1984 Lubow et al Endodontic flap design: analysis and recommendations for current usage
|
|
|
- Ginger Baldwin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surgical Endodontics Endodontic flap design 1984 Lubow et al Endodontic flap design: analysis and recommendations for current usage Most important factor in flap design is blood supply therefore widest at the base. Then consider regional anatomy BVs and nerves. Incisions should not be over defects. Then closure - Flap should be replaced so as to cover all surgically exposed sites. Relieving incisions at least one tooth mesial or distal to the surgical site to cover the surgical area. 6 flap designs semilunar, triangular, rectangular, trapezoidal, vertical incision and Luebke- Oschsenbein all full thickness Semilunar contraindicated when a fenestration or dehiscence is present along incision line often leads to scarring. Triangular flap useful for short roots. Horizontal incision in gingival sulcus, with vertical relieving incision extending to alveolar mucosa interproximally. Trapezoidal and rectangular horizontal incision in gingival sulcus with vertical relieving incisions. Relieving incision are not placed directly over a root or bony prominence which may have an inadequate supply. Luebke-Oschsenbein horizontal incision placed a minimum of 2mm from the depth of the gingival sulcus, the incision line then curves gently to form the vertical components of the flap. Give excellent access and vision and adequate blood supply, not interfere with the aesthetics at the gingival margin. Disadvantage 2mm of attached gingiva should be present coronal to the line of incision, minimal attached gingiva at the surgical site, unpredictable scar formation Authors recommend - Full-thickness dissection with easily recognizable landmarks and straight-line incisions. A bevelled horizontal incision is designed to incorporate the maximum amount of facial keratinised tissue into the body of the flap, while leaving the interproximal tissues untouched. Starts in the sulcus bevelled and cuts across papillae leaving intact. The resultant flap is easily replaced with interrupted sutures to the stable interproximal papillae. Disadvantages full thickness may lead to dehiscences/fenestrations. May have gingival aesthetic probs Kramper et al Comparative study of the wound healing of 3 types of flap design (on dogs)
2 Semilunar, submarginal incision in the attached gingivae, intrasulcular. submarginal better except in the development of scar formation. Inflammatory changes persisted longer in the semilunar and intrasulcular incisions and retarded wound healing. Loss of alveolar bone occurred in the submarginal and semilunar incisions Intrasulcular led to healing by second intention (granulation) due to problems with reapproximation of the wound edges. Loss of alveolar bone and gingival recession. But no scarring visible Submarginal easy to replace and primary intention healing. Tensile strength of the submarginal incision wound will be greater at 60 days than the semilunar and intrasulcular incision wounds.scar tissue present Semilunar due to greater vascularity in alveolar mucosa, incision likely to lead to increased hemorrhage. Often leads to overextension or damage to the wound margins for access and visibility. The requirement of a minimum of 2mm of attached gingiva is of great important in the prevention of mucogingival problems. Triangular flap designs are acceptable if adequate access can be achieved without trauma to the wound margins. Trapezoidal flap designs are not necessary as blood supply should be good enough. Choice between intrasulcular and submarginal must be first based on the anatomical location of the pathological lesion. The only requisite is that a fibrin clot be established and maintained into which the tissue elements are able to migrate. However, since postop trauma cannot always be avoided, it is prudent to place the incision over healthy bone so the intact periosteum can provide a firm base for suturing the surgical flap into place. Retraction of a full thickness flap will expose alveolar crestal bone, causing some loss of that bone, possible recession of the marginal gingiva, or at least lengthening of the epithelial attachment Moiseiwitsch Avoiding the mental foramen during periapical surgery 3 steps during presurgical diagnosis, flap design and surgery are presented. Preop diagnosis PA and panoramic. Or vertically placed standard periapical and standard view. Flap design Place single relieving incision distally as access created without stretching mental neurovascular bundle. Could cut groove into bone to prevent retractor slipping. Surgical technique nerve damage often by strectching or crushing of bundle with retractor. Try to stop retractor from slipping.
