The Influence of Cervical Cavity Shape on the Restoration Material Retention A finite element method study
|
|
|
- Blake Holland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Influence of Cervical Cavity Shape on the Restoration Material Retention A finite element method study ANAMARIA FLORESCU, STEFAN MANEA, VIOLETA HANCU, ROXANA MANU*, CORNELIA FLORENTINA BICLESANU Titu Maiorescu University of Bucharest, Faculty of Dentistry, Department of Dental Specialities, 67A, Gheorghe Petrascu Str, , Bucharest, Romania Present study examines, by means of finite element method, the influence of cervical cavity shape on tensions distribution caused by occlusal overload of the teeth with abfraction lesion. Same force values are applied to four 3-D lower premolar finite element models, representing four different cavity shapes. An extracted lower premolar which presented an abfraction lesion has been used. The restoration was achieved by using ER adhesive systems and Giomers. The premolar was scanned and the resulting sections were processed and converted into a 3D digital format. Thus, a model of finite elements which presented a restored wedge-shaped cavity in the cervical dental area was obtained. Then, by modifying the shape and dimensions, there were created another 3 modified-shape cavities. Forces of different magnitudes (45-150N), exerted at a 45 degree angle on buccal cusp, have been applied. A wedge-shaped cavity with a short occlusal side does not show tension in the cervical region, nor in the distal angle of the restoration up to a force of 100N. So, in order to increase the retention of the abfraction restoration, changing the shape of the cavity could be the treatment of choice. Clinical relevance In order to avoid costly and unethical research, by means of FEM, different shapes of cervical cavities were easily created and conditions that influence retention of abfraction restoration were tested. Keywords: cavity shape, noncarious cervical lesions (NCCL), abfraction, finite element method (FEM) The restoration of non-carious cervical lesions (NCCL) is a difficult one because of many factors, including sclerotic dentin, the occlusal overstress, the small thickness, or lack, of enamel at the cervical level, incorrect tooth-brushing techniques, nutritional habits, restorative materials properties, etc. From a clinical point of view, the predominant NCCL forms are the V-shaped lesions or the wedge-shaped ones, characteristic of the abfractions or abrasions, as well as the concave, rounded/dish-like lesions which are characteristic of dental erosions [1-4]. The tensions resulting from occlusal overstress are distributed to the enamel, dentin and the restoration material (the composite resin, adhesive system) [5].This concentration of tensions at the cement-enamel junction (CEJ) [6] is responsible not only for the development of wedge-shape cervical lesions (abfraction), but also for the loss of restorations. When restorative treatment is needed, it is not advisable to transform a wedge-shaped lesion into a concave lesion, with the aim to increase retention. Although this is clinically doable, a lot of healthy dental tissue would be sacrificed, and thus be in contradiction to the principles of the minimum invasive therapy. Since the shape of the cavity may be a factor that would influence the restoration retention, modifying the abovementioned shape might favour long-term restoration retention. According to P. Magne [7], performing research on patients may prove both costly and unethical, and, in order to avoid it, virtual models, as well as simulations, have gained their ever larger presence in live experiments or clinical trials. The aim of the study is to compare, by means of the finite element method (FEM), the most comprehensive in vitro investigation method in restorative dentistry that allows for realistic simulations [8, 9],the levels of tension generated under the action of the same force values which are applied to four 3-D lower premolar finite element models, representing four different cavity shapes, as well as to simulate the conditions that might lead to the increase in the retention of the cervical restoration by sacrificing the least dental tissue. Finite element method comprises analyzing stress, deformation and propagation of the fracture line in a structure. When a force is applied to a structure, deformation and stress arise, and if stresses are excessive and go beyond the elastic limit, can cause fractures in the materials [10]. Analysis by FEM is particularly useful in detecting risk areas, giving us the possibility to study the distribution of stresses and strains of a mechanically loaded structure [11]. Experimental part For the study, a lower premolar extracted for periodontal reasons was used; it presented an abfraction with a smooth, hard, shiny surface, without any carious process. The premolar was kept in physiological serum for 24 hours, then in T chloramine until the time of the experiment. The tooth was cleaned with a rubber cup and abrasive paste (Clean Polish, Kerr). A superficial dentin layer was removed and the edges were smoothed by means of a round burs (RA 1, Dia Tessin) on low speed. Restoration was achieved using etch and rinse (ER) 3- step adhesive systems (Gluma Solid Bond, Heraeus Kulzer) and Giomers (Beautifil low flow FO2 and Beautifil II, Shofu Dental Corporation), whose compositions are shown in table 1 [12, 13]. * roxanamanu2012@yahoo.com; Phone
2 Table 1 MATERIAL COMPOSITION Table 2 REQUIRED CONSTANT DATA The premolar was scanned by means of the Micro CT, while the resulting 0.5mm-wide longitudinal and transversal sections were processed by means the DICOM software. The scanned images were converted into a 3D digital format by means of the MIMICS software and processed in Abaqus /CAE in order to be analysed through the finite element method. Thus, a model of finite elements which presented a restored wedge-shaped cavity in the cervical dental region (model 1) was obtained, while the necessary data was taken from available literature [12-16] (table 2). On this finite elements model, by modifying the shape and dimensions, as shown in figure 1, there were created another 3 modified-shape cavities. A wedge-shaped cavity with a very rounded axial angle was created on the second model. On the 3 rd and 4 th models, wedge-shaped cavities with unequal sides were made, with the cervical side longer than the occlusal side on the 3 rd model, thus making an degree angle with the long dental axis; at the same time, on the 4 th model, the cervical side was shorter than the occlusal one and perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth. In the end, the 4 premolar finite elements models with 4 different types of cavities are presented (fig. 1). In the case of a functional occlusion, there is a vertical stress on the lateral side of the arch; the average occlusal force is 100N, but it may vary between 70 and 150N [17]. At the same time, this force may vary according to the exact position of the tooth in the arch, the gender of the patient, the type of tooth (the force has a low value with the incisors and a maximum with the first molar) [18]. Occlusal forces generated during oral functions, nonfunction and premature contacts give rise to significant tensile stresses in the cervical enamel [14]. In order to simulate the most dangerous effects on a restored tooth, forces of different magnitudes were exerted on these models at a 45 degree angle and applied mainly MATERIALE PLASTICE 54 No
