Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma: A Case Report and Review of Literature S. Moghe, M.K. Gupta, A. Pillai, A. Maheswari
|
|
|
- Christiana Carr
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Report Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma: A Case Report and Review of Literature S. Moghe, M.K. Gupta, A. Pillai, A. Maheswari Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, People s Dental Academy, People s University, Bhopal (Received January, 2013) (Accepted June, 2013) Abstract: Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma or so called Giant cell epulis is the most common oral giant cell lesion.it usually presents as a purplish-red soft tissue nodule consisting of multinucleated giant cells in a background of mononuclear stromal cells and extravasated red blood cells. This lesion probably does not represent a true neoplasm but it may be a reactive in nature which is believed to be stimulated by local irritation or trauma, but the cause is not known with certainty. A case of peripheral giant cell granuloma arising at the left maxillary premolar region in a 18 year old boy is being reported here. The lesion was completely excised upto the periosteum level; there was no residual or recurrence of swelling or bony defect apparent in the area of biopsy after a follow-up period of 1 year. Key Words: Peripheral giant cell Granuloma, Epulis. Introduction: Peripheral giant cell granuloma (PGCG) is the most common oral giant cell lesion as a soft tissue extra-osseous purplish-red nodule. This lesion is probably not a true neoplasm but could be a reactive in nature. The initiating stimulus is believed to be due to local irritation or trauma but the cause is not known with certainity. It has also been termed as a peripheral giant cell reparative granuloma; but whether it is in fact reparative, has not been established and their osteoclastic activity appears doubtful. Their membrane receptors for calcitonin, demonstrated by immuno -histochemistry and their osteoclastic activity when cultured in vitro are evidence that they are osteoclasts (Bonetti et al, 1990; Lim & Gibbins 1995; Mighell et al, 1996), whereas other authors have suggested that the lesion is formed by cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system (Carvalho et al, 1995). The PGCG bears a close microscopic resemblance to the central giant cell granuloma, and hence some pathologists believe that it may represent a soft tissue counterpart of the central bony lesion (Katsikeris et al, 1988). The lesion can be sessile or pedunculated, penetrating through periodontal membrane and may or may not be ulcerated. Occasionally lesions arise from the periosteum overlying edentulous area. Secondary ulceration due to trauma may give the lesions a focal yellow zone caused by the formation of fibrin clot over the ulcer Corresponding Author: Dr. Swapnil Moghe, Sr. Lecturer, Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, People s Dental Academy, People s University, Bhopal Phone No. : , swap2112@gmail.com Lesions can become large, sometimes attaining a size upto 2 cm. The clinical appearance is similar to the more common pyogenic granuloma, although the PGCG is often more bluish-purple as compared with the bright-red colour of a typical pyogenic granuloma. Recently, the PGCG associated with dental implants has been reported (Hirshberg et al, 2003). Although the PGCG develops within soft tissue, superficial resorption of the underlying alveolar bony crest is sometimes seen. On occasion, it may be difficult to determine whether the mass arose as a peripheral lesion or a central giant cell granuloma eroding through the cortical plate into the gingival soft tissues (Chadwick et al, 1989; Giansanti & Waldrom, 1969). Rarely a giant cell epulis may be due to hyperparathyroidism, representing the so-called osteoclastic brown tumours associated with this endocrine disorder (Smith et al, 1988; Burkes & White, 1989) and is then likely to be associated with other lesions in bones and changes in the blood chemistry. The extra-osseous lesions of cherubism involving the gingiva appear very similar to giant cell epulide. However, the other distinctive clinical and radiological features of cherubism indicate the correct diagnosis (Odell & Morgan, 1998). Histologically, PGCG is composed of nodules of multinucleated giant cells in a background of plump ovoid and spindle-shaped mesenchymal cells and extravasated red blood cells. The giant cells may contain only a few nuclei or up to several dozen. Some of them are large, vesicular nuclei; others are small, pyknotic nuclei. The origin of the giant cell is unknown. People s Journal of Scientific Research 55
2 Case Report A 18 year old boy was referred to the Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, People s Dental Academy, Bhopal for an non-tender exophytic lesion in the left maxillary premolar region since May, 2010 (Fig. I). Since then the lesion had gradually increased in size. It bled from time to time but the patient did not seek any treatment. The patient had no significant medical history. The clinical differential diagnoses included PGCG, pyogenic granuloma and haemangioma. The excisional biopsy was undertaken upto the periosteum level under local anaesthesia, and Fig. III: Irritational factor as seen during exploration of lesion. Fig. I: A red exophytic, non-painful lesion arising in the maxillary left premolar area haemostasis was achieved by electrocautery and Surgicel. The irritational factor was seen during exploration of lesion (Fig. III).To prevent recurrence of tumour, denuded bone was treated with Carnoy s solution. Chlorhexidine mouth rinse was prescribed post-operatively twice a day for 7 days. On gross examination, the excised nodule was red in colour and measured 30 x 20 x 35mm in maximum dimension. There was periodontal bone loss in the maxillary left canine region (Fig. II). Due to the extensive nature of lesion, there was displacement of maxillary left canine. Histologically, the overlying epithelium was composed of aggregates of multinucleated giant cells Fig. II: Bone loss associated with the lesion, as seen on the occlusal view. Fig. IV. Photomicrograph showing aggregates of multinucleated giant cells in a background of mononuclear stromal cells, extravasated erythrocytes and deposits of haemosiderin (H & E Stain, 100X). People s Journal of Scientific Research 56
