The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
|
|
|
- Clarence Crawford
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
2 477 Immediate Provisionalization of Dental Implants in Grafted Alveolar Ridges in the Esthetic Zone: A 5-Year Evaluation Lyndon F. Cooper, DDS, PhD 1 /Glenn Reside, DDS 2 Filiep Raes, DDS, MSc, PhD 3 /Joan Soliva Garriga, DDS, DMD 4 Luís Giner Tarrida, DDS, DMD, PhD 5 /Jörg Wiltfang, MD, DMD 6 Matthias Kern, DMD 7 /Hugo De Bruyn, DDS, PhD 8 This clinical study assessed at 5 years both implant survival and peri-implant tissue architecture of immediately provisionalized implants placed 4 to 6 months following augmentation with demineralized bovine bone allograft and collagen membrane. Of 23 implants in 19 patients, one implant failed prior to loading (95.6% survival). Implant tissue relationships were stable following implant placement; marginal bone level changes from implant placement to 5 years (mean ± SD: 0.18 ± 0.79 mm, range: 1.6 to 1.4 mm, P =.51), the mesial and distal papilla length changes (mesial mean ± SD: 1.14 ± 0.92 mm, P <.001; distal mean ± SD: 0.74 ± 1.46 mm, P =.04), and the unchanged mucosal zenith location (mean ± SD: 0.24 ± 0.93 mm, P =.15) were recorded. There were no major surgical complications during the 5-year period. When augmentation is required, subsequent dental implant placement in the anterior maxilla may be achieved using immediate placement and provisionalization protocol to attain osseointegration success and stable peri-implant tissue responses. (Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent 2014;34: doi: /prd.2022) 1 Stallings Distinguished Professor and Chairman, Department of Prosthodontics, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, USA. 2 Associate Professor, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, North Carolina, USA. 3 Assistant Professor, Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Dental School, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium. 4 Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, Dentistry School, Universitat Internacional de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain. 5 Vice Dean, Research Department, Dentistry School, Universitat Internacional de Catalunya, Barcelona, Spain. 6 Professor and Head, Department of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, University of Schleswig-Holstein, Kiel, Germany. 7 Department of Prosthodontics, Propaedeutics and Dental Materials; School of Dentistry; Christian-Albrechts University at Kiel; Kiel, Germany. 8 Professor and Chairman, Department of Periodontology and Oral Implantology, Dental School, Faculty of Medicine and Health Sciences, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium; Visiting Professor, Department of Prosthodontics, University of Malmö, Malmö, Sweden. Correspondence to: Dr Lyndon F. Cooper, 330 Brauer Hall, CB#7450, University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill, NC ; lyndon_cooper@unc.edu 2014 by Quintessence Publishing Co Inc. The replacement of a single anterior maxillary tooth is predictably achieved using endosseous dental implants. 1,2 Recent investigations have extended reported outcomes from implant survival data to include important information about esthetic outcomes using objective scoring of soft tissues (pink esthetic score or PES 3 ) and supported crowns. 4 In addition, interest is emerging about patient-based outcomes related to satisfaction. 5 Several systematic reviews indicate high implant survival and shortterm esthetic success associated with high patient satisfaction. The replacement of a failing or missing anterior tooth may be a consequence of trauma, caries, periodontal disease, or anodontia. The clinical presentation of the tooth or the residual alveolar ridge strongly influences the procedural course of therapy, and different protocols, including immediate placement and provisionalization, immediate provisionalization, early placement, or conventional placement in healed alveolar ridges, have been advocated. Several investigators reported that high implant survival and Volume 34, Number 4, 2014
3 478 esthetic success may be achieved for either immediate placement with provisionalization or immediate provisionalization of implants placed in healed ridges. 6,7 An early placement protocol has been alternatively advocated. 4,8 In the anterior maxillary alveolar ridge, the local conditions for esthetic implant placement and restoration are often unfavorable because of multiple architectural factors. 9 Irrespective of the clinician s preference, when considering implant placement into extraction sockets or alveolar ridges, there will be situations when bone grafting is required. Alveolar bone grafting and socket preservation procedures are commonly performed, and many different methods for bone augmentation have been evaluated. The use of autogenous bone, allogeneic bone substitutes, and recombinant osteoinductive agents with or without occlusive membranes have been illustrated and are supported by case series. When considering prospective, comparative studies, Esposito et al 10 concluded that there was little data to distinguish the outcomes of one or another material or technique. In a separate review 11 it was concluded that there is merit in selecting procedures that are simpler and less invasive, involve less risk of complications, and reach their goals most expeditiously. A recent systematic review suggested that adequate alveolar bone augmentation may be achieved using particulate xenograft or allograft materials beneath barrier membranes. 