One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A Case Series
|
|
|
- Noel Barber
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology /3:62-68 One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A Case Series Othman Shibly, Ahmad Kutkut, and Jasim M. Albandar 1 Center for Dental Studies, State University of New York at 2 Buffalo, Buffalo, NY; Department of Restorative Dentistry, University of Kentucky College of Dentistry, Lexington, KY; 3 Periodontal Diagnostics Research Laboratory, Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Temple University School of Dentistry, Philadelphia, PA Abstract Objective: The aim of this one-year, re-entry case series was to evaluate clinically the amount of bone regeneration following the placement of immediate implants in fresh extraction sockets where bone allograft has been used to treat horizontal gaps and buccalbone dehiscence defects in periodontally compromised patients. Methods: Sixteen patients consented to participate, each having one immediate implant with 3 mm buccal dehiscence bone defects and 2 mm horizontal defects between the implant and socket wall. Peri-implant defects were treated using a demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft and a bioresorbable collagen membrane. Measurements of the vertical and horizontal bone defects were performed at 4 sites: buccally, mesially, distally and lingually, and were done at baseline and at 1-year follow-up. Results: The mean reduction in vertical defects between baseline and re-entry for all sites was 2.42 mm (p = ). Compared to lingual sites, the buccal sites showed the greatest resolution in vertical defects dimension (6.37 mm), followed by proximal sites (0.78 mm). The overall mean reduction in horizontal defects was 1.59 mm (p < ). Compared to lingual sites, the buccal sites showed the greatest resolution in horizontal gap dimension (3.2 mm), followed by proximal sites (0.8 mm). Age, defect location in the mouth and implant length did not show significant effects on the reduction in defect dimension during the first year. Conclusions: A partially missing buccal plate was not a critical factor for implant success and bone regeneration of immediate implants in patients with a history of periodontal disease regardless of the time of implant loading (immediate/conventional).. Key words: Bone regeneration; bone remodeling; immediate; periodontal disease; wound healing. Introduction Correspondence to: Othman Shibly, DDS, MS Center for Dental Studies, Department of Periodontics and Endodontics, University at Buffalo School of Dental Medicine, 250 Squire Hall, Buffalo, NY shibly@buffalo.edu Phone: , Fax: A common presentation when a dental implant is placed immediately after tooth extraction is the presence of a residual gap between the coronal part of the implant and the socket's bony walls. This gap may compromise osseointegration and esthetics at the implant site. The use of barrier membranes and bonegrafting materials to fill the peri-implant defect around immediate implants has resulted in improved quality and quantity of regenerated bone. (Nemcovsky et al., 2000; Rosenquist and Ahmed, 2000; Shibly et al., 2010; Tehemar et al., 2003). It has been shown that immediate implants have a high survival rate when autogenous bone graft is used to fill the peri-implant defects around these implants. (Schwartz-Arad and Chaushu, 1997; Cochran, 1999). Other authors (Becker et al., 1994; Block and Kent, 1991; Gher et al., 1994) have shown favorable results using demineralized, freeze-dried bone allografts (DFDBA) for the same purpose. Furthermore, the presence of an intact buccal- International Academy of Periodontology
2 Othman Shibly et al: Buccal Bone Regeneration at Implants 63 crestal wall of the alveolar ridge is a major consideration when immediate implants are placed into extraction sites. The contemporary view is that the width of the buccal wall should be at least 2 mm to maintain the alveolar bone level at the implant platform (Qahash et al., 2008). Immediate implant placement in patients with a history of periodontal disease is challenging because of the partial or complete loss of the buccal plate, particularly in the anterior zone. Recently, Funato et al. (2007) proposed a classification system for use when planning treatment for immediate implants and described certain indications and limitations of immediate placement of implants based on the characteristics of the buccal bone and soft tissue profile. According to these recommendations, deficient buccal bone that deviates from the alveolar housing is considered a contraindication to immediate placement of implants. In this case, a delayed implant placement approach was recommended instead. The location where the implant is placed (anterior/posterior), as well as the thickness of the buccal-bone crest and the size of the horizontal buccal gap, significantly influenced the amount of hard tissue alteration that occurred during the period of healing following immediate