Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial
|
|
|
- Miranda Lane
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Interproximal Papilla Levels Following Early Versus Delayed Placement of Single-Tooth Implants: A Controlled Clinical Trial Lars Schropp, DDS, PhD /Flemming Isidor, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont /Lambros Kostopoulos, MS, DDS, PhD 3 / Ann Wenzel, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont 4 Purpose: The aim of this study was to evaluate interproximal papillae and clinical crown height following the placement of single-tooth implants according to early and delayed protocols. Materials and Methods: Forty-five patients were randomly allocated to either the early group or the delayed group. They were treated with a single-tooth acid-etched Osseotite implant in the maxillary or mandibular anterior or premolar region an average of days (in the case of early placement) or 3 months (in the case of delayed placement) following tooth extraction. Interproximal papilla dimensions and clinical crown height were evaluated using a score index in 39 patients who attended a follow-up visit 6 to 8 months after prosthesis delivery. The patients were evaluated in photographs taken week after crown placement (baseline) and approximately.5 years after crown placement (follow-up). Results: It was demonstrated by logistic regression the risk of presenting no papilla or a negative papilla was 7 times greater at baseline for delayed cases than for early cases (33% versus 8%). However, the soft tissue fill in the proximal spaces improved significantly from baseline to the.5-year follow-up in both groups, with no significant difference between the groups found at follow-up. The papilla height almost years after implant placement was inversely correlated with patient age. The clinical crown height was acceptable in significantly more cases in the early group than in the delayed group at follow-up. Half of the crowns in the delayed group exhibited an inappropriate height; of these, almost two thirds were assessed to be too short. Discussion and Conclusion: Early placement of single-tooth implants may be preferable to delayed implant placement technique in terms of early generation of interproximal papillae and the achievement of an appropriate clinical crown height, but no difference in papilla dimensions was seen at.5 years after seating of the implant crown. INT J ORAL MAXILLOFAC IMPLANTS 5;: Key words: delayed implant placement, dental implants, early implant placement, esthetics of dental prostheses, mucosa The success of treatment with dental implants for replacement of or more missing teeth is well documented in both clinical and experimental studies. 4 Until recently, success criteria have mainly Assistant Professor, Department of Prosthetic Dentistry, Royal Dental College, University of Aarhus, Denmark. Professor, Department of Prosthetic Dentistry, Royal Dental College, University of Aarhus, Denmark. 3 Associate Professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Royal Dental College, University of Aarhus, Denmark. 4 Professor, Department of Oral Radiology, Royal Dental College, University of Aarhus, Denmark. Correspondence to: Dr Lars Schropp, Department of Prosthetic Dentistry, Royal Dental College, Aarhus University, Vennelyst Boulevard 9, 8 Århus C, Denmark. Fax: lschropp@odont.au.dk focused on technical and functional aspects of the implant. Commonly used criteria for success are achievement of osseointegration, maintenance of a stable peri-implant marginal bone level, and high survival rates. 5 However, when dealing with implantsupported restorations in the anterior region, treatment success will also depend on the esthetic outcome. Currently, patients have great expectations that prosthetic restorations look like their natural teeth. Particularly with single-tooth replacements, there are high demands upon the clinician, who must ensure that the artificial crown is integrated harmoniously with the existing dentition. Obviously, the appearance of the restoration in terms of color, shape, and surface structure has a great influence on the esthetic outcome. Another factor that may be important for obtaining a favorable esthetic result The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 753
2 following implant treatment is the preservation or creation of harmonious soft tissue contours of the peri-implant mucosa, with distinct papillae. Several approaches have been suggested for improving the esthetics in relation to implant treatment 6,7 : tissue augmentation including bone and/or connective tissue grafting, 8,9 guided bone regeneration, orthodontic extrusion,, modification of surgical procedures 3 7 (suturing and incision techniques, eg, the punch technique 5 ), and development of various implant and abutment designs. 8 Most of these options for optimizing the esthetic result are associated with increased financial costs and may prolong the treatment period. Another approach may be immediate placement of the implant, alternatively combined with the immediate provision of temporary prostheses. 3 When implants are placed in fresh extraction sockets, there may be peri-implant bone defects. To ensure bone formation in these gaps and osseointegration of the entire implant surface, bone reconstructive procedures (grafting, guided tissue regeneration) have been applied. However, in a recent study 4 it was shown that 3-wall infrabony defects with a maximum of 5 mm between the parallel walls, a maximum depth of 4 mm, and a perpendicular width of up to mm are capable of healing spontaneously. It has never been determined whether the presence of bone defects just after implant placement has an impact on peri-implant soft tissue conditions, including the appearance of the interproximal papillae. Most previous investigations that have focused on peri-implant soft tissue conditions are case studies, and to the authors knowledge, no randomized, controlled clinical studies exist.,,5 9 The aim of this prospective, randomized clinical study was to evaluate the dimensions of the interproximal papillae and the clinical crown height following early and delayed placement of single-tooth implants week after crown placement and at a follow-up visit approximately.5 years after crown placement. MATERIALS AND METHODS The study population consisted of 45 consecutive patients treated with Osseotite implants (3i/Implant Innovations, Palm Beach Gardens, FL) in the maxillary or mandibular anterior or premolar region. Two different treatment protocols for implant placement were applied: early implantation and delayed implantation. The patients were randomly allocated to of these groups at the initial examination. The implants in the early group were placed between 3 and 5 days following extraction of the tooth to be replaced (mean = days), while implant placement in the delayed group was performed after a healing period of approximately 3 months. No membranes were used. Grafting with autogenous bone in cases of fenestrations or dehiscences where implant threads had been exposed was done at implant placement surgery solely in the delayed group, whereas grafting of these types of defects was done at abutment connection surgery in both groups. After 3 months, a -piece or -piece EP healing abutment (3i/Implant Innovations) was connected to the implants to allow guided soft tissue healing for 4 to 6 weeks. A single-tooth ceramometal restoration was fabricated for 4 patients. Details on the study groups and the surgical treatment procedures have been described in a previous article. 