ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect Of Strong Organic Acids On Dentinal Tubules Of Teeth- A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study
|
|
|
- Curtis Woods
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IJCMR 445 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect Of Strong Organic Acids On Dentinal Tubules Of Teeth- A Scanning Electron Microscopic Study Daksh Sharma 1, Shreedhar Balasundari 2, Kamboj Mala 3, Natarajan S 4 ABSTRACT Introduction: The head and neck is a complex structure of both soft and hard tissues. Natural teeth are the most durable of all tissues, being denser and chemically more inert. This study is an attempt to observe changes caused by strong inorganic acids (hydrochloric acid, nitric acid and sulphuric acid) to human maxillary first premolar teeth under scanning electron microscope. Changes were also noted at different time periods to determine the best decalcifying agent among these acids. Material and Methods: A total of 40 human maxillary first premolar teeth were collected. All the teeth were placed in 10% formalin (immediately after extraction). After fixation in formalin for hours, teeth were immersed in their respective acids 10 in 37% HCl, 10 in 65% HNO 3, 10 in 96% H 2 SO 4 and 10 normal teeth were immersed in normal saline. Discussion: We conclude that 37% HCl took the minimum time to dissolute the teeth immersed and also showed the maximum change in number and diameter of dentinal tubules as compared to time taken by other two acids. But the structural changes were more in 65% HNO 3 as compared to other two acids. Conclusion: Work done on presence of intertubular dentin, occlusion of dentinal tubules and presence of crystals make this study unique. Additional studies with larger sample size would further help to assess the structural changes in dentin of the acid treated tooth. Keywords: Teeth; Dentine, Strong Organic Acids, Scanning Electron Microscope How to cite this article: Daksh Sharma, Shreedhar Balasundari, Kamboj Mala, Natarajan S. Effect of strong organic acids on dentinal tubules of teetha scanning electron microscopic study. International Journal of Contemporary Medical Research. 2015;2(2): Source of Support: Nil Conflict of Interest: None 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor and Head, 4 Professor, Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, Career Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences and Hospital, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, 3 Senior Professor and Head, Department of Oral Pathology and Microbiology, Post Graduate Institute of Dental Sciences, Rohtak, Haryana, India Corresponding author: Dr. Mala Kamboj, 31/9J, Medical Enclave, PGIMS, Rohtak INTRODUCTION Head and neck is a complex structure of both soft and hard tissues. 1 Natural teeth are the most durable, being denser and chemically more inert. 2 When teeth first form they are composed of soft tissue resembling the consistency of a jelly fish. As the body matures, this soft tissue mineralizes by a process of incorporating minerals into its specialized soft tissue, making teeth and bone hard and strong. 3 Soft tissues pose little resistance to histochemical techniques. Presence of high inorganic content like calcium and phosphorus in teeth, make it very hard to prepare for microscopic examinations. 2 Decalcification is done to make teeth suitable for viewing under microscope. The aim is to remove calcium salts from mineralized tissue using chemical solutions like acids and chelating agents, while preserving the organic portions. 1 It is carried out by chemical agents, either with acids to form soluble calcium or with chelating agents that bind to calcium ions. Acids decalcifiers are divided into 2 groups: 1. Strong inorganic acids: like HNO 3 and HCl. They decalcify rapidly and cause considerable change in tooth immersed in them. 2. Weak organic acids: like formic acid, picric acid and acetic acid. Studies have been done on teeth using these acids. 4 Dentinal tubules extend through entire thickness of the dentin from the DEJ to the pulp. The
2 446 tubules follow an S-shaped path from the outer surface to the perimeter of pulp in coronal dentin. They are tapered structures measuring approx 2.5 µm in dia near the pulp, 1.2 µm in mid portion of dentin & 900 nm near DEJ. In the coronal parts of the young premolar and molar teeth, number of tubules range from 59,000 to 76,000 per sq mm at the pulpal surface, with approx half as many per sq mm near the enamel. Dentinal tubules are delimited by a collar of more highly calcified matrix called peritubular dentin. 5 Peritubular dentin is a mineralized deposit formed centripetally in the dentinal tubules with advancing age, so that the tubular diameter is smaller in teeth from older persons. 6 It extends for about 1 to 2 µm. 7 To observe these minute structures of dentinal tubules normally and the ultra structural changes after being subjected to decalcification, SEMs are used. As Thomas Huxley said In a scientific work, those who refuse to go beyond fact, rarely get as far as fact. Thus, limiting ourselves only to light microscopy would mean to handicap ourselves. Looking beyond and trying to study the surface details and ultra structural changes caused by the strong organic acids on normal teeth with the help of SEM is what we have done in our study. Thus, this study is an attempt to observe changes caused by strong inorganic acids (HCl, HNO 3 and H 2 SO 4 ) to human maxillary first premolar teeth under SEM. Changes were also noted at different time periods to determine the best decalcifying agent among these acids. MATERIALS AND METHODS Source of Data The study was conducted on extracted teeth and only the non carious maxillary first premolar teeth which were extracted for orthodontic or periodontal reasons were used. These teeth were free of any restorations. A total of 40 human maxillary first premolar teeth were collected. Method to observe changes under naked eye All teeth were placed in 10% formalin (immediately after extraction). After fixation in formalin for hrs teeth were immersed in their respective acids 10 in 37%HCl, 10 in 65% HNO 3, 10 in 96% H 2 SO 4 and 10 normal teeth were immersed in normal saline. Changes in teeth were observed after specific time intervals in all acids. Changes were clicked and recorded in Nikon 255 camera. Teeth which had sufficient amount of crown portion left after acid immersion were kept in plastic containers containing distilled water. These teeth were used for observing and analyzing changes in density and diameter of dentinal tubule. Method to observe changes under SEM The SEM specimens were coated with gold palladium coating by EMITECH Sputter for two minutes and were fed into the (ZEISS Evo Special edition ) Scanning Electron Microscope, after mounting over the metallic stub. Each specimen was scanned at the lesional surface accelerating voltage of 10kV. The chosen magnification was x3000. The areas selected for photography were those where maximum width of the dentinal tubules was visible. Only the images of the representative areas were photographed. Maximum fields in the areas of interest on the SEM specimens were observed. As the teeth specimens were acid treated, the clicked surfaces showed uneven changes at fixed magnification. The normal samples (control group) were scanned first to form a base for the interpretation of samples with lesions. Then the acid immersed samples were subjected to a preliminary scan to note the changes. Based on preliminary trial scan and review of literature, the following features were looked for in the teeth of HCl, HNO 3 and H 2 SO Diameter and density of dentinal tubules. 2. Distinctness of peritubular and intertubular dentin 3. Presence of crystals within the tubules and its nature. The data obtained was entered in a master chart for further interpretation and analysis. Inclusion criteria 1. Crown surface closer to pulp of maxillary first premolars 2. Age: yrs 3. Teeth extracted for orthodontic and periodontal purposes
