The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
|
|
|
- Reynold Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
2 175 Immediate Implant Placement and Provisionalization After Long-Axis Root Fracture and Complete Loss of the Facial Bony Lamella Robert Noelken, Dr Med Dent* Martin Kunkel, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med Dent** Wilfried Wagner, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med Dent*** The aim of this research was to explore the performance of a flapless surgical approach for immediate implant placement, simultaneous alveolar ridge augmentation, and immediate provisionalization in patients with complete loss of the facial bony lamella resulting from long-axis root fracture. Eighteen NobelPerfect implants were placed in 16 patients (follow-up, 13 to 36 months) who had sustained complete loss of the facial bony lamellae. Implants were inserted simultaneous to subperiostal bone augmentation with autogenous bone chips and underwent immediate provisionalization. Outcome variables included implant success, marginal bone levels, and pink esthetic score (PES). All implants achieved excellent primary stability. There were no implant losses. On average, interproximal marginal bone levels stabilized at 1.0 to 1.3 mm above the first thread. Postoperative cone beam computed tomography scans were available for 16 implant sites and confirmed restoration of the facial lamella in the vast majority of patients. Marginal esthetics, as assessed by the PES, was by and large preserved (mean postoperative PES, 12.5). Oral hygiene was highly predictive for the esthetic result. Survival rates, marginal bone levels, and esthetic results suggest a proof-of-principle for the new flapless immediate implant placement technique in patients with complete loss of the facial bony lamella. Oral hygiene status may be considered as a negative prognostic factor for the esthetic outcome. (Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2011;31: ) * Private Practice, Lindau/Lake Constance, Germany; Research Fellow, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University Hospital Mainz, Mainz, Germany. ** Professor and Head, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University Hospital Bochum, Bochum, Germany. *** Professor and Head, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University Hospital Mainz, Mainz, Germany. Correspondence to: Dr Robert Noelken, Paradiesplatz 7-13, D Lindau/Lake Constance, Germany; fax: ; praxis@dr-noelken.de. Bone loss resulting from vertical root fracture 1 3 poses a challenging problem in dental implant dentistry. Since the microbiotic and mechanical sequelae of vertical root fractures typically induce the loss of alveolar bone, and rather often complete resorption of the facial bony lamella, 4 typical requirements for immediate implant placement and especially immediate loading most often will not be fulfilled. 5,6 For these reasons, implant restoration is often performed as a two- or three-stage procedure Staged approaches, however, imply major drawbacks with regard to the preservation of the residual bone level 11,12 and the marginal gingival contour. 13,14 The respective involuntary changes have been demonstrated clearly to compromise the long-term esthetic results Immediate implant placement and immediate provisionalization substantially add to the preservation of the marginal structure It was the remarkable esthetic outcome achieved in a recently published series on NobelPerfect implants 22 that prompted the authors to transfer Volume 31, Number 2, 2011
3 176 the concept of immediate implant placement and provisionalization to the challenging situation of longitudinal root fractures. The rationale emerged from the observation that a layer of autologous bone chips placed in the gap between the implant and the facial soft tissues resulted in the restoration of a stable facial bone layer regardless of the dimension of a preexisting facial bony defect. Thus, the aim of this study was to systematically explore the performance of a new flapless immediate implant placement technique when applied in patients with complete loss of the facial bony lamella. Specifically, this communication reports implant success rates and focuses on the clinical, radiographic, and esthetic outcomes within a followup period of 13 to 36 months. Method and materials From April 2004 to December 2006, 16 patients (5 men, 11 women; mean age, 43 years; range, 25 to 64 years) were enrolled in this study. Inclusion criteria were as follows: tooth loss in the esthetic zone following a long-axis root fracture, complete loss of the facial bony lamella, high primary stability expected, and request for an immediate provisional prosthetic restoration. Exclusion criteria included previous radiation therapy, systemic bone diseases, and permanent immunosuppressive medication. Overall, 18 implants were inserted. In the