Revitalization Teeth: A Prospective Case Series
|
|
|
- David Thomas
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2018; 6(2): doi: /j.ajcem ISSN: (Print); ISSN: (Online) Case Report Revitalization Teeth: A Prospective Case Series Christian Holscher 1, *, Kerstin Galler 2 1 Integra, Department of Integra Medical Research, Luxemburg, Luxembourg 2 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Periodontology, University Medical Center, Regensburg, Germany address: * Corresponding author To cite this article: Christian Holscher, Kerstin Galler. Revitalization Teeth: A Prospective Case Series. American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine. Vol. 6, No. 2, 2018, pp doi: /j.ajcem Received: March 3, 2018; Accepted: March 19, 2018; Published: April 10, 2018 Abstract: In addition to caries, dental trauma is one of the most common causes of damage to permanent teeth and pulp. Pulp necrosis or damage to Hertwig s epithelial root sheath (HERS) leads to arrested tooth root development in immature teeth. Pulp necrosis can be treated by revitalization, a biology-based treatment alternative to apexification. Induction of a blood clot inside the root canal can lead to healing of periapical lesions and increased root length and thickness. Traumatic impact as the cause of pulp necrosis may affect the treatment outcome negatively, depending on the severity of damage to HERS. Revitalization procedures in four teeth with pulp necrosis following dental trauma were performed using a standardized treatment protocol. Three teeth were dislocated, the fourth tooth was avulsed. Each patient exhibited at least two clinical signs of pulp necrosis as well as radiographic evidence of apical periodontitis. X-rays were taken using individualized film holders (IFH) to reliably assess the treatment outcome. Revitalization treatment was performed without instrumentation of the canal walls, but disinfection with sodium hypochlorite and intracanal dressing with triple antibiotic paste (TAP) for three weeks. Provocation of bleeding was induced in a second visit, the blood clot was covered with collagen followed by calcium silicate cement, and teeth were sealed with resin composite. Clinical and radiographic follow-ups were performed after 1, 3, 6 and 12 months. An increase of root length and thickness was evident in the three teeth with dislocation injuries. In one case, formation of mineralized tissue below the calcium silicate cement was observed. The tooth which had been avulsed and replanted showed resorption of the apical root area. The observations made in this study support the assumption that a separation of HERS and the cells that form pulp and dentin during tooth root development may negatively affect the outcome after a standardized revitalization procedure. The consistent implementation of standardized treatment protocols and the use of IFH are helpful receiving a reliable treatment outcome. Keywords: Revascularization, Maturogenesis, Regeneration, Dental Trauma, Hertwig s Epithelial Root Sheath (HERS), Root Canal Treatment 1. Introduction Tooth root development in humans begins after the completion of crown formation and is controlled by the cells of Hertwig s epithelial root sheath (HERS). Epithelial cells, which are derived from the cervical loop of the enamel organ, proliferate and extend in an apical direction to determine the root number, shape and length. Among other functions, HERS cells instruct the underlying mesenchymal stem cells of the apical papilla to differentiate into odontoblasts to form root dentin and pulp [1]. HERS is a transient structure, it becomes fenestrated as root formation continues and is subsequently reduced to the epithelial rests of Malassez (ERM) [2-3]. If pulp necrosis occurs in a premature tooth with incomplete root formation, stem cells of the apical papilla will eventually perish and no longer be available to differentiate and form pulp cells and dentin. Pilot experiments by Huang et al. in minipigs have shown that surgical removal of the apical papilla at an early stage of root development led to arrested root development [4]. Similarly, odontoblast differentiation inevitably stops after a growth arrest of HERS. Radicular
2 American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2018; 6(2): dysplasia as a consequence occurs mainly due to trauma or in association with dentin disorders [5]. Revitalization procedures aim at the recruitment of stem cells of the apical papilla, which can repopulate the root canal, undergo differentiation and form dental pulp. After provocation of bleeding, stem cells of the apical papilla are flushed in with the blood stream and accumulate in the canal [6]. An increase of root length and thickness is described after revitalization in multiple case reports and case series [7-9]. Whereas the role of stem cells of the apical papilla in this process has been assessed and described, evidence on the influence of HERS cells is sparse. However, an intact HERS may be required in order to allow for continued root formation after a revitalization procedure. Traumatic impact, especially avulsion but possibly also severe dislocation injuries may cause a disruption of the epithelial cell layer and thus a separation of epithelial and mesenchymal cells. It can be speculated that this spatial disruption will abolish the signaling cues indispensable for mesenchymal cell differentiation and thus in an irreversible arrest of root development. Numerous case reports demonstrate the success of revitalization procedures in premolars with structural abnormalities, such as dentes evaginati. Interesting observations, which show the completion of root tip formation separated from the coronal part of the root after dislocation shed light on unfavorable conditions for a completion of root formation [10]. From a biological point of view, it appears feasible to assume that severe dislocation injuries with damage to HERS may result in impaired regeneration and failure to induce a completion of root formation. 2. Clinical Cases Four teeth with pulp necrosis in three patients after dental trauma were treated with revitalization procedures. The medical history was without pathological findings in all cases, and tetanus shots had been given recently. After comprehensive discussion of the risks and possible outcomes of revitalization treatment, consent of the patients and parents was obtained. Case 1 A 7-year-old boy experienced an accident at school and was referred to the Department of Conservative Dentistry at the University of Goettingen due to a luxation injury of both upper middle incisors. Both teeth 11 and 21 were dislocated 3 to 4 mm in a palatal direction and showed mobility grade II. The teeth were free of caries, tooth 21 presented with a dentin-enamel fracture without pulp exposure, which was sealed with a flowable composite. Diagnostic testing was inconclusive to cold, but the patient reported sensitivity to palpation and percussion. Periodontal probing depths were within normal limits (1 and 2 mm). The teeth were repositioned and splinted flexibly for 2 weeks. Case 2 An 8-year-old girl was referred after an accident during swimming lessons at school. Tooth 11 was dislocated in a palatal direction and presented with an enamel fracture at the distal edge, which was sealed with flowable composite resin. The tooth was splinted with a flexible splint for 2 weeks. Case 3 An 11-year-old girl was referred after she had suffered a hit from a horse. Tooth 11 was avulsed, but promptly transferred to a dentosafe box (Medice, Iserlohn, Germany) and stored for approximately 30 minutes. Tooth 12 presented with a subluxation injury and mobility grade I. Tooth 11 was replanted and stabilized flexibly with a splint for 15 days. Additional lacerations of the gingiva were sutured. 3. Material and Methods 3.1. Diagnostic For all patients, soft chow for one week and the use of chlorhexidine mouth rinse for oral hygiene were recommended. Follow-ups were conducted weekly during the first month post injury, including clinical and radiographic examinations. Additional diagnostics included electric pulp testing (EPT) or, if ankyloses was suspected, the use of a periotest device (Medizintechnik Gulden, Modautal, Germany). Endodontic treatment was initiated if at least two clinical signs or symptoms (e.g. negative response to vitality testing with cold or EPT, tenderness to percussion, pain) were present in combination with radiographic evidence of apical periodontitis Revitalization After informed written consent, revitalization procedures were conducted in all cases and in accordance with the current guidelines [7, 11]. The procedural details were identical for all cases, following a standardized protocol (figure 1). All treatment steps were performed by only one experienced endodontic specialist. After rubber dam isolation, an access cavity was prepared and the diagnosis of pulp necrosis was clinically confirmed in all cases. Root canal length was determined electrometrically and additionally controlled under an operating microscope. The root canal walls were left intact, no mechanical instrumentation was performed, and canals were irrigated with 10 ml of 3% sodium hypochlorite for 60 seconds with a NaviTip cannula (G 30 Ultradent, Munich, Germany) 2 mm above the endometrically determined canal length. Patients did not experience pain throughout the treatment with exception of provocation of bleeding by instrumentation beyond the apex, which was dolorous despite local anesthesia in all cases. Provocation of bleeding was performed in the second visit two to three times before sufficient influx of blood into the canal was achieved. Insertion of a collagen matrix (PARASORB Cone, RESORBA Medical GmbH, Nürnberg, Germany) provided a thrust block, which allowed for condensation of the tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine, Septodont, France) against the blood clot.