3 2002 Velvart - Papilla base incision: a new approach to recession-free healing of the interdental papilla after endodontic surgery To evaluate a new incision technique: the papilla base incision. The papilla base flap, consisting of the papilla base incision and two releasing incisions, was used to expose the bone. The papilla base incision consisted of a shallow first incision at the base of the papilla and a second incision directed to the crestal bone, creating a split thickness flap in the area of the papilla base. Further apically a full thickness flap was raised. In patients with healthy marginal periodontal conditions the papilla base incision allows rapid and predictable recession-free healing following marginal surgical exposure of the soft
4 tissues. One month postoperatively the majority of the incisions were completely or partially invisible. No noticeable space was created beneath the contact point area. When the distance from the contact point to the bone was 5 mm or less, the papilla was present almost 100% of the time. With a distance of 6 mm, the papilla was present 56% of the time, and when the distance measured 7 mm or more, the papilla was present 27% of the time or less. Intro - Endodontic surgery requires exposure of the bone covering the root(s) and the apices. To achieve access, a full thickness flap must be raised, which consists of gingival and mucosal tissue as well as periosteum. To mobilize the flap, various modes of incisions can be selected including horizontal incisions (sulcular and submarginal) and vertical releasing incisions (Gutmann & Harrison 1991a). The papilla base incision (above) required two different incisions at the base of the papilla. 1 The first shallow incision severed the epithelium and connective tissue to the depth of 1.5 mm from the surface of the gingiva. The incision was placed at the level of the lower third of the papilla in a slight curved line going from one side of the papilla to the other (Fig. 1). The incision started and ended in a 90 degree angle between the border of the tooth and the gingiva (see lines in Fig. 1 above). 2 The scalpel was then placed to the base of the previously created shallow incision at the base of the papilla and subsequently inclined apically, almost parallel to the long axis of the tooth, aiming at the crestal bone margin. With this second incision a split thickness flap was prepared in the apical third of the base of the papilla. The incision ended at the crestal bone level, where the periosteum was separated from the bone (Fig. 2). From there on the preparation continued in a full thickness muco periosteal flap. Buccally over the tooth the vertical incision and papilla base incision were joined by an intrasulcular incision. The scalpel was moved within the sulcus, dissecting the gingiva to the crestal bone. The sulcular incision reached from the releasing incision to the start of the papilla base incision,
5 or from one papilla to the next papilla. The flap was mobilized and retracted, during the root-end resection and filling. The flap closure was initiated from the releasing incisions. For the vertical incisions 6/0 (Supramid, B. Braun, Neuhausen, Switzerland) interrupted polyamide sutures were used. The papilla base incision was sutured with two or three polypropylene 7/0 (Prolene, Ethicon, Norderstedt, Germany) interrupted sutures depending on the width of the papilla. It is of utmost importance to preserve epithelial and connective tissue attachment at its original level and traumatize the attachment apparatus as little as possible during the incision in order to obtain rapid healing through primary intention. This can be obtained by: 1 complete and sharp incision of the tissues; 2 avoiding crushing of the tissues; 3 preventing drying of the tissues during the procedure; and 4 perfect adaptation of wound edges upon closure (Gutmann & Harrison 1991b). The wound edges are perfectly reapproximated without tension on the suture. Tension will compromise blood circulation on both the papilla and the split flap and cause delayed healing. It was shown by Pini Prato et al. (2000) that greater tension reduced root coverage in coronally advanced flaps. a) Wound closure of the papilla base incision with three polypropylene sutures; (b) sutures removed after 4 days. A minimum of two sutures is required, one at each side of the papilla base incision for perfect reapproximation of the wound edges. The key point of the Papilla base incision is to avoid thinning of the split flap. The epithelium of the partial thickness portion of the flap needs support by underlying connective tissue, which has to be thick enough to maintain vitality through sufficient blood supply. If this goal cannot be obtained, the tissue will necrotize, resulting in a tissue defect, followed by scar formation. On the other hand, excessive thickness of the connective tissue layer of the split flap portion could compromise the survival of the unreflected buccal papilla. The ideal thickness of a partial thickness flap is unknown.
6 2005 Velvart and Peters - Soft Tissue Management in Endodontic Surgery Complete, recession-free and predictable healing of gingival tissue is one important goal of endodontic surgical treatment. Several studies have identified factors that influence the prognosis of endodontic surgery (4 11). According to Friedman (12) they can be divided into preoperative-, operative-, and postoperative factors. Success rates vary between 25% and 98% depending on the study (13, 14). An important anatomical consideration during endodontic surgery is the course of blood vessels supplying alveolar mucosa and gingiva. Four interconnected pathways of blood supply exist: the subepithelial capillaries of the gingiva and alveolar mucosa, the vascular network within the periosteum, the intraseptal arteries in the bone marrow and the plexus of the periodontium. Accessing the apical pathology - an evaluation of the size and position of the expected periradicular pathology in relation to the root, neurovascular structures and the sinus has to take place, including assessment of the local blood supply to the soft tissues in and around the designated flap area. Triangular Flap This type of surgical flap comprises a horizontal incision extending at least one tooth mesially and distally to the involved area combined with one releasing vertical incision forms a triangular flap (Fig. 4). Usually, the releasing incision is performed on the mesial part of the flap. The triangular flap is mainly indicated for correction of problems in the cervical and midroot portions, such as in cases with cervical root resorptions, perforations and in resections of very short roots. The main advantages of this flap design are minimal disruption of the blood supply to the mobilized tissues and easy repositioning of the wound edges. As in all intrasulcular horizontal incisions, recession may result after the healing process. Fig 4
