Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting.
|
|
|
- Bryce Jennings
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting. Samuel Lee, DDS*, Grace Kang-Lee, DDS, Kwang-Bum Park, DDS, MS, PhD, Thomas Han, DDS, MS Abstract Background: The placement of dental implants in posterior maxilla is often a challenge due to pneumatization of maxillary sinus. Dental surgeons have predictably overcome these obstacles by performing bone grafting procedures such as lateral window technique (modified Caldwell-Luc). But, mobidity has been a concerned due to postoperative brusing, pain, and swelling. To reduce the mobidity, many internal (crestal) approaches to sinus grafting were introduced using osteotome, reamers, tapping drills, piezo, ISM, HSC, etc. But still, all these internal techniques for sinus grafting are difficult to predict their results because of lack of visibility when opening sinus floor and manipulating Schneiderian membrane. Purpose: Presenting a new sinus grafting technique that is systematic and predictable. This system utilizes crestal approach to reduce morbidity. Unlike the other crestal approaches to sinus grafting, the uniqueness of this system is that it is not a blind technique and the result of membrane elevation is comparable to that of lateral approach. Conclusion: The new systematic approach to internal sinus grafting is simple, predictable, without morbidity associated with lateral window technique. KEY WORDS: Sinus, grafting, Lift, dental implants, lateral window, crestal window, internal sinus lift, crestal sinus lift, sinus elevation, osteotome, Schneiderian, sinus membrane, minimally invasive sinus surgery Introduction The treatment of posterior edentulism has been a challenge for dental physicians due to a poor bone quality and quantity (due to pneumatization of maxillary sinus). We have overcome these obstacles by bone condensing and bone grafting into a maxillary sinus under the Schneiderian membrane Bone grafting into sinus have produced predictable results enabling clinicians to place longer implants for more stable prosthesis with better and long term outcome. 3 However, morbidity associated with the lateral window grafting procedure has been a concern. 5, 6, 7, 15, 17, 18 Severe brusing, swelling, and pain are the common postoperative complications due to a flap elevation beyond the mucogingival junction. 5, 6, 7, 15, 17, 18 The intraoperative complication that arises from the rupture of intraosseous branch of posterior superiorior artery (branch of maxillary artery) is panic-striken 15. Moreover, the technical nature of lateral window procedure is easily accompanied with the possibility of the Schneiderian membrane perforation while opening an window and elevating a sinus membrane. Therefore, nowadays, many internal (crestal) approaches to sinus grafting have been introduced such as osteotome 5, 6, 7, reamers 17, tapping drills 18, piezo, ISM 17, HSC 15, etc. Nevertheless, all the internal techniques for sinus grafting to this date are unpredictable for average clinicians, because of the lack of visibility when opening the sinus floor and manipulating the Schneiderian membrane. A standard diameter implant (4.0mm) has been a great solution for premolar areas, but it has some limitations in the molar area resulting a poor emergence profile 21, fracture of implants 20, crestal bone strain 19, and a narrow occlusal table. Minimum of 5mm to 8mm implants in diameter will overcome the poor bone quality by increasing the bone to implant contact surface area as well as making a superior emergence profile 21. Such diameter of implants in molar area also decreases the fracture rate of implants, crestal bone stress, and allows fabrication of a natural size occlusal table 20. 1
2 Use of wide diameter implants, which is more appropriate for molar restorations as described above, has opened a new door to sinus grafting. Crestal window, instead of lateral window, is made with trephine bur to elevate a sinus membrane and graft bone into the sinus with a direct visualization (not a blind technique like previous crestal approach techniques published). The new innovation in sinus grafting described in this paper makes sinus grafting easy and predictable, without the cost of morbidity associated with the lateral window technique. position. For example, if implant placement on #2, 3, and 4 are anticipated and #3 site is the lowest sinus floor, #3 site is used to lift sinus membrane. The rationale behind this method is that the elevation is done from the bottom to up. That being the case, this approach is easier to elevate from the lowest point. Description of the Innovation/Method Flap Elevation Incision design that is at least 2 mm more palatal than the implant position and a flap elevation that does not open beyond the mucogingival junction is recommended (figure 1). This type of incision design allows minimal pain, prevention of oral antral communication in case of perforation, unilateral retraction of flap, and an option of doing one or two stage implant placement without losing keratinized tissue. Figure 1. Palatal incision for minimal pain, prevention of oral antral communication in case of perforation, unilateral retraction of flap, and allows option of doing one or two stage implant placement without losing keratinized tissue. Location of crestal window Lowest point of sinus floor is located with an aid of panoramic radiograph (figure 2). It is more favorable if this position coincides with implant Figure 2. Internal sinus lift initiated from lowest location. Crestal window with set of specially designed trephine burs # Round windows is made on the crestal bone with a specially designed trephine bur which is 1 mm smaller in diameter than the final implant size. For example, if 6 mm implant is anticipated, 4.0 mm inner diameter and 5.0 mm outer diameter is used. Unlike the conventional trephine that uses rpm with an ample amount of irrigation, this technique utilizes a lower speed, rpm without irrigation, for that reason it is called the Waterless technique. 18 Waterless technique has many advantages of not using saline irrigation. For instance, a patient is more comfortable during the waterless procedure, a surgeon is able to collect more autogenous bone, and this technique is more friendly to vital structures such as sinus membrane, lingual plate, buccal wall, arteries, and nerves. Moreover, this technique enables implant position and angulation more precise because it is performed at a lower speed 18. Trephining at a precise location can be challenging due to a drifting nature of the trephine bur. In order to minimize heating of bone and to maximize visualization and precision of trephine bur, a newly designed pointed trephine # is used at the speed of 2
