Clinical progress of teeth and implant displaced into the maxillary sinus: retrospective clinical study
|
|
|
- Kristian Bond
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Oral Biology Research, 2017; December 31, 41(4): Copyright c 2017, Oral Biology Research Institute DOI: /obr Original Article ORAL BIOLOGY RESEARCH Clinical progress of teeth and implant displaced into the maxillary sinus: retrospective clinical study So-Hyun Kim 1 and Young-Kyun Kim 1,2 * 1 Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Section of Dentistry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam 13620, Republic of Korea 2 Professor, Department of Dentistry and Dental Research Institute, School of Dentistry, Seoul National University, Seoul 03080, Republic of Korea (Received Aug 28, 2017; Accepted Sep 11, 2017) ABSTRACT Because of the unique anatomical characteristics of the maxillary sinus, a tooth or implant may be accidentally displaced into the maxillary sinus for various reasons. The medical records, including symptoms, clinical examinations, a description of surgery and radiographs, were reviewed for 19 patients who were treated for the displacement of a tooth and implants into the maxillary sinus, between 2003 and Sixteen cases (84%) were implant displacement, while three other cases (16%) involved tooth displacement. Eleven cases (57.9%) were asymptomatic, while eight cases (42.1%) displayed symptoms. Psychological stress and nasal obstruction were the most common signs and symptoms, followed by nasal discharge, pain, and purulent discharge. Attempts at removal of the displaced material were made in 14 out of 19 (74%) cases; 5 patients (26%) were observed with using antibiotics. For removal, a majority of patients underwent surgery with the Caldwell-Luc approach while using general anesthesia. All of the symptoms disappeared after removing the displaced material. In these cases, clinicians should perform thorough assessments of the local anatomy using radiography prior to treatment. The appropriate healing period and type of treatment should be selected based the patient s bone quality and bone mass, while avoiding an excessive use of instruments. KEY WORDS: Implant, Maxillary sinus, Tooth Introduction Because dental procedures are performed in very near to the patient, a sudden movement by the patient or a careless movement by the dentist may cause displacement of the tooth, implant, or fragment of instrument into the soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial area. In particular, residual tooth roots or implants placed in the maxilla are often displaced into the maxillary sinus or infratemporal fossa. This is primarily due to the use of inappropriate manipulation, sudden movement by the patient during treatment, or the lack of residual bone for implantation. *Corresponding author: Young-Kyun Kim Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Section of Dentistry, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, 82 Gumi-ro 173beon-gil, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 13620, Republic of Korea Tel.: , Fax: kyk0505@snubh.org Especially in the posterior maxillary area, low bone density, poor bone quality, rapid alveolar bone resorption, and pneumatization of the maxillary sinus often lead to loss of implant s primary stability. In addition, marginal bone loss during healing may then hinder secondary implant stability and cause the implant to be displaced accidentally into the maxillary sinus [1, 2]. Implantation via the crestal approach in patients with the inadequate residual bone or poor bone quality may also result in displacement of the implant into the maxillary sinus. Displacement of material into the maxillary sinus not only results in medical complications but also may cause a patient to lose trust in the medical staff, potentially ending in a medical dispute. Therefore, it is important that dentists perform meticulous preoperative assessments and consider each patient s unique anatomy prior to placing dental implants. In spite of this, displacement of material into the maxillary sinus may still occur, and quick and accurate followup treatment would minimize secondary complications
2 So-Hyun Kim and Young-Kyun Kim and restore a patient s trust in the medical staff. However, little data exists that identifies the problems resulting from displacement of material into the maxillary sinus and the appropriate treatment for this. Accordingly, this study aims to identify the types of implants and teeth commonly displaced into the maxillary sinus, as well as the symptoms, complications, and treatments associated with displacement. We also present some representative case reports detailing displacement of the foreign body into the maxillary sinus. Materials and Methods The medical records including symptoms, clinical examinations, description of surgery and radiographs were reviewed for 19 patients who visited the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery at the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital between 2003 and 2015 to be treated for displacement of foreign body into the maxillary sinus. This retrospective clinical study was approved by the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Institutional Review Board (B ). Thirteen patients were male (68%) and six were female (32%). The patients ages ranged from 21 to 67 years, with a mean age of years. Sixteen cases (84%) involved implant displacement while three cases (16%) involved tooth displacement. There were 11 cases with the right (57.9%) and eight cases with the left (42.1%) sinus. Regarding the time of displacement, each eight cases (42%) occurred during the implant surgery (primary and secondary) and after the implant surgery. In three cases (16%), it occurred during the tooth extraction procedure. Among the cases where it occurred during the implant surgery, in six cases it occurred during the primary surgery and in two cases were during the secondary surgery (Table 1). Results Eleven cases (57.9%) remained asymptomatic while eight Table 1. Time of displacement Time of displacement Patients % During the implant surgery 8 42 After the implant surgery (Postoperative) 8 42 During tooth extraction 3 16 Total Table 2. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms Patients (Including a duplication) Psychological stress 4 Nasal obstruction 4 Nasal discharge 3 Pain (headache, sinus pain, on palpation) 3 Purulent discharge 2 Table 3. Types of treatment Treatment Patients % Removal alone Removal + bone augmentation or re-implantation Observation 5 26 Removal + irrigation followed by observation cases (42.1%) had symptoms associated with the displaced material. In five cases, patients had multiple signs and symptoms (For example, Headache and nasal obstruction). Psychological stress and nasal obstruction were the most common symptoms, followed by nasal discharge, pain, and purulent discharge (Table 2). Patients with psychological stress had uncomfortable feelings associated with foreign material present within their bodies or developed fear associated with implant surgery; in one severe case, the patient developed a panic disorder. Treatments included removal of the displaced teeth or implant (53%), observation and use of antibiotics (26%), bone augmentation or re-implantation after removal of the displaced material (11%), and failed removal followed by irrigation and antibiotic therapy (11%) (Table 3). During the period of observation, pain medications, antibiotics, and radiographic imaging were prescribed. Removal of the displaced material was performed under general anesthesia in 12 out of the 14 cases in which it was attempted, while local anesthesia was used for the remaining two cases. The Caldwell-Luc approach was used in 13 cases and endoscopy was performed by an ENT in one case (Table 3). Symptoms developed in one case with tooth displacement and eight cases with implant displacement. Complications associated with displacement included maxillary sinusitis (seven cases) and oral-maxillary sinus fistula (two cases, one with tooth displacement, and one with implant displacement). All symptoms disappeared after removing the displaced material. In one of the five cases in which the displaced material was not immediately
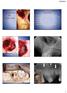
3 Teeth and implant displaced into the maxillary sinus removed and only observed, the implant was removed three years later by an ENT specialist, due to bilateral paranasal sinusitis. In two cases where had attempted the removal but failed, the symptoms eventually resolved in one case and the remaining case was lost to follow-up. Case Reports Case 1: Tooth displacement and removal A 26-year-old female patient was undergoing extraction of the #28 tooth when it was displaced into the maxillary sinus. She developed purulent discharge and signs of maxillary sinusitis, which did not resolve with a two-week course of antibiotics, pain medications in a local dental clinic. The patient visited a local ENT clinic that referred her to our institution. The panoramic and occipitomental (Water s) radiograph showed displacement of the #28 tooth into the maxillary sinus, thickening of the left maxillary sinus mucosa, and an oral-maxillary sinus fistula (Fig. 1). Under general anesthesia, a 1.5-cm sinus window was created in the anterior wall of the maxillary sinus via the Caldwell-Luc approach. An endoscope was then inserted to explore the location of the displaced tooth and associated inflammation of the maxillary sinus. After removing the displaced tooth and surrounding inflamed tissue, the maxillary sinus was irrigated with normal saline and suture was done with 4-0 vicryl. After the surgery, the incision was dressed and antibiotics were prescribed. We ceased observation of the patient when the clinical symptoms resolved completely approximately two months postoperatively (Fig. 2). Case 2: Implant displacement and removal A 54-year-old male patient presented to our institution for discomfort in the right facial area. Implants had been placed at #15, 16, and 17, approximately three months prior to presentation and re-implantation had been performed at #15 a month ago. Pain medication had been prescribed a week prior to presentation, which was effective in controlling the pain in the right side of his face and implant sites. The patient visited our institution when the right nasal obstruction and foul-smelling nasal discharge persisted. Other than controlled hypertension, the patient did not have any notable medical history. On examination, Fig. 1. Case 1: Displacement of the #28 tooth: Panoramic and occipitomental (Water s) views taken at the first examination. Fig. 2. Case 1: Panoramic and occipitomental (Water s) views obtained two months after removal of the displaced tooth
4 So-Hyun Kim and Young-Kyun Kim Fig. 3. Case 2: Displacement of the #17 implant into the maxillary sinus: Panoramic and occipitomental (Water s) views taken at the first examination. Fig. 4. Case 2: Displacement of the #17 implant: First CT. Fig. 5. Case 2: Displacement of the #16 implant into the maxillary sinus; change in position of the #17 implant. the patient had tenderness in the right posterior maxillary region. A panorama view revealed displacement of the #17 implant into the maxillary sinus while Water s view showed increased radiopacity of the right maxillary sinus (Fig. 3). Computed tomography confirmed increased radiopacity of the entire right maxillary sinus and revealed the 3-dimensional position of the displaced implant (Fig. 4). The height of the residual bone in the posterior region was approximately 3 mm due to pneumatization of the maxillary sinus. The patient visited the hospital approximately one month later for the removal of the #17 implant. He reported that another panorama view had been obtained a few days previously that revealed displacement of a second implant. The new images were reviewed, which confirmed that the #16 implant was also displaced into the maxillary sinus and that the #17 implant had migrated within the maxillary sinus (Fig. 5). A flap over the #14-18 teeth was elevated and a lateral window into the maxillary sinus was created under general anesthesia. Purulent material present in the maxillary Fig. 6. Case 2: Panorama and CT after removing #16 and #17 implants