3 Fig. 1 Shapes and dimensions of cavities Fig. 2 The appearance of the first enamel fissure at a 45N force to the premolar buccal cusp. The values of the forces applied were: 45N, 60N, 90N, 105N, 120N, 150N. The tested forces, within functional occlusion, do not produce dental modifications, but, when applied at 45 degree angle, they create non-functional conditions, permitting an actual simulation of overstrain. Results and discussions When a 45 N force is tested, the first enamel fissure, located in the distal angle of lesions, may appear on models 1, 2 and 4. Tension levels are different depending on the shape of the cavity, high tension levels being observed on these models. On the 3 rd model, the same force generates tensions located in an area under the lesions distal angle, towards the cervical region of the tooth (fig.2). The fissure development and the increases of tensions can be observed as a result of increasing the force to 60 N. In all models, fissures have the tendency to evolve towards the cervical area (fig. 3). Fig.4 Tension distribution in distal angles of restorations for the models at 90 N At 90 N force, distal and mesial angles of restorations belonging to models 1, 2 and 4 showed very low and low tension levels, while the 3rd model presented the lowest tension in the distal angles of restorations and increased tension level in the mesial angle of the restorations. These differences are probably due to the asymmetry of the tooth and to the differences between giomer s and dentin s composition and properties. Also, an accumulation of tensions can be observed on the cervical side of models 1, 2, and 4 as well; they affect both the tooth and the restoration. With this value of the force, the cervical tensions affect only the tooth, and not the restoration in the case of model 3 (fig. 4). By increasing the force to 100N, highest level of tension concentrated in the cervical region of the restorations is observed for model 4and the lowest level for model 3. Models 1 and 2 show similar tension levels (fig. 5). Fig. 5 Models with tension distribution at distal angles at 100N Fig. 3 Evolution of the crack on the enamel towards the gingival area at 60N 113
4 Fig.6 Tension distribution for models at 150N (distal angle of the restoration) Fig. 7 Tension pressure distribution for models at 150N (mesial angle of the restoration) At 150 N, the observed tensions maintain the same pattern in all 4 models (fig. 6); high tension levels have been observed in the cervical region of models 1, 2 and 4, except for model 3, who showed the highest tension concentration in its restoration mesial angle (fig. 7). The aim of the study was to compare, by means of the finite element method (FEM), the levels of tension generated under the action of the same force values which are applied to four 3-D lower premolar finite element models, representing four different cavity shapes, as well as to simulate the conditions that might lead to the increase in the retention of the cervical restoration by sacrificing the least dental tissue. For models with wedge-shaped cavity (model 1), rounded wedge tip (model 2) and the wedge with a shorter cervical side (model 4), at a 45N force, a tension concentration in the distal angle of the restoration and the appearance of the first fissures in the enamel are observed. At a higher force of 60N, the evolution of the fissure towards the cervical margin of the restoration is observed. For the same models, at 90N, due to the difference in tension between dentin and Giomer, lower tension levels are observed in distal angles of the restoration; likewise, mild tension in the cervical region appears. At 100N, the highest tension concentration is recorded if there is a wedge-shaped cavity with a short cervical side (model 4) and the lowest tension concentration appears in wedge-shaped cavity with a short occlusal side (model 3). For wedge-shaped cavities with a short occlusal side (model 3), there is a tension concentration on the mesial angle of the restoration only at 90N, the level is greater than those of other models. Otherwise, the wedge-shaped cavity with a short occlusal side does not show tension in the cervical region, nor in the distal angle of the restoration up to a force of 100N. At 120N, the restorations exceed the permitted adhesive tension and therefore may detach. Presence of high stress concentration in the mesio-axial and disto-axial proximities of Class V lesion was also reported by Shubhashini [19] when tensile load was applied on that tooth. The stress concentration is in the immediate vicinity of the restored area and was also found to be inversely proportional to the Young s modulus value of the restorative material used [19]. Although the dish-like cavity shows a much more favourable retention for NCCL restorations than wedgeshaped cavities do, as shown by E. Eliguzeloglu [20], the transformation of a wedge-shaped lesion into a rounded lesion requires a great sacrifice of healthy tooth tissue, which is often not accepted by the patient, and also contradicts the principles of minimal invasive therapy. Turning a wedge-shaped cavity into a wedge-shaped cavity with a shorter occlusal wall (a minimally invasive manoeuvre in comparison with creating a rounded shaped cavity), and restoration with Giomers could be measures taken in order to increase the dental abfraction restoration retention. Conclusions Changing the shape of the cervical cavity through minimally invasive treatments along with Giomer direct adhesive restoration could be the best choice of noncarious lesions treatment with long term results. Acknowledgement Authors want to acknowledge the support of Stefan Cristian Castravete, General Manager, CAELYNX Europe. References 1.ADDY, M., EMBERY, G., EDGAR, M., ORCHARDSON, R., Tooth Wear and Sensitivity- Clinical advances in restorative dentistry, 1 st. edition, Ed. Martin Dunitz Ltd., Martin Dunitz Publishers, London ; 2000, p.3-76, p GRIPPO, J., J Am Dent Assoc., 135, no. 10, 2004, p.1376; 3.BARTLETT, D., SHAH, P. A., J Dent Res., 85, 2006, p.306; 4.LUSSI, A., Dental Erosion-From Diagnosis to Terapy. Monographs in Oral Science, Karger Publishers, Basel, editor GM Whitford, 20, 2006, p. 3, p.10, p. 23; 5.VAN MEERBEEK, B., BRAEM, M., LAMBRECHTS, P., VANHERLE, G., Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 70, 1993, p.308; 6.ROMEED, S.A., MALIK, R., DUNNE, S.M., Int J Dent., 30; 2012: Epub 2012 Jul 30; 7.MAGNE, P., Dent Mat., 23, nr. 5, 2007, p.539; 8.TANTBIROJN, D., VERSLUIS, A., PINTADO, M.R., DELONG, R., DOUGLAS, W.H., Dent Mater., 20, 2004, p.535; 9.VERSLUIS, A., TANTBIROJN, D., PINTADO, M.R., DELONG, R., DOUGLAS, W.H., Dent Mater., 20, 2004, p. 554; 10.COMAN, C., GHERGIC, D.L., PATROI, D.N., TARCOLEA, M., COMANEANU, R.M., BARBU, H.M., Mat. Plast.,53, no.1, 2016, p MATERIALE PLASTICE 54 No
5 11.ORMENISAN, A., TARCOLEA, M., SUCIU, M., GRIGORAS, R.I., BERESESCU, F.G., VLASCEANU, D., HANCU, V., COMANEANU, R.M., Mat. Plast., 52, no. 3, 2015, p *** 13.*** 14.ROMEED, S.A., FOK, S.L., WILSON, N.H., Journal of Oral Rehabilitation., 33, 2006, p. 209; 15.POIATE, I.A.V.P. et al., Brazilian Oral Research 23, nr.2, 2009, p.161; 16.KIM, K.-H., WOO, S.-G., SON, K., PARK, J.-K., Proceedings of the 18 th IASTED International Conference Modelling and Simulation, 2007, Montreal, Quebec, Canada; 17.MOTTA, A.B., PEREIRA, L.C., DA CUNHA, A.R.C.C., ABAQUS Users Conference, 2006, p.329; 18.FERRARIO, V. F., SFORZA, C., SERRAO, G., DELLAVIA, C., TARTAGLIA, G.M., J Oral Rehab., 31, nr.1, 2004, p.18; 19.SHUBHASHINI, N., MEENA, N., SHETTY, A., KUMARI, A., NAVEEN, D.N., J Conserv Dent., 11, no. 3, 2008, p. 121; 20.ELIGUZELOGLU, E., ERASLAN, O., OMURLU, H., ESKITASCIOGLU, G., BELLI, S., European Journal of Dentistry, 5, 2011, p. 180 Manuscript received:
Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations:
 1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
1 Lec.7 د.عبد املنعم اخلفاجي CLASS V CAVITY PREPARATION FOR AMAGLAM Indications The selection of amalgam as a restorative material for class V cavity should involve the following considerations: 1- Caries:
how to technique Issue How to improve the longevity of porcelain veneers.
