Cécile Baron 1, Carine Guivier-Curien 2, Vu-Hieu Nguyen 3, Salah Naili 3. Monastery Banz, June 29 th, 2017
|
|
|
- Ashley McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Bone repair and ultrasound stimulation : an insight into the interaction of LIPUS with the lacuno-canalicular network of cortical bone through a multiscale computational study. Cécile Baron 1, Carine Guivier-Curien 2, Vu-Hieu Nguyen 3, Salah Naili 3 1 Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS, ISM UMR 7287, Marseille France 2 Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS, Ecole Centrale, IRPHE UMR 7342, Marseille France 3 Université Paris Est, MSME UMR 8208 CNRS, Créteil France Monastery Banz, June 29 th, 2017 Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
2 Ultrasound waves and living tissues UltraSounds (US) interact with living tissues : destroy (HIFU) and repair (LIPUS) What is LIPUS? Low Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation LIPUS stimulates bone healing : Large literature (Duarte 1983, Pilla et al. 1990, Heckman et al. 1994, Takikawa et al. 2000, Hemery et al. 2011,...) FDA approval since 1994 Commercial device : Exogen R Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
3 Ultrasound waves and living tissues UltraSounds (US) interact with living tissues : destroy (HIFU) and repair (LIPUS) What is LIPUS? Low Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation LIPUS stimulates bone healing : Large literature (Duarte 1983, Pilla et al. 1990, Heckman et al. 1994, Takikawa et al. 2000, Hemery et al. 2011,...) FDA approval since 1994 Commercial device : Exogen R What mechanisms are responsible? Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
4 Ultrasound waves and living tissues UltraSounds (US) interact with living tissues : destroy (HIFU) and repair (LIPUS) What is LIPUS? Low Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation LIPUS stimulates bone healing : Large literature (Duarte 1983, Pilla et al. 1990, Heckman et al. 1994, Takikawa et al. 2000, Hemery et al. 2011,...) FDA approval since 1994 Commercial device : Exogen R What mechanisms are responsible? Thermal effects and Mechanical effects Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
5 Ultrasound waves and living tissues UltraSounds (US) interact with living tissues : destroy (HIFU) and repair (LIPUS) What is LIPUS? Low Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation LIPUS stimulates bone healing : Large literature (Duarte 1983, Pilla et al. 1990, Heckman et al. 1994, Takikawa et al. 2000, Hemery et al. 2011,...) FDA approval since 1994 Commercial device : Exogen R What mechanisms are responsible? Thermal effects and Mechanical effects But how? Open question! (Claes et al. 2007, Padilla et al. 2014) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
6 Ultrasound waves and living tissues UltraSounds (US) interact with living tissues : destroy (HIFU) and repair (LIPUS) What is LIPUS? Low Intensity Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulation LIPUS stimulates bone healing : Large literature (Duarte 1983, Pilla et al. 1990, Heckman et al. 1994, Takikawa et al. 2000, Hemery et al. 2011,...) FDA approval since 1994 Commercial device : Exogen R What mechanisms are responsible? Thermal effects and Mechanical effects But how? Open question! (Claes et al. 2007, Padilla et al. 2014) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
7 Bone Tissue How is cortical bone tissue organized? Porous and multiscale : vascular porosity (HV) : Havers and Volkman canals (Ø 100 µm) lacuno-canalicular network (LCN) : lacunae (Ø 10 µm) + canaliculi (Ø< 1 µm) Bone cells : osteocytes Mechanotransduction Fluid shear stress on osteocyte bone remodelling Cowin et al. 1991, Klein-Nulend et al Cortical bone = double-level porous medium Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
8 Bone Tissue How is cortical bone tissue organized? Porous and multiscale : vascular porosity (HV) : Havers and Volkman canals (Ø 100 µm) lacuno-canalicular network (LCN) : lacunae (Ø 10 µm) + canaliculi (Ø< 1 µm) Bone cells : osteocytes Mechanotransduction Fluid shear stress on osteocyte bone remodelling Cowin et al. 1991, Klein-Nulend et al Cortical bone = double-level porous medium Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
9 Hypothesis and aims Hypothesis : US excitation at meso-scale level induces fluid shear stress on osteocytes at micro-scale level Locks : Multiscale phenomena to understand and analyze Multiphysics : acoustics, fluid and structure Coupling multiscale and multiphysics Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
10 Hypothesis and aims Hypothesis : US excitation at meso-scale level induces fluid shear stress on osteocytes at micro-scale level Locks : Multiscale phenomena to understand and analyze Multiphysics : acoustics, fluid and structure Coupling multiscale and multiphysics Development of relevant FE models to understand LIPUS mechanisms Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
11 Hypothesis and aims Hypothesis : US excitation at meso-scale level induces fluid shear stress on osteocytes at micro-scale level Locks : Multiscale phenomena to understand and analyze Multiphysics : acoustics, fluid and structure Coupling multiscale and multiphysics Development of relevant FE models to understand LIPUS mechanisms Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
12 Models Biphasic medium Model + US : ModBone Vascular pores (HV) = fluid phase HV pores reconstructed from binarized µct images (22.5 µm) Poroelastic bone matrix (PBM) RX image anisotropic solid (Scheiner et al. 2015) + LCN equivalent medium (Biot s model) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
13 Models Biphasic medium Model + US : ModBone Vascular pores (HV) = fluid phase HV pores reconstructed from binarized µct images (22.5 µm) Poroelastic bone matrix (PBM) RX image anisotropic solid (Scheiner et al. 2015) + LCN equivalent medium (Biot s model) Ultrasound stimulation (US) from Exogen device f=1 MHz, pressure=2 kpa, duty cycle=20%, pulse duration=1 ms, Øtransducer=20 mm Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
14 Models Biphasic medium Model + US : ModBone Vascular pores (HV) = fluid phase HV pores reconstructed from binarized µct images (22.5 µm) Poroelastic bone matrix (PBM) RX image anisotropic solid (Scheiner et al. 2015) + LCN equivalent medium (Biot s model) Ultrasound stimulation (US) from Exogen device f=1 MHz, pressure=2 kpa, duty cycle=20%, pulse duration=1 ms, Øtransducer=20 mm 2-2 P (kpa) 1 MHz t (ms) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
15 Models Biphasic medium Model + US : ModBone Vascular pores (HV) = fluid phase HV pores reconstructed from binarized µct images (22.5 µm) Poroelastic bone matrix (PBM) RX image anisotropic solid (Scheiner et al. 2015) + LCN equivalent medium (Biot s model) Ultrasound stimulation (US) from Exogen device f=1 MHz, pressure=2 kpa, duty cycle=20%, pulse duration=1 ms, Øtransducer=20 mm 2-2 P (kpa) 1 MHz t (ms) water US HV PBM Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
16 Models Osteocyte Model : ModOst Osteocyte cell (solid phase) Extracellular matrix, ECM (solid phase) Interstitial Fluid (IFluid) (fluid phase) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
17 Models Osteocyte Model : ModOst Osteocyte cell (solid phase) Extracellular matrix, ECM (solid phase) Interstitial Fluid (IFluid) (fluid phase) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
18 Models Osteocyte Model : ModOst Osteocyte cell (solid phase) Extracellular matrix, ECM (solid phase) Interstitial Fluid (IFluid) (fluid phase) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
19 FE simulation 2D and 3D coupling between acoustics and fluid and fluid-solid interaction Software : Comsol Multiphysics ModBone (2D) : US stimulation at the mesoscale Time-dependent problem Weak form of wave propagation in poroelastic medium + boundary conditions (Nguyen et al. 2010) x bone 0.7 mm, x water 0.4 mm and t 0.1µs 40h to simulate a single cycle propagation. Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
