Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review
|
|
|
- Poppy York
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review article ISSN (print) / ISSN (online) Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review Youngjune Jang, Euiseong Kim* Microscope Center, Department of Conservative Dentistry and Oral Science Research Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea Epinephrine is one of the most widely-used vasoconstrictors in dental treatment including endodontic microsurgery. However, the systemic safety of epinephrine has been in debate for many years because of its potential risk to cause cardiovascular complications. The purpose of this review was to assess the cardiovascular effect of epinephrine use in endodontic microsurgery. Endodontic microsurgery directly applies epinephrine into the bone cavity, and the amount is reported to be much larger than other dental surgeries. Moreover, when considering that systemic potency of intraosseous application is reported to be comparable to intravenous application, the systemic influence of epinephrine could be increased in endodontic microsurgery. Besides, pre-existing cardiovascular complications or drug interactions can enhance its systemic influence, resulting in increased susceptibility to cardiovascular complications. Although clinical studies have not reported significant complications for patients without severe systemic complications, many epinephrine-induced emergency cases are warning the cardiovascular risk related with pre-existing systemic disease or drug interactions. Epinephrine is a dose-sensitive drug, and its hypersensitivity reaction can be fatal to patients when it is related to cardiovascular complications. Therefore, clinicians should recognize the risk, and the usage of pre-operative patient evaluation, dose control and patient monitoring are required to ensure patient s safety during endodontic microsurgery. (Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4): ) Key words: Cardiovascular diseases; Drug interactions; Endodontic microsurgery; Epinephrine; Hemostasis; Vasoconstrictor agents Received August 3, 2013; Revised September 8, 2013; Accepted September 8, Jang Y; Kim E, Microscope Center, Department of Conservative Dentistry and Oral Science Research Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea *Correspondence to Euiseong Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD. Professor, Microscope Center, Department of Conservative Dentistry and Oral Science Research Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, 50 Yonsei-ro, Seodaemungu, Seoul, Korea TEL, ; FAX, ; , andyendo@yuhs. ac Introduction Epinephrine is one of the most widely-used vasoconstrictors in dentistry. However, because of the characteristics as a hormone that influences main organs simultaneously, it has been argued as a potential risk factor that can cause cardiovascular complications. For this reason, many studies have been published to evaluate the safety of epinephrine in dental treatment However most of them were conducted with tooth extraction 2-13 and periodontal surgery, 14 and there have been only few studies for endodontic microsurgery to this date. 15,16 Endodontic microsurgery has a unique feature in regard of epinephrine application, especially in intra-operative hemostasis. Almost perfect bleeding control is needed for proper inspection of the resected root surface and retro-filling of the root-end cavity, which are the most important components of endodontic microsurgery For this This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( by-nc/3.0) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Copyrights The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry. 187
2 Jang Y and Kim E reason, direct application of epinephrine into the bone cavity has been commonly selected by many clinicians, which has been confirmed as an effective way to ensure hemostasis during surgery. 17 However, due to additional doses of epinephrine and the administration route (intraosseous route) that affects the systemic circulation more directly than other routes, the systemic influence of epinephrine could be increased in endodontic microsurgery, resulting in increased susceptibility to the cardiovascular complications. 15,16,20,21 As the success rate and long-term prognosis of endodontic microsurgery is validated, it is becoming a standard treatment option in the endodontic field It is the time to focus on not only the long-term prognosis of endodontic microsurgery, but also the systemic safety during treatments. Therefore, the purposes of this review were to assess the cardiovascular effect of epinephrine use in endodontic microsurgery, and to make clinical suggestions that can reduce the risk of epinephrine. Review Pharmacology of epinephrine Epinephrine is one of the principal hormones that affect adrenergic receptors of autonomic nervous system. 25 It modulates various functions of the body simultaneously by affecting different subtypes of the adrenergic receptor. Epinephrine induces vasoconstriction of the mucosa, skin, and internal organs by affecting α1 adrenergic receptor, and increases blood glucose level by affecting α2 adrenergic receptor. It also influences β1 adrenergic receptor to increase cardiac output by changing heart rate and contraction force, and it induces vasodilatation of the skeletal muscles, liver and relaxation of bronchial smooth muscle by affecting β2 receptor. In the dental field, epinephrine serves as a local vasoconstrictor in local anesthetics or gingival retraction cords. 26,27 And it is also used in endodontic microsurgery as a hemostatic agent to control the bleeding in the bone cavity. 17 In this way, most dentists only use the effect of epinephrine to α1 receptor. On the other hand, epinephrine is being used for various purposes in the medical field. It is injected in case of acute hypotensive crisis to elevate the blood pressure immediately, and it is also administered to induce defibrillation in case of cardiac arrest. In acute asthma attack, it is inhaled to induce bronchodilation. Epinephrine is not just a simple hemostatic agent but a hormone that modulates main organs of the body. In this regard, its action on β1 adrenergic receptor can cause unsuspected cardiovascular complications during dental surgery if we are not aware of its nature. Predisposing risk factors related with epinephrine 1. Pre-existing Cardiovascular disease Patients with cardiovascular diseases are increasing in dental practices in recent years. Such patients are vulnerable to the stress induced by dental treatment, and more susceptible to drug side effects compared to healthy patients. Therefore, the possibility of medical emergency during dental treatment is more likely in these patients. Cardiovascular complications of epinephrine on patients with hypertension have been a concern in dental practice. Bader et al. conducted systematic review to identify cardiovascular complications in hypertensive patients caused by epinephrine contained in anesthetic solutions studies were initially searched, and finally six studies of them were analyzed. This revealed that the effect of epinephrine was not significant during dental surgery in hypertensive patients compared with normotensive patients. However, as the author commented, the number of subjects was too small and the information about predisposing medical diagnoses and medication status was restricted. Moreover, analyzed studies were associated with tooth extraction and minor dental surgery, not endodontic microsurgery. Meanwhile, it is not difficult to find epinephrine emergency cases in patient with pre-existing cardiovascular disease. Lee et al. reported occurrence of cardiac arrest induced by submucosal injection of epinephrine in a patient with variant angina. 28 When 1.5% lidocaine with 1 : 100,000 epinephrine was injected (about 7.5 ml) in the nasal mucosa for septoplasty, sudden ventricular tachycardia was observed, followed by cardiac arrest. Kim et al. also reported two cases that showed acute elevation of blood pressure with severe chest tightness during endoscopic submucosal dissection after submucosal injection of 1 : 100,000 epinephrine. 29 One of the cases was diagnosed as myocardiac infarction. 2. Drug interactions 1) Non-selective β blocker Epinephrine induces vasoconstriction on mucosa, skin, and internal organs by affecting α1 adrenergic receptor. It also induces vasodilatation of skeletal muscle by affecting β2 adrenergic receptor at the same time so that rapid increase of blood pressure can be prevented. However such mechanism can be disturbed by nonselective β blocker because it blocks the action of β1 and β2 adrenergic receptor Therefore epinephrine behaves as a pure agonist of α adrenergic receptor inducing acute hypertensive crisis, followed by reflex bradycardia, and cardiac arrest in the worst case when it is administered 188