implant placement into an extraction socket. The thickness of the buccal-bone crest significantly influenced not only the amount of horizontal gap fill, but also the amount of vertical crestal resorption. The implant sites in the anterior segment of the dentition respond differently than posterior sites (horizontal ridge reduction, gap fill and vertical crest resorption) and this may suggest that anterior sites are more susceptible to ridge alterations at implant placement than posterior sites (Ferrus et al., 2010; Shibly et al., 2010). The purpose of this case series report was to evaluate the amount of bone regeneration of partial or complete buccal-plate defects around implants when they were placed immediately after extraction, and to study the effect of patient characteristics, such as age and gender, and local factors, including the type of site (buccal, lingual, mesial and distal), defect location (maxillary/mandibular, anterior/posterior), implant length and whether loading was immediate or conventional in patients with a history of periodontal disease. Materials and Methods Subjects The study subjects included 16 patients comprising a subset of a larger group of 55 subjects used in a previous clinical trial that was designed to study various outcomes following placement of immediate implants in fresh extraction sites (Shibly et al., 2010). The subjects ranged in age from 25 to 75 years (mean 58.4 y) and included 7 males and 9 females. They were recruited from among patients who had been actively treated for periodontal disease and were on a periodontal maintenance program at the State University of New York at Buffalo. The inclusion criteria were presence of a nonrestorable tooth that was scheduled for extraction and indicated for placement of an immediate dental implant to replace the extracted tooth. Further, the extraction site should have a buccal dehiscence bone defect of at least 3 mm and an open defect (gap) of at least 2 mm adjacent to the implant after implant installation. This paper will report only on subjects who consented to a re-entry protocol one year postoperatively. The exclusion criteria were bruxism, smoking, and having a compromised general health condition that could negatively affect the healing potential of periimplant tissue, including uncontrolled diabetes, immunodeficiency, kidney or liver disease, chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer or arthritis, and severely impaired cardiovascular function. The subjects completed a health history and signed an informed consent form. The study was approved by the university's Institutional Review Board. Surgical procedure A sulcular incision was performed around the nonrestorable tooth and care was taken to preserve the attached gingiva and papillae. After elevation of the flap, the tooth was extracted atraumatically. The extraction socket was debrided of any granulation tissue and osteotomy was performed. The dental implant was installed directly into the alveolar bone and placed 3 mm apically to the cemento-enamel junction of the neighboring teeth. The implant had initial stability after insertion as evidenced by a minimum torque of 35 Ncm. The implant placed was a parallelwalled implant with bone and soft tissue stimulating capacity biomaterial on the surface (NobelReplace Straight Groovy, with TiUnite surface, Nobel Biocare, Yorba Linda, CA USA). To ensure adequate nourishment for the graft, bone corticotomy was performed around the implant using a round bur size 2 on high speed. Bone defects adjacent to the implant were filled with sterile, demineralized, freeze-dried bone graft (DFDBA; OraGRAFT, LifeNet Health, Virginia Beach, VA). The defect was covered with a bioresorbable collagen membrane (Resorbable Collagen Membranes, Tissue Specialists, Little Rock, AR). Six subjects enrolled in this follow-up report were in the immediate loading group and an abutment was screwed into the implant for these subjects. A temporary resin crown was fabricated and temporarily cemented onto the abutment; the gingival flap was adapted around the crown and sutured in place. The other 10 subjects were in the conventional loading group; a releasing incision for the buccal tissue was performed to allow for primary closure over the
3 64 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology /3 Table 1. Bone defects (mm) measured at baseline and at re-entry one year later, by type of defect and site. Vertical defects Site No. of sites Baseline One Year Mean SD Mean SD % fill Buccal Lingual Mesial Distal Horizontal defects (gap) SD, standard deviation Buccal Lingual Mesial Distal implant. The implant was surgically uncovered three months postoperatively and a healing abutment was placed, followed by a fabrication of final restoration within four weeks of uncovering the implant. Postoperative care Sutures were removed 7 to 10 days after surgery. Patients were advised to clean the surgical area gently with a cotton swab moistened with 0.12% chlorhexidine gluconate (Peridex, Zila