 Issue 4 2013 How to improve the longevity of porcelain veneers. 1. Avoid finishing on a resin composite restoration. longer term weak spot Although tempting in the interests of minimal tooth removal, finishing
Issue 4 2013 How to improve the longevity of porcelain veneers. 1. Avoid finishing on a resin composite restoration. longer term weak spot Although tempting in the interests of minimal tooth removal, finishing
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV.
 Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Preparation and making fillings Class V., III., IV. Class V. Cervical defects - Dental caries - Non carious lesions (erosion, abrasion, V shaped defects) Types of defects Caries Erosion Abrasion V shaped
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations The outline form
 Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Lec. 3-4 Dr. Saif Alarab Clinical Technique for Class I Amalgam Restorations Class I refers to -Restorations on the occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth, - The occlusal two thirds of facial and lingual
Finite element analysis of thermal stress distribution in different restorative materials used in class V cavities
 Original Article Finite element analysis of thermal stress distribution in different restorative materials used in class V cavities MS Guler, C Guler 1, F Cakici 2, EB Cakici 2, S Sen 3 Department of Maritime
Original Article Finite element analysis of thermal stress distribution in different restorative materials used in class V cavities MS Guler, C Guler 1, F Cakici 2, EB Cakici 2, S Sen 3 Department of Maritime
Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up
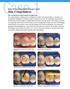 Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
Case 1 This case study focuses on the restoration of an upper molar. Filtek LS Low Shrink Posterior Restorative System Case 1: Cusp build-up The existing, inadequate restoration led to the development
2. Gap closure and replacement of the missing tooth 35 with directly modelled bridge region 34-36
 GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
GrandTEC Test Kit Dear User, This Test Kit has been put together to enable you to test GrandTEC on the model before using it in a clinical situation. GrandTEC is a resin-impregnated glass fibre strip.
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry. Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer)
 Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Part II National Board Review Operative Dentistry Module 3D General Questions Answers in BOLD (usually the first answer) Howard E. Strassler, DMD University of Maryland Dental School With special acknowledgements
Tooth Abfraction in Relationship to Occlusal Load Stresses: A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. I (Oct. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org Tooth Abfraction in Relationship to Occlusal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. I (Oct. 2017), PP 80-84 www.iosrjournals.org Tooth Abfraction in Relationship to Occlusal
OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH
 ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska,
ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 OUR EXPERIENCE WITH GRADIA DIRECT IN THE RESTORATION OF ANTERIOR TEETH Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska,
ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT
 ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska 1, R. Pirinska
ISSN: 1312-773X (Online) Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers) 2006, vol. 12, issue 2 ADHESIVE RECONSTRUCTION IN HELP OF THE ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT Snezhanka Topalova-Pirinska 1, R. Pirinska
Ceramic Based Aesthetic CAD/CAM Restorative
 Ceramic Based Aesthetic CAD/CAM Restorative Create Natural Aesthetics with High-Strength Materials SHOFU Block HC and Disk HC are the latest generation of hybrid-ceramic restorative materials for use with
Ceramic Based Aesthetic CAD/CAM Restorative Create Natural Aesthetics with High-Strength Materials SHOFU Block HC and Disk HC are the latest generation of hybrid-ceramic restorative materials for use with
CLASS II CAVITY PREPARATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL CLASS II
 CLASS II CAVITY PREPARATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL CLASS II Contact area carious lesion Proximal view Vertical section - Buccal view Class II carious lesions are diagnosed using bitewing radiographs.
CLASS II CAVITY PREPARATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AN IDEAL CLASS II Contact area carious lesion Proximal view Vertical section - Buccal view Class II carious lesions are diagnosed using bitewing radiographs.
Fuji II LC. A Perfect Choice
 A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
A Perfect Choice is a remarkable restorative material The world s first resin-reinforced glass ionomer has remained the benchmark for light cured glass ionomer cements, delivering more than 15 years of
Metal-Free Restorations PROCEDURES FOR POSTERIOR DIRECT & SEMI-DIRECT COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS D I D I E R D I E T S C H I. For.
