Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation
|
|
|
- Lorraine Blake
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE pissn eissn Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation Wang Peng, Il-Kyu Kim, Hyun-Young Cho, Sang-Pill Pae, Bum-Sang Jung, Hyun-Woo Cho, Ji-Hoon Seo Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Department of Dentistry, Inha University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea Abstract (J Korean ;39: ) Objectives: The posterior maxillary region often provides a limited bone volume for dental s. Maxillary sinus elevation via inserting a bone graft through a window opened in the lateral sinus wall has become the most common surgical procedure for increasing the alveolar bone height in place of dental s in the posterior maxillary region. The purpose of this article is to assess the change of bone volume and the clinical effects of dental placement in sites with maxillary sinus floor elevation and autogenous bone graft through the lateral window approach. Materials and Methods: In this article, the analysis data were collected from 64 dental s that were placed in 24 patients with 29 lacks of the bone volume posterior maxillary region from June 2004 to April 2011, at the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inha University Hospital. Panoramic views were taken before the surgery, after the surgery, 6 months after the surgery, and at the time of the final The influence of the factors on the grafted bone material resorption rate was evaluated according to the patient characteristics (age and gender), graft material, installation stage, size, placement region, local infection, surgical complication, and residual alveolar bone height. Results: The bone graft resorption rate of male patients at the final follow-up was significantly higher than the rate of female patients. The single autogenous bone-grafted site was significantly more resorbed than the autogenous bone combined with the Bio-Oss grafted site. The installation stage and residual alveolar height showed a significant correlation with the resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft material. The success rate and survival rate of the were 92.2% and 100%, respectively. Conclusion: Maxillary sinus elevation procedure with autogenous bone graft or autogenous bone in combination with Bio-Oss is a predictable treatment method for rehabilitation. Key words: Dental s, Maxillary sinus floor augmentation, Maxillary sinus, Alveolar bone grafting, Bone resorption [paper submitted / revised / accepted ] I. Introduction Dental s are increasingly being used to replace missing teeth 1. Note, however, that there are common problems in the posterior maxillary region such as restriction in the anatomic location, alveolar bone atrophy after prolonged edentulate state, resorption of alveolar bone in patients with periodontitis, and pneumatized sinus cavities causing lack of alveolar bone height. Likewise, lack of bone mass hampers restoration in the posterior maxillary region. Il-Kyu Kim Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Department of Dentistry, Inha University School of Medicine, 27, Inhang-ro, Jung-gu, Incheon , Korea TEL: FAX: kik@inha.ac.kr CC This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Copyright 2013 The Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons. All rights reserved. Boyne and James 2 (1980) reported on the elevation of the maxillary sinus floor in patients with large, pneumatized sinus cavities in preparation for the placement of blade s. Obviously, in the posterior maxillary region, reduction of vertical bone height is often limited to standard placement. Elevation of the maxillary sinus floor is the option to solve this problem. Various surgical techniques have been presented to use the sinus cavity for elevating the sinus membrane and placing bone graft materials. Tatum 3 first proposed dental placement in sites with bone graft for sinus floor elevation through the lateral window approach technique and its clinical application. This technology expanded the indication of the posterior maxillary region, having the advantages of direct vision when performing surgery, control of the elevated height, effective protection of the sinus mucosa, convenience of bone graft, and accurate positioning. In the study published by Wallace and Froum 4, they showed a high success rate using this technology for restoration. This work was supported by Inha University Research Grant. 274
2 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation As technology and bone grafting developed, maxillary sinus bone grafting became a popular form of surgery. Nonetheless, the graft material for maxillary sinus bone grafting has become an object of controversy. Bone grafting materials used for maxillary sinus graft include autogenous bone, allogenous bone, xenogenous bone, and synthetic bone. As the principle of new bone to be formed by autogenous bone, grafted bone exhibits osteoconductivity for osteoblast maturity by stimulating the osteoprogenitor cell of adjacent tissue or plays the role of passive substrate for the osteoprogenitor cell 5. Meanwhile, autogenous bone graft has the limit of bone yield but the advantage of no tissue rejection. This study sought to assess the change of bone volume and success and survival rates of placement in sites with bone graft for the elevation of maxillary sinus floor according to the patient s characteristics (age and gender), graft material, placement stage, size, placement region, local infection, surgical complication, and residual alveolar bone height. 1. Case selection II. Materials and Methods A total of 79 patients underwent dental restorations using sinus floor elevation from June 2004 to April 2011 at the Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Inha University Hospital (Incheon, Korea). At least 55 patients failed to comply with the follow-up principle or had systemic diseases, so the remaining 24 patients were included in the analysis. A total of 65 dental s were inserted. One was not inserted into the bone graft region, and this was also excluded from the analysis. Therefore, 64 s were included in this analysis. A total of 47 s were inserted using two-stage surgery, and 17 s, using one-stage surgery. Among 24 patients, 5 patients received bilateral surgery. At least 6 patients had single missing tooth, whereas 18 patients had multiple missing tooth. After a healing period of 6 to 13 months (average: 8.8 months), the prostheses were restored. The follow-up period was 24 to 68 months (average: 32.4 months). This study was conducted after obtaining approval from the Institutional Review Board. 