Ability of Hydroxyapatite-Bone Morphologenetic Protein (BMP) Complex to Induce Dentin Formation in Dogs
|
|
|
- Godwin Wilkerson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 70(5): , December, 1993 Ability of Hydroxyapatite-Bone Morphologenetic Protein (BMP) Complex to Induce Dentin Formation in Dogs By Fumihiko SUWA, Lianjia Yang, Yoshikuni OHTA, Yi-Ru FANG, Hiromi IKE and Taka-aki DEGUCHI Department of Anatomy, Osaka Dental University 5-31, Otemae 1-chome, Chuo-ku, Osaka 540, Japan Department of Oral Pathology, The Fourth Military Medical University, Faculty of Stomatology, Xian, China -Received for Publication, August 18, Key Words: Dentinogenesis, Osteogenesis, HAP, BMP, Dog Summary: This histological investigation examined the formation and differentiation of pulp cells under the influence of HAP/BMP complex. HAP/BMP complex was implanted in exposed pulp of the mandibular premolars and alveolar bone defect in the dog. Sequential changes in these areas were examined mainly under a light microscope and partly under a scanning electron microscope. Two weeks after the operation, fibroblast-like cells proliferated right beneath the implanted complex, and after 3 weeks, dentin including dentin tubules grew in the pulp. After four weeks a dentin bridge composed of osteoid dentin was found, and after 8 weeks this dentin calcified and covered the defective surface of the root and adhered to two types: tubular dentin and osteodentin. This complex exhibited outstanding ability to induce dentinogenesis and osteogenesis. In the embryo, dentinogenesis, which depends upon the differentiation of dental pulp cells, occurs after proliferation of the dental papilla and differentiation to odontoblasts. Cytogenetic and histogenetic influences are retained, and are capable of continuous dentin renewal throughout the postfetal life in a manner analogous to that of bone tissues (Cat 1989). There has been experimental evidence to show that mesenchymal cells are able to differentiate into odontoblasts without the influence of epithelial cells of the enamel organ when the dental pulp of the mature permanent tooth is injured. It has been suggested that some inductive factor(s) may exist in the epithelium of the enamel organ and the necrotic layer of the injured pulp (Chao-How 1978). However, the mechanisms of differentiation of dental pulp cells and the initiation of dentinogenesis have not been elucidated. In the past 20 years, knowledge about bone morphogenetic protein (BMP), including its purification, physiochemical characteristics and recombinant human BMP protein, has greatly increased (Wang 1988, Wozney et al. 1988, Wozney 1989). Dentinal BMP was extracted from human and bovine teeth by Kawai and Urist (1989) and Bessho et al. (1991). Their pioneering work demonstrated that BMP was clearly a protein stored in the dentin matrix and possibly in matrices of enamel and cement. However, much less progress has been made in the field of cellular differentiation in human and mammalian dental pulp cells. The effect of BMP complex on the differentiation of dental pulp cells has not been reported. The histological aspects of dentin formation and the differentiation of pulp cells developing under the influence of hydroxyapatite-bmp complex are described here. Materials and Methods 1. Dissociative extraction of BMP Partially purified BMP was obtained from a demineralized bovine bone which was prepared by sequential extractions, as shown in Table 1. The gelatinized insoluble bone matrix was chemically extracted with 4 M guanidine-hc1 (GuHC1)/0.5 M CaCl2, including 1.0 mm N-ethylmaleimide (NEM) for 24 hr at room temperature. This extract was dialyzed against distilled water for 3 days at 4 C, then the retentate was heated in the dialysis bags to 35 C each time gelling occurred, and centrifuged (40,000 x g, 20 min, at 4 C). The precipitate was redissolved in 4M GuHC1/0.05 CaC1,. The 4M GuHC1-soluble proteins were dialyzed in 0.25 M sodium citrate-citric acid buffer (ph 3.1). Following 195
2 196 F. Suwa et al. Table 1. Method of purifying BMP from decalcified bovine bones thick, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for light microscopic examinations. In numerical order hr C Remarks Results dialysis, the retentate was heated to 40 C, and centrifuged (40,000 x g, 60 min, at 35 C). The precipitate was washed in distilled water and 1:1 chloroformmethanol, and lyophilized at 4 C. 2. Preparation of hydroxyapatite (HAP)/BMP complex BMP was redissolved in 4 M GuHC1, to which porous HAP (pores: iLtm in diameter) was added. This complex was dialyzed against distilled water 24 hr at 4 C and lyophilized. The dried HAP/ BMP complex was examined under a scanning electron microscope (accelerating voltage 20 kv). 3. Bioassay The HAP combined with BMP by dialysis was implanted in the interfascicular tissue (pouch) of a femoral muscle of the mouse. HAP alone was implanted in the muscle as a control. After 1, 2, 3 and 4 weeks the implanted region was dissected out with surrounding tissues, and immediately fixed in 10% formalin for histological examinations. 4. Dentin inductive activity of HAP/BMP complex in dogs Four male adult dogs (average body weight 22 kg) were empolyed for this experiment. After the dogs were anesthetized by an intramuscular injection of sodium pentobarbital (Nembutal 0.5 ml/kg), the unilateral mandibular premolars were cut at the cemento-enamel junction. Alveolar ridges were reduced 2-3 mm in height. The HAP/BMP complex was implanted in the exposed pulp and bone defect, and the wound was closed by gingival ligation. HAP alone was implanted in defects of the opposite mandibular premolars as a control. Two, 3, 4 and 8 weeks after operation, the dogs were killed and the implanted areas were dissected out, fixed in 10% formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned at 5 [inn 1. Osteoinductive activity of HAP/BMP complex Scanning electron microscopy revealed that the surface of the complex was covered with BMP. Pores of HAP were occupied by a large amount of BMP (Fig. 1). Seven days after implantation of the complex into the interfascicular tissue, many mesenchymal cells proliferated around the granules of the complex. A few lymphocytes could be found. At 14 days, no new bone formation was found, but the mesenchymal cells had begun to differentiate into osteoblasts. By three weeks, a thin layer of new bone rimming the HAP granules was found. By four weeks, the new bone had become thickened, and new bone formation was also seen in the center of the granules (Fig. 2). In the control group, new bone formation was not found at this time (Fig. 3). 2. HAP/BMP-induced dentin formation in dogs One week after implantation, dental pulps were completely capped with HAP/BMP complex and were free of inflammation. A thin, necrotic layer was found on the surface of the exposed pulp. By two weeks, fibroblast-like cells were proliferating in a wide area just beneath the HAP/BMP complex, but a dentin bridge had not formed. By three weeks, regular dentin was induced in the pulp, and many dentin tubules in the shape of normal dentin were observed (Fig. 4). Odontoblasts were observed around the newly formed dentin. From the fourth week after the operation, the rate of dentin formation increased, and a dentin bridge composed of osteodentin without any dentin tubules was formed (Fig. 5). By eight weeks, the osteodentin bridge had calcified. Newly formed bone covered the surface of the dentin defect of the root and adhered to the new bone rimming the HAP granules (Fig. 6). In the control group with HAP alone, a dentin bridge was not found by eight weeks. The granules of the complex were surrounded by a fibrous tissue (Fig. 7). Discussion It is well-known that BMP is an efficient boneinducing protein, and may induce the differentiation of mesenchymal cells into chondro- and osteocytes in soft tissues and bone defect (Urist et al. 1983). Implantation of BMP in a thigh muscle pouch of the mouse consistently induces new cartilage formation