3 42 Christian Holscher and Kerstin Galler: Revitalization Teeth: A Prospective Case Series Figure 1. Standardized treatment protocol according to the Clinical Considerations for a Regenerative Procedures of the AAE [11]. (IFH: individual film holder; WL: working length; TAP: triple-antibiotic-paste; CEJ: cemento-enamel junction) Evaluation of the Treatment Outcome In order to assess the progress after treatment with a series of radiographs, each patient received an individually adapted film holder (IFH). The position of the front teeth was retained using silicone impressions, which allowed for reproducible imaging with identical angulation (figure 2). X-rays were taken after adhesive seal of the cavity in order to avoid the risk of contamination of the root canal. enamel-cementum junction, the vertical plane at the anatomically prominent structure of the sutura palatina media. The superimposed image created from 3 radiographs (figures 3D, 4D, 5D) shows the root tip in red (directly after revitalization), orange (first follow-up) and blue (second follow up), respectively, in order to visualize changes Follow up Figure 2. Radiographs were taken using individualized film holders (IFH). Consecutive radiographs were superimposed using a special software (GIMP; Version ) such that a standardized evaluation of root development was possible. To superimpose images, the horizontal plane was aligned at the Case 1 Figure 3. A: Preoperative radiograph. B: One month after revitalization treatment. C: 6-month follow-up. D: Evaluation after 6 months after superimposition of three radiographic images. An increase of root length is visible as well as a narrowing of the canal in the apical area. E: Clinical image after 6 months.
4 American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2018; 6(2): During follow-ups, no pain, swelling, sinus tracts or tenderness to percussion or palpation were observed in any case. Probing depths were physiological, and apical periodontitis diminished in all cases. In neither case, ankylosis or discoloration was observed. A slight increase in root length was detectable along with a narrowing of the apical part of the canal after 6 months (Case 1, figure 3) and after 12 months (Case 2, figure 4). The radiograph in Case 1 taken after 6 months showed dentin bridging 2 mm below the tricalcium silicate cement (figure 6) and in the apical region (figure 3c). Case 3 presents with resorption of the root tip (figure 5). Whether an increase of root thickness has occurred remains speculative. 4. Discussion Case 2 Figure 4. A: Postoperative radiograph. B: 6 months after revitalization treatment. C: 12-month follow-up. D: Evaluation after 6 months after superimposition of three radiographic images. An increase of root length is visible as well as a narrowing of the canal in the apical area. E: Clinical image after 12 months. Case 3 Figure 5. A: Postoperative radiograph. B: One month after revitalization treatment. C: 6-month follow-up. D: Evaluation after 6 months after superimposition of three radiographic images. The root is distinctly shortened compared to the initial situation. E: Clinical image after 6 months. Figure 6. In case 1, a possible formation of a mineralized barrier (bridging) below the tricalcium silicate cement is visible after 6 months. Approximately one third of all adolescents suffer from dental trauma until their twentieth year [12-14]. Dislocation injuries account for 73.4%, avulsion for 8-9.2% [15]. In more than half of all damaged teeth, fractures of enamel or dentin can be observed. Teeth which present with combined injuries of dislocation and fractures to enamel and dentin, which are observed in 31.6% of dental trauma cases, appear to have a higher risk of developing pulp necrosis, even without pulp exposure [15]. The risk of pulp necrosis increases from 4.8% in isolated injuries to 56.5% for combined injuries [16]. As a cause, compromised blood circulation is suspected, which leads to impaired immunoresponse of the pulpal tissue after traumatic impact. Both case 1 and 2 presented with a combination of dislocation and enamel-dentin fractures. Exposed dentin was sealed with dentin bonding during attachment of the splint. Whether pulpal necrosis occurred as a consequence of the dislocation injury or the enamel-dentin fracture remains uncertain. Since cold testing after dental trauma has limited informative value regarding pulp vitality [17-18], at least two clinical symptoms in combination with radiographic findings of apical periodontitis were required in this study to validate the diagnosis of pulp necrosis. The suspected diagnosis was confirmed after accessing the root canal. Since root development was not complete in either case, revitalization procedures were chosen as the best treatment option. After informed consent, the treatment protocol was identical for all three patients. It complies with the guidelines and consideration of the AAE and ESE [7, 11]. After preparation of the access cavity, necrotic tissue was found in all cases. Sufficient disinfection is a pre-requisite for successful regeneration [19], therefore, the removal of debris and smear layer and a disruption of the biofilm inside the root canal is essential. Instrumentation of the root canal walls, however, weakens the thin dentin walls of immature teeth even further. Therefore, mechanical debridement was deferred, but passive ultrasonic activation of the disinfection irrigant was considered indispensable. Ultrasonic activation in teeth with open apices may cause undesirable effects in the population of stem cells of the apical papilla and thus affect the outcome negatively. Histological studies also show that despite pulp necrosis and apical periodontitis, vital tissue
5 44 Christian Holscher and Kerstin Galler: Revitalization Teeth: A Prospective Case Series remnants can still be present inside the root canal [20], and it might be beneficial to preserve these islands of cells. The goal is to achieve maximum reduction of microorganisms, but at the same time prevent damage to the cells and tissues that are involved in regeneration and repair. As an intracanal medicament, triple antibiotic paste consisting of ciprofloxacine, metronidazole and cefuroxim was used. Calcium hydroxide, the alternative intracanal medicament, disinfects due to its high ph, which stays stable for up to two weeks [21]. It induces a mineralized barrier, but can cause cell necrosis to a depth of 1.5 mm, as shown in histologic studies after direct pulp capping [22]. Whereas calcium hydroxide has been found to be uncritical with stem cells of the apical papilla [23], triple antibiotic paste was used in the first published report by Banchs and Trope [24] and therefore the medicament of choice for most case reports published so far. The reported clinical success rates with TAP ranged between 91% [25] and 93% [26]. However, antibiotic pastes have cytotoxic effects as well [27-29]. Therefore, low concentrations between 0.39 mg/ml [28] and 0.1 mg/ml [23] are recommended to date. For triple antibiotic pastes, minocycline has been replaced with cefuroxim to avoid tooth discoloration [30-32]. In the described cases, triple antibiotic paste was prepared in a liquid consistency and inserted into the canal by use of a syringe in a controlled manner under an operating microscope. The clinical images document that tooth discolorations were not observed in any of the cases. Mineral trioxide aggregate, which has been commonly used after revitalization procedures, can cause discolorations after contact with blood. The tricalcium silicate cement used in this study contains circonium dioxide as a radiopacifier, which does not lead to discoloration, and may therefore be a suitable material to cover the blood clot during revitalization procedures. Whereas a slight increase in root length and thickness were observed in cases 1 and 2, case 3 shows apical resorption of the treated tooth at the 6-month follow-up. This might be the consequence of disruption of apical papilla and HERS caused by avulsion of the tooth. Without instruction and control by the epithelial cells of HERS, the stem cells of the apical papilla might not be able to differentiate and form pulp cells, odontoblasts and root dentin, which could explain why there was no increase in root length. It can be speculated that an ingrowth of clastic cells caused the resorption at the apex. However, periotest results do not provide any indication of replacement resorption and ankylosis. In both cases 1 and 2, an increase in root length was observed, along with internal mineralized barrier formation in case 1. This mineralized tissue formation was also observed in a recently published case report [33]. The teeth did not respond to cold testing and EPT after revitalization. This might be due to formation of ectopic tissue inside the root canal [30, 34-35], or, more likely, due to the large distance between the location where the stimulus was placed and the tissue. Thus, the nociceptive stimulus was not triggered. An increase in root thickness cannot be proven explicitly in this study, which might be due to the short time frame of follow-ups. It should be mentioned that comparable studies report an increase of thickness rather than root length with similar follow-up periods of 12 months [36-37]. The prognosis for the cases presented here is estimated to be good, all teeth are without signs and symptoms of inflammation and apical radiolucency s are decreasing. Survival rates after revitalization amount to 95%, success rates are stated to be 78% [36]. Comparing revitalization and apexification, revitalization appears to entail more unfavorable side effects (discoloration, pain, reinfection), but can induce an increase of root length and thickness, which do not take place after apexification [38]. 5. Conclusion The assumption that the outcome after revitalization procedures may be compromised after severe dislocation injuries and avulsion due to a disruption of HERS and SCAP seems plausible. Nevertheless, this has to be confirmed in clinical studies with sufficient sample sizes. The consistent implementation of standardized treatment protocols and the use of individual film holders are helpful receiving a reliable treatment outcome. Conflict of Interest The authors declared no potential conflict of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. References [1] D Souza R. Development of the pulpodentin complex. In: Goodis HE, ed: Seltzer and Bender s Dental Pulp. Carol Stream, IL: Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc; [2] Diekwisch TG. The developmental biology of cementum. Int J Dev Biol. 2001; 45: [3] Nanci A (2003). Development of the tooth and its supporting tissues. In: Ten Cate s oral histology: development, structure, and function. 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby, pp [4] Huang GT, Sonoyama W, Liu Y, Liu H, Wang S, Shi S. The hidden treasure in apical papilla: the potential role in pulp/dentin regeneration and bioroot engineering. J Endod. 2008; 34: [5] Luder HU. Malformations of the tooth root in humans. Front Physiol. 2015; 27:307. [6] Lovelace TW, Henry MA, Hargreaves KM, Diogenes A. Evaluation of the delivery of mesenchymal stem cells into the root canal space of necrotic immature teeth after clinical regenerative endodontic procedure. J Endod. 2011; 37: [7] Galler KM, Krastl G, Simon S, Van Gorp G, Meschi N, Vahedi B, Lambrechts P. European Society of Endodontology position statement: Revitalization procedures. Int Endod J. 2016; 49: [8] Hargreaves KM, Diogenes A, Teixeira FB. Treatment options: biological basis of regenerative endodontic procedures. J Endod. 2013; 39:30-43.
