The clinical use of endosseous implants has
|
|
|
- Stanley Morton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial of 3i Machined-Surface Implants: Results After 6 Years of Follow-up Dietmar Weng, DDS, Dr Med Dent 1 /Zhimon Jacobson, DDS 2 /Dennis Tarnow, DDS 3 / Markus B. Hürzeler, DDS, Dr Med Dent, PhD 4 /Ove Faehn, DDS 5 / Farshid Sanavi, DMD, PhD 6 /Pål Barkvoll, DDS, PhD 7 /Renée M. Stach, DDS 8 Purpose: In this prospective multicenter clinical study, 1,179 3i standard threaded and self-tapping implants were followed for up to 6 years and monitored according to established success criteria. Materials and Methods: A total of 493 patients (240 men and 253 women) with a mean age of 45.1 years at implant surgery were enrolled at 6 research centers after being screened for exclusion criteria. Implants were placed according to a 2-stage surgical protocol with a minimum of 4 months of submerged healing in the mandible and 6 months in the maxilla. Restorations included 633 prostheses, the majority of which were fixed partial dentures in the posterior mandible or maxilla or single-tooth replacements in the anterior maxilla. Results: One hundred four implants (8.8%) did not meet success criteria and were designated as failures, and 222 implants (18.8%) were lost to follow-up. The cumulative success rate according to life table methods was 91.1% at 6 years. Discussion: Sixty percent of the failed implants were short ( 10 mm long), and their cumulative success rate as a group at 6 years was 89.0%, compared to 93.1% for longer implants (P.05). Thirty-three percent of all failures were implants placed in the posterior maxilla, for a 5-year cumulative success rate of 87.4%. Conclusion: It appears that limited bone dimensions and poor-quality bone have an impact on the performance of these machined-surface implants. (INT J ORAL MAXILLOFAC IMPLANTS 2003;18: ) Key words: bone quality, clinical trial, endosseous dental implants, surface properties 1 Associate Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dental Medicine, Bavarian Julius-Maximilians-University of Würzburg, Germany. 2 Professor, Boston University School of Graduate Dentistry, Boston, Massachusetts. 3 Associate Professor and Chairman, Department of Implant Dentistry, College of Dentistry, New York University, New York, New York. 4 Private Practice, Institute for Periodontology and Implantology, Munich, Germany. 5 Private Practice, Oslo, Norway. 6 Clinical Associate Professor and Director of Periodontal Graduate Clinic and Implant Clinic, School of Dental Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. 7 Professor and Head, Department of Oral Surgery and Oral Medicine, University of Oslo, Norway; Chairman, Institute of Clinical Dentistry, University of Oslo, Norway. 8 Medical Writer, Clinical Research Department, Implant Innovations, Palm Beach Gardens, Florida. Reprint requests: Dr Dietmar Weng, Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dental Medicine, Bavarian Julius-Maximilians-University of Würzburg, Pleicherwall 2, Würzburg, Germany. Fax: dietmar.weng@mail.uni-wuerzburg.de The clinical use of endosseous implants has enriched the therapeutic spectrum of restorative dentistry like few other innovations in the last century. Since the introduction of the first welldocumented implant system, 1 many others have followed, exhibiting similar as well as different material properties and design features. Because of the steadily increasing number of implant restorations, the necessity has emerged to establish objective, system-independent criteria for defining long-term success of dental implants. The search for such criteria was first initiated at the National Institutes of Health Harvard Consensus Development Conference in The currently accepted and established criteria are based on a series of other proposals for implant success criteria 3,4 and were subsequently refined and reinforced in the Toronto Consensus Report in To be considered successful, an implant must meet the following requirements 5 : The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 417
2 Fig 1 1. The resultant implant support does not preclude the placement of a planned functional and esthetic prosthesis that is satisfactory to both patient and dentist. 2. There is no pain, discomfort, altered sensation, or infection attributable to the implants. 3. Individual unattached implants are immobile when tested clinically. 4. The mean vertical bone loss is less than 0.2 mm annually following the first year of function. The objective of this study was to evaluate the long-term performance of 3i standard threaded and self-tapping implants (Implant Innovations, Palm Beach Gardens, FL). The following is the first description of a prospective clinical trial on 3i machined-surface implants with well-defined success criteria over an observation time of up to 6 years. MATERIALS AND METHODS The 3i self-tapping implant. Six research centers (5 university clinics and 1 private clinic) located in the United States (3 institutions) and in Europe (3 institutions) participated in this prospective, multicenter clinical trial. Patients had to be able to tolerate conventional surgical and restorative procedures and had to be willing and able to comply with all aspects of the treatment and follow-up schedule. The patients health status was evaluated in a preoperative screening. Presence of 1 or several of the following conditions, determined either by direct examination or historical documentation, was reason for exclusion from the study: alcoholism or drug abuse, mental illness, evidence or suspicion of unwillingness to comply with longterm follow-up, uncontrolled diabetes, hemophilia, metabolic bone disorder, history of renal failure, corticosteroid treatment, anticoagulant therapy, radiation treatment to the head or neck, previous bone graft at the intended site, current chemotherapy, untreated or uncontrolled periodontal pathology, current pregnancy at the time of evaluation, and severe bruxing or clenching habits. The test designs to be implanted in the patients were 3i standard