3 Ability of HAP-BMP Complex to Induce Dentin Formation 197 by the 7th day, woven bone by the 14th day, and lamellar bone by the 21st day (Urist et al. 1984). But BMP extracted from bone matrix by chemical methods is limited in amount. After implantation of BMP alone, it dissolves readily in the tissue fluid. In recent studies on the development of new implantable biomaterials as bone substitutes in the reparation of bone defect, BMP bound to 3-TCP, HAP and human fibrin have been investigated (Urist et al. 1979, Kawamura et al. 1988, Mieki 1990). Mieki (1990) reported that the osteoinductive activity of HAP/BMP complex was higher than that of BMP alone. A porous HAP combined with BMP by dialysis was used for our experiment. The results revealed that the complex induced new bone formation around the granules of the material by the 21st day. Proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal cells were observed before new bone formation. Since new bone is induced in the center of the granules after three weeks, the complex retains higher osteoinductive activity. Because the differentiation and development of odontoblasts, osteo- and chondrocytes are essential to both new dentin and bone formation, investigators have been looking for a substance or factor that can induce the differentiation of odontoblasts. Some researchers (Sampath et al. 1983, Urist et al. 1984) found that BMP was present not only in the bone matrix of rats, pigs and humans, but also in the dentin of rabbits and humans. Yang and Yan (1990) demonstrated that BMP might be found in human tooth anlages such as human predentin, and cells of the outer and inner enamel epithelium. It may be possible that BMP synthesized by the inner enamel epithelium is secreted into the pulp and thus induces the mesenchymal cells of the pulp to differentiate into odontoblasts, which produce the dentin matrix. There has been experimental evidence to indicate that crude BMP may induce the differentiation of pulp cells into odontoblasts in vivo and in vitro (Nakashima 1992). The dentins induced by HAP/BMP complex in the present study were of two types: osteodentin and regular tubular dentin. This feature may be related to the characteristics of the BMP that penetrates into the pulp tissue. Each particle of BMP may become the center of differentiation of dental pulp cells. Those cells adjacent to the BMP acquire sufficient stimulation for differentiation into typical odontoblasts, which secrete regular tubular dentin. But many pulp cells are induced by the complex to differentiate into immature odontoblasts, which produce the osteodentin. In the present experiment, the osteodentin bridge induced by HAP/BMP complex was produced over a time period that was more rapid than in the control group. Therefore, it can be said that this complex could be used as a substitute for the existing commonly used capping agents. On the other hand, the osteodentin bridge induced by HAP/BMP complex repairs not only pulp but also the dentin defect of roots (Fig. 6). The development of alveolar bone depends upon the growth of the tooth root. Alveolar atrophy occurs without sufficient stimulation of the root, as suggested by Cat (1989). This experiment provides further evidence that the dental pulp and dentin defect of the root are repaired by osteodentin, and thereby the living root can be retained in the alveolar bone. It, therefore, is possible to prevent the atrophy of alveolar bone. Literature cited 1) Bessho, K., Tanaka, N., Matsumoto, J., Tagawa, T. & Murata, M.: Human dentin matrix-derived bone morphogenetic protein. J. Dent. Res., 1991;70(3): ) Cat, A. R. T.: Oral Histology. Development, Structure and Function. 3rd ed. C. V. Mosby Co., 59-79, ) Chao-How, C.: An experimental autoradiographic study on healing of pulp wound following pulpotomy in dogs with tritiated thymidine. Shikwa Gakuho 1978;78: (in Japanese) 4) Kawamura, M., Urist, M. R.: Human fibrin is a physiologic delivery system for bone morphogenetic protein. Clin. Orthop., 1988;235: ) Kawai, T., Urist, M. R.: Bovine tooth-derived bone morphogenetic protein. J. Dent. Res., 1989;68: ) Mieki, A.: Bone inductive activity of13-tricalcium phosphatebone morphogenetic protein complex. Aichi Gakuin Daigaku Shigakkai Shi, 1990:28: (in Japanese) 7) Nakashima, M.: Mitogenetic and dentin-inductive effects of crude bone morphogenetic protein from bone and dentin in primary adult pulp cell culture. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Athol., 1992;73(4) : ) Sampath, T. K., Reddi, A. H.: Homology of bone-inductive protein from human, monkey, bovine, and rat extracellular matrix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1983;80: ) Urist, M. R., Mukulski, A., Lietze, A.: A solubilized and insolubilized bone morphgenetic protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1979;76: ) Urist, M. R., Lietze, A., Dawson, E.: P-tricalcium phosphate delivery system for bone morphogenetic protein. Clin. Orthop., 1984;187: ) Urist, M. R., Huo, Y. K., Brownell, A. G., Hohl, W. M.. Buyske, J., Lietze, A., Tempst, P., Hunkapillcr, M.. Delange, R.J.: Purification of bovine bone morphogenctic protein by hydroxyapatite chromatography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1983;81: ) Wang, E. A., Rosen, V., Cordes, P., Hewick, R. M., Kriz, M. J., Luxenberg, D. P., Sibley, B. S., Wozney, J. M.: Purification and characterization of other distinct bone-inducing factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1988:85: ) Wozney, J. M., Rosen, V., Celeste, A. J., Mitsock, L. M., Whitters, M. J., Kriz, R. W., Hewick, R. M., Wang, F. A.: Novel regulators of bone formation: Molecular clones and activities. Science, 1988;242: ) Wozney, J. M.: Bone morphogenetic proteinṣ Prog. Growth Factor Res., 1989;1( ) Yang, L., Yan, J.: Immunohistochemical observations
4 198 F. Suwa et al. on bone morphogenetic protein in normal and abnormal conditions. Clin. Orthop., : Explanation of Figures Plate I Fig. la. Fig. lb. Porous HAP. Surfaces of HAP are combined with BMP. Pores (GB) are occupied by BMP. Fig. 2. Fig. 3. Four weeks after implantion of HAP/BMP complex, new bone (arrows) is rimming the granules of the complex. HE staining x 66. Four weeks after implantion of the granules of HAP, as a control group, the granules of HAP are covered with fibrous tissue (arrow). HE staining x 66.