20 FE simulation 2D and 3D coupling between acoustics and fluid and fluid-solid interaction Software : Comsol Multiphysics ModBone (2D) : US stimulation at the mesoscale Time-dependent problem Weak form of wave propagation in poroelastic medium + boundary conditions (Nguyen et al. 2010) x bone 0.7 mm, x water 0.4 mm and t 0.1µs 40h to simulate a single cycle propagation. water US PBM HV input parameters : US stimulation parameters f=1mhz, pressure=2 kpa, duty cycle=20%, pulse duration=1 ms, Øtransducer=10 mm surrounding fluid properties = water bone material properties = anisotropic poroelasticity (Scheiner et al. 2015, Goulet et al. 2008, Nguyen et al. 2010, Cowin et al. 2009) output parameter : IFluid pressure gradient Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
21 FE simulation 2D and 3D coupling between acoustics and fluid and fluid-solid interaction Software : Comsol Multiphysics ModBone (2D) : US stimulation at the mesoscale Time-dependent problem Weak form of wave propagation in poroelastic medium + boundary conditions (Nguyen et al. 2010) x bone 0.7 mm, x water 0.4 mm and t 0.1µs 40h to simulate a single cycle propagation. input parameters : US stimulation parameters f=1mhz, pressure=2 kpa, duty cycle=20%, pulse duration=1 ms, Øtransducer=10 mm surrounding fluid properties = water P (kpa) bone material properties = anisotropic poroelasticity (Scheiner et al. 2015, Goulet et al. 2008, Nguyen et al. 2010, Cowin et al. 2009) output parameter : IFluid pressure gradient MHz water US HV t (ms) PBM Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
22 Results and Discussion : ModBone Acoustic pressure and IFluid pressure (Pa) t = 4 µs t = 20 µs IFluid pressure (IFluid P) difference induced by US stimulation on 1 cycle Max IFluid P periosteum IFluid P endosteum Pa IFluid P gradient = 3.8 Pa/µm IFluid P gradient 30 Pa /µm (Anderson et al. 2005, Verbruggen et al. 2012, 2014) 8-times lower than previous studies considering physiological mechanical loading. Fluid shear stress on osteocyte? Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
23 Results and Discussion : ModBone Acoustic pressure and IFluid pressure (Pa) t = 4 µs t = 20 µs IFluid pressure (IFluid P) difference induced by US stimulation on 1 cycle Max IFluid P periosteum IFluid P endosteum Pa IFluid P gradient = 3.8 Pa/µm IFluid P gradient 30 Pa /µm (Anderson et al. 2005, Verbruggen et al. 2012, 2014) 8-times lower than previous studies considering physiological mechanical loading. Fluid shear stress on osteocyte? Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
24 FE simulation ModOst (3D) : Fluid Structure Interaction Model (one-way coupling) input parameter : IFluid P gradient from ModBone : 3.8 Pa/µm output parameter : fluid shear stress on osteocyte : τ IFluid domain : newtonian, ρ=997 kg/m 3, µ= kg.m 1.s 1 Solid domain : linear elastic, ECM : E=16.6 GPa, ν=0.38 ; osteocyte : E=4.47 kpa, ν=0.3 Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
25 Results and Discussion : ModOst 0.6 Fluid shear stress on osteocyte (cell body and processes) τ max 0.6 Pa (McGarry et al. 2004) Shear stress patterns obviously related to simple symmetrical geometry and boundary conditions Shear stress levels in agreement with literature and consistent patterns with higher values on processes than on cell body (Anderson et al. 2005, Verbruggen et al. 2014) Theoretical shear stress interval for osteocyte under physiological load : Pa (Weinbaum et al. 1994) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
26 Results and Discussion : ModOst 0.6 Fluid shear stress on osteocyte (cell body and processes) τ max 0.6 Pa (McGarry et al. 2004) Shear stress patterns obviously related to simple symmetrical geometry and boundary conditions Shear stress levels in agreement with literature and consistent patterns with higher values on processes than on cell body (Anderson et al. 2005, Verbruggen et al. 2014) Theoretical shear stress interval for osteocyte under physiological load : Pa (Weinbaum et al. 1994) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
27 Limitations of the study a realistic model of the bone callus? geometry healing tissues properties Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
28 Limitations of the study a realistic model of the bone callus? geometry healing tissues properties Water Cortical bone Woven bone Cartilage Granular tissue Bailon-Plaza et al. 2001, Claes et Heigele 1999 Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
29 Limitations of the study a realistic model of the bone callus? geometry healing tissues properties Water Cortical bone Woven bone Cartilage Granular tissue Bailon-Plaza et al. 2001, Claes et Heigele 1999 Vascular porosity? Goulet et al Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
30 Limitations of the study a realistic model of the bone callus? Pa Pa Pa Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
31 Limitations of the study a realistic model of the lacuno-canaliculi system? Image from Creatis (Lyon, France) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
32 Conclusion and Perspectives 2-scale numerical model to investigate the mechanical effects of LIPUS on osteocytes. Fluid shear stress lower than the lower bound of prediction interval under physiological load Poroelastic model and US LCN permeability m 2 (Cowin et al. 2009) treatment duration (15 min) vs 1 cycle (1 ms) : cumulative effect to investigate stimulation frequency higher than physiological loading (1-100 Hz) pulsed ultrasound : 2 frequencies repetition frequency and signal frequency pulse duration = 1 ms vs signal period = 1 µs Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
33 Conclusion and Perspectives 2-scale numerical model to investigate the mechanical effects of LIPUS on osteocytes. Fluid shear stress lower than the lower bound of prediction interval under physiological load Poroelastic model and US LCN permeability m 2 (Cowin et al. 2009) treatment duration (15 min) vs 1 cycle (1 ms) : cumulative effect to investigate stimulation frequency higher than physiological loading (1-100 Hz) pulsed ultrasound : 2 frequencies repetition frequency and signal frequency pulse duration = 1 ms vs signal period = 1 µs 1 ms relaxation time of fluid in canaliculi (Swan et al. 2004) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
34 Conclusion and Perspectives 2-scale numerical model to investigate the mechanical effects of LIPUS on osteocytes. Fluid shear stress lower than the lower bound of prediction interval under physiological load Poroelastic model and US LCN permeability m 2 (Cowin et al. 2009) treatment duration (15 min) vs 1 cycle (1 ms) : cumulative effect to investigate stimulation frequency higher than physiological loading (1-100 Hz) pulsed ultrasound : 2 frequencies repetition frequency and signal frequency pulse duration = 1 ms vs signal period = 1 µs 1 ms relaxation time of fluid in canaliculi (Swan et al. 2004) Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
35 Conclusion and Perspectives 2-scale numerical model to investigate the mechanical effects of LIPUS on osteocytes. Fluid shear stress lower than the lower bound of prediction interval under physiological load Osteocyte process model Zoom on the osteocyte process into the canaliculi GAG fibers strain amplification You et al Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
36 Conclusion and Perspectives 2-scale numerical model to investigate the mechanical effects of LIPUS on osteocytes. Fluid shear stress lower than the lower bound of prediction interval under physiological load Osteocyte process model Zoom on the osteocyte process into the canaliculi GAG fibers strain amplification You et al Drag forces F d F s =2πaLτ N F d N a = 0.22 µm : process radius ; L = 20 µm : process length. Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
37 Conclusion and Perspectives Tissue scale Microscopic scale Thank you for your attention. Any questions (or answers)? Baron, Guivier-Curien et al. US and bone healing Monastery Banz, June 29 th, / 16
38
39 Equations Wave propagation in the anisotropic poroelastic matrix (from Nguyen et al. 2012) boundary conditions : pressure and stress fields continuity + open pore condition (continuity of the normal relative velocity between fluid and solid)
40 Poroelastic cortical bone properties Transverse isotropic extralacunar matrix (GPa) (Scheiner et al. 2015) Mass density : ρ=1.9 g/cm 3 Isotropic LCN permeability : m 2 (Smith et al. 2002, Cowin et al. 2009) Other Biot s parameters from NGuyen et al φ=5%, α 1 =0.11, α 2 =0.15, M = 35.6 GPa.