4 Clinical photographs of the implant crowns, including at least adjacent tooth on each side, if present, were obtained week after seating of the prosthetic restoration (baseline) and at a visit (follow-up) 6 to 8 months later (corresponding to approximately years after implant placement). All photographs were digitized with a resolution of,6 dpi with a flatbed scanner with a transparency module (Seiko Epson, Nagano, Japan) and compressed to JPEG format. Blinded evaluation of the interproximal papillae mesial and distal to the implant restoration, as well as the clinical implant crown height, was carried out by an experienced prosthodontist who had not been involved in the treatment. Assessments were made of 39 patients ( women, 8 men) with a mean age of 49 years (range 3 to 76 years), who attended a follow-up visit to the clinic approximately.5 years after seating of the prosthetic restoration (9 in the early group; in the delayed group). The distribution of implant regions can be seen in Fig. The observer examined the photographs of the patients in a random order on a 9-inch cathode ray tube (CRT) computer monitor. He was allowed to manipulate the size of the photographs. The photographs taken at baseline and follow-up were randomly mixed. The interproximal spaces were assessed using a modification of the Papilla Index described by Jemt 5 : a score of = no papilla or a negative papilla; a score of = less than half of the height of the proximal area occupied by soft tissue; a score of = at least half of the height of the proximal area occupied by soft tissue (Figs and 3). Likewise, the clinical crown height was evaluated as follows: a score of = too long; a score of = too short; a score of 3 = appropriate. The observer was instructed to focus on the level of the marginal mucosa compared to that of the adjacent teeth rather than the incisal/occlusal extension of the crown. The scores for the papillae and the crown 754 Volume, Number 5, 5
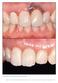
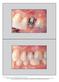
3 Fig Distribution of implant regions. CI = central incisor, LI = lateral incisor, C = canine, PM = premolar Early Delayed No. of implants CI LI C PM Maxilla CI LI C PM Mandible Fig An implant site (left) at baseline and (right) at the.5-year follow-up. The papillae received scores of mesially and distally at baseline. At follow-up, both papillae received scores of. Fig 3 An implant site (left) at baseline and (right) at the.5-year follow-up. The papillae received scores of mesially and distally at baseline. At follow-up, both papillae received scores of. height at baseline and follow-up were recorded. Twenty percent of the photographs were selected at random and re-evaluated by the same observer 6 weeks later. To determine the reproducibility of the method used for evaluating the parameters, the percentage of agreement between the first and second assessments was calculated. Agreement between the first and second recordings was 88% for clinical height assessments. Papilla scores of the first assessment were identical to the scores of the second assessment 8% of the time on the mesial side and 87% on the distal side. The clinical attachment levels were measured at the teeth adjacent to the implant site just before implant placement. Average of the buccal and lingual attachment levels at the tooth surfaces facing the implant site were recorded. Data Analysis Frequencies for the papilla and clinical crown height scores were calculated. Differences in papilla scores between the early and delayed groups were tested by means of the Mann-Whitney test. recorded at baseline were compared with the scores at the.5- year follow-up and tested for significant difference by the Wilcoxon signed rank test for paired data. Data on papilla assessments were also dichotomized using thresholds: () a score of versus all The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 755
4 Mesial papilla Distal papilla Mesial + distal papilla 7 7 Follow-up 6 Follow-up 6 Follow-up Fig 4 Frequency of scores for mesial and distal papillae at week after crown placement (baseline) and at the.5-year follow-up (total for the early and delayed groups). Table Average Frequencies of Mesial and Distal Papillae with the of and Week After Crown Placement () and at the.5-year Follow-up Score Early (%) P Delayed (%) P P* 8 33 <. NS <. Follow-up 8 3 NS 3 6 NS <. <. Follow-up NS *Indicates significance of the difference between the early and delayed groups. P <.5 was considered significant. other scores and () a score of versus all other scores.thereafter, differences in the frequencies of the scores between the early and delayed groups were tested by means of tests, and differences between baseline and follow-up by McNemar s test. Logistic regression analysis was applied to calculate the risk indicators for having no papilla or a negative papilla (score of ) and for receiving a score of, respectively. Correlations between papilla scores at baseline and at.5-year follow-up, respectively, and clinical attachment levels just before implant placement at teeth surfaces adjacent to the implant site were tested for statistical significance by means of Spearman s rho test. Likewise, correlations between papilla scores and patient age were tested. Additionally, logistic regression models were made with papilla scores at baseline and.5-year follow-up, respectively, as the dependent variables and patient age, gender, and clinical attachment level at teeth adjacent to the implant site as independent variables. Papilla scores were dichotomized into groups: scores of or and scores of. Age and clinical attachment level were entered into the model as continuous variables. In a second model, patient ages were divided into groups: those equal to or older than the median age (5 years) and those younger than the median age. Distribution of the papilla scores for implant sites associated with a peri-implant bone defect at implant placement was compared with the distribution for implant sites not associated with a defect, and tests were used for testing the difference. Data on clinical crown height assessments were dichotomized into groups: scores of or (too long or too short) and scores of 3 (appropriate), and differences in the frequencies of the scores between the early and delayed groups at baseline and followup were tested by means of tests, and differences between baseline and follow-up by McNemar s test. The level of statistical significance was set at P <.5. RESULTS The distribution of papilla scores based on clinical photographs obtained week after crown placement (baseline) and at the.5-year follow-up is presented in Fig 4. Both for the mesial and distal papillae, significantly higher scores, ie, more favorable scores, were recorded at.5-year follow-up compared with baseline (P <.5). No significant differences between the early and delayed groups were found at either time point (P >.). In the following, overall data for the mesial and distal papillae are described (average percentages are stated). At baseline, % of the interproximal spaces were associated with no papilla or a negative papilla (score of ). After.5 years, 5% of the sites received a score of (Fig 4). No negative papillae were seen. When the early and delayed groups were analyzed separately, a significant difference between baseline and.5-year follow-up was revealed only in the delayed group (Table ). In this group, 33% of the sites received a score of at baseline versus 3% after.5 years (P <.). In the early group, 8% of the sites 756 Volume, Number 5, 5