3 50 rpm without irrigation (figure 3). The pointed trephine is used to mark the location for the crestal window, and only drills into the cortical bone of the crest (figure 4). The second step of this system utilizes the trephine that has adjustable stopper #. One millimeter short of the sinus floor from the crestal ridge is estimated with an aid of radiograph, and the stopper trephine is used to set that length inside the trephine. For example, if 6 mm of bone height is anticipated, then the stopper is set at 5 mm within the trephine. Using 50 rpm speed, the stopper trephine is used to take the bone core out (figure 5). If the sinus floor is weak and relatively flat, the sinus floor will fracture off and expose the Schneiderian membrane (figure 6). However, if the sinus floor is dense or in on incline plane, it will leave about 1 mm of cortical bone (floor of sinus). to mark the position of implant not penetrating more than 2 mm. Figure 5. Stopper trephine used at 50 rpm 1 mm short of sinus floor. Figure 3. Pointed trephine to mark precise location of crestal window position. Figure 6. Flat sinus floor will be taken out with trephine bur leaving just sinus membrane most of time. If cortical bone is still intact after the use of the trephine bur, then the sinus diamond bur # is used to open the sinus floor without perforating the sinus membrane (figure 7 and 8). This is done very predictably because of the formula below: Pressure = Force / Area Figure 4. After use of pointed trephine. Pointe trephine is used The force is minimized by utilizing the stopper at the shoulder of the diamond bur. The diamond surface will grind out bone rather than cutting it. These fine bone particles will act as a buffer between the sinus membrane and the diamond bur creating a larger 3
4 surface contact, which in turn reduces the pressure on the membrane. In addition, a large diameter diamond bur is used, rather than a small one to increase the surface area, which in fact, also decreases the pressure on the Scheiderian membrane. This concept is similar to the nail bed (figure 7), that does not pucture magician s skin. osteotomy depending on the incline plane of the sinus floor. Once a slight drop into the sinus membrane is felt, the elevation of the membrane is initiated with the mushroom sinus elevator (figure 9), and it is also used to break away the remaining ledges of the bone that interfere with the sinus membrane elevation (figure 10). Subsequently, the Cobra sinus elevator # is used to further elevate the sinus membrane, and to scrape the sinus floor to promote bleeding in the sinus cavity (figure 11 and 12). figure 7. diamond bur that minimizes pressure on sinus membrane by putting minimal force and maximizing contract surface. Figure 9. elevation. Mushroom elevator to initial sinus membrane Figure 8. After the use of the sinus diamond bur. the membrane is still intact. Next, the mushroom elevator # is used as a probe to feel the sinus floor to detect any membrane exposure. Sinus floor is never flat, therefore it is common to find an initial sinus opening not on the center of osteotomy, rather on the corner of Figure 10. Mushroom elevator to break away ledge of bone that interferes with sinus elevation. 4
5 Figure 11. Cobra elevator to further elevate sinus floor distally and medially. Also used to scrape sinus floor to promote bleeding. Figure 12. vertical condensation of autogenous bone (graft collected from the trephine) only to just above residual bone height. Figure 11. Cobra elevator to further elevate sinus floor mesially and laterally. Also used to scrape sinus floor to promote bleeding. Bone Condensing The lateral condensation (figure 13) of bone is more critical than the vertical condensation (figure 12) to decrease the pressure on the sinus membrane. This method facilitates a healing time by increasing the blood supply from the lateral and medial walls, thus this leads to a better prognosis and long term success. By the way, the cross sectional slide from the CT scan is crucial to verify the elevation of lateral and medial walls rather than a dome shape graft as seen in the most internal techniques (figure 28, 30, 35). Figure 13. Lateral condensation of bone graft to increase blood supply by graft entering lateral and medial wall, instead of making dome shape grafting as seen on other internal sinus grafting procedures. Insertion of implant Skipping the last drill in the sequence of implant drills is recommended to achieve a better bone compaction and improve the initial stabilization of implant (figure 14). If an implant is loose, a larger healing cap is recommended to prevent implant dropping into sinus cavity, especially if the residual bone height is short. 5