41 Poroelastic healing tissues properties 4 weeks_ Isotropic solid matrix Granular tissue Cartilage Woven bone (GPa) (GPa) (GPa) φ=90% α 1 =0.98 α 2 =0.96 M = 2.2 MPa ρ= 1.01 g/cm 2 φ=80% α 1 =0.98 α 2 =0.96 M = 2.4 MPa ρ= 1.04 g/cm 2 φ=50% α 1 =0.976 α 2 =0.955 M = 2.55 MPa ρ= 1.25 g/cm 2
42 Mechanical properties of healing tissue E ν k p GradPress τ max (GPa) (m 2 ) (Pa/µm) (Pa) Cortical bone Woven bone Immature bone
43 Mechanical properties of healing tissue E ν k p GradPress τ max (GPa) (m 2 ) (Pa/µm) (Pa) Cortical bone Woven bone Immature bone
44 Mesh
Interaction of ultrasound with cortical bone as a two-level porous medium: a multiscale computational study.
 Interaction of ultrasound with cortical bone as a two-level porous medium: a multiscale computational study. Cécile Baron 1, Carine Guivier-Curien 2, Vu-Hieu Nguyen 3, Salah Naili 3 1 Aix-Marseille Université,
Interaction of ultrasound with cortical bone as a two-level porous medium: a multiscale computational study. Cécile Baron 1, Carine Guivier-Curien 2, Vu-Hieu Nguyen 3, Salah Naili 3 1 Aix-Marseille Université,
How to understand the effects of LIPUS on bone healing? A multiscale computational investigation
 How to understand the effects of LIPUS on bone healing? A multiscale computational investigation Cécile Baron 1, Carine Guivier-Curien 2, Vu-Hieu Nguyen 3, Salah Naili 3 1 Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS,
How to understand the effects of LIPUS on bone healing? A multiscale computational investigation Cécile Baron 1, Carine Guivier-Curien 2, Vu-Hieu Nguyen 3, Salah Naili 3 1 Aix-Marseille Université, CNRS,
Introduction to Biomedical Engineering: Basic concepts and Bone Biomechanics
 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering: Basic concepts and Bone Biomechanics Fall 2016, AKUT G. Rouhi Biomechanics The field of biomechanics applies principles of mechanics to study the structure and function
Introduction to Biomedical Engineering: Basic concepts and Bone Biomechanics Fall 2016, AKUT G. Rouhi Biomechanics The field of biomechanics applies principles of mechanics to study the structure and function
Design and Simulation of Blocked Blood Vessel for Early Detection of Heart Diseases
 Proceedings of the 215 2nd International Symposium on Physics and Technology of Sensors, 8-1th March, 215, Pune, India Design and Simulation of Blocked Blood Vessel for Early Detection of Heart Diseases
Proceedings of the 215 2nd International Symposium on Physics and Technology of Sensors, 8-1th March, 215, Pune, India Design and Simulation of Blocked Blood Vessel for Early Detection of Heart Diseases
E. Sassaroli and B. E. O Neill. The Methodist Hospital Research Institute Houston TX
 Lowering of the Interstitial Fluid Pressure as a Result of Tissue Compliance Changes during High Intensity Focused Ultrasound Exposure: Insights from a Numerical Model E. Sassaroli and B. E. O Neill The
Lowering of the Interstitial Fluid Pressure as a Result of Tissue Compliance Changes during High Intensity Focused Ultrasound Exposure: Insights from a Numerical Model E. Sassaroli and B. E. O Neill The
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Finite-element study of vibration effect to fracture healing of a human tibia
 Finite-element study of vibration effect to fracture healing of a human tibia Leonid Maslov 1, Jean-Baptiste Etheve 2, Nikolay Sabaneev 3 Ivanovo State Power Engineering University, Ivanovo, Russia 1 Corresponding
Finite-element study of vibration effect to fracture healing of a human tibia Leonid Maslov 1, Jean-Baptiste Etheve 2, Nikolay Sabaneev 3 Ivanovo State Power Engineering University, Ivanovo, Russia 1 Corresponding
Thomas A. Metzger, Stephen A. Schwaner, Jonelle M. Shudick, Anthony J. LaNeve, Glen L. Niebur. University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN, USA.
 Mechanical Stimuli in Bone Marrow During Physiologic Loading Thomas A. Metzger, Stephen A. Schwaner, Jonelle M. Shudick, Anthony J. LaNeve, Glen L. Niebur. University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN, USA.
Mechanical Stimuli in Bone Marrow During Physiologic Loading Thomas A. Metzger, Stephen A. Schwaner, Jonelle M. Shudick, Anthony J. LaNeve, Glen L. Niebur. University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, IN, USA.
Bone Quantitative Ultrasound
 Bone Quantitative Ultrasound Pascal Laugier Guillaume Haïat Editors Bone Quantitative Ultrasound ABC Editors Pascal Laugier Université Pierre et Marie Curie CNRS Laboratoire d Imagerie Parametrique 15,
Bone Quantitative Ultrasound Pascal Laugier Guillaume Haïat Editors Bone Quantitative Ultrasound ABC Editors Pascal Laugier Université Pierre et Marie Curie CNRS Laboratoire d Imagerie Parametrique 15,
Non-Newtonian pulsatile blood flow in a modeled artery with a stenosis and an aneurysm
 Non-Newtonian pulsatile blood flow in a modeled artery with a stenosis and an aneurysm I. Husain, C. Langdon and J. Schwark Department of Mathematics Luther College University of Regina Regina, Saskatchewan
Non-Newtonian pulsatile blood flow in a modeled artery with a stenosis and an aneurysm I. Husain, C. Langdon and J. Schwark Department of Mathematics Luther College University of Regina Regina, Saskatchewan
Ismail et al. / International Medical Device and Technology Conference 2017
 ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of Cement Line Shielding on the Stress Distribution in Single Osteon with Different Haversian Canal Diameters and e A.A. Ismail a *, R. Daud a,, A.K. Junoh b, N.A.M. Zain b, M.I.
ORIGINAL PAPER Effect of Cement Line Shielding on the Stress Distribution in Single Osteon with Different Haversian Canal Diameters and e A.A. Ismail a *, R. Daud a,, A.K. Junoh b, N.A.M. Zain b, M.I.
