University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten Willemijn
|
|
|
- Duane Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten Willemijn IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version below. Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Publication date: 2016 Link to publication in University of Groningen/UMCG research database Citation for published version (APA): Slagter, K. W. (2016). Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone. [Groningen]: Rijksuniversiteit Groningen. Copyright Other than for strictly personal use, it is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Take-down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Downloaded from the University of Groningen/UMCG research database (Pure): For technical reasons the number of authors shown on this cover page is limited to 10 maximum. Download date:
2 Immediate single-tooth implant placement in bony defects in the aesthetic zone: a 1-year randomized controlled trial. This chapter is an edited version of the manuscript: Slagter KW, Meijer HJ, Bakker NA, Vissink A, Raghoebar GM. Immediate single-tooth implant placement in bony defects in the esthetic zone: a 1-year randomized controlled trial. Journal of Periodontology. Epub ahead of publication. 2016;15:
3 Abstract Aim: To assess whether outcome of immediate implant placement in the aesthetic zone in bony defects was non-inferior to delayed implant placement after one year regarding marginal bone level (MBL). Materials and Methods: Forty patients with a failing tooth in the aesthetic zone and a labial bony defect of 5 mm after removal of a tooth were randomly assigned for immediate (n=20) or delayed (n=20) implant placement. Second stage surgery and provisionalization occurred after three months healing. Follow-up was at 1 month and 1 year after definitive crown placement. The study was powered to detect a difference in MBL of >0.9 mm. Buccal bone thickness, soft tissue peri-implant parameters, aesthetic indexes and patients satisfaction were also assessed. Results: One year after definitive crown placement, MBL level loss was 0.9±0.6 mm mesially and 0.9±0.6 mm distally for the immediate group and 0.5±0.1 mm and 0.68±0.6 mm for the delayed group, respectively. Regarding differences in means, non-inferiority was observed after 1 year (mesially: immediate vs. delayed: difference in mean 0.0 mm (95%CI to 0.30 mm, p=0.0, distally: immediate vs. delayed: difference in mean 0.21 mm (95%CI to 0.51 mm, p=0.58). No significant differences in the outcome variables were observed. Conclusion: Immediate implant placement with delayed provisionalization was non-inferior to delayed implant placement with delayed provisionalization in labial bony defects of 5 mm regarding change in MBL. Although not powered for other outcome variables, no clinically relevant differences were observed in these variables. 76
4 Introduction The survival of immediately placed and provisionalized implants in the aesthetic zone is very high. 1,2,3 However, it is not just implant survival that determines the success of an implant treatment as implant treatment in the aesthetic zone is also in need of a favourable hard and soft peri-implant tissue outcome.,5 A recent randomized clinical trial 6 verified this for marginal bone level (MBL) in extraction sockets with no bony defects and showed that indeed the MBL outcome is favourable too. Although unknown to what extent the peri-implant soft tissues react on missing support of hard peri-implant tissues, it has been hypothesized that the risk on developing facial gingival recession is low when the bone labially from the implants has no dehiscences and a sufficient thickness at implant placement. 7 In this respect, it was reported that large U- and UU-shaped defects are accompanied by more gingival recession 1-year after immediate tooth replacement, reason why Kan et al 8 recommended a delayed approach, viz. to combine implant placement with hard and/or soft tissue grafting when a labial bone defect is present at implant placement. Recently, however, it was reported that newer techniques allow for a favorable treatment outcome of implants placed in fresh extractions sockets with labial plate dehiscences Thus, an intact labial plate is presumably not essential to allow for immediate implant placement with a favorable outcome. No studies yet assessed the treatment outcome of implants placed in fresh extraction sockets with labial plate dehiscences in the aesthetic zone in a prospective, randomized clinical trial design. Therefore, the aim of this randomized controlled trial was to assess whether the 1 year treatment outcome of immediate implant placement and delayed provisionalization is non-inferior regarding change in marginal bone level (MBL) to delayed implant placement and delayed provisionalization in case of implant placement in fresh extraction sockets with labial bony defects of 5 mm in the aesthetic zone. Materials and methods Study design Between January 2010 and January 2012 all eligible consecutive patients >18 years with a failing tooth in the maxillary aesthetic zone (incisor, canine or first premolar) referred for single tooth implant treatment were asked to join this randomized clinical trial. Pre-operative, a cone beam computed tomography (CBCT)-scan was made to assess whether there was sufficient bone on the palatal side to place an implant as for primary stability of the implant sufficient palatinal bone is necessary in case of labial dehiscence. Patients were excluded from participation in this study when they met one or more of the following criteria: inadequate oral hygiene, insufficient mesio-distal width for implant placement, periodontal disease, smoking, ASA (American Society of Anesthesiologists) score II 12, and a bony defect of <5 mm in vertical direction of the labial socket wall after removal of the tooth. The size of the bony defect was determined after extraction of the failing tooth. The shape of the osseous defect was assessed by a bone sounding technique with a periodontal probe at the buccal, the mesial, and distal aspect of the failing tooth, and the mesial and distal aspect of the immediately adjacent teeth. 77
