Maxillary 3-implant removable prostheses without palatal coverage on Locator abutments a case series
|
|
|
- Aron Weaver
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Maxillary 3-implant removable prostheses without palatal coverage on Locator abutments a case series Arild Mo, Department of Clinical Dentistry, Faculty of Health Sciences, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, Norway Carl Hjortsjö, Department of Prosthetic Dentistry and Oral Function, Institute of Clinical Dentistry, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway Heming Olsen-Bergem, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Institute of Clinical Dentistry, University of Oslo, Oslo, Norway Asbjørn Jokstad, Department of Clinical Dentistry, Faculty of Health Sciences, UiT The Arctic University of Norway, Tromsø, Norway Running title: 3-implant maxillary removable prosthesis Corresponding author: Dr. Asbjørn Jokstad Department of Clinical Dentistry Faculty of Health Sciences UiT The Arctic University of Norway 9037 Tromsø Phone: (+47) asbjorn.jokstad@uit.no 1
2 Abstract Objectives: To present the clinical outcomes of patients with an edentulous maxilla treated with a removable prosthesis without palatal coverage retained by Locator abutments on three titanium implants. Material and Methods: All the patients in a private dental clinic consecutively treated up to six years earlier were invited for a follow-up examination (n=23). Two implants were placed bilaterally and one implant anteriorly in a tripod pattern. All patients underwent a clinical and radiological examination and completed questionnaires related to their experiences and satisfaction with the reconstructions. The prosthesis and implants were examined for adverse biological or technical aspects. Patient satisfaction and quality of life outcomes were collected using a self-reported Denture Satisfaction Scale and OHIP-20. Statistical analyses were limited to descriptive statistics. Results: Twenty-one of 23 invited participants consented to participate. We report in this paper the outcomes of the study participants who had received their implants more than 2 years ago (n=12). None of their 36 implants gave any indications of mobility or tenderness upon percussion. Suppuration was observed on one implant. Probing around the implants caused no (53%) or minor bleeding (47%). The incidence of adverse biological and technical events was near non-existent. The rates of replacement of male attachments varied, as did any changes of male attachment retention force. All participants described the task of insertion and removal of the prosthesis as unproblematic. The marginal bone loss ranged between 0 and 5.3 mm. The OHIP-20 and the Denture Satisfaction Questionnaire scores were high. Conclusions: The results in this clinical study are positive and promising. Admittedly, the study design is purely retrospective and observational with a small participant cohort, so the technical solution of placing three implants in the edentulous maxilla to retain a removable prosthesis should be appraised further in more controlled studies. Keywords: Dentures; Follow-Up Studies; Edentulous; Patient Satisfaction; Quality of Life; Retrospective Studies; Self Report; Titanium 2
3 Introduction Patients with a fully edentulous maxilla who desire an implant-retained prosthesis may receive different treatments, depending on general and local conditions (Zarb et al. 2013). The literature abounds with descriptions of technical solutions, ranging from a fixed solution retained by 4 axial or tilted implants and upwards (Heydecke et al. 2012) or a removable solution supported by 2 up to 10 splinted or free-standing implants (Roccuzzo et al. 2012). Initiatives to define the standard of care for the fully edentulous maxilla by critically appraising and comparing the cost-effectiveness of different prosthodontic solutions have not yet reached consensus (Schley et al. 2011). Patients restored with a maxillary removable prosthesis appear to require more maintenance visits when the prosthesis is retained by two splinted or free-standing implants in comparison to four implants that have been splinted with a cast or milled bar (Slot et al. 2010, Raghoebar et al. 2014). Whether the costs associated with the additional maintenance needs in the end outweighs the added costs of two additional implants and bars is still uncertain (Stoumpis & Kohal 2011, Bassi et al. 2013, Dudley 2013). Moreover, current reviews on this topic refer to data from primary studies where the non-splinted implants were fitted mostly with ball attachment systems of various designs, which likely have introduce confounding by virtue of variations in resistance against wear and degradation in the oral environment (Alsabeeha et al. 2009). In late 2007, two patients were referred to a private specialist clinic practice in Norway where the three first authors of this paper is affiliated (A.M., C.H. & H.O-B.). The two patients wished to restore a fully edentulous maxilla with a prosthesis supported by implants. Both patients expressed a desire for a fixed solution. However, it became clear during the clinical examinations that only a few intraoral positions were suitable for a surgical placement of a dental implant without prior surgical site enhancement. Both patients were reluctant to endure augmentation surgery to enable the placement of several implants to retain a complete fixed dental prosthesis. At the time, one systematic review had concluded that the evidence foundation for choosing the optimal design for a maxillary removable prosthesis was limited only to ball- and bar-solutions, as well as weak and rather contradictory (Sadowsky 2007). However, another 3
4 contemporaneous paper describing results of a small case series alleged that stud-type attachments on four or six unsplinted implants could successfully retain a maxillary removable prosthesis without a palatal coverage (Cavallaro & Tarnow 2007). The concept of a palate-free prosthesis appealed to both patients. From a clinical perspective, the prevailing consensus on standard of care at the time was that the implants had to be minimum 10 mm long, and placed surgically with a best possible relative parallelism and perpendicularly to the axial load vector. A second element was to achieve a maximal anterior-posterior spread of the implants intraorally. For the two patients, however, combining these requirements with the anatomical constraints in the edentulous maxilla allowed only space for the placement of three implants. After weighing up the positive aspects versus risks of possible adverse outcomes, both patients agreed with the surgeon-prosthodontist team to plan for a removable prosthesis without a palatal coverage retained by three free-standing implants fitted with Locator abutments (Zest Anchors, LLC, Escondido, CA, USA) (Figure 1). At the first recall examination after the completion of the treatment, both patients reported remarkably high satisfaction with their new prosthesis. The positive outcomes prompted therefore the clinicians to provide the same solution for a third and fourth patient with limited bone and unwilling to undergo bone augmentation surgery. Although anecdotal, the clinicians perceived the treatment approach as beneficial, while the incidence of patient-reported problems seemed minor. The technical solution was therefore subsequently offered to other patients who for different reasons decided not to proceed with site augmentation to enable placement of multiple implants in the maxilla. The objective of this report is to present the clinical outcomes of the first 21 consecutive patients with an edentulous maxilla treated with a removable prosthesis without palatal coverage retained by Locator abutments on three implants, one placed in the central incisor region and the two other in a more or less equilateral distance from the central implant. 4
