Effect of mouth wash extracted from Salvadora persica (Miswak) on dental plaque formation: A clinical trail
|
|
|
- Stephen Evans
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Medicinal Plants Research Vol. 4(14), pp , 18 July, 2010 Available online at ISSN Academic Journals Full Length Research Paper Effect of mouth wash extracted from (Miswak) on dental plaque formation: A clinical trail Fouad Hussein Al-Bayaty 1 *, Aiman Hamad AI-Koubaisi 2, Nidhal Abdul Wahid Ali 3 and Mahmood Ameen Abdulla 4 1 Department of Restorative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, University Teknologi MARA Shah Alam, Malaysia. 2 Faculty of Dentistry, Baghdad University, Baghdad, Iraq. 3 Faculty of Dentistry, Al Mustansrya University, Mustansrya, Iraq. 4 Department of Molecular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University Malaya, Malaysia. Accepted 17 June, 2010 Chewing sticks or Miswak are used for teeth cleaning in many parts of the world, these Miswaks are believed to contain chemical substances which inhibit plaque formation and gingivitis. In the present study, (Miswak) was extracted with 60% ethanol and was examined for its toxic effect, assessed its antibacterial activity and evaluated clinically for its effect on dental plaque formation. A 4 day plaque regrowth, double - blind, crossover design was used in which 10 dental students volunteers were rendered plaque free (0.3), ceased tooth cleaning, then, asked to rinse twice daily for 1.5 min each time with 10 ml of chlorhexidine 0.2% mouth rinse and three times daily for 1.5 min each time with 10 ml of S. persica 10% solution and placebo mouth rinse. On day five, plaque was scored by the plaque index system (PLI). A wash out period of 2 days was allowed in which the volunteers returned to self- performed plaque control, then a new test period was initiated. Statistical analysis showed that the mean PLI score were 1.48 for S. persica mouth rinse, 0.48 for chlorhexidine and 2.07 for placebo mouth rinse. Acute toxicity test revealed no mortality among the experimental animals which is an indication that S. persica crude extract solution is well tolerated, disk diffusion test showed a marked antibacterial effect in vitro and this effect is concentration dependent, had an effect in in vivo, but this effect cannot be considered absolute. Key words: Mouthwash, Miswak, dental plaque. INTRODUCTION Supragingival plaque control is largely the responsibility of the individual, using tooth brushes and interdental cleaning devices, however; mechanical plaque eradication is considered for most as time consuming, requires above average of motivation, skill and is more difficult for handicapped people (Lindhe, 2003). Also, the prevalence of gingivitis, from young age in all population, and the occurrence or recurrence of periodontal disease is high (Brown et al., 1996). These observations suggest that mechanical cleaning alone by a considerable proportion of individuals is insufficiently good to maintain gingival health and, in the susceptible individual, to prevent *Corresponding author. drfouadhm@yahoo.com. Tel: Fax: periodontal disease occurrence and progression or recurrence. This supports the concept of employing agents to control plaque and require minimal cooperation and skill in their use This is the concept, which underlies, chemical supra gingival plaque control. A number of chemical agents which have antiseptic or antimicrobial action have been used, with variable success, to inhibit supragingival plaque formation and the development of gingivitis. Among these are; phenolic compounds, Bis-biguanidaes, Pyrimidines, Quaternary ammnium compounds, Oxygenating agents, halogens, heavy metal salts (Mandel, 1988). And among these agents, chlorhexidine is, thus far, the most studied and effective antiseptic for plaque inhibition and prevention of gingivitis when used twice daily as mouth rinse (Ribeiro et al., 2007). But in oral use as a mouth rinse chlorhexidine
2 Al-Bayaty et al has been reported to have a number of side effects including: brown discoloration of the teeth, some restorative materials and mucosa, bitter taste, and sometime sloughing of oral mucosa which restricts its general use. Other chemical antiplaque agents have been tested, none has shown equal or better results than chlorhexidine without eliciting unfavourable side effects (Hellden et al., 1981; Addy et al., 1995). In order to overcome such side effects the world health organization (WHO) advice researchers to investigate the possible use of natural products such as herb and plant extracts. Herb and plant extract have been used in oral hygiene products for many years if not centuries (Mandel, 1988). A number of clinical studies have shown the effects of using mouth washes extracted from herbs such as Sanguinarina (Abbas et al., 1985), Myrtus communis (Walid and Fouad, 2001), Qureucus infectoria (Walid and Fouad, 2000), Capparis spinosa (Fouad and Wassan, 2001) and Cinnamon (Fouad et al., 2000) in the prevention of dental plaque accumulation and subsequent gingival inflammation. is a medicinal plant whose roots have been used by many people in Africa, South America, Middle East and Asia. The precise method for the use of the Miswak was recorded by Babylonian 5000 B.C. and the fashion ultimately spread throughout the Greek and Romanian empire. In fact, the chewing stick which is known as Miswak or siwak among Moslems had fallen into general use by the time the holly prophet Mohammed started his mission in about 543 A.D. Prophet Mohammed said that the Miswak is an implement for the cleaning of teeth and pleases Allah (Lewis, 1980). One of Mohammed s biographers wrote: Even the approach of death did not keep the prophet from demanding the siwak because it is the most elegant thing that one can use, and the most fitting to be found beautiful. For it makes the teeth white, clarifies the understanding, makes the breath fragrant, extinguishes the gall, dries up the phlegm, strengthens the gums around the teeth, makes the glance clear, sharpens the power of the vision, opens the bowels and whets the appetite (Almas, 2001). S. persica, a very popular plant in the middle east, contains a number of identified antimicrobial and other prophylactic components including fluoride (Al-Lafi and Ababneh, 1995), alkaloids (Khalessi et al., 2004), sulphur compounds (Ezmirly et al., 1979), glucosinolates (Darmani et al., 2006) and volatile oils such as benzyl isothiocyanate (Khalessi et al., 2004). It has been demonstrated that extracts of S. Persica improved gingival health and inhibited growth of cariogenic bacteria (Khalessi et al., 2004). Another study showed that Streptococcus mutans was more susceptible to Miswaks antimicrobial activity than Lactobacilli (Almas and Al-Zeid, 2004). In this regards, Almas et al. (2005) compared antimicrobial activity of eight commercially available mouth rinses and 50% Miswaks extract against seven microorganisms. They found that mouth rinses containing chlorhexidine had the maximum antibacterial activity, while Miswak extract had low antibacterial activity. Additionally, Sofrata et al. (2007) showed that mouth rinsing with S. persica extract, compared with water rinsing, resulted in protracted elevation of plaque ph and the difference between two groups was statistically significant at 30 min. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended and encouraged the use of these sticks as an effective tool for oral hygiene (WHO 1987), it cleans the dental structures and prevent problems in two ways: by mechanical action of the soft wood fibres, and by therapeutic action of a chemical constituent of the chewing stick itself (Almas, 2001). From the above it is not clear if the plant has any chemical anti dental plaque property. For this reason the present study addresses the problem with the following objectives: to determine antibacterial activity of S. Persica alcoholic extract in vitro, to evaluate acute toxicity profile of its ethanol extract and to determine clinically the effect of the S. persica extract on dental plaque formation when used as mouthwash. MATERIALS AND METHODS Alcoholic extraction of S. persica chewing sticks Two hundred grams of chewing sticks were cut using a sharp knife, then ground to powder using a food blender. The powder was extracted with one litre of 60% ethanol; the mixture was left for 24 h. Then filtered through Whatman No.1 filter paper.the extract was autoclaved at 40 C until it becomes dry (Al- Jebbory, 1994). Assessment of antibacterial activity The antibacterial activity of the S. persica extract was evaluated by using the disk diffusion test technique (British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy, 2005) sterile paper disks were moisted for 15 min in 1, 3, 5 and 10% solution of plant extract and 0.2% Chlorhexidine solution as positive control and distilled water as a negative control. Supra gingival plaque was collected by using sterilized periodontal probes from 10 patients, the plaque samples were pooled, streaked on blood agar plate, incubated at 37 C for 48 h. The cultured dental plaque was transferred into nutrient broth and incubated for 24 h at 37 C. Blood agar plate streaked by previously cultured broth with supragingival plaque using loop wire then, these disks were placed on the streaked blood agar plate; the plate was incubated at 37 for 24 h and examined for zone of inhibition. This procedure was repeated four times (Christofilogiannis, 2001). Evaluation of the toxicological profile of the extract The acute toxicity test was studied in group of 32 male albino mice which were injected intra peritonealy per body weight with varying concentration of plant extract (10, 30, 50 and 100 mg/ml). Then the concentration of the injected extract was increased to 2 g/kg. The acute toxicity LD 50 was calculated as the geometric mean of the dose that resulted in 100% lethality and that which caused no lethality at all (Goth, 1978).
