We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
|
|
|
- Gerald Anderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3, , M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 154 Countries delivered to TOP 1% most cited scientists 12.2% Contributors from top 500 universities Selection of our books indexed in the Book Citation Index in Web of Science Core Collection (BKCI) Interested in publishing with us? Contact book.department@intechopen.com Numbers displayed above are based on latest data collected. For more information visit
2 18 Virtual Planning for Dental Implant Placement Using Guided Surgery Vinicius Nery Viegas, Celso Gustavo Schwalm Lacroix, Rogério Miranda Pagnoncelli and Marília Gerhardt de Oliveira Pontifícia Universidade Católica do Rio Grande do Sul Brazil 1. Introduction Technical and scientific advances in diagnostic and therapeutic methods in the biomedical field have substantially increased the predictability and longevity of the outcomes of restorative surgical procedures. In contemporary oral implantology, bioprototyping techniques based on computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing (CAD/CAM) technology have proven to be valuable aids in diagnosis, treatment planning, and surgical intervention. Among other aspects, use of these technologies improves preoperative planning, makes it easier for patients to understand proposed procedures, increases the predictability of treatment, and may reduce surgical morbidity. The preliminary stages that precede dental implant surgery are as important as the actual operative intervention itself, or even more so. Inadequate placement of implants may injure important anatomical structures or lead to aesthetic or functional compromise of the prosthetic stage of oral rehabilitation. Implant planning and placement can be based solely on computed tomography data and surgical guides fashioned after diagnostic models. However, direct three-dimensional visualization of the surgical site and real-model simulation of the intended surgical procedure can play a significant role in obtaining outcomes that are more consistent with the original treatment plan. Biomedical prototypes, or biomodels, provide faithful reproductions of the patient s bone condition, thus enabling this type of assessment. Likewise, the surgery itself can be made safer and less invasive with use of individualized surgical guides for implant placement. The development of software programs for implant placement planning and the integration of these software packages with rapid prototyping methods have made fabrication of such guides possible. The process of obtaining and reformatting computed tomography (CT) data, planning implant placement over a virtual model, fabricating a surgical guide with prototyping methods, and using this guide or template during dental implant surgery with specifically designed systems may be referred to as guided implant surgery. 2. Principles of guided surgery Guided implant surgery is based on the combination of virtual surgical planning and prototyping techniques. Rapid prototyping can be defined as a set of technology-based
3 400 Implant Dentistry The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry processes that enable fabrication of three-dimensional, concrete objects from a computeraided design (CAD) project. The objective of rapid prototyping is to create a real model with the same geometric features of the virtual model, which can then undergo real-world manipulation for a variety of purposes (James et al., 1998; Peltola et al., 2008). The greatest challenges in the surgical and prosthetic stages of dental implant surgery are due to diagnostic failure and poor case planning (Lal et al., 2006). The American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology (AAOMR) recommends that any evaluation of the available bony architecture for diagnosis and planning of extensive implant-based oral rehabilitation include CT imaging (Almog et al., 2006). In this context, Jacobs et al. (1999) assessed the reliability of two-dimensional CT images for implant placement planning. The Jacobs study was performed on 100 partially or fully edentulous patients who underwent CT scanning and subsequent implant placement. Available bone height was measured below the maxillary sinus and nasal fossa and above the mandibular canal, and a 1.5 mm safety margin was respected. Planning took into account implant number, location, and size, available bone height, and possible anatomic complications, such as bony dehiscences and fenestrations, maxillary sinus perforation, absence of primary stability, and poor implant positioning in light of the required biomechanical and cosmetic outcome. The authors found that, in some cases, placement of implants according to plan was impossible, mostly due to intraoperative findings that had been missed or underestimated on CT images. Agreement between planned and intraoperative implant number and sites was satisfactory. Of the 416 planned implants, 395 were successfully placed. However, the authors found weak agreement between the size of the planned implant and that of the implant actually placed (44%). Implants were shorter or longer than planned in 110 and 74 of the 395 successful cases respectively. According to the authors, CT images can be used for preoperative planning of the number of implants, as well as for choice of implant sites. However, CT scans are not sufficiently reliable for precise determination of implant size or for prevention of intraoperative anatomic complications, and can thus reduce the predictability of the implant placement procedure (Jacobs et al., 1999). Thus, in light of the need for implementation of available treatment planning resources in implantology, virtual planning and rapid prototyping techniques have come to provide an excellent choice in the search for satisfactory outcomes with lower intra- and postoperative complication rates (Choi et al., 2002; Almog et al., 2006). Biomedical prototypes and virtual evaluation provide the ability to visualize and manipulate the surgical sites, measure the patient s bony structures, and simulate the surgical intervention itself. These preoperative procedures increase predictability of the chosen technique, improve applicability of the surgical plan, and can shorten operative time (Choi et al., 2002; Sarment et al., 2003a; Sarment et al., 2003b; Meurer et al., 2008). Erickson et al. (1999) surveyed the opinions of oral and maxillofacial surgeons about the use of stereolithographic models for diagnosis, treatment planning, preoperative surgical simulation, and construction of alloplastic implants for anatomical reconstruction. Seventysix models were constructed in the study period. Prototypes were used by 69% of respondents as a diagnostic aid during the planning phase, and played a role in treatment planning in 92% of cases. Seventy-three percent of respondents used the models to instruct patients as to the planned procedure. Preoperative surgical simulation was employed in 38% of cases. Seventy-seven percent of surgeons reported reductions in operative time when