12 Following healing and initial consolidation of the grafted alveolar ridge, the eventuality of implant placement can be met by different clinical approaches that include two-stage, one-stage, and immediate provisionalization protocols. Expedited therapies often appeal to patients. When implants cannot be placed in extraction sockets or healed ridges and bone augmentation is required, the subsequent placement of the implant may be achieved using an immediate provisionalization procedure. The outcomes of immediate provisionalization of implants placed into recently grafted bone have not been fully investigated. As part of a larger, prospective study of immediate provisionalization of implants placed in extraction sockets and healed ridges, several patients required bone grafting to support future implant placement. Here, the 5-year outcome of immediately provisionalized implants placed in recently grafted bone is reported. Implant survival, marginal bone level, and soft tissue architectural changes were evaluated. Method and materials This data is a subset of data representing patients enrolled in a fourcenter investigation comparing immediate placement and provisionalization with immediate provisionalization of maxillary implants in the esthetic zone. The details of this investigation are reported elsewhere. 6,13 According to an institutional review board approved protocol, 139 patients were recruited for implant placement. At the time of surgery, anatomical or volumetric conditions that precluded implant placement for immediate placement and/or provisionalization were identified in 21 patients. A guided bone regeneration (GBR) procedure was performed using anorganic bovine bone (Bio-Oss, Geistlich) and a resorbable collagen membrane (Bio-Gide or Bio- Mend, Geistlich). Primary closure was obtained, and the sites were left to heal for a period of 4 to 6 months, after which implant placement was performed. Implant placement and restoration Briefly, following uneventful healing of the grafted alveolus, 3.5- to 5.0- mm wide and 11- to 17-mm long implants (OsseoSpeed, Dentsply) were placed under local anesthesia using a modified protocol. Preoperative analgesics (eg, 800 mg ibuprofen) and antibiotics (1 g amoxicillin or 600 mg clindamycin) were prescribed. Transmucosal punches were used for flapless access in the majority of cases; however, conventional flaps were performed in seven of the patients. Osteotomies were created to depth but undersized with respect to diameter (3.2-mm diameter for 3.5- and 4.5-mm implants or 3.7-mm diameter for 4.0- and 5.0-mm implants). For 4.5- and 5.0-mm implants, conical tapered drills were required. The stability of the implant was visually and tactilely assessed at the time of placement. Immediate provisionalization The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
4 479 procedures were performed using Direct Abutment or Profile BiAbutment (Dentsply) and acrylic crowns. Abutments were placed with finger pressure (approximately 15 to 20 Ncm). The crowns were adjusted to be free of centric or eccentric contacts. A periapical radiograph was taken to (1) evaluate implant placement, (2) ensure abutment placement, (3) discover residual cement, and (4) serve as a baseline for evaluation of marginal bone level changes. Postoperative prescriptions for analgesics, antimicrobial mouthrinse (0.12% chlorhexidine gluconate), and antibiotics (amoxicillin 500 mg, three times daily for 5 to 7 days) were given to all patients. Instructions for oral hygiene included the maintenance of conventional toothbrushing and flossing, with local restrictions around the provisional crown for the first 7 to 10 days. Eight weeks after implant, abutment, and provisional crown placement, the provisional crown was removed, and the abutment was retightened to 25 Ncm. An impression was taken of the abutment, and a definitive all-ceramic (Procera [Nobel Biocare] or Lava [3M Espe]) crown was fabricated using conventional prosthodontic procedures. At 11 to 12 weeks, the definitive crown was cemented, and a periapical radiograph was taken. Follow-up evaluation Individuals were evaluated at 26 weeks and annually for 5 years following provisional crown placement. The initial clinical treatment and follow-up evaluation are illustrated longitudinally in Fig 1. Implant immobility was assessed clinically. Implant failure was indicated by pain, peri-implant radiolucency, and/or mobility. Abutment and crown complications and failures were recorded. Plaque and bleeding scores were recorded at four points for each crown (mesiolingual, distolingual, mesiobuccal, and distobuccal). The gingival zenith score (linear distance from the gingival zenith to the incisal edge reference) and the papilla score (linear distance from the papilla tip to the incisal edge reference of adjacent tooth) were recorded to the nearest 0.5 mm. Periapical radiographs were taken by a long cone paralleling technique at implant placement, definitive crown cementation, and at 6 months and yearly for the 5-year follow-up period (Fig 2). A radiologist, independent from the group of investigators, performed all the radiographic interpretations. The distance of the mesial and distal interproximal bone to the reference point (the outer aspect of the implant bevel) was measured to the nearest 0.1 mm. A mean of these two measurements was calculated for each implant, and the changes from baseline, ie, implant placement, were calculated for each subsequent time point. Statistical analysis Descriptive statistics were used in analyzing patient group and implant characteristics. A nonparametric test, Wilcoxon signed rank test, was used to analyze differences between visits or time intervals in terms of hard and soft tissue parameters. The level of significance was set at 0.05 for each test. Results Among the 21 patients, 19 had 23 implants placed with primary stability that were included in this 5-year evaluation. Two implants did not achieve primary stability, were not immediately provisionalized, and therefore were not included in the subsequent analyses. Of the 23 implant sites, 16 were placed in sites developed from extraction sockets and 7 were placed in augmented healed ridges. After the 4- to 6-month graft healing period, 23 implants were placed with acceptable primary stability and were restored with provisional crowns. The study cohort included 7 women (mean ± SD age: 41 ± 19 years) and 12 men (mean ± SD age: 39 ± 16 years). Among these, all were nonsmokers, with three reporting previous tobacco use. The bone quality estimates included 9 (39%) type 2 and 12 (52%) type 3. Bone quantity was high (91% types A and B). No canine sites were represented among the patients; the 23 implants were widely distributed among incisor and premolar sites (Table 1). One implant was determined to be mobile at the time of definitive crown impression (67 days following placement) and was removed. One implant was lost to follow-up after the 6-month evaluation as a result of patient relocation. The calculated implant survival at 5 years was 95.6%. Volume 34, Number 4, 2014
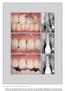
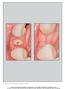
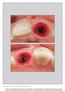
5 480 Fig 1 Longitudinal photographic documentation of peri-implant mucosal conditions illustrating the present investigation of implants placed into grafted alveolar bone. Fig 1a Preoperative condition of the dentition, with a resinbonded fixed dental prosthesis replacing the maxillary left and right lateral incisors. b Figs 1b to 1d Grafting of the alveolar ridge at the maxillary lateral incisor positions using demineralized bovine bone mineral and a collagen membrane. Note the substantial defect present. a c d Fig 1e Alveolar ridges and mucosa 4 months following ridge augmentation procedure. Figs 1f and 1g Left and right lateral incisor provisional crowns and mucosal tissues 8 weeks following implant placement. Figs 1h and 1i One week following definitive crown placement. Figs 1j and 1k One year following placement of definitive crowns. Figs 1l and 1m Three years following definitive crown placement. Figs 1n and 1o Five years following placement of definitive crowns. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
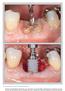
6 481 Fig 2 Longitudinal radiographic assessment of implant therapy illustrating the present investigation of implants placed in grafted alveolar bone. Figs 2a and 2b Preoperative condition of implant sites. Figs 2c and 2d Implant placement: 3.5-mm MicroThread implants (AstraTech Dental Implant System, Dentsply Implants) placed within the available alveolar bone in the maxillary left and right lateral incisor positions. The interproximal subcrestal positioning is consistent with crestal placement at the buccal bone crest. Figs 2e and 2f Crestal bone level at abutment tightening, prior to final impression. Note the approximation of the bone to the implant-abutment interface. Figs 2g and 2h One-year radiographic evaluation of the all-ceramic restorations and abutments on implants. Note that abutments of different heights were utilized to accommodate the differences in tissue height. Table 1 Implant positions Central incisor Lateral incisor First Canine premolar Second premolar Total n % Figs 2i and 2j Three-year radiographic evaluation. Volume 34, Number 4, 2014