 PROCEDURES FOR POSTERIOR DIRECT & SEMI-DIRECT COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS Metal-Free Restorations D I D I E R D I E T S C H I The Geneva Smile Center D.M.D, PhD, Privat-Docent 2, Quai Gustave Ador 1207 Geneva
PROCEDURES FOR POSTERIOR DIRECT & SEMI-DIRECT COMPOSITE RESTORATIONS Metal-Free Restorations D I D I E R D I E T S C H I The Geneva Smile Center D.M.D, PhD, Privat-Docent 2, Quai Gustave Ador 1207 Geneva
Semi-Direct Composite Restorations- A Clinical Report
 MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Semi-Direct Composite Restorations- A Clinical Report Berhanuddin Muhamad Asyraf, Tong Wah Lim Faculty of Dentistry, University Teknologi MARA, Malaysia ABSTRACT In nowadays world,
MALAYSIAN DENTAL JOURNAL Semi-Direct Composite Restorations- A Clinical Report Berhanuddin Muhamad Asyraf, Tong Wah Lim Faculty of Dentistry, University Teknologi MARA, Malaysia ABSTRACT In nowadays world,
Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth
 Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Dental Journal Mahidol Dental Journal Original Article Scanning electron microscope characterization of abrasion in human teeth B.Sc., D.D.S., Specialty Certificate in Oral Pathology, M.S. Department of
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation
 Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Prosthodontist and Instructional Designer Introduction Welcome! This module is developed to guide dental students in
Advance Dental Simulation Module on Crown Preparation Ranier M. Adarve, DMD, MS, MHPE Prosthodontist and Instructional Designer Introduction Welcome! This module is developed to guide dental students in
Performance Assessment of Various Molar Crown Designs
 2012 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology IPCBEE vol. 34 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Assessment of Various Molar Crown Designs Rashmi Uddanwadiker
2012 2nd International Conference on Biomedical Engineering and Technology IPCBEE vol. 34 (2012) (2012) IACSIT Press, Singapore Performance Assessment of Various Molar Crown Designs Rashmi Uddanwadiker
1 Use with caution in some situations.
 Issue 27 2013 How to obtain optimum results with ceramic inlays. There is now a comprehensive range of reports on the clinical performance of ceramic inlays over a period of 8 to 15+ years. This has enabled
Issue 27 2013 How to obtain optimum results with ceramic inlays. There is now a comprehensive range of reports on the clinical performance of ceramic inlays over a period of 8 to 15+ years. This has enabled
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials
 Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
Direct composite restorations for large posterior cavities extended range of applications for high-performance materials A case study by Ann-Christin Meier, Dr. med. dent., Stapelfeld, Germany When large
A new cavity classifica
 Scientific articles Australian Dental Journal 1998;43:(3):153-9 A new cavity classifica t i o n Graham J. Mount, BDS(Syd), DDSc(Adel), FRACDS* W. Rory Hume, BDS, PhD, DDSc, FRACDS Abstract With the development
Scientific articles Australian Dental Journal 1998;43:(3):153-9 A new cavity classifica t i o n Graham J. Mount, BDS(Syd), DDSc(Adel), FRACDS* W. Rory Hume, BDS, PhD, DDSc, FRACDS Abstract With the development
Hands-on Posterior Tooth Preparation. Practical Skills Courses, SWL, 25/11/2016
 Hands-on Posterior Tooth Preparation Practical Skills Courses, SWL, 25/11/2016 Hands-On Didactic Teaching A Tooth-Friendly-Approach - Hands-on Tooth Preparation Course - Dental Simulation to include: Posterior
Hands-on Posterior Tooth Preparation Practical Skills Courses, SWL, 25/11/2016 Hands-On Didactic Teaching A Tooth-Friendly-Approach - Hands-on Tooth Preparation Course - Dental Simulation to include: Posterior
TOOTH PREPARATION. (Boucher's Clinical Dental Terminology, 4th ed, p239)
 Budapest, 2017 TOOTH PREPARATION The selected form given to a natural tooth when it is reduced by instrumentation to receive a prosthesis (e.g. artificial crown or a retainer for a fixed or removable prosthesis)
Budapest, 2017 TOOTH PREPARATION The selected form given to a natural tooth when it is reduced by instrumentation to receive a prosthesis (e.g. artificial crown or a retainer for a fixed or removable prosthesis)
Key words : Non-carious cervical lesion, Stress distribution, Composite resin, Elastic modulus, Finite element analysis
 대한치과보존학회지 : Vol. 33, No. 3, 2008 The influence of combining composite resins with different elastic modulus on the stress distribution of class V restoration: A three-dimensional finite element study Jeong-Kil
대한치과보존학회지 : Vol. 33, No. 3, 2008 The influence of combining composite resins with different elastic modulus on the stress distribution of class V restoration: A three-dimensional finite element study Jeong-Kil
how to technique How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. Disadvantages. 1 Issue Full coverage crown. >>
 Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Issue 37 2013 How to treat a cracked, but still inact, cusp. 1 Full coverage crown. >> Advantages. A full crown can splint all sections of the tooth together. 1 Disadvantages. 1 Encircles crown and acts
Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location
 Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
Original paper Dental Materials Journal 21 (1): 32-43, 2002 Anisotropy of Tensile Strengths of Bovine Dentin Regarding Dentinal Tubule Orientation and Location Toshiko INOUE, Hidekazu TAKAHASHI and Fumio
For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Matrix
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Paul C Belvedere* Adjunct Professor,
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC DENTAL SCIENCE Case Report For the Perfect Class V and All Cervical Area Gingival Margins when Placing Direct Composites, Create an Injection Molding Paul C Belvedere* Adjunct Professor,
NATIONAL EXAMINING BOARD FOR DENTAL NURSES
 NATIONAL EXAMINING BOARD FOR DENTAL NURSES NATIONAL DIPLOMA EXAMINATION DENTAL CHARTING NEBDN is a limited company registered in England & Wales No. 5580200 Registered with the Charity Commisioners No.
NATIONAL EXAMINING BOARD FOR DENTAL NURSES NATIONAL DIPLOMA EXAMINATION DENTAL CHARTING NEBDN is a limited company registered in England & Wales No. 5580200 Registered with the Charity Commisioners No.
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material
 Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Continually Fluoride Releasing Aesthetic Dental Restorative Material Research is our best product Image provided by Dr. Sushil Koirala BEAUTIFIL II More than just filling BEAUTIFIL II stands out for its
Clinical use of Filtek Silorane. Low Shrink Posterior Restorative
 Clinical use of Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative In collaboration with Dr. Gabriel Krastl Department of Periodontology, Endodontics and Cariology at the University of Basel Dental Hospital
Clinical use of Filtek Silorane Low Shrink Posterior Restorative In collaboration with Dr. Gabriel Krastl Department of Periodontology, Endodontics and Cariology at the University of Basel Dental Hospital
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown. By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi
 Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
Morphology of an Anatomic Crown By: Assistant Professor Dr. Baydaa Ali Al - Rawi October 4, 2009 Elevated landmarks Depressed landmarks A) Elevated landmarks : 1. Dental lobe : is one of the primary centers
No Prep And Minimal Prep Veneers
 Ajay Juneja No Prep And Minimal Prep Veneers 12 Apr 2016 It has been now an established entity for more then two decades since No Preparation Ceramic Veneers are being used. The very ideology of preserving
Ajay Juneja No Prep And Minimal Prep Veneers 12 Apr 2016 It has been now an established entity for more then two decades since No Preparation Ceramic Veneers are being used. The very ideology of preserving
Contraindicated internal bleaching what to do?
