Lack of sufficient bone height in the posterior maxilla
|
|
|
- Rafe Reynolds
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Computerized Tomography Assisted Calculation of Sinus Augmentation Volume Gerald Krennmair, MD, DMD, PhD 1 /Martin Krainhöfner, MD, DMD 2 /Harald Maier 3 / Michael Weinländer, MD, DMD 4 /Eva Piehslinger, MD, DMD, PhD 5 Purpose: This study was intended to calculate the augmentation volume for a sinus lift procedure based on cross-sectional computerized tomography (CT) scans for 2 different augmentation heights. Materials and Methods: Based on area calculations of cross-sectional CT scans, the volume of additional bone needed was calculated for 44 sinus lift procedures. The amount of bone volume needed to raise the sinus floor to heights of both 12 and 17 mm was calculated. Results: To achieve a sinus floor height of 12 mm, it was necessary to increase the height by a mean of 7.2 ± 2.1 mm (range, 3.0 to 10.5 mm), depending on the residual ridge height; to achieve a height of 17 mm, a mean of 12.4 ± 2.0 mm (range, 8.5 to 15.5 mm) was required (P <.01). The calculated augmentation volume for an augmentation height of 12 mm was 1.7 ± 0.9 cm 3 ; for an augmentation height of 17 mm, the volume required was 3.6 ± 1.5 cm 3. Increasing the height of the sinus lift by 5 mm, ie, from 12 mm to 17 mm augmentation height, increased the augmentation volume by 100%. A significant correlation was found between augmentation height and the calculated sinus lift augmentation volume (r = 0.78, P <.01). Discussion and Conclusion: Detailed preoperative knowledge of sinus lift augmentation volume is helpful as a predictive value in deciding on a donor site for harvesting autogenous bone and on the ratio of bone to bone substitute to use. Calculation of the augmentation size can help determine the surgical approach and thus perioperative treatment and the costs of the surgery for both patients and clinicians. (Basic Science) INT J ORAL MAXILLOFAC IMPLANTS 2006;21: Key words: augmentation volume, computerized tomography, sinus lift augmentation Lack of sufficient bone height in the posterior maxilla frequently precludes standard implant placement in this region. Since the 1980s, many investigators have used internal sinus augmentation (sinus floor elevation) to allow implant placement in the posterior maxillary region in patients who initially present with insufficient bone height. 1 3 After successful internal maxillary sinus augmentation, anchorage of dental implants is possible even in cases in which the posterior maxillary region has undergone severe bone resorption. 3 5 Traditional internal sinus 1 University Professor and Clinical Lecturer, Department of Prosthodontics, Dental School, University of Vienna, Austria. 2 Assistant, Department of Prosthodontics, Dental School, University of Vienna, Austria. 3 Student, Dental School, University of Vienna. 4 Private Practice in Oral Implantology and Implant Prosthetics, Vienna, Austria. 5 Head, Department of Prosthodontics, Dental School, University of Vienna, Austria. Correspondence to: Univ-Prof DDr Med Gerald Krennmair, Trauneggsiedlung 8, 4600 Wels, Austria. Fax: krennmair@aon.at. augmentation and implant placement using the lateral window approach are accomplished as either a 1- step or a 2-step surgical procedure. 3 6 In this surgical technique, a hinged opening is made in the facial antral wall and inverted to create a space for the graft material. 1 Various types of grafting material (eg, autogenous bone, xenogenic bone, combinations of these materials) have been used successfully. The graft material is placed between the antral floor and the elevated sinus membrane (including the inverted bone plate) Although there have been some modifications of the surgical techniques in recent years, 15,16 the original technique described by Boyne and James is still in use today. 1 Autogenous bone can be harvested from the iliac crest, the metaphysis of the tibia, and several intraoral mandibular sites such as the symphyseal or retromolar area and the maxillary tuberosity Detailed knowledge of the bone volume needed prior to surgery may be helpful in selecting the optimal donor site. Preoperative knowledge of the required bone volume minimizes the extent of the surgical procedure as well as the potential complications encountered and reduces hospital costs and expenses for the patient The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 907
2 A 1 A 2 A n a TH 17 AH 17 TH 12 AH 12 b Fig 2 CT scans with superimposed vertical reference lines. The total height (TH) lines indicate the total height needed to accommodate (a) a 15-mm-long implant or (b) a 10-mm-long implant; The augmentation height (AH) lines indicate the amount by which the current height must be increased (TH = AH + residual ridge height). Fig 1 CT panoramic images showing the mesiodistal extension of the planned sinus augmentation and the available cross-sectional scans. A total maxillary sinus volume of approximately 15 cm 3 has been reported in the literature (ie, anatomic and radiographic studies). 25 In a cadaveric study, Uchida and colleagues 25 described a total sinus volume of 14 cm 3. They also measured the sinus floor volume for simulated sinus lift procedures and found that, depending on the procedure and implant length, it was necessary to increase the bone volume of the antral floor by 1 to 7 cm 3. Few clinical investigations regarding sinus augmentation volume (ie, the amount by which it is necessary to increase the sinus volume) as determined prior to surgery have been carried out. 25,26 Computerized tomography (CT) and software programs may be used to obtain sectional images of the maxillary sinus and the adjacent antral floor Detailed cross-sectional CT scans allow calculation of the augmentation volume for various implant lengths and residual ridge heights. The aim of the present study was to measure the sinus augmentation volume using preoperative cross-sectional CT scans and to calculate the required graft volume for several augmentation heights and implant lengths. MATERIALS AND METHODS The present study included 31 patients (18 men and 13 women; mean age, 53.1 ± 7.2 years, range, 36 to 68 years) with unilateral (n = 18) or bilateral (n = 13) edentulous posterior maxillae. Overall, 44 posterior maxillary regions scheduled for sinus lift procedures for implant treatment were studied. Basic radiographic diagnostic evaluation consisted of a conventional orthopantomogram. In addition, a dental CT was performed from which CT panoramic images and reformatted CT cross-sectional scans were prepared. Axial CT radiographic examinations were carried out using a Somatom Plus S machine (125 kv, 520 m As, matrix ; Siemens, Munich, Germany). Axial