threaded implants and 3i self-tapping implants (Fig 1). These implants feature a machined surface and an external hexagon. The lengths (7, 8.5, 10, 13, 15, and 18 mm) and diameters (3.25, 3.75, 4, 5, and 6 mm) of the individual implants varied from subject to subject, depending on the bone width and depth at each site. To standardize surgical procedures, all centers were equipped with the same surgical drill units, handpieces, and surgical instruments. Furthermore, study monitors assessed and reviewed all surgical procedures to ensure intercenter reliability. The implants were placed according to the manufacturer s guidelines in a 2-stage process to guarantee complete bony fixation before loading. Concomitant hard tissue grafting or augmentation procedures precluded inclusion in the study. At the time of surgery, the clinical assessment of bone quality was recorded based on hand-felt perception of the drilling resistance and categorized into 1 of 3 classes of bone quality. Bone quality was scored by the clinician as dense, normal, or soft. Surgical uncovering of the implants was done after a healing period of 4 months in the mandible and 6 months in the maxilla. During soft tissue healing after stage 2 surgery, fabrication of the prosthetic restorations was completed. At the time of prosthesis placement, baseline measurements were obtained. They consisted of clinical and radiographic parameters and were repeated at 6 months, 1 year, 18 months, and 2, 3, 4, and 5 years after prosthesis placement. Clinical parameters included the assessment of: Individual and unattached implant mobility, as determined by the lateral application of pressure by 2 opposing instruments to the implant Probing depths at mesial, distal, buccal, and lingual sites, ie, distance in mm between the mucosal margin and the bottom of the probable pocket with a non-standardized periodontal probe; care was taken not to disturb any soft tissue attachment Peri-implant mucosal health at 4 sites, including gingival levels, amount of keratinized gingiva, amount of recession, gingival inflammation, and presence of hyperplastic mucosa or suppuration 418 Volume 18, Number 3, 2003
3 Table 1 Distribution of Implants by Study Center No. of No. of No. of No. of Failure rate Center patients restorations implants placed implant failures by center % % % % % % Totals % In measuring gingival levels, a standard reference point was established from which measurements were made in millimeters, ie, the implant/abutment interface. All measurements apical to the reference point were expressed as negative numbers; all coronally oriented measurements were reported as positive numbers. Gingival inflammation was categorized by severity using the following scale: 0 = no inflammation, 1 = mild inflammation (color change only), 2 = moderate inflammation (bleeding upon probing), and 3 = severe inflammation (spontaneous bleeding). Radiographic parameters were obtained from periapical and panoramic radiographs made at baseline, 6 months, and 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 years and included mesial and distal bone level measurements as well as descriptions of peri-implant radiolucencies. Acquisition of periapical radiographs was standardized by use of a customized template fabricated at the time of prosthesis placement. Bone level measurements estimated to the nearest 0.01 mm were performed by 1 calibrated examiner on serial radiographs according to standard operating procedures. Average mesial and distal bone level measurements were calculated for all implants. The mean implant value was the average of the mean mesial and distal measurements. Bone loss was the difference in bone level measurements from the baseline established at prosthesis loading compared to each follow-up evaluation. In addition to the surgical and implant measurements, prosthodontic parameters were assessed at follow-up evaluations. Categories rated by the clinicians on a scale from 1 to 4 included prosthesis retention, prosthesis stability, esthetics, and phonetics. The Cornell Medical Index 6,7 was used to evaluate patient satisfaction in the categories comfort, fit, speech, appearance, ability to chew, ability to taste, and general satisfaction. Each category was graded as 1 (excellent), 2 (good), 3 (fair), or 4 (poor). Changes in medical status and disclosure of new adverse events (unanticipated negative effects, eg, implant failure, fracture of implant components) were also recorded at each recall visit. In this study an implant was considered successful If it was immobile when tested individually and unattached to other implants In the absence of peri-implant radiolucency While no persistent or irreversible signs and symptoms such as pain, discomfort, altered sensation, or infection attributable to the implant were observed If there was loss of marginal bone crestal levels no greater than 0.2 mm per year after the first year of function If the resultant implant support did not preclude the placement of a planned functional and esthetic prosthesis that was satisfactory to both patient and the investigator Implants were classified as successful, failed, or censored (eg, not used as a result of death, buried because of poor position for restoration, or if the patient was lost to follow-up) and analyzed by survival analysis distribution according to life table methods. RESULTS A total of 493 patients 240 men (49%) and 253 women (51%) with a mean age of 45.1 ± 15.1 years were enrolled in the study across 6 investigational centers. Of these, 78 (16%) were smokers and 1% had diabetes. A breakdown of enrollment by center is included in Table 1. A total of 1,179 implants were placed in the 493 patients. The diameters and lengths of implants used in this study are described in Table 2. The majority of implants (61.8%) were 3.75 mm in diameter. Of the implants placed, 48.5% were short in length, ie, 10 mm or less. Five hundred nine (41.4%) of the implants were placed in the maxilla and 972 (79.1%) in premolar or molar areas of the mandible or the maxilla. Two hundred seventy-four (23.2%) were located in the posterior maxilla The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 419