6 Figure 14. slow insertion of implant. Under prepping osteotomy is crucial to achieve good initial stabilization. Then adjacent implants can be inserted after sufficient sinus grafting. Case report 1 This is a 29 years old female asian patient who had an extraction of #14 three months prior to implant surgery and #15 edetulism for 5 years. She is a non smoker and a healthy individual. A preoperative radiograph shows 4-6 mm of a residual bone height. Ostium is wide open and there were no signs of sinusitis. Figure 16. Cross section of sinus shows thin sinus membrane, no signs of sinus disease and patency of ostium. Sinus floor is relatively flat. The cross section of CT shows healthy sinus, but her sinus membrane is thin and gingival bio type is a thin type as well. There is no known study correlating between the gingival biotype and the thickness of a sinus membrane, but through the author s clinical experience it is observed that a thin gingival biotype tends to have a thinner sinus membrane unless he/she is a smoker. Figure 15. preoperative radiograph showing only 4-6 mm of residual bone height. figure 17. after bone core is removed sinus floor came out with it. Thin sinus membrane is observed with some bone ledge still intact (which can be removed with mushroom elevator). 6
7 The patient s sinus floor is relatively flat, thus it was expected that the sinus floor can be removed with the bone core after the use of trephine with the stopper (figure 17). Trephine at the low speed, 50 rpm ( Waterless technique ) is used to take out the bone core. The rotation of the bone core within the trephine bur is a clinical indication that the sinus floor is broken and no further apical pressure of trephine is recommended to avoid cutting the sinus membrane. Autogenous bone collected from the trephine is made into a particulate graft and condensed into the maxillary sinus. After the elevation of sinus membrane, slow bone compaction is introduced by inserting a condenser no more than the initial height of the residual bone (figure 18). Then, the lateral condensation is achieved by the use of sinus spreader (figure 19) Figure 18. vertical condensation into sinus no more than initial height of sinus floor. Figure 19. after lateral condensation with spreader. Figure 20. after suture. Notice that by doing palatal incision we have preserved attached gingiva on buccal side. Implant osteotomy is under-drilled in diameter, so a good initial stability is achieved by allowing one stage implant surgery as well as condensing a poor quality bone. Initially, we started the surgery with the palatal incision, so we have an option of doing two stage surgery with the incision line away from the implant site as well as one stage with the preservation of keratinized tissue (figure 20). Panoramic and CT scan should be taken after the surgery to verify proper grafting of maxillary sinus without perforation. It is more important to note the horizontal compaction of the bone graft touching the medial and lateral walls, which maximize the blood supply to the graft and determines the longevity of the graft after loading. 7
8 Figure 21. Postoperative radiograph. Note excellent lateral condensation of graft reaching medial and lateral wall of sinus. Case 2 This is a 53 years old male asian patient who is healthy and a non-smoker. Ostium is patent and no sign of sinus disease is detected. The lowest point on the sinus floor was located on #3 area with the residual bone height of 6.5mm. In this case, due to a high bone density of the sinus floor, the trephine core came out without the sinus floor. Sinus diamond bur was used to expose the Scheneiderian membrane safely (figure 22). Then, elevation of membrane and bone grafting was achieved using DFDBA ** mixed with autogenous bone graft (figure 22). Overgrafting was planned due to a high shrinkage rate of DFDBA ** (figure 23). Figure 23. 6X8.5mm and 4X10mm implant placed after grafting with DFDB and autogenous bone graft internally into maxillary sinus. To anticipate shrinkage, over grafting has been achieved. Case 3 This is a 60 years old asian patient who is a smoker, otherwise healthy individual. The residual bone height is only about 1.5mm on #14 site. #14 site was used to lift the sinus (because it is the lowest point), then #13 implant was placed after grafting. Sinus diamond bur is used to penetrate into the bone directly instead of using the trephine bur because the residual bone height is only 1.5 mm. figure 22. after 5 mm trephine, sinus floor was still intact. Therefore, Sinus diamond bur used to grind out the floor. Visualization of sinus membrane is clearly seen. 8
9 figure 24. after use of sinus diamond bur. Note sinus membrane on the center of the ring. Moreover, thinner residual bone height permits a better access and visualization. The elevation of membrane with the cobra elevator is easier if there is less residual bone height, because there are less interference of bone on the instrument while elevating the membrane. Movement of the Scheneiderian membrane is observed as a patient is breathing. This serves as a confirmation that the sinus membrane is intact after elevation. Then, as a final step prior to bone grafting, the cobra elevator is used to make bleeding surface inside the sinus by scraping the floor. figure 25. after elevation of membrane with mushroom elevator. After a visual confirmation of the sinus membrane exposure, the membrane elevation was done with the mushroom elevator. Then, the ledge of bone was removed with osteotomy drill at low speed using the waterless technique (figure 26). After removal of the ledge of bone, introduction of cobra elevator was possible to further elevate the sinus membrane in all directions. Bone condensed into the sinus, then implant was inserted with skipping the last drill sequence (4.3 mm diameter drill instead of 4.6 mm drill for 5.1 mm implant). A good primary stabilization was achieved (figure 27). figure 27. Postoperative radiograph showing 12 mm of elevation from #14 site. Only 1-2 mm residual bone height. figure 26. ledge of bone removed with 4.3 mm implant osteotomy drill at low speed (Waterless technique 18 ). As seen on the figure 26, the crestal window technique is easier if a residual bone height is thin. 9 figure 28. Postoperative radiograph showing good lateral condensation. Note relatively thick sinus membrane due to smoking.