4 Virtual Planning for Dental Implant Placement Using Guided Surgery 401 prototypes were used, 38% reported improvement in surgical access, and 46% noted that more complex procedures were made safer and more predictable by preoperative study of prototype models. Despite the wide applicability of biomodels (in 96% of treatment phases) only 15% of surgeons that responded to the survey believed that rapid prototyping had played an essential role in proper treatment. Nevertheless, the authors stressed the validity of prototypes as a tool for obtaining more predictable and lasting results. In a similar study, Erben et al. (2002) interviewed 38 oral and maxillofacial surgeons to determine the main indications for biomodels and the key benefits provided by their use in preoperative planning. Models were used in planning placement of osseointegrated implants and other procedures. Surgeons noted that use of biomedical prototypes improved the quality of diagnosis, enabled preoperative simulation of planned interventions, made it easier for patients to understand the procedure and provided intraoperative guidance. Wulf et al. (2003) published a study conducted between September 1999 and April 2002 in order to assess the relevance of biomedical prototypes in the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative stages of maxillofacial surgery. Fifty-four surgeons described their experiences on a total of 466 cases. This study corroborated the advantages of biomodel use described in the aforementioned investigations. In dental implantology, bioprototyping techniques are not limited to model construction and analysis. With the advent of sophisticated data acquisition methods and image manipulation and virtual planning software, fabrication of rapid-prototyped surgical guides and templates have made it possible to achieve more reliable agreement between the planned and final position of dental implants. This improved predictability of implant and prosthesis positions is based on the concepts of guided surgery (Garg, 2006; Rosenfeld et al., 2006). 3. Guided surgery in dental implantology Fabrication of a surgical guide that faithfully reproduces planned implant positions can play an essential role in the success of implant-based oral rehabilitation (Ganz, 2003). Surgical templates fashioned using conventional methods have some drawbacks that can make successful aesthetic and functional outcomes more difficult to achieve. The diagnostic models on which these guides are based provide a rigid, non-functional representation of the soft tissues that cover the alveolar ridge, which prevents visualization of the underlying bone anatomy of the region of interest and consequently makes it impossible to decide on a definitive orientation for implants (Lal et al., 2006). Guided surgery can be used in rehabilitation of fully or partially edentulous patients, or even for single teeth. Likewise, guides can be mucosa-supported (tissue-borne), toothsupported (tooth-borne), or bone-supported (bone-borne). In guided surgery for rehabilitation of fully edentulous arches, certain steps must be followed prior to implant position planning: a. placement of diagnostic models on a semi-adjustable articulator; b. diagnostic wax-up; c. duplicate of wax-up for fabrication of acrylic-resin CT guide; d. placement of at least six 1.5 to 2 mm-diameter holes on the vestibular region of the guide and filling with radiopaque material;
5 402 Implant Dentistry The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry e. interocclusal registration with addition or condensation silicone for guidance during CT scanning; f. occlusal CT view of guide and interocclusal record; g. isolated scan of guide (for flapless procedures) (Parel & Triplett, 2004; Balshi et al., 2006; Marchack, 2007; Sanna et al., 2007; Van Assche et al., 2007). CT slices acquired in the DICOM file format must be converted with the aid of a specific software package prior to manipulation and reformatting into 3D images. During this process, the isolated radiographic guide scan is superimposed onto its occlusal view, using the radiopaque points as landmarks (Parel & Triplett, 2004; Balshi et al., 2006; Marchack, 2007; Sanna et al., 2007; Van Assche et al., 2007). The threshold for the case is also defined during this stage (Souza et al., 2003). Files obtained during this step can then be opened in implant position planning software. These applications provide axial, panoramic, and three-dimensional reconstructions of CT slices (Marchack, 2007; Sanna et al., 2007; Van Assche et al., 2007). They also enable manipulation of the panoramic reconstruction curve on the axial plane, providing orthogonal slices for assessment of alveolar ridge thickness in the vestibulolingual or vestibulopalatal direction (Parel & Triplett, 2004; Sanna et al., 2007; Van Assche et al., 2007). Virtual planning gives implantologists the ability to choose the precise location, orientation, and dimensions of implants, abutments and other fixtures. Implant emergence and the relationship of the implant to the future prosthesis can also be visualized and adjusted as convenient. In short, virtual planning can overcome the limitations of conventional surgical guides (Lal et al., 2006). Several virtual planning and guided surgery systems are available on the market. Each has its own particularities that should be taken into account by the implantologist, according to therapeutic indication, cost-benefit ratio, and learning curve for clinical use. The final stage of planning consists of defining the sites for placement of two or more anchor pins for the surgical guide, which are inserted through the vestibular aspect of the guide, between the implants (Balshi et al., 2006; Marchack, 2007; Sanna et al., 2007). After planning is complete, files are sent to a medical prototyping facility, where they will be converted into an appropriate format for prototype fabrication (Parel & Triplett, 2004; Marchack, 2007; Sanna et al., 2007; Van Assche et al., 2007). With implant positions established, a surgical guide is designed on the basis of the virtual model and sent to the prototyping station, where it is then fabricated (Lal et al., 2006). Three types of surgical guides or templates can be manufactured with rapid prototyping methods to improve the predictability of osseointegrated implant-based oral rehabilitation. Bone-supported (or bone-borne) guides are placed after the mucoperiosteal flap has been raised. Their advantages include positional stability during implant placement and the possibility of direct visualization of anatomical structures. The need for broader surgical exploration, however, may be regarded as a drawback of this type of guide, which is usually reserved for partially or fully edentulous arches (Tardieu et al., 2003; Garg, 2006; Lal et al., 2006). In mucosa-supported (or tissue-borne) surgical guides, templates, anchor pins are placed transmucosally. The drilling sequence for implant placement begins with a tissue punch or extractor, with the guide in place (Parel & Triplett, 2004; Marchack, 2007; Sanna et al., 2007). These guides are indicated in fully edentulous patients. Use of the double-scan technique, in
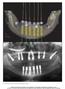
6 Virtual Planning for Dental Implant Placement Using Guided Surgery 403 which two independent scans of the radiographic guide individually and in occlusion are obtained, is mandatory in these cases. The key advantage of this method is the possibility of performing allows minimally invasive flapless procedures, which make for an easier intraoperative and postoperative period (Garg, 2006). Tooth-supported (or tooth-borne) surgical guides, as the name implies, are supported by the patient s remaining teeth. They are indicated in rehabilitation of single teeth or partially partially edentulous regions, and provide good outcomes when used for minimally invasive flapless surgery (Garg, 2006). Once the prototyped guide is ready, implant placement may proceed as recommended for each system (Figures 1 and 2). Fig. 1. Guided surgery for complete upper arch rehabilitation. a) Three-dimensional view of preoperative planning. Note radiopaque markers used to superimpose scans of the guide (isolated and in occlusion). Dentaslice software package (Bioparts, Brazil). b) Preoperative implant positioning. c) Five implants in place. Note insertion of anchor pins into stereolithographic guide. Neoguide system (Neodent, Brazil). d) Postoperative panoramic radiograph. Note similarity to virtual planning.