5 Distal papilla score at baseline Distal papilla score at follow-up a Clinical attachment level (mm) b Clinical attachment level (mm) Distal papilla score at baseline Distal papilla score at follow-up c Age d Age Fig 5 Correlations between clinical attachment level just before implant placement at the tooth surface distal to the implant site and the distal papilla score (a) at baseline and (b) at the.5-year follow-up. Correlations between patient age and distal papilla score (c) at baseline and (d) at the.5-year follow-up. A circle represents case, and each additional sunflower petal represents case. A red fit line indicates statistically significant correlation. received a score of both at baseline and at the follow-up. Testing the difference between the groups by logistic regression, an odds ratio (OR) of 7. was found, which means that the risk of presenting no papilla or a negative papilla at baseline was 7. times greater in the delayed group than in the early group (P <.5). In the early group, at least half of the height of the proximal area was occupied with soft tissue (score of ) in 3% of the cases at baseline and in 57% at the.5-year follow-up (Table ). The corresponding values in the delayed group were 6% (baseline) and 63% (follow-up). This improved soft tissue fill at the.5-year follow-up was statistically significant in both groups (P <.). A statistically significant correlation between papilla score recorded week after seating of the implant crown and clinical attachment level at the tooth surface adjacent to the implant site measured just before implant surgery was found for the distal papilla (P =.) (Fig 5a) but not for the mesial papilla (P =.9). At the.5-year follow-up, the scores for neither the neither mesial nor distal papillae correlated with the clinical attachment levels (P >.9) (Fig 5b). No correlation was found between papilla scores mesial and distal to the implant crown and patient age at baseline (P >.5) (Fig 5c); however, at the.5- year follow-up, papilla scores correlated significantly with age (P <.5) (Fig 5d). These data were supported by logistic regression analyses. Of the independent variables tested, only patient age was shown to be a risk indicator for having a papilla score of or two years after implant placement. Patients The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 757
6 No defect Defect year follow-up Early Delayed year follow-up Fig 6 Frequency of mesial and distal papilla scores at sites associated with peri-implant bone defects just after implant placement and those without bone defects (combined total for early and delayed groups). Evaluations at week after crown placement (baseline) and.5-year follow-up. Fig 7 Frequency of clinical crown height scores in the early and the delayed groups at baseline and.5-year follow-up. of 5 years or older had a significantly higher risk of presenting a papilla occupying less than half of the height of the proximal area at follow-up than younger patients (OR = 6.4, P =.3 mesially; OR = 9.3, P =.3 distally). The percentages of the papilla scores,, and for proximal implant sites associated with a periimplant bone defect at implant surgery did not differ considerably from sites not associated with a bone defect (Fig 6). At baseline, 4% (3 of 54) of implant sites without a bone defect received a papilla score of versus. 4% (3 of ) of the sites associated with a defect. At.5-year follow-up, the percentages of the papilla scores for implant sites with and without a bone defect were almost the same. Assessments of clinical crown height showed no significant differences between the baseline and the.5-year follow-up examination. The height of the implant crown was determined to be appropriate in 68% of the cases at baseline in the early group; after.5 years, 83% of the crowns were at a proper height (P =.5). The corresponding numbers in the delayed group were 45% at baseline and 5% at follow-up (P >.99). Sixty percent of the crowns that were determined to have an inappropriate height in the delayed group at follow-up were too short. A significant difference between the groups was found at the.5-year follow-up (P <.4). The distribution of the clinical crown height scores between the early and delayed groups is presented in Fig 7. DISCUSSION In the present controlled clinical investigation, no significant differences were found between early and delayed placement of single-tooth implants following tooth extraction in regard to interproximal papilla dimensions.5 years after implant crown placement. Furthermore, it was revealed that the soft tissue fill in the proximal spaces improved significantly between week after seating of the restoration (baseline) and the.5-year follow-up in both groups. This finding is supported by a study by Chang and associates, 3 who found that papilla height adjacent to implant-supported single-tooth replacements improved over an average observation period of 38 months. Similarly, Jemt 5 has reported that a significant spontaneous regeneration of the papillae took place during a period of to 3 years in relation to single-tooth implants. He found that half or more of the height of the papilla was present in 5% of the proximal spaces at placement but in 88% at follow-up, a difference of.8 times. This is in agreement with the data of the present study; in the present study, at least half of the height of the proximal area was filled with soft tissue in.8 times more cases at follow-up than at baseline (57% versus 3%) in the early group and.5 times more cases in the delayed group (6% versus 4%). Overall data for the early and delayed groups showed that less than half of the height of the proximal area was filled with soft tissue at baseline in 758 Volume, Number 5, 5
7 more than 7% of the sites and approximately % were associated with no papilla or a negative papilla. During the.5-year observation period, the appearance of the papilla improved significantly in both groups. Nevertheless, less than half of the height of the proximal area was filled with soft tissue in 4% of the cases at follow-up for both groups. When evaluating the results of this study, it is important to take age and the general periodontal conditions of the patients into consideration. Most likely, it is possible to obtain a more favorable appearance of the papillae in patients without pre-existing periodontal disease. This is supported by previous studies, which have demonstrated that the crestal bone level has an influence on the volume of the interproximal dental and peri-implant papilla. 