10 A cross section from the CT scan shows that the medial and lateral walls are fully elevated to maximize the blood supply to the graft (figure 28). Note the thickness of the Scheneiderian membrane on the unelevated lateral and medial wall, which is usually thickened due to smoking. Case 4 This is a 53 years old patient who is healthy, but a heavy smoker. The Scheneiderian membrane is often thickened in smokers as discussed in case 3, which makes surgical elevation of membrane much more predictable. This author feels comfortable doing a sinus lift procedure if the thickness of the Scheneiderian membrane is less than 3mm, no clinical sign of sinusitis, and a patent ostium. vertical condensation (figure 30). Then, two more implants have been placed mesially on #13 and #14 area (figure 31). DFDB tends to resorb faster and cause more shrinkage than other bone graft materials; therefore, overgrafting of the material is indicated. However, advantage is that it is not too radiopaque. Therefore, when it gets replaced by a true bone, the clinician can have a visual confirmation by observing radiopacity from the newly formed bone as well and the new cortical bone formation on the new sinus floor (figure 32). figure 29. Preoperative radiograph showing lowest sinus floor around #15 with 2 mm of residual bone height. #15 site was used to elevate sinus membrane using crestal approach. figure 31. Insertion of 4X10 mm implant into #13 and #14 site after bone grafting from #15 site. figure 30. After proper sinus grafting and insertion of 6X10 mm implant. Note the graft touching medial and lateral wall of sinus wall on the cross sectional view. A preoperative radiograph shows only 2mm of bone height on #15 area (figure 29). The lowest point (#15) is used to elevate the sinus membrane and insert bone graft material. DFDB (1.5cc) was used mostly with the lateral condensation rather than the figure 32. Two year post operative showing new cortical bone formed on sinus floor confirming natural morphology of true 10
11 bone. Note shrinkage of bone graft due to faster resorbing nature of DFDB. Case 6 The is a 39 years old asian patient who does not have a history of sinusitis and is not a smoker. Ostium patency is observed on the CT scan, and there is no clinical sign of sinus disease was detected prior to surgery. However, the residual bone height is only about 2 mm around #14 and #15 area (figure 33). Under prepping of osteotomy is crucial in this case to achieve a successful initial stabilization. As discussed above, the crestal window approach is easier if the residual bone height is thin like in this case. To avoid a bone shrinkage as observed in case 5, the author used a long lasting membrane (Lambone ** ) under the Scheneiderian membrane. figure 34. after soaking resorbable membrane, Lambone, in tetracycline for 10 min, roll it up like Korean rice roll ( Kim Bap technique ) and insert into sinus cavity. figure 35. Preoperative cross section on the left and postoperative cross section on the right. Note good lateral compaction of bone against sinus wall and membrane on top of graft to protect it from shrinkage. figure 33. Preoperative panoramic radiograph showing clear sinus cavity, but severe pneumatization leaving only 1-2 mm bone height at lowest point. The crestal window in this case is only 4 mm in diameter. Therefore, insertion of the resorbable membrane is achieved by rolling the membrane ( Kim Bap Technique ) after soaking in saline with tetracycline 19 (figure 34). Lambone is tough and has an excellent plasticity, so once it is inserted into the sinus cavity via the crestal window, it will open up (go back to original shape) (figure 35). 11
12 figure 36. Postoperative radiograph after internal sinus grafting and insertion of 4X10 mm on #13, 5X10 mm on #14, and 5X10mm on #15. Discussion As shown on many clinical cases above, the new Crestal Window Technique allows elevation of the Scheneiderian membrane predictably without the mobidity associated with the lateral window technique, because the flap elevation does not extend beyond the mucogingival juction. With proper instruments (mushroom, cobra, bone carrier, vertical condenser, and lateral condenser) and tools (pointed trephine, trephine with stopper, and sinus diamond bur), the crestal window approach is predictable and results in similar outcome as the lateral window technique in terms of membrane elevation and bone condensing. However, as perforations do occur in the lateral window technique, perforations also can occur in the crestal window technique (mostly during membrane manipulation rather than during opening the crestal window). Perforation of sinus membrane In case of perforation, a primary closure is achieved since palatal incision was made. This prevents the possibility of oral antral communication especially in a case where the residual bone height is very thin. Non-resorbable membrane is recommended to be placed over the crestal window to prevent the soft tissue ingrowth. After 2-3 months after healing, a reattempt of the crestal window is most likely to be successful because a repaired sinus membrane (previously torn) is tougher in nature. Because of the low post operative discomfort associated with the procedure, patients accept the second attempt without much objection. Time to load implant The best indicator that the graft turned into a true bone without doing biopsy is an observation of new cortical bone formation on the newly formed sinus floor (figure 32). Typically it takes month for every 1 mm of bone grafting. For example, if 5 mm of bone graft elevation was done, the new cortical bone will be formed around 8 months later (3 + 5 = 8 12 months). But, this formula slightly varies depending on the buccal lingual dimension of the sinus cavity. Conclusion The new innovative Crestal Window technique is a good alternative to the conventional lateral window technique. This technique results in a similar outcome as the lateral window technique without the mobidity associated with the procedure. Unlike other crestal approach to sinus lift, it is unique in that it is not a blind technique, and it does not result in a dome shape grafting (because the membrane is fully elevated palatally and laterally before the introduction of bone graft). The only disadvantage is that it requires use of 4.5 mm or larger implant placement. However, as discussed earlier, 5.0 mm diameter or larger should be used for the molar site anyway for a better emergence profile, less risk of implant fracture, and less crestal bone stress by minimizing the bending moment force. 