7 404 Implant Dentistry The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry Fig. 2. Guided surgery for partial anterior-superior rehabilitation. a) Preoperative planning. Nobelguide software system (Nobel Biocare, Sweden) b) Implant position, immediately after surgery. c) Palatal emergence of implants, in accordance with virtual planning. d) Final result: porcelain-fused-to-metal restoration. 4. Final remarks Implant planning has always been a major challenge of dental practice. CT is often unable to provide precise definitions of implant size and will not always be useful in preventing anatomical complications during surgery. Loubele et al (2007) found that bony dimensions were underestimated on the basis of measurements taken from several CT scans. Likewise, Suomalainen et al. (2008) reported errors in measurement of bone dimensions on CT images. These setbacks are even more critical when planning implants for patients with little available bone tissue. The advent of virtual planning and rapid prototyping techniques has led to a shift in this paradigm. Biomedical prototypes have made it possible for the implantologist to visualize and directly manipulate areas of interest, thus narrowing the gap between pre- and intraoperative findings (Choi et al., 2002; Sarment et al., 2003a; Meurer et al., 2008). Virtual planning permits three-dimensional analysis of implant position. Its clinical application guided surgery optimizes intra- and postoperative outcomes, as it can reduce surgical morbidity and improve the predictability of the proposed treatment plan. Studies on guided surgery have gained prominence in the dentistry literature since the early 2000s. Gateno et al. (2003) studied the fit precision of stereolithographic surgical splints and that of conventional acrylic resin splints. Their results indicated that stereolithographic
8 Virtual Planning for Dental Implant Placement Using Guided Surgery 405 splints had a high degree of accuracy of seating, thus enabling transfer of virtual treatment plans directly to the patient during surgery. Van Assche et al. (2007) evaluated the precision of transfer of computer-based planning for implant placement in four partially edentulous human jaws with soft tissues present. All stages of guided surgery were performed on the anatomical specimens, from molding and diagnostic wax-up to placement of implants (a total of 12). Postoperative cone-beam CT scans were obtained and superimposed onto preoperative scans in a virtual environment. Placed implants had a mean angular deviation of 2 degrees (range, degrees) from the planned position, whereas mean linear deviation was 1 mm ( mm) at the hex and 2 mm ( mm) at the apical implant tip. The authors conclude that cone-beam CT images can be used in computer-based implant planning for guided implant surgery with rapid-prototyped guides (Van Assche et al., 2007). Viegas et al. (2010) conducted an experiment on 11 dry human mandibles to assess transfer of virtual implant position planning to surgery. Implant positions were standardized and simulated in an appropriate software package, using preoperative cone-beam CT scans as a basis. Models and surgical guides for each mandible were fabricated using stereolithography methods. Simulated surgeries, including implant placement and removal, were first performed on each prototype. Implants were then placed into the mandible replicas. Analysis of results was based on standardized postoperative CT scanning of prototypes and replicas for visualization of the implant beds. Superposition of pre- and post-operative three-dimensional models enabled assessment of the linear distance and angle between the long axes of planned and placed implants. Linear measurements made directly on models were used to assess the validity of prototype-simulated procedures as a tool for treatment planning in oral implantology. The variations in distance between the coronal, central, and apical regions of the 22 implants evaluated in this study were, on average, <0.41 mm. Mean deviation in angle was 1.45 ± 0.89 degrees for implants placed on the right and 0.70 ± 0.30 degrees for implants placed on the left. Comparison of samples by means of Student s t test, using a reference value of zero, showed statistically significant differences for all measurements (p < 0.05). The correlation between implant bed positions in each mandible was fair to very good, depending on the distance analyzed and on the method used for interpretation of measurements. This study found that real-life deviation from planned dental implant positions determined by means of virtual planning and simulated surgery on a biomedical prototype were within a range that indicates the reliability of guided surgery as a method of dental implant placement. In a clinical study, Nickenig and Eitner (2007) evaluated transfer of virtual implant plans to the operative field by means of the guided surgery technique. A total of 102 patients took part in the study (250 implants). Implants were placed into the posterior area of the mandible in 55.4% of cases. Eighteen cases (7.2%) involved rehabilitation of fully edentulous arches. Computer-based virtual planning based on cone-beam CT scans was used in all cases. Flapless surgery was used for placement of 147 implants (58.8%) and all patients had uneventful intraoperative courses. In 98.4% of patients, there were no issues with surgical guide fit or instrumentation. Reduced interocclusal distance limited applicability of the technique in four patients. Initial plans were changed in eight cases, when raising the mucoperiosteal flap revealed a need for modifications in manipulation of the available bone tissue and simultaneous
9 406 Implant Dentistry The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry implant placement. Regarding predictability of implant size, only one implant had to be replaced with a smaller-diameter equivalent due to insufficient bone thickness. Postoperative panoramic radiographs showed that anatomical structures such as the maxillary sinus, mandibular canal, mental foramen, and neighboring teeth were spared as planned. Comparison of postoperative radiographs and panoramic reconstructions created by the planning software revealed substantial differences in implant angle in nine cases. The authors concluded that virtual plans based on cone-beam CT scans can be reproduced during implant placement surgery, and constitute a reliable method for defining implant position and size, preventing anatomical complications, and enabling wider use of flapless surgery (Nickenig & Eitner, 2007). The minor variations between planned and actual implant placement in the aforementioned studies show that computer-based treatment plans can be reliably transferred to the operative environment by means of the guided surgery technique. Furthermore, another key advantage of this procedure is the possibility of immediate loading of functional prostheses. Implant planning and positioning should not only take into account successful intraosseous implant placement, but also ensure that the future prosthesis is passively and securely seated on its fixtures. Prosthetic options for offsetting deviations in implant position vary according to the chosen guided surgery system. Even so, the current literature reveals a concern with the longevity of these implants. Sanna, Molly, and Van Steenberghe (2007) evaluated the survival of 183 implants (30 patients) placed for rehabilitation of fully edentulous arches with the guided surgery technique, using cone-beam CT scanning, tissue-borne guides, and immediate loading. The results showed that guided placement of dental implants followed by immediate loading of fixed prostheses was associated with survival rates similar to those obtained with the same mode of rehabilitation on implants reopened after the osseointegration period. Schneider et al. (2009) conducted a systematic review to assess the accuracy and clinical applications of guided implant surgery. A literature search yielded 3120 titles, eight of which met the inclusion criteria in terms of accuracy and 10 in terms the clinical performance. Meta-regression analysis revealed a mean deviation of 1.07 mm at the entry point (95% CI, mm) and 1.63 mm at the apex (95% CI, mm). No significant differences between the studies were found regarding method of template production or template support and stabilization. Early surgical complications occurred in 9.1% of cases. Limited access for instrumentation and fracture of the surgical guide were the sole technique-related complications observed all others were equally possible during conventional implant placement procedures. Early prosthetic complications occurred in 18.8% and late prosthetic complications in 12% of cases. Noteworthy prosthesis-related complications included misfit of abutment to bridge, extensive adjustments of the occlusion, and incomplete seating of the prosthesis. The most common delayed complications were screw loosening and prosthesis fracture. Implant survival rates, assessed in six clinical studies with a total of 537 implants most loaded immediately after flapless implantation procedures ranged between 91 and 100%. Studies such as these related justify the relevance of investigations that seek improvement toward increasingly accurate and safe methods that are beneficial to patients and dentists alike, such as virtual planning and guided surgery.
