Effectiveness of full- and partial-mouth disinfection on halitosis in periodontal patients
|
|
|
- Samson Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 57, No. 1, 1-6, 2015 Original Effectiveness of full- and partial-mouth disinfection on halitosis in periodontal patients Léo G. Soares 1), Lisiane Castagna 1), Sérgio C. Weyne 2), Denise G. Silva 3), Márcio E. V. Falabella 3,4), and Eduardo M. B. Tinoco 1) 1) Department of Periodontology, University of the Estate of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil 2) Department of Dentistry, University of Estácio de Sá, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil 3) Department of Periodontology, University of Grande Rio, Duque de Caxias, Brazil 4) Department of Periodontology, Federal University of Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil (Received July 31, 2014; Accepted December 18, 2014) Abstract: To compare the effectiveness of full- and partial-mouth disinfection for halitosis control, patients were assigned to treatment with full-mouth therapy (complete scaling and root planing in one stage within 24 h) or conventional therapy in quadrants (scaling and root planing performed by quadrant over a period of 4 weeks) (n = 90 for each group). Both groups were then subdivided: half the patients scraped their tongue daily and half did not. The patients were then evaluated by halimeter, organoleptic testing, and tongue coating index. Halimeter evaluation showed greater reduction of sulfide gases after full-mouth therapy than after conventional therapy (P < 0.001). However, organoleptic testing and the tongue coating index showed no difference among the four treatment groups. There was also no difference in relation to tongue scraping. In conclusion, halimeter evaluation showed that the reduction in volatile sulfur compounds was significantly greater after full-mouth therapy than after conventional therapy. However, this difference was not observed in organoleptic evaluation. (J Oral Sci 57, 1-6, 2015) Keywords: halitosis; periodontitis; scaling and root planning; bad breath; full-mouth. Correspondence to Dr. Léo Guimarães Soares, Rua Ministro Viveiros de Castro, 32/902, Copacabana, Rio de Janeiro , RJ, Brazil dr_leog@hotmail.com doi.org/ /josnusd.57.1 DN/JST.JSTAGE/josnusd/57.1 Introduction Halitosis can be a serious social problem, but standard dental treatments and mouthwashes (1), which contain chlorhexidine (CHX) or chlorine dioxide (2), are not ideal treatments. The main cause of halitosis is bacterial putrefaction of organic substrates in the oral cavity (3). These bacteria may be present in subgingival plaque, and there is no specific bacterial species responsible for production of volatile sulfur compounds (VSC) (4). Bacteria that produce VSC colonize the lingual dorsum and are responsible for development of halitosis (1). Porphyromonas, Prevotella, Actinobacillus, and Fusobacterium species are the most frequently identified organisms. However, only a small number of studies have investigated bacterial colonization in detail (5). Periodontal patients have high levels of VSC and may have more tongue coating as compared with healthy patients (6,7). Periodontal treatment removes dental calculus and cement contaminated with toxins or microorganisms (8). Debridement with conventional instrumentation is performed by quadrant (with a 1-week interval between quadrants) or at a single session (fullmouth disinfection), the preferred approach for treatment of periodontal infections (9). Halitosis treatment attempts to eliminate oral pathologies and control bacterial biofilm, thereby efficiently reducing the oral microbiota. Treatment must be accompanied by professional dental prophylaxis, i.e., removal of dental cavities and plaque retentive factors (10). Intraoral conditions such as insufficient dental hygiene, periodontitis, and tongue coating are the leading causes
2 2 of halitosis (85% of cases). Therefore, dental care professionals are the first to be confronted with this problem (5). Tongue cleaning removes about 70% of oral sulfides and is therefore essential in oral care (11). Effective halitosis treatment is believed to require the use of scrapers to remove the tongue coating and biofilm covering the tongue dorsum (12). This removal is often described as the most effective treatment for halitosis (13). A clear treatment plan should be designed for patients with halitosis, which are mainly periodontal patients (14). In the present study we compared the effectiveness of full- and partial-mouth disinfection for control of halitosis. Materials and Methods Study design This intervention study (Fig. 1) was performed between May 2010 and September 2011 and was designed (15-17) to compare the effects of conventional and fullmouth periodontal treatments on halitosis in periodontal patients. Consecutive patients with periodontal disease were randomly divided into four groups: PTSS+CHX+TS: Full-mouth periodontal therapy in a single session plus CHX mouthwash, with tongue scraping PTSS+CHX: Full-mouth periodontal therapy in a single session plus CHX, without tongue scraping PTQ+TS: Conventional periodontal therapy in quadrants, with tongue scraping PTQ TS: Conventional periodontal therapy in quadrants, without tongue scraping The patients in groups PTSS+CHX+TS and PTQ+TS received tongue scrapers daily and appropriate instruction in tongue scraping technique. CHX was included based on the results of a previous study of full-mouth periodontal therapy (15). The 15-mL solution of 0.2% CHX, without alcohol, was used twice daily for 60 s. Patient selection Patients were selected if they satisfied the inclusion criteria, namely, absence of dental decay; presence of generalized chronic periodontitis (8) with at least 20 teeth and a probing pocket depth (PPD) 5 mm in at least six sites; absence of systemic disease, as documented by their primary care physician; no periodontal treatment in the previous 12 months; no use of antibiotics in the previous 6 months; no history of radiation therapy for the neck or head; and no current smoking. Factors such as diet, food impaction, oral hygiene, and hyposalivation Fig. 1 Study flowchart *Evaluated by halimeter, organoleptic testing, Visible plaque index (VPI), Gingival bleeding index (GBI), Winkel Tongue Coating Index (WTCI), Probing on pocket depth (PPD), Clinical attachment level (CAL), and Bleeding on pocket probing (BoP); PTSS+CHX+TS, full-mouth periodontal therapy in a single session plus CHX mouthwash, with tongue scraping; PTSS+CHX, full-mouth periodontal therapy in a single session plus CHX, without tongue scraping; PTQ+TS, conventional periodontal therapy in quadrants, with tongue scraping; PTQ TS, conventional periodontal therapy in quadrants, without tongue scraping. were also well controlled in this study by the examiner at each appointment. All participants were informed of the importance and purpose of the study and provided written informed consent. The study was previously approved by the Ethics Committee of University of the Estate of Rio de Janeiro ( ). Sample size was determined based on the findings of previous studies. The estimated number of individuals required to reach a power of 0.8 for the design of this study was 15 patients per group (standard deviation of the error, 1.84; detectable difference, 2.43). Therefore, we enrolled 90 participants, 44 women and 46 men, aged years (average ± 14.26). Experimental phase No specific instruction was given for brushing/rinsing technique, but the volunteers were strongly encouraged
