Ridge resorption resulting from tooth loss often
|
|
|
- Caren Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CLINICAL Horizontal Bone Augmentation Using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography Case Series Alberto Monje, DDS 1 * Florencio Monje, MD, PhD 2 Federico Hernández-Alfaro, MD, DDS, PhD 3 Raúl Gonzalez-García, MD, PhD 2 Fernando Suárez-López del Amo, DDS 1 Pablo Galindo-Moreno, DDS, PhD 4 Jesús Montanero-Fernández, PhD 5 Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MS, PhD 1 The aim of the present study was to use cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) to assess horizontal bone augmentation using block grafts, harvested from either the iliac crest (IC) or mandibular ramus (MR) combined with particulate xenograft and a collagen membrane for in the severe maxillary anterior ridge defects (cases Class III-IV according to Cadwood and Howell s classification). Fourteen healthy partially edentulous patients requiring extensive horizontal bone reconstruction in the anterior maxilla were selected for the study. Nineteen onlay block grafts (from IC or MR) were placed. The amount of horizontal bone gain was recorded by CBCT at 3 levels (5, 7, and 11 mm from the residual ridge) and at the time of bone grafting as well as the time of implant placement ( 5 months). Both block donor sites provided enough ridge width for proper implant placement. Nonetheless, IC had significantly greater ridge width gain than MR (Student t test) (4.93 mm vs 3.23 mm). This was further confirmed by nonparametric Mann-Whitney test (P ¼.007). Moreover, mean pristine ridge and grafted ridge values showed a direct association (Spearman coefficient of correlation ¼.336). A combination of block graft, obtained from the IC or MR, combined with particulate xenograft then covered with an absorbable collagen membrane is a predictable technique for augmenting anterior maxillary horizontal ridge deficiency. Key Words: bone graft, mandibular ramus, iliac crest, horizontal bone augmentation, block graft INTRODUCTION Ridge resorption resulting from tooth loss often compromises ideal implant placement. Hence, in these situations bone augmentation is often recommended to provide the required ridge width and height. Generally speaking, guided bone regeneration, 1 ridge splitting, block graft, or distraction osteogenesis have all been applied 1 Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine, University of Michigan School of Dentistry, Ann Arbor, Mich. 2 Center of Implantology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (CICOM), Badajoz, Spain. Department of Oral Surgery and Implantology, The International University of Catalonia, Barcelona, Spain. 4 Department of Oral Surgery and Implantology, University of Granada, Granada, Spain. 5 Department of Mathematics, University of Extremadura, Badajoz, Spain. * Corresponding author, amonjec@umich.com DOI: /AAID-JOI-D for this purpose and have shown some promising results. 2,3 Nonetheless, autogenous block graft remains one of the main methods for reconstructing severely resorbed maxilla. 4 These block grafts can be harvested from intraoral or extraoral sites. Although endochondral or intramembranous type block grafts can be used, endonchondral block grafts, such as iliac crest (IC), undergo the creeping substitution process, which takes longer and results in a greater amount of bone resorption. Nyström et al 5 observed a reduction in width of IC onlay block grafts from 12.2 mm to 8.7 mm at 12 months. On the contrary, intramembranous block grafts, such as mandibular ramus (MR) or chin, undergo reverse creeping substitution, which means it takes longer for the graft to resorb; hence, it can hold space for the bone to fill in for a longer period. 6 When this type of graft was used to graft the anterior maxilla, 60% resorption was reported. 7 Similar findings were also observed in an animal study (56% resorption of intramembranous blocks). 8 However, endonchondral bone blocks display a more complete graft 366 Vol. XLI/Special Issue/2015
2 Monje et al resorption during healing. 8 In addition, intraoral block grafts are more convenient for clinicians to harvest and use for horizontal bone augmentation. Furthermore, harvesting grafts from intraoral sites reduces costs, and the procedure is often performed as an outpatient procedure. 9 In contrast, extraoral sources provide larger blocks and are often selected for more extensive reconstructions. After block grafts are fixed, particulate grafts are often added for filling the gaps and augmenting the site. Bovinederived bone substitute (Bio-Oss, GeistlichPharma AG, Wolhousen, Switzerland), an osteoconductive material, has shown to be predictable in augmenting alveolar ridges horizontally as it not only acts as a space maintainer but also holds space longer because it resorbs very slowly. 13 A recent randomized controlled trial compared the use of autogenous block grafts with or without particulate anorganic bovine bone (ABB). 14 Results from this study demonstrated that packing ABB around block grafts minimized block graft resorption. 14 Moreover, in order to exclude unwanted cells into the wound, a membrane is often used to protect the grafts. 15,16 Although some authors have shown the inefficacy of using membranes when performing onlay block grafts, 17 others have noted a higher membrane exposure rate and subsequent infection with the use of membrane. 7,18 However, compared with nonresorbable membranes, bioabsorbable membranes have made the process easier as they avoid the drawbacks associated with nonresorbable membranes while achieving similar outcomes. 