4 Table 2 Length and Diameter Distribution of Implants Implant length (mm) Implant diameter (mm) Total Total Percent of implants placed Maxillary implants Mandibular implants Total Anterior Posterior Percent of restorations Single-tooth replacement Short-span fixed prostheses ( 5 units) Long-span fixed prostheses ( 5 units) Fig 2 Proportion of implants placed by location. Fig 3 Distribution of prosthetic restorations. Percent cumulative success Fig months Life table distribution for all implants. (Fig 2). One hundred eighty-three (15.6%) implants were placed in bone described as dense, 816 (69.5%) in normal bone, and 175 (14.9%) in soft bone. Altogether, 633 prostheses were placed in the 493 patients. Distribution of these 633 prostheses can be seen in Fig 3. A majority of restorations (371, or 59%) were fixed partial dentures in the posterior areas of the mandible or the maxilla, followed by 253 (40%) single-tooth replacements, and a few long-span fixed prostheses (1%). The results of gingival assessments (gingival levels, keratinized gingiva, probing depths, and gingival inflammation) indicated that peri-implant mucosa maintained good health throughout the follow-up period, with only slight changes from baseline. Stable marginal crestal bone levels were observed throughout the follow-up period, with a mean bone loss of 0.67 mm between loading and 4- year evaluations. This report provides an interim analysis after a mean observation time of 72.0 ± 6.4 months after implant placement. Mean elapsed time from implant placement to stage 2 surgery was 6.8 months and from implant placement to loading was 15.5 months. Of the implants characterized as successful, 80.5% reached the 5-year evaluation time point. One hundred four implants (8.8%) did not meet success criteria and were designated as failures, and 222 implants (18.8%) were lost to follow-up. Reasons for loss to follow-up were death, geographic relocation, and economic reasons. Eight hundred fifty-three of the surviving 957 implants were considered successful according to the aforementioned 420 Volume 18, Number 3, 2003
5 Fig 5 Prosthetic outcomes for all restorations, as rated by clinicians. 0 months = Prosthetic loading date. Good Excellent 1.0 Rating Retension Stability Esthetics Phonetics Fig 6 Cornell Medical Index of patient satisfaction as scored by patients. 0 months = Prosthetic loading date Excellent Comfort Fit Speech Appearance Ability to chew Ability to taste General satisfaction Percent cumulative success All implants Short implants Implants in posterior maxilla Short implants in posterior maxilla Percent cumulative success mm (n = 475) 8.5 mm (n = 70) 7 mm (n = 27) Fig 7 Life table distribution for implants by length and location. Fig 8 Life table distribution for short implants by individual length. criteria. The cumulative success rate according to life table methods was 91.1% at 5 years post-loading, and the survival distribution is illustrated in Fig 4. Most implant failures (87, or 83.7%) occurred prior to prosthesis placement (ie, loading), and only 12 failures occurred 18 months post-prosthesis placement. Most of the 104 implants designated as failures were subsequently removed. The reasons for failure were mobility (84), continuous radiolucency (20), persistent pain (20), persistent signs of infection (14), violation of the mandibular canal (1), and/or other (11). Prosthetic outcomes and patient satisfaction with their prostheses were favorable and are illustrated in Figs 5 and 6. The type of occlusion observed for most prostheses was group function or anterior disclusion. Most clinicians rated the retention, stability, esthetics, and phonetics of the prostheses as excellent or good. Sixty percent of all failed implants were short ( 10 mm), and the cumulative success rate for these short implants was 89.0%, a significantly lower rate than the cumulative success rate for all implants of 91.1% (Fig 7). Failure of the short implants included 26% of 7-mm implants, 19% of 8.5-mm implants, and 9% of 10-mm implants (Fig 8). The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 421
6 Another group of implants that failed at a relatively higher rate were those placed in the posterior maxilla. These constituted 33% of all failures with a cumulative success rate at 5 years of 87.4% (Fig 7). DISCUSSION A major reason for the success of dental implants has been the development of implant designs and surgical procedures that result in a direct boneimplant interface that can be stable long term. This condition is generally referred to as osseointegration. It is achieved by careful control of the conditions of treatment, notably atraumatic surgical preparation of the implant site by the use of copiously irrigated drilling at low speed and high torque under aseptic conditions, use of biocompatible implant materials such as titanium, and the imposition of a healing period during which no load is placed on the implant. 8 Osseointegration is characterized by immobility of the implant, lack of radiolucency around the implant, and the absence of soft tissue between bone and the major portion of the implant surface on histologic examination. 9 Stable osseointegration can be considered a criterion of implant success, and the parameters established in the present study for implant success served to determine the existence of osseointegration. Since the initiation of this study, implant designs have evolved to include surface modifications with greater roughness that act to not only anchor the implant more firmly in the bone soon after placement, but also to promote better clot retention and bone regeneration. 