Research Effect of tetracycline HCL (periodontal plus AB) on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans levels in chronic periodontitis
|
|
|
- Lesley Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ISSN Research Effect of tetracycline HCL (periodontal plus AB) on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans levels in chronic periodontitis Sneha Kataria 1, Kabbur Thippanna Chandrashekar 1*, Rohit Mishra 1, Vandana Tripathi 1, Ankit Galav 1 and Upasana Sthapak 1 1 Department of Periodontics, Hitkarini Dental College and Hospital, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India. *Corresponding author: Kabbur Thippanna Chandrashekar ktcshekars@gmail.com Editor approved: Ronell Bologna-Molina University of the Republic, Uruguay Received: 31 October 2014 Revised: 09 January 2015 Accepted: 21 January 2015 Published: 31 January Chandrashekar et al; licensee Vernon Innovative Publishers. licenses/by/4.0. Abstract Objectives: To evaluate the efficacy of tetracycline fiber (used as local drug delivery) along with scaling and root planing for the treatment of chronic periodontitis, and compare the results with those ensuing after scaling and root planing alone. Material and methods: A total of 50 patients were selected for the study. The treatment sites were divided into two groups by a split mouth technique. In each patient, periodontal pockets were treated with scaling and root planing alone (control site), or treated by scaling and root planing followed by placement of tetracycline fiber (test site), with the aim of evaluating Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in chronic periodontitis. Gingival index, probing depth, clinical attachment levels and quantitative and qualitative analysis of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans was carried out at and 14 day after treatment. The significance of any difference between test and control sites was tested using independent sample Student s t tests. Results: After fourteen days, there was a statistically significant improvement in all variables including gingival index score, pocket probing depth, clinical attachment levels and reduction in colony counts of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. However, inter group comparison showed statistically significant improvement only in the colony count of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in the test group. Conclusion: When compared with scaling and root planing alone, tetracycline fiber therapy along with scaling and root planing improves periodontal parameters and significantly reduces bacterial colony count in treatment of chronic periodontitis. Keywords: Collagen, periodontitis, tetracycline fibers, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans Introduction Chronic Periodontitis is defined as an infectious disease resulting in inflammation within the supporting tissues of the teeth, progressive attachment and bone loss and is characterized by pocket formation and/or recession of the gingiva and mainly prevalent in adults, but can occur at any age. Even though it is a multifactorial disease, the primary etiology is the presence of plaque and calculus. Progression of attachment loss usually occurs slowly, but periods of rapid progression can occur. It is known to be associated with a variable microbial pattern [1]. The most common periodontal microbiota associated with chronic periodontitis includes aerobic, anaerobic, gram How to cite this article: Kataria, S., Chandrashekar, K.T., Mishra, R., Tripathi, V., Galav, A. and Sthapak, U. (2015). Effect of tetracycline HCL (periodontal plus AB) on Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans levels in chronic periodontitis. Archives of Oral and Dental Research, 2:1. Retrieved
2 positive and gram negative bacterial flora. Amongst the anaerobic bacteria, the most commonly implicated bacteria include Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, Prevotella intermedia and Campylobacter rectus, as they are found in increased quantity in active sites and their elimination by therapy is associated with improved clinical features [2]. Among these bacteriae also, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is found in most diseased sites and may compose as much as 90% of the total cultivable bacteria [3]. It is thus considered as the most important pathogen for periodontitis and refractory periodontitis. The conventional periodontal therapy aims at complete elimination of the primary etiologic factor, plaque and other predisposing factors such as calculus, over hanging restorations, faulty prosthesis etc [4]. Scaling and Root Planning (SRP) forms a vital part of the first phase of periodontal therapy, as it leads to significant improvement in the clinical parameters [5]. However, different patients respond differently to mechanical therapy and the period over which the improved results can be maintained also varies in different individuals. The microbiological profile of an individual plays an important role in the outcome of mechanical therapy [2]. Since the mechanical therapy fails to eliminate bacteria which penetrate the connective tissue, the use of antibiotics as adjuncts to SRP has been advocated. In a systematic review, Haffajee et al., (2003) concluded that the use of systemic antibiotics leads to improved clinical parameters as compared to treatment with scaling alone [6]. However, the disadvantages like development of resistant strains, incidence of super infections and systemic side effects limit their wide spread use. Also, systemically administered antibiotics fail to penetrate the periodontal biofilm which requires an antibiotic strength of about 500 times greater than the usual therapeutic dose [7]. Local application of antibiotic or antiseptic in direct contact with the root surface can reduce or eliminate pathogenic organisms that could not be eradicated mechanically [5]. They also offer the advantages of high concentrations at the target sites with reduced systemic dosing, fewer applications, and high patient acceptability. The local delivery system maintains effective intra-pocket levels of antibacterial agents for extended period of time, so that they can alter subgingival flora and influence the healing of attachment apparatus [4]. Amongst the various antibiotics used for local application, tetracycline is favoured due to its better resorption, protein binding capability, diffusion into tissue structures, and prolonged duration of action. These unique drugs constitute the only class of antimicrobials tested to date that achieve higher concentrations in gingival fluid than in blood. Tetracyclines also help to increase reattachment or regeneration by enhancing fibroblast activity and conditioning of root surfaces by inhibiting collagenase activity [6]. Since, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is one of the most pathogenic bacteria responsible for all forms of periodontal diseases, the present clinical study, a split-mouth randomized control trial, was aimed to compare the effect of resorbable tetracycline fibres (Periodontal Plus AB ) as an adjunct to scaling and root planing on clinical parameters and the levels of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in adults diagnosed with chronic periodontitis. Materials and methods Source of data This clinical study was conducted in the Department of Periodontics, Hitkarini Dental College and Hospital, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India. Fifty patients were selected including both males and females in the age group of years diagnosed with chronic periodontitis. Selection of patients Patients diagnosed with chronic periodontitis with probing depth of 5 mm and radiographic evidence of bone loss at atleast two non-adjacent sites were selected. The patients who were able to maintain good oral hygiene and had not received any antibiotics in the past six months were included in the study. None of the patients had received any periodontal treatment before the examination. Patients were excluded if they had any systemic disease such as diabetes, if they were allergic to tetracycline fibres, pregnant or lactating or were using any medicated mouthrinse on a routine basis. The study design was approved by the ethical committee of Hitkarini Dental College & Hospital, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India. Clinical trial design A written informed consent form explaining the nature of the study and procedure for local drug delivery was obtained all the patients. In each patient, the treatment sites were divided into two groups randomly by the split-mouth technique: Test Group A (SRP+Periodontal Plus AB) and Control Group B (SRP alone). All clinical parameters and plaque samples were collected at (zero days) and 14 th day respectively. Tetracycline fibers (Periodontal Plus AB (Advanced Biotech Products, Chennai, India)) Figure 1 the product contains 25 mg pure fibrilar collagen, containing approximately 2 mg of evenly impregnated tetracycline HCL, sterilized by gamma radiation with shelf life of 2 years. It releases tetracycline and it gets dissolve in the period of 8-12 days. Periodontal Plus AB Fibers are available in strips containing four individually packed and separable sterile product packs. Clinical measurements Gingival index [9], pocket probing depth and clinical attachment level were recorded at and repeated on 14 th day after the treatment. Probing pocket depth The pocket depth was measured using a Hu Freidy UNC 15 probe 2