3 1448 J. Med. Plant. Res. Measurement of the elimination of S. persica extract from the oral cavity Quantitative assessments of the release of S. persica extract was evaluated in saliva using Electronic spectrophotometer. Saliva sample were collected from five dental students volunteer who was instructed to rinse their mouth with 10 ml of 10% S. persica solution for 2 min. following the morning meal. They were also instructed not to change their eating and drinking habits. Following the rinse, 3 ml of unstimulated saliva was collected in small test tubes 16 times according to fixed time schedule. The first sample was taken 5 min after expectorating the mouth wash and the last one 24 h later. Then 1 ml of saliva mixed with 2 ml 2 M NaOH and 20 ml of chloroform in glass stoppered flask, 15 ml of the organic phase is aspirated and transferred to a test tube, 4 ml 0.1 M glycine buffer were added with PH adjusted to 2.10 ± ml of the buffer transferred to a 1 cm cavette and the extinction at 360 nm was measured against buffer as reference. The extinction of the unknown (Ex) and the mean value of the extinction of the standard (Est) and the blanks (Ebl) were used for calculating the amount of S. persica extracts in the unknown sample using the following equation. Mg in the sample = Clinical trial preparation Ex - Ebl x (mg in the standard) Est- Ebl Three different mouthwash preparations were tested in the study: 1) Placebo mouthwash: Distilled water as negative control. 2) mouth wash: Alcoholic extract, at a concentration of 10 mg/ml 3) Chlorhexidine mouth wash: 0.2% chlorhexidine digluconate as a positive control. The rinsing preparations were filled in identical but coded bottles. An instruction of usage was written on it. Preparation of volunteers The nature of the trial was explained to each volunteer verbally by the examining clinician. During a preparatory period of 2 weeks, the participants were exposed to a professional plaque control measure (Axelssen and Lindhe, 1981a and b). The oral hygiene session were conducted by the examining clinician and required at least min each. At the end of this preparatory period, each participant received a professional scaling and polishing. Study design The study was a double blind, crossover design. A group of 10 male dental students, 22 years of age volunteered to participate in this clinical trial from the College of Dentistry, University of Baghdad. They had total of 275 teeth and 1100 teeth surfaces. These volunteers participated in three test periods; each period lasted five days from Saturday - Wednesday, in which each volunteer was instructed to rinse with each of the following mouth rinses: 1) The test solution: S. persica alcoholic extract at 10% concentration. The instruction was to rinse three times daily with 10 ml of the solution at duration of 1.5 min. 2) The positive control: 0.2% chlorhexidine digluconate solution. 10 ml, 2 times, each time 1.5 min duration. 3) The negative control: Distilled water 10 ml, 3 times daily each times 1.5 min duration. And during which, all mechanical oral hygiene measures were withdrawn, they were also instructed not to change their eating and drinking habits, at the end of each test period a washout period of 2 days was allowed during which the volunteers were instructed to resume the previous mechanical plaque control measures (Abbas et al., 1985; Axelssen and Lindhe, 1981a). The volunteers were asked to fill out a questionnaire concerning their opinion about the taste and other side effects of the rinsing solution like ulceration, change in the test and burning sensation in the mouth. Clinical examination A single clinician carried out all examinations, the presence and amount of plaque was examined and scored on day 5 using the plaque index system PLI (Silness and Loe, 1964). Subjects selection criteria The subjects enrolled in this study had to satisfy the following criteria: 1) Male dental student volunteers who should have at least 20 teeth with good alignment (wisdom teeth were excluded). 2) None of the volunteers were wearing fixed or removable orthodontic appliances or partial dentures. Subjects were excluded from the study if they had any of the following: 1) A history of epilepsy, convulsion or fainting spells. 2) Hepatitis or other liver disease within the last 12 months. 3) Systemic diseases such as hypertension, blood diseases and heart diseases. 4) Allergy or hyper sensitivity to chlorhexidine. 5) Use of antibiotics within seven days of the baseline. 6) Presence of periodontal tissue breakdown or pathological lesion (Siegrist et al., 1986). Statistical analysis The statistical analysis was carried out using the student s t-test with 5% significance level. Separate analysis was made for the individual mean, for the mean for group of teeth and tooth surfaces. RESULTS Extraction product 200 g of S. persica was yield to alcoholic extract of approximately 15 g. Antibacterial activity test The inhibition zone of the various concentrations, which were recorded after 24 h incubation at 37 C are shown in Table 1. The best antibacterial activity in vitro (12 mm)
4 Al-Bayaty et al Table 1. Inhibition zone of types of solution. Types of mouth wash Inhibition zone (mm) 1 mg/ml S. persica mg/ml S. persica mg/ml S. persica mg/ml S. persica % Chlorhexidine Distilled water Table 2. Concentration of alcoholic extract of in saliva. Time S. Persia 10 mg/ml solution (mg/ml) After 5 min 6.7 After 1 h 4.54 After 2 h 3.79 After 3 h 3.04 After 4 h 2.29 After 5 h 1.03 After 6 h 0.5 After 8 h 0 After 10 h 0 Table 4, 5 and 6 represent a summary of a comparative significance between different mouth washes regarding their effect on dental plaque formation. The statistical analysis of data showed that: 1) Avery highly significant deference (p < 0.001) between and placebo mouth rinse for plaque index scores in all tooth surfaces. 2) mouth rinse resulted in a very highly significant (p < 0.001) higher plaque index scores than the 0.2% Chlorhexidine mouth rinse in all groups of teeth and tooth surfaces. Figures 1 illustrates the percentage distribution of (PLI) scores for the three mouthwashes in all teeth surfaces. For score (0) Chlorhexidine was 54%, S. persica was 8.6% and placebo was 0.5% for score (1) Chlorhexidine was 43.4% S. persica was 35% and placebo was 22.5% for score (2), Chlorhexidine was 2.6% S. persica was 55.9% and placebo was 45.7%. For score (3), Chlorhexidine was 0%, S. persica was 0.5% and placebo was 31.2%. Figures 2 and 3 show the percentage distribution of PLI scores for mandibular and maxillary teeth respectively. Figures 4 and 5 show the percentage distribution of PLI scores for buccal, lingual teeth surfaces respectively. DISCUSSION was obtained with 10 mg/ml concentration, 5 mg/ml concentration shows significant but, however, less than that of 10 mg/ml whereas 1 and 3 mg/ml failed to show significant activity. Acute toxicity The procedure of acute toxicity test revealed no mortality among the experimental animals, which, in turn, indicates that this substance is well tolerated. Measurement of the elimination of S. persica extract from the oral cavity The concentration of the 10 mg/ml S. persica solution in saliva at various time points are shown in Table 2. Results from electronic spectrophotometer revealed traces of extract after 6 h, then vanishes at 8 h. Clinical trial Table 3 demonstrated that the mean plaque index scores for the maxillary and mandibular teeth after 5 days of daily rinsing with S. persica, and placebo mouth rinses were 1.48, 0.48 and 2.07, respectively. There is a continued interest in identifying efficient antiplaque agents that could be used daily without side effects (Prabuseenivasan et Al., 2006). Folk medicine is a potential source of medicaments and has recently become a focus of dental research (Fouad et al., 2000; Walid and Fouad, 2000 and 2001; Fouad and Wassan, 2001). Chewing sticks or Miswaks are still popular compared with the use of modern tooth brushes, the type of chewing sticks used in the Middle East is derived from the plant S. persica (Almas, 2001). Alcoholic extraction of S. persica yielded 15 gm for each 200 gm of sticks; this is considered as a commercially valued (Almas and Al-Zeid, 2004). The in vitro activity of S. persica, revealed that its action is a concentration dependent, where 10 mg/ml solution produced the greatest zone of inhibition around each paper disc in the agar diffusion assay (Table 1) when compared with other solutions. Yet the inhibition zones were less pronounced that of Chlorhexidine solution at all concentrations this result was in agreement with that presented by Almas et al. (2005). The acute toxicity test (single dose toxicity) is still of considerable importance for the assessment of risk posed by new chemical substances, and for better control of natural and synthetic agents in the human environment (Zbinden and Flury-Roversi, 1981). Evaluation of toxicological profile of the extract by intra peritoneal
5 1450 J. Med. Plant. Res. Table 3. The mean plaque index scores for all surfaces: All teeth, maxillary teeth and mandibular teeth. All teeth Maxillary teeth Mandibular teeth Mean S.D. E Mean S.D. E Mean S.D. E S. persica Chx Table 4. A summary of a comparative significance between different mouth washes. Regarding their effect on dental plaque formation. versus S. persica S. persica versus water All teeth VHS VHS Maxillary teeth VHS VHS Mandibular teeth VHS VHS : Chlorhexidine; VHS: Very highly significant. P < Table 5. A summary of a comparative significance between different mouth washes. Regarding their effect on dental plaque formation. versus S. persica S. persica versus water Incisors and canines VHS VHS Premolars VHS VHS Molars VHS VHS : Chlorhexidine; VHS: Very highly significant. P < Table 6. A summary of a comparative significance between different mouth washes. Regarding their effect on dental plaque formation. versus S. persica S. persica versus water Approximal surfaces VHS VHS Buccal surfaces VHS VHS lingual surfaces VHS VHS : Chlorhexidine; VHS: Very highly significant. P < injection did not cause death among the experimental animals even with a very high does which was 2.04 g/kg. Therefore; the extract is considered as a well-tolerated substance and so the LD50-test is without practical or theoretical relevance. This is according to Zbinden and Flury-Roversi (1981) who stated that substances that are well tolerated by small rodents at oral doses of 5 g/kg and parenteral doses 2 g/kg should not be subject to a LD50- test. This result is in accordance with that presented by Abo Al-Samh and Al-Nazhan (1997). The spectrophotometer assessments were carried out using the Electronic spectrophotometer in the present study to measure the
6 Al-Bayaty et al Figure 1. The percentage distribution of all surfaces according to plaque index scores. Figure 2. The percentage distribution of mandibular tooth surfaces according to plaque index scores. releases of solution from oral cavity has certain limitation and does not give the accurate picture. But rather an approximate one of the substantivity when compared with the radioisotopes technique, which was used for Chlorhexidine by Bonesvoll et al. (1974). Traces of S. persica 10 mg/ml solution were detected up to 6 h after expectoration; this substantivity in approxi- mate but it gives a comparable gross picture. Therefore; volunteers were instructed to rinse their mouth with the solution three times daily in order to make a relatively accurate comparison. Five-day experimental period length was chosen because plaque accumulation reaches measurable volumes after 4-5 days of no oral hygiene (Theilade et al., 1966).