sections were made parallel to the alveolar ridge of the maxilla at 1-mm intervals.the axial scans were reformatted into panoramic images, and proportional 1-mm crosssectional views were obtained from the axial scans using the dental CT software program (Siemens) In the CT panoramic images the mesiodistal extension of the planned sinus augmentation was determined using the number (A 1 A n, Fig 1) of available cross-sectional scans (Fig 1). Vertical reference lines were superimposed on the scans (Fig 2). For a 10-mm-long implant, a reference line of 12 mm was used; this included a 2-mm safety margin. For a 15- mm-long implant, a 17-mm-long reference line was used. The total height (TH) was the height of the residual bone plus the amount by which it would be necessary to augment the sinus to place an implant of the desired length (ie, the augmentation height [AH]). When calculating the augmentation volume, 2 mm of augmentation height were added to compensate for the possibility of graft resorption. To determine the maximum AH, the AH reference line was drawn from the lowest point of the sinus floor; a horizontal line was then drawn across the scan for determination of the required volume for each implant length (Fig 3). 908 Volume 21, Number 6, 2006
3 Fig 3 Cross-sectional CT scans with the necessary AHs for 10- or 15-mm-long implants shown. AH 17 AH 12 Fig 4 Area calculation on cross-sectional CT scans. All 1-mm cross-sectional scans were converted to digital images with an HP 1210 scanner (Hewlett- Packard, Palo Alto, CA) and then processed with Photoshop 5.0 LE (Adobe, San Jose, CA; Figs 3 and 4). Using a PC cursor the surface was defined on the respective cross-sectional scan and the pixel number of the surface was determined (Fig 4). Summation of the individual pixels and their defined size (1 pixel = mm) produced the surface areas of the individual cross-sectional scans at the given heights. Using the previously determined anterior-posterior distance (Fig 1), the number of cross-sectional scans required was defined. The overall volume (V) was determined using the formula V = n A n, where n was the sum of the surface areas of the individual cross sections. Volume calculation was carried out in this manner for all planned sinus lifts with adequate consideration of residual alveolar ridge height (RRH). The augmentation volumes for augmentation heights of 12 and 17 mm were calculated and compared. The volumes determined were given in absolute numbers, but they were also compared as relative figures for the varying augmentation heights. A simple correlation was calculated for the calculated volumes and the required augmentation heights defined. Means ± SD and simple correlations were compared using the Student t test. P values of.05 were considered significant. RESULTS Using CT data the maximum AH required and the augmentation volume required to achieve THs of 12 and 17 mm were calculated for 44 maxillary posterior areas. The maxillary posterior areas had a mean ± SD RRH of 4.5 ± 2.1 mm (range, 2.0 to 8.5 mm). The maximum AH required for elevation from the most caudal point of the sinus lift floor to the level of the horizontal reference line was calculated for heights of 12 or 17 mm. For an AH of 12 mm, an elevation of 7.2 ± 2.1 mm (range, 3.0 to 10.5 mm) was required; to obtain an AH of 17 mm, elevation of 12.4 ± 2.0 mm (range, 8.5 to 15.5 mm) was required (P <.01). To achieve a TH of 12 mm, mean augmentation volume of 1.7 ± 0.9 cm 3 (range, cm 3 ) needed to be achieved; for a TH of 17 mm, the mean augmentation volume was 3.6 ± 1.5 cm 3 (range, cm 3 ). The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 909
4 60 AH 12 mm AH 17 mm Volume (cm 3 ) No. of sinus lifts (augmentations) Fig 5 Individual augmentation volumes of all maxillary sinus areas (n = 44) where sinus augmentation was planned relative to intended augmentation height. In Fig 5 the individual augmentation volumes of all maxillary sinuses are shown in relation to the different AHs (12 or 17 mm). Figure 6 shows the relationship of augmentation volumes for augmentation heights of 12 mm (V AH12 ) and 17 mm (V AH17 ). An increase of elevation of 5 mm, ie, from an augmentation height of 12 mm to a height of 17 mm, was associated with an increase of 100% for the augmentation volume. A significant correlation was found between the required AH and the calculated sinus lift volume (r = 0.78, P <.01). Figure 7 shows the correlation between AH and augmentation volume for all cases (n = 88): The necessary volume in cm was equal to 0.352x 8.073, where x was the augmentation height in mm DISCUSSION Results of numerous clinical studies have shown that autogenous bone alone or in combination with xenogenic bone substitute is the graft material of choice for elevation of the maxillary sinus floor to achieve a sufficient height for implant placement in atrophic posterior maxillary regions. 2 5,10 14 Autogenous bone material may be harvested from intraoral donor sites (the ascending ramus, the retromolar area, the mandibular symphyseal region, and the maxillary tuberosity) or extraoral ones (eg, the ilium, tibia, or cranium) ,30,31 Sailer, 6 Uchida and associates, 25 and Montazem and colleagues 31 described the bone graft volume which can be harvested from the mandibular symphyseal region as ranging from 3 to 6 cm 3. The varying dimension between buccal and lingual cortical bone results in variable bone volume and limits the volume of intraoral symphyseal bone available for transplantation. 31,32 Excessive harvesting of symphyseal bone may lead to damage of the roots of adjacent anterior teeth and cause neurosensory disturbances. 17,19,23,31,32 Based on anatomic investigations and calculations, the bone volume of the ascending ramus and the retromolar area is about 2 to 3 cubic centimeters. 30,33 Use of the retromolar area or the ascending ramus is often limited because of atrophyrelated resorption of the mandible and the risk of injury of the inferior alveolar nerve bundle. 30,33 In contrast, extraoral donor sites allow the harvest of larger amounts of bone range of bone. 20,22 Detailed knowledge of the volume of bone required prior to surgery is helpful to determine the amount of bone to be harvested and thus to select an adequate donor site. 17 Preoperative knowledge of the sinus augmentation size may minimize potential intraoperative complications at donor sites and can also be used to estimate the costs of additional xenogenic graft materials used. 19,23,24 A review of recent studies has suggested that implants to be placed in the poste- 910 Volume 21, Number 6, 2006