19,20 Hence, collagen and other bioabsorbable membranes have often been used as tissue barriers for bone augmentation to minimize graft resorption and promote primary wound closure. 14,21 The aim of this study was to use cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT) to evaluate the amount of horizontal bone gain achieved by use of the iliac crest or mandibular ramus, particulate xenograft, and a collagen membrane to correct severe maxillary anterior ridge defect. MATERIALS AND METHODS Fourteen healthy partially edentulous patients requiring extensive horizontal bone reconstruction in the anterior maxilla (class III-IV atrophy according to Cawood and Howell classification 22 ) were enrolled in this study from November 2011 to September Patients enrolled in the study had to meet the following inclusion criteria: age between 18 and 85 years, no systemic diseases or conditions known to alter bone metabolism, and adequate oral hygiene. Patients were excluded if they were pregnant, smokers, or taking medications known to modify bone metabolism or if they had had taken antibiotics for more than 2 weeks in the previous 3 months. Overall, 19 onlay block grafts, either IC or MR, were placed. For isolated small defects, MR was used; for cases with extensive atrophy, IC was used. Harvesting procedures of the ramus block graft Under local anesthesia and intravenous conscious sedation, an incision was made in the posterior mandible following the external oblique ridge. A full-thickness flap was reflected, exposing the lateral aspect of the ramus. Rectangular grafts were harvested using fissure burs to delineate the block and curved chisels and mallet to detach the graft. Sharp edges around the blocks were subsequently smoothed with a large bur. Harvesting procedures of the iliac crest block graft Under general anesthesia with local anesthesia, an incision was performed in the anterior iliac crest. A rectangular-shaped bone block was marked with a fissure bur and harvested using a saw blade and then harvested using a chisel. The amount of bone harvested was according to the patient s needs. Recipient site preparation At the recipient site, a midcrestal incision was performed with intrasulcular and vertical releasing incisions, after which a fullthickness flap was reflected. The block graft was adapted to the recipient sites and anchored to the residual ridge by 1 or 2 titanium fixation screws 1.5 mm in diameter (Level One 1.5 Neuro, KLS Martin LP, Jacksonville, Fla). After achieving stability of the graft, sharp edges were smoothed using a fissure bur. Bio-Oss, a bone substitute of bovine origin, was packed around the pristine ridge to act as a recipient bed and fill any voids. Then, a collagen absorbable membrane (Bio-Gide, Geistlich- Pharma AG) was placed over the graft. Finally, the buccal flap was scored to ensure a tension-free closure, and the flaps were sutured with both absorbable and nonresorbable sutures (Cytoplast Suture, Osteogenics Biomedical Inc, Lubbock, Tex). CBCT examination Image from the maxillary arch of the patients were acquired by CBCT i-cat Model (Imaging Sciences International LLC, Hatfield, Pa). The imaging parameters were set at 120 kvp, 18.66mAs, scan time 20 seconds, resolution 0.4 mm, and a field of view that varied based on the scanned region. The amount of horizontal bone was measured before bone-grafting surgery and at the time of implant placement ( 5 months) (Figure 1). All the measurements were performed by the same calibrated examiner (A.M.). Presence of teeth adjacent to or opposing the edentulous span was required to identify the position measured at both time points. Each graft was plotted on the sagittal images at approximately the midface using the i-cat Vision (Imaging Sciences International LLC) (Figure 2). Then, a perpendicular line was drawn following residual bone inclination. Subsequently, 3 horizontal lines recorded bone width at 5, 7, and 11 mm from the crest. In cases where the titanium fixation screw blocked an accurate measurement, the measure was performed at the closest clear area to the fixation screw. Error in radiographic assessment was determined through repeated measurements of 5 randomly selected patients. The mean difference was mm between the measurements. Statistical analysis Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS (version 19, IBM, Chicago, Ill). Because of the small sample size, statistical analysis was based on a descriptive analysis of both groups. A Mann- Whitney test was used to contrast the influence of type of graft. Journal of Oral Implantology 367
3 Horizontal Bone Augmentation Assessed by CBCT FIGURES 1 4. FIGURE 1. (a) Depiction of the measurements at all levels for a pristine ridge. (b) Depiction of the measurements at all levels for a grafted ridge. FIGURE 2. (a) Sagittal view of the measured ridge before bone grafting surgery plotted by cone-beam computerized tomography (CBCT). (b) Sagittal view of the measured ridge before implant placement ( 5 months after the grafting surgery) plotted by CBCT. FIGURE 3. Plot for pristine ridge for patients with mean values for paired data. FIGURE 4. Plot for grafted ridge for patients with mean values for paired data. 368 Vol. XLI/Special Issue/2015