2. Preoperative examination Patients received clinical examination over 3 months after tooth extraction, and they were suitable for surgery. At least 24 patients had no systemic diseases affecting bone healing, but 3 patients had chronic maxillary sinusitis (CMS). Preoperative panoramic taking was performed to assess bone volume at both the ation and donor sites to ensure the optimal position of the graft and. The bone quality, residual bone height, and existing maxillary sinus morphology were also evaluated on panoramic views. 3. Type of graft material Autogenous bone was harvested from the mandibular ramus or iliac crest, and then crushed into particulates. Bio-Oss (Geistlich Pharma AG, Wolhusen, Switzerland) was used as xenogenous bone. Autogenous bone alone or composite graft consisting of autogenous bone and Bio-Oss was used as grafting material. After sinus elevation, if the created space for grafting was small with 1 or 2 tooth sites included, autogenous bone was used alone; if not, composite graft was used. 4. Surgical methods The surgery for 18 patients was performed under local anesthesia, and the other 6 patients were treated under general anesthesia by one surgeon. The surgery was started with a trapezoid incision made on the alveolar ridge crest, and a fullthickness flap was then raised to expose the lateral antral wall of the sinus fully. After the flap was raised to the desired level, a window was created with a round bur as trapdoor on the lateral buttress of the maxilla. The bottom of the window was located 5 mm above the edge of the maxillary sinus floor. The size of the trapdoor should be determined according to the number of dental s, should be conducive to peel the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus, and should be smaller than the area of the lateral wall of the maxillary sinus. The height of this trapdoor should not exceed the width of the sinus to allow a final horizontal position of the new floor. A space was created after the sinus membrane was elevated by the intruded trapdoor. Finally, the bone block was rotated into the top of the space. After peeling the mucous membrane, the movement of bone block and mucous membrane could be seen together with respiration; thus indicating that the maxillary sinus membrane was integrated. The socket should be gradually expanded and prepared as the bed. Because of the low density of bone in the maxillary molar region, the use of osteotome needs to achieve better primary stability. The prepared graft material 275
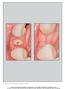
3 J Korean ;39: was grafted in the elevated maxillary sinus cavity, and then placement was performed. All of the s used were External Implant RBT (BioHorizons Implant Systems Inc., Birmingham, AL, USA). If the residual bone height and bone density are too low, primary stability would be jeopardized. Therefore, two-stage surgery should be performed. 5. Radiological examination The panoramic images were traced on paper, and all measurements were performed by calibration. The amount of bone augmentation A was evaluated by measuring the distance from the bottommost part of the fixture threads to the uppermost part of the bone graft material on a center-line of fixture after the surgery.(fig. 1) The same measuring method was applied on a panorama taken 6 months after the surgery B and on the final follow-up C. The amount of resorption of bone graft material A-B 6 months after the surgery and A-C at the final follow-up time was calculated. The resorption rate was calculated as (A-B)/A 100% on 6 months after the surgery and (A-B)/A 100% at the final follow-up time. To measure marginal bone resorption, the distance between the bottommost part of fixture threads to the top of the alveolar crest as represented in a panorama was measured. The measuring method was based on the panorama obtained im- mediately after the inserted surgery and at the final follow-up time. 6. Postoperative maintenance All patients took antibiotics to prevent infection and control edema after the surgery. The rest of the treatment was the same as the routine ation operation. Patients were advised not to blow their nose to avoid pressing on the sinus mucosa. Sutures were removed 7 to 10 days later. 7. Statistical analysis on the resorption rate of bone graft material With each measurement, statistical analysis on bone resorption 6 months after the surgery and final follow-up was performed using independent-sample t-test and ANOVA by age, gender, placement stage, graft materials, size, placement region, local infection, surgical complication, and residual alveolar bone height. P-values less than 0.05 were considered significant. 8. Follow-up principles All patients were asked to make a return visit within 1, 3, and 6 months of the surgery and to undergo regular reexamination each year. The contents of the re-examination included the extent of stability and condition of tissue surrounding the. Patients should take a panoramic radiograph at each return visit and compare the resorption condition of the edge bone surrounding the. Based on the panorama and medical records, preoperative and postoperative complications were examined; the success rates of the s were evaluated according to the criteria of Albrektsson et al. 6 at the time of final III. Results 1. Bone resorption rate by age and gender Fig. 1. The measurements for evaluating the amount of bone augmentation. (A: measure of the distance between the uppermost part of bone graft material and the lowermost partof the fixture threads on the panorama, B: measuring of the amount of bone augmentation 6 months after the surgery, C: measuring of the amount of bone augmentation on final follow-up, dotted line: bone resorption) The 24 patients who received 64 s for restoration were included for analysis. A total of 18 male patients received 21 bone grafts, whereas 6 female patients received 8 bone grafts. Patients age ranged from 18 to 68 years old, with mean age of 49.4 years. The resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft in the 41 to 50-year-old age group was 23.0% and 32.7% on 6 months 276