10 Prospective clinical studies have shown that an implant with a dual acid-etched surface performs at a high success rate While the 1,179 machined-surface implants in the present long-term study showed a cumulative success rate of 91.1%, which falls within the guidelines for implant success of at least 85% at 5 years 3 and is similar to success rates reported for other machined-surface implants, 15 they did not achieve success rates as high as the more recently manufactured acid-etched implants. Because of the large number of implants in the current study, an attempt at failure analysis is possible. As can be seen from the Fig 4 life table distribution, there was a consistent decline in the cumulative success rate, and after 18 months the curve flattened out into a steady state with fewer failures. With respect to implant dimensions and locations, it appears that short implants ( 10 mm) failed at a higher rate than longer implants. This is also consistent with the findings of other clinical reports on machined-surface implants. The failure rate of these short implants increased as the length of the implant decreased. The cumulative success rate for the short implants was 88.7% at 6 years, which includes a 26% failure of 7-mm implants. In comparison, the 5-year cumulative success rate for long implants was 93.1%. Frequently, short implants are placed where there are inadequate bony dimensions and the bone tends to be of a softer clinically assessed quality, such as in the posterior maxilla where space is limited by the maxillary sinus. Implants are at greater risk in areas of the jaw where bone density is often quite low, the bone height is reduced, and functional load is high. In this report there was a greater percentage of implant failures in the posterior maxilla, where a cumulative success rate of 86.2% was achieved for 274 implants. One third of all implant failures were those implants placed in the posterior maxilla, where 27.4% of the implants were placed in bone described as soft, which is almost twice the frequency of soft bone for all implants. Furthermore, for the short implants placed in the posterior maxilla the success rate was only 80.6%, perhaps indicating the contribution of implant length and bone quality to clinical outcomes. It appears that the limitations of bone dimensions and more common occurrence of poor-quality bone had an impact on the outcome of machined-surface implants placed in the posterior maxilla. Another observation regarding the failure pattern in this study was that 95.2% of all implant failures (ie, 99 of 104) occurred within the first 3 years after implant placement. This finding is consistent with another study of machined-surface implants, 16 in which 97.9% of the failures occurred before the third year of follow-up (274 out of 280). Lindh and coworkers 17 conducted a meta-analysis of implants in partially edentulous patients. In 19 studies with a total of 2,686 predominantly machined-surface implants, 95.3% of all failures were recorded within 3 years after implant loading. These failure patterns seem to support the US Food and Drug Administration s recent proposal 18 to change the clinical follow-up period of root-form endosseous implants for Premarket Approval Applications from 5 to 3 years, at least as far as machined-surface implants are concerned. CONCLUSION Survival analysis indicated that after 6 years of follow-up, 3i machined-surface implants achieved a cumulative success rate of 91.1% in this patient population. Short implants failed at a higher rate (11.0%) than longer implants (6.9%), and more failures were located in the posterior maxilla (33% of 422 Volume 18, Number 3, 2003
7 all failures). Additional analyses of this data set will be published in subsequent manuscripts. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This study was supported by Implant Innovations, Palm Beach Gardens, Florida. REFERENCES 1. Brånemark P-I, Hansson B-O, Adell R, et al. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Suppl 1977;16: Schnitman PA, Shulman LB. Recommendations of the Consensus Development Conference on Dental Implants. J Am Dent Assoc 1979;98: Albrektsson T, Zarb G, Worthington P, Eriksson AR. The long-term efficacy of currently used dental implants: A review and proposed criteria of success. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1986;1: Albrektsson T, Isidor F. Consensus Report of Session V. In: Lang NP, Karring T (eds). Proceedings of the 1st European Workshop on Periodontology. London: Quintessence, 1993: Zarb GA, Albrektsson T (eds). Consensus report: Towards optimized treatment outcomes for dental implants. Int J Prosthodont 1998;11: Monroe RT, Whiskin FE, Bonacich P, Jewell WO. The Cornell Medical Index questionnaire as a measure of health in older people. J Gerontol 1965;20: Cheraskin E, Ringsdorf WM, Setyaadmadja AT, Barett RA. Predictive dentistry: The Cornell Medical Index health questionnaire (general response) and dental findings. NY J Dent 1967;34: Adell R, Lekholm U, Brånemark P-I. Surgical procedures. In: Brånemark P-I, Zarb GA, Albrektsson T (eds). Tissue- Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry. Chicago: Quintessence, 1985: Brånemark P-I. Introduction to osseointegration. In: Brånemark P-I, Zarb GA, Albrektsson T (eds). Tissue-Integrated Prostheses: Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry. Chicago: Quintessence, 1985: Davies JE. Mechanisms of endosseous integration. Int J Prosthodont 1998;11: Sullivan DY, Sherwood RL, Porter SS. Long-term performance of Osseotite implants: A 6-year clinical follow-up. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2001;22: Grunder U, Gaberthuel T, Boitel N, et al. Evaluating the clinical performance of the Osseotite implant: Defining prosthetic predictability. Compend Contin Educ Dent 1999; 20: Lazzara RJ, Porter SS, Testori T, Galante J, Zetterqvist L. A prospective multicenter study evaluating loading of Osseotite implants two months after placement: One-year results. J Esthet Dent 1998;10: Testori T, Wiseman L, Woolfe S, Porter SS. A prospective multicenter study of the Osseotite implant: A four-year interim report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2001;16: Esposito M, Hirsch J-M, Lekholm U, Thomsen P. Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (I). Success criteria and epidemiology. Eur J Oral Sci 1998;106: Albrektsson T, Dahl E, Enbom L, et al. Osseointegrated oral implants: A Swedish multicenter study of 8139 consecutively inserted Nobelpharma implants. J Periodontol 1988;59: Lindh T, Gunne J, Tillberg A, Molin M. A meta-analysis of implants in partial edentulism. Clin Oral Implants Res 1998; 9: U.S. Food and Drug Administration: Class II Special Controls Guidance Document: Root-form Endosseous Dental Implants and Abutments; Draft Guidance for Industry and FDA html The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 423