4 Monje et al The correlation between mean values of pristine ridge and grafted ridge was analyzed using the Spearman test. Limitations of the study Possible bias may arise from the present study because of its retrospective nature. Neither the surgical procedures nor patient enrollment were randomized or masked. All the patients were enrolled from a cohort of consecutively treated patients who fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Furthermore, some bias may emerge from the measurements as only 2 CBCTs were taken (1 before the surgery and the other before implant placement [ 5 months]) to avoid an unnecessary radiograph exposure to the patients. In any event, we aimed to report horizontal bone augmentation and not resorption of these types of grafts, which has already been reported previously Furthermore, precautions must be exercised when interpreting the study results because of the small sample size. However, in order to carry out a thorough study and overcome the limitations of a retrospective study, we selected only cases that would likely produce, with minimum risk of bias, precise results. RESULTS Table 1 displays the mean width of each ridge from all the levels measured (pristine and grafted). Mean values for pristine ridge at each measured level (5, 7, and 11 mm) were 4.41 mm, 5.31 mm, and 5.91 mm, respectively. An increase in width was found for grafted ridge: 8.63 mm, 9.22, mm and 9.72 mm for levels 5, 7, and 11 mm, respectively. We included 5 patients with 2 grafts each, so to control the subject factor, we used the mean value obtained of both grafts for these subjects (Table 2). Figures 3 and 4 present the results for pristine ridge and grafted ridge, respectively, and show the mean values of the paired data. Data showed that the IC group had significantly greater ridge width gain than the MR group in the mean value obtained from the 3 levels of grafted ridges measured. The Student t test for independent samples confirmed this finding. Nonetheless, because of the small sample size, the nonparametric test Mann-Whitney (Table 3) was also used to assess the influence of type of graft, and the same result (P ¼.007) was found. As expected, no difference was identified in the pristine ridge (P ¼.897). At baseline, no difference was noted at pristine ridge (5.25 mm and 5.16 mm for the MR and IC groups, respectively). However, the IC group had a mean horizontal bone gain of 4.93 mm vs 3.23 mm in the MR group. Nonetheless, both procedures achieved proper ridge width (5 mm) for implant placement. Mean pristine ridge and grafted ridge values showed a direct association. In other words, the higher the values obtained in pristine ridge the higher the values in grafted ridge. The Spearman coefficient of correlation was.336, even though this was not found to be significant (P ¼.159). DISCUSSION Results obtained from this study suggest that IC and MR block grafts, in combination with ABB and then covered with an absorbable collagen membrane, are a predictable approach for augmenting severely reabsorbed anterior maxilla horizontal deficient ridges. Generally speaking, the IC group had a gain of 4.93 mm bone width, while the MR group had a mean gain of 3.23 mm when assessed by CBCT. Consequently, a statistically significant difference was found between both groups, thus showing a clear tendency for the IC group to obtain greater horizontal bone augmentation (P ¼.007), though both procedures ended up achieving proper ridge width (5 mm) for implant placement. Hence, the results obtained from this study suggest that the source of bone block does not matter, as long as the voids are filled and the site is secured with a barrier membrane under the primary wound closure. It is important to note that this study had a short follow-up and, thus, further long-term studies are needed to verify this finding as endochondral origin bone takes longer to resorb than intramembranous origin block graft. In this sense, it is also worth mentioning that other factors (eg, graft size) might determine the final bone augmentation achieved and the resorption rate over time. As a result, IC might result in a greater amount of bone gain compared with other grafts because of the size of the blocks that can be obtained. As mentioned previously, clinical trials with a longer follow-up are needed to validate this assumption. Interestingly, our study found out that IC had significant more bone fill than MR (P ¼.007) despite the higher graft resorption expected from the IC. 5,26,27 Because both block grafts resulted in a similar outcome for reconstruction of the anterior maxilla, the choice between the 2 depends on other factors. In contrast to intraoral block grafts, IC bone blocks provide a much larger amount of bone for horizontal augmentation. The choice of donor site was based not only on the residual ridge width but also on the amount of graft needed to reconstruct the sites. Hence, in larger areas or when more bone graft is needed, clinicians often opt to use IC instead of MR. However, MR has higher patient acceptance because it is less invasive and is easier to harvest. 28 It is important to note that adding an ABB to fill the voids created between the graft and recipient bed might minimize bone graft resorption because of its osteoconductive properties and the slow graft resorption rate as demonstrated in many previous publications. 14,21,29,30 Furthermore, placement of a collagen barrier membrane over the graft sites might exclude unwanted cells from the wound, protect the wound, and therefore promote bone regeneration. 15 From the histologic and immunohistochemical standpoints no difference was found between the sites treated with or without membrane when block graft was used as the graft materials.. 31,32 However, recent studies have shown that using a membrane during block graft procedures actually minimizes bone resorption. 14,31,32 Our study did not aim to show the efficacy of placing a barrier membrane and its influence in bone resorption. However, we noted that the additional use of ABB and absorbable membrane had successful outcomes for proper implant placement compared with the results in previous studies where these biomaterials were not used. 5,7 The potential concerns in this study are the small sample size and short study period; in addition, no randomization was performed. Therefore, future studies with randomization, a Journal of Oral Implantology 369