initial phase of the study, patients received NobelPerfect implants (Nobel Biocare) with a 1.5-mm machined scalloped collar (n = 3). Beginning in November 2005, NobelPerfect Groovy implants (Nobel Biocare) with a TiUnite-surfaced scalloped collar were inserted (n = 15). Thirteen implants replaced maxillary incisors, and 5 implants were inserted in the maxillary first premolar region. Surgical technique All surgical interventions were performed using a flapless protocol. The condemned teeth were extracted, with care taken to maintain the lateral and oral alveolar socket walls and the gingival architecture. Hereafter, implant sites were prepared according to the manufacturer s instructions. The implants were placed in contact with the oral lamella of the socket. The scalloped implant neck was placed approximately 2 mm apical to the circumferential soft tissue margin. All implant sites allowed for a 16-mmlong implant to be placed. Implant diameters were 3.5 mm in four implants, 4.3 mm in seven implants, and 5.0 mm in seven implants. To restore the facial bony contour, simultaneous bone grafting was performed by condensing bone chips to the bottom of the facial defect with a plugger. All autogenous bone grafts were harvested at the mandibular ramus. Additional soft tissue grafts were not used. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
4 177 Immediate restoration In patients undergoing single-tooth replacement, manufactured acrylic teeth were adjusted on top of titanium abutments. For multiple tooth replacements, provisional restorations were fabricated by a lab technician. All provisional restorations were free of occlusal contacts. For further stabilization, all implants were splinted. Patients received clindamycin (starting 2 days preoperatively for 1 week) for perioperative bacterial control. After a minimum of 3 months, the definitive crowns were fabricated using porcelain-fused-to-metal or Procera zirconia technology (Nobel Biocare) and were cemented using a long-lasting temporary cement (Improv, Alvelogro) or a glass-ionomer cement (Ketac-Cem, 3M ESPE). Follow-up and definition of outcome variables Patients were examined at the time of implant placement and at least 13 months later. The primary outcome variables were as follows: Implant success according to the criteria established by Buser et al. 23 Peri-implant probing depth, registered at six sites around the implants (mesiofacial, facial, distofacial, mesiolingual, lingual, distolingual). Status of the interproximal marginal bone level, determined using digital radiographs with a commercial Rinn holder. Specifically, the vertical distance between the mesial and distal bone level and the prominence of the first thread was measured. Attachment levels crestal to the first thread were designated as positive values. Status of the facial bone level, determined using cone bean computed tomography (CBCT) data. Specifically, the bone level was determined by the reconstruction according to the long axis of the implants. The Sulcular Bleeding Index (SBI) according to Mühlemann and Son, 24 measured prior to surgery and at each follow-up visit. The pink esthetic score (PES) according to Fürhauser et al, 25 measured prior to surgery and at each follow-up visit. Statistical analysis Survival probabilities were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method. The endpoint of interest was implant failure according to the criteria established by Buser et al. 23 The analysis exploring the link between marginal bone level and the PES was completed using Spearman rankbased correlations. Subpopulations within the study group (improved vs decreased PES) were compared using nonparametric U tests. Paired observations (oral vs facial probing depth, pre- vs postoperative PES) were compared using the Wilcoxon matched pairs test. The reported P values were two-sided. All calculations were completed using SPSS for Windows (version 12, IBM). Volume 31, Number 2, 2011
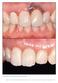
5 178 Fig 1 Typical treatment protocol for single-tooth replacement. Fig 1a Initial clinical aspect of the right central incisor. The marginal tissues showed slight swelling. Fig 1b After extraction of the affected tooth, a long-axis root fracture was visible. Fig 1d (left) Intraoperative aspect after reconstruction of the facial lamella with autogenous bone chips from the ramus. Note the slight overextension of the bone graft to achieve a favorable marginal contour after the consolidation phase. Fig 1e (right) CBCT image 5 months after implant placement. Three-dimensional imaging in the sagittal view shows the complete reconstitution of the facial bony lamella. Fig 1c Intraoperative view after removal of the tooth. The entire facial lamella underwent resorption. Figs 1f and 1g (left) Clinical and (right) radiographic outcomes 19 months after immediate implant placement, immediate provisionalization, and definitive restoration delivery. Complete osseointegration of the implant and favorable marginal bone level at approximately 1.5 mm coronal to the first thread was noticed. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