3 447 Exclusion criteria 1. Carious teeth 2. Restored teeth STATISTICAL ANALYSIS Continuous data was summarized in Mean ± SD while discrete (categorical) in %. All analyses were performed on STATISTICA statistical software (Windows version 6.0). RESULT Morphological changes The morphological changes in teeth of three groups (37% HCl, 65% HNO 3 and 96% H 2 SO 4 ) over the periods (0.5 hr to 96 hrs) were summarized in Table 1. The teeth were immersed separately in different containers containing the 3 different acids. At various intervals, the samples were taken out of the container and examined for any morphological changes; photographed and placed back in the containers. The specimens were under observation until they had completely dissolved or precipitated completely. Among acids, the 100% dissolution of teeth without any remnants was evident earliest in 37% HCl at after 8 hrs; 65% HNO 3 showed 100% dissolution without any remnants after 15 hrs and 96% H 2 SO 4 showed complete dissolution after 96 hrs. Normal dentinal tubule diameter and density: Closer to the pulp was measured by SEM and summarized in Table 2. Change in diameter of dentinal tubules and density of dentinal tubules/field: The changes in diameter and density of dentinal tubules of Group 2 (37% HCl), Group 3 (65% HNO 3 ) and Group 4 (96% H 2 SO 4 ) were observed up to complete dissolution. Observations are summarized in Table 3. Type of morphological changes like Intertubular dentin, Occluded tubules and Presence of crystals (calcification) closer to the pulp of all four groups up to complete dissolution (except Group 1) were observed. Distribution of Intertubular dentin and distribution of Occluded tubules were assessed according to four type i.e. (-) denotes absent, (+) denotes fewly present, (++) denotes moderately present, (+++) denotes significantly present. They are summarized in Table 4. DISCUSSION Teeth are the hardest tissues in the body, consisting of enamel, dentin and cementum, and have a highly mineralized extracellular matrix. 11 Unlike soft tissues, which can be easily sectioned and analyzed, teeth require complete demineralization in order to prepare proper sections for histological analysis. The process of decalcification is done to study the structure of tooth, pulp calcifications, and also to evaluate the biological response of dental pulp to restorative material. 1 There have been studies conducted on diameter and density of dentinal tubules in human permanent teeth when viewed under light microscopes, scanning electron microscope and transmission electron microscope. But to best of our knowledge there has been no study on effects of strong inorganic acids on dentin with density and diameter changes in dentinal tubules in human permanent teeth under scanning electron microscope. Therefore the present study was undertaken to observe the changes in dentin and within dentinal tubules in maxillary first premolars. We also observed the changes in intertubular dentin, occlusion of dentinal tubules and the presence of crystals. Changes were also noted at different time periods to determine the better decalcifying agent among these acids. There have been few studies conducted over the morphological changes when teeth were immersed in strong inorganic acids. The changes were seen for specific time duration until the teeth dissolute or there was complete fragmentation of teeth as in case of 96% H 2 SO 4. Jadhav et al worked with 37% HCL, 65% HNO 3 and 96% H 2 SO 4 and came up with the conclusion that 37% HCL took minimum time in tooth dissolution followed by 65% HNO 3 and lastly by 96% H 2 SO In an another study by Alessandra Mazza et al comprising of four acids 37% HCL, 65% HNO 3, 96% H 2 SO 4 and Aqua Regia (chloroazotic acid-hcl/nitric acid 1:3), it was found that 96% H 2 SO 4 took the maximum time to
4 448 Figure-1: Scanning electron micrographic figures of teeth immersed in 37% HCl, 65% HNO3, 95% H2SO4 at various hours to monitor the changes in the dentinal tubules of teeth. dissolve the teeth immersed among the four inorganic acids.9 Our results are in agreement with the above studies and we found complete dissolution of teeth immersed in 37% HCl in 8 hrs, 65% HNO3 in 15 hrs and 96% H2SO4 in 96 hrs respectively. We used Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) in place of light microscope as SEM is a powerful method for the investigation of surface structures. Electrons in SEM penetrate into the sample within a small depth, so that it is suitable for surface topology, for every kind of samples. This INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CONTEMPORARY MEDICAL RESEARCH Volume 2 Issue 2
5 449 Table-1: Morphological changes in teeth of three groups over the periods Observation periods 0.5 hr Group 2 (37% HCl) Presence of effervescence in solution in 10/10 (100%) with color alterations in 7/10 teeth (70%) Group 3 (65%HNO 3 ) Presence of effervescence in 8/10 teeth (80%) with yellow color deposit over teeth in 10 /10 teeth (100%) Group 4 (96% H 2 SO 4 ) No Change 1 hr 2 hr 4 hr Transparency in 7/10 teeth with color alterations in 10/10 teeth Disintegration of apical third of root with crack extending from incisal surface to middle third of crown in 7/10 teeth. Disintegration of middle third of root in 8/10 teeth. Yellow colored residue deposited over tooth in 8/10 teeth (80%) and transparency present. Disintegration of apical third without any crack on the crown in 8/10 teeth. Disintegration of middle third of root in 10/10 teeth No Change No Change Presence of white precipitate seen in 4/10 teeth (40%) 8 hr Complete dissolution in 10/10 teeth without any remnants Splitting of teeth in 9/10 teeth (90%) Presence of white precipitate seen in 7/10 teeth (70%) 15 hr - Complete dissolution in 10/10 teeth without any remnants. Increase in white precipitate seen in 10/10 teeth with partial dissolution of apical third of root present in 3/10 teeth 20 hr hr - - Partial dissolution of apical third of root seen in 4/10 teeth (40%) Partial dissolution of apical third of root seen in 6/10 teeth. Tooth was recognized in 10/10 teeth. White precipitate increased in 6/10 teeth 48 hr - - White precipitate was increased in 8/10 teeth with fragmentation of teeth in 6/10 teeth. Tooth was recognizable in 8/10 teeth. 72 hr hr - - White precipitate was increased in 10/10 teeth with fragmentation of teeth in 7/10 teeth. Tooth was still recognisable in 4/10 teeth. Complete dissolution in 10/10 teeth. Inference: 37% HCL took minimum time to dissolute the teeth followed by 65% HNO 3 and lastly by 96% H 2 SO 4