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Endosseous cylindric implants are well accepted
 Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Case study 2. A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant
 Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Endosseous dental implants initially showed very
 Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
The surgical placement of dental implants has
 Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Preliminary Data of a Prospective Clinical Study on the Osseotite NT Implant: 18-month Follow-up
 Preliminary Data of a Prospective Clinical Study on the Osseotite NT Implant: 18-month Follow-up Mithridade Davarpanah, MD, DDS 1 / Mihaela Caraman, DDS 2 /Serge Szmukler-Moncler, DDS, PhD 3 / Boris Jakubowicz-Kohen,
Preliminary Data of a Prospective Clinical Study on the Osseotite NT Implant: 18-month Follow-up Mithridade Davarpanah, MD, DDS 1 / Mihaela Caraman, DDS 2 /Serge Szmukler-Moncler, DDS, PhD 3 / Boris Jakubowicz-Kohen,
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
The Self-tapping and ICE 3i Implants: A Prospective 3-Year Multicenter Evaluation
 The Self-tapping and ICE 3i Implants: A Prospective 3-Year Multicenter Evaluation Mithridade Davarpanah, MD, DDS 1 /Henry Martinez, DDS 2 /Jean-François Tecucianu, MD, DDS 3 / Gil Alcoforado, DDS 4 /Daniel
The Self-tapping and ICE 3i Implants: A Prospective 3-Year Multicenter Evaluation Mithridade Davarpanah, MD, DDS 1 /Henry Martinez, DDS 2 /Jean-François Tecucianu, MD, DDS 3 / Gil Alcoforado, DDS 4 /Daniel
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols
 Group 3 Consensus Statements Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols Hans-Peter Weber, DMD, Dr Med Dent 1 /Dean Morton, BDS, MS 2 /German O. Gallucci, DMD,
Group 3 Consensus Statements Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols Hans-Peter Weber, DMD, Dr Med Dent 1 /Dean Morton, BDS, MS 2 /German O. Gallucci, DMD,
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
John P. Zarb, BA, DDS George A. Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
 C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Implant Prosthodontic Management of Anterior Partial Edentulism: Long-Term Follow-Up of a Prospective Study John P. Zarb, BA, DDS George A. Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
C L I N I C A L P R A C T I C E Implant Prosthodontic Management of Anterior Partial Edentulism: Long-Term Follow-Up of a Prospective Study John P. Zarb, BA, DDS George A. Zarb, BChD, DDS, MS, MS, FRCD(C)
Implant osseointegration and successful restoration
 Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Table of Contents. 1 Immediate occlusal loading of NanoTite PREVAIL Implants: A prospective 1-year clinical and radiographic study
 Table of Contents 1 Immediate occlusal loading of NanoTite PREVAIL Implants: A prospective 1-year clinical and radiographic study 3 Immediate provisionalization of NanoTite Implants in support of single-tooth
Table of Contents 1 Immediate occlusal loading of NanoTite PREVAIL Implants: A prospective 1-year clinical and radiographic study 3 Immediate provisionalization of NanoTite Implants in support of single-tooth
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
During the last 30 years, endosseous oral
 Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
Influence of Variations in Implant Diameters: A 3- to 5-Year Retrospective Clinical Report Carl-Johan Ivanoff, DDS*/Kerstin Gröndahl, DDS, PhD**/Lars Sennerby, DDS, PhD***/ Christina Bergström, MSc****/Ulf
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study
 Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note
 Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Bone Reduction Surgical Guide for the Novum Implant Procedure: Technical Note Stephen M. Parel, DDS 1 /Steven L. Ruff, CDT 2 /R. Gilbert Triplett, DDS, PhD 3 /Sterling R. Schow, DMD 4 The Novum System
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 255 Multicenter Retrospective Analysis
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 255 Multicenter Retrospective Analysis
For more than 20 years, the standard protocol for
 Immediate Loading of Splinted Locking-Taper Implants: 1-Year Survival Estimates and Risk Factors for Failure Mohammed S. Erakat, BS 1 /Sung-Kiang Chuang, DMD, MD 2 /Roy H. Yoo, DMD 3 / Meghan Weed, BS
Immediate Loading of Splinted Locking-Taper Implants: 1-Year Survival Estimates and Risk Factors for Failure Mohammed S. Erakat, BS 1 /Sung-Kiang Chuang, DMD, MD 2 /Roy H. Yoo, DMD 3 / Meghan Weed, BS
The influence of radiotherapy on osseointegration
 Experience with Osseointegrated Implants Placed in Irradiated Tissues in Japan and the United States Atsushi Niimi, DDS, DMSc*/Minoru Ueda, DDS, PhD**/ Eugene E. Keller, DDS, PhD***/Philip Worthington,
Experience with Osseointegrated Implants Placed in Irradiated Tissues in Japan and the United States Atsushi Niimi, DDS, DMSc*/Minoru Ueda, DDS, PhD**/ Eugene E. Keller, DDS, PhD***/Philip Worthington,
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos,
NanoTite Tapered Implants: An Implant Designed For Performance. Review And Clinical Results
 NanoTite Tapered Implants: An Implant Designed For Performance Review And Clinical Results NanoTite Tapered Implants: Review and Clinical Results INTRODUCTION For more than ten years and with documentation
NanoTite Tapered Implants: An Implant Designed For Performance Review And Clinical Results NanoTite Tapered Implants: Review and Clinical Results INTRODUCTION For more than ten years and with documentation
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis
 Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
While the protocol for direct bone-to-implant
 Immediate Functional Loading of Brånemark System Implants in Edentulous Mandibles: Clinical Report of the Results of Developmental and Simplified Protocols Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD 1 / Thomas J. Balshi,
Immediate Functional Loading of Brånemark System Implants in Edentulous Mandibles: Clinical Report of the Results of Developmental and Simplified Protocols Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD 1 / Thomas J. Balshi,
STABILITY OF IMPLANTS AND NATURAL TEETH MONTHS OF FUNCTION AS DETERMINED BY THE PERIOTEST OVER 60 CLINICAL
 CLINICAL STABILITY OF IMPLANTS AND NATURAL TEETH AS DETERMINED BY THE PERIOTEST OVER 60 MONTHS OF FUNCTION Sheldon Winkler, DDS Harold F. Morris, DDS, MS J. Robert Spray, DDS KEY WORDS Implant Natural
CLINICAL STABILITY OF IMPLANTS AND NATURAL TEETH AS DETERMINED BY THE PERIOTEST OVER 60 MONTHS OF FUNCTION Sheldon Winkler, DDS Harold F. Morris, DDS, MS J. Robert Spray, DDS KEY WORDS Implant Natural
A simple approach to preserve keratinized mucosa around implants using a pre-fabricated implantretained stent: a report of two cases
 Case Report J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:194-200 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.4.194 A simple approach to preserve keratinized mucosa around implants using a pre-fabricated implantretained stent: a report
Case Report J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:194-200 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.4.194 A simple approach to preserve keratinized mucosa around implants using a pre-fabricated implantretained stent: a report
Young-Jin Park, DDS,* and Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:1338-1344, 2010 Retrospective Chart Analysis on Survival Rate of Fixtures Installed at the Tuberosity Bone for Cases With Missing Unilateral Upper Molars: A Study of 7 Cases Young-Jin
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys
 The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
Areview of recent studies concerning molar. Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report
 Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
Single Molar Replacement with a Progressive Thread Design Implant System: A Retrospective Clinical Report George E. Romanos, Dr med dent 1 /Georg H. Nentwig, Prof Dr med dent 2 Many clinical studies have
ADEA COHAEP SYMPOSIA: TURF WARS
 ADEA COHAEP SYMPOSIA: TURF WARS October 30, 2015 8:00 9:30 a.m. Chicago, IL Saulius E. Drukteinis, D.M.D., M.S., Ph.D. Associate Professor, Director, Predoctoral Periodontology Nova Southeastern University
ADEA COHAEP SYMPOSIA: TURF WARS October 30, 2015 8:00 9:30 a.m. Chicago, IL Saulius E. Drukteinis, D.M.D., M.S., Ph.D. Associate Professor, Director, Predoctoral Periodontology Nova Southeastern University
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 827 Thirty-Two Year Success of Dental Implants in Periodontally Compromised Dentition Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 Glenn J. Wolfinger,
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
The Importance of Implant Surface Characteristics in the Replacement of Failed Implants
 The Importance of Implant Surface Characteristics in the Replacement of Failed Implants Ghada Alsaadi, DDS, MSc 1 /Marc Quirynen, DDS, PhD 2 /Daniel van Steenberghe, MD, PhD, Dr hc 3 Purpose: The purpose
The Importance of Implant Surface Characteristics in the Replacement of Failed Implants Ghada Alsaadi, DDS, MSc 1 /Marc Quirynen, DDS, PhD 2 /Daniel van Steenberghe, MD, PhD, Dr hc 3 Purpose: The purpose
INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY HISTORY OF DENTAL IMPLANTS EUGENIA PROKOPETS, DDS LSU PERIODONTICS
 INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY HISTORY OF DENTAL IMPLANTS EUGENIA PROKOPETS, DDS LSU PERIODONTICS Thank you Dr. Simmons BEFORE THE COMMON ERA 16TH AND 17TH CENTURIES Archeological records from China
INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY HISTORY OF DENTAL IMPLANTS EUGENIA PROKOPETS, DDS LSU PERIODONTICS Thank you Dr. Simmons BEFORE THE COMMON ERA 16TH AND 17TH CENTURIES Archeological records from China
Frequency and Type of Prosthetic Complications Associated with Interim, Immediately Loaded Full-Arch Prostheses: A 2-Year Retrospective Chart Review
 Frequency and Type of Prosthetic Complications Associated with Interim, Immediately Loaded Full-Arch Prostheses: A 2-Year Retrospective Chart Review Carl Drago, DDS, MS, FACP 1,2,3 1 Department of Dental
Frequency and Type of Prosthetic Complications Associated with Interim, Immediately Loaded Full-Arch Prostheses: A 2-Year Retrospective Chart Review Carl Drago, DDS, MS, FACP 1,2,3 1 Department of Dental
Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps Jay R. Beagle Despite the continued debate regarding the need for
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps Jay R. Beagle Despite the continued debate regarding the need for
Clinical Evaluation of Dental Implants with Surfaces Roughened by Anodic Oxidation, Dual Acid-Etched Implants, and Machined Implants
 Clinical Evaluation of Dental Implants with Surfaces Roughened by Anodic Oxidation, Dual Acid-Etched Implants, and Machined Implants Alexandre-Amir Aalam, DDS 1 /Hessam Nowzari, DDS, PhD 2 Purpose: The
Clinical Evaluation of Dental Implants with Surfaces Roughened by Anodic Oxidation, Dual Acid-Etched Implants, and Machined Implants Alexandre-Amir Aalam, DDS 1 /Hessam Nowzari, DDS, PhD 2 Purpose: The
G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM
 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
CHAPTER. 1. Uncontrolled systemic disease 2. Retrognathic jaw relationship
 CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
CHAPTER 7 Immediate Implant Supported Restoration of the Edentulous Arch Stephen G. Alfano and Robert M. Laughlin Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Naval Medical Center San Diego, San Diego,
The restoration of partially and completely