5 Horizontal Bone Augmentation Assessed by CBCT TABLE 1 Mean bone width and standard deviations of the measured spans for pristine ridge and grafted ridge Donor Site Graft (N) Patient (N) Pristine Ridge (mm) SD Grafted Ridge (mm) SD Mandibular ramus Iliac crest TABLE 2 Mean bone width and for each subject included in the present study for pristine ridge and grafted ridge Donor Site Patient (N) Pristine Ridge (mm) Grafted Ridge (mm) Mandibular ramus Iliac crest TABLE 3 Differences in terms of horizontal bone augmentation between iliac crest grafted ridges and mandibular ramus grafted ridges 5 months after grafting surgery Pristine Ridge (mm) Grafted Ridge (mm) Donor Site Mandibular ramus Mean Median SD N 8 8 Iliac crest Mean Median SD N 6 6 Student t test P ¼0.846 P ¼0.001 Mann-Whitney test P ¼0.897 P ¼ Vol. XLI/Special Issue/2015
6 Monje et al larger sample size, and a longer follow-up are needed to verify the findings reported in this study. CONCLUSION Within the limitations of the present study, a combination of block graft obtained from the IC or MR, combined with particulate xenograft and then covered with an absorbable collagen membrane is a predictable technique in augmenting anterior maxillary horizontal ridge deficiency. ABBREVIATIONS ABB: anorganic bovine bone CBCT: cone-beam computerized tomography IC: iliac crest MR: mandibular ramus ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors want to thank FEDICOM Foundation (Foundation for the study of Implantology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery), Badajoz, Spain, for financial support. We would also like to thank Ms. Purificación Barragán, Center of Implantology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery (CICOM), Badajoz, Spain, for her help in collecting and organizing the data and Mr. Victor Cortés- Tabares (our radiologist), CICOM, Badajoz, Spain, for his idea in developing this research. We also thank Dr. Raul Gonzalez- García for providing the measuring depiction. REFERENCES 1. Hammerle CH, Jung RE, Feloutzis A. A systematic review of the survival of implants in bone sites augmented with barrier membranes (guided bone regeneration) in partially edentulous patients. J Clinical Periodontol. 2002;29(suppl 3): ; discussion Faysal U, Cem SB, Atilla S. Effects of different consolidation periods on bone formation and implant success in alveolar distraction osteogenesis: a clinical study. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2013;41: Gonzalez-Garcia R, Monje F, Moreno C. Alveolar split osteotomy for the treatment of the severe narrow ridge maxillary atrophy: a modified technique. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;40: Tessier P, Kawamoto H, Matthews D, et al. Autogenous bone grafts and bone substitutes tools and techniques: I. A 20,000-case experience in maxillofacial and craniofacial surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2005;116:6S 24S; discussion 92S 94S. 5. Nyström E, Nilson H, Gunne J, Lundgren S. A 9 14 year follow-up of onlay bone grafting in the atrophic maxilla. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009; 38: Burchardt H. The biology of bone graft repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1983;(174): Widmark G, Andersson B, Ivanoff CJ. Mandibular bone graft in the anterior maxilla for single-tooth implants. Presentation of surgical method. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1997;26: Ozaki W, Buchman SR. Volume maintenance of onlay bone grafts in the craniofacial skeleton: micro-architecture versus embryologic origin. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1998;102: Schwartz-Arad D, Levin L. Intraoral autogenous block onlay bone grafting for extensive reconstruction of atrophic maxillary alveolar ridges. J Periodontol. 2005;76: Araujo MG, Liljenberg B, Lindhe J. Dynamics of Bio-Oss Collagen incorporation in fresh extraction wounds: an experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2010;21: Araujo MG, Sonohara M, Hayacibara R, Cardaropoli G, Lindhe J. Lateral ridge augmentation by the use of grafts comprised of autologous bone or a biomaterial. An experiment in the dog. J Clin Periodontol. 2002;29: Cardaropoli G, Araujo M, Hayacibara R, Sukekava F, Lindhe J. Healing of extraction sockets and surgically produced augmented and non-augmented defects in the alveolar ridge. An experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol. 2005;32: Wetzel AC, Stich H, Caffesse RG. Bone apposition onto oral implants in the sinus area filled with different grafting materials. A histological study in beagle dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1995;6: Cordaro L, Torsello F, Morcavallo S, di Torresanto VM. Effect of bovine bone and collagen membranes on healing of mandibular bone blocks: a prospective randomized controlled study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22: Melcher AH. On the repair potential of periodontal tissues. J Periodontol. 1976;47: Hardwick R, Hayes BK, Flynn C. Devices for dentoalveolar regeneration: an up-to-date literature review. J Periodontol. 