4 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation after the surgery and on the final follow-up, respectively; these were higher than the rates of other age groups. Note, however, that the difference in the resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft by patients age was not significant. (Table 1) The resorption rate of the maxillary sinus bone graft of the male patients group was 21.7% and 31.1% on 6 months after the surgery and on the final follow-up, respectively; these were higher than the resorption rate of the female patients group.(table 2) In particular, the bone resorption rate in the male patients group on the final follow-up was significantly higher than that in female patients (P<0.05). Note, however, that the difference in the resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft by patients gender--6 months after the surgery-- was not significant. 2. Bone resorption rate by graft material At least 14 (48.3%) cases utilized autogenous bone graft material, and 15 (51.7%) cases, autogenous bone in combination with Bio-Oss. The harvested autogenous bone was used in the mandibular ramus (95.3%) and in the iliac crest bone (4.7%). The mixing proportion of autogenous bone and Bio- Oss was 2 : 1 or 3 : 1. The resorption rate of bone graft material in the group with single autogenous bone graft was 23.1% and 32.1% on 6 months after the surgery and on the final follow-up, respectively. The resorption rate of bone graft material in the group with combined graft of autogenous bone and Bio-Oss was 18.9% and 28.6% on 6 months after the surgery and on the final follow-up, respectively. Bone graft resorption rate in the single autogenous bone material group was significantly higher than that in the autogenous bone with Bio-Oss material group (P<0.05).(Table 3) 3. Bone resorption rate by placement stage The decision to perform one-stage or two-stage surgery was mainly based on the available residual bone height and the possibility of achieving primary stability for the inserted s. In this study, cases wherein one-stage surgery was performed when the residual bone height remained higher than 5 mm were selected, including those wherein two-stage surgery was the option when residual bone height remained lower than 5 mm. A total of 17 s were used in onestage surgery, i.e., ation simultaneously done with sinus floor elevation. On the other hand, 47 s were used in the two-stage surgery, which involved sinus floor elevation with delayed placement, i.e., 4 to 12 months after Table 1. Resorption rate of bone material by age Age (yr) * 23.0* 20.9* 20.3* 29.2* 32.7* 29.4* 29.8* : resorption rate of bone material 6 months after the Table 3. Resorption rate of bone material by graft material Graft material ABG ABG+Bio-Oss * 18.9* 32.1* 28.6* (ABG: autogenous bone graft) : resorption rate of bone material 6 months after the Bio-Oss: Switzerland-made particulate graft material. Table 2. Resorption rate of bone material by gender Patients gender Male Female * 28.3* : resorption rate of bone material 6 months after the Table 4. Resorption rate of bone material by placement stage Implant placement stage 1-Stage surgery 2-Stage surgery * 20.6* 32.8* 29.5* : resorption rate of bone material 6 months after the 277
5 J Korean ;39: sinus grafting. The resorption rate of the maxillary sinus bone graft in the one-stage surgery group was significantly higher than that in the two-stage surgery group (P<0.05).(Table 4) 4. Bone resorption rate by size Out of a total of 64 s, there were 20 s with diameter of 4 mm and 44 s with diameter of 5 mm. The length was 9 mm in 4 s, 10.5 mm in 15 s, 11.5 mm in 7 s, 12 mm in 27 s, and 13 mm in 11 s. There was no significant correlation between the diameter, length of inserted, and bone resorption rate. (Table 5) 5. Bone resorption rate by placement region Out of a total of 64 s, 3 were placed in the first premolar region, 14, in the second premolar region, 27, in the first molar region, and 20, in the second molar region. Among these, the first molar region showed the highest resorption rate with 22.7% and 32.6% on 6 months after the Table 5. Resorption rate of bone material by size Fixture Length (mm) Diameter (mm) 4 5 Table 6. Resorption rate of bone material by placement region Placement region 1st premolar 2nd premolar 1st molar 2nd molar * 23.2* 23.1* 20.7* 18.9* 20.1* 20.5* 20.3* 21.5* 22.7* 20.9* 28.7* 32.5* 32.3* 30.1* 27.8* 30.1* 30.5* : resorption rate of bone material 6 months after the 29.8* 30.7* 32.6* 30.8* : resorption rate of bone material 6 months after the surgery and on the final follow-up, respectively, whereas the first premolar region showed the lowest resorption rate with 20.3% and 29.8% on 6 months after the surgery and on the final follow-up, respectively. Note, however, that the difference in resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft by placement region was not significant.(table 6) 6. Bone resorption rate by local infection and surgical complication Among the 29 maxillary sinus bone graft surgeries of 24 patients, 3 (10.3%) cases suffered from CMS. In 4 (13.8%) maxillary sinuses, perforation of the sinus membrane occurred when the sinus membrane was elevated, but they were cured without any specific abnormality in the perforated region. Local infection and surgical complication did not wield significant impact on the resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft.(table 7) 7. Bone resorption rate by residual bone height In this study, the range of residual bone height was 1.89 to 6.56 mm. This study divided the residual alveolar bone height into two groups: less than 4 mm (22 s) and over 4 mm (42 s). The resorption rate of maxillary Table 7. Resorption rate of bone material according to local infection and surgical complication Sinus disease CMS Perforation None * 22.6* 21.3* 27.4* 30.2* 28.9* (CMS: chronic maxillary sinusitis) : resorption rate of bone material 6 months after the Perforation: maxillary sinus perforation. Table 8. Resorption rate of bone material by residual bone height Residual bone height (mm) <4 > * 22.9* 28.5* 32.6* : resorption rate of bone material 6 months after the 278
6 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation Table 9. Implant placement stage and marginal bone resorption Implant placement stage 1-Stage surgery 2-Stage surgery sinus bone graft in the higher residual bone height group (>4 mm) was significantly higher than that in the lower residual bone height group (<4 mm) (P<0.05).(Table 8) 8. Clinical evaluation and marginal bone resorption During the healing and follow-up period of these 24 patients, the s did not exhibit any sign or symptom of pain, infection, and neuropathy. In addition, the panoramic views did not show peri- radiolucency, with the s exhibiting no mobility. Therefore, the dental survival rate was pegged at 100%. According to the panoramic views taken immediately after the surgery and at the final follow-up time, the average marginal bone resorption of all 64 s was 1.28 mm during an average monitoring period of 2.7 years. Marginal bone resorption due to the difference in placement stage showed a statistically significant difference at the final follow-up time, with the one-stage surgery group exhibiting less resorption.