8,3 The results of the present study indicated that there may be a correlation between the clinical attachment level present at the tooth surface adjacent to the implant site before implant placement and the height of the papilla week after the seating of the crown. However, after.5 years, the papilla score did not correlate with the clinical attachment level. To evaluate whether age could be a predictor for the appearance of interproximal papillae adjacent to single-tooth implant crowns, tests for correlation between age and papilla score as well as logistic regression analyses were performed. The results revealed that no correlation existed between age and papilla level assessed week after seating of the crown. In contrast, a highly statistically significant correlation between age and papilla level at followup was found. At that point, only 4% of the interproximal spaces were filled less than half of the height with soft tissue in patients younger than 5 years, versus 6% among the older patients. Thus, these data strongly suggest that the improvement of interproximal papilla height in relation to singletooth implants over a period of.5 years is more pronounced among younger patients than older patients. Future investigations should focus on the relationship between papilla generation and patient age, and studies with larger patient samples must confirm the results of this study before a definitive conclusion can be made. It was striking that the risk of having no papilla or a negative papilla present one week after crown placement was 7 times greater for patients in the delayed group than for those in the early group (33% versus 8% of the sites). However, during the observation period, a substantial improvement was observed in the delayed group; only 3% of the papillae received score after.5 years. A possible explanation for the difference between the groups could be that implant placement soon after tooth extraction may provide for preservation of bone tissue, 3 which in turn will have an impact on the soft tissue conditions. Previous investigations indicated only that the position of the soft tissue margin is related to the level of bone support around the implants. 33,34 It was of interest to investigate whether the presence of proximal peri-implant bone defects at implant surgery influences the height of the papillae. In the present study, it was observed that the papilla scores were not dependent on whether the proximal implant sites were associated with a bone defect. This finding could be explained by the substantial amount of bone formation actually occurring in these defects during the first 3 months following implant placement. 4 Further bone generation can be expected within the first.5 years postplacement. Data on clinical crown height revealed that the height was appropriate in significantly more cases in the early group than in the delayed group at the follow-up examination. Improvement was found in both groups at the follow-up examination, although this improvement was not statistically significant. At follow-up, 83% of the implant crowns in the early group were assessed to have a proper height, compared with only 5% in the delayed group. Those crowns in the early group whose height was considered inappropriate were all too long. In contrast, almost two thirds of the crowns in the delayed group with an inappropriate height were assessed to be too short. This contradicts the general clinical expectation that delayed implant placement should result in long implant-supported crowns because of the resorption of the alveolar ridge occurring the first 3 to 6 months after tooth extraction. On the other hand, this observation is in agreement with a recent study 35 which found that the major dimensional changes of the alveolar ridge following tooth extraction take place in the buccolingual direction and that only minor changes in height occur. Reshaping of the soft tissue might be a possibility to achieve appropriate crown heights. However, the implant crowns that were determined to be too short in this study were not associated with an excess of soft tissue buccally. In the present study, early implant placement was defined as a delay of 3 to 5 days between tooth extraction and implant placement. The rationale for using this protocol was the ability to include teeth with periapical lesions; the protocol also enabled the staff to coordinate the performance of presurgical radiography and surgery. Obviously, this modification of the immediate implant placement technique might have an impact on the appearance of the interproximal papillae and clinical crown height. Intraobserver reproducibility of the evaluation method was found to be high. When the first and The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 759
8 second scorings of clinical crown height were compared, an agreement of almost 9% was found. The recordings of the first assessment of the papillae corresponded to those of the second assessment in more than 8% of the cases. However, it is obvious that the evaluation criteria are by nature subjective. The results of this controlled clinical study demonstrated that the early placement of singletooth implants in the anterior and premolar regions may be preferable to a delayed placement protocol in terms of early generation of interproximal papillae with a favorable shape and volume adjacent to implant-supported crowns. Furthermore, it was revealed that an appropriate clinical crown height could be achieved in significantly more cases in the early group than in the delayed group. An improvement of the soft tissue appearance during the.5- year observation period was demonstrated in both groups. It should be emphasized that the implants were placed using conventional methods; no advanced techniques for preservation of the soft tissues were used. However, a flap design at the abutment operation to provide establishment of attached mucosa at the buccal aspect of the implant was applied. Despite the fact that only 6% of the proximal areas were at least half-filled with soft tissue.5 years after placement of the implant crowns, a questionnaire survey 36 showed that the patients were highly satisfied with the general appearance of their restorations. Clinical crown height and the dimensions of the interproximal papillae have certainly a great influence on the esthetic outcome of implant-supported restorations. For this reason, it is of utmost importance to inform patients carefully prior to implant treatment about the possibilities for restoring the natural appearance of peri-implant soft tissues. It is likewise important to moderate patient expectations and explain that it is not always possible to preserve the papillae or to ensure appropriate clinical crown height, particularly in patients with previous periodontal disease. Conversely, the patients should also be informed about the possibility of spontaneous improvement of the peri-implant soft tissue appearance during the following years. However, one should bear in mind that this improvement over time may be related to patient age. CONCLUSION The present study demonstrated that early implant placement was superior to delayed placement of single-tooth implants in regard to early generation of interproximal papillae. The early and the delayed protocols performed equally well in achievement of soft tissue fill in the interproximal spaces adjacent to the implant crown at.5 years after seating of the restoration. The papilla height years after implant placement was inversely correlated with patient age in this patient population. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This project was supported by 3i Implant Innovations, Palm Beach, Florida. REFERENCES. Adell R, Lekholm U, Rockler B, Brånemark P-I. A 5-year study of osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Int J Oral Surg 98;: Jemt T, Lekholm U, Adell R. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of partially edentulous patients: A preliminary study on 876 consecutively placed fixtures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 989;4: Schmitt A, Zarb GA.The longitudinal clinical effectiveness of osseointegrated dental implants for single-tooth replacement. Int J Prosthodont 993;6: Norton MR. Biologic and mechanical stability of single-tooth implants: 4- to 7-year follow-up. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res ;3:4. 5. van Steenberghe D, Quirynen M, Naert I. Survival and success rates with oral endosseous implants. In: Lang NP, Karring T, Lindhe J (eds). Proceedings of the 3rd European Workshop on Periodontology: Implant Dentistry. Ittingen: Quintessence, 999: Shearer BH. Osseointegrated implants: a review of the literature. Int Dent J 995;45: de Lange GL. Aesthetic and prosthetic principles for single tooth implant procedures: an overview. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 995;7: Stambaugh R. Aesthetic ridge and extraction site augmentation for anterior implant placement without barrier membrane. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 997;9: Price RB, Price DE. Esthetic restoration of a single-tooth dental implant using a subepithelial connective tissue graft: a case report with 3-year follow-up. Int J Periodont Restor Dent 999;9:9.. Hermann JS, Buser D. Guided bone regeneration for dental implants. Curr Opin Periodontol 996;3: Salama H, Salama M, Kelly J.The orthodontic-periodontal connection in implant site development. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 996;8: Francischone CE, Costa CG, Francischone AC, Ribeiro HT, Silva RJ. Controlled orthodontic extrusion to create gingival papilla: a case report. Quintessence Int ;33: Schwartz-Arad D, Chaushu G. Immediate implant placement: a procedure without incisions. J Periodontol 998;69: Tinti C, Benfenati SP.The ramp mattress suture: a new suturing technique combined with a surgical procedure to obtain papillae between implants in the buccal area. Int J Periodont Restor Dent ;: Auty C, Siddiqui A. Punch technique for preservation of interdental papillae at nonsubmerged implant placement. Implant Dent 999;8: Volume, Number 5, 5
9 6. Takei HH, Han TJ, Carranza FA Jr, Kenney EB, Lekovic V. Flap technique for periodontal bone implants. Papilla preservation technique. J Periodontol 985;56:4. 7. Flanagan D. An incision design to promote a gingival base for the creation of interdental implant papillae. J Oral Implantol ;8: Gadhia MH, Holt RL. A new implant design for optimal esthetics and retention of interproximal papillae. Implant Dent 3;: Lazzara RJ. Managing the soft tissue margin: the key to implant aesthetics. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 993;5: Wöhrle PS. Nobel Perfect esthetic scalloped implant: rationale for a new design. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 3;5 Suppl : Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K, Lozada J. Immediate placement and provisionalization of maxillary anterior single implants: - year prospective study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 3; 8: Kan JY, Rungcharassaeng K. Interimplant papilla preservation in the esthetic zone: A report of six consecutive cases. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 3;3: Touati B, Guez G. Immediate implantation with provisionalization: from literature to clinical implications. Pract Proced Aesthet Dent ;4: Schropp L, Kostopoulos L, Wenzel A. Bone healing following immediate versus delayed placement of titanium implants into extraction sockets: a prospective clinical study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 3;8: Jemt T. Regeneration of gingival papillae after single-implant treatment. Int J Periodont Restor Dent 997;7: Grunder U. Stability of the mucosal topography around single-tooth implants and adjacent teeth: -year results. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent ;: Jemt T. Restoring the gingival contour by means of provisional resin crowns after single-implant treatment. Int J Periodont Restor Dent 999;9: Salama H, Salama MA, Garber D, Adar P.The interproximal height of bone: a guidepost to predictable aesthetic strategies and soft tissue contours in anterior tooth replacement. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent 998;: Garber DA, Salama MA, Salama H. Immediate total tooth replacement. Compend Contin Educ Dent ;: 6, Chang M, Wennström JL, Ödman P, Andersson B. Implant supported single tooth replacements compared to contralateral natural teeth. Crown and soft tissue dimensions. Clin Oral Implants Res 999;: Tarnow DP, Magner AW, Fletcher P.The effect of the distance from the contact point to the crest of bone on the presence or absence of the interproximal dental papilla. J Periodontol 99;63: Denissen HW, Kalk W, Veldhuis HA, van Waas MA. Anatomic consideration for preventive implantation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 993;8: Abrahamsson I, Berglundh T, Wennstrom J, Lindhe J.The periimplant hard and soft tissues at different implant systems. A comparative study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 996;7: Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Dimension of the periimplant mucosa. Biological width revisited. J Clin Periodontol 996;3: Schropp L, Wenzel A, Kostopoulos L, Karring T. Bone healing and soft tissue contour changes following single-tooth extraction: A clinical and radiographic -month prospective study. Int J Periodont Restor Dent 3;3: Schropp L, Isidor F, Kostopoulos L, Wenzel A. Patient experience of, and satisfaction with, delayed-immediate vs. delayed single-tooth implant placement. Clin Oral Implants Res 4; 5: The International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants 76
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
The effect of peri-implant bone exposure on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2012;42:20-24 http://dx.doi.org/10.5051/jpis.2012.42.1.20 on soft tissue healing and bone loss in two adjacent implants Seung-Yun Shin 1, Seung-Boem Kye 1, Jongrak
The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration
 IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Successful osseointegration of implants has been
 Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
Therapeutic Management for Immediate Implant Placement in Sites with Periapical Deficiencies Where Coronal Bone Is Present: Technique and Case Report Cyril I. Evian, DMD 1 /Ahmed Al-Momani, BDS 2 /Edwin
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE IMPACT OF IMMEDIATE AND NON-IMMEDIATE PROVISIONALIZATION ON THE SOFT TISSUE ESTHETICS OF FINAL RESTORATIONS ON IMMEDIATELY PLACED IMPLANTS Chong-Hyun Han 1, DDS, PhD, Jeong-Won Paik 2,
The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org ( this information is current as of July 11, 2011):
 Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
Implants or Pontics: Decision Making for Anterior Tooth Replacement Frank Spear J Am Dent Assoc 2009;140;1160-1166 The following resources related to this article are available online at jada.ada.org (
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets
 Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
The refinement of adhesive technology and contemporary
 CONTINUING EDUCATION 3 4 THE INTERPROXIMAL HEIGHT OF BONE: A GUIDEPOST TO PREDICTABLE AESTHETIC STRATEGIES AND SOFT TISSUE CONTOURS IN ANTERIOR TOOTH REPLACEMENT Henry Salama, DMD* Maurice A. Salama, DMD
CONTINUING EDUCATION 3 4 THE INTERPROXIMAL HEIGHT OF BONE: A GUIDEPOST TO PREDICTABLE AESTHETIC STRATEGIES AND SOFT TISSUE CONTOURS IN ANTERIOR TOOTH REPLACEMENT Henry Salama, DMD* Maurice A. Salama, DMD
Ten tips that everyone should know before performing a treatment involving implants in the aesthetic zone.