5 Teeth and implant displaced into the maxillary sinus sinus was removed with saline irrigation. After removal of the two displaced implants, the maxillary sinus mucosa was elevated and the perforated mucosa was repaired with a resorbable collagen membrane (BioArm: ACE Surgical Supply Company Inc., Brockton, MA, USA and Tisseel: Baxter AG, Wien, Austria). Bone augmentation of the maxillary sinus was performed (ExFuse: Hanmi Medicare Inc., Seoul, South Korea), after which time the window was sutured closed. Four months after the surgery, panorama and CT images confirmed that the radiopacity of the right maxillary sinus had nearly resolved completely. The patient was also noted to be asymptomatic (Fig. 6). Case 3: Observation without removal of the displaced implant A 55-year-old female patient presented for evaluation after having undergone bone augmentation and implantation at the #16 and #17 teeth at a local clinic one year previously. The #17 implant had been removed, and the #16 implant was displaced into the maxillary sinus, when the patient was referred to our institution. She had symptoms of temporomandibular disorders but none of maxillary sinusitis. Observation over the past year and a current panorama view (Fig. 7) showed no evidence of right maxillary sinusitis, so regular monitoring was recommended. There were no notable changes in the patient s clinical signs or in the appearance of the implant at the one- and six-month follow-up (Fig. 8) visits, and the patient did not return to the hospital for approximately 2.5 years. The patient then re-presented with tickling around the right side of the nose and frequent sneezing. A panorama view showed that the implant was further displaced into the Fig. 8. Case 3: Panorama view obtained six months after the first examination. Fig. 7. Case 3: Displacement of the #16 implant. Fig. 9. Case 3: Panorama and CT images obtained 2.5 years after the first examination
6 So-Hyun Kim and Young-Kyun Kim maxillary sinus (Fig. 9). Computed tomography revealed maxillary sinusitis on the side contralateral to the displaced implant and bilateral paranasal sinusitis (Fig. 9). The patient was then referred to the ENT department and the displaced implant was removed via endoscopy. All of the patient s symptoms then resolved. Discussion Maxillary posterior teeth or implants may be displaced into the maxillary sinus during extraction or implantation due to the anatomical structure of this area. One study reported that % of the material introduced into the paranasal sinus is iatrogenic [3]. Therefore clinicians must take precautions when extracting posterior teeth because inappropriate handling of instruments without full visualization of the area or use of excessive force may displace the tooth or residual roots into the maxillary sinus [3, 4]. Further, the risk of displacement increases when the implantation is performed with the maxillary sinus mucosa lifted via the crestal approach in patients with inadequate bone mass or poor bone quality secondary to pneumatization. Several studies have reported that a lateral approach is preferred for the maxillary sinus lift when the height of the residual bone is less than 4-5 mm [5, 6]. In this study, approximately 84% of the cases of displacement into the maxillary sinus involved an implant while 16% involved a tooth. Displacement occurred more frequently in male patients (68%) than it did in female patients (32%). Displacement was as likely to occur during implant surgery as it was to occur after. In other words, there is a risk that implants may be displaced into the maxillary sinus not only during but also after surgery owing to marginal bone resorption, which calls for careful observation on the part of the surgeon. All cases of tooth displacement occurred during the extraction procedure, suggesting that clinicians should take precautions when maneuvering instruments during the extraction of maxillary posterior teeth. Discomfort, paresthesia when in close proximity to a nerve, pain, swelling, maxillary sinusitis, cellulitis, and abscess formation have been suggested as potential complications of displacement of a foreign body into the maxillary sinus [4, 7, 8]. In our study, more than half of the patients (57.9%) were asymptomatic, with the remaining 42.1% complaining of symptoms associated with maxillary sinusitis and psychological stress. The main symptoms noted were nasal obstruction, nasal discharge, and pain. Seven patients (37%) were definitively diagnosed with maxillary sinusitis, and in severe cases, patients developed an oral-maxillary sinus fistula. Although the majority of patients were asymptomatic, the fact that the patients with psychological stress suffered from insomnia due to a foreign body sensation, fear of dental treatment, and even a severe panic disorder allows us to speculate that these patients suffered from severe pain. Furthermore, in one case, the displacement negatively affected the patient s trust in the medical staff, which eventually led to a medical dispute. It is important to note that even if a patient does not show any symptoms in the short-term, an implant or tooth may eventually cause maxillary sinusitis by impairing the mobility of the maxillary sinus cilia, inducing a foreign body reaction, or obstructing the nasal meatus by moving within the maxillary sinus [9-11]. Treatment consisted of removal of the displaced material or observation. Removal was attempted in most cases, but observation while treating with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory medications, and steroids was chosen for patients without clinical symptoms. The symptoms mostly resolved in both patients who were observed from the beginning and in those patients who were later placed on observation after the displaced material could not be removed. The clinical symptoms resolved in all cases that were followed, but two were lost to follow-up. Whether the displaced material must be removed or not is still controversial. Some arguing that all displaced materials must be removed even in asymptomatic patients in order to prevent psychological stress and other secondary complications [12, 13]. Due to the anatomy of the maxillary sinus, which has ciliated mucosa and an empty cavity, displaced material can continue to move within it, necessitating regular imaging to closely monitor the location of the material. Furthermore, once symptoms of maxillary sinusitis, infection, and neuropathy develop, the displaced material must be removed promptly, at which time the patient should be referred to an oral-maxillofacial specialist or an ENT. If material is displaced into the maxillary sinus during surgery, the surgeon should immediately try to remove the displaced material while ensuring a full field of view via hemostasis and saline irrigation. The material may be removed via powerful suction or water pressure, or it can be removed manually by carefully detaching the maxillary sinus mucosa. However, probing without a full field of