20 * Dr. Samuel Lee is in private practice, First Choice Dental Group, Buena Park, CA, USA. He is the inventor of the tools described in this article. Dr. Grace Kang-Lee is in private practice, First Choice Dental Group, Buena Park, CA, USA. Dr. Kwang-bum Park is in private practice, Mir Dental Hospital, Dae Gu, Korea Dr. Thomas Han, is in private practice, WPD, Los Angeles, CA, and also is clinical professor at Periodontal Department at UCLA. # All instruments mentioned above relating to Crestal Window Sinus Grafting is manufactured by Megagen Implant, Inc. ** DFDB is purchased from Pacific Coast Tissue Bank, Los Angeles, CA. Lambone is purchased from Pacific Coast Tissue Bank, Los Angeles, CA. Disclosure The author of this article is the inventor of this Crestal Window Sinus System, and has financial interest with the product. References 1. Tatum H Jr. Maxillary and sinus implant reconstruction. Dent Clin North Am 1986; 30:
13 2. Boyne PJ, James RA. Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J Oral Surg 1980; 38: Misch CE. Maxillary sinus augmentation for endosteal implants: organized alternative treatment plans. Int J Oral Implant 1987; 4: Garg JN, Quinones CR Augmentation of the maxillary sinus. A surgical technique. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 1997; 9: Summers RB. The osteotome technique: part 3 less invasive methods of the elevating the sinus floors. Compendium 1994; 15: Summers RB. The osteotome technique: part 2 the ridge expansion osteotomy (REO) procedure. Compendium 1994;15: Summers RB. A new concept in maxillary implant surgery: The osteotome technique. Compendium 1994; 15: Bori JE. A new sinus lift procedure: Sa-4/ O. Dent Implantology Update 1991; 2: Smiler DG. The sinus lift graft: basic technique and variations. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 1997; 9: Bruschi GB. Scipioni A, Calesini G, Bruschi E. Localize Management of the sinus floor with simultaneous implant Placement: a clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1998;13: Toffler M. Site development in the posterior maxilla using Osteocompression and apical alveolar displacement. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2001;22: Fugazzotto PA, De PS. Sinus floor augmentation at the time of maxillary molar extraction: success and failure rates of 137 implants in function for up to 3 years. J Periodontol 2002; 73: Winter AA, Pollack AS, Odrich RB. Placement of implants in the severely atrophic posterior maxilla using localized management of the sinus floor: a preliminary study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2002; 17: Soltan M, Smiler DG. Antral membrane balloon elevation. J Oral Implantol 2005; 31: Chen L, Cha J. An 8-year retrospective study: 1,100 patients receiving 1,557 implants using the minimally invasive hydraulic sinus condensing technique. J Periodontol 2005; 76: Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review. Ann Periodontol 2003; 8: Yamada J, Park H. Internal Sinus Manipulation (ISM) procedure: a Technical Report. Clinical Implant Dentistry and Related Research, volume 9, Number 3, Lee S, Lee G. Minimally invasive sinus grafting with autogenous bone, Implant Tribune, Feb Vol 3 Issue Petrie C et al. Increasing implant diameter resulted in 3.5-fold reduction in crestal strain. Clin Oral Impl Res ; Davarpanah M. et al, Wide diameter implants: New concepts. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2001;21; Degidi M, Piatelli A, Iezzi G, Carinci F. Wide- Diameter Implant: Analysis of Clinical Outcome of 304 Fixtures. J Periodontol 2007;78:
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Subantral Augmentation Utilizing the Zimmer. Sinus Lift Balloon Technique
 Copyright 2010 by Zimmer Dental Inc. Subantral Augmentation Utilizing the Zimmer Sinus Lift Balloon Technique Geraldo Nicolau Rodrigues, Americo Yuti Katayama, Ronald F. Cardoso The edentulous posterior
Copyright 2010 by Zimmer Dental Inc. Subantral Augmentation Utilizing the Zimmer Sinus Lift Balloon Technique Geraldo Nicolau Rodrigues, Americo Yuti Katayama, Ronald F. Cardoso The edentulous posterior
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT. simultaneous implant placement and is an alternative Summer s osteotome both clinical use as well as the
 BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift
 Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
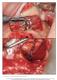 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla,
 Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
PLACEMENT OF DENTAL IMPANT IN POSTERIOR MAXILLARY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRAFT: A CASE REPORT
 CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
T he cortical bone of the maxillary
 KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
C O N T E N T S. Introduction of DASK. Crestal Approach. Lateral Approach. Dentium - For Dentists By Dentists
 C O N T E N T S Introduction of DASK Crestal Approach Lateral Approach OSTEON TM Sinus & Lifting Dentium - For Dentists By Dentists 03 Introduction of DASK Drills for Crestal Approach The distance from
C O N T E N T S Introduction of DASK Crestal Approach Lateral Approach OSTEON TM Sinus & Lifting Dentium - For Dentists By Dentists 03 Introduction of DASK Drills for Crestal Approach The distance from
DASK-0912 [Rev.3] Distributed by. DASK_rev3_1127: 레이아웃 오? 4:53 페이지 1. Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.