5 For allocation to either group a computerized random number generator was used. A research-nurse not involved in the study blindly allocated the patients to (Figure 1 and 2): - An immediate group: immediate placed implant (NobelActive, Nobel Biocare AB, Goteborg, Sweden) and delayed provisionalization; - A delayed group: delayed placed implant (NobelActive, Nobel Biocare AB, Goteborg, Sweden) and delayed provisionalization. Informed consent was obtained from all patients. The study was approved by the local medical ethical committee (NL ) and registered in a trial register (ISRCTN ). Surgical protocol Preoperatively, patients started prophylactic antibiotic therapy (amoxicillin 500mg t.i.d. for 7 days or clindamycin 300mg q.i.d. in case of amoxicillin allergy). Oral disinfection consisted of a 0.2% chlorhexidine mouthwash, twice daily for 7 days. All surgeries were performed under local anesthesia and performed by the same experienced oral and maxillofacial surgeon (GR). In all cases, the failing teeth were removed with a sulcular incision, careful detachment of the periodontal ligament and use of periotomes. After removal of the tooth, the alveolus was meticulously cleansed and any alveolar debridement was removed with a sterile gauze. If the sterile gauze was still contaminated, more cleaning took place. Before implant placement, bone grafts were harvested from the maxillary tuberosity with the use of chisels. The wound of the bone graft in the tuberosity region was closed with Vicryl -0 (Ethicon, Johnson&Johnson, Amersfoort, The Netherlands). Immediate placement group: The implant site was prepared on the palatal side of the alveolus following the protocol of the manufacturer using a surgical template based on the ideal position of the prospective implant crown. The last used burr, depending on the diameter of the implant, was placed in the prepared alveolus. Next, the tuberosity bone graft was shaped with the use of a forceps to match the labial bony defect. The bone graft was placed in the extraction socket, with the cortical side facing the periosteum, under the periosteum covering the labial plate defect. A mixture of autologous bone and Bio-Oss (Geistlich, Wolhusen, Switzerland) spongiosa granules ( mm) was thightly packed into the remaining space between the burr and the bone graft. Regarding the corono-apical position of the implants (NobelActive, Nobel Biocare AB, Goteborg, Sweden) the shoulder of the implant was placed at a depth of 3 mm apical to the most apical aspect of the prospective clinical crown, with help of the surgical template. Immediately after implant placement a corresponding cover screw was placed. To achieve an optimal aesthetic outcome, next a soft tissue graft, harvested from tuberosity region where the bone graft was taken from, was placed on top of the bone graft and implant according to the method described in detail by Raghoebar et al. 13 The wound was closed with Ethilon 5-0 (Ethicon, Johnson&Johnson, Amersfoort, The Netherlands). During the three months osseointegration phase, patients were allowed to wear a removable partial denture not interfering with the wound. After three months, the implant was uncovered by a small incision at the site of the cover screw, followed by an implant-level impression according to the procedure described in the prosthetic protocol section. 78
6 Figure 1. Cohort flow diagram. Enrollment Assessed for eligibility (n=0) Excluded (n=0) Not meeting inclusion criteria (n=0) Declined to participate (n=0) Other reasons (n=0) Randomized (n=0) Allocated to intervention (n=20) Received allocated intervention (n=20) Did not receive allocated interven tion (give reasons) (n=0) Allocation Allocated to intervention (n=20) Received allocated intervention (n=20) Did not receive allocated interven tion (give reasons) (n=0) Lost to follow-up (give reasons) (n=0) Discontinued intervention (give reasons) (n=0) Follow-Up Lost to follow-up (give reasons) (n=0) Discontinued intervention (give reasons) (n=0) Analysed (n=20) Excluded form analysis (give reasons) (n=0) Analysis Analysed (n=20) Excluded form analysis (give reasons) (n=0) 79
7 Pre-operative TPre Day 0 (T0) 3 months (T3) 6 months (T6) 12 months (T12) 18 months (T18) Inclusion Healing phase Prosthetic phase Screening and Measurements Follow-up phase Extraction & Implant placement & Delayed provisionalization Second phase surgery & Provisional crown Definitive crown and Follow-up Follow-up Figure 2A. Schedule of visits and procedures study group immediate placement and delayed provisionalization. 80
8 Pre-operative TPre Day 0 (T0) 3 months (T3) 6 months (T6) 9 months (T9) 12 months (T12) 18 months (T18) 21 months (T21) Inclusion Healing phase Prosthetic phase Screening and Measurements Follow-up phase Extraction & Guided Bone Regeneration Implant placement Second phase Definitive crown surgery and Follow-up & Provisional crown Follow-up Figure 2b. Schedule of visits and procedures study group delayed placement and delayed provisionalization. 81
9 Delayed placement group: The alveolus was locally augmented with the same procedure as described for the immediate group, with exception of placement of an implant. After 3 months a pedicled mucoperiosteal flap was raised to expose the maxilla, after which the NobelActive implant was placed according to the requirements of the manufacture using a surgical template. The implants were placed, comparable to the implants placed in the immediate placement group, 3 mm below the cervical junction of the adjacent teeth. The wound was primary closed with Ethilon 5-0 (Ethicon, Johnson&Johnson, Amersfoort, The Netherlands). After three months the implant was uncovered following the same procedure as described for the immediate group, again followed by an implant-level impression. Patients were allowed to wear a removable partial denture until the provisionalization took place. Prosthetic protocol An implant-level impression was made immediately after uncovering the implant. After the impression was taken, a corresponding healing abutment was placed. A screw-retained provisional crown composed of an engaging temporary abutment and composite was then fabricated in the dental laboratory. This same day, the provisional crown was fastened directly onto the implant with 20 Ncm by a manual torque wrench. A final open tray impression using polyether impression material (Impregum Penta, 3M ESPE, Seefeld, Germany) was taken at implant level after a provisional phase of 3 months in both groups. In the dental laboratory, one lab technician made the digital design of the definitive crown to the desired form of the abutment. This digital design was used to retrieve individualized zirconia abutments (NobelProcera, Nobel Biocare AB, Goteborg, Sweden). Depending on the location of the screw access hole, the final crown was either cement-retained or screw-retained. Abutment screws were torqued with 32 Ncm. Cement-retained crowns were cemented with glass ionomer cement (Fuji Plus, GC Europe, Leuven, Belgium). All prosthetic procedures were performed by a single experienced prosthodontist (HM). Outcome measures Primary outcome measure of this study was the change in marginal peri-implant bone level (MBL) proximal to the implant, from placement of the implant to one month (T1) after connecting the definitive crown and from placement of the implant to one year (T12) after connecting the definitive crown. Secondary outcome measures included buccal bone thickness (BBT), implant survival, change in interproximal peri-implant mucosa (IML) and midfacial peri-implant mucosal level (MML) as compared with the gingival level of the pre-operative failing tooth. Furthermore, papilla volume, health of keratinized gingiva, amount of plaque, amount of bleeding and pocket probing depth were assessed. Aesthetic outcome was assessed by means of objective indices (Implant Crown Aesthetic Index (ICAI) 1, the pink esthetic score (PES) 15 and the white esthetic score (WES). 16,17 Patients satisfaction was assessed using the Oral Health Impact Profile (OHIP) index 18 and the Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) 19 on a 0-10 scale. Radiographic assessments To calculate changes in MBL, one month (T1) and one year (T12) after placement of the definitive crown, a standardized digital peri-apical radiograph was taken with an individualized aiming device 20, pre- 82