3 3 to use the same technique on each test day. Patients assigned to tongue scraping were instructed to use a Kolbe cleaner to scrape their tongue, using three strokes over the dorsum of the tongue. The participants were also instructed to avoid eating/drinking on the evening before treatment, until they were tested. Test participants reported to the dental school in the morning at the scheduled time. The patients were instructed to avoid oral hygiene measures in the morning, to permit measurement of morning bad breath (2). The presence of halitosis was evaluated with a previously calibrated halimeter (Interscan Corp. Halimeter, Chatsworth, CA, USA) and organoleptic testing. The halimeter was a VSC monitor that collects volatile sulfur gases from the mouths of patients and expresses VSC concentrations in parts per billion (ppb) (18). The organoleptic test is considering the gold standard for evaluation because of its clinical relevance: the human nose can inhale more than 10,000 odors, not only sulfur gases (19). In addition, organoleptic testing was performed by the same calibrated examiner, who inhaled breath from the mouths of patients and assigned a score of 0 4 (0 = no odor; 1 = natural odor; 2 = distance about 15 cm; 3 = about 50 cm; 4 = >50 cm) (19). The kappa coefficient of agreement was for the organoleptic test. The patients were also evaluated with the visible plaque index (VPI) (20), which evaluates the presence (1) and absence (0) plaque, and with the gingival bleeding index (GBI) (20). All surfaces of four sites of the teeth were examined, and the presence or absence of gingival bleeding was determined by light inspection of the gingival sulcus with a periodontal probe. The number of gingival margins with bleeding was expressed as a percentage of the total number of gingival margins. Assessment of an index of tongue coating (Winkel Tongue Coating Index; WTCI) (21) was done as follows: the dorsum of the tongue was divided into six sextants: three in the back and three in the front. The tongue coating in each sextant was scored as 0 (no coverage), 1 (mild coverage), or 2 (severe coverage). The total value for tongue coating was the sum of the values from the six areas (score range, 0 12). The tongues of participants were photographed, and these photographs were clinically assessed by the same calibrated examiner. The kappa coefficient of agreement was A periodontal examination was performed at baseline and at 30, 60, and 90 days after treatment. These examination also included (22) assessment of probing on pocket depth (PPD) (the distance from the gingival margin to the bottom of pocket), clinical attachment level (CAL) (the distance from the cement-enamel junction to the bottom of the pocket), and bleeding on pocket probing (BoP) (presence/absence of bleeding 30 s after probing). These measurements were performed at four points (mesial, buccal, distal, and palatal/lingual) by a calibrated examiner using a periodontal probe (University of North Carolina type, 15 mm; Hu-Friedy, Chicago, IL, USA; kappa coefficient, 0.988). Periodontal therapy was then performed for all teeth, with ultrasonic debridement (tip P10; Cavitron, Dentsply, Tulsa, OK, USA) and McCall 13/14 and 17/18 and Gracey 5/6, 7/8, 11/12, and 13/14 manual curettes and Hirschfeld #5-11 periodontal files (Hu-Friedy) for root planning and supra- and subgingival scaling with anesthetic blocking of the region. Conventional therapy required four visits per patient; full-mouth therapy required one visit. The first re-evaluation (PPD, CAL, and BoP) was performed 30 days after the end of treatment (22). The same measurements were made at 60 and 90 days after the end of treatment. The patients did not receive supragingival or subgingival treatment after the initial periodontal treatment, only instruction in oral hygiene, when necessary. The treatments successful, and no patients required dental surgery during 90 days after completion of treatment. Statistical analysis The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to determine if the values were parametric. The significance of differences between treatment groups was analyzed using ANOVA and then the Tukey test. All differences were considered significant at P < Statistical analyses were performed using the SigmaPlot statistical software package (Systat Software Inc., San Jose, CA, USA). Results ANOVA showed significant differences (P < 0.001) among groups in halimeter, organoleptic, and WTCI values. Tables 1 and 2 show the results of periodontal and halitosis assessment in the different treatment groups at baseline and 90 days after treatment. Halimeter testing showed similar results between fullmouth treatments (PTSS+CHX+TS vs. PTSS+CHX; Fig. 2) and between conventional treatments (PTQ+TS vs, PTQ TS; Fig. 2) at 30, 60, and 90 days. Reduction of VSC was significantly greater (P < 0.001) in patients receiving a full-mouth treatment (PTSS+CHX+TS and PTSS+CHX; Fig. 2) than for those receiving a conventional therapy (PTQ+TS and PTQ TS). Organoleptic testing at 30, 60, and 90 days showed no significant difference between treatment groups.
4 4 Table 1 Baseline values for periodontal and halitosis variables, by intervention group PTSS+CHX+TS PTSS+CHX PTQ+TS PTQ-TS VPI (%) ± ± ± ± 7.44 GBI (%) ± ± ± ± BOP (%) ± ± ± ± PPD (mm) 6.28 ± ± ± ± 1.33 CAL (mm) 7.25 ± ± ± ± 1.61 OLS (mean ± SD) 1.5 ± ± ± ± 0.4 VSC (mean ± SD) 109 ± ± ± ± 37 WTCI (mean ± SD) 4.7 ± ± ± ± 2.7 PTSS: periodontal therapy in a single session (full-mouth), CHX: chlorhexidine rinsing, TS: tongue scraping, PTQ: conventional periodontal therapy in quadrants, VPI: visible plaque index, GBI: gingival bleeding index, PPD: pocket probing depth, CAL: clinical attachment level, BOP: bleeding on probing, OLS: organoleptic score (0-4), VSC: volatile sulfide compounds (ppb), WTCI: Winkel tongue coating index (0-12). Table 2 Values for periodontal and halitosis variables at 90 days after treatment, by intervention group PTSS+CHX+TS PTSS+CHX PTQ+TS PTQ-TS VPI (%) 6.99 ± ± ± ± 3.99 GBI (%) ± ± ± ± BOP (%) ± ± ± ± PPD (mm) 3.99 ± ± ± ± 1.61 CAL (mm) 6.01 ± ± ± ± 2.22 OLS (mean ± SD) 0.4 ± ± ± ± 0.5 VSC (mean ± SD) 53 ± ± ± 7 54 ± 11 WTCI (mean ± SD) 1.6 ± ± ± ± 0.7 PTSS: periodontal therapy in a single session (full-mouth), CHX: chlorhexidine rinsing, TS: tongue scraping, PTQ: conventional periodontal therapy in quadrants, VPI: visible plaque index, GBI: gingival bleeding index, PPD: pocket probing depth, CAL: clinical attachment level, BOP: bleeding on probing, OLS: organoleptic score (0-4), VSC: volatile sulfide compounds (ppb), WTCI: Winkel tongue coating index (0-12). WTCI at 30, 60, and 90 days showed a reduction of tongue coating in all groups but no significant difference between the four treatment groups. At 90 days, patients who had received full-mouth treatment with tongue scraping (group PTSS+CHX+TS) had a greater reduction in tongue coating. There was no significant difference between patient groups in baseline tongue coating index. Organoleptic testing showed a significant difference when compared the different periods (30, 60, and 90 days; P < 0.001) in group PTQ+TS, which experienced a decrease in halitosis throughout the 90-day observation period. At 90 days there was no statistical difference in periodontal parameters between full-mouth and conventional therapies. However, PPD, CAL, and BoP showed that both therapies significantly reduced clinical parameters at 30, 60, and 90 days, as compared with baseline values. Discussion Several reports have identified periodontitis as an important cause of halitosis (7,23-26). In this interventional study, patients received one of four treatments in order to compare the effectiveness of full-and partial-mouth disinfection for control of halitosis. A previous study (16) restricted enrollment to patients with a tongue coating index greater than 4 on the WTCI and an organoleptic measurement greater than 2. The present study used different inclusion criteria, as did another previous study (4). A previous study (15) found that full-mouth treatment was more effective than conventional therapy in quadrants at controlling halitosis. Patients who received the combination of full-mouth treatment+chx+cpc for 2 months improved on organoleptic testing but not on VSC halimeter testing. The authors of that study used only nonsurgical periodontal treatment, without tongue scraping. The present results showed the opposite: halimeter testing at 30, 60, and 90 days showed a better result in patients receiving full-mouth treatment than in those receiving conventional treatment. No difference was seen on organoleptic testing. Another study from the same group (27), found a significant reduction in VSC