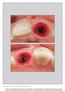
6 179 Fig 2 Patient with the worst outcome in the case series. Fig 2a (right) Initial clinical aspect showing a long-axis root fracture with complete loss of the facial lamella, a fistula, and a recession-type defect. Fig 2b (left) Radiographic outcome 15 months after immediate implant placement showing excessive bone loss following overextrusion of cement. Fig 2c (right) Clinical aspect at final examination. There was a lack of inflammation despite severe bone resorption. The marginal soft tissue level improved, but the overall PES score was unchanged. Results All patients fully attended the followup. Although the facial bony lamella was completely absent, all implants yielded sufficient primary stability for immediate placement of the provisional restoration. Figure 1 illustrates the typical treatment protocol for a single-tooth replacement. Figure 2 presents the preoperative aspects and final outcome of the patient with the worst clinical outcome in terms of marginal bone level. This implant was classified as a failure because of excessive bone loss. Implant success Within the follow-up period (13 to 36 months; median, 22 months), no implant had to be removed. No major loss of marginal bone was observed except for in one patient (Fig 2). On retrospective analysis, this excessive bone loss occurred because of an initially unrecognized cement overextrusion to the sulcus at the time of delivering the definitive crown. Four months later, this patient presented with purulent sulcular outflow. Although the cement was removed and secondary augmentation was performed, the defect did not recover. The implant did not show an unfavorable esthetic outcome or renewed suppuration through the final examination (Fig 2c). Nevertheless, this implant was considered a failure. Thus, the success rate, according to the criteria of Buser et al, 23 was 94% (mean survival, 34 months; 95% confidence interval, 31 to 38 months) (Fig 3). Volume 31, Number 2, 2011
7 180 Survival Censored observation Time (mo) PES PES preoperative PES postoperative PES unchanged Patient no. Fig 3 Kaplan-Meier estimate for implant survival. Fig 4 Pre- and postoperative PES ratings. In approximately 70% of implants, the esthetic status was improved or preserved compared with the initial situation. Probing depth Mean peri-implant probing depth ranged from 3.7 mm (facial) to 4.6 mm (disto-oral). Probing depths indicated no inferior bone level on the facial aspect (mean, 3.7 mm) when compared to the oral aspect (mean, 3.9 mm). By contrast, the distolingual probing depth was slightly higher than the distobuccal (4.6 vs 4.2 mm), reflected in a moderate trend toward a difference (P =.073, Wicoxon matched pairs analysis). Thus, the data suggest no relevant differences between marginal tissue levels at the preserved oral and reconstructed facial aspects of the implants. In the complication case (Fig 2), probing depths of up to 9 mm were observed. Marginal bone level Referring to the contour of the first thread, the average interproximal marginal bone level was 1.3 mm (range, 2.6 to 2.7 mm) at the mesial aspect and 1.0 mm (range, 3.9 to 3.1 mm) at the distal aspect. The respective values in the complication case were 2.6 and 3.9 mm. Excluding the complication case, the average interproximal marginal bone level was 1.6 mm (range, 0.0 to 2.7 mm) at the mesial aspect and 1.3 mm (range, 0.0 to 3.1 mm) at the distal aspect. When the interproximal marginal bone level was considered as a function of time, there was no correlation between the marginal bone status and the length of the follow-up period (r = 0.368, P =.133; Spearman rank correlation coefficient). Follow-up CBCTs were available for 16 patients. The reconstruction of up to 10 slices within the long axis of the implants confirmed gross reconstitution of the facial bony lamella in all patients (Fig 1e). However, in 4 patients, single slices suggested small longitudinal zones of incomplete bone coverage in the midline at the facial prominence measuring 0.5 to 1.0 mm in width. PES Improvement of the PES was noticed in 8 implant sites. In 5 sites, the esthetic status was unchanged, while 5 sites sustained a slight to moderate decrease (Fig 4). Thus, overall, the PES remained unchanged by the intervention (P =.646, Wilcoxon matched pairs test). At the final The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