3 Figure 1. Periodontal Plus AB (Tetracycline fibers). fixed reference point (FRP) on the stent to the base of the pocket (BOP) (Figure 2) and the fixed reference point to the free gingival margin (GM). Probing pocket depth was obtained by subtracting distance of the Fixed Reference Point to Gingival Margin Fixed Reference Point to Base of Pocket. The measurement was recorded to the nearest millimetre and the recording was entered into the customized performa made for the study for each patient. The customized occlusal stents were stored on the prepared study casts to minimize distortion and to record on the 14 th day. Clinical attachment level The customized occlusal stent was placed on the selected teeth and the probe was gently inserted along the groove on the stent. The distance the fixed reference point on the stent to the base of the pocket and distance fixed reference point to the Cemento-Enamel Junction (CEJ) were recorded. Clinical attachment level was obtained by subtracting the distance of fixed reference point to cemento enamel junction fixed reference point to base of pocket. After the clinical parameters were recorded at, the tetracycline fibres (Periodontal Plus AB) were placed at the respective site (Figure 3) and the treated areas were given periodontal pack to isolate the area and to restrict the effect of the tetracycline fibres to particular sites for at least a week. The patient was informed to report to the clinic in case of any irritation or dysfunction. After the placement of Periodontal Plus AB drug, patients were instructed not to floss and probe the area with tongue, finger or toothpick and report immediately, if the material or pack is dislodged before the scheduled recall visit or if any pain, swelling or irritation occurred. Collection of subgingival plaque samples Sub gingival plaque samples were collected at and 14 days after the treatment. Samples were collected with complete aseptic precautions. The tooth was first isolated with cotton rolls, gently dried by air syringe and the supragingival plaque was removed. Care was taken not to disturb the subgingival plaque. Two sterile paper points were inserted in the gingival sulcus for 10 sec. The paper points which were contaminated by saliva or blood were discarded. The paper points were immediately placed in thioglycolate transport medium and transported to the laboratory for microbiological evaluation (Figures 4 and 5). Microbiological lab investigations The samples were processed within 24 hours. Each sample was first inoculated on Wilkins Chalgren Agar Medium [11] (Figure 6). The plates were incubated in vacuum dessicator at 37 C under anaerobic conditions. After seven days, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans colonies were seen as star shaped (Figure 7). Bacteria the pure culture were subjected to various tests. Figure 2. Measurement of probing depth using UNC 15 periodontal probe and acrylic stent. Figure 3. Placement of tetracycline fibres in periodontal pocket. 3
4 Figure 6. Wilkins chalgren agar medium. Figure 4. Collecting of subgingival plaque sample using paper points. Figure 7. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans colonies. study for analysis of data using SPSS for Windows (Statistical Presentation System Software, 1999, SPSS Inc, New York) version Figure 5. Thioglycolate transport medium. Identification was confirmed based on cell morphology (rod shaped), Gram stain reaction (Gram negative), biochemical and enzymatic tests including Indole test (negative), Carbohydrate fermentation test (positive for glucose, lactose and sucrose), Gas production test (H 2 s) (negative), Catalase test (positive). Data analysis Independent t and Paired t test, were employed in the present Results The gingival index, pocket probing depth, clinical attachment level and colony forming units for one hundred sites in fifty patients were assessed. Gingival index Comparative analysis of test and control group at revealed mean scores of 1.17±0.568 and 1.35±0.489 respectively with a t value of t= indicating no significant difference between the two groups (p>0.05). At 14 th day mean of test and control group were 0.74±0.681 and 0.56±0.399 with a t value is t= indicating no significant difference between two groups (p>0.05). However, statistically significant reduction was seen 4
5 in both the groups baselline (p<0.05) (Table 1, Graph 1). Probing pocket depth Comparative analysis of test and control group at revealed mean scores of 5.80±1.105 and 6.10±1.252 respectively with a t value of t= indicating no significant difference between the two groups (p>0.05). At 14 th day, mean value of test group is 3.90±1.119 and control group is 4.25±1.251 resulting in a t value of t= indicating no significant difference between the two groups (p>0.05) (Table 2, Graph 2). Clinical attachment level The mean gain in clinical attachment level when compared to 14 th day in test and control groups was 13.15±1.631 to 14.45±2.481 and 11.80±1.473 (10.10%) to 12.95±2.523 (10.60%) respectively indicating no significant difference between the two groups (Table 3, Graph 3). Colony forming units The mean colony forming units/ml in test group at was ± (Figure 8) which reduced to 18.57±9.748 (91.1%) on 14 th day (Figure 9) and mean colony forming units/ml in control group at was ± (Figure 10) which reduced to ± (51%) on the 14 th day (Figure 11). On comparison between the two groups, test group revealed 91.1% Table 1. Mean gingival index before and after treatment. Plaque Index Experimental sites (Group A) Mean±SD % Change Control sites (Group B) Mean±SD % Change P value Baseline 1.17± ± t=1.0435; 14 th day 0.74± % 0.56± % t=0.9917; Significance 0 day v/s 15 days * Significant t=3.270; p<0.05 t=6.786; p< Table 2. Mean probing depth before and after treatment. Plaque index Experimental sites (Group A) Control sites (Group B) P value Mean±SD Baseline 5.8± th day 3.9±1.119 Significance 0 day v/s 14 days * Significant Mean Value Graph 2 Plaque Index Baseline 13.15± th day 11.8±1.473 % Change Mean±SD ± % 4.25±1.251 % Change -- t=0.8033; 33.70% t=0.9324; t=27.606; p< t=14.091; p< Mean PPD 0 Day 14 Day Experimental sites (Group A) Mean±SD % Change Control sites (Group B) Mean±SD % Change ± % 12.95±2.523 Group A Group B Table 3. Mean relative attachment level before and after treatment. Significance 0 day v/s 14 days * Significant t=27.606; p< t=14.091; p< P value -- t=1.9581; 10.10% t= Mean GI Group A Group B Day 14 Day Graph 1 Graph 3 Mean Value Mean Value Mean RAL 0 Day 14 Day Group A Group B 5
6 Figure 8. Growth of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans seen in sample test group. Figure 11. Growth of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans seen in 14 th day sample control group. reduction in colonies of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, compared to 51.0% of control group (Table 4, Graph 4). Discussion The present clinical study was conducted to evaluate efficacy Figure 9. Growth of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans seen in 14 th day sample test group. Table 4. Mean CFU before and after treatment. Plaque Index Experimental sites (Group A) Mean±SD % Change Baseline 245.5± th day 18.57±9.748 Significance 0 day v/s 14 days Control sites (Group B) Mean±SD % Change ± % 136± P value -- t=2.3374; p<0.05* 50.00% t= ; p<0.0001** t=13.228; p< t=12.292; p< **Highly significant *Significant Mean CFU Figure 10. Growth of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans seen in sample control group. Mean Value Graph 4 0 Day 14 Day Group A Group B 6