5 Ability of HAP-BMP Complex to Induce Dentin Formation 199 Plate I
6 200 F. Suwa et al. Plate II Fig. 4. Three weeks after implantation of HAP/BMP complex in the dog pulp, regular dentin (arrows) is observed. HE staining x 13. Fig. 5. Fig. 6. A dentin bridge composed of osteodentin (0) is formed by 4 weeks after the operation. D: normal dentin, H: HAP granules. HE staining x 66. By 8 weeks, the osteodentin bridge (B) is calcified. New bone covers the cutting surface of the root dentin (D) and continues to new bone (arrows) of HAP granules (H). HE staining x 33. Fig. 7. In the control group, new bone formation is not observed at 8 weeks. H: HAP granules HE staining x 33.
7 A hl II l\ ol I A P- ( (nriplc Indu,_ I kilt urmatlun 101 Platt: 11
BONE TISSUE. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
BONE TISSUE Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology BONE FUNCTION Support Protection (protect internal organs) Movement (provide leverage system for skeletal muscles, tendons, ligaments
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp 1- Coronal pulp
 Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Lec. 11 & 12 Dr. Ali H. Murad Dental pulp Is the soft connective tissue located in the central portion of each tooth. All pulps have similar morphologic characteristic, such as a soft, gelatinous consistency
Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
Biology Dr. Khalida Ibrahim BONE TISSUE Bone tissue is a specialized form of connective tissue and is the main element of the skeletal tissues. It is composed of cells and an extracellular matrix in which
06 Tooth Development and Eruption
 + 06 Tooth Development and Eruption Tooth development Root development PDL and alveolar bone development Primary tooth eruption and shedding Permanent tooth eruption Q. Where and how tooth starts to form?
+ 06 Tooth Development and Eruption Tooth development Root development PDL and alveolar bone development Primary tooth eruption and shedding Permanent tooth eruption Q. Where and how tooth starts to form?
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alginate, tooth-shaped, for constructs, encapsulated pulp cells in, 589 590 Antibiotic paste, triple, change in root length and width
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alginate, tooth-shaped, for constructs, encapsulated pulp cells in, 589 590 Antibiotic paste, triple, change in root length and width
Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis)
 Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
Lecture four Dr. Wajnaa Oral Histology Dentin Formation(Dentinogenesis) Dentinogenesis begins at the cusp tips after the odontoblasts have differentiated and begin collagen production. Dentinogenesis growth
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary
 SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
SalvinOss Xenograft Bone Graft Material In Vivo Testing Summary Summary of In Vivo Use Of Bioresorbable Xenograft Bone Graft Materials In The Treatment Of One-Walled Intrabony Defects In A Canine Model
Development of teeth. 5.DM - Pedo
 Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
Development of teeth 5.DM - Pedo Tooth development process of continuous changes in predetermined order starts from dental lamina A band of ectodermal cells growing from the epithelium of the embryonic
CAP STAGE. Ans 1 The following are the stages of tooth development :
 Ans 1 The following are the stages of tooth development : 1. Bud stage 2. Cap stage 3. Bell stage 4. Advanced bell stage 5. Formation of Hertwig s epithelial root sheath BUD STAGE 1. Around the eighth
Ans 1 The following are the stages of tooth development : 1. Bud stage 2. Cap stage 3. Bell stage 4. Advanced bell stage 5. Formation of Hertwig s epithelial root sheath BUD STAGE 1. Around the eighth
DENTIN-PULP COMPLEX. Erlina Sih Mahanani. School of Dental sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia. Erlina Sih Mahanani
 DENTIN-PULP COMPLEX School of Dental sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Introduction Overview anatomy & histology of dentin and pulp. Development of dentin and pulp Structure of dentin and pulp Dentin
DENTIN-PULP COMPLEX School of Dental sciences Universiti Sains Malaysia Introduction Overview anatomy & histology of dentin and pulp. Development of dentin and pulp Structure of dentin and pulp Dentin
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue
 Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
Chapter 6: Skeletal System: Bones and Bone Tissue I. Functions A. List and describe the five major functions of the skeletal system: 1. 2. 3.. 4. 5.. II. Cartilage A. What do chondroblasts do? B. When
botiss dental bone & tissue regeneration biomaterials collacone max Innovative composite matrix socket preservation form-fitting resorbable composite
 dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 botiss regeneration system maxresorb flexbone* collacone.. max
dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 botiss regeneration system maxresorb flexbone* collacone.. max
botiss biomaterials bone & tissue regeneration collacone max Innovative composite matrix socket preservation form-fitting resorbable composite
 bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 Socket preservation safeguarding your sockets collacone.. max flexbone*
bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials socket preservation Innovative composite matrix form-fitting resorbable composite 1 Socket preservation safeguarding your sockets collacone.. max flexbone*
Bone augmentation with biomaterials
 Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
Role of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in Periodontics
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 6, June 2016 804 Role of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in Periodontics Dr.Jaishree Tukaram Kshirsagar, MDS, Dr.Aruna Kaveri
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 6, Issue 6, June 2016 804 Role of Bone Morphogenetic Proteins in Periodontics Dr.Jaishree Tukaram Kshirsagar, MDS, Dr.Aruna Kaveri
The Histology of Dentin
 The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