8 181 Table 1 Mean pre- and postoperative PES values Variable Preoperative Postoperative Mesial papilla Distal papilla Level of soft tissue margin SBI (%) Soft tissue contour Alveolar process contour Soft tissue color Soft tissue texture Total Reduced PES (n = 5) Improved or equal PES (n = 13) Fig 5 SBI according to esthetic outcome. When comparing the implants with reduced postoperative PES scores to those with improved or equal scores, the preoperative SBI emerged as a simple predictive parameter. examination, the mean PES amounted to 12.5 (range, 10.0 to 14.0), while the preoperative PES averaged 12.2 (range, 8.0 to 14.0). The detailed values of the PES are given in Table 1. Thus, the integrity of the gingival architecture could be largely maintained with this flapless approach. The most critical single PES item in this cohort was the alveolar process contour. In 12 implant sites, the natural appearance of this zone was preserved, but another 6 sites showed a slight to moderate loss of the bony contour. When looking at potential determinants of the PES, neither demographic or anamnestic data nor the interproximal marginal bone level were predictive for the postoperative esthetic outcome. However, the SBI was strongly associated with the esthetic outcome, with an increased SBI score suggesting an improved likelihood of a decrease in the esthetic score and vice versa (P =.002, U test) (Fig 5). Discussion This analysis addressed the clinical performance of a new flapless immediate implant placement and augmentation technique in patients with complete loss of the facial bony lamella because of vertical root fractures. Clinical reports on this issue are rare. Evian et al 26 reported the therapeutic management for immediate implant placement in sites with periapical deficiencies where the marginal bone was preserved. They raised a flap in the apical region without compromising the integrity of the coronal bone and gingiva. However, this technique is not suitable for complete facial bony defects. To get one step further, a flapless approach was combined with a subperiostal ridge augmentation via bone chips for reconstruction of the entire facial alveolar wall. This treatment concept provides continuous bony support of the marginal gingiva and promises prevention of the collapse of the marginal contour. Since primary stability is the cornerstone of immediate provisionalization, 16-mm-long implants were used and splinted to the neighboring teeth or other implants to assure maximum anchorage and to distribute stress to the surrounding bone. 27 It remains open whether the specific implant design and surface or the surgical concept is the key to the support of the marginal contour Volume 31, Number 2, 2011
9 182 and the reconstitution of the bony lamella. However, although all patients had extended defects of the facial alveolar bone lamella, the clinical outcome parameters were in line with the results reported for immediate loading of standard platform 5,6,18 21 or scalloped implants in favorable bone conditions. Thus, success rates, marginal bone levels, and esthetic results suggest a proof-of-principle for this flapless immediate implant placement and augmentation technique. It is remarkable that the results are in striking contrast to several previous reports suggesting that soft tissue compromise and gingival recession could hardly be avoided, regardless of immediate 35 or delayed 33 provisionalization. However, there are fundamental differences between these studies and the current case series. In this study, the gingival architecture was preserved, implants were placed at the oral aspect of the alveolar contour allowing for bony reconstruction within the envelope, and allografts were avoided. Taken together, these details might explain the rather stable esthetic outcome, since they all contribute to minimal inflammatory reactions, which otherwise might promote renewed bone resorption and consecutive soft tissue collapse. Due to the restriction of the case series to longitudinal root fractures, only a limited number of patients were included in this cohort. However, even with the small patient sample, oral hygiene emerged as a relevant predictive factor for esthetic outcome. In spite of the promising results, implant-supported tooth replacement in the esthetic zone remains a critical issue, especially when the alveolar bone is lost because of inflammatory resorption. Although, on average, a favorable interproximal bone level was maintained and comparable PES ratings were obtained at pre- and postoperative evaluations, the data presented in Fig 4 indicate that a relevant proportion of the patients experienced some esthetic compromise. It remains to be explored whether these drawbacks may be avoided by a strict patient selection based on oral hygiene parameters such as the SBI or by further refinements of the surgical approach. However, by applying the protocol specified above, preservation or improvement of the esthetic status was achieved in two thirds of the patients. Conclusion Survival rates, marginal bone levels, and esthetic results suggest a proof-of-principle for a flapless immediate implant placement technique in patients with complete loss of the