10 Virtual Planning for Dental Implant Placement Using Guided Surgery References Almog, D. M., Benson, B. W., Wolfgang, L., Frederiksen, N. L. & Brooks, S. L. (2006). Computerized tomography-based imaging and surgical guidance in oral implantology. J Oral Implantol, Vol. 32, No. 1, pp , ISSN Balshi, S. F., Wolfinger, G. J. & Balshi, T. J. (2006). Surgical planning and prosthesis construction using computed tomography, CAD/CAM technology, and the Internet for immediate loading of dental implants. J Esthet Restor Dent, Vol. 18, No. 6, pp ; discussion , ISSN Choi, J. Y., Choi, J. H., Kim, N. K., Kim, Y., Lee, J. K., Kim, M. K., Lee, J. H. & Kim, M. J. (2002). Analysis of errors in medical rapid prototyping models. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg, Vol. 31, No. 1, (February 2002), pp , ISSN Erben, C., Vitt, K. & Wulf, J. (2002). The Phidias validation study of reported benefits from use of stereolithographic models. Phidias Newsletter, Vol. [S.I.], No. 8, (March 2002), pp , ISSN Erickson, D. M., Chance, D., Schmitt, S. & Mathis, J. (1999). An opinion survey of reported benefits from the use of stereolithographic models. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, Vol. 57, No. 9, (September), pp , ISSN Ganz, S. D. (2003). Use of stereolithographic models as diagnostic and restorative aids for predictable immediate loading of implants. Pract Proced Aesthet Dent, Vol. 15, No. 10, (November-December 2003), pp ; quiz 772, ISSN Garg, A. K. (2006). Surgical templates in implant dentistry. Dent Implantol Update, Vol. 17, No. 6, (June 2006), pp , ISSN Gateno, J., Xia, J., Teichgraeber, J. F., Rosen, A., Hultgren, B. & Vadnais, T. (2003). The precision of computer-generated surgical splints. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, Vol. 61, No. 7, (July 2006), pp , ISSN Jacobs, R., Adriansens, A., Naert, I., Quirynen, M., Hermans, R. & Van Steenberghe, D. (1999). Predictability of reformatted computed tomography for pre-operative planning of endosseous implants. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, Vol. 28, No. 1, (January 1999), pp , ISSN X James, W. J., Slabbekoorn, M. A., Edgin, W. A. & Hardin, C. K. (1998). Correction of congenital malar hypoplasia using stereolithography for presurgical planning. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, Vol. 56, No. 4, (April 1998), pp , ISSN Lal, K., White, G. S., Morea, D. N. & Wright, R. F. (2006). Use of stereolithographic templates for surgical and prosthodontic implant planning and placement. Part I. The concept. J Prosthodont, Vol. 15, No. 1, (January-February 2006), pp , ISSN X Loubele, M., Guerrero, M. E., Jacobs, R., Suetens, P. & van Steenberghe, D. (2007). A comparison of jaw dimensional and quality assessments of bone characteristics with cone-beam CT, spiral tomography, and multi-slice spiral CT. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, Vol. 22, No. 3, (May-June 2007), pp , ISSN Marchack, C. B. (2007). CAD/CAM-guided implant surgery and fabrication of an immediately loaded prosthesis for a partially edentulous patient. J Prosthet Dent, Vol. 97, No. 6, (June 2007), pp , ISSN Meurer, M. I., Meurer, E., Silva, J. V. L. d., Bárbara, A. S., Nobre, L. F., Oliveira, M. G. d. & Silva, D. N. (2008). [Acquisition and manipulation of computed tomography images of the maxillofacial region for biomedical prototyping]. Radiol. bras, Vol. 41, No. 1, (January-February 2008), pp , ISSN
11 408 Implant Dentistry The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry Nickenig, H. J. & Eitner, S. (2007). Reliability of implant placement after virtual planning of implant positions using cone beam CT data and surgical (guide) templates. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, Vol. 35, No. 4-5, (June-July 2007), pp , ISSN Parel, S. M. & Triplett, R. G. (2004). Interactive imaging for implant planning, placement, and prosthesis construction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, Vol. 62, No. 9 Suppl 2, (September 2004), pp , ISSN Peltola, S. M., Melchels, F. P., Grijpma, D. W. & Kellomaki, M. (2008). A review of rapid prototyping techniques for tissue engineering purposes. Ann Med, Vol. 40, No. 4, pp , ISSN Rosenfeld, A. L., Mandelaris, G. A. & Tardieu, P. B. (2006). Prosthetically directed implant placement using computer software to ensure precise placement and predictable prosthetic outcomes. Part 1: diagnostics, imaging, and collaborative accountability. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, Vol. 26, No. 3, (June 2006), pp , ISSN Sanna, A. M., Molly, L. & van Steenberghe, D. (2007). Immediately loaded CAD-CAM manufactured fixed complete dentures using flapless implant placement procedures: a cohort study of consecutive patients. J Prosthet Dent, Vol. 97, No. 6, (June 2007), pp , ISSN Sarment, D. P., Al-Shammari, K. & Kazor, C. E. (2003a). Stereolithographic surgical templates for placement of dental implants in complex cases. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent, Vol. 23, No. 3, (June 2003), pp , ISSN Sarment, D. P., Sukovic, P. & Clinthorne, N. (2003b). Accuracy of implant placement with a stereolithographic surgical guide. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, Vol. 18, No. 4, (July- August 2003), pp , ISSN Schneider, D., Marquardt, P., Zwahlen, M. & Jung, R. E. (2009). A systematic review on the accuracy and the clinical outcome of computer-guided template-based implant dentistry. Clin Oral Implants Res, Vol. 20 No. Suppl 4, (September 2009), pp , ISSN Souza, M. A. d., Centeno, T. M. & Pedrini, H. (2003). [Integrating 3D reconstruction of tomographic images and rapid prototyping for fabrication of medical models]. Rev. bras. eng. biomed, Vol. 19, No. 2, (Augoust 2003), pp , ISSN Suomalainen, A., Vehmas, T., Kortesniemi, M., Robinson, S. & Peltola, J. (2008). Accuracy of linear measurements using dental cone beam and conventional multislice computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol, Vol. 37, No. 1, (January 2008), pp , ISSN X Tardieu, P. B., Vrielinck, L. & Escolano, E. (2003). Computer-assisted implant placement. A case report: treatment of the mandible. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants, Vol. 18, No. 4, (July-August 2003), pp , ISSN Van Assche, N., van Steenberghe, D., Guerrero, M. E., Hirsch, E., Schutyser, F., Quirynen, M. & Jacobs, R. (2007). Accuracy of implant placement based on pre-surgical planning of three-dimensional cone-beam images: a pilot study. J Clin Periodontol, Vol. 34, No. 9, (September 2007), pp , ISSN Viegas, V. N., Dutra, V., Pagnoncelli, R. M. & de Oliveira, M. G. (2010). Transference of virtual planning and planning over biomedical prototypes for dental implant placement using guided surgery. Clin Oral Implants Res, Vol. 21, No. 3, (March 2010), pp , ISSN Wulf, J., Vitt, K. D., Erben, C. M., Bill, J. S. & Busch, L. C. (2003). Medical biomodelling in surgical applications: results of a multicentric European validation of 466 cases. Stud Health Technol Inform, Vol. 94, No. pp , ISSN
12 Implant Dentistry - The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry Edited by Prof. Ilser Turkyilmaz ISBN Hard cover, 476 pages Publisher InTech Published online 30, September, 2011 Published in print edition September, 2011 Since Dr. Branemark presented the osseointegration concept with dental implants, implant dentistry has changed and improved dramatically. The use of dental implants has skyrocketed in the past thirty years. As the benefits of therapy became apparent, implant treatment earned a widespread acceptance. The need for dental implants has resulted in a rapid expansion of the market worldwide. To date, general dentists and a variety of specialists offer implants as a solution to partial and complete edentulism. Implant dentistry continues to advance with the development of new surgical and prosthodontic techniques. The purpose of Implant Dentistry - The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry is to present a comtemporary resource for dentists who want to replace missing teeth with dental implants. It is a text that integrates common threads among basic science, clinical experience and future concepts. This book consists of twenty-one chapters divided into four sections. How to reference In order to correctly reference this scholarly work, feel free to copy and paste the following: Vinicius Nery Viegas, Celso Gustavo Schwalm Lacroix, Rogeŕio Miranda Pagnoncelli and Mariĺia Gerhardt de Oliveira (2011). Virtual Planning for Dental Implant Placement Using Guided Surgery, Implant Dentistry - The Most Promising Discipline of Dentistry, Prof. Ilser Turkyilmaz (Ed.), ISBN: , InTech, Available from: InTech Europe University Campus STeP Ri Slavka Krautzeka 83/A Rijeka, Croatia Phone: +385 (51) Fax: +385 (51) InTech China Unit 405, Office Block, Hotel Equatorial Shanghai No.65, Yan An Road (West), Shanghai, , China Phone: Fax:
13 2011 The Author(s). Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial- ShareAlike-3.0 License, which permits use, distribution and reproduction for non-commercial purposes, provided the original is properly cited and derivative works building on this content are distributed under the same license.