 C L I N I C A L Contraindicated internal bleaching what to do? Maciej Zarow 1 Before the reconstruction of a root canal-treated anterior tooth, the walking bleach technique should always be considered.
C L I N I C A L Contraindicated internal bleaching what to do? Maciej Zarow 1 Before the reconstruction of a root canal-treated anterior tooth, the walking bleach technique should always be considered.
Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect
 Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2007 Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect S. JIAN*, J. TING*, T. YING &W.DONG-MEI
Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2007 Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the application of attachment for obturator framework in unilateral maxillary defect S. JIAN*, J. TING*, T. YING &W.DONG-MEI
Clinical Technique/Case Report
 Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
Operative Dentistry, 2008, 33-3, 345-349 Clinical Technique/Case Report Modified Matrix Band Design for Ultra-conservative Posterior Restorations S Deliperi Clinical Relevance The combination of minimally
أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل CROWN AND BRIDGE جامعة تكريت كلية. Lec. (2) طب االسنان
 Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Lec. (2) CROWN AND BRIDGE أ.م. هدى عباس عبد اهلل Patient selection and examination A thorough diagnosis must first be made of the patient's dental condition, considering both hard and soft tissues. this
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars
 Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
Permanent 2 nd Maxillary Molars In comparison to the first max molar First molars appears in the oral cavity at the age of 6 years old.. While 2 nd molar 3 rd molar Max. 2 nd molar have long roots (sometimes
Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice
 Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Calogero Bugea Endodontics Cracked Tooth: How to manage it in daily practice 5 Feb 2016 Tooth Fractures are not rare, surface cracks, or craze lines, are relatively common in teeth. In most of cases they
Cutting instruments. Instruments
 Instruments أﻧﺲ اﻟﻌﺒﯿﺪي. د The removal and shaping of tooth structure are essential aspects of restorative dentistry. Initially this was a difficult process accomplished entirely by the use of - Hand instruments.
Instruments أﻧﺲ اﻟﻌﺒﯿﺪي. د The removal and shaping of tooth structure are essential aspects of restorative dentistry. Initially this was a difficult process accomplished entirely by the use of - Hand instruments.
R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology
 Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(4):1395 1400 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Microscopic aspects of the hybrid layer formed by the SE 1-step Futurabond
Rom J Morphol Embryol 2014, 55(4):1395 1400 ORIGINAL PAPER R J M E Romanian Journal of Morphology & Embryology http://www.rjme.ro/ Microscopic aspects of the hybrid layer formed by the SE 1-step Futurabond
***Handout*** Adhesive Dentistry Harald O. Heymann, DDS MEd Dentin Bonding Rewetting/Desensitization
 ***Handout*** Adhesive Dentistry Harald O. Heymann, DDS MEd Dentin Bonding * Regardless of the type dentinal adhesive used, the primary mechanism for dentin adhesion is still establishment of the hybrid
***Handout*** Adhesive Dentistry Harald O. Heymann, DDS MEd Dentin Bonding * Regardless of the type dentinal adhesive used, the primary mechanism for dentin adhesion is still establishment of the hybrid
A clinical case involving severe erosion of the maxillary anterior teeth restored with direct composite resin restorations
 SETHI A clinical case involving severe erosion of the maxillary anterior teeth restored with direct composite resin restorations Sanjay Sethi, BDS (Lond.) Square Mile Dental Centre, 7-9 White Kennett Street,
SETHI A clinical case involving severe erosion of the maxillary anterior teeth restored with direct composite resin restorations Sanjay Sethi, BDS (Lond.) Square Mile Dental Centre, 7-9 White Kennett Street,
Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation
 Ajay Juneja Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation 1 Feb 2016 The rationale of having minimal preparation and having ceramic veneers cemented to enamel in order for the
Ajay Juneja Shadeguides Ceramic Veneers: Tooth Preparation for Enamel Preservation 1 Feb 2016 The rationale of having minimal preparation and having ceramic veneers cemented to enamel in order for the
Lecture. Permanent maxillary premolars
 Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
Lecture Permanent maxillary premolars Permanent premolars The maxillary premolars are four in number: two in the right and two in the left. They are posterior to the canines and anterior to the molars.
MINIMAL INTERVENTION DENTISTRY THE PENN COMPOSITE STENT
 SCD Case Study MINIMAL INTERVENTION DENTISTRY THE PENN COMPOSITE STENT The Penn Composite Stent is a treatment technique following the principles of Minimal Intervention Dentistry. What is Minimal Intervention
SCD Case Study MINIMAL INTERVENTION DENTISTRY THE PENN COMPOSITE STENT The Penn Composite Stent is a treatment technique following the principles of Minimal Intervention Dentistry. What is Minimal Intervention
Dzakovich Conclusions
 Definitions Attrition Tooth wear resulting from contact between opposing teeth. Erosion A gradual tooth-surface loss process caused by an electrolytic or chemical mechanism without bacteria being involved.
Definitions Attrition Tooth wear resulting from contact between opposing teeth. Erosion A gradual tooth-surface loss process caused by an electrolytic or chemical mechanism without bacteria being involved.
Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement
 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1035 CLINICAL ARTICLE Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate Tooth Replacement Natural Tooth Pontic using Fiber-reinforced Composite for Immediate
Results:Mean microleakage score of group G1, G2 and G3 was 2.86 ± 1.43, 1.86 ± 1.65 and 2.46 ± 1.50 respectively.
 Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class 2 Cavities Restored with A Nanohybrid Composite Using Three Different Increment Techniques-
Journal of Oral Health & Community Dentistry original article Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class 2 Cavities Restored with A Nanohybrid Composite Using Three Different Increment Techniques-
CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATION 36MO
 INTERNATIONAL PEER REVIEW CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATION 36MO Leung Kwan Yu, Steve BDS II - Class 2019, The University of Hong Kong instruments Mirror Periodontal probe Hatchets Gingival margin trimmers
INTERNATIONAL PEER REVIEW CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATION 36MO Leung Kwan Yu, Steve BDS II - Class 2019, The University of Hong Kong instruments Mirror Periodontal probe Hatchets Gingival margin trimmers
Ribbond-Direct Composite on an Endo Premolar
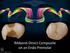 Ribbond-Direct Composite on an Endo Premolar The Problem. What to do next? The Problem Best aesthetics will be to leave the facial enamel intact. The risk the tooth is biomechanically weak following removal
Ribbond-Direct Composite on an Endo Premolar The Problem. What to do next? The Problem Best aesthetics will be to leave the facial enamel intact. The risk the tooth is biomechanically weak following removal
Available online at ScienceDirect
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 1251 1257 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 Comparative Study
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 69 ( 2014 ) 1251 1257 24th DAAAM International Symposium on Intelligent Manufacturing and Automation, 2013 Comparative Study
Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes. **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures**
 Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures** This review notes compiled and prepared by my sister for her own study, as a last day review session for
Dental Anatomy High Yield Notes **Atleast 35 questions comes from these areas of old lectures** This review notes compiled and prepared by my sister for her own study, as a last day review session for
Paper submission. Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case
 Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
Paper submission Denture repair with the application of a magnetic attachment to the inner crown of a telescopic crown: A 3-year follow-up case A. Izumida Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Tohoku
KaVo SONICflex tips overview. SONICflex Tip book. Comprehensive user reports on the KaVo tips may be found at
 KaVo SONICflex tips overview SONICflex Tip book. Comprehensive user reports on the KaVo tips may be found at www.kavo.com/spitzen KaVo SONICflex tips overview NEW Variety developed to a fine point. retro
KaVo SONICflex tips overview SONICflex Tip book. Comprehensive user reports on the KaVo tips may be found at www.kavo.com/spitzen KaVo SONICflex tips overview NEW Variety developed to a fine point. retro
Advanced Probing Techniques
 Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
Module 21 Advanced Probing Techniques MODULE OVERVIEW The clinical periodontal assessment is one of the most important functions performed by dental hygienists. This module begins with a review of the
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary Vol.:9 No.:2 2012
 MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
MDJ Evaluation the effect of eugenol containing temporary fillings on shear bond strength of composite restoration Dr. Farid G. Numan B.D.S., M.Sc Abstract The purpose of this in-vitro study was to evaluate
CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATIONS. Amalgam restorations that restore one or both of the proximal surfaces of the tooth
 CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATIONS Amalgam restorations that restore one or both of the proximal surfaces of the tooth Initial Tooth Preparation Occlusal outline form (occlusal step).the occlusal outline form
CLASS II AMALGAM RESTORATIONS Amalgam restorations that restore one or both of the proximal surfaces of the tooth Initial Tooth Preparation Occlusal outline form (occlusal step).the occlusal outline form
Achieving Excellence In Lustre
 Achieving Excellence In Lustre FAM Dr. Suhas Lele is a 1980 graduate of University of Mumbai. He is founder of Vision Invisible Dental academy. Vision Invisible envisage to train practicing dental professionals
Achieving Excellence In Lustre FAM Dr. Suhas Lele is a 1980 graduate of University of Mumbai. He is founder of Vision Invisible Dental academy. Vision Invisible envisage to train practicing dental professionals
Preclinical Dentistry. I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects. Lenka Roubalíková
 Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
Preclinical Dentistry I. Dental Caries Non carious lesions: trauma, erosion. abrasion, wedge shaped defects Lenka Roubalíková Understanding dental caries crown pulp chamber neck root canal root Dental
The Role of Cuspal Flexure And the Weakening Effect of occlusal Amalgam Restoration in the Development of Abfraction Lesions A Finite Element Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2017), PP 10-17 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Cuspal Flexure And the Weakening
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2017), PP 10-17 www.iosrjournals.org The Role of Cuspal Flexure And the Weakening
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PERIODONTAL STRESSES IN FIXED PROSTHODONTICS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PERIODONTAL STRESSES IN FIXED PROSTHODONTICS Valeria Pendefunda, Arina Ciocan Pendefunda, Nicoleta Ioanid, Alina Apostu, Oana Ţănculescu Odontology, Periodontology and Fixed
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF PERIODONTAL STRESSES IN FIXED PROSTHODONTICS Valeria Pendefunda, Arina Ciocan Pendefunda, Nicoleta Ioanid, Alina Apostu, Oana Ţănculescu Odontology, Periodontology and Fixed
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Evaluation of Microleakage in Composite-Composite and Amalgam-Composite Interfaces in Tooth with Preventive Resin Restoration (Ex-viva)
 Original Article Evaluation of Microleakage in Composite-Composite and Amalgam-Composite Interfaces in Tooth with Preventive Resin Restoration (Ex-viva) H. Afshar 1, A. Jafari 2, M. R. Khami 2,3, S. Razeghi
Original Article Evaluation of Microleakage in Composite-Composite and Amalgam-Composite Interfaces in Tooth with Preventive Resin Restoration (Ex-viva) H. Afshar 1, A. Jafari 2, M. R. Khami 2,3, S. Razeghi
Reference to primary publication Properties of alginates in ZWP 4/2014 Xantalgin Crono - Introduction
 Reference to primary publication in ZWP 4/2014 Dr. Marcus Holzmeier, Wuerzburg Xantalgin Crono - Highly accurate alginate impressions. Introduction Even today when digital impression techniques are gaining
Reference to primary publication in ZWP 4/2014 Dr. Marcus Holzmeier, Wuerzburg Xantalgin Crono - Highly accurate alginate impressions. Introduction Even today when digital impression techniques are gaining
Primary Teeth Chapter 18. Dental Anatomy 2016
 Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Primary Teeth Chapter 18 Dental Anatomy 2016 Primary Teeth - Introduction Synonyms deciduous teeth, baby teeth, temporary teeth, milk teeth. There are 20 primary teeth, designated as A thru T in the Universal