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF DENTAL IMPLANT FRACTURES. ACASE HISTORY Firas A. M. AL Quran, PhD, MSc Med; Bashar A. Rashan, MS; Ziad N. AL-Dwairi, PhD The widespread use of endosseous osseointegrated implants
Safety and esthetics with
 Safety and esthetics with dental implants A guide for patients Dear reader, Implant restorations follow nature's example. You can have the functions of natural teeth completely restored and thus maintain
Safety and esthetics with dental implants A guide for patients Dear reader, Implant restorations follow nature's example. You can have the functions of natural teeth completely restored and thus maintain
MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT
 ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT ROMESH SONI a, HARAKH CHAND BARANWAL
ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) MULTIDIRECTIONAL APPROACH OF ORAL REHABILITATION WITH IMPLANTS IN A PATIENT WITH LIMITED MOUTH OPENING: A CASE REPORT ROMESH SONI a, HARAKH CHAND BARANWAL
Don t Let Life Pass You By Because Of Oral Bone Loss
 Don t Let Life Pass You By Because Of Oral Bone Loss Ask For Dental Implant Solutions From BIOMET 3i Scan With Your Smartphone! In order to scan QR codes, your mobile device must have a QR code reader
Don t Let Life Pass You By Because Of Oral Bone Loss Ask For Dental Implant Solutions From BIOMET 3i Scan With Your Smartphone! In order to scan QR codes, your mobile device must have a QR code reader
Early Loading of Osseotite Implants 2 Months After Placement in the Maxilla and Mandible: A 5-year Report
 Early Loading of Osseotite Implants 2 Months After Placement in the Maxilla and Mandible: A 5-year Report Daniel Sullivan, DDS 1 /Giampaolo Vincenzi, MD, DDS 2 /Sylvan Feldman, DDS, MLA 3 Purpose: In this
Early Loading of Osseotite Implants 2 Months After Placement in the Maxilla and Mandible: A 5-year Report Daniel Sullivan, DDS 1 /Giampaolo Vincenzi, MD, DDS 2 /Sylvan Feldman, DDS, MLA 3 Purpose: In this
A Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Survival Rates of Implants in the Mandible
 A Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Survival Rates of Implants in the Mandible Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 /Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD, FACP 2 / Brett E. Stein 3 /Stephen F. Balshi, MBE 4 Purpose:
A Long-term Retrospective Analysis of Survival Rates of Implants in the Mandible Thomas J. Balshi, DDS, PhD, FACP 1 /Glenn J. Wolfinger, DMD, FACP 2 / Brett E. Stein 3 /Stephen F. Balshi, MBE 4 Purpose:
Since the early 1980s, when the concept of
 Retention of Teeth Versus Extraction and Implant Placement: Treatment Preferences of Dental Faculty and Dental Students Peter M. Di Fiore, D.D.S., M.S.; Lawrence Tam, D.D.S.; Ha T. Thai, D.D.S.; Eugene
Retention of Teeth Versus Extraction and Implant Placement: Treatment Preferences of Dental Faculty and Dental Students Peter M. Di Fiore, D.D.S., M.S.; Lawrence Tam, D.D.S.; Ha T. Thai, D.D.S.; Eugene
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate
 AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This
 1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
1- Implant-supported vs. implant retained distal extension mandibular partial overdentures and residual ridge resorption. Abstract Purpose: This retrospective study in male patients sought to examine posterior
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 07 Page July 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
CHAPTER 1. General Introduction
 CHAPTER 1 General Introduction Chapter 1 The loss of remaining natural teeth and provision of artificial removable dentition is a major and irreversible procedure for the patient. The main limitations
CHAPTER 1 General Introduction Chapter 1 The loss of remaining natural teeth and provision of artificial removable dentition is a major and irreversible procedure for the patient. The main limitations
Computer-guided minimally invasive
 CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
CASE REPORT Guided Flapless Surgery With Immediate Loading for the High Narrow Ridge Without Grafting Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1,2 Sang J. Lee, DMD, MMSc 2 * Guillaume J. Campard, DMD, MMSc 3 Maria
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Please visit the C.E. Pavilion to validate your course attendance Or If There s a Line Go cdapresents.com
 UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
 A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
A New Procedure Reduces Laboratory Time to 6 Hours for the Elaboration of Immediate Loading Prostheses with a Titanium Frame Following Implant Placement Huard C, Bessadet M, Nicolas E, Veyrune JL * International
م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION
 Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
Lec.1 م.م. طارق جاسم حممد REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE INTRODUCTION االسنان طب Prosthodontics is the branch of dentistry pertaining to the restoration and maintenance of oral function, comfort, appearance,
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy
 The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants. by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD
 Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Utilizing Digital Treatment Planning and Guided Surgery in Conjunction with Narrow Body Implants by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Implant dentistry is undergoing some amazing transformations. With the
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report
 Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Mandibular implant-supported hybrid prostheses
 Occlusal Contacts of Edentulous Patients with Mandibular Hybrid Dentures Opposing Maxillary Complete Dentures Tetsuya Suzuki, DDS, PhD*/Hiroshi Kumagai, DDS, PhD**/ Nobuyuki Yoshitomi, DDS, PhD***/Edwin
Occlusal Contacts of Edentulous Patients with Mandibular Hybrid Dentures Opposing Maxillary Complete Dentures Tetsuya Suzuki, DDS, PhD*/Hiroshi Kumagai, DDS, PhD**/ Nobuyuki Yoshitomi, DDS, PhD***/Edwin
This Presentation Is Trademarked by Lawrence H. Zager, D.D.S.