 Ten tips that everyone should know before performing a treatment involving implants in the aesthetic zone. Introduction Francisco Teixeira Barbosa. Private practice. Barcelona. Spain. Nowadays, implantology
Ten tips that everyone should know before performing a treatment involving implants in the aesthetic zone. Introduction Francisco Teixeira Barbosa. Private practice. Barcelona. Spain. Nowadays, implantology
The Brånemark osseointegration method, using titanium dental implants (fixtures)
 Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Early Failures in 4,641 Consecutively Placed Brånemark Dental Implants: A Study From Stage 1 Surgery to the Connection of Completed Prostheses Bertil Friberg, DDS/Torsten Jemt, DDS, PhD/Ulf Lekholm, DDS,
Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Page 1 of 10 Issue Date: March 2005, Posted On: 5/2/2005 Dental Implant Placement in the Maxillary Anterior Region: Guidelines for Aesthetic Success Michael Tischler, DDS Figure 1. A 43-year-old female
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps
 CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps Jay R. Beagle Despite the continued debate regarding the need for
CLINICAL AND RESEARCH REPORTS Developing Keratinized Mucosa Around Nonsubmerged Dental Implants. Part I: The Use of Vascularized Flaps Jay R. Beagle Despite the continued debate regarding the need for
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Since the introduction of osseointegrated dental implants
 CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
CLINICAL Papilla Formation in Response to Computer-Assisted Implant Surgery and Immediate Restoration Paul A. Schnitman, DDS, MSD 1 * Chie Hayashi, DDS, PhD, MMSc 2 This retrospective analysis was undertaken
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 559 Emergence Profile Design Based on Implant Position in the Esthetic Zone Marius Steigmann, DDS 1,2 Alberto Monje, DDS 3 Hsun-Liang Chan,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 559 Emergence Profile Design Based on Implant Position in the Esthetic Zone Marius Steigmann, DDS 1,2 Alberto Monje, DDS 3 Hsun-Liang Chan,
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Patients esthetic demands and
 Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Predictable Periimplant Gingival Esthetics: Use of the Natural Tooth as a Provisional following Implant Placement ROBERT C. MARGEAS, DDS* ABSTRACT Maintaining the interdental papilla and bone height following
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
(Images are at the end of article)
 Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Long term provisionalization during periodontal surgery and extraction site tissue grafting: A Case Review Michael Tischler, DDS Diplomate American Board Of Oral Implantology/Implant Dentistry (Images
Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
 International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
International Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 125146, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/125146 Research Article Interdental Papilla Length and the Perception of Aesthetics in Asymmetric Situations
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association
 All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
All Dentistry is Cosmetic Betsy Bakeman, DDS Arkansas State Dental Association Patients have traditionally sought treatment when concerned with the way their teeth look, function or feel. Over the past
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
Endosseous dental implants initially showed very
 Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
Five-mm-Diameter Implants without a Smooth Surface Collar: Report on 98 Consecutive Placements Franck Renouard, DDS*/Jean-Pierre Arnoux, DDS**/David P. Sarment, DDS*** In recent years, indications for
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 313 Timing, Positioning, and Sequential Staging in Esthetic Implant Therapy: A Four-Dimensional Perspective Akiyoshi Funato, DDS* Maurice
PETER GEHRKE, DR. MED. DENT.* MARKUS LOBERT, DR. MED. DENT. GÜNTER DHOM, DR. MED. DENT.
 Reproducibility of the Pink Esthetic Score Rating Soft Tissue Esthetics Around Single-Implant Restorations with Regard to Dental Observer Specialization PETER GEHRKE, DR. MED. DENT.* MARKUS LOBERT, DR.
Reproducibility of the Pink Esthetic Score Rating Soft Tissue Esthetics Around Single-Implant Restorations with Regard to Dental Observer Specialization PETER GEHRKE, DR. MED. DENT.* MARKUS LOBERT, DR.
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
In the esthetic zone, osseointegration
 CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
Implant Site Development Part I
 REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
REVIEW ARTICLE Implant Site Development Part I 1 Umang Nayar, 2 Shankar Iyer IJCID Implant Site Development Part I 1 Consultant, Dental Surgeon and Periodontist at Max Health Care, New Delhi, Professor
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 27 Flapless Implant Surgery in the Esthetic Region: Advantages and Precautions Tae-Ju Oh, DDS, MS 1 /Jeffrey Shotwell, DDS, MS 2 Edward
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
The surgical placement of dental implants has
 Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS,
 Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
Cr e a t i o n a n d Preservation o f Na t u ra l So f t Tissue Em e r g e n c e Profiles Ar o u n d Dental Implants in the Esthetic Zone by Paul S. Petrungaro, DDS, MS, FICD, FACD, DICOI Chicago, IL Lake
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5
 Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Restoring esthetics by immediately loaded implant placement Jurel SK 1, Gupta DS 2, Agarwal H 3, Singh RD 4, Aggarwal KK 5 Case Report 1 Dr. Sunit K Jurel MDS, Assistant professor Department of Prosthodontics
Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed in Healed Sockets: A Cross-sectional Study
 JDSOR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1099 Implants Placed in Healed Sockets Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed
JDSOR ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1099 Implants Placed in Healed Sockets Dentascan Evaluation of Hard Tissue Changes around Implants Placed
INTRODUCTION. Jun-Won Hong 1, DDS, MS, Seung-Geun Ahn 1, DDS, PhD, Dae-Ho Leem 2, DDS, PhD, Jae-Min Seo 1 *, DDS, MS
 CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.52 Immediate placement and functional loading of implants on canine with fixed partial denture for a patient having canine protected occlusion: a case