7 of tetracycline fibres as an adjunct to scaling and root planing for the treatment of chronic periodontitis and its effect on the subgingival levels of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Fifty patients were enrolled in the study and were treated with either combination of SRP and tetracycline fibres or SRP alone. Statistical analysis of the results showed that there was significant improvement in the clinical parameters as compared to in both the groups; however, the inter-group comparison was not significant. While on comparison of the change in the colony forming units of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans as obtained the subgingival plaque samples, significant improvement were seen in the test group. The prevalence of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans is nearly 90% in localized juvenile periodontitis, 30-50% in severe adult periodontitis, and also encountered frequently in rapidly progressing periodontitis. Factors that promote Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans colonization and persistence in the oral cavity include adhesins, bacteriocins, invasins and antibiotic resistance [11]. Studies have shown that Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans cannot be completely eradicated the subgingival sites by mechanical therapy alone [12]. Persistence of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans after treatment has been correlated with its frequency before treatment. Individuals showing evidence of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans in a multitude of sites appear to be more difficult to treat than patients with few positive sites only. Also, deeper pockets show a greater resistance to eradication of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans [13]. It has been suggested that a possible explanation for this might be that Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans invades the gingival tissues and therefore are more difficult to eradicate using non-surgical therapy [12]. Various studies have shown that successful reduction of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and improvement in clinical results was seen with employment of combination of therapeutic modalities, i.e., mechanical as well as chemotherapeutic [14]. When compared to other commercially available antibiotics for use as local drug delivery agents, tetracycline provides better results in terms of clinical [15] and microbiological status [16]. However, studies on the duration of the maintenance of the improved periodontal status have been contradictory. Aimetti M et al., (2004) reported absence of recolonization of periodontal pocket by periopathogens over a 12 months follow up period after treatment with SRP and tetracycline fibres [17]. While, Man-Ying Wong (1999) reported recolonization by bacteria as early as 3 6 months [18]. It was suggested that the bacteria the other untreated niches of the oral cavity, such as cheek, tongue mucosa, saliva, or untreated sites may contribute to reinfection of the pockets and explain the insignificant response to local tetracycline therapy [18]. Since the present study was of fourteen days, it is beyond its scope to comment on duration over which the reduction in the level of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans can be maintained. Administration of an antibiotic directly into the periodontal pocket provides various advantages. Apart bypassing first Archives of Oral and Dental Research pass metabolism, systemic side effects and maintaining higher concentration at the diseased site, development of resistance to antibiotics, when administered locally, has also not yet been observed for periopathogens. Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans strains have been found to be most susceptible to amoxicillin/clavulanic acid, tetracycline and metronidazole with 0%, 0.8% and 20.8% nonsusceptible isolates, respectively [19]. The susceptibility of the different strains of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans varies according to geographic location also. It was found that 100% of subgingival Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans isolated Spanish patients grew on tetracycline-containing agar plates versus 0% isolated Dutch patients [20]. The present study definitively concludes that the strain of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans found in Indian population is susceptible to tetracycline. Conclusion Chemotherapeutic agents act as a useful adjunct to conventional mechanical therapy in patients with refractory periodontitis, in medically compromised patients and for patients where surgical intervention is contraindicated. Since, the susceptibility of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans to antibiotics decreases with maturation of biofilm, [21] the first requirement of periodontal therapy is to disrupt the established biofilm. As evident this study, it can be assumed that tetracycline fibre therapy along with scaling and root planing is more effective than scaling and root planing alone. However, further long term studies should be undertaken to obtain more clinical evidence for regular use of this material on clinical parameter for a larger sample. Limitation of the study The present clinical trial was conducted for a short duration of forteen days. Also, the other putatuive periodontal pathogens were not assessed and thus, no conclusions can be drawn on their effect on periodontitis and efficacy of tetracyclline fibres against these bacteria. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions All authors contributed equally to the manuscript. Acknowledgement The study was conducted in Hitkarini Dental College and Hospital, Jabalpur, Madhya Pradesh, India. The authors wish to acknowledge the assistance of Daksh Pathological Laboratories for their assistance with the anaerobic microbiological culture and data collection and interpretation. References 1. Glossary of periodontal terms th edition. 2. Haffajee, A. D., Cugini, M. A., Dibart, S., Smith, C., Kent, R. L., Jr. and Socransky, S. S. (1997). Clinical and microbiological features 7
8 of subjects with adult periodontitis who responded poorly to scaling and root planing. J Clin Periodontol, 24, Kornman, K. S. and Robertson, P. B. (1985). Clinical and microbiological evaluation of therapy for juvenile periodontitis. J Periodontol, 56, Newman, Takei, Klokkevold, Carranza: Clinical Periodontology. 10th edition, Drisko, C. H. (2001). Nonsurgical periodontal therapy. Periodontol 2000, 25, Golub, L. M., Suomalainen, K. and Sorsa, T. (1992). Host modulation with tetracyclines and their chemically modified analogues. Curr Opin Dent, 2, Haffajee, A. D., Socransky, S. S. and Gunsolley, J. C. (2003). Systemic anti-infective periodontal therapy. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol, 8, Greenstein, G. (2005). Changing periodontal concepts: treatment considerations. Compend Contin Educ Dent, 26, 81-2, Lenox, J. A. and Kopczyk, R. A. (1973). A clinical system for scoring a patient s oral hygiene performance. J Am Dent Assoc, 86, Wilkins, T. D. and Chalgren, S. (1976). Antimicrobial Agents. Chemother, 10, Paula, M., Fives-Taylor, Diane Hutchins Meyer., Keith, P. Mintz. and Catherine Brissette (2000). Virulence factors of Actinobacillus actinornycetemconzitans. Periodontology, 20, Renvert, S., Wikstrom, M., Dahlen, G., Slots, J. and Egelberg, J. (1990). On the inability of root debridement and periodontal surgery to eliminate Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans periodontal pockets. J Clin Periodontol, 17, Mombelli, A., Gmur, R., Gobbi, C. and Lang, N. P. (1994). Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in adult periodontitis. II. Characterization of isolated strains and effect of mechanical periodontal treatment. J Periodontol, 65, Pavicic, M. J., van Winkelhoff, A. J., Douque, N. H., Steures, R. W. and de Graaff, J. (1994). Microbiological and clinical effects of metronidazole and amoxicillin in Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans-associated periodontitis. A 2-year evaluation. J Clin Periodontol, 21, Kinane, D. F. and Radvar, M. (1999). A six-month comparison of three periodontal local antimicrobial therapies in persistent periodontal pockets. J Periodontol, 70, Goodson, J. M., Tanner, A., McArdle, S., Dix, K. and Watanabe, S. M. (1991). Multicenter evaluation of tetracycline fiber therapy. III. Microbiological response. J Periodontal Res, 26, Aimetti, M., Romano, F., Torta, I., Cirillo, D., Caposio, P. and Romagnoli, R. (2004). Debridement and local application of tetracycline-loaded fibres in the management of persistent periodontitis: results after 12 months. J Clin Periodontol, 31, Wong, M. Y., Lu, C. L., Liu, C. M. and Hou, L. T. (1999). Microbiological response of localized sites with recurrent periodontitis in maintenance patients treated with tetracycline fibers. J Periodontol, 70, Kulik, E. M., Lenkeit, K., Chenaux, S. and Meyer, J. (2008). Antimicrobial susceptibility of periodontopathogenic bacteria. J Antimicrob Chemother, 61, van Winkelhoff, A. J., Herrera Gonzales, D., Winkel, E. G., Dellemijn-Kippuw, N., Vandenbroucke-Grauls, C. M. and Sanz, M. (2000). Antimicrobial resistance in the subgingival microflora in patients with adult periodontitis. A comparison between The Netherlands and Spain. J Clin Periodontol, 27, Takahashi, N., Ishihara, K., Kato, T. and Okuda, K. (2007). Susceptibility of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans to six antibiotics decreases as biofilm matures. J Antimicrob Chemother, 59,
Research Center, India. 2 Professor And Dean, Department Of Periodontics And Implantology, Hitkarini Dental College And