 This Presentation Is Trademarked by Lawrence H. Zager, D.D.S.! The next presentation is from the private collection of patient s treated in my practice with the use of implants and other prosthetic devices
This Presentation Is Trademarked by Lawrence H. Zager, D.D.S.! The next presentation is from the private collection of patient s treated in my practice with the use of implants and other prosthetic devices
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Implants- immediate restoration of postextraction edentation both esthetically and functionally
 Implants- immediate restoration of postextraction edentation both esthetically and functionally Otilia Stana (Gag), LileIoana Elena, Freiman Paul, Mugur Popescu, Elisei Gabriela, Sebesan Voicu, Vincze
Implants- immediate restoration of postextraction edentation both esthetically and functionally Otilia Stana (Gag), LileIoana Elena, Freiman Paul, Mugur Popescu, Elisei Gabriela, Sebesan Voicu, Vincze
SPECIAL SUPPLEMENT. Inside this issue: 2014 No. 3. Peri-implant disease Implant surface: An evolution Summaries of select scientific publications
 www.jird.com SPECIAL SUPPLEMENT Inside this issue: Peri-implant disease Implant surface: An evolution Summaries of select scientific publications Official Publication of The Institute for Implant and Reconstructive
www.jird.com SPECIAL SUPPLEMENT Inside this issue: Peri-implant disease Implant surface: An evolution Summaries of select scientific publications Official Publication of The Institute for Implant and Reconstructive
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Dentatus ANEW Narrow Diameter Implants. Expanding Implantology with More Treatment Options
 Dentatus ANEW Narrow Diameter Implants Expanding Implantology with More Treatment Options The Versatility of Dentatus ANEW LONG-TERM RESTORATIONS INTERIM SOLUTIONS LONG-TERM RESTORATIONS Many dentists
Dentatus ANEW Narrow Diameter Implants Expanding Implantology with More Treatment Options The Versatility of Dentatus ANEW LONG-TERM RESTORATIONS INTERIM SOLUTIONS LONG-TERM RESTORATIONS Many dentists
Hiron Andreaza da Cunha, MS 1 /Carlos Eduardo Francischone, DMD 2 /Hugo Nary Filho, DDS 3 / Rubelisa Cândido Gomes de Oliveira, BDS 4
 A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
A Comparison Between Cutting Torque and Resonance Frequency in the Assessment of Primary Stability and Final Torque Capacity of and TiUnite Single-Tooth Implants Under Immediate Loading Hiron Andreaza
Implant Site Development Part I
 REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
Long-term success of osseointegrated implants
 Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
Against All Odds A No Bone Solution Long-term success of osseointegrated implants depends on the length of the implants used and the quality and quantity of bone surrounding these implants. As surgical
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
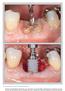 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
Successful osseointegration of implants has been
 Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
Many of the problems reported by conventional
 Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Maxillary Overdentures Retained by Splinted and Unsplinted Implants: A Retrospective Study Timo O. Närhi, DDS, PhD 1 /Miluska Hevinga, DDS 2 / Ralph A. C. A. Voorsmit, DDS, PhD 3 /Warner Kalk, DDS, PhD
Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report
 CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration: An Editorial White Paper*
 Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration: An Editorial White Paper* Alan Meltzer, DMD, MScD; Harold Baumgarten, DMD; Tiziano Testori, MD, DDS; Paolo Trisi, DDS, PhD Published by Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration:
Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration: An Editorial White Paper* Alan Meltzer, DMD, MScD; Harold Baumgarten, DMD; Tiziano Testori, MD, DDS; Paolo Trisi, DDS, PhD Published by Pressure Necrosis And Osseointegration:
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options
 Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Module 2 Introduction to immediate full arch fixed implant treatment - surgical options First Name Last Name Objectives Identify the need and opportunity to treat full arch patients with fixed detachable
Ankylos. Scientific Summary
 Ankylos Scientific Summary Implanting TissueCare For over 25 years, the Ankylos implant system stands for stable, long-term esthetics. The results from numerous publications and long-term clinical experience
Ankylos Scientific Summary Implanting TissueCare For over 25 years, the Ankylos implant system stands for stable, long-term esthetics. The results from numerous publications and long-term clinical experience
More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution.
 More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution. Expand your patient pool with an innovative solution. With the Straumann PURE Ceramic Implant, clinicians have an additional option to convince
More than pure esthetics. The natural and strong solution. Expand your patient pool with an innovative solution. With the Straumann PURE Ceramic Implant, clinicians have an additional option to convince