1995;66: Kusiak JF, Zins JE, Whitaker LA. The early revascularization of membranous bone. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1985;76: Piette E, Alberius P, Samman N, Linde A. Experience with e-ptfe membrane application to bone grafting of cleft maxilla. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1995;24: Hammerle CH, Lang NP. Single stage surgery combining transmucosal implant placement with guided bone regeneration and bioresorbable materials. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2001;12: Tawil G, El-Ghoule G, Mawla M. Clinical evaluation of a bilayered collagen membrane (Bio-Gide) supported by autografts in the treatment of bone defects around implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001;16: Hernandez-Alfaro F, Sancho-Puchades M, Guijarro-Martinez R. Total reconstruction of the atrophic maxilla with intraoral bone grafts and biomaterials: a prospective clinical study with cone beam computed tomography validation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2013;28: Cawood JI, Howell RA. A classification of the edentulous jaws. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1988;17: Johansson B, Grepe A, Wannfors K, Hirsch JM. A clinical study of changes in the volume of bone grafts in the atrophic maxilla. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2001;30: Sbordone C, Toti P, Guidetti F, Califano L, Bufo P, Sbordone L. Volume changes of autogenous bone after sinus lifting and grafting procedures: A 6-year computerized tomographic follow-up. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2013;41: Sbordone L, Toti P, Menchini-Fabris GB, Sbordone C, Piombino P, Guidetti F. Volume changes of autogenous bone grafts after alveolar ridge augmentation of atrophic maxillae and mandibles. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2009;38: Sbordone C, Toti P, Guidetti F, Califano L, Santoro A, Sbordone L. Volume changes of iliac crest autogenous bone grafts after vertical and horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation of atrophic maxillas and mandibles: a 6-year computerized tomographic follow-up. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2012; 70: Chiapasco M, Zaniboni M, Boisco M. Augmentation procedures for the rehabilitation of deficient edentulous ridges with oral implants. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17(suppl 2): Touzet S, Ferri J, Wojcik T, Raoul G. Complications of calvarial bone harvesting for maxillofacial reconstructions. J Craniofac Surg. 2011;22: von Arx T, Buser D. Horizontal ridge augmentation using autogenous block grafts and the guided bone regeneration technique with collagen membranes: a clinical study with 42 patients. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2006;17: Maiorana C, Beretta M, Salina S, Santoro F. Reduction of autogenous bone graft resorption by means of bio-oss coverage: a prospective study. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2005;25: Donos N, Kostopoulos L, Karring T. Alveolar ridge augmentation using a resorbable copolymer membrane and autogenous bone grafts. An experimental study in the rat. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002;13: Adeyemo WL, Reuther T, Bloch W, et al. Healing of onlay mandibular bone grafts covered with collagen membrane or bovine bone substitutes: a microscopical and immunohistochemical study in the sheep. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2008;37: Journal of Oral Implantology 371
Key Words: bone graft, mandibular ramus, iliac crest, horizontal bone augmentation, block graft
 CLINICAL Horizontal Bone Augmentation Using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography Case Series Alberto Monje,
CLINICAL Horizontal Bone Augmentation Using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-Beam Computerized Tomography Case Series Alberto Monje,
Horizontal Bone Augmentation using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate
 Horizontal Bone Augmentation using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-beam Computed tomography Case Series Alberto Monje (corresponding
Horizontal Bone Augmentation using Autogenous Block Grafts and Particulate Xenograft in the Severe Atrophic Maxillary Anterior Ridges: A Cone-beam Computed tomography Case Series Alberto Monje (corresponding
Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla
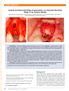 CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
Posterior mandible and vertical augmentation
 CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
Comparison of implant primary stability between maxillary edentulous ridges receiving intramembranous origin block grafts
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18732 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18732 Comparison of implant primary stability between maxillary edentulous ridges
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.18732 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.18732 Comparison of implant primary stability between maxillary edentulous ridges
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Years of research and advancement in
 Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
Immediate Implants with Guided Bone Regeneration Using Titanium Mesh and Alloplast in an Infected Site: A Case Report Mahesh et al Dr. Lanka Mahesh 1 Dr. Ajay Bibra 2 Dr. Vishal Gupta 3 Abstract Years
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
e153 Resident, Department of Periodontics and Oral Medicine, University of Michigan School of Dentistry, Ann Arbor, Michigan, USA.
