ORIGINAL RESEARCH. Nitesh Kumar Sharma 1, Anushree Prasad 2 INTRODUCTION.
|
|
|
- Mervyn Welch
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluation of Efficacy of Tetracycline as a Local Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis as an Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing A Clinical and Microbiological Study Nitesh Kumar Sharma 1, Anushree Prasad 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: Tetracycline and its derivatives has shown to be highly effective in the treatment of chronic periodontitits. Since there are very limited microbiological study conducted to evaluate the efficacy of tetracycline fibers as a local drug therapy, the study has been taken up to evaluate the efficacy of locally delivered tetracycline fibers (Periodontal AB Plus) in conjuction with scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis in the patients who are not willing to undergo periodontal flap surgery. Material and methods: The present study is a randomized clinical trial with split mouth design in which a total no.of 35 patients who were diagnosed with generalized chronic moderate periodontitis, consisting of both genders (Male : Female =16 : 19), aged between 25 to 60 years were selected. These selected sites were randomly divided into test group and control group Test group - included 35 sites that were selected for the placement of Periodontal Plus AB; Tetracycline fibers (local drug delivery) after scaling and root planing. Control group - included 35 sites that were treated with scaling and root planing alone (without local drug delivery).clinical parameters taken were the PI, GI, SBI, probing depth (PD), and clinical attachment level (CAL). Anaerobic culture was done to compare the total colony forming unit before and after the treatment. Clinical parameters were assesed at base line, 30 days and 90 days whereas the total count was calculated at baseline, 30 days and 90 days. Result: Results showed a significant improvement in all the clinical parameters. There was significant decrease in mean probing depth from base line to 90 days, and also there was significant gain in CAL in the test group as compared to control group. There was a significant reduction in the total colony count from base line to 21 days in both the group, but more reduction was observed in the test group. After 21 days to 90 days there was significant increase in the total colony count in both the group, but less increase was observed in test group. Conclusion: Within the limits of this study and on the basis of the clinical and microbiological parameters, it can be concluded that tetracycline fiber therapy enhances the benefits of SRP in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. Keywords: Tetracycline, Local Drug Delivery System, Chronic Periodontitis, Scaling and Root Planing, Clinical and Microbiological Study INTRODUCTION Periodontal diseases represent a group of localized microbial induced infections involving the gingival and supporting tissues of the teeth, resulting in progressive loss of attachment and formation of periodontal pockets. There is considerable evidence implicating facultative and anaerobic bacteria as a primary cause of periodontal disease. The control of prevalence and progression of periodontal disease requires a reduction of sub-gingival microbial plaque mass or at least a suppression of periodontopathic bacteria. 1 Periodontal diseases are routinely treated by mechanical procedures which include meticulous scaling and root planing in conjunction with patient s proper plaque control. Mechanical therapy may however fail to eliminate the pathogenic bacteria because of their location within gingival tissues or in other areas inaccessible to periodontal instruments. 2 Subgingival microbial recolonization after scaling and root planing occurs slowly. Periodontal debridement may not eradicate these species like A. actinomycetemcomitans and P.gingivalis due to their invasive potential into gingival epithelial cells and subepithelial connective tissue, and their high affinity for crevicular epithelium and dentinal tubule. Consequently, this has led to adjunctive use of antimicrobials, assuming that chemical aids would compensate for technical shortcomings and prevent early microbial re-colonization to ultimately ensure the best chance for clinical improvements. 3 Antimicrobial therapy has also been directed at specific bacteria associated with clinically diseased sites to help augment the mechanical treatment aimed at the removal of sub-gingival calculus and toxins. However, the inability to achieve and maintain therapeutic concentrations of the antibiotic in the crevicular fluid with systemic administration can limit its effectiveness. 4 Also, the Systemic administration of antimicrobial agents requires frequent dosing which is associated with the risk of developing resistant organisms and super infection as well as adverse effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances. 5 Pitcher et al. observed that mouth rinses and agents used during supra-gingival irrigation do not predictably reach beyond 5 mm into the periodontal pocket. For antimicrobial agents to be effective, the concentration of the drug should be adequate at the site and also there should be prolonged drug microbial contact. 6 In order to overcome the drawbacks associated with systemic and conventional mode of therapy, local drug delivery systems were developed, which is used in this study. 7 The antimicrobial agents used as local drug delivery agents include tetracycline, ofloxacin, clindamycin, chlorhexidine, etc. Tetracycline as well its derivatives doxycycline and 1 Senior Resident, RIMS, Ranchi, 2 Senior Dental Officer, ECHS Army Hospital, Jamshedpur, India Corresponding author: Dr. Nitesh Kumar Sharma, Senior Resident, Rims, Ranchi, India How to cite this article: Nitesh Kumar Sharma, Anushree Prasad. Evaluation of efficacy of tetracycline as a local drug delivery system in the treatment of chronic periodontitis as an adjunct to scaling and root planing a clinical and microbiological study. International Journal of Contemporary Medical Research 2017;4(5): Volume 4 Issue 5 May 2017 ICV (2015): ISSN (Online): X; (Print):
2 minocycline are the most commonly used antimicrobial agents in the treatment of periodontal infections. Tetracycline also binds to the root surfaces and can be released in active form over extended periods of time. The sub-lethal concentration of tetracycline reduces adherence and co-aggregation properties of a number of disease associated bacteria including P. gingivalis and P. intermedia Tetracyclines are semi-synthetic chemotherapeutic agents which are bacteriostatic in action and hence are effective against rapidly multiplying bacteria. Tetracycline have been incorporated into a variety of delivery systems (nonresorbable or bioresorbable) for insertion into periodontal pockets. These include hollow fibers (Goodson et al., 1979), ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer fibers (Goodson et al., 1983), ethyl cellulose fibers (Friedman and Golomb, 1982), acrylic strips (Addy et al., 1982), collagen preparations (Minabe et al., 1989), and hydroxypropyl cellulose films (Noguchi et al., 1984). 11 Recently, a new local drug delivery system, Periodontal Plus AB, which contains 25 mg pure fibrilar collagen with approximately 2 mg of evenly impregnated tetracycline hydrochloride (Advanced Biotech Products, Chennai, India) have been introduced for the treatment of gingival and periodontal diseases. 11 The present three month study was designed to reduce the surgical intervention in the treatment of periodontal pocket and to use locally available material so as to reduce the financial burden on the patient and thereby making cost effective management. Since there are limited microbiological studies conducted to evaluate the efficacy of tetracycline fibers as a local drug therapy, the study has been taken up to evaluate the efficacy of locally delivered tetracycline fibers (Periodontal AB Plus) in conjuction with scaling and root planing in the treatment of chronic periodontitis in the patients who are not willing to undergo periodontal flap surgery. MATERIAL AND METHODS The present study was a randomized clinical trial with split mouth design in which a total no.of 35 patients who were diagnosed with generalized chronic moderate periodontitis, consisting of both genders (Male : Female =16 : 19), aged between 25 to 60 years were selected from the outpatient department of periodontics, Rama dental college hospital and research centre, Kanpur. The study was performed for a period of 3 months, and the patients were selected under the following criteria. Inclusion criteria 1. Patients diagnosed as generalized chronic periodontitis. 