7 482 Table 2 Marginal bone level values (mm) at the various examinations IP DR (IP + 12 weeks) IP + 1 year IP + 3 years IP + 5 years n Mean SD Maximum Minimum Median P value* IP = implant placement; DR = definitive restoration. *Wilcoxon signed rank test. Cumulative % of implants Loss Bone level change (mm) from IP to 5 years Fig 3 Cumulative graph illustrating interproximal bone level changes between implant placement (IP) and the 5-year follow-up. In this study, the relationship of the reference point (the outer aspect of the implant bevel) to the interproximal crest at implant placement was reported by the Gain investigator as supracrestal (concave), crestal (flat), or subcrestal (convex) and was most frequently flat (20/23), indicating that clinicians achieved crestal implant placement. Marginal bone levels were measured from implant placement to 5 years. The position of the average marginal bone level (mesial and distal) over the 5-year follow-up period is presented in Table 2. As noted, the marginal bone levels were stable over the 5 years. The mean ± SD marginal bone level change after 5 years was 0.18 ± 0.79 mm (range: 1.6 to 1.4 mm). The distribution of marginal bone level changes is presented in Fig 3. Half of the sites (9/18) recorded no bone loss or bone gain, while only four sites displayed more than 1 mm of interproximal marginal bone loss after 5 years. The affiliated peri-implant coronal plaque and bleeding indices were consistently 15% or lower (Table 3). The direct intraoral measurement of papillae revealed the increased interproximal dimension of approximately 1 mm within the first year following implant and crown placement. This increase in interproximal soft tissue remained throughout the 5-year period (Table 4). Regarding the buccal soft tissues, the direct measurement of the distance from the incisal edge to the peri-implant mucosal zenith demonstrated minor reductions (mean ± SD tissue growth: 0.24 ± 0.93 mm) in this dimension over the 5-year period (Table 5). When comparing the change in the peri-implant mucosal zenith location for implants placed in grafted bone using a flapped versus flapless procedure, minor tissue recession occurred at implants placed using flaps ( 0.21 mm ± 1.07) versus flapless procedures (+0.46mm ± 0.80). The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
8 483 Table 3 Percentage of surfaces exhibiting bleeding on gentle probing and plaque IP + 2 weeks IP + 8 weeks DR (IP + 12 weeks) IP + 1 year IP + 3 years IP + 5 years Bleeding Plaque IP = implant placement; DR = definitive restoration. Table 4 Changes in papilla dimensions (mm) from implant and provisional crown placement* Impression (IP + 8 weeks) DR (IP + 12 weeks) IP +1 year IP + 3 years IP + 5 years Papillae M D M D M D M D M D n Mean SD Maximum Minimum Median P value <.001 <.001 <.001 <.001 < IP = implant placement; DR = definitive restoration; M = mesial; D = distal. *Positive values indicate gain; negative values indicate loss. Wilcoxon signed rank test. Discussion This study evaluated implant survival and peri-implant tissue response following immediate provisionalization of implants placed into recently grafted alveolar ridges and sockets. After a healing period of 4 to 6 months following augmentation using demineralized bovine bone mineral and a collagen barrier membrane, sufficient bone was available for placement of implants with primary stability in the majority of patients. However, initial primary stability was not achieved for 2 of 25 implants planned for the 21 patients. The immediate provisionalization of the implants resulted in one early implant loss without late failures and produced high implant survival after Table 5 Mean changes (mm) in gingival zenith location (relative to incisal edge) from definitive crown placement* IP + 1 year IP + 3 years IP + 5 years n Mean SD Maximum Minimum Median P value IP = implant placement. *Positive values indicate gain; negative values indicate loss. Wilcoxon signed rank test. a 5-year follow-up period (95.6%). In the related prospective study comparing immediate provisionalization of implants placed into ungrafted sockets or healed ridges, the same high implant survival (96%) was recorded at 3 years. 13 In a systematic review of alveolar augmentation and implant placement, Jensen and Terheyden 14 indicated that several combinations of bone grafting materials and procedures permit implant placement and are associated with high implant Volume 34, Number 4, 2014
9 484 survival. In another review, 15 it was concluded that bone grafting procedures as performed in this study are effective in promoting augmentation in postextraction sites. The authors concluded that survival rates over 95% may be expected for both immediate and early placement. The present investigation is in agreement with this review regarding implant survival and tissue stability associated with later implant placement. However, the related study involving immediate placement and provisionalization also demonstrated the same magnitude of tissue stability, calling in question the fundamental causes of tissue stability and the potential reasons for tissue instability. 