 e153 Comparison of Microstructures Between Block Grafts from the Mandibular Ramus and Calvarium for Horizontal Bone Augmentation of the Maxilla: A Case Series Study Alberto Monje, DDS 1 /Florencio Monje,
e153 Comparison of Microstructures Between Block Grafts from the Mandibular Ramus and Calvarium for Horizontal Bone Augmentation of the Maxilla: A Case Series Study Alberto Monje, DDS 1 /Florencio Monje,
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Long-term success for osteointegrated
 CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
Vertical and horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation
 CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Volume changes of autogenous bone grafts after alveolar ridge augmentation of atrophic maxillae and mandibles
 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009; 38: 1059 1065 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.06.024, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Pre-Implant Surgery Volume changes of autogenous bone
Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009; 38: 1059 1065 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.06.024, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Pre-Implant Surgery Volume changes of autogenous bone
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
Osseointegrated implants are a very reliable means
 Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
Intramembranous autogenous bone graft is the gold
 CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Augmentation in Two Stages of Atrophic Alveolar Bone Prior to Dental Rehabilitation: A Case Report
 Augmentation in Two Stages of Atrophic Alveolar Bone Prior to Dental Rehabilitation: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The aim of this report is to describe a significantly deficient case of alveolar bone that
Augmentation in Two Stages of Atrophic Alveolar Bone Prior to Dental Rehabilitation: A Case Report Abstract Aim: The aim of this report is to describe a significantly deficient case of alveolar bone that
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Innovative Treatment Concepts IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY
 Innovative Treatment Concepts IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY LEADING REGENERATION CLINICAL CASES Dr. J. Aranda Onlay grafting for horizontal augmentation 8 Prof. Dr. D. Buser et al. Onlay grafting for
Innovative Treatment Concepts IN ORAL AND MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY LEADING REGENERATION CLINICAL CASES Dr. J. Aranda Onlay grafting for horizontal augmentation 8 Prof. Dr. D. Buser et al. Onlay grafting for
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE
 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic. Review
 Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Peri-implant Augmentation
 Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
A Case Report by Dr. Daniel Gober Geistlich Mucograft for the treatment of multiple adjacent recession defects: A more palatable option The Situation A 35 year old male presented in my practice with a
Maxillary Sinus Lateral Wall Thickness and Their Morphologic Patterns in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla
 Maxillary Sinus Lateral Wall Thickness and Their Morphologic Patterns in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla Alberto Monje, D.D.S.*, Andrés Catena PhD Florencio Monje, MD, PhD, Raúl Gonzalez-García MD, PhD,
Maxillary Sinus Lateral Wall Thickness and Their Morphologic Patterns in the Atrophic Posterior Maxilla Alberto Monje, D.D.S.*, Andrés Catena PhD Florencio Monje, MD, PhD, Raúl Gonzalez-García MD, PhD,
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique. Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang*
 CASE REPORT The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang* Introduction: Horizontal ridge width reduction after tooth extraction is a common clinical scenario. As such, when implant-supported
CASE REPORT The Sandwich Bone Augmentation Technique Jia-Hui Fu* and Hom-Lay Wang* Introduction: Horizontal ridge width reduction after tooth extraction is a common clinical scenario. As such, when implant-supported
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Intraoral and extraoral autologous bone block graft techniques: A review of the recent literature
 International Journal of Contemporary Dental and Medical Reviews (2016), Article ID 030316, 5 Pages REVIEW ARTICLE Intraoral and extraoral autologous bone block graft techniques: A review of the recent
International Journal of Contemporary Dental and Medical Reviews (2016), Article ID 030316, 5 Pages REVIEW ARTICLE Intraoral and extraoral autologous bone block graft techniques: A review of the recent
Local Intraoral Autologous Bone Harvesting for Dental Implant Treatment: Alternative Sources and Criteria of Choice. Private Practice, Rome, Italy 2
 REVIEW Local Intraoral Autologous Bone Harvesting for Dental Implant Treatment: Alternative Sources and Criteria of Choice Federico Brugnami, 1 Alfonso Caiazzo 2 and Cataldo Leone 3 1 Private Practice,
REVIEW Local Intraoral Autologous Bone Harvesting for Dental Implant Treatment: Alternative Sources and Criteria of Choice Federico Brugnami, 1 Alfonso Caiazzo 2 and Cataldo Leone 3 1 Private Practice,
ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report
 ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report Yaqian Chen, Qingqing Wu, Yi Man State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China