2. Patients having A. two contra-lateral sites with 5 mm periodontal pocket with active lesion, and radiographic evidence of bone loss B. Clinical attachment loss 3 5 mm at the base line, 3. Patients who had not undergone any surgical or nonsurgical periodontal therapy in the past 6 months, and patient who are not willing for surgical therapy. 4. Patients able to follow verbal or written oral hygiene instructions. Exclusion criteria 1. Patients who had taken antibiotic therapy in the past 6 months. 2. Patients with a history of using antimicrobial mouthrinses within 2 months of the baseline visit or on routine basis. 3. Patients having history of allergy to tetracycline 4. Pregnant woman and lactating mothers. 5. Patients with periodontal pockets in which the depth of the pockets corresponded to the apex of the tooth as in probable endodontic-periodontic conditions. 6. Medically compromised patients. 7. Teeth with furcation involvements. 8. Known smokers and smokeless tobacco. Thirty five patients with a total of 70 sites who were diagnosed with generalized chronic periodontitis were selected. These selected sites were randomly divided into test group and control group. Test group - included 35 sites that were selected for the placement of Periodontal Plus AB; Tetracycline fibers (local drug delivery) after scaling and root planing. Control group - included 35 sites that were treated with scaling and root planing alone (without local drug delivery). Clinical examination for the base line parameters were done after obtaining written consent from each patient who had participated in the study. The ethical clearance obtained from ethical committee of Rama dental college, hospital and research centre, Kanpur. Clinical parameters Sulcular Bleeding Index (Muhlemann and Sons 1971) were evaluated at base line, 1 month and 3 months post-therapy. Soft tissue parameters Soft tissue changes were evaluated by measuring Reduction in Interproximal probing pocket depth, at base line, 30 day and 3 months Gain in Interproximal Clinical attachment level. at base line, 30 day and 3 months The measurement were taken using UNC -15 probe and fixed reference point (occlusal stent). Interproximal Probing pocket depth was recorded preoperative by noting the distance from Gingival margin to the base of pocket. Probing pocket depth = {Reference point (RP) to base of pocket (BOP) Reference point (RP) to Gingival margin (GM)} Probing depth measurement was done from gingival margin to the base of pocket using UNC-15 graduated probe at baseline, 30 days, and 3 months post-therapy. Clinical attachment level = {Reference point (RP) to base of pocket (BOP) Reference point (RP) to Cemento-enamel junction (CEJ)} Microbiological study for total colony count Anaerobic culture was done to compare the total colony forming unit before and after the treatment. For the collection of subgingival samples the selected sites were isolated using cotton rolls. Sterile absorbable paper points (size 45 75) were used for the collection of plaque samples. Total Anaerobic bacterial count was measured by colony counter. ISSN (Online): X; (Print): ICV (2015): Volume 4 Issue 5 May
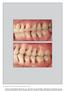
3 Tetracycline fibers (Periodontal Plus AB) The product contains 25 mg pure fibrilar collagen, containing approximately 2 mg of evenly impregnated tetracycline HCl. Periodontal Plus AB Fibers are available in strips containing four individually packed and separable sterile product packs. Just before placement, fibers was soaked with saline in a sterile dappen dish. Soaked fibers was placed at the prepared site and gently pushed inside the pocket, so that the material fills the depths and curves of the pocket. The site was sealed with coe-pak to prevent ingress of oral fluids and to prevent the dislodgement of fiber. RESULT As showen in table -1, at base line plaque score showed no statistically difference (p = 0.101) between control and test group. Also after 30 days there was no significant difference in the mean plaque score between test and control group (p = 0.749). However at 90 days, there was a significant difference between test and control group (p < 0.001), with greater improvement in the test group. At base line gingival index score showed no statistically difference (p = 0.101) between control and test group. After 30 days there was significant difference in the mean plaque score between test and control group (p = 0.106). However at 90 days, there was a greater significant difference between test and control group (p < 0.006), with greater improvement in the test group. At base line mean sulcular bleeding score showed statistically difference (p < 0.001) between control and test group with the test group showing more mean sulcular bleeding score. However After 30 days there was not much significant difference in the mean sulcular bleeding score between test and control group (p = 0.106). At 90 days, there was a greater significant difference between test and control group (p < 0.001), with greater improvement in the test group. Inter group Comparison of mean values for test and control for colony forming units (log CFU showed no statistically significant difference between the control group and test group (p > 0.001) for total anaerobic colony count at base line. However After 30 days there was significant difference in the total anaerobic colony count between test and control group (p < 0.001) with more reduction for total colony count seen in test group. At 90 days,there was an increase in total colony count for both the group, but still lesser than at the base line colony count and there was a greater significant difference between test and control group (p < 0.001), with much less rebound in the test group.(p < 0.001). At base line mean probing depth showed statistically difference (p = 0.001) between control and test group with the test group showing more mean probing depth. Mean probing depth for the control group was 6.69 ± 0.63, whereas for test group it was 6.94 ± However After 30 days there was much significant difference in the mean probing depth between test and control group (p = 0.106). At 30 days the mean probing depth for test group was reduced to 4.51 ± 0.56, in comparison to control group,in which it is reduced to 5.66 ± At 90 days, there was a greater significant difference between test and control group (p < 0.001), with greater Figure-1: Test site Measuring of probing pocket depth and CAL using acrylic stent at base line. Figure-2: Placement of Periodontal Plus AB at test site Figure-3: Measuring of probing pocket depth and CAL using acrylic stent at 3 months. 90 th day (mean ± sd) 30 th day (mean ± sd) Base line (mean ± sd) Control Test p- value Control Test p- value Control Test p- value Plaque index (PI) 2.63 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.53 < 0.001; sig Gingival index (GI) 2.62 ± ± ± ± ± ± ; sig Sulcuar bleeding index (SBI) 3.47 ± ± 0.34 <0.001; sig 2.15 ± ± ± ± 0.37 < 0.001; sig Colony forming unit (CFUs) 7.61 ± ± ± ± 0.21 <0.001; sig 7.46 ± ± 0.13 <0.001; sig Probing depth (PD) 6.69 ± ± ± ±.56 < 0.001; sig 4.71 ± ± 0.61 < 0.001; sig Clinical attachment loss (CAL) 6.46 ± ± ± ± ± ± 0.38 <0.001; sig Table-1: Intergroup comparison for test and control at base line, 30th day, and 90th day 1000 Volume 4 Issue 5 May 2017 ICV (2015): ISSN (Online): X; (Print):