7 Rectangular and Trapezoidal Flap Rectangular and trapezoidal flaps are an extension of the triangular flap with a second vertical releasing incision. Most frequesntly used flaps. As the blood vessels run mostly parallel to the long axis of the teeth from the apical to the coronal direction, one consideration is to disrupt the least number of vascular structures. The longer the flap length the more important is the ratio between the length and width of the flap (54). Several authors advocate a length-width ratio of 2:1 Submarginal Flap The most popular submarginal flap is the flap design by Ochsenbein and Luebke (56). Two releasing vertical incisions are connected by a scalloped horizontal incision. The submarginal flap is only to be used, when there is a broad zone of attached gingiva with a minimum of 2 mm. Advantage of leaving the marginal gingiva untouched and it does not expose any restoration margins. As crestal bone is not denuded, the risk of attachment loss is minimized. In rare situations, because of insufficient treatment planning and poor surgical technique, necrosis of the unreflected tissue might occur because of deprivation of blood supply to this area. The recession resulting from such tissue breakdown can have devastating effects on the esthetic outcome of surgical treatment. Possible scar tissue formation is another disadvantage of the submarginal flap. Semilunar Flap Placing either a straight or a curved horizontal incision in the alveolar mucosa that extends all the way to the bone creates a semilunar flap. The only advantage of this flap design is the fact that the marginal tissue remains untouched and thus no recession will occur. On the other hand, many disadvantages accompany its use. A semilunar flap will provide only limited access to the surgical area. Additionally, placement of the incision over the bony
8 defect means that the wound cannot be closed over sound bone structure. Furthermore, the content of elastic fibers and muscle attachments of alveolar mucosa is high, both of which exert pulling forces on the reapproximated surgical wound margins SURGICAL SITE CLOSURE After irrigation with saline solution to remove debris, the wound edges are reapproximated carefully to allow primary intention healing (52). Compression of the repositioned flap with a saline-moistened piece of gauze is necessary to create a thin fibrin layer between flapped tissue and cortical bone (53, 58, 59). Replacement of a thin blood clot with parallel fibrin fibers by new fibrous tissue results in collagen adhesion (58). SUTURES: TECHNIQUES AND MATERIALS Bacterial colonization is an important factor leading to tissue reactions to intraoral sutures. When comparing histological tissue response of different suture materials, monofilament sutures (e.g. nylon, gut, steel, and chromic gut) produced smaller inflammatory reaction than multifilament materials (e.g. silk, siliconized silk, polyester, teflonized polyester, cotton, or linen) In general, monofilament synthetic sutures are least traumatic, allow less bacterial migration and are the materials of choice. Sutures should not act as ligatures and tension created by sutures should be minimal (45). Tension can be reduced by using a greater number of sutures and by choosing fine microsurgical materials (28). While full flaps are best secured using vertical mattress sutures and anchor sutures, limited flaps are best retained using interrupted, fine-diameter sutures.
9 Examples of commonly employed suture techniques. (A) interrupted suture, (B) anchor suture, (C) sling suture, and (D) vertical mattress suture Reprinted with permission from (102). SUTURE REMOVAL A perisutural epithelial sleeve develops at 3 days and can enrobe the entire suture track after 7 days (66). An intense inflammatory response to suture materials and the trauma of suture placement is visible after 3 days (66). As resealing of epithelium at the wound margin is evident within 2 days, suture removal can take place after 48 h but should take place no longer than 96 h after placement. CRITICAL REVIEW OF SOFT TISSUE HEALING Healing Process Healing takes place in several phases that overlap and coexist: wounding, clotting and inflammation, epithelial healing, connective tissue healing, proliferation, maturation, and remodelling Within 24 h, polymorphonuclear leukocytes and macrophages start migrating into a blood clot. Stimulated macrophages play a central role in angiogenesis and new collagen synthesis. After 4 days an epithelial barrier has formed. Healing and reattachment of an elevated flap to cortical bone is a slower procedure, the periosteum does not survive reflection (58). Granulation tissue replaces the thin fibrin clot between the flap and cortical bone after 4 days, and fibrous connective tissue replaces granulation tissue by 14 days. Vertical releasing incision that creates a compromised tissue area (arrow). The proximal, unreflected tissue portion will most probably necrotize because of insufficient blood supply. A dashed line indicates the desired incision course, beginning in a 90-degree angle to the gingival marginal. Keeping the flap moist at all times helps avoids shrinkage and dehydration
10 Patient Related Factors Both the type of tissue involved and the type of surgical wound determine the healing process (78). Patients with a thick tissue biotype tend to display coronal soft tissue regrowth to the former level in crown lengthening procedures, whereas patients with a thin tissue biotype do not. The integrity and thickness of underlying bone plays a role in mucogingival stability. Among other principles (incision and flap design, atraumatic and gentle tissue management), a passive and tension-free wound closure is fundamental for proper wound healing and for a successful functional and esthetic outcome. Changing the size of the suture material and accordingly the size of the needle as in microsuturing is much less traumatic. Papilla Preservation/Protection Sulcular full thickness flap is used in periradicular surgery. In this flap technique the buccal papilla is mobilized and becomes part of the flap (89). Ideally, the sulcular incision should dissect the buccal from the lingual papilla. The conventional sulcular flap results in considerable retraction of papilla height after 1 month and 3 months postsurgically. Straight-line incisions during endodontic surgery, without mobilization or inclusion of the papilla into the buccal flap, lead to a clear indentation line where the incision was placed. No longer acceptable. Depending on the incision site, the following materials have been used: Vertical incisions should be sutured with 6/0 sutures, because of close proximity to inserting muscles in the mucosa, which might exert some tension to the wound during mastication and speech. As nylon monofilament materials are somewhat stiff in size 6/0, softer material, such as polyamide (Supramid ) was preferred. This material is a multifilament suture, with a coating providing monofilamentous appearance with a smooth surface. For closure of the horizontal incision and the delicate area of the papillae, we recommend polypropylene interrupted sutures with a size of 7/0 or smaller (Fig. 21). As the wound edges should be perfectly adapted to each other, depending on the dimensions of the papilla two or three interrupted sutures are needed. Suture removal performed after 3 to 5 days promoted rapid healing. The critical area for suture removal after 2 to 3 days is the apical portion of the vertical releasing incision the mucosal wound, in particular in the region with muscle tension, which might require 24 to 48 h longer to initiate healing. Papilla base flaps have allowed virtually recession free healing after endodontic surgery.