A CAD/CAM flapless surgical technique and immediate prosthesis: a clinical report
 JOURNAL of OSSEOINTEGRATION > ROGÉRIO MARGONAR 1, THALLITA PEREIRA QUEIROZ 2, ELCIO MARCANTONIO 3, ERIKA OLIVEIRA DE ALMEIDA 4, ELCIO MARCANTONIO JÚNIOR 5 1 DDS, MS, PhD, Department of Health Sciences,
JOURNAL of OSSEOINTEGRATION > ROGÉRIO MARGONAR 1, THALLITA PEREIRA QUEIROZ 2, ELCIO MARCANTONIO 3, ERIKA OLIVEIRA DE ALMEIDA 4, ELCIO MARCANTONIO JÚNIOR 5 1 DDS, MS, PhD, Department of Health Sciences,
Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow
 Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow Ahmad Kutkut, DDS, MS, FICOI, DICOI Director of Predoctoral Implant Program Chair UKCD Implant Board ahmad.kutkut@uky.edu Disclaimer Neither I or any of my immediate
Digital Implant Dentistry Workflow Ahmad Kutkut, DDS, MS, FICOI, DICOI Director of Predoctoral Implant Program Chair UKCD Implant Board ahmad.kutkut@uky.edu Disclaimer Neither I or any of my immediate
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
GuidedService. The ultimate guide for precise implantations
 GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
GuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations ABGuidedService The ultimate guide for precise implantations At A.B. Dental we've brought implantology into the future with a 3D digitally planned
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer-guided minimally invasive
 CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 49 A Protocol for Immediate Placement of a Prefabricated Screw-Retained Provisional Prosthesis Using Computed Tomography and Guided Surgery
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 49 A Protocol for Immediate Placement of a Prefabricated Screw-Retained Provisional Prosthesis Using Computed Tomography and Guided Surgery
Computer-aided design/computer-assisted manufacturing
 Use of a Digitally Planned and Fabricated Mandibular Complete Denture for Easy Conversion to an Immediately Loaded Provisional Fixed Complete Denture. Part 1. Planning and Surgical Phase Jaime L. Lozada,
Use of a Digitally Planned and Fabricated Mandibular Complete Denture for Easy Conversion to an Immediately Loaded Provisional Fixed Complete Denture. Part 1. Planning and Surgical Phase Jaime L. Lozada,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Navigation in Implant Dentistry
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Short Communication Navigation in Implant Dentistry Varun Menon P* Craniomaxillofacial Surgery and Implantology Center, Thrissur, Kerala, India *Corresponding Author:
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Short Communication Navigation in Implant Dentistry Varun Menon P* Craniomaxillofacial Surgery and Implantology Center, Thrissur, Kerala, India *Corresponding Author:
Accuracy of Computer-Guided Implant Surgery by a CAD/CAM and Laser Scanning Technique
 Accuracy of Computer-Guided Implant Surgery by a CAD/CAM and Laser Scanning Technique Xue Zhu ZHAO 1, Wei Hua XU 2, Zhi Hui TANG 1, Min Jie WU 1, Jie ZHU 1, Si CHEN 1 Objectives: To explore the method
Accuracy of Computer-Guided Implant Surgery by a CAD/CAM and Laser Scanning Technique Xue Zhu ZHAO 1, Wei Hua XU 2, Zhi Hui TANG 1, Min Jie WU 1, Jie ZHU 1, Si CHEN 1 Objectives: To explore the method
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS
 DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
DIGITAL DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT PLANNING FOR PLACEMENT AND RESTORATION OF SINGLE IMPLANTS IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA By Timothy Kosinski, DDS Dental implants have undergone many positive advances in recent
An Introduction to Dental Implants
 An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
THE USE OF KEYSTONE EASYGUIDE CT SCANNING SOFTWARE FOR DIAGNOSIS, DIRECTION AND DEPTH DETERMINATION
 CT DIAGNOSTICS IN 3D IMPLANT TREATMENT PLANNING THE USE OF KEYSTONE EASYGUIDE CT SCANNING SOFTWARE FOR DIAGNOSIS, DIRECTION AND DEPTH DETERMINATION Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Assistant Clinical Professor
CT DIAGNOSTICS IN 3D IMPLANT TREATMENT PLANNING THE USE OF KEYSTONE EASYGUIDE CT SCANNING SOFTWARE FOR DIAGNOSIS, DIRECTION AND DEPTH DETERMINATION Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Assistant Clinical Professor
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Implant Studio Patient Case
 Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Implant Studio Patient Case Full mouth rehabilitation Case information On first visit, the patient was wearing a removable partial denture on lower jaw
Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Implant Studio Patient Case Full mouth rehabilitation Case information On first visit, the patient was wearing a removable partial denture on lower jaw
Much has been written about the success of various
 Simplified Guide for Precise Implant Placement: A Technical Note Brent D. Kennedy, MD, DDS*/Thomas A. Collins, Jr, DDS**/ Patrick C. W. Kline, DMD, MD** Ideal implant placement is ultimately determined
Simplified Guide for Precise Implant Placement: A Technical Note Brent D. Kennedy, MD, DDS*/Thomas A. Collins, Jr, DDS**/ Patrick C. W. Kline, DMD, MD** Ideal implant placement is ultimately determined
Implant restoration in the aesthetic zone using guided surgery and immediate functional loading
 Prachatipat Hospital Prathumtani Province Dr. Nawakamon Suriyan Implant restoration in the aesthetic zone using guided surgery and immediate functional loading Digital Workflow: clinical patient information
Prachatipat Hospital Prathumtani Province Dr. Nawakamon Suriyan Implant restoration in the aesthetic zone using guided surgery and immediate functional loading Digital Workflow: clinical patient information
Computer Aided Diagnosis and Design of Implant Abutments
 Article submitted for publication to Journal of Prosthodontics David A. Felton Computer Aided Diagnosis and Design of Implant Abutments Jef M. van der Zel, PhD, MSc, Professor Computerized Dentistry Academic
Article submitted for publication to Journal of Prosthodontics David A. Felton Computer Aided Diagnosis and Design of Implant Abutments Jef M. van der Zel, PhD, MSc, Professor Computerized Dentistry Academic
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry
 Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Guided implant placement using the trephine drill nonsleeve and immediate provisional crown or bridge in the esthetic zone
 Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 8(5) pp. 054-059, August 2017 DOI: http:/dx.doi.org/10.14303/jmms.2017.050 Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2017 International
Journal of Medicine and Medical Sciences Vol. 8(5) pp. 054-059, August 2017 DOI: http:/dx.doi.org/10.14303/jmms.2017.050 Available online http://www.interesjournals.org/jmms Copyright 2017 International
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Accuracy of guided osteotomy using dental implant treatment-planning software in combination with an optical scan of a dental cast
 POSEIDO. 2014;2(4) Accuracy of software- guided implant osteotomy 253 Research article Accuracy of guided osteotomy using dental implant treatment-planning software in combination with an optical scan
POSEIDO. 2014;2(4) Accuracy of software- guided implant osteotomy 253 Research article Accuracy of guided osteotomy using dental implant treatment-planning software in combination with an optical scan
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
Title: Integration of 3D anatomical data obtained by CT imaging and 3D optical scanning for Computer Aided Implant Surgery
 Author's response to reviews Title: Integration of 3D anatomical data obtained by CT imaging and 3D optical scanning for Computer Aided Implant Surgery Authors: Gianni Frisardi (frisardi@tin.it) Giacomo
Author's response to reviews Title: Integration of 3D anatomical data obtained by CT imaging and 3D optical scanning for Computer Aided Implant Surgery Authors: Gianni Frisardi (frisardi@tin.it) Giacomo
Guided surgery for single-implant placement: A critical review
 Guided surgery for single-implant placement: A critical review Abstract Objective Marco Tallarico, a Silvio Mario Meloni, b Luigi Canullo, a Erta Xhanari c & Giovanni Polizzi d a Private practice, Rome,
Guided surgery for single-implant placement: A critical review Abstract Objective Marco Tallarico, a Silvio Mario Meloni, b Luigi Canullo, a Erta Xhanari c & Giovanni Polizzi d a Private practice, Rome,
CLINICAL REPORT Use of Stereolithographic Templates for Surgical and Prosthodontic Implant Planning and Placement. Part II.