3 Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery with non-selective β blocker. 35 Foster and Aston reported case series of drug interaction between epinephrine and non-selective β blocker. 35 When % lidocaine or xylocaine with 1 : 100,000-1 : 200,000 epinephrine was subcutaneously injected to patients in medication with propranolol for eyelid-plasty and facial plasty, there was acute elevation of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and one of the patient experienced cardiac arrest. 2) Monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor and tricyclic antidepressant MAO inhibitor and tricyclic antidepressant acts on axon terminal and synaptic space where epinephrine is secreted. MAO inhibitor blocks MAO from breaking up transmitter molecules that epinephrine concentration is increased at axon terminal. Tricyclic antidepressant inhibits the reuptake of neurotransmitters from synaptic space to axon terminal, and also increases epinephrine concentration at synaptic space. Therefore, both MAO inhibitor and tricyclic antidepressants induce the effect of overdose administration of epinephrine ,36,37 Boakes et al. conducted clinical study to evaluate drug interaction between epinephrine and tricyclic antidepressant in patients taking imipramine 25 mg t.i.d, and observed significant elevation of blood pressure in experimental group compared to control group. 37 In this way, he reported clinical synergistic interaction between the two drugs. Intrinsic risk factors of endodontic microsurgery related with epinephrine 1. Dose of epinephrine A small amount of epinephrine is routinely injected as a vasoconstrictor with local anesthetic solution for conventional dental surgery and the quantity is about mg (Table 1). However, additional amount of epinephrine is applicated in endodontic microsurgery for hemostasis of access bone cavity. 17 Epinephrine contained in one Racellet #3 pellet is equivalent to 15.3 amples of 2% lidocaine with 1 : 100,000 epinephrine, and total epinephrine dose used in endodontic microsurgery for hemostasis is reported to mg (Table 2). 15,16 Therefore, approximately times larger amount of epinephrine is used in endodontic microsurgery compared with other dental surgery or plastic surgery. In case of systemic emergencies like anaphylaxis or cardiac arrest, generally mg of epinephrine is injected intravenously to induce immediate cardiac excitation or assist cardiac defibrillation. Therefore, the amount of epinephrine we are using in endodontic microsurgery might be too large and its safety should be confirmed before application. Table 1. Dose of epinephrine administered on anesthetic injection Product 2% lidocaine with 1 : 100,000 2% lidocaine with 1 : 50,000 epinephrine epinephrine 17,38-40 Epinephrine concentration 1 : 100,000 1 : 50,000 Epinephrine dose mg/ample mg/ample Number of ample used in microsurgery 2-3 amples 2-3 amples 17 Total epinephrine dose mg mg Table 2. Dose of epinephrine administered on hemostasis Product Racellet #3 Epinephrine concentration (in effective concentration) Epinephrine dose/pellet (in effective concentration) Number of pellet used in microsurgery Total epinephrine dose (in effective concentration) CollaCote soaked in epinephrine solution (Racepinephrine) Cotton soaked in epinephrine solution (Bosmin) N/A : 1,000 (Racepinephrine) 1 : 1,000 (Bosmin) mg/pellet mg mg/cotton 1-7 pellets pellets cottons mg mg mg 189
4 Jang Y and Kim E 2. Administration route of epinephrine Most of epinephrine is applicated through intraosseous route in endodontic microsurgery. Therefore the systemic potency of intraosseous route should be compared with other pathways like subcutaneous, submucous, or intravenous routes to estimate the amount of risk. Cancellous bone is known to be highly vascularized with much of capillary distribution. Wood et al. observed heart rate after local anesthetic injection, and compared intraosseous injection with infiltration injection in terms of heart rate change. 20 Significant increase in heart rate was indentified in intraosseous injection compared with infiltration injection during injection and after 2 minutes. Hoskins et al. used swine model to compare intraosseous injection with IV injection in terms of inflow capacity to systemic circulation as he measured aortic concentration of epinephrine 480 seconds after injection. 21 Intraosseous injection through sternum resulted 86% of epinephrine concentration in relative dose compared with IV injection, and intraosseous injection via tibia showed 65% of epinephrine concentration compared with IV injection. According to this result, he suggested intraosseous injection of epinephrine as a second choice when IV injection is difficult in cardiovascular emergencies. On the basis of these studies, we can expect that cardiovascular effect of intraosseous route is comparable to intravenous route, and stronger than subcutaneous or submucosal route. Clinical studies and case reports Two clinical studies were found, which examined cardiovascular effects of epinephrine during endodontic surgery (Table 3). 15,16 Vickers et al. evaluated 17 ASA I or II patients who underwent endodontic surgery with the use of topical epinephrine for hemostasis. 16 Racemic epinephrine pellets (Racellet #3) were applied into bone cavity to achieve hemostasis during surgery, and blood pressure and pulse rate was measured pre- and postoperatively and during the surgery. Results indicated that there was no significant change in blood pressure and pulse rate. Vy et al. evaluated 42 patients who received topical epinephrine placement during endodontic surgery. 15 Racemic epinephrine was delivered with collagen sponge into bony crypt for hemostasis, and blood pressure and pulse rate was measured pre- and postoperatively and during the surgery. Other than slight increase of pulse rate on anesthetic injection, results showed no evident changes in blood pressure or pulse rate during surgical procedure. Vy et al. pointed out that epinephrine is not applied by injection mode, but applied topically. As topically applied epinephrine causes immediate local vasoconstriction of capillaries in bone cavity surface, there is little chance of large amount of epinephrine to be absorbed into the systemic circulation. This can be one of the reasons why there are rare emergency situations in the routine endodontic microsurgery. Table 3. Clinical studies Author Vickers et al. (2002) 16 Vy et al. (2004) 15 Subjects Medical status ASA I or II Normal Treatment Epinephrine type Epinephrine dose (effective concentration) BP/HR recording BP change PR change Endodontic surgery with root-end resection & filling Racemic epinephrine (Racellet #3) Endodontic surgery with root-end filling Racemic epinephrine (Racepinephrine) Collagen sponge (Colla-cote) mg mg Before treatment (baseline) At epinephrine application, and 1, 5, 10 min after placement Before dismissal Between groups Before treatment (baseline) After anesthetic injection After epinephrine application Before dismissal during surgical procedure during surgical procedure 190
5 Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery These clinical studies indicate that epinephrine can be considered as a stable hemostatic agent if it is applied in controlled volume, and for normal patients without severe systemic complications. Although existing clinical studies are not warning about potential systemic complication of epinephrine use in endodontic microsurgery, they still cannot guarantee that epinephrine can be used safely in all endodontic microsurgery cases. Only 59 patients without significant systemic disease were evaluated, and there is no data for patients with predisposing systemic diseases such as cardiovascular disease. Many emergency cases during surgery induced by epinephrine administration have been reported in various fields of medical society, and most of them are related with predisposing cardiovascular complications or drug interactions (Table 4). 28,29,35,41,42 Therefore epinephrine application should be carefully considered in such cases. Epinephrine is a dose-sensitive drug and has narrow safety margin. 25 It should be noticed that there are always hyper-responders in each drug, and such hypersensitivity reaction can lead to fatal result when it is related to cardiovascular complication like these cases. Clinical suggestion 1. Pre-operative patient evaluation Medical history should be thoroughly investigated to find out pre-existing cardiovascular disease or any possible drug interactions ,36,37 Such patients are classified as high-risk group, and substitute hemostatic agent should be considered instead of epinephrine. 2. Dose control Dose control of epinephrine is the first thing to do for risk management. It is recommended to use quantifiable products, and there are commercial products like Racellet pellets (Pascal International, Bellevue, WA, USA). One Racellet #3 pellet contains 0.55 mg of racemic epinephrine (0.275 mg in effective concentration), therefore clinician can easily estimate the whole epinephrine amount administered. To use cotton soaked in epinephrine solution is not an effective way in measuring epinephrine dose, because the solution volume absorbed to the cotton is not Table 4. Case reports of cardiovascular emergencies related with local epinephrine injection on oral & maxillofacial region Author Foster and Aston (1983) 35 Sex/Age Epinephrine dose (mg) F/ F/ Pre-op BP (mm Hg) and PR (bpm) 110/ Post-op BP (mm Hg) and PR (bpm) 190/ / Additional side effect F/ unknown 200/110 Cardiac arrest F/ F/ M/ Ferry et al. (1986) 41 M/ unknown Umino et al. (1994) 42 M/ Lee et al. (2010) 28 M/ Kim et al. (2011) 29 F/73 unknown F/ / / / / / / / / / / / / Myocardiac infarction Atrial fibrillation Cardiac arrest Myocardiac infarction Myocardiac infarction 191