A DAMAGE/REPAIR MODEL FOR ALVEOLAR BONE REMODELING
 A DAMAGE/REPAIR MODEL FOR ALVEOLAR BONE REMODELING M. Mengoni 1 and J.-P. Ponthot 2 1. ABSTRACT Tooth movements obtained through orthodontic appliances result from a complex biochemical process of bone
A DAMAGE/REPAIR MODEL FOR ALVEOLAR BONE REMODELING M. Mengoni 1 and J.-P. Ponthot 2 1. ABSTRACT Tooth movements obtained through orthodontic appliances result from a complex biochemical process of bone
The University of Sydney Slide 1
 The University of Sydney Slide 1 SIMULATION DRIVEN BIOMEDICAL DESIGN Lecture 4 Presented by Dr Paul Wong AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 2 Simulation Types There is more to
The University of Sydney Slide 1 SIMULATION DRIVEN BIOMEDICAL DESIGN Lecture 4 Presented by Dr Paul Wong AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 2 Simulation Types There is more to
Lesson 03: Sound Wave Propagation and Reflection. This lesson contains 15 slides plus 14 multiple-choice questions.
 Lesson 03: Sound Wave Propagation and Reflection This lesson contains 15 slides plus 14 multiple-choice questions. Accompanying text for the slides in this lesson can be found on pages 8 through 14 in
Lesson 03: Sound Wave Propagation and Reflection This lesson contains 15 slides plus 14 multiple-choice questions. Accompanying text for the slides in this lesson can be found on pages 8 through 14 in
The table below shows the density and velocity of waves in two different substances. Density / kg m 3 Velocity / m s 1
 Q1.(a) When ultrasound is incident at an interface between two different media some energy is transmitted and some is reflected. The ratio of the reflected energy intensity I r to the incident energy intensity
Q1.(a) When ultrasound is incident at an interface between two different media some energy is transmitted and some is reflected. The ratio of the reflected energy intensity I r to the incident energy intensity
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY. Computational Simulation of Fracture Repair in Stem Cell Seeded Defects under Different. Mechanical Loading.
 UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Computational Simulation of Fracture Repair in Stem Cell Seeded Defects under Different Mechanical Loading by Saghar Nasr A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN
UNIVERSITY OF CALGARY Computational Simulation of Fracture Repair in Stem Cell Seeded Defects under Different Mechanical Loading by Saghar Nasr A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF GRADUATE STUDIES IN
Quiz 6. Cartilage and Bone
 Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
Quiz 6 Cartilage and Bone MCQs X type (true or false): 1. Cartilage tissue: a. Has a rich blood supply. b. Develops from mesenchyme. c. Has ability for a quick regeneration. d. Has chondrocytes as precursor
Stretching Cardiac Myocytes: A Finite Element Model of Cardiac Tissue
 Megan McCain ES240 FEM Final Project December 19, 2006 Stretching Cardiac Myocytes: A Finite Element Model of Cardiac Tissue Cardiac myocytes are the cells that constitute the working muscle of the heart.
Megan McCain ES240 FEM Final Project December 19, 2006 Stretching Cardiac Myocytes: A Finite Element Model of Cardiac Tissue Cardiac myocytes are the cells that constitute the working muscle of the heart.
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM TYPES OF BONES
 SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
SKELETAL TISSUES CHAPTER 7 By John McGill Supplement Outlines: Beth Wyatt Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell INTRODUCTION TO THE SKELETAL SYSTEM STRUCTURE Organs: Bones Related Tissues: Cartilage and Ligaments
An effort is made to analyse the stresses experienced by the human femur. In order
 Finite Element Analysis of Human Femur Bone U N Mughal 1, H A Khawaja 2*, M Moatamedi 1, M Souli 3 1. Narvik University College, Norway 2. UiT-The Arctic University of Norway, Norway 3. University of Lille,
Finite Element Analysis of Human Femur Bone U N Mughal 1, H A Khawaja 2*, M Moatamedi 1, M Souli 3 1. Narvik University College, Norway 2. UiT-The Arctic University of Norway, Norway 3. University of Lille,
Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers in Ultrasound Elasticity Imaging. Timothy J Hall Medical Physics Department University of Wisconsin AIUM 2012
 Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers in Ultrasound Elasticity Imaging Timothy J Hall Medical Physics Department University of Wisconsin AIUM 2012 Proposed Biomarkers Shear wave speed for quantifying liver fibrosis
Quantitative Imaging Biomarkers in Ultrasound Elasticity Imaging Timothy J Hall Medical Physics Department University of Wisconsin AIUM 2012 Proposed Biomarkers Shear wave speed for quantifying liver fibrosis
Osteocytes The galaxy within
 Osteocytes The galaxy within Buenzli PR, Sims NA. Quantifying the osteocyte network in the human skeleton. Bone 2015;75:144-50. Buenzli and Sims present a fascinating insight into the intergalactic vastness
Osteocytes The galaxy within Buenzli PR, Sims NA. Quantifying the osteocyte network in the human skeleton. Bone 2015;75:144-50. Buenzli and Sims present a fascinating insight into the intergalactic vastness
Numerical and experimental simulation of the effect of long bone fracture healing stages on ultrasound transmission across an idealized fracture
 Numerical and experimental simulation of the effect of long bone fracture healing stages on ultrasound transmission across an idealized fracture S. Gheduzzi, S. P. Dodd, and A. W. Miles Department of Mechanical
Numerical and experimental simulation of the effect of long bone fracture healing stages on ultrasound transmission across an idealized fracture S. Gheduzzi, S. P. Dodd, and A. W. Miles Department of Mechanical
Peggers Super Summaries Basic Sciences Bone
 Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
2/11/2009. Evidence for the Molecular, Cellular and Physiological Effects of Microstreaming and Cavitation at MHz and khz Ultrasound Frequencies
 Evidence for the Molecular, Cellular and Physiological Effects of Microstreaming and Cavitation at MHz and khz Ultrasound Frequencies ISEPA : Las Vegas : Feb 2009 Professor Tim Watson University of Hertfordshire
Evidence for the Molecular, Cellular and Physiological Effects of Microstreaming and Cavitation at MHz and khz Ultrasound Frequencies ISEPA : Las Vegas : Feb 2009 Professor Tim Watson University of Hertfordshire
S. N. Khan 1, R. M. Warkhedkar 2, A. Shyam 3, B. R. Patil 4
 IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) ISSN(e) : 2278-1684, ISSN(p) : 2320 334X, PP : 40-44 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation between BMD and Radio intensity of Human Bones for Strength
IOSR Journal of Mechanical and Civil Engineering (IOSR-JMCE) ISSN(e) : 2278-1684, ISSN(p) : 2320 334X, PP : 40-44 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation between BMD and Radio intensity of Human Bones for Strength
Investigation of Geometric Effect on the Ultrasonic Processing of Liquids
 Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 5-2016 Investigation of Geometric Effect on the Ultrasonic Processing of Liquids Pravan Pasumarthi Clemson University, ppasuma@clemson.edu Follow this and
Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 5-2016 Investigation of Geometric Effect on the Ultrasonic Processing of Liquids Pravan Pasumarthi Clemson University, ppasuma@clemson.edu Follow this and
Cerebrospinal fluid flow in the upper cervical canal in patients with the Chiari I malformation
 Cerebrospinal fluid flow in the upper cervical canal in patients with the Chiari I malformation Kent-Andre Mardal K. H. Støverud, S. Linge, G. Rutkowska, I. Drøsdal, H.P. Langtangen, V. Haughton Outline
Cerebrospinal fluid flow in the upper cervical canal in patients with the Chiari I malformation Kent-Andre Mardal K. H. Støverud, S. Linge, G. Rutkowska, I. Drøsdal, H.P. Langtangen, V. Haughton Outline
AlN/ZnO/Silicon Structure Combining Surface Acoustic Waves and Waveguiding Layer Acoustic Wave
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Paris AlN/ZnO/Silicon Structure Combining Surface Acoustic Waves and Waveguiding Layer Acoustic Wave O. Legrani*, O. Elmazria*, S. Zhgoon +, L.