CASE REPORT http://dx.doi.org/10.4047/jap.2012.4.1.52 Immediate placement and functional loading of implants on canine with fixed partial denture for a patient having canine protected occlusion: a case
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Special reprint from
 Special reprint from Copyright 2007 by Quintessence Publ Co, Inc Volume 27 Number 5 October 2007 451 Fig 1d (left) View of the 1.3-mm twist drill preparing the osteotomy for implant placement. Fig 1e
Special reprint from Copyright 2007 by Quintessence Publ Co, Inc Volume 27 Number 5 October 2007 451 Fig 1d (left) View of the 1.3-mm twist drill preparing the osteotomy for implant placement. Fig 1e
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12 Accepted on:22/05/12
 SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
SURGICAL RECONSTRUCTION OF INTERDENTAL PAPILLA USING AN INTERPOSED SUBEPITHELIAL CONNECTIVE TISSUE GRAFT: A CASE REPORT ijcrr Vol 04 issue 12 Category: Case Report Received on:22/04/12 Revised on:07/05/12
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
 Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
Platform switching for marginal bone preservation around dental implants: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Atieh MA, Ibrahim HM, Atieh AH. J Periodontol. 2010 Oct;81(10):1350-66. BACKGROUND: Platform
New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of a Case Series
 See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295813926 New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of
See discussions, stats, and author profiles for this publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/295813926 New Surgical Protocol to Create Interimplant Papilla: The Preliminary Results of
The clinical use of endosseous implants has
 A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial of 3i Machined-Surface Implants: Results After 6 Years of Follow-up Dietmar Weng, DDS, Dr Med Dent 1 /Zhimon Jacobson, DDS 2 /Dennis Tarnow, DDS 3 / Markus B. Hürzeler,
A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Trial of 3i Machined-Surface Implants: Results After 6 Years of Follow-up Dietmar Weng, DDS, Dr Med Dent 1 /Zhimon Jacobson, DDS 2 /Dennis Tarnow, DDS 3 / Markus B. Hürzeler,
Initially, implant dentistry was focused on
 CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
Review Article. ISSN (Print)
 Scholars Journal of Dental Sciences (SJDS) Sch. J. Dent. Sci., 2015; 2(4):296-301 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Journal of Dental Sciences (SJDS) Sch. J. Dent. Sci., 2015; 2(4):296-301 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique
 e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
e116 Pouch Roll Technique for Implant Soft Tissue Augmentation: A Variation of the Modified Roll Technique Sang-Hoon Park, DDS, MS* Hom-Lay Wang, DDS, MSD, PhD** This paper presents three cases of peri-implant
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study
 Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
MODIFIED SINGLE ROLL FLAP APPROACH FOR SIMULTANEOUS IMPLANT PLACEMENT AND GINGIVAL AUGMENTATION
 Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Journal of IMAB ISSN: 1312-773X https://www.journal-imab-bg.org https://doi.org/10.5272/jimab.2017233.1667 Journal of IMAB - Annual Proceeding (Scientific Papers). 2017 Jul-Sep;23(3): Case report MODIFIED
Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function
 Young-Il Kang* Dong-Won Lee* Kwang-Ho Park Ik-Sang Moon Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function Authors affiliations: Young-Il Kang*, Dong-Won Lee*, Ik-Sang
Young-Il Kang* Dong-Won Lee* Kwang-Ho Park Ik-Sang Moon Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function Authors affiliations: Young-Il Kang*, Dong-Won Lee*, Ik-Sang
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
 International Extraction Journal Defect: of Clinical Assessment, Implant Dentistry, Classification January-April and Management 2009;1(1):1-11 Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
International Extraction Journal Defect: of Clinical Assessment, Implant Dentistry, Classification January-April and Management 2009;1(1):1-11 Extraction Defect: Assessment, Classification and Management
INTRODUCTION. long-term results in the restoration of both totally and partially
 CLINICAL RESTORATION OF THE SOFT-TISSUE MARGIN IN SINGLE-TOOTH IMPLANT IN THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Jamil Awad Shibli, DDS, MS, PhD Susana d Avila, DDS, MS KEY WORDS Dental implants Subepithelial connective
CLINICAL RESTORATION OF THE SOFT-TISSUE MARGIN IN SINGLE-TOOTH IMPLANT IN THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Jamil Awad Shibli, DDS, MS, PhD Susana d Avila, DDS, MS KEY WORDS Dental implants Subepithelial connective
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported
 PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
PROSTHODONTICS Significance of crown shape in the replacement of a central incisor with a single implantsupported crown Luca Gobbato, DDS 1 /Gianluca Paniz, DDS 2 /Fabio Mazzocco, DDS 3 / Andrea Chierico,
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study
 Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
The Socket Shield Technique A case Report
 The Socket Shield Technique A case Report Haseeb H. Al-Dary Private Practice, Amman Jordan dary_haseeb@yahoo.com ABSTRACT In the aim of achieving an optimal esthetic result, implant dentistry has become
The Socket Shield Technique A case Report Haseeb H. Al-Dary Private Practice, Amman Jordan dary_haseeb@yahoo.com ABSTRACT In the aim of achieving an optimal esthetic result, implant dentistry has become
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate
 AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry Certificate The AO Certificate in Implant Dentistry provides an opportunity for AO members to demonstrate that they have attained a level of education and experience
Bernt Andersson, DDS, Odont Dr/PhD;* Sibel Bergenblock, DDS; Björn Fürst, DDS; Torsten Jemt, DDS, Odont Dr/PhD
 Long-Term Function of Single-Implant Restorations: A 17- to 19-Year Follow-Up Study on Implant Infraposition Related to the Shape of the Face and Patients Satisfactioncid_381 1..10 Bernt Andersson, DDS,
Long-Term Function of Single-Implant Restorations: A 17- to 19-Year Follow-Up Study on Implant Infraposition Related to the Shape of the Face and Patients Satisfactioncid_381 1..10 Bernt Andersson, DDS,