![DASK-0912 [Rev.3] Distributed by. DASK_rev3_1127: 레이아웃 오? 4:53 페이지 1. Specifications are subject to change without prior notice. DASK-0912 [Rev.3] Distributed by. DASK_rev3_1127: 레이아웃 오? 4:53 페이지 1. Specifications are subject to change without prior notice.](/thumbs/90/104476783.jpg) DASK_rev3_1127: 레이아웃 1 09. 12. 02 오? 4:53 페이지 1 Distributed by Specifications are subject to change without prior notice. DASK-0912 [Rev.3] HEAD OFFICE 3105 Trade Tower 159, Samsung-dong, Gangnam-gu, Seoul,
DASK_rev3_1127: 레이아웃 1 09. 12. 02 오? 4:53 페이지 1 Distributed by Specifications are subject to change without prior notice. DASK-0912 [Rev.3] HEAD OFFICE 3105 Trade Tower 159, Samsung-dong, Gangnam-gu, Seoul,
complications (Zitzmann and Schaerer,
 Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Zurich Open Repository and Archive. Sinus floor elevation using an osteotome technique without grafting materials or membranes
 University of Zurich Zurich Open Repository and Archive Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich http://www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2008 Sinus floor elevation using an osteotome technique without grafting materials
University of Zurich Zurich Open Repository and Archive Winterthurerstr. 190 CH-8057 Zurich http://www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2008 Sinus floor elevation using an osteotome technique without grafting materials
Sinus elevation with short implant
 Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
CONTENTS. Introduction to DASK. Crestal Approach. Lateral Approach
 Specifications are subject to change without notice. Sales office: 11075 Knott Ave., Suite A Cypress, CA 90630 Tel 1-877-304-6752 Fax 1-714-890-6360 Homepage / E-mail: www.dentiumusa.com / info@dentiumusa.com
Specifications are subject to change without notice. Sales office: 11075 Knott Ave., Suite A Cypress, CA 90630 Tel 1-877-304-6752 Fax 1-714-890-6360 Homepage / E-mail: www.dentiumusa.com / info@dentiumusa.com
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery
 An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
SCA Kit Sinus Crestal Approach Kit
 SCA Kit Sinus Crestal Approach Kit Introduction 3S of SCA Kit SCA Kit Composition Component(I-drill) Component(S-Reamer) Component(Stopper) Component(Depth Gauge) Component(Bone carrier) Component(Bone
SCA Kit Sinus Crestal Approach Kit Introduction 3S of SCA Kit SCA Kit Composition Component(I-drill) Component(S-Reamer) Component(Stopper) Component(Depth Gauge) Component(Bone carrier) Component(Bone
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
IJCMR 73. REVIEW ARTICLE Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgeries: An Overview
 IJCMR 73 REVIEW ARTICLE Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgeries: An Overview Riddhi Katara, 1 D. Gopalakrishnan, 2 Tuhina Tyagi, 1 Disha Kataria, 1 Gurbani Kaur, 1 Archana Singh 3 ABSTRACT Maxillary
IJCMR 73 REVIEW ARTICLE Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgeries: An Overview Riddhi Katara, 1 D. Gopalakrishnan, 2 Tuhina Tyagi, 1 Disha Kataria, 1 Gurbani Kaur, 1 Archana Singh 3 ABSTRACT Maxillary
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation
 42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re. Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T
 Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
03 Best combination for thin ridge
 MILAkit TM BonEx kit TM 03 Best combination for thin ridge Joel A. Gonzales RDA Product Specialist Email: Cell: joelg@megagenus.com (480) 440-3927 Thor MEGAGEN Implant 28 29 Why Thor? 1. Simple & Strong
MILAkit TM BonEx kit TM 03 Best combination for thin ridge Joel A. Gonzales RDA Product Specialist Email: Cell: joelg@megagenus.com (480) 440-3927 Thor MEGAGEN Implant 28 29 Why Thor? 1. Simple & Strong
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Crestal endoscopic approach for evaluating sinus membrane elevation technique
 Elian and Barakat International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2018) 4:15 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0126-6 International Journal of Implant Dentistry TECHNICAL ADVANCES ARTICLE Crestal endoscopic
Elian and Barakat International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2018) 4:15 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40729-018-0126-6 International Journal of Implant Dentistry TECHNICAL ADVANCES ARTICLE Crestal endoscopic
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
English. Perfectly in tune. Satelec Surgical Tips
 English Perfectly in tune Satelec Surgical Tips SATELEC, World Leader - Inventor of the piezoelectric technology applied to dentistry, - Constant R&D investments, in partnership with clinicians, universities
English Perfectly in tune Satelec Surgical Tips SATELEC, World Leader - Inventor of the piezoelectric technology applied to dentistry, - Constant R&D investments, in partnership with clinicians, universities
The Uniti implant system is designed to be simple to learn and use. A seamless surgical protocol renders the system user friendly.
 Surgical Manual The Uniti implant system is designed to be simple to learn and use. A seamless surgical protocol renders the system user friendly. For the experienced practitioner it will take no more
Surgical Manual The Uniti implant system is designed to be simple to learn and use. A seamless surgical protocol renders the system user friendly. For the experienced practitioner it will take no more
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation Vol. 3, No. 1, January 2011
 SHORT DENTAL IMPLANTS IN THE MAXILLAR SINUS FLOOR TRANSCRESTAL ELEVATION Valentin Topalo 1, Fahim Atamni 2 1 Ph. D, Professor 2 Doctor of Medicine, Postdoctorand Orthopedic Dentistry, Oromaxillofacial
SHORT DENTAL IMPLANTS IN THE MAXILLAR SINUS FLOOR TRANSCRESTAL ELEVATION Valentin Topalo 1, Fahim Atamni 2 1 Ph. D, Professor 2 Doctor of Medicine, Postdoctorand Orthopedic Dentistry, Oromaxillofacial
Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3.
 DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
Clinical Perspectives
 Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
Clinical Perspectives Inside This Issue: Revised Drilling Guidelines For Parallel Walled Implants Case Presentation By: Pär-Olov Östman, DDS, PhD, MD Volume 8, Issue 1 Recommended Drilling Guidelines For
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Pre op Failed endodontic treatment with sinus involvement.
 Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
Case #1 of 10 consecutive extraction sockets grafted with Socket Graft Putty, covered with Socket Seal and sealed with Periacryl. I D # HEU This patient is a 66 year old female. Pre op Failed endodontic
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
continuing education 2
 continuing education 2 Sinus Augmentation Osteotome Sinus Augmentation with Less Than 5 mm of Native Bone: A Membrane Visualization Technique Using a Tapered Platform-Switching Implant David Anson, DDS;
continuing education 2 Sinus Augmentation Osteotome Sinus Augmentation with Less Than 5 mm of Native Bone: A Membrane Visualization Technique Using a Tapered Platform-Switching Implant David Anson, DDS;
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Young-Jin Park, DDS,* and Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
DIOnavi. Brochure Ver.2. Product Introduction: DIOnavi. Clinical Case Report
 DIOnavi. Brochure Ver.2 Product Introduction: DIOnavi. Clinical Case Report Evolved for Precision and Stability Digital Navigation Implant 04 Product Introduction: DIOnavi. One-Step Protocol 10 Clinical
DIOnavi. Brochure Ver.2 Product Introduction: DIOnavi. Clinical Case Report Evolved for Precision and Stability Digital Navigation Implant 04 Product Introduction: DIOnavi. One-Step Protocol 10 Clinical
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up
 Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Enhancing implant stability with osseodensification a case report with 2-year follow-up Dr. Salah Huwais discusses how osseodensification facilitates ridge expansion with enhanced implant stability Introduction
Effectively restoring a grossly atrophic maxilla
 Augmentation Grafting of the Maxillary Sinus and Simultaneous Implant Placement in Patients with 3 to 5 mm of Residual Alveolar Bone Height Michael Peleg, DMD*/Ziv Mazor, DMD**/Arun K. Garg, DMD*** This
Augmentation Grafting of the Maxillary Sinus and Simultaneous Implant Placement in Patients with 3 to 5 mm of Residual Alveolar Bone Height Michael Peleg, DMD*/Ziv Mazor, DMD**/Arun K. Garg, DMD*** This
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Nabil Nadji A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE
 CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF SHORT IMPLANTS PLACED IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA WITH THE INDIRECT SINUS ELEVATION TECHNIQUE AND IN THE POSTERIOR MANDIBLE: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY WITH UP TO 5-YEAR FOLLOW-UP. by Nabil
CLINICAL OUTCOMES OF SHORT IMPLANTS PLACED IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA WITH THE INDIRECT SINUS ELEVATION TECHNIQUE AND IN THE POSTERIOR MANDIBLE: A RETROSPECTIVE STUDY WITH UP TO 5-YEAR FOLLOW-UP. by Nabil
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes
 Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Innovative Sinus Lift Technology
 Dynamic Implant Valve Approach Innovative Sinus Lift Technology UpHeal Dental Ltd. >> DIVA Sinus Lift Technology is here! DIVA s Unique Features and Innovations: > > DIVA is a new sinus lift technology
Dynamic Implant Valve Approach Innovative Sinus Lift Technology UpHeal Dental Ltd. >> DIVA Sinus Lift Technology is here! DIVA s Unique Features and Innovations: > > DIVA is a new sinus lift technology
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Sinus Floor Elevation. Treatment Concepts
 Sinus Floor Elevation Treatment Concepts Geistlich Family supports your way to regeneration together for more satisfied patients Dr. Andreas Geistlich CONTENTS 3 Maxillary sinus floor augmentation 4 5
Sinus Floor Elevation Treatment Concepts Geistlich Family supports your way to regeneration together for more satisfied patients Dr. Andreas Geistlich CONTENTS 3 Maxillary sinus floor augmentation 4 5
Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs
 Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Surgical Manual. Step By Step Techniques
 Surgical Manual Step By Step Techniques Table of Contents Pre-Surgical 1 8 Measurement of Bone 2 Bone Classification 3 Implant Size Selection 4 5 Surgical Template Fabrication 6 8 Instrumentation 9 11
Surgical Manual Step By Step Techniques Table of Contents Pre-Surgical 1 8 Measurement of Bone 2 Bone Classification 3 Implant Size Selection 4 5 Surgical Template Fabrication 6 8 Instrumentation 9 11
4766 Research Dr. San Antonio, TX insightdentalsystems.com
 OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
OVERVIEW OF THE INSIGHT DENTAL IMPLANT DELIVERY SYSTEM The IDS system comes in a unit dose implant system where its advantage provides sterile instrumentation in one single-use kit. It is organized to
Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft
 The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
Ridge Split Procedure
 Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Ridge Split Procedure in the Atrophic Maxilla Udatta Kher B.D.S., M.D.S. Loss of teeth causes extensive resorption of the alveolar ridge. In the maxilla the resorption pattern occurs towards the midline,
Immediate Implant Placement With Ridge Split in A Siebert's Class 1 Defect - A Case Report
 Immediate Implant Placement With Ridge Split in A Siebert's Class 1 Defect - A Case Report Arjun. M. R 1, Nandini Manjunath 2 1, 2 Department of Periodontics, A. J. Institute of Dental Sciences, India
Immediate Implant Placement With Ridge Split in A Siebert's Class 1 Defect - A Case Report Arjun. M. R 1, Nandini Manjunath 2 1, 2 Department of Periodontics, A. J. Institute of Dental Sciences, India
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Comparison of Lateral Window and Osteotome Techniques in Sinus Augmentation: Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation
 Original Article Comparison of Lateral Window and Osteotome Techniques in Sinus Augmentation: Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation N. Esfahanizadeh 1, A. R. Rokn 2, M. Paknejad 3, P. Motahari
Original Article Comparison of Lateral Window and Osteotome Techniques in Sinus Augmentation: Histological and Histomorphometric Evaluation N. Esfahanizadeh 1, A. R. Rokn 2, M. Paknejad 3, P. Motahari
The Internatonal Journal of Periodontics & Restoraive Dentistry
 The Internatonal Journal of Periodontics & Restoraive Dentistry 3 Incisive Vessel Based Palatal Flap for the Reconstruction of Anterior Maxillary Soft Tissues [Au: Text has been edited heavily. Please
The Internatonal Journal of Periodontics & Restoraive Dentistry 3 Incisive Vessel Based Palatal Flap for the Reconstruction of Anterior Maxillary Soft Tissues [Au: Text has been edited heavily. Please
Product Catalog. Others make Implants to sell... Tatum Surgical makes Implants to treat your Patients.