7 1452 J. Med. Plant. Res. Figure 3. The percentage distribution of maxillary tooth surfaces according to plaque index scores. Figure 4. The percentage distribution of buccal surfaces according to plaque index scores. S. persica mouthwash inhibited plaque formation and yielded to mean PLI score lower than that of placebo, but also higher than that recorded for Chlorhexidine (Table 7) in most part of dentition. Therefore; S. persica had a very highly significant (p < 0.001) effect on plaque accumulation in comparison with placebo this finding was in accordance with that presented by Sofrata et al. (2007). Nonetheless, Chlorhexidine showed a very highly significant reduction in the overall bacterial plaque accumulation when compared with S. persica. Irrespective of the agents that have been used, plaque tends to be predominant on mandibular surfaces than on maxillary surfaces (Table 3, Figures 2 and 3), on buccal surfaces than on lingual surfaces (Table 8, Figures 4 and 5). This is in agreement with Moran et al. (1995). This is probably attributable to the masticatory and tongue actions. More on posterior teeth than on anterior (Table 4A), this is consistent with Axelsson and Lindhe (1987). Also plaque accumulations tend to be predo-minant on interproximal teeth surfaces (Table 8, Figures 4, and 5). This is in agreement with Lang et al. (1982). Eight of ten volunteers complain from the taste of the plant extract solution, two of ten showed a reversible staining of teeth. Other than these, they expressed on
8 Al-Bayaty et al Figure 5. The percentage distribution of lingual surfaces according to plaque index scores. Table 7. The mean plaque index scores for group of teeth. Incisors and canines Premolars Molars Mean S.D. E Mean S.D. E Mean S.D. E Table 8. The mean plaque index scores for group of teeth. Approximal surfaces Buccal surfaces Lingual surfaces Mean S.D. E S.D. E Mean S.D. E major side effects. Overall observations indicate that S. persica crude extract solution is well tolerated showed a marked antibacterial effect in vitro and this effect is concentration dependent, has an effect in in vivo, but this effect cannot be considered absolute. It is note worthy to mention that the chewing sticks, which have been tested in the present study, were cut from the tree one month earlier, kept in a plastic package, closed tightly and kept in the freezer at -5 C in order to keep them fresh. The fresher the stick, it seems the more effective it will be. In summary, the rational explanation of the attractiveness of S. persica chewing stick as a tool for teeth cleaning is: - Cheapness, safeness, its shape is like brush, contains chemical constituents with variable actions. - It seems to be two in one, which means it, gathers the tooth paste and tooth brush in one implement named Miswak. Conclusions S. persica alcoholic extract produced remarkable antibacterial activity in vitro at 10 mg/ml concentration, is well tolerated and safe. As a mouth rinse is less effective
9 1454 J. Med. Plant. Res. than chlorhexidine in preventing plaque accumulation and more effective than placebo on dental plaque accumulation. REFERENCES Abbas DK, Thrane P, Othman SJ (1985). Effectiveness of veadent as a plaque inhibiting mouthwash. Scand. J. Dent. Res., 93: Abo Al-Samh D, Al-Nazhan S (1997). In vitro study of the cytotoxicity of the Miswak ethanolic extract. Saudi Dent. J. 9: Addy M, Moran M, Newcomb R, Warren P (1995a). The comparative tea staining potential of phenolic, Chlorhexidine and antiadhesive mouth-rinses. J. Clin. Periodontol., 22: Al-Jebbory A (1994). Ethnopharmacology. AL-Hauria house press, Baghdad. pp Almas K, Skaug N, Ahmad I (2005). An in vitro antimicrobial comparison of Miswak extract with commercially available non-alcohol mouth rinses. Int. J. Dent. Hyg., 3: Almas K., Al-Zeid Z (2004). The immediate antimicrobial effect of a toothbrush and Miswak on cariogenic bacteria: A clinical study. J. Contemp. Dent. Pract., 5: Almas K. ( 2001). The effects of extracts of chewing sticks (Salvadora persica) on healthy and periodontaly involved human dentin A SEM study. Indian J. Dent. Res., 12: Al-Lafi T, Ababneh H (1995). The effect of the extract of the Miswak (chewing sticks) used in Jordan and the Middle East on oral bacteria. Int. Dent. J., 45: Axelssen P, Lindhe J (1981a). Effect of controlled oral hygiene procedures on caries and periodontal disease in adults.results after 6 yrs. J. Clin. Periodontol., 8: Axelssen P, Lindhe J (1981b).The significance of maintenance care in the treatment of periodontal disease. J. Clin. Periodontol., 8: Axelssen P, Lindhe J(1987). Efficacy of moth rinses in inhibiting dental plaque and gingivitis in man. J. Clin. Periodontol., pp Bonesvell P, lokken P, Rola G, Paus PN (1974).Retention of chlorhexidine in the human oral cavity after mouth rinses. Arch. Biol., 19: British Society for Antimicrobial Chemotherapy: basic disc diffusion method for antimicrobial susceptibility testing, version4.[ 2005_final_nh_apr il_2.pdf] Brown LJ, Albandar JM, Brunelle JA, Lee H (1996). Early-onset periodontitis: progression of attachment loss during 6 years. J. Periodontol., 67: Christofilogiannis P (2001).Current inoculation method in MIC determination. Aquacultu, 196: Darmani H, Nusayr T, Al-Hiyasat AS (2006). Effects of extracts of Miswak and d e m on proliferation of Balbl C 3T3 fibroblasts and viability of cariogenic bacteria. Int. J. Dent. Hyg., 4: Ezmlrly ST, Cheng JC, Wilson SR (1979). Saudi Arabian medcinal plants: Planta. Med., 35: Fouad H, Mahmouad, Wassan HZ (2001).The efficacy of Capparis Spinosa herbal extract as an antiplaque agent. J. College. Dentistry., 10: Fouad H, Mahmouad, Waleed H, Nidhal A (2000) The effect of cinnamon extract on staphylococcus aureas &Escherichia coli in vitro study. J. College. Dentistry., 7: Goth A (1978). Drugs safety and effectiveness in medical pharmacology.c.v. Mosby, U.S.A. p. 42. Hellden L, Comosci D, Hoch J, Tinanoff N(1981). Clinical study to compare the effect of stannous fluoride and chlorhexidine mouth rinses on plaque formation. J. Clin. Periodontol., 8: Khalessi AM, Pack AR, Thomson WM, Tomkins GR (2004). An in vitro study of the plaque control efficacy of Persica: A commercially available herbal mouthwash containing extracts of Salvadora Persica. Int. Dent. J., 54: Lang NP, Hotz P, Graf H, Gerring AH, Saxer UP (1982). Effects of supervised chlorhexidine mouth rinse in children. A longitudinal clinical trial. J. Periodont. Res., 17: Lewis EM (1980). Plants used for teeth cleaning throughout the world. J. Prev. Dent., 6: Lindhe J (2003). Clinical Periodontology and Implant Dentistry, fourth edition, Blackwell Munksgaard Publication. Mandel ID (1988). Chemotherapeutic agents for controlling plaque &gingivitis J Clin. Periodontol. 15: Moran J, Addy M, Wades W, Milson S, McAndrew R, Newcombe RG (1995).The effect of oxidizing mouth rinse compared with chlorhexidine on salivary bacterial counts and plaque regrowth. J. Clin. Periodontol., 22: Prabuseenivasan S, Jayakumar M, Ignacimuthu S (2006).In vitro activity of some plant essential oils. BMC Complementary. Alternative. Med., 6(39): 1-8. Ribeiro LG, Hashizume LN, Maltz M (2007).The effect of different formulations of chlorhexidine in reducing level of mutan streptococci in the oral cavity. J. Dent., 35: Siegrist BE, Gusberti FA, Brecx MC, Weber HP, Lang NP (1986). Efficacy of supervised rinsing with chlorhexidine digluconate in comparison of phenolic and plant alkaloid compounds. J. Periodont. Res., 21(16): Silness J, Joe H (1964). Periodontal disease in pregnancy.ii. Correlation between oral hygiene and periodontal condition. Acta Odonto. Scand.pp Sofrata A, Lingstrom P, Balloon M, Gustafsson A ( 2007). The effect of Miswak extract on plaque ph. An in vivo study. Caries Res., 41: Theilade E, Wright WH, Jensen SB, Loe H (1966). Experimental gingivitis in man. A longitudinal clinical and bacteriological investigation. Periodont. Res., 1: Walid H, Fouad H( 2000).The effect of mouth wash extracted from Qureucus infectoria on dental plaque formation. J Coll. Dent., 6: Walid H, Fouad H (2001). The effect of Myrtus Communis extract mouth wash on newly dental plaque. J. Coll. Dent., 8: World Health Organization. (1987).Prevention of oral diseases. Geneva: WHO. Zbinden G, Flury-Roversi M (1981). Significance of the LD50-test for the toxicological evaluation of chemical substances. Arch. Toxicol., 47:
Evaluation of Potential Effect of Menthol Solution on Oral Hygiene Status of Dental Students in a University in Iraq
 Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research April 2015; 14 (4): 687-692 ISSN: 1596-5996 (print); 1596-9827 (electronic) Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001
Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research April 2015; 14 (4): 687-692 ISSN: 1596-5996 (print); 1596-9827 (electronic) Pharmacotherapy Group, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Benin, Benin City, 300001
MDJ Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Cinnamomum Vol.:6 No.:4 2009
 MDJ Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Extract on Cariogenic Microorganisms of the Dental Plaque In-Vitro Study and Scanning Electron Microscopic Assessment Dr. Nidhal Abdul
MDJ Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity of Cinnamomum Zeylanicum Extract on Cariogenic Microorganisms of the Dental Plaque In-Vitro Study and Scanning Electron Microscopic Assessment Dr. Nidhal Abdul
Antibacterial Effects of Persica and Matrica Herbal Mouthwashes on Common Oral Microorganisms: An In Vitro Study
 107 2 / 35 / 1390 / : *** ** #* * ** *** 89 /12/10 : 89/9/15 : Antibacterial Effects of Persica and Matrica Herbal Mouthwashes on Common Oral Microorganisms: An In Vitro Study Mostafa Sadeghi*#, Reza Bahramabadi**,
107 2 / 35 / 1390 / : *** ** #* * ** *** 89 /12/10 : 89/9/15 : Antibacterial Effects of Persica and Matrica Herbal Mouthwashes on Common Oral Microorganisms: An In Vitro Study Mostafa Sadeghi*#, Reza Bahramabadi**,
Comparison of the antibacterial effects of persica mouthwash with chlorhexidine on streptococcus mutans in orthodontic patients
 DARU Vol. 14, No. 4 2006 178 Comparison of the antibacterial effects of persica mouthwash with chlorhexidine on streptococcus mutans in orthodontic patients * Salehi P., Momeni Danaie Sh. Department of
DARU Vol. 14, No. 4 2006 178 Comparison of the antibacterial effects of persica mouthwash with chlorhexidine on streptococcus mutans in orthodontic patients * Salehi P., Momeni Danaie Sh. Department of
Comparison of Fluoridated Miswak and Toothbrushing with Fluoridated Toothpaste on Plaque Removal and Fluoride Release
 Hosam Baeshen et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2035 Comparison of Fluoridated Miswak and Toothbrushing with Fluoridated Toothpaste on Plaque Removal and Fluoride Release 1 Hosam Baeshen,
Hosam Baeshen et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2035 Comparison of Fluoridated Miswak and Toothbrushing with Fluoridated Toothpaste on Plaque Removal and Fluoride Release 1 Hosam Baeshen,
The Immediate Antimicrobial Effect of a Toothbrush and Miswak on Cariogenic Bacteria: A Clinical Study
 The Immediate Antimicrobial Effect of a Toothbrush and Miswak on Cariogenic Bacteria: A Clinical Study Abstract The aim of this study was to assess the antimicrobial activity of the miswak chewing stick
The Immediate Antimicrobial Effect of a Toothbrush and Miswak on Cariogenic Bacteria: A Clinical Study Abstract The aim of this study was to assess the antimicrobial activity of the miswak chewing stick
Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children
 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108 Nidhi ORIGINAL Gupta, Manohar ARTICLE Bhat Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children 1
Citation for published version (APA): Van Strydonck, D. A. C. (2013). Chlorhexidine and the control of plaque and gingivitis
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Chlorhexidine and the control of plaque and gingivitis Van Strydonck, D.A.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Van Strydonck, D. A. C. (01).
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Chlorhexidine and the control of plaque and gingivitis Van Strydonck, D.A.C. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Van Strydonck, D. A. C. (01).
THE ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF DIFFERENT MOUTHWASHES IN MALAYSIA. Mat Ludin, C.M., and Md Radzi, J.
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 8, No. 2, July 2001 (14-18) ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF DIFFERENT MOUTHWASHES IN MALAYSIA Mat Ludin, C.M., and Md Radzi, J. Department of
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 8, No. 2, July 2001 (14-18) ORIGINAL ARTICLE THE ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF DIFFERENT MOUTHWASHES IN MALAYSIA Mat Ludin, C.M., and Md Radzi, J. Department of
Cognitive Impairment and Oral Health
 Geriatric Lectures Series: Cognitive Impairment and Oral Health Dr. Leo Marchini, DDS, MSD, PhD Department of Preventive and Community Dentistry University of Iowa College of Dentistry and Dental Clinics
Geriatric Lectures Series: Cognitive Impairment and Oral Health Dr. Leo Marchini, DDS, MSD, PhD Department of Preventive and Community Dentistry University of Iowa College of Dentistry and Dental Clinics
Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study.
 ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study. Dr. Yashika Jain Senior Lecturer, Institution: SGT Dental College & Hospital,
ISSN: 2278 0211 (Online) Effect of temperature change of 0.2% chlorhexidine rinse on matured human plaque: an in vivo study. Dr. Yashika Jain Senior Lecturer, Institution: SGT Dental College & Hospital,
Efficacy Evaluation of a Chlorine Dioxide Containing Toothpaste (DioxiBrite ) on Plaque and Gingivitis. A Clinical Study
 Efficacy Evaluation of a Chlorine Dioxide Containing Toothpaste (DioxiBrite ) on Plaque and Gingivitis A Clinical Study Principle Investigator Laura Mueller-Joseph RDH, Ed.D. State University of New York
Efficacy Evaluation of a Chlorine Dioxide Containing Toothpaste (DioxiBrite ) on Plaque and Gingivitis A Clinical Study Principle Investigator Laura Mueller-Joseph RDH, Ed.D. State University of New York
Product Information Clinpro Prophy Powder 4 Bottles à 100 g
 Ordering Information Item No. Product Information 671 Clinpro Prophy Powder 4 Bottles à 1 g Clinpro Prophy Powder 12613 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Cherry Fine 12657 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Mint
Ordering Information Item No. Product Information 671 Clinpro Prophy Powder 4 Bottles à 1 g Clinpro Prophy Powder 12613 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Cherry Fine 12657 Clinpro Prophy Paste 2 à 2 g Mint
Strengthening the teeth and decreasing the effects of acid and bacteria on the teeth. Sodium Fluoride
 Dento plus mouthwash has a powerful formula that ensures the full coverage for all types of dental infections. Dento plus mouthwash adds to its formula the power of natural analgesics, natural anti inflammatory,
Dento plus mouthwash has a powerful formula that ensures the full coverage for all types of dental infections. Dento plus mouthwash adds to its formula the power of natural analgesics, natural anti inflammatory,
Comparing the Effectiveness of Two Fluoride Mouthrinses on Streptococcus Mutans
 115 2 / 35 / 1390 / ** #* * * ** 89/12/18 : 89/8/5 : Comparing the Effectiveness of Two Fluoride Mouthrinses on Streptococcus Mutans Maryam Karami*, Roomina Mazaheri*#, Manoochehr Mesripour** * Assistant
115 2 / 35 / 1390 / ** #* * * ** 89/12/18 : 89/8/5 : Comparing the Effectiveness of Two Fluoride Mouthrinses on Streptococcus Mutans Maryam Karami*, Roomina Mazaheri*#, Manoochehr Mesripour** * Assistant
Chapter 14 Outline. Chapter 14: Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders. Dental Caries. Dental Caries. Prevention. Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders
 Chapter 14 Outline Chapter 14: Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Dental caries Prevention Gingivitis Prevention Tooth hypersensitivity Pathophysiology Treatment 2 Hygiene-Related
Chapter 14 Outline Chapter 14: Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Hygiene-Related Oral Disorders Dental caries Prevention Gingivitis Prevention Tooth hypersensitivity Pathophysiology Treatment 2 Hygiene-Related
In vitro Antimicrobial Comparison of Chlorhexidine, Persica Mouthwash and Miswak Extract
 JCDP 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1111 In vitro Antimicrobial Comparison of Chlorhexidine, Persica Mouthwash and Miswak Extract ORIGINAL RESEARCH In vitro Antimicrobial Comparison of Chlorhexidine, Persica