5 Materials and Methods The Norwegian regional research ethics board approved the research protocol prior to commencing the study (ref. 2013/1446/REK Nord). All the patients in a private dental clinic consecutively treated with a maxillary removable prosthesis without palatal coverage supported by three dental implants were invited to participate in a follow-up examination (n=23). The patients received a free implant hygiene session and prosthesis cleaning, but no fiduciary compensation. Additional information required from the participants in this clinical study beyond routine care was a request to submit two treatment satisfaction questionnaires. The questionnaire response data were managed according to directives established by the Norwegian patient privacy ombudsperson. The current study cohort consists of all consecutive patients with an edentate maxilla, alternatively with terminal maxillary teeth, restored with a removable prosthesis without palatal coverage retained by Locator abutments on three implants. The patients with terminal teeth received in all cases an interim immediate prosthesis while the jaw healed for 3 to 5 months prior to implant surgery. None of the patients received any form of site augmentation or extraction socket grafting. The patients received commercially available implants made from titanium with a microrough surface surgically placed according to the manufacturer s instructions. During 2007 to 2010, implant systems from 3 different manufacturers were used, i.e., Osseospeed (Astra Tech, Mølndal, Sweden), Osstem (Osstem, Seoul, Korea) and Straumann SLA tissue level and bone level implants (Straumann, Waldenburg, Switzerland). In brief, the surgical procedures included antibiotics use at the discretion of the oral surgeon, local anesthetics, full flap incisions, placement of two implants bilaterally and one implant anteriorly with relative parallelism in sites considered radiographically to have the best bone. Hence, the implants were placed in the 15-13, and regions. At the onset around 2007, emphasis was made to place the implants with the best possible relative parallelism perpendicularly to the axial loading, but this constraint became less rigid few years later. All implants were located submerged under the 5
6 mucosa during the healing period, while the existing removable prosthesis was relieved and lined with a soft silicone-based reline material (GC Reline Soft, GC Corp., Leuven, Belgium). After approximately 3-4 months of healing, Locator abutments (ZEST Anchors, Escondido, CA, USA) were fitted to the implants, and new prostheses were made from heat-cured poly-methyl-methacrylate. All prostheses were reinforced with a metal alloy framework made from cobalt-chromium. All prostheses were constructed with prefabricated acrylic teeth (Premium and Mondial PALA Teeth, Heraeus Kulzer GmbH, Hanau, Germany) designed with a bilateral balanced occlusion, which were in a few situations lingualized due to the dentition of the mandible, and without anterior contacts in habitual occlusion. All prostheses incorporated three Locator male attachments with active retention, i.e., 680 (blue), 1361 (pink) or 2268 (clear) grams of retentive force. The choice of the male attachment retentive force was based principally on the patient-reported ease of placing and loosening their prosthesis. All patients were taught how to practice optimal home oral care, explained the need to seek regular maintenance care and requirement to uphold good oral hygiene. All patients were invited to return to the specialist clinic practice for follow-up dental care, or to continue to receive dental care from their regular dentist. Base-line recording Before the commencement of treatments, all patients had self-reported general health conditions that could entail risk of adverse outcomes. Recordings were made of general and local factors that could affect the prognosis of the implants and prosthesis, including the occurrence of systemic disease, regular medication use and smoking status. Presurgery and post-operative panoramic radiographs taken at the day of implant surgery, complemented with radiographs taken at the second-stage surgery upon the connection of abutments. Follow-up examinations All patients underwent a clinical and radiological examination and completed questionnaires related to changes in general health aspects, as well as their 6
7 experiences and satisfaction with the reconstructions and eventual need for repair sessions during the last year. Intra-oral status The radiographic examination comprised an orthopantomogram. The clinical examination included a basic periodontal examination with the use of an UNC-15 (University of North Carolina) manual periodontal probe. Outcomes measured were the presence or absence of peri-implant suppuration or fistula, the modified plaque and sulcus bleeding indices (Mombelli et al. 1987) and the probing depth (Buser et al. 1990). Examination of prosthesis and implants The removable prosthesis was carefully examined for any technical flaws. Adverse technical events included loss of retention, or fracture and/or chipping of the removable prosthesis. Adverse mechanical events included loosening of the male attachment or fracture of an implant. The stability of all implants was assessed, and any sign of mobility along with pain and discomfort was interpreted as a definitive sign of implant failure. The male attachment were replaced with new attachments of the same or more retentive force if the patient reported problems with placing and loosening their prosthesis, or complaints of dislodgment during function. The patients were also advised to replace the attachments in case of noticeable wear facets or ledges on the central pillar of the nylon attachment. The detached male attachments rings were not subjected to further detailed examinations Patient satisfaction and quality of life outcomes Patient-based outcomes were collected using a self-reported Denture Satisfaction Scale (Allen et al. 2001) and the short form version of the Oral Health Impact Profile questionnaire (OHIP-20) (Allen & Locker, 2002). The scores from the Denture Satisfaction Scale were analyzed globally and related to functional status. The OHIP scores was also analyzed globally and next divided into function-related questions as well as questions related to psychosocial issues. Sub-scale scores were created by summing the responses to the respective questions. 7
8 Radiographic analyses All radiographs were analyzed by using public domain software (ImageJ, U.S. National Institute of Health, USA) by an independent examiner. Reference bone levels on the mesial and distal sides were determined by measuring the distance between the implant platform and the most apical point of the alveolar crestal bone surrounding the implant. The loss in crestal bone height in relation to the implant shoulder over the observation period was calculated relative to the bone level measured on the radiographs made at the time of implant placement, alternatively at the time of abutment placement. Statistical analyses of clinical and radiographic parameters Statistical analyses were limited to descriptive statistics applied on the clinical and radiographic data, and questionnaire outcomes. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS software version 22 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Results Twenty-three consecutive patients with an edentulous maxilla have been provided with a removable prosthesis without palatal coverage retained by Locator abutments on three implants. All received invitation to partake in this clinical study. Twenty-one consented, while one patient has passed away and another declined because of a stroke. Of the consenting participants, 12 have received their implants more than 2 years ago, and the data from this cohort of study participants is described in detail below. The average age of the six male and six female participants was 69 years (SD = 9), with a period of edentate maxilla ranging between 3 months and 10 years (average 3 years). Seven of the 12 participants conveyed that the primary reason for electing the removable option on three implants was caused by lack of enough bone for more implants, while the remaining five stated that financial considerations influenced their decision to proceed with a removable solution. Each study participant had received three implants of either Astra Tech, (n=7) or Straumann SLA (n=5), between 2 to 6 years earlier (Table 1). The majority of the 8