10 operatively (Tpre), immediately following implant placement (baseline T0), one month (T1), and twelve months (T12) after definitive crown placement. The vertical distance from the shoulder of the implant to the first-bone-to-implant contact was measured at the distal and mesial site of the implant. The radiographs of T1 and T12 were analyzed using the manufacturer-provided implant diameter as a reference. Measurements were performed independently by two examiners (KS and Harry Slagter), after which the average of both measurements was used. To calculate buccal bone thickness (BBT) labial of the implant, one month (T1) and one year (T12) after placement of the definitive crown a CBCT scan was made. The scanner (icat 3D exam scanner,kavo Dental GmbH, Biberach, Germany) was validated for measuring bone thickness by Fourie et al. 21 To allow for reproducible measurements, a CBCT imaging and software protocol was developed and validated. 22 Area of interest was the distance from the central axis of the implant to the outer contour of the buccal bone at the neck of the implant. Buccal bone thickness measurements (in mm) were performed calculating the distance to the buccal bone outline minus the radius of the interior contour of the implant (as provided by the implant company). Measurements were performed independently by two examiners (KS and HM), after which the average of both measurements was used. Survival rate Survival rate was defined as the percentage of functional implants one year after definitive crown placement. The criteria for successful osseointegration according to Smith & Zarb (1989) were adapted. Photographic assessments Before implant placement (Tpre) at T1 and at T12, standardized digital photographs (Nikon D300s, Nikon Corporation,Yurakucho, Tokyo, Japan) were taken using a technique as described earlier.17 A manual periodontal probe (Williams Color-Coded probe; Hu-Friedy, Chicago, IL, USA) with known dimensions was held in close proximity and parallel to the long axis of the adjacent tooth to calibrate the photographs. Full screen analysis of the photographs was performed using a digital picture editing program (Keynote, Apple Inc, Cupertino, CA, USA). The changes in IML and in MML were compared with the original gingival level of the failing tooth. These measurements were independently performed by two examiners (KS and Harry Slagter) after which the average of both measurements was used. Clinical assessments The following clinical variables were assessed at T1 and T12 at the implant and adjacent teeth before implant placement (Tpre): - Papilla volume: assessing the mesial and distal papilla adjacent to the implant using the papilla index 23 ; - Amount of plaque: assessed at four sites per implant/adjacent tooth (mesial, buccal, distal and palatinal) using the modified plaque index 2 ; - Amount of bleeding: using the modified sulcus bleeding index 2 ; - Gingiva: using the gingival Index 25 ; 83
11 - Probing pocket depth: assessed at four sites per implant/adjacent tooth (mesial, buccal, distal and palatinal) using a manual periodontal probe (Williams Color-Coded probe; Hu-Friedy, Chicago, IL, USA) measuring to the nearest 1 mm. All data were recorded by a single one blinded examiner (KS). Aesthetic assessments The aesthetic outcome was assessed on standardized digital photographs (Nikon D300s, Nikon Corporation,Yurakucho, Tokyo, Japan taken at Tpre and T1, and T12 in both groups. An additional photograph was taken of implant crowns replacing the lateral of canine capturing the contra lateral tooth. Peri-implant mucosa and implant crown aesthetic outcomes were determined using ICAI 1 and PES-WES. 16,17 Measurements were performed independently by two examiners (KS and Diederik Hentenaar). Patients satisfaction Patients satisfaction was surveyed at T1 and T12 using the validated OHIP-1 questionnaire. Overall satisfaction was assessed using a 100-mm visual analogue scale (VAS). Statistical analysis For determination of the sample size, G*power version 3.1 was used. 26 A radiographic change in MBL of >0.9 mm (SD 1 mm) after 12 months of definitive crown placement was regarded as a relevant difference between study groups. 1 With an expected effect-size of 0.9 mm, an alpha of 0.05 and a power of 0.80, 38 patients were required, 19 in each group. 0 patients were included to account for anticipated dropout rate. Shapiro-Wilk test, together with normality plots were used to assess normal distribution of the continuous variables. Differences between groups were evaluated by one-way analyses of variance (ANOVA) for continuous data and by Fisher s exact test or chi-square test for categorical data. Regarding MBL, T-tests for equality of means with associated confidence intervals (CI) were calculated. If the difference of 0.9 did not pass the 95% CI borders, non-inferiority was considered established. In case of uncertainty of the significance because of the relatively small number of patients analysed and the large number of outcomes, Bonferroni correction was considered in case of a p-value 0.01<>0.05. A p-value of 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance. All analyses were performed using SPSS (PASW Statistics 20.0, SPSS Inc.; IBM Corporation, Chicago, IL, USA). Results Inter-and intra-observer correlation The inter- and intra-observer correlations for both the radiographic and photographic measurements were very high. For details see Slagter et al. 6 Patients Baseline characteristics and treatment specifications of the immediate group (n=20) and delayed group (n=20) are shown in Table 1 and Figure 3 and. All patients received their assigned treatment (Figure 1). No extensive bleedings at the donor and receptor site were observed. 8