5 V AH17 :V AH No. of sinus lifts (augmentations) Fig 6 Relationship between augmentation volume for the 2 AHs for each sinus area studied. rior maxilla should be at least 13 mm in length to achieve long-term success. 3,5 Thus, in the present study calculations were carried out for the placement of a 15-mm implant; in addition, 2 mm were added to the necessary AH to account for graft resorption. 34,35 The results of the calculations in the present study demonstrate that for cases with reduced residual ridge height elevation of up to 15 mm is associated with an augmentation volume of up to 5 to 6 cm 3. This size is tantamount to the maximum dimension of the mandibular symphyseal donor site and exceeds the maximum amount of bone that can be harvested from the ascending ramus or the retromolar area. 3,17 20,30 33 A sinus augmentation volume of 5 to 6 cm 3 may require the use of an extraoral donor site or a bone substitute. 11,12 Thus, calculation of the augmentation volume may affect donor site selection, which in turn affects the method of anesthesia, peri- and postoperative treatment, and patient cost. Knowledge of the anticipated augmentation size is especially helpful for the calculation of the amount of bone substitute used. 11 The obtained correlations and mathematical model presented here may be helpful in establishing preoperative estimates of the amount of bone to harvest and the amount of bone substitute to use. The literature includes a wide range of different recommendations about the ratio of autogenous bone to bone substitute to use ,34 However, high Fig 7 AV (cm 3 ) AH (mm) Correlation between AH and volume. success rates have been presented recently for sinus augmentation with xenogenic bone substitutes alone or with several mixtures of autologous bone and xenogenic substitutes at ratios of 1:3 or 1:4. 3,5,11,14 Therefore preoperative CT calculation of sinus augmentation volume may also determine the amount (and/or ratio) of xenogenic substitute to use and provide predictive information on surgical and material costs for the patients ,34 Several investigators have previously reported on donor site, graft bone volume, and implant length in conjunction with bone grafting in the maxillary sinus The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 911
6 floor. 25,26 In an anatomic model as well as in a CT investigation, the calculated bone graft volumes ranged from 2 to 15 cm 3. 25,26 The findings reported for the present study confirm the data described by Uchida and associates, 25 who reported that the augmentation volume required for a 10-mm elevation would be 1.5 ± 0.9 cm 3. In this study, the bone volume required for a 15- mm elevation was smaller, possibly because the preexisting alveolar ridge was included in the calculations made in the present study. In contrast, the study of Uchida and associates 26 only used axial scans, and the residual ridge was not considered. The present study shows that cross-sectional CT scans define the width and height of the residual ridge and allow for an exact calculation of the height and volume of augmentation. Cross-sectional CT scans also provide information on surrounding structures Images of the maxillary posterior areas using cross-sectional CT scans may be useful in selecting the appropriate surgical approach and may also be useful when deciding whether to use the conventional lateral approach or the crestal osteotome technique. 1,15,16,27,28 However, there are also critical limitations of the use of radiographic calculations such as those presented in the present and former studies. Clinically, the contour of the sinus lift will not always follow the straight lines drawn on CT scans. Because of concavities and convexities in clinical situations, radiographic calculations only provide useful approximations of volume Interesting findings were obtained in the present study when the relative volumes of sinus lift augmentation for different augmentation heights were compared. It was found that increasing the augmentation height from 12 mm to 17 mm resulted in a significant increase of bone augmentation volume. With an increase of augmentation height of 5 mm, the augmentation volume increased by 100%. With the present findings showing a maximum sinus augmentation volume of 5 to 6 cm, 3 and with previous studies demonstrating that at least 2 to 3 cm 3 of bone can be harvested from intraoral donor sites, intraoral sites should be given preference over extraoral donor sites. 17,18,30,31 Using the bone harvested from intraoral sites, unilateral as well as bilateral sinus floor elevation may be carried out with bone from intraoral sites alone if there is not substantial atrophy. 3,5,11 Based on the calculations described and using the recommended ratios of bone to bone substitute (1:4), extraoral bone harvesting is only necessary in patients with contraindications for intraoral mandibular harvesting sites, maxillae with severe bilateral atrophy, or maxillae for which both external and internal (onlay) grafting are needed. REFERENCES 1. Boyne PJ, James RA. Grafting of the maxillary sinus floor with autogenous marrow and bone. J Oral Surg 1980;38: Kent JN, Block MS. Simultaneous maxillary sinus floor bone grafting and placement of hydroxylapatite-coated implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1989;47: Wallace SS, Froum SJ. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants: A systematic review. Ann Periodontol 2003;8: Valentini P, Abensur DJ. Maxillary sinus grafting with anorganic bovine bone: A clinical report of long-term results. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2003;18: Hallman M, Nordin T. Sinus floor augmentation with bovine hydroxyapatite mixed with fibrin glue and later placement of nonsubmerged implants: A retrospective study in 50 patients. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2004;19: Sailer HF. A new method of inserting endosseous implants in totally atrophic maxillae. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 1989;17: Stricker A,Voss PJ, Gutwald R, Schramm A, Schmelzeisen R. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation with autogenous bone grafts to enable placement of SLA-surfaced implants: Preliminary results after 15 to 40 months. Clin Oral Implants Res 2003;14: Quinones CR, Hurzeler MB, Schupbach P, Arnold DR, Strub JR, Caffesse RG. Maxillary sinus augmentation using different grafting materials and dental implants in monkeys. Part IV. Evaluation of hydroxyapatite-coated implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 1997;8: Haas R, Donath K, Fodinger M,Watzek G. Bovine hydroxyapatite for maxillary sinus grafting: Comparative histomorphometric findings in sheep. Clin Oral Implants Res 1998;9: Khoury F. Augmentation of the sinus floor with mandibular bone block and simultaneous implantation: A 6-year clinical investigation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1999;14: Hallman M, Sennerby L, Lundgren S. A clinical and histologic evaluation of implant integration in the posterior maxilla after sinus floor augmentation with autogenous bone, bovine hydroxyapatite, or a 20:80 mixture. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2002;17: Maiorana C, Redemagni M, Rabagliati M, Salina S.Treatment of maxillary ridge resorption by sinus augmentation with iliac cancellous bone, anorganic bovine bone, and endosseous implants: A clinical and histologic report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2000;15: Peleg M, Mazor Z, Garg AK. Augmentation grafting of the maxillary sinus and simultaneous implant placement in patients with 3 to 5 mm residual alveolar bone height. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1999;14: Cordioli G, Mazzocco C, Schepers E, Brugnolo E, Majzoub Z. Maxillary sinus floor augmentation using bioactive glass granules and autogenous bone with simultaneous implant placement. Clinical and histological findings. Clin Oral Implants Res 2001;12: Summers RB.The osteotome technique: Part 3 Less invasive methods of elevating the sinus floor. Compend Contin Educ Dent 1994;15: Toffler M. Osteotome-mediated sinus floor elevation: A clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2004;19: Misch CM. Comparison of intraoral donor sites for onlay grafting prior to implant placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1997;12: Misch CM. Use of the mandibular ramus as a donor site for onlay grafting. J Oral Implantol 2000; 26: Volume 21, Number 6, 2006
7 19. Clavero J, Lundgren S. Ramus or chin grafts for maxillary sinus inlay and local onlay augmentation: Comparison of donor site morbidity and complications. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2003;5: Jakse N, Seibert FJ, Lorenzoni M, Eskici A, Pertl C. A modified technique of harvesting tibial cancellous bone and its use for sinus grafting. Clin Oral Implants Res 2001;12: Iturriaga MT, Ruiz CC. Maxillary sinus reconstruction with calvarium bone grafts and endosseous implants. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2004;62: Cricchio G, Lundgren S. Donor site morbidity in two different approaches to anterior iliac crest bone harvesting. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2003;5: Raghoebar GM, Louwerse C, Kalk WW, Vissink A. Morbidity of chin bone harvesting. Clin Oral Implants Res 2001;12: Kalk WW, Raghoebar GM, Jansma J, Boering G. Morbidity from iliac crest bone harvesting. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1996;54: Uchida Y, Goto M, Katsuki T, Akiyoshi T. A cadaveric study of maxillary sinus size as an aid in bone grafting of the maxillary sinus floor. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1998;56: Uchida Y, Goto M, Katsuki T, Soejima Y. Measurement of maxillary sinus volume using computerized tomographic images. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1998;13: Peleg M, Chaushu G, Mazor Z, Ardekian L, Bakoon M. Radiological findings of the post-sinus lift maxillary sinus: A computerized tomography follow-up. J Periodontol 1999;70: Cavalcanti MG, Ruprecht A, Vannier MW. 3-D volume rendering using multislice CT for dental implants. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 2002;31: Nakagawa Y, Kobayashi K, Ishii H, et al. Preoperative application of limited cone beam computerized tomography as an assessment tool before minor oral surgery. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2002;31: Gungormus M,Yavuz MS.The ascending ramus of the mandible as a donor site in maxillofacial bone grafting. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2002;60: Montazem A, Valauri DV, St-Hilaire H, Buchbinder D.The mandibular symphysis as a donor site in maxillofacial bone grafting: A quantitative anatomic study. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2000;58: Park HD, Min CK, Kwak HH,Youn KH, Choi SH, Kim HJ.Topography of the outer mandibular symphyseal region with reference to the autogenous bone graft. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2004;33: Bedrossian E,Tawfilis A, Alijanian A.Veneer grafting: A technique for augmentation of the resorbed alveolus prior to implant placement. A clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2000;15: Hatano N, Shimizu Y, Ooya K. A clinical long-term radiographic evaluation of graft height changes after maxillary sinus floor augmentation with a 2:1 autogenous bone/xenograft mixture and simultaneous placement of dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 2004;15: Shlomi B, Horowitz I, Kahn A, Dobriyan A, Chaushu G.The effect of sinus membrane perforation and repair with Lambone on the outcome of maxillary sinus floor augmentation: A radiographic assessment. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2004;19: Tepper G, Haas R, Zechner W, Krach W, Watzek G.Three-dimensional finite element analysis of implant stability in the atrophic posterior maxilla: A mathematical study of the sinus floor augmentation. Clin Oral Implants Res 2002;13: The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 913
8 914 Volume 21, Number 6, 2006
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting
 44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
44 The Application of Cone Beam CT Image Analysis for the Mandibular Ramus Bone Harvesting LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Lee, Jang-yeol, Youn, Pil-sang, Kim, Hyoun-chull, Lee Sang-chull Ⅰ. Introduction
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Intramembranous autogenous bone graft is the gold
 CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
CASE LETTER CBCT Morphologic Analysis of Edentulous Posterior Mandible for Mandibular Body Bone Graft Jae-Min Song, DDS, MSD, PhD 1 Jae-Yeol Lee, DDS, MSD, PhD 1,2 Yong-Deok Kim, DDS, MSD, PhD 2,3 * INTRODUCTION
Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane
 10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
10.5005/JP-Journals-10012-1077 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Correlation between Gingival Phenotype, Residual Ridge Height and the Schneiderian Membrane BC Deepthi, Shilpa Shetty, CL Satish Babu, P Rohit, DM Mallikarjuna,
The placement of endosseous implants may be difficult
 Measurement of Maxillary Sinus Volume Using Computerized Tomographic Images Yuki Uchida, DDS, PhD*/Masaaki Goto, DDS, PhD**/ Takeshi Katsuki, DDS, PhD***/Yoshikazu Soejima, DDS, PhD**** This study measured
Measurement of Maxillary Sinus Volume Using Computerized Tomographic Images Yuki Uchida, DDS, PhD*/Masaaki Goto, DDS, PhD**/ Takeshi Katsuki, DDS, PhD***/Yoshikazu Soejima, DDS, PhD**** This study measured
A Radiographic Analysis of Anatomical Variation at The Mandibular Sites of Intraoral Bone Harvesting