The Histology of Dentin Pauline Hayes Garrett, D.D.S. Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore This material was taken from: Essentials of Oral
o~ r;'c' - OSTEOARTHRITIS
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2001) 9, Supplement A, S102-S108 2001 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0451, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on IDE~l Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2001) 9, Supplement A, S102-S108 2001 OsteoArthritis Research Society International doi:10.1053/joca.2001.0451, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com on IDE~l Osteoarthritis
The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic
 1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
1 1 INTRODUCTION The treatment of destructive periodontal disease, due to specific periodontopathic bacteria, aims at the regeneration of a periodontal attachment composed of new cementum, alveolar bone
Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane
 Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane Pericardium GBR/GTR Membrane Facts - CE since 2009 - so far no serious clinical complication or objection - approx. 250.000 successful clinical treatments
Scientific & Clinical Evidence Jason membrane Pericardium GBR/GTR Membrane Facts - CE since 2009 - so far no serious clinical complication or objection - approx. 250.000 successful clinical treatments
One step close to growing a new set of dentures.
 One step close to growing a new set of dentures. A team headed up by Dr. Jinhua Yu of the Institute of Stomatology at Nanjing University, China, has continued to lay the foundation for a whole new line
One step close to growing a new set of dentures. A team headed up by Dr. Jinhua Yu of the Institute of Stomatology at Nanjing University, China, has continued to lay the foundation for a whole new line
Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians. with Marnie Hayward
 Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians with Marnie Hayward Salivary glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual Salivary glands position Parotid glands Lie below ear and behind angle
Dental Anatomy and Physiology for Clinical Dental Technicians with Marnie Hayward Salivary glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual Salivary glands position Parotid glands Lie below ear and behind angle
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH
 PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH PRO-STIM Injectable Inductive Graft TECHNICAL MONOGRAPH Headline Contents Headline Appendix 4 5 7 8 13 14 Clinical Benefits Self-Forming Porous Scaffold
Development of Bone Canaliculi During Bone Repair
 Development of Bone Canaliculi During Bone Repair K. KUSUZAKI, 1 N. KAGEYAMA, 1 H. SHINJO, 1 H. TAKESHITA, 1 H. MURATA, 1 S. HASHIGUCHI, 1 T. ASHIHARA, 2 and Y. HIRASAWA 1 Departments of 1 Orthopaedic
Development of Bone Canaliculi During Bone Repair K. KUSUZAKI, 1 N. KAGEYAMA, 1 H. SHINJO, 1 H. TAKESHITA, 1 H. MURATA, 1 S. HASHIGUCHI, 1 T. ASHIHARA, 2 and Y. HIRASAWA 1 Departments of 1 Orthopaedic
Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy
 Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy von Alexandrina L. Dumitrescu 1. Auflage Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy Dumitrescu schnell und portofrei erhältlich bei beck-shop.de DIE FACHBUCHHANDLUNG
Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy von Alexandrina L. Dumitrescu 1. Auflage Chemicals in Surgical Periodontal Therapy Dumitrescu schnell und portofrei erhältlich bei beck-shop.de DIE FACHBUCHHANDLUNG
Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs
 Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Current Applied Physics 5 (2005) 507 511 www.elsevier.com/locate/cap Evaluation of different grafting materials in three-wall intra-bony defects around dental implants in beagle dogs Ui-Won Jung a, Hee-Il
Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway
 Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway Jieyuan Zhang, Xiaolin Liu, Haiyan Li, Chunyuan Chen, Bin Hu, Xin Niu, Qing
Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signalling pathway Jieyuan Zhang, Xiaolin Liu, Haiyan Li, Chunyuan Chen, Bin Hu, Xin Niu, Qing
BEGO BIOMATERIALS When the result counts
 BEGO BIOMATERIALS When the result counts Partners in Progress INTRO Challenge what exists get the right answers We practise systematic thinking with a passion and we are never satisfied with the status
BEGO BIOMATERIALS When the result counts Partners in Progress INTRO Challenge what exists get the right answers We practise systematic thinking with a passion and we are never satisfied with the status
Fish Skin Grafts Promote Superior Cell Ingrowth Compared to Amnion Allografts, Human Cadaver Skin and Mammalian Extracellular Matrix (ECM)
 Fish Skin Grafts Promote Superior Cell Ingrowth Compared to Amnion Allografts, Human Cadaver Skin and Mammalian Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Christopher L. Winters, DPM American Health Network Indianapolis,
Fish Skin Grafts Promote Superior Cell Ingrowth Compared to Amnion Allografts, Human Cadaver Skin and Mammalian Extracellular Matrix (ECM) Christopher L. Winters, DPM American Health Network Indianapolis,
2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J DENTAL TISSUE REPLACEMENT AND REGENERATION
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s/massachusetts General Hosp. VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J DENTAL TISSUE REPLACEMENT AND REGENERATION
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Harvard Medical School Brigham and Women s/massachusetts General Hosp. VA Boston Healthcare System 2.79J/3.96J/BE.441/HST522J DENTAL TISSUE REPLACEMENT AND REGENERATION
Bone Grafting for Socket Preservation
 Bone Grafting for Socket Preservation Dr. Karl R. Koerner Normal extraction facial bone loss. Excessive force. Commonly the thickness of facial bone. Hussain, A. et al. Ridge preservation comparing a nonresorbable
Bone Grafting for Socket Preservation Dr. Karl R. Koerner Normal extraction facial bone loss. Excessive force. Commonly the thickness of facial bone. Hussain, A. et al. Ridge preservation comparing a nonresorbable
DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth.