4 improvement in the test group. Mean probing depth for the test group gets reduced to 3.51 ± 0.61 in comparison to control group in which it was reduced to 4,71 ± At base line clinical attachment level for control group was 6.46 ± 0.89, and for test group it was 6.66 ± 0.73, which was statistically significant p < On 30 day clinical attachment level changes to 5.46 ± 0.89 for control group and 4.77 ± 0.94 for the test group. So the gain in clinical attachment level from base line to 30 day was 1.00 ± 0.24 for control group, whereas the gain in clinical attachment level for the test group was 1.89 ± 0.8, which was statistically significant p < On 90 th day, clinical attachment level changes to 4.46 ± 0.89 for control group and 3.17 ± 0.38 for the test group. So the gain in clinical attachment level from base line to 90 days was 2.00 ± 0.24 for the control group, whereas the gain in clinical attachment level for the test group was 3.49 ± 0.66, which was highly significant; p < in comparison to control group. DISCUSSION The presence of bacterial plaque represents the principal etiological factor involved in the initiation and progression of periodontitis. These bacterial plaque or biofilms are difficult therapeutic targets as they are not easily disrupted. 12 In a non sterile environment such as the mouth, it is virtually impossible to completely prevent their formation. 13 Essential goal of current periodontal therapy is successful management of the suspected bacterial pathogens to the extent that destruction of the periodontium is arrested. A number of different nonsurgical and surgical therapies have been successful in achieving this goal. Mechanical debridement with or without surgical manipulations, to disrupt the subgingival flora and to provide clean, smooth, and biological compatible roots surfaces, had been the therapy to treat periodontal diseases till the early 1970s. Mechanical therapy may however fail to eliminate the pathogenic bacteria because of their location within gingival tissues or in other areas inaccessible to periodontal instruments. 14 Most widely used local drug delivery system reports in periodontal literature are of Tetracycline as reported by Goodson, 7 Metronidazole by Addy et al. 15 Chlorhexidine by Addy et al. and Ofloxacin by Hoffler et al. 16 In the present study, collagen-impregnated tetracycline fibers was used which was found to be advantageous among other drugs. Tetracyclines are superior to other antibiotics as they are the only class of antibiotics which has the ability for retention to the tooth cementum and soft tissues. They are the only antibiotics, which can achieve higher levels of gingival fluid concentrations than serum levels. 17 Tetracycline has also been to inhibit collagenase activity, collagen degradation and bone resorption as reported by Golub et al. 18 The substantivity of tetracyclines have proved to be effective against gram-positive and gramnegative anaerobic microflora associated with chronic adult periodontitis. They exert their antimicrobial effect by inhibiting protein synthesis. 5 Maiden et al. 19 reported that in vitro testing has shown probable periodontal pathogens including P. gingivalis, Fusobacterium nucleatum, P. intermedia, Eikenella corrodens, Wolinella recta, and A. actinomycetemcomitans are susceptible to local Tetracycline concentrations achieved in periodontal pocket with a controlled release device. Therefore, tetracycline is suitable to local delivery and as adjuncts to mechanical therapy in management of periodontal disease. According to Betty N.A. Vandekerckhove, 22 treatment with tetracycline-impregnated fibers converted refractory sites to stable areas. The ability of locally delivered tetracycline to stop recurrent disease may be related not only to its antibacterial effect, 23 but also to its secondary effects on the collagen breakdown. 24 It also enhances Fibroblast attachment to root structure. 25 In addition, there is a substantivity of tetracycline through its binding to dentin, as proven in vitro and in vivo. The present study was designated to access the clinical efficiency of tetracycline-impregnated bio-degradable collagen fibers, by evaluating the changes in plaque index and gingival index, sulcular bleeding index, changes in probing pocket depth and clinical attachment level. Also the changes in total anaerobic colony count was evaluated over a period of 3 months. In the present study, statistically significant reduction in plaque score and gingival index score from baseline to 3 months for both treatment group (P<0.001) was observed. However better result in the reduction in plaque score and gingival index score was observed in the test group. This might be attributed to the enforced oral hygiene instruction or Howthorne phenomenon, 26 which have played a role in the reduction of the plaque score. Similar observations were made by Minabe et al. 27 Heijl et al., 28 Mehta et al.,[5] and Friesen et al. 29 who found low levels of plaque index scores and gingival index score. The sulcular bleeding index also showed statistically significant reduction from base line to 30 days and at 3 months in both the control and test group, however in comparison to control group, test group showed more statistically significant reduction in sulcular bleeding index. Our study is in accordance with the study conducted by Minabe and Nishimura et al 27, Heijl and Dahlen et al 28, Goodson JM and Armitage GC et al 30, Tonetti and Cortenilli et al 31, Pini Prato et al 32, D. F Kinane et al 20, Newman, Korman, Doherthy et al 4 etc. Decrease in bleeding on probing could be attributed to the fact that these local drug delivery system maintain adequate antimicrobial drug level over a sufficient period of time. This sustained concentration of tetracyclines at very high level, greater than 1.6 mg/ml in the crevicular fluid over 10 days Our study showed, a highly statistical significant (P< 0.001) reduction in probing depth from baseline to 3 months in both control and test group. On comparison between the two groups, the probing depth reduction at all time points was greater in the scaling plus tetracycline fiber group than the scaling and root planning alone group, which was statistically significant (P<0.01 The results are in accordance with the findings of Goodson et al., 11 Minabe et al. 16 Newman et al. 4 Tonetti et al. 24 and Mehta et al. 5 Minabe M et al 14 observed greater reduction in probing pocket depth in tetracycline plus SRP group. Our study reports a significant gain in clinical attachment level from baseline to 3 months in both the treated sites (P<0.001); On comparison between the two group, the gain in CAL at all time points was significantly greater in the scaling plus tetracycline fiber group than the scaling and root planing alone group (P<0.01). From base line to 3 months, mean gain in CAL was 2.45 ± 0.66 in the test group, whereas in the control group the mean gain in CAL was 1.35 ± The percentage gain in the case of test group was 36.78% whereas in the case of control ISSN (Online): X; (Print): ICV (2015): Volume 4 Issue 5 May
5 group it was 20.89%, from base line to 3 months. Our study was in accordance to the study conducted by Goodson et al. 23 Heijl et al. 13 Minabe et al., 22 Newman et al., 4 Drisko et al., 5 and Kinane and Radvar. 20 Minabe et al. found gain of clinical attachment level around 2 mm, and suggested that the local application of antibiotic using a local drug delivery in combination with root debridement may contribute to clinical attachment gain. The reduction in probing depth and gain in CAL can be attributed to the fact that local tetracycline therapy and SRP causes the arrest of disease progression by altering the subgingival microbiota and to create a more healthy sub-gingival environment. In addition to the antimicrobial effects, it is possible that tetracycline fiber may have effects on the local periodontal environment. These effects may include chemical conditioning of the root surface. This concept is supported by the results of Southard et al. 10 In an experimental study with monkeys, Blomlof et al. 12 observed a New attachment on the chemically conditioned cementum surfaces. In our study, the high concentrations of tetracycline HCl over 10 days allowed clinically normal healing, achieving cliical attachment gains similar to scaling and root planning or even better than scaling and root planing. Another explanation may be that the tetracycline fiber affects the host response 15 via the anticollagenase activity of tetracycline. Terranova et al. 22 reported that tetracycline treatment of root surfaces markedly enhanced binding of fibronectin and fibroblasts. It was also noted that preconditioning of root surfaces with tetracycline HCl enhanced the migration of periodontal ligament cells. Present study reports sites receiving SRP + Periodontal Plus AB (tetracycline) and sites receiving SRP alone exhibited similar total colony count at base line. At 21 day post treatment there was a statistically significant reduction in the total anaerobic colony count in both the test and control group; p < 0.001; with more statistically significant reduction observed in the test group. From base line to 21 days, the mean