6 American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine 2018; 6(2): [9] Wigler R, Kaufman AY, Lin S, Steinbock N, Hazan-Molina H, Torneck CD. Revascularization: a treatment for permanent teeth with necrotic pulp and incomplete root development. J Endod : [10] Jung IY, Kim ES, Lee CY, Lee SJ. Continued development of the root separated from the main root. J Endod. 2011; 37: [11] AAE Position Statement (2013). Scope of Endodontics: Regenerative Endodontics. Available at: 7/06/scopeofendo_regendo.pdf. [12] Glendor U. Epidemiology of traumatic dental injuries--a 12 year review of the literature. Dent Traumatol. 2008; 24: [13] Oginni AO, Adekoya-Sofowora CA. Pulpal sequelae after trauma to anterior teeth among adult Nigerian dental patients. BMC Oral Health 2007; 7:11. [14] Jarvinen S. Fractured and avulsed permanent incisors in Finnish children. A retrospective study. Acta Odontol Scand. 1979; 37: [15] Lauridsen E, Hermann NV, Gerds TA, Ahrensburg SS, Kreiborg S, Andreasen JO. Combination injuries 3. The risk of pulp necrosis in permanent teeth with extrusion or lateral luxation and concomitant crown fractures without pulp exposure. Dent Traumatol. 2012; 28: [16] Viduskalne I, Care R. Analysis of the crown fractures and factors affecting pulp survival due to dental trauma. Stomatologija. 2010; 12: [17] Bhaskar S, Rappaport H. Dental vitality tests and pulp status. J Am Dent Assoc. 1973; 86: [18] Andreasen J, Andreasen F (1994). Textbook and Color Atlas of Traumatic Injuries to the Teeth, 3rd edn. Copenhagen: Munksgaard. [19] Lin LM, Shimizu E, Gibbs JL, Loghin S, Ricucci D. Histologic and histobacteriologic observations of failed revascularization/revitalization therapy: a case report. J Endod. 2014; 40: [20] Ricucci D, Pascon EA, Pitt Ford TR, Langeland K. Epithelium and bacteria in periapical lesions. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2006; 101: [21] Tronstad L, Andreasen JO, Hasselgren G, Kristerson L, Riis I. ph changes in dental tissues after root canal filling with calcium hydroxide. J Endod. 1981; 7: [22] Meadow D, Lindner G, Needleman H. Oral trauma in children. Pediatr Dent. 1984; 6: [23] Ruparel NB, Teixeira FB, Ferraz CC, Diogenes A. Direct effect of intracanal medicaments on survival of stem cells of the apical papilla. J Endod. 2012; 38: [24] Banchs F, Trope M. Revascularization of immature permanent teeth with apical periodontitis: new treatment protocol? J Endod. 2004; 30: [25] Torabinejad M, Nosrat A, Verma P, Udochukwu O. Regenerative endodontic treatment or mineral trioxide aggregate apical plug in teeth with necrotic pulps and open apices: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Endod. 2017; 43: [26] Chan EKM, Desmeules M, Cielecki M, Dabbagh D, Ferraz dos Santos B. Longitudinal cohort study of regenerative endodontic treatment for immature necrotic permanent teeth. J Endod. 2017; 43: [27] Phumpatrakom P, Srisuwan T. Regenerative capacity of human dental pulp and apical papilla cells after treatment with a 3-antibiotic mixture. J Endod. 2014; 40: [28] Chuensombat S, Khemaleelakul S, Chattipakorn S, Srisuwan T. Cytotoxic effects and antibacterial efficacy of a 3-antibiotic combination: an in vitro study. J Endod. 2013; 39: [29] Bezgin T, Sönmez H. Review of current concepts of revascularization/ revitalization. Dent Traumatol. 2015; 31: [30] Thibodeau B, Teixeira F, Yamauchi M, Caplan DJ, Trope M. Pulp revascularization of immature dog teeth with apical periodontitis. J Endod. 2007; 33: [31] Miller EK, Lee JY, Tawil PZ, Teixeira FB, Vann WF Jr. Emerging therapies for the management of traumatized immature permanent incisors. Pediatr Dent. 2012; 34: [32] Montero-Miralles P, Martín-González J, Alonso-Ezpeleta O, Jiménez-Sánchez MC, Velasco-Ortega E, Segura-Egea JJ. Effectiveness and clinical implications of the use of topical antibiotics in regenerative endodontic procedures: a review. Int Endod J. 2018; 26. [in press]. [33] Mehrvarzfar P, Abbott PV, Akhavan H, Savadkouhi ST. Modified Revascularization in Human Teeth Using an Intracanal Formation of Treated Dentin Matrix: A Report of Two Cases. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2017; 7: [34] Wang X, Jong G, Lin LM, Shimizu E. EphB-EphrinB interaction controls odontogenic/osteogenic differentiation with calcium hydroxide. J Endod. 2013; 39: [35] Andreasen JO, Bakland LK. Pulp regeneration after non-infected and infected necrosis, what type of tissue do we want? A review. Dental Traumatol. 2012; 28: [36] Alobaid AS, Cortes LM, Lo J, Nguyen TT, Albert J, Abu-Melha AS, Lin LM, Gibbs JL. Radiographic and clinical outcomes of the treatment of immature permanent teeth by revascularization or apexification: a pilot retrospective cohort study. J Endod. 2014; 40: [37] Saoud TM, Zaazou A, Nabil A, Moussa S, Lin LM, Gibbs JL. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of traumatized immature permanent necrotic teeth after revascularization/revitalization therapy. J Endod. 2014; 40: [38] Kahler B, Rossi-Fedele G, Chugal N, Lin LM. An Evidence-based Review of the Efficacy of Treatment Approaches for Immature Permanent Teeth with Pulp Necrosis. J Endod. 2017; 43:
Management of Permanent Tooth Dental Trauma in Children and Young Adolescents
 Management of Permanent Tooth Dental Trauma in Children and Young Adolescents Jessica Y. Lee DDS, MPH, PhD Chair and Distinguished Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry University of North Carolina
Management of Permanent Tooth Dental Trauma in Children and Young Adolescents Jessica Y. Lee DDS, MPH, PhD Chair and Distinguished Professor Department of Pediatric Dentistry University of North Carolina
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH
 FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
FRACTURES AND LUXATIONS OF PERMANENT TEETH 1. Treatment guidelines and alveolar bone Followup Procedures INFRACTION Clinical findings Radiographic findings Treatment Follow-Up Favorable Outcome Unfavorable
Trauma to the Central Incisor: The Story So Far
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Review Article Trauma to the Central Incisor: The Story So Far Dania Siddik* Consultant Paediatric Dentist, Guy s & St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK *Corresponding
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Review Article Trauma to the Central Incisor: The Story So Far Dania Siddik* Consultant Paediatric Dentist, Guy s & St Thomas NHS Foundation Trust, London, UK *Corresponding
The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries
 The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
The Recommended Guidelines of the American Association of Endodontists for The Treatment of Traumatic Dental Injuries 2013 American Association of Endodontists Revised 9/13 The Recommended Guidelines of
European Society of Endodontology position statement: Revitalization procedures
 doi:10.1111/iej.12629 European Society of Endodontology position statement: Revitalization procedures European Society of Endodontology developed by: K. M. Galler 1, G. Krastl 2, S. Simon 3, G. Van Gorp
doi:10.1111/iej.12629 European Society of Endodontology position statement: Revitalization procedures European Society of Endodontology developed by: K. M. Galler 1, G. Krastl 2, S. Simon 3, G. Van Gorp
Post natal mesenchymal cells possibility to regenerate and repair dental structures.