16 The stated risk factors of thin tissue biotype, facial malposition of the implant, and a thin or damaged facial bone wall were averted by the present grafting of deficient alveolar ridges or sockets. Jung et al 17 reported on the comparison of implant placement in alveolar ridges augmented using demineralized bovine bone allograft and collagen membranes with or without recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2. None of the 34 implants in 11 patients were lost in either grafting situation; there were insignificant changes in the marginal bone levels over the 5-year evaluation period. In a related work, Benić et al 18 demonstrated 100% implant survival for implants in concomitantly grafted bone and 94.1% implant survival for implants placed in native alveolar bone. They concluded that implants placed with concomitant bone regeneration did not perform differently from implants placed into native bone with respect to implant survival, marginal bone height, and peri-implant soft tissue parameters. The osseointegration of implants does not appear to be negatively impacted by the presence of healed or healing demineralized bone allograft. This may reflect the relative abundance of native alveolar bone supporting the implant and/or the integrity of the osseointegration process within regenerated bone. Importantly, the present study did not include any canine sites (or traumatically avulsed teeth), which may have required more significant alveolar reconstruction that could challenge optimal esthetic outcomes. There is sufficient histologic evidence that titanium implants are integrated within regenerated bone. Bone-to-implant contact is not negatively impacted by the presence of residual xenograft or allograft particles in the augmented sites. In a canine model, implants placed in deproteinized bovine bone mineral (DBBM; BioOss) 3 months after grafting showed equivalent osseointegration to implants placed in healed ridges following a 4-month healing period. 19 In a primate model, osseointegration within tissues regenerated using DBBM and a collagen membrane was confirmed. 20 In a surgical defect model in dogs, histology revealed that DBBM grafts placed around implants at placement resulted in a normal range of boneto-implant contact (30% to 40%). At 4 months, however, some of the newly formed bone resorbed. 21 Bio-Oss exhibited osteo conductive properties and was recommended for GBR procedures in dehiscence defects with respect to vertical and horizontal growth of bone. Norton et al 22 illustrated that the new bone volume created by augmentation procedures using this method was approximately 25% vital bone (with approximately 25% residual matrix), and this tissue supported the successful osseointegration of dental implants (97%). It should be noted that some controversy remains regarding the value of graft material to the process of osseointegration at subsequent implant placement. In a canine buccal defect model, it was concluded that significant bone-to-implant contact was not achieved at DBBMgrafted sites. 23 In a recent consideration of the bone-to-implant contact achieved at microimplants placed into grafted sinuses, Browaeys et al 24 concluded that osseointegration in sinus bone grafts mixed with Bio- Oss was poor. This result may not be limited to the type of material: Spin- Neto et al 25 indicated similar limitations in osseointegration achieved clinically using an allogeneic bone graft. Rasmusson et al 26 directly compared the implant stability and survival of implants placed in grafted maxillary bone and intact maxillary bone and found no difference in implant performance. In the present scenario, the high implant survival may reflect that much of the implant was placed in native alveolar bone. Clinical alveolar regeneration and subsequent dental implant osseointegration can be achieved using the protocol utilized in this study. The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
10 485 The present investigation involved a relatively brief healing period of 4 to 6 months following augmentation. There is some evidence that longer healing periods may not be required for consolidation of xenogenic bone grafts. However, clearly this time frame does not permit complete integration or resorption of the xenograft. The clinical procedures reflect this; intact xenograft particles were occasionally displaced from the healing tissue sites during the preparation of the osteotomy for implant placement. A longer healing period could favor further graft consolidation and improve the intraoperative experience for the clinician. However, it is noted that high implant survival and 5-year peri-implant tissue stability suggests that sufficient consolidation occurred prior to or continued following implant placement, provisionalization, and function. The logistical and temporal advantages of immediate provisionalization 4 to 6 months following ridge augmentation merit consideration. First, a decision to avoid implant placement in a socket or insufficient alveolar ridge in favor of augmentation should always be made where needed. Second, the augmentation prior to implant placement simplifies the procedure and permits soft tissue closure at the time of grafting. Third, immediate provisionalization within the recently grafted site accelerates