6 Jang Y and Kim E uniform, ranging mg/pellet. Excess application should be avoided. As Kim and Rethnam recommended, to use only one epinephrine cotton followed by sterile dry cottons might be an alternative way in case bleeding is not severe Patient monitoring Electrocardiogram should be measured during endodontic microsurgery as well as blood pressure and pulse rate, because there is possibility of cardiac arrhythmia and it is impossible to detect it without electrocardiogram. All parameters must be checked in real-time to deal with emergency immediately. Conclusions The effect of epinephrine administration during endodontic microsurgery has not been fully investigated. Clinical studies to date do not provide sufficient information about potential systemic complications of epinephrine use in endodontic microsurgery, meanwhile case reports and case series are warning about the risk. Clinicians should be aware of the nature of epinephrine, and should pay attention to its potential risk when treating patient with endodontic microsurgery, especially for medically compromised patients. Further research is strongly recommended to evaluate the cardiovascular effect of epinephrine application during endodontic microsurgery, and to establish standard guidelines that can guarantee safety of patients with various systemic conditions during endodontic microsurgery. Conflict of Interest: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported. References 1. Bader JD, Bonito AJ, Shugars DA. A systematic review of cardiovascular effects of epinephrine on hypertensive dental patients. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2002;93: Silvestre FJ, Salvador-Martínez I, Bautista D, Silvestre- Rangil J. Clinical study of hemodynamic changes during extraction in controlled hypertensive patients. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2011;16:e Ogunlewe MO, James O, Ajuluchukwu JN, Ladeinde AL, Adeyemo WL, Gbotolorun OM. Evaluation of haemodynamic changes in hypertensive patients during tooth extraction under local anaesthesia. West Indian Med J 2011;60: Conrado VC, de Andrade J, de Angelis GA, de Andrade AC, Timerman L, Andrade MM, Moreira DR, Sousa AG, Sousa JE, Piegas LS. Cardiovascular effects of local anesthesia with vasoconstrictor during dental extraction in coronary patients. Arq Bras Cardiol 2007;88: Meral G, Tasar F, Sayin F, Saysel M, Kir S, Karabulut E. Effects of lidocaine with and without epinephrine on plasma epinephrine and lidocaine concentrations and hemodynamic values during third molar surgery. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 2005; 100:e Miura K, Matsumura K, Nakamura Y, Kurokawa H, Kajiyama M, Takata Y. Suppression of cardiac sympathetic nervous system during dental surgery in hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res 2000;23: Blinder D, Manor Y, Shemesh J, Taicher S. Electrocardiographic changes in cardiac patients having dental extractions under a local anesthetic containing a vasopressor. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1998;56: Meechan JG. Plasma potassium changes in hypertensive patients undergoing oral surgery with local anesthetics containing epinephrine. Anesth Prog 1997;44: Blinder D, Shemesh J, Taicher S. Electrocardiographic changes in cardiac patients undergoing dental extractions under local anesthesia. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1996;54: Abraham-Inpijn L, Borgmeijer-Hoelen A, Gortzak RA. Changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and electrocardiogram during dental treatment with use of local anesthesia. J Am Dent Assoc 1988;116: Meyer FU. Hemodynamic changes of local dental anesthesia in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther Toxicol 1986;24: Vernale CA. Cardiovascular responses to local dental anesthesia with epinephrine in normotensive and hypertensive subjects. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1960;13: Cheraskin E. Use of epinephrine with local anesthesia in hypertensive patients. III. Effect of epinephrine on blood pressure and pulse rate. J Am Dent Assoc 1958; 57: Davenport RE, Porcelli RJ, Iacono VJ, Bonura CF, Mallis GI, Baer PN. Effects of anesthetics containing epinephrine on catecholamine levels during periodontal surgery. J Periodontol 1990;61: Vy CH, Baumgartner JC, Marshall JG. Cardiovascular effects and efficacy of a hemostatic agent in periradicular surgery. J Endod 2004;30: Vickers FJ, Baumgartner JC, Marshall G. Hemostatic efficacy and cardiovascular effects of agents used during endodontic surgery. J Endod 2002;28: Kim S, Rethnam S. Hemostasis in endodontic microsurgery. Dent Clin North Am 1997;41: Song M, Shin SJ, Kim E. Outcomes of endodontic micro-resurgery: a prospective clinical study. J Endod 192
7 Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery 2011;37: Cho YW, Kim E. Is stopping of anticoagulant therapy really required in a minor dental surgery? How about in an endodontic microsurgery? Restor Dent Endod 2013;38: Wood M, Reader A, Nusstein J, Beck M, Padgett D, Weaver J. Comparison of intraosseous and infiltration injections for venous lidocaine blood concentrations and heart rate changes after injection of 2% lidocaine with 1 : 100,000 epinephrine. J Endod 2005;31: Hoskins SL, do Nascimento P Jr, Lima RM, Espana-Tenorio JM, Kramer GC. Pharmacokinetics of intraosseous and central venous drug delivery during cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Resuscitation 2012;83: Kim E, Song JS, Jung IY, Lee SJ, Kim S. Prospective clinical study evaluating endodontic microsurgery outcomes for cases with lesions of endodontic origin compared with cases with lesions of combined periodontal-endodontic origin. J Endod 2008;34: Setzer FC, Shah SB, Kohli MR, Karabucak B, Kim S. Outcome of endodontic surgery: a meta-analysis of the literature-part 1: Comparison of traditional rootend surgery and endodontic microsurgery. J Endod 2010;36: Song M, Chung W, Lee SJ, Kim E. Long-term outcome of the cases classified as successes based on shortterm follow-up in endodontic microsurgery. J Endod 2012;38: Katzung B, Masters S, Trevor A. Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. 12th ed. Columbus: McGraw-Hill; 2011: p Chu WS, Park SH, Ahn DK, Kim SK. Effect of local anesthesia on pulpal blood flow in mechanically stimulated teeth. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31: Lee JS, Kim SK. The influence of epinephrine concentration in local anesthetics on pulpal and gingival blood flows. J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28: Lee JY, Hong SJ, Chon JY, Kwon SY. Cardiac arrest induced by submucosal injection of epinephrine in a patient with variant angina. Rhinology 2010;48: Kim HH, Park MI, Park SJ, Moon W. Myocardial infarction thought to be provoked by local epinephrine injection during endoscopic submucosal dissection. J Clin Med Res 2011;3: Hersh EV, Giannakopoulos H. Beta-adrenergic blocking agents and dental vasoconstrictors. Dent Clin North Am 2010;54: Sugimura M, Hirota Y, Shibutani T, Niwa H, Hori T, Kim Y, Matsuura H. An echocardiographic study of interactions between pindolol and epinephrine contained in a local anesthetic solution. Anesth Prog 1995;42: Yagiela JA. Adverse drug interactions in dental practice: interactions associated with vasoconstrictors. Part V of a series. J Am Dent Assoc 1999;130: Pallasch TJ. Vasoconstrictors and the heart. J Calif Dent Assoc 1998;26: , Ferguson-Myrthil N. Vasopressor use in adult patients. Cardiol Rev 2012;20: Foster CA, Aston SJ. Propranolol-epinephrine interaction: a potential disaster. Plast Reconstr Surg 1983;72: Gómez-Moreno G, Guardia J, Cutando A, Calvo-Guirado JL. Pharmacological interactions of vasoconstrictors. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2009;14:e Boakes AJ, Laurence DR, Teoh PC, Barar FS, Benedikter LT, Prichard BN. Interactions between sympathomimetic amines and antidepressant agents in man. Br Med J 1973;1: Gutmann JL, Frazier LW Jr, Baron B. Plasma catecholamine and haemodynamic responses to surgical endodontic anaesthetic protocols. Int Endod J 1996; 29: Buckley JA, Ciancio SG, McMullen JA. Efficacy of epinephrine concentration in local anesthesia during periodontal surgery. J Periodontol 1984;55: Witherspoon DE, Gutmann JL. Haemostasis in periradicular surgery. Int Endod J 1996;29: Ferry DR, Henry RL, Kern MJ. Epinephrine-induced myocardial infarction in a patient with angiographically normal coronary arteries. Am Heart J 1986;111: Umino M, Ohwatari T, Shimoyama K, Nagao M. Unexpected atrial fibrillation during tooth extraction in a sedated elderly patient. Anesth Prog 1994;41:
Clinical assessment of the safe use local anaesthesia with vasoconstrictor agents in cardiovascular compromised patients: A systematic review
 e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.889984 Received: 2013.11.03 Accepted: 2013.12.13 Published: 2014.03.10 Clinical assessment of the safe use local anaesthesia with vasoconstrictor agents in cardiovascular
e-issn 1643-3750 DOI: 10.12659/MSM.889984 Received: 2013.11.03 Accepted: 2013.12.13 Published: 2014.03.10 Clinical assessment of the safe use local anaesthesia with vasoconstrictor agents in cardiovascular
Suppression of Cardiac Sympathetic Nervous System during Dental Surgery in Hypertensive Patients
 207 Original Article Suppression of Cardiac Sympathetic Nervous System during Dental Surgery in Hypertensive Patients Keiko MIURA, Kiyoshi MATSUMURA*, Yoshito NAKAMURA*, Minoru KAJIYAMA, and Yutaka TAKATA*
207 Original Article Suppression of Cardiac Sympathetic Nervous System during Dental Surgery in Hypertensive Patients Keiko MIURA, Kiyoshi MATSUMURA*, Yoshito NAKAMURA*, Minoru KAJIYAMA, and Yutaka TAKATA*
Hypertension represents one of the most
 AJH 1998;11:1376 1380 Changes in Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Variability During Dental Surgery Kiyoshi Matsumura, Keiko Miura, Yutaka Takata, Hideo Kurokawa, Minoru Kajiyama, Isao Abe, and Masatoshi
AJH 1998;11:1376 1380 Changes in Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Variability During Dental Surgery Kiyoshi Matsumura, Keiko Miura, Yutaka Takata, Hideo Kurokawa, Minoru Kajiyama, Isao Abe, and Masatoshi
A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean university hospital pediatric dental clinic
 Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2016;16(3):203-208 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2016.16.3.203 A survey of dental treatment under general anesthesia in a Korean
Physiology and Pharmacology
 Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake Vasoactivity Local
Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake Vasoactivity Local
Evaluation of Changing Serum Blood Glucose Levels after Local Anesthetic Injection during Tooth Extraction
 Evaluation of Changing Serum Blood Glucose Levels after Local Anesthetic Injection during Tooth Extraction Original Article Kamal Qaranizade 1, Eshagh Lasemi 2, Hamidreza Mahaseni Aghdam 3, Farshid Malihi
Evaluation of Changing Serum Blood Glucose Levels after Local Anesthetic Injection during Tooth Extraction Original Article Kamal Qaranizade 1, Eshagh Lasemi 2, Hamidreza Mahaseni Aghdam 3, Farshid Malihi
Chapter 9. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives 9/11/2012. Cardiac Arrhythmias. Define electrical therapy
 Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Chapter 9 Cardiac Arrhythmias Learning Objectives Define electrical therapy Explain why electrical therapy is preferred initial therapy over drug administration for cardiac arrest and some arrhythmias
Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology
 Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology Drugs act on Sympathetic NS (adrenergic system) Adrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics), adrenergic agonists, or alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists Antiadrenergic
Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology Drugs act on Sympathetic NS (adrenergic system) Adrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics), adrenergic agonists, or alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists Antiadrenergic
Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of lidocaine with adrenaline and lidocaine with clonidine in maxillary infiltration anesthesia.
 ISSN(Online): XXXXXX Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of lidocaine with adrenaline and lidocaine with clonidine in maxillary infiltration anesthesia. Dr. Pranay Yajurvedi 1, Dr. Navin Shah 2, Dr.
ISSN(Online): XXXXXX Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of lidocaine with adrenaline and lidocaine with clonidine in maxillary infiltration anesthesia. Dr. Pranay Yajurvedi 1, Dr. Navin Shah 2, Dr.
HOW LOW CAN YOU GO? HYPOTENSION AND THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT.
 HOW LOW CAN YOU GO? HYPOTENSION AND THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT. Donna M. Sisak, CVT, LVT, VTS (Anesthesia/Analgesia) Seattle Veterinary Specialists Kirkland, WA dsisak@svsvet.com THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT
HOW LOW CAN YOU GO? HYPOTENSION AND THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT. Donna M. Sisak, CVT, LVT, VTS (Anesthesia/Analgesia) Seattle Veterinary Specialists Kirkland, WA dsisak@svsvet.com THE ANESTHETIZED PATIENT
a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline, isoprenaline, dopamine, dobutamine
 1 Adrenergic or sympathetic agonist: Are classified according to: I)- according to the chemical structure a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline,
1 Adrenergic or sympathetic agonist: Are classified according to: I)- according to the chemical structure a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline,
MA. Hemodynamic and ventilatory changes during implant. with intravenous conscious sedation
 Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 0 Jul ;6 ():e-. Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral.6.e http://dx.doi.org/doi:0.7/medoral.6.e Hemodynamic and ventilatory changes during
Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 0 Jul ;6 ():e-. Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral.6.e http://dx.doi.org/doi:0.7/medoral.6.e Hemodynamic and ventilatory changes during
Cortisol Level and Hemodynamic Changes During Tooth Extraction at Hypertensive and Normotensive Patients
 ORIGINAL PAPER 2015 Zana Bajrami Agani, Alberto Benedetti, Vjosa Hamiti Krasniqi, Jehona Ahmedi, Zana Sejfija, Mergime Prekazi Loxha, Arben Murtezani, Aida Namani Rexhepi, Zana Ibraimi This is an Open
ORIGINAL PAPER 2015 Zana Bajrami Agani, Alberto Benedetti, Vjosa Hamiti Krasniqi, Jehona Ahmedi, Zana Sejfija, Mergime Prekazi Loxha, Arben Murtezani, Aida Namani Rexhepi, Zana Ibraimi This is an Open
Delayed bleeding after implant surgery in patients taking novel oral anticoagulants: a case report
 Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):143-147 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.143 Delayed bleeding after implant surgery in patients taking novel oral anticoagulants:
Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(2):143-147 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.2.143 Delayed bleeding after implant surgery in patients taking novel oral anticoagulants:
Neosynephrine. Name of the Medicine
 Name of the Medicine Neosynephrine Phenylephrine hydrochloride 1% injection Neosynephrine Presentation Neosynephrine is a clear, colourless, aqueous solution, free from visible particulates, in sterile
Name of the Medicine Neosynephrine Phenylephrine hydrochloride 1% injection Neosynephrine Presentation Neosynephrine is a clear, colourless, aqueous solution, free from visible particulates, in sterile
PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker
 PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
Pharmacology of Local Anaesthetic drugs
 Pharmacology of Local Anaesthetic drugs Local Anaesthetics Lidocaine hydrochloride (Xylocaine) Lidocaine hydrochloride + 1:200,000 adrenaline Bupivacaine hydrochloride (Marcain) Bupivacaine hydrochloride
Pharmacology of Local Anaesthetic drugs Local Anaesthetics Lidocaine hydrochloride (Xylocaine) Lidocaine hydrochloride + 1:200,000 adrenaline Bupivacaine hydrochloride (Marcain) Bupivacaine hydrochloride
PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP
 PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP Brand or Product Name [Product name] Tablet 2mg [Product name] Tablet 4mg [Product name] Syrup 2mg/5ml Name and Strength of Active Substance(s)
PACKAGE INSERT TEMPLATE FOR SALBUTAMOL TABLET & SALBUTAMOL SYRUP Brand or Product Name [Product name] Tablet 2mg [Product name] Tablet 4mg [Product name] Syrup 2mg/5ml Name and Strength of Active Substance(s)
Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate).
 VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
VENTOL Composition Each ml of Ventol solution for inhalation contains 5 mg Salbutamol (as sulphate). Respiratory Solution Action Salbutamol is a short-acting, relatively selective beta2-adrenoceptor agonist.
The Systemic Effect Of Topical Timolol On Some Cardiovascular Parameters In Owerri Municipality
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 The Systemic Effect Of Topical Timolol On Some Cardiovascular Parameters In Owerri Municipality G Oze, M Emegwamuo, P Eleanya, H
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Third World Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 The Systemic Effect Of Topical Timolol On Some Cardiovascular Parameters In Owerri Municipality G Oze, M Emegwamuo, P Eleanya, H
International Journal of Research and Review E-ISSN: ; P-ISSN:
 International Journal of Research and Review www.ijrrjournal.com E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Short Communication Rate Pressure Product in Diabetic Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy at Rest and Under
International Journal of Research and Review www.ijrrjournal.com E-ISSN: 2349-9788; P-ISSN: 2454-2237 Short Communication Rate Pressure Product in Diabetic Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy at Rest and Under
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Angina pectoris due to coronary atherosclerosis : Atenolol is indicated for the long term management of patients with angina pectoris.
 Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Lonet Tablet Description Lonet contains Atenolol, a synthetic β1 selective (cardioselective) adrenoreceptor blocking agent without membrane stabilising or intrinsic sympathomimetic (partial agonist) activity.
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment
 Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
Intraoperative and Postoperative Arrhythmias: Diagnosis and Treatment Karen L. Booth, MD, Lucile Packard Children s Hospital Arrhythmias are common after congenital heart surgery [1]. Postoperative electrolyte
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Given the trade and/or generic name of an adrenergic blocking agent, classify that agent as either an alpha or beta blocker.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 Adrenergic Blocking Agents. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-5. LESSON OBJECTIVES 8-1. Given a group of statements, select the statement that best describes one of the
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS)
 DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
DRUG CLASSES BETA-ADRENOCEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (BETA-BLOCKERS) Beta-blockers have been widely used in the management of angina, certain tachyarrhythmias and heart failure, as well as in hypertension. Examples
Facial blanching after inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia: an unusual complication
 Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(4):317-321 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.4.317 Facial blanching after inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia: an unusual
Case Report pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2017;17(4):317-321 https://doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2017.17.4.317 Facial blanching after inferior alveolar nerve block anesthesia: an unusual
Haemostatic agents in apical surgery. A systematic review
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.21109 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.21109 Haemostatic agents in apical surgery. A systematic review Adrià CléOvejero
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.21109 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.21109 Haemostatic agents in apical surgery. A systematic review Adrià CléOvejero
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul
 Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) د. م. أ. وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul Sympathetic (Adrenergic) nervous system 3 Objectives At end of this lecture, the
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS) د. م. أ. وحدة اليوزبكي Department of Pharmacology- College of Medicine- University of Mosul Sympathetic (Adrenergic) nervous system 3 Objectives At end of this lecture, the
Adverse drug interactions in dental practice
 University "Goce Delchev" Shtip Faculty of Medical science Adverse drug interactions in dental practice Assistant professor Mаrija Darkovska-Serafimovska INTERACTION interaction is a situation in which
University "Goce Delchev" Shtip Faculty of Medical science Adverse drug interactions in dental practice Assistant professor Mаrija Darkovska-Serafimovska INTERACTION interaction is a situation in which
Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, University of Dental Medicine, Mandalay
 Original Article Comparative Study of the Anesthetic Efficacy of Articaine and Lignocaine in Mandibular First Molars Hnin Ei Phyo 1, Linn Pe Than 2, Htay Htay Yi 2, Ko Ko Maung 2 1 Department of Oral &
Original Article Comparative Study of the Anesthetic Efficacy of Articaine and Lignocaine in Mandibular First Molars Hnin Ei Phyo 1, Linn Pe Than 2, Htay Htay Yi 2, Ko Ko Maung 2 1 Department of Oral &
Norepinephrine (Levophed )
 Norepinephrine (Levophed ) Scope C3IFT CCT Generic Name: Norepinephrine Trade Name: Levophed Chemical Class: Therapeutic Class: Actions: Pharmacokinetics: Vasopressor Vasopressor Mechanism of Action: Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (Levophed ) Scope C3IFT CCT Generic Name: Norepinephrine Trade Name: Levophed Chemical Class: Therapeutic Class: Actions: Pharmacokinetics: Vasopressor Vasopressor Mechanism of Action: Norepinephrine
AUTONOMIC DRUGS: ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS AND SYMPATHOMIMETICS. Lecture 4
 AUTONOMIC DRUGS: ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS AND SYMPATHOMIMETICS Lecture 4 Introduction (review) 5 key features of neurotransmitter function, which can be targets for pharmacotherapy Synthesis Storage Release
AUTONOMIC DRUGS: ADRENOCEPTOR AGONISTS AND SYMPATHOMIMETICS Lecture 4 Introduction (review) 5 key features of neurotransmitter function, which can be targets for pharmacotherapy Synthesis Storage Release
B-blockers. Effects not related to Beta-Blockade
 B-blockers Effects not related to Beta-Blockade It has been suggested that some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity is desirable to prevent untoward effects such as asthma or excessive bradycardia. Pindolol
B-blockers Effects not related to Beta-Blockade It has been suggested that some intrinsic sympathomimetic activity is desirable to prevent untoward effects such as asthma or excessive bradycardia. Pindolol
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
Angina Pectoris Dr. Shariq Syed
 Angina Pectoris Dr. Syed 1 What is Angina Pectoris (AP)? Commonly known as angina is chest pain often due to ischemia of the heart muscle, Because of obstruction or spasm of the coronary arteries 2 What
Angina Pectoris Dr. Syed 1 What is Angina Pectoris (AP)? Commonly known as angina is chest pain often due to ischemia of the heart muscle, Because of obstruction or spasm of the coronary arteries 2 What
Properties of Pressure
 OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
Hypotension After Local Anesthetic Infiltration Into The Oral Submucosa During Oral And Maxillofacial Surgery
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 34 Number 1 Hypotension After Local Anesthetic Infiltration Into The Oral Submucosa During Oral And Maxillofacial K Satoh, A Ohashi, M Kumagai, M
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Anesthesiology Volume 34 Number 1 Hypotension After Local Anesthetic Infiltration Into The Oral Submucosa During Oral And Maxillofacial K Satoh, A Ohashi, M Kumagai, M
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER. EPHEDRINE HCl STEROP 10mg/ml EPHEDRINE HCl STEROP 50mg/ml Solution for injection. Ephedrine Hydrochloride
 PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER EPHEDRINE HCl STEROP 10mg/ml EPHEDRINE HCl STEROP 50mg/ml Solution for injection Ephedrine Hydrochloride Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using
PACKAGE LEAFLET: INFORMATION FOR THE USER EPHEDRINE HCl STEROP 10mg/ml EPHEDRINE HCl STEROP 50mg/ml Solution for injection Ephedrine Hydrochloride Read all of this leaflet carefully before you start using
ENDODONTOLOGY BLOOD-LESS OPERATING FIELD AN ENDODONTIST S ENIGMA HEMOSTASIS IN PERIRADICULAR SURGERY A REVIEW
 AN ENDODONTIST S ENIGMA HEMOSTASIS IN PERIRADICULAR SURGERY A REVIEW Inamdar Saquib * Sureshchandra B. ** ABSTRACT It is indeed a very true saying that necessesity is the mother of all inventions. How
AN ENDODONTIST S ENIGMA HEMOSTASIS IN PERIRADICULAR SURGERY A REVIEW Inamdar Saquib * Sureshchandra B. ** ABSTRACT It is indeed a very true saying that necessesity is the mother of all inventions. How
General anesthesia. No single drug capable of achieving these effects both safely and effectively.