facial bony lamella. Oral hygiene status may be considered as a negative prognostic factor for the esthetic outcome. Acknowledgment This work was supported in part by a grant from Nobel Biocare to Dr Robert Noelken and Prof Wilfried Wagner. References 1. Reeh ES, Messer HH, Douglas WH. Reduction in tooth stiffness as a result of endodontic and restorative procedures. J Endod 1989;15: Zhi-Yue L, Yu-Xing Z. Effects of post-core design and ferrule on fracture resistance of endodontically treated maxillary central incisors. J Prosthet Dent 2003;89: Milot P, Stein RS. Root fracture in endodontically treated teeth related to post selection and crown design. J Prosthet Dent 1992;68: Ricucci D, Bergenholtz G. Bacterial status in root-filled teeth exposed to the oral environment by loss of restoration and fracture or caries A histobacteriological study of treated cases. Int Endod J 2003;36: Wöhrle PS. Single-tooth replacement in the aesthetic zone with immediate provisionalization: Fourteen consecutive case reports. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 1998;10: Kan JYK, Rungcharassaeng K. Immediate placement and provisionalization of maxillary anterior single implants: A surgical and prosthodontic rationale. Pract Periodontics Aesthetic Dent 2000;12: Keith JD Jr, Salama MA. Ridge preservation and augmentation using regenerative materials to enhance implant predictability and esthetics. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2007;28: Cardaropoli G, Araújo M, Hayacibara R, Sukekava F, Lindhe J. Healing of extraction sockets and surgically produced augmented and non-augmented defects in the alveolar ridge. An experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol 2005;32: Salama H, Salama MA, Garber DA, Adar P. Developing optimal peri-implant papillae within the esthetic zone: Guided soft tissue augmentation. J Esthet Dent 1995;7: Evian CI, al-maseeh J, Symeonides E. Soft tissue augmentation for implant dentistry. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2003;24: , , Carlsson GE, Bergman B, Headgård B. Changes in contour of the maxillary alveolar process under immediate dentures. A longitudinal clinical and x-ray cephalometric study covering 5 years. Acta Odontol Scand 1967;25: The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
10 Becker W, Ochsenbein C, Tibbetts L, Becker BE. Alveolar bone anatomic profiles as measured from dry skulls. Clinical ramifications. J Clin Periodontol 1997;24: Spear FM. Maintenance of the interdental papilla following anterior tooth removal. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 1999; 11: Tarnow DP, Magner AW, Fletcher P. The effect of the distance from the contact point to the crest of bone on the presence or absence of the interproximal dental papilla. J Periodontol 1992;63: Salama H, Salama MA, Garber D, Adar P. The interproximal height of bone: A guidepost to predictable aesthetic strategies and soft tissue contours in anterior tooth replacement. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 1998;10: Ko CC, Douglas WH, DeLong R, et al. Effects of implant healing time on crestal bone loss of a controlled-load dental implant. J Dent Res 2003;82: Kan JYK, Rungcharassaeng K. Site development for anterior implant esthetics: The dentulous site. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2001;22: , 228, Lazzara RJ. Immediate implant placement into extraction sites: Surgical and restorative advantages. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 1989;9: Gelb DA. Immediate implant surgery: Three-year retrospective evaluation of 50 consecutive cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1993;8: Hui E, Chow J, Li D, Liu J, Wat P, Law H. Immediate provisional for single-tooth implant replacement with Brånemark system: Preliminary report. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2001;3: Kan JYK, Rungcharassaeng K, Lozada J. Immediate placement and provisionalization of maxillary anterior single implants: 1-year prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2003;18: Noelken R, Morbach T, Kunkel M, Wagner W. Immediate function with Nobel- Perfect implants in the anterior dental arch. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2007;27: Buser D, Mericske-Stern R, Bernard JP, et al. Long-term evaluation of non-submerged ITI implants. Part 1: 8-year life table analysis of a prospective multi-center study with 2359 implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 1997;8: Mühlemann HR, Son S. Gingival sulcus bleeding A leading symptom in initial gingivitis. Helv Odontol Acta 1971;15: Fürhauser R, Florescu D, Benesch T, Haas R, Mailath G, Watzek G. Evaluation of soft tissue around single-tooth implant crowns: The pink esthetic score. Clin Oral Implants Res 2005;16: Evian CI, Al-Momani A, Rosenberg ES, Sanavi F. Therapeutic management for immediate implant placement in sites with periapical deficiences where coronal bone is present: Technique and case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2006; 21: Bergkvist G, Simonsson K, Rydberg K, Johansson F, Dérand T. A finite element analysis of stress distribution in bone tissue surrounding uncoupled or splinted dental implants. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2008;10: Rocci A, Gottlow J. Esthetic outcome of immediately loaded scalloped implants placed in extraction sites using flapless surgery. A 6 months report of 4 cases. Appl Osseo Res 2004;4: Wöhrle PS. Nobel Perfect esthetic scalloped implant: Rationale for a new design. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2003; 5(suppl 1): Nowzari H, Chee W, Yi K, Pak M, Ho Chung W, Rich S. Scalloped dental implants: A retrospective analysis of radiographic and clinical outcomes of 17 NobelPerfect implants in 6 patients. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2006;8: McAllister BS. Scalloped implant designs enhance interproximal bone levels. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2007;27: Kan JYK, Rungcharassaeng K, Liddelow G, Henry P, Goodacre CJ. Periimplant tissue response following immediate provisional restoration of scalloped implants in the esthetic zone: A one-year pilot prospective multicenter study. J Prosthet Dent 2007;97(suppl):S109 S118 [erratum 2008;99:167]. 33. Evans CJD, Chen ST. Esthetic outcomes of immediate implant placements. Clin Oral Implants Res 2008;19: Chen ST, Darby IB, Reynolds EC. A prospective clinical study of non-submerged immediate implants: Clinical outcomes and esthetic results. Clin Oral Implants Res 2007;18: Kan JYK, Rungcharassaeng K, Sclar A, Lozada JL. Effects of the facial osseous defect morphology on gingival dynamics after immediate tooth replacement and guided bone regeneration: 1-year results. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2007;65(suppl 1): [erratum 2008;66: ]. Volume 31, Number 2, 2011
Successful osseointegration of implants has been
 Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Immediately provisionalized OsseoSpeed TM Profile implants inserted into extraction sockets: 3-year results
 Robert Noelken Fabienne Oberhansl Martin Kunkel Wilfried Wagner Immediately provisionalized OsseoSpeed TM Profile implants inserted into extraction sockets: 3-year results Authors affiliations: Robert
Robert Noelken Fabienne Oberhansl Martin Kunkel Wilfried Wagner Immediately provisionalized OsseoSpeed TM Profile implants inserted into extraction sockets: 3-year results Authors affiliations: Robert
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of July 11, 2011):
 Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration
 IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
In the esthetic zone, osseointegration
 CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
Multidisciplinary Approach in Restoration of Form, Function and Aesthetics of Grossly Decayed Anterior Teeth
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(1):48-52 Multidisciplinary Approach in Restoration of Form, Function and Aesthetics of Grossly Decayed Anterior Teeth Vyapaka Pallavi From the Department of Conservative
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(1):48-52 Multidisciplinary Approach in Restoration of Form, Function and Aesthetics of Grossly Decayed Anterior Teeth Vyapaka Pallavi From the Department of Conservative
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Peri-implant Augmentation
 Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Restorative Dentistry and Papilla Reconstruction in Reduced Periodontium
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT Restorative Dentistry and Papilla Reconstruction in Reduced Periodontium Robert Azzi, Daniel Etienne, Bernard Schweitz Restoring the loss of periodontal soft and hard tissues
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORT Restorative Dentistry and Papilla Reconstruction in Reduced Periodontium Robert Azzi, Daniel Etienne, Bernard Schweitz Restoring the loss of periodontal soft and hard tissues
The refinement of adhesive technology and contemporary
 CONTINUING EDUCATION 3 4 THE INTERPROXIMAL HEIGHT OF BONE: A GUIDEPOST TO PREDICTABLE AESTHETIC STRATEGIES AND SOFT TISSUE CONTOURS IN ANTERIOR TOOTH REPLACEMENT Henry Salama, DMD* Maurice A. Salama, DMD
CONTINUING EDUCATION 3 4 THE INTERPROXIMAL HEIGHT OF BONE: A GUIDEPOST TO PREDICTABLE AESTHETIC STRATEGIES AND SOFT TISSUE CONTOURS IN ANTERIOR TOOTH REPLACEMENT Henry Salama, DMD* Maurice A. Salama, DMD
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Revisions for CDT 2016
 Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Since the introduction of osseointegrated dental implants
 CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Immediate implant placement in a single staged
 Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes
 Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior
 Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