9 implants had been placed in the maxilla characterized according to the Lekholm and Zarb jaw grading system as shape C, with the bone qualities 3 (n=21) or 2 (n=6) or 4 (n=3). Six implants had been placed in a maxilla characterized as shape D and having the bone qualities 3 (n=3) or 2 (n=3). Ten of the 12 study participants attended their regular dentists for regular dental care, while two continued the maintenance care at the specialist clinic practice. At the time of clinical examination, 10 of the 12 study participants reported that they did not remove their prosthesis during the nighttime, and seven of these showed clinical signs of denture stomatitis. None of the 36 implants showed any indications of mobility or tenderness upon percussion. Suppuration was observed on one implant. On the individual implant level, the plaque levels was generally good with no (61%) or minor (25%) plaque levels. Probing around the implants did not cause bleeding (53%), or elicited only minor bleeding (47%). There was no relationship between the performance of the removable prosthesis and three implants in the maxilla, nor patient satisfaction as a function of the state of the dentition in the mandible, i.e., natural teeth (n=3), partial edentate without (n=3) and with (n=1) removable prosthesis, natural teeth combined with fixed prosthesis (n=2), removable complete prosthesis (n=1), or removable tooth-retained complete prosthesis (n=2). The incidence of adverse biological and technical events was near non-existent as reported by the study participants and recorded in the patient charts. No implants were lost. None of the Locator abutments showed any clinically relevant wear. The rates of replacements of male attachments varied, as did any changes of male attachment retention force (Table 2). While 3 participants had not replaced any male attachments, the remaining participants replaced their male attachments between 2 to 59 months after prosthesis delivery (average 25 months). At this point two participants received male attachments with more retention than inserted originally. Five participants undertook a second replacement between 16 to 46 months after prosthesis delivery (average 31 months). Two participants had replaced their male attachments 9
10 respectively three and five times over the follow-up time period. All participants described the task of insertion and removal of the prosthesis as unproblematic. The marginal bone loss around the supporting implants measured on the radiographs ranged between 0 and 5.3 mm, with a mean of 0.4 mm (SD 0.7) (Table 3). In one situation a mid-placed implant where suppuration and approximately 5 mm marginal bone loss was observed after approximately 2 years. Further bone loss was avoided after an open flap surgery with implant surface debridement and decontamination procedures, and the bone level has remained stable since the surgery. The bone loss appeared to be similar for the anterior middle implants (Mean 0.4 mm, (SD 0.8)) versus the posteriorly placed implants (Mean 0.4mm (SD 0.6)). The patient satisfaction scores, as judged by the OHIP-20 scores were good in general, with relatively minor variation amongst the study participants (Table 4). The satisfaction scores described according to the denture satisfaction questionnaire appeared to be good, as the respondents were totally (n=5) or very (n=6) or reasonably satisfied (n=1) with their denture (Table 5). Moreover, the participants described the surgery as totally (n=6) or very (n=6) satisfactory. As to a question of whether they would redo the surgery again if needs arose, six responded with a yes, without any hesitation, two stated yes, very probably, and four answered with a yes, probably. Discussion The results in this clinical study are positive and promising, but admittedly, the current study cohort is too small to recommend authoritatively that the described technical solution should be adopted. However, a case can be made that the solution makes sense from a theoretical biomechanical perspective. The center of the accumulated load in the maxilla upon maximal occlusion is located some distance posteriorly to the palatal incisal papilla and this area has, albeit in another context, been referred to as the center of force (Olivieri et al. 1998), alternatively the occlusal load center (Shinogaya et al. 2001, 2002). Conceptually, a removable prosthesis should ably resist displacement caused by vertical and lateral forces if it is supported by a three-legged frame projecting equidistantly from this center and with reasonably equilateral 10
11 distances between the three implant positions. The idea of tripodizing implants in this manner to support a removable maxillary prosthesis seems not to have received much attention in the basic sciences literature (Brunski 2014). Clinically, the notion has been appraised in two separate patient cohorts by a research group in New Zealand, with relative positive outcomes in the first cohort after 1 year (Payne et al. 2004), 2 years (Al- Zubeibi et al. 2011) and 10 years (Ma al. 2015), as well as in the smaller second cohort after 1 year (Osman et al. 2013). The Locator system include a male attachment that is made from nylon with varying retention force against the abutment. They are intended to be replaced due to a gradual loss of retentive force caused by their wear against the abutment upon prosthesis dislodgment. The study participants in the current cohort experienced different incidences of replacements, which corroborates observations made in other clinical studies (Vere et al. 2012, Cordaro et al. 2013, Ma et al. 2015). Likely, the extent of wear of attachment systems is multifactorial (Alsabeeha et al. 2009), in line with other tribological phenomena intraorally. The wear of the attachment is primarily localized on the central pillar and is circumferential unless there is a relative angulation, which induce more localized wear facets or ledges relative to the implant angulation (Rabbani et al. 2015). A weakness of the current study is that no measurements were made of the patientreported OHIP and denture satisfaction scores before commencing the prosthetic treatment, so there are no comparisons between before and after treatment. Moreover, OHIP likely changes over time, which was not addressed in the current follow-up study. Nevertheless, the study participants reported good OHIP (table 4) and satisfaction (table 5) scores, judged in comparison with analogous studies of maxillary removable prostheses without palatal coverage and retained by stud-type attachments on e.g., 2 (Zembic et al. 2013, Zembic & Wismeijer 2014), 3 (Al-Zubeidi et al. 2011) or 4 (Troeltzsch et al. 2013, Wang et al. 2015) free-standing implants. The study participants commented particularly the value of avoiding a palatal coverage, which allowed them to feel the food texture, temperature and to some extent taste. Interestingly, this patient feedback diverge somewhat from conclusions based on experimental cross-over studies over several months stating that patients have only minor or no opinions about 11
12 preference for palatal coverage (de Albuquerque Jr et al. 2000, Zembic & Wismeijer 2014). In contrast, on balance, it has been theorized that palatal coverage inhibits bolus formation during mastication, which is required for comfortable swallowing. The wearers therefore increase the number of mastication strokes until the swallowing threshold to compensate for the lowered masticatory performance (Sato et al. 2013). Moreover, palatal coverage affects the oral perception adversely, possibly because of a reduction of the intraoral stereognostic abilities (Kumamoto et al. 2010). Some individuals may adapt and others may maladapt to these circumstances. The observation that patients report effortlessness insertion and removal of the prosthesis corroborates earlier findings (Vere et al. 2012). From an economic perspective, the described technical solution appear to be more affordable than a bar-retained or a fixed solution. Estimates of the relative costs of the actual supraconstruction, as based on prices obtained from a commercial dental laboratory in Norway, is 1:1.8 and 1:2.9 versus a bar-retained prosthesis on 4 implants and a fixed solution on 6 implants respectively (raw numbers: NOK14373 vs NOK vs NOK 41853). Obviously, the costs over time depend on accrued maintenance time and need to replace worn components. In the past, investigators have raised concern that patients with an implant-supported prosthesis without a palatal coverage may experience more mechanical and technical adverse outcomes compared to those without (Palmqvist et al. 1994, Widbom et al. 2004, Sadowsky 2007, Slot et al. 2010, Raghoebar et al. 2014). In the current study, however, the incidence of repairs so far has been very low, consistent with studies on removable palatal-free maxillary prostheses retained by Locator abutments (Cordaro et al. 2013, Wang et al. 2015) A factor to consider with regard to a possible failure of an implant is that a remake of the removable prosthesis on a tripod solution is not necessarily required. The small vertical space required by a Locator attachment system facilitates the retrofitting into the existing prosthesis, as compared to the vertical space required to accommodate the retentive elements of a ball or bar-solution into the prosthesis. The replacement implant may positioned in the same osteotomy site, or in an alternative position. Moreover, there is no longer a great emphasis on placing multiple implants in a relative parallel vertical alignment since several clinical studies show minor effects of non-axial loading 12