12 Table 1. Baseline characteristics and treatment specifications per study group. Variable Immediate group (n=20) Delayed group (n=20) Age Mean±SD Range 3.7 ± ± Gender Male Female Cause of tooth loss Fracture (crown or root) Agenesis Caries Endodontic failure Periodontal failure Root resorption Bone defect Mean±SD (mm) 8.35 ± ±1.76 Implant location Incisor 1 Incisor 2 Canine Implant length 13 mm 15 mm 18 mm Implant diameter 3.5 mm.3 mm Type of final restoration Screw-retained Cement-retained
13 Three patients (immediate: group 1; delayed: group 2) had an antral perforation due to harvesting the tuberosity bone. The wound overlying the antral perforation was primary closed and healing was uneventful. Wound healing at the grafting/implantation site was undisturbed with the exception of one patient (group 2) in whom a small bone sequester had to be removed. After removal of the bone sequester, wound healing was uneventful and the remaining bone was sufficient for implant placement. No complications were observed during the follow up. Marginal bone level MBL loss at the mesial and distal site after 1 month and 12 months after placement of the definitive crown was comparable for both treatment approaches (Table 2). Non-inferiority for the change in MBL between the groups was observed, both for the 1 month (mesially: immediate group vs. delayed group: difference in mean 0.0 mm (95%CI-0.2- to 0.23 mm, p=0.83, distally: 0.23 mm (95%CI-0.8 to 0.5 mm, p=0.70) and 1 year (mesially: 0.0 mm (95%CI to 0.30, p=0.0, distally: 0.21mm (95%CI to 0.51 mm, p=0.58) time point. Buccal bone level Mean buccal bone thickness at the neck of the implant 1 month and 12 months after placement of the definitive crown is shown in Table 2. Buccal bone thickness did not change between between T1 and T12. Survival rate One year implant survival rate was 100% in both groups. Interproximal and midfacial peri-implant mucosal level IML and MML, did not change significantly between with time in both groups (Table 2). Clinical outcome Plaque, bleeding and gingival indexes as well as the pocket probing depth were low and remained low throughout the study period (Table 3). Aesthetic assessments At the 1-year evaluation, no significant differences in ICAI as well as PES/WES were seen between the groups (Table 2). The aesthetic outcome was mainly dependent on the appearance of the implant crown and less by the aspect of the peri-implant mucosa, and did not differ between the groups. Patients satisfaction OHIP-1 scores did not differ between the groups (Table ; p>0.05). Overall satisfaction scores one year after placement of the crown were 8.±1. and 8.1±1.3 for the immediate and delayed group, respectively. 86
14 Table 2. Changes regarding marginal bone level, marginal soft tissue level and aesthetic evaluation from pre-operative (Tpre), one month (T1) to 12 months (T12) after definitive crown placement. Tpre Tpre P-value T1 T1 P-value T12 T12 P-value Mean (sd) Mean (sd) Mean (sd) Mean (sd) Mean (sd) Mean (sd) Variable Group A Group B Group A Group B Group A Group B Marginal bone level in mm(±sd) Mesial of implant 0.9 (±0.6) 0.5 (±0.1) (±0.39) 0.51 (±0.3) 0.7 Distal of implant 0.71 (±0.51) 0.8 (±0.7) (±0.51) 0.5 (±0.5) 0.18 BBTchanges in mm Buccal of implant (mean ±sd) 1.01 (±0.55) 0.79 (±0.6) (±0.7) 0.71 (±0.28) 0.07 Marginal soft tissue level changes in mm (±sd) Mesial of implant 0.15 (±0.18) 0.18 (±0.16) (±0.16) 0.15 (±0.16) 0.99 Distal of implant 0.17 (±0.16) 0.23 (±0.17) (±0.18) 0.21 (±0.17) 0.53 Mid-facial of implant 0.13 (±0.28) 0.30 (±0.9) (±0.28) 0.3 (±0.55) 0.17 PES 7.00 (2.10) 6.90 (1.30) (1.66) 7.0 (1.59) (1.59) 7.0 (1.6) 0.79 WES 5.00 (2.33) 5.0 (1.65) (1.73) 7.60 (1.09) (0.90) 7.90 (1.08) 0.79 PES/WES (3.0) (3.6) (2.20) (1.71) (2.05) (2.11) 0.50 ICAI 9.60 (6.5) 1.10 (8.57) (2.18) 6.20 (3.9) (2.38) 5.2 (.10)
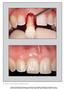
15 3a 3b 3c 3b 3d Figure 3. Immediate implant treatment with delayed provisionalization. a Clinical situation pre-operative. b. Pre-operative radiograph. c. Clinical situation post-operative. d. Post-operative radiograph. 88
16 a b c d Figure. Delayed implant treatment with delayed provisionalization. a Clinical situation pre-operative. b. Pre-operative radiograph. c. Clinical situation post-operative. d. Post-operative radiograph. 89
17 Table 3. Clinical outcome measures pre-operative (Tpre), and one month (T1) and 12 months (T12) after definitive crown placement. Tpre Tpre P- value T1 T1 P- value T12 T12 P- value Variable Immediate group Delayed group Immediate group Delayed group Immediate group Delayed group Papilla index: 0/1/2/3/ Mesial (#patient) Distal (#patient) Gingival index: 0/1/2/3 (#patient) Plaque index: 0/1/2/3 (#patient) Bleeding index: 0/1/2/3 (#patient) 0/7/2/11/0 2/6/6/6/ /5/3/11/0 2/8//6/ /3/8/9/0 0/6/5/9/ /7/5/8/0 2/6/6/6/ /5/8/6/0 5/6/5// /3/8/9/0 0/7/7/6/ /1/0/1 17/1/1/ /2/0/0 20/0/0/ /2/0/0 20/0/0/ /2/0/0 20/0/0/ /0/0/0 20/0/0/0 NA 18/1/1/0 20/0/0/ /9/2/0 9/6/3/ /7/1/0 12/8/0/ /9/0/0 15/5/0/ Pocket depth in mm Mesial (mean ±sd) Distal (mean ±sd) Buccal (mean ±sd) 3.0± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± ± Palatal (mean ±sd) 2.2± ± ±0. 2.9± ± ±
18 91
19 Table. Oral Health Impact Profile18scores at baseline (T1) and one year (T12) of functioning. Mean OHIP-1 T1 P-value T12 P-value Immediate group Delayed group Immediate group Delayed group Variable never/hardly ever/ occasionally/fairly often/very often never/hardly ever/ occasionally/fairly often/very often Question 1 Have you had trouble pronouncing any words because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/17/3/0/0 0/1/5/1/ /19/1/0/0 0/16/3/1/ Question 2 Have you felt that your sense of taste has worsened because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/18/2/0/0 0/16/2/2/ /19/1/0/0 0/18/1/1/ Question 3 Have you had a painful aching in your mouth? 0/11/7/2/0 0/9/10/1/ /9/9/2/0 0/10/8/2/ Question Have you found it uncomfortable to eat any foods because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/12/7/1/0 0/11/5// /16/3/1/0 0/16/2/2/ Question 5 Have you been self-conscious of your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/10///2 0/11//5/ /13//3/0 0/15/3/1/ Question 6 Have you felt tense because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/12/5/3/0 0/1/3/3/ /11/5//0 0/16/1/3/ Question 7 Has your diet been unsatisfactory because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/17/3/0/0 0/16//0/ /19/1/0/0 0/16//0/ Question 8 Have you had to interrupt meals because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/18/2/0/0 0/18/2/0/ /18/2/0/0 0/20/0/0/