 Lec. 7 Dr. Ali H.Murad DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth. Physical properties: 1-Dentin is pale yellow in color,
Lec. 7 Dr. Ali H.Murad DENTIN It a hard vital tissue, surrounds the pulp & underlies the enamel on the crown & the cementum on the roots of the teeth. Physical properties: 1-Dentin is pale yellow in color,
A scanning electron microscope study of the capillary loops
 Jpn.J.Oral Biol.,28:239-244,1986. A scanning electron microscope study of the capillary loops of oral epithelial papillae using corrosive resin casts I.Gingiva,alveolar mucosa,and buccal mucosa Yoshiaki
Jpn.J.Oral Biol.,28:239-244,1986. A scanning electron microscope study of the capillary loops of oral epithelial papillae using corrosive resin casts I.Gingiva,alveolar mucosa,and buccal mucosa Yoshiaki
Bones. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
 Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Bones Osteocytes : Are responsible for maintenance of bones Present in lacunae, and send processes. Unable to divide. The division of bones anatomically is : long, short, irregular, flat and sesamoid.
Osteogenic Efficiency of Demineralized and Lyophylized Xenogeneic Bone and Syngeneic Dentine Implants in Mice
 PL-ISSN 0015-5497 (print), ISSN 1734-9168 (online) Folia Biologica (Kraków), vol. 61 (2013), No 1-2 Institute of Systematics and Evolution of Animals, PAS, Kraków, 2013 doi:10.3409/fb61_1-2.25 Osteogenic
PL-ISSN 0015-5497 (print), ISSN 1734-9168 (online) Folia Biologica (Kraków), vol. 61 (2013), No 1-2 Institute of Systematics and Evolution of Animals, PAS, Kraków, 2013 doi:10.3409/fb61_1-2.25 Osteogenic
Inflammatory pulp conditions DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY
 Inflammatory pulp conditions DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY Inflammation is the single most important disease process affecting the dental pulp. Pulpitis
Inflammatory pulp conditions DR.AHMED IBRAHIM AL-JOBORY B.D.S. M.SC. CONSERVATIVE DEPARTMENT/ BAGHDAD UNIVERSITY Inflammation is the single most important disease process affecting the dental pulp. Pulpitis
Oral cavity Lab exercises
 Oral cavity Lab exercises Slide #190 (GT-1-32). Oral cavity, goat. large conical buccal papillae stratified squamous epithelium keratinized or non-keratinized no muscularis mucosae connective tissue represents
Oral cavity Lab exercises Slide #190 (GT-1-32). Oral cavity, goat. large conical buccal papillae stratified squamous epithelium keratinized or non-keratinized no muscularis mucosae connective tissue represents
Surgical Therapy. Tuesday, April 2, 13. Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS
 Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Surgical Therapy Alessan"o Geminiani, DDS, MS Periodontal Flap: a surgical procedure in which incisions are made in the gingiva or mucosa to allow for separation of the epithelium and connective tissues
Chapter 4. Cartilage and Bone. Li Shu-Lei instructor. Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University
 Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Chapter 4 Cartilage and Bone Li Shu-Lei instructor Dept. Histology and Embryology, School of Basic Medical Sciences, Jilin University I Cartilage a specialized connective tissue Characterizers: Cartilage
Derived copy of Bone *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
OpenStax-CNX module: m57739 1 Derived copy of Bone * Shannon McDermott Based on Bone by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0 By
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury
 Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Foundation Revolutionary Bone Augmentation Material. Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Regional Partner
 Foundation Revolutionary Bone Augmentation Material Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Regional Partner Easy Placement, Effective Results Tooth extraction. Socket is curetted and bone is exposed. Insertion
Foundation Revolutionary Bone Augmentation Material Thinking ahead. Focused on life. Regional Partner Easy Placement, Effective Results Tooth extraction. Socket is curetted and bone is exposed. Insertion
Dentinogenesis and dentin permeability
 Dentinogenesis and dentin permeability Dr. Gábor Varga February, 2016 Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry, Semmelweis University Radiograph of teeth dentin is the major component Molar longitudinal
Dentinogenesis and dentin permeability Dr. Gábor Varga February, 2016 Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry, Semmelweis University Radiograph of teeth dentin is the major component Molar longitudinal
Bone augmentation with maxgraft
 Patient information bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with maxgraft established safe X100 natural Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the jaw bone loss
Patient information bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with maxgraft established safe X100 natural Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the jaw bone loss
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using Various Bone Substitutes -A Web Form of Titanium Fibers Promotes Rapid Bone Development-
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 53, No. 5, pp. 257-263 2007 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using Various Bone Substitutes -A Web Form of Titanium Fibers Promotes Rapid Bone Development- HIROSHI MASAGO 1, YASUYUKI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 53, No. 5, pp. 257-263 2007 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation Using Various Bone Substitutes -A Web Form of Titanium Fibers Promotes Rapid Bone Development- HIROSHI MASAGO 1, YASUYUKI
TOX 2017 Magyar Toxikológusok Társasága Tudományos konferencia Bükfürdő, Október
 TOX 2017 Magyar Toxikológusok Társasága Tudományos konferencia Bükfürdő, Október 11-13. Histopathological evaluation of the teeth in regulatory studies: what are the needs and what can we learn from it
TOX 2017 Magyar Toxikológusok Társasága Tudományos konferencia Bükfürdő, Október 11-13. Histopathological evaluation of the teeth in regulatory studies: what are the needs and what can we learn from it
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 and decorin expression in old fracture fragments and surrounding tissues
 Bone morphogenetic protein 2 and decorin expression in old fracture fragments and surrounding tissues X.G. Han 1, D.K. Wang 2, F. Gao 3, R.H. Liu 1 and Z.G. Bi 1 1 Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated
Bone morphogenetic protein 2 and decorin expression in old fracture fragments and surrounding tissues X.G. Han 1, D.K. Wang 2, F. Gao 3, R.H. Liu 1 and Z.G. Bi 1 1 Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated
and Non-Human MODULE No.17: Structural Variation in Teeth- Human and Non-Human
 SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag MODULE No.17: Structural Variation in Teeth- Human and FSC_P11_M17 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Structure of Human
SUBJECT Paper No. and Title Module No. and Title Module Tag MODULE No.17: Structural Variation in Teeth- Human and FSC_P11_M17 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction 3. Structure of Human
ULTRASONIC DEVICE IN BONE CUTTING
 Acta orthop. scand. 52, 5-10, 1981 ULTRASONIC DEVICE IN BONE CUTTING A Histological and Scanning Electron Microscopical Study H. ARO*, H. KALLIONIEMI**, A. J. AHO* & P. KELLOKUMPU-LEHTINEN*** *Department
Acta orthop. scand. 52, 5-10, 1981 ULTRASONIC DEVICE IN BONE CUTTING A Histological and Scanning Electron Microscopical Study H. ARO*, H. KALLIONIEMI**, A. J. AHO* & P. KELLOKUMPU-LEHTINEN*** *Department
ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM. Dr. Fatin Awartani
 ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM Part II Cementum and Alveolar bone Associate Professor Periodontal division King Saud university Cementum Calcified mesenchymal tissue that forms the outer covering of the anatomic
ANATOMY OF THE PERIODONTIUM Part II Cementum and Alveolar bone Associate Professor Periodontal division King Saud university Cementum Calcified mesenchymal tissue that forms the outer covering of the anatomic
Oral manifestations of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Type VII: histological examination of a primary tooth
 PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1990 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 12, Number 2 Oral manifestations of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Type VII: histological examination of a primary tooth
PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY/Copyright 1990 by The American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Volume 12, Number 2 Oral manifestations of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome Type VII: histological examination of a primary tooth
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
Semester Credits: 3 Lecture Hours: 3. Prerequisites:
 Revised: Fall 2015 Semester Credits: 3 Lecture Hours: 3 21THistology DNH 115 Admission into dental hygiene program. Prerequisites: Course Description: Presents a study of the microscopic and macroscopic
Revised: Fall 2015 Semester Credits: 3 Lecture Hours: 3 21THistology DNH 115 Admission into dental hygiene program. Prerequisites: Course Description: Presents a study of the microscopic and macroscopic
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
B U I L D S T R O N G B O N E F A S T
 B U I L D S T R O N G B O N E F A S T Putty MIS Particulate Morsels A BIOACTIVE SYNTHETIC BONE FOR FASTER HEALING NovaBone is a 100% bioactive synthetic material composed from elements that occur naturally
B U I L D S T R O N G B O N E F A S T Putty MIS Particulate Morsels A BIOACTIVE SYNTHETIC BONE FOR FASTER HEALING NovaBone is a 100% bioactive synthetic material composed from elements that occur naturally
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
Pediatric endodontics. Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR
 Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 4,000 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
Structure of an Incisor
 MAMMALIAN TEETH Mammals have different types and shapes of teeth and they are thus termed Heterodonts. Those which have teeth of the same size and shapes are termed as Homodonts. In mammals teeth consist
MAMMALIAN TEETH Mammals have different types and shapes of teeth and they are thus termed Heterodonts. Those which have teeth of the same size and shapes are termed as Homodonts. In mammals teeth consist
Periodontal ligament
 Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
Periodontal ligament The periodontium The periodontium includes: The gingiva Cementum Periodontal ligament Alveolar bone Def: The periodontal ligament is the dense fibrous connective tissue that occupies
Ossification and Bone Remodeling
 Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
Ossification and Bone Remodeling Pre-natal Ossification Embryonic skeleton: fashioned from fibrous membranes or cartilage to accommodate mitosis. 2 types of pre-natal ossification (bone formation) 1.
What We Know About Life in Jaw Bones?
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Clinical Image What We Know About Life in Jaw Bones? Elena Mokhireva* Dental surgeon, Russian Federation, Hospital & Health Care, Russia *Corresponding Author: Elena
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Clinical Image What We Know About Life in Jaw Bones? Elena Mokhireva* Dental surgeon, Russian Federation, Hospital & Health Care, Russia *Corresponding Author: Elena
Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Department of Anatomy, Glasgow University
 THE UPTAKE OF LABELLED SULPHATE INJECTED INTO THE HOST ANIMAL BY CARTILAGE HOMOGRAFTS By G. M. WYBURN, D.Sc., F.R.F.P.S.G., and P. BACSICH, D.Sc., M.D. Department of Anatomy, Glasgow University INTRODUCTION
THE UPTAKE OF LABELLED SULPHATE INJECTED INTO THE HOST ANIMAL BY CARTILAGE HOMOGRAFTS By G. M. WYBURN, D.Sc., F.R.F.P.S.G., and P. BACSICH, D.Sc., M.D. Department of Anatomy, Glasgow University INTRODUCTION
Peggers Super Summaries Basic Sciences Bone
 Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
Bone Overview & Turnover BONES Function o Support o Protection o Assisting movement o Storage of minerals o Production of red blood cells from marrow Types o Cancellous o Compact with Haversian systems
GRAFTON DEMINERALIZED BONE: FIBER TECHNOLOGY AND PERFORMANCE IMPLICATIONS
 GRAFTON DEMINERALIZED BONE: FIBER TECHNOLOGY AND PERFORMANCE IMPLICATIONS Based Upon the Published Source: Martin GJ, Jr., Boden SD, Titus L, Scarborough NL. New formulations of demineralized bone matrix
GRAFTON DEMINERALIZED BONE: FIBER TECHNOLOGY AND PERFORMANCE IMPLICATIONS Based Upon the Published Source: Martin GJ, Jr., Boden SD, Titus L, Scarborough NL. New formulations of demineralized bone matrix
Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health. Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory
 Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory Pulp Is a viscous connective tissue of collagen fibers and ground substance supporting the vital cellular, vascular, and nerve structures
Restorative Dentistry and it s related to Pulp health Dr.Ahmed Al-Jobory Pulp Is a viscous connective tissue of collagen fibers and ground substance supporting the vital cellular, vascular, and nerve structures
Effect of BMPs on Hematopoietic Injury of Acute Radiation Sickness in Mice. Tian Qiong*, Zhang Shaozhang*, Pu Qin*, Zhang Fake*, Hannah X.H.