JCDP 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1111 In vitro Antimicrobial Comparison of Chlorhexidine, Persica Mouthwash and Miswak Extract ORIGINAL RESEARCH In vitro Antimicrobial Comparison of Chlorhexidine, Persica
Paraclinical Effects of Miswak Extract on Dental Plaque
 Original Article Paraclinical Effects of Miswak Extract on Dental Plaque Hamid Reza Poureslami DDS, MSc*, Abbas Makarem DDS, MSc**, Faraz Mojab PhD*** ABSTRACT Introduction: The Persian toothbrush tree
Original Article Paraclinical Effects of Miswak Extract on Dental Plaque Hamid Reza Poureslami DDS, MSc*, Abbas Makarem DDS, MSc**, Faraz Mojab PhD*** ABSTRACT Introduction: The Persian toothbrush tree
Assessment of Knowledge of Oral Hygiene Aids among Dentists
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 10, Issue 5 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 60-64 Assessment of Knowledge of Oral Hygiene Aids among Dentists
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 10, Issue 5 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 60-64 Assessment of Knowledge of Oral Hygiene Aids among Dentists
Developed by: The Inter Tribal Council of Arizona, Inc. Dental Clinical and Prevention Support Center
 Inter Tribal Council of Arizona, Inc. Dental Clinical and Prevention Support Center 2214 North Central Avenue, Suite 100 Phoenix, Arizona 85004 602-258-4822 602-258-4825 fax www.itcaonline.com Developed
Inter Tribal Council of Arizona, Inc. Dental Clinical and Prevention Support Center 2214 North Central Avenue, Suite 100 Phoenix, Arizona 85004 602-258-4822 602-258-4825 fax www.itcaonline.com Developed
Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases. As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
 Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
Melissa Rudzinski Preventive Dentistry Shaunda Clark November 2013 Bacterial Plaque and Its Relation to Dental Diseases As a hygienist it is important to stress the importance of good oral hygiene and
Effect of P.betle in Dentifrice on Streptococcus mutans of Schoolchildren
 Effect of P.betle in Dentifrice on Streptococcus mutans of Schoolchildren Sutadi H*.,Desiree S*.,Anni.TD*.,Felicia S*., Mangundjaja S** *Department of Paediatric Dentistry and **Department of Oral Biology
Effect of P.betle in Dentifrice on Streptococcus mutans of Schoolchildren Sutadi H*.,Desiree S*.,Anni.TD*.,Felicia S*., Mangundjaja S** *Department of Paediatric Dentistry and **Department of Oral Biology
Dental caries prevention. Preventive programs for children 5DM
 Dental caries prevention Preventive programs for children 5DM Definition of Terms Preventive dentistry: usage of all the means to achieve and maintain the optimal oral health prevention of dental caries,
Dental caries prevention Preventive programs for children 5DM Definition of Terms Preventive dentistry: usage of all the means to achieve and maintain the optimal oral health prevention of dental caries,
Phytochemical screening and antibacterial properties of Garcinia kola
 2013; 2(3): 34-38 Online at: www.phytopharmajournal.com Research Article ISSN 2230-480X JPHYTO 2013; 2(3): 34-38 2013, All rights reserved Phytochemical screening and antibacterial properties of Garcinia
2013; 2(3): 34-38 Online at: www.phytopharmajournal.com Research Article ISSN 2230-480X JPHYTO 2013; 2(3): 34-38 2013, All rights reserved Phytochemical screening and antibacterial properties of Garcinia
LEMONGRASS OIL MOUTHWASH AND ITS ANTIPLAQUE EFFICACY: AN IN-VITRO STUDY USING SPECTROPHOTOMETER
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 03 LEMONGRASS OIL MOUTHWASH AND ITS ANTIPLAQUE EFFICACY: AN IN-VITRO STUDY USING SPECTROPHOTOMETER Kukkamalla Meena
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 03,Issue 03 LEMONGRASS OIL MOUTHWASH AND ITS ANTIPLAQUE EFFICACY: AN IN-VITRO STUDY USING SPECTROPHOTOMETER Kukkamalla Meena
INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVE
 ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to examine a mouthwash containing essential oils and herbal extracts, effect on whole mouth and posterior dorsum tongue malodor over a 90 day period. Sixty healthy
ABSTRACT The purpose of this study was to examine a mouthwash containing essential oils and herbal extracts, effect on whole mouth and posterior dorsum tongue malodor over a 90 day period. Sixty healthy
The inhibitory effects of different mouthwash brands on the zone of inhibition of. Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli
 The inhibitory effects of different mouthwash brands on the zone of inhibition of Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli George Kendros Bio 2290 Section 001 TM Gray 2013 04 10 Abstract The use of mouthwash
The inhibitory effects of different mouthwash brands on the zone of inhibition of Micrococcus luteus and Escherichia coli George Kendros Bio 2290 Section 001 TM Gray 2013 04 10 Abstract The use of mouthwash
In vitro antimicrobial activity of Miswak extracts against some oral pathogenic isolates Received in: 18/11/2009 Accepted in: 14/1/2010
 In vitro antimicrobial activity of Miswak extracts against some oral pathogenic Received in: 18/11/29 Accepted in: 14/1/21 Abdul Ghany Omer * Sozan Muhsin Qarani ** Amera Kamal Khalil *** ABSTRACT Background
In vitro antimicrobial activity of Miswak extracts against some oral pathogenic Received in: 18/11/29 Accepted in: 14/1/21 Abdul Ghany Omer * Sozan Muhsin Qarani ** Amera Kamal Khalil *** ABSTRACT Background
Course #:
 Welcome to Lesson 7: Indicators of Problems of the Dental Health for Individuals with Disabilities webcast series. Please adjust your computer volume so that it is at a comfortable listening level for
Welcome to Lesson 7: Indicators of Problems of the Dental Health for Individuals with Disabilities webcast series. Please adjust your computer volume so that it is at a comfortable listening level for
A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran
 Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Received 26 October 2007; Accepted 11 February 2008 A Clinical Evaluation of Anatomic Features of Gingiva in Dental Students in Tabriz, Iran Adileh Shirmohammadi 1 Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 * Ardeshir Lafzi
Comparative Evaluation of Effect of Chlorhexidine And Sodium Fluoride Mouthwashes on Plaque
 Comparative Evaluation of Effect of Chlorhexidine And Sodium Fluoride Mouthwashes on Plaque Sunanda Sundas 1, Arati Rao 2 1 Head, Department of Pedodontics, Peoples Dental College & Hospital, Kathmandu,
Comparative Evaluation of Effect of Chlorhexidine And Sodium Fluoride Mouthwashes on Plaque Sunanda Sundas 1, Arati Rao 2 1 Head, Department of Pedodontics, Peoples Dental College & Hospital, Kathmandu,
Food, Nutrition & Dental Health Summary
 By Liz Pearson, RD www.lizpearson.com Food, Nutrition & Dental Health Summary Canadian Health Measures Survey (2007 to 2009) 57% of 6 11 year olds have or have had a cavity 59% of 12 19 year olds have
By Liz Pearson, RD www.lizpearson.com Food, Nutrition & Dental Health Summary Canadian Health Measures Survey (2007 to 2009) 57% of 6 11 year olds have or have had a cavity 59% of 12 19 year olds have
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement
 Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
Clinical Management of an Unusual Case of Gingival Enlargement Abstract Aim: The purpose of this article is to report a case of conditioned gingival enlargement managed by nonsurgical periodontal therapy.
30/01/2012. Aim. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. We know that. Learning Objectives. Diagnosing. Treatment planning.
 Aim Advanced Partial Dentures A contradiction or a true advance? Looking to the Partial denture option Learning Objectives Diagnosing Treatment planning Learning Objectives Expectations have greatly overtaken
Aim Advanced Partial Dentures A contradiction or a true advance? Looking to the Partial denture option Learning Objectives Diagnosing Treatment planning Learning Objectives Expectations have greatly overtaken
Best Practices in Oral Health for Older Adults -How to Keep My Bite in My Life!
 Best Practices in Oral Health for Older Adults -How to Keep My Bite in My Life! Mr. has most of his natural teeth. Mr. JB Age 78. In for rehab from stroke; will return home. Non-dominant hand/arm paralyzed.
Best Practices in Oral Health for Older Adults -How to Keep My Bite in My Life! Mr. has most of his natural teeth. Mr. JB Age 78. In for rehab from stroke; will return home. Non-dominant hand/arm paralyzed.