3 in a background of mononuclear stromal cells, extravasated red blood cells and deposits of haemosiderin (Fig. IV). After a period of 6 months, no residual or recurrence of swelling or bony defect was seen. The patient was then referred to the Department of Prosthodontics and the Department of Periodontics for a new partial denture and periodontal treatment. Discussion: The etiology and nature of PGCG (giant cell epulide) still remains undecided. In the past, several hypotheses had been proposed to explain the nature of multinucleated giant cells, one of them is that they are osteoclasts left from physiological resorption of teeth or reaction to injury to periosteum. Now there is a strong evidence that these cells are osteoclasts as they have been shown to possess receptors for calcitonin and were able to excavate bone in vitro (Flanagan et al 1988). The study of Lim & Gibbins (1995) confirmed that the multinucleated giant cells reacted strongly for a monoclonal antibody (MB1) which reacts with lymphocytes and a proportion of T cells and monocytes. The MB1 antibody has previously been shown to be expressed by osteoclasts in fetal bone. Interestingly, the re-expression of the blood vessels in the lesion for the widely used endothelial cell marker factor VIII related antigen had failed to demonstrate the presence of blood vessels other than on the periphery of the lesion although these lesions appear to be extremely vascular in nature. There is also a growing body of opinion that giant cells may simply represent a reactionary component of the lesion and are derived via blood stream from bone marrow mononuclear cells and may be present only in response to an yet unknown stimulus from the stroma. This concept is based on the results of some more recent studies using cell culture and transplantation (el Mofty & Osdoby, 1985; Cohen et al, 1988) in which the giant cells have been found to be short lived and to disappear early in culture in contrast to the active proliferation of the stromal cells. A study by Wulling et al (2001) revealed that the stromal cells secrete a variety of cytokines and differentiation factors, including Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP1), Osteoclast differentiation factor (ODF), and Macrophage-colony stimulating factor (M-CSF). These molecules are monocyte chemo-attractants and are essential for osteoclast differentiation, this suggest that the stromal cell stimulates blood monocyte immigration into tumour tissue and enhances their fusion into osteoclast like multinucleated giant cells. Further more, the recently identified membrane-bound protein family a disintegrin and metalloprotease (ADAM) is considered to play a role in the multinucleation of osteoclasts and macrophage derived giant cells from mononuclear precursor cells (Abe et al, 1999). In a recent study by Liu et al (2003), in situ hybridization was carried out to detect the mrna expression of the receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL), that is shown to be essential in the osteoclastogenesis, its receptor RANKL and its decoy receptor osteopritegrin (OPG). They concluded that RANKL and OPG expressed in these lesions may play on important role in the formation of multinucleated giant cells. There are no pathognomonic clinical features whereby these lesions can be differentiated from other forms of gingival enlargement including pyogenic granuloma, fibrous epulis, peripheral ossifying fibroma, inflammatory fibrous hyperplasia, peripheral odontogenic fibroma, hemangiomacaverosum and papilloma. Microscopic examination is required for the definitive diagnosis(carranza & Hogan, 2012; Chaparro-Avendano et al, 2005). Generally, this lesion is clinically indistinguishable from a pyogenic granuloma, although a PGCG is more likely to cause bone resorption than pyogenic granuloma, the differences are otherwise minimal (Regezi et al, 2008). Microscopically, the lesion arises from, or is at least attached to the periodontal ligament or mucoperiosteum. The most characteristic histological features include a non-encapsulated highly cellular mass with abundant giant cells, inflammation, interstitial hemorrhage, hemosiderin deposits and mature bone or osteoid. Fibroblasts are the basic element of peripheral giant cell granulomas. Scattered among the plump, young fibroblasts are numerous multinucleated giant cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm which appear to be non-functional in the usual sense of phagocytosis and bone resorption(regezi et al, 2008). Two types of giant cells are mainly found, one representing metabolically active cells (Type I) and the other representing dying cells (Type II). The origin of these cells has not been defined yet. However, a striking similarity between these cells and osteoclasts does exist (Katsikeris et al, 1988). Both the type of People s Journal of Scientific Research 57
4 cells consists of multiple, large, ovoid, vesicular, somewhat translucent nuclei with prominent nucleoli and the nuclear chromatin was located peripherally on distinct nuclear membrane. Type I cells vary in size, often exceeding 100µ in diameter.the type II cells are fewer in number, have smaller and more irregular nuclei than type I. The nucleoli are not easily seen and the cytoplasm stains deeply eosinophilic and granular than the type I cells (Bhaskar et al, 1971). Despite ultrastructural studies, the true nature of the giant cells in PGCG remains debatable (Bonetti et al, 1990).Inflammation is a constant finding but is varied not only in degree but also in location. The inflammatory cells consist primarily of lymphocytes, plasma cells, histiocytes and occasional polymorphonuclear cells. Rarely, ulceration was an associated feature (Bhaskar et al, 1971). Vascular proliferation, especially capillary, was found in a study of Peralles et al (2006). Calcified tissue which is found in some of the lesions varying from small amorphous foci to well developed trabeculae (Bhaskar et al, 1971). The woven bone or lamellar bone is thought to be produced by mononuclear stromal cells, which resemble latent proliferative osteoblasts or osteoprogenitor cells. Thus, it is not surprising that woven bone and lamellar bone are formed in PGCG (Dayan et al, 1990). No correlation was found between amount of bone with location or reported duration of the lesion (Giansanti & Waldron, 1969). The histologic appearance is similar to that of a giant cell granuloma of the jaw, but for the fact that the epulis has a covering of stratified squamous epithelium (Regezi et al, 2008). In rare instances, both a soft tissue and intraosseous lesion can co-exist. The overlying mucosal surface is ulcerated in about 50% cases. A clear zone of dense fibrous connective tissue usually separates the giant cell proliferation from the mucosal surface (Neville et al, 2009). Treatment consists of local surgical excision down to the underlying bone, for extensive clearing of the base (Neville et al, 2009).Removal of local factors or irritants is also required(regezi et al, 2008). If resection is only superficial, the growth may recur. Exposure of all bony walls following thorough surgical resection responds satisfactorily most of the times. Recurrence rate of % (average 9.9%) has been reported in various epidemiologic studies (Mighell et al, 1996). A recurrence rate of 5% has been reported by Giansanti & Waldron (1969). Recurrence is believed to be related to lack of inclusion of the periosteum or periodontal ligament in the excised specimen (Regezi et al, 2008). A re-excision must be performed for these cases (Neville et al, 2009). Aggressive tendencies or malignant transformation of these lesions has never been reported (Katsikeris et al, 1988). The treatment rendered in this case was surgical excision to the bone, chemical cauterization and curettage followed by oral prophylaxis.the 1 year follow-up has shown no recurrence indicating that the given treatment along with maintenance of a good oral hygiene is sufficient to treat PGCG. References: 1. Abe E, Mocharla H, Yamate T, Taguchi Y. Monolages SC: Meltrin-alpha, a fusion protein involved in multinucleated giant cell and osteoclast formation. Calcified Tissue International, 1999;64(6): Bhaskar SN, Cutright DE, Beasley JD, Perez B: Giant cell reparative granuloma (peripheral): report of 50 cases. Journal of Oral Surgery, 1971;29(2): Bonetti F, Pelosi G, Martignoni G, Mombello A, Zamboni G, Pea M, Scarpa A, Chilosi M: Peripheral giant cell granuloma: evidence for osteoclastic differentiation. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine & Oral Pathology, 1990;70(4): Burkes EJ (Jr.), White RP (Jr.): A peripheral giant-cell granuloma manifestation of primary hyperparathyroidism: report of case. Journal of the American Dental Association, 1989;118(1): Carranza FA, Hogan EL: Peridontal Pathology-Gingival Enlargements. In: Carranza s Clinical Periodontology. MG Newman, H Takei, PR Klokkevold, RA Rarranga (Eds.); 10 th Edn.; Elsevier Saunders, St Louis; 2012.pp Carvalho YR, Loyola AM, Gomez RS, Araujo VC: Peripheral giant cell granuloma. An immunohistochemical and ultrastructural study. Oral Diseases, 1995;(1)1: Chadwick BL, Crawford PJ, Aldred MJ: Massive giant cell epulis in a child with familial cyclic neutropenia. British Dental Journal, 1989;16(8): Chaparro-Avendano AV, Berini-Aytés L, Gay-Escoda C: Peripheral giant cell granuloma. A report of five cases and review of literature. Medicina Oral, Patologia, Oral & Cirugia Buccal, 2005;10(1): Cohen MA, Grossman ES, Thompson SH: Features of central giant cell granuloma of the jaws xenografted in nude mice. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine & Oral Pathology, 1988;66(2): Dayan D, Buchner A, Spirer S: Bone formation in Peripheral giant cell granuloma. Journal of Periodontology, 1990; 61(7): People s Journal of Scientific Research 58
5 11. Eversole LR, Rovin S: Reactive lesions of the gingiva. Journal of Oral Pathology, 1972;1(1): el-mofty SK, Osdoby P: Growth behavior and lineage of isolated and cultured cells derived from giant cell granuloma of the mandible. Journal of Oral Pathology, 1985;14(7): Flanagan AM, Nui B, Tinkler SM, Horton MA, Williams MD, Chambers DJ: The multinucleated giant cell granulomas of the jaws are osteoclasts. Cancer, 1988;62(6): Giansanti JS, Waldron CA: Peripheral giant cell granuloma: review of 720 cases. Journal of Oral Surgery, 1969;17(10): Hirshberg A, Kozlovsky A, Schwartz-Arad D, Mardinger O, Kaplan I: Peripheral giant cell granuloma associated with dental implants. Journal of Periodontology, 2003;74(9): Katsikeris N, Kakarantza-Angelopoulou E, Angelopoulos AP: Peripheral giant cell granuloma. Clinicopathologic study of 224 new cases and review of 956 reported cases. International Journal of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery, 1988;17(2): Lim L, Gibbins JR: Immunohistochemical and ultra structural evidence of a modified microvasculature in the giant cell granuloma of the jaws. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology, Oral Radiology & Endodontics, 1995;79(2): Liu B, Yu SF, Li TJ: Multinucleated giant cells in various forms of giant cell containing lesions of the jaws express features of osteoclasts. Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine, 2003; 32(6): Mighell AJ, Robinson PA, Hume WJ: PCNA and Ki-67 immunoreactivity in multinucleated cells of giant cell fibroma and peripheral giant cell granuloma. Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine, 1996; 25(5): Neville B, Allen CM, Damm DD, Bouquot JE: Soft Tissue Tumors. In: Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology. 3 rd Edn.; Elsevier Saunders, St. Louis; 2009.pp Odell EW, Morgan PR: Biopsy Pathology of the Oral Tissues (Biopsy pathology series 22). Chapman & Hall Medical, London, 1998.pp Peralles PG, Viana APB, Azevedo ALR, Pires FR: Gingival and alveolar hyperplastic reactive lesions: clinicopathological study of 90 cases. Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences, 2006; 5(18): Regezi JA, Sciubba JJ, Jordan RCK. Red-Blue lesions: In: Oral Pathology: Clinical Pathologic Correlations. 5 th Edn.; Elsevier Saunders, St. Louis; 2008.pp Smith BR, Fowler CB, Svane TJ: Primary hyperparathyroidism presenting as a peripheral giant cell granuloma. Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, 1988;46(1): Wulling M, Engels C, Jesse N, Werner M, Delling G, Kaiser E: The nature of giant cell tumor of bone. Journal of Cancer Research & Clinical Oncology, 2001;127(8): Source of Support : Nil. Conflict of Interest: None declared. People s Journal of Scientific Research 59
Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child
 Volume 2016, Article ID 7536304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7536304 Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child Afsaneh Nekouei, Alireza Eshghi,
Volume 2016, Article ID 7536304, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7536304 Case Report A Review and Report of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a 4-Year-Old Child Afsaneh Nekouei, Alireza Eshghi,
Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma A Review and Case Report
 Case Report Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma A Review and Case Report Dr. Somya Maheshwari *, Dr. Girish Bhutada, Dr Vaishakhi Baisane, Dr Devendra Palve Name & Address of Institution: Swargiya Dadasaheb
Case Report Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma A Review and Case Report Dr. Somya Maheshwari *, Dr. Girish Bhutada, Dr Vaishakhi Baisane, Dr Devendra Palve Name & Address of Institution: Swargiya Dadasaheb
Clinical Presentation and Management of Peripheral Giant Cell Granulomas in Children: 2 Cases Report
 10.1515/bjdm-2016-0007 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Clinical Presentation and Management of Peripheral Giant Cell Granulomas in Children: 2 Cases Report SUMMARY
10.1515/bjdm-2016-0007 BALKAN JOURNAL OF DENTAL MEDICINE ISSN 2335-0245 STOMATOLOGICAL SOCIETY Clinical Presentation and Management of Peripheral Giant Cell Granulomas in Children: 2 Cases Report SUMMARY
Reactive Hyperplastic Lesions of the Gingiva: A Retrospective Study of 260 Cases
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1142 Sangeetha Ramu, Charlotte Rodrigues ORIGINAL RESEARCH Reactive Hyperplastic Lesions of the Gingiva: A Retrospective Study of 260 Cases Sangeetha Ramu, Charlotte Rodrigues
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1142 Sangeetha Ramu, Charlotte Rodrigues ORIGINAL RESEARCH Reactive Hyperplastic Lesions of the Gingiva: A Retrospective Study of 260 Cases Sangeetha Ramu, Charlotte Rodrigues
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report
 Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
Case Report Article Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma of the Maxilla: Case Report José Carlos Martins Junior*, Frederico Santos Keim**, Mariana Schmidt Kreibich**. * Oral and maxillofacial surgeon at Hospital
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses. Gingival Lesions
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Masses Gingival Lesions Gingival/Alveolar Ridge Masses Parulis Periodontal Abscess Tori and Exostoses Reactive Proliferations Peripheral Odontogenic Cysts Peripheral Odontogenic
Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma Mimicking Pyogenic Granuloma -A Case Report
 American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics Case Report Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma Mimicking Pyogenic Granuloma -A Case Report Sivakumarashankari, Gaurav*, Jayanthi K and Kamala R Dept.
American Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics Case Report Peripheral Ossifying Fibroma Mimicking Pyogenic Granuloma -A Case Report Sivakumarashankari, Gaurav*, Jayanthi K and Kamala R Dept.
Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child: A Case Report
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 370242, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2012/370242 Case Report A Giant Cell Fibroma and Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia in a Young Child:
PERIPHERAL'GIANT'CELL' GRANULOMA:'A'CASE'REPORT)
 KOTA,Kasim* KODANDA,Ram* JAISEKHARAN,VP* PERIPHERALGIANTCELL GRANULOMA:ACASEREPORT ABSTRACT Peripheral giant cell granuloma(pgcg is a non neoplastic reactive lesionofthegingiva,originatingfromtheperiosteumorperiodontal
KOTA,Kasim* KODANDA,Ram* JAISEKHARAN,VP* PERIPHERALGIANTCELL GRANULOMA:ACASEREPORT ABSTRACT Peripheral giant cell granuloma(pgcg is a non neoplastic reactive lesionofthegingiva,originatingfromtheperiosteumorperiodontal
Clinical and Histologic Features of 26 Canine Peripheral Giant Cell Granulomas (Formerly Giant Cell Epulis)
 Diagnostic Pathology Clinical and Histologic Features of 26 Canine Peripheral Giant Cell Granulomas (Formerly Giant Cell Epulis) Veterinary Pathology 49(6) 1018-1023 ª The Author(s) 2012 Reprints and permission:
Diagnostic Pathology Clinical and Histologic Features of 26 Canine Peripheral Giant Cell Granulomas (Formerly Giant Cell Epulis) Veterinary Pathology 49(6) 1018-1023 ª The Author(s) 2012 Reprints and permission:
Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
 Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects Original Article Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects Original Article Correlation of Histopathologic Features with Demographic, Gross and Radiographic Findings in Giant Cell Granulomas of the Jaws
EAR, NOSE, THROAT DISORDERS
 EAR, NOSE, THROAT DISORDERS A Case of Recurrent Pyogenic Granuloma of Gingiva ABSTRACT A case of pyogenic granuloma of gingiva is presented. Aetiology factors, clinical presentations and different treatment
EAR, NOSE, THROAT DISORDERS A Case of Recurrent Pyogenic Granuloma of Gingiva ABSTRACT A case of pyogenic granuloma of gingiva is presented. Aetiology factors, clinical presentations and different treatment
Case Report Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a Child Associated with Ectopic Eruption and Traumatic Habit with Control of Four Years
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 6725913, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6725913 Case Report Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a Child Associated
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 6725913, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6725913 Case Report Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma in a Child Associated
Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report. A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 13 Number 1 Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi Citation A Narwal,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 13 Number 1 Paraosteal Osteosarcoma of Mandible: A Case Report A Narwal, A Hooda, R Sen, V Singh, A Gupta, S Bala, D Sethi Citation A Narwal,
The Modified Latero-Coronally-Positioned Flap After Excision Of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 12 Number 1 The Modified Latero-Coronally-Positioned Flap After Excision Of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma G Gassmann, A Dannan, W Grimm Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 12 Number 1 The Modified Latero-Coronally-Positioned Flap After Excision Of Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma G Gassmann, A Dannan, W Grimm Citation
Gingival Aggressiveness during Pregnancy
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org ISSN (e)-2347-176x Gingival Aggressiveness during Pregnancy Authors Dr Arvind Garg 1, Dr Asmita Arora 2, Dr Shweta Aggarwal 3, Dr Arun Garg 4 Dr Viniti Goel 5 1 Professor &
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org ISSN (e)-2347-176x Gingival Aggressiveness during Pregnancy Authors Dr Arvind Garg 1, Dr Asmita Arora 2, Dr Shweta Aggarwal 3, Dr Arun Garg 4 Dr Viniti Goel 5 1 Professor &
Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia: Two Case Reports
 American Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Case Report http://ivyunion.org/index.php/maxillofacial Page 1 of 7 Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia: Two Case Reports Narjiss. Akerzoul 1*, Saliha. Chbicheb
American Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Case Report http://ivyunion.org/index.php/maxillofacial Page 1 of 7 Focal Fibrous Hyperplasia: Two Case Reports Narjiss. Akerzoul 1*, Saliha. Chbicheb
Reactive hyperplastic lesions of the oral cavity: A ten year observational study on North Indian Population
 Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.50670 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.50670 Reactive hyperplastic lesions of the oral cavity: A ten year observational
Journal section: Oral Medicine and Pathology Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.50670 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.50670 Reactive hyperplastic lesions of the oral cavity: A ten year observational
Gingival and alveolar hyperplastic reactive lesions: clinicopathological study of 90 cases
 Braz J Oral Sci. JulySeptember 26 Vol. 5 Number 8 Pryscilla Giglio Peralles Ana Paula Borges Viana André Luiz da Rocha Azevedo 2 Fábio Ramôa Pires 3 DDS; formerly undergraduating students; School of Dentistry,
Braz J Oral Sci. JulySeptember 26 Vol. 5 Number 8 Pryscilla Giglio Peralles Ana Paula Borges Viana André Luiz da Rocha Azevedo 2 Fábio Ramôa Pires 3 DDS; formerly undergraduating students; School of Dentistry,
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare case report
 Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
Annals of Dental Research (2013) Vol 3 (1): 10-14 HATAM Publishers: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.hgpub.com www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma: A rare
THE CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA, A CASE OF RECURRENCE AFTER 22 YEARS. SARINDER SINGH, B.D.S. Department of Oral Surgery, Guy s Hospital, London
 British Journal of Oral Surgery (1982) 20, 109-116 @ The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-I 17x/82/00080109$02.00 THE CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA, A CASE OF RECURRENCE AFTER 22 YEARS SARINDER
British Journal of Oral Surgery (1982) 20, 109-116 @ The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-I 17x/82/00080109$02.00 THE CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA, A CASE OF RECURRENCE AFTER 22 YEARS SARINDER
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report
 Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
Peripheral Odontogenic Fibroma : A Case Report Vinayak V Meharwade 1, Vidya V Meharwade 2 1- Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology, Sinhgad Dental College and Hospital, Pune, Maharashtra, India.