 A Radiographic Analysis of Anatomical Variation at The Mandibular Sites of Intraoral Bone Harvesting CBCT risk assessment in mandibular grafting Key Words: Donor site, CBCT, Mandible, Implant bone, Grafting
A Radiographic Analysis of Anatomical Variation at The Mandibular Sites of Intraoral Bone Harvesting CBCT risk assessment in mandibular grafting Key Words: Donor site, CBCT, Mandible, Implant bone, Grafting
FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION
 original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
original articles FIVE-YEAR FOLLOW-UP OF IMPLANTS PLACED SIMULTANEOUSLY WITH INFERIOR ALVEOLAR NERVE LATERALISATION OR TRANSPOSITION Stefan Peev 1, Borislav Ivanov 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Tihomir Georgiev
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
Prevalence and management of Schneiderian membrane perforations during sinus-lift procedures
 Federico Hernández-Alfaro Marta Marín Torradeflot Carlos Marti Prevalence and management of Schneiderian membrane perforations during sinus-lift procedures Authors affiliations: Federico Hernández-Alfaro,
Federico Hernández-Alfaro Marta Marín Torradeflot Carlos Marti Prevalence and management of Schneiderian membrane perforations during sinus-lift procedures Authors affiliations: Federico Hernández-Alfaro,
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
The potential of the horizontal ramus of the mandible as a donor site for block and. particular grafts in pre-implant surgery
 Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009; 38: 1173 1178 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.07.006, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Pre-implant Surgery The potential of the horizontal ramus
Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2009; 38: 1173 1178 doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.07.006, available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com Clinical Paper Pre-implant Surgery The potential of the horizontal ramus
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3.
 DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT. simultaneous implant placement and is an alternative Summer s osteotome both clinical use as well as the
 BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
BONE SPREADING TECHNIQUE A CASE REPORT AUTHORS: Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD*, João Carlos Paixão** ABSTRACT: Bone spreading technique (BST) is horizontal augmentation with minimal trauma for simultaneous
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
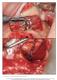 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
Nasal floor elevation combined with dental implant placement
 1 Nasal floor elevation combined with dental implant placement Ziv Mazor, DMD * Adi Lorean, DMD ** Eitan Mijiritsky Liran Levin, DMD * Private Practice, Ra anana, Israel ** Private Practice, Tiberius,
1 Nasal floor elevation combined with dental implant placement Ziv Mazor, DMD * Adi Lorean, DMD ** Eitan Mijiritsky Liran Levin, DMD * Private Practice, Ra anana, Israel ** Private Practice, Tiberius,
Posterior mandible and vertical augmentation
 CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Long-term success for osteointegrated
 CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
CASE REPORT Symphyseal Bone Cylinders Tapping With the Dental Implant Into Insufficiency Bone Situated Esthetic Area at One-Stage Surgery: A Case Report and the Description of the New Technique Umut Tekin,
A Review of Survival Rates for Implants Placed in Grafted Maxillary Sinuses Using Meta-analysis
 A Review of Survival Rates for Implants Placed in Grafted Maxillary Sinuses Using Meta-analysis Darryl C. Tong, BDS*/Kim Rioux**/Mark Drangsholt, DDS, MPH***/ O. Ross Beirne, DMD, PhD**** A variety of
A Review of Survival Rates for Implants Placed in Grafted Maxillary Sinuses Using Meta-analysis Darryl C. Tong, BDS*/Kim Rioux**/Mark Drangsholt, DDS, MPH***/ O. Ross Beirne, DMD, PhD**** A variety of
Effects of Maxillary Sinus Graft on the Survival of Endosseous Implants: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 8-2008 Effects of Maxillary Sinus Graft on the Survival of Endosseous Implants: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 8-2008 Effects of Maxillary Sinus Graft on the Survival of Endosseous Implants: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re. Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T
 Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.6.274 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation Wang Peng, Il-Kyu Kim, Hyun-Young Cho, Sang-Pill
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.6.274 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation Wang Peng, Il-Kyu Kim, Hyun-Young Cho, Sang-Pill
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2013) Vol. 52, Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2013) Vol. 52, Page 544 554 Role of Multislice Dental CT in Assessment of Dental Implants Safa A Elaty *, Ahmed M Monib *, Yasser A Mohamed *,Ahmed F Abd
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2013) Vol. 52, Page 544 554 Role of Multislice Dental CT in Assessment of Dental Implants Safa A Elaty *, Ahmed M Monib *, Yasser A Mohamed *,Ahmed F Abd
Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla
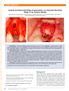 CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
CASE REPORT Vertical and Horizontal Ridge Augmentation of a Severely Resorbed Ridge in the Anterior Maxilla Alberto Monje,* Florencio Monje, Fernando Suarez,* Raúl González-García, Laura Villanueva-Alcojol,
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig
 Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Dec 19, 2016 Monday Morning Pearls of Practice by Bobby Baig baig@buildyoursmile.com Prosthodontic Associates 2300 Yonge St, suite 905 Toronto, M4P1E4 www.buildyoursmile.com CBCT and Implant Dentistry:
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Osseointegrated implants are a very reliable means
 Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
Computed tomography for dental implants: the influence of the gantry angle and mandibular positioning on the bone height and width
 (2005) 34, 9 15 q 2005 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Computed tomography for dental implants: the influence of the gantry angle and mandibular positioning on the
(2005) 34, 9 15 q 2005 The British Institute of Radiology http://dmfr.birjournals.org RESEARCH Computed tomography for dental implants: the influence of the gantry angle and mandibular positioning on the
Which Hard Tissue Augmentation Techniques Are the Most Successful in Furnishing Bony Support for Implant Placement?