Bone Grafting and Immediate Implant Placement in the Anterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Whether a consequence of periodontal disease, caries or trauma to the root, losing an anterior tooth is psychologically
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS,
 Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
Implant Site Development Part I
 REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Biology of periodontal and periimplant. The ideal soft tissue profile around teeth and implants
 The ideal soft tissue profile around teeth and implants Biology of periodontal and periimplant tissues Individualized abutment Péter Windisch Prof. Dr. Med. Dent. Head Of The Department Of Periodontology
The ideal soft tissue profile around teeth and implants Biology of periodontal and periimplant tissues Individualized abutment Péter Windisch Prof. Dr. Med. Dent. Head Of The Department Of Periodontology
Replacing Hopeless Retained Deciduous Teeth in Adults Utilizing Dental Implants: Concepts and Case Presentation Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 7 Issue Date: November 2005, Posted On: 12/1/2005 Replacing Hopeless Retained Deciduous Teeth in Adults Utilizing Dental Implants: Concepts and Case Presentation Michael Tischler, DDS Hopeless
Page 1 of 7 Issue Date: November 2005, Posted On: 12/1/2005 Replacing Hopeless Retained Deciduous Teeth in Adults Utilizing Dental Implants: Concepts and Case Presentation Michael Tischler, DDS Hopeless
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
 International Extraction Journal Defect: of Clinical Assessment, Implant Dentistry, Classification January-April and Management 2009;1(1):1-11 Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
International Extraction Journal Defect: of Clinical Assessment, Implant Dentistry, Classification January-April and Management 2009;1(1):1-11 Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery. Dr.maryam khosravi
 Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
Principles of Periodontal flap surgery Dr.maryam khosravi Goals of periodontal SURGICAL phase 1 - Controlling or eliminating periodontal disease. 2 Correcting anatomic conditions that may a. favor periodontal
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic case report.
 European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
European International Journal of Science and Technology Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 Treatment of dental recessions in the esthetic zone by gingival and osseous recontouring. A multidisciplinary perio-prosthodontic
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Use of the natural tooth as a provisional after immediate implant placement
 Use of the natural tooth as a provisional after immediate implant placement By Robert Margeas, DDS Research on the preservation of the tissue architecture, reduction of surgical sequences and greater aesthetic
Use of the natural tooth as a provisional after immediate implant placement By Robert Margeas, DDS Research on the preservation of the tissue architecture, reduction of surgical sequences and greater aesthetic
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes BARRY P. LEVIN, DMD*, SERGIO RUBINSTEIN, DDS, LOUIS F. ROSE, DDS, MD ** ABSTRACT
CLINICAL ARTICLE Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes BARRY P. LEVIN, DMD*, SERGIO RUBINSTEIN, DDS, LOUIS F. ROSE, DDS, MD ** ABSTRACT
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
Available online at International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp , December, 2015
 z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Peri-implant health and peri-implant bone stability after immediate implant placement
 2 First report of a two-year retrospective study with a newly developed bone-level implant system Peri-implant health and peri-implant bone stability after immediate implant placement DR-MEDIC STOM. HENRIETTE
2 First report of a two-year retrospective study with a newly developed bone-level implant system Peri-implant health and peri-implant bone stability after immediate implant placement DR-MEDIC STOM. HENRIETTE
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
It is well-known that osseointegrated implants do not
 Infraposition of Implant-Retained Maxillary Incisor Crown Placed in an Adult Patient: Case Report Roberto Cocchetto, MD, DDS 1 /Luigi Canullo, DDS 2 /Renato Celletti, MD, DDS 3 Several studies have clearly
Infraposition of Implant-Retained Maxillary Incisor Crown Placed in an Adult Patient: Case Report Roberto Cocchetto, MD, DDS 1 /Luigi Canullo, DDS 2 /Renato Celletti, MD, DDS 3 Several studies have clearly
Immediate versus early implant placement
 Point and Counterpoint Coordinator: Mauro Tosta Immediate versus early implant placement Washington SANTANA MSc in Dentistry, Federal University of Goiás (UFG). Professor of Implantodontics, IKO-Goiânia.