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD A CASE REPORT
 International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
International Journal of Innovation Sciences and Research Vol.4, No, 4, pp. 139-143, April- 2015 CASE STUDY Available online at http://www.ijisr.com CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA IN A 10 YEAR OLD CHILD
Case Presentation: Figure 1. Palatal lesion. Figure 2. Panoramic xray
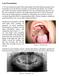 Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
Case Presentation: A 10-year-old girl presented with a hard palatal mass that had been progressively increasing in size for the last 4 months, as reported by her dentist. Two months previously, her dentist
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT
 MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
MANSOURA UNIVERSITY FACULTY OF DENTISTRY ORAL PATHOLOGY DEPT THIRD YEAR Course Director: Dr. Nadia M. Lotfy Professor of Oral Pathology Dr. Manal Mohamed Zyada Associate Professor of Oral Pathology Oral
ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS: A RARE CASE REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Oral Focal Micinosis: A Rare Case Sharma E. et al 178 CASE REPORT ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS: A RARE CASE REPORT OF TWO CASES Sharma Ena 1, Nadella Manjari 1, Chatterjee Anirban 1, Alampalli Ramesh 1 ABSTRACT
Oral Focal Micinosis: A Rare Case Sharma E. et al 178 CASE REPORT ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS: A RARE CASE REPORT OF TWO CASES Sharma Ena 1, Nadella Manjari 1, Chatterjee Anirban 1, Alampalli Ramesh 1 ABSTRACT
Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst
 doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2591.2006.01107.x CLINICAL ARTICLE Periapical central giant cell granuloma misdiagnosed as odontogenic cyst T. Lombardi 1, M. Bischof 1,2, R. Nedir 1,2, D. Vergain 1, C. Galgano 3,
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report
 Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Case report: Central Giant Cell Granuloma of Mandible A Case Report 1Dr Praveen Kumar, 2 Dr Balreddy P., 3 Dr Sridhar Reddy B., 4 Dr Sanjeev Naik, 5Dr. Sujitha Reddy Patil 1Post Graduate, Department of
Original Article. A Survey of Soft Tissue Tumor-Like Lesions of Oral Cavity: A Clinicopathological Study
 Iranian Journal of Pathology (28)3 (2), 81-81 87 Original Article A Survey of Soft Tissue Tumor-Like Lesions of Oral Cavity: A Clinicopathological Study Maryam Assadat Hashemi Pour 1, M Rad 1, A Mojtahedi
Iranian Journal of Pathology (28)3 (2), 81-81 87 Original Article A Survey of Soft Tissue Tumor-Like Lesions of Oral Cavity: A Clinicopathological Study Maryam Assadat Hashemi Pour 1, M Rad 1, A Mojtahedi
Case Report Soft Tissue Reconstruction with Free Gingival Graft Technique following Excision of a Fibroma
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 248363, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/248363 Case Report Soft Tissue Reconstruction with Free Gingival Graft Technique following Excision of a
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 248363, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/248363 Case Report Soft Tissue Reconstruction with Free Gingival Graft Technique following Excision of a
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
A 24 year old male patient presented with a swelling on the dorsal aspect of left foot since 3 years. He was operated thrice before, outside, for
 A 24 year old male patient presented with a swelling on the dorsal aspect of left foot since 3 years. He was operated thrice before, outside, for same. Came to us with recurrence since last one year with
A 24 year old male patient presented with a swelling on the dorsal aspect of left foot since 3 years. He was operated thrice before, outside, for same. Came to us with recurrence since last one year with
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws
 Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Differential Diagnosis of Radiolucent Lesions of the Jaws Multilocular Multilocular Radiolucencies Odontogenic Keratocyst Botryoid Odontogenic Cyst Glandular odontogenic Cyst Invasive Ameloblastoma Central
Peripheral ossifying fibroma: a clinical and immunohistochemical study of four cases
 95 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 1, 95-99, 2010 Original Peripheral ossifying fibroma: a clinical and immunohistochemical study of four cases José A. García de Marcos 1), María J. García de Marcos
95 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 52, No. 1, 95-99, 2010 Original Peripheral ossifying fibroma: a clinical and immunohistochemical study of four cases José A. García de Marcos 1), María J. García de Marcos
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
PERIPHERAL CEMENTO-OSSIFYING FIBROMA- A CASE REPORT
 PERIPHERAL CEMENTO-OSSIFYING FIBROMA- A CASE REPORT Dr.V.Gopinath, 1 Dr.V.Krishna, 2 Dr.Pramod kumar 3 1. Professor and Head, Department Of Periodontology, Department Of Periodontology, Rungta College
PERIPHERAL CEMENTO-OSSIFYING FIBROMA- A CASE REPORT Dr.V.Gopinath, 1 Dr.V.Krishna, 2 Dr.Pramod kumar 3 1. Professor and Head, Department Of Periodontology, Department Of Periodontology, Rungta College
Fibroma - A misnomer : Case Series
 Case Report Abstract Fibroma - A misnomer : Case Series NUJHS Vol. 5, No.4, December 2015, ISSN 2249-7110 Riya Verghese, Amitha Ramesh, Rahul Bhandary, Biju Thomas & Nishita L. Philip 1 2,3 4 5 Post Graduate,
Case Report Abstract Fibroma - A misnomer : Case Series NUJHS Vol. 5, No.4, December 2015, ISSN 2249-7110 Riya Verghese, Amitha Ramesh, Rahul Bhandary, Biju Thomas & Nishita L. Philip 1 2,3 4 5 Post Graduate,
CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT
 IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
IJCRR Section: Healthcare Sci. Journal Impact Factor 4.016 Case Report CENTRAL GIANT CELL GRANULOMA PRESENTING AS UNILOCULAR RADIOLUCENCY IN POSTERIOR MANDIBLE A CASE REPORT S. Aruleena Shaminey 1, G.
Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation
 Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
Aswath et al. 51 CASE IN IMAGES OPEN ACCESS Pimary hyperparathyroidism as central giant cell granuloma of the jaws: Pre and post treatment pattern of clinical and radiographic presentation Nalini Aswath,
Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 36th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA Oct. 14-17, 2011 Jeju, Korea Next Congress: http://www.ivis.org October 14(Fri) ~ 17(Mon) 2011 ICC Jeju, Korea 2011 WSAVA
Maxillary Pyogenic Granuloma: A Case Report.
 RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Maxillary Pyogenic Granuloma: A Case Report. Nalini MS*, Shivaprasad BM, Savita S and Sonali Chakrarborthy. Department of Periodontics, Rajarajeshwari Dental
RESEARCH AND REVIEWS: JOURNAL OF DENTAL SCIENCES Maxillary Pyogenic Granuloma: A Case Report. Nalini MS*, Shivaprasad BM, Savita S and Sonali Chakrarborthy. Department of Periodontics, Rajarajeshwari Dental
Retrospective analysis of the clinical features of 530 cases of reactive lesions of oral cavity
 Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2014), 1, 1 6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Retrospective analysis of the clinical features of 530 cases of reactive lesions of oral cavity Santosh Hunasgi 1, Anila
Journal of Advanced Clinical & Research Insights (2014), 1, 1 6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Retrospective analysis of the clinical features of 530 cases of reactive lesions of oral cavity Santosh Hunasgi 1, Anila
Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaw and Giant Cell Tumor of Long Bones (Comparative Study)
 GIANT THE IRAQI CELL POSTGRADUATE GRANULOMA MEDICAL JOURNAL Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaw and Giant Cell Tumor of Long Bones (Comparative Study) Omar
GIANT THE IRAQI CELL POSTGRADUATE GRANULOMA MEDICAL JOURNAL Histopathological and Immunohistochemical Study of Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaw and Giant Cell Tumor of Long Bones (Comparative Study) Omar
Ameloblastic Carcinoma of the Mandible: a Rare Case Report
 IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
IBIMA Publishing Journal of Research and Practice in Dentistry http://www.ibimapublishing.com/journals/dent/dent.html Vol. 2015 (2015), Article ID 672596, 6 pages DOI: 10.5171/2015.672596 Case Report Ameloblastic
AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 04, Issue 03 AMELOBLASTIC FIBROMA: A RARE CASE REPORT Namratha Patil 1 1.Sr lecturer, dept of oral medicine and radiology, KAHES VK
Asymptomatic Alveolar Swelling After a Tooth Extraction
 Continuing Education Brought to you by Asymptomatic Alveolar Swelling After a Tooth Extraction Course Author(s): Michaell A. Huber, DDS; Anne Cale Jones, DDS; H. Stan McGuff, DDS; Online Case: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/professional-education/case-challenges/case-challenge-064
Continuing Education Brought to you by Asymptomatic Alveolar Swelling After a Tooth Extraction Course Author(s): Michaell A. Huber, DDS; Anne Cale Jones, DDS; H. Stan McGuff, DDS; Online Case: www.dentalcare.com/en-us/professional-education/case-challenges/case-challenge-064
Surgical Diode Laser Excision for Peripheral Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma: A Case Report and Literature Review
 Surgical Diode Laser Excision for Peripheral Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma: A Case Report and Literature Review Tanveer Alam a, Ali Azhar Dawasaz b, Naresh Thukral c, Daya Jangam d a Postgraduate Student,
Surgical Diode Laser Excision for Peripheral Cemento-Ossifying Fibroma: A Case Report and Literature Review Tanveer Alam a, Ali Azhar Dawasaz b, Naresh Thukral c, Daya Jangam d a Postgraduate Student,
JCDP ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 JCDP Omar Kujan et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1629 Immunohistochemical Comparison of p53, Ki-67, CD68, Vimentin, α-smooth Muscle Actin and Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin in Oral Peripheral
JCDP Omar Kujan et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1629 Immunohistochemical Comparison of p53, Ki-67, CD68, Vimentin, α-smooth Muscle Actin and Alpha-1-Antichymotrypsin in Oral Peripheral
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2008) Young Researchers Gavasova and Budev EPULIS FISSURATUM CLINICAL APPEARANCE AND TREATMENT. Dr G.Gavasova, Dr I.
 EPULIS FISSURATUM CLINICAL APPEARANCE AND TREATMENT Dr G.Gavasova, Dr I.Budev Medical University, Faculty of Dental Medicine Oral Surgery Department Head: Prof. Dr D. Atanasov, Ph.D, MD. Summary Continuous
EPULIS FISSURATUM CLINICAL APPEARANCE AND TREATMENT Dr G.Gavasova, Dr I.Budev Medical University, Faculty of Dental Medicine Oral Surgery Department Head: Prof. Dr D. Atanasov, Ph.D, MD. Summary Continuous
Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report
 457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
457 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 457-461, 2009 Case Report Central odontogenic fibroma of the mandible: a case report Ioanna Daskala 1), Demos Kalyvas 2), Markos Kolokoudias 2), Dimitris Vlachodimitropoulos
Gingival and alveolar ridge tumor-like overgrowth lesions
 Gingival and alveolar ridge tumor-like overgrowth lesions Salwan Y.H. Bede, B.D.S., F.I.B.M.S. (1) ABSTRACT Background: Tumor-like overgrowth lesions of the oral mucosa are pathological growths that project
Gingival and alveolar ridge tumor-like overgrowth lesions Salwan Y.H. Bede, B.D.S., F.I.B.M.S. (1) ABSTRACT Background: Tumor-like overgrowth lesions of the oral mucosa are pathological growths that project
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies
 Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Inter-radicular Radiolucencies Differential Diagnosis Laterally Displaced Radicular Cyst Accessory canals Root fracture Lateral Periodontal Cyst Botryoid variant Odontogenic Keratocyst Incisive Canal Cyst
Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
Normal thyroid tissue
 Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Thyroid Pathology Overview Normal thyroid tissue Normal thyroid tissue with follicles filled with colloid. Thyroid cells form follicles, spheres of epithelial cells (always single layered in health, usually
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Metabolic & Endocrine disorders of bone:
 Metabolic & Endocrine disorders of bone: Osteoporosis: Bone apposition < bone resorption Risk factors: Postmenopausal women Hyperthyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Cushing s syndrome bone quantity: thin cortex
Metabolic & Endocrine disorders of bone: Osteoporosis: Bone apposition < bone resorption Risk factors: Postmenopausal women Hyperthyroidism Hyperparathyroidism Cushing s syndrome bone quantity: thin cortex
Case Report. A Reticent Intraoral Growth - Peripheral Giant Cell Granuloma
 Medicine Case Report 1 2 3 4 Dr. Abhay Kulkarni, Dr. Rajendra Birangane, Dr. Sanjeev Onkar, Dr.Pratik.C.Parkarwar Kulkarni A, Birangane R, Onkar S, Parkarwar PC. A Reticent Intraoral Growth - Peripheral
Medicine Case Report 1 2 3 4 Dr. Abhay Kulkarni, Dr. Rajendra Birangane, Dr. Sanjeev Onkar, Dr.Pratik.C.Parkarwar Kulkarni A, Birangane R, Onkar S, Parkarwar PC. A Reticent Intraoral Growth - Peripheral
A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1
 A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1 1 Animal Health Trust, Newmarket, UK 2 608 Equine and Farm Vets, Rowington, UK Signalment: Horse,
A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1 1 Animal Health Trust, Newmarket, UK 2 608 Equine and Farm Vets, Rowington, UK Signalment: Horse,
SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE
 African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
African Journal of Oral Health Volume 3 Numbers 1&2, 2006:1-5 REFEREED ARTICLE SQUAMOUS ODONTOGENIC TUMOUR: REPORT OF FIVE CASES FROM NIGERIA AND REVIEW OF LITERATURE Adebiyi K.E., Odukoya O., Taiwo, E.O.