6 450 Table-2: Normal Dentinal Tubule Diameter And Density Measured By SEM Tooth number Chosen areas Diameter of dentinal tubules (µm) Density of dentinal tubules/field (no) 1. Closer to the pulp Closer to the pulp Closer to the pulp Closer to the pulp Closer to the pulp Closer to the pulp Closer to the pulp Closer to the pulp Closer to the pulp Closer to the pulp Inference: Tubule diameter ranges from 1.8 to 2.6 µm and number/field from 52.0 to Table-3: Summary (Mean ± SD) Of Changes In Diameter (µm) Of Dentinal Tubules And Changes In Density/Field (No.) Of Three Groups Over The Periods Observation Diameter (µm) of dentinal tubules Density/field (no.) of dentinal tubules periods Groups Group 2 (37% HCL) Group 3 (65% HNO 3 ) Group 4 (96% H 2 SO 4 ) Group 2 (37% HCL) Group 3 (65% HNO 3 ) Group 4 (96% H 2 SO 4 ) 0.5 hr 2.44 ± 0.29 No change No change ± 6.78 No change No change 1 hr 3.42 ± ± 0.17 No change ± ± 1.73 No change 2 hr 3.83 ± ± 0.16 No change ± ± 1.49 No change 4 hr 2.13 ± ± ± ± ± ± hr Complete Complete ± 2.37 ± ± ± 4.43 dissolution dissolution hr - Complete Complete ± 2.49 ± dissolution dissolution hr ± ± hr ± ± hr ± ± hr ± ± hr - - Complete dissolution % change (pre to final reading) 12.7% (in 3.5 hrs) 17.4% (in 7 hrs) 33.6% (68 hrs) 71.0% (in 3.5 hrs) 27.1% (in 7 hrs) 93.6% (68 hrs) Inference: Maximum diameter change according to time taken was seen in 37% HCL > 65% HNO 3 > 96%H 2 SO 4. Inference: Maximum change in number of tubules/field according to time taken was seen in 37% HCL, followed by 65% HNO 3 and lastly by 96%H 2 SO 4. technique provides a large depth of field, which means the area of the sample that can be viewed in focus at the same time is actually quite large. According to Tencate, normal dentinal tubule diameter is approximately 2.5 µm in diameter near the pulp. 5 Our SEM findings were also in agreement as the diameter of dentinal tubules of all samples ranged from 1.8 to 2.6 µm with mean (± SD) 2.16 ± 0.28 µm at closer to the pulp. Density of dentinal tubules/field (no.) of all samples ranged from 52.0 to with mean (± SD) ± Correlation analysis revealed a significant (p>0.05) and negative (inverse) correlation (r= -0.65, p<0.05) between diameter of dentinal tubules and density of dentinal tubules/field. This finding of ours is new
7 451 Table-4: Frequency distribution of Changes in Intertubular dentin, Occluded tubules and Presence of Crystals among the four groups Groups Intertubular Dentin Occluded Tubules Presence of Crystals Yes No Group 1(n=10) 10(100%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 8(80%) 2(20%) 0 (0%) 0(0%) 10(100%) Group 2(n=10) 7 (70%) 3 (30%) 0 (0%) 6(60%) 4(40%) 0 (0%) 9(90%) 1(10%) Group 3(n=10) 8 (80%) 2 (20%) 0 (0%) 2(20%) 8(80%) 0 (0%) 8(80%) 2(20%) Group 4 (n=10) 0 (0%) 10 (100%) 0 (0%) 1(10%) 8(80%) 0 (0%) 2(20%) 0(0%) χ 2 value (DF=3) P value P<0.001(Highly Significant) 0.016(Significant) P<0.001(Highly Significant) in the field of dentinal tubules as previous authors counted the number of dentinal tubules in mm 2. During decalcification of teeth in acid there are findings that the peritubular dentin to a large extent is dissolved. Decalcification of the peritubular dentin preceded that of the intertubular regions, not only in areas where the tubules opened on the experimental surface but also in areas where they were orientated parallel to this surface, indicating that the peritubular zone represents the most easily demineralized part of dentin. The peritubular zone became completely demineralized throughout most of the lesion. The tubule diameter measured on decalcified sections thus gives an excessively high value. 6 Our findings were in agreement as there is increase in diameter of dentinal tubules in all the three acids for certain time periods i.e 1hr, 2hr in 37% HCL, 1hr, 2hr, 4hr in 65% HNO 3 and 15hr in 96% H 2 SO 4. After certain time period i.e. (4 hr in HCL, 8hr in HNO 3 ) there was decrease in diameter of dentinal tubules. There was a unique finding in case of 96% H 2 SO 4 that changes in diameter of dentinal tubules were not persistent as in the other two acids. The maximum mean value of number of dentinal tubules per field was seen in 37% HCL in 1 hr (110.90) of immersion whereas the minimum number per field was seen in 96% H 2 SO 4 in 72 hr (2). Changes in proportion of intertubular dentin fewly present was significantly (p<0.001) higher in normal tooth, 37% HCL and 65% HNO 3 as compared to 96%H 2 SO 4 while moderately present was significantly higher in 96% H 2 SO 4 as compared to normal tooth, 37% HCL and 65% HNO 3.Similarly, comparing the proportion of Occluded tubules between the four groups. In other words, the proportion of Occluded tubules fewly present was significantly higher in normal tooth and 37% HCL as compared to 65% HNO 3 and 96% H 2 SO 4 while moderately present was significantly higher in 65% HNO 3 and 96%H 2 SO 4 as compared to normal tooth and 37% HCL. Further, comparing the proportion of presence of crystals between the four groups, the presence of crystals was significantly higher in 37% HCL, 65% HNO 3 and as 96% H 2 SO 4 compared to normal tooth. These findings of SEM are new in its kind. Through our study we conclude that 37% HCL took the minimum time to dissolute the teeth immersed and also showed the maximum change in number and diameter of dentinal tubules as compared to time taken by other two acids. But the structural changes were more in 65% HNO 3 as compared to other two acids. Our study was one of its kind as we worked on untouched and unrevealed effects of three commonly used strong acids on dentinal changes of human permanent maxillary first premolars. CONCLUSION The changes of dentin under effect of strong inorganic acids were best appreciated on SEM because of its large depth of field and range of magnification which is relatively wide and allows the investigator to easily focus on an area of interest. To the best of our knowledge there has been no work done previously to assess the presence of intertubular dentin, occlusion of
8 452 dentinal tubules and presence of crystals in observing the changes of strong inorganic acids on teeth. REFERENCES 1. Sanjai K, Kumarswamy J, Archana P, Papaiah L, Jayaram S, Krishnan L. Evaluation and comparison of different decalcifying agents on human teeth. Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 2012; 16: Zappa J. Comparison of different decalcification methods to hard teeth tissues morphological analysis. Dent Med Probl 2005; 42: David B Ferguson: Oral Bioscience, Churchill Livingstone Harcourt Publications John D. Bancroft and Marilyn Gamble. Theory and practice of histological techniques. 6th ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier; 2008 p Nanci A. Tencate s: Development, Structure and Function. Oral histology. 7thed. Mosby; 2008 p Kvaal S.I, Koppang H.S, Solheim T. Relationship between age and deposit of peritubular dentine. Gerodontology 1994; 11: Mjor A Ivar. Dentin Permeability: The basis for understanding pulp reactions and adhesive technology. Braz Dent J 2009; 20: Cho A, Suzuki S, Hatakeyama J, Haruyama N, Kulkarni A. A method for rapid demineralization of teeth and bones. The Open Dentistry Journal 2010;4: Mazza Alessandra, Merlati Giuseppe, Savio Caterina, Fassina Giovvani, Menghini Paolo and Danesino Paolo. Observations on dental structures when placed in contact with acids: Experimental studies to aid identification processes. J Forensic Sci 2005;50: Jadhav Kiran, Gupta Nidhi, Mujib Ahmed BR, Amberkar S Vikram. Effects of acids on the teeth and its relevance in postmortem identification. Journal of Forensic Dental Sciences 2009;1: Kubinek Roman, Zapletalova Zdena,Vujtek Milan, Novotny Radko, Kolarova Hana and Chmelickova Hana. Examination of Dentin surface using AFM and SEM. Modern research and educational topics in microscopy Formatex, 2007; Garberoglio R. and Brannstrom M. Scanning electron microscopic investigation of human dentinal tubules. Archs Oral Biol 1976; 21:
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
The Histology of Dentin
 The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth.
