Long-term outcome of dental implants after maxillary augmentation with and without bone grafting
|
|
|
- Daniella Angelica Gibbs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi: /medoral Long-term outcome of dental implants after maxillary augmentation with and without bone grafting Manuel Cara-Fuentes 1, Jesús Machuca-Ariza 2, Alberto Ruiz-Martos 3, Mª Carmen Ramos-Robles 4, Ildefonso Martínez-Lara 5 1 DMD. Private practice, Almeria, Spain 2 DMD. Private practice, Malaga, Spain 3 DMD. Private practice, Madrid, Spain 4 MD, DDS, PhD. Collaborator Professor, Department of Oral Medicine, School of Dentistry, Granada, Spain 5 MD, PhD. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeon at University Hospital, Associate Professor of Health Sciences School of Dentistry, Granada, Spain Correspondence: Avda. Europa 177, La Mojonera, Almería, Spain, manolocaraf@gmail.com Please cite this article in press as: Cara-Fuentes M, Machuca-Ariza J, Ruiz-Martos A, Ramos-Robles Mª C, Martínez-Lara I. Long-term outcome of dental implants after maxillary augmentation with and without bone grafting. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. (2016), doi: /medoral Received: 14/09/2015 Accepted: 22/11/2015 Abstract Background: This study aims to evaluate the technique of sinus bone reformation, which consists of elevating the sinus membrane and placement the implant without bone graft, compared with the widely-used technique involving raising the maxillary sinus and grafting, using animal hydroxyapatite as the filler, while simultaneously fixing the implants. Material and Methods: This is a retrospective study on two groups of patients who underwent elevation of the sinus membrane and simultaneous placement of the implant. The grafting technique was applied to one group, while the other had no graft. An alveolar ridge height of 4 to 7 mm was necessary. Radiological control was undertaken at 6 months and one year post-prosthetic loading. In each group 38 implants were placed. Results: No significant behavioural differences were observed in the implants according to the Albrektsson success criteria. Implant failure was observed in 2 implants from the bone grafting group (success rate 93%) and in 1 implant from the reformation group (success rate 97%). In this group, bone formation was observed on both sides of each implant, the bone gain was measured using image management software (2.7±0.9mm mesial and 2.6±0.9mm distal). There was no correlation between mesial and distal bone gain and implant s length. Conclusions: The results indicate that bone reformation is a valid technique in cases involving atrophy of the posterior maxilla. Primary stability, maintenance of space by the implant, and the formation of a blood clot are crucial in this technique in order to achieve bone formation around the implant. It is an alternative to the conventional technique of sinus lift with filling material, and has several advantages over this procedure, including a lower infection risk, as it does not involve a biomaterial, reduced cost, a simpler technique, and better acceptance by the patient. Key words: Bone formation, sinus membrane elevation, maxillary sinus, bone grafting.
2 Introduction Implant placement in the posterior maxilla is frequently conditioned by a loss in bone height of the alveolar ridge, the most widespread treatment being the elevation and grafting of the maxillary sinus with different materials. Currently, the most-used synthetic material is hydroxyapatite, which is slowly resorbed, providing sufficient time for bone maturation and remodelling, maintaining the stability of the space gain in the maxillary sinus through time (1). A variation on the conventional sinus elevation technique is sinus bone reformation. This consists of sinus membrane raising according to the conventional technique, placement the implant, and placing the membrane over it, without the use of a grafting. It has been found that in the space below the membrane, where the implant is placed, there may be ossification that contributes to bone formation around the implant (2). In 2003, Lundgren et al. (3) described spontaneous bone formation in the maxillary sinus three months after extirpating an intrasinusal cyst, having had to raise the sinus membrane to stitch. In 2006, Palma et al. (4) after carrying out experimental studies on goats, showed that the amount of bony tissue increase after elevating the maxillary sinus, either with or without autogenous grafting, is similar after 6 months of healing. In 2007, Thor and Sennerby (5) put implants in the sinus without grafting, suggesting that the titanium surface of the implants demonstrated sufficient thrombogenicity. Activating the coagulation system and platelets affects cell and bone growth. The implant provides a vertical limit for the upper position of the elevated maxillary sinus membrane, while the space is maintained by the formation of a blood clot (6). Sufficient bone is needed to obtain adequate primary stability. It is thought that when the minimum height is less than 5 mm, there should be a sufficient layer of cortical bone in the sinus floor to achieve stability (7). Several authors (2,8-10) have obtained satisfactory results with this technique, at least as good as those employing the conventional procedure. Material and Methods This work involves a retrospective study on two groups of clinical cases, where the patients underwent sinus membrane elevation and implant insertion in a single surgical phase. The sinus bone reformation technique, without bone grafting, was applied to one group and 38 implants were inserted. The other group also involved 38 implants, as well as the use of animal hydroxyapatite filler (Biooss, Geistlich Pharma AG, Wolhusen, Switzerland). The criterion for selecting the surgical technique in the patients was geographical, based on the working location of each of the professionals. The inclusion criteria for this study were: sinus elevation with bone reformation or grafting and simultaneous insertion of the implants, with an alveolar ridge height of between 4 and 7 mm; availability of at least the initial panoramic radiograph and the 1-year post-prostheticloading control radiograph; clinical control of the patient at least a year after the prosthetic loading; no irreparable sinus membrane perforation; and absence of any maxillary sinus pathology. Those cases lacking any of the inclusion criteria were excluded from the study. The patients corresponding to each group were reviewed by the same professionals that carried out the treatments, according to their normal working protocols. The integration and survival of the implants through time has been evaluated using the success/failure criteria defined by Albrektsson (11) in 1986, applied to each implant individually. In the reformation group the implants used were Zimmer SPB, SPWB and TSV, and Phibo. In the conventional elevation group, Phibo and Biomet implants were employed. This study was performed in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was approved by the research ethics committee of the Stomatology Department of the Dentistry School of Granada University, and written informed consent was obtained before participation. - Surgical technique All the operations were made under local anaesthetic. A full-thickness crestal incision was made with distal unloading, as well as mesial incision in some cases to avoid the inclusion and injury of the