20 Question 9 Have you found it difficult to relax because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/1/1/5/0 0/17/2/1/ /16/3/1/0 0/17/3/0/ Question 10 Have you been a bit embarrassed because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/15/5/0/0 0/13/6/1/ /17/2/1/0 0/13/3/1/1 0.5 Question 11 Have you been a bit irritable with other people because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/16/2/2/0 0/17/2/0/ /15/5/0/0 0/16/2/2/ Question 12 Have you had difficulty doing your usual jobs because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/11/7/1/1 0/12/7/1/ /17/3/0/0 0/16/3/1/ Question 13 Have you felt that life in general was less satisfying because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/1//1/0 0/15/3/2/ /18/1/1/0 0/18/1/1/ Question 1 Have you been totally unable to function because of problems with your teeth, mouth or dentures? 0/19/1/0/0 0/20/0/0/ /19/0/1/0 0/17/3/0/
21 Discussion The present study showed that immediate placement with delayed provisionalization was not inferior to delayed placement with delayed provisionalization at a level of >0.9 mm MBL. Although not a priori powered to compare the other outcome variables, no clinically relevant differences were observed regarding clinical, esthetic and patient-reported outcomes too. Immediate placement offers a shorter treatment time due to the lower number of surgical procedures by combining extraction, implant placement, and bone grafting in one operative procedure Clinical outcomes Change in MBL in this study is considerably less than the generally accepted magnitude of up to 1 mm for the first year after implant placement described in the systematic review of Lang et al. 1 and the 0.81±0.8 mm according to the systematic review of Slagter et al. 3 concerning immediate implant placement. It has to be mentioned that MBL loss usually predominantly occurs during the first year after immediate implant placement and hardly progresses thereafter. 1 Thus, the 1-year results are considered to reflect the level of MBL related to a specific treatment in healthy subjects, a result that supports the immediate implant placement approach. A successful aesthetic outcome is presumably dependent on establishment of an optimal threedimensional implant position within the available bone dimensions as well as the maintenance of adequate buccal bone over the buccal implant surface. 30,31 In the present study, the buccal bone thickness appeared at least to be stable up to 1 year after implant placement and provisionalization in both patient groups and was thus considered to be independent of timing of implant insertion. Literature regarding BBT is scarce. Comparison with other studies, although measured in a different study design, learned that in the present study BBT after 1 year for immediate placed implants was more than the value of 0.16 mm thickness reported in the immediate implant group of Raes et al. 32 but less than the 2.12 mm BBT reported by Degidi et al. 33 For the delayed placed implants, BBT in the present study was more than the 0.20 mm reported by Raes et al. 32 Regarding the peri-implant soft tissues, the phenomenon biotype has been reported to affect the aesthetic result. 3 Possibly the thickness of the mucosa can positively influence the stability of the peri-implant soft tissues. In future studies, the effect of biotype on treatment outcome should be an integral part of the treatment design. Aesthetic assessments Although not upfront powered, the PES/WES and ICAI scores were comparable for the studied approaches and were comparable to results published in the literature regarding immediately and delayed placed single tooth implants placed in the aesthetic zone. 16,35,36 The scores of the pink component of PES/WES and ICAI were favorable and comparable for the immediate and delayed approaches, again supporting immediate placement of implants in larger bony defects when primary stability of the implant can be achieved. 9
22 Patients satisfaction In the field of implant dentistry there is an increasing focus on patient-reported outcome measures. 37 Immediate placement with immediate provisionalization is associated with high satisfaction rates. 38 This is in line with the satisfaction perceived by patients with immediate implant placement in this study. Regarding the OHIP-1, no differences were observed between both groups during the entire follow-up, again in line with other studies regarding immediate implant placement. 39,0 The two protocols, while yielding comparable results in terms of clinical outcomes and patient satisfaction, differed considerably in time to teeth and the number of scheduled visits (Figure 2), with the immediate implant placement reducing both the time and visit number to final restoration. Limitation The procedure to replace a failing tooth in the aesthetic zone with a bony defect with an immediate implant is a complex procedure. Raghoebar et al 13 showed that gingival mid-labial aesthetics most benefitted from a full thickness palatal graft compared to a connective tissue graft or closing with a membrane. Due to the complexity of this procedure, to achieve an optimal result it was recommended that the surgery should be done by experienced surgeons. 13 Therefore, in the current study all surgeries were performed by one single experienced surgeon. The latter approach compromises the applicability of the reported approach for general applications. Conclusion Immediate placement with delayed provisionalization is non-inferior regarding a change in MBL of >0.9 mm to delayed placement with delayed provisionalization in labial bony defects of 5 mm in the aesthetic zone after a 1-year follow-up. In addition, although not powered for these outcome variables, no clinically relevant differences in other outcomes were observed. 95
23 References Lang NP, Pun L, Lau KY, Li KY, Wong MC. A systematic review on survival and success rates of implants placed immediately into fresh extraction sockets after at least 1 year. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012;23: Lin GH, Chan HL, Wang HL. The effect of currently available surgical and restorativeinterventions on reducing mid-facial mucosal recession of single-tooth immediate placed implants: a systematic review. J Periodontol 201;85: Slagter KW, den Hartog L, Bakker NA, Vissink A, Meijer HJ, Raghoebar GM. Immediate placement of dental implants in the esthetic zone: a systematic review and pooled analysis. J Periodontol 201;85:e Den Hartog L, Slater JJ, Vissink A, Meijer HJ, Raghoebar GM. Treatment outcome of immediate, early and conventional single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone: a systematic review to survival, bone level, soft-tissue, aesthetics and patient satisfaction. J Clin Periodontol 2008;35: Cosyn J, Hooghe N, De Bruyn H. A systematic review on the frequency of advanced recession following single immediate implant treatment. J Clin Periodontol 2012;39: Ahead of print. Slagter KW, Meijer HJ, Bakker NA, Vissink A, Raghoebar GM. Feasibility of immediate placement of single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone: a 1-year randomized controlled trial. [published online ahead of print June 26, 2015]. J Clin Periodontol 2015; doi: /jcpe Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K. Site development for anterior single implant esthetics: the dentulous site. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2001;22:221-6, 228, Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Sclar A, Lozada JL. Effects of the facial osseous defect morphology on gingival dynamics after immediate tooth replacement and guided bone regeneration: 1-year results. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007;65: Noelken R, Kunkel M, Wagner W. Immediate implant placement and provisionalization after long-axis root fracture and complete loss of the facial bony lamella. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2011;31: da Rosa JC, Rosa AC, da Rosa DM, Zardo CM. Immediate Dentoalveolar Restoration of compromised sockets: a novel technique. Eur J Esthet Dent 2013;8: Ahead of print. Sarnachiaro GO, Chu SJ, Sarnachiaro E, Gotta SL, Tarnow DP. Immediate implant placement into extraction sockets with labial plate dehiscence defects: a clinical case series. [published online ahead of print April 27, 2015]. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2015; doi: /cid Little JP. Consistency of ASA grading. Anaesthesia 1995;50: Raghoebar GM, Slater JJ, Hartog L, Meijer HJ, Vissink A. Comparison of procedures for immediate reconstruction of large osseous defects resulting from removal of a single tooth to prepare for insertion of an endosseous implant after healing. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2009;38: Meijer HJ, Stellingsma K, Meijndert L, Raghoebar GM. A new index for rating aesthetics of implant-supported single crowns and adjacent soft tissues - the Implant Crown Aesthetic Index. Clin Oral Implants Res 2005;16: Furhauser R, Florescu D, Benesch T, Haas R, Mailath G, Watzek G. Evaluation of soft tissue around single-tooth implant crowns: the pink esthetic score. Clin Oral Implants Res 2005;16:639-6.
24 16. Belser UC, Grutter L, Vailati F, Bornstein MM, Weber HP, Buser D. Outcome evaluation of early placed maxillary anterior single-tooth implants using objective esthetic criteria: a cross-sectional, retrospective study in 5 patients with a 2- to -year follow-up using pink and white esthetic scores. J Periodontol 2009;80: Buser D, Halbritter S, Hart C, et al. Early implant placement with simultaneous guided bone regeneration following single-tooth extraction in the esthetic zone: 12-month results of a prospective study with 20 consecutive patients. J Periodontol 2009;80: van der Meulen MJ, John MT, Naeije M, Lobbezoo F. Developing abbreviated OHIP versions for use with TMD patients. J Oral Rehabil 2012;39: Carlsson AM. Assessment of chronic pain. I. Aspects of the reliability and validity of the visual analogue scale. Pain 1983;16: Meijndert L, Meijer HJ, Raghoebar GM, Vissink A. A technique for standardized evaluation of soft and hard peri-implant tissues in partially edentulous patients. J Periodontol 200;75: Fourie Z, Damstra J, Schepers RH, Gerrits PO, Ren Y. Segmentation process significantly influences the accuracy of 3D surface models derived from cone beam computed tomography. Eur J Radiol 2012;81:e Online-only article. Slagter KW, Raghoebar GM, Vissink A, Meijer HJA. Inter- and intraobserver reproducibility of buccal bone measurements at dental implants with cone beam computed tomography in the esthetic region. International Journal of Implant Dentistry 2015, 1:8; doi: /s Jemt T. Regeneration of gingival papillae after single-implant treatment. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1997;17(): Mombelli A, van Oosten MA, Schurch E,Jr, Land NP. The microbiota associated with successful or failing osseointegrated titanium implants. Oral Microbiol Immunol 1987;2: Löe H. The Gingival Index, the Plaque Index and the Retention Index Systems. J Periodontol. 1967;38: Faul F, Erdfelder E, Buchner A, Lang AG. Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods 2009;1: De Rouck T, Collys K, Cosyn J. Single-tooth replacement in the anterior maxilla by means of immediate implantation and provisionalization: a review. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2008;23: De Rouck T, Collys K, Wyn I, Cosyn J. Instant provisionalization of immediate single-tooth implants is essential to optimize esthetic treatment outcome. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009;20: den Hartog L, Raghoebar GM, Stellingsma K, Vissink A, Meijer HJ. Immediate non-occlusal loading of single implants in the aesthetic zone: a randomized clinical trial. J Clin Periodontol 2011;38: Buser D, Martin W, Belser UC. Optimizing esthetics for implant restorations in the anterior maxilla: anatomic and surgical considerations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 200; Grunder U, Gracis S, Capelli M. Influence of the 3-D bone-to-implant relationship on esthetics. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2005;25:
25 32. Raes F, Renckens L, Aps J, Cosyn J, De Bruyn H. Reliability of circumferential bone level assessment around single implants in healed ridges and extraction sockets using cone beam CT. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2013;15: Degidi M, Daprile G, Nardi D, Piattelli A. Immediate provisionalization of implants placed in fresh extraction sockets using a definitive abutment: the chamber concept. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2013;33: Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Lozada JL, Zimmerman G. Facial gingival tissue stability following immediate placement and provisionalization of maxillary anterior single implants: a 2- to 8-year follow-up. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2011;26: den Hartog L, Raghoebar GM, Slater JJ, Stellingsma K, Vissink A, Meijer HJ. Singletooth implants with different neck designs: a randomized clinical trial evaluating the aesthetic outcome. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2013;15: Santing HJ, Raghoebar GM, Vissink A, den Hartog L, Meijer HJ. Performance of the Straumann Bone Level Implant system for anterior single-tooth replacements in augmented and nonaugmented sites: a prospective cohort study with 60 consecutive patients. Clin Oral Implants Res 2013;2: McGrath C, Lam O, Lang N. An evidence-based review of patient-reported outcome measures in dental implant research among dentate subjects. J Clin Periodontol 2012;39: Hartlev J, Kohberg P, Ahlmann S, Andersen NT, Schou S, Isidor F. Patient satisfaction and esthetic outcome after immediate placement and provisionalization of single-tooth implants involving a definitive individual abutment. Clin Oral Implants Res 201;25: Raes F, Cooper LF, Tarrida LG, Vandromme H, De Bruyn H. A case-control study assessing oralhealth-related quality of life after immediately loaded single implants in healed alveolar ridges or extraction sockets. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012;23: Raes F, Cosyn J, De Bruyn H. Clinical, Aesthetic, and Patient-Related Outcome of Immediately Loaded Single Implants in the Anterior Maxilla: A Prospective Study in Extraction Sockets, Healed Ridges, and Grafted Sites. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2013;15:
26 99
27 100
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of an impacted maxillary canine: two case reports
 Zuiderveld et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0013-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of
Zuiderveld et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:13 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0013-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Immediate placement and provisionalization of an implant after removal of
Inter- and intraobserver reproducibility of buccal bone measurements at dental implants with cone beam computed tomography in the esthetic region
 Slagter et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:8 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0007-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Inter- and intraobserver reproducibility of buccal bone measurements at dental
Slagter et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2015) 1:8 DOI 10.1186/s40729-015-0007-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Inter- and intraobserver reproducibility of buccal bone measurements at dental
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study
 Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
AOS Adelaide Novembre Acknowledgement Dr Andre HaEngh for some clinical pictures
 Pa#ent- centered implant treatment giving reliability through simplicity (part 2- when bone is not where we want it to be) Hugo De Bruyn & Stefan Vandeweghe AOS Adelaide Novembre 2011 Acknowledgement Dr
Pa#ent- centered implant treatment giving reliability through simplicity (part 2- when bone is not where we want it to be) Hugo De Bruyn & Stefan Vandeweghe AOS Adelaide Novembre 2011 Acknowledgement Dr
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
In the esthetic zone, osseointegration
 CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5
 Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Peri-implant Augmentation
 Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Treatment outcome of two adjacent implant crowns with different implant platform designs in the aesthetic zone Tymstra, Nynke; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan; den Hartog, Laurens;
University of Groningen Treatment outcome of two adjacent implant crowns with different implant platform designs in the aesthetic zone Tymstra, Nynke; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan; den Hartog, Laurens;
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Immediate implant placement, with or without simultaneous implant provisionalization,
 Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
University of Groningen. Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke
 University of Groningen Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.05.013 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.04.003 10.1002/hed.24053 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
University of Groningen Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.05.013 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.04.003 10.1002/hed.24053 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Immediate non-occlusal loading of single implants in the aesthetic zone den Hartog, Laurens; Raghoebar, Gerry; Stellingsma, Cornelius; Vissink, Arjan; Meijer, Hendrikus Published
University of Groningen Immediate non-occlusal loading of single implants in the aesthetic zone den Hartog, Laurens; Raghoebar, Gerry; Stellingsma, Cornelius; Vissink, Arjan; Meijer, Hendrikus Published
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Performance of the Straumann Bone Level Implant system for anterior single-tooth replacements in augmented and nonaugmented sites Santing, Hendrik J.; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink,
University of Groningen Performance of the Straumann Bone Level Implant system for anterior single-tooth replacements in augmented and nonaugmented sites Santing, Hendrik J.; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink,
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Dental treatment for two adjacent missing teeth in the maxillary aesthetic zone Tymstra, Nynke; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan; Meijer, Hendrikus Published in: CLINICAL ORAL IMPLANTS
University of Groningen Dental treatment for two adjacent missing teeth in the maxillary aesthetic zone Tymstra, Nynke; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan; Meijer, Hendrikus Published in: CLINICAL ORAL IMPLANTS
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen A Technique for Standardized Evaluation of Soft and Hard Peri-Implant Tissues in Partially Edentulous Patients Meijndert, Leo; Meijer, Hendrikus; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan
University of Groningen A Technique for Standardized Evaluation of Soft and Hard Peri-Implant Tissues in Partially Edentulous Patients Meijndert, Leo; Meijer, Hendrikus; Raghoebar, Gerry; Vissink, Arjan
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
University of Groningen. Soft tissue development in the esthetic zone Patil, Ratnadeep Chandrakant
 University of Groningen Soft tissue development in the esthetic zone Patil, Ratnadeep Chandrakant IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Soft tissue development in the esthetic zone Patil, Ratnadeep Chandrakant IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Clinical Paper Pre-Implant Surgery
 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009; 38: 736 743 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.03.002, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Pre-Implant Surgery Comparison of procedures for immediate
Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009; 38: 736 743 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.03.002, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Pre-Implant Surgery Comparison of procedures for immediate
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla
 Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla Franck Bonnet, DDS Private Practice, Cannes, Le Cannet, France Director
Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla Franck Bonnet, DDS Private Practice, Cannes, Le Cannet, France Director
Initial findings and treatment plan
 12 STARGET 1 I 10 s t r a u m a n n CADCAM s o l u t i o n s A n dr ea s Gr a f MDT, Dr. Karin Wolleb and D r. R onal d J ung Individual anterior esthetics Pa rt 1 : t h e p o ssib i l ities o f S traum
12 STARGET 1 I 10 s t r a u m a n n CADCAM s o l u t i o n s A n dr ea s Gr a f MDT, Dr. Karin Wolleb and D r. R onal d J ung Individual anterior esthetics Pa rt 1 : t h e p o ssib i l ities o f S traum