 Lec. 7 Dr. Ali H.Murad DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth. Physical properties: 1-Dentin is pale yellow in color,
Lec. 7 Dr. Ali H.Murad DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth. Physical properties: 1-Dentin is pale yellow in color,
Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study
 ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
ISSN 0970-4388 Etching with EDTA- An in vitro study BOGRA P a, KASWAN S b ABSTRACT: In the present study, 25% EDTA, in gel form, was used to analyse its micromorphological effects on tooth surfaces with
Diameter and Density of Dentinal Tubule in Human Primary Teeth
 Original Article Diameter and Density of Dentinal Tubule in Human Primary Teeth Jittikarn Sikanta 1, Sitthichai Wanachantararak 2 and Varisara Sirimaharaj 1 1 Department of Orthodontics and Pediatric Dentistry,
Original Article Diameter and Density of Dentinal Tubule in Human Primary Teeth Jittikarn Sikanta 1, Sitthichai Wanachantararak 2 and Varisara Sirimaharaj 1 1 Department of Orthodontics and Pediatric Dentistry,
Comparison of the microstructure of crown and root dentin by a scanning electron microscopic study
 J Dent Sci 2010;5(1):14 20 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the microstructure of crown and root dentin by a scanning electron microscopic study Chia-Yi Chu, 1 Tien-Chun Kuo, 2,3 Shu-Fang Chang, 1 Yow-Chyun
J Dent Sci 2010;5(1):14 20 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the microstructure of crown and root dentin by a scanning electron microscopic study Chia-Yi Chu, 1 Tien-Chun Kuo, 2,3 Shu-Fang Chang, 1 Yow-Chyun
DENTIN-PULP COMPLEX. Erlina Sih Mahanani. School of Dental sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia. Erlina Sih Mahanani
 DENTIN-PULP COMPLEX School of Dental sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Introduction Overview anatomy & histology of dentin and pulp. Development of dentin and pulp Structure of dentin and pulp Dentin
DENTIN-PULP COMPLEX School of Dental sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Introduction Overview anatomy & histology of dentin and pulp. Development of dentin and pulp Structure of dentin and pulp Dentin
Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Structure and mechanical properties of teeth. Advisors: M.A. Meyers & E. A. Olevsky Student :Yen-Shan Lin Date: 6/23/2008
 Structure and mechanical properties of teeth Advisors: M.A. Meyers & E. A. Olevsky Student :Yen-Shan Lin Date: 6/23/2008 Outline Basic structure and components of teeth Mechanical properties 1. tubule
Structure and mechanical properties of teeth Advisors: M.A. Meyers & E. A. Olevsky Student :Yen-Shan Lin Date: 6/23/2008 Outline Basic structure and components of teeth Mechanical properties 1. tubule
Confocal laser scanning microscopy study of dentinal tubules in dental caries stained with alizarin red
 Archives of Orofacial Sciences (2008), 3(1): 2-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Confocal laser scanning microscopy study of dentinal tubules in dental caries stained with alizarin red A.F. Marzuki, S.M. Masudi * School
Archives of Orofacial Sciences (2008), 3(1): 2-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Confocal laser scanning microscopy study of dentinal tubules in dental caries stained with alizarin red A.F. Marzuki, S.M. Masudi * School
Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis)
 Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Preclinical Dentistry. I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects. Lenka Roubalíková
 Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
XPS surface analysis of human tooth samples with EnviroESCA
 Application Note #000396 KeyWords XPS, Human Tissue, Tooth, Measurements, Surface Analysis XPS surface analysis of human tooth samples with EnviroESCA Human teeth from an adult and a baby were studied
Application Note #000396 KeyWords XPS, Human Tissue, Tooth, Measurements, Surface Analysis XPS surface analysis of human tooth samples with EnviroESCA Human teeth from an adult and a baby were studied
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
DEFENSE MECHANISM OF DENTINE AND PULP AGAINST INJURY
 DEFENSE MECHANISM OF DENTINE AND PULP AGAINST INJURY DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY MEMBER OF IRAQI ENDODONTICS SOCIETY The reaction in dentine are
DEFENSE MECHANISM OF DENTINE AND PULP AGAINST INJURY DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY MEMBER OF IRAQI ENDODONTICS SOCIETY The reaction in dentine are
Decalcification and Clearing of Bone eg. Fibula. Salem Kharwa Clinical Anatomy Medical School
 Decalcification and Clearing of Bone eg. Fibula Salem Kharwa Clinical Anatomy Medical School Bone composition Bone consists of cells (osteocytes) surrounded by a calcified matrix containing collagen fibres.
Decalcification and Clearing of Bone eg. Fibula Salem Kharwa Clinical Anatomy Medical School Bone composition Bone consists of cells (osteocytes) surrounded by a calcified matrix containing collagen fibres.