 Effect of BMPs on Hematopoietic Injury of Acute Radiation Sickness in Mice Tian Qiong*, Zhang Shaozhang*, Pu Qin*, Zhang Fake*, Hannah X.H.** Abstract Purpose: To investigate the effect of Bone morphogenetic
Effect of BMPs on Hematopoietic Injury of Acute Radiation Sickness in Mice Tian Qiong*, Zhang Shaozhang*, Pu Qin*, Zhang Fake*, Hannah X.H.** Abstract Purpose: To investigate the effect of Bone morphogenetic
BIOACTIVE SYNTHETIC GRAFT
 B U I L D S T R O N G B O N E F A S T Putty Particulate Morsels A BIOACTIVE SYNTHETIC BONE FOR FASTER HEALING NovaBone is a 100% bioactive synthetic material composed from elements that occur naturally
B U I L D S T R O N G B O N E F A S T Putty Particulate Morsels A BIOACTIVE SYNTHETIC BONE FOR FASTER HEALING NovaBone is a 100% bioactive synthetic material composed from elements that occur naturally
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
In Vivo Heat-stimulus Triggered Osteogenesis
 In Vivo Heat-stimulus Triggered Osteogenesis Kunihiro Ikuta 1, Hiroshi Urakawa 1, Eiji Kozawa 1, Shunsuke Hamada 1, Naoki Ishiguro 2, Yoshihiro Nishida 1. 1 Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 2 Nagoya Graduated
In Vivo Heat-stimulus Triggered Osteogenesis Kunihiro Ikuta 1, Hiroshi Urakawa 1, Eiji Kozawa 1, Shunsuke Hamada 1, Naoki Ishiguro 2, Yoshihiro Nishida 1. 1 Nagoya University, Nagoya, Japan, 2 Nagoya Graduated
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue
 The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
The Skeletal System:Bone Tissue Dynamic and ever-changing throughout life Skeleton composed of many different tissues cartilage, bone tissue, epithelium, nerve, blood forming tissue, adipose, and dense
BioVin Collagen Membrane
 BioVin Collagen Membrane Resorbable cross-linked collagen membrane BioVin Bovine Bone Bovine Bone Substitute OToss Synthetic Bone Synthetic Resorbable Biphasic Calcium Phosphate OToss Synthetic Bone Inject
BioVin Collagen Membrane Resorbable cross-linked collagen membrane BioVin Bovine Bone Bovine Bone Substitute OToss Synthetic Bone Synthetic Resorbable Biphasic Calcium Phosphate OToss Synthetic Bone Inject
L-PRF Leukocyte-Platelet Rich Fibrin
 Patient information bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials L-PRF Leukocyte-Platelet Rich Fibrin innovative How to naturally support wound healing safe natural Wound healing What happens when a
Patient information bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials L-PRF Leukocyte-Platelet Rich Fibrin innovative How to naturally support wound healing safe natural Wound healing What happens when a
Tooth eruption and movement
 Tooth eruption and movement Dr. Krisztián Nagy Diphydont dentition Deciduous dentition primary dentition Diphydont dentition Permanent dentition secondary dentition Mixed Dentition: Presence of both dentitions
Tooth eruption and movement Dr. Krisztián Nagy Diphydont dentition Deciduous dentition primary dentition Diphydont dentition Permanent dentition secondary dentition Mixed Dentition: Presence of both dentitions
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation
 Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
Cytoflex Barrier Membrane Clinical Evaluation Historical Background Guided tissue regeneration is a well established concept in the repair of oral bone defects. The exclusion of soft tissue epithelial
PRP Usage in Today's Implantology
 Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
Bone modeling and remodeling How does a bone form without augmentation?
 Overview on Bone formation,bone grafts materials, and Augma Biomaterials bone cements Bone modeling and remodeling How does a bone form without augmentation? Bone Modeling Initial formation of a bone A
Overview on Bone formation,bone grafts materials, and Augma Biomaterials bone cements Bone modeling and remodeling How does a bone form without augmentation? Bone Modeling Initial formation of a bone A
THE NEXT FRONTIER OF BONE REGENERATION
 THE NEXT FRONTIER OF BONE REGENERATION where Technology meets Nature swiss made SmartBone is new composite bone substitute specifically developed for bone regeneration in oral and maxillofacial reconstructive
THE NEXT FRONTIER OF BONE REGENERATION where Technology meets Nature swiss made SmartBone is new composite bone substitute specifically developed for bone regeneration in oral and maxillofacial reconstructive
In the last decade of the 20 th century, special emphasis was put on an emerging field of science: Tissue engineering,which combines the state of the
 In the last decade of the 20 th century, special emphasis was put on an emerging field of science: Tissue engineering,which combines the state of the art materials science with concepts from the life sciences.
In the last decade of the 20 th century, special emphasis was put on an emerging field of science: Tissue engineering,which combines the state of the art materials science with concepts from the life sciences.