 CLINICAL REPORT Use of Stereolithographic Templates for Surgical and Prosthodontic Implant Planning and Placement. Part II. A Clinical Report Kunal Lal, DDS, MS; 1 George S. White, DDS; 2 Dennis N. Morea,
CLINICAL REPORT Use of Stereolithographic Templates for Surgical and Prosthodontic Implant Planning and Placement. Part II. A Clinical Report Kunal Lal, DDS, MS; 1 George S. White, DDS; 2 Dennis N. Morea,
Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow
 Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information On first visit,
Jung-plant dental office Dr. Jae-min, Lee D.D.S. Full mouth rehabilitation with digital workflow Solutions featured: 3Shape TRIOS 3Shape Dental System 3Shape Implant Studio Case information On first visit,
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,500 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant Planning: A Clinical Study
 JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry
 Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology
 Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
Restorative Driven Implant Solutions Utilizing the Latest Technology Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD As a general dentist who has placed nearly 7,000 dental implants, I
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment
 Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY
 NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY MANUAL Grand Morse Connection Helix Implant GRAND POSSIBILITIES WITH A LIMITLESS SOLUTION. GRAND MORSE NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY. 4 5 6 CONTENTS 1. CLINICAL STEP BY STEP OF GRAND
NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY MANUAL Grand Morse Connection Helix Implant GRAND POSSIBILITIES WITH A LIMITLESS SOLUTION. GRAND MORSE NEODENT GUIDED SURGERY. 4 5 6 CONTENTS 1. CLINICAL STEP BY STEP OF GRAND
CBCT as an Emerging Gold Standard for Presurgical Planning in Implant Restorations
 10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1344 M Shiva Shankar et al CASE REPORT CBCT as an Emerging Gold Standard for Presurgical Planning in Implant Restorations M Shiva Shankar, Bhupinder Pal, Nitesh Rai, Digvijaya
10.5005/jp-journals-10011-1344 M Shiva Shankar et al CASE REPORT CBCT as an Emerging Gold Standard for Presurgical Planning in Implant Restorations M Shiva Shankar, Bhupinder Pal, Nitesh Rai, Digvijaya
SCD Case Study. Implant-supported overdentures
 SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide
 Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
THE EXPANDING INFLUENCE OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY AND THE APPLICATION OF COMPUTER-GUIDED IMPLANTOLOGY
 CONTINUING EDUCATION 10 THE EXPANDING INFLUENCE OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY AND THE APPLICATION OF COMPUTER-GUIDED IMPLANTOLOGY George A. Mandelaris, DDS, MS* Alan L. Rosenfeld, DDS MANDELARIS 20 5 JUNE Implant
CONTINUING EDUCATION 10 THE EXPANDING INFLUENCE OF COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY AND THE APPLICATION OF COMPUTER-GUIDED IMPLANTOLOGY George A. Mandelaris, DDS, MS* Alan L. Rosenfeld, DDS MANDELARIS 20 5 JUNE Implant
The success of implant reconstruction depends
 Fabrication of a Dual-Purpose Surgical Template for Correct Labiopalatal Positioning of Dental Implants Murat C. Cehreli, DDS 1 /Saime Şahin, DDS, PhD 2 An implant-supported prosthesis can potentially
Fabrication of a Dual-Purpose Surgical Template for Correct Labiopalatal Positioning of Dental Implants Murat C. Cehreli, DDS 1 /Saime Şahin, DDS, PhD 2 An implant-supported prosthesis can potentially
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02,Issue 01 RESTORATION OF A FULLY EDENTULOUS PATIENT UTILIZING SIMPLE TECHNIQUES FOR IMPRESSION AND FABRICATION OF A HYBRID BRIDGE
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
CT Scan Technology. An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D.
 CT Scan Technology An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D. GANZ, DMD / USA Abstract Implant dentistry, one of the most predictable
CT Scan Technology An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D. GANZ, DMD / USA Abstract Implant dentistry, one of the most predictable
Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid
 Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid Implant-Level Restoration Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol The Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid offers a fixed, all-ceramic implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid Implant-Level Restoration Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol The Element-Z Screw-Retained Hybrid offers a fixed, all-ceramic implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee
 Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee Jung-plant Dental office 1 PROLOGUE How can we deal with the immediate loading implant cases easier and more accurate
Guided immediate loading implant surgery planned with Implant Studio D.D.S. Jae-min, Lee Jung-plant Dental office 1 PROLOGUE How can we deal with the immediate loading implant cases easier and more accurate
Dental implant placement is a sensitive surgical
 Implant Locating and Placement Based on a Novel Tactile Imaging and Registration Concept: A Technical Note Haim Tal, DMD, MDent, PhD 1 /Kurt A. Schicho, DSc, MD 2 /Michal Shohat, DMD 3 Computed-assisted
Implant Locating and Placement Based on a Novel Tactile Imaging and Registration Concept: A Technical Note Haim Tal, DMD, MDent, PhD 1 /Kurt A. Schicho, DSc, MD 2 /Michal Shohat, DMD 3 Computed-assisted
A Novel Stereolithographic Surgical Guide Template for Planning Treatment Involving a Mandibular Dental Implant
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66:1446-1454, 2008 A Novel Stereolithographic Surgical Guide Template for Planning Treatment Involving a Mandibular Dental Implant Sakineh Nikzad, DDS, MSc,* and Abbas Azari, DDS,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66:1446-1454, 2008 A Novel Stereolithographic Surgical Guide Template for Planning Treatment Involving a Mandibular Dental Implant Sakineh Nikzad, DDS, MSc,* and Abbas Azari, DDS,
BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Intraoperative Computerized Navigation for Flapless Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in the Edentulous Mandible
 Intraoperative Computerized Navigation for Flapless Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in the Edentulous Mandible Nardy Casap, DMD, MD 1 /Eyal Tarazi, DMD 2 /Alon Wexler, DMD 2 /Uri Sonnenfeld, DMD
Intraoperative Computerized Navigation for Flapless Implant Surgery and Immediate Loading in the Edentulous Mandible Nardy Casap, DMD, MD 1 /Eyal Tarazi, DMD 2 /Alon Wexler, DMD 2 /Uri Sonnenfeld, DMD
Application of CAD/CAM dental implant surgical templates in immediate implant surgery in esthetic area : A case report
 ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 8 Issue 6 BTAIJ, 8(6), 2013 [861-865] Application of CAD/CAM dental implant surgical templates in immediate implant surgery in esthetic area : A case report Zhenyan Lin 1, Yongbo
ISSN : 0974-7435 Volume 8 Issue 6 BTAIJ, 8(6), 2013 [861-865] Application of CAD/CAM dental implant surgical templates in immediate implant surgery in esthetic area : A case report Zhenyan Lin 1, Yongbo
Assessment of Response of Dental Clinicians and Patients towards Different Imaging Modalities Used In Diagnostic Evaluation of Dental Implant Therapy.