 Product Catalog Others make Implants to sell... Tatum Surgical makes Implants to treat your Patients. Advantages of Tatum Implant System: 1. Only one surgical procedure is required to place and load the
Product Catalog Others make Implants to sell... Tatum Surgical makes Implants to treat your Patients. Advantages of Tatum Implant System: 1. Only one surgical procedure is required to place and load the
Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane
 10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation. Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics
 A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
Annals of Dental Research
 P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S.
 THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
One in four sinus lift procedures can be
 11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
SURGICAL MANUAL. Step By Step Techniques
 SURGICAL MANUAL Step By Step Techniques TABLE OF CONTENTS PRE-SURGICAL 1 8 MEASUREMENT OF BONE.......................... 2 BONE CLASSIFICATION........................... 3 IMPLANT SIZE SELECTION.........................
SURGICAL MANUAL Step By Step Techniques TABLE OF CONTENTS PRE-SURGICAL 1 8 MEASUREMENT OF BONE.......................... 2 BONE CLASSIFICATION........................... 3 IMPLANT SIZE SELECTION.........................
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
Typically, the posterior maxilla demonstrates
 CASE LETTER Trephine Core: An Alternative Sinus Lift Technique Lanka Mahesh, BDS, MS 1 Gregori M. Kurtzman, DDS, MAGD, DICOI 2 * Sagrika Shukla, BDS 3 INTRODUCTION Typically, the posterior maxilla demonstrates
CASE LETTER Trephine Core: An Alternative Sinus Lift Technique Lanka Mahesh, BDS, MS 1 Gregori M. Kurtzman, DDS, MAGD, DICOI 2 * Sagrika Shukla, BDS 3 INTRODUCTION Typically, the posterior maxilla demonstrates
IMPACTED CANINES. Unfortunately, this important tooth is the second most common tooth to be impacted after third molars
 IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
IMPACTED CANINES After we talked about impacted third molars, today we ll discuss about maxillary impacted canines in upper dental arch, how to manage these cases as a dental surgeon. You will study about
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Redefining Regeneration
 Redefining Regeneration Taking Volume to the MAX One Product, One Treatment, Real VOLUME Buccal Bone Loss Socket Preservation Lateral / Vertical Augmentation Grafting Material Scaffold Barrier (4-6 months)
Redefining Regeneration Taking Volume to the MAX One Product, One Treatment, Real VOLUME Buccal Bone Loss Socket Preservation Lateral / Vertical Augmentation Grafting Material Scaffold Barrier (4-6 months)
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 1. Implant Locations. Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla. Anatomy and risk factors Option 1: Short implants
 T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
Derma S O F T T I S S U E A U G M E N TAT I O N. Acellular dermal matrix
 Derma A XENOGENIC GRAFT FOR S O F T T I S S U E A U G M E N TAT I O N Acellular dermal matrix A xenogenic graft for soft tissue augmentation CHARACTERISTICS Obtained from derma of porcine origin, using
Derma A XENOGENIC GRAFT FOR S O F T T I S S U E A U G M E N TAT I O N Acellular dermal matrix A xenogenic graft for soft tissue augmentation CHARACTERISTICS Obtained from derma of porcine origin, using
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review of Anatomy and Lateral Sinus Lift Technique
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. 2016), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. 2016), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review
Periodontal Disease. Radiology of Periodontal Disease. Periodontal Disease. The Role of Radiology in Assessment of Periodontal Disease
 Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Radiology of Periodontal Disease Steven R. Singer, DDS srs2@columbia.edu 212.305.5674 Periodontal Disease! Includes several disorders of the periodontium! Gingivitis! Marginal Periodontitis! Localized
Flapless Dental Implantation using Cortex Implants
 Flapless Dental Implantation using Cortex Implants By Dr. Meir Mamraev DMD LLB W e P r o v e I t E v e r y D a y The following case study discusses the flapless implant surgery approach using the Cortex
Flapless Dental Implantation using Cortex Implants By Dr. Meir Mamraev DMD LLB W e P r o v e I t E v e r y D a y The following case study discusses the flapless implant surgery approach using the Cortex
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