CASE REPORT PLAQUE TYPE ORAL VERRUCOUS HYPERPLASIA AND IRRITATIONAL FIBROMA: A REPORT OF CONJOINT OCCURRENCE
 CASE REPORT PLAQUE TYPE ORAL VERRUCOUS HYPERPLASIA AND IRRITATIONAL FIBROMA: A REPORT OF CONJOINT OCCURRENCE Alphy Alphonsa Sebastian, Hasan Subhi 1. Phd student, Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Pathology,
CASE REPORT PLAQUE TYPE ORAL VERRUCOUS HYPERPLASIA AND IRRITATIONAL FIBROMA: A REPORT OF CONJOINT OCCURRENCE Alphy Alphonsa Sebastian, Hasan Subhi 1. Phd student, Department of Oral Medicine and Oral Pathology,
Flow Cytometry. Hanan Jafar (2017)
 1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
EAR, NOSE, THROAT DISORDERS
 EAR, NOSE, THROAT DISORDERS Clinico-Pathological Quiz ABSTRACT A case of a fleshy, granular, pedunculated growth from the oral cavity will be presented. A differential diagnosis of similar growths from
EAR, NOSE, THROAT DISORDERS Clinico-Pathological Quiz ABSTRACT A case of a fleshy, granular, pedunculated growth from the oral cavity will be presented. A differential diagnosis of similar growths from
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
IRA-International Journal of Applied Sciences ISSN Vol. 03 Issue 02 (May, 2016) Paper DOI:
 IRA-International Journal of Applied Sciences ISSN 2455-4499 Vol. 03 Issue 02 (May, 2016) Paper DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.21013/jas.v3.n2.p8 Pathophysiology of Giant Cell Formation in Giant Cell Tumor
IRA-International Journal of Applied Sciences ISSN 2455-4499 Vol. 03 Issue 02 (May, 2016) Paper DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.21013/jas.v3.n2.p8 Pathophysiology of Giant Cell Formation in Giant Cell Tumor
Pregnancy Tumor JOHSR CASE REPORT ABSTRACT CASE REPORT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 JOHSR CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10042-1029 1 Shwetha Chikkaboraiah, 2 Rajiv Nidasale Puttaswamaiah, 3 Sushama R Galgali ABSTRACT Aim: The aim of this case report is to present a case of rapidly growing
JOHSR CASE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10042-1029 1 Shwetha Chikkaboraiah, 2 Rajiv Nidasale Puttaswamaiah, 3 Sushama R Galgali ABSTRACT Aim: The aim of this case report is to present a case of rapidly growing
Case Report Peripheral ossifying fibroma in Pregnancy: A multifactorial consequence Suramya S 1, Gujjari SK 2, Sreeshyla HS 3
 Case Report Peripheral ossifying fibroma in Pregnancy: A multifactorial consequence Suramya S 1, Gujjari SK 2, Sreeshyla HS 3 1 Dr Suramya S MDS, Post graduate student Periodontology suramya.1986@gmail.com
Case Report Peripheral ossifying fibroma in Pregnancy: A multifactorial consequence Suramya S 1, Gujjari SK 2, Sreeshyla HS 3 1 Dr Suramya S MDS, Post graduate student Periodontology suramya.1986@gmail.com
Case Report Giant Cell Fibroma of Tongue: Understanding the Nature of an Unusual Histopathological Entity
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 864512, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/864512 Case Report Giant Cell Fibroma of Tongue: Understanding the Nature of an Unusual Histopathological Entity Wanjari
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 864512, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/864512 Case Report Giant Cell Fibroma of Tongue: Understanding the Nature of an Unusual Histopathological Entity Wanjari
TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES
 Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Traumatic Bone Cyst Kumar S. et al 183 CASE REPORT TRAUMATIC BONE CYST OF IDIOPATHIC ORIGIN? A REPORT OF TWO CASES Kumar Satish 1, S. Padmashree 1, Jayalekshmy Rema 1 ABSTRACT BACKGROUND: Traumatic bone
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course. Histo Exam #3 KEY
 2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
2015 Descriptive Vet Path Course Histo Exam #3 KEY Test 3, Slide 1 Tissue from a guinea pig. MORPHOLOGIC DIAGNOSIS: Heart: Multifocally and randomly (1 pt), within the left and right ventricular myocardium
A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report
 Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report A Rare case of Tubercular Gingivitis Case Report *Dr. Ansh Chugh 1, Dr. Firoz A Hakkim 2, Dr. Rajesh. V 3, Dr. Raghava Sharma 4 1: JUNIOR RESIDENT IN GENERAL MEDICINE 2: SENIOR RESIDENT IN
Case Report Giant Cell Fibroma in a Two-Year-Old Child
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 7058356, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7058356 Case Report Giant Cell Fibroma in a Two-Year-Old Child Anna Carolina Volpi Mello-Moura, 1,2 Ana
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2016, Article ID 7058356, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7058356 Case Report Giant Cell Fibroma in a Two-Year-Old Child Anna Carolina Volpi Mello-Moura, 1,2 Ana
THE OHIO JOURNAL OF SCIENCE
 THE OHIO JOURNAL OF SCIENCE PUBLISHED BY THE OHIO STATE; UNIVERSITY SCIENTIFIC SOCIETY VOLUME XVIII 'NOVEMBER, 1917 No. 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS FORRMAN AND REED Tumors in Dogs. II 1 WAI/TON The Axial Rotation
THE OHIO JOURNAL OF SCIENCE PUBLISHED BY THE OHIO STATE; UNIVERSITY SCIENTIFIC SOCIETY VOLUME XVIII 'NOVEMBER, 1917 No. 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS FORRMAN AND REED Tumors in Dogs. II 1 WAI/TON The Axial Rotation
CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT
 Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Mucocele and epidermoid cyst CONCURRENT EXTRAVASATION MUCOCELE AND EPIDERMOID CYST OF THE LOWER LIP: A CASE REPORT Wen-Chen Wang, Li-Min Lin, Yee-Hsiung Shen, 1 Yu-Ju Lin, and Yuk-Kwan Chen Departments
Synonyms. Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma
 Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
Nephrogenic Adenoma Synonyms Nephrogenic metaplasia Mesonephric adenoma Definition Benign epithelial lesion of urinary tract with tubular, glandular, papillary growth pattern Most frequently in the urinary
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES ISSN:
 PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. A CASE REPORT DENTURE INDUCED INFLAMMATORY
PACIFIC JOURNAL OF MEDICAL SCIENCES {Formerly: Medical Sciences Bulletin} ISSN: 2072 1625 Pac. J. Med. Sci. (PJMS) www.pacjmedsci.com. Email: pacjmedsci@gmail.com. A CASE REPORT DENTURE INDUCED INFLAMMATORY
SURGICAL'MANAGEMENT'OF' PLEXIFORM'AMELOBLASTOMA:'A' CASE'REPORT'
 HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
HARSH,Ashutosh* PUROHIT,Pragya* PUROHIT,NC** ADLAKHA,Twisha*** SURGICALMANAGEMENTOF PLEXIFORMAMELOBLASTOMA:A CASEREPORT ABSTRACT Ameloblastoma is a benign but locally invasive neoplasm of odontogenicepithelium.patientsusuallypresentlateafterthetumor
Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws: A Short Series and Review of Literature
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1086 ORIGINAL RESEARCH WJD Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws: A Short Series and Review of Literature 1 SK Mathur, 2 Parveen Rana Kundu, 3 Sugandha Mohan, 4 Virender Singh
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1086 ORIGINAL RESEARCH WJD Central Giant Cell Granuloma of the Jaws: A Short Series and Review of Literature 1 SK Mathur, 2 Parveen Rana Kundu, 3 Sugandha Mohan, 4 Virender Singh