respective papillae. Mucoperiosteal flaps were raised with the precaution of leaving the whole lateral wall of the upper jaw uncovered. The access window was made with a No. 8 round bur hand piece, always respecting certain limits, locating it at the lower edge, two millimetres above the antral floor. After separating the window with a curette, the integrity of the sinus membrane was examined. In patients with bone reformation, bony windows were always attempted, which could be put back on later. These were made with a piezoelectric motor creating a bevel to allow their subsequent replacement. In the group using animal hydroxyapatite, Bio-oss, the implant and filler were put in simultaneously, aiming to infra-prepare in order to achieve greater primary stability of the implants. Antrostomy closure was performed with a resorbable membrane (Bio-Gide, Geistlish Biomaterials, Switzerland). In the bone reformation group, after the bony window was removed, the sinus membrane was detached conventionally, including dissection of the palatal wall, to avoid it becoming tense after insertion of the implant. Later, the integrity of the sinus membrane was exam-
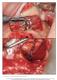
3 ined to verify that there was no tearing and the implants were placed, also with infra-preparation. Once fixed, the sinus membrane was placed over the implant and the formation of clotting within the sinus was checked. In most cases it was possible to stably replace the bony window (Fig. 1); a resorbable membrane (Bio-Gide, Geistlish Biomaterials, Switzerland) was used when replacement was impossible. measured in millimetres. It is measured from the implant-prosthesis join, just as when measuring the residual bone, to the last bone-implant join in the maxillary sinus; the difference from the original measurement is the newly formed mesial and distal bone (Fig. 2 a, b). Data graphics and statistical analysis were performed using Prism 5 (GraphPad). Mann-Whitney tests was applied to evaluate differences between the groups and Spearman correlation coefficient was calculated between bone gain and implant s length. We used Fisher s exact test to compared adverse events in the two study groups. For categorical data, the X² test was used. Kaplan-Meier estimates was used to describe the proportion Fig. 1. Bony window repositioning after implants placement using bone reformation technique. - Radiological analysis When the implants were placed a periapical and/or panoramic x-ray was taken, which was used for measuring the existing residual alveolar height in each case, utilising a specific radiological image management programme (BDSWIN, Dürr Dental, AG, Bietigheim- Bissingen, Germany). It is calibrated to the length of the implant, which is known. It is measured in millimetres from the implant-prosthesis connection (for the Zimmer SPB and SPWB implants we have to take into account the two millimetres corresponding to the polished transepithelial area) up to the last point of bone-implant contact when entering the maxillary sinus, mesially and distally from each implant. Radiological control took place 6 months and one year after prosthetic loading. The radiographs enable an assessment of new bone formation around the implants, the degree of resorption of the filler, and the loss of bone at the coronal level in the implants (horizontal and vertical resorption). Bone formation in the reformation cases was also measured with radiological image treatment software (BDSWIN, Dürr Dental, AG, Bietigheim-Bissingen, Germany). The newly formed bone was Fig. 2. Panoramic view of one implant using sinus bone reformation and bony window repositioning at different times. a. At the time of surgery. b. 36 months after surgery. Bone gain is observed on both sides of the implant. a b
4 of implants who failed during follow-up. P < 0.05 was regarded as statistically significant. Values are presented as means ± s.d. unless otherwise stated. Results The first group comprises 26 patients, 11 men and 15 women aged between 32 and 71, on whom a total of 28 maxillary sinus elevations were performed, with the simultaneous insertion of 38 osseointegrated implants, using the sinus bone reformation technique. The second group includes a total of 25 patients, 15 men and 10 women aged from 31 to 69, on whom 29 maxillary sinus elevations were performed, with the simultaneous insertion of 38 osseointegrated implants, but grafting the sinus with hydroxyapatite of bovine origin (Bio-Oss ) (Table 1.) The mean follow-up time after loading was 924 and 1177 days in the bone grafting and bone reformation group respectively. There was no statistical differences between the implant length and diameter among patients who underwent dental implant placement using bone grafting compared to those who underwent bone reformation (p 0.94 and 0.09 respectively). The mean mesial and distal bone gain were 2.7 and 2.6 mm respectively in the bone reformation group. Horizontal, but not vertical, bone resorption was significantly higher in patients with bone grafting compared to those in the bone reformation group (p ). In the reformation group, there was no correlation between mesial and distal bone gain and implant s length (Fig. 3. a, b). In addition, bone gain was similar among those patients who had bony window compared to those who underwent closure with resorbable membrane (p 0.2). Implant failure was observed in 2 patients from the bone grafting group and in 1 patient from the bone reformation group. Implant survival at 70 months after loading was similar among patients with bone grafting and those with bone reformation (93% vs 97% respectively) (Fig. 3.c). Side effects (sinusitis, bleeding or suppuration) were observed in 7 of 25 patients in the bone grafting group and in 5 of 26 patients from the bone reformation group. No statistical difference was observed among the two groups. Discussion It is difficult to compare the great number of studies on maxillary sinus elevation techniques available in the literature due to the differences in inclusion criteria, type of implants, patient follow-up, quantity of residual bone present, techniques used, phases of treatment, type of grafting material used, and evaluation methods. Similarly, the definition of success based on histomorphometric parameters is not comparable, as these depend on clinical evolution and short- or long-term response. In planning the present study, we tried to evaluate the sinus bone reformation technique and, at the same time, compare it with a widely-used technique with predictable results that are increasingly supported in the literature, as is the case of sinus elevation and grafting with hydroxyapatite of bovine origin (Bio-Oss ). In order to decrease the clinical and technical variability, it Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients and implants. Group Bone grafting Reformation p Number of patients Male: female ratio 15:10 11:15 Age in years 53 ± ± Number of total implants Implant s length (mm) 11.2± ± Implant s Diameter in mm 4.1±0.3 4± Mesial bone height 5.3± ± Distal bone height 4.5± ± Mesial bone gain 2.7±0.9 Distal bone gain 2.6±0.9 Vertical resorption (mm) 0.6± ± Horizontal resorption (mm) 0.8± ± Healing time (days) 245.6± ± Time from loading to last follow-up ± ± Implant failure 2/38 1/38 1 Number of patients with side effects (sinusitis, bleeding, suppuration) 7/25 5/26 0.5