13 of implants in the maxilla (Malo et al. 2005, Testori et al. 2008, Tealdo et al. 2008). Nevertheless, the inter-abutment divergence should not exceed 20 degrees according to the manufacturer of the Locator attachment system. A criticism of the current data is that the follow-up time of these first twelve consecutive patients vary from two to 6 years, and that the study design is purely retrospective and observational. A second patient cohort is currently under recruitment for a prospective study, with an aspiration that the future clinical observation will corroborate these first promising findings. References Allen, F. & Locker, D. (2002) A modified short version of the oral health impact profile for assessing health-related quality of life in edentulous adults. The International Journal of Prosthodontics 15, Allen, P.F., McMillan, A.S. & Walshaw, D. (2001) A patient-based assessment of implant-stabilized and conventional complete dentures. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 85, Alsabeeha, N.H., Payne, A.G. & Swain, M.V. (2009) Attachment systems for mandibular two-implant overdentures: a review of in vitro investigations on retention and wear features. The International Journal of Prosthodontics 22: Al-Zubeidi, M.I., Alsabeeha, N.H., Thomson, W.M. & Payne, A.G. (2012) Patient satisfaction with maxillary 3-implant overdentures using different attachment systems opposing mandibular 2-implant overdentures. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 14 Suppl 1:e Bassi, F., Carr, A.B., Chang, T.L., Estafanous, E.W., Garrett, N.R. & et al. (2013) Economic outcomes in prosthodontics. The International Journal of Prosthodontics 26: Brunski, J.B. (2014) Biomechanical aspects of the optimal number of implants to carry a cross-arch full restoration. European Journal of Oral Implantology 7 Suppl 2:S
14 Buser, D., Weber, H.P. & Lang, N.P. (1990) Tissue integration of non-submerged implants. 1-year results of a prospective study with 100 ITI hollow-cylinder and hollow-screw implants. Clinical Oral Implants Research 1: Cavallaro, J.S. & Tarnow, D.P. (2007) Unsplinted Implants Retaining Maxillary Overdentures with Partial Palatal Coverage: Report of 5 Consecutive Cases. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 22: Cordaro, L., Torsello, F., Mirisola di Torresanto, V. & Baricevic, M. (2013) Rehabilitation of an edentulous atrophic maxilla with four unsplinted narrow diameter titanium-zirconium implants supporting an overdenture. Quintessence International 44: de Albuquerque Jr., R.F., Lund, J.P., Tang, L., Larivée, J., de Grandmont, P., Gauthier, G. & Feine, J.S. (2000) Within-subject comparison of maxillary long-bar implant-retained prostheses with and without palatal coverage: patient-based outcomes. Clinical Oral Implants Research 11: Dudley, J. (2013) Maxillary implant overdentures: current controversies. Australian Dental Journal 58: Heydecke, G., Zwahlen, M., Nicol, A., Nisand, D., Payer, M., Renouard, F., Grohmann, P., Mühlemann, S. & Joda, T. (2012) What is the optimal number of implants for fixed reconstructions: a systematic review. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23 Suppl 6: Kumamoto, Y., Kaiba, Y., Imamura, S. & Minakuchi, S. (2010) Influence of palatal coverage on oral function - oral stereognostic ability and masticatory efficiency. Journal of Prosthodontic Research 54: Ma, S., Tawse-Smith, A., De Silva, R.K., Atieh, M.A., Alsabeeha, N.H. & Payne, A.G. (2015) Maxillary Three-Implant Overdentures Opposing Mandibular Two-Implant Overdentures: 10-Year Surgical Outcomes of a Randomized Controlled Trial. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research [Epub doi: /cid.12325] Malo, P., Rangert, B. & de Araujo Nobre, M. (2005) All-on-4 immediate-function concept with Brånemark System implants for completely edentulous maxillae: a 1- year retrospective clinical study. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 7 Suppl 1: S
15 Mombelli, A., van Oosten, M.A.C., Schürch Jr., E. & Lang, N.P. (1987) The microbiota associated with successful or failing osseointegrated titanium implants. Oral Microbiology Immunology 2, Olivieri, F., Kang, K.H., Hirayama, H. & Maness, W.L. (1998) New method for analyzing complete denture occlusion using the center of force concept: a clinical report. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 80: Osman, R.B., Payne, A.G., Duncan, W. & Ma, S. (2013) Zirconia implants supporting overdentures: a pilot study with novel prosthodontic designs. The International Journal of Prosthodontics 26: Palmqvist, S., Sondell, K. & Swartz, B. (1994) Implant-supported maxillary overdentures: outcome in planned and emergency cases. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 9: Payne, A.G., Tawse-Smith, A., Thomson, W.M., Duncan, W.D. & Kumara, R. (2004) One-stage surgery and early loading of three implants for maxillary overdentures: a 1-year report. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 6: Rabbani, S., Juszczyk, A.S., Clark, R.K. & Radford, D.R. (2015) Investigation of retentive force reduction and wear of the locator attachment system with different implant angulations. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 30: Raghoebar, G.M., Meijer, H.J., Slot, W., Slater, J.J. & Vissink, A. (2014) A systematic review of implant-supported overdentures in the edentulous maxilla, compared to the mandible: How many implants? European Journal of Oral Implantology 7: Roccuzzo, M., Bonino, F., Gaudioso, L., Zwahlen, M. & Meijer, H.J. (2012) What is the optimal number of implants for removable reconstructions? A systematic review on implant-supported overdentures. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23 Suppl 6: Sadowsky, S.J. (2007) Treatment considerations for maxillary implant overdentures: a systematic review. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 97:
16 Sato, T., Furuya, J., Tamada,Y. & Kondo, H. (2013) Impacts of palatal coverage on bolus formation during mastication and swallowing and subsequent adaptive changes. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 40: Schley, J.S. & Wolfart, S. (2011) Which prosthetic treatment concepts present a reliable evidence-based option for the edentulous maxilla related to number and position of dental implants? European Journal of Oral Implantology 4: Shinogaya, T., Tanaka, Y., Toda, S. & Hayakawa, I. (2002) A new approach to evaluating occlusal support by analyzing the center of the bite force. Clinical and Oral Investigations 6: Shinogaya, T., Bakke, M., Thomsen, C.E., Vilmann, A., Sodeyama, A. & Matsumoto, M. (2001) Effects of ethnicity, gender and age on clenching force and load distribution. Clinical and Oral Investigations 5: Slot, W., Raghoebar, G.M., Vissink, A., Huddleston Slater, J.J. & Meijer, H.J. (2010) A systematic review of implant-supported maxillary overdentures after a mean observation period of at least 1 year. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 37: Stoumpis, C. & Kohal, R.J. (2011) To splint or not to splint oral implants in the implant-supported overdenture therapy? A systematic literature review. Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 38: Testori, T., Del Fabbro, M., Capelli, M., Zuffetti, F., Francetti, L. & Weinstein, R.L. (2008) Immediate occlusal loading and tilted implants for the rehabilitation of the atrophic edentulous maxilla: 1-year interim results of a multicenter prospective study. Clinical Oral Implants Research 19: Tealdo, T., Bevilacqua, M., Pera, F., Menini, M., Ravera, G., Drago, C. & Pera, P. (2008) Immediate function with fixed implant-supported maxillary dentures: a 12- month pilot study. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry 99: Troeltzsch, M., Troeltzsch, V., Brodine, A.H., Frankenberger, R., Messlinger, K. & Troeltzsch, M. (2013) Clinical performance and peri-implant parameters of 132 implants supporting locator-retained overdentures: a case series of 33 patients. The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 28:
17 Vere, J., Hall, D., Patel, R. & Wragg, P. (2012) Prosthodontic maintenance requirements of implant-retained overdentures using the Locator attachment system. The International Journal of Prosthodontics 25: Wang, F., Monje, A., Huang, W., Zhang, Z., Wang, G. & Wu, Y. (2015) Maxillary four implant-retained overdentures via locator attachment: intermediate-term results from a retrospective study. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research [Epub doi: /cid.1233] Widbom, C., Soderfeldt, B. & Kronstrom, M. (2005) A retrospective evaluation of treatments with implant-supported maxillary overdentures. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 7: Zarb, G., Eckert, S.E., Jacob, R.F. & Zarb, J.P. (2013) Additional treatment planning options for both edentulous and potentially edentulous patients. In: Prosthodontic Treatment for Edentulous Patients. Zarb, G., Hobkirk, J.A., Eckert, S.E. & Jacob, R.F (eds). Ed.13. St.Louis: Elsevier, Zembic, A. & Wismeijer, D. (2014) Patient-reported outcomes of maxillary implantsupported overdentures compared with conventional dentures. Clinical Oral Implants Research 25: Zembic, A., Tahmaseb, A. & Wismeijer, D. (2015) Within-subject comparison of maxillary implant-supported overdentures with and without palatal coverage. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research 17:
18 Table 1. Lengths and diameters (mm) of implants (n=12 patients x 3 implants) L 8 or or Total ø 13 3, , ,0 / , Total:
19 Table 2. The frequency of replacements of Locator male attachments indicated by months since delivery of prosthesis and attachment retention force represented by color codes. (B)lue: 680 Grams, (P)ink: 1361 Grams, (C)lear: 2268 Grams. (n=12 study participants) Replace #1 (mths) Color Replace #2 (mths) Color Replace #3 (mths) Color Replace #4 (mths) Color Replace #5 (mths) Color Baseline Followup (mths) PCP 22 Blue 41 Blue 54 Pink 58 Pink 74 Clear 74 PPP 8 Pink 34 Pink 43 Pink 33 P-C 26 Pink 46 Clear 50 PPP 15 Pink 17 #2Pink 1Clear 41 CPP 2 Pink 16 Pink 28 BBB 59 Pink 66 PPP 41 Pink 72 BBB 33 Blue 46 BBB 19 Pink 26 BBB - 36 BBB - 47 PPP - 28 Average:
20 Table 3. Peri-implant bone loss of the study participants (n=12 patients, each with 3 implants) recorded radiographically at their last clinical examination (2,3,4 or 6 years). 2 yrs 3 yrs 4 yrs 6 yrs N=2 patients, 6 implants N=5 patients, 15 implants N=3 patients, 9 implants N=2 patients, 6 implants mm mes dis mes dis mes dis mes dis 0-0, , , ,9 4-4,9 5+ 1* 1* * Suppuration and rapid bone destruction observed after approximately 2 years around the anterior implant. Process ceased following open flap surgery, implant surface debridement and decontamination procedures. Bone level remaining stable since the surgery. 20
21 Table 4. OHIP-20 total and subscale scores for study participants treated with a removable prosthesis with partial palatal coverage retained by three free-standing implants fitted with Locator abutments (n=12). Mean SD Median min max Total 29, Functional Limitation Physical Pain Psychological Discomfort Physical Disability Psychological Disability Social Disability Handicap Functional Psychosocial 11, Table 5. Satisfaction scores with the surgical aspect and the maxillary prosthesis reported by the study participants treated with a removable prosthesis with partial palatal coverage retained by three free-standing implants fitted with Locator abutments (n=12 patients) Totally satisfied Very satisfied Reasonably satisfied 1. How satisfied are you with your denture? How satisfied are you with the retention of your denture? 3. How satisfied are you with the stability of your denture? 4. How satisfied are you with the comfort of your denture? 5. How satisfied are you with the occlusion of your denture? 6. How satisfied are you with the appearance/ aesthetics of your denture? 7. How satisfied are you with the ability to speak with your dentures?
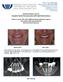
22 Figure 1. The first patient in the current study cohort that received a removable prosthesis with partial palatal coverage retained by three free-standing implants fitted with Locator abutments. At the time, the implants were placed with best possible relative parallelism perpendicularly to the axial loading and a maximum anterio-posterior spread of the implants. Post-implant surgery radiograph (top) from fall 2007, other figures from fall
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment
 Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
Conus Concept: A Rewarding Complete Denture Treatment Complete dentures have largely become the domain of the denturist due to the dissatisfaction general dentists feel with this treatment. Multiple visits,
MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT
 ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT ROMESH SONI a, HARAKH CHAND BARANWAL
ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT ROMESH SONI a, HARAKH CHAND BARANWAL
BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
SCD Case Study. Implant-supported overdentures
 SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
SCD Case Study Implant-supported overdentures An implant-retained overdenture may be indicated in patients with changed anatomy, neuromuscular disorders, significant gag reflex or considerable ridge resorption
Implant osseointegration and successful restoration
 Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Basic information on the. Straumann Pro Arch TL. Straumann Pro Arch TL
 Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
Basic information on the Straumann Pro Arch TL Straumann Pro Arch TL Contents 1. Introduction 2 1.1 Discover more treatment options with the 4 mm Short Implant 2 2. Technical information 3 3. Step-by-step
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
The effect of attachment type and implant number on satisfaction and quality of life of mandibular implant-retained overdenture wearers
 Original Article The effect of attachment type and implant number on satisfaction and quality of life of mandibular implant-retained overdenture wearers Emre Mumcu, Hakan Bilhan and Onur Geckili Department
Original Article The effect of attachment type and implant number on satisfaction and quality of life of mandibular implant-retained overdenture wearers Emre Mumcu, Hakan Bilhan and Onur Geckili Department
Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report
 Case report AODMR Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report Sheren Fatima 1, Rajarshi Basu 2, Neelkamal Hallur 3, Aaisha Siddiqua 4, Syed Zakaullah 4, Sumaiyya 2, Chaitanya
Case report AODMR Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report Sheren Fatima 1, Rajarshi Basu 2, Neelkamal Hallur 3, Aaisha Siddiqua 4, Syed Zakaullah 4, Sumaiyya 2, Chaitanya
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Immediate fixed teeth a treatment concept for edentulous patients
 52 Maxillary rehabilitation using the All-on-4 concept Immediate fixed teeth a treatment concept for edentulous patients DR DUSAN VASILJEVIC AND VLADAN VASILJEVIC, FRIEDEBURG, GERMANY The number of edentulous
52 Maxillary rehabilitation using the All-on-4 concept Immediate fixed teeth a treatment concept for edentulous patients DR DUSAN VASILJEVIC AND VLADAN VASILJEVIC, FRIEDEBURG, GERMANY The number of edentulous
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois Phone: Fax:
 Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Samantha W. Chou, D.M.D. 2325 N. Southport Ave. Chicago, Illinois 60614 Phone: 312-608-6881 Fax: 773-296-0601 Samanthawchou@gmail.com What is our role as the dentist? "We live in a culture in which people
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers
 Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
Turk J Med Sci 31 (2001) 445-449 TÜB TAK Filiz KEYF Frequency of the Various Classes of Removable Partial Dentures and Selection of Major Connectors and Direct/Indirect Retainers Received: November 30,
Evaluation of subjective satisfaction of dental implant patients
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.525/jkaoms.204.40.3.30 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Evaluation of subjective satisfaction of dental implant patients Young-Kyun Kim, Hyun-Suk Kim, Yang-Jin Yi 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/0.525/jkaoms.204.40.3.30 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Evaluation of subjective satisfaction of dental implant patients Young-Kyun Kim, Hyun-Suk Kim, Yang-Jin Yi 2,
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide
 Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Implant Restorations: A Step-By-Step Guide Drago, Carl DDS, MS ISBN-13: 9780813828831 Table of Contents Contributors. Foreword. Acknowledgments. Chapter 1. Introduction To Implant Dentistry. 1. Introduction.