(table 9) In 5 patients, 5 s exhibited increased marginal bone resorption. Two s in two male patients with CMS, one in one male patient with perforation of the sinus membrane, and two s in one male patient and one female patient without any disease showed more than 2.0 mm progressive marginal bone resorption during an average monitoring period of 2.7 years. Therefore, the success rate of the s was 92.2%. IV. Discussion Mean of resorption (mm) 1.17* 1.58* After the loss of the maxillary molar tooth, the alveolar bone shows rapid resorption, and the size of the maxillary sinus also increases. Therefore, only the thin bone wall between the oral cavity and the maxillary sinus may remain. To place an for such patients, bone graft is done for bone augmentation. Maxillary sinus bone graft surgery is now predictable and is regarded as a safe surgical procedure. Most of the bone graft materials are known to yield a good result in terms of the survival rate of, but the maxillary sinus bone graft materials may be absorbed over time 7. According to Wang and Luo 8, age was one of the major factors influencing bone resorption. In this study, the bone resorption rate of patients in the 41 to 50-year-old age group was 23.0% on 6 months after the surgery and 32.7% at the final follow-up time; these were higher than the rates of the other age groups. Note, however, that the difference in bone resorption rate by patient s age was not statistically significant.(table 1) Andreasen et al. 9 reported that the gender of the patient was significantly related to bone resorption activity and observed a different degree of bone resorption, noting that it was higher in women than in men. In contrast, this study found the bone graft resorption rate in the male patients group at the time of final follow-up to be significantly higher than that in the female patients group. Nonetheless, the difference in bone graft resorption rate by patients gender 6 months after the surgery was not significant.(table 2) Various materials have been used for grafting the sinus floor. The bone graft materials can be categorized into four groups: autogenous bone, allogenous bone, xenogenous bone, and synthetic bone. These bone graft materials can be used alone or in combination with each other. Autogenous bone has been considered the gold standard 10 of bone graft material for a long time because of its osteoconductive, osteoinductive, and osteogenic properties 11. According to Dragoo and Sullivan 12, autogenous bone is a bone graft material with the highest regenerative capability when it comes to alveolar bone defects. Autogenous bone including calvarium, tibia, ribs, or iliac bone can be used. Due to problems such as inconvenience of hospitalization, general anesthesia, postoperative pain, and burden of medical expenses, however, its use has been limited. Alternatively, autogenous bone from the oral cavity such as mental region, mandibular ramus, and zygomatic region has often been used 13. In particular, mandibular ramus bone has high ratio of cortical bone, but the harvest of the ramus bone is difficult. Nonetheless, it is the preferred bone graft material for the maxillary sinus due to the low risk of edema and nerve injury compared to mental bone. When maxillary sinus bone graft using autogenous bone was performed, many cases exhibited considerable bone resorption over time. Furthermore, a study reported that using 100% autogenous bone as bone graft material enabled faster absorption compared to using autogenous bone in combination with bone substitutes. At present, autogenous bone in combination with bone substitutes is used widely
7 J Korean ;39: A histological analysis proved that using bone graft material combining autogenous bone and Bio-Oss enables shortening the time of formation of new bone 15. No studies have shown that autogenous bone and bone substitute mixing ratio differences have an impact on the success rate of dental s, however. Hatano et al. 16 performed simultaneous placement with maxillary sinus bone grafting using autogenous bones and xenogeneic bones (Bio-Oss) mixed at a 2 : 1 ratio and conducted a long-term clinical evaluation. They found that the survival of s after 2 to 3 years was 94.2%, and that the height of the maxillary sinus floor was similar to the level of the apex area or slightly lower. They confirmed that, even in cases grafted with a mixture of autogenous and xenogeneic bones, repneumatization progressed continuously for 2 to 3 years, and that no great change was observed after that. They also concluded that stable maintenance of the height of maxillary sinus bone grafting materials played an important role in success. Kim et al. 17 also reported the results of clinical studies on sinus bone resorption after sinus bone grafting and placement. In their study, the mean height of the remaining alveolar bone before the surgery, immediately after the surgery, and 1 year after the surgery was 4.9 mm, 19.0 mm, and 17.2 mm, respectively, in group I (xenograft + minimal amount of autogenous bone) and 4.0 mm, 19.2 mm, and 17.8 mm, respectively, in group II (allograft + xenograft + minimal amount of autogenous bone). In this study, the resorption rate after the single graft of autogenous bone was 23.1% and 32.1% on 6 months after the surgery and on the final followup, respectively, whereas the resorption rate after a combined graft of autogenous bone and Bio-Oss was 18.9% and 28.6% on 6 months after the surgery and on the final follow-up, respectively. The difference in bone resorption rate by graft material (single autogenous bone or autogenous bone in combination with Bio-Oss) was statistically significant (P<0.05). (Table 3) Some researchers suggested that, with higher residual bone height (>5 mm), the could have better primary stability, and that it would be suitable for maxillary sinus elevation with bone graft and one-stage surgery. When the residual bone height was lower than 5 mm, two-stage surgery was recommended 18,19. Corinaldesi et al. 20 showed that patients undergoing the simultaneous approach (20 sites) showed mean residual bone height of 5.9±1.77 mm (range, 4 to 9 mm) at baseline. Among patients undergoing the delayed approach (14 sites), mean residual bone height decreased to 3.5±1.16 mm (range, 1.5 to 5 mm). In this study, the mean residual bone height of the one-stage surgery group and twostage surgery group was 5.67 mm and 3.91 mm, respectively. The resorption rate of the maxillary sinus bone graft in the one-stage surgery group was significantly higher than that in the two-stage surgery group. This is because one-stage surgery for these cases all involved single autogenous bone graft material.(table 4) Some studies reported that the small surface area of had risk of increasing the resorption rate 21. In this study, however, there was no correlation between the size and resorption rate.