5 M e s ia l b o n e g a in (m m ) r p Im p la n t's le n g th (m m ) a D is ta l b o n e g a in (m m ) r p Im p la n t's le n g th (m m ) b p c I m p la n t s u r v iv a l (% ) B o n e r e f o rm a tio B o n e g ra ftin g M o n th s a fte r p ro s th e s is lo a d in g Fig. 3. a Bone gain according to implant s length (mesial).b. Bone gain according to implant s length (distal). c. Long-term implant survival. (Kaplan-Meier). Implants at risk Reformation Bone grafting was decided only to include those cases where the sinus treatment with grafting and implant fixing was carried out in a single phase, as happens in sinus bone reformation. The initial clinical conditions are similar, i.e., the height of the remaining bone theoretically becomes the deciding factor determining the possibility of these procedures, making it feasible to compare the two surgical techniques. Inserting the implants at the same time as the elevation and sinus grafting is a widely-used technique that is well-documented clinically. Blomquist et al. (12) pointed out the advantage of this technique in minimising both costs and surgery time, as well as the fact that the loading can be carried out beforehand, thus maintaining the graft. Many studies (13-15) indicate that there are no clinical or histological differences between the immediate placement of the implant after maxillary sinus elevation and delayed insertion. The height of the remaining bone is a determining factor when choosing whether to insert the implants in one or two phases, as if there is a height of less than 5 mm there are problems fixing them at the same time as the subantral graft (16,17). In both study groups, most cases involved the positioning of implants with a residual crestal bone height of 5 mm. In certain cases, 4 mm of residual crestal bone was enough to achieve adequate primary stability. No difference was observed between the results obtained according to the available bone height
6 and primary stability is considered more important that the amount of residual crestal bone present. A study has recently been published with even less residual bone in which immediate prosthetic loading was carried out (18). For various reasons, many of the studies published on the use of the bovine hydroxyapatite Bio-oss are not useful for comparing with this group. These include delayed implant placement, its use with another filler, no patient follow-up specified, no reference made to the prior bone height in the residual ridge, or no success rate shown. The results obtained in our study are similar to some of those published that were conducted under equivalent conditions (19-22). Sinus bone reformation offers a series of advantages over the conventional grafting technique: it needs no graft material; a second surgical field is not necessary (if it is autologous bone); there is less morbidity (in the case of autologous bone); a lower infection risk; no risk of the graft material failing; it is cheaper; the technique is simpler; and there is greater patient acceptance when no filler is inserted. Various theories have been put forth to explain the osteoformation that occurs without the use of a graft. Srouji et al. (23) showed that the cells derived from the sinus membrane can grow in culture expressing osteoprogenitor cell markers and osteogenic differentiation can be induced, as well as new bone formation in transplant area. This provides evidence of the presence of osteoprogenitor cells within the Schneider membrane. An important factor in this process is the elevation of the membrane and the exposure of the medial sinus wall, because mesenchymal cells migrate from the exposed sinus wall. Since bone formation requires the recruitment, migration and differentiation of pluripotent mesenchymal cells into osteoblasts, it points to the periosteum of the sinus membrane being another possible source of bone-forming cells (24). Maintaining the integrity of the maxillary sinus membrane, making sure it stays raised for there to be enough space to build bone, and forming a blood clot, are prerequisites for bone formation in cases of reformation. The space is maintained thanks to the primary stability of the implant onto which the membrane is deposited, creating a limit, and the formation of a blood clot. Certain studies use different methods to support the sinus membrane and achieve the tenting effect, including: the use of the patient s own venous blood (25), absorbable gelatine sponges (26), equine-collagen sponges (4), fibrin-rich blocks with concentrated growth factors (27), perforated cylindrical device with hydroxyapatite (28), and star- and H-shaped polyactide devices (29). In most reformation cases the bony window was replaced enabling the maxillary sinus to be maintained as an isolated cavity, favouring bone formation according to the principles of guided bone regeneration. As an alternative, resorbable membranes were used. The bone gain was similar in both. Sohn and Cricchio recommend replacing the bony window (26,29), with Sohn pointing out its hypothetical osteoinductive power (26). For this reason, the reformation fulfils the requirements suggested by Gurtner et al. (30) as essential elements for achieving success in bone regeneration: stem cells, anchorage elements, and growth factors. The results obtained for the reformation group in our work are similar to those of various other studies (2,5,6,8-10). No bone gain differences between mesial and distal side of the implants were found. These results present the technique as a clear alternative to elevation of the maxillary sinus with grafting material; it shows similar results, especially when considering practical issues such as safety and cost. Although the final validation of this technique must undoubtedly come from an analysis of the long-term success of the implants, it is also necessary to understand the intrasinus boneformation process, particularly those aspects relating to timing, quantity and arrangement, that determine when an implant can receive total functional loading, and the most effective number and arrangement of implants to be fixed in each situation. After an analysis of the results of the study a series of questions are raised that should be looked at in more extensive future studies. These issues include: where the bone forms preferentially (the implants and/or walls of the maxillary sinus); the timing of the bone formation; the influence of the amount of crestal bone remaining; the importance of the quantity of implants introduced into the maxillary sinus; the effect of replacing the bone access window; and the number of implants necessary to maintain the membrane s vertical limit. Conclusions 1. The results of this study as well as those present in the literature, are similar to, and even sometimes better than, those achieved through the traditional elevation of the maxillary sinus, independent of the bone graft used. 2. The bone reformation can be considered a suitable procedure for inserting implants in cases of posterior maxilla atrophy, where insufficient bone remains for the conventional placement of implants. 3. This technique entails a series of advantages over conventional maxillary sinus elevation with subantral graft: it does not involve grafting, there is less morbidity, a lower infection risk, it is cheaper, and it is better accepted by the patient. 4. Studies involving a larger sample size and longer follow-up period are necessary for determining the factors that influence the degree of bone formation.