 Assessment of Response of Dental Clinicians and Patients towards Different Imaging Modalities Used In Diagnostic Evaluation of Dental Implant Therapy. Khairnar Mayur Sudhakar, Raut Darshana Hemant, Bakshi
Assessment of Response of Dental Clinicians and Patients towards Different Imaging Modalities Used In Diagnostic Evaluation of Dental Implant Therapy. Khairnar Mayur Sudhakar, Raut Darshana Hemant, Bakshi
Additive manufacturing in maxillofacial reconstruction
 Additive manufacturing in maxillofacial reconstruction Luciana Laura Dincă 1,*, Alexandra Banu 1 and Aurelian Vișan 1 1 Politehnica University of Bucharest, Department of Manufacturing Technology, Splaiul
Additive manufacturing in maxillofacial reconstruction Luciana Laura Dincă 1,*, Alexandra Banu 1 and Aurelian Vișan 1 1 Politehnica University of Bucharest, Department of Manufacturing Technology, Splaiul
Interesting Case Series. Virtual Surgical Planning in Orthognathic Surgery
 Interesting Case Series Virtual Surgical Planning in Orthognathic Surgery Suraj Jaisinghani, MS, a Nicholas S. Adams, MD, b,c Robert J. Mann, MD, b,c,d John W. Polley, MD, b,c,d, and John A. Girotto, MD,
Interesting Case Series Virtual Surgical Planning in Orthognathic Surgery Suraj Jaisinghani, MS, a Nicholas S. Adams, MD, b,c Robert J. Mann, MD, b,c,d John W. Polley, MD, b,c,d, and John A. Girotto, MD,
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING
 UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING -=- & UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING ----CBCTi-------iTERO------ NewTom VGi *Vertical Patient Positioning
UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING -=- & UNDERSTANDING DIGITAL DENTISTRY: CBCT AND INTRA-ORAL 30 SCANNING ----CBCTi-------iTERO------ NewTom VGi *Vertical Patient Positioning
Use of Technology for Improved Implant Use in The OMS Practice AAOMS 93rd Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA
 Use of Technology for Improved Implant Use in The OMS Practice AAOMS 93rd Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA Image Navigation Surgery For Implant Placement - A Comparison To Guided Stent Use Robert W. Emery
Use of Technology for Improved Implant Use in The OMS Practice AAOMS 93rd Annual Meeting, Philadelphia, PA Image Navigation Surgery For Implant Placement - A Comparison To Guided Stent Use Robert W. Emery
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2013) Vol. 52, Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2013) Vol. 52, Page 544 554 Role of Multislice Dental CT in Assessment of Dental Implants Safa A Elaty *, Ahmed M Monib *, Yasser A Mohamed *,Ahmed F Abd
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2013) Vol. 52, Page 544 554 Role of Multislice Dental CT in Assessment of Dental Implants Safa A Elaty *, Ahmed M Monib *, Yasser A Mohamed *,Ahmed F Abd
Computer Guided Implant Placement - Why it s a Sound Investment For Dentists
 Computer Guided Implant Placement - Why it s a Sound Investment For Dentists Computer Guided Implant Placement 1 Table of Contents Overview Meeting the Challenges of Patient Demands 3 Free-hand Workflow
Computer Guided Implant Placement - Why it s a Sound Investment For Dentists Computer Guided Implant Placement 1 Table of Contents Overview Meeting the Challenges of Patient Demands 3 Free-hand Workflow
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options
 Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Case study 25. Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla Using Short Implants. Dr. Ariel Labanca Mitre
 Case study 25 Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla Using Short Implants Dr. Ariel Labanca Mitre Oral Implantology Specialist Prosthodontics Specialist Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla
Case study 25 Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla Using Short Implants Dr. Ariel Labanca Mitre Oral Implantology Specialist Prosthodontics Specialist Implantology Solutions for Atrophic Maxilla
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Hybrid Denture bridges have a well-documented history
 Conversion of Acrylic Hybrid Dentures to Monophase Zirconia Bridge Michael Tischler DDS, José Echeverry CDT, Darwin Bagley CDT Hybrid Denture bridges have a well-documented history greater than 40 years
Conversion of Acrylic Hybrid Dentures to Monophase Zirconia Bridge Michael Tischler DDS, José Echeverry CDT, Darwin Bagley CDT Hybrid Denture bridges have a well-documented history greater than 40 years
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Simplant. Guided Surgery. delivering restorative driven implant treatment
 Simplant Guided Surgery delivering restorative driven implant treatment Simplant the key to unlocking digital potential As part of the Denstsply Sirona Implants Digital Solutions offering, Simplant delivers
Simplant Guided Surgery delivering restorative driven implant treatment Simplant the key to unlocking digital potential As part of the Denstsply Sirona Implants Digital Solutions offering, Simplant delivers
Even faster thanks to ExpertEase Immediate restoration directly following implant placement. new
 Even faster thanks to ExpertEase Immediate restoration directly following implant placement new The Initial Situation: Patients want beautiful teeth quickly preferably directly after the implantation Patients
Even faster thanks to ExpertEase Immediate restoration directly following implant placement new The Initial Situation: Patients want beautiful teeth quickly preferably directly after the implantation Patients
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
KAREN O. From Failure to Fantastic
 KAREN O From Failure to Fantastic THE Pi TEAM THOMAS J. BALSHI, DDS, PhD, FACP GLENN J. WOLFINGER, DMD, FACP JAMES R. BOWERS, DDS IAN SMITH, DMD KAREN O Karen suffered from painful and swollen gum tissue
KAREN O From Failure to Fantastic THE Pi TEAM THOMAS J. BALSHI, DDS, PhD, FACP GLENN J. WOLFINGER, DMD, FACP JAMES R. BOWERS, DDS IAN SMITH, DMD KAREN O Karen suffered from painful and swollen gum tissue
Restore your patients quality of life. Solutions for all edentulous indications
 Restore your patients quality of life. Solutions for all edentulous indications 2 Solutions for all edentulous indications «I just wanted to have my smile back, and I truly feel they fixed it just the
Restore your patients quality of life. Solutions for all edentulous indications 2 Solutions for all edentulous indications «I just wanted to have my smile back, and I truly feel they fixed it just the
EFFECT OF SMOKING HABBITS ON ACCURACY OF SUPPORTED STEREOLITHOGRAPHIC SURGICAL. J. D'haese & H. De Bruyn
 EFFECT OF SMOKING HABBITS ON ACCURACY OF IMPLANT PLACEMENT USING MUCOSALLY SUPPORTED STEREOLITHOGRAPHIC SURGICAL GUIDES J. D'haese & H. De Bruyn 1 ABSTRACT Background: Smoking is considered as a factor
EFFECT OF SMOKING HABBITS ON ACCURACY OF IMPLANT PLACEMENT USING MUCOSALLY SUPPORTED STEREOLITHOGRAPHIC SURGICAL GUIDES J. D'haese & H. De Bruyn 1 ABSTRACT Background: Smoking is considered as a factor