(table 5) According to Kim and Lee 22, there was no correlation with the placement region. Similarly, this study found no significant difference by placement region.(table 6) Cheong et al. 23 reported that 105 maxillary sinuses in 87 patients showed high prevalence of sinus disease. This result supported the fact that maxillary sinus disease was very common among patients who were planning ation in the maxillary posterior areas. In this study, CMS developed in 3 (10.3%) cases. Note, however, that neither maxillary sinus bone grafting material loss nor failure occurred. CMS did not show significant correlation with the resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft.(table 7) According to Pjetursson et al. 24, the most common intraoperative complication was the perforation of the sinus membrane. The mean prevalence of membrane perforation was 19.5%, and range was 0 to 58.3%. Significant statistical correlation was found between residual alveolar bone height and membrane perforation. Due mainly to technical difficulties, maxillary sinus membrane perforation occurs more frequently with a small height of residual alveolar bone. The study by Ardekian et al. 25 found no statistical difference in the success rate of the immediate s placed with sinus bone grafting in patients whose membrane was perforated versus those patients in whom an intact membrane was maintained. In our study, perforation of the sinus membrane was observed in 4 (13.8%) patients. Nevertheless, perforation of the sinus membrane did not show significant correlation with the resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft.(table 7) According to Jensen et al. 26, residual alveolar bone height had the most influence on the survival rate of the placed after maxillary sinus elevation, and, if the height was 7 mm or less, bone graft must be done for placement. The study by Herzberg et al. 21 showed that residual bone height of less than 4 mm tended to promote graft material resorption. Note, however, that this study showed the opposite 280
8 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation result. The resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft in the higher residual bone height group (>4 mm) was significantly higher than that for the lower residual bone height group (<4 mm). This is because, with higher residual bone height (>4 mm), single autogenous bone graft material was used for the elevation of maxillary sinus floor.(table 8) Herzberg et al. 21 examined 70 patients with 212 s placed in 81 maxillary sinus regions during the period 1995 to 2000 and reported 95.5% and 83.7% cumulative survival and success rates, respectively, for 4.5 years. The study of Kim et al. 27 showed that the mean marginal bone resorption around the s was 0.69 mm 1 year after prosthodontic loading. Marginal bone resorption of more than 1.5 mm occurred in 9 s, for a success rate of 88%. Kim et al. 17 also reported mean marginal bone loss--1 year after prosthodontic loading and after 20.8 months follow-up--of 0.6 mm and 0.7 mm, respectively, in group 1 (xenograft + minimal amount of autogenous bone). At least 3 s showed bone resorption of more than 1.5 mm within 1 year of loading, for a success rate of 93.9%. On the other hand, mean marginal bone loss 1 year after prosthodontic loading and after 19.7 months follow-up was 0.7 mm and 1.0 mm, respectively, in group 2 (allograft + xenograft + minimal amount of autogenous bone). A total of 4 s showed bone resorption of more than 1.5 mm within 1 year of loading, for a success rate of 83.3%. In this study, marginal bone resorption was measured to be a minimum of 0.61 mm to a maximum of 3.54 mm and a mean of 1.28 mm during an average of 2.7 years after prostheses placement. The one-stage surgery and two-stage surgery showed significant differences in marginal bone resorption, with less bone resorption observed in the former.(table 9) Two s in two male patients with CMS, one in one male patient with perforation of the sinus membrane, and two s in one male patient and one female patient without any disease showed more than 2.0 mm progressive marginal bone resorption during an average monitoring period of 2.7 years. Furthermore, overall, no falling off or looseness, pain, infection and abnormal feeling, or inflammation in the peri- was observed for the 64 s. The panoramic views showed no shadows during the 24 to 68 months follow-up period. Therefore, the success rate and survival rate of the were 92.2% and 100%, respectively. V. Conclusion This study reported the clinical findings on sinus elevation surgery with immediate placement and subsequent placement using autogenous bone graft or autogenous bone in combination with Bio-Oss graft. Based on the evaluation results on the resorption level using the panoramic views taken before the surgery, immediately after the surgery, 6 months after the surgery, and final follow-up time, the following conclusions were drawn: 1. The bone graft resorption rate in the male patients group on the final follow-up was significantly higher than that in the female patients group; note, however, that there was no significant difference in bone resorption rate by patients gender 6 months after surgery. 2. The bone resorption rate after single autogenous bone graft was significantly higher compared to the autogenous bone combined with Bio-Oss. 3. The resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft in the one-stage surgery group was significant higher than that in the two-stage surgery group. 4. The resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft in the higher residual bone height group (>4 mm) was significant higher than that in the residual bone height group (<4 mm). 5. There was no significant correlation with the resorption rate of maxillary sinus bone graft among patients age, size, placement region, local infection, and surgical complication. 6. During an average monitoring period of 2.7 years, the success rate and survival rate of the were 92.2% and 100%, respectively. The results suggest that maxillary sinus floor elevation with autogenous bone graft through the lateral window approach technique is feasible and safe, and that the elevation of maxillary sinus floor is predictable in rehabilitation for patients with reduced vertical bone height in the posterior maxillary region. References 1. Smith LP, Ng M, Grubor D, Chandu A. Outcomes of dental s placed in a surgical training programme. Aust Dent J 2009; 54: Boyne PJ, James RA. Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J Oral Surg 1980;38: Tatum H Jr. Maxillary and sinus reconstructions. Dent Clin North Am 1986;30: Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental s. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol 2003;8: Mellonig JT, Bowers GM, Bailey RC. Comparison of bone graft materials. Part I. New bone formation with autografts and allografts determined by Strontium-85. J Periodontol 1981;52: Albrektsson T, Zarb G, Worthington P, Eriksson AR. The long- 281