reduction in total anaerobic colony count was (3.78 ± 0.21) in the case of test group, whereas it was (1.04 ± 0.10) for the control group. More statistically significant reduction observed in the test group at 21 days, compared with the control for total anaerobic colony count, proves the efficacy of the drug tetracycline fiber as an antimicrobial agent. However the total anaerobic colony count showed a significant increase from 21 days to 3 months in both the groups, but less significant increase in total count in the test group. CONCLUSION Within the limits of this study and on the basis of the clinical and microbiological parameters, it can be concluded that tetracycline fiber therapy enhances the benefits of SRP in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. There was greater improvement in all the clinical signs of priodontitis and also significant reduction in anaerobic colony count as compared to scaling and root planing alone. The adjunctive benefit of the fiber was maintained for 3 months following therapy without additional fiber treatment. SRP and locally delivered tetracycline therapy are completely different treatment modalities that work by different mechanisms. Locally delivered tetracycline therapy has a specific purpose, to control localized infection, whereas scaling is utilized to remove calculus and other deposits. Hence, a combination of scaling and local drug delivery results in added benefits in the control of periodontal disease. REFERENCES 1. Helderman WH. Microbial etiology of Periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1981;8: Van Winkelhoff AJ, Rams TE, Slots J. Systemic antibiotics in periodontics. Periodontology ;10: Marc Quirynen, Wim Teughels, Marc De Soete and Daniele Van Steenberghe Topical antiseptics and antibiotics in the initial therapy of chronic periodontitis. Microbiological aspects perio ;28: Newman MG, Kornman KS, Doherty FM et al. A 6-Month Multi-Center Evaluation of Adjunctive Tetracycline Fiber Therapy Used in Conjunction With Scaling and Root Planing in Maintenance Patients: Clinical Results. J Periodontol. 1994;65: Sadaf N, Anoop B, Dakshina B et al. Evaluation of efficacy of tetracycline fibers in conjunction with scaling and root planing in patients with chronic periodontitis. J Ind Soc Periodontol. 2012;16: Pitcher GR, Newman HN, Strahan JD. As referred in effects of subgingival irrigation on Periodontal Status. J Periodontol. 1987;58: Goodson JM, Haffajee A, Socransky SS. Periodontal therapy by local delivery of tetracycline. J Clin Periodontol. 1979;6: Cattabriga M, Pedrazzoli V, Cattabriga A, Pannuti E, Trapani M, Verrocchi GC et al. Tetracycline fiber used alone or with scaling and root planing in periodontal maintenance patients: Clinical results. Quintessence International. 1996; 27: Hanes PJ, Purvis JP. Local anti-infective therapy: Pharmacological agents. A Systematic Review. Ann Periodontal. 2003;8: Baker PJ, Evans RT, Coburn RA, Genco RJ. Tetracycline and its derivatives strongly bind to and are released from the tooth surface in active form. J Periodontol. 1983;54: Sachdeva S, Agarwal V et al. Evaluation of commercially available biodegradable tetracycline fiber therapy in chronic periodontitis. J Ind Soc Periodontol. 2011;15: Listagarten M.A., Lindhe J., Hellden L. Effects of tetracycline and/or scaling on human periodontal disease, Clinical, microbiological and histopathological observation. J Clin Periodontol. 1978;5: Lindhe J., Heijl L., Goodson J.M. et al. Local tetracycline delivery using hollow fiber devices in periodontal therapy. J Clin Periodontol. 1979;6: Williams B.L, Osterberg S.K.A et al. Long term effect of tetracycline on subgingival microflora in chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol. 1979; 6: Addy M. Handley R. Newman H. N et al. The development and in vitro evaluation of acrylic strips and dialysis tubing for local drug delivery. J Periodontol. 1982;53: Kornman K.S, Karl E.H. et al. The effect of long term low dose tetracycline therapy on the subgingival microflora in refractory adult periodontitis. J Periodontol. 1999;53: Goodson J.M, Holborow D., Hogan P. et al. Monolithic tetracycline containing fibers for controlled delivery to periodontal pockets. J Periodontol. 1983: Lindhe J., Liljenberg B., Adielson et al Local tetracycline delivery using hollow fiber devices in periodontal therapy Volume 4 Issue 5 May 2017 ICV (2015): ISSN (Online): X; (Print):
6 J Clin Periodontol. 1979;6: Lundstrom A., Johansson L.A. Hamp S.E. et al. Effect of combined systemic antimicrobial therapy and mechanical plaque control in patients with recurrent periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol. 1984;11: Addy M. Langeroudi M. Comparison of the emmediate effects on the subgingival microflora of acrylic strips containing 40% chlorohexidine, metronidazole, or tetracycline. J Clin Periodontol. 1984; Goodson J. M. Offenbacher T S., Periodontal Disease Treatment by Local Drug Delivery. J. Periodontol. 1985;5: Mabri T.W., Yukna R.A. et al. Freezed dried bone allograft combined with tetracycline in the treatment of juvenile periodontitis. J Periodontol. 1985;56: Moskow B.S. Repair of an extensive periodontal defect after tetracycline administration. J Periodontol 1986;57: Christenson L. Zambon J.J et al Topical application of tetracycline HCL in human periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 1993;20: Terranova V.P., Franzetti L.C. et al. A biochemical approach to periodontal regeneration tetracycline treatment of dentin promotes fibroblast adhesion and growth. J Periodontal Res. 1986;21: Source of Support: Nil; Conflict of Interest: None Submitted: ; Accepted: ; Published: ISSN (Online): X; (Print): ICV (2015): Volume 4 Issue 5 May
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
JMSCR Volume 2 Issue 7 Page July
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 1.1147 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Clinical Evaluation of Locally Delivered 10% Doxycycline Hyclate Gel as An Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in the Treatment of Chronic
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 1.1147 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Clinical Evaluation of Locally Delivered 10% Doxycycline Hyclate Gel as An Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in the Treatment of Chronic
Journal of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
 Comparison of Systemic Ciprofloxacin in Elimination of A.a from Active Sites with Combination of Metronidzole and Amoxicillin in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled
Comparison of Systemic Ciprofloxacin in Elimination of A.a from Active Sites with Combination of Metronidzole and Amoxicillin in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder
 ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
Periodontitis is characterized by
 Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Povidone Iodine vs Tetracycline Fibers- To Analyse the Therapeutic Effect Suchetha A 1, Garg A 2, Lakshmi P 3,Sapna N 4, Mundinamane DB 5,
Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Povidone Iodine vs Tetracycline Fibers- To Analyse the Therapeutic Effect Suchetha A 1, Garg A 2, Lakshmi P 3,Sapna N 4, Mundinamane DB 5,
Research Effect of tetracycline HCL (periodontal plus AB) on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans levels in chronic periodontitis
 ISSN 2058-7813 Research Effect of tetracycline HCL (periodontal plus AB) on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans levels in chronic periodontitis Sneha Kataria 1, Kabbur Thippanna Chandrashekar 1*, Rohit
ISSN 2058-7813 Research Effect of tetracycline HCL (periodontal plus AB) on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans levels in chronic periodontitis Sneha Kataria 1, Kabbur Thippanna Chandrashekar 1*, Rohit
Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
Research Center, India. 2 Professor And Dean, Department Of Periodontics And Implantology, Hitkarini Dental College And
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 100-107 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Tetracycline Hydrochloride
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 100-107 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Tetracycline Hydrochloride
Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS
 Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS Guidelines for use of antibiotics in periodontal therapy 1. The clinical
Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS Guidelines for use of antibiotics in periodontal therapy 1. The clinical
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient. Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club
 Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Chlorhexidine chip and tetracycline fibers as adjunct to scaling and root planing A clinical study
 Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2009 - Volume 8, Number 4 Chlorhexidine chip and tetracycline fibers as adjunct to scaling and root planing A clinical study Ruchi Srivastava 1 ; Pushpendra
Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2009 - Volume 8, Number 4 Chlorhexidine chip and tetracycline fibers as adjunct to scaling and root planing A clinical study Ruchi Srivastava 1 ; Pushpendra
Current Chemotherapeutic Modalities Available in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease
 Current Chemotherapeutic Modalities Available in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Paul Tolmie, D.D.S. Kenneth Rasenberger, D.D.S. Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. The Changing Views of Plaque and Periodontal
Current Chemotherapeutic Modalities Available in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Paul Tolmie, D.D.S. Kenneth Rasenberger, D.D.S. Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. The Changing Views of Plaque and Periodontal
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment. Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD
 TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
Periodontal Regeneration
 Periodontal Regeneration Regeneration The most ideal treatment Attempts to recreate the tissues destroyed by periodontitis Cement, bone and ligament Reduces the risk for recession and sensitivity (could
Periodontal Regeneration Regeneration The most ideal treatment Attempts to recreate the tissues destroyed by periodontitis Cement, bone and ligament Reduces the risk for recession and sensitivity (could
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
Original Research. which are considered important in causation of gingivitis and periodontitis. 1,2
 Tetracycline hydrochloride and spiramycin sub gingival irrigation in chronic Received: 20 th January 2015 Accepted: 15 th April 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research
Tetracycline hydrochloride and spiramycin sub gingival irrigation in chronic Received: 20 th January 2015 Accepted: 15 th April 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research
Please visit the C.E. Pavilion to validate your course attendance Or If There s a Line Go cdapresents.com
 UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers
 http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
Role of antibiotics in periodontal therapy
 BANGLADESH JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Volume-8 No. 4; October 2009 Review article Abstract Manas D 1, Srinivas SR 2, Jithendra KD 3 Loeshe in 1976 propounded the Specific Plaque Hypothesis and efforts
BANGLADESH JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Volume-8 No. 4; October 2009 Review article Abstract Manas D 1, Srinivas SR 2, Jithendra KD 3 Loeshe in 1976 propounded the Specific Plaque Hypothesis and efforts
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters
 Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Reimbursement Guide. ATRIDOX Insurance Reimbursement Guide for the submission of insurance claims
 Reimbursement Guide Insurance Reimbursement Guide f the submission of insurance claims General reimbursement & submission infmation Reimbursement infmation Submission of insurance claims Pre-determination
Reimbursement Guide Insurance Reimbursement Guide f the submission of insurance claims General reimbursement & submission infmation Reimbursement infmation Submission of insurance claims Pre-determination
Initial Therapy. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS. Oral sulcular epithelium. Oral. epithelium. Junctional. epithelium. Connective tissue.
 Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS
 THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different...
![2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different... 2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different...](/thumbs/89/99584051.jpg) 2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different... Risks associated with Periodontal disease 1 Diabetes Diabetic patients are more likely to develop periodontal disease, which in turn
2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different... Risks associated with Periodontal disease 1 Diabetes Diabetic patients are more likely to develop periodontal disease, which in turn
The dentogingival junction to the
 Volume 79 Number 10 RedefiningtheBiologicWidthinSevere, Generalized, Chronic Periodontitis: Implications for Therapy M. John Novak,* Huda M. Albather, and John M. Close Background: Previous studies demonstrated
Volume 79 Number 10 RedefiningtheBiologicWidthinSevere, Generalized, Chronic Periodontitis: Implications for Therapy M. John Novak,* Huda M. Albather, and John M. Close Background: Previous studies demonstrated
Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis Takeo Fujii, Pao-Li Wang, Yoichiro Hosokawa, Shinichi Shirai, Atsumu Tamura, Kazuhiro
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis Takeo Fujii, Pao-Li Wang, Yoichiro Hosokawa, Shinichi Shirai, Atsumu Tamura, Kazuhiro
- BANA Hydrolysis as a Comparative Tool in the Evaluation of Amoxicillin and Azithromycin in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article - BANA Hydrolysis as a Comparative Tool in the Evaluation of Amoxicillin and Azithromycin in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis Rosaiah
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article - BANA Hydrolysis as a Comparative Tool in the Evaluation of Amoxicillin and Azithromycin in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis Rosaiah
The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study)
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study) To cite this article:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study) To cite this article:
Periodontist-Dental Hygienist Collaboration in Periodontal Care for Chronic Periodontitis: An 11-year Case Report
 ull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 177 186 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0039 Periodontist-Dental Hygienist Collaboration in Periodontal Care for Chronic Periodontitis: An 11-year Case Report
ull Tokyo Dent Coll (2017) 58(3): 177 186 Case Report doi:10.2209/tdcpublication.2016-0039 Periodontist-Dental Hygienist Collaboration in Periodontal Care for Chronic Periodontitis: An 11-year Case Report
Volume 2 Issue
 Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study.
 ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study. Dr. Yashika Jain Senior Lecturer, Institution: SGT Dental College & Hospital,
ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study. Dr. Yashika Jain Senior Lecturer, Institution: SGT Dental College & Hospital,
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the. Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System
 Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Surgical Procedure in Guided Tissue Regeneration with the Inion GTR Biodegradable Membrane System 1 Introduction This presentation familiarizes you with the basic steps how to use the Inion GTR membrane
Periodontal Treatment Protocol Department of Orthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester
 Periodontal Treatment Protocol Department of Orthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester 1. Periodontal Assessment Signs of perio disease: - Gingivae become red/purple - Gingivae
Periodontal Treatment Protocol Department of Orthodontics and Restorative Dentistry, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester 1. Periodontal Assessment Signs of perio disease: - Gingivae become red/purple - Gingivae
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT HESKA PERIOceutic Gel 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each unit dose contains: 2.1 Active substance Doxycycline
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT HESKA PERIOceutic Gel 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each unit dose contains: 2.1 Active substance Doxycycline
Materials and Methods: Literature review and Authors opinion.
 Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic
 1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
Microbiota and Oral Disease Prof. Dennis Cvitkovitch
 1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Overview of Periodontics for the General Practicioner
 Overview of Periodontics for the General Practicioner Nashville Area Dental Continuing Education August 27, 2008 Phillip D. Woods, DDS, MPH Commander, USPHS BOP National Periodontal Consultant Diplomate,
Overview of Periodontics for the General Practicioner Nashville Area Dental Continuing Education August 27, 2008 Phillip D. Woods, DDS, MPH Commander, USPHS BOP National Periodontal Consultant Diplomate,
NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS
 NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS March 30, 2015 Dear Oxyfresh Professional: We are thrilled to share with you the exciting results of a NEW 12-month, double blind clinical study published in the International
NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS March 30, 2015 Dear Oxyfresh Professional: We are thrilled to share with you the exciting results of a NEW 12-month, double blind clinical study published in the International
Periodontal (Gum) Disease
 Periodontal (Gum) Disease If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you re not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases
Periodontal (Gum) Disease If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you re not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases
Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing I. Clinical findings
 J Clin Periodontol 24; 31: 132 14 Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 24 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing I. Clinical findings D. A. Apatzidou
J Clin Periodontol 24; 31: 132 14 Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 24 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing I. Clinical findings D. A. Apatzidou
Implementing Hygiene Systems for Increased Productivity
 Implementing Hygiene Systems for Increased Productivity Rachel Wall, RDH, BS Phone 704-541-0995 Fax 866-645-4469 Rachel@inspiredhygiene.com www.inspiredhygiene.c Copyright 2014. Revised 2017 Inspired Hygiene
Implementing Hygiene Systems for Increased Productivity Rachel Wall, RDH, BS Phone 704-541-0995 Fax 866-645-4469 Rachel@inspiredhygiene.com www.inspiredhygiene.c Copyright 2014. Revised 2017 Inspired Hygiene
Antimicrobials in treatment of periodontal disease -A review
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 4, Issue 5 (Jan.- Feb. 2013), PP 19-23 Antimicrobials in treatment of periodontal disease -A review
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 4, Issue 5 (Jan.- Feb. 2013), PP 19-23 Antimicrobials in treatment of periodontal disease -A review
The ultimate goal in periodontal
 Volume 71 Number 4 Interleukin-1 Gene Polymorphisms and Long-Term Stability Following Guided Tissue Regeneration Therapy* Massimo De Sanctis and Giovanni Zucchelli Background: Specific interleukin (IL)-1
Volume 71 Number 4 Interleukin-1 Gene Polymorphisms and Long-Term Stability Following Guided Tissue Regeneration Therapy* Massimo De Sanctis and Giovanni Zucchelli Background: Specific interleukin (IL)-1
Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018
 Dental Policy Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: 04-901 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018 Description This document addresses periodontal maintenance. Note:
Dental Policy Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: 04-901 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018 Description This document addresses periodontal maintenance. Note:
Research Article. Chlorhexidine varnish: An attempt to vanish moderate periodontitis
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(1):339-345 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Chlorhexidine varnish: An attempt to vanish moderate
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(1):339-345 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Chlorhexidine varnish: An attempt to vanish moderate
Home care. Home care. Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice. Professional care. BSP Roadshows 2008/9
 3. Periodontal Treatment BSP Roadshows 2008/9 Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice 3. Periodontal Treatment Phil Ower www.periocourses.co.uk Why is it so important? Oral hygiene methods what s
3. Periodontal Treatment BSP Roadshows 2008/9 Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice 3. Periodontal Treatment Phil Ower www.periocourses.co.uk Why is it so important? Oral hygiene methods what s
Department of Oral Surgery, Heinrich Heine University, D Düsseldorf, Germany.
 Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Bone Levels - From Hypothesis To Facts
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 6, Issue 5 (May.- Jun. 2013), PP 19-23 Bone Levels - From Hypothesis To Facts Savitha B 1, Priyanka
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 6, Issue 5 (May.- Jun. 2013), PP 19-23 Bone Levels - From Hypothesis To Facts Savitha B 1, Priyanka
Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease
 Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Mr P.Renton-Harper Specialist in Periodontics prh@perio.co.uk www.perio.co.uk Periodontal Disease A bacterial infection in a susceptible
Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Mr P.Renton-Harper Specialist in Periodontics prh@perio.co.uk www.perio.co.uk Periodontal Disease A bacterial infection in a susceptible
Periodontal Microbiology (Dental Plaque)
 Periodontal Microbiology (Dental Plaque) Dental plaque Dental plaque is soft deposits that form the biofilm adhering to the tooth surface of other hard surface in the oral cavity, including removable and
Periodontal Microbiology (Dental Plaque) Dental plaque Dental plaque is soft deposits that form the biofilm adhering to the tooth surface of other hard surface in the oral cavity, including removable and
IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE Module 5 Treatment Planning
 IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE Module 5 Treatment Planning Dental Hygiene Solutions Module 5 Dentalhygiene.solutions 1 Please take time to view the Documentation Bonus Video Module 5 Point Clinical Philosophy 1.
IMPLEMENTATION GUIDE Module 5 Treatment Planning Dental Hygiene Solutions Module 5 Dentalhygiene.solutions 1 Please take time to view the Documentation Bonus Video Module 5 Point Clinical Philosophy 1.
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Periodontal Microbiology. Dr. Csifó-Nagy Boróka Department of Periodontology Semmelweis University
 Periodontal Microbiology Dr. Csifó-Nagy Boróka Department of Periodontology Semmelweis University 2016 Topics introduction, historical perspective pathogens of destructive periodontal diseases microbial
Periodontal Microbiology Dr. Csifó-Nagy Boróka Department of Periodontology Semmelweis University 2016 Topics introduction, historical perspective pathogens of destructive periodontal diseases microbial
Khosropanah H., et al J Dent Shiraz Univ Med Scien June; 13(2): 44-48
 Original Article The Clinical Effectiveness of Subgingival Irrigation with Povidone-Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide in Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Periodontitis Khosropanah H. a, Koohpeima F.
Original Article The Clinical Effectiveness of Subgingival Irrigation with Povidone-Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide in Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Periodontitis Khosropanah H. a, Koohpeima F.
Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2013) 54(4): 243 250 Case Report Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report Akiyo Komiya-Ito,
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2013) 54(4): 243 250 Case Report Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report Akiyo Komiya-Ito,
STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT. Cynthia Fong, RDH, MS
 STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 9:00 a.m. 12 Noon STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course provides
STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 9:00 a.m. 12 Noon STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course provides
Antimicrobial Treatment for Advanced Periodontal Disease
 Antimicrobial Treatment for Advanced Periodontal Disease James S. Kohner, DDS DISCLOSURES December 15, 2011 Editor's Note: This author's case report is based on the work of Jorgen Slots, DDS, DMD, PhD,
Antimicrobial Treatment for Advanced Periodontal Disease James S. Kohner, DDS DISCLOSURES December 15, 2011 Editor's Note: This author's case report is based on the work of Jorgen Slots, DDS, DMD, PhD,
History Why we need to classify?