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study
 Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Construction of Removable Partial Denture
 Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
Construction of Removable Partial Denture Peter Hermann Department of Prosthodontics Semmelweis University Treatment options for edentulous spaces Fixed prosthodontics (crowns/bridges) Removable prosthodontics
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate
 AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION
 Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report
 Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
Rehabilitation of Resorbed Mandibular Ridge with Implant Supported Overdenture- A Clinical Report 1 2 1 1 Mittal R, Saxena D, Rao S, Kumar M Abstract: Statement of Problem: Complete denture rehabilitation
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,500 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Consequences of insufficient treatment planning for flapless implant surgery for a mandibular overdenture: A clinical report
 Consequences of insufficient treatment planning for flapless implant surgery for a mandibular overdenture: A clinical report Avinash S., BDS, MS a University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, Conn.
Consequences of insufficient treatment planning for flapless implant surgery for a mandibular overdenture: A clinical report Avinash S., BDS, MS a University of Connecticut Health Center, Farmington, Conn.
 A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols
 Group 3 Consensus Statements Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols Hans-Peter Weber, DMD, Dr Med Dent 1 /Dean Morton, BDS, MS 2 /German O. Gallucci, DMD,
Group 3 Consensus Statements Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols Hans-Peter Weber, DMD, Dr Med Dent 1 /Dean Morton, BDS, MS 2 /German O. Gallucci, DMD,
4. What about age? There is no age limit. After puberty, anyone can get dental implants.
 Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
CASE REPORT. Prosthetic rehabilitation of edentulous mandible with two-implant retained fixed hybrid prosthesis: A case report.
 1828 CASE REPORT Prosthetic rehabilitation of edentulous mandible with two-implant retained fixed hybrid prosthesis: A case report Meisha Gul, Muhammad Rizwan Nazeer, Robia Ghafoor Abstract Removable complete
1828 CASE REPORT Prosthetic rehabilitation of edentulous mandible with two-implant retained fixed hybrid prosthesis: A case report Meisha Gul, Muhammad Rizwan Nazeer, Robia Ghafoor Abstract Removable complete
Removable Partial Dentures
 Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Removable Partial Dentures Replacement of missing teeth Fixed partial denture Removable partial denture Complete removable Transitional denture Partial removable Implant retained prosthodontics No prosthetic
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options
 Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Solid Zirconia Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis (Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) BruxZir. FIRST Appointment. The BruxZir
 (Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol C The BruxZir Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis offers a fixed, all-zirconia implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
(Protocol C All-CAD with Multi-Unit Abutments) Step-by-Step Restorative Protocol C The BruxZir Full-Arch Implant Prosthesis offers a fixed, all-zirconia implant solution for edentulous patients desiring
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
It has been proposed that partially edentulous maxillectomy
 CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
CLASSICAL ARTICLE Basic principles of obturator design for partially edentulous patients. Part II: Design principles Mohamed A. Aramany, DMD, MS* Eye and Ear Hospital of Pittsburgh and University of Pittsburgh,
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS
 REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG020.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
REMOVABLE PROSTHODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG020.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
Straumann SmartOne. Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance. Step 2 Maintenance visit
 Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Preserving the Integrity of Facial Structures with Implant-Retained Overdentures
 Preserving the Integrity of Facial Structures with Implant-Retained Overdentures Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has
Preserving the Integrity of Facial Structures with Implant-Retained Overdentures Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has
Design and Manufacturing of Titanium Attachment for Single Implant Retained Mandibular Overdenture: A Review
 Original article: Design and Manufacturing of Titanium Attachment for Single Implant Retained Mandibular Overdenture: A Review *RupaliRaut 1, Dr. S. B. Jaju 2, Dr. N. H. Rathi 3 1Student, M. Tech CAD/CAM,
Original article: Design and Manufacturing of Titanium Attachment for Single Implant Retained Mandibular Overdenture: A Review *RupaliRaut 1, Dr. S. B. Jaju 2, Dr. N. H. Rathi 3 1Student, M. Tech CAD/CAM,
A Clinical Study of Edentulous Patients Rehabilitated According to the All on Four Immediate Function Protocol
 A Clinical Study of Edentulous Patients Rehabilitated According to the All on Four Immediate Function Protocol Roberto Crespi, MD, MS 1 /Raffaele Vinci, MD, DMD 2 /Paolo Capparé, MD 3 / George E. Romanos,
A Clinical Study of Edentulous Patients Rehabilitated According to the All on Four Immediate Function Protocol Roberto Crespi, MD, MS 1 /Raffaele Vinci, MD, DMD 2 /Paolo Capparé, MD 3 / George E. Romanos,
Principles of. By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah
 Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
Principles of By: Dr. Ahmad Rabah 1. Utilize what's present: Whenever possible, select a design that fits the teeth and soft tissues, rather than choosing one that requires tissue alteration. When minimal
The costs and benefits of prosthodontic interventions:
 PROSTHODONTICS 4th year - Fall 2008 The costs and benefits of prosthodontic interventions: Treatment outcomes in prosthodontics and importance of oral hygiene compliance and good control routines Asbjørn
PROSTHODONTICS 4th year - Fall 2008 The costs and benefits of prosthodontic interventions: Treatment outcomes in prosthodontics and importance of oral hygiene compliance and good control routines Asbjørn
Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction with Hybrid Restorations
 Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
Philip L. Fava II, DMD, MDSc Robert A. Levine, DDS, FCPP, FISPPS 9880 Bustleton Ave, Suite 211 Philadelphia, PA 19115 PADentalImplants.com 215-677-8686 Featured Patient Case #1: Complete Mouth Reconstruction
In 1977, Lew1 developed a passive
 CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry
 Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Devoted to the Advancement of Implant Dentistry Our ultimate goal is to provide you and your patients with the highest standards in implant case planning
Fixed full-arch implant-supported acrylic resin prostheses
 Tooth Fractures in Fixed Full-Arch Implant-Supported Acrylic Resin Prostheses: A Retrospective Clinical Study Javier Ventura, PhD, DMD 1 /Emilio Jiménez-Castellanos, PhD, DMD 2 / José Romero, PhD, DMD
Tooth Fractures in Fixed Full-Arch Implant-Supported Acrylic Resin Prostheses: A Retrospective Clinical Study Javier Ventura, PhD, DMD 1 /Emilio Jiménez-Castellanos, PhD, DMD 2 / José Romero, PhD, DMD
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Role of the implant design on immediate loading Critical appraisal of the evidence from clinical trials
 Role of the implant design on immediate loading Critical appraisal of the evidence from clinical trials Asbjørn Jokstad, DDS, PhD UiT The Arctic University of Norway University of Toronto # Publications
Role of the implant design on immediate loading Critical appraisal of the evidence from clinical trials Asbjørn Jokstad, DDS, PhD UiT The Arctic University of Norway University of Toronto # Publications
Radiographic Stent for Simplified Placement of Implants in the Mandible
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1086 CASE REPORT Radiographic Stent for Simplified Placement of Implants in the Mandible ABSTRACT This article aims to present a modified yet simple technique for the placement
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1086 CASE REPORT Radiographic Stent for Simplified Placement of Implants in the Mandible ABSTRACT This article aims to present a modified yet simple technique for the placement
Restoring Straumann implants. with Locator abutments.