 Post natal mesenchymal cells possibility to regenerate and repair dental structures. Received: February 2014 Accepted: April 2014 Martha Siragusa. msiragus@arnet.com.ar DDS, PhD. Endodontics Departments
Post natal mesenchymal cells possibility to regenerate and repair dental structures. Received: February 2014 Accepted: April 2014 Martha Siragusa. msiragus@arnet.com.ar DDS, PhD. Endodontics Departments
Chronicles of Dental Research
 CASE REPORT Pulp Revascularization of Non vital Immature Young Permanent Tooth: A case report. Vikrant Kumar 1, Chhaya Sharma 1, Romana Nisar 1, Sheeba Hassan 1, Pooja Tiwari 1 Abstract Traumatic injuries
CASE REPORT Pulp Revascularization of Non vital Immature Young Permanent Tooth: A case report. Vikrant Kumar 1, Chhaya Sharma 1, Romana Nisar 1, Sheeba Hassan 1, Pooja Tiwari 1 Abstract Traumatic injuries
MANAGEMENT OF ROOT RESORPTION- A REBIRTH CASE REPORTS DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ENDODONTICS
 MANAGEMENT OF ROOT RESORPTION- A REBIRTH CASE REPORTS AUTHORS Dr. SHALINI.H, PG Student Dr. B. RAMAPRABHA, MDS Professor Dr. M. KAVITHA, MDS Professor and HOD DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ENDODONTICS
MANAGEMENT OF ROOT RESORPTION- A REBIRTH CASE REPORTS AUTHORS Dr. SHALINI.H, PG Student Dr. B. RAMAPRABHA, MDS Professor Dr. M. KAVITHA, MDS Professor and HOD DEPARTMENT OF CONSERVATIVE DENTISTRY AND ENDODONTICS
Pulp Prognosis of Crown-Related Fractures, in Relation to Presence of Luxation Injury and Root Development Stage
 Pulp Prognosis of Crown-Related Fractures, in Relation to Presence of Luxation Injury and Root Development Stage Didem Atabek, Alev Alacam, Itır Aydintug, İlknur Baldag Department of Pedodontics, Faculty
Pulp Prognosis of Crown-Related Fractures, in Relation to Presence of Luxation Injury and Root Development Stage Didem Atabek, Alev Alacam, Itır Aydintug, İlknur Baldag Department of Pedodontics, Faculty
The traumatic injury of an immature permanent tooth can lead to the loss of pulp
 Regenerative Treatment of an Immature, Traumatized Tooth With Apical Periodontitis: Report of a Case Elisabetta Cotti, DDS, MS, Manuela Mereu, DDS, and Daniela Lusso, DDS Abstract This case report describes
Regenerative Treatment of an Immature, Traumatized Tooth With Apical Periodontitis: Report of a Case Elisabetta Cotti, DDS, MS, Manuela Mereu, DDS, and Daniela Lusso, DDS Abstract This case report describes
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS
 GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATISED INCISORS Dentists need to understand that the decision to remove or not reimplant an avulsed incisor must be made very carefully. The loss of such a tooth in
Revascularization of Non-vital Permanent Teeth with Open Apices: A New Treatment Modality
 Original Article Revascularization of Non-vital Permanent Teeth with Open Apices: A New Treatment Modality Naila Amir Ali 1 and Anser Maxood 2 1. Assistant Prof, DHQ Hospital Quetta 2. Prof, Dental Department,
Original Article Revascularization of Non-vital Permanent Teeth with Open Apices: A New Treatment Modality Naila Amir Ali 1 and Anser Maxood 2 1. Assistant Prof, DHQ Hospital Quetta 2. Prof, Dental Department,
Dental Trauma in the Pediatric Population
 Dental Trauma in the Pediatric Population Juan F. Yepes DDS, MD, MPH, MS, DrPH Associate Professor of Pediatric Dentistry Indiana University School of Dentistry James Whitcomb Hospital for Children jfyepes@iupui.edu
Dental Trauma in the Pediatric Population Juan F. Yepes DDS, MD, MPH, MS, DrPH Associate Professor of Pediatric Dentistry Indiana University School of Dentistry James Whitcomb Hospital for Children jfyepes@iupui.edu
Current concepts in the management of dental trauma
 Current concepts in the management of dental trauma S ALBADRI BDS, PHD, MFDS, MPAEDENT, FDS (PAED DENT),FHES READER /HONORARY CONSULTANT IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Introduction ØAround one in ten children
Current concepts in the management of dental trauma S ALBADRI BDS, PHD, MFDS, MPAEDENT, FDS (PAED DENT),FHES READER /HONORARY CONSULTANT IN PAEDIATRIC DENTISTRY Introduction ØAround one in ten children
REVASCULARIZATION AN OVERVIEW
 REVASCULARIZATION AN OVERVIEW Marri Sai Archana 1 *, Varri Sujana 2, Bolla Nagesh 3, Polavarapu Jaya Krishna Babu 4 1. Senior Lecturer, M.D.S, Department of Conservative Dentistry, Sibar Institute of Dental
REVASCULARIZATION AN OVERVIEW Marri Sai Archana 1 *, Varri Sujana 2, Bolla Nagesh 3, Polavarapu Jaya Krishna Babu 4 1. Senior Lecturer, M.D.S, Department of Conservative Dentistry, Sibar Institute of Dental
Conservative treatment of immature teeth with apical periodontitis using triple antibiotic paste disinfection
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2016) 11, 196e201 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Conservative treatment of immature teeth with apical periodontitis
Journal of Dental Sciences (2016) 11, 196e201 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect journal homepage: www.e-jds.com CASE REPORT Conservative treatment of immature teeth with apical periodontitis
Pulp regeneration after non-infected and infected necrosis, what type of tissue do we want? A review
 Dental Traumatology 2011; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2011.01057.x Pulp regeneration after non-infected and infected necrosis, what type of tissue do we want? A review REVIEW ARTICLE Jens O. Andreasen 1,
Dental Traumatology 2011; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2011.01057.x Pulp regeneration after non-infected and infected necrosis, what type of tissue do we want? A review REVIEW ARTICLE Jens O. Andreasen 1,
Guidelines for the evaluation and management of traumatic dental injuries
 Dental Traumatology 2001; 17: 193 196 Copyright C Munksgaard 2001 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600-4469 Editor s note The International Association of Dental Traumatology
Dental Traumatology 2001; 17: 193 196 Copyright C Munksgaard 2001 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600-4469 Editor s note The International Association of Dental Traumatology
MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT Nabi Shahnaz
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 05 MTA PULPOTOMY ASSOCIATED APEXOGENESIS OF HUMAN PERMANENT MOLAR WITH IRREVERSIBLE PULPITIS: A CASE REPORT Nabi Shahnaz
Healing of external inflammatory root resorption - a case report
 Healing of external inflammatory root resorption - a case report Mithra N. Hegde * Deepak Pardal ** ABSTRACT Case report describes a radiographic follow-up of healing of external inflammatory root resorption
Healing of external inflammatory root resorption - a case report Mithra N. Hegde * Deepak Pardal ** ABSTRACT Case report describes a radiographic follow-up of healing of external inflammatory root resorption
REIMPLANTATION OF AVULSED TOOTH- A CASE REPORT
 Case Report REIMPLANTATION OF AVULSED TOOTH- A CASE REPORT Grover PS 1, Kaur S 2 1 Senior Consultant, 2 Junior Consultant, Dr. Grover s Dental and Implant Center, Ludhiana ABSTRACT This paper describes
Case Report REIMPLANTATION OF AVULSED TOOTH- A CASE REPORT Grover PS 1, Kaur S 2 1 Senior Consultant, 2 Junior Consultant, Dr. Grover s Dental and Implant Center, Ludhiana ABSTRACT This paper describes
SOUTH CALGARY ENDODONTICS
 Spring 2016 SOUTH CALGARY ENDODONTICS ISSUE 1 FALL 2014 www.southcalgaryendo.ca 403-474-1893 Drs. Staniloff, Kolosowski and Smorang are pleased to announce: Mission Endodontics and South Calgary Endodontics
Spring 2016 SOUTH CALGARY ENDODONTICS ISSUE 1 FALL 2014 www.southcalgaryendo.ca 403-474-1893 Drs. Staniloff, Kolosowski and Smorang are pleased to announce: Mission Endodontics and South Calgary Endodontics
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alginate, tooth-shaped, for constructs, encapsulated pulp cells in, 589 590 Antibiotic paste, triple, change in root length and width