7 References 1. Zitzmann, NV; Scharer, P. Sinus elevation procedures in the resorbed posterior maxilla. Comparison of the crestal and lateral aproaches. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998; 85: Lundgren, S; Andersson, S; Gualini, F; Sennerby, L. Bone reformation with sinus membrane elevation: a new surgical technique for maxillary sinus floor augmentation.clin Implant Dent Relat Res.2004;6(3): Lundgren, S; Andersson, S; Sennerby, L. Spontaneous bone formation in the maxillary sinus after removal of a cyst: coincidence or consequence? Clin Implant Dent Relat Res. 2003; 5: Palma, VC; Magro-Filho, O; de Oliveira, JA; Lundgren, S; Salata, LA; Sennerby, L. Bone reformation and implant integration following maxillary sinus membrane elevation: An experimental study in primates. Clin Imp Dent Relat Res.2006; 8: Thor, A; Sennerby, L: Hirsch, JM; Rasmusson, L. Bone formation at the maxillary sinus floor following simultaneous elevation of the mucosal lining and implant installation without graft material. An evaluation of 20 patients treated with 44 astra tech implants Sup 1; 65: Chen, T; Chang, H; Leung, K-W; Lai, YL; Kao, S. Implant placement inmediately after the lateral approach of the trap door window procedure to create a maxillary sinus lift without bone grafting: A-2 year retrospective evaluation of 47 implants in 33 patients. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007; 65: Lundgren, S ; Cricchio, G ; Palma, VC ; Salata, LA ; Sennerby, L. Sinus membrane elevation and simultaneous insertion of dental implants : A new surgical technique in maxillary sinus floor augmentation. Periodontology 2000, 2008 ; 47(1) : Sohn, DS; Lee, JS; Ahn, MR; Shin, HI. New bone formation in the maxillary sinus without bone grafts. Implant Dent 2008: Sep; 17 (3): Gabbert, O; Kodo, A; Schmitter, M; Rammelsberg, P Implants placed in combination with an internal sinus lift without graft material: an analysis of short-term failure. Journal Clinical Periodontology 2009; 36: , 10. Jeong, SM; Choi, BH; Li, J; Xuan, F. A retrospective study of the effects of sinus membrane elevation on bone formation around implants placed in the maxillary sinus cavity. Oral Surg, Oral Med, Oral Pathol, Oral Radiol and Endod. 2009; 107(3): 364-8, 11. Albrektsson, T ; Zarb, G ; Worthington, P ; Eriksson, AR. The long term efficacy of currently used dental implants : a review and proposed criteria of success. The Int Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implats, 1986 ;11:25-34, 12. Blomquist, J ; Alberius, P ; Isaksson, S. Retrospective analysis of one-stage maxillary sinus augmentation with endosseous implants. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1996;11: Jensen, OT; Shulman,L; Block, M; Iacono, V. Report of the sinus consensus conference of Int J Oral Implant. 1998; 13 supl: Wallace, S; Froum, S. Effect of maxillary sinus augmentation on the survival of endosseous dental implants. A systematic review. Ann Periodontolo. 2003; 8: Del Fabbro, M; Rosano, G; Taschieni, S. Implants survival rates alter maxillary sinus augmentation. Eur J Oral Sci. 2008; 116: Smiler, DG ; Johnson, PW ; Lozada, JL. Sinus lift grafts and endosseous implants. Treatment of the atrophic posterios maxilla. Dent Clin North Am ; 36 : Misch, CE. Maxillary sinus augmentation for endosteal implants organized alternative treatment plans. Int J Oral Implant. 1987; 4: Cricchio, G; Imburgia, M; Sennerby, L; Lundgren, S. Inmediate loading of implants placed simultaneously with sinus membrane elevation in the posterior atrophic maxilla: a two-year follow-up study on 10 patients. Clin Implant Dentistry and Related Research. 2014; 16: Tawil, G; Mawla, M. Sinus floor elevation using a bovine bone mineral (Bio-oss ) with or without the concomitant use of a bilayered collagen barrier (Bio-Gide ): a clinical report of inmediate and delayed implant placement. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2001; 16: Hallman, M; Sennerby, L; Lundgren, S. A clinical and histologic evaluation of implants integration in the posterior maxilla after sinus floor augmentation with autogenous bone, bovine hydroxiapatite, or a 20:80 mixture. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2002; 17: Valentini, P; Abensur, D. Maxillary sinus grafting with anorganic bovine bone: a clinical report of long-term results. Int J Oral of Maxillofac Imp Jul-Aug; 18(4): Mardinger, O; Manor, I; Mijiritsky, E; Hirshberg, A. Maxillary sinus augmentation in the presence of antral pseudocyst: a clinical approach. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007; 103: Srouji, S; Kizhner, T; Ben David, D; Riminucci, M; Bianco, P; Livne, E. The Schneiderian membrane contains osteoprogenitor cells: in vio and in vitro study. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2009; 84: Dong-Seok, S; Ji-Soo, L; Mi-Ra, A; Hong- In, S New bone formation in teh maxillary sinus without bone grafts. Implant Dentistry 2008; Sept 17(3): Hatano, N ; Sennerby, L ; Lundgren, S : Maxillary sinus augmentation using sinus membrane elevation and peripheral venous blood for implant-supported rehabilitation of the atrophic posterior maxilla : case series. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res (9) : Sohn, DS, Moon, JW, Moon, KN ; Cho, SC ; Kang, PS. New bone formation in the maxillary sinus using only absorbable gelatin sponge. Journal of Oral Maxillofac Surg 2010 ; 68 : Sohn, DS ; Heo, JU ; Kwak, DH ; Kim, DE ; Kim, JM ; Moon, JW ; Lee, JH ; Park, IS. Bone regeneration in the maxillary sinus using an autologous fibrin-rich block with concentrated growth factors alone. Implant Dentistry ; 20 (5) : Johansson, LA ; Isaksson, S ; Adolfsson, E ; Lindh, C ; Sennerby, L. Bone regeneration using a hollow hydroxyapatite space-maintaining device for maxillary sinus floor augmentation. A clinical pilot study. Clin Imp Dent Relat Research ; 14(4) : Cricchio, G ; Sennerby, L ; Lundgren, S ; Sinus bone formation and implant survival after sinus membrane elevation and implant placement : a 1- to 6- year follow-up study. Clin Oral Implant Res ; 22 : Gurtner, GC; Callaghan, MJ; Longaker, MT. Progress and potential for regenerative medicine. Annual Review of Medicine. 2007; 58: Acknowledgments The autors claim to have no financial interest in any company or any of the products mentioned in this article.
Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material- A case Report
 A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
A CASE REPORT ISSN: 2321-4988 D.Shiva kumar et al. /JPR:BioMedRx: An International Journal 2013,1(8), Available online through www.jpronline.info Maxillary sinus augmentation without any graft material-
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:0.7/medoral..e Pre-operative evaluation of the volume of bone graft in sinus lifts by means of CompuDent Oscar Arias-Irimia, Cristina Barona-Dorado,
One in four sinus lift procedures can be
 11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
11 Volume 5, Issue 1: Summer 2017 Inspyred: The alternative EAO voice Handling perforations of the sinus membrane A new approach using advanced platelet-rich fi brin (A-PRF) One in four sinus lift procedures
International Journal of Implant Dentistry. Takahiro Kaneko *, Satoshi Nakamura, Shunsuke Hino, Norio Horie and Tetsuo Shimoyama
 Kaneko et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2016) 2:16 DOI 10.1186/s40729-016-0049-z International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Open Access Continuous intra-sinus bone regeneration
Kaneko et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2016) 2:16 DOI 10.1186/s40729-016-0049-z International Journal of Implant Dentistry CASE REPORT Open Access Continuous intra-sinus bone regeneration
Christopher Riben and Andreas Thor. 1. Introduction
 International Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 105483, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/105483 Review Article The Maxillary Sinus Membrane Elevation Procedure: Augmentation of Bone around Dental Implants without
International Dentistry Volume 2012, Article ID 105483, 9 pages doi:10.1155/2012/105483 Review Article The Maxillary Sinus Membrane Elevation Procedure: Augmentation of Bone around Dental Implants without
Maxillary sinus floor augmentation procedures
 New Bone Formation Following Sinus Membrane Elevation Without Bone Grafting: Histologic Findings in Humans Jae-Jin Ahn, DDS, MS, PhD 1 /Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD 2 /Gerard Byrne, DDS 3 / Jae-Hyun Kim,
New Bone Formation Following Sinus Membrane Elevation Without Bone Grafting: Histologic Findings in Humans Jae-Jin Ahn, DDS, MS, PhD 1 /Sung-Am Cho, DDS, MS, PhD 2 /Gerard Byrne, DDS 3 / Jae-Hyun Kim,
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Research. Vol. 3, No. 4 Autumn 2016
 Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Research Vol. 3, No. 4 Autumn 2016 Primary stability of implants inserted following sinus lift and bone graft in the posterior of the maxilla Mehdi Sezavar 1, Mohammad Reza
Journal of Craniomaxillofacial Research Vol. 3, No. 4 Autumn 2016 Primary stability of implants inserted following sinus lift and bone graft in the posterior of the maxilla Mehdi Sezavar 1, Mohammad Reza
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Vertical and horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation
 CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants
 Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
Factors affecting changes in sinus graft height between and above the placed implants Ofer Mardinger, DMD, BMedSc, a Gavriel Chaushu, DMD, MSc, b Sheli Sigalov, DMD, c Ran Herzberg, DMD, d Binyamin Shlomi,
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up
 643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
643 The Use of Freeze-Dried Bone Allograft as an Alternative to Autogenous Bone Graft in the Atrophic Maxilla: A 3-Year Clinical Follow-up Marco Aurélio Bianchini, DDS, MSc, PhD 1 André R. Buttendorf,
Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years
 Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Original Article Comparison of Peri-Implant Bone Loss and Survival of Maxillary Intrasinus and Extrasinus Implants After 2 Years AR. Rokn 1,2, AAR. Rasouli Ghahroudi 3,4, S. Hemati 5, A. Soolari 6 1 Associate
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 413 Schneiderian Membrane Perforation Rate During Sinus Elevation Using Piezosurgery: Clinical Results of 100 Consecutive Cases Stephen
Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3.
 DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
DOI: 1018044/Medinform.201631.370 Sinus floor elevation with lateral approach and five-year follow-up Stefan Peev 1, Tihomir Georgiev 2, Elitsa Sabeva 1, Georgi Papanchev 2, Vladimir Panov 3. 1. Department
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
Effects of Maxillary Sinus Graft on the Survival of Endosseous Implants: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
 University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 8-2008 Effects of Maxillary Sinus Graft on the Survival of Endosseous Implants: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
University of Pennsylvania ScholarlyCommons Departmental Papers (Dental) Penn Dental Medicine 8-2008 Effects of Maxillary Sinus Graft on the Survival of Endosseous Implants: A 10-Year Retrospective Study
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation Surgery with Autogenous Bone Grafts as Ceiling Raghoebar, Gerry; Meijer, Hendrikus; Telleman, Gerdien; Vissink, Arjan Published in: Clinical Implant
University of Groningen Maxillary Sinus Floor Augmentation Surgery with Autogenous Bone Grafts as Ceiling Raghoebar, Gerry; Meijer, Hendrikus; Telleman, Gerdien; Vissink, Arjan Published in: Clinical Implant
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation
 Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Complications of postoperative swelling of the maxillary sinus membrane after sinus floor augmentation Abstract Objective The aim of this article was to investigate postoperative swelling of the maxillary
Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla
 IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
IJOICR 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1036 RECENT TECHNICAL ADVANCES Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified Approach to Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla Crestal Sinus Augmentation: A Simplified
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
A New Technique for Minimally Invasive Maxillary Lateral Sinus Augmentation: a Case Report
 A New Technique for Minimally Invasive Maxillary Lateral Sinus Augmentation: a Case Report Xiu Lian HU 1, Xian ZHOU 1, Jian Hui LI 1, Ye LIN 1 Numerous techniques are described for lateral sinus augmentation,
A New Technique for Minimally Invasive Maxillary Lateral Sinus Augmentation: a Case Report Xiu Lian HU 1, Xian ZHOU 1, Jian Hui LI 1, Ye LIN 1 Numerous techniques are described for lateral sinus augmentation,
Evaluation of Sinus Floor Augmentation with Simultaneous Implant Placement Using Platelet-Rich Fibrin as Sole Grafting Material
 Evaluation of Sinus Floor Augmentation with Simultaneous Implant Placement Using Platelet-Rich Fibrin as Sole Grafting Material Nobutaka Tajima, DDS, PhD 1 /Seigo Ohba, DDS, PhD 2 / Takashi Sawase, DDS,
Evaluation of Sinus Floor Augmentation with Simultaneous Implant Placement Using Platelet-Rich Fibrin as Sole Grafting Material Nobutaka Tajima, DDS, PhD 1 /Seigo Ohba, DDS, PhD 2 / Takashi Sawase, DDS,
THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS. Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel GTO I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E
 GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
GTO THE NEW STANDARD OF EXCELLENCE IN BIOMATERIALS Collagenated heterologous cortico-cancellous bone mix + TSV Gel R E G E N E R A T I O N S C I E N C E I N S P I R E D B Y N A T U R E A unique biotechnology
Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.6.274 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation Wang Peng, Il-Kyu Kim, Hyun-Young Cho, Sang-Pill
ORIGINAL ARTICLE http://dx.doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2013.39.6.274 pissn 2234-7550 eissn 2234-5930 Assessment of the autogenous bone graft for sinus elevation Wang Peng, Il-Kyu Kim, Hyun-Young Cho, Sang-Pill
Sinus elevation with short implant
 Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
Sinus elevation with short implant Authors: Prof. Dr Mauro Marincola, Prof. Dr Dr Rolf Ewers, Prof. Giorgio Lombardo (University of Verona) & Prof. Miguel Simancas Pallares (University of Cartagena), Austria/Italy/Colombia
World Congress of Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Bone Surgery 2015, Busan Korea, May Pre-Congress Workshop 1
 World Congress of Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Bone Surgery 2015, Busan Korea, May 01-03 Pre-Congress Workshop 1 Course Director Prof. Dong-Seok Sohn S-dental Date May 1(Fri) 2015, 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM $800
World Congress of Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Bone Surgery 2015, Busan Korea, May 01-03 Pre-Congress Workshop 1 Course Director Prof. Dong-Seok Sohn S-dental Date May 1(Fri) 2015, 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM $800
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift
 Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Minimally invasive implant dentistry with short or narrow implants Ridge splitting and crestal and internal sinus lift Prof. Mauro Marincola 1, Dr Daniel Hernández-González 1, Dr Jaime Guzmán-De Ávila
Subantral Augmentation Utilizing the Zimmer. Sinus Lift Balloon Technique
 Copyright 2010 by Zimmer Dental Inc. Subantral Augmentation Utilizing the Zimmer Sinus Lift Balloon Technique Geraldo Nicolau Rodrigues, Americo Yuti Katayama, Ronald F. Cardoso The edentulous posterior
Copyright 2010 by Zimmer Dental Inc. Subantral Augmentation Utilizing the Zimmer Sinus Lift Balloon Technique Geraldo Nicolau Rodrigues, Americo Yuti Katayama, Ronald F. Cardoso The edentulous posterior
Annals of Dental Research
 P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
P a g e 1 ADR 7 (1), 1-6, 2017 Journal Homepage: www.hgpub.com/ojs2/index.php/adr Direct Sinus Lift with Putty Alloplastic Bone Substitute for Simultaneous Implant Placement A Case Report Chander Prakash*,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla,
 Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
Staged Sinus Floor Elevation Using the Crestal Core Elevation (CCE) Procedure: A Review of the Technique Michael, DDS Abstract In the moderately to severely atrophic maxilla, trephined cores measuring
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure
 Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Seung-Yun Shin 1, You-Jeong Hwang 2, Jung-Hoon Kim 3,4, Yang-Jo Seol 3,
Long-term results of new deproteinized bovine bone material in a maxillary sinus graft procedure pissn 2093-2278 eissn 2093-2286 Seung-Yun Shin 1, You-Jeong Hwang 2, Jung-Hoon Kim 3,4, Yang-Jo Seol 3,
Procedure Manual and Catalog
 Procedure Manual and Catalog TM Why SynthoGraft? SynthoGraft offers a unique structure which provides stability, while its micro-porosity allows for rapid vascularization and subsequent resorption. Although
Procedure Manual and Catalog TM Why SynthoGraft? SynthoGraft offers a unique structure which provides stability, while its micro-porosity allows for rapid vascularization and subsequent resorption. Although
Sinus Floor Elevation. Treatment Concepts
 Sinus Floor Elevation Treatment Concepts Geistlich Family supports your way to regeneration together for more satisfied patients Dr. Andreas Geistlich CONTENTS 3 Maxillary sinus floor augmentation 4 5
Sinus Floor Elevation Treatment Concepts Geistlich Family supports your way to regeneration together for more satisfied patients Dr. Andreas Geistlich CONTENTS 3 Maxillary sinus floor augmentation 4 5
T he cortical bone of the maxillary
 KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