 Restoring Straumann implants with Locator abutments. 1 1 Straumann is the industrial partner of the ITI (International Team for Implantology) in the areas of research, development, and education. Contents.
Restoring Straumann implants with Locator abutments. 1 1 Straumann is the industrial partner of the ITI (International Team for Implantology) in the areas of research, development, and education. Contents.
Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete Denture and Mandibular Teeth supported Overdenture
 Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
Case Report imedpub Journals www.imedpub.com Periodontics and Prosthodontics DOI: 10.21767/2471-3082.100041 Prosthodontic Management of Combination Syndrome Case with Metal Reinforced Maxillary Complete
IMMEDIATE LOADED IMPLANTS IN EDENTULOUS PATIENTS: CLINICAL AND TECHNICAL ASPECTS USING BIOTEC TRE AND KORUM SP IMPLANTS
 ARTICLES MB IMMEDIATE LOADED IMPLANTS IN EDENTULOUS PATIENTS: CLINICAL AND TECHNICAL ASPECTS USING BIOTEC TRE AND KORUM SP IMPLANTS F. Vedove, F. Soda Smile Service, Bassano del Grappa, Vicenza, Italy
ARTICLES MB IMMEDIATE LOADED IMPLANTS IN EDENTULOUS PATIENTS: CLINICAL AND TECHNICAL ASPECTS USING BIOTEC TRE AND KORUM SP IMPLANTS F. Vedove, F. Soda Smile Service, Bassano del Grappa, Vicenza, Italy
Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research. DOI: /sjodr. ISSN (Print) Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website:
 DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
DOI:10.21276/sjodr Saudi Journal of Oral and Dental Research Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-1300 (Print) ISSN 2518-1297 (Online)
Università degli Studi di Milano, Department of Biomedical, Surgical and Dental Sciences, Research Centre in Oral Implantology, Milan, Italy
 Implant success rates in full-arch rehabilitations supported by upright and tilted implants: a retrospective investigation with up to five years of follow-up Luca Francetti 1,2, Andrea Rodolfi 1,2, Bruno
Implant success rates in full-arch rehabilitations supported by upright and tilted implants: a retrospective investigation with up to five years of follow-up Luca Francetti 1,2, Andrea Rodolfi 1,2, Bruno
Peri-implant health, clinical outcome and patient-centred outcomes of implant-supported overdentures in the mandible and the maxilla
 www.nature.com/bdjopen ARTICLE OPEN Peri-implant health, clinical outcome and patient-centred outcomes of implant-supported overdentures in the mandible and the maxilla David Offord 1, Grant Mathieson
www.nature.com/bdjopen ARTICLE OPEN Peri-implant health, clinical outcome and patient-centred outcomes of implant-supported overdentures in the mandible and the maxilla David Offord 1, Grant Mathieson
Effects of Reinforcement on Denture Strain in Maxillary Implant Overdentures: An In Vitro Study Under Various Implant Configurations
 Effects of Reinforcement on Denture Strain in Maxillary Implant Overdentures: An In Vitro Study Under Various Implant Configurations Toshihito Takahashi, DDS, PhD 1 /Tomoya Gonda, DDS, PhD 2 /Yoshinobu
Effects of Reinforcement on Denture Strain in Maxillary Implant Overdentures: An In Vitro Study Under Various Implant Configurations Toshihito Takahashi, DDS, PhD 1 /Tomoya Gonda, DDS, PhD 2 /Yoshinobu
Mini implants for Stabilization of partial dentures
 Systematically to the goal Mini implants for Stabilization of partial dentures Winfried Walzer Prostheses are still considered by many to be aesthetically pleasing, cost-effective, but often associated
Systematically to the goal Mini implants for Stabilization of partial dentures Winfried Walzer Prostheses are still considered by many to be aesthetically pleasing, cost-effective, but often associated
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Rehabilitation of a Patient with Completely Edentulous Maxillary Arch using All on 4 Concept of Implantation
 IJopRD K Harshakumar et al CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1179 Rehabilitation of a Patient with Completely Edentulous Maxillary Arch using All on 4 Concept of Implantation 1 K Harshakumar, 2 Nimisha
IJopRD K Harshakumar et al CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10019-1179 Rehabilitation of a Patient with Completely Edentulous Maxillary Arch using All on 4 Concept of Implantation 1 K Harshakumar, 2 Nimisha
The restoration of partially and completely
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
CHAPTER 1. General Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 General Introduction Chapter 1 The loss of remaining natural teeth and provision of artificial removable dentition is a major and irreversible procedure for the patient. The main limitations
CHAPTER 1 General Introduction Chapter 1 The loss of remaining natural teeth and provision of artificial removable dentition is a major and irreversible procedure for the patient. The main limitations
Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture Using Modified Impression Technique: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 10 Ver.VII (Oct. 2015), PP 102-107 www.iosrjournals.org Prosthodontic Rehabilitation with Overdenture
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. To systematically appraise the impact of mechanical/technical risk factors on
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. To systematically appraise the impact of mechanical/technical risk factors on
Multi-Unit Abutment System SIC Safe on Four. Optimum use of available bone by angled placement of implants
 Multi-Unit Abutment System SIC Safe on Four Optimum use of available bone by angled placement of implants Multi-Unit Abutment System SIC Safe on Four Safe on Four The SIC Safe on Four system is a further
Multi-Unit Abutment System SIC Safe on Four Optimum use of available bone by angled placement of implants Multi-Unit Abutment System SIC Safe on Four Safe on Four The SIC Safe on Four system is a further
Opening minds and expanding practice revenue opportunities
 GIVE YOUR PATIENTS THE FREEDOM TO EAT, SPEAK AND LAUGH AGAIN. Opening minds and expanding practice revenue opportunities Since the McGill Consensus in 2002, the dental industry has recognized that implant-supported
GIVE YOUR PATIENTS THE FREEDOM TO EAT, SPEAK AND LAUGH AGAIN. Opening minds and expanding practice revenue opportunities Since the McGill Consensus in 2002, the dental industry has recognized that implant-supported
Prosthetic RehabilitationofaPatientwithAlzheimersDiseaseusingaCombinedBallBarandClipRetainedImplantSupportedOverdentureA Case Report
 Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
Global Journal of Medical Research: J Dentistry & Otolaryngology Volume 17 Issue 2 Version 1.0 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Mandibular implant-supported hybrid prostheses