 General anesthesia General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic, amnesia, and unconscious reflexes, while causing muscle relaxation and suppression of undesirable
General anesthesia General anesthesia is essential to surgical practice, because it renders patients analgesic, amnesia, and unconscious reflexes, while causing muscle relaxation and suppression of undesirable
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION LEVOPHED. (norepinephrine bitartrate injection USP) 1 mg norepinephrine/ ml
 PRESCRIBING INFORMATION LEVOPHED (norepinephrine bitartrate injection USP) 1 mg norepinephrine/ ml Sympathomimetic Amine for Use in Hypotensive Emergencies Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway
PRESCRIBING INFORMATION LEVOPHED (norepinephrine bitartrate injection USP) 1 mg norepinephrine/ ml Sympathomimetic Amine for Use in Hypotensive Emergencies Pfizer Canada Inc. 17300 Trans-Canada Highway
Esshagh Lasemi 1, Mehdi Sezavar 1, Leyla Habibi 2, Seyfollah Hemmat 3, Farzin Sarkarat 1, Zahra Nematollahi 4 INTRODUCTION
 Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2015;15(4):201-205 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2015.15.4.201 Articaine (4%) with epinephrine (1:100,000 or 1:200,000) in inferior
Original Article pissn 2383-9309 eissn 2383-9317 J Dent Anesth Pain Med 2015;15(4):201-205 http://dx.doi.org/10.17245/jdapm.2015.15.4.201 Articaine (4%) with epinephrine (1:100,000 or 1:200,000) in inferior
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adverse drug events, polypharmacy and perioperative considerations in elderly patients, 377 389 Age, and risk of postoperative urinary retention,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adverse drug events, polypharmacy and perioperative considerations in elderly patients, 377 389 Age, and risk of postoperative urinary retention,
Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point Using the Cricoid Cartilage as Landmark Through X-ray Review
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
Autonomic Nervous System Keri Muma Bio 6 Organization of the Nervous System Efferent Division Somatic Nervous System Voluntary control Effector = skeletal muscles Muscles must be excited by a motor neuron
The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine. Some adrenergic drugs act directly on the adrenergic
 Adrenergic drugs The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine. Some adrenergic drugs act directly on the adrenergic receptor (adrenoceptor) by activating it
Adrenergic drugs The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine. Some adrenergic drugs act directly on the adrenergic receptor (adrenoceptor) by activating it
Local Anaesthetics Predictable Profound Performance
 Local Anaesthetics Predictable Profound Performance Competence you can trust 3M local anaesthetics A better choice for patients With 3M local anaesthetics, you can rely on an effective and well-tolerated
Local Anaesthetics Predictable Profound Performance Competence you can trust 3M local anaesthetics A better choice for patients With 3M local anaesthetics, you can rely on an effective and well-tolerated
Lujain Hamdan. Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem. Mohammed khatatbeh
 12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
12 Lujain Hamdan Ayman Musleh & Yahya Salem Mohammed khatatbeh the last lecture, we have studied the differences between the two divisions of the ANS: sympathetic and parasympathetic pathways which work
ADULT DRUG REFERENCE Drug Indication Adult Dosage Precautions / Comments
 ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
ADENOSINE Paroxysmal SVT 1 st Dose 6 mg rapid IV 2 nd & 3 rd Doses 12 mg rapid IV push Follow each dose with rapid bolus of 20 ml NS May cause transient heart block or asystole. Side effects include chest
Ganglionic Blockers. Ganglion- blocking agents competitively block the action of
 Ganglionic Blockers Ganglion- blocking agents competitively block the action of acetylcholine and similar agonists at nicotinic (Nn) receptors of both parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic ganglia.
Ganglionic Blockers Ganglion- blocking agents competitively block the action of acetylcholine and similar agonists at nicotinic (Nn) receptors of both parasympathetic and sympathetic autonomic ganglia.
Arrhythmias. 1. beat too slowly (sinus bradycardia). Like in heart block
 Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
Arrhythmias It is a simple-dysfunction caused by abnormalities in impulse formation and conduction in the myocardium. The heart is designed in such a way that allows it to generate from the SA node electrical
Dr. Vishaal Bhat. anti-adrenergic drugs
 Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Dr. Vishaal Bhat anti-adrenergic drugs Divisions of human nervous system Human Nervous system Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system Includes neurons and
Management Of Medical Emergencies. Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS
 Management Of Medical Emergencies Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS Z.S. Messieha Associate Professor, Anesthesiology University Of Illinois At Chicago Necessity Of Emergency Protocol Aging patient population.
Management Of Medical Emergencies Zakaria S. Messieha, DDS Z.S. Messieha Associate Professor, Anesthesiology University Of Illinois At Chicago Necessity Of Emergency Protocol Aging patient population.
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs. ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani
 Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
Adrenergic agonists Sympathomimetic drugs ANS Pharmacology Lecture 4 Dr. Hiwa K. Saaed College of Pharmacy/University of Sulaimani 2017-2018 Adrenergic agonists The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that
Autonomic Pharmacology
 Autonomic Pharmacology ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR BLOCKERS Adrenergic-receptor antagonists block the effects of sympathetic stimulation and adrenergic agonists mediated through - and -receptors. Adrenergic receptor
Autonomic Pharmacology ADRENERGIC RECEPTOR BLOCKERS Adrenergic-receptor antagonists block the effects of sympathetic stimulation and adrenergic agonists mediated through - and -receptors. Adrenergic receptor
Salapin: Salbutamol BP 2mg as sulphate in each 5mL of a raspberry cola flavoured, sugar free syrup.
 Salapin Salbutamol Syrup 2mg/5mL Qualitative and quantitative composition Salapin: Salbutamol BP 2mg as sulphate in each 5mL of a raspberry cola flavoured, sugar free syrup. Clinical particulars Therapeutic
Salapin Salbutamol Syrup 2mg/5mL Qualitative and quantitative composition Salapin: Salbutamol BP 2mg as sulphate in each 5mL of a raspberry cola flavoured, sugar free syrup. Clinical particulars Therapeutic
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology
 d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
d) Cardiovascular System Higher Human Biology What can your remember about the heart and blood vessels? What is the Cardiovascular System? The cardiovascular system, also known as the circulatory system,
Efficacy of the Computer-Controlled Injection System STA TM, the Ligmaject, and the dental
 Clinical Efficacy of the Computer-Controlled Injection System STA TM, the Ligmaject, and the dental syringe for intraligamentary anesthesia in restorative patients Marco Ferrari 1, Maria Crysanti Cagidiaco
Clinical Efficacy of the Computer-Controlled Injection System STA TM, the Ligmaject, and the dental syringe for intraligamentary anesthesia in restorative patients Marco Ferrari 1, Maria Crysanti Cagidiaco
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Implantable cardioverter defibrillators for the treatment of arrhythmias and cardiac resynchronisation therapy for the treatment of heart failure (review
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CLINICAL EXCELLENCE Implantable cardioverter defibrillators for the treatment of arrhythmias and cardiac resynchronisation therapy for the treatment of heart failure (review
DBL EPHEDRINE SULFATE INJECTION
 Ephedrine Sulfate USP Description DBL EPHEDRINE SULFATE INJECTION The molecular formula of Ephedrine Sulfate is (C 10 H 15 NO) 2 H 2 SO 4. Its molecular weight is 428.5. The CAS registry number of Ephedrine
Ephedrine Sulfate USP Description DBL EPHEDRINE SULFATE INJECTION The molecular formula of Ephedrine Sulfate is (C 10 H 15 NO) 2 H 2 SO 4. Its molecular weight is 428.5. The CAS registry number of Ephedrine
Anaesthetic Efficacy of the Anterior Middle Superior Nerve Block for Extraction of Maxillary Anterior Teeth
 Anaesthetic Efficacy of the Anterior Middle Superior Nerve Block for Extraction of Maxillary Anterior Teeth 1 2 3 5 Bansal S, Kukreja P, Kumar S, Sharma M, Rakshak AK, Jha KB Abstract: Aim: The aim of
Anaesthetic Efficacy of the Anterior Middle Superior Nerve Block for Extraction of Maxillary Anterior Teeth 1 2 3 5 Bansal S, Kukreja P, Kumar S, Sharma M, Rakshak AK, Jha KB Abstract: Aim: The aim of
Cardiac Pathophysiology
 Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Cardiac Pathophysiology Evaluation Components Medical history Physical examination Routine laboratory tests Optional tests Medical History Duration and classification of hypertension. Patient history of
Bisoprolol Fumarate 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg Tablet
 Bisoprolol Fumarate 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg Tablet Description Betapro is a preparation of Bisoprolol Fumarate. Bisoprolol is used alone or in combination with other medications to treat high blood pressure.