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 100-107 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Tetracycline Hydrochloride
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 100-107 www.iosrjournals.org Effect of Tetracycline Hydrochloride
Periodontitis is characterized by
 Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Povidone Iodine vs Tetracycline Fibers- To Analyse the Therapeutic Effect Suchetha A 1, Garg A 2, Lakshmi P 3,Sapna N 4, Mundinamane DB 5,
Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Povidone Iodine vs Tetracycline Fibers- To Analyse the Therapeutic Effect Suchetha A 1, Garg A 2, Lakshmi P 3,Sapna N 4, Mundinamane DB 5,
Journal of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
 Comparison of Systemic Ciprofloxacin in Elimination of A.a from Active Sites with Combination of Metronidzole and Amoxicillin in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled
Comparison of Systemic Ciprofloxacin in Elimination of A.a from Active Sites with Combination of Metronidzole and Amoxicillin in Patients with Aggressive Periodontitis: A Randomized Double Blind Controlled
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder
 ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
ARESTIN (minocycline hcl) subgingival powder Coverage for services, procedures, medical devices and drugs are dependent upon benefit eligibility as outlined in the member's specific benefit plan. This
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
Please visit the C.E. Pavilion to validate your course attendance Or If There s a Line Go cdapresents.com
 UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
Materials and Methods: Literature review and Authors opinion.
 Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
Haffajee AD, Bogren A, Hasturk H et al. Subgingival microbiota of chronic periodontitis subjects from different geographic locations. J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31:996-1002. Purpose: To compare the subgingival
- BANA Hydrolysis as a Comparative Tool in the Evaluation of Amoxicillin and Azithromycin in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article - BANA Hydrolysis as a Comparative Tool in the Evaluation of Amoxicillin and Azithromycin in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis Rosaiah
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article - BANA Hydrolysis as a Comparative Tool in the Evaluation of Amoxicillin and Azithromycin in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis Rosaiah
Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS
 Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS Guidelines for use of antibiotics in periodontal therapy 1. The clinical
Systemic antibiotics Vs Local antibiotics in the Treatment of Periodontal Diseases BY: ABRAHEEM JAMAL ABRAHEEM & AYOUB NAGIBB BURWEISS Guidelines for use of antibiotics in periodontal therapy 1. The clinical
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient. Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club
 Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
ORIGINAL RESEARCH. Nitesh Kumar Sharma 1, Anushree Prasad 2 INTRODUCTION.
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Evaluation of Efficacy of Tetracycline as a Local Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis as an Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing A Clinical and
ORIGINAL RESEARCH www.ijcmr.com Evaluation of Efficacy of Tetracycline as a Local Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis as an Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing A Clinical and
Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease
 Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Mr P.Renton-Harper Specialist in Periodontics prh@perio.co.uk www.perio.co.uk Periodontal Disease A bacterial infection in a susceptible
Microbial and Genetic Testing in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Mr P.Renton-Harper Specialist in Periodontics prh@perio.co.uk www.perio.co.uk Periodontal Disease A bacterial infection in a susceptible
What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers
 http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
JMSCR Volume 2 Issue 7 Page July
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 1.1147 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Clinical Evaluation of Locally Delivered 10% Doxycycline Hyclate Gel as An Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in the Treatment of Chronic
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 1.1147 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Clinical Evaluation of Locally Delivered 10% Doxycycline Hyclate Gel as An Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in the Treatment of Chronic
Role of antibiotics in periodontal therapy
 BANGLADESH JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Volume-8 No. 4; October 2009 Review article Abstract Manas D 1, Srinivas SR 2, Jithendra KD 3 Loeshe in 1976 propounded the Specific Plaque Hypothesis and efforts
BANGLADESH JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCE Volume-8 No. 4; October 2009 Review article Abstract Manas D 1, Srinivas SR 2, Jithendra KD 3 Loeshe in 1976 propounded the Specific Plaque Hypothesis and efforts
JSS Medical and Dental College and Hospital, JSS University, Mysore, India *Author for Correspondence
 CLINICAL, MICROBIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR STUDY OF PORPHYROMONAS GINGIVALIS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS *Mayuri Vajawat 1, Vijay Kumar 2, K.G. Rajeshwari 3 and P.C. Deepika 4 1&4 Department of
CLINICAL, MICROBIOLOGICAL AND MOLECULAR STUDY OF PORPHYROMONAS GINGIVALIS IN PATIENTS WITH CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS *Mayuri Vajawat 1, Vijay Kumar 2, K.G. Rajeshwari 3 and P.C. Deepika 4 1&4 Department of
Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis Takeo Fujii, Pao-Li Wang, Yoichiro Hosokawa, Shinichi Shirai, Atsumu Tamura, Kazuhiro
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Effect of Systemically Administered Azithromycin in Early Onset Aggressive Periodontitis Takeo Fujii, Pao-Li Wang, Yoichiro Hosokawa, Shinichi Shirai, Atsumu Tamura, Kazuhiro
Periodontal Microbiology. Dr. Csifó-Nagy Boróka Department of Periodontology Semmelweis University
 Periodontal Microbiology Dr. Csifó-Nagy Boróka Department of Periodontology Semmelweis University 2016 Topics introduction, historical perspective pathogens of destructive periodontal diseases microbial
Periodontal Microbiology Dr. Csifó-Nagy Boróka Department of Periodontology Semmelweis University 2016 Topics introduction, historical perspective pathogens of destructive periodontal diseases microbial
Current Chemotherapeutic Modalities Available in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease
 Current Chemotherapeutic Modalities Available in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Paul Tolmie, D.D.S. Kenneth Rasenberger, D.D.S. Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. The Changing Views of Plaque and Periodontal
Current Chemotherapeutic Modalities Available in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Paul Tolmie, D.D.S. Kenneth Rasenberger, D.D.S. Chris van Kesteren, D.D.S. The Changing Views of Plaque and Periodontal
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment. Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD
 TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
TwinLight TM Periodontal Treatment Tomaž Lipoglavšek, DMD REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE 2 The available evidence consistently shows that therapies intended to arrest and control periodontitis depend primarily
Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis
 157 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 46, No. 3, 157-161, 2004 Original Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis Mohammad Hossein Salari and Zainab Kadkhoda Department
157 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 46, No. 3, 157-161, 2004 Original Rate of cultivable subgingival periodontopathogenic bacteria in chronic periodontitis Mohammad Hossein Salari and Zainab Kadkhoda Department
Additive or Synergistic Antimicrobial Effects of Amoxicillin and Metronidazole on Whole Plaque Samples: A Preliminary Report
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2011 13/1: 11 16 Additive or Synergistic Antimicrobial Effects of Amoxicillin and Metronidazole on Whole Plaque Samples: A Preliminary Report Clemens
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2011 13/1: 11 16 Additive or Synergistic Antimicrobial Effects of Amoxicillin and Metronidazole on Whole Plaque Samples: A Preliminary Report Clemens
An Investigation of Antibiotic Resistance of Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Peri-implantitis Lesions
 Original Article An Investigation of Antibiotic Resistance of Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Peri-implantitis Lesions Z. Kadkhoda 1, S. Torabi 2, A. Aliramezani 3.