7 Teeth and implant displaced into the maxillary sinus view is not recommended, as this may cause the substance to be further displaced into the tissue [8]. Surgeons must also note that the displaced material may be located in a position different from that shown in the radiographs due to the fluidity of the maxillary sinus mucosa. In cases where the material cannot be removed, the surgeon should irrigate the wound adequately, apply sterile gauze, and use antibiotics, pain medications, and serial radiographs while observing clinical symptoms to evaluate progress. Furthermore, the patient should be instructed to avoid severe coughing or sneezing episodes as much as possible [8]. In our study, attempts at removal of the displaced material were made in 14 out of 19 (74%) cases, 12 of which were performed under general anesthesia (85.7%) while two were performed under local anesthesia. Most surgeries (n=13) were performed using the Caldwell-Luc approach. Endoscopic assistance could be used aid the surgeon in accurately locating and removing the material. Minimally invasive, endoscopic removal has been on the rise in recent years and has been reported to be safe, causing little soft tissue damage and resulting in good outcomes [4, 10-12]. Remaining normal maxillary sinus mucosa must not be removed because it has the potential to heal completely after removal of the displaced material. Although all of the cases reviewed in this study had good outcomes after removal of the displaced material and numerous other studies have noted that removing the material eliminated severe complications, preventing the displacement of material into the maxillary sinus in the first place would be the best scenario. This is considering the fact that removal of the material under general anesthesia may inflict psychological stress and that displacement of the teeth or implants in the first place could be detrimental to the doctor-patient relationship. To this end, clinicians should perform thorough assessments of the local anatomy using radiography and CT prior to treatment. A careful choice between the crestal and lateral approach should be made depending on the height of the residual bone. The appropriate healing period and type of treatment should be chosen based the patient s bone quality and bone mass while avoiding the excessive use of instruments. Conflict of Interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests. ORCID So-Hyun Kim Young-Kyun Kim References 1. González-García A, González-García J, Diniz-Freitas M, García-García A, Bullón P. Accidental displacement and migration of endosseous implants into adjacent craniofacial structures: a review and update. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2012;17: doi: /medoral Iida S, Tanaka N, Kogo M, Matsuya T. Migration of a dental implant into the maxillary sinus. A case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2000;29: doi: / S (00) Bouquet A, Coudert JL, Bourgeois D, Mazoyer JF, Bossard D. Contributions of reformatted computed tomography and panoramic radiography in the localization of third molars relative to the maxillary sinus. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2004;98: doi: /j.tripleo Gao QM, Yang C, Zheng LY, Hu YK. Removal of Long- Term Broken Roots Displaced Into the Maxillary Sinus by Endoscopic Assistant. J Craniofac Surg 2016;27: doi: /SCS Fugazzotto PA. Augmentation of the Posterior Maxilla: A Proposed Hierarchy of Treatment Selection. J Periodontol 2003;75: doi: /jop Pjetursson BE, Rast C, Brägger U, Schmidlin K, Zwahlen M, Lang NP. Maxillary sinus floor elevation using the osteotome technique with or without grafting material. Part I : Implant survival and patient's perception. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009;20: doi: /j x. 7. Woolley EJ, Patel M. Subdural empyema resulting from displacement of a root into the maxillary antrum. Br Dent J 1997;182: Kim YK, Lee YJ, Yoon PY, Choi YH, Kim SG. Complication Q&A in dentistry. Seoul: DaehanNarae Publishing; P Eltas A, Dundar S, Eltas SD, Altun O, Yolcu U, Saybak A. Accidental Displacement of Dental Implants Into Both Maxillary Sinuses During Surgery. J Oral Implantol 2015;41: doi: /AAID-JOI-D de Jong MA, Rushinek H, Eliashar R. Removal of dental implants displaced into the maxillary sinus: A case series. Eur J Oral Implantol 2016;9: Kitamura A, Removal of a migrated dental implant from
8 So-Hyun Kim and Young-Kyun Kim a maxillary sinus by transnasal endoscopy. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007;45: doi: /j.bjoms Matti E, Emanuelli E, Pusateri A, Muniz CC, Pagella F. Transnasal Endoscopic Removal of Dental Implants from the Maxillary Sinus. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2013;28: doi: /jomi Chiapasco M, Felisati G, Maccari A, Borloni R, Gatti F, Di Leo F. The management of complications following displacement of oral implants in the paranasal sinuses: a multicenter clinical report and proposed treatment protocols. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;38: doi: /j.ijom
Reconstruction of large oroantral defects using a pedicled buccal fat pad
 Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Migration of foreign bodies
 CASE LETTER Atraumatic Removal of an Asymptomatic Migrated Dental Implant Into the Maxillary Sinus: A Case Report Spiros Tsodoulos, DDS, MD, PhD Irene Karabouta, DDS, MD, PhD* Margarita Voulgaropoulou,
CASE LETTER Atraumatic Removal of an Asymptomatic Migrated Dental Implant Into the Maxillary Sinus: A Case Report Spiros Tsodoulos, DDS, MD, PhD Irene Karabouta, DDS, MD, PhD* Margarita Voulgaropoulou,
Complex Exodontia. Jone Kim, DDS, MS
 Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Title endoscope. Kitamura, Akira; Zeredo, Jorge L. Implant dentistry, 19(1), pp.16-20; Issue Date
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Migrated maxillary implant removed endoscope. Kitamura, Akira; Zeredo, Jorge L Citation Implant dentistry, 19(1), pp.16-20; Issue Date 2010-02 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/24593
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Migrated maxillary implant removed endoscope. Kitamura, Akira; Zeredo, Jorge L Citation Implant dentistry, 19(1), pp.16-20; Issue Date 2010-02 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10069/24593
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan
 Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
Treatment of dental implant displacement into the maxillary sinus
 An et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:35 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0133-1 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery REVIEW Open Access Treatment of dental implant displacement
An et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2017) 39:35 DOI 10.1186/s40902-017-0133-1 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery REVIEW Open Access Treatment of dental implant displacement
Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers
 Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
Tikrit Journal for Dental Sciences 1(2013)107-112 Maxillary Sinus Measurements in Different Age Groups of Human Cadavers Mohammad A. Abd-alla BDS, MSc., Ph.D. (1) Abdul-Jabbar J. Mahdi BDS, MSc., Ph.D.