Anti-gingivitis Effects of Acacia arabica-containing Toothpaste
 Anti-gingivitis Effects of Acacia arabica-containing Toothpaste Pradeep S. TANGADE 1, Anmol MATHUR 1, Amit TIRTH 1, Soumik KABASI 1 Objective: To evaluate the anti-plaque and anti-gingivitis properties
Anti-gingivitis Effects of Acacia arabica-containing Toothpaste Pradeep S. TANGADE 1, Anmol MATHUR 1, Amit TIRTH 1, Soumik KABASI 1 Objective: To evaluate the anti-plaque and anti-gingivitis properties
Soeherwin Mangundjaja., Abdul Muthalib., Ariadna Djais Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry Universitas Indonesia
 THE EFFECT OF DENTIFRICE CONTAINING ENZYME ON SALIVARY MUTANS STREPTOCOCCAL LEVEL IN ORTHODONTIC PATIENTS Soeherwin Mangundjaja., Abdul Muthalib., Ariadna Djais Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry
THE EFFECT OF DENTIFRICE CONTAINING ENZYME ON SALIVARY MUTANS STREPTOCOCCAL LEVEL IN ORTHODONTIC PATIENTS Soeherwin Mangundjaja., Abdul Muthalib., Ariadna Djais Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry
EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTION MEDIA ON PERIODONTAL HEALTH AMONG HEARING IMPAIRED CHILDREN
 EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTION MEDIA ON PERIODONTAL HEALTH AMONG HEARING IMPAIRED CHILDREN Malee Arunakul, Yosvimol Kuphasuk 2 and Romcharee Boonyathanasit 3 Department of Pediatric Dentistry,
EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL HYGIENE INSTRUCTION MEDIA ON PERIODONTAL HEALTH AMONG HEARING IMPAIRED CHILDREN Malee Arunakul, Yosvimol Kuphasuk 2 and Romcharee Boonyathanasit 3 Department of Pediatric Dentistry,
Comparative effect of neemstick and toothbrush on plaque removal and gingival health A clinical trial
 J.Adv Oral Research All Rights Res ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparative effect of neemstick and toothbrush on plaque removal and gingival health A clinical trial Ajay Bhambal* Sonal Kothari SudhanshuSaxena Manish
J.Adv Oral Research All Rights Res ORIGINAL RESEARCH Comparative effect of neemstick and toothbrush on plaque removal and gingival health A clinical trial Ajay Bhambal* Sonal Kothari SudhanshuSaxena Manish
Safe Breath Rinse. To eliminate and prevent bad breath
 Safe Breath Rinse To eliminate and prevent bad breath Bad breath a very common problem Bad breath (halitosis) has been a problem since time immemorial. Home remedies recommended 2,000 years ago are very
Safe Breath Rinse To eliminate and prevent bad breath Bad breath a very common problem Bad breath (halitosis) has been a problem since time immemorial. Home remedies recommended 2,000 years ago are very
Linking Research to Clinical Practice
 Prevention of Root Caries Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical dental
Prevention of Root Caries Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS Linking Research to Clinical Practice The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical dental
JCD RESEARCH ARTICLE ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative Evaluation of the Plaque 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1186 Inhibitory Effect of a Herbal Extract Comparative Evaluation of the Plaque Inhibitory Effect of a Herbal Extract containing
RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative Evaluation of the Plaque 10.5005/jp-journals-10031-1186 Inhibitory Effect of a Herbal Extract Comparative Evaluation of the Plaque Inhibitory Effect of a Herbal Extract containing
Effects of Two Iranian Herbal Extracts of Malva sylvestris and. Salvadora persica on Two Oral Streptococci
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Effects of Two Iranian Herbal Extracts of Malva sylvestris and Salvadora persica on Two Oral Streptococci Surena Vahabi 1 * Shahrooz Habibi
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Effects of Two Iranian Herbal Extracts of Malva sylvestris and Salvadora persica on Two Oral Streptococci Surena Vahabi 1 * Shahrooz Habibi
Effects of a Chewable Sodium Bicarbonate Oral Composition of Plaque and Gingivitis
 Volume 2 Number 1 Winter Issue, 2001 Effects of a Chewable Sodium Bicarbonate Oral Composition of Plaque and Gingivitis Abstract The purpose of this pilot study was to evaluate the ef fects of an effervescent
Volume 2 Number 1 Winter Issue, 2001 Effects of a Chewable Sodium Bicarbonate Oral Composition of Plaque and Gingivitis Abstract The purpose of this pilot study was to evaluate the ef fects of an effervescent
Our Teeth. Word List: find each word from the list below in the table above (just circle each word on the table and cross it off from your list)
 Your Teeth Our Teeth B I L L E V Q I Z Q Q V E J E U Q A L P S Q A V S R Q E D Y E E G L E M A N E Y R V J R R G R L E A I Y T I V A C E B R A B Q O A C A P N C X M I L K T E E T H L M X O L M I Z T E
Your Teeth Our Teeth B I L L E V Q I Z Q Q V E J E U Q A L P S Q A V S R Q E D Y E E G L E M A N E Y R V J R R G R L E A I Y T I V A C E B R A B Q O A C A P N C X M I L K T E E T H L M X O L M I Z T E
Available online Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(6):758-764 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 comparison of plain Chlorhexidine (0.2%) and Chlorhexidine
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(6):758-764 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 comparison of plain Chlorhexidine (0.2%) and Chlorhexidine
Citation for published version (APA): Azaripour, A. (2016). Structure and function of the human periodontium: Science meets the clinician
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Structure and function of the human periodontium Azaripour, A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Azaripour, A. (2016). Structure and function
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Structure and function of the human periodontium Azaripour, A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Azaripour, A. (2016). Structure and function
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer. Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients
 Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
Dental care and treatment for patients with head and neck cancer Department of Restorative Dentistry Information for patients i Why have I been referred to the Restorative Dentistry Team? Treatment of
International Journal of Public Health Dentistry
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative study to assess the effect of chewing stick and toothbrush on oral hygiene and periodontal status among Indian population Raghavendra M. Shetty; Sunaina Shetty; Sachin B. M;
RESEARCH ARTICLE Comparative study to assess the effect of chewing stick and toothbrush on oral hygiene and periodontal status among Indian population Raghavendra M. Shetty; Sunaina Shetty; Sachin B. M;
Caring for your Dentures
 DENTURES SERIES Caring for your Dentures It s important that your dentures, like natural teeth, be kept free from plaque and tartar. This prevents permanent staining and bad breath. Use a denture brush
DENTURES SERIES Caring for your Dentures It s important that your dentures, like natural teeth, be kept free from plaque and tartar. This prevents permanent staining and bad breath. Use a denture brush
#1065 Effect of an Essential Oil Herbal Mouthwash on Oral Malodor
 #1065 Effect of an Essential Oil Herbal Mouthwash on Oral Malodor H. Malmström DDS, Rita Cacciato RDH, Michael Yunker DDS, YF. Ren DDS, PhD, MPH, Eastman Department of Dentistry, Division of General Dentistry,
#1065 Effect of an Essential Oil Herbal Mouthwash on Oral Malodor H. Malmström DDS, Rita Cacciato RDH, Michael Yunker DDS, YF. Ren DDS, PhD, MPH, Eastman Department of Dentistry, Division of General Dentistry,
Antimicrobial Activity of Dentifrice Containing Xylitol on Mutans Streptococci
 Antimicrobial Activity of Dentifrice Containing Xylitol on Mutans Streptococci Elza Auerkari Ibrahim and Soeherwin Mangundjaja Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry Universitas Indonesia Abstract
Antimicrobial Activity of Dentifrice Containing Xylitol on Mutans Streptococci Elza Auerkari Ibrahim and Soeherwin Mangundjaja Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry Universitas Indonesia Abstract
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PREVORA STAGE 1
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PREVORA STAGE 1 (Chlorhexidine Acetate) 10% w/v Antimicrobial Agent CHX Technologies Inc. Date of Preparation: 4800 Dundas Street West August 18, 2004 Suite 105 Toronto, ON M9A 1B1 Product
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PREVORA STAGE 1 (Chlorhexidine Acetate) 10% w/v Antimicrobial Agent CHX Technologies Inc. Date of Preparation: 4800 Dundas Street West August 18, 2004 Suite 105 Toronto, ON M9A 1B1 Product
Root Dentine Sensitivity
 Indian Medical Gazette JULY 2012 269 Original Study Root Dentine Sensitivity Jyoti Ajay Khade, Associate Professor, Dept. of Dentistry, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) Adilabad, A.P.
Indian Medical Gazette JULY 2012 269 Original Study Root Dentine Sensitivity Jyoti Ajay Khade, Associate Professor, Dept. of Dentistry, Rajiv Gandhi Institute of Medical Sciences (RIMS) Adilabad, A.P.
How to look after your mouth. Cancer Services Information for patients
 How to look after your mouth Cancer Services Information for patients i Is my mouth at risk? There are many things that can affect your mouth. If you answer yes to any of the following, you may be at risk
How to look after your mouth Cancer Services Information for patients i Is my mouth at risk? There are many things that can affect your mouth. If you answer yes to any of the following, you may be at risk
When Teeth Go Bad How nurse advice can help reduce recurrences of dental disease. Callum Blair BVMS MRCVS
 When Teeth Go Bad How nurse advice can help reduce recurrences of dental disease Callum Blair BVMS MRCVS Dental disease is a common condition affecting cats and dogs. An often quoted statistic is that
When Teeth Go Bad How nurse advice can help reduce recurrences of dental disease Callum Blair BVMS MRCVS Dental disease is a common condition affecting cats and dogs. An often quoted statistic is that
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE)
 Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Adult 16+ years Oral Health Promotion - individually tailored optimal daily oral care Version 3.0 Date approved: October 2016 Approved by: The Board Review due:
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Adult 16+ years Oral Health Promotion - individually tailored optimal daily oral care Version 3.0 Date approved: October 2016 Approved by: The Board Review due:
Oil pulling as an adjunct to scaling and root planing: A Clinico-Microbial study
 International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 4 Issue 6 June 2015 PP. 38-44 Oil pulling as an adjunct to scaling and root planing: A
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Science Invention ISSN (Online): 2319 6718, ISSN (Print): 2319 670X Volume 4 Issue 6 June 2015 PP. 38-44 Oil pulling as an adjunct to scaling and root planing: A
Linking Research to Clinical Practice
 Linking Research to Clinical Practice Non Fluoride Caries Preventive Agents Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical
Linking Research to Clinical Practice Non Fluoride Caries Preventive Agents Denise M. Bowen, RDH, MS The purpose of Linking Research to Clinical Practice is to present evidence based information to clinical
Complete Mouth Care System Stimulate natural repair with Dr. Ellie's Complete Mouth Care System
 ELLIE PHILLIPS DDS Complete Mouth Care System It only takes 5 minutes, twice a day, to protect your smile and improve your oral health. Stimulate natural repair with Dr. Ellie's Complete Mouth Care System»
ELLIE PHILLIPS DDS Complete Mouth Care System It only takes 5 minutes, twice a day, to protect your smile and improve your oral health. Stimulate natural repair with Dr. Ellie's Complete Mouth Care System»
Health and fitness. Diabetes and Oral Care by Ms. Kanchan Naikawadi, Preventive Healthcare Specialist Indus Health
 Health and fitness Alll about how to keep one self in good health... Live Life Healthy... Diabetes and Oral Care by Ms. Kanchan Naikawadi, Preventive Healthcare Specialist Indus Health Ms. Kanchan Naikawadi,
Health and fitness Alll about how to keep one self in good health... Live Life Healthy... Diabetes and Oral Care by Ms. Kanchan Naikawadi, Preventive Healthcare Specialist Indus Health Ms. Kanchan Naikawadi,
84% of subjects in the experimental group had no bleeding at Week 6 compared to 0% in the control group. See Figure 2.