Biomechanics of Solids
 Biomechanics of Solids Devendra Bajaj Graduate Student, LAMP Department of Mechanical Engineering UMBC ENCH 484/693: Biomedical Engineering. (April 18, 2007) Historical Facts Leonardo da Vinci 1452-1519
Biomechanics of Solids Devendra Bajaj Graduate Student, LAMP Department of Mechanical Engineering UMBC ENCH 484/693: Biomedical Engineering. (April 18, 2007) Historical Facts Leonardo da Vinci 1452-1519
Preparation Techniques of Luminal and Hard Tissues for Scanning Electron Microscopy
 Preparation Techniques of Luminal and Hard Tissues for Scanning Electron Microscopy Y. Ersoy Canillioglu and G. Erkanli Senturk Bahcesehir University, School of Medicine, Department of Histology and Embryology,
Preparation Techniques of Luminal and Hard Tissues for Scanning Electron Microscopy Y. Ersoy Canillioglu and G. Erkanli Senturk Bahcesehir University, School of Medicine, Department of Histology and Embryology,
Core build-up using post systems
 Core build-up using post systems Dr. Gergely Pataky Department of Conservative Dentistry What to speak about today General considerations Classification of post systems Dowel-core or fibre post? Biologic
Core build-up using post systems Dr. Gergely Pataky Department of Conservative Dentistry What to speak about today General considerations Classification of post systems Dowel-core or fibre post? Biologic
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry. Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS
 KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
KING SAUD UNIVERSITY College of Dentistry Department of Restorative Dental Sciences DIVISION OF ENDODONTICS COURSE OUTLINE 323 RDS Pre-Clinical Endodontics Three (3) Credit Hours Third Year 2014-2015 Prepared
Medical NBDE-II. Dental Board Exams Part I.
 Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Dentinogenesis and dentin permeability
 Dentinogenesis and dentin permeability Dr. Gábor Varga February, 2016 Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry, Semmelweis University Radiograph of teeth dentin is the major component Molar longitudinal
Dentinogenesis and dentin permeability Dr. Gábor Varga February, 2016 Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry, Semmelweis University Radiograph of teeth dentin is the major component Molar longitudinal
Key words: Nd: YAG laser, acid resistance, fluoride
 Combination Effects of Nd: YAG Laser Irradiation and Fluoride Application to Root Surface on Acid Resistance Nobuyori Nagai, Mitsuo Fukuda, Shingo Minoura, Yasuo Yamada, Jun Tako, Koji Miwa, Takashi Noguchi,
Combination Effects of Nd: YAG Laser Irradiation and Fluoride Application to Root Surface on Acid Resistance Nobuyori Nagai, Mitsuo Fukuda, Shingo Minoura, Yasuo Yamada, Jun Tako, Koji Miwa, Takashi Noguchi,
Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA in the Apical Sealing Ability of Lased And Unlased Root Canal Walls - A Pilot Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 6 Ver. XIV (June 2016), PP 100-104 www.iosrjournals.org Comparison of White MTA And Grey MTA
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth
 New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
IJBPAS, September, 2015, 4(9), Special Issue: ISSN: AGE ESTIMATION USING DIGITAL PANORAMIC RADIOGRAPHY
 : 124-129 ISSN: 2277 4998 AGE ESTIMATION USING DIGITAL PANORAMIC RADIOGRAPHY AREZOU TORKIAN E Mail: Torkian_ar@yahoo.com ABSTRACT One of the interesting applications of forensic deontology is age estimation
: 124-129 ISSN: 2277 4998 AGE ESTIMATION USING DIGITAL PANORAMIC RADIOGRAPHY AREZOU TORKIAN E Mail: Torkian_ar@yahoo.com ABSTRACT One of the interesting applications of forensic deontology is age estimation
CAP STAGE. Ans 1 The following are the stages of tooth development :
 Ans 1 The following are the stages of tooth development : 1. Bud stage 2. Cap stage 3. Bell stage 4. Advanced bell stage 5. Formation of Hertwig s epithelial root sheath BUD STAGE 1. Around the eighth
Ans 1 The following are the stages of tooth development : 1. Bud stage 2. Cap stage 3. Bell stage 4. Advanced bell stage 5. Formation of Hertwig s epithelial root sheath BUD STAGE 1. Around the eighth
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
Chapter 5. Investigation of in vitro Dental Erosion by Optical Techniques
 Chapter 5 Investigation of in vitro Dental Erosion by Optical Techniques 5.1 INTRODUCTION 5 Dental erosion is becoming an increasing predicament in dentistry and can be attributed to either exogenous
Chapter 5 Investigation of in vitro Dental Erosion by Optical Techniques 5.1 INTRODUCTION 5 Dental erosion is becoming an increasing predicament in dentistry and can be attributed to either exogenous
Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2013, Article ID 902861, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/902861 Case Report Typical Radiographic Findings of Dentin Dysplasia Type 1b with Dental Fluorosis S. Venkata
Institution : College of Dentistry Academic Department : Maxillofacial surgery and Diagnostic sciences
 Institution : College of Dentistry Academic Department : Maxillofacial surgery and Diagnostic sciences [MDS] Program : Bachelor of Dentistry [ BDS ] Course : Oral Biology Course Coordinator : Saleem Shaikh
Institution : College of Dentistry Academic Department : Maxillofacial surgery and Diagnostic sciences [MDS] Program : Bachelor of Dentistry [ BDS ] Course : Oral Biology Course Coordinator : Saleem Shaikh
Dental Anatomy and Occlusion
 CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
CHAPTER 53 Dental Anatomy and Occlusion Ma Lou C. Sabino DDS, and Emily G. Smythe, DDS What numerical system is used most commonly in the United States for designating the adult dentition? Pediatric dentition?
Comparison of removal of endodontic smear layer using NaOCl, EDTA, and different concentrations of maleic acid A SEM study
 Endodontology, Vol. 15, 2003 Comparison of removal of endodontic smear layer using NaOCl, EDTA, and different concentrations of maleic acid A SEM study *Prabhu SG **Rahim N ***Bhat KS ***Mathew J ABSTRACT
Endodontology, Vol. 15, 2003 Comparison of removal of endodontic smear layer using NaOCl, EDTA, and different concentrations of maleic acid A SEM study *Prabhu SG **Rahim N ***Bhat KS ***Mathew J ABSTRACT
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs
 Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Paper submission. Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case
 Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Journal of Oral & Dental Health
 Research Article X-ray Microanalysis of ormal Primary Tooth Dentine and Primary Tooth Dentine in Teeth Diagnosed Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type II oren JG 1 *, Sabel 1 and Cornell DH 2 Journal of Oral
Research Article X-ray Microanalysis of ormal Primary Tooth Dentine and Primary Tooth Dentine in Teeth Diagnosed Dentinogenesis Imperfecta Type II oren JG 1 *, Sabel 1 and Cornell DH 2 Journal of Oral
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice
 Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
1 24% 25 49% 50 74% 75 99% Every time or 100% 2. Do you assess caries risk for individual patients in any way? Yes
 1. When you examine patients to determine if they have a primary caries lesion, on what percent of these patients do you use airdrying to help diagnose the lesion? Never or 0% (skip to question 3) 1 24%
1. When you examine patients to determine if they have a primary caries lesion, on what percent of these patients do you use airdrying to help diagnose the lesion? Never or 0% (skip to question 3) 1 24%
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV.
 Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT
 ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska 1, R. Pirinska
ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska 1, R. Pirinska
Oral Embryology and Histology
 Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary Vol.:9 No.:2 2012
 MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
6610 NE 181st Street, Suite #1, Kenmore, WA
 660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
660 NE 8st Street, Suite #, Kenmore, WA 9808 www.northshoredentalacademy.com.08.900 READ CHAPTER The Professional Dental Assistant (p.-9) No Key Terms Recall Questions:,,,, and 6 CLASS SYLLABUS DAY READ
Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry
 Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry Vol. 2014(2014), Article ID 639870, 27 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2014.639870 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2014 Megha Jain, Sowmya Kasetty and Sudheendra
Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry Vol. 2014(2014), Article ID 639870, 27 minipages. DOI:10.5171/2014.639870 www.ibimapublishing.com Copyright 2014 Megha Jain, Sowmya Kasetty and Sudheendra
(Received February 6, 1935.)
 272 6 I2.3II.1:577. i6c THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN D ON THE CALCIUM CONTENT OF THE DENTINE. BY E. WILFRED FISH. (From the Hale Research Laboratory, Royal Dental Hospital, London.) (Received February 6, 1935.)
272 6 I2.3II.1:577. i6c THE EFFECT OF VITAMIN D ON THE CALCIUM CONTENT OF THE DENTINE. BY E. WILFRED FISH. (From the Hale Research Laboratory, Royal Dental Hospital, London.) (Received February 6, 1935.)
Effect of sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidin and EDTA on dentin microhardness
 Effect of sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidin and EDTA on dentin microhardness Received: 11/1/2015 Accepted: 18/5/2015 Diyar Khalid Bakr* Sazan Sherdil Saleem** Basam Kareem Amin* Abstract Background and
Effect of sodium hypochlorite, chlorhexidin and EDTA on dentin microhardness Received: 11/1/2015 Accepted: 18/5/2015 Diyar Khalid Bakr* Sazan Sherdil Saleem** Basam Kareem Amin* Abstract Background and
Abstract. A Case Of External Resorption
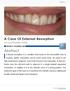 SHGDDS 1 BY Steven H. Goldstein, DDS Abstract External resorption is a condition that leads to the irreversible loss of enamel, dentin, cementum, and in some cases bone. Its cause is not fully understood,
SHGDDS 1 BY Steven H. Goldstein, DDS Abstract External resorption is a condition that leads to the irreversible loss of enamel, dentin, cementum, and in some cases bone. Its cause is not fully understood,
COURSE CURRICULUM FOR AESTHETIC DENTISTRY
 COURSE CURRICULUM FOR AESTHETIC DENTISTRY Esthetic Dentistry is actually the fourth dimension in clinical dentistry. In addition to biologic, Physiologic, and mechanical factors, all of which must be understood
COURSE CURRICULUM FOR AESTHETIC DENTISTRY Esthetic Dentistry is actually the fourth dimension in clinical dentistry. In addition to biologic, Physiologic, and mechanical factors, all of which must be understood
The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic
 1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
Requisite Approval must be attached
 Requisite Approval must be attached Multicultural Supplement must be attached CITRUS COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT DEPARTMENT Health Occupations COURSE NUMBER DENT 100 TITLE Dental Assisting Basics THIS COURSE
Requisite Approval must be attached Multicultural Supplement must be attached CITRUS COMMUNITY COLLEGE DISTRICT DEPARTMENT Health Occupations COURSE NUMBER DENT 100 TITLE Dental Assisting Basics THIS COURSE
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core
 Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
Dowel restorations Treatment with a post and core A post and core is a dental restoration used to sufficiently buildup tooth structure for future restoration with a crown when there is not enough tooth
Research Article. University, Mangalore Corresponding author Dr. Junaid Ahmed
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) ISSN 2320-6691 Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2013; 1(5):427-431 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) ISSN 2320-6691 Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2013; 1(5):427-431 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific
Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes. **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures**
 Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures** This review notes compiled and prepared by my sister for her own study, as a last day review session for
Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures** This review notes compiled and prepared by my sister for her own study, as a last day review session for
Adper Easy Bond. Self-Etch Adhesive. Technical Product Profile
 Adper Easy Bond Self-Etch Adhesive Technical Product Profile Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Product Description... 4 Composition...5-8 Background... 5 Mechanism of Adhesion to Enamel
Adper Easy Bond Self-Etch Adhesive Technical Product Profile Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction... 4 Product Description... 4 Composition...5-8 Background... 5 Mechanism of Adhesion to Enamel
PG Cert Contemporary Restorative and Aesthetic Dentistry (Level I)
 PG Cert Contemporary Restorative and Aesthetic Dentistry (Level I) www.dominic-hassall-training.co.uk DAY 1 Periodontology Module Contemporary Periodontics Course introduction and philosophy o Cosmetic,
PG Cert Contemporary Restorative and Aesthetic Dentistry (Level I) www.dominic-hassall-training.co.uk DAY 1 Periodontology Module Contemporary Periodontics Course introduction and philosophy o Cosmetic,
Effect of Casein Phosphopeptide amorphous Calcium. and Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate
 IJCPD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of CPP-ACP 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1447 and Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate Effect of Casein Phosphopeptide amorphous Calcium Phosphate and Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate
IJCPD ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of CPP-ACP 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1447 and Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate Effect of Casein Phosphopeptide amorphous Calcium Phosphate and Calcium Sodium Phosphosilicate
REVIEW OF AGE ESTIMATION TECHNIQUE DEPENDING ON DEPOSITION OF SECONDARY DENTIN
 Review Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 03 REVIEW OF AGE ESTIMATION TECHNIQUE DEPENDING ON DEPOSITION OF SECONDARY DENTIN Sonune Shrikant 1, Shete Mrinal 2, Karande
Review Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 03 REVIEW OF AGE ESTIMATION TECHNIQUE DEPENDING ON DEPOSITION OF SECONDARY DENTIN Sonune Shrikant 1, Shete Mrinal 2, Karande
Near-UV light detection
 C L I N I C A L Near-UV light detection Javier Tapia Guadix 1 Near-UV light induced fluorescence has already proven to be very useful as an alternative to classic caries-detector dyes. However its potential
C L I N I C A L Near-UV light detection Javier Tapia Guadix 1 Near-UV light induced fluorescence has already proven to be very useful as an alternative to classic caries-detector dyes. However its potential
The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study)
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study) To cite this article:
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS The effect of root surface conditioning on smear layer removal in periodontal regeneration (a scanning electron microscopic study) To cite this article:
6/8/12 THE LEGEND OF WORMS
 1 INTRODUCTION DEFINITION EARLY THEORIES Legend of worms Humoral theory Vital theory Chemical theory Parasitic theory Chemicoparasitic theory Proteolytic theory Proteolysis- chelation theory Sucrose chelation
1 INTRODUCTION DEFINITION EARLY THEORIES Legend of worms Humoral theory Vital theory Chemical theory Parasitic theory Chemicoparasitic theory Proteolytic theory Proteolysis- chelation theory Sucrose chelation
GOVERNMENT GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA. N$4.00 WINDHOEK - 5 September 2014 No. 5550
 GOVERNMENT GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA N$4.00 WINDHOEK - 5 September 2014 No. 5550 CONTENTS Page GOVERNMENT NOTICE No. 138 Regulations relating to minimum requirements of study for registration,
GOVERNMENT GAZETTE OF THE REPUBLIC OF NAMIBIA N$4.00 WINDHOEK - 5 September 2014 No. 5550 CONTENTS Page GOVERNMENT NOTICE No. 138 Regulations relating to minimum requirements of study for registration,
Electronic Dental Records
 Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
Electronic Dental Records Dr. Douglas K Benn, Professor of Maxillofacial Radiology & Director of Oral Diagnostic Systems, University of Florida and Health Conundrums LLC 8/2/2008 Dr Benn, University of
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary
 SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
Age estimation of indian adults from orthopantomographs
 Forensic Dentistry Forensic Dentistry Age estimation of indian adults from orthopantomographs Sudhanshu Saxena (a) (a) Department of Public Health Dentistry, People s College of Dental Sciences and Research
Forensic Dentistry Forensic Dentistry Age estimation of indian adults from orthopantomographs Sudhanshu Saxena (a) (a) Department of Public Health Dentistry, People s College of Dental Sciences and Research
DENTAL TRAUMA IN DECIDUOUS TEETH
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Dental Trauma in Deciduous Teeth must be made in conjunction with
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage your health. All decisions about the management of Dental Trauma in Deciduous Teeth must be made in conjunction with
Effects of Citric Acid and EDTA on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces: A SEM Study
 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1166 Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effects of Citric Acid and EDTA on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces: A SEM Study Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad,
10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1166 Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH Effects of Citric Acid and EDTA on Periodontally Involved Root Surfaces: A SEM Study Sunkara Shree Ramalinga Prasad,
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(7): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(7):915-932 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Comparative evaluation of dentinal tubule occlusion
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(7):915-932 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Comparative evaluation of dentinal tubule occlusion
TOOTH DISCOLORATION. Multimedia Health Education. Disclaimer
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage dental health. All decisions about the management of tooth discoloration must be made in conjunction with your dentist
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage dental health. All decisions about the management of tooth discoloration must be made in conjunction with your dentist
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor
 Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study
 Original Research In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study ASHUTOSH * ASEEM P. TIKKU ** ANIL CHANDRA ** PROMILA VERMA *** RAKESH K. YADAV
Original Research In vitro evaluation of root canal preparation with plastic endodontic rotary finishing file - A SEM study ASHUTOSH * ASEEM P. TIKKU ** ANIL CHANDRA ** PROMILA VERMA *** RAKESH K. YADAV
Microstructure of primary tooth dentin. David A. Sumikawa, DDS, MS Grayson W. Marshall, DDS, MPH, PhD Lauren Gee, MPH Sally J.
 Scientific Article Microstructure of primary tooth dentin David A. Sumikawa, DDS, MS Grayson W. Marshall, DDS, MPH, PhD Lauren Gee, MPH Sally J. Marshall, PhD Dr. Sumikawa is in private pediatric dental
Scientific Article Microstructure of primary tooth dentin David A. Sumikawa, DDS, MS Grayson W. Marshall, DDS, MPH, PhD Lauren Gee, MPH Sally J. Marshall, PhD Dr. Sumikawa is in private pediatric dental
Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity
 Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity Nicolas Elian, DDS Private Practice Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey David Geon U Kim, DDS, MS Faculty and Research Coordinator
Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity Nicolas Elian, DDS Private Practice Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey David Geon U Kim, DDS, MS Faculty and Research Coordinator
Operative dentistry. Lec: 10. Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE):
 Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
Operative dentistry Lec: 10 د.عبذالمنعم الخفاجي Zinc oxide eugenol (ZOE): There are 2 types: 1) Unreinforced ZOE (ordinary type): supplied as powder (zinc oxide + some additives like zinc acetate, white
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
The Dental Board of California - Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001
 The Dental Board of California - Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001 As required by Chapter 801, Statutes of 1992, the Dental Board of California has prepared this fact
The Dental Board of California - Dental Materials Fact Sheet Adopted by the Board on October 17, 2001 As required by Chapter 801, Statutes of 1992, the Dental Board of California has prepared this fact
EFFICACY OF AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, G.C. TOOTH MOUSSE AND GLUMA DESENSITIZER IN TREATING DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY : A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 02 EFFICACY OF AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, G.C. TOOTH MOUSSE AND GLUMA DESENSITIZER IN TREATING DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 02 EFFICACY OF AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, G.C. TOOTH MOUSSE AND GLUMA DESENSITIZER IN TREATING DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY
Incremental lines in root cementum of human teeth: An approach to their role in age estimation using polarizing microscopy
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Incremental lines in root cementum of human teeth: An approach to their role in age estimation using polarizing microscopy Pooja Aggarwal, Susmita Saxena, Puja Bansal Department of Oral
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Incremental lines in root cementum of human teeth: An approach to their role in age estimation using polarizing microscopy Pooja Aggarwal, Susmita Saxena, Puja Bansal Department of Oral
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Primary Teeth Chapter 18. Dental Anatomy 2016
 Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
LOUISIANA MEDICAID PROGRAM ISSUED: 08/18/14 REPLACED: 09/15/13 CHAPTER 16: DENTAL SERVICES APPENDIX A: EPSDT DENTAL PROGRAM FEE SCHEDULE PAGE(S) 16
 APPENDIX A: FEE SCHEDULE DENTAL PROGRAM FEE SCHEDULE Provided in the table on the following pages are the reimbursable dental procedure codes and fees for the Medicaid of Louisiana, EPSDT Dental Program.
APPENDIX A: FEE SCHEDULE DENTAL PROGRAM FEE SCHEDULE Provided in the table on the following pages are the reimbursable dental procedure codes and fees for the Medicaid of Louisiana, EPSDT Dental Program.