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift
 Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re. Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T
 Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Postoperative malocclusion after maxillofacial fracture management: a retrospective case study
 Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0167-z Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery REVIEW Open Access Postoperative malocclusion
Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:27 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0167-z Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery REVIEW Open Access Postoperative malocclusion
Case Report Unusual Case of Osseointegrated Dental Implant Migration into Maxillary Sinus Removed 12 Years after Insertion
 Hindawi Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2017, Article ID 9634672, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9634672 Case Report Unusual Case of Osseointegrated Dental Implant Migration into Maxillary Sinus
Hindawi Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2017, Article ID 9634672, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/9634672 Case Report Unusual Case of Osseointegrated Dental Implant Migration into Maxillary Sinus
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
 WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
WHAT IS FUNCTIONAL ENDOSCOPIC SINUS SURGERY (FESS)? The nasal telescope has greatly changes the evaluation and treatment of rhino-sinusitis. This instrument, which provides a view of the structures in
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Sinus Surgery. Middle Meatus
 Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Sinus Surgery Introduction Sinus surgery is a very common and safe operation. Your doctor may recommend that you have sinus surgery. The decision whether or not to have sinus surgery is also yours. This
Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary. Zanco J. Med. Sci., Vol. 16, No. (2), 2012
 Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary sinus to the alveolar bone crest, using digital panoramic imaging system, in Erbil city Received: 10/2/2011 Accepted: 13/9/2011 Sarkawt H. Ali* Saeed
Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary sinus to the alveolar bone crest, using digital panoramic imaging system, in Erbil city Received: 10/2/2011 Accepted: 13/9/2011 Sarkawt H. Ali* Saeed
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation
 Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Maxillary tuberosity fracture and ophthalmologic complications following removal of maxillary third molar
 Oral Surgery ISSN 1752-2471 CASE REPORT Maxillary tuberosity fracture and ophthalmologic complications following removal of maxillary third molar J. Baba 1, T. Iwai 2, H. Endo 1, N. Aoki 1 & I. Tohnai
Oral Surgery ISSN 1752-2471 CASE REPORT Maxillary tuberosity fracture and ophthalmologic complications following removal of maxillary third molar J. Baba 1, T. Iwai 2, H. Endo 1, N. Aoki 1 & I. Tohnai
CASE REPORT SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES
 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 18: 128-32, 2016 * * *, * * SUMMARY The present article reports the late removal of a wisdom tooth displaced into the maxillary
SCIENTIFIC ARTICLES Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 18: 128-32, 2016 * * *, * * SUMMARY The present article reports the late removal of a wisdom tooth displaced into the maxillary
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery
 An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION
 original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
Evaluation of subjective satisfaction of dental implant patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.525/jkaoms.204.40.3.30 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Evaluation of subjective satisfaction of dental implant patients Young-Kyun Kim, Hyun-Suk Kim, Yang-Jin Yi 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.525/jkaoms.204.40.3.30 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Evaluation of subjective satisfaction of dental implant patients Young-Kyun Kim, Hyun-Suk Kim, Yang-Jin Yi 2,
A Preferable Technique for Protecting the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: Coronectomy
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 7:13-138, 9 A Preferable Technique for Protecting the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: Coronectomy Dogan Dolanmaz, DDS, PhD,* Gulsun Yildirim, DDS, PhD, Kubilay Isik, DDS, PhD, Korhan Kucuk,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 7:13-138, 9 A Preferable Technique for Protecting the Inferior Alveolar Nerve: Coronectomy Dogan Dolanmaz, DDS, PhD,* Gulsun Yildirim, DDS, PhD, Kubilay Isik, DDS, PhD, Korhan Kucuk,
Detecting a sinus perforation.
 Extractions and the Sinus Dentistry s Black Hole. Detecting a sinus perforation. How to know when you have a small perforation? Need: Adequate light (headlight preferred) Small suction tip (2 mm diameter)
Extractions and the Sinus Dentistry s Black Hole. Detecting a sinus perforation. How to know when you have a small perforation? Need: Adequate light (headlight preferred) Small suction tip (2 mm diameter)
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter. Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July Volume 2
 Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Limited To Endodontics Newsletter LTE Limited To Endodontics A Practice Of Endodontic Specialists July 1 2009 Volume 2 Endodontic Treatment For The Compromised Tooth The goal of endodontic therapy is to
Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre
 Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/130 Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre B G Prakash 1, Suhasini Biyyapu 2 1 Professor, Department of ENT, JSS Medical College,
Original Article DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/130 Incidence of Odontogenic Sinusitis Experience in a Tertiary Care Centre B G Prakash 1, Suhasini Biyyapu 2 1 Professor, Department of ENT, JSS Medical College,
Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation
 42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
Title. Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu. CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5. Issue Date
 Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Title Bilateral hypoplasia of the maxillary sinus : swelli Author(s)Matsushita, Kazuhiro; Yamamoto, Hidekazu CitationBritish journal of oral and maxillofacial surgery, 5 Issue Date 2017-04 Doc URL http://hdl.handle.net/2115/68826
Keywords: Biomechanics, Biostatistics, Maxilla, Maxillary sinus, Sinus floor augmentation.
 Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
A CASE REPORT OF ORO ANTAL FISTULA TREATED WITH A COMBINATION TECHNIQUE OF BUCCAL ADVANCEMENT FLAP AND BUCCAL FAT PAD
 Case Report: A CASE REPORT OF ORO ANTAL FISTULA TREATED WITH A COMBINATION TECHNIQUE OF BUCCAL ADVANCEMENT FLAP AND BUCCAL FAT PAD 1 Dr Gopal Sharma, 2 Dr Jaya Mukherjee, 3 Dr Bhagyashree Purandare 1Head
Case Report: A CASE REPORT OF ORO ANTAL FISTULA TREATED WITH A COMBINATION TECHNIQUE OF BUCCAL ADVANCEMENT FLAP AND BUCCAL FAT PAD 1 Dr Gopal Sharma, 2 Dr Jaya Mukherjee, 3 Dr Bhagyashree Purandare 1Head
Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis
 Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis 저자저널명발행기관 NDSL URL Na, Ji Yeon ; Kang, Joo Hyun ; Choi, Seong-Ho ; Jeong, Ho-Gul ; Han, Sang-Sun 大韓齒科醫師協會誌 = The journal of the Korean
Squamous cell carcinoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking periodontitis 저자저널명발행기관 NDSL URL Na, Ji Yeon ; Kang, Joo Hyun ; Choi, Seong-Ho ; Jeong, Ho-Gul ; Han, Sang-Sun 大韓齒科醫師協會誌 = The journal of the Korean
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS
 INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
INDIANA HEALTH COVERAGE PROGRAMS PROVIDER CODE TABLES Note: Due to possible changes in Indiana Health Coverage Programs (IHCP) policy or national coding updates, inclusion of a code on the code tables
Facial blanching after inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia: an unusual complication
 Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(4):317-321 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.4.317 Facial blanching after inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia: an unusual
Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(4):317-321 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.4.317 Facial blanching after inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia: an unusual
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Retained Metallic Foreign body- A Diagnostic and Surgical Challenge
 Retained Metallic Foreign body- A Diagnostic and Surgical Challenge Shaila M Agrawal, Aisshwarya Patel *, Aseem Sharma Department of Oral and Maxillofacial and Reconstructive surgery, Modern Dental College
Retained Metallic Foreign body- A Diagnostic and Surgical Challenge Shaila M Agrawal, Aisshwarya Patel *, Aseem Sharma Department of Oral and Maxillofacial and Reconstructive surgery, Modern Dental College
DISEASES AND SURGERY OF SINUS MAXILLARIS
 DISEASES AND SURGERY OF SINUS MAXILLARIS Diseases of sinus maxillaris Anatomical disorders Oronasal fistules Sinus apertus Radix in sinus maxillaris Cysts Imflammations Tumors Injuries Preprosthetic disorders
DISEASES AND SURGERY OF SINUS MAXILLARIS Diseases of sinus maxillaris Anatomical disorders Oronasal fistules Sinus apertus Radix in sinus maxillaris Cysts Imflammations Tumors Injuries Preprosthetic disorders
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT OF ACCIDENTALLY DISPLACED MANDIBULAR THIRD MOLAR INTO
 SURGICAL MAAGEMET OF ACCIDETALLY DISPLACED MADIBULAR THIRD MOLAR ITO THE PTERYGOMADIBULAR SPACE: A CASE REPORT I-Yueh Huang, 1,2 Chao-Ming Chen, 1 Sung-Wen Chang, 3,4 Chia-Fu Yang, 1 Chung-Ho Chen, 1,2
SURGICAL MAAGEMET OF ACCIDETALLY DISPLACED MADIBULAR THIRD MOLAR ITO THE PTERYGOMADIBULAR SPACE: A CASE REPORT I-Yueh Huang, 1,2 Chao-Ming Chen, 1 Sung-Wen Chang, 3,4 Chia-Fu Yang, 1 Chung-Ho Chen, 1,2
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
Healing pattern of the mucous membrane after tooth extraction in the maxillary sinus
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:23-29 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.1.23 Healing pattern of the mucous membrane after tooth extraction in the maxillary sinus Ji-Young Yoo, Sung-Hee Pi, Yun-Sang
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:23-29 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.1.23 Healing pattern of the mucous membrane after tooth extraction in the maxillary sinus Ji-Young Yoo, Sung-Hee Pi, Yun-Sang
T he cortical bone of the maxillary
 KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
PRE-OP and POST-OP SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS
 PRE-OP and POST-OP SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS Darlene Sorrell, DMD, is not an oral surgeon. AIDC is an out-patient facility. 29 years of experience in IHS. Advanced General Practice Residency. No access
PRE-OP and POST-OP SURGICAL CONSIDERATIONS Darlene Sorrell, DMD, is not an oral surgeon. AIDC is an out-patient facility. 29 years of experience in IHS. Advanced General Practice Residency. No access
Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.1.37 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases Young-Kyun Kim 1, Su-Gwan Kim
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.1.37 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases Young-Kyun Kim 1, Su-Gwan Kim
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Paranasal sinus foreign bodies (FB) are. Iatrogenic foreign bodies in the maxillary synus: between malpraxis and medico-legal consequences
 Rom J Leg Med [23] 14-18 [2015] DOI: 10.4323/rjlm.2015.14 2015 Romanian Society of Legal Medicine Iatrogenic foreign bodies in the maxillary synus: between malpraxis and medico-legal consequences Claudiu
Rom J Leg Med [23] 14-18 [2015] DOI: 10.4323/rjlm.2015.14 2015 Romanian Society of Legal Medicine Iatrogenic foreign bodies in the maxillary synus: between malpraxis and medico-legal consequences Claudiu
Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report
 Vol. 31 No. 3, December 2012 Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report In-Seong Jeon, Min-Suk Heo 1, Kyu-Ho Yoon 2, Kwang-Heung Han
Vol. 31 No. 3, December 2012 Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report In-Seong Jeon, Min-Suk Heo 1, Kyu-Ho Yoon 2, Kwang-Heung Han
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature:
 CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
CBCT Specific Guidelines for South African Practice as Indicated by Current Literature: CF Hoogendijk Maxillo- facial and Oral surgery: Trauma: 1. Facial trauma for the confirmation or exclusion of fractures