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Alginate, tooth-shaped, for constructs, encapsulated pulp cells in, 589 590 Antibiotic paste, triple, change in root length and width
Indication for Intentional Replantation of Teeth
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. V (Dec. 2017), PP 36-42 www.iosrjournals.org Indication for Intentional Replantation
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 12 Ver. V (Dec. 2017), PP 36-42 www.iosrjournals.org Indication for Intentional Replantation
Regenerative Endodontic Procedure using Platelet-Rich Fibrin to Treat Traumatized Immature Permanent Tooth: a Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 5 Ver. VI (May. 2015), PP 36-40 www.iosrjournals.org Regenerative Endodontic Procedure using
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 5 Ver. VI (May. 2015), PP 36-40 www.iosrjournals.org Regenerative Endodontic Procedure using
Case Report Pulp Revascularization in Immature Permanent Tooth with Apical Periodontitis Using Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
 Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 564908, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/564908 Case Report Pulp Revascularization in Immature Permanent Tooth with Apical Periodontitis Using Mineral Trioxide
Case Reports in Medicine, Article ID 564908, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/564908 Case Report Pulp Revascularization in Immature Permanent Tooth with Apical Periodontitis Using Mineral Trioxide
Non-Surgical management of Apical third root fracture with MTA: A Case report
 International Journal Dental and Medical Sciences Research (IJDMSR) ISSN: 2393-073X Volume1, Issue 2 (Jul- 2017), PP 05-09 www.ijdmsr.com Non-Surgical management of Apical third root fracture with MTA:
International Journal Dental and Medical Sciences Research (IJDMSR) ISSN: 2393-073X Volume1, Issue 2 (Jul- 2017), PP 05-09 www.ijdmsr.com Non-Surgical management of Apical third root fracture with MTA:
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision
 Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
Large periapical lesion: Healing without knife and incision Ridhima Suneja College of Dentistry, Gulf Medical University, Ajman, UAE ABSTRACT Three dimensional obturation of root space has always yielded
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
Emergency Management of Trauma
 Aims and Objectives Emergency Management of Trauma Susan Parekh/Paul Ashley Unit of Paediatric Dentistry Knowledge and understanding of the following: Epidemiology of traumatic injuries Classification
Aims and Objectives Emergency Management of Trauma Susan Parekh/Paul Ashley Unit of Paediatric Dentistry Knowledge and understanding of the following: Epidemiology of traumatic injuries Classification
Pediatric endodontics. Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR
 Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Pediatric endodontics Diagnosis, Direct and Indirect pulp capping DR.SHANKAR WHY TO PRESERVE PRIMARY TEETH? The preservation of the primary dentition until their normal anticipated exfoliation can be justified
Journal of Dental & Oro-facial Research Vol. 14 Issue 01 Jan. 2018
 Journal of Dental & Oro-facial Research Vol. 14 Issue 01 Jan. 2018 Management of Non-Vital Teeth with Open Apices using MTA: Two Case Reports *Karan Narang 1, Mohini Nayak 2, Abdul Wahed, 3 John V. George
Journal of Dental & Oro-facial Research Vol. 14 Issue 01 Jan. 2018 Management of Non-Vital Teeth with Open Apices using MTA: Two Case Reports *Karan Narang 1, Mohini Nayak 2, Abdul Wahed, 3 John V. George
September 19. Title: In vitro antibacterial activity of different endodontic irrigants. Author: Claudia Poggio et al.
 2012 September 19 Title: In vitro antibacterial activity of different endodontic irrigants. Author: Claudia Poggio et al. Journal: Dental Traumatology 2012; 28: 205-209 Reviewer: Arnav R. Mistry, DMD Purpose:
2012 September 19 Title: In vitro antibacterial activity of different endodontic irrigants. Author: Claudia Poggio et al. Journal: Dental Traumatology 2012; 28: 205-209 Reviewer: Arnav R. Mistry, DMD Purpose:
Australian Dental Journal
 Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association Australian Dental Journal 2016; 61:(1 Suppl): 120 127 doi: 10.1111/adj.12403 Life cycles of traumatized teeth: long-term
Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association Australian Dental Journal 2016; 61:(1 Suppl): 120 127 doi: 10.1111/adj.12403 Life cycles of traumatized teeth: long-term
CONTENTS. Endodontic therapy Permanent open apex teeth Intracanal Medication. A. Introduction I. Problems II. III. IV. B. Research C.
 CONTENTS A. Introduction I. Problems II. III. IV. Endodontic therapy Permanent open apex teeth Intracanal Medication B. Research C. Conclusion INTRODUCTION A. Problems 1. In permanent teeth with open apex
CONTENTS A. Introduction I. Problems II. III. IV. Endodontic therapy Permanent open apex teeth Intracanal Medication B. Research C. Conclusion INTRODUCTION A. Problems 1. In permanent teeth with open apex
Examination of teeth and gingiva
 Examination of teeth and gingiva Siriporn Chattipakorn, DDS, PhD. SUBJECTIVE HISTORY Chief complaint In patient s own words My tooth hurts when I chew hard foods I can t drink cold drink I have bad breath
Examination of teeth and gingiva Siriporn Chattipakorn, DDS, PhD. SUBJECTIVE HISTORY Chief complaint In patient s own words My tooth hurts when I chew hard foods I can t drink cold drink I have bad breath
Paediatric Dentistry Avulsion: Case reports
 Australian Dental Journal 1997;42.(6):361-6 Paediatric Dentistry Avulsion: Case reports J. E. Rutar, BDSc(Qld), GCEd(Qld)* Abstract Children may present at a dental surgery for management of oro-facial
Australian Dental Journal 1997;42.(6):361-6 Paediatric Dentistry Avulsion: Case reports J. E. Rutar, BDSc(Qld), GCEd(Qld)* Abstract Children may present at a dental surgery for management of oro-facial
CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF DIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES PERFORMED BY POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS
 CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF DIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES PERFORMED BY POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS Monica Monea Alexandru Sitaru Tudor Hantoiu Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty
CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF DIRECT PULP CAPPING PROCEDURES PERFORMED BY POSTGRADUATE STUDENTS Monica Monea Alexandru Sitaru Tudor Hantoiu Department of Odontology and Oral Pathology, Faculty
Case Report Revascularization in Immature Permanent Teeth with Necrotic Pulp and Apical Pathology: Case Series
 Hindawi Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2017, Article ID 3540159, 8 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3540159 Case Report Revascularization in Immature Permanent Teeth with Necrotic Pulp and Apical Pathology:
Hindawi Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2017, Article ID 3540159, 8 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3540159 Case Report Revascularization in Immature Permanent Teeth with Necrotic Pulp and Apical Pathology:
Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics. Pain History. Patient Assessment. Examination. Examination 11/07/2014
 Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics Diagnosis, pulpitis, perio-endo. Treatment planning & case selection Patients assessment Special tests which help us diagnose pulpal disease How reliable are they?
Principles of diagnosis in Endodontics Diagnosis, pulpitis, perio-endo. Treatment planning & case selection Patients assessment Special tests which help us diagnose pulpal disease How reliable are they?
Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment of an Infected Immature Dens Invaginatus with the Aid of Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
 Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 403045, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/403045 Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment of an Infected Immature Dens Invaginatus with the Aid of Cone-Beam
Case Reports in Dentistry, Article ID 403045, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/403045 Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment of an Infected Immature Dens Invaginatus with the Aid of Cone-Beam
Autotransplantation and restoration of an avulsed anterior tooth: A multidisciplinary approach
 Autotransplantation and restoration of an avulsed anterior tooth: A multidisciplinary approach Yuli Berlin-Broner 1 Ysidora Torrealba 2 Liran Levin 3 1 Division of Endodontics, Faculty of Medicine and
Autotransplantation and restoration of an avulsed anterior tooth: A multidisciplinary approach Yuli Berlin-Broner 1 Ysidora Torrealba 2 Liran Levin 3 1 Division of Endodontics, Faculty of Medicine and
Revascularization in Immature and Mature Teeth with Necrotic Pulp: A Clinical Study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Revascularization 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2438 of Teeth with Necrotic Pulp Revascularization in Immature and Mature Teeth with Necrotic Pulp: A Clinical Study 1 Padmaraj S Neelamurthy,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Revascularization 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2438 of Teeth with Necrotic Pulp Revascularization in Immature and Mature Teeth with Necrotic Pulp: A Clinical Study 1 Padmaraj S Neelamurthy,
Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report
 Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report Mithra N. Hegde, BDS, MDS, FPFA; Aditya Shetty, BDS, MDS; Rekha Sagar, BDS, MDS
Management of a Type III Dens Invaginatus using a Combination Surgical and Non-surgical Endodontic Therapy: A Case Report Mithra N. Hegde, BDS, MDS, FPFA; Aditya Shetty, BDS, MDS; Rekha Sagar, BDS, MDS
Treatment and orthodontic movement of a root-fractured maxillary central incisor with an immature apex: 10-year follow-up
 doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01790.x CASE REPORT Treatment and orthodontic movement of a root-fractured maxillary central incisor with an immature apex: 10-year follow-up A. Mendoza 1, E. Solano 2 & J.
doi:10.1111/j.1365-2591.2010.01790.x CASE REPORT Treatment and orthodontic movement of a root-fractured maxillary central incisor with an immature apex: 10-year follow-up A. Mendoza 1, E. Solano 2 & J.
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children
 Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
Dental materials and cements, and its use in children Study objective Discuss the role and importance of cements in paediatric dentistry Calcium hydroxide This is a colourless crystal or white powder prepared
DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES
 International Association of Dental Traumatology DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES Revised 2012 CONTENT: Section 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth Section 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth Section 3. Traumatic
International Association of Dental Traumatology DENTAL TRAUMA GUIDELINES Revised 2012 CONTENT: Section 1. Fractures and luxations of permanent teeth Section 2. Avulsion of permanent teeth Section 3. Traumatic
Multiple Dentoalveolar Traumatic Lesions: Report of a Case and Proposition of Dental Polytrauma as a New Term
 Multiple Dentoalveolar Traumatic Lesions: Report of a Case and Proposition of Dental Polytrauma as a New Term Abstract Traumatic injuries to permanent teeth are common, and dramatic episodes can occur
Multiple Dentoalveolar Traumatic Lesions: Report of a Case and Proposition of Dental Polytrauma as a New Term Abstract Traumatic injuries to permanent teeth are common, and dramatic episodes can occur
Minimal Management of Traumatically Luxated Immature Maxillary Permanent Incisors
 imedpub Journals http://journals.imedpub.com Journal of Orthodontics & Endodontics Minimal Management of Traumatically Luxated Immature Maxillary Permanent Incisors Peter M. Di Fiore 1 Diplomate, American
imedpub Journals http://journals.imedpub.com Journal of Orthodontics & Endodontics Minimal Management of Traumatically Luxated Immature Maxillary Permanent Incisors Peter M. Di Fiore 1 Diplomate, American
Treatment of necrotic immature teeth is very challenging in endodontics. Immature
 Drawbacks and Unfavorable Outcomes of Regenerative Endodontic Treatments of Necrotic Immature Teeth: A Literature Review and Report of a Case Ali Nosrat, DDS, MS,* Negar Homayounfar, DDS, MS, and Kaveh
Drawbacks and Unfavorable Outcomes of Regenerative Endodontic Treatments of Necrotic Immature Teeth: A Literature Review and Report of a Case Ali Nosrat, DDS, MS,* Negar Homayounfar, DDS, MS, and Kaveh
Histological Evaluation of Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Immature Permanent Teeth with Different Scaffolds- a Systematic Review
 Volume 120 No. 5 2018, 549-563 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ Histological Evaluation of Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Immature Permanent
Volume 120 No. 5 2018, 549-563 ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ http://www.acadpubl.eu/hub/ Histological Evaluation of Regenerative Endodontic Treatment in Immature Permanent
Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice
 Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Profile of articles addressed to dental pulp revascularization in PubMed database
 ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2015 Apr-Jun;12(2):166-71 Original Research Article Profile of articles addressed to dental pulp revascularization in PubMed database Renata Grazziotin-Soares
ISSN: Electronic version: 1984-5685 RSBO. 2015 Apr-Jun;12(2):166-71 Original Research Article Profile of articles addressed to dental pulp revascularization in PubMed database Renata Grazziotin-Soares
Rehabilitation of esthetics after dental avulsion and impossible replantation: A case report
 2018; 4(1): 265-269 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 265-269 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 13-11-2017 Accepted: 14-12-2017 Dr. El harram Sara Postgraduate Student,
2018; 4(1): 265-269 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 265-269 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 13-11-2017 Accepted: 14-12-2017 Dr. El harram Sara Postgraduate Student,
Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: Report of Two Cases with Different Clinical Management and Outcomes
 Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: Report of Two Cases with Different Clinical Management and Outcomes Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad¹, Noushin Shokouhinejad 2, Salma Pirmoazen 3 1 Assistant Professor,
Case Report Regenerative Endodontic Treatment: Report of Two Cases with Different Clinical Management and Outcomes Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad¹, Noushin Shokouhinejad 2, Salma Pirmoazen 3 1 Assistant Professor,
SEALING AND HEALING : Management of internal resorption perforation Case reports
 SEALING AND HEALING : Management of internal resorption perforation Case reports with Authors ( Department of Conservative dentistry and Endodontics, TamilNadu Government Dental College, Chennai- 600 003):
SEALING AND HEALING : Management of internal resorption perforation Case reports with Authors ( Department of Conservative dentistry and Endodontics, TamilNadu Government Dental College, Chennai- 600 003):
The use of MTA in teeth with necrotic pulps and open apices 1
 Dental Traumatology 2002; 18: 217 221 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600 4469 The use of MTA in teeth with necrotic pulps and open
Dental Traumatology 2002; 18: 217 221 Copyright # Blackwell Munksgaard 2002 Printed in Denmark. All rights reserved DENTAL TRAUMATOLOGY ISSN 1600 4469 The use of MTA in teeth with necrotic pulps and open
Intensive care for the immature pulp Maintaining pulp vitality after a traumatic injury
 Nine-year-old Josh is racing down a hill on his mountain bike. The bike hits a rock and Josh lands on the trail. His mouth is bloody. His front tooth feels funny. He gets up, dusts himself off and rides
Nine-year-old Josh is racing down a hill on his mountain bike. The bike hits a rock and Josh lands on the trail. His mouth is bloody. His front tooth feels funny. He gets up, dusts himself off and rides
The Endodontics Introduction. By: Thulficar Al-Khafaji BDS, MSC, PhD
 The Endodontics Introduction By: Thulficar Al-Khafaji BDS, MSC, PhD Introduction Definition Endodontology form function health of the dental pulp and the periradicular tissues that surround the root(s)
The Endodontics Introduction By: Thulficar Al-Khafaji BDS, MSC, PhD Introduction Definition Endodontology form function health of the dental pulp and the periradicular tissues that surround the root(s)
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth
 New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
New Edition Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth A Decision Guide American Association of Endodontists www.aae.org/treatmentoptions TREATMENT PLANNING CONSIDERATIONS The Treatment Options for the
This is a repository copy of Regenerative endodontics: a true paradigm shift or a bandwagon about to be derailed?.
 This is a repository copy of Regenerative endodontics: a true paradigm shift or a bandwagon about to be derailed?. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/111345/
This is a repository copy of Regenerative endodontics: a true paradigm shift or a bandwagon about to be derailed?. White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/111345/
Sports Dentistry: Treating the athletes in your practice.