Pharmaceuticals, Fort Collins, CO) twice daily for two weeks. The definitive final crown was placed in both groups after three months. Follow-up evaluations were at 3, 6 and 12 months. Measurement of bone defects All 16 subjects consented to the re-entry procedure in which a full thickness flap was elevated to expose the bone around the implant. The elevation of the flap was conservative to allow direct measurement of the bony defect around the implant. No vertical releasing incision was done, and the flap was replaced and secured with sutures. Two variables were measured clinically during the surgical procedures at baseline and one year postoperatively. The first measurement assessed the vertical distance between the implant shoulder and the base of the bone defect at 4 sites: buccally, mesially, distally and lingually. The second variable assessed the horizontal gap between the implant and the bone socket walls at the same four sites. An experienced examiner who was not aware of the patients' group assignments performed the clinical measurements in millimeters using a UNC-15 periodontal probe. The procedures were performed at the Center for Dental Studies, School of Dental Medicine, State University of New York at Buffalo, NY. Both the surgeon and the restorative dentist were aware of the patients' group assignments; however, they did not perform the measurements of the variables. Data analysis The restricted maximum likelihood method (Wolfinger et al., 1994) was used to fit multiple regression models to study the effect of local factors and patient information on the change in defect measurements during the 1-year follow-up period. Local factors included the type of site (buccal, lingual, mesial and distal), defect location (maxillary anterior, maxillary posterior and mandibular posterior) and implant length. Patient information included age (years) and gender. The treatment group (immediate or conventional loading) also was entered in the model. The analysis used the defects as the unit of analysis and adjusted for the covariance due to clustering of sites within subjects. The modeling was performed stepwise, and separately, for vertical and horizontal defects. Variables that showed an alpha value > 0.1 were removed from the model. The analysis was performed using SAS version 9.2 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC). Results Sixteen implants were placed, one in each subject. Five implants were placed in the anterior maxilla, 7 in the posterior maxilla and 4 in the posterior mandible. A total of 64 defects in 16 subjects were measured at baseline and at the follow-up visit 1 year postoperatively. At baseline, the vertical and horizontal defects were most pronounced at the buccal sites (Table 1). The mean reduction in vertical defects between baseline and re-entry for all sites predicted in the regression analysis was 2.42 mm (p = ). The final
4 Othman Shibly et al: Buccal Bone Regeneration at Implants 65 Table 2. Regression analysis* of the change in vertical defects dimension during one year Variable Coefficient Intercept 2.55 Buccal sites (vs. lingual) 3.82 Proximal sites (vs. lingual) SE p < *Mixed regression model procedure (adjusted R = 71.9%). SE, standard error Table 3. Regression analysis* of the change in horizontal defects (gap) dimension during one year. Variable Coefficient SE p Intercept < Buccal sites (vs. lingual) < Proximal sites (vs. lingual) Females (vs. males) Immediate loading (vs. conventional loading) *Mixed regression model procedure (adjusted R = 57.3%). SE, standard error model, shown in Table 2, indicated that the type of site (buccal, lingual, proximal) had a significant effect on the magnitude of reduction in the vertical defects dimension (p = ). Compared to lingual sites, the buccal sites showed the greatest resolution in vertical defects dimension (6.37 mm), followed by proximal sites (0.78 mm). Other variables assessed in this study did not have a significant effect on vertical defects. The results were similar when the percentage of defect fill was used as a response variable in the model. The mean reduction in horizontal defects for all sites predicted in the regression analysis was 1.59 mm (p < ). In the final regression model (Table 3), variables with significant effects were the type of site (p = ), gender (p = 0.025) and treatment group (p = 0.036). Compared to lingual sites, the buccal sites showed the greatest resolution in horizontal gap dimension (3.2 mm), followed by proximal sites (0.8 mm). The reduction in gap dimension was significantly higher in males than females (p = 0.025) and in the conventional loading groups than the immediate loading groups (p = 0.036). A test of the interaction effect of sex and loading type showed no significant effect. Age, defect location in the mouth and implant length did not show significant effects on the reduction in gap dimension during the first year. Discussion This investigation reported a case series of patients who consented to re-entry aimed at