Original Article An Investigation of Antibiotic Resistance of Aggregatibacter Actinomycetemcomitans and Porphyromonas Gingivalis in Peri-implantitis Lesions Z. Kadkhoda 1, S. Torabi 2, A. Aliramezani 3.
Received 18 June 2004; returned 6 August 2004; revised 1 December 2004; accepted 8 December 2004
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 55, 347 351 doi:10.1093/jac/dki013 Advance Access publication 4 February 2005 Concentrations and in vivo antibacterial activity of spiramycin and metronidazole
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (2005) 55, 347 351 doi:10.1093/jac/dki013 Advance Access publication 4 February 2005 Concentrations and in vivo antibacterial activity of spiramycin and metronidazole
NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS
 NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS March 30, 2015 Dear Oxyfresh Professional: We are thrilled to share with you the exciting results of a NEW 12-month, double blind clinical study published in the International
NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS March 30, 2015 Dear Oxyfresh Professional: We are thrilled to share with you the exciting results of a NEW 12-month, double blind clinical study published in the International
FACULTY OF HEALTH SCIENCES INSTITUTE OF CLINICAL DENTISTRY
 Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
Periodontopathic Bacteria: A Microbiological View
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 873-877 http://www.ijcmas.com Review Article Periodontopathic Bacteria: A Microbiological View Bhadoria Kiran 1 *, Jana A.M 2 and Shrivastav Archana 1 1 Department
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 873-877 http://www.ijcmas.com Review Article Periodontopathic Bacteria: A Microbiological View Bhadoria Kiran 1 *, Jana A.M 2 and Shrivastav Archana 1 1 Department
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS
 THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences PERIODONTAL PATHOGENS AMONG PRE PUBERTAL, PUBERTAL AND POST PUBERTAL GIRLS, IN CHENNAI, INDIA.
 Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 PERIODONTAL PATHOGENS AMONG PRE PUBERTAL, PUBERTAL AND POST PUBERTAL GIRLS, IN CHENNAI, INDIA. KANAKAM ELIZABETH
Research Article Microbiology International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 PERIODONTAL PATHOGENS AMONG PRE PUBERTAL, PUBERTAL AND POST PUBERTAL GIRLS, IN CHENNAI, INDIA. KANAKAM ELIZABETH
Overview of Periodontics for the General Practicioner
 Overview of Periodontics for the General Practicioner Nashville Area Dental Continuing Education August 27, 2008 Phillip D. Woods, DDS, MPH Commander, USPHS BOP National Periodontal Consultant Diplomate,
Overview of Periodontics for the General Practicioner Nashville Area Dental Continuing Education August 27, 2008 Phillip D. Woods, DDS, MPH Commander, USPHS BOP National Periodontal Consultant Diplomate,
Initial Therapy. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS. Oral sulcular epithelium. Oral. epithelium. Junctional. epithelium. Connective tissue.
 Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Antimicrobial Treatment for Advanced Periodontal Disease
 Antimicrobial Treatment for Advanced Periodontal Disease James S. Kohner, DDS DISCLOSURES December 15, 2011 Editor's Note: This author's case report is based on the work of Jorgen Slots, DDS, DMD, PhD,
Antimicrobial Treatment for Advanced Periodontal Disease James S. Kohner, DDS DISCLOSURES December 15, 2011 Editor's Note: This author's case report is based on the work of Jorgen Slots, DDS, DMD, PhD,
One-stage, full-mouth disinfection: fiction or reality?
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 50, 2009, 39 51 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2009 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 disinfection: fiction or reality? WIM TEUGHELS,CHRISTEL DEKEYSER,MARK
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 50, 2009, 39 51 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2009 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 disinfection: fiction or reality? WIM TEUGHELS,CHRISTEL DEKEYSER,MARK
Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 60:1234-1240, 2002 Microbial Complexes Detected in the Second/Third Molar Region in Patients With Asymptomatic Third Molars Raymond P. White, Jr, DDS, PhD,* Phoebus N. Madianos,
Microbiota and Oral Disease Prof. Dennis Cvitkovitch
 1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
1 Professor Dennis Cvitkovitch Faculty of Dentistry Dental Research Institute University of Toronto The human microbiome We are a composite species: eukaryotic, bacterial, archeal Every human harbors over
Course Title: DH 118 A Clinical Dental Hygiene I-Lecture Term: Fall
 Course Objective 1. Relate the history of dental hygiene to the concept of preventive dentistry and describe the dental hygienist's scope of practice. 1.1. Relate the history of the dental hygiene profession
Course Objective 1. Relate the history of dental hygiene to the concept of preventive dentistry and describe the dental hygienist's scope of practice. 1.1. Relate the history of the dental hygiene profession
Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study
 Clin Oral Invest (2017) 21:717 724 DOI 10.1007/s00784-016-1941-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study M. A. Stokman
Clin Oral Invest (2017) 21:717 724 DOI 10.1007/s00784-016-1941-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study M. A. Stokman
actinomycetemcornitans and
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 20, 1999, 341-362 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright 8 Munksgaard 1999 PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 ISSN 0906-6713 Ecological considerations in the treatment of Actinobacillus
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 20, 1999, 341-362 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Copyright 8 Munksgaard 1999 PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 ISSN 0906-6713 Ecological considerations in the treatment of Actinobacillus
Linking Research to Clinical Practice
 Probiotics and Oral Health Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical dental
Probiotics and Oral Health Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical dental
Volume 2 Issue
 Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Clinical and microbiological characterization of periodontal abscesses
 J Clin Periodontol 2005; 32: 1213 1218 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00839.x Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Clinical and microbiological characterization of periodontal abscesses Jaramillo A, Arce
J Clin Periodontol 2005; 32: 1213 1218 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2005.00839.x Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Clinical and microbiological characterization of periodontal abscesses Jaramillo A, Arce
Khosropanah H., et al J Dent Shiraz Univ Med Scien June; 13(2): 44-48
 Original Article The Clinical Effectiveness of Subgingival Irrigation with Povidone-Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide in Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Periodontitis Khosropanah H. a, Koohpeima F.