5 5 Fig. 2 Percent reduction in halimeter measurements, by treatment group, at 30, 60, and 90 days The box-plots show the upper and lower quartiles of the averages. Outliers are shown as separate points (Tukey test, P > 0.05 between groups: * φ # ω π, no difference between groups). PTSS+CHX+TS, full-mouth periodontal therapy in a single session plus CHX mouthwash, with tongue scraping; PTSS+CHX, full-mouth periodontal therapy in a single session plus CHX, without tongue scraping; PTQ+TS, conventional periodontal therapy in quadrants, with tongue scraping; PTQ TS, conventional periodontal therapy in quadrants, without tongue scraping. and tongue coating among patients with moderate periodontitis who received full-mouth therapy, as was noted in the present study. Two studies (23,28) found a compatible concentration of VSC and the periodontal parameters, the authors showed that periodontal patients had more VSC. In the present study, we noted a nonsignificant reduction in periodontal parameters (data not shown) in all periodontal groups. A previous study (29) measured VSC in 210 periodontal pockets of 70 patients and found that PPD and radiographic bone loss were positively associated with VSC levels. In another study (16), VSC concentrations were not significantly correlated with average PPD, CAL, or VPI. Only BoP was related to VSC concentrations. These findings suggest that halitosis is more severe in persons within inflammatory conditions (30). In the current study, the reduction in BoP was greater at 30 and 60 days, but not at 90 days, in patients receiving fullmouth therapy. A previous study (31) evaluated the effects of periodontal treatment and tongue cleaning on oral halitosis parameters and found that periodontal treatment was quite important and that tongue cleaning was somewhat important in reducing halitosis in periodontitis patients. A study (32) comparing full-mouth scaling and root planning with quadrant scaling and root planning in 40 patients with chronic periodontitis over a period of 6 months found that full-mouth therapy was not more effective. Nevertheless, both modalities were efficacious. Those findings were confirmed by our results. A halimeter study (4) of 127 patients showed a significant decrease in VSC after rinsing with CHX for 7 days. The authors concluded that, in addition to periodontal treatment, use of antiseptics can reduce halitosis. However, in the present study we found a reduction in halitosis in all groups; thus, CHX was not the determining factor. Some studies (27,30,33) that compared full-mouth and conventional therapies and included CHX groups and placebo found no effect for CHX during 6 months of follow-up. In the present study, the patient groups receiving full-mouth treatment also received CHX, but the results for these groups did not significantly differ, which confirms the findings of earlier studies. A systematic review (34) showed that full-mouth treatment, with or without antiseptics, had no significant clinical benefit for patients with chronic periodontitis. In conclusion, halimeter evaluation showed that reduction in halitosis was significantly greater after fullmouth therapy than after conventional therapy. However, organoleptic testing showed no difference between treatment groups. Tongue scraping had no effect on halitosis. Acknowledgments The authors express their sincere gratitude to Prof. Alix Young and Grazyna Jonski, from the University of Oslo in Norway, and Prof. Antonio Leal Neto, from Brazil. References 1. Krespi YP, Shrime MG, Kacker A (2006) The relationship between oral malodor and volatile sulfur compound-producing bacteria. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 135, Soares LG, Guaitolini RL, Weyne SC, Falabella MEV, Tinoco EMB, Silva DG (2013) The effect of a mouthrinse containing chlorine dioxide in the clinical reduction of volatile sulfur compounds. Gen Dent 61, Scully C, El-Maaytah M, Porter SR, Greenman J (1997) Breath odor: etiopathogenesis, assessment and management. Eur J Oral Sci 105, Bosy A, Kulkarni GV, Rosenberg M, McCulolloch CA (1994) Relationship of oral malodor to periodontitis: evidence of independence in discrete subpopulations. J Periodontol 65, Bollen CML, Beikler T (2012) Halitosis: the multidisciplinary approach. Int J Oral Sci 4,
6 6 6. Yaegaki K, Sanada K (1992) Volatile sulfur compounds in mouth air from clinically healthy subjects and patients with periodontal disease. J Periodontal Res 27, Loesche WJ, Kazor C (2002) Microbiology and treatment of halitosis. Periodontol , The American Academy of Periodontology (1999) International workshop for a classification of periodontal diseases and conditions. Ann Periodontol 4i, Quirynen M, Bollen CM, Vandekerckhove BN, Dekeyser C, Papaioannou W, Eyssen H (1995) Full- vs. partial-mouth disinfection in the treatment of periodontal infections: shortterm clinical and microbiological observations. J Dent Res 74, Greenman J (1999) Microbial aetiology of halitosis. In: Dental plaque revisited: oral biofilms in health and disease, Newman HN, Wilson M eds, Bioline Cardiff, Rosenberg M (2006) Bad breath and periodontal disease: how related are they? J Clin Periodontol 33, Oliveira-Neto JM, Sato S, Pedrazzi V (2013) How to deal with morning bad breath: a randomized, crossover clinical trial. J Indian Soc Periodontol 17, Yaegaki K (2012) Advances in breath odor research: re-evaluation and newly-arising sciences. J Breath Res 6, doi: / /6/1/ Corrao S (2011) Halitosis: new insight into a millennial old problem. Intern Emerg Med 6, Quirynen M, Mongardini C, van Steenberghe D (1998) The effect of a 1-stage full-mouth disinfection on oral malodor and microbial colonization of the tongue in periodontitis: a pilot study. J Periodontol 69, Tsai CC, Chou HH, Wu TL, Yang YH, Ho KY, Wu YM et al. (2008) The levels of volatile sulfur compounds in mouth air from patients with chronic periodontitis. J Periodontal Res 43, Van der Sleen MI, Slot DE, Van Trijffel E, Winkel EG, Van der Weijden GA (2010) Effectiveness of mechanical tongue cleaning on breath odour and tongue coating: a systematic review. Int J Dent Hyg 8, Rosenberg M, Septon I, Eli I, Bar-Ness R, Gelernter I, Brenner S et al. (1991) Halitosis measurement by an industrial sulphide monitor. J Periodontol 62, Falcão DP, Vieira CN, Batista de Amorim RF (2012) Breaking paradigms: a new definition for halitosis in the context of pseudo-halitosis and halitophobia. J Breath Res 6, doi: / /6/1/ Ainamo J, Bay I (1975) Problems and proposals for recording gingivitis and plaque. Int Dent J 25, Winkel EG, Roldán S, Van Winkelhoff AJ, Herrera D, Sanz M (2003) Clinical effects of a new mouthrinse containing chlorhexidine, cetylpyridinium chloride and zinc-lactate on oral halitosis. A dual-center, double-blind placebo-controlled study. J Clin Periodontol 30, Axelsson P, Lindhe J (1981) The significance of maintenance care in the treatment of periodontal disease. J Clin Periodontol 8, Miyazaki H, Sakao S, Katoh Y, Takehara T (1995) Correlation between volatile sulphur compounds and certain oral health measurements in the general population. J Periodontol 66, Söder B, Johansson B, Söder PO (2000) The relation between foetor ex ore, oral hygiene and periodontal disease. Swed Dent J 24, Nogueira Filho GR, Duarte PM, Toledo S, Tabchoury CP, Cury JA (2002) Effect of triclosan dentifrices on mouth volatile sulphur compounds and dental plaque trypsin-like activity during experimental gingivitis development. J Clin Periodontol 29, Soares LG, Tinoco EMB (2014) Prevalence and related parameters of halitosis in general population and periodontal patients. OA Dent 2, Quirynen M, Mongardini C, de Soete M, Pauwels M, Coucke W, van Eldere J et al. (2000) The role of chlorhexidine in the one-stage full-mouth disinfection treatment of patients with advanced adult periodontitis. Long-term clinical and microbiological observations. J Clin Periodontol 27, Liu XN, Shinada K, Chen XC, Zhang BX, Yaegaki K, Kawaguchi Y (2006) Oral malodor-related parameters in the Chinese general population. J Clin Periodontol 33, Morita M, Wang HL (2001) Relationship between sulcular sulfide level and oral malodor in subjects with periodontal disease. J Periodontol 72, Apatzidou AD, Bakirtzoglou E, Vouros I, Karagiannis V, Papa A, Konstantinidis A (2013) Association between oral malodour and periodontal disease-related parameters in the general population. Acta Odontol Scand 71, Pham TA, Ueno M, Zaitsu T, Takehara S, Shinada K, Lam PH et al. (2011) Clinical trial of oral malodor treatment in patients with periodontal diseases. J Periodontal Res 46, Apatzidou DA, Kinane DF (2004) Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing. I. Clinical findings. J Clin Periodontol 31, Wennstrom JL, Tomasi C, Bertelle A, Dellasega E (2005) Full-mouth ultrasonic debridement versus quadrant scaling and root planing as an initial approach in the treatment of chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 32, Lang NP, Tan WC, Krähenmann MA, Zwahlen M (2008) A systematic review of the effects of full-mouth debridement with and without antiseptics in patients with chronic periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 35, 8-21.