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Paris AlN/ZnO/Silicon Structure Combining Surface Acoustic Waves and Waveguiding Layer Acoustic Wave O. Legrani*, O. Elmazria*, S. Zhgoon +, L.
Oil Transmission Pipelines Condition Monitoring Using Wavelet Analysis and Ultrasonic Techniques
 Engineering, 2013, 5, 551-555 doi:10.4236/eng.2013.56066 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Oil Transmission Pipelines Condition Monitoring Using Wavelet Analysis and Ultrasonic
Engineering, 2013, 5, 551-555 doi:10.4236/eng.2013.56066 Published Online June 2013 (http://www.scirp.org/journal/eng) Oil Transmission Pipelines Condition Monitoring Using Wavelet Analysis and Ultrasonic
Bone density and shape adapt to loading. Bone remodeling simulation models. Bone remodeling. But... Frost: mechanostat theory. Bone remodeling theory
 Bone density and shape adapt to loading Bone remodeling simulation models Turkey Ulna experiments (Rubin et al) Sheep ulnar osteotomy (McNamara) Bert van Rietbergen Bone is deposited in regions of high
Bone density and shape adapt to loading Bone remodeling simulation models Turkey Ulna experiments (Rubin et al) Sheep ulnar osteotomy (McNamara) Bert van Rietbergen Bone is deposited in regions of high
Vascular Mechanobiology: growth and remodeling in the aorta in health and disease
 Vascular Mechanobiology: growth and remodeling in the aorta in health and disease Dr.-Ing. Christian J. Cyron Technical University of Munich funded by the German Research Foundation (Emmy-Noether Grant
Vascular Mechanobiology: growth and remodeling in the aorta in health and disease Dr.-Ing. Christian J. Cyron Technical University of Munich funded by the German Research Foundation (Emmy-Noether Grant
BONE FRACTURE & HEALING Lecture 9
 BONE FRACTURE & HEALING Lecture 9 Presented by Paul Wong, PhD AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 1 Mechanical Responses of Bone Biomaterial mechanics Failure Body kinematics
BONE FRACTURE & HEALING Lecture 9 Presented by Paul Wong, PhD AMME4981/9981 Semester 1, 2016 The University of Sydney Slide 1 Mechanical Responses of Bone Biomaterial mechanics Failure Body kinematics
Computational Simulation of Penetrating Trauma in Biological Soft Tissues using the Material Point Method
 Computational Simulation of Penetrating Trauma in Biological Soft Tissues using the Material Point Method Irina IONESCU* +, James GUILKEY* ++, Martin BERZINS*, Robert M. KIRBY*, Jeffrey WEISS* + *Scientific
Computational Simulation of Penetrating Trauma in Biological Soft Tissues using the Material Point Method Irina IONESCU* +, James GUILKEY* ++, Martin BERZINS*, Robert M. KIRBY*, Jeffrey WEISS* + *Scientific
Evaluation of dental implant induced bone remodelling by using a 2D Finite Element model
 5 th Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics, ACAM 2007 10-12 December 2007, Brisbane, Australia Evaluation of dental implant induced bone remodelling by using a 2D Finite Element model Daniel Lin 1,a,
5 th Australasian Congress on Applied Mechanics, ACAM 2007 10-12 December 2007, Brisbane, Australia Evaluation of dental implant induced bone remodelling by using a 2D Finite Element model Daniel Lin 1,a,
Advanced FE Modeling of Absorbable PLLA Screws
 Advanced FE Modeling of Absorbable PLLA Screws Jorgen Bergstrom, Ph.D., David Quinn, Ph.D., Eric Schmitt jbergstrom@veryst.com, LLC September 14, 2011 Introduction Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction
Advanced FE Modeling of Absorbable PLLA Screws Jorgen Bergstrom, Ph.D., David Quinn, Ph.D., Eric Schmitt jbergstrom@veryst.com, LLC September 14, 2011 Introduction Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction
Hierarchical Microimaging of Bone Structure and Function
 Hierarchical Microimaging of Bone Structure and Function Prof. Ralph Müller, PhD Institute for Biomechanics, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland 1 Motivation and aims Engineering endpoints have become an important
Hierarchical Microimaging of Bone Structure and Function Prof. Ralph Müller, PhD Institute for Biomechanics, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland 1 Motivation and aims Engineering endpoints have become an important
Using Computational Fluid Dynamics Model to Predict Changes in Velocity properties in Stented Carotid Artery
 Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Paris (COMSOL Conference) Using Computational Fluid Dynamics Model to Predict Changes in Velocity properties in Stented Carotid Artery Vaidehi
Excerpt from the Proceedings of the COMSOL Conference 2010 Paris (COMSOL Conference) Using Computational Fluid Dynamics Model to Predict Changes in Velocity properties in Stented Carotid Artery Vaidehi
Therapeutic Ultrasound
 THERAPEUTIC ULTRASOUND Therapeutic is a form of MECHANICAL energy Mechanical vibration at increasing frequencies is known as sound energy. Below 16Hz, these vibrations are not recognizable as sound The
THERAPEUTIC ULTRASOUND Therapeutic is a form of MECHANICAL energy Mechanical vibration at increasing frequencies is known as sound energy. Below 16Hz, these vibrations are not recognizable as sound The
Simulation of bone indentation
 Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 113 Simulation of bone indentation S. Kasiri 1, G. Reilly 1,2 & D. Taylor 1 1 Trinity Centre for Bioengineering, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland 2 Institute of Technology
Modelling in Medicine and Biology VII 113 Simulation of bone indentation S. Kasiri 1, G. Reilly 1,2 & D. Taylor 1 1 Trinity Centre for Bioengineering, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland 2 Institute of Technology
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Computational Modelling in the Development of Novel Passive Strain Sensors for Orthopedic Implants
 Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 5-2016 Computational Modelling in the Development of Novel Passive Strain Sensors for Orthopedic Implants Hunter Pelham Clemson University, hlpelham@gmail.com
Clemson University TigerPrints All Theses Theses 5-2016 Computational Modelling in the Development of Novel Passive Strain Sensors for Orthopedic Implants Hunter Pelham Clemson University, hlpelham@gmail.com
Descriptions of NDT Projects Fall 2004 October 31, 2004
 Descriptions of NDT Projects Fall 2004 October 31, 2004 Introduction There are two separate NDT labs in Magister: ULTRA for ultrasound and EDDY for eddy current. Both labs are equipped with mechanical