KIM ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 26, NUMBER 3 2017 351 Sinus Membrane Elevation by the Crestal Approach Using a Novel Drilling System Young-Kyun Kim, DDS, PhD,* Ji-Young Lee, DDS, Jin-Woo Park, DDS,
Since the proximity of the maxillary sinus may result
 Incidence, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Sinus Graft Infection After Sinus Floor Elevation: A Clinical Study Istvan A. Urban, DMD, MD 1 /Heiner Nagursky, PhD 2 / Christopher Church, MD, MS 3 /Jaime L. Lozada,
Incidence, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Sinus Graft Infection After Sinus Floor Elevation: A Clinical Study Istvan A. Urban, DMD, MD 1 /Heiner Nagursky, PhD 2 / Christopher Church, MD, MS 3 /Jaime L. Lozada,
Posterior mandible and vertical augmentation
 CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
CASE REPORT Bilateral Vertical Ridge Augmentation With Block Grafts and Guided Bone Regeneration in the Posterior Mandible: A Case Report Maria A. Peñarrocha* Jose A. Vina Laura Maestre David Peñarrocha-Oltra
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report
 Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
Alveolar Ridge Augmentation with Titanium Mesh and Particulate Allograft A Case Report Dr. Pratibha Borasi, Dr. Praneeta Kamble Department of Periodontics, Nair Hospital Dental College, Mumbai, Maharashtra,
I n the edentulous posterior maxilla,
 IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 0, NUMBER 0 2012 1 Minimally Invasive Sinus Augmentation Using Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Vibration and Hydraulic Pressure: A Multicenter Retrospective Study Ji-Min Kim, DDS,*
IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 0, NUMBER 0 2012 1 Minimally Invasive Sinus Augmentation Using Ultrasonic Piezoelectric Vibration and Hydraulic Pressure: A Multicenter Retrospective Study Ji-Min Kim, DDS,*
Bone augmentation with biomaterials
 Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
Patient information dental bone & tissue regeneration botiss biomaterials Bone augmentation with biomaterials established safe natural X100 Implantation stability is crucial for success Atrophy of the
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 07 Page July 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re. Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T
 Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Dental Implant Treatment with Diffe Title for Sinus Floor Elevation-A Case Re Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Seta, S; Tak Author(s) T; Kakizawa, T Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 4 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/200
Maxillary Sinus Augmentation:
 Earn 4 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: Fixed Restorations in the Compromised Posterior Maxilla A Peer-Reviewed Publication
Earn 4 CE credits This course was written for dentists, dental hygienists, and assistants. Maxillary Sinus Augmentation: Fixed Restorations in the Compromised Posterior Maxilla A Peer-Reviewed Publication
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
Oral Health and Dentistry
 Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Page 107 to 118 Volume 1 Issue 2 2017 Case Report Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 Full Mouth Implants Rehabilitation of a Patient with Ectodermal Dysplasia After 3-Ds Ridge Augmentation and Bilateral
Endosseous cylindric implants are well accepted
 Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
Soft Tissue Exposure of Endosseous Implants Between Stage I and Stage II Surgery as a Potential Indicator of Early Crestal Bone Loss Joseph A. Toljanic, DDS*/Mark L. Banakis, DDS**/Leslee A. K. Willes,
PRP Usage in Today's Implantology
 Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
Volume 1, December 2004 www.implant.co.il PRP Usage in Today's Implantology by Dr. R. Shapira Introduction: Treating patients suffering from hematological disorders or using anticoagulant medications always
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
 227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
227 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 45, No. 4, 227-232, 2003 Case report Treatment planning in a case of restoration of the maxilla and mandible using osseointegrated implants with four types of bone graft
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus.
 Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, Karasoulos D, Felice P, Alissa R, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. Cochrane Database
Interventions for replacing missing teeth: augmentation procedures of the maxillary sinus. Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Rees J, Karasoulos D, Felice P, Alissa R, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. Cochrane Database
Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report
 Vol. 31 No. 3, December 2012 Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report In-Seong Jeon, Min-Suk Heo 1, Kyu-Ho Yoon 2, Kwang-Heung Han
Vol. 31 No. 3, December 2012 Differential application of a repair technique for large perforations of the Schneiderian membrane: case report In-Seong Jeon, Min-Suk Heo 1, Kyu-Ho Yoon 2, Kwang-Heung Han
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 141 Screw Spreading: Technical Considerations and Case Report Renato Sussumu Nishioka, DDS, PhD, MSc* Alberto Noriyuki Kojima, DDS, PhD,
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation. Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics
 A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
A Retrospective Analysis of Maxillary Sinuses and Implant Survival after Lateral Window Sinus Augmentation Marlon Foote, DDS Periodontics Boyne, 1980 Maxillary Sinus Augmentations Maxillary sinus augmentation,
Osseointegrated implants are a very reliable means
 Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
Tridimensional Reconstruction of Knife-Edge Edentulous Maxillae by Sinus Elevation, Onlay Grafts, and Sagittal Osteotomy of the Anterior Maxilla: Preliminary Surgical and Prosthetic Results Matteo Chiapasco,
The use of endosseous implants is currently a routine
 Evaluation of 31 Zygomatic Implants and 74 Regular Dental Implants Used in 16 Patients for Prosthetic Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Cross-Arch Fixed Bridges Jonas P. Becktor, DDS;* Sten Isaksson,
Evaluation of 31 Zygomatic Implants and 74 Regular Dental Implants Used in 16 Patients for Prosthetic Reconstruction of the Atrophic Maxilla with Cross-Arch Fixed Bridges Jonas P. Becktor, DDS;* Sten Isaksson,
Hydrodynamic ultrasonic maxillary sinus lift: Review of a new technique and presentation of a clinical case
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.17430 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17430 Hydrodynamic ultrasonic maxillary sinus lift: Review of a new technique and
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Review doi:10.4317/medoral.17430 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.17430 Hydrodynamic ultrasonic maxillary sinus lift: Review of a new technique and
Sinus Augmentation Studies Methods and Definition
 FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
FDA approved indications for Infuse Bone Graft in the Maxillofacial Skeleton Alveolar Ridge Augmentation (Buccal Wall Defects) in the Maxilla Maxillary Sinus Floor augmentation Sinus Augmentation Studies
School of Dentistry, Federal University of Santa Catarina (UFSC), Florianópolis, SC, Brazil
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2016 18/4: 102 108 A Step-by-Step Management of Extraction Sites in Areas of Maxillary Sinus Pneumatization: A Literature Review and a Case Presentation