11 Comparison of different sizes of scalpel blades. Top is the regular blade size #15, middle blade represents the smaller #15C and bottom shows the microblade with double sided cutting edges.
Soft Tissue Management in Endodontic Surgery
 JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 31, NO. 1, JANUARY 2005 REVIEW Soft Tissue Management in Endodontic Surgery Peter Velvart, DMD,
JOURNAL OF ENDODONTICS Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2004 by The American Association of Endodontists VOL. 31, NO. 1, JANUARY 2005 REVIEW Soft Tissue Management in Endodontic Surgery Peter Velvart, DMD,
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of endodontic surgery
 Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask
 Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
Everything You Wanted to Know About Extractions but Were Afraid to Ask Tooth extraction is a surgical procedure with serious potential complications and should only be performed by a trained veterinarian.
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
Minimally invasive techniques for periodontal regeneration
 2016; 2(12): 230-234 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 230-234 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-10-2016 Accepted: 05-11-2016 Dr. Rizwan M Sanadi Professor,
2016; 2(12): 230-234 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2016; 2(12): 230-234 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 04-10-2016 Accepted: 05-11-2016 Dr. Rizwan M Sanadi Professor,
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER. Brook A. Niemiec, DVM
 DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Diplomate, European Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry San Diego Vet Dental
DENTAL EXTRACTIONS MADE EASIER Brook A. Niemiec, DVM Diplomate, American Veterinary Dental College Diplomate, European Veterinary Dental College Fellow, Academy of Veterinary Dentistry San Diego Vet Dental
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
I J Pre Clin Dent Res 2014;1(2):49-53 April-June All rights reserved International Journal of Preventive & Clinical Dental Research Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and
Principles of Endodontic Surgery
 1 Principles of Endodontic Surgery Categories of endodontic surgery 1- Periapical surgery. 2- Hemisection/root amputation. 3- Intentional replantation. 4- Corrective surgery. 1- PERIAPICAL SURGERY (i.e.,
1 Principles of Endodontic Surgery Categories of endodontic surgery 1- Periapical surgery. 2- Hemisection/root amputation. 3- Intentional replantation. 4- Corrective surgery. 1- PERIAPICAL SURGERY (i.e.,
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Surgical Endodontics. Year 5 DDS - November Dr. Ahmad El-Ma aita
 Surgical Endodontics Year 5 DDS - November 2014 Dr. Ahmad El-Ma aita Outline: 1- Definitions 2- Range of surgical endodontics 3- Indications and contraindications 4- Peri-radicular surgery: Clinical and
Surgical Endodontics Year 5 DDS - November 2014 Dr. Ahmad El-Ma aita Outline: 1- Definitions 2- Range of surgical endodontics 3- Indications and contraindications 4- Peri-radicular surgery: Clinical and
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY
 MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY DR.H.Gharati Periodontist & Dental Implant Specialist Assistant Professor, School Of Dentistry Friedman(1957): DEFINITION Mucogingival surgery, Surgical
MUCOGINGIVAL THERAPY PERIODONTAL PLASTIC SURGERY DR.H.Gharati Periodontist & Dental Implant Specialist Assistant Professor, School Of Dentistry Friedman(1957): DEFINITION Mucogingival surgery, Surgical
Educational Training Document
 Educational Training Document Table of Contents Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer Page: 2 Part 2: Line Item Grade Sheets Page: 3 Release: 11/2016 Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer The
Educational Training Document Table of Contents Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer Page: 2 Part 2: Line Item Grade Sheets Page: 3 Release: 11/2016 Page 1 of 6 Part 1: Resource Document Disclaimer The
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth
 New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
SURGICAL TREATMENT OF GINGIVAL RECESSION WITH SOFT TISSUE GRAFT PROCEDURE
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2018243.2149 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2018 Jul-Sep;24(3) Literature review
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2018243.2149 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2018 Jul-Sep;24(3) Literature review
SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT A PREDICTABLE INDICATOR FOR ROOT COVERAGE
 SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT A PREDICTABLE INDICATOR FOR ROOT COVERAGE Munishwar Singh* * 201 Military Dental Centre, C/o 99 APO, India Keywords: Gingival recession, Root coverage procedure, Connective
SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT A PREDICTABLE INDICATOR FOR ROOT COVERAGE Munishwar Singh* * 201 Military Dental Centre, C/o 99 APO, India Keywords: Gingival recession, Root coverage procedure, Connective
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Many techniques have been proposed for root coverage:
 Case Series Localized Gingival Recessions Treated With the Original Envelope Technique: A Report of 50 Consecutive Patients Jaime A. Vergara* and Raul G. Caffesse Background: The surgical techniques used
Case Series Localized Gingival Recessions Treated With the Original Envelope Technique: A Report of 50 Consecutive Patients Jaime A. Vergara* and Raul G. Caffesse Background: The surgical techniques used
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