 Aiming to Cover: MSc ADVANCED GENERAL DENTAL PRACTICE Classification & Recognition of Periodontal Disease Classification of periodontal disease Recognition of Disease DR MIKE MILWARD BDS (Birmingham),
Aiming to Cover: MSc ADVANCED GENERAL DENTAL PRACTICE Classification & Recognition of Periodontal Disease Classification of periodontal disease Recognition of Disease DR MIKE MILWARD BDS (Birmingham),
Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases. As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
 Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
JSS Medical and Dental College and Hospital, JSS University, Mysore, India *Author for Correspondence
 CLINICAL, MICROBIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR STUDY OF PORPHYROMONAS GINGIVALIS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS *Mayuri Vajawat 1, Vijay Kumar 2, K.G. Rajeshwari 3 and P.C. Deepika 4 1&4 Department of
CLINICAL, MICROBIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR STUDY OF PORPHYROMONAS GINGIVALIS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS *Mayuri Vajawat 1, Vijay Kumar 2, K.G. Rajeshwari 3 and P.C. Deepika 4 1&4 Department of
The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT The Treatment of Gingival Recession Associated with Deep Corono-Radicular Abrasions (CEJ step) a Case Series Giovanpaolo Pini-Prato, Carlo Baldi, Roberto Rotundo, Debora Franceschi,
Objectives: What s Your Therapeutic Goal?
 Objectives: List differences Magnetorestrictive scalers vs Piezoelectric Understand role of ultrasonic scaling and biofilm management Compare ultrasonic scaling versus hand instrumentation List advantages
Objectives: List differences Magnetorestrictive scalers vs Piezoelectric Understand role of ultrasonic scaling and biofilm management Compare ultrasonic scaling versus hand instrumentation List advantages
Influence of Smoking on Long-Term Clinical Results of Intrabony Defects Treated With Regenerative Therapy
 Influence of Smoking on Long-Term Clinical Results of Intrabony Defects Treated With Regenerative Therapy Paul S. Rosen,* Manuel H. Marks? and Mark A. Reynolds* 1159 This retrospective study compares the
Influence of Smoking on Long-Term Clinical Results of Intrabony Defects Treated With Regenerative Therapy Paul S. Rosen,* Manuel H. Marks? and Mark A. Reynolds* 1159 This retrospective study compares the
The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment
 The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment Authors_Prof. Tzi Kang Peng, Taiwan & Prof. Georgi Tomov, Bulgaria _Introduction With oral implantology experience its Renaissance, the
The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment Authors_Prof. Tzi Kang Peng, Taiwan & Prof. Georgi Tomov, Bulgaria _Introduction With oral implantology experience its Renaissance, the
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
Systemic antibiotics in the treatment of periodontal disease
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 28, 2002, 106 176 Copyright C Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 ISSN 0906-6713 Systemic antibiotics in the treatment of periodontal disease
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 28, 2002, 106 176 Copyright C Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 ISSN 0906-6713 Systemic antibiotics in the treatment of periodontal disease
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Case Report Treatment strategy for guided tissue regeneration in various class II furcation defect: Case series Pushpendra Kumar Verma 1, Ruchi Srivastava 1, K. K. Gupta 2, T. P.
Dental Research Journal Case Report Treatment strategy for guided tissue regeneration in various class II furcation defect: Case series Pushpendra Kumar Verma 1, Ruchi Srivastava 1, K. K. Gupta 2, T. P.
Paula Matesanz-Pérez 1, Elena Figuero 1, Antonio Bascones-Martínez 1,3, Mariano Sanz 2 and David Herrera 2 1 Graduate Periodontology, Faculty of
 J Clin Periodontol 2013; 40: 227 241 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12026 A systematic review on the effects of local antimicrobials as adjuncts to subgingival debridement, compared with subgingival debridement alone,
J Clin Periodontol 2013; 40: 227 241 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12026 A systematic review on the effects of local antimicrobials as adjuncts to subgingival debridement, compared with subgingival debridement alone,
Have you been diag nosed with PERIODONTAL DISEASE
 Have you been diag nosed with PERIODONTAL DISEASE What you need to know about Periodontal Disease? Periodontal disease (also called gum disease) is a chronic, bacterial infection of the gums that can destroy
Have you been diag nosed with PERIODONTAL DISEASE What you need to know about Periodontal Disease? Periodontal disease (also called gum disease) is a chronic, bacterial infection of the gums that can destroy
FACULTY OF HEALTH SCIENCES INSTITUTE OF CLINICAL DENTISTRY
 Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
Treatment of juvenile periodontitis with microbiologically modulated periodontal therapy (Keyes Technique)
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright @1985 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 7 Number 4 Treatment of juvenile periodontitis with microbiologically modulated periodontal therapy (Keyes Technique)
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright @1985 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 7 Number 4 Treatment of juvenile periodontitis with microbiologically modulated periodontal therapy (Keyes Technique)
-70% Visible plaque index(vpi) -60% Bleeding on probing (BOP) -10% Probing depth (PD)
 Deep studies carried out by the Second University of Naples show the effectiveness of SoWash System and its accessories. After only 14 days use of SoWash System: -70% Visible plaque index(vpi) -60% Bleeding
Deep studies carried out by the Second University of Naples show the effectiveness of SoWash System and its accessories. After only 14 days use of SoWash System: -70% Visible plaque index(vpi) -60% Bleeding
Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports
 0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
ELIMINATE POCKETS. Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease
 ELIMINATE POCKETS Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease CONSEQUENTLY Periodontal pockets should be eliminated
ELIMINATE POCKETS Periodontal pocket is the consequence of periodontal infection But also a major risk factor for the further progression of disease CONSEQUENTLY Periodontal pockets should be eliminated
Locally delivered doxycycline improves the healing following non-surgical periodontal therapy in smokers
 J Clin Periodontol 4; : 589 595 doi:./j.-5x.4.54.x Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 4 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Locally delivered doxycycline improves the healing following non-surgical periodontal
J Clin Periodontol 4; : 589 595 doi:./j.-5x.4.54.x Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 4 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Locally delivered doxycycline improves the healing following non-surgical periodontal
Transient Tooth Discoloration After Periodontal Instrumentation of an Aggressive Periodontitis. A Case Report
 Transient Tooth Discoloration After Periodontal Instrumentation of an Aggressive Periodontitis. A Case Report Julio C Rincon A*, Zahida Oakley*, Paul Abbott *Department of Periodontology and Implant Dentistry.
Transient Tooth Discoloration After Periodontal Instrumentation of an Aggressive Periodontitis. A Case Report Julio C Rincon A*, Zahida Oakley*, Paul Abbott *Department of Periodontology and Implant Dentistry.