evaluating the amount of buccal-bone regeneration and the pattern of remodeling around 16 immediate implants with partially missing buccal plate; 6 implants were immediately loaded after placement and 10 implants had conventional loading as part of a previously published protocol (Shibly et al., 2010). Although the consent form of the main study included re-entry evaluation, only 16 patients agreed to do re-entry at one year follow-up. Hence, randomization and study power, which was achieved in the original study, were compromised in this follow-up, re-entry study. Despite these shortcomings, this case series provides useful information regarding bone regeneration around implants. In the present investigation the surgical protocols that included the application of bone grafting material and membrane in combination with immediate loading (unsubmerged healing) or conventional loading (submerged healing) resulted in coronal displacement of the mucogingival junction in some cases, especially in the conventional loading group. The reason is that the surgical protocol for conventional loading requires a releasing incision for the buccal tissue to allow for
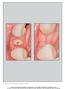
5 66 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology /3 Fig. 1A Fig. 1B Fig. 1C Figure 1. Stages of procedure for the treatment group immediate implant with immediate loading. A) An implant was placed immediately after extraction of tooth number 7 showing partial loss of buccal plate. B) A demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft was placed and covered with collagen membrane. Temporary abutment in place. C) One year re-entry showing significant bone regeneration of the buccal plate. primary closure over the implant (Shibly et al., 2010). The pattern of buccal-bone remodeling in both groups indicates that the problem associated with complete or partial loss of the buccal plate prior to implant placement in a fresh extraction socket can be overcome if an appropriate guided bone regeneration (GBR) procedure is implemented and if there is enough interproximal and lingual bone to allow the implant initial stability. We have previously reported a 1-year implant survival rate of 95% using this protocol (Shibly et al., 2010). However, when immediate placement results in a fenestrated implant or a dehiscence defect, the surgeon must decide whether additional bone augmentation procedures should be conducted or, alternatively, whether a delayed approach would be a better choice. Furthermore, studies show that when the defect around the immediate implant is a selfmaintained, four-wall bony defect, it may heal without performing a GBR procedure (Arau jo, et al., 2006; Botticelli et al., 2004; Ferrus et al., 2010; Funato et al., 2007; Nevins et al., 2006; Shibly et al., 2010). The results of this study suggest that applying the GBR principle to large bony defects, including loss of the buccal bone, at the time of implant placement in fresh extraction sockets may result in clinically successful bone regeneration around the implant at the defect site. This finding is consistent with recent studies suggesting that when a large buccal defect or dehiscence existed at the time of placement of an immediate implant, GBR application is necessary to regenerate bone around the implant to maintain the soft and hard tissues. Augmentation of larger defects usually dictates the use of a barrier membrane with or without bone grafting materials (Gher et al., 1994; Nemcovsky et al., 2000; Rosenquist and Ahmed, 2000; Shibly et al., 2010; Tehemar et al., 2003). In this study, clinical evaluation at the re-entry surgery showed that in general the implants were clinically stable, asymptomatic and free of osseous defects. The probing and measurements of hard tissue around the implants were indicative of new hard tissue filling the peri-implant defect, and thus indicative of buccal-bone regeneration. This finding agrees with results of other studies (Covani et al., 2008; Ferrus et al., 2010; Mardinger et al., 2009) and is consistent with the hypothesis that the main factors necessary to induce bone healing are initial implant stability, presence of bony walls capable of maintaining a firm blood clot, and the use of barrier membranes and bone-grafting materials when a buccal-bone defect exists. The peri-implant osseous gap originally observed in our study at baseline was clinically filled by hard tissue, which could not be probed. The bone regeneration that filled the vertical gap was not influenced by patients' age or gender, or local factors, such as defect location (maxillary/mandibular, anterior/posterior) and length of implants. On the other hand, the bone fill of the horizontal gap was modestly higher (statistically significant at p < 0.05) in males than females, and in the conventional group than the immediate loading group. However, generalizing these results must be done with caution because of the relative small sample size, lack of randomization and unequal groups.