OPERATION TECHNIQUES OF DENTOALVEOLAR SURGERY. Semmelweis University - Oral Surgery Department
 OPERATION TECHNIQUES OF DENTOALVEOLAR SURGERY Semmelweis University - Oral Surgery Department MINOR ORAL SURGERY (DENTOALVEOLAR SURGERY) MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY (Head and Neck Surgery) SURGICAL THERAPY SURGICAL
OPERATION TECHNIQUES OF DENTOALVEOLAR SURGERY Semmelweis University - Oral Surgery Department MINOR ORAL SURGERY (DENTOALVEOLAR SURGERY) MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY (Head and Neck Surgery) SURGICAL THERAPY SURGICAL
GINGIVAL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES
 Gingival Surgical Procedures GINGIVAL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES! limited to the gingival and not involving underlying osseous structures! Gingival Curettage! Gingivectomy! Gingivoplasty! Gingival Flap Gingival
Gingival Surgical Procedures GINGIVAL SURGICAL TECHNIQUES! limited to the gingival and not involving underlying osseous structures! Gingival Curettage! Gingivectomy! Gingivoplasty! Gingival Flap Gingival
Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession
 World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
World Journal of Medical Sciences 10 (2): 117-121, 2014 ISSN 1817-3055 IDOSI Publications, 2014 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.wjms.2014.10.2.82175 Double Papillary Flap - A Treatment for Gingival Recession 1 1 1
Maryland AGD AE and Socket Grafting 2015
 The Goodacre Study 5 year retrospective study looked at Crown & Bridge Caries Single crowns 1% FPD abutments 17% Periodontal Involvement Single crowns
The Goodacre Study 5 year retrospective study looked at Crown & Bridge Caries Single crowns 1% FPD abutments 17% Periodontal Involvement Single crowns
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the. Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System
 Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
Esthetic Crown Lengthening for Upper Anterior Teeth: Indications and Surgical Techniques Mohammad Assaf Assistant Professor, Faculty of Dentistry, Al-Quds University, Jerusalem, Palestine. ABSTRACT Correspondence
Core build-up using post systems
 Core build-up using post systems Dr. Gergely Pataky Department of Conservative Dentistry What to speak about today General considerations Classification of post systems Dowel-core or fibre post? Biologic
Core build-up using post systems Dr. Gergely Pataky Department of Conservative Dentistry What to speak about today General considerations Classification of post systems Dowel-core or fibre post? Biologic
Socket Graft Plus. Case Presentation. Ideal Bone Graft for All Socket Grafting Situations. Case #1
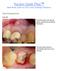 Socket Graft Plus Ideal Bone Graft for All Socket Grafting Situations Case Presentation Case #1 Tooth #3 presents with a buccal parulis, ensuring a buccal alveolar fenestration. The tooth will be remove
Socket Graft Plus Ideal Bone Graft for All Socket Grafting Situations Case Presentation Case #1 Tooth #3 presents with a buccal parulis, ensuring a buccal alveolar fenestration. The tooth will be remove
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
The Effect of Flap Design on Wound Healing after Periapical Surgery: A Comparative Study.
 ISSN: 1812 1217 The Effect of Flap Design on Wound Healing after Periapical Surgery: A Comparative Study. Mohammad S. Suleiman BDS, MSc (Lect) Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery College of Dentistry,
ISSN: 1812 1217 The Effect of Flap Design on Wound Healing after Periapical Surgery: A Comparative Study. Mohammad S. Suleiman BDS, MSc (Lect) Dept of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery College of Dentistry,
Townie Guest Editorial. Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options. Daniel J. Melker, DDS. fig. 1
 Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options Daniel J. Melker, DDS Attached connective tissue (a.k.a. attached tissue) in the simplest terms is the body s only barrier between the underlying
Gingival Attachment Loss: Evaluation and Surgical Options Daniel J. Melker, DDS Attached connective tissue (a.k.a. attached tissue) in the simplest terms is the body s only barrier between the underlying
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
WILLIAM B. BOHANNAN DDS, MD PROFESSIONAL CORPORATION
 7.12.18 WILLIAM B. BOHANNAN DDS, MD RE: Samuel Bower Site #6 To whom it may concern: Mr. Bower and his parents wish to seek additionally opinions for site #6. They are trying to decide if further surgery
7.12.18 WILLIAM B. BOHANNAN DDS, MD RE: Samuel Bower Site #6 To whom it may concern: Mr. Bower and his parents wish to seek additionally opinions for site #6. They are trying to decide if further surgery
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
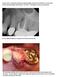 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment
 SCIENTIFIC SESSION Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment Essayist: Roberto Pontoriero Introduction In periodontally involved patients, periodontal therapy usually results in various degrees of soft-tissue
SCIENTIFIC SESSION Osseous surgery in periodontal treatment Essayist: Roberto Pontoriero Introduction In periodontally involved patients, periodontal therapy usually results in various degrees of soft-tissue
Gum Graft? Patient Need a. Does My. 66 JANUARY 2017 // dentaltown.com. by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky
 by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky was born in Dallas and attended college at the University of Texas at Austin. He continued his education at Baylor College of Dentistry in Dallas, where he
by Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky Dr. Brian S. Gurinsky was born in Dallas and attended college at the University of Texas at Austin. He continued his education at Baylor College of Dentistry in Dallas, where he
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery
 CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
CASE SERIES 1 OPEN ACCESS Management of millers class III marginal tissue recession associated with endodontic lesion: Report of two cases managed using second stage surgery Sangeeta ABSTRACT Introduction:
Periodontal ligament
 Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report Veena Ashok. P. MDS, Bhargav Neetha BDS Abstract: Gingival recession is defined as Displacement of soft tissue margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction
CASE REPORT Free Gingival Autograft: A Case Report Veena Ashok. P. MDS, Bhargav Neetha BDS Abstract: Gingival recession is defined as Displacement of soft tissue margin apical to the cemento-enamel junction
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE. Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic
 MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
MAXILLARY INJECTION TECHNIQUE Chinthamani Laser Dental Clinic Introduction A number of injection techniques are available to aid in providing clinically adequate anesthesia of the teeth and soft and hard
The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
The primary objective of dental suturing is
 CLINICAL SUTURING FOR OPTIMAL SOFT-TISSUE MANAGEMENT Lee H. Silverstein, DDS, MS; Gregori M. Kurtzman, DDS; Peter C. Shatz, DDS Establishing nontension primary wound closure of various soft tissue flaps
CLINICAL SUTURING FOR OPTIMAL SOFT-TISSUE MANAGEMENT Lee H. Silverstein, DDS, MS; Gregori M. Kurtzman, DDS; Peter C. Shatz, DDS Establishing nontension primary wound closure of various soft tissue flaps
Clinical Application of Modified Apically Repositioned Flap in Class III/IV Gingival Recession Cases
 J Harjeet Singh et al SE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1200 linical pplication of Modified pically Repositioned Flap in lass III/IV Gingival Recession ases 1 Harjeet Singh, 2 Manab Kosala, 3 Vivek apurao
J Harjeet Singh et al SE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1200 linical pplication of Modified pically Repositioned Flap in lass III/IV Gingival Recession ases 1 Harjeet Singh, 2 Manab Kosala, 3 Vivek apurao
ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM. Dr. Fatin Awartani
 ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM Part II Cementum and Alveolar bone Associate Professor Periodontal division King Saud university Cementum Calcified mesenchymal tissue that forms the outer covering of the anatomic
ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM Part II Cementum and Alveolar bone Associate Professor Periodontal division King Saud university Cementum Calcified mesenchymal tissue that forms the outer covering of the anatomic
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
Surgical removal of wisdom teeth
 Oral surgery/dr.hazem Lecture #8 Rand Herzallah Surgical removal of wisdom teeth Wisdom teeth extraction is harder than the extraction of any other teeth; because of: 1) The anatomical location of the
Oral surgery/dr.hazem Lecture #8 Rand Herzallah Surgical removal of wisdom teeth Wisdom teeth extraction is harder than the extraction of any other teeth; because of: 1) The anatomical location of the
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Esthetic Crown Lengthening
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
Principles of Complicated Exodontia
 Principles of Complicated Exodontia Larry J. Peterson CHAPTER CHAPTER OUTLINE PRINCIPLES OF FLAP DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT, AND MANAGEMENT Design Parameters for Soft Tissue Flaps Types of Mucoperiosteal Flaps
Principles of Complicated Exodontia Larry J. Peterson CHAPTER CHAPTER OUTLINE PRINCIPLES OF FLAP DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT, AND MANAGEMENT Design Parameters for Soft Tissue Flaps Types of Mucoperiosteal Flaps
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 433 Lip Repositioning for Reduction of Excessive Gingival Display: A Clinical Report Ari Rosenblatt, DMD, DDS* Ziv Simon, DMD, MSc* Excessive
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 433 Lip Repositioning for Reduction of Excessive Gingival Display: A Clinical Report Ari Rosenblatt, DMD, DDS* Ziv Simon, DMD, MSc* Excessive
TWO-STEP SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR ROOT COVERAGE (FREE GINGIVAL GRAFT AND CORONALLY POSITIONED FLAP) - A CASE REPORT
 TWO-STEP SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR ROOT COVERAGE (FREE GINGIVAL GRAFT AND CORONALLY POSITIONED FLAP) - A CASE REPORT Dr Prashant Bhusari*, Dr Apoorva Saxena**, Dr Jaya Jain***,Dr Rashmi Rathore***, Dr Aditi
TWO-STEP SURGICAL PROCEDURE FOR ROOT COVERAGE (FREE GINGIVAL GRAFT AND CORONALLY POSITIONED FLAP) - A CASE REPORT Dr Prashant Bhusari*, Dr Apoorva Saxena**, Dr Jaya Jain***,Dr Rashmi Rathore***, Dr Aditi
Application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9mm implant in a narrow interdental space
 C A S E R E P O R T Application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9mm implant in a narrow interdental space Michael Kristensen 1 This case report describes the application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9 mm implant
C A S E R E P O R T Application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9mm implant in a narrow interdental space Michael Kristensen 1 This case report describes the application of the Straumann BLT Ø 2.9 mm implant
Figure (2-6): Labial frenum and labial notch.