Research Article Halitosis Related Parameters from Patients with Chronic Periodontitis
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Halitosis Related Parameters from Patients with Chronic Periodontitis Soares LS 1, Castagna L 1, Weyne SC 2, Silva DG 3, Falabella MEV 3 and Tinoco
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Halitosis Related Parameters from Patients with Chronic Periodontitis Soares LS 1, Castagna L 1, Weyne SC 2, Silva DG 3, Falabella MEV 3 and Tinoco
ISSN % 47
 ISSN 1560-1587 7 30 60% 7 The Taiwan J Oral Med Sci 007; 3:7-68 Printed in Taiwan, All rights reserved Tonzetich 1 volatile sulfide compounds,vcsc VSCs 90% amines skatole indole VSCs Yaegaki -ketobutyrate
ISSN 1560-1587 7 30 60% 7 The Taiwan J Oral Med Sci 007; 3:7-68 Printed in Taiwan, All rights reserved Tonzetich 1 volatile sulfide compounds,vcsc VSCs 90% amines skatole indole VSCs Yaegaki -ketobutyrate
The levels of volatile sulfur compounds in mouth air from patients with chronic periodontitis
 J Periodont Res 2008; 43: 186 193 All rights reserved The levels of volatile sulfur compounds in mouth air from patients with chronic periodontitis Ó 2007 The Authors. Journal compilation Ó 2007 Blackwell
J Periodont Res 2008; 43: 186 193 All rights reserved The levels of volatile sulfur compounds in mouth air from patients with chronic periodontitis Ó 2007 The Authors. Journal compilation Ó 2007 Blackwell
Prevalence of oral malodor and related factors among adults in Akita Prefecture
 J Med Dent Sci 2007; 54: 159 165 Original Article Prevalence of oral malodor and related factors among adults in Akita Prefecture Masayuki Ueno 1, Tomohito Yanagisawa 1, Kayoko Shinada 1, Satoko Ohara
J Med Dent Sci 2007; 54: 159 165 Original Article Prevalence of oral malodor and related factors among adults in Akita Prefecture Masayuki Ueno 1, Tomohito Yanagisawa 1, Kayoko Shinada 1, Satoko Ohara
A PILOT STUDY OF THE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUBSTANTIVITY OF A NEW ANTI-HALITOSIS MOUTHRINSE
 A PILOT STUDY OF THE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUBSTANTIVITY OF A NEW ANTI-HALITOSIS MOUTHRINSE Binkley, Kenneth A., DDS., Colvard, Michael J., DDS., MS., Oester, Michael, PhD. ABSTRACT A cysteine challenge test
A PILOT STUDY OF THE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUBSTANTIVITY OF A NEW ANTI-HALITOSIS MOUTHRINSE Binkley, Kenneth A., DDS., Colvard, Michael J., DDS., MS., Oester, Michael, PhD. ABSTRACT A cysteine challenge test
Impact of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on oral malodor and microbial load of saliva
 대한치주과학회지 : Vol. 37, No. 1, 2007 Impact of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on oral malodor and microbial load of saliva Myung-Jin Kim, Sung-Jo Kim, Jeom-Il Choi, Ju-Youn Lee * Department of Periodontology,
대한치주과학회지 : Vol. 37, No. 1, 2007 Impact of nonsurgical periodontal therapy on oral malodor and microbial load of saliva Myung-Jin Kim, Sung-Jo Kim, Jeom-Il Choi, Ju-Youn Lee * Department of Periodontology,
Reduction of oral levels of volatile sulfur compounds (VSC) by professional toothcleaning and oral hygiene instruction in nonhalitosis
 Oral Health Prev Dent. 2004;2(4):397-401. Related Articles, Links Reduction of oral levels of volatile sulfur compounds (VSC) by professional toothcleaning and oral hygiene instruction in nonhalitosis
Oral Health Prev Dent. 2004;2(4):397-401. Related Articles, Links Reduction of oral levels of volatile sulfur compounds (VSC) by professional toothcleaning and oral hygiene instruction in nonhalitosis
#1065 Effect of an Essential Oil Herbal Mouthwash on Oral Malodor
 #1065 Effect of an Essential Oil Herbal Mouthwash on Oral Malodor H. Malmström DDS, Rita Cacciato RDH, Michael Yunker DDS, YF. Ren DDS, PhD, MPH, Eastman Department of Dentistry, Division of General Dentistry,
#1065 Effect of an Essential Oil Herbal Mouthwash on Oral Malodor H. Malmström DDS, Rita Cacciato RDH, Michael Yunker DDS, YF. Ren DDS, PhD, MPH, Eastman Department of Dentistry, Division of General Dentistry,
HCD Deutscher 1 SHM Derman 1 AG Barbe 1 R Seemann 2 MJ Noack 1. Abstract 1 INTRODUCTION REVIEW ARTICLE
 Accepted: 16 July 2017 DOI: 10.1111/idh.12306 REVIEW ARTICLE The effect of professional tooth cleaning or non- surgical periodontal therapy on oral halitosis in patients with periodontal diseases. A systematic
Accepted: 16 July 2017 DOI: 10.1111/idh.12306 REVIEW ARTICLE The effect of professional tooth cleaning or non- surgical periodontal therapy on oral halitosis in patients with periodontal diseases. A systematic
Patients with periodontal disease
 J Periodontol January 2001 Relationship Between Sulcular Sulfide Level and Oral Malodor in Subjects With Periodontal Disease Manabu Morita* and Hom-Lay Wang Background: The relationship between oral malodor
J Periodontol January 2001 Relationship Between Sulcular Sulfide Level and Oral Malodor in Subjects With Periodontal Disease Manabu Morita* and Hom-Lay Wang Background: The relationship between oral malodor
Clinical correlates of oral malodour in a population of patients attending a preventive clinic in Pretoria, South Africa
 Clinical correlates of oral malodour in a population of patients attending a preventive clinic in Pretoria, South Africa SADJ August 2011, Vol 66 no 7 p326 - p331 O A Ayo-Yusuf: BDS, MSc (Odont), MPH,
Clinical correlates of oral malodour in a population of patients attending a preventive clinic in Pretoria, South Africa SADJ August 2011, Vol 66 no 7 p326 - p331 O A Ayo-Yusuf: BDS, MSc (Odont), MPH,
INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVE
 ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to examine a mouthwash containing essential oils and herbal extracts, effect on whole mouth and posterior dorsum tongue malodor over a 90 day period. Sixty healthy
ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to examine a mouthwash containing essential oils and herbal extracts, effect on whole mouth and posterior dorsum tongue malodor over a 90 day period. Sixty healthy
Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Halitosis
 28 2 (2007 6 ) J Korean Oriental Med 2007;28(2):13-21 원저 김진성 류봉하 Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Halitosis Jin-sung Kim Bong-ha Ryu 3rd Department of Internal Medicine Hospital of Oriental Medicine
28 2 (2007 6 ) J Korean Oriental Med 2007;28(2):13-21 원저 김진성 류봉하 Clinical Characteristics of Patients with Halitosis Jin-sung Kim Bong-ha Ryu 3rd Department of Internal Medicine Hospital of Oriental Medicine
Evaluation of a stabilized chlorine dioxide paste-rinse combination regimen vs. a phenol-related rinse regimen.
 Evaluation of a stabilized chlorine dioxide paste-rinse combination regimen vs. a phenol-related rinse regimen. Steven J. Spindler, D.D.S.* and Gregg A. Spindler** The relative clinical efficacy was compared
Evaluation of a stabilized chlorine dioxide paste-rinse combination regimen vs. a phenol-related rinse regimen. Steven J. Spindler, D.D.S.* and Gregg A. Spindler** The relative clinical efficacy was compared
Oral hygiene practices and self-perceived halitosis among dental students
 Oral hygiene practices and self-perceived halitosis among dental students Ghufran A. Hasan, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background: represents a common dental condition, although sufferers are often not
Oral hygiene practices and self-perceived halitosis among dental students Ghufran A. Hasan, B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background: represents a common dental condition, although sufferers are often not
Oral halitosis and oral hygiene practices among dental students
 Oral halitosis and oral hygiene practices among dental students Barzan A. Al-Atrooshi B.D.S, M.Sc (1) Abeer S. Al-Rawi B.D.S, M.Sc (1) ABSTRACT Background: Oral halitosis is a very important problem, because
Oral halitosis and oral hygiene practices among dental students Barzan A. Al-Atrooshi B.D.S, M.Sc (1) Abeer S. Al-Rawi B.D.S, M.Sc (1) ABSTRACT Background: Oral halitosis is a very important problem, because
Life Science Journal 2014;11(10)
 The Effect of Salvadora persica L. Sticks on Bacterial Counts and Oral Odor: A Crossover Clinical Study Mohammed Abdullah Alqumber Department of Laboratory Medicine, Faculty of Applied Medical Sciences,
The Effect of Salvadora persica L. Sticks on Bacterial Counts and Oral Odor: A Crossover Clinical Study Mohammed Abdullah Alqumber Department of Laboratory Medicine, Faculty of Applied Medical Sciences,
Effect of Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy on the Concentration of Volatile Sulfur Compound in Mouth Air of a Group of Nigerian Young Adults
 Original Article Effect of Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy on the Concentration of Volatile Sulfur Compound in Mouth Air of a Group of Nigerian Young Adults Ehizele AO, Akhionbare O Department of Periodontics,