Descriptions of NDT Projects Fall 2004 October 31, 2004 Introduction There are two separate NDT labs in Magister: ULTRA for ultrasound and EDDY for eddy current. Both labs are equipped with mechanical
Assessing potential cracking zones in embankment dams
 Southern Cross University epublications@scu 23rd Australasian Conference on the Mechanics of Structures and Materials 2014 Assessing potential cracking zones in embankment dams Ke He University of New
Southern Cross University epublications@scu 23rd Australasian Conference on the Mechanics of Structures and Materials 2014 Assessing potential cracking zones in embankment dams Ke He University of New
VISUALIZATION OF TRANSDUCER-PRODUCED SOUND FIELDS IN SOLIDS
 VISUALIZATION OF TRANSDUCER-PRODUCED SOUND FIELDS IN SOLIDS Wolfgang Sachse* Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Cornell University, Ithaca, New York - 14853 ABSTRACT Broadband ultrasonic pulses
VISUALIZATION OF TRANSDUCER-PRODUCED SOUND FIELDS IN SOLIDS Wolfgang Sachse* Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Cornell University, Ithaca, New York - 14853 ABSTRACT Broadband ultrasonic pulses
JADAVPUR UNIVERSITY & 2 SCHOOL OF BIOSCIENCE AND ENGINEERING ABHIRUP ROY CHOUDHURY 1, KRITTIKA DASGUPTA 2, ABHIJIT CHANDA 1,2, DEBABRATA NAG 1
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2010 India ABHIRUP ROY CHOUDHURY 1, KRITTIKA DASGUPTA 2, ABHIJIT CHANDA 1,2, DEBABRATA NAG 1 1 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING & 2 SCHOOL OF BIOSCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2010 India ABHIRUP ROY CHOUDHURY 1, KRITTIKA DASGUPTA 2, ABHIJIT CHANDA 1,2, DEBABRATA NAG 1 1 DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING & 2 SCHOOL OF BIOSCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
Modeling of the Impact of Blood Vessel Flow on the Temperature Distribution during Focused Ultrasound Treatments
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Modeling of the Impact of Blood Vessel Flow on the Temperature Distribution during Focused Ultrasound Treatments Elisabetta Sassaroli, King C. P. Li, Brian
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 2010 Boston Modeling of the Impact of Blood Vessel Flow on the Temperature Distribution during Focused Ultrasound Treatments Elisabetta Sassaroli, King C. P. Li, Brian
What are the parts of the skeletal system? Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues. Growth of Cartilage. Bones come in many shapes
 Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
Chapter 6- Part I Bones and Skeletal Tissues Components of the skeletal system Classification of Bone (bone shapes) Functions of bone Bone structure Microscopic structure of bone and bone cells What are
The extracellular matrix, interstitial fluid and ions as a mechanical signal transducer in articular cartilage
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1999) 7, 41 58 1999 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/99/010041+18 $12.00/0 Article No. joca.1998.0161, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1999) 7, 41 58 1999 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/99/010041+18 $12.00/0 Article No. joca.1998.0161, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
The Physics of Ultrasound. The Physics of Ultrasound. Claus G. Roehrborn. Professor and Chairman. Ultrasound Physics
 The Physics of Ultrasound Pipe Organ 10-8000 Emission Dog 452-1080 Man 85-1100 Spectrum Bat 10,000-120,000 Porpoise 7000-120,000 Claus G. Roehrborn Professor and Chairman 10 20 Cycles per second Reception
The Physics of Ultrasound Pipe Organ 10-8000 Emission Dog 452-1080 Man 85-1100 Spectrum Bat 10,000-120,000 Porpoise 7000-120,000 Claus G. Roehrborn Professor and Chairman 10 20 Cycles per second Reception
Modeling of Thermal Damage from Focused Ultrasound Exposures for Heterogeneous Tissues
 Modeling of Thermal Damage from Focused Ultrasound Exposures for Heterogeneous Tissues Adam C. Waspe, PhD adam.waspe@sickkids.ca Aug. 11, 2014 * Some content adapted from lecture notes from Rajiv Chopra
Modeling of Thermal Damage from Focused Ultrasound Exposures for Heterogeneous Tissues Adam C. Waspe, PhD adam.waspe@sickkids.ca Aug. 11, 2014 * Some content adapted from lecture notes from Rajiv Chopra
BEE 453. May 4, Ravi Sood, David Nahlik, Weston Nichols, and Evan Graham
 Laser Irradiation of Tumors for the Treatment of Cancer: An Analysis of Blood Flow, Temperature and Oxygen Transport BEE 453 May 4, 2007 Ravi Sood, David Nahlik, Weston Nichols, and Evan Graham 2 Executive
Laser Irradiation of Tumors for the Treatment of Cancer: An Analysis of Blood Flow, Temperature and Oxygen Transport BEE 453 May 4, 2007 Ravi Sood, David Nahlik, Weston Nichols, and Evan Graham 2 Executive
Annular Array Transducer and Matched Amplifier for Therapeutic Ultrasound
 ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 35, 4, 653 660 (2010) DOI: 10.2478/v10168-010-0049-6 Annular Array Transducer and Matched Amplifier for Therapeutic Ultrasound Wojciech SECOMSKI, Andrzej NOWICKI, Janusz WÓJCIK, Marcin
ARCHIVES OF ACOUSTICS 35, 4, 653 660 (2010) DOI: 10.2478/v10168-010-0049-6 Annular Array Transducer and Matched Amplifier for Therapeutic Ultrasound Wojciech SECOMSKI, Andrzej NOWICKI, Janusz WÓJCIK, Marcin
Cartilage & bone. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
Cartilage & bone Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES describe the microscopic structure, distribution and growth of the different types of Cartilage
TRANSDUCER MODELS FOR THE FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF ULTRASONIC NDT PHENOMENA. R. L. Ludwig, D. Moore and W. Lord
 TRANSDUCER MODELS FOR THE FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF ULTRASONIC NDT PHENOMENA R. L. Ludwig, D. Moore and W. Lord Electrical Engineering Department Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado 80523
TRANSDUCER MODELS FOR THE FINITE ELEMENT SIMULATION OF ULTRASONIC NDT PHENOMENA R. L. Ludwig, D. Moore and W. Lord Electrical Engineering Department Colorado State University Fort Collins, Colorado 80523
Feng Xiujuan National Institute of Metrology (NIM),China
 The acoustic calibration service in transportation at NIM Feng Xiujuan National Institute of Metrology (NIM),China 1. Calibration requirements 2. Calibration service at NIM 2.1 Microphone 2.2 Ultrasonic
The acoustic calibration service in transportation at NIM Feng Xiujuan National Institute of Metrology (NIM),China 1. Calibration requirements 2. Calibration service at NIM 2.1 Microphone 2.2 Ultrasonic
b. Adult bones produce 2.5 million RBCs each second.
 Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Ch 6 Skeletal System I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. The skeletal system consists of: 1. bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments B. Living bone is not Gr. dried up 1. It is dynamic and adaptable
Stress Wave Focusing Transducers
 UCRL-K-130697 PREPRINT Stress Wave Focusing Transducers Steven R. Visuri, Richard A. London, Luiz Da Silva This paper was prepared for submittal to Optical Society of America, Spring Topical Meetings Orlando,
UCRL-K-130697 PREPRINT Stress Wave Focusing Transducers Steven R. Visuri, Richard A. London, Luiz Da Silva This paper was prepared for submittal to Optical Society of America, Spring Topical Meetings Orlando,
inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering August 2000, Nice, FRANCE
 1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 3.6 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD (FEM) MODEL FOR THE HEARING
1 inter.noise 2000 The 29th International Congress and Exhibition on Noise Control Engineering 27-30 August 2000, Nice, FRANCE I-INCE Classification: 3.6 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD (FEM) MODEL FOR THE HEARING
Heat Drain Device for Ultrasound Imaging Probes ESAOTE SPA
 Heat Drain Device for Ultrasound Imaging Probes ESAOTE SPA L. Spicci, G. Vigna TRANSDUCER STRUCTURE OVERVIEW Finished probe Complete transducer Silicon lens Filling resin INTRODUCTION Electrical driving
Heat Drain Device for Ultrasound Imaging Probes ESAOTE SPA L. Spicci, G. Vigna TRANSDUCER STRUCTURE OVERVIEW Finished probe Complete transducer Silicon lens Filling resin INTRODUCTION Electrical driving
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
APPLICATION OF COMPOSITE FRACTURE MECHANICS TO BONE FRACTURE ANALYSIS USING ABAQUS XFEM
 APPLICATION OF COMPOSITE FRACTURE MECHANICS TO BONE FRACTURE ANALYSIS USING ABAQUS XFEM Presenter: David Reid Dassault Systemes UK Ltd SIMULIA david.reid@3ds.com 01925 885971 07825 308031 Work by: Xiaoliang
APPLICATION OF COMPOSITE FRACTURE MECHANICS TO BONE FRACTURE ANALYSIS USING ABAQUS XFEM Presenter: David Reid Dassault Systemes UK Ltd SIMULIA david.reid@3ds.com 01925 885971 07825 308031 Work by: Xiaoliang
In vivo non invasive quantitative assessment of passive diastolic stiffness of infarcted myocardium using Shear Wave Imaging
 Munich, August 28th 2012 European Society of Cardiology In vivo non invasive quantitative assessment of passive diastolic stiffness of infarcted myocardium using Shear Wave Imaging Mathieu Pernot 1, Wei-Ning
Munich, August 28th 2012 European Society of Cardiology In vivo non invasive quantitative assessment of passive diastolic stiffness of infarcted myocardium using Shear Wave Imaging Mathieu Pernot 1, Wei-Ning
Dynamic Role of the Cardiac Jelly
 61 Chapter 6 Dynamic Role of the Cardiac Jelly Before looping, when the embryonic heart is still a straight tube, the cardiac jelly occupies the bulk of the heart tube walls. Despite its preeminence in
61 Chapter 6 Dynamic Role of the Cardiac Jelly Before looping, when the embryonic heart is still a straight tube, the cardiac jelly occupies the bulk of the heart tube walls. Despite its preeminence in
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS. These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore.
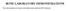 BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
Acoustic Radiation Force Based Imaging: An Overview
 Acoustic Radiation Force Based Imaging: An Overview Kathy Nightingale, Michael Wang, Stephen Rosenzweig, Veronica Rotemberg, Samantha Lipman, Ned Rouze, Mark Palmeri Department of Biomedical Engineering
Acoustic Radiation Force Based Imaging: An Overview Kathy Nightingale, Michael Wang, Stephen Rosenzweig, Veronica Rotemberg, Samantha Lipman, Ned Rouze, Mark Palmeri Department of Biomedical Engineering
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion
 Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Development of Ultrasound Based Techniques for Measuring Skeletal Muscle Motion Jason Silver August 26, 2009 Presentation Outline Introduction Thesis Objectives Mathematical Model and Principles Methods
Edinburgh Imaging Academy online distance learning courses
 Course: Biomechanics Semester 1 / Autumn 10 Credits Each Course is composed of Modules & Activities. Modules: Biomechanics basics Ultrasound advanced Cardiovascular IMSc IMSc IMSc Each Module is composed
Course: Biomechanics Semester 1 / Autumn 10 Credits Each Course is composed of Modules & Activities. Modules: Biomechanics basics Ultrasound advanced Cardiovascular IMSc IMSc IMSc Each Module is composed
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS
 OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
OSSEOUS TISSUE & BONE STRUCTURE PART I: OVERVIEW & COMPONENTS The Skeletal System Skeletal system includes: bones of the skeleton, cartilages, ligaments, and connective tissues What are the functions of
Simulation of Chemotractant Gradients in Microfluidic Channels to Study Cell Migration Mechanism in silico
 Simulation of Chemotractant Gradients in Microfluidic Channels to Study Cell Migration Mechanism in silico P. Wallin 1*, E. Bernson 1, and J. Gold 1 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Applied Physics,
Simulation of Chemotractant Gradients in Microfluidic Channels to Study Cell Migration Mechanism in silico P. Wallin 1*, E. Bernson 1, and J. Gold 1 1 Chalmers University of Technology, Applied Physics,
Available online at ScienceDirect. The Malaysian International Tribology Conference 2013, MITC2013
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 68 ( 2013 ) 109 115 The Malaysian International Tribology Conference 2013, MITC2013 The Effects of Surface Curvature on Cartilage
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 68 ( 2013 ) 109 115 The Malaysian International Tribology Conference 2013, MITC2013 The Effects of Surface Curvature on Cartilage
A Thesis. presented to. the Faculty of California Polytechnic State University, San Luis Obispo. In Partial Fulfillment
 An Investigation of Humeral Stress Fractures in Racing Thoroughbreds using a 3D Finite Element Model in Conjunction with a Bone Remodeling Algorithm A Thesis presented to the Faculty of California Polytechnic
An Investigation of Humeral Stress Fractures in Racing Thoroughbreds using a 3D Finite Element Model in Conjunction with a Bone Remodeling Algorithm A Thesis presented to the Faculty of California Polytechnic
Finite Element Analysis of Radius and Ulna. Eli Pavlatos April 24, 2013
 Finite Element Analysis of Radius and Ulna Eli Pavlatos April 24, 2013 Outline Review bone biomechanics bone behavior during fracture Stress analysis concepts properties of bone for models Fracture simulations
Finite Element Analysis of Radius and Ulna Eli Pavlatos April 24, 2013 Outline Review bone biomechanics bone behavior during fracture Stress analysis concepts properties of bone for models Fracture simulations
HiFFUT A New Class of Transducer
 HiFFUT A New Class of Transducer Kick-Off Meeting Dr Andrew Feeney, Postdoctoral Research Fellow My Background I obtained a Master s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Glasgow in 2010
HiFFUT A New Class of Transducer Kick-Off Meeting Dr Andrew Feeney, Postdoctoral Research Fellow My Background I obtained a Master s degree in Mechanical Engineering from the University of Glasgow in 2010
Comparison of biophysical stimuli for mechano-regulation of tissue differentiation during fracture healing
 ARTICLE IN PRESS Journal of Biomechanics 39 (2006) 1507 1516 www.elsevier.com/locate/jbiomech www.jbiomech.com Comparison of biophysical stimuli for mechano-regulation of tissue differentiation during
ARTICLE IN PRESS Journal of Biomechanics 39 (2006) 1507 1516 www.elsevier.com/locate/jbiomech www.jbiomech.com Comparison of biophysical stimuli for mechano-regulation of tissue differentiation during
aneurysm initiation and fully developed aneurysms
 Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive Faculty and Researcher Publications Faculty and Researcher Publications Collection 2015 Investigation of material modeling in fluid structure interaction analysis
Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive Faculty and Researcher Publications Faculty and Researcher Publications Collection 2015 Investigation of material modeling in fluid structure interaction analysis
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION Subject:- Anatomy, Physiology and Health Education Class:- B.P. Ed. Semester- I Presented By:- Dr. Mahesh Singh Dhapola Cell Theory All living things are made up of cells.
DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICAL EDUCATION Subject:- Anatomy, Physiology and Health Education Class:- B.P. Ed. Semester- I Presented By:- Dr. Mahesh Singh Dhapola Cell Theory All living things are made up of cells.
Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance?