 SECTION 2 Which Hard Tissue Augmentation Techniques Are the Most Successful in Furnishing Bony Support for Implant Placement? Tara L. Aghaloo, DDS, MD 1 /Peter K. Moy, DMD 2 Purpose: A variety of techniques
SECTION 2 Which Hard Tissue Augmentation Techniques Are the Most Successful in Furnishing Bony Support for Implant Placement? Tara L. Aghaloo, DDS, MD 1 /Peter K. Moy, DMD 2 Purpose: A variety of techniques
Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary. Zanco J. Med. Sci., Vol. 16, No. (2), 2012
 Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary sinus to the alveolar bone crest, using digital panoramic imaging system, in Erbil city Received: 10/2/2011 Accepted: 13/9/2011 Sarkawt H. Ali* Saeed
Evaluation of proximity of the floor of the maxillary sinus to the alveolar bone crest, using digital panoramic imaging system, in Erbil city Received: 10/2/2011 Accepted: 13/9/2011 Sarkawt H. Ali* Saeed
Endosseous Implants and Bone Augmentation in the Partially Dentate Maxilla: An Analysis of 17 Patients with a Follow-up of 29 to 101 Months
 Endosseous Implants and Bone Augmentation in the Partially Dentate Maxilla: An Analysis of 17 Patients with a Follow-up of 29 to 101 Months Jonas P. Becktor, DDS, PhD 1 / Sten Isaksson, MD, DDS, PhD 2
Endosseous Implants and Bone Augmentation in the Partially Dentate Maxilla: An Analysis of 17 Patients with a Follow-up of 29 to 101 Months Jonas P. Becktor, DDS, PhD 1 / Sten Isaksson, MD, DDS, PhD 2
Effectively restoring a grossly atrophic maxilla
 Augmentation Grafting of the Maxillary Sinus and Simultaneous Implant Placement in Patients with 3 to 5 mm of Residual Alveolar Bone Height Michael Peleg, DMD*/Ziv Mazor, DMD**/Arun K. Garg, DMD*** This
Augmentation Grafting of the Maxillary Sinus and Simultaneous Implant Placement in Patients with 3 to 5 mm of Residual Alveolar Bone Height Michael Peleg, DMD*/Ziv Mazor, DMD**/Arun K. Garg, DMD*** This
Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years
 Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Jonas P. Becktor, DDS, PhD,* Hadar Hallström, LDS, Sten Isaksson, MD, DDS, PhD, and Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66:780-786, 2008 The Use of Particulate Bone Grafts From the Mandible for Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation Before Placement of Surface-Modified Implants: Results From Bone Grafting
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66:780-786, 2008 The Use of Particulate Bone Grafts From the Mandible for Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation Before Placement of Surface-Modified Implants: Results From Bone Grafting
Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation
 42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
42 Distribution of the maxillary artery related to sinus graft surgery for implantation LvingWell Dental Hospital LivingWell Institute of Dental Research Jang-yeol Lee, Hyoun-chull Kim, Il-hae Park, Sang-chull
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants
 Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry
 Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Group 1 and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Contemporary Surgical and Radiographic Techniques in Implant Dentistry Michael M. Bornstein, PD Dr Med Dent 1 /Bilal Al-Nawas, Prof Dr Med, Dr Med
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
International Journal of Implant Dentistry. Takahiro Kaneko *, Satoshi Nakamura, Shunsuke Hino, Norio Horie and Tetsuo Shimoyama
 Kaneko et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2016) 2:16 DOI 10.1186/s40729-016-0049-z International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Open Access Continuous intra-sinus bone regeneration
Kaneko et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2016) 2:16 DOI 10.1186/s40729-016-0049-z International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Open Access Continuous intra-sinus bone regeneration
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Intraoral and extraoral autologous bone block graft techniques: A review of the recent literature
 International Journal of Contemporary Dental and Medical Reviews (2016), Article ID 030316, 5 Pages REVIEW ARTICLE Intraoral and extraoral autologous bone block graft techniques: A review of the recent
International Journal of Contemporary Dental and Medical Reviews (2016), Article ID 030316, 5 Pages REVIEW ARTICLE Intraoral and extraoral autologous bone block graft techniques: A review of the recent
Reconstruction and rehabilitation
 CLINICAL Minimally Invasive Subnasal Elevation and Antral Membrane Balloon Elevation Along With Bone Augmentation and Implants Placement Efraim Kfir, DMD 1 Vered Kfir, DMD 2 Moshe Goldstein, DMD 3 Ziv
CLINICAL Minimally Invasive Subnasal Elevation and Antral Membrane Balloon Elevation Along With Bone Augmentation and Implants Placement Efraim Kfir, DMD 1 Vered Kfir, DMD 2 Moshe Goldstein, DMD 3 Ziv
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic. Review
 Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Vertical Bone Augmentation for Implant Placement in the Mandible a Systematic Review A dissertation submitted to the University of Manchester for the degree of Master of Science in Dentistry (Oral and
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft
 Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft & Puros Block Allograft Puros Cancellous Particulate Allograft The Natural Choice For Healthy 1 Bone Growth. 1. Proven, Predictable Regeneration Acts as an osteoconductive
Dental implants offer a predictable treatment
 Histologic evaluation of a 12-year-old threaded hydroxyapatite-coated implant placed in conjunction with subantral augmentation procedure: A clinical report Periklis Proussaefs, DDS, MS, a Henry-Savajol
Histologic evaluation of a 12-year-old threaded hydroxyapatite-coated implant placed in conjunction with subantral augmentation procedure: A clinical report Periklis Proussaefs, DDS, MS, a Henry-Savajol
The use of endosseous implants is currently a routine
 Evaluation of 31 Zygomatic Implants and 74 Regular Dental Implants Used in 16 Patients for Prosthetic Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Cross-Arch Fixed Bridges Jonas P. Becktor, DDS;* Sten Isaksson,
Evaluation of 31 Zygomatic Implants and 74 Regular Dental Implants Used in 16 Patients for Prosthetic Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Cross-Arch Fixed Bridges Jonas P. Becktor, DDS;* Sten Isaksson,
In 1977, Lew1 developed a passive
 CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
CLINICAL AN OVERVIEW OF THE LEW ATTACHMENT: CLINICAL REPORTS Jack Piermatti, DMD Sheldon Winkler, DDS KEY WORDS Lew attachment Atrophic mandible Subperiosteal implant Root form implant Although the Lew
PLACEMENT OF DENTAL IMPANT IN POSTERIOR MAXILLARY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRAFT: A CASE REPORT
 CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
CSE REPORT PLCEMENT OF DENTL IMPNT IN POSTERIOR MXILLRY RIDGE USING INDIRECT SINUS LIFT TECHNIQUE WITHOUT GRFT: CSE REPORT S.P.S Sooch 1, Puja 2, Seema ggarwal 3 (e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599 (p) ISSN Print:
Benefits of CBCT in Implant Planning
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1032 CLINICAL SCIENCE 1 Gregori M Kurtzman, 2 Douglas F Dompkowski 1 Private General Practice in Silver Spring, Maryland, USA 2 Private Periodontal Practice in Bethesda, Maryland,