 The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
The anatomy of the edentulous ridge in the maxilla and mandible is very important for the design of a complete denture. The consistency of the mucosa and architecture of the underlying bone is different
Geistlich Fibro-Gide. The Alternative Soft-Tissue Graft
 Geistlich Fibro-Gide The Alternative Soft-Tissue Graft Geistlich Fibro-Gide shows comparable results to connective tissue grafts in terms of change in soft-tissue volume over time., This demonstrates that
Geistlich Fibro-Gide The Alternative Soft-Tissue Graft Geistlich Fibro-Gide shows comparable results to connective tissue grafts in terms of change in soft-tissue volume over time., This demonstrates that
TASKS. 2. Apply a disclosing agent to make the plaque visible.
 TASKS EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS Personal protective equipment Assortment of nylon, soft-bristled toothbrushes Assortment of dental Floss, waxed and nonwaxed Disclosing solution Face mirror 3. Demonstrate
TASKS EQUIPMENT AND MATERIALS Personal protective equipment Assortment of nylon, soft-bristled toothbrushes Assortment of dental Floss, waxed and nonwaxed Disclosing solution Face mirror 3. Demonstrate
RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS. The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4
 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS 1 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS RESISTANT TO EXPOSURE The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4 RELIABLE BARRIER
RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS 1 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS RESISTANT TO EXPOSURE The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4 RELIABLE BARRIER
DENTAL SUTURES. Testimonials. Juraj Brozović DMD, PhD Split Croatia
 DENTAL SURGERY DENTAL SUTURES Testimonials Juraj Brozović DMD, PhD Split Croatia RESORBA sutures are a vital part of my everyday surgical armamentarium due to their bioinert and tensile properties. SUPRAMID
DENTAL SURGERY DENTAL SUTURES Testimonials Juraj Brozović DMD, PhD Split Croatia RESORBA sutures are a vital part of my everyday surgical armamentarium due to their bioinert and tensile properties. SUPRAMID
DENTAL SUTURE BOOKLET. RESORBA Oral Sutures state of the art wound closure. Our Distributor
 DENTAL SUTURE BOOKLET RESORBA Oral Sutures state of the art wound closure Our Distributor Juraj Brozović Split Croatia RESORBA sutures are a vital part of my everyday surgical armamentarium due to their
DENTAL SUTURE BOOKLET RESORBA Oral Sutures state of the art wound closure Our Distributor Juraj Brozović Split Croatia RESORBA sutures are a vital part of my everyday surgical armamentarium due to their
A Fantastic Aprroach for Multiple Recession Coverage: Vestibular Incision Subperiosteal Tunnel Access Technique (Vista)-A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2016), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org A Fantastic Aprroach for Multiple Recession
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. I (Feb. 2016), PP 52-56 www.iosrjournals.org A Fantastic Aprroach for Multiple Recession
أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل CROWN AND BRIDGE جامعة تكريت كلية. Lec. (2) طب االسنان
 Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Incisions Flap design Closure of Wounds
 Incisions Flap design Closure of Wounds Intekhab Islam Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Incision and Flap Design 1 Outline Incisions Flaps Closure of wounds Incision and Flap Design 2 Incisions Access to
Incisions Flap design Closure of Wounds Intekhab Islam Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Incision and Flap Design 1 Outline Incisions Flaps Closure of wounds Incision and Flap Design 2 Incisions Access to
Complex Exodontia. Jone Kim, DDS, MS
 Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic case report.
 European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
ELIMINATE POCKETS. Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease
 ELIMINATE POCKETS Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease CONSEQUENTLY Periodontal pockets should be eliminated
ELIMINATE POCKETS Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease CONSEQUENTLY Periodontal pockets should be eliminated
Treatment of Altered Passive Eruption: Periodontal Plastic Surgery of the Dentogingival Junction
 CASE REPORT Publication Treatment of Altered Passive Eruption: Periodontal Plastic Surgery of the Dentogingival Junction Roberto Rossi, DDS, MScD Private Practice Genoa, Italy Remo Benedetti, MD, DDS Private
CASE REPORT Publication Treatment of Altered Passive Eruption: Periodontal Plastic Surgery of the Dentogingival Junction Roberto Rossi, DDS, MScD Private Practice Genoa, Italy Remo Benedetti, MD, DDS Private
A New Papilla Preservation Technique for Periodontal Regeneration of Severely Compromised Teeth. Jose A. Moreno Rodríguez and Raúl G.