Original Article The Clinical Effectiveness of Subgingival Irrigation with Povidone-Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide in Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Periodontitis Khosropanah H. a, Koohpeima F.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT
 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1049 Shubangi Mani et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Microbiological Evaluation of Chlorine Dioxide Based Mouthwash and Toothpaste in Periodontitis Patients along with Combination
10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1049 Shubangi Mani et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Microbiological Evaluation of Chlorine Dioxide Based Mouthwash and Toothpaste in Periodontitis Patients along with Combination
PERIODONTAL (GUM) DISEASE & IT S TREATMENT
 PERIODONTL (GUM) DISESE & IT S TRETMENT What do healthy gums look like? In a healthy mouth, gums are pink and do not bleed on tooth brushing. They are firm and cannot be easily separated from teeth. What
PERIODONTL (GUM) DISESE & IT S TRETMENT What do healthy gums look like? In a healthy mouth, gums are pink and do not bleed on tooth brushing. They are firm and cannot be easily separated from teeth. What
Implementing Hygiene Systems for Increased Productivity
 Implementing Hygiene Systems for Increased Productivity Rachel Wall, RDH, BS Phone 704-541-0995 Fax 866-645-4469 Rachel@inspiredhygiene.com www.inspiredhygiene.c Copyright 2014. Revised 2017 Inspired Hygiene
Implementing Hygiene Systems for Increased Productivity Rachel Wall, RDH, BS Phone 704-541-0995 Fax 866-645-4469 Rachel@inspiredhygiene.com www.inspiredhygiene.c Copyright 2014. Revised 2017 Inspired Hygiene
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
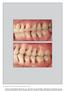 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
Dental Water Jet. By: Jennifer Buffington, Lindsay Hunt, Ruth Gardner
 Dental Water Jet By: Jennifer Buffington, Lindsay Hunt, Ruth Gardner What is a Dental Water Jet? A home, dental self-care device that uses a stream of pulsating water to irrigate the subgingival sulcus
Dental Water Jet By: Jennifer Buffington, Lindsay Hunt, Ruth Gardner What is a Dental Water Jet? A home, dental self-care device that uses a stream of pulsating water to irrigate the subgingival sulcus
Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018
 Dental Policy Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: 04-901 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018 Description This document addresses periodontal maintenance. Note:
Dental Policy Subject: Periodontal Maintenance Guideline #: 04-901 Publish Date: 03/15/2018 Status: Revised Last Review Date: 02/05/2018 Description This document addresses periodontal maintenance. Note:
Research Article Full Mouth Disinfection Versus Scaling and Root Planing per Quadrant in Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Full Mouth Disinfection Versus Scaling and Root Planing per Quadrant in Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review Maísa Casarin 1 *, Danilo Antonio
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Full Mouth Disinfection Versus Scaling and Root Planing per Quadrant in Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review Maísa Casarin 1 *, Danilo Antonio
Probiotics In Gingivitis Management: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jordi Espadaler, PhD. Director of Innovation
 Probiotics In Gingivitis Management: A Randomized Clinical Trial Jordi Espadaler, PhD. Director of Innovation espadaler@ab-biotics.com Improving oral care Mechanical plaque removal, brushing and rinsing
Probiotics In Gingivitis Management: A Randomized Clinical Trial Jordi Espadaler, PhD. Director of Innovation espadaler@ab-biotics.com Improving oral care Mechanical plaque removal, brushing and rinsing
Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
Show biofilm the red card
 Show biofilm the red card BIOFILM-ERASER 1 A NEW APPLICATION Effective treatment for periodontal and peri-implant inflammation Periodontitis and peri-implantitis are bacterial inflammations with similar
Show biofilm the red card BIOFILM-ERASER 1 A NEW APPLICATION Effective treatment for periodontal and peri-implant inflammation Periodontitis and peri-implantitis are bacterial inflammations with similar
Rare case of generalised aggressive periodontitis in the primary dentition
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2014 Rare case of generalised aggressive periodontitis in the primary dentition
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2014 Rare case of generalised aggressive periodontitis in the primary dentition
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis
 CLINICAL REPORT 295 Ajay Mahajan, Jaya Dixit, Umesh Verma An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis KEY WORDS antimicrobial therapy, clinical findings,
CLINICAL REPORT 295 Ajay Mahajan, Jaya Dixit, Umesh Verma An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis KEY WORDS antimicrobial therapy, clinical findings,
Original Research. which are considered important in causation of gingivitis and periodontitis. 1,2
 Tetracycline hydrochloride and spiramycin sub gingival irrigation in chronic Received: 20 th January 2015 Accepted: 15 th April 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research
Tetracycline hydrochloride and spiramycin sub gingival irrigation in chronic Received: 20 th January 2015 Accepted: 15 th April 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research
Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases. As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
 Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
Efficacy of Azithromycin in Comparison with Metronidazole in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis
 ISSN: 1812 1217 Efficacy of zithromycin in Comparison with Metronidazole in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis Jawna a K Mammdoh BDS, MSc ( Lec.) Department of dental basic sciences College of Dentistry,
ISSN: 1812 1217 Efficacy of zithromycin in Comparison with Metronidazole in the Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis Jawna a K Mammdoh BDS, MSc ( Lec.) Department of dental basic sciences College of Dentistry,
Kerry Hyland-Lepicek, RDH
 The Oravital System: A Paradigm Shift in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease There is substantial evidence indicating that most forms of periodontal disease are specific infections caused by an overgrowth
The Oravital System: A Paradigm Shift in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease There is substantial evidence indicating that most forms of periodontal disease are specific infections caused by an overgrowth
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of April 21, 2011 ):
 EFFICIENT ANTIMICROBIAL TREATMENT IN PERIODONTAL MAINTENANCE CARE JØRGEN SLOTS and MICHAEL G. JORGENSEN J Am Dent Assoc 2000;131;1293-1304 The following resources related to this article are available
EFFICIENT ANTIMICROBIAL TREATMENT IN PERIODONTAL MAINTENANCE CARE JØRGEN SLOTS and MICHAEL G. JORGENSEN J Am Dent Assoc 2000;131;1293-1304 The following resources related to this article are available
Periodontal Maintenance
 Periodontal Maintenance Friday, February 20, 2015 1:06 PM Periodontal disease control always begins with patient education - Plaque control, diet, smoking cessation, impact that systemic health has on
Periodontal Maintenance Friday, February 20, 2015 1:06 PM Periodontal disease control always begins with patient education - Plaque control, diet, smoking cessation, impact that systemic health has on
Periodontal disease is characterized by progressive periodontal pathogens. It is known that coronary heart disease is
 ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
ISSN: 0975-766X CODEN: IJPTFI Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com PREVALENCE OF PERIODONTAL DISEASES IN PATIENTS WITH CORONARY HEART DISEASE Niha Naveed* BDS student, Saveetha
Reimbursement Guide. ATRIDOX Insurance Reimbursement Guide for the submission of insurance claims
 Reimbursement Guide Insurance Reimbursement Guide f the submission of insurance claims General reimbursement & submission infmation Reimbursement infmation Submission of insurance claims Pre-determination
Reimbursement Guide Insurance Reimbursement Guide f the submission of insurance claims General reimbursement & submission infmation Reimbursement infmation Submission of insurance claims Pre-determination
Periodontal Microbiology (Dental Plaque)
 Periodontal Microbiology (Dental Plaque) Dental plaque Dental plaque is soft deposits that form the biofilm adhering to the tooth surface of other hard surface in the oral cavity, including removable and
Periodontal Microbiology (Dental Plaque) Dental plaque Dental plaque is soft deposits that form the biofilm adhering to the tooth surface of other hard surface in the oral cavity, including removable and
2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different...
