-017-3037-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Disagreement between the results from three commercial tests for the detection of Borrelia-specific serum
Viramed Biotech AG Borrelia B31 IgG ViraStripe
 - 1 - Viramed Biotech AG Borrelia B31 IgG ViraStripe A line blot serologic assay for the detection of IgG-specific antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi in human serum The Borrelia B31 IgG ViraStripe
- 1 - Viramed Biotech AG Borrelia B31 IgG ViraStripe A line blot serologic assay for the detection of IgG-specific antibodies against Borrelia burgdorferi in human serum The Borrelia B31 IgG ViraStripe
Cotinine (Mouse/Rat) ELISA Kit
 Cotinine (Mouse/Rat) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2264 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Cotinine (Mouse/Rat) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2264 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
EVALUATION OF LYME DISEASE TESTS. I would like to thank Dr. Dumler for his reply to my letter expressing concerns regarding
 Note: Andrew Onderdonk, editor of The Journal of Clinical Microbiology has refused to ask Dumler to dislose the results of his study or explain his erroneous arithmetic. Dumler has not provided results
Note: Andrew Onderdonk, editor of The Journal of Clinical Microbiology has refused to ask Dumler to dislose the results of his study or explain his erroneous arithmetic. Dumler has not provided results
Canine CRP Detection Kit
 Canine CRP Detection Kit Catalog # 6027 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use Acute phase proteins (APPs) are blood proteins released from hepatocytes as an integral part of acute phase
Canine CRP Detection Kit Catalog # 6027 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use Acute phase proteins (APPs) are blood proteins released from hepatocytes as an integral part of acute phase
Borrelia B31 ViraChip IgG Test Kit
 Borrelia B31 ViraChip IgG Test Kit Intended Use: The Viramed Biotech AG Borrelia B31 ViraChip IgG Test Kit is an in vitro qualitative protein microarray assay for the detection of IgG antibodies to Borrelia
Borrelia B31 ViraChip IgG Test Kit Intended Use: The Viramed Biotech AG Borrelia B31 ViraChip IgG Test Kit is an in vitro qualitative protein microarray assay for the detection of IgG antibodies to Borrelia
Vaccines - Canine
 Vaccines - Canine 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com What is a vaccine? The word vaccine comes from the discovery of an English country doctor, Dr. Edward Jenner. Dr. Jenner discovered that people given a
Vaccines - Canine 803-808-7387 www.gracepets.com What is a vaccine? The word vaccine comes from the discovery of an English country doctor, Dr. Edward Jenner. Dr. Jenner discovered that people given a
STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA Kit
 STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2171 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com I. INTRODUCTION STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA2171 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com I. INTRODUCTION STAT1 (ps727) (Human/Mouse) ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent
A European Multicenter Study of Immunoblotting in Serodiagnosis of Lyme Borreliosis
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2000, p. 2097 2102 Vol. 38, No. 6 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. A European Multicenter Study of Immunoblotting
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, June 2000, p. 2097 2102 Vol. 38, No. 6 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. A European Multicenter Study of Immunoblotting
SIV p27 Antigen ELISA Catalog Number:
 INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK SIV p27 Antigen ELISA is for research use only and is not intended for in vitro diagnostic use. The RETRO-TEK SIV p27 Antigen ELISA is an enzyme linked immunoassay used to detect
INTENDED USE The RETRO-TEK SIV p27 Antigen ELISA is for research use only and is not intended for in vitro diagnostic use. The RETRO-TEK SIV p27 Antigen ELISA is an enzyme linked immunoassay used to detect
Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex Assay
 Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex Assay For the detection of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex (ospa- and p41(flagellin) genes) using the BD MAX TM system. Instructions for use (Version 1.0
Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex Assay For the detection of Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato complex (ospa- and p41(flagellin) genes) using the BD MAX TM system. Instructions for use (Version 1.0
Anti-Borrelia burgdorferi antibody profile in post-lyme disease syndrome
 CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 March 2011 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.00002-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 16 March 2011 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:10.1128/cvi.00002-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H1N1 (Swine Flu 2009) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Helicobacter pylori IgA ELISA Kit
 Helicobacter pylori IgA ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0964 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Helicobacter pylori IgA ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0964 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit
 2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
2009 H1N1 Influenza ( Swine Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA kit Catalog Number : SEK001 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as
Acute parvovirus B19 infection frequently causes false positive results in the
 CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 0 December 00 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:0./cvi.000-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
CVI Accepts, published online ahead of print on 0 December 00 Clin. Vaccine Immunol. doi:0./cvi.000-0 Copyright 00, American Society for Microbiology and/or the Listed Authors/Institutions. All Rights
Insulin (Porcine/Canine) ELISA
 Insulin (Porcine/Canine) ELISA For the quantitative measurement of insulin in Porcine/Canine serum and plasma (EDTA) For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 80-INSPO-E01
Insulin (Porcine/Canine) ELISA For the quantitative measurement of insulin in Porcine/Canine serum and plasma (EDTA) For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 80-INSPO-E01
Received 23 November 1998/Returned for modification 8 March 1999/Accepted 6 April 1999
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1999, p. 2241 2247 Vol. 37, No. 7 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Validity of Interpretation Criteria
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1999, p. 2241 2247 Vol. 37, No. 7 0095-1137/99/$04.00 0 Copyright 1999, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Validity of Interpretation Criteria
against Infection with Several Isolates of Borrelia burgdorferi
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1994, p. 618-622 0095-1 137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright 1994, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 3 Ability of Canine Lyme Disease Vaccine To Protect Hamsters
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Mar. 1994, p. 618-622 0095-1 137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright 1994, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 3 Ability of Canine Lyme Disease Vaccine To Protect Hamsters
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Kit. purified polyclonal antibody raised against the full length recombinant p24 is used.
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Kit 80-001 1 kit 96 assays This kit can measure the amount of HIV-1 Gag p24 antigen in cell culture medium handily by a sandwich ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method. p24 antigen
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Kit 80-001 1 kit 96 assays This kit can measure the amount of HIV-1 Gag p24 antigen in cell culture medium handily by a sandwich ELISA (Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay) method. p24 antigen
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual)
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
Received 22 November 2004/Returned for modification 14 January 2005/Accepted 17 April 2005
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 2005, p. 3602 3609 Vol. 43, No. 8 0095-1137/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.43.8.3602 3609.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Aug. 2005, p. 3602 3609 Vol. 43, No. 8 0095-1137/05/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jcm.43.8.3602 3609.2005 Copyright 2005, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Rubella virus IgG ELISA Kit
 Rubella virus IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0223 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
Rubella virus IgG ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0223 96 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle of
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176
 human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
Serodiagnosis of Early Lyme Disease
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1994, p. 1733-1738 0095-1137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright 1994, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 7 Use of Recombinant OspC from Borrelia burgdorferi for Serodiagnosis
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 1994, p. 1733-1738 0095-1137/94/$04.00+0 Copyright 1994, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 32, No. 7 Use of Recombinant OspC from Borrelia burgdorferi for Serodiagnosis
H5N1 ( Avian Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA Pair Set
 H5N1 ( Avian Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK002 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
H5N1 ( Avian Flu ) Hemagglutinin ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK002 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (CMV) IgM ELISA Kit Protocol
 CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (CMV) IgM ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat. No.:EK-310-91) 330 Beach Road, Burlingame CA Tel: 650-558-8898 Fax: 650-558-1686 E-Mail: info@phoenixpeptide.com www.phoenixpeptide.com INTENDED USE The
CYTOMEGALOVIRUS (CMV) IgM ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat. No.:EK-310-91) 330 Beach Road, Burlingame CA Tel: 650-558-8898 Fax: 650-558-1686 E-Mail: info@phoenixpeptide.com www.phoenixpeptide.com INTENDED USE The