 RESEARCH BOOKLET A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating the Anti-Gingivitis Efficacy of an Oral Hygiene Regimen consisting of an Interactive Power Toothbrush, a Two-Step Stannous Fluoride Dentifrice and
RESEARCH BOOKLET A Randomized Clinical Trial Evaluating the Anti-Gingivitis Efficacy of an Oral Hygiene Regimen consisting of an Interactive Power Toothbrush, a Two-Step Stannous Fluoride Dentifrice and
Confidence for you comfort for your patient
 Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder For supra- and subgingival cleaning Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder with TCP For added sensitivity relief Confidence for you comfort for your patient f TCP functionalized Tri-Calcium
Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder For supra- and subgingival cleaning Clinpro Glycine Prophy Powder with TCP For added sensitivity relief Confidence for you comfort for your patient f TCP functionalized Tri-Calcium
Toothbrushing Frequency as It Relates to Plaque Development and Gingival Health*
 Toothbrushing Frequency as It Relates to Plaque Development and Gingival Health* by NIKLAUS P. LANG* BOYD R. CUMMING*** HARALD LÖE** EPIDEMIOLOGICAL and experimental studies have demonstrated that gingival
Toothbrushing Frequency as It Relates to Plaque Development and Gingival Health* by NIKLAUS P. LANG* BOYD R. CUMMING*** HARALD LÖE** EPIDEMIOLOGICAL and experimental studies have demonstrated that gingival
GSK Medicine: Study Number: Title: Rationale: Phase: Study Period Study Design: Group 1 (Test Group) Group 2 (Reference group):
 The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The study listed may include approved and non-approved uses, formulations or treatment regimens. The results reported in any single study may not reflect the overall results obtained on studies of a product.
The comparison of 0.05% sodium fluoride and 0.2% chlorhexidine usage and aquadest to the plaque index on fixed orthodontic patients
 Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2007, 18(1):20-27. The comparison of 0.05% sodium fluoride and 0.2% chlorhexidine usage and aquadest to the plaque index on fixed orthodontic patients Veronica Vera D.
Padjadjaran Journal of Dentistry 2007, 18(1):20-27. The comparison of 0.05% sodium fluoride and 0.2% chlorhexidine usage and aquadest to the plaque index on fixed orthodontic patients Veronica Vera D.
PERINATAL CARE AND ORAL HEALTH
 PERINATAL CARE AND ORAL HEALTH Lakshmi Mallavarapu, DDS Terry Reilly Health Services Boise, Idaho CE objectives Recognize the necessity of Oral Care during Perinatal Period Examine and assess teeth and
PERINATAL CARE AND ORAL HEALTH Lakshmi Mallavarapu, DDS Terry Reilly Health Services Boise, Idaho CE objectives Recognize the necessity of Oral Care during Perinatal Period Examine and assess teeth and
THE USE OF VACCUM FORM RETAINERS FOR RELAPSE CORRECTION
 THE USE OF VACCUM FORM RETAINERS FOR RELAPSE CORRECTION Azrul Hafiz Abdul Aziz 1 and Haslinda Ramli 2 1,2 Islamic Science University of Malaysia, Faculty of Dentistry, Level 15, Tower B, Persiaran MPAJ,
THE USE OF VACCUM FORM RETAINERS FOR RELAPSE CORRECTION Azrul Hafiz Abdul Aziz 1 and Haslinda Ramli 2 1,2 Islamic Science University of Malaysia, Faculty of Dentistry, Level 15, Tower B, Persiaran MPAJ,
MODULE 5 IMPACTS OF DRY MOUTH. Welcome to. Module 5. Impacts of Dry Mouth
 Welcome to Module Impacts of Dry Mouth IMPACTS OF DRY MOUTH According to Oralieve research, nearly 90% of Dental Professionals believe that the incidence of the cases of dry mouth is on the rise. 1 * Living
Welcome to Module Impacts of Dry Mouth IMPACTS OF DRY MOUTH According to Oralieve research, nearly 90% of Dental Professionals believe that the incidence of the cases of dry mouth is on the rise. 1 * Living
In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial effect of miswak against common oral pathogens
 Open Access Original Article In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial effect of miswak against common oral pathogens Saima Naseem 1, Khursheed Hashmi 2, Fatima Fasih 3, Shaheen Sharafat 4, Rafiq Khanani 5
Open Access Original Article In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial effect of miswak against common oral pathogens Saima Naseem 1, Khursheed Hashmi 2, Fatima Fasih 3, Shaheen Sharafat 4, Rafiq Khanani 5
A PILOT STUDY OF THE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUBSTANTIVITY OF A NEW ANTI-HALITOSIS MOUTHRINSE
 A PILOT STUDY OF THE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUBSTANTIVITY OF A NEW ANTI-HALITOSIS MOUTHRINSE Binkley, Kenneth A., DDS., Colvard, Michael J., DDS., MS., Oester, Michael, PhD. ABSTRACT A cysteine challenge test
A PILOT STUDY OF THE EFFECTIVENESS AND SUBSTANTIVITY OF A NEW ANTI-HALITOSIS MOUTHRINSE Binkley, Kenneth A., DDS., Colvard, Michael J., DDS., MS., Oester, Michael, PhD. ABSTRACT A cysteine challenge test
Dental Care and Health An Update. Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI
 Dental Care and Health An Update Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI WHO s Definition of Health? Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of
Dental Care and Health An Update Dr. Ranjini Pillai, DDS, MPH, FAGD, FICOI WHO s Definition of Health? Health is a state of complete physical, mental, and social wellbeing and not merely the absence of
Oral Health Status of Pregnant Women
 Oral Health Status of Pregnant Women Ingrida Vasiliauskiene Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 5:57-61, 2003 SUMMARY The aim of the study was to determine the prevalence and severity
Oral Health Status of Pregnant Women Ingrida Vasiliauskiene Stomatologija, Baltic Dental and Maxillofacial Journal, 5:57-61, 2003 SUMMARY The aim of the study was to determine the prevalence and severity
The Effect of Fragaria x ananassa Infusum on Salivary Mutans Streptococci
 The Effect of Fragaria x ananassa Infusum on Salivary Mutans Streptococci Harun.A Gunawan.,AR. Putri.,H.Widodo., S Mangundjaja Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry Universitas Indonesia Jakarta
The Effect of Fragaria x ananassa Infusum on Salivary Mutans Streptococci Harun.A Gunawan.,AR. Putri.,H.Widodo., S Mangundjaja Department of Oral Biology Faculty of Dentistry Universitas Indonesia Jakarta
Effect of Manuka honey, chlorhexidine gluconate and xylitol on the clinical levels
 Contemp Clin Dent. 2010 Oct-Dec; 1(4): 214 217. doi: 10.4103/0976-237X.76386 PMCID: PMC3220139 Effect of Manuka honey, chlorhexidine gluconate and xylitol on the clinical levels of dental plaque Prathibha
Contemp Clin Dent. 2010 Oct-Dec; 1(4): 214 217. doi: 10.4103/0976-237X.76386 PMCID: PMC3220139 Effect of Manuka honey, chlorhexidine gluconate and xylitol on the clinical levels of dental plaque Prathibha
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
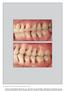 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 395 Clinical Case Report on Treatment of Generalized Aggressive Periodontitis: 5-Year Follow-up Kai-Fang Hu, DDS, MD 1 /Ya-Ping Ho, DDS,
Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports
 0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
0 Class II Furcations Treated by Guided Tissue Regeneration in Humans: Case Reports R.G. Caffesse, B.A. Smith/ B. Duff, E.C. Morrison, D. Merrill/ and W. Becker In the cases reported here, the response
How to maintain good oral health
 How to maintain good oral health Health Education and Promotion Program 2015, MMM Healthcare, LLC - PMC Medicare Choice, LLC Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-737-01-050514-E M&P-PRD-TEM-030-032511-S
How to maintain good oral health Health Education and Promotion Program 2015, MMM Healthcare, LLC - PMC Medicare Choice, LLC Reproduction of this material is prohibited. MP-HEP-PPT-737-01-050514-E M&P-PRD-TEM-030-032511-S
Journal of Medical Science & Technology
 Original Article Journal of Medical Science & Technology Open Access Effect of Black tea as mouth rinse among selected school children with dental plaque Radhika 1, B Vanaja Kumari 1 1 Community health
Original Article Journal of Medical Science & Technology Open Access Effect of Black tea as mouth rinse among selected school children with dental plaque Radhika 1, B Vanaja Kumari 1 1 Community health
Knowledge, Attitude and Practice about Oral Health among General Population of Peshawar
 SHORT COMMUNICATION Knowledge, Attitude and Practice about Oral Health among General Population of Peshawar Farzeen Khan, Aisha Ayub 3 and Zeeshan Kibria 1 ABSTRACT To determine the level of knowledge
SHORT COMMUNICATION Knowledge, Attitude and Practice about Oral Health among General Population of Peshawar Farzeen Khan, Aisha Ayub 3 and Zeeshan Kibria 1 ABSTRACT To determine the level of knowledge
Evaluation of the Amount and Type of Microorganisms in Tooth Brushes and Miswak after Immediate Brushing
 ARC Journal of Dental Science Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018, PP 15-21 ISSN No. (Online) 2456-0030 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2456-0030.0301005 www.arcjournals.org Evaluation of the Amount and Type of Microorganisms
ARC Journal of Dental Science Volume 3, Issue 1, 2018, PP 15-21 ISSN No. (Online) 2456-0030 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.20431/2456-0030.0301005 www.arcjournals.org Evaluation of the Amount and Type of Microorganisms
Periodontal Diagnosis Form
 Periodontal Diagnosis Form Notes on the use of the form 1. The form that follows is a comprehensive analysis of your patient, taking into account many factors that might contribute to oral conditions.