Bisoprolol Fumarate 2.5 mg, 5 mg and 10 mg Tablet Description Betapro is a preparation of Bisoprolol Fumarate. Bisoprolol is used alone or in combination with other medications to treat high blood pressure.
Bleeding Management with Extractions
 Bleeding Management with Extractions WHAT YOU WILL LEARN IN THIS SEGMENT: What is INR? Do you stop Coumadin before extractions or not? If not, how many teeth can be removed per appointment? Which local
Bleeding Management with Extractions WHAT YOU WILL LEARN IN THIS SEGMENT: What is INR? Do you stop Coumadin before extractions or not? If not, how many teeth can be removed per appointment? Which local
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 11: Vasoactive Agents Question No. 1 of 10 1. Vascular smooth muscle contraction is triggered by a rise in. Question #01 (A) Luminal calcium (B) Extracellular calcium (C) Intracellular
Titrating Critical Care Medications
 Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Cardiac chest pain or suspected Myocardial Infarction.
 s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
s Aspirin Platelet aggregation inhibitor. Anti-inflammatory agent and an inhibitor of platelet function. Useful agent in the treatment of various thromboembolic diseases such as acute myocardial infarction.
In the name of GOD. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension
 In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
In the name of GOD Animal models of cardiovascular diseases: myocardial infarction & hypertension 44 Presentation outline: Cardiovascular diseases Acute myocardial infarction Animal models for myocardial
A COPD medication delivery device option: an overview of the NEOHALER
 A COPD medication delivery device option: an overview of the NEOHALER 2017 Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. All rights reserved 9/17 RESP019-17 Indication and Boxed Warning INDICATION ARCAPTA NEOHALER (indacaterol)
A COPD medication delivery device option: an overview of the NEOHALER 2017 Sunovion Pharmaceuticals Inc. All rights reserved 9/17 RESP019-17 Indication and Boxed Warning INDICATION ARCAPTA NEOHALER (indacaterol)
Anaesthetic efficacy of periodontal ligament injection of 2% lidocaine with 1:80,000 adrenaline
 ISSN: 1812 1217 Anaesthetic efficacy of periodontal ligament injection of 2% lidocaine with 1:8, adrenaline Shehab A Hamad BDS, MSc (Lect) Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery College of Dentistry,
ISSN: 1812 1217 Anaesthetic efficacy of periodontal ligament injection of 2% lidocaine with 1:8, adrenaline Shehab A Hamad BDS, MSc (Lect) Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery College of Dentistry,
ASTHALIN Respirator Solution (Salbutamol sulphate)
 Published on: 28 Jan 2016 ASTHALIN Respirator Solution (Salbutamol sulphate) Composition Each 1 ml contains: Salbutamol Sulphate IP equivalent to Salbutamol IP.. 5 mg Dosage Form Solution for inhalation
Published on: 28 Jan 2016 ASTHALIN Respirator Solution (Salbutamol sulphate) Composition Each 1 ml contains: Salbutamol Sulphate IP equivalent to Salbutamol IP.. 5 mg Dosage Form Solution for inhalation
ADRENERGIC AGONISTS. Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1. Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev. Date: September 16, Materials on: Exam #2
 ADRENERGIC AGONISTS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 16, 2010 Materials on: Exam #2 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 9 1 ADRENERGIC NEUROTRANSMISSION Pre-Synaptic
ADRENERGIC AGONISTS Course: Integrated Therapeutics 1 Lecturer: Dr. E. Konorev Date: September 16, 2010 Materials on: Exam #2 Required reading: Katzung, Chapter 9 1 ADRENERGIC NEUROTRANSMISSION Pre-Synaptic
Images have been removed from the PowerPoint slides in this handout due to copyright restrictions.
 Percutaneous Coronary Intervention https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bssqnhylvma Types of PCI Procedures Balloon Angioplasty Rotational Atherectomy Coronary Stent Balloon Inflation Rotational Atherectomy
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bssqnhylvma Types of PCI Procedures Balloon Angioplasty Rotational Atherectomy Coronary Stent Balloon Inflation Rotational Atherectomy
Pheochromocytoma: Effects of Catecholamines
 36 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 8 Pheochromocytoma: Effects of Catecholamines Helen Ames is a 51-year-old homemaker who experienced what she thought were severe menopausal symptoms. These awful "attacks"
36 PHYSIOLOGY CASES AND PROBLEMS Case 8 Pheochromocytoma: Effects of Catecholamines Helen Ames is a 51-year-old homemaker who experienced what she thought were severe menopausal symptoms. These awful "attacks"
Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP
 What Is Cardiac Stress Testing? Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP A Cardiac Stress Test is a test used to measure the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. Cardiac
What Is Cardiac Stress Testing? Chad Morsch B.S., ACSM CEP A Cardiac Stress Test is a test used to measure the heart's ability to respond to external stress in a controlled clinical environment. Cardiac
Student Contribution THE USE OF VASOPRESSIN IN THE TREATMENT OF CARDIAC ARREST A CASE STUDY. Aaron Turner, SA Ambulance Service
 ISSN 1447-4999 Student Contribution THE USE OF VASOPRESSIN IN THE TREATMENT OF CARDIAC ARREST A CASE STUDY Aaron Turner, SA Ambulance Service INTRODUCTION Despite widespread use, current methods of treatment
ISSN 1447-4999 Student Contribution THE USE OF VASOPRESSIN IN THE TREATMENT OF CARDIAC ARREST A CASE STUDY Aaron Turner, SA Ambulance Service INTRODUCTION Despite widespread use, current methods of treatment
EPINEPHRINE Injection, USP 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Ampul Protect from light until ready to use.