Original Article Effect of Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy on the Concentration of Volatile Sulfur Compound in Mouth Air of a Group of Nigerian Young Adults Ehizele AO, Akhionbare O Department of Periodontics,
Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing I. Clinical findings
 J Clin Periodontol 24; 31: 132 14 Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 24 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing I. Clinical findings D. A. Apatzidou
J Clin Periodontol 24; 31: 132 14 Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 24 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Quadrant root planing versus same-day full-mouth root planing I. Clinical findings D. A. Apatzidou
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS
 THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
THE EFFICIENCY OF INITIAL PHASE TREATMENT IN CHRONIC MARGINAL PERIODONTITIS Adriana Monea, Lecturer, DMD, PhD Department of Odontology and Periodontology Faculty of Dental Medicine, UMF Tîrgu-Mureş, Romania
Prevalence and Factors Related to Tongue Coating among a Sample of Jordanian Royal Medical Services Dental Outpatients
 Prevalence and Factors Related to Tongue Coating among a Sample of Jordanian Royal Medical Services Dental Outpatients Rana A. Omor BDS*, Musab A. Arabeyat BDS*, Ayman N. Hiasat BDS**, Mahasen S. Ajarmeh
Prevalence and Factors Related to Tongue Coating among a Sample of Jordanian Royal Medical Services Dental Outpatients Rana A. Omor BDS*, Musab A. Arabeyat BDS*, Ayman N. Hiasat BDS**, Mahasen S. Ajarmeh
Safe Breath Rinse. To eliminate and prevent bad breath
 Safe Breath Rinse To eliminate and prevent bad breath Bad breath a very common problem Bad breath (halitosis) has been a problem since time immemorial. Home remedies recommended 2,000 years ago are very
Safe Breath Rinse To eliminate and prevent bad breath Bad breath a very common problem Bad breath (halitosis) has been a problem since time immemorial. Home remedies recommended 2,000 years ago are very
NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS
 NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS March 30, 2015 Dear Oxyfresh Professional: We are thrilled to share with you the exciting results of a NEW 12-month, double blind clinical study published in the International
NEW 12-MONTH CLINICAL STUDY RESULTS March 30, 2015 Dear Oxyfresh Professional: We are thrilled to share with you the exciting results of a NEW 12-month, double blind clinical study published in the International
Case Report A Case Report of Tooth Wear Associated with a Patient s Inappropriate Efforts to Reduce Oral Malodor Caused by Endodontic Lesion
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 9, Article ID 778, 5 pages doi:.55/9/778 Case Report A Case Report of Tooth Wear Associated with a Patient s Inappropriate Efforts
Hindawi Publishing Corporation International Journal of Dentistry Volume 9, Article ID 778, 5 pages doi:.55/9/778 Case Report A Case Report of Tooth Wear Associated with a Patient s Inappropriate Efforts
Non surgical management of periodontitis related halitosis among adults
 Original Article Non surgical management of periodontitis related halitosis among adults Hossam A. Eid 1,2 1 Department of Oral Medicine, Oral Diagnosis and Periodontology, Faculty of Dentistry, Suez Canal
Original Article Non surgical management of periodontitis related halitosis among adults Hossam A. Eid 1,2 1 Department of Oral Medicine, Oral Diagnosis and Periodontology, Faculty of Dentistry, Suez Canal
A randomised clinical trial to assess control of oral malodour by a novel dentifrice containing 0.1%w w o-cymen-5-ol, 0.6%w w zinc chloride
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE International Dental Journal 2011; 61 (Suppl. 3): 60 66 doi: 10.1111/j.1875-595X.2011.00051.x A randomised clinical trial to assess control of oral malodour by a novel dentifrice containing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE International Dental Journal 2011; 61 (Suppl. 3): 60 66 doi: 10.1111/j.1875-595X.2011.00051.x A randomised clinical trial to assess control of oral malodour by a novel dentifrice containing
IMPACT OF DIFFERENT ORAL HYGIENE AIDS FOR THE REDUCTION OF MORNING BAD BREATH AMONG DENTAL STUDENTS: A CROSSOVER CLINICAL TRIAL
 DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-627 Original Research IMPACT OF DIFFERENT ORAL HYGIENE AIDS FOR THE REDUCTION OF MORNING BAD BREATH AMONG DENTAL STUDENTS: A CROSSOVER CLINICAL TRIAL SHAIJAL GODHA, PRALHAD L DASAR,
DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-627 Original Research IMPACT OF DIFFERENT ORAL HYGIENE AIDS FOR THE REDUCTION OF MORNING BAD BREATH AMONG DENTAL STUDENTS: A CROSSOVER CLINICAL TRIAL SHAIJAL GODHA, PRALHAD L DASAR,
Effect of DioxiRinse Mouthwash on Oral Malodor
 Effect of DioxiRinse Mouthwash on Oral Malodor A Clinical and Microbiological Pilot Study April 8, 2002 Principal Investigator: Sushma Nachnani University Health Resources Group, Inc. 5714 Canterbury Drive
Effect of DioxiRinse Mouthwash on Oral Malodor A Clinical and Microbiological Pilot Study April 8, 2002 Principal Investigator: Sushma Nachnani University Health Resources Group, Inc. 5714 Canterbury Drive
Halitosis: A Short Overview
 CASE REPORTS Halitosis: A Short Overview Jens Kaltschmitt, Peter Eickholz Occurrence of halitosis, breath malodour or bad breath may indicate certain medical problems (e.g. periodontitis) and may cause
CASE REPORTS Halitosis: A Short Overview Jens Kaltschmitt, Peter Eickholz Occurrence of halitosis, breath malodour or bad breath may indicate certain medical problems (e.g. periodontitis) and may cause
Halitosis is caused by odorous
 Volume 77 Number 7 Development of a Compact and Simple Gas Chromatography for Oral Malodor Measurement Takatoshi Murata,* Anton Rahardjo, Yuki Fujiyama, Takayuki Yamaga, Mariko Hanada, Ken Yaegaki, i and
Volume 77 Number 7 Development of a Compact and Simple Gas Chromatography for Oral Malodor Measurement Takatoshi Murata,* Anton Rahardjo, Yuki Fujiyama, Takayuki Yamaga, Mariko Hanada, Ken Yaegaki, i and
Full-mouth treatment concepts for chronic periodontitis: a systematic review
 J Clin Periodontol 2008; 35: 591 604 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01239.x Full-mouth treatment concepts for chronic periodontitis: a systematic review Eberhard J, Jervøe-Storm P-M, Needleman I, Worthington
J Clin Periodontol 2008; 35: 591 604 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01239.x Full-mouth treatment concepts for chronic periodontitis: a systematic review Eberhard J, Jervøe-Storm P-M, Needleman I, Worthington
Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (JDMS) ISSN: 2279-0853, ISBN: 2279-0861. Volume 1, Issue 4 (Sep-Oct. 2012), PP 36-41 Mechanical Non Surgical Therapy: An Indispensable Tool 1 Ashu Bhardwaj,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Use of brushes, rinses, and cooling solutions in oral care van der Sluijs, E.; Slot, D.E.; van der Weijden, G.A. Published in: Link to publication Citation for published
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Use of brushes, rinses, and cooling solutions in oral care van der Sluijs, E.; Slot, D.E.; van der Weijden, G.A. Published in: Link to publication Citation for published
Breath Odors of Oral Origin (Oral Malodor)
 Breath Odors of Oral Origin (Oral Malodor) Breath odor or halitosis denotes any type of disagreeable scent felt on a person s breath during exhalation and speech. These odors have many different causes
Breath Odors of Oral Origin (Oral Malodor) Breath odor or halitosis denotes any type of disagreeable scent felt on a person s breath during exhalation and speech. These odors have many different causes
Halitosis is the term used to define
 Volume 80 Number 1 Prevalence of Halitosis in Young Male Adults: A Study in Swiss Army Recruits Comparing Self-Reported and Clinical Data Michael M. Bornstein,* Bruce L. Stocker, Rainer Seemann, Walter
Volume 80 Number 1 Prevalence of Halitosis in Young Male Adults: A Study in Swiss Army Recruits Comparing Self-Reported and Clinical Data Michael M. Bornstein,* Bruce L. Stocker, Rainer Seemann, Walter
Oral hygiene reinforcement in the simplified periodontal treatment of 1 hour
 J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41: 149 156 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12200 Oral hygiene reinforcement in the simplified periodontal treatment of 1 hour Danae A. Apatzidou, Penelope Zygogianni, Dimitra Sakellari and
J Clin Periodontol 2014; 41: 149 156 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12200 Oral hygiene reinforcement in the simplified periodontal treatment of 1 hour Danae A. Apatzidou, Penelope Zygogianni, Dimitra Sakellari and
Influence of menstrual cycle and salivary ß-estradiol on volatile sulfur compound
 Received: 25 Oct. 2011 Accepted: 24 Apr. 2012 Original Article Influence of menstrual cycle and salivary ß-estradiol on volatile sulfur compound Shahla Kakoei DDS, MSc 1, Fahimeh Barkhori DDS 2, Ali Mirzazadeh