 Sports Dentistry: Treating the athletes in your practice. November 3, 2011 David P. Croglio, DDS 2503 Kensington Avenue Amherst, New York 14226 716-839-2820 dmdjcro@aol.com Section 1 Introduction to Sports
Sports Dentistry: Treating the athletes in your practice. November 3, 2011 David P. Croglio, DDS 2503 Kensington Avenue Amherst, New York 14226 716-839-2820 dmdjcro@aol.com Section 1 Introduction to Sports
A combined approach with passive and active repositioning of a traumatically intruded immature permanent incisor
 H.-J. Kim*-**, Y.-I. Kim***, K.-S. Min**-**** *Department of Conservative Dentistry, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea **Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry and Institute
H.-J. Kim*-**, Y.-I. Kim***, K.-S. Min**-**** *Department of Conservative Dentistry, Pusan National University Hospital, Busan, Korea **Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry and Institute
Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer
 Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer Abstract Aim: The focus of this study was to examine the staining potential of calcium hydroxide
Staining Potential of Calcium Hydroxide and Monochlorophenol Following Removal of AH26 Root Canal Sealer Abstract Aim: The focus of this study was to examine the staining potential of calcium hydroxide
Transient Tooth Discoloration After Periodontal Instrumentation of an Aggressive Periodontitis. A Case Report
 Transient Tooth Discoloration After Periodontal Instrumentation of an Aggressive Periodontitis. A Case Report Julio C Rincon A*, Zahida Oakley*, Paul Abbott *Department of Periodontology and Implant Dentistry.
Transient Tooth Discoloration After Periodontal Instrumentation of an Aggressive Periodontitis. A Case Report Julio C Rincon A*, Zahida Oakley*, Paul Abbott *Department of Periodontology and Implant Dentistry.
Reposition of intruded permanent incisor by a combination of surgical and orthodontic approach: a case report
 Reposition of intruded permanent incisor by a combination of surgical and orthodontic approach: a case report Ki-Taeg Jang* / Jung-Wook Kim** / Sang-Hoon Lee*** / Chong-Chul Kim**** / Se-Hyun Hahn*****
Reposition of intruded permanent incisor by a combination of surgical and orthodontic approach: a case report Ki-Taeg Jang* / Jung-Wook Kim** / Sang-Hoon Lee*** / Chong-Chul Kim**** / Se-Hyun Hahn*****
A'REVITALIZATION'PROTOCOL'LEAD' TO'DIFFERENT'OUTCOMES'IN' ADJACENT'TEETH'
 PATEL,Suhag* ZAFAR,Salwa** SINGH,Abhishek*** JAIN,Neetika*** CHOUDHARY,Ronak* AREVITALIZATIONPROTOCOLLEAD TODIFFERENTOUTCOMESIN ADJACENTTEETH ABSTRACT Regenerative Endodontic Procedures can be defined
PATEL,Suhag* ZAFAR,Salwa** SINGH,Abhishek*** JAIN,Neetika*** CHOUDHARY,Ronak* AREVITALIZATIONPROTOCOLLEAD TODIFFERENTOUTCOMESIN ADJACENTTEETH ABSTRACT Regenerative Endodontic Procedures can be defined
Pulpal treatment in young permanent teeth CHALLENGES IN PULPAL TREATMENT OF YOUNG PERMANENT TEETH A REVIEW
 Review CHALLENGES IN PULPAL TREATMENT OF YOUNG PERMANENT TEETH A REVIEW Anantharaj.A 1,Praveen.P 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3, Prathibha Rani.S 4, Sudhir.R 5,Murali Krishnan.B 6 1 Professor and Head, 2,3
Review CHALLENGES IN PULPAL TREATMENT OF YOUNG PERMANENT TEETH A REVIEW Anantharaj.A 1,Praveen.P 2, Karthik Venkataraghavan 3, Prathibha Rani.S 4, Sudhir.R 5,Murali Krishnan.B 6 1 Professor and Head, 2,3
Effect of sodium hypochlorite on human pulp cells: an in vitro study
 Effect of sodium hypochlorite on human pulp cells: an in vitro study Mark D. Essner, DDS, a Amjad Javed, MSc, PhD, b and Paul D. Eleazer, DDS, MS, c Birmingham, Alabama UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA SCHOOL OF
Effect of sodium hypochlorite on human pulp cells: an in vitro study Mark D. Essner, DDS, a Amjad Javed, MSc, PhD, b and Paul D. Eleazer, DDS, MS, c Birmingham, Alabama UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA SCHOOL OF
Root fractures: the influence of type of healing and location of fracture on tooth survival rates an analysis of 492 cases
 Dental Traumatology 2012; 28: 404 409; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2012.01132.x Root fractures: the influence of type of healing and location of fracture on tooth survival rates an analysis of 492 cases Jens
Dental Traumatology 2012; 28: 404 409; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2012.01132.x Root fractures: the influence of type of healing and location of fracture on tooth survival rates an analysis of 492 cases Jens
Australian Dental Journal
 Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association Australian Dental Journal 2016; 61:(1 Suppl): 95 106 doi: 10.1111/adj.12401 Management of incompletely developed teeth
Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association Australian Dental Journal 2016; 61:(1 Suppl): 95 106 doi: 10.1111/adj.12401 Management of incompletely developed teeth
Intrusive luxation of 60 permanent incisors: a retrospective study of treatment and outcome
 Dental Traumatology 2011; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2011.01088.x Intrusive luxation of 60 permanent incisors: a retrospective study of treatment and outcome Georgios Tsilingaridis 1, Barbro Malmgren 1,2,
Dental Traumatology 2011; doi: 10.1111/j.1600-9657.2011.01088.x Intrusive luxation of 60 permanent incisors: a retrospective study of treatment and outcome Georgios Tsilingaridis 1, Barbro Malmgren 1,2,
Iwaya et al (1) showed that a human immature permanent tooth with necrotic pulp
 Histologic Observation of a Human Immature Permanent Tooth with Irreversible Pulpitis after Revascularization/Regeneration Procedure Emi Shimizu, DDS, PhD,* George Jong, DDS,* Nicola Partridge, PhD, Paul
Histologic Observation of a Human Immature Permanent Tooth with Irreversible Pulpitis after Revascularization/Regeneration Procedure Emi Shimizu, DDS, PhD,* George Jong, DDS,* Nicola Partridge, PhD, Paul
Healing of Extensive Periapical Lesions by means of Conventional Endodontic treatment a Report of Two Cases
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Apr. 2015), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org Healing of Extensive Periapical Lesions
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 4 Ver. VIII (Apr. 2015), PP 87-91 www.iosrjournals.org Healing of Extensive Periapical Lesions
Treatment of Extrusive Luxation in Permanent Teeth: Literature Review with Systematic Criteria
 REVIEW ARTICLE Treatment of Extrusive Luxation in Permanent Teeth: Literature 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2024 Review with Systematic Criteria Treatment of Extrusive Luxation in Permanent Teeth: Literature
REVIEW ARTICLE Treatment of Extrusive Luxation in Permanent Teeth: Literature 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2024 Review with Systematic Criteria Treatment of Extrusive Luxation in Permanent Teeth: Literature
Management of Dens Invagenatus (DI) in a Young Permanent Tooth
 Case report AODMR Management of Dens Invagenatus (DI) in a Young Permanent Tooth Preeti M Tippashetty 1, Vedavathi Boregowda 2, Veena S Pai 2, Sijo P Mathew 1, Gis George 1, Roopa R Nadig 3 1 Post Graduate
Case report AODMR Management of Dens Invagenatus (DI) in a Young Permanent Tooth Preeti M Tippashetty 1, Vedavathi Boregowda 2, Veena S Pai 2, Sijo P Mathew 1, Gis George 1, Roopa R Nadig 3 1 Post Graduate
Single-Step Apexification with Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA) Case Reports
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Feb. 2016), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Single-Step Apexification with Mineral
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 2 Ver. VIII (Feb. 2016), PP 49-53 www.iosrjournals.org Single-Step Apexification with Mineral
Dental Trauma in children I. 5DM PEDO
 Dental Trauma in children I. 5DM PEDO Childhood is a risky period of life considering trauma (high risk and incidence of injuries) Injuries to the teeth can severely harm a child in these aspects: functional
Dental Trauma in children I. 5DM PEDO Childhood is a risky period of life considering trauma (high risk and incidence of injuries) Injuries to the teeth can severely harm a child in these aspects: functional
Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:6 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0006-0 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics Eyal Rosen 1 Igor Tsesis 1 Received: 15 June 2017 / Accepted: 9 July 2017 / Published
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth: A Decision Guide
 Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth: A Decision Guide www.aae.org/treatmentoptions ROOT AMPUTATION, HEMISECTION, BICUSPIDIZATION Case One Hemisection of the distal root of tooth #19. 13 mo. Recall
Treatment Options for the Compromised Tooth: A Decision Guide www.aae.org/treatmentoptions ROOT AMPUTATION, HEMISECTION, BICUSPIDIZATION Case One Hemisection of the distal root of tooth #19. 13 mo. Recall
ADVANCES IN PEDIATRIC DENTISTRY
 TRIAGE TRAUMATIC DENTAL INJURIES: Critical Steps Kaneta R. Lott, DDS LottSeminars.com EDUCATE INSPIRE LEAD GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC DENTAL INJURIES www.iadt dentaltrauma.org DENTAL TRAUMA
TRIAGE TRAUMATIC DENTAL INJURIES: Critical Steps Kaneta R. Lott, DDS LottSeminars.com EDUCATE INSPIRE LEAD GUIDELINES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC DENTAL INJURIES www.iadt dentaltrauma.org DENTAL TRAUMA
Management of Internal Resorption with Perforation
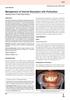 Mahendran Kavitha et al CSE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10047-0054 1 Mahendran Kavitha, 2 K Girija, 3 Shekar Shobana STRCT Internal root resorption is a pathologic intraradicular process in which there
Mahendran Kavitha et al CSE REPORT 10.5005/jp-journals-10047-0054 1 Mahendran Kavitha, 2 K Girija, 3 Shekar Shobana STRCT Internal root resorption is a pathologic intraradicular process in which there
Australian Dental Journal
 Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association Australian Dental Journal 2014; 59: 240 244 doi: 10.1111/adj.12164 Management of traumatically intruded young permanent
Australian Dental Journal The official journal of the Australian Dental Association Australian Dental Journal 2014; 59: 240 244 doi: 10.1111/adj.12164 Management of traumatically intruded young permanent
Pulp biology update: Is regeneration possible or is it just pulp fiction?