ß-tricalcium phosphate used with onlay graft for horizontal bone augmentation yielded preferable result: a case report Yaqian Chen, Qingqing Wu, Yi Man State Key Laboratory of Oral Diseases, West China
Volumetric stability of autogenous bone graft with mandibular body bone: cone-beam computed tomography and three-dimensional reconstruction analysis
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.5.232 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Volumetric stability of autogenous bone graft with mandibular body bone: cone-beam computed tomography and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2015.41.5.232 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Volumetric stability of autogenous bone graft with mandibular body bone: cone-beam computed tomography and
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
Ridge Augmentation. Selection of Applicable Abstracts and Posters. Using Titanium-Reinforced PTFE Membranes
 Ridge Augmentation Selection of Applicable Abstracts and Posters Using Titanium-Reinforced PTFE Membranes Gultekin BA, Cansiz E, Borahan MO. Clinical and 3-Dimensional Radiographic Evaluation of Autogenous
Ridge Augmentation Selection of Applicable Abstracts and Posters Using Titanium-Reinforced PTFE Membranes Gultekin BA, Cansiz E, Borahan MO. Clinical and 3-Dimensional Radiographic Evaluation of Autogenous
Horizontal bone augmentation by means of guided bone regeneration
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft
 The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
 227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Sanju P. Jose
 Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Envelope approach for onlay bone grafting: Preliminary surgical and prosthetic results
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 : Preliminary surgical and prosthetic results Federico Hernández-Alfaro
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.16.e45 : Preliminary surgical and prosthetic results Federico Hernández-Alfaro
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry
 Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Bone grafts are widely used in the reconstruction of
 RESEARCH Cone Beam Computerized Tomography Measurement of Alveolar Ridge at Posterior Mandible for Implant Graft Estimation Wenjian Zhang, DDS, MS, PhD 1 * Justin Tullis, BS 2 Robin Weltman, DDS, MS 3
RESEARCH Cone Beam Computerized Tomography Measurement of Alveolar Ridge at Posterior Mandible for Implant Graft Estimation Wenjian Zhang, DDS, MS, PhD 1 * Justin Tullis, BS 2 Robin Weltman, DDS, MS 3
Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging
 Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Bone Grafting: Essential Indications and Techniques in Implant Dentistry Limited bone availability makes implant placement challenging and sometimes unpredictable. Candidates for implant therapy must have
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using the Allograft Bone Shell Technique
 Mogammad Thabit Peck CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1755 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using the Allograft Bone Shell Technique Mogammad Thabit Peck ABSTRACT Background: The loss of teeth, whether
Mogammad Thabit Peck CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1755 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation using the Allograft Bone Shell Technique Mogammad Thabit Peck ABSTRACT Background: The loss of teeth, whether
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
Revisions for CDT 2016
 Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Revisions for CDT 2016 This document was developed from preliminary actions of the Code Maintenance Committee (CMC). This document has been compared to the CMC meeting notes and the ASCII file. This document
Autogenous bone graft alone or associated with titanium mesh for vertical alveolar ridge augmentation: a controlled clinical trial
 Mario Roccuzzo Guglielmo Ramieri Marco Bunino Sid Berrone Autogenous bone graft alone or associated with titanium mesh for vertical alveolar ridge augmentation: a controlled clinical trial Authors affiliations:
Mario Roccuzzo Guglielmo Ramieri Marco Bunino Sid Berrone Autogenous bone graft alone or associated with titanium mesh for vertical alveolar ridge augmentation: a controlled clinical trial Authors affiliations:
Comprehensive Dental Implantology
 Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
Annals of Dental Research
 P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes
 Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Sandwich bone graft for vertical augmentation of the posterior maxillary region: a case report with 9-year follow-up
 Tanaka et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:20 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0063-9 International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Sandwich bone graft for vertical augmentation of
Tanaka et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:20 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0063-9 International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Sandwich bone graft for vertical augmentation of
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 07 Page July 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION
 original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 1. Implant Locations. Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla. Anatomy and risk factors Option 1: Short implants