1 PERIODONTIUM: THE TOOTH SUPPORTING STRUCTURES 1 2 MICROSCOPIC ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM 21
 Contributors xiii Preface for Course Instructors xv Acknowledgments xviii PART 1: THE PERIODONTIUM IN HEALTH 1 PERIODONTIUM: THE TOOTH SUPPORTING STRUCTURES 1 Tissues of the periodontium 3 Nerve supply,
Contributors xiii Preface for Course Instructors xv Acknowledgments xviii PART 1: THE PERIODONTIUM IN HEALTH 1 PERIODONTIUM: THE TOOTH SUPPORTING STRUCTURES 1 Tissues of the periodontium 3 Nerve supply,
An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis
 CLINICAL REPORT 295 Ajay Mahajan, Jaya Dixit, Umesh Verma An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis KEY WORDS antimicrobial therapy, clinical findings,
CLINICAL REPORT 295 Ajay Mahajan, Jaya Dixit, Umesh Verma An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis KEY WORDS antimicrobial therapy, clinical findings,
2017 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout
 2017 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Kimberly Miller, RDH Course 8123: Principle Based Periodontal Therapy and Treatment Planning! Thursday, April 6 9 am - 4:30 pm Principle Based Periodontal Therapy
2017 Oregon Dental Conference Course Handout Kimberly Miller, RDH Course 8123: Principle Based Periodontal Therapy and Treatment Planning! Thursday, April 6 9 am - 4:30 pm Principle Based Periodontal Therapy
Probiotics In Gingivitis Management: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jordi Espadaler, PhD. Director of Innovation
 Probiotics In Gingivitis Management: A Randomized Clinical Trial Jordi Espadaler, PhD. Director of Innovation espadaler@ab-biotics.com Improving oral care Mechanical plaque removal, brushing and rinsing
Probiotics In Gingivitis Management: A Randomized Clinical Trial Jordi Espadaler, PhD. Director of Innovation espadaler@ab-biotics.com Improving oral care Mechanical plaque removal, brushing and rinsing
Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
The New periodontal Disease : The Inflammatory and Risky am ow Gingivitis Periodontitis Periodontitis Chronic Periodontitis
 The New periodontal Disease : Inflammatory and Risky Sam Low slow@dental.ufl.edu Gingivitis Condition is reversible But, if left untreated may progress to periodontitis with loss of attachment of connective
The New periodontal Disease : Inflammatory and Risky Sam Low slow@dental.ufl.edu Gingivitis Condition is reversible But, if left untreated may progress to periodontitis with loss of attachment of connective
The use of antimicrobial
 Antimicrobial mouthrinses and the management of periodontal diseases Introduction to the supplement Ira B. Lamster, DDS, MMSc The use of antimicrobial mouthrinses is an approach to limiting the accumulation
Antimicrobial mouthrinses and the management of periodontal diseases Introduction to the supplement Ira B. Lamster, DDS, MMSc The use of antimicrobial mouthrinses is an approach to limiting the accumulation
Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis
 157 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 46, No. 3, 157-161, 2004 Original Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis Mohammad Hossein Salari and Zainab Kadkhoda Department
157 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 46, No. 3, 157-161, 2004 Original Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis Mohammad Hossein Salari and Zainab Kadkhoda Department
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT
 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1049 Shubangi Mani et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Microbiological Evaluation of Chlorine Dioxide Based Mouthwash and Toothpaste in Periodontitis Patients along with Combination
10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1049 Shubangi Mani et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Microbiological Evaluation of Chlorine Dioxide Based Mouthwash and Toothpaste in Periodontitis Patients along with Combination
When Teeth Go Bad How nurse advice can help reduce recurrences of dental disease. Callum Blair BVMS MRCVS
 When Teeth Go Bad How nurse advice can help reduce recurrences of dental disease Callum Blair BVMS MRCVS Dental disease is a common condition affecting cats and dogs. An often quoted statistic is that
When Teeth Go Bad How nurse advice can help reduce recurrences of dental disease Callum Blair BVMS MRCVS Dental disease is a common condition affecting cats and dogs. An often quoted statistic is that
Linking Research to Clinical Practice
 Is Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy Cost Effective? Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information
Is Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy Cost Effective? Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery
 Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
Contemporary Periodontal Surgery Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. CPCC Dental Hygiene Program October 18, 2011 Surgical Management of Periodontitis Periodontal Plastic Surgery Soft tissue and esthetics Dental
actinomycetemcornitans and
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 20, 1999, 341-362 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright 8 Munksgaard 1999 PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 ISSN 0906-6713 Ecological considerations in the treatment of Actinobacillus
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 20, 1999, 341-362 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright 8 Munksgaard 1999 PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 ISSN 0906-6713 Ecological considerations in the treatment of Actinobacillus
Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
Received 18 June 2004; returned 6 August 2004; revised 1 December 2004; accepted 8 December 2004
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 55, 347 351 doi:10.1093/jac/dki013 Advance Access publication 4 February 2005 Concentrations and in vivo antibacterial activity of spiramycin and metronidazole
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 55, 347 351 doi:10.1093/jac/dki013 Advance Access publication 4 February 2005 Concentrations and in vivo antibacterial activity of spiramycin and metronidazole
Using an Antibiotic Rinse System
 Using an Antibiotic Rinse System An Adjunct in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Dr. Gerald Pearson, B.Sc., D.D.S., Dip. Perio drgepearson@ bellnet.ca Sherri Legere, RDH sherri.legere@ rogers.com Anne
Using an Antibiotic Rinse System An Adjunct in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Dr. Gerald Pearson, B.Sc., D.D.S., Dip. Perio drgepearson@ bellnet.ca Sherri Legere, RDH sherri.legere@ rogers.com Anne
: Dr. Mark S. Putt, University Park Research Inc., 6415 Mutual Drive, Fort Wayne, IN 46825, USA. E- :
 Research Article A 6-month clinical investigation of custom tray application of peroxide gel with or without doxycycline as adjuncts to scaling and root planing for treatment of periodontitis MARK S. PUTT,
Research Article A 6-month clinical investigation of custom tray application of peroxide gel with or without doxycycline as adjuncts to scaling and root planing for treatment of periodontitis MARK S. PUTT,
Dental Water Jet. By: Jennifer Buffington, Lindsay Hunt, Ruth Gardner
 Dental Water Jet By: Jennifer Buffington, Lindsay Hunt, Ruth Gardner What is a Dental Water Jet? A home, dental self-care device that uses a stream of pulsating water to irrigate the subgingival sulcus
Dental Water Jet By: Jennifer Buffington, Lindsay Hunt, Ruth Gardner What is a Dental Water Jet? A home, dental self-care device that uses a stream of pulsating water to irrigate the subgingival sulcus
Show biofilm the red card
 Show biofilm the red card BIOFILM-ERASER 1 A NEW APPLICATION Effective treatment for periodontal and peri-implant inflammation Periodontitis and peri-implantitis are bacterial inflammations with similar
Show biofilm the red card BIOFILM-ERASER 1 A NEW APPLICATION Effective treatment for periodontal and peri-implant inflammation Periodontitis and peri-implantitis are bacterial inflammations with similar