9 J Korean ;39: term efficacy of currently used dental s: a review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1986;1: Scarano A, Degidi M, Iezzi G, Pecora G, Piattelli M, Orsini G, et al. Maxillary sinus augmentation with different biomaterials: a comparative histologic and histomorphometric study in man. Implant Dent 2006;15: Wang X, Luo Y. Influencing factors on bone resorption after alveolar bone grafting. Zhonghua Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi 2005;40: Andreasen JO, Paulsen HU, Yu Z, Schwartz O. A long-term study of 370 autotransplanted premolars. Part III. Periodontal healing subsequent to transplantation. Eur J Orthod 1990;12: Tong DC, Rioux K, Drangsholt M, Beirne OR. A review of survival rates for s placed in grafted maxillary sinuses using meta-analysis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1998;13: Klijn RJ, Meijer GJ, Bronkhorst EM, Jansen JA. A meta-analysis of histomorphometric results and graft healing time of various biomaterials compared to autologous bone used as sinus floor augmentation material in humans. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 2010;16: Dragoo MR, Sullivan HC. A clinical and histological evaluation of autogenous iliac bone grafts in humans. I. Wound healing 2 to 8 months. J Periodontol 1973;44: Misch CM. Comparison of intraoral donor sites for onlay grafting prior to placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1997;12: Valentini P, Abensur DJ. Maxillary sinus grafting with anorganic bovine bone: a clinical report of long-term results. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2003;18: Tawil G, Mawla M. Sinus floor elevation using a bovine bone mineral (Bio-Oss) with or without the concomitant use of a bilayered collagen barrier (Bio-Gide): a clinical report of immediate and delayed placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2001;16: Hatano N, Shimizu Y, Ooya K. A clinical long-term radiographic evaluation of graft height changes after maxillary sinus floor augmentation with a 2:1 autogenous bone/xenograft mixture and simultaneous placement of dental s. Clin Oral Implants Res 2004;15: Kim YK, Yun PY, Kim SG, Kim BS, Ong JL. Evaluation of sinus bone resorption and marginal bone loss after sinus bone grafting and placement. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2009;107:e McCarthy C, Patel RR, Wragg PF, Brook IM. Sinus augmentation bone grafts for the provision of dental s: report of clinical outcome. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2003;18: Fugazzotto PA, Vlassis J. Long-term success of sinus augmentation using various surgical approaches and grafting materials. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1998;13: Corinaldesi G, Pieri F, Sapigni L, Marchetti C. Evaluation of survival and success rates of dental s placed at the time of or after alveolar ridge augmentation with an autogenous mandibular bone graft and titanium mesh: a 3- to 8-year retrospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2009;24: Herzberg R, Dolev E, Schwartz-Arad D. Implant marginal bone loss in maxillary sinus grafts. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2006; 21: Kim BJ, Lee JH. The retrospective study of survival rate of s with maxillary sinus floor elevation. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2010;36: Cheong CS, Cho BH, Hwang DS, Jung YH, Naa KS. Evaluation of maxillary sinus using cone-beam CT in patients scheduled for dental in maxillary posterior area. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;35: Pjetursson BE, Tan WC, Zwahlen M, Lang NP. A systematic review of the success of sinus floor elevation and survival of s inserted in combination with sinus floor elevation. J Clin Periodontol 2008;35(8 Suppl): Ardekian L, Oved-Peleg E, Mactei EE, Peled M. The clinical significance of sinus membrane perforation during augmentation of the maxillary sinus. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2006;64: Jensen OT, Shulman LB, Block MS, Iacono VJ. Report of the Sinus Consensus Conference of Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1998;13(Suppl): Kim YK, Yun PY, Im JH. Clinical retrospective study of sinus bone graft and placement. J Korean Assoc Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg 2008;30:
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re. Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T
 Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Retrospective Study of Bone Resorption after Maxillary Sinus Bone Graft
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2011.4.2.59 Ji-A Moon 1, Min-Sung Cho 2, Seung-Gon Jung 2, Min-Suk Kook 2, Hong-Ju Park 2, Hee-Kyun Oh 2 1. Department of Dental Science, School of Dentistry,
http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2011.4.2.59 Ji-A Moon 1, Min-Sung Cho 2, Seung-Gon Jung 2, Min-Suk Kook 2, Hong-Ju Park 2, Hee-Kyun Oh 2 1. Department of Dental Science, School of Dentistry,
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.1.37 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases Young-Kyun Kim 1, Su-Gwan Kim
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.1.37 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Familial tooth bone graft for ridge and sinus augmentation: a report of two cases Young-Kyun Kim 1, Su-Gwan Kim
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants
 Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years
 Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Effects of Maxillary Sinus Graft on the Survival of Endosseous Implants: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 8-2008 Effects of Maxillary Sinus Graft on the Survival of Endosseous Implants: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 8-2008 Effects of Maxillary Sinus Graft on the Survival of Endosseous Implants: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure
 Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Seung-Yun Shin 1, You-Jeong Hwang 2, Jung-Hoon Kim 3,4, Yang-Jo Seol 3,
Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Seung-Yun Shin 1, You-Jeong Hwang 2, Jung-Hoon Kim 3,4, Yang-Jo Seol 3,
Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla
 CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
Posterior mandible and vertical augmentation
 CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
Keywords: Biomechanics, Biostatistics, Maxilla, Maxillary sinus, Sinus floor augmentation.
 Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
Research Article Journal of Periodontal J Periodontal Implant Sci 2013;43:58-63 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2013.43.2.58 Peri-implant bone length changes and survival rates of implants penetrating the
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3.
 DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Reconstruction of large oroantral defects using a pedicled buccal fat pad
 Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
Yang et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2018) 40:7 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40902-018-0144-6 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery CASE REPORT Open Access Reconstruction
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Vertical and horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation
 CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
One in four sinus lift procedures can be
 11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 1. Implant Locations. Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla. Anatomy and risk factors Option 1: Short implants
 T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Sinus Floor Elevation. Treatment Concepts
 Sinus Floor Elevation Treatment Concepts Geistlich Family supports your way to regeneration together for more satisfied patients Dr. Andreas Geistlich CONTENTS 3 Maxillary sinus floor augmentation 4 5
Sinus Floor Elevation Treatment Concepts Geistlich Family supports your way to regeneration together for more satisfied patients Dr. Andreas Geistlich CONTENTS 3 Maxillary sinus floor augmentation 4 5
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
 227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
Intramembranous autogenous bone graft is the gold
 CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report
 Vol. 31 No. 3, December 2012 Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report In-Seong Jeon, Min-Suk Heo 1, Kyu-Ho Yoon 2, Kwang-Heung Han
Vol. 31 No. 3, December 2012 Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report In-Seong Jeon, Min-Suk Heo 1, Kyu-Ho Yoon 2, Kwang-Heung Han
Annals of Dental Research
 P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report
 ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report Yaqian Chen, Qingqing Wu, Yi Man State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China
ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report Yaqian Chen, Qingqing Wu, Yi Man State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Healing pattern of the mucous membrane after tooth extraction in the maxillary sinus
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:23-29 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.1.23 Healing pattern of the mucous membrane after tooth extraction in the maxillary sinus Ji-Young Yoo, Sung-Hee Pi, Yun-Sang
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:23-29 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.1.23 Healing pattern of the mucous membrane after tooth extraction in the maxillary sinus Ji-Young Yoo, Sung-Hee Pi, Yun-Sang
Osseointegrated implants are a very reliable means
 Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
A New Technique for Minimally Invasive Maxillary Lateral Sinus Augmentation: a Case Report
 A New Technique for Minimally Invasive Maxillary Lateral Sinus Augmentation: a Case Report Xiu Lian HU 1, Xian ZHOU 1, Jian Hui LI 1, Ye LIN 1 Numerous techniques are described for lateral sinus augmentation,
A New Technique for Minimally Invasive Maxillary Lateral Sinus Augmentation: a Case Report Xiu Lian HU 1, Xian ZHOU 1, Jian Hui LI 1, Ye LIN 1 Numerous techniques are described for lateral sinus augmentation,
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
A Review of Survival Rates for Implants Placed in Grafted Maxillary Sinuses Using Meta-analysis
 A Review of Survival Rates for Implants Placed in Grafted Maxillary Sinuses Using Meta-analysis Darryl C. Tong, BDS*/Kim Rioux**/Mark Drangsholt, DDS, MPH***/ O. Ross Beirne, DMD, PhD**** A variety of
A Review of Survival Rates for Implants Placed in Grafted Maxillary Sinuses Using Meta-analysis Darryl C. Tong, BDS*/Kim Rioux**/Mark Drangsholt, DDS, MPH***/ O. Ross Beirne, DMD, PhD**** A variety of
Young-Jin Park, DDS,* and Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION
 original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
Years of research and advancement in
 Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
International Journal of Implant Dentistry. Takahiro Kaneko *, Satoshi Nakamura, Shunsuke Hino, Norio Horie and Tetsuo Shimoyama
 Kaneko et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2016) 2:16 DOI 10.1186/s40729-016-0049-z International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Open Access Continuous intra-sinus bone regeneration
Kaneko et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2016) 2:16 DOI 10.1186/s40729-016-0049-z International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Open Access Continuous intra-sinus bone regeneration
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
REASONS TO USE R.T.R.