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series NABIL KHZAM, BDS, MPhil, DClinDent*, NIKOS MATTHEOS, DDS, MASc, PhD, DAVID ROBERTS,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series NABIL KHZAM, BDS, MPhil, DClinDent*, NIKOS MATTHEOS, DDS, MASc, PhD, DAVID ROBERTS,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Esthetic evaluation of implant-supported single crowns: a comparison of objective and patient-reported outcomes
 Altay et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2019) 5:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0153-3 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Open Access Esthetic evaluation of implant-supported
Altay et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2019) 5:2 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0153-3 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Open Access Esthetic evaluation of implant-supported
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study
 Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
University of Groningen. Single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone den Hartog, Laurens
 University of Groningen Single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone den Hartog, Laurens IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
University of Groningen Single-tooth implants in the aesthetic zone den Hartog, Laurens IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it.
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 175 Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization After Long-Axis Root Fracture and Complete Loss of the Facial Bony Lamella Robert
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 175 Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization After Long-Axis Root Fracture and Complete Loss of the Facial Bony Lamella Robert
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Submission to Clinical Oral Implants Research (adjusted version)
 Submission to Clinical Oral Implants Research (adjusted version) Title A prospective cohort study on the impact of smoking on soft tissue alterations around single implants Running title Soft tissue alterations
Submission to Clinical Oral Implants Research (adjusted version) Title A prospective cohort study on the impact of smoking on soft tissue alterations around single implants Running title Soft tissue alterations
MINI System CASE REPORT. Name: Dr. Achraf Souayah Na<on: Tunisia
 MINI System SE REPORT Name: Dr. chraf Souayah Na
MINI System SE REPORT Name: Dr. chraf Souayah Na
An Introduction to Dental Implants
 An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
An Introduction to Dental Implants Aims: This article provides an introduction to dental implants, outlining the categories of dental implants, the phases involved in implant dentistry and assessing a
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 2. Introduction Surgical challenges to treat esthetic implant failures Treatment options & case reports Conclusions
 T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
BUILDING A. Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation. 70 OCTOBER 2016 // dentaltown.com
 BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
BUILDING A MANDI Achieving total reconstruction in a single operation by Dr. Fayette C. Williams Fayette C. Williams, DDS, MD, FACS, is clinical faculty at John Peter Smith Hospital in Fort Worth, Texas,
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Prosthodonticstown. Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites. clinical. Table I
 Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
Prosthodonticstown clinical Immediate Implant Placement in Fresh Extraction Sites Charles A. Babbush, DDS, MScD Table I Benefits Of Immediate Implantation Improved prosthesis fabrication and/or design
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
SCD Case Study. Implant-supported overdentures
 SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Integrating Natural Hard and Soft Tissue
 ACCREDITATION ESSENTIALS Integrating Natural Hard and Soft Tissue An Implant-Supported Restoration in the Esthetic Zone Somkiat Aimplee, DDS, MSc The successful replacement of anterior teeth with implants
ACCREDITATION ESSENTIALS Integrating Natural Hard and Soft Tissue An Implant-Supported Restoration in the Esthetic Zone Somkiat Aimplee, DDS, MSc The successful replacement of anterior teeth with implants
Then and Now. Implant Therapy:
 Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report
 Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
University of Groningen. Restorative dentistry done digitally Schepke, Ulf
 University of Groningen Restorative dentistry done digitally Schepke, Ulf IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
University of Groningen Restorative dentistry done digitally Schepke, Ulf IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
An esthetic zone implant
 clinical brief inside my practice peer to peer spotlight tech profile Surgical and Prosthetic Treatment of a Failed Maxillary Central Incisor Immediate implant placement is a key to success Robert A. Levine,
clinical brief inside my practice peer to peer spotlight tech profile Surgical and Prosthetic Treatment of a Failed Maxillary Central Incisor Immediate implant placement is a key to success Robert A. Levine,
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Inclusive Tooth Replacement System
 Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area
 CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 401 Guidelines for Selecting the Implant Diameter During Immediate Implant Placement of a Fresh Extraction Socket: A Case Series Ariádene
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior
 Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
Peri-implant health and peri-implant bone stability after immediate implant placement
 2 First report of a two-year retrospective study with a newly developed bone-level implant system Peri-implant health and peri-implant bone stability after immediate implant placement DR-MEDIC STOM. HENRIETTE
2 First report of a two-year retrospective study with a newly developed bone-level implant system Peri-implant health and peri-implant bone stability after immediate implant placement DR-MEDIC STOM. HENRIETTE
Case Report - Dr. Arthur Weiss
 High Esthetic Solutions with a Team Approach to Implant Dentistry The placement of hybrid abutments in the highly esthetic anterior zone Introduction Proper planning with a team approach ensures that highly
High Esthetic Solutions with a Team Approach to Implant Dentistry The placement of hybrid abutments in the highly esthetic anterior zone Introduction Proper planning with a team approach ensures that highly