 Occlusal Contacts of Edentulous Patients with Mandibular Hybrid Dentures Opposing Maxillary Complete Dentures Tetsuya Suzuki, DDS, PhD*/Hiroshi Kumagai, DDS, PhD**/ Nobuyuki Yoshitomi, DDS, PhD***/Edwin
Occlusal Contacts of Edentulous Patients with Mandibular Hybrid Dentures Opposing Maxillary Complete Dentures Tetsuya Suzuki, DDS, PhD*/Hiroshi Kumagai, DDS, PhD**/ Nobuyuki Yoshitomi, DDS, PhD***/Edwin
Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function
 Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function Joseph B. Breitman, DMD, FACP, 1,2 Scott Nakamura, DMD, 3 Arnold L. Freedman, DDS, 4 & Irving L. Yalisove, DDS
Telescopic Retainers: An Old or New Solution? A Second Chance to Have Normal Dental Function Joseph B. Breitman, DMD, FACP, 1,2 Scott Nakamura, DMD, 3 Arnold L. Freedman, DDS, 4 & Irving L. Yalisove, DDS
Overdenture: A Way of Preventive Prosthodontics
 CASE REPORT Overdenture: A Way of Preventive Prosthodontics Gorakhnath B Shinde 1 and Wadkar AP 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: doi:... 1 Post Graduate Student 2 Professor and PG Guide Department of Prosthodontics
CASE REPORT Overdenture: A Way of Preventive Prosthodontics Gorakhnath B Shinde 1 and Wadkar AP 2 Quick Response Code ABSTRACT: doi:... 1 Post Graduate Student 2 Professor and PG Guide Department of Prosthodontics
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Frequency and Type of Prosthetic Complications Associated with Interim, Immediately Loaded Full-Arch Prostheses: A 2-Year Retrospective Chart Review
 Frequency and Type of Prosthetic Complications Associated with Interim, Immediately Loaded Full-Arch Prostheses: A 2-Year Retrospective Chart Review Carl Drago, DDS, MS, FACP 1,2,3 1 Department of Dental
Frequency and Type of Prosthetic Complications Associated with Interim, Immediately Loaded Full-Arch Prostheses: A 2-Year Retrospective Chart Review Carl Drago, DDS, MS, FACP 1,2,3 1 Department of Dental
REMOVABLE IMPLANT- SUPPORTED PROSTHESIS
 Dr. Loredana Mazzaferri REMOVABLE IMPLANT- SUPPORTED PROSTHESIS 40 Giunchi Emanuele Luca Cattin Fig. 1a Initial situation Fig. 1b after implant surgery Fig. 1c former situation Fig. 2a Fig. 2b Fig. 3 Fig.
Dr. Loredana Mazzaferri REMOVABLE IMPLANT- SUPPORTED PROSTHESIS 40 Giunchi Emanuele Luca Cattin Fig. 1a Initial situation Fig. 1b after implant surgery Fig. 1c former situation Fig. 2a Fig. 2b Fig. 3 Fig.
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
J. Mark Thomason Guido Heydecke Jocelyne S. Feine Janice S. Ellis. 168 c 2007 The Authors. Journal compilation c 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard
 J. Mark Thomason Guido Heydecke Jocelyne S. Feine Janice S. Ellis How do patients perceive the benefit of reconstructive dentistry with regard to oral health-related quality of life and patient satisfaction?
J. Mark Thomason Guido Heydecke Jocelyne S. Feine Janice S. Ellis How do patients perceive the benefit of reconstructive dentistry with regard to oral health-related quality of life and patient satisfaction?
ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD)
 ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD) is a dental prosthesis which artificially supplies teeth and associated structure in a partially edentulous arch, made from acrylic resin and can be inserted and
ACRYLIC REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE(RPD) is a dental prosthesis which artificially supplies teeth and associated structure in a partially edentulous arch, made from acrylic resin and can be inserted and
While the protocol for direct bone-to-implant
 Immediate Functional Loading of Brånemark System Implants in Edentulous Mandibles: Clinical Report of the Results of Developmental and Simplified Protocols Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD 1 / Thomas J. Balshi,
Immediate Functional Loading of Brånemark System Implants in Edentulous Mandibles: Clinical Report of the Results of Developmental and Simplified Protocols Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD 1 / Thomas J. Balshi,
SPLINTED DYNAMIC UCLA FOR THREE PROSTHODONTICALLY UNFAVOURABLE IMPLANTS IN AN ESTHETIC REGION: A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 02 SPLINTED DYNAMIC UCLA FOR THREE PROSTHODONTICALLY UNFAVOURABLE IMPLANTS IN AN ESTHETIC REGION: A CASE REPORT D. R. Prithviraj
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03, Issue 02 SPLINTED DYNAMIC UCLA FOR THREE PROSTHODONTICALLY UNFAVOURABLE IMPLANTS IN AN ESTHETIC REGION: A CASE REPORT D. R. Prithviraj
The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study
 26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
SCD Case Study. Attachments in Prosthodontics
 SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
SCD Case Study Attachments in Prosthodontics Precision attachments are retention units milled out of alloy. They have male and female parts that fit together with tolerances of 10 microns. It is important
University of Groningen. Implant treatment for patients with severe hypodontia Filius, Marieke Adriana Pieternella
 University of Groningen Implant treatment for patients with severe hypodontia Filius, Marieke Adriana Pieternella IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
University of Groningen Implant treatment for patients with severe hypodontia Filius, Marieke Adriana Pieternella IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors
 Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
Evaluation of fixed partial denture in relation to gingival recession and other factors Faiza M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc. (1) Zainab M. Abdul Ameer,B.D.S., M. Sc (2) ABSTRACT Background: Gingival recession
G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM
 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
Many of the problems reported by conventional
 Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Comparative Evaluation of Bone in Mandibular Implant Retained Overdentures Using Delayed and Immediate Loading Protocol: An In-Vivo Study
 J Indian Prosthodont Soc (Apr-June 2013) 13(2):113 121 DOI 10.1007/s13191-012-0240-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Evaluation of Bone in Mandibular Implant Retained Overdentures Using Delayed and Immediate
J Indian Prosthodont Soc (Apr-June 2013) 13(2):113 121 DOI 10.1007/s13191-012-0240-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Evaluation of Bone in Mandibular Implant Retained Overdentures Using Delayed and Immediate
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama
 Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
Lect. 14 Prosthodontics Dr. Osama Principles of Removable Partial Denture Design Difference in Prosthesis Support and Influence on Design: For a tooth-supported prosthesis, the movement potential is less