Point and Counterpoint Coordinator: Mauro Tosta Immediate versus early implant placement Washington SANTANA MSc in Dentistry, Federal University of Goiás (UFG). Professor of Implantodontics, IKO-Goiânia.
Nicholas Caplanis DMD MS 6/13/2012
 Considerations In The Esthetic Zone Nick Caplanis DMD MS Private Practice Periodontics and Implant Surgery Mission Viejo, California Nick@drcaplanis.com Assistant Professor Loma Linda University Anatomic
Considerations In The Esthetic Zone Nick Caplanis DMD MS Private Practice Periodontics and Implant Surgery Mission Viejo, California Nick@drcaplanis.com Assistant Professor Loma Linda University Anatomic
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area
 CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
Course Objectives. HDA 2018 Dental Implant Complications. What are some common failures / problems we all encounter?
 HDA 2018 Dental Implant Complications 1 Course Objectives - Understand protocols for diagnosing and treatment planning to minimize complications - Recognize and manage intraoperative complications during
HDA 2018 Dental Implant Complications 1 Course Objectives - Understand protocols for diagnosing and treatment planning to minimize complications - Recognize and manage intraoperative complications during
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 335 Considerations of Implant Abutment and Crown Contour: Critical Contour and Subcritical Contour Huan Su, DDS* Oscar González-Martín,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 335 Considerations of Implant Abutment and Crown Contour: Critical Contour and Subcritical Contour Huan Su, DDS* Oscar González-Martín,
Anterior Restoration Splinting Implant with Natural Tooth: A Clinical Report
 Anterior Restoration Splinting Implant with Natural Tooth: A Clinical Report Seoung-Jin Hong, Yi-Hyung Woo, Kung-Rock Kwon, Janghyun Paek* Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, KyungHee University,
Anterior Restoration Splinting Implant with Natural Tooth: A Clinical Report Seoung-Jin Hong, Yi-Hyung Woo, Kung-Rock Kwon, Janghyun Paek* Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, KyungHee University,
Proven stability, high esthetics NobelReplace Conical Connection
 Proven stability, high esthetics NobelReplace Conical Connection Proven tapered implant body with a tight sealed connection NobelReplace Conical Connection combines the original tapered implant body with
Proven stability, high esthetics NobelReplace Conical Connection Proven tapered implant body with a tight sealed connection NobelReplace Conical Connection combines the original tapered implant body with
Abstract. A Case Of External Resorption
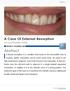 SHGDDS 1 BY Steven H. Goldstein, DDS Abstract External resorption is a condition that leads to the irreversible loss of enamel, dentin, cementum, and in some cases bone. Its cause is not fully understood,
SHGDDS 1 BY Steven H. Goldstein, DDS Abstract External resorption is a condition that leads to the irreversible loss of enamel, dentin, cementum, and in some cases bone. Its cause is not fully understood,
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Inclusive Tooth Replacement System
 Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
Optimizing Anterior Esthetics with the Inclusive Tooth Replacement System by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant treatment has changed so much over the years. In the past it was acceptable to place
MINI System CASE REPORT. Name: Dr. Achraf Souayah Na<on: Tunisia
 MINI System SE REPORT Name: Dr. chraf Souayah Na
MINI System SE REPORT Name: Dr. chraf Souayah Na
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
Then and Now. Implant Therapy:
 Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
Implant Therapy: Then and Now by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry has come a long way since blade and subperiostal implants were widely used. Improvements in implant design and site preparation
Dental Implants and Esthetics
 Continuing Education Brought to you by Dental Implants and Esthetics Course Author(s): Charles J. Goodacre, DDS, MSD; Chad J. Anderson, MS, DMD CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists,
Continuing Education Brought to you by Dental Implants and Esthetics Course Author(s): Charles J. Goodacre, DDS, MSD; Chad J. Anderson, MS, DMD CE Credits: 1 hour Intended Audience: Dentists, Dental Hygienists,