6 Othman Shibly et al: Buccal Bone Regeneration at Implants 67 At one-year re-entry, all peri-implant gaps assessed from the internal socket wall to the implant surface were healed and the horizontal defects were filled with bone. However, the vertical buccal defects showed mean reduction in the bone effect from 9.63 to an average residual vertical defect of approximately 3 mm. In a few implants threads were still exposed on the buccal aspect (Figure 1). Figure 1 (implant #7 with cemented crown) shows mucosal recession and metal transparency, which is an obvious esthetic concern, particularly in the anterior area. Based on this clinical observation, GBR was successful in obtaining significant bone regeneration. However, it did not result in complete resolution of the buccal defect. This may be attributed to various reasons, including immediate placement, immediate loading protocol or buccal implant placement. A major limitation of this investigation is the lack of histological analysis to describe the characteristics of the tissue that came into contact with the implant. The amount of bone regeneration found in this study was based on clinical appearance and probing. Histological evaluation would have given a definite answer as to whether we observed true bone or dense connective tissues. Also, the present findings of a significantly greater reduction in gap dimension in males than females and in the conventional than immediate loading groups should be validated in another betterpowered study. Conclusions This case series report suggests that bone regeneration was successful around implants placed immediately in fresh sockets, regardless of whether the time of loading of the implant was immediately after placement or delayed. A partially missing buccal plate was not a critical factor for the stability and successful osseointegration of immediate implants, and these defects could heal clinically using GBR. Measurements performed at re-entry surgery showed significant bone regeneration of the buccal plate as a result of the GBR procedure. Even complete loss of the buccal plate did not pose a challenge to an immediately placed implant in the esthetic zone if an adequate amount of lingual and interproximal bone was available to ensure initial stability and a GBR procedure was used. This case series showed some regeneration of the buccal bone in all 16 cases that consented to re-entry. However, future studies, including histological evaluation, are needed to validate these findings. Also, placement of immediate implants must be done cautiously in the anterior zone of periodontally compromised patients, as this report did not show complete resolution of the buccal plate, which may impose an esthetic concern that can be manifested by buccal mucosal recession. An adequately powered, prospective, randomized, Fig. 2A Fig. 2B Fig. 2C Figure 2. Stages of procedure for the treatment group immediate implant with conventional loading. A) An implant was placed immediately after extraction of tooth number 6. B) A demineralized freeze-dried bone allograft was placed and covered with collagen membrane. C) One year re-entry showing significant bone regeneration of the buccal plate. clinical trial will be valuable to study the effects of patient characteristics and local factors.
7 68 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology /3 Acknowledgments The study was supported by grant from Nobel Biocare Services AG. References Araújo, M., Wennström, J. and Lindhe, J. Modeling of the buccal and lingual bone walls of fresh extraction sites following implant installation. Clinical Oral Implants Research 2006; 17: Becker, W., Becker, B.E., Polizzi, G. and Bergstrom, C. Autogenous bone grafting of bone defects adjacent to implants placed into immediate extraction sockets in patients: A prospective study. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 1994; 14: Block, M.S. and Kent, J.N. Placement of endosseous implants into tooth extraction sites. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 1991; 49: Botticelli, D., Berglundh, T. and Lindhe, J. Hard-tissue alterations following immediate implant placement in extraction sites. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 2004; 31: Cochran, D.L., Schenk, R., Wozney, J.M. and Jones, A.A. Recombinant human BMP protein-2 stimulation of bone formation around endosseous dental implants. Journal of Periodontology 1999; 70: Covani, U., Cornelini, R. and Barone, A. Buccal bone augmentation around immediate implants with and without flap elevation: A modified approach. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 2008; 23: Ferrus, J., Cecchinato, D., Pjetursson, E.B., Lang, N.P., Sanz, M. and Lindhe, J. Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets. Clinical Oral Implants Research 2010; 21: Funato, A., Salama, M.A., Ishikawa, T., et al. Timing, positioning, and sequential staging in esthetic implant therapy: A fourdimensional perspective. International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2007; 27: Gher, M.E., Quintero, G., Assad, D., Monaco, E. and Richardson, A.E. Bone grafting and guided bone regeneration for immediate dental implants in humans. Journal of Periodontology 1994; 65: Mardinger, O., Chaushu, G., Ghelfan, O. and Nissan, J. Intrasocket reactive soft tissue for primary closure after augmentation of extraction sites with severe bone loss before implant placement. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 2009; 67: Nemcovsky, C.E., Moses, O., Artzi, Z. and Gelernter, I. Clinical coverage of dehiscence defects in immediate implant procedures: Three surgical modalities to achieve primary soft tissue closure. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 2000; 15: Nevins, M., Camelo, M., De Paoli, S., et al. A study of the fate of the buccal wall of extraction sockets of teeth with prominent roots. International Journal of Periodontics and Restorative Dentistry 2006; 26: Qahash, M., Susin, C., Polimeni, G., Hall, J. and Wikesjö, U.M. Bone healing dynamics at buccal peri-implant sites. Clinical Oral Implants Research 2008; 19: Rosenquist, B. and Ahmed, M. The immediate replacement of teeth by dental implants using homologous bone membranes to seal the sockets: Clinical and radiographic findings. Clinical Oral Implants Research 2000; 11: Schwartz-Arad, D. and Chaushu, G. Placement of implant into fresh extraction sites: 4 to 7 years retrospective evaluation of 95 immediate implants. Journal of Periodontology 1997; 68: Shibly, O., Al-Ghamdi, A. and Al-Sabbagh, M. Guidelines for immediate implant placement in periodontally compromised patients. Dental Learning 2010; 4:1-8. Shibly, O., Patel, N., Albandar, J.M. and Kutkut, A. Bone regeneration around implants in periodontally compromised patients: A randomized clinical trial of the effect of immediate implant with immediate loading. Journal of Periodontology 2010; 81: Tehemar, S., Hanes, P. and Sharawy, M. Enhancement of osseointegration of implants placed into extraction socket of healthy and periodontally diseased teeth by using graft material and eptfe membrane, or a combination. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 2003; 5: Wolfinger, R.D., Tobias, R.D. and Sall, J. Computing Gaussian likelihoods and their derivatives for general linear mixed models. SIAM J Scientific Computing 1994; 15:
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets
 Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Initially, implant dentistry was focused on
 CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Vertical and/or horizontal alveolar
 CLINICAL Vascularized Connective Tissue Flap for Bone Graft Coverage Alan S. Herford, DDS, MD 1 * Todd C. Cooper, DDS 1 Carlo Maiorana, DDS, MD 2 Marco Cicciù, DDS, PhD 2 Alveolar defects are characterized
CLINICAL Vascularized Connective Tissue Flap for Bone Graft Coverage Alan S. Herford, DDS, MD 1 * Todd C. Cooper, DDS 1 Carlo Maiorana, DDS, MD 2 Marco Cicciù, DDS, PhD 2 Alveolar defects are characterized
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Sanju P. Jose
 Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
The immediate placement of dental implants
 CASE REPORT Bone Regeneration Around Immediate Implants Utilizing a Dense Polytetrafluoroethylene Membrane Without Primary Closure: A Report of 3 Cases Jonathan Waasdorp, DMD, MS 1 * Sylvan Feldman, DDS,
CASE REPORT Bone Regeneration Around Immediate Implants Utilizing a Dense Polytetrafluoroethylene Membrane Without Primary Closure: A Report of 3 Cases Jonathan Waasdorp, DMD, MS 1 * Sylvan Feldman, DDS,
Conventional immediate implant placement and immediate placement with socket-shield technique Which is better
 International Journal of Clinical Medicine Research 2014; 1(5): 176-180 Published online December 30, 2014 (http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijcmr) ISSN: 2375-3838 Conventional immediate implant placement
International Journal of Clinical Medicine Research 2014; 1(5): 176-180 Published online December 30, 2014 (http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijcmr) ISSN: 2375-3838 Conventional immediate implant placement
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
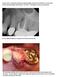 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Clinical outcome of submerged vs. non-submerged implants placed in fresh extraction sockets
 Luca Cordaro Ferruccio Torsello Mario Roccuzzo Clinical outcome of submerged vs. non-submerged implants placed in fresh extraction sockets Author s affiliations: Luca Cordaro, Ferruccio Torsello, Eastman
Luca Cordaro Ferruccio Torsello Mario Roccuzzo Clinical outcome of submerged vs. non-submerged implants placed in fresh extraction sockets Author s affiliations: Luca Cordaro, Ferruccio Torsello, Eastman
Thick vs. Thin Gingival Biotypes: A Key Determinant in Treatment Planning for Dental Implants
 r s Thick vs. Thin Gingival Biotypes: A Key Determinant in Treatment Planning for Dental Implants richard t. kao, dds, phd; mark c. fagan, ms, dds; and gregory j. conte, ms, dmd abstract During the treatment
r s Thick vs. Thin Gingival Biotypes: A Key Determinant in Treatment Planning for Dental Implants richard t. kao, dds, phd; mark c. fagan, ms, dds; and gregory j. conte, ms, dmd abstract During the treatment
SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT
 MAVEN CASE REPORT SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT Dr. Parthasarathi Biswas 1, Dr. Debajyoti Mondal 1, Dr. B Praveena Devi 1, Dr. Indrasri Das 2, Dr. Somen Bagchi 3,
MAVEN CASE REPORT SOCKET WHETHER TO PRESERVE IT NOW OR TO CREATE LATER? - A CASE REPORT Dr. Parthasarathi Biswas 1, Dr. Debajyoti Mondal 1, Dr. B Praveena Devi 1, Dr. Indrasri Das 2, Dr. Somen Bagchi 3,
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials mucoderm 3D-Regenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials 3DRegenerative Tissue Graft strictly biologic mucoderm Soft Tissue Graft Indications mucoderm is a collagen tissue matrix derived of animal dermis
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging
 Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Immediate Implant Placement: A Review
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. IV (May. 2017), PP 90-95 www.iosrjournals.org Immediate Implant Placement: A Review
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. IV (May. 2017), PP 90-95 www.iosrjournals.org Immediate Implant Placement: A Review
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT
 ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT * Mishal Piyush Shah 1 and Sheela Kumar Gujjari 2 1 Department of
ALVEOLAR RIDGE AUGMENTATION UTILIZING PLATELET RICH FIBRIN IN COMBINATION WITH DEMINERALIZED FREEZE-DRIED BONE ALLOGRAFT A CASE REPORT * Mishal Piyush Shah 1 and Sheela Kumar Gujjari 2 1 Department of
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Socket Graft Plus. Case Presentation. Ideal Bone Graft for All Socket Grafting Situations. Case #1
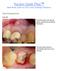 Socket Graft Plus Ideal Bone Graft for All Socket Grafting Situations Case Presentation Case #1 Tooth #3 presents with a buccal parulis, ensuring a buccal alveolar fenestration. The tooth will be remove
Socket Graft Plus Ideal Bone Graft for All Socket Grafting Situations Case Presentation Case #1 Tooth #3 presents with a buccal parulis, ensuring a buccal alveolar fenestration. The tooth will be remove
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter
 THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
Immediate implant placement in a single staged
 Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Immediate implants at fresh extraction sockets: from myth to reality
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 132 152 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Immediate implants at fresh extraction
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 132 152 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Immediate implants at fresh extraction
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Early implant placement: 3D radiographic study on the fate of buccal wall
 Early implant placement: 3D radiographic study on the fate of buccal wall A. Lanza 1-2, F. Scognamiglio 1, G. De Marco 1, F. Di Francesco 1, F. Femiano 1-3, M. Lanza 4, A. Itro 5 1 DD-Multidisciplinary
Early implant placement: 3D radiographic study on the fate of buccal wall A. Lanza 1-2, F. Scognamiglio 1, G. De Marco 1, F. Di Francesco 1, F. Femiano 1-3, M. Lanza 4, A. Itro 5 1 DD-Multidisciplinary
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes
 Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up
 Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya. botiss. dental bone & tissue regeneration. biomaterials. strictly biologic
 Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE biologic potential bovine block & granules: pure bone mineral
Clinical cases by Dr. Fernando Rojas-Vizcaya dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials strictly biologic botiss BTR system: BONE biologic potential bovine block & granules: pure bone mineral
Analysis of the socket bone wall dimensions in the upper maxilla in relation to immediate implant placement
 Guy Huynh-Ba Bjarni E. Pjetursson Mariano Sanz Denis Cecchinato Jorge Ferrus Jan Lindhe Niklaus P. Lang Analysis of the socket bone wall dimensions in the upper maxilla in relation to immediate implant
Guy Huynh-Ba Bjarni E. Pjetursson Mariano Sanz Denis Cecchinato Jorge Ferrus Jan Lindhe Niklaus P. Lang Analysis of the socket bone wall dimensions in the upper maxilla in relation to immediate implant
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Original Article Clinical and biometrical evaluation of socket preservation using demineralized freeze dried bone allograft with and without the palatal connective tissue as a biologic
Dental Research Journal Original Article Clinical and biometrical evaluation of socket preservation using demineralized freeze dried bone allograft with and without the palatal connective tissue as a biologic
Prosthodonticstown. Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites. clinical. Table I
 Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS
 The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
Gingivectomy, excision gingival, each quadrant Gingivoplasty, each quadrant
 Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
Dental in Nature Oral Surgery Effective CDT D3410 surgery - anterior D3421 surgery bicuspid (first root) D3425 surgery molar (first root) D3426 D3427 surgery (each additional root) Periradicular surgery