CPD Article ISSUE 59. Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future
 CPD Article ISSUE 59 Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future BIDST CPD This learning session has been judged as being equivalent to one hour of verifiable CPD. To claim your verifiable CPD
CPD Article ISSUE 59 Proud of our History, Looking Forward to the Future BIDST CPD This learning session has been judged as being equivalent to one hour of verifiable CPD. To claim your verifiable CPD
Contents Graduate Diploma of Dental Implantology
 Graduate Diploma of Dental Implantology Information Brochure Contents Graduate Diploma of Dental Implantology DOH 551 Introduction to Dental Implants and Basic Restorative Implantology Module 1 Fundamentals
Graduate Diploma of Dental Implantology Information Brochure Contents Graduate Diploma of Dental Implantology DOH 551 Introduction to Dental Implants and Basic Restorative Implantology Module 1 Fundamentals
Dentatus ANEW Narrow Diameter Implants. Expanding Implantology with More Treatment Options
 Dentatus ANEW Narrow Diameter Implants Expanding Implantology with More Treatment Options The Versatility of Dentatus ANEW LONG-TERM RESTORATIONS INTERIM SOLUTIONS LONG-TERM RESTORATIONS Many dentists
Dentatus ANEW Narrow Diameter Implants Expanding Implantology with More Treatment Options The Versatility of Dentatus ANEW LONG-TERM RESTORATIONS INTERIM SOLUTIONS LONG-TERM RESTORATIONS Many dentists
Young-Jin Park, DDS,* and Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
A FAMILY FULL OF SMILES
 A FAMILY FULL OF SMILES Prologue The saga started years ago. As a poor southern boy, when Danny had a toothache, the normal protocol was to extract the offending tooth. Subsequently, as an adult, Dan chewed
A FAMILY FULL OF SMILES Prologue The saga started years ago. As a poor southern boy, when Danny had a toothache, the normal protocol was to extract the offending tooth. Subsequently, as an adult, Dan chewed
TABLE OF CONTENTS P. 4-5 P. 6-7 P. 8-9 P P P P
 Full Smile Solution TABLE OF CONTENTS P. 4-5 P. 6-7 P. 8-9 P. 10-11 P. 12-13 P. 14-15 P. 16-17 FULL SMILE SOLUTION MGUIDE PROCESS ADVANTAGES CUSTOM SOLUTIONS MGUIDE SURGICAL SETS MCENTER REQUIRED SOURCES
Full Smile Solution TABLE OF CONTENTS P. 4-5 P. 6-7 P. 8-9 P. 10-11 P. 12-13 P. 14-15 P. 16-17 FULL SMILE SOLUTION MGUIDE PROCESS ADVANTAGES CUSTOM SOLUTIONS MGUIDE SURGICAL SETS MCENTER REQUIRED SOURCES
EasyLineImplant. Guided Surgery
 EasyLineImplant Guided Surgery Guided surgery Guided Surgery represents an improvement in the traditional surgery, increasing the advantages for clinicians and patients. The guided procedure allows reaching
EasyLineImplant Guided Surgery Guided surgery Guided Surgery represents an improvement in the traditional surgery, increasing the advantages for clinicians and patients. The guided procedure allows reaching
CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions
 CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions 2 V2R CT Scanning Protocol \\ Contents Contents General requirements... 3 V2R Dual Scan Protocol... 5 V2R Single Scan Protocol... 8 Overview... 10
CT Scanning Protocol For V2R Guided Surgery Solutions 2 V2R CT Scanning Protocol \\ Contents Contents General requirements... 3 V2R Dual Scan Protocol... 5 V2R Single Scan Protocol... 8 Overview... 10
Orthodontic-prosthetic implant anchorage in a partially edentulous patient
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2011) 6, 176e180 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Clinical Report Orthodontic-prosthetic implant anchorage in a partially edentulous patient
Journal of Dental Sciences (2011) 6, 176e180 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Clinical Report Orthodontic-prosthetic implant anchorage in a partially edentulous patient
SIMPLANT Guided Surgery delivering restorative-driven implant treatment
 SIMPLANT Guided Surgery delivering restorative-driven implant treatment SIMPLANT the key to unlocking digital potential As part of the DENTSPLY Implants Digital Solutions portfolio, SIMPLANT digital implant
SIMPLANT Guided Surgery delivering restorative-driven implant treatment SIMPLANT the key to unlocking digital potential As part of the DENTSPLY Implants Digital Solutions portfolio, SIMPLANT digital implant
Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research. DOI: /sjodr. ISSN (Print) Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website:
 DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
Screw hole-positioning guide and plate-positioning guide: A novel method to assist mandibular reconstruction
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 301e305 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Screw hole-positioning guide and plate-positioning guide: A novel method
Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 301e305 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Screw hole-positioning guide and plate-positioning guide: A novel method
Ideal treatment of the impaired
 RESEARCH IMPLANTS AS ANCHORAGE IN ORTHODONTICS: ACLINICAL CASE REPORT Dale B. Herrero, DDS KEY WORDS External anchorage Pneumatized Often, in dental reconstruction, orthodontics is required for either
RESEARCH IMPLANTS AS ANCHORAGE IN ORTHODONTICS: ACLINICAL CASE REPORT Dale B. Herrero, DDS KEY WORDS External anchorage Pneumatized Often, in dental reconstruction, orthodontics is required for either
The clinical significance COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY BASED IMAGING AND SURGICAL GUIDANCE IN ORAL IMPLANTOLOGY RESEARCH
 RESEARCH COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY BASED IMAGING AND SURGICAL GUIDANCE IN ORAL IMPLANTOLOGY Dov M. Almog, DMD B. W. Benson, DDS, MS L. Wolfgang, DDS N. L. Frederiksen, DDS, PhD S. L. Brooks, DDS, MS KEY
RESEARCH COMPUTERIZED TOMOGRAPHY BASED IMAGING AND SURGICAL GUIDANCE IN ORAL IMPLANTOLOGY Dov M. Almog, DMD B. W. Benson, DDS, MS L. Wolfgang, DDS N. L. Frederiksen, DDS, PhD S. L. Brooks, DDS, MS KEY
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Placement of Posterior Mandibular and Maxillary Implants in Patients with Severe Bone Deficiency: A Clinical Report of Procedure
 Placement of Posterior Mandibular and Maxillary Implants in Patients with Severe Bone Deficiency: A Clinical Report of Procedure Leonard Krekmanov, DDS, PhD 1 The purpose of this investigation was to modify
Placement of Posterior Mandibular and Maxillary Implants in Patients with Severe Bone Deficiency: A Clinical Report of Procedure Leonard Krekmanov, DDS, PhD 1 The purpose of this investigation was to modify
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
The removable implant supported prosthesis for the upper jaw
 Implant placement in the atrophied maxilla The removable implant supported Drs. Alan Rosenfeld and George Mandelaris Diplomates, American Board of Periodontology Initial Exam: Patient with ill fitting,
Implant placement in the atrophied maxilla The removable implant supported Drs. Alan Rosenfeld and George Mandelaris Diplomates, American Board of Periodontology Initial Exam: Patient with ill fitting,