Nasal floor elevation combined with dental implant placement
 1 Nasal floor elevation combined with dental implant placement Ziv Mazor, DMD * Adi Lorean, DMD ** Eitan Mijiritsky Liran Levin, DMD * Private Practice, Ra anana, Israel ** Private Practice, Tiberius,
1 Nasal floor elevation combined with dental implant placement Ziv Mazor, DMD * Adi Lorean, DMD ** Eitan Mijiritsky Liran Levin, DMD * Private Practice, Ra anana, Israel ** Private Practice, Tiberius,
One in four sinus lift procedures can be
 11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
Chronic Sinusitis. Acute Sinusitis. Sinusitis. Anatomy of the Paranasal Sinuses. Sinusitis. Medical Topics - Sinusitis
 1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
1 Acute Chronic is the inflammation of the inner lining of the parnasal sinuses due to infection or non-infectious causes such as allergies or environmental pullutants. If the inflammation lasts more than
Clinical details: Details of scan: CONE BEAM CT REPORT: Name: H. B. Gender: Reason for referral: Referred by:
 Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Name: H. B. Gender: Male DOB: 11/12/1950 Age: 64 Date taken: 16/11/2015 Date reported: 19/11/2015 Clinical details: Reason for referral: Referred by: Investigate symptoms related to left TMJ. Reconstructed
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Assessment of the Relationship between the Maxillary Sinus Floor and Maxillary Posterior Teeth Roots using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
 Abbas Shokri et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1589 Assessment of the Relationship between the Maxillary Sinus Floor and Maxillary Posterior Teeth Roots using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Abbas Shokri et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1589 Assessment of the Relationship between the Maxillary Sinus Floor and Maxillary Posterior Teeth Roots using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Tooth extraction involves general risks such as
 GETTING by Dr. Andonis Terezides Andonis Terezides, DDS, graduated from the University of California at Davis with a degree in biological anthropology. He attended the University of Maryland School of
GETTING by Dr. Andonis Terezides Andonis Terezides, DDS, graduated from the University of California at Davis with a degree in biological anthropology. He attended the University of Maryland School of
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Abstract. Cenk Kilic a Kivanc Kamburoglu b Selcen Pehlivan Yuksel c Tuncer Ozen d
 An Assessment of the Relationship between the Maxillary Sinus Floor and the Maxillary Posterior Teeth Root Tips Using Dental Cone-beam Computerized Tomography Cenk Kilic a Kivanc Kamburoglu b Selcen Pehlivan
An Assessment of the Relationship between the Maxillary Sinus Floor and the Maxillary Posterior Teeth Root Tips Using Dental Cone-beam Computerized Tomography Cenk Kilic a Kivanc Kamburoglu b Selcen Pehlivan
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
CLOSURE OF OROANTRAL COMMUNICATION WITH PLATELET-RICH FIBRIN
 Original rticle International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 05 CLOSURE OF ORONTRL COMMUNICTION WITH PLTELET-RICH FIRIN Waseem itar 1, Mounzer ssad 2 1. MSc, Department of oral and
Original rticle International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 05 CLOSURE OF ORONTRL COMMUNICTION WITH PLTELET-RICH FIRIN Waseem itar 1, Mounzer ssad 2 1. MSc, Department of oral and
Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case Report?
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550023 Volume 2, Issue 2 Case Report Autologous Bone Augmentation in Combination with an Ameloblastoma in the Maxillary Region- A Case
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Potential Complications
 Potential Complications The risk of complications associated with wisdom teeth removal is less than 0.5 percent when performed by an experienced oral surgeons who uses contemporary techniques and surgical
Potential Complications The risk of complications associated with wisdom teeth removal is less than 0.5 percent when performed by an experienced oral surgeons who uses contemporary techniques and surgical
2: Canullo L, Tallarico M, Penarrocha D, Meloni SM, Penarrocha M. Abstracts. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016;9 Suppl 1:9-54. PubMed PMID:
 1: Tallarico M, Xhanari E, Pisano M, De Riu G, Tullio A, Meloni SM. Single post-extractive ultra-wide 7 mm-diameter implants versus implants placed in molar healed sites after socket preservation for molar
1: Tallarico M, Xhanari E, Pisano M, De Riu G, Tullio A, Meloni SM. Single post-extractive ultra-wide 7 mm-diameter implants versus implants placed in molar healed sites after socket preservation for molar
Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane
 10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases
 Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
Cholesterol granuloma of the jaws: report of two cases Pages with reference to book, From 15 To 17 Alper Alkan, Osman Etoz ( Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Erciyes University, Faculty of
Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.6.274 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation Wang Peng, Il-Kyu Kim, Hyun-Young Cho, Sang-Pill
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.6.274 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation Wang Peng, Il-Kyu Kim, Hyun-Young Cho, Sang-Pill
Measurement of the Maxilla and Zygoma as an Aid in Installing Zygomatic Implants
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59:1193-1198, 2001 Measurement of the Maxilla and Zygoma as an Aid in Installing Zygomatic Implants Yuki Uchida, DDS, PhD,* Masaaki Goto, DDS, PhD, Takeshi Katsuki DDS, PhD, and
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 59:1193-1198, 2001 Measurement of the Maxilla and Zygoma as an Aid in Installing Zygomatic Implants Yuki Uchida, DDS, PhD,* Masaaki Goto, DDS, PhD, Takeshi Katsuki DDS, PhD, and
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
complications (Zitzmann and Schaerer,
 Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3.
 DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
2018 Dental Code Set For dates of service from 1/1/ /31/2018
 D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
D0120 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION - ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0140 LIMITED ORAL EVALUATION - PROBLEM FOCUSED D0150 COMPREHENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION - NEW OR ESTABLISHED PATIENT D0160 DETAILED AND EXTENSIVE ORAL EVALUATION
2018 Dental Code Set
 D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
D0120 D0140 D0150 D0160 D0180 D0210 D0220 D0230 D0240 D0250 D0251 D0270 D0272 D0273 D0274 D0277 D0290 D0310 D0330 D0340 D0350 D0393 D0470 D0502 PERIODIC ORAL EVALUATION ESTABLISHED PATIENT LIMITED ORAL
Case Report Intraoral management of iatrogenically displaced lower third molar roots in the sublingual space: a report of 2 cases
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19591-19595 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0013767 Case Report Intraoral management of iatrogenically displaced lower third molar roots in the sublingual space: a report
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(10):19591-19595 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0013767 Case Report Intraoral management of iatrogenically displaced lower third molar roots in the sublingual space: a report
ENDOSCOPIC REMOVAL OF SUPERNUMERARY
 ENDOSCOPIC REMOVAL OF SUPERNUMERARY TOOTH FROM THE NASAL CAVITY OF A CHILD: A CASE REPORT M. CLEMENTINI 1, A. MORLUPI 1, C. AGRESTINI 1, M. DI GIROLAMO 1, S. DI GIROLAMO 2, L. OTTRIA 1 1 Department of
ENDOSCOPIC REMOVAL OF SUPERNUMERARY TOOTH FROM THE NASAL CAVITY OF A CHILD: A CASE REPORT M. CLEMENTINI 1, A. MORLUPI 1, C. AGRESTINI 1, M. DI GIROLAMO 1, S. DI GIROLAMO 2, L. OTTRIA 1 1 Department of
ISSN: Volume 4 Issue Faciomaxillary prosthesis in rehabilitation. After maxillectomy. A clinical study
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 Faciomaxillary prosthesis in rehabilitation After maxillectomy A clinical study Prasad c Parimala V Vijjaykanth M Sivakumar P Department of Dental Surgery Govt. Stanley
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 4 Issue 4 2014 Faciomaxillary prosthesis in rehabilitation After maxillectomy A clinical study Prasad c Parimala V Vijjaykanth M Sivakumar P Department of Dental Surgery Govt. Stanley
adjacent craniofacial structures: A review and update
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.18032 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18032 Accidental displacement and migration of endosseous implants into adjacent
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.18032 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18032 Accidental displacement and migration of endosseous implants into adjacent
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions. Koskela, Sanna
 https://helda.helsinki.fi Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions Koskela, Sanna 2017-03 Koskela, S, Suomalainen, A, Apajalahti, S & Venta, I 2017, ' Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions
https://helda.helsinki.fi Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions Koskela, Sanna 2017-03 Koskela, S, Suomalainen, A, Apajalahti, S & Venta, I 2017, ' Malpractice claims related to tooth extractions
Principles of endodontic surgery
 Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Oro-antral fistulae and fractured tuberosities
 Oro-antral fistulae and fractured tuberosities G. Bell 1 IN BRIEF Most oro-antral fistulae and tuberosity fractures are predictable and avoidable. Simple modification of surgical technique will reduce
Oro-antral fistulae and fractured tuberosities G. Bell 1 IN BRIEF Most oro-antral fistulae and tuberosity fractures are predictable and avoidable. Simple modification of surgical technique will reduce
Minimal invasive horizontal ridge augmentation using subperiosteal tunneling technique
 Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0087-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Minimal invasive horizontal
Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0087-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Minimal invasive horizontal
Pathophysiology and Etiology
 Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
Sinusitis Pathophysiology and Etiology Sinusitis is inflammation of the mucosa of one or more sinuses. It can be either acute chronic. Chronic sinusitis is diagnosed if symptoms are present for more than
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 07 Page July 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
The future of health is digital
 Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Dated: XX/XX/XXXX Name: XXXXXXXX XXXXXXXXXXX Birth Date: XX/XX/XXXX Date of scan: XX/XX/XXXX Examination of the anatomical volume: The following structures are reviewed and evaluated for bilateral symmetry,
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
PLACEMENT OF DENTAL IMPANT IN POSTERIOR MAXILLARY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRAFT: A CASE REPORT
 CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
Journal of American Science 2014;10(10)
 Introduction of a combined approach to retrieve a displaced maxillary third molar from the infra-temporal fossa complicating a mismanaged facial pain: A case report Ehab Helmi Ghali 1 (MB.ChB., BDS, MS,
Introduction of a combined approach to retrieve a displaced maxillary third molar from the infra-temporal fossa complicating a mismanaged facial pain: A case report Ehab Helmi Ghali 1 (MB.ChB., BDS, MS,
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP)
 REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
Extractions and the Maxillary Sinus
 Extractions and the Maxillary Sinus Four levels of sinus membrane involvement: Level One: Sinus membrane showing within the socket after an extraction. Not perforated. Level Two: 1-2mm tear. Level three:
Extractions and the Maxillary Sinus Four levels of sinus membrane involvement: Level One: Sinus membrane showing within the socket after an extraction. Not perforated. Level Two: 1-2mm tear. Level three:
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Bilateral Diplopia and Abducent Nerve Palsy Secondary to Odontogenic Sinusitis: An Unusual Presentation
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Bilateral Diplopia and Abducent Nerve Palsy Secondary to Odontogenic Sinusitis: An Unusual Presentation Samer Malas, MD* Hiba Al-Reefy, MB, BCh,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Bilateral Diplopia and Abducent Nerve Palsy Secondary to Odontogenic Sinusitis: An Unusual Presentation Samer Malas, MD* Hiba Al-Reefy, MB, BCh,
01/05/2014. Background. Minimally invasive tooth extraction. Thomas Dietrich Professor of Oral Surgery University of Birmingham, School of Dentistry
 Background Remodelling of alveolar bone following extraction Minimally invasive tooth extraction Thomas Dietrich Professor of Oral Surgery University of Birmingham, School of Dentistry 2 weeks 4 weeks
Background Remodelling of alveolar bone following extraction Minimally invasive tooth extraction Thomas Dietrich Professor of Oral Surgery University of Birmingham, School of Dentistry 2 weeks 4 weeks
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