Original Article. in depth, 4 mm in mesiodistal width and 3 mm occlusogingival
 Original Article A Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class V Composite Restorations using a Fifth Generation Adhesive and a Glass Ionomer Bonding Agent - An In Vitro Dye Leakage Study Dipali Shah
Original Article A Comparative Evaluation of Microleakage in Class V Composite Restorations using a Fifth Generation Adhesive and a Glass Ionomer Bonding Agent - An In Vitro Dye Leakage Study Dipali Shah
INDICATIONS. Fixed Appliances are indicated when precise tooth movements are required
 DEFINITION Fixed Appliances are devices or equipments that are attached to the teeth, cannot be removed by the patient and are capable of causing tooth movement. INDICATIONS Fixed Appliances are indicated
DEFINITION Fixed Appliances are devices or equipments that are attached to the teeth, cannot be removed by the patient and are capable of causing tooth movement. INDICATIONS Fixed Appliances are indicated
Essentials of. Dental Assisting. Edition 6. Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird
 Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
Essentials of Dental Assisting Edition 6 Debbie S. Robinson Doni L. Bird CHAPTER21 Restorative Procedures http://evolve.elsevier.com/robinson/essentials/ LEARNING OBJECTIVES KEY TERMS 1. Pronounce, define,
Learning and applying the Natural Layering Concept
 I industry report _ natural layering concept Learning and applying the Natural Layering Concept Author_ Prof Didier Dietschi, Switzerland Right_Dentine samples of the Miris 2 system, developed according
I industry report _ natural layering concept Learning and applying the Natural Layering Concept Author_ Prof Didier Dietschi, Switzerland Right_Dentine samples of the Miris 2 system, developed according
Incisal Edge Abrasion Caused By An Unusual Eating Habit
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 6 Number 1 W Amin, A Kassab, N Salim Citation W Amin, A Kassab, N Salim.. The Internet Journal of Dental Science. 2007 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Dental Science Volume 6 Number 1 W Amin, A Kassab, N Salim Citation W Amin, A Kassab, N Salim.. The Internet Journal of Dental Science. 2007 Volume 6 Number 1. Abstract
Used Products. Variolink N LC. Proxyt fluoride-free. OptraStick. Ivoclean. Monobond N. OptraDam. N-Etch. Tetric N-Bond.
 Used Products TOOTH - Veneer - Glass-ceramics - Variolink N LC - Tetric N-Bond Variolink N LC The microfilled, purely light-curing luting composite system Proxyt fluoride-free Prophy paste without fluoride
Used Products TOOTH - Veneer - Glass-ceramics - Variolink N LC - Tetric N-Bond Variolink N LC The microfilled, purely light-curing luting composite system Proxyt fluoride-free Prophy paste without fluoride
WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2
 C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
C L I N I C A L WaveOne Gold reciprocating instruments: clinical application in the private practice: Part 2 Peet van der Vyver 1 and Martin Vorster 2 1 Department of Odontology, School of Dentistry, University
Simply saves tooth structure. The occlusal onlay.
 Simply saves tooth structure. The occlusal onlay. The traditional approach: PFM crowns are the traditional restoration method for extensive defects in the hard substance of premolars and molars. Advantages:
Simply saves tooth structure. The occlusal onlay. The traditional approach: PFM crowns are the traditional restoration method for extensive defects in the hard substance of premolars and molars. Advantages:
5,6 Significant improvements of the dentin bond
 Porcelain Jacket Crowns: Back to the Future Through Bonding Pascal Magne, PhD, DMD 1 Michel Magne, MDT, BS 2 Inge Magne, CDT 2 More than 50 years before bonding to tooth structure (and especially to dentin)
Porcelain Jacket Crowns: Back to the Future Through Bonding Pascal Magne, PhD, DMD 1 Michel Magne, MDT, BS 2 Inge Magne, CDT 2 More than 50 years before bonding to tooth structure (and especially to dentin)
Principle Investigators: Overview of Study Methods: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz
 Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
Principle Investigators: Dr. John Burgess Dr. Carlos Muñoz Overview of Study Methods: Subjects in need of Class I and/or Class II restorations were enrolled in two clinical trials conducted in US dental
Key points for starting off
 Key points for starting off First off, the five questions to ask yourself about a loose tooth before identifying it are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Category (incisor, canine, premolar or molar)? Permanent or deciduous?
Key points for starting off First off, the five questions to ask yourself about a loose tooth before identifying it are: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Category (incisor, canine, premolar or molar)? Permanent or deciduous?
روپ قداص رتکد ناشخرد یاھدادعتسا رتفد
 CLASS II (pp 658-664 664, 696-708 708) دکتر صادق پور دفتر استعدادھای درخشان Seven Steps of Cavity Preparation 1) Establish the outline form 2) Establish resistance form 3) Establish retention form 4) Provide
CLASS II (pp 658-664 664, 696-708 708) دکتر صادق پور دفتر استعدادھای درخشان Seven Steps of Cavity Preparation 1) Establish the outline form 2) Establish resistance form 3) Establish retention form 4) Provide
Frictional Behavior and Surface Failure of Human Enamel
 Frictional Behavior and Surface Failure of Human Enamel J. M. POWERS, R. G. CRAIG, and K. C. LUDEMA School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48104, USA, and College of Engineering,
Frictional Behavior and Surface Failure of Human Enamel J. M. POWERS, R. G. CRAIG, and K. C. LUDEMA School of Dentistry, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan 48104, USA, and College of Engineering,
Ⅰ. INTRODUCTION. Department of Conservative dentistry, College of Dentistry, Pusan National University
 Effects of occlusal load on the stress distribution of four cavity configurations of noncarious cervical lesions: A three-dimensional finite element analysis study Effects of occlusal load on the stress
Effects of occlusal load on the stress distribution of four cavity configurations of noncarious cervical lesions: A three-dimensional finite element analysis study Effects of occlusal load on the stress
Press Release. Press Contact. The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results
 Press Release The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results by Dr. Arzu Tuna and Dr. Umut Baysal, Attendorn, Germany Composite restorations have always
Press Release The concept for Class II restoration Delicate preparation, rapid procedure and reliable results by Dr. Arzu Tuna and Dr. Umut Baysal, Attendorn, Germany Composite restorations have always
EFFICACY OF AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, G.C. TOOTH MOUSSE AND GLUMA DESENSITIZER IN TREATING DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY : A RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIAL
 Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 02 EFFICACY OF AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, G.C. TOOTH MOUSSE AND GLUMA DESENSITIZER IN TREATING DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY
Original Article International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 01,Issue 02 EFFICACY OF AMORPHOUS CALCIUM PHOSPHATE, G.C. TOOTH MOUSSE AND GLUMA DESENSITIZER IN TREATING DENTIN HYPERSENSITIVITY
The power of four: Aesthetic treatment in the anterior area.