 Pulp biology update: Is regeneration possible or is it just pulp fiction? Hal Duncan, Division of Restorative Dentistry and Periodontology, Dublin Dental University Hospital, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland
Pulp biology update: Is regeneration possible or is it just pulp fiction? Hal Duncan, Division of Restorative Dentistry and Periodontology, Dublin Dental University Hospital, Trinity College Dublin, Ireland
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS
 NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.03 Effective Date: January 1, 2018 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
Regenerative Endodontics
 Regenerative Endodontics Dental infections in immature teeth: ü Arrested dental development ü Premature tooth loss Classic Treatments: 1. Conventional Root Canal Therapy -Teeth no longer develop becoming
Regenerative Endodontics Dental infections in immature teeth: ü Arrested dental development ü Premature tooth loss Classic Treatments: 1. Conventional Root Canal Therapy -Teeth no longer develop becoming
PULP REVASCULARIZATION OF A NECROTIC INFECTED IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 03 PULP REVASCULARIZATION OF A NECROTIC INFECTED IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Muhamad
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 03 PULP REVASCULARIZATION OF A NECROTIC INFECTED IMMATURE PERMANENT TOOTH: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Muhamad
Endodontic Treatment After Autotransplantation of Tooth with Complete Root Formation
 Endodontic Treatment After Autotransplantation of Tooth with Complete Root Formation Caio Cesar Souza 1, Carlos Eduardo da Silveria Bueno 1, Augusto Shogi Kato 1, Rina Andrea Pelegrine 1 Ana Paula Simezo
Endodontic Treatment After Autotransplantation of Tooth with Complete Root Formation Caio Cesar Souza 1, Carlos Eduardo da Silveria Bueno 1, Augusto Shogi Kato 1, Rina Andrea Pelegrine 1 Ana Paula Simezo
Questions for final state exam
 Questions for final state exam 1. 1. Estetic filling in operative dentistry 2. Pulp-dentin organ, morphology and functions, pulp-periodontal complex 3. The process(es) of tooth eruption, disorders linked
Questions for final state exam 1. 1. Estetic filling in operative dentistry 2. Pulp-dentin organ, morphology and functions, pulp-periodontal complex 3. The process(es) of tooth eruption, disorders linked
5. Injuries to the tooth supporting structures in the permanent dentition
 Research Signpost Trivandrum Kerala, India Dental and Maxillofacial Trauma Challenges in Low and Middle Income Countries, 2018: 79-96 ISBN: 978-81-308-0577-1 Editors: Febronia Kokulengya Kahabuka, Irene
Research Signpost Trivandrum Kerala, India Dental and Maxillofacial Trauma Challenges in Low and Middle Income Countries, 2018: 79-96 ISBN: 978-81-308-0577-1 Editors: Febronia Kokulengya Kahabuka, Irene
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS
 NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.02 Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
NON-SURGICAL ENDODONTICS UnitedHealthcare Dental Coverage Guideline Guideline Number: DCG009.02 Effective Date: February 1, 2017 Table of Contents Page INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE...1 BENEFIT CONSIDERATIONS...1
Surgical Retreatment of an Invaginated Maxillary Central Incisor Following Overfilled Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report
 Surgical Retreatment of an Invaginated Maxillary Central Incisor Following Overfilled Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report Hakan Ozbas a Rustem Kemal Subay b Melike Ordulu c ABSTRACT This case report presents
Surgical Retreatment of an Invaginated Maxillary Central Incisor Following Overfilled Endodontic Treatment: A Case Report Hakan Ozbas a Rustem Kemal Subay b Melike Ordulu c ABSTRACT This case report presents
Sequelae and prognosis of intruded primary incisors: a retrospective study
 Scientic Article Sequelae and prognosis of intruded primary incisors: a retrospective study Gideon Holan, DMD Diana Ram, Dr. Odontol Dr. Holan is senior lecturer and Dr. Ram is instructor, Department of
Scientic Article Sequelae and prognosis of intruded primary incisors: a retrospective study Gideon Holan, DMD Diana Ram, Dr. Odontol Dr. Holan is senior lecturer and Dr. Ram is instructor, Department of
Comparison of MTA and Ca(OH) 2 for the apexification of necrotic immature permanent teeth An Evidence Based Report
 Comparison of MTA and Ca(OH) 2 for the apexification of necrotic immature permanent teeth An Evidence Based Report Allison Clark, Anthony Pino, Danielle Attoe, Fatemeh Farzin, Keith Li, Malisa Gambacorta
Comparison of MTA and Ca(OH) 2 for the apexification of necrotic immature permanent teeth An Evidence Based Report Allison Clark, Anthony Pino, Danielle Attoe, Fatemeh Farzin, Keith Li, Malisa Gambacorta
Here are some frequently asked questions about Endodontic treatment:
 Here are some frequently asked questions about Endodontic treatment: What is an "Endodontist"? Endodontists are dentists who specialize in treating the soft inner tissue of your tooth's roots. After they
Here are some frequently asked questions about Endodontic treatment: What is an "Endodontist"? Endodontists are dentists who specialize in treating the soft inner tissue of your tooth's roots. After they
Clinical Guideline on Management of Acute Dental Trauma
 120 Clinical Guidelines American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Clinical Guideline on Management of Acute Dental Trauma Originating Council Council on Clinical Affairs Review Council Council on Clinical
120 Clinical Guidelines American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Clinical Guideline on Management of Acute Dental Trauma Originating Council Council on Clinical Affairs Review Council Council on Clinical
Update of Management and root canal treatment of non-vital immature permanent incisor teeth guideline 2010
 Update of Management and root canal treatment of non-vital immature permanent incisor teeth guideline 2010 Clinical Guidelines in Paediatric Dentistry Management and Root Canal Treatment of Non-Vital Immature
Update of Management and root canal treatment of non-vital immature permanent incisor teeth guideline 2010 Clinical Guidelines in Paediatric Dentistry Management and Root Canal Treatment of Non-Vital Immature
Principles of endodontic surgery
 Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.
Principles of endodontic surgery Note: the doctor said that this lecture mainly contain notes, so we should study it from the book for further information (chapter 18) principles of endodontic surgery.