 A New Papilla Preservation Technique for Periodontal Regeneration of Severely Compromised Teeth Jose A. Moreno Rodríguez and Raúl G. Caffesse Introduction: Periodontal regeneration of hopeless teeth represents
A New Papilla Preservation Technique for Periodontal Regeneration of Severely Compromised Teeth Jose A. Moreno Rodríguez and Raúl G. Caffesse Introduction: Periodontal regeneration of hopeless teeth represents
Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations:
 1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
CAD/CAM PREPARATION GUIDELINES & TISSUE MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES RECOMMENDATIONS FOR OPTIMAL SCANNING, DESIGNING, AND MILLING
 CAD/CAM PREPARATION GUIDELINES & TISSUE MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES RECOMMENDATIONS FOR OPTIMAL SCANNING, DESIGNING, AND MILLING CROWN PREPARATION GUIDELINES IDEAL CROWN PREPARATIONS POSTERIOR RESTORATIONS Rounded
CAD/CAM PREPARATION GUIDELINES & TISSUE MANAGEMENT TECHNIQUES RECOMMENDATIONS FOR OPTIMAL SCANNING, DESIGNING, AND MILLING CROWN PREPARATION GUIDELINES IDEAL CROWN PREPARATIONS POSTERIOR RESTORATIONS Rounded
Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) Three quarter (¾ )crown: Uses: Indications ---- For posterior teeth ;
 Lecture.9 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) *It is a cast metal crown restoration that cover only a part of the clinical crown, most commonly used type of partial veneer crown
Lecture.9 Dr.Adel F.Ibraheem Partial Veneer Crown(Three quarter crown) *It is a cast metal crown restoration that cover only a part of the clinical crown, most commonly used type of partial veneer crown
HeliMEND Advanced. Absorbable Collagen Membrane. Instructions for Use
 HeliMEND Advanced Absorbable Collagen Membrane Instructions for Use 2 Indications HeliMEND Advanced absorbable collagen membrane is an absorbable, implantable material that is indicated for guided tissue
HeliMEND Advanced Absorbable Collagen Membrane Instructions for Use 2 Indications HeliMEND Advanced absorbable collagen membrane is an absorbable, implantable material that is indicated for guided tissue
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor
 Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
soft tissue mucoderm botiss native stable 3-dimensional 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft Handling, Clinical Application and Cases
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft Handling, Clinical Application and Cases by PD Dr. med. dent. Adrian Kasaj soft tissue native stable 3-dimensional
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft Handling, Clinical Application and Cases by PD Dr. med. dent. Adrian Kasaj soft tissue native stable 3-dimensional
Central Incisor DR.Ahmed Al-Jobory B.D.S.,M.Sc. Conservative Department
 Dental Anatomy Lecture 3 Central Incisor DR.Ahmed Al-Jobory B.D.S.,M.Sc. Conservative Department The permanent maxillary Incisors Maxillary incisor are four in number. The maxillary central incisor is
Dental Anatomy Lecture 3 Central Incisor DR.Ahmed Al-Jobory B.D.S.,M.Sc. Conservative Department The permanent maxillary Incisors Maxillary incisor are four in number. The maxillary central incisor is
Efficacy of Lateral Pedicle Graft in the Treatment of Isolated Gingival Recession Defects
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 3 Issue 1 January 2014 PP.46-50 Efficacy of Lateral Pedicle Graft in the Treatment of
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 3 Issue 1 January 2014 PP.46-50 Efficacy of Lateral Pedicle Graft in the Treatment of
RAJ M. SAINI, DDS, MSD
 Restoring and Maintaining Periodontal Health with Orthodontic Treatment RAJ M. SAINI, DDS, MSD rajmsaini@yahoo.com Diplomate Of The American Board Of Orthodontics Clinical Professor Of Orthodontics New
Restoring and Maintaining Periodontal Health with Orthodontic Treatment RAJ M. SAINI, DDS, MSD rajmsaini@yahoo.com Diplomate Of The American Board Of Orthodontics Clinical Professor Of Orthodontics New
Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 509319, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/509319 Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 509319, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/509319 Case Report Esthetic Root Coverage with Double Papillary Subepithelial Connective Tissue Graft: A Case Report
22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24
 Erick Sato Case Report Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #24 22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24 Subjective: Chief Complaint: My tooth is dark, and my dentist referred me for
Erick Sato Case Report Non-Surgical Root Canal Therapy #24 22 yo female presented for evaluation and treatment of tooth #24 Subjective: Chief Complaint: My tooth is dark, and my dentist referred me for
,5 mm mm
 Mini luxators These mini luxators have an anatomically curved blade to adapt to the tooth root. Through a slight rotating movement the periodontal ligaments can be cut cleanly, at the same time dilating
Mini luxators These mini luxators have an anatomically curved blade to adapt to the tooth root. Through a slight rotating movement the periodontal ligaments can be cut cleanly, at the same time dilating
Clinical applications of minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE SERIES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Clinical applications of minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery Sangeeta Singh, Saravanan SP, Devendra Srivastava, Raghvendra MH, A.
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE SERIES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Clinical applications of minimally invasive periodontal plastic surgery Sangeeta Singh, Saravanan SP, Devendra Srivastava, Raghvendra MH, A.
CLINICAL. Free gingival grafts to manage recession when and how? Matthew B M Thomas CLINICAL
 CLINICAL CLINICAL Free gingival grafts to manage recession when and how? Matthew B M Thomas Gingival recession results from displacement of the gingival margin below the cemento-enamel junction leading
CLINICAL CLINICAL Free gingival grafts to manage recession when and how? Matthew B M Thomas Gingival recession results from displacement of the gingival margin below the cemento-enamel junction leading
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