Periodontal Diagnosis Form Notes on the use of the form 1. The form that follows is a comprehensive analysis of your patient, taking into account many factors that might contribute to oral conditions.
PATIENT INFORMATION DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH
 PATIENT INFORMATION DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH www.dentalcareireland.ie DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH People with poor diabetes control can be more prone to oral health problems such as gum disease, dry mouth,
PATIENT INFORMATION DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH www.dentalcareireland.ie DIABETES AND ORAL HEALTH People with poor diabetes control can be more prone to oral health problems such as gum disease, dry mouth,
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, :54 AM
 Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
Plaque and Occlusion in Periodontal Disease Wednesday, February 25, 2015 9:54 AM 1. The definition of Trauma From Occlusion: Primary TFO, Secondary TFO, and Combined TFO 2. Clinical and Radiographic signs
An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis
 CLINICAL REPORT 295 Ajay Mahajan, Jaya Dixit, Umesh Verma An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis KEY WORDS antimicrobial therapy, clinical findings,
CLINICAL REPORT 295 Ajay Mahajan, Jaya Dixit, Umesh Verma An intriguing case of gingival enlargement associated with generalised aggressive periodontitis KEY WORDS antimicrobial therapy, clinical findings,
Higher plants produced hundreds to thousands of diverse chemical compounds with different biological activities (Hamburger and Hostettmann, 1991).
 4. ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYSALIS MINIMA L. 4.1. Introduction Use of herbal medicines in Asia represents a long history of human interactions with the environment. Plants used for traditional medicine
4. ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF PHYSALIS MINIMA L. 4.1. Introduction Use of herbal medicines in Asia represents a long history of human interactions with the environment. Plants used for traditional medicine
Studies have long shown that adding fluoride
 WELCOME Is Fluoride in Drinking Water Bad for You? Studies have long shown that adding fluoride to drinking water has helped prevent tooth decay in children and adults. Now, a recent study out of Australia
WELCOME Is Fluoride in Drinking Water Bad for You? Studies have long shown that adding fluoride to drinking water has helped prevent tooth decay in children and adults. Now, a recent study out of Australia
Structure of an Incisor
 MAMMALIAN TEETH Mammals have different types and shapes of teeth and they are thus termed Heterodonts. Those which have teeth of the same size and shapes are termed as Homodonts. In mammals teeth consist
MAMMALIAN TEETH Mammals have different types and shapes of teeth and they are thus termed Heterodonts. Those which have teeth of the same size and shapes are termed as Homodonts. In mammals teeth consist
Dear Editor, There are many approaches to reducing the presence of bacteria. Keeping the mouth wet
 Dear Editor, There have recently been several articles and inquiries related to Dry Mouth Syndrome published in the Victoria Advocate and the tooth decay related to decreased salivary flow. Tooth decay
Dear Editor, There have recently been several articles and inquiries related to Dry Mouth Syndrome published in the Victoria Advocate and the tooth decay related to decreased salivary flow. Tooth decay
CAries Management By Risk Assessment"(CAMBRA) - a must in preventive dentistry
 CAries Management By Risk Assessment"(CAMBRA) - a must in preventive dentistry Nanda Kishor KM* *MDS, Reader, Department of Conservative and Endodontics Pacific Dental College, Udaipur, Rajasthan, India
CAries Management By Risk Assessment"(CAMBRA) - a must in preventive dentistry Nanda Kishor KM* *MDS, Reader, Department of Conservative and Endodontics Pacific Dental College, Udaipur, Rajasthan, India
Dr. Prabhati Gupta, 1 Dr. Suhail Majid Jan, 2 Dr. Roobal Behal. 3 1,2,3 (Department of Periodontics, Govt. Dental College, Srinagar)
 Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 5~ Issue 6 (218) pp: 3-34 ISSN(Online) : 2394-76X ISSN (Print):2394-751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Comparative Evaluation
Quest Journals Journal of Medical and Dental Science Research Volume 5~ Issue 6 (218) pp: 3-34 ISSN(Online) : 2394-76X ISSN (Print):2394-751 www.questjournals.org Research Paper Comparative Evaluation
Esthetic Crown Lengthening
 Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
Esthetic Crown Lengthening Esthetic Crown Lengthening ACCELERATED OSTEOGENIC ORTHODOTNICS (WILKODONTICS) It is a technique developed by Wilko brothers. has roots in orthopedics, back to the early 1900s
Small Animal Dentistry. Presented by: Rebecca Dodge, CVT
 Small Animal Dentistry Presented by: Rebecca Dodge, CVT Topics to be discussed Anatomy and oral examination Common dental problems for canines and felines Client knowledge and prevention tips Anatomy Dog
Small Animal Dentistry Presented by: Rebecca Dodge, CVT Topics to be discussed Anatomy and oral examination Common dental problems for canines and felines Client knowledge and prevention tips Anatomy Dog
IJCPD ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION /jp-journals
 Deepika Jauhari et al Original research 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-195 Comparative Evaluation of the Effects of Mouthrinse, Mouthrinse and Oil Pulling on the Caries Activity and Streptococcus mutans Count
Deepika Jauhari et al Original research 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-195 Comparative Evaluation of the Effects of Mouthrinse, Mouthrinse and Oil Pulling on the Caries Activity and Streptococcus mutans Count
The effects of the MYO appliance in children with malocclusions of the primary dentition
 The effects of the MYO appliance in children with malocclusions of the primary dentition Kevin Bourke The myofunctional device variously called: "Munchee," "Chewer" MYO or O.P. device has been extensively
The effects of the MYO appliance in children with malocclusions of the primary dentition Kevin Bourke The myofunctional device variously called: "Munchee," "Chewer" MYO or O.P. device has been extensively
Seniors Oral Care
 For information about oral health care, please contact the Ontario Dental Association at 416-922-3900 or visit www.youroralhealth.ca The Ontario Dental Association gratefully acknowledges UBC ELDERS Education,
For information about oral health care, please contact the Ontario Dental Association at 416-922-3900 or visit www.youroralhealth.ca The Ontario Dental Association gratefully acknowledges UBC ELDERS Education,
CARIES RISK ASSESSMENT FORM FOR AGE 0 TO 5 YEARS Instructions on reverse Patient Name: I.D. # Age Date Initial/baseline exam date Recall/POE date
 CARIES RISK ASSESSMENT FORM FOR AGE 0 TO 5 YEARS Instructions on reverse Patient Name: I.D. # Age Date Initial/baseline exam date Recall/POE date Respond to each question in sections 1, 2, and 3 with a
CARIES RISK ASSESSMENT FORM FOR AGE 0 TO 5 YEARS Instructions on reverse Patient Name: I.D. # Age Date Initial/baseline exam date Recall/POE date Respond to each question in sections 1, 2, and 3 with a
Periodontal (Gum) Disease
 Periodontal (Gum) Disease If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you re not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases
Periodontal (Gum) Disease If you have been told you have periodontal (gum) disease, you re not alone. An estimated 80 percent of American adults currently have some form of the disease. Periodontal diseases
Other common oral problems DR ANDREW DAVIES FRCP CONSULTANT IN PALLIATIVE MEDICINE ROYAL SURREY COUNTY HOSPITAL, GUILDFORD, UK
 Other common oral problems DR ANDREW DAVIES FRCP CONSULTANT IN PALLIATIVE MEDICINE ROYAL SURREY COUNTY HOSPITAL, GUILDFORD, UK Outline Epidemiology OASis study Poor oral hygiene Halitosis Taste disturbance
Other common oral problems DR ANDREW DAVIES FRCP CONSULTANT IN PALLIATIVE MEDICINE ROYAL SURREY COUNTY HOSPITAL, GUILDFORD, UK Outline Epidemiology OASis study Poor oral hygiene Halitosis Taste disturbance