Received: 25 Oct. 2011 Accepted: 24 Apr. 2012 Original Article Influence of menstrual cycle and salivary ß-estradiol on volatile sulfur compound Shahla Kakoei DDS, MSc 1, Fahimeh Barkhori DDS 2, Ali Mirzazadeh
Comparison of the Psychological Condition of Chinese Patients with or without Halitosis Complaints
 Comparison of the sychological Condition of Chinese atients with or without Halitosis Complaints Jing WANG 1,2, Lu HE 1 Objective: To investigate the psychological condition of Chinese patients with or
Comparison of the sychological Condition of Chinese atients with or without Halitosis Complaints Jing WANG 1,2, Lu HE 1 Objective: To investigate the psychological condition of Chinese patients with or
Title: EFFECTS OF FIXED AND REMOVABLE SPACE MAINTAINERS ON HALITOSIS
 Author s response to reviews Title: EFFECTS OF FIXED AND REMOVABLE SPACE MAINTAINERS ON HALITOSIS Authors: Elif Yıldızer Keriş (dtelifkaya@gmail.com) didem atabek (dtdidem@hotmail.com) kahraman gungor
Author s response to reviews Title: EFFECTS OF FIXED AND REMOVABLE SPACE MAINTAINERS ON HALITOSIS Authors: Elif Yıldızer Keriş (dtelifkaya@gmail.com) didem atabek (dtdidem@hotmail.com) kahraman gungor
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Objectives: The aim of this work was to evaluate saliva and tongue coating ph in
 www.scielo.br/jaos Saliva and tongue coating ph before and after use of mouthwashes and relationship with parameters of halitosis Elen de Souza TOLENTINO 1, Luiz Eduardo Montenegro CHINELLATO 2, Olinda
www.scielo.br/jaos Saliva and tongue coating ph before and after use of mouthwashes and relationship with parameters of halitosis Elen de Souza TOLENTINO 1, Luiz Eduardo Montenegro CHINELLATO 2, Olinda
Efficacy of chlorine dioxide mouthwash in reducing oral malodor: A 2 week randomized, double blind, crossover study
 Received: 5 June 2018 Revised: 14 August 2018 Accepted: 19 August 2018 DOI: 10.1002/cre2.131 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of chlorine dioxide mouthwash in reducing oral malodor: A 2 week randomized, double
Received: 5 June 2018 Revised: 14 August 2018 Accepted: 19 August 2018 DOI: 10.1002/cre2.131 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of chlorine dioxide mouthwash in reducing oral malodor: A 2 week randomized, double
Mouthrinses for the treatment of halitosis (Review)
 Fedorowicz Z, Aljufairi H, Nasser M, Outhouse TL, Pedrazzi V This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2008, Issue
Fedorowicz Z, Aljufairi H, Nasser M, Outhouse TL, Pedrazzi V This is a reprint of a Cochrane review, prepared and maintained by The Cochrane Collaboration and published in The Cochrane Library 2008, Issue
Tongue Hygiene and Its Significance in the Control of Halitosis
 10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1107 Sandeep REVIEW Anant ARTICLE Lawande, Gayatri Sandeep Lawande Tongue Hygiene and Its Significance in the Control of Halitosis Sandeep Anant Lawande, Gayatri Sandeep Lawande
10.5005/jp-journals-10026-1107 Sandeep REVIEW Anant ARTICLE Lawande, Gayatri Sandeep Lawande Tongue Hygiene and Its Significance in the Control of Halitosis Sandeep Anant Lawande, Gayatri Sandeep Lawande
Halitosis-A warning sign?
 Review article Halitosis-A warning sign? 1Dr. Swati Gupta, 2 Dr. Richa Gupta 1MDS Periodontology( Manipal university) 2Research pool officer in anatomy (Post Graduate institute of medical science and research)
Review article Halitosis-A warning sign? 1Dr. Swati Gupta, 2 Dr. Richa Gupta 1MDS Periodontology( Manipal university) 2Research pool officer in anatomy (Post Graduate institute of medical science and research)
Home care. Home care. Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice. Professional care. BSP Roadshows 2008/9
 3. Periodontal Treatment BSP Roadshows 2008/9 Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice 3. Periodontal Treatment Phil Ower www.periocourses.co.uk Why is it so important? Oral hygiene methods what s
3. Periodontal Treatment BSP Roadshows 2008/9 Core Values for Treating Patients in Practice 3. Periodontal Treatment Phil Ower www.periocourses.co.uk Why is it so important? Oral hygiene methods what s
Oral malodor, also known as bad breath,
 Oral malodor ADA COUNCIL ON SCIENTIFIC AFFAIRS Oral malodor, also known as bad breath, is a common complaint among the general population. Recently, this area has witnessed growing technology and communications,
Oral malodor ADA COUNCIL ON SCIENTIFIC AFFAIRS Oral malodor, also known as bad breath, is a common complaint among the general population. Recently, this area has witnessed growing technology and communications,
Comparative effects of various commercially available mouthrinse formulations on oral malodour
 (211) 17, 1886 doi:1.1111/j.161-825.21.1714.x Ó 21 John Wiley & Sons A/S All rights reserved www.wiley.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative effects of various commercially available mouthrinse formulations
(211) 17, 1886 doi:1.1111/j.161-825.21.1714.x Ó 21 John Wiley & Sons A/S All rights reserved www.wiley.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparative effects of various commercially available mouthrinse formulations
Impact of tongue cleansers on microbial load and taste
 J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31: 506 510 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2004.00507.x Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2004 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Impact of tongue cleansers on microbial load and
J Clin Periodontol 2004; 31: 506 510 doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.2004.00507.x Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2004 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved Impact of tongue cleansers on microbial load and
Halitosis amongst students in tertiary institutions in Lagos state
 Halitosis amongst students in tertiary institutions in Lagos state *Joda AE, Olukoju OO Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Bio-pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Lagos Abstract Background: Halitosis
Halitosis amongst students in tertiary institutions in Lagos state *Joda AE, Olukoju OO Department of Clinical Pharmacy and Bio-pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Lagos Abstract Background: Halitosis
Research Article Correlations between Perceived Oral Malodor Levels and Self-Reported Oral Complaints
 International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 343527, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/343527 Research Article Correlations between Perceived Oral Malodor Levels and Self-Reported Oral Complaints
International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 343527, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/343527 Research Article Correlations between Perceived Oral Malodor Levels and Self-Reported Oral Complaints
Kerry Hyland-Lepicek, RDH
 The Oravital System: A Paradigm Shift in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease There is substantial evidence indicating that most forms of periodontal disease are specific infections caused by an overgrowth
The Oravital System: A Paradigm Shift in the Treatment of Periodontal Disease There is substantial evidence indicating that most forms of periodontal disease are specific infections caused by an overgrowth
Self-Perception of Halitosis among Undergraduate Students of Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences - A Questionnaire Based Study
 Self-Perception of Halitosis among Undergraduate Students of Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences - A Questionnaire Based Study Humagain M, 1 Dixit S, 2 Bhandari B, 1 Khanal S, 1 Singh PK 3
Self-Perception of Halitosis among Undergraduate Students of Kathmandu University School of Medical Sciences - A Questionnaire Based Study Humagain M, 1 Dixit S, 2 Bhandari B, 1 Khanal S, 1 Singh PK 3
Research Article Full Mouth Disinfection Versus Scaling and Root Planing per Quadrant in Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Full Mouth Disinfection Versus Scaling and Root Planing per Quadrant in Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review Maísa Casarin 1 *, Danilo Antonio
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Research Article Full Mouth Disinfection Versus Scaling and Root Planing per Quadrant in Aggressive Periodontitis: A Systematic Review Maísa Casarin 1 *, Danilo Antonio
The effect of smoking on bleeding on probing after nonsurgical periodontal therapy: a quasi-experimental study
 Original Research Periodontics The effect of smoking on bleeding on probing after nonsurgical periodontal therapy: a quasi-experimental study Rodrigo ARDAIS Ticiane de Góes MÁRIO Jociana BOLIGON Karla
Original Research Periodontics The effect of smoking on bleeding on probing after nonsurgical periodontal therapy: a quasi-experimental study Rodrigo ARDAIS Ticiane de Góes MÁRIO Jociana BOLIGON Karla
Essentials of Periodontal Management in General Practice