 T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation
 Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
We Want to Keep You Smiling. Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide
 We Want to Keep You Smiling Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Strong Bone for a Healthier Smile Strong and healthy teeth provide a feeling of well-being, self-confidence and
We Want to Keep You Smiling Bone Regeneration with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Strong Bone for a Healthier Smile Strong and healthy teeth provide a feeling of well-being, self-confidence and
Hands-on Cadaver Intensive Course in Advanced Implant Surgery: Hard and Soft Tissue Management
 Implant Surgery: Hard and Soft Tissue Management 2017-2018 Presentation of the course There is a high demand for specialized training in the field of advanced implantology. The opportunity to perform complex
Implant Surgery: Hard and Soft Tissue Management 2017-2018 Presentation of the course There is a high demand for specialized training in the field of advanced implantology. The opportunity to perform complex
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Socket Treatment. Procedure Guide
 Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
Socket Treatment Procedure Guide www.implantdirect.com 888.649.6425 Extraction Healing and Ridge Resorption The Why Working with patients to educate them on the benefits of bone maintenance post extraction
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP)
 REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
REFERENCES for PLATELET RICH PLASMA (PRP) Daif ET. Autologous blood injection as a new treatment modality for chronic recurrent temporomandibular joint dislocation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral
P rimary or mechanical implant
 IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 0, NUMBER 0 2013 1 Effect of Location on Primary Stability and Healing of Dental Implants Alberto Monje, DDS,* Fernando Suarez, DDS,* Carlos Andrés Garaicoa, DDS, Florencio Monje,
IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 0, NUMBER 0 2013 1 Effect of Location on Primary Stability and Healing of Dental Implants Alberto Monje, DDS,* Fernando Suarez, DDS,* Carlos Andrés Garaicoa, DDS, Florencio Monje,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants
 Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
B. Alper Gultekin, 1 Elcin Bedeloglu, 2 T. Emre Kose, 3 and Eitan Mijiritsky Introduction
 BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4987437, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4987437 Clinical Study Comparison of Bone Resorption Rates after Intraoral Block Bone and Guided Bone
BioMed Research International Volume 2016, Article ID 4987437, 9 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/4987437 Clinical Study Comparison of Bone Resorption Rates after Intraoral Block Bone and Guided Bone
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation
 Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Case Report Treatment of an Erratic Extraction Socket for Implant Therapy in a Patient with Chronic Periodontitis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 1746961, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1746961 Case Report Treatment of an Erratic Extraction Socket for Implant Therapy in a Patient with Chronic
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 1746961, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1746961 Case Report Treatment of an Erratic Extraction Socket for Implant Therapy in a Patient with Chronic
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift
 Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3.
 DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
Deep-Frozen Allogeneic Onlay Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Ridges: A Preliminary Study
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:1300-1306, 2009 Deep-Frozen Allogeneic Onlay Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Ridges: A Preliminary Study Antonio Barone, DDS, PhD, MSc,* Paolo Varanini,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 67:1300-1306, 2009 Deep-Frozen Allogeneic Onlay Bone Grafts for Reconstruction of Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Ridges: A Preliminary Study Antonio Barone, DDS, PhD, MSc,* Paolo Varanini,
2: Canullo L, Tallarico M, Penarrocha D, Meloni SM, Penarrocha M. Abstracts. Eur J Oral Implantol. 2016;9 Suppl 1:9-54. PubMed PMID:
 1: Tallarico M, Xhanari E, Pisano M, De Riu G, Tullio A, Meloni SM. Single post-extractive ultra-wide 7 mm-diameter implants versus implants placed in molar healed sites after socket preservation for molar
1: Tallarico M, Xhanari E, Pisano M, De Riu G, Tullio A, Meloni SM. Single post-extractive ultra-wide 7 mm-diameter implants versus implants placed in molar healed sites after socket preservation for molar
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
MINERVA MEDICA COPYRIGHT
 MINERVA STOMATOL 2013;62(Suppl. 1 to No. 12):59-68 Success of bone grafts in atrophic posterior edentulous mandible: literature review P. PROCACCI 1, V. LORA 2, A. ROSSETTO 1, F. GELPI 2, S. MARCONCINI
MINERVA STOMATOL 2013;62(Suppl. 1 to No. 12):59-68 Success of bone grafts in atrophic posterior edentulous mandible: literature review P. PROCACCI 1, V. LORA 2, A. ROSSETTO 1, F. GELPI 2, S. MARCONCINI