APOSTILA(DE(ARTIGOS( ( WEBINAR( INSTALAÇÃO*DE*IMPLANTES*NA*REGIÃO*POSTERIOR*DE* MAXILA*COM*POUCA*DISPONIBILIDADE*ÓSSEA* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
 APOSTILA(DE(ARTIGOS( ( WEBINAR( INSTALAÇÃO*DE*IMPLANTES*NA*REGIÃO*POSTERIOR*DE* MAXILA*COM*POUCA*DISPONIBILIDADE*ÓSSEA* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * DR.(EDUARDO(DIAS( 2015( CONTINUING EDUCATION 34
APOSTILA(DE(ARTIGOS( ( WEBINAR( INSTALAÇÃO*DE*IMPLANTES*NA*REGIÃO*POSTERIOR*DE* MAXILA*COM*POUCA*DISPONIBILIDADE*ÓSSEA* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * DR.(EDUARDO(DIAS( 2015( CONTINUING EDUCATION 34
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 61 Incision Design and Soft Tissue Management to Maintain or Establish an Interproximal Papilla Around Integrated Implants: A Case Series
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 61 Incision Design and Soft Tissue Management to Maintain or Establish an Interproximal Papilla Around Integrated Implants: A Case Series
Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
 Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
Journal of Dental Sciences (2012) 7, 373e378 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.e-jds.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison between different papillary recession classification systems
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report The Socket Science of Immediate Implants - Case Report Sanjay Kaul 1**, Shantipriya Reddy 2*, Soumya Kambali
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report The Socket Science of Immediate Implants - Case Report Sanjay Kaul 1**, Shantipriya Reddy 2*, Soumya Kambali
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Immediate implant placement in a single staged
 Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Bone and Crescent Shaped Free Gingival Grafting for Anterior Immediate Implant Placement: Technique and Case Report Han et al Thomas Han, DDS, MS 1 2 Abstract Immediate implant placement in a single staged
Available online at International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp , December, 2015
 z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
z Available online at http://www.journalcra.com International Journal of Current Research Vol. 7, Issue, 12, pp.24212-24216, December, 2015 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CURRENT RESEARCH ISSN: 0975-833X REVIEW
Amount of bone loss after maxillary dental implant loading in smoker and non-smoker patients
 Amount of bone loss after maxillary dental implant loading in smoker and non-smoker patients Taha Y. Hamad, B.D.S., H.D.D., M.Sc. (1) Background: Excessive crestal bone loss after dental implant occurs
Amount of bone loss after maxillary dental implant loading in smoker and non-smoker patients Taha Y. Hamad, B.D.S., H.D.D., M.Sc. (1) Background: Excessive crestal bone loss after dental implant occurs
Restoration of Congenitally Missing Lateral Incisors with Single Stage Implants: An Interdisciplinary Approach
 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1045 CASE REPORT Restoration of Congenitally Missing Lateral Incisors with Single Stage Implants: An Interdisciplinary Approach 1 Mitha M Shetty, 2 Akshai KR Shetty, 3 N Kalavathy,
10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1045 CASE REPORT Restoration of Congenitally Missing Lateral Incisors with Single Stage Implants: An Interdisciplinary Approach 1 Mitha M Shetty, 2 Akshai KR Shetty, 3 N Kalavathy,
Buccal Bone Resorption Around Posterior Implants After Surgery: A 1-Year Prospective Study
 Buccal Bone Resorption Around Posterior Implants After Surgery: A 1-Year Prospective Study Toshio Takuma, DDS 1,2 /Keiji Oishi, DDS, PhD 3 /Tomofusa Manabe, DT 2 / Satoshi Yoneda, DDS, PhD 4 /Toshihiko
Buccal Bone Resorption Around Posterior Implants After Surgery: A 1-Year Prospective Study Toshio Takuma, DDS 1,2 /Keiji Oishi, DDS, PhD 3 /Tomofusa Manabe, DT 2 / Satoshi Yoneda, DDS, PhD 4 /Toshihiko
Clinical outcome of submerged vs. non-submerged implants placed in fresh extraction sockets
 Luca Cordaro Ferruccio Torsello Mario Roccuzzo Clinical outcome of submerged vs. non-submerged implants placed in fresh extraction sockets Author s affiliations: Luca Cordaro, Ferruccio Torsello, Eastman
Luca Cordaro Ferruccio Torsello Mario Roccuzzo Clinical outcome of submerged vs. non-submerged implants placed in fresh extraction sockets Author s affiliations: Luca Cordaro, Ferruccio Torsello, Eastman
Since the report of Adell and associates, 1 well-documented
 Immediate Loading of an Implant Following Implant Site Development Using Forced Eruption: A Case Report Young-Seok Park, DDS, MSD 1 /Ki-Young Yi, DDS 2 /Seong-Cheol Moon, DDS, MSD, PhD 3 / Young-Chul Jung,
Immediate Loading of an Implant Following Implant Site Development Using Forced Eruption: A Case Report Young-Seok Park, DDS, MSD 1 /Ki-Young Yi, DDS 2 /Seong-Cheol Moon, DDS, MSD, PhD 3 / Young-Chul Jung,
Case study 2. A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant
 Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations
 Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
Dental Implant Treatment Planning and Restorative Considerations Aldo Leopardi, BDS, DDS, MS Practice Limited to Implant, Fixed and Removable Prosthodontics Greenwood Village, Colorado www.knowledgefactoryco.com
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A Case Series
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2012 14/3:62-68 One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2012 14/3:62-68 One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The patient gave a history of hypertension and gastritis for which was taking Lacidipine 4mg, Omeprazole 20mg and Simvastatin 40mg.
 A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
A.S. was referred by her general dental practitioner for assessment for possible implant placement to restore the space where her bridge replacing her maxillary central incisors had recently failed. Fig
G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM
 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
Vertical and/or horizontal alveolar
 CLINICAL Vascularized Connective Tissue Flap for Bone Graft Coverage Alan S. Herford, DDS, MD 1 * Todd C. Cooper, DDS 1 Carlo Maiorana, DDS, MD 2 Marco Cicciù, DDS, PhD 2 Alveolar defects are characterized
CLINICAL Vascularized Connective Tissue Flap for Bone Graft Coverage Alan S. Herford, DDS, MD 1 * Todd C. Cooper, DDS 1 Carlo Maiorana, DDS, MD 2 Marco Cicciù, DDS, PhD 2 Alveolar defects are characterized