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL SECOND EDITION
 VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
VETERINARY HEMATOLOGY ATLAS OF COMMON DOMESTIC AND NON-DOMESTIC SPECIES SECOND EDITION COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL CHAPTER ONE HEMATOPOIESIS GENERAL FEATURES All blood cells have a finite life span, but in normal
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position
 A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
A Case Report of Odontogenic Keratocyst in Anterior Mandibule Position Malihe Moeini 1, Seyed Ehsan Anvar 2, Rasool Barzegari Bafghi 3* 1.Resident of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology, Faculty of Dentistry,
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC RESEARCH
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC RESEARCH How to cite this article : PAI K,GUPTA A.INTRAVASCULAR EPITHELIOID HAEMANGIOMA OF TEMPORAL ARTERY: A DIAGNOSTIC DIFFICULTY Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC RESEARCH How to cite this article : PAI K,GUPTA A.INTRAVASCULAR EPITHELIOID HAEMANGIOMA OF TEMPORAL ARTERY: A DIAGNOSTIC DIFFICULTY Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic
Problem diagnoses. Current issues in Anatomic pathology. Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity 5/29/2009
 Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Current issues in Anatomic pathology Problem Diagnoses in Tumors of the Oral Cavity Richard Jordan DDS PhD FRCPath Professor of Oral Pathology & Pathology Director, UCSF Oral Pathology Diagnostic Laboratory
Deposition of Bone by the Osteoblasts. Bone is continually being deposited by osteoblasts, and it is continually being resorbed where osteoclasts are
 Bone remodeling Deposition of Bone by the Osteoblasts. Bone is continually being deposited by osteoblasts, and it is continually being resorbed where osteoclasts are active. This mechanism is always is
Bone remodeling Deposition of Bone by the Osteoblasts. Bone is continually being deposited by osteoblasts, and it is continually being resorbed where osteoclasts are active. This mechanism is always is
Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases
 (2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
(2010) 39, 57 63 2010 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org CASE REPORT Ossifying fibromas of the jaw bone: 20 cases Y Liu 1, M You 1, H Wang*,1, Z Yang 1, J Miao 1, K Shimizutani
Flow Cytometry. What is flow cytometry?
 Flow Cytometry Flow Cytometry What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence
Flow Cytometry Flow Cytometry What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence
An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report
 J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
J. Int Oral Health 2010 Case Report All right reserved An unusual site of Adenomatoid Odontogenic Tumor: A rare case report Sapna Panjwani*, Anjana Bagewadi**, Vaishali Keluskar*** *Post Graduate Student
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
Aggressive Pregnancy Tumor Mimicking A Malignant Neoplasm: A Case Report
 Aggressive Pregnancy Tumor Mimicking A Malignant Neoplasm: A Case Report Khansa Ababneh, BDS, PhD, FDSRCSEd; Taiseer Al-Khateeb, BDS, MScD, FDSRCSEd, FFDRCSI Abstract Aim: The aim of this report is to
Aggressive Pregnancy Tumor Mimicking A Malignant Neoplasm: A Case Report Khansa Ababneh, BDS, PhD, FDSRCSEd; Taiseer Al-Khateeb, BDS, MScD, FDSRCSEd, FFDRCSI Abstract Aim: The aim of this report is to
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Osteoma of Mandibular Condyle as Ca Title Pain and Limited-mouth-opening: Cas. Yonezu, H; Wakoh, M; Otonari, T; Sa Author(s) Hashimoto, S; Uchiyama, T
 Osteoma of Mandibular Condyle as Ca Title Pain and Limited-mouth-opening: Cas Yonezu, H; Wakoh, M; Otonari, T; Sa Author(s) Hashimoto, S; Uchiyama, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/417
Osteoma of Mandibular Condyle as Ca Title Pain and Limited-mouth-opening: Cas Yonezu, H; Wakoh, M; Otonari, T; Sa Author(s) Hashimoto, S; Uchiyama, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/417
HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY
 Bosnian-British School of Pathology November 2012 HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY Slide seminar: Oral Pathology Preferred Diagnoses Dr A Sandison, Slide seminar: Pathology of the Oral Cavity Page 1 of 5 1. Female
Bosnian-British School of Pathology November 2012 HEAD AND NECK PATHOLOGY Slide seminar: Oral Pathology Preferred Diagnoses Dr A Sandison, Slide seminar: Pathology of the Oral Cavity Page 1 of 5 1. Female
A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1986 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 8 Number 2 A survey of biopsied oral lesions in pediatric dental patients Robert L. Skinner, MS W.D. Davenport,
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions. An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling. John L. Alonge, MS, DDS
 Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis of Oral Lesions An Interactive Lecture Using Audience Response Polling John L. Alonge, MS, DDS Goals 1. Review the diagnostic process needed to formulate a differential diagnosis
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Seyed Mohammad Razavi, Roya Yahyaabadi* Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.8.2279 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:03/17/2018 Acceptance:06/29/2018 Comparative Study of Correlation between Angiogenesis Markers (CD31) and Ki67 Marker with
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.8.2279 RESEARCH ARTICLE Editorial Process: Submission:03/17/2018 Acceptance:06/29/2018 Comparative Study of Correlation between Angiogenesis Markers (CD31) and Ki67 Marker with
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Pyogenic granuloma A case report (Crocker and Hartzell s disease A Commoner)
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 6 Ver. 2 (June. 2018), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org Pyogenic granuloma A case report (Crocker
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 6 Ver. 2 (June. 2018), PP 69-73 www.iosrjournals.org Pyogenic granuloma A case report (Crocker
Brown Tumours: A Case of a Non-Healing Tooth Socket
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report Brown Tumours: A Case of a Non-Healing Tooth Socket Natalie Bradley 1 *, Neha P Shah 2, Selvam Thavaraj 3 and Jerry Kwok 2 1 Kent Community Health Foundation
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report Brown Tumours: A Case of a Non-Healing Tooth Socket Natalie Bradley 1 *, Neha P Shah 2, Selvam Thavaraj 3 and Jerry Kwok 2 1 Kent Community Health Foundation
Case Series Oral lipomas: A report of two cases ABSTRACT
 International Journal of Medicine and Biomedical Research Volume 3 Issue 1 January April 2014 www.ijmbr.com Michael Joanna Publications Case Series Oral lipomas: A report of two cases Omisakin O.O 1*,
International Journal of Medicine and Biomedical Research Volume 3 Issue 1 January April 2014 www.ijmbr.com Michael Joanna Publications Case Series Oral lipomas: A report of two cases Omisakin O.O 1*,