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report The Socket Science of Immediate Implants - Case Report Sanjay Kaul 1**, Shantipriya Reddy 2*, Soumya Kambali
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report The Socket Science of Immediate Implants - Case Report Sanjay Kaul 1**, Shantipriya Reddy 2*, Soumya Kambali
Then and Now. Implant Therapy:
 Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Implant Site Development Part I
 REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Interface with Professional Partners
 Interface with Professional Partners Develop site v Site ready v Choose Implant Systemic Evaluation Initial radiographs Models/Photos Treat Refer Planning Clinical Evaluation Surgical template Restorative
Interface with Professional Partners Develop site v Site ready v Choose Implant Systemic Evaluation Initial radiographs Models/Photos Treat Refer Planning Clinical Evaluation Surgical template Restorative
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 15 No. 03 July 16
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Complex Exodontia. Jone Kim, DDS, MS
 Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
Complex Exodontia Jone Kim, DDS, MS Diplomate, American Board of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Lecturer, UCLA School of Dentistry, Dept. of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Principle of Complex Exodontia Principle
RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS. The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4
 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS 1 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS RESISTANT TO EXPOSURE The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4 RELIABLE BARRIER
RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS 1 RELIABLE WHEN IT COUNTS RESISTANT TO EXPOSURE The unique collagenase-resistant membrane protects bone graft and supports treatment success even when exposed 4 RELIABLE BARRIER
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Dental implants certainly have
 CLINICAL Facial Wall Defect Grafting Techniques in Preparation for a Dental Implant by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Dental implants certainly have become a popular method of restoring missing teeth. The
CLINICAL Facial Wall Defect Grafting Techniques in Preparation for a Dental Implant by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Dental implants certainly have become a popular method of restoring missing teeth. The
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
In 1981, Dr. Albrektsson, a member of
 Osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability in the maxilla: part II case report with 2-year follow-up Drs. Ann Marie Hofbauer and Salah Huwais offer another case study
Osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability in the maxilla: part II case report with 2-year follow-up Drs. Ann Marie Hofbauer and Salah Huwais offer another case study
GBR membrane for ideal regeneration
 GBR membrane for ideal regeneration 1) i-gen Lingual Extension should be considered for a large defect. Need to have at least 1mm of space above the platform of a fixture: Make this space with a pre-existing
GBR membrane for ideal regeneration 1) i-gen Lingual Extension should be considered for a large defect. Need to have at least 1mm of space above the platform of a fixture: Make this space with a pre-existing
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Bridge Flap: A Sine Qua Non For Mucogingival Deformities Debajyoti Mondal, Anju L, Rajul Choradia, Somen
GBR membrane for ideal regeneration. i-gen TM. 2mm. >2.5mm. Lingual Extension. >100 blunt angle
 REGENERATION 02/03 Design Concept GBR membrane for ideal regeneration i-gen TM Description Single A type Small IG1W4509 Single A type Regular IG1W5510 Single A type Wide IG1W6511 Single B type Small IG2W0918
REGENERATION 02/03 Design Concept GBR membrane for ideal regeneration i-gen TM Description Single A type Small IG1W4509 Single A type Regular IG1W5510 Single A type Wide IG1W6511 Single B type Small IG2W0918
Identification of Stability Changes for Immediately Placed Dental Implants
 Identification of Stability Changes for Immediately Placed Dental Implants Jason D. West, DDS, MS 1 /Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 2 Purpose: To evaluate the changes in stability of immediately placed implants
Identification of Stability Changes for Immediately Placed Dental Implants Jason D. West, DDS, MS 1 /Thomas W. Oates, DMD, PhD 2 Purpose: To evaluate the changes in stability of immediately placed implants
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior
 Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Immediate implantation and provisionalization: single-tooth restoration in the esthetic zone
 Immediate implantation and provisionalization: single-tooth restoration in the esthetic zone Authors_Susan McMahon, DMD, and Karrah Petruska _c.e. credit part II This article qualifies for C.E. credit.
Immediate implantation and provisionalization: single-tooth restoration in the esthetic zone Authors_Susan McMahon, DMD, and Karrah Petruska _c.e. credit part II This article qualifies for C.E. credit.