 3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic. Review
 Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift
 Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Long-term success for osteointegrated
 CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
I. Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2012.38.2.71 pissn 22347550 eissn 22345930 Study on the position of the posterior superior alveolar artery in relation to the performance of the maxillary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2012.38.2.71 pissn 22347550 eissn 22345930 Study on the position of the posterior superior alveolar artery in relation to the performance of the maxillary
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
The use of endosseous implants is currently a routine
 Evaluation of 31 Zygomatic Implants and 74 Regular Dental Implants Used in 16 Patients for Prosthetic Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Cross-Arch Fixed Bridges Jonas P. Becktor, DDS;* Sten Isaksson,
Evaluation of 31 Zygomatic Implants and 74 Regular Dental Implants Used in 16 Patients for Prosthetic Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Cross-Arch Fixed Bridges Jonas P. Becktor, DDS;* Sten Isaksson,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla,
 Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
Space maintenance in autogenous fresh demineralized tooth blocks with platelet rich plasma for maxillary sinus bone formation: a prospective study
 DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1886-1 RESEARCH Open Access Space maintenance in autogenous fresh demineralized tooth blocks with platelet rich plasma for maxillary sinus bone formation: a prospective study Eun
DOI 10.1186/s40064-016-1886-1 RESEARCH Open Access Space maintenance in autogenous fresh demineralized tooth blocks with platelet rich plasma for maxillary sinus bone formation: a prospective study Eun
Effectiveness of guided bone regeneration and protein collagen sponge on socket preservation post tooth-extraction.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (12): 5402-5407 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effectiveness of guided bone regeneration and protein collagen sponge on socket preservation post tooth-extraction. Tao Wang
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (12): 5402-5407 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Effectiveness of guided bone regeneration and protein collagen sponge on socket preservation post tooth-extraction. Tao Wang
Case study 2. A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant
 Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
T he cortical bone of the maxillary
 KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation
 42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT. simultaneous implant placement and is an alternative Summer s osteotome both clinical use as well as the
 BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
complications (Zitzmann and Schaerer,
 Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Comprehensive Dental Implantology
 Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan
 Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Assessment of the relationship between maxillary sinus floor and maxillary posterior teeth root apices using spiral CT scan Zainab Abdulhasan Hussein, B.D.S. (1) (2) Lamia H. Al-Nakib, B.D.S., M.Sc. ABSTRACT
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
골내결손부에서의치주조직재생 : 증례보고
 ISSN 1229-5418 Implantology 2015; 19(4): 228~232 골내결손부에서의치주조직재생 : 증례보고 김설희, 김태일서울대학교치의학대학원치주과학교실 Periodontal Regeneration in Intrabony Defects: A Case Report Sul-hee Kim, Tae-il Kim Department of Periodontology,
ISSN 1229-5418 Implantology 2015; 19(4): 228~232 골내결손부에서의치주조직재생 : 증례보고 김설희, 김태일서울대학교치의학대학원치주과학교실 Periodontal Regeneration in Intrabony Defects: A Case Report Sul-hee Kim, Tae-il Kim Department of Periodontology,
We Want to Keep You Smiling. Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide
 We Want to Keep You Smiling Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Strong Bone for a Healthier Smile Strong and healthy teeth provide a feeling of well-being, self-confidence and
We Want to Keep You Smiling Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Strong Bone for a Healthier Smile Strong and healthy teeth provide a feeling of well-being, self-confidence and
Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report
 CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
Abstract. Introduction. Case Report
 Chettinad Health City Medical Journal Case Report Ridge using Titanium Mesh, PRF and Autogenous Bone Graft with Implant Placement Dr.Vinayak S Gowda*, Dr.B.Meena Priya** *Professor, Department of Periodontics,
Chettinad Health City Medical Journal Case Report Ridge using Titanium Mesh, PRF and Autogenous Bone Graft with Implant Placement Dr.Vinayak S Gowda*, Dr.B.Meena Priya** *Professor, Department of Periodontics,
Minimal invasive horizontal ridge augmentation using subperiosteal tunneling technique
 Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0087-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Minimal invasive horizontal
Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2016) 38:41 DOI 10.1186/s40902-016-0087-8 Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery RESEARCH Open Access Minimal invasive horizontal
Lack of sufficient bone height in the posterior maxilla
 Computerized Tomography Assisted Calculation of Sinus Augmentation Volume Gerald Krennmair, MD, DMD, PhD 1 /Martin Krainhöfner, MD, DMD 2 /Harald Maier 3 / Michael Weinländer, MD, DMD 4 /Eva Piehslinger,
Computerized Tomography Assisted Calculation of Sinus Augmentation Volume Gerald Krennmair, MD, DMD, PhD 1 /Martin Krainhöfner, MD, DMD 2 /Harald Maier 3 / Michael Weinländer, MD, DMD 4 /Eva Piehslinger,
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS
 A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
A WIDE RANGE OF REGENERATIVE SOLUTIONS INDICATIONS: 1/ SOCKET AND RIDGE PRESERVATION 2/ FILLING OF EXTRACTION SOCKETS Biomaterials offers portfolio of regenerative materials for implantology, aimed at
School of Dentistry, Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC), Florianópolis, SC, Brazil
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2016 18/4: 102 108 A Step-by-Step Management of Extraction Sites in Areas of Maxillary Sinus Pneumatization: A Literature Review and a Case Presentation
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2016 18/4: 102 108 A Step-by-Step Management of Extraction Sites in Areas of Maxillary Sinus Pneumatization: A Literature Review and a Case Presentation