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2016 18/4: 102 108 A Step-by-Step Management of Extraction Sites in Areas of Maxillary Sinus Pneumatization: A Literature Review and a Case Presentation
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery
 An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
An Assessment of the Efficacy of Sinus Balloon Technique on Transcrestal Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation Surgery Huda Moutaz Asmael, B.D.S. (1) Thair Abdul Lateef, B.D.S., H.D.D., F.I.B.M.S. (2) ABSTRACT
Flapless Crestal Sinus Augmentation: Hydraulic Technique
 C15 12/30/2015 11:13:50 Page 152 CHAPTER 15 Flapless Crestal Sinus Augmentation: Hydraulic Technique Byung-Ho Choi Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine,
C15 12/30/2015 11:13:50 Page 152 CHAPTER 15 Flapless Crestal Sinus Augmentation: Hydraulic Technique Byung-Ho Choi Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine,
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study
 26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
26 News No.26 January 2011 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone Height: A Preliminary 6-Month Clinical Study Make it Simple 2 The Use Of 6mm Long Implants In Cases With Limited Bone
Simultaneous Indirect Sinus Lift and Implant Insertion. Case Report for Extreme Bone Resorption
 26 Simultaneous Indirect Sinus Lift and Implant Insertion. Case Report for Extreme Bone Resorption Faaiz Alhamdani, PhD, College of Dentistry, Ibn Sina University for Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences,
26 Simultaneous Indirect Sinus Lift and Implant Insertion. Case Report for Extreme Bone Resorption Faaiz Alhamdani, PhD, College of Dentistry, Ibn Sina University for Medical and Pharmaceutical Sciences,
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Immediate Implant Placement in Deficient Bone Sites
 clinical Raj Chopra BSc, DDS Immediate Implant Placement in Deficient Bone Sites THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN PEER-REVIEWED. Introduction The presence of a low-lying sinus floor and inadequate bone volume often
clinical Raj Chopra BSc, DDS Immediate Implant Placement in Deficient Bone Sites THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN PEER-REVIEWED. Introduction The presence of a low-lying sinus floor and inadequate bone volume often
Prevalence and management of Schneiderian membrane perforations during sinus-lift procedures
 Federico Hernández-Alfaro Marta Marín Torradeflot Carlos Marti Prevalence and management of Schneiderian membrane perforations during sinus-lift procedures Authors affiliations: Federico Hernández-Alfaro,
Federico Hernández-Alfaro Marta Marín Torradeflot Carlos Marti Prevalence and management of Schneiderian membrane perforations during sinus-lift procedures Authors affiliations: Federico Hernández-Alfaro,
More than bone regeneration. A total solution.
 More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
More than bone regeneration. A total solution. More than a dental implant company. A total solution. When it comes to treatment options, your patients want positive results both functionally and esthetically.
Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review of Anatomy and Lateral Sinus Lift Technique
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. 2016), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 1 Ver. IV (Jan. 2016), PP 29-33 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Sinus Floor Elevation: Review
The Essential Choice. With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability
 The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
The Essential Choice With the Benefits of Biologic Predictability Documented, Reliable, Experienced is the essential choice for your daily regenerative needs. Throughout our long history and dedication
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Sinus elevation by in situ utilization of bone scrapers: technique and results
 Sinus elevation by in situ utilization of bone scrapers: technique and results Pedro Martos Díaz 1, Luis Naval Gías 2, Jesús Sastre Pérez 3, Raúl González García 1, Fernando Bances del Castillo 3, María
Sinus elevation by in situ utilization of bone scrapers: technique and results Pedro Martos Díaz 1, Luis Naval Gías 2, Jesús Sastre Pérez 3, Raúl González García 1, Fernando Bances del Castillo 3, María
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 2. Introduction Surgical challenges to treat esthetic implant failures Treatment options & case reports Conclusions
 T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books. International authors and editors. Our authors are among the TOP 1%
 We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
We are IntechOpen, the first native scientific publisher of Open Access books 3,350 108,000 1.7 M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our authors are among the 151 Countries
Contemporary Implant Dentistry
 Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Contemporary Implant Dentistry C H A P T ER 1 4 O F C O N T E M P OR A R Y O R A L A N D M A X I L L OFA C IA L S U R G E RY B Y : D R A R A S H K H O J A S T EH Dental implant is suitable for: completely
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Strong bone for beautiful teeth. Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide
 Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
Strong bone for beautiful teeth Patient Information I Bone reconstruction with Geistlich Bio-Oss and Geistlich Bio-Gide Contents Smiling is the most beautiful way to show your teeth 3 What are the causes
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Tooth out what's next?
 Tooth out what's next Content >> Treatment Options >> Clinical Cases >> Product Information >> Product related FAQs >> Why Ridge Preservation > Minimise invasion: Bone volume preservation > Minimise invasion:
Tooth out what's next Content >> Treatment Options >> Clinical Cases >> Product Information >> Product related FAQs >> Why Ridge Preservation > Minimise invasion: Bone volume preservation > Minimise invasion:
complications (Zitzmann and Schaerer,
 Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
Inadequate height and width of alveolar process is considered as the most common limiting factor for implant placement in maxillary alveolar process. Subsequent to tooth extraction, the decrease of occlusal
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 1. Implant Locations. Implant Placement in the Posterior Maxilla. Anatomy and risk factors Option 1: Short implants
 T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
T O P I C S Day 1 Factors influencing the long-term stability of dental implants Surgical procedures in posterior sites: Standard implant placement with or without flap elevation Surgical procedures in
REASONS TO USE R.T.R.
 3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
3 REASONS TO USE R.T.R. AFTER EACH EXTRACTION Fully resorbable ß-TCP material RTR 3raisons 120x280.indd 1 16/06/15 10:52 1AVOID SPONTANEOUS RIDGE RESORPTION After tooth extraction, spontaneous healing
regeneration 6 (GBR), and sinus augmentation
 551 Sinus Augmentation Utilizing Anorganic Bovine Bone (Bio-Oss) with Absorbable and Nonabsorbable Membranes Placed over the Lateral Window: Histomorphometric and Clinical Analyses Stephen 5. Wallace,
551 Sinus Augmentation Utilizing Anorganic Bovine Bone (Bio-Oss) with Absorbable and Nonabsorbable Membranes Placed over the Lateral Window: Histomorphometric and Clinical Analyses Stephen 5. Wallace,