 EPINEPHRINE Injection, USP 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Ampul Protect from light until ready to use. DESCRIPTION Epinephrine Injection, USP 1:1000 is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution. Each ml contains epinephrine
EPINEPHRINE Injection, USP 1:1000 (1 mg/ml) Ampul Protect from light until ready to use. DESCRIPTION Epinephrine Injection, USP 1:1000 is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution. Each ml contains epinephrine
Crisis Management During Liver Transplant Surgery Liver and Intensive Care Group of Europe Newcastle upon Tyne 2005
 Crisis Management During Liver Transplant Surgery Liver and Intensive Care Group of Europe Newcastle upon Tyne 2005 M. Susan Mandell M.D. Ph. D. Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Health
Crisis Management During Liver Transplant Surgery Liver and Intensive Care Group of Europe Newcastle upon Tyne 2005 M. Susan Mandell M.D. Ph. D. Department of Anesthesiology University of Colorado Health
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide
 Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
Lab Period: Name: Physiology Chapter 14 Blood Flow and Blood Pressure, Plus Fun Review Study Guide Main Idea: The function of the circulatory system is to maintain adequate blood flow to all tissues. Clinical
BIMM118. Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ganglia close to the innervated organs Myelinated axons Ganglia close to the spinal column Preganglionic axons are myelinated; postganglionic axons are
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ganglia close to the innervated organs Myelinated axons Ganglia close to the spinal column Preganglionic axons are myelinated; postganglionic axons are
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 8
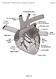 Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Figure 8-1 Figure 8-2 Figure 8-3 Figure 8-4 Figure 8-5 Figure 8-7 Figure 8-8 Figure 8-9 TABLE 8-1 Blood Flow Through the Heart The right atrium receives blood from all tissues, except the lungs, through
Establishing Dental Treatment Guidelines for Adult Patients with Uncontrolled Hypertension Attending Acute Care.
 Establishing Dental Treatment Guidelines for Adult Patients with Uncontrolled Hypertension Attending Acute Care. John C Comisi, DDS Assistant Professor, MUSC-College of Dental Medicine We all have them
Establishing Dental Treatment Guidelines for Adult Patients with Uncontrolled Hypertension Attending Acute Care. John C Comisi, DDS Assistant Professor, MUSC-College of Dental Medicine We all have them
Adrenergic Agonists 1
 Adrenergic Agonists 1 THE ADRENERGIC NEURON Adrenergic neurons release norepinephrine as the primary neurotransmitter. These neurons are found in the central nervous system (CNS) and also in the sympathetic
Adrenergic Agonists 1 THE ADRENERGIC NEURON Adrenergic neurons release norepinephrine as the primary neurotransmitter. These neurons are found in the central nervous system (CNS) and also in the sympathetic
Agency 71. Kansas Dental Board (Authorized by K.S.A and (Authorized by K.S.A and
 Agency 71 Kansas Dental Board Articles 71-4. CONTINUING EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS. 71-5. SEDATIVE AND GENERAL ANAESTHESIA. 71-11. MISCELLANEOUS PROVISIONS. Article 4. CONTINUING EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS 71-4-1.
Agency 71 Kansas Dental Board Articles 71-4. CONTINUING EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS. 71-5. SEDATIVE AND GENERAL ANAESTHESIA. 71-11. MISCELLANEOUS PROVISIONS. Article 4. CONTINUING EDUCATION REQUIREMENTS 71-4-1.
Clinical Competency Name: Post-operative use of Metaraminol in Recovery
 Clinical Competency Name: Post-operative use of Metaraminol in Recovery Trainee name: Title: Ward or department: Method of assessment: Clinical assessor: Name: Title: Professional assessor: Name: Title:
Clinical Competency Name: Post-operative use of Metaraminol in Recovery Trainee name: Title: Ward or department: Method of assessment: Clinical assessor: Name: Title: Professional assessor: Name: Title:
Cardiac Drugs: Chapter 9 Worksheet Cardiac Agents. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate.
 Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
Complete the following. 1. drugs affect the rate of the heart and can either increase its rate or decrease its rate. 2. drugs affect the force of contraction and can be either positive or negative. 3.
ADVERSE REACTIONS Most common adverse reactions during treatment: nausea, vomiting, and tachycardia. (6)
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AKOVAZ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AKOVAZ. AKOVAZ (ephedrine sulfate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AKOVAZ safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AKOVAZ. AKOVAZ (ephedrine sulfate
These drugs produce effects similar to the sympathetic nervous system
 Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
Terms adrenergic Drugs mydriasis sympathetic nervous system adrenergic drugs adrenergic mechanism of action positive inotropic effect positive chronotropic effect positive dromotropic effect adrenergic
Anesthetic Efficacy of Different Ropivacaine Concentrations for Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block
 SCIENTIFIC REPORT Anesthetic Efficacy of Different Ropivacaine Concentrations for Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Eman El-Sharrawy, MBBCh, MSc, MD,* and John A. Yagiela, DDS, PhD *Faculty of Dentistry, Tanta
SCIENTIFIC REPORT Anesthetic Efficacy of Different Ropivacaine Concentrations for Inferior Alveolar Nerve Block Eman El-Sharrawy, MBBCh, MSc, MD,* and John A. Yagiela, DDS, PhD *Faculty of Dentistry, Tanta
Cardiology. Objectives. Chapter
 1:44 M age 1121 Chapter Cardiology Objectives art 1: Cardiovascular natomy and hysiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia nalysis (begins on p. 1127) fter reading art 1 of this chapter, you should be able
1:44 M age 1121 Chapter Cardiology Objectives art 1: Cardiovascular natomy and hysiology, ECG Monitoring, and Dysrhythmia nalysis (begins on p. 1127) fter reading art 1 of this chapter, you should be able
Received: 21 July 2017 Accepted: 26 Nov. 2017
 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22122/johoe.v7i3.366 Published by Vesnu Publications Received: 21 July 2017 Accepted: 26 Nov. 2017 Onset and duration of 2% lidocaine as inferior alveolar nerve block versus buccal/lingual
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.22122/johoe.v7i3.366 Published by Vesnu Publications Received: 21 July 2017 Accepted: 26 Nov. 2017 Onset and duration of 2% lidocaine as inferior alveolar nerve block versus buccal/lingual
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to
 Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
Hypertension The normal radial artery blood pressures in adults are: Systolic arterial pressure: 100 to 140 mmhg. Diastolic arterial pressure: 60 to 90 mmhg. These pressures are called Normal blood pressure
LUNCH AND LEARN. Sterile Drug Products Used in the Anesthesia Practice Setting: Part 2. February 10, 2017
 LUNCH AND LEARN Sterile Drug Products Used in the Anesthesia Practice Setting: Part 2 February 10, 2017 Featured Speaker: Julie A. Golembiewski, PharmD Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Pharmacy
LUNCH AND LEARN Sterile Drug Products Used in the Anesthesia Practice Setting: Part 2 February 10, 2017 Featured Speaker: Julie A. Golembiewski, PharmD Clinical Associate Professor, Department of Pharmacy
WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA
 CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
CARDIAC DRUG REVIEW WHAT DO YOU SEE WHEN YOU STIMULATE BETA VASODILATE BRONCHODILATE +CHRONOTROPE +INOTROPE EPI S OTHER NAME? ADRENALIN WHAT DOES EPI DO THAT NOREPI AND DOPAMINE DO NOT DO? BETA 2 BRONCHODILATOR
Instruct patient and caregivers: Need for constant monitoring Potential complications of drug therapy
 Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
Assessment Prior to administration: Assess patient for chest pain, dysrhythmias, and vital signs (initially and throughout therapy) Obtain complete medical history, including allergies, especially heart
Cardiovascular Effects of Local Anesthesia with Vasoconstrictor during Dental Extraction in Coronary Patients
 Cardiovascular Effects of Local Anesthesia with Vasoconstrictor during Dental Extraction in Coronary Patients Valeria C. L. S. Conrado, Januário de Andrade, Gabriella A. M. C. de Angelis, Ana Carolina
Cardiovascular Effects of Local Anesthesia with Vasoconstrictor during Dental Extraction in Coronary Patients Valeria C. L. S. Conrado, Januário de Andrade, Gabriella A. M. C. de Angelis, Ana Carolina
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT. Vicks Sinex, 0.5 mg/ml, nasal spray solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION
 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Vicks Sinex, 0.5 mg/ml, nasal spray solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Oxymetazoline hydrochloride 0.5 mg/ml 1 spray (50 l) contains approximately 25
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Vicks Sinex, 0.5 mg/ml, nasal spray solution 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Oxymetazoline hydrochloride 0.5 mg/ml 1 spray (50 l) contains approximately 25