LOUISIANA MEDICAID PROGRAM ISSUED: 09/15/13 REPLACED: 03/28/13 CHAPTER 16: DENTAL SERVICES APPENDIX A: EPSDT DENTAL PROGRAM FEE SCHEDULE PAGE(S) 16
 APPENDIX A: FEE SCHEDULE DENTAL PROGRAM FEE SCHEDULE Provided in the table on the following pages are the reimbursable dental procedure codes and fees for the Medicaid of Louisiana, EPSDT Dental Program.
APPENDIX A: FEE SCHEDULE DENTAL PROGRAM FEE SCHEDULE Provided in the table on the following pages are the reimbursable dental procedure codes and fees for the Medicaid of Louisiana, EPSDT Dental Program.
06 Tooth Development and Eruption
 + 06 Tooth Development and Eruption Tooth development Root development PDL and alveolar bone development Primary tooth eruption and shedding Permanent tooth eruption Q. Where and how tooth starts to form?
+ 06 Tooth Development and Eruption Tooth development Root development PDL and alveolar bone development Primary tooth eruption and shedding Permanent tooth eruption Q. Where and how tooth starts to form?
T O O T H A T L A S C O U R S E G U I D E A S S I S T A N T E D I T I O N
 T O O T H A T L A S C O U R S E G U I D E A S S I S T A N T E D I T I O N The information in this guide was prepared by ehuman with contributions from: Cara Miyasaki, RDHEF, MS, Foothill College Kay Murphy,
T O O T H A T L A S C O U R S E G U I D E A S S I S T A N T E D I T I O N The information in this guide was prepared by ehuman with contributions from: Cara Miyasaki, RDHEF, MS, Foothill College Kay Murphy,
ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM. Dr. Fatin Awartani
 ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM Part II Cementum and Alveolar bone Associate Professor Periodontal division King Saud university Cementum Calcified mesenchymal tissue that forms the outer covering of the anatomic
ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM Part II Cementum and Alveolar bone Associate Professor Periodontal division King Saud university Cementum Calcified mesenchymal tissue that forms the outer covering of the anatomic
UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS SCHOOL OF DENTAL MEDICINE
 UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS SCHOOL OF DENTAL MEDICINE Competencies for Graduates of the DMD Program Introduction The UNLV School of Dental Medicine Competency statements describe the level of skills
UNIVERSITY OF NEVADA LAS VEGAS SCHOOL OF DENTAL MEDICINE Competencies for Graduates of the DMD Program Introduction The UNLV School of Dental Medicine Competency statements describe the level of skills
MORPHOLOGICAL AND DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHICAL DENTAL ANATOMY OF ADULT BUFFALOES
 Original Article Buffalo Bulletin (April-June 2017) Vol.36 No.2 MORPHOLOGICAL AND DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHICAL DENTAL ANATOMY OF ADULT BUFFALOES R.K. Singh 1, R.P. Pandey 1, S. Purohit 1, S.P. Singh 2, *, A.K.
Original Article Buffalo Bulletin (April-June 2017) Vol.36 No.2 MORPHOLOGICAL AND DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHICAL DENTAL ANATOMY OF ADULT BUFFALOES R.K. Singh 1, R.P. Pandey 1, S. Purohit 1, S.P. Singh 2, *, A.K.
Identification and qualitative Analysis. of Renal Calculi
 Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
Identification and qualitative Analysis of Renal Calculi 1 -Renal Calculi: Kidney stones, renal calculi or renal lithiasis (stone formation) are small, hard deposits that form inside your kidneys. The
Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 3 Ver. V. (Mar. 2014), PP 26-30 Erupting Compound Odontome - A case report Dr. Sahana Srinath
In vitro evaluation of root canals obturated with four different techniques. Part 3: Obturation of lateral canals
 64 > research In vitro evaluation of root canals obturated with four different techniques. Part : Obturation of lateral canals SADJ July, Vol 67 no 6 p64 - p69 FS Botha, C van der Merwe, PJ van der Vyver,
64 > research In vitro evaluation of root canals obturated with four different techniques. Part : Obturation of lateral canals SADJ July, Vol 67 no 6 p64 - p69 FS Botha, C van der Merwe, PJ van der Vyver,
Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd
 Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd upon completion of the articulator mounting and a thorough assessment of the occlusal requirements, the practitioner should be able to perform the proper arrangement
Selection and arrangement of teeth in rpd upon completion of the articulator mounting and a thorough assessment of the occlusal requirements, the practitioner should be able to perform the proper arrangement
DENTAL CARIES CARACTERISTICS, HANDPIECES, HAND INSTRUMENTS, (USED IN PHANTOM LAB) HYSTOPATHOLOGY. BURS. 3rd year, 1st semester
 DENTAL CARIES CARACTERISTICS, HYSTOPATHOLOGY. HANDPIECES, HAND INSTRUMENTS, BURS. (USED IN PHANTOM LAB) 3rd year, 1st semester DENTAL CARIES CARIES Dental caries is a multifactorial chronic, irreversible
DENTAL CARIES CARACTERISTICS, HYSTOPATHOLOGY. HANDPIECES, HAND INSTRUMENTS, BURS. (USED IN PHANTOM LAB) 3rd year, 1st semester DENTAL CARIES CARIES Dental caries is a multifactorial chronic, irreversible
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
GENERAL DENTISTRY & COMPREHENSIVE CARE
 GENERAL DENTISTRY & COMPREHENSIVE CARE Case Studies Volume 1 375 East Main Street East Islip, NY 11730 631-581-5121 www.drforlano.com Thank you for considering us for your general dental needs. All phases
GENERAL DENTISTRY & COMPREHENSIVE CARE Case Studies Volume 1 375 East Main Street East Islip, NY 11730 631-581-5121 www.drforlano.com Thank you for considering us for your general dental needs. All phases
IN VITRO COMPARISON OF RETENTION AND MARGINAL LEAKAGE OF PROVISIONAL CROWNS CEMENTED WITH PROVISIONAL CEMENT ENRICHED WITH THREE DIFFERENT ADDITIVES
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 06 IN VITRO COMPARISON OF RETENTION AND MARGINAL LEAKAGE OF PROVISIONAL CROWNS CEMENTED WITH PROVISIONAL CEMENT ENRICHED
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 06 IN VITRO COMPARISON OF RETENTION AND MARGINAL LEAKAGE OF PROVISIONAL CROWNS CEMENTED WITH PROVISIONAL CEMENT ENRICHED
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Ankylosed primary teeth with no permanent successors: What do you do? -- Part 1
 Ankylosed primary teeth with no permanent successors: What do you do? -- Part 1 March 3, 2015 By David M. Sarver, DMD, MS The clinical problem You have a seven-year-old patient who comes to your office
Ankylosed primary teeth with no permanent successors: What do you do? -- Part 1 March 3, 2015 By David M. Sarver, DMD, MS The clinical problem You have a seven-year-old patient who comes to your office