 1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
1 2 Which type of collagen forms the coarse collagen fibres in dense regular and irregular connective tissues? Which compound is reponsible for the viscous character of the ground substance? 3 Which class
Analysis of the effects of plaque deposits on the blood flow through human artery
 ISSN 2395-1621 Analysis of the effects of plaque deposits on the blood flow through human artery #1 Sajid S. Mulani, #2 Pankaj I. Jagad 1 sajidsmulani21@gmail.com 2 pjjagad.scoe@sinhgad.edu #12 Department
ISSN 2395-1621 Analysis of the effects of plaque deposits on the blood flow through human artery #1 Sajid S. Mulani, #2 Pankaj I. Jagad 1 sajidsmulani21@gmail.com 2 pjjagad.scoe@sinhgad.edu #12 Department
Stress Shadowing and Fracture Interference in GOHFER R. D. Barree
 Stress Shadowing and Fracture Interference in GOHFER R. D. Barree Stress Shadow or Interference: When hydraulic fracture treatments are carried out in horizontal wells, the spacing of multiple transverse
Stress Shadowing and Fracture Interference in GOHFER R. D. Barree Stress Shadow or Interference: When hydraulic fracture treatments are carried out in horizontal wells, the spacing of multiple transverse
Keywords: Angioplasty, Explicit finite elements method, Tube hidroforming, Stents.
 Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/evento/10wccm AN ANALYSIS OF THE CONTACT BETWEEN THE STENT AND THE ARTERY USING TUBE HIDROFORMING SIMULATION
Blucher Mechanical Engineering Proceedings May 2014, vol. 1, num. 1 www.proceedings.blucher.com.br/evento/10wccm AN ANALYSIS OF THE CONTACT BETWEEN THE STENT AND THE ARTERY USING TUBE HIDROFORMING SIMULATION
The Musculoskeletal System. Chapter 46
 The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
The Skeletal System PART A
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
: Biomedical Signal Processing
 : Biomedical Signal Processing 0. Introduction: Biomedical signal processing refers to the applications of signal processing methods, such as Fourier transform, spectral estimation and wavelet transform,
: Biomedical Signal Processing 0. Introduction: Biomedical signal processing refers to the applications of signal processing methods, such as Fourier transform, spectral estimation and wavelet transform,
39th Annual UIA Symposium. Metrology research for External Beam Cancer Therapy. K.-V. Jenderka
 39th Annual UIA Symposium Metrology research for External Beam Cancer Therapy K.-V. Jenderka P B Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Braunschweig Department Sound www.ptb.de Topics Overview Therapeutic
39th Annual UIA Symposium Metrology research for External Beam Cancer Therapy K.-V. Jenderka P B Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt Braunschweig Department Sound www.ptb.de Topics Overview Therapeutic
INSPECTION THROUGH AN OVERLAY REPAIR WITH A SMART FLEXIBLE ARRAY PROBE.
 INSPECTION THROUGH AN OVERLAY REPAIR WITH A SMART FLEXIBLE ARRAY PROBE. Ph. Brédif (*), G. Selby (**), S. Mahaut (*), O. Casula (*) (*) CEA/DRT, Saclay, France (**) EPRI, USA 1. ABSTRACT Contact inspection
INSPECTION THROUGH AN OVERLAY REPAIR WITH A SMART FLEXIBLE ARRAY PROBE. Ph. Brédif (*), G. Selby (**), S. Mahaut (*), O. Casula (*) (*) CEA/DRT, Saclay, France (**) EPRI, USA 1. ABSTRACT Contact inspection
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,100 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Parameter Optimization for FEM based modeling of singlet oxygen during PDT using COMSOL
 Presented at the COMSOL Conference 21 Boston COMSOL Conference, Boston, 1/8/21 Parameter Optimization for FEM based modeling of singlet oxygen during PDT using COMSOL Xing Liang, Ken Kang-Hsin Wang, and
Presented at the COMSOL Conference 21 Boston COMSOL Conference, Boston, 1/8/21 Parameter Optimization for FEM based modeling of singlet oxygen during PDT using COMSOL Xing Liang, Ken Kang-Hsin Wang, and
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Phased Array Ultrasonics and Eddy Current Examination for Graphite Components
 Phased Array Ultrasonics and Eddy Current Examination for Graphite Components www.inl.gov June 22, 2011 12 th International Symposium on Nondestructive Characterization of Materials Blacksburg, Virginia
Phased Array Ultrasonics and Eddy Current Examination for Graphite Components www.inl.gov June 22, 2011 12 th International Symposium on Nondestructive Characterization of Materials Blacksburg, Virginia
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics.
 In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
In-Silico approach on Offset placement of implant-supported bridges placed in bone of different density in Orthodontics. Chandrasenan.P 1, Vishnu.G 2, Akshay K Nair 3 1M Tech student, Department of Mechanical
Graftys. Cross-selling. Indications. Comparison. Basic Science. Graftys 415 rue Claude Nicolas Ledoux Aix en Provence Cedex 4
 2015 Graftys Cross-selling Indications Comparison Graftys 415 rue Claude Nicolas Ledoux 13854 Aix en Provence Cedex 4 www.graftys.com Basic Science Graftys QuickSet Training 1 Where to use QuickSet? Revision
2015 Graftys Cross-selling Indications Comparison Graftys 415 rue Claude Nicolas Ledoux 13854 Aix en Provence Cedex 4 www.graftys.com Basic Science Graftys QuickSet Training 1 Where to use QuickSet? Revision
RESEARCH REPOSITORY.
 RESEARCH REPOSITORY This is the author s final version of the work, as accepted for publication following peer review but without the publisher s layout or pagination. The definitive version is available
RESEARCH REPOSITORY This is the author s final version of the work, as accepted for publication following peer review but without the publisher s layout or pagination. The definitive version is available
Permanent deformation of bridge abutment on liquefiable soils
 Permanent deformation of bridge abutment on liquefiable soils Akihiro TAKAHASHI 1, Hideki SUGITA 1 & Shunsuke TANIMOTO 1 ABSTRACT Seismic response of a bridge abutment located near a river dyke is the
Permanent deformation of bridge abutment on liquefiable soils Akihiro TAKAHASHI 1, Hideki SUGITA 1 & Shunsuke TANIMOTO 1 ABSTRACT Seismic response of a bridge abutment located near a river dyke is the
Proceedings Amorphous SiC/c-ZnO-Based Lamb Mode Sensor for Liquid Environments
 Proceedings Amorphous SiC/c-ZnO-Based Lamb Mode Sensor for Liquid Environments Cinzia Caliendo 1, *, Muhammad Hamidullah 1 and Farouk Laidoudi 2 1 Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnologies, IFN-CNR,
Proceedings Amorphous SiC/c-ZnO-Based Lamb Mode Sensor for Liquid Environments Cinzia Caliendo 1, *, Muhammad Hamidullah 1 and Farouk Laidoudi 2 1 Institute of Photonics and Nanotechnologies, IFN-CNR,
-the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its formation and remodeling throughout life.
 Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
Biology 325 Fall 2004 BONES AND SKELETAL TISSUES Introduction -skeleton contains cartilage and bones -the emphasis on this section is the structure and function of bone tissue and on the dynamics of its
IMECE TISSUE- AND CELL-LEVEL STRESS DISTRIBUTIONS OF THE HEART VALVE TISSUE DURING DIASTOLE
 Proceedings of the ASME 2013 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE2013 November 15-, 2013, San Diego, California, USA IMECE2013-63229 TISSUE- AND CELL-LEVEL STRESS DISTRIBUTIONS
Proceedings of the ASME 2013 International Mechanical Engineering Congress & Exposition IMECE2013 November 15-, 2013, San Diego, California, USA IMECE2013-63229 TISSUE- AND CELL-LEVEL STRESS DISTRIBUTIONS