/TLv/ A classification of the edentulous jaws. Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery. iiiii!iii!iii! ] BASAL
![/TLv/ A classification of the edentulous jaws. Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery. iiiii!iii!iii! ] BASAL /TLv/ A classification of the edentulous jaws. Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery. iiiii!iii!iii! ] BASAL](/thumbs/72/66558540.jpg) Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery A classification of the edentulous jaws J. I. awood ~ and R. A. Howell 2 ~Maxillofacial Unit, Royal Infirmary, hester, UK, 2Liverpool Dental Hospital, Liverpool, UK J. L awood
Trauma; Preprosthetic Surgery A classification of the edentulous jaws J. I. awood ~ and R. A. Howell 2 ~Maxillofacial Unit, Royal Infirmary, hester, UK, 2Liverpool Dental Hospital, Liverpool, UK J. L awood
In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla,
 Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S.
 THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
THE USE OF TEMPORARY ANCHORAGE DEVICES FOR MOLAR INTRUSION & TREATMENT OF ANTERIOR OPEN BITE By Eduardo Nicolaievsky D.D.S. Skeletal anchorage, the concept of using the facial skeleton to control tooth
Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa Region in Patients requiring Dental Implants A Cone Beam Computed Tomography Study
 Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa via 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2427 Cone Beam Computed Tomography ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa Region
Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa via 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-2427 Cone Beam Computed Tomography ORIGINAL ARTICLE Assessment of Lingual Concavities in Submandibular Fossa Region
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2012; 42 : 219-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5624/isd.2012.42.4.219 Assessment of the relationship between the maxillary molars and adjacent structures using cone beam computed tomography
Abstract. Introduction. Case Report
 Chettinad Health City Medical Journal Case Report Ridge using Titanium Mesh, PRF and Autogenous Bone Graft with Implant Placement Dr.Vinayak S Gowda*, Dr.B.Meena Priya** *Professor, Department of Periodontics,
Chettinad Health City Medical Journal Case Report Ridge using Titanium Mesh, PRF and Autogenous Bone Graft with Implant Placement Dr.Vinayak S Gowda*, Dr.B.Meena Priya** *Professor, Department of Periodontics,
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE
 INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE Joint Degree Master Program: Implantology and Dental Surgery (M.Sc.) Specialized Modules: List of individual modules Specialized Module 1 Basic principles of implantology
Comprehensive Dental Implantology
 Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
Comprehensive Dental Implantology Surgical Course Presented by: Dr Chan Siew Luen BDS (Singapore) MDS Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery (HK) FAMS (Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery) CPE TBC 3 Modules covering topics
complications (Zitzmann and Schaerer,
 Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Bone grafts are widely used in the reconstruction of
 RESEARCH Cone Beam Computerized Tomography Measurement of Alveolar Ridge at Posterior Mandible for Implant Graft Estimation Wenjian Zhang, DDS, MS, PhD 1 * Justin Tullis, BS 2 Robin Weltman, DDS, MS 3
RESEARCH Cone Beam Computerized Tomography Measurement of Alveolar Ridge at Posterior Mandible for Implant Graft Estimation Wenjian Zhang, DDS, MS, PhD 1 * Justin Tullis, BS 2 Robin Weltman, DDS, MS 3
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review of Anatomy and Lateral Sinus Lift Technique
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. 2016), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. 2016), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review
CASE REPORT. CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration
 Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Computer Aided Implantology Academy Newsletter - Newsletter 20 - July 2009 CASE REPORT CBCT-Assisted Treatment of the Failing Long Span Bridge with Staged and Immediate Load Implant Restoration Case Report
Prevalence, Height, and Location of Antral Septa in Iranian Patients Undergoing Maxillary Sinus Lift
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Prevalence, Height, and Location of Antral Septa in Iranian Patients Undergoing Maxillary Sinus Lift Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 Amir Reza Babaloo
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Research Article Prevalence, Height, and Location of Antral Septa in Iranian Patients Undergoing Maxillary Sinus Lift Masoumeh Faramarzie 1 Amir Reza Babaloo
Moderately to severely resorbed edentulous
 The Zygomatic Implant: Preliminary Data on Treatment of Severely Resorbed Maxillae. A Clinical Report Edmond Bedrossian, DDS, FACD, FACOMS 1 /Lambert Stumpel III, DDS 2 / Michael Beckely, DDS 3 /Thomas
The Zygomatic Implant: Preliminary Data on Treatment of Severely Resorbed Maxillae. A Clinical Report Edmond Bedrossian, DDS, FACD, FACOMS 1 /Lambert Stumpel III, DDS 2 / Michael Beckely, DDS 3 /Thomas
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 1. Implant Locations. Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla. Anatomy and risk factors Option 1: Short implants
 T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
One in four sinus lift procedures can be
 11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
Placement of Posterior Mandibular and Maxillary Implants in Patients with Severe Bone Deficiency: A Clinical Report of Procedure
 Placement of Posterior Mandibular and Maxillary Implants in Patients with Severe Bone Deficiency: A Clinical Report of Procedure Leonard Krekmanov, DDS, PhD 1 The purpose of this investigation was to modify
Placement of Posterior Mandibular and Maxillary Implants in Patients with Severe Bone Deficiency: A Clinical Report of Procedure Leonard Krekmanov, DDS, PhD 1 The purpose of this investigation was to modify
Comparison of implant survival with implants placed in acceptable and compromised bone: a literature review
 J Maxillofac Oral Surg 8(1):1 7 COMPARATIVE STUDY Comparison of implant survival with implants placed in acceptable and compromised bone: a literature review Stefan Ihde 1 Sigmar Kopp 2 Thomas Maier 3
J Maxillofac Oral Surg 8(1):1 7 COMPARATIVE STUDY Comparison of implant survival with implants placed in acceptable and compromised bone: a literature review Stefan Ihde 1 Sigmar Kopp 2 Thomas Maier 3
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
BONE SPREADER TECHNIQUE: APRELIMINARY 3-YEAR STUDY Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, MSc, PhD; Francisley Avila Souza, DDS, MSc
 RESEARCH BONE SPREADER TECHNIQUE: APRELIMINARY 3-YEAR STUDY Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, MSc, PhD; Francisley Avila Souza, DDS, MSc The purpose of this study was to observe the clinical outcome of bone
RESEARCH BONE SPREADER TECHNIQUE: APRELIMINARY 3-YEAR STUDY Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, MSc, PhD; Francisley Avila Souza, DDS, MSc The purpose of this study was to observe the clinical outcome of bone
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting.
 Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting. Samuel Lee, DDS*, Grace Kang-Lee, DDS, Kwang-Bum Park, DDS, MS, PhD, Thomas Han, DDS, MS Abstract
Crestal Window Sinus Lift, minimally invasive, predictable, and systematic approach to sinus grafting. Samuel Lee, DDS*, Grace Kang-Lee, DDS, Kwang-Bum Park, DDS, MS, PhD, Thomas Han, DDS, MS Abstract
Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant Planning: A Clinical Study
 JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
JCDP Original Research Reliability of OPG and CBCT 10.5005/jp-journals-00000-0000 in Presurgical Implant Planning Reliability of Orthopantomography and Cone-beam Computed Tomography in Presurgical Implant
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
ISSN: 2395-6429 International Journal of Current Medical and Pharmaceutical Research Available Online at http://www.journalcmpr.com DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24327/23956429.ijcmpr20170169 RESEARCH ARTICLE
MASTERS SERIES 2010 ACCELERATED IMPLANT DENTISTRY EDUCATION. San Francisco April-September Miami March-August CREDIT HOURS
 MASTERS SERIES 2010 Level II Implant Continuum Advanced Continuum Miami March-August 2010 San Francisco April-September 2010 ACCELERATED IMPLANT DENTISTRY EDUCATION 120 CREDIT HOURS Arun K. Garg, D.M.D.
MASTERS SERIES 2010 Level II Implant Continuum Advanced Continuum Miami March-August 2010 San Francisco April-September 2010 ACCELERATED IMPLANT DENTISTRY EDUCATION 120 CREDIT HOURS Arun K. Garg, D.M.D.
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
A rare crestal branch of inferior alveolar nerve: case report 1 Mahdi Niknami 1 Reza Es haghi * 2 Hamed Mortazavi 3 Hadi Hamidi
 Journal Dental School 2012; 30(2):132-135 Case Report A rare crestal branch of inferior alveolar nerve: case report 1 Mahdi Niknami 1 Reza Es haghi * 2 Hamed Mortazavi 3 Hadi Hamidi 1 Assistant Professor,
Journal Dental School 2012; 30(2):132-135 Case Report A rare crestal branch of inferior alveolar nerve: case report 1 Mahdi Niknami 1 Reza Es haghi * 2 Hamed Mortazavi 3 Hadi Hamidi 1 Assistant Professor,
Measurements of the mandibular canal by multidetector computed tomography
 Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2012 - Volume 11, Number 2 Measurements of the mandibular canal by multidetector computed tomography Frederico Sampaio Neves 1, Daniel Fernandes Tourinho 2,
Original Article Braz J Oral Sci. April June 2012 - Volume 11, Number 2 Measurements of the mandibular canal by multidetector computed tomography Frederico Sampaio Neves 1, Daniel Fernandes Tourinho 2,
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Hands-on Cadaver Intensive Course in Advanced Implant Surgery: Hard and Soft Tissue Management
 Implant Surgery: Hard and Soft Tissue Management 2017-2018 Presentation of the course There is a high demand for specialized training in the field of advanced implantology. The opportunity to perform complex
Implant Surgery: Hard and Soft Tissue Management 2017-2018 Presentation of the course There is a high demand for specialized training in the field of advanced implantology. The opportunity to perform complex
CT Scan Technology. An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D.
 CT Scan Technology An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D. GANZ, DMD / USA Abstract Implant dentistry, one of the most predictable
CT Scan Technology An Evolving Tool for Avoiding Complications and Achieving Predictable Implant Placement and Restoration SCOTT D. GANZ, DMD / USA Abstract Implant dentistry, one of the most predictable
A Prospective Randomized Study of 1- and 2-Stage Sinus Inlay Bone Grafts: 1-Year Follow-up
 A Prospective Randomized Study of 1- and 2-Stage Sinus Inlay Bone Grafts: 1-Year Follow-up Karin Wannfors, DDS, PhD 1 /Björn Johansson, DDS 2 /Mats Hallman, DDS 3 /Tomas Strandkvist, DDS 3 The purpose
A Prospective Randomized Study of 1- and 2-Stage Sinus Inlay Bone Grafts: 1-Year Follow-up Karin Wannfors, DDS, PhD 1 /Björn Johansson, DDS 2 /Mats Hallman, DDS 3 /Tomas Strandkvist, DDS 3 The purpose