 Essentials of Periodontal Management in General Practice Phil Ower MSc BDS MGDSRCS Specialist in Periodontics Briars Dental Centre, Newbury and www.periocourses.co.uk Introduction Effective management
Essentials of Periodontal Management in General Practice Phil Ower MSc BDS MGDSRCS Specialist in Periodontics Briars Dental Centre, Newbury and www.periocourses.co.uk Introduction Effective management
Cause related therapy: Professional mechanical plaque control Zsuzsanna Papp Prof. István Gera
 Cause related therapy: Professional mechanical plaque control Zsuzsanna Papp Prof. István Gera Periodontal Clinic, Semmelweis University, Budapest 2017.02.14. Complex periodontal therapy Systemic phase
Cause related therapy: Professional mechanical plaque control Zsuzsanna Papp Prof. István Gera Periodontal Clinic, Semmelweis University, Budapest 2017.02.14. Complex periodontal therapy Systemic phase
Clinical Efficacy of a New Mouthwash Containing Essential Oil of Cardamom in Reducing Volatile Sulphur Coumpounds Concentration
 Original Article Int J Clin Prev Dent 2014;10(4):237-242 ㆍ http://dx.doi.org/10.15236/ijcpd.2014.10.4.237 ISSN (Print) 1738-8546 ㆍ ISSN (Online) 2287-6197 Clinical Efficacy of a New Mouthwash Containing
Original Article Int J Clin Prev Dent 2014;10(4):237-242 ㆍ http://dx.doi.org/10.15236/ijcpd.2014.10.4.237 ISSN (Print) 1738-8546 ㆍ ISSN (Online) 2287-6197 Clinical Efficacy of a New Mouthwash Containing
Efficacy Evaluation of a Chlorine Dioxide Containing Toothpaste (DioxiBrite ) on Plaque and Gingivitis. A Clinical Study
 Efficacy Evaluation of a Chlorine Dioxide Containing Toothpaste (DioxiBrite ) on Plaque and Gingivitis A Clinical Study Principle Investigator Laura Mueller-Joseph RDH, Ed.D. State University of New York
Efficacy Evaluation of a Chlorine Dioxide Containing Toothpaste (DioxiBrite ) on Plaque and Gingivitis A Clinical Study Principle Investigator Laura Mueller-Joseph RDH, Ed.D. State University of New York
OralChroma Used worldwide by dentists and researchers
 OralChroma Used worldwide by dentists and researchers Oral Gas Analysis and Oral Health Monitoring OVERVIEW 1. OralChroma & The Dental Practice A pre-examination oral health analysis device Individually
OralChroma Used worldwide by dentists and researchers Oral Gas Analysis and Oral Health Monitoring OVERVIEW 1. OralChroma & The Dental Practice A pre-examination oral health analysis device Individually
Clinical efficacy of phase I therapy combined with a triclosan/copolymer dentifrice on generalized chronic periodontitis
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2010) 5, 216e220 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Original Article Clinical efficacy of phase I therapy combined with a triclosan/copolymer
Journal of Dental Sciences (2010) 5, 216e220 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com Original Article Clinical efficacy of phase I therapy combined with a triclosan/copolymer
Sulphur By-Product: The Relationship between Volatile Sulphur Compounds and Dental Plaque-Induced Gingivitis
 Sulphur By-Product: The Relationship between Volatile Sulphur Compounds and Dental Plaque-Induced Gingivitis Abstract The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between volatile sulphur
Sulphur By-Product: The Relationship between Volatile Sulphur Compounds and Dental Plaque-Induced Gingivitis Abstract The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship between volatile sulphur
One-stage, full-mouth disinfection: fiction or reality?
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 50, 2009, 39 51 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2009 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 disinfection: fiction or reality? WIM TEUGHELS,CHRISTEL DEKEYSER,MARK
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 50, 2009, 39 51 Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved Ó 2009 John Wiley & Sons A/S PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 disinfection: fiction or reality? WIM TEUGHELS,CHRISTEL DEKEYSER,MARK
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Volatile sulphur compounds in morning breath of human volunteers Snel, Johannes; Burgering, Maurits; Smit, Bart; Noordman, Wouter; Tangerman, Albert; Winkel, Edwin; Kleerebezem,
University of Groningen Volatile sulphur compounds in morning breath of human volunteers Snel, Johannes; Burgering, Maurits; Smit, Bart; Noordman, Wouter; Tangerman, Albert; Winkel, Edwin; Kleerebezem,
Your Pet s Dentistry Procedure
 Your Pet s Dentistry Procedure Does your pets breath smell? Periodontal disease is the most common disease in dogs and cats. Without adequate care and attention, periodontal disease can result in pain,
Your Pet s Dentistry Procedure Does your pets breath smell? Periodontal disease is the most common disease in dogs and cats. Without adequate care and attention, periodontal disease can result in pain,
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters
 Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
Impact of Photodynamic Therapy Applied by FotoSan on Periodontal Tissues Clinical Parameters REVIEWED PAPER Most patients visiting dental surgeries suffer from various types of periodontopathies. Since
What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers
 http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2017/v72no8a8 < 387 What s new for the clinician? Summaries of and excerpts from recently published papers SADJ September 2017, Vol 72 no 8 p387- p391 Compiled and
Please visit the C.E. Pavilion to validate your course attendance Or If There s a Line Go cdapresents.com
 UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
COMPARISON OF HAND AND ULTRASONIC INSTRUMENTATION ON PERIODONTAL PARAMETERS IN GHANAIAN PATIENTS WITH MODERATE CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS
 March 216 Vol. 5, No. 1 PostgraduateMedical Journal of Ghana COMPARISON OF AND INSTRUMENTATION ON PERIODONTAL PARAMETERS IN GHANAIAN PATIENTS WITH MODERATE CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS Abstract Vasco E, Kwamin
March 216 Vol. 5, No. 1 PostgraduateMedical Journal of Ghana COMPARISON OF AND INSTRUMENTATION ON PERIODONTAL PARAMETERS IN GHANAIAN PATIENTS WITH MODERATE CHRONIC PERIODONTITIS Abstract Vasco E, Kwamin
Screenings, Indices Their influence on the treatment plan (Berne concept)
 Screenings, Indices Their influence on the treatment plan (Berne concept) 1. 2. 3. 4. Garguilo AW, Wentz FM, Orban B. Dimensions and relations of thedentogingival junction in humans. J Periodontol 1961;
Screenings, Indices Their influence on the treatment plan (Berne concept) 1. 2. 3. 4. Garguilo AW, Wentz FM, Orban B. Dimensions and relations of thedentogingival junction in humans. J Periodontol 1961;
Application of a portable gas chromatograph for quantitative measurement of canine oral malodor
 Fundamental Toxicological Sciences (Fundam. Toxicol. Sci.) Vol.4, No.1, 23-29, 2017 23 Original Article Application of a portable gas chromatograph for quantitative measurement of canine oral malodor Naoki
Fundamental Toxicological Sciences (Fundam. Toxicol. Sci.) Vol.4, No.1, 23-29, 2017 23 Original Article Application of a portable gas chromatograph for quantitative measurement of canine oral malodor Naoki
How to Handle Halitosis Examinations?
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Curd Bollen* (DDS, PhD, MSc perio) Department of Periodontology Halitosis Implantology, Oral Clinical Center, Netherlands *Corresponding Author: Oral Care Center Dr. Bollen - Eyckholtstraat
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS Curd Bollen* (DDS, PhD, MSc perio) Department of Periodontology Halitosis Implantology, Oral Clinical Center, Netherlands *Corresponding Author: Oral Care Center Dr. Bollen - Eyckholtstraat
Other common oral problems DR ANDREW DAVIES FRCP CONSULTANT IN PALLIATIVE MEDICINE ROYAL SURREY COUNTY HOSPITAL, GUILDFORD, UK
 Other common oral problems DR ANDREW DAVIES FRCP CONSULTANT IN PALLIATIVE MEDICINE ROYAL SURREY COUNTY HOSPITAL, GUILDFORD, UK Outline Epidemiology OASis study Poor oral hygiene Halitosis Taste disturbance
Other common oral problems DR ANDREW DAVIES FRCP CONSULTANT IN PALLIATIVE MEDICINE ROYAL SURREY COUNTY HOSPITAL, GUILDFORD, UK Outline Epidemiology OASis study Poor oral hygiene Halitosis Taste disturbance
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
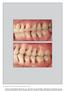 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
Available online Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(6):758-764 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 comparison of plain Chlorhexidine (0.2%) and Chlorhexidine
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(6):758-764 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 comparison of plain Chlorhexidine (0.2%) and Chlorhexidine
Initial Therapy. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS. Oral sulcular epithelium. Oral. epithelium. Junctional. epithelium. Connective tissue.
 Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
Oral sulcular epithelium Junctional epithelium E Oral epithelium Initial Therapy Connective tissue Bone Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Non-surgical Therapy Scaling: Instrumentation of the crown and root
3 Post 30 sec. rinse (ppb) Percent Reduction > Average % Reduction
 Testing Prevotella intermedia Trial Dentist Chlorhexidine Water 1 Baseline (ppb) 114 96 71 1 Post sec. rinse (ppb) 13 Percent Reduction 86 86 2 Baseline (ppb) 77 44 63 2 Post sec. rinse (ppb) 1 7 7 Percent
Testing Prevotella intermedia Trial Dentist Chlorhexidine Water 1 Baseline (ppb) 114 96 71 1 Post sec. rinse (ppb) 13 Percent Reduction 86 86 2 Baseline (ppb) 77 44 63 2 Post sec. rinse (ppb) 1 7 7 Percent
Results: The raw data for each test species are shown in the series of tables below:
 FINAL REPORT Grant Number 1785 (BR1); Contract with Dentist Select Action Date: 5/15/12 Budget Period: 6/15/12 to 9/15/12 Contacts: Dr. Richard Downs, Abbadent Dental; Dr. Gerard St-Cyr, CEO, Dentist Select
FINAL REPORT Grant Number 1785 (BR1); Contract with Dentist Select Action Date: 5/15/12 Budget Period: 6/15/12 to 9/15/12 Contacts: Dr. Richard Downs, Abbadent Dental; Dr. Gerard St-Cyr, CEO, Dentist Select
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation. Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman
 Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
Principles of Periodontal Instrumentation Periodontology I - 4th year 23/2/2012 Dr. Murad Shaqman Outline Classification of periodontal instruments General principles of instrumentation Principles of scaling
Linking Research to Clinical Practice
 Is Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy Cost Effective? Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information
Is Non Surgical Periodontal Therapy Cost Effective? Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information
Response of molars and non-molars to a strict supragingival control in periodontal patients
 Periodontics Response of molars and non-molars to a strict supragingival control in periodontal patients Patrícia Daniela elchiors Angst (a) Flávia Benetti Piccinin (a) Rui Vicente Oppermann (a) Rosemary
Periodontics Response of molars and non-molars to a strict supragingival control in periodontal patients Patrícia Daniela elchiors Angst (a) Flávia Benetti Piccinin (a) Rui Vicente Oppermann (a) Rosemary
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT
 10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1049 Shubangi Mani et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Microbiological Evaluation of Chlorine Dioxide Based Mouthwash and Toothpaste in Periodontitis Patients along with Combination
10.5005/jp-journals-10029-1049 Shubangi Mani et al ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical and Microbiological Evaluation of Chlorine Dioxide Based Mouthwash and Toothpaste in Periodontitis Patients along with Combination
Comparison of halitosis parameters and sialometry between patients subjected to head and neck radiotherapy and patients with periodontal disease
 Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2011 - Volume 10, Number 2 Comparison of halitosis parameters and sialometry between patients subjected to head and neck radiotherapy and patients with periodontal
Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2011 - Volume 10, Number 2 Comparison of halitosis parameters and sialometry between patients subjected to head and neck radiotherapy and patients with periodontal
Smell It Like It Is: Addressing Halitosis
 Smell It Like It Is: Addressing Halitosis Tracey Jacobs, BSDH, RDH Manager, Professional Education South tracey.jacobs@philips.com Tracey is a graduate of the University of Alabama School of Dentistry
Smell It Like It Is: Addressing Halitosis Tracey Jacobs, BSDH, RDH Manager, Professional Education South tracey.jacobs@philips.com Tracey is a graduate of the University of Alabama School of Dentistry
The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment
 The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment Authors_Prof. Tzi Kang Peng, Taiwan & Prof. Georgi Tomov, Bulgaria _Introduction With oral implantology experience its Renaissance, the
The use of the LiteTouch Er:YAG laser in peri-implantitis treatment Authors_Prof. Tzi Kang Peng, Taiwan & Prof. Georgi Tomov, Bulgaria _Introduction With oral implantology experience its Renaissance, the
Review article AODMR. Halitosis: An oversimplified complex issue
 Review article AODMR Halitosis: An oversimplified complex issue Kartika Chawla, Salem Tariq Shaikh 1 Department of Periodontology & Oral Implantology, Private Practitioner, New Delhi, India, Department
Review article AODMR Halitosis: An oversimplified complex issue Kartika Chawla, Salem Tariq Shaikh 1 Department of Periodontology & Oral Implantology, Private Practitioner, New Delhi, India, Department
Manabu Nakano 1*, Eiju Shimizu 2, Hiroyuki Wakabayashi 1, Koji Yamauchi 1 and Fumiaki Abe 1
 Nakano et al. BMC Oral Health (2016) 16:37 DOI 10.1186/s12903-016-0199-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess effects of the single
Nakano et al. BMC Oral Health (2016) 16:37 DOI 10.1186/s12903-016-0199-7 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess effects of the single
Effect of Clindamycin Hydrochloride on Oral Malodor, Plaque, Calculus, and Gingivitis in Dogs with Periodontitis*
 J. M. Warrick, G. A. Inskeep, T. D. Yonkers, G. K. Stookey, and T. H. Ewing Effect of Clindamycin Hydrochloride on Oral Malodor, Plaque, Calculus, and Gingivitis in Dogs with Periodontitis* Janice M. Warrick,
J. M. Warrick, G. A. Inskeep, T. D. Yonkers, G. K. Stookey, and T. H. Ewing Effect of Clindamycin Hydrochloride on Oral Malodor, Plaque, Calculus, and Gingivitis in Dogs with Periodontitis* Janice M. Warrick,
Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93.
 Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
Julia Collins Den 1200 Journal #4 1. Demographics Patient is J.S. age 29, Heavy/II 2. Assessment Patient had no significant findings in medical history. Her vital signs were 130/99, pulse 93. Patient does
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement
 Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Khosropanah H., et al J Dent Shiraz Univ Med Scien June; 13(2): 44-48
 Original Article The Clinical Effectiveness of Subgingival Irrigation with Povidone-Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide in Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Periodontitis Khosropanah H. a, Koohpeima F.
Original Article The Clinical Effectiveness of Subgingival Irrigation with Povidone-Iodine and Hydrogen Peroxide in Treatment of Moderate to Severe Chronic Periodontitis Khosropanah H. a, Koohpeima F.
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
FACULTY OF HEALTH SCIENCES INSTITUTE OF CLINICAL DENTISTRY
 Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
Professor Gottfried Schmalz Editor-in-Chief Clinical Oral Investigations Universität Regensburg Fakultät für Medizin Poliklinik für Zahnerhatungskunde und Parodontologie Frans-Josef-Strauss-Allee 11 93053
Reimbursement Guide. ATRIDOX Insurance Reimbursement Guide for the submission of insurance claims
 Reimbursement Guide Insurance Reimbursement Guide f the submission of insurance claims General reimbursement & submission infmation Reimbursement infmation Submission of insurance claims Pre-determination
Reimbursement Guide Insurance Reimbursement Guide f the submission of insurance claims General reimbursement & submission infmation Reimbursement infmation Submission of insurance claims Pre-determination
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient. Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club
 Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Maintenance in the Periodontally Compromised Patient Dr. Van Vagianos January 22, 2009 Charlotte Dental Hygiene Study Club Periodontal Maintenance for Natural Teeth and Implants What is Periodontal Maintenance?
Prevention and therapy of periodontal diseases and oral malodour van der Sluijs, E.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prevention and therapy of periodontal diseases and oral malodour van der Sluijs, E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van der Sluijs, E. (2017).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prevention and therapy of periodontal diseases and oral malodour van der Sluijs, E. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): van der Sluijs, E. (2017).
Periodontal (Gum) Disease
 Periodontal (Gum) Disease If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you re not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases
Periodontal (Gum) Disease If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you re not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases
significant proportion of the general population affected by this condition.
 Indian Journal of Dental Sciences. September 2013 Issue:3, Vol.:5 All rights are reserved www.ijds.in Review Article Indian Journal of Dental Sciences E ISSN NO. 2231-2293 P ISSN NO. 0976-4003 Diagnosis
Indian Journal of Dental Sciences. September 2013 Issue:3, Vol.:5 All rights are reserved www.ijds.in Review Article Indian Journal of Dental Sciences E ISSN NO. 2231-2293 P ISSN NO. 0976-4003 Diagnosis
JCDP. Original research ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 JCDP Original research Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2372 Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 by One-stage
JCDP Original research Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2372 Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 Evaluation of Clinical Periodontal Indices and Serum Interleukin-27 by One-stage