Remaining dentin thickness Shallow cavity depth Preparation 0.5 mm into dentin (ideal depth) Moderate cavity depth Remaining dentin over pulp of at le
 Deep carious lesions management Remaining dentin thickness Shallow cavity depth Preparation 0.5 mm into dentin (ideal depth) Moderate cavity depth Remaining dentin over pulp of at least 1-2 mm Deep cavity
Deep carious lesions management Remaining dentin thickness Shallow cavity depth Preparation 0.5 mm into dentin (ideal depth) Moderate cavity depth Remaining dentin over pulp of at least 1-2 mm Deep cavity
Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration
 Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration One toolbox for your needs! Tefguide 9000 742 401 12x24 mm pc 1 Osgide 9000 701 520 15 x 20 mm pc 1 Osbone 9000 800 255 250-1000 μm 0.25 cc 5 Product Specifications
Guided Tissue and Bone Regeneration One toolbox for your needs! Tefguide 9000 742 401 12x24 mm pc 1 Osgide 9000 701 520 15 x 20 mm pc 1 Osbone 9000 800 255 250-1000 μm 0.25 cc 5 Product Specifications
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Strong bone for beautiful teeth. Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide
 Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
P105 Predictable Bone Grafting for Site Preparation for Implants and Prosthetics Workshop JAMES GRISDALE, DDS THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 26
 P105 Predictable Bone Grafting for Site Preparation for Implants and Prosthetics Workshop JAMES GRISDALE, DDS THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 26 Please complete the speaker evaluation form in the Midwinter Meeting
P105 Predictable Bone Grafting for Site Preparation for Implants and Prosthetics Workshop JAMES GRISDALE, DDS THURSDAY, FEBRUARY 26 Please complete the speaker evaluation form in the Midwinter Meeting
Regeneration Bone Grafting & Soft Tissue Management
 Regeneration Bone Grafting & Soft Tissue Management OSTEON TM II Table of Contents Bone Graft Material OSTEON TM II Collagen 04 OSTEON TM Collagen 06 OSTEON TM II 08 OSTEON TM 12 ORTHOPEDIC OSTEON TM 14
Regeneration Bone Grafting & Soft Tissue Management OSTEON TM II Table of Contents Bone Graft Material OSTEON TM II Collagen 04 OSTEON TM Collagen 06 OSTEON TM II 08 OSTEON TM 12 ORTHOPEDIC OSTEON TM 14
Pattern of bone resorption after extraction
 Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
Teeth loss Pattern of bone resorption after extraction 50% in 1st year 2/ 3 in first 3 months Reich KM, Huber CD, Lippnig WR, Um C, Watzek G, Tangl S. (2011, 17). Atrophy of Residual Alveolar Ridge following
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS
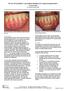 The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
The Use of DynaMatrix Extracellular Membrane for Gingival Augmentation: A Case Series Dr. Stephen Saroff, DDS LOCALIZED RECESSION ON TOOTH #25 DUE TO BONE RECESSION (PRE OP) Introduction Tissue grafting
Characteristics of Seminar the number Iof odontoblasts
 Characteristics of Seminar the number Iof odontoblasts in human Sangtean dental Kongpan pulp post-mortem 52312346 Marko Vavpotič a,tomaž Turk b, Draga Štiblar Martinčic c, Jože Balažic a a Institue of
Characteristics of Seminar the number Iof odontoblasts in human Sangtean dental Kongpan pulp post-mortem 52312346 Marko Vavpotič a,tomaž Turk b, Draga Štiblar Martinčic c, Jože Balažic a a Institue of
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
CHAPTER 6 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Bone is made up of several different tissues working together: bone, cartilage, dense connective tissue, epithelium, various blood forming tissues, adipose
Ozonated Olive Oil Enhances the Growth of Granulation Tissue in a Mouse Model of Pressure Ulcer
 Ozone: Science and Engineering, 29: 503 507 Copyright # 2007 International Ozone Association ISSN: 0191-9512 print / 1547-6545 online DOI: 10.1080/01919510701618205 Ozonated Olive Oil Enhances the Growth
Ozone: Science and Engineering, 29: 503 507 Copyright # 2007 International Ozone Association ISSN: 0191-9512 print / 1547-6545 online DOI: 10.1080/01919510701618205 Ozonated Olive Oil Enhances the Growth
Oral Histology. Alveolar bone or process: Functions of alveolar bone: Chemical composition: Development of the alveolar process: Dr.
 Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
الكيمياء احليوية لألنسجة املتخصصة. Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 الكيمياء احليوية لألنسجة املتخصصة Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues BCH 443 Biochemistry of specialized Tissues Course Symbol & No. : BCH 443 Credit Hours : 2 (2+0) Prerequisite : BCH 347 Class schedule
الكيمياء احليوية لألنسجة املتخصصة Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues BCH 443 Biochemistry of specialized Tissues Course Symbol & No. : BCH 443 Credit Hours : 2 (2+0) Prerequisite : BCH 347 Class schedule
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs
 Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Applications in Dermatology, Dentistry and LASIK Eye Surgery using LASERs http://www.medispainstitute.com/menu_laser_tattoo.html http://www.life123.com/bm.pix/bigstockphoto_close_up_of_eye_surgery_catar_2264267.s600x600.jpg
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Medical NBDE-II. Dental Board Exams Part I.
 Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
PROCHONDRIX CARTILAGE RESTORATION MATRIX CONTAINS GROWTH FACTORS NECESSARY FOR HYALINE CARTILAGE REGENERATION
 A L L O S O U R C E PROCHONDRIX CARTILAGE RESTORATION MATRIX CONTAINS GROWTH FACTORS NECESSARY FOR HYALINE CARTILAGE REGENERATION Ryan Delaney MS; Carolyn Barrett BS, MBA; Peter Stevens PhD, MBA AlloSource,
A L L O S O U R C E PROCHONDRIX CARTILAGE RESTORATION MATRIX CONTAINS GROWTH FACTORS NECESSARY FOR HYALINE CARTILAGE REGENERATION Ryan Delaney MS; Carolyn Barrett BS, MBA; Peter Stevens PhD, MBA AlloSource,
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS. These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore.
 BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
BONE LABORATORY DEMONSTRATIONS These demonstrations are found on the bulletin boards outside the MCO Bookstore. COMPACT & TRABECULAR BONE - LM When viewed under the polarizing light microscope, the layering