 3M SM Health Care Academy The power of four: Aesthetic treatment in the anterior area. Drs Ajay Juneja and Lamberto Villani, Dubai, United Arab Emirates In aesthetic dentistry, the recommendation that
3M SM Health Care Academy The power of four: Aesthetic treatment in the anterior area. Drs Ajay Juneja and Lamberto Villani, Dubai, United Arab Emirates In aesthetic dentistry, the recommendation that
J Bagh College Dentistry Vol. 27(1), March 2015 The influence of
 The influence of shifting the class I cavity position prepared in posterior teeth buccally and lingualy on stress distribution (Finite element analysis study) Abdulsalm Rasheed Al-Zahawi, B.D.S., H.D.D.,
The influence of shifting the class I cavity position prepared in posterior teeth buccally and lingualy on stress distribution (Finite element analysis study) Abdulsalm Rasheed Al-Zahawi, B.D.S., H.D.D.,
IFURH0017.V04 NOV2017 INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CLINICAL PROCEDURE
 IFURH0017.V04 NOV2017 H Y B R I D INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CLINICAL PROCEDURE OVC PROCEDURE 1. OVC Selection Determine the mesial-distal (M-D) distance of the affected tooth using the appropriate Selector
IFURH0017.V04 NOV2017 H Y B R I D INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE CLINICAL PROCEDURE OVC PROCEDURE 1. OVC Selection Determine the mesial-distal (M-D) distance of the affected tooth using the appropriate Selector
DISCOVER A NEW APPROACH TO COMFORT. Clinically proven immediate and lasting sensitivity relief with just one application!
 Clinically proven immediate and lasting sensitivity relief with just one application! PLUS the stain removal strength you trust! DISCOVER A NEW APPROACH TO COMFORT PERFORMANCE meets PROTECTION For better
Clinically proven immediate and lasting sensitivity relief with just one application! PLUS the stain removal strength you trust! DISCOVER A NEW APPROACH TO COMFORT PERFORMANCE meets PROTECTION For better
EQUIA. Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System
 EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
EQUIA EQUIA Fil EQUIA Coat + Self-Adhesive, Bulk Fill, Rapid Restorative System From the World Leader in Glass Ionomer Technology - A Complete Glass Ionomer Based Bulk Fill Rapid Restorative System Class
Medical NBDE-II. Dental Board Exams Part I.
 Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Medical NBDE-II Dental Board Exams Part I http://killexams.com/exam-detail/nbde-ii Question: 149 Anatomically, the term "clinical root" can be defined as which of the following: A. The space in the tooth
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor
 Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
Lecture 2 Maxillary central incisor Generally The deciduous tooth appears in the mouth at 3 18 months of age, with 6 months being the average and is replaced by the permanent tooth around 7 8 years of
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 ABSTRACT Purpose: Evaluation of stress distribution maxilla under parafunctional loading on short dental implant using 3-dimensional (3D) finite element models. Material and method: 3D maxillary and mandibular
ABSTRACT Purpose: Evaluation of stress distribution maxilla under parafunctional loading on short dental implant using 3-dimensional (3D) finite element models. Material and method: 3D maxillary and mandibular
Dr.Zainab. second. step): The. proximal
 Class II Amalgam Restorations Dr.Zainab This section introduces the principles and techniques of a Class II tooth preparation for an amalgam restoration involving a carious lesion on one proximal surface.
Class II Amalgam Restorations Dr.Zainab This section introduces the principles and techniques of a Class II tooth preparation for an amalgam restoration involving a carious lesion on one proximal surface.
LMArte. Sculpt masterpieces
 LMArte Sculpt masterpieces LMArte LMArte by Style Italiano Designed by Walter Devoto DDS and Angelo Putignano MD, DDS. Esthetic layering - succeed with LM-Arte LM-Arte is a set of innovative instruments
LMArte Sculpt masterpieces LMArte LMArte by Style Italiano Designed by Walter Devoto DDS and Angelo Putignano MD, DDS. Esthetic layering - succeed with LM-Arte LM-Arte is a set of innovative instruments
Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity
 Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity Nicolas Elian, DDS Private Practice Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey David Geon U Kim, DDS, MS Faculty and Research Coordinator
Management of Inadequate Margins and Gingival Recession Presenting as Tooth Sensitivity Nicolas Elian, DDS Private Practice Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey David Geon U Kim, DDS, MS Faculty and Research Coordinator
Amalgam restoration of posterior proximal cavities with deep and concave gingival outlines
 Amalgam restoration of posterior proximal cavities with deep and concave gingival outlines M. Darveniza, MDSc, FRACDS* Abstract A technique for making a matrix and wedges for amalgam restoration of deep
Amalgam restoration of posterior proximal cavities with deep and concave gingival outlines M. Darveniza, MDSc, FRACDS* Abstract A technique for making a matrix and wedges for amalgam restoration of deep
3M Restorative Solution Guide. Make your featuring. choice!
 Restorative Solution Guide Make your featuring choice! workflow precision impression restoration Feasible Simple Repeatable Success simplified Ultimate featuring Efficient composite Esthetic adhesive Economic
Restorative Solution Guide Make your featuring choice! workflow precision impression restoration Feasible Simple Repeatable Success simplified Ultimate featuring Efficient composite Esthetic adhesive Economic
1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
 1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
1 1. What is the highest and sharpest cusp on the lower first deciduous molar? a. mesiobuccal b. distobuccal c. distolingual d.mesiolingual 2. Which of the following is NOT the correct location of an embrasure?
A conservative restorative smile makeover
 C L I N I C A L A conservative restorative smile makeover Aneta Grzesinska 1 Introduction The patient was a 37-year-old female who presented to the practice requesting six porcelain veneers for her upper
C L I N I C A L A conservative restorative smile makeover Aneta Grzesinska 1 Introduction The patient was a 37-year-old female who presented to the practice requesting six porcelain veneers for her upper
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary
 Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
Dental Morphology and Vocabulary Palate Palate Palate 1 2 Hard Palate Rugae Hard Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate Palate Palate Soft Palate 4 Palate Hard Palate Soft Palate Maxillary Arch (Maxilla) (Uppers)