![2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different... 2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different...](/thumbs/89/99584051.jpg) 2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different... Risks associated with Periodontal disease 1 Diabetes Diabetic patients are more likely to develop periodontal disease, which in turn
2.5 mg dental insert [chlorhexidine digluconate] Uniquely different... Risks associated with Periodontal disease 1 Diabetes Diabetic patients are more likely to develop periodontal disease, which in turn
Using an Antibiotic Rinse System
 Using an Antibiotic Rinse System An Adjunct in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Dr. Gerald Pearson, B.Sc., D.D.S., Dip. Perio drgepearson@ bellnet.ca Sherri Legere, RDH sherri.legere@ rogers.com Anne
Using an Antibiotic Rinse System An Adjunct in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease Dr. Gerald Pearson, B.Sc., D.D.S., Dip. Perio drgepearson@ bellnet.ca Sherri Legere, RDH sherri.legere@ rogers.com Anne
Detection of predominant subgingival periopathogens around submerged and non submerged hydroxy apatite implants
 [Downloaded free from http://www.jdionline.org on Sunday, January 26, 2014, IP: 201.22.186.203] Click here to download free Android application for this journa ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of predominant
[Downloaded free from http://www.jdionline.org on Sunday, January 26, 2014, IP: 201.22.186.203] Click here to download free Android application for this journa ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of predominant
Pathogens in Relation to Periodontal Status
 J Dent Res 74(11): 1789-1793, November, 1995 Salivary Levels of Suspected Periodontal Pathogens in Relation to Periodontal Status and Treatment B. von Troil-Lindenl*, H. Torkko2, S. Alaluusua3, H. Jousimies-Somer4,
J Dent Res 74(11): 1789-1793, November, 1995 Salivary Levels of Suspected Periodontal Pathogens in Relation to Periodontal Status and Treatment B. von Troil-Lindenl*, H. Torkko2, S. Alaluusua3, H. Jousimies-Somer4,
Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study.
 ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study. Dr. Yashika Jain Senior Lecturer, Institution: SGT Dental College & Hospital,
ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study. Dr. Yashika Jain Senior Lecturer, Institution: SGT Dental College & Hospital,
Diabetes and Periodontal Disease. Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres. Literature Review 1 11/4/08
 1 Diabetes and Periodontal Disease Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres Literature Review 1 11/4/08 2 Introduction Diabetes is a cardiovascular condition that effects an estimated 20 million people in the United
1 Diabetes and Periodontal Disease Brianne Neelis & Katie Torres Literature Review 1 11/4/08 2 Introduction Diabetes is a cardiovascular condition that effects an estimated 20 million people in the United
Chlorhexidine chip and tetracycline fibers as adjunct to scaling and root planing A clinical study
 Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2009 - Volume 8, Number 4 Chlorhexidine chip and tetracycline fibers as adjunct to scaling and root planing A clinical study Ruchi Srivastava 1 ; Pushpendra
Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. October/December 2009 - Volume 8, Number 4 Chlorhexidine chip and tetracycline fibers as adjunct to scaling and root planing A clinical study Ruchi Srivastava 1 ; Pushpendra
Committee and study is carried out for one month i.e, from December 2015 January 2016.
 Association between Gram-Negative Enteric Rods, Porphyromonas gingivalis and Changes in Clinical Parameters in Chronic Periodontitis: An Observational Study Bhavya.B 1, Ashwini.S 2, Shruthi.K.R 3 Department
Association between Gram-Negative Enteric Rods, Porphyromonas gingivalis and Changes in Clinical Parameters in Chronic Periodontitis: An Observational Study Bhavya.B 1, Ashwini.S 2, Shruthi.K.R 3 Department
GOALS FOR THE PERIODONTAL PATIENT
 1 Goals for the Periodontal Patient: 1. Modify Risk Factors a. Overall goal is total health. b. Research shows that oral health is related to total health c. #1 preventable risk fact is tobacco use d.
1 Goals for the Periodontal Patient: 1. Modify Risk Factors a. Overall goal is total health. b. Research shows that oral health is related to total health c. #1 preventable risk fact is tobacco use d.
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT HESKA PERIOceutic Gel 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each unit dose contains: 2.1 Active substance Doxycycline
ANNEX I SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF VETERINARY MEDICINAL PRODUCT HESKA PERIOceutic Gel 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each unit dose contains: 2.1 Active substance Doxycycline
A Pilot Study Comparing the Outcome of Scaling/Root Planing With and Without Perioscope Technology
 A Pilot Study Comparing the Outcome of Scaling/Root Planing With and Without Perioscope Technology Christine M. Blue, BSDH, MS; Patricia Lenton, RDH, MA; Scott Lunos, MS; Kjersta Poppe, RDH, MS; Joy Osborn,
A Pilot Study Comparing the Outcome of Scaling/Root Planing With and Without Perioscope Technology Christine M. Blue, BSDH, MS; Patricia Lenton, RDH, MA; Scott Lunos, MS; Kjersta Poppe, RDH, MS; Joy Osborn,
IJEDS ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 Ameet Mani et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1145 Efficacy of Oral Probiotics as an Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in Nonsurgical Treatment Outcome of Generalized Chronic Periodontitis
Ameet Mani et al Original Research 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1145 Efficacy of Oral Probiotics as an Adjunct to Scaling and Root Planing in Nonsurgical Treatment Outcome of Generalized Chronic Periodontitis
Home care. Home care. Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice. Professional care. BSP Roadshows 2008/9
 3. Periodontal Treatment BSP Roadshows 2008/9 Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice 3. Periodontal Treatment Phil Ower www.periocourses.co.uk Why is it so important? Oral hygiene methods what s
3. Periodontal Treatment BSP Roadshows 2008/9 Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice 3. Periodontal Treatment Phil Ower www.periocourses.co.uk Why is it so important? Oral hygiene methods what s
Therapy of hopeless teeth a case of long-term tooth preservation in a patient with generalised aggressive periodontitis
 CLINICAL REPORT 251 Publication Matthias Pelka, Anselm Petschelt Therapy of hopeless teeth a case of long-term tooth preservation in a patient with generalised aggressive periodontitis Matthias Pelka,
CLINICAL REPORT 251 Publication Matthias Pelka, Anselm Petschelt Therapy of hopeless teeth a case of long-term tooth preservation in a patient with generalised aggressive periodontitis Matthias Pelka,
Research Article. Chlorhexidine varnish: An attempt to vanish moderate periodontitis
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(1):339-345 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Chlorhexidine varnish: An attempt to vanish moderate
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(1):339-345 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Chlorhexidine varnish: An attempt to vanish moderate
Department of Oral Surgery, Heinrich Heine University, D Düsseldorf, Germany.
 Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Lasers Surg Med. 2007 Jun;39(5):428-40 Immunohistochemical characterization of periodontal wound healing following nonsurgical treatment with fluorescence controlled Er:YAG laser radiation in dogs. Schwarz
Have you been diag nosed with PERIODONTAL DISEASE
 Have you been diag nosed with PERIODONTAL DISEASE What you need to know about Periodontal Disease? Periodontal disease (also called gum disease) is a chronic, bacterial infection of the gums that can destroy
Have you been diag nosed with PERIODONTAL DISEASE What you need to know about Periodontal Disease? Periodontal disease (also called gum disease) is a chronic, bacterial infection of the gums that can destroy
Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 307 308 Actinomycetes, 307 308 Actinomycosis, in oral cavity, 288 290 Aggregatibacter, 308 309 Amoxicillin, in odontogenic infections,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Actinobacteria, 307 308 Actinomycetes, 307 308 Actinomycosis, in oral cavity, 288 290 Aggregatibacter, 308 309 Amoxicillin, in odontogenic infections,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
Clinical UM Guideline
 Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Gingivectomy or Gingivoplasty Guideline #: 04-202 Current Effective Date: 07/01/2016 Status: Reviewed Last Review Date: 07/10/2017 Description This document addresses gingivectomy
Clinical UM Guideline Subject: Gingivectomy or Gingivoplasty Guideline #: 04-202 Current Effective Date: 07/01/2016 Status: Reviewed Last Review Date: 07/10/2017 Description This document addresses gingivectomy
Aggressive and chronic periodontitis
 J Periodontol February 2005 Prevalence of Periodontopathic Bacteria in Aggressive Periodontitis Patients in a Chilean Population Marta Gajardo,* Nora Silva,* Leyla Gómez,* Rubén León, Beatriz Parra, Adolfo
J Periodontol February 2005 Prevalence of Periodontopathic Bacteria in Aggressive Periodontitis Patients in a Chilean Population Marta Gajardo,* Nora Silva,* Leyla Gómez,* Rubén León, Beatriz Parra, Adolfo
Clinical Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Fidelis III Nd:Yag Laser as an Adjunct to Conventional Periodontal Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis
 BALKAN JOURNAL OF STOMATOLOGY ISSN 1107-1141 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Clinical Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Fidelis III Nd:Yag Laser as an Adjunct to Conventional Periodontal Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis
BALKAN JOURNAL OF STOMATOLOGY ISSN 1107-1141 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Clinical Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Fidelis III Nd:Yag Laser as an Adjunct to Conventional Periodontal Treatment of Chronic Periodontitis
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
NEWSLETTER ABOUT LIGHT ACTIVATED DISINFECTION MARCH FotoSanNewsletter
 FotoSanNewsletter Biofilm modulation In this issue we will discuss Bacterial Replacement Therapy (BRT) - a new highly effective method to change a pathogen biofilm to non-pathogen. 1 Reduce the bacteria
FotoSanNewsletter Biofilm modulation In this issue we will discuss Bacterial Replacement Therapy (BRT) - a new highly effective method to change a pathogen biofilm to non-pathogen. 1 Reduce the bacteria
ABSTRACT. Keywords: Scaling and root-planning (SRP), chlorhexidine gluconate (CHX), (N-benzoyl-d L-arginine-2-napthylamide) BANA
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.4.DE7 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Effects Of Scaling And Root Planing And 0.2 % Chlorhexidine Rinse On Clinical And Microbiological Parameters In
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.4.DE7 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Effects Of Scaling And Root Planing And 0.2 % Chlorhexidine Rinse On Clinical And Microbiological Parameters In
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus in Chronic Generalized Periodontitis via Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Pilot Study
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus in Chronic Generalized Periodontitis via Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Pilot Study Thomas George Veliyaveetil
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Detection of Herpes Simplex Virus in Chronic Generalized Periodontitis via Polymerase Chain Reaction: A Pilot Study Thomas George Veliyaveetil
Bone Levels - From Hypothesis To Facts
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 6, Issue 5 (May.- Jun. 2013), PP 19-23 Bone Levels - From Hypothesis To Facts Savitha B 1, Priyanka
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 6, Issue 5 (May.- Jun. 2013), PP 19-23 Bone Levels - From Hypothesis To Facts Savitha B 1, Priyanka
Commercial DNA Probes Reveal Colonization Patterns of Periodontopathogens in Chronic Periodontitis
 RESEARCH REPORTS Commercial DNA Probes Reveal Colonization Patterns of Periodontopathogens in Chronic Periodontitis W. Keung Leung, Lijian Jin, Birgitta Söder, Esmonde F. Corbet In the present study, detection
RESEARCH REPORTS Commercial DNA Probes Reveal Colonization Patterns of Periodontopathogens in Chronic Periodontitis W. Keung Leung, Lijian Jin, Birgitta Söder, Esmonde F. Corbet In the present study, detection
Fusobacteria Bacteremia Post Full Mouth Disinfection Therapy: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VI (July. 2015), PP 77-81 www.iosrjournals.org Fusobacteria Bacteremia Post Full Mouth
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VI (July. 2015), PP 77-81 www.iosrjournals.org Fusobacteria Bacteremia Post Full Mouth
Product Information Clinpro Prophy Powder 4 Bottles à 100 g
 Ordering Information Item No. Product Information 671 Clinpro Prophy Powder 4 Bottles à 1 g Clinpro Prophy Powder 12613 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Cherry Fine 12657 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Mint
Ordering Information Item No. Product Information 671 Clinpro Prophy Powder 4 Bottles à 1 g Clinpro Prophy Powder 12613 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Cherry Fine 12657 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Mint
STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT. Cynthia Fong, RDH, MS
 STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 9:00 a.m. 12 Noon STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course provides
STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT 2014 Kentucky Dental Association Louisville, KY Friday, March 14, 2014 9:00 a.m. 12 Noon STRAIGHTFORWARD ULTRASONIC DEBRIDEMENT COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course provides
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Specific Egg Yolk Antibody (Ovalgen PG) as a Novel Supportive Immunotherapy for Periodontitis
 7 th Vietnam International Dental Exhibition and congress (VIDEC) Aug 7-9, 2014 Specific Egg Yolk Antibody (Ovalgen PG) as a Novel Supportive Immunotherapy for Periodontitis Nguyen Van Sa, Ph.D Immunology
7 th Vietnam International Dental Exhibition and congress (VIDEC) Aug 7-9, 2014 Specific Egg Yolk Antibody (Ovalgen PG) as a Novel Supportive Immunotherapy for Periodontitis Nguyen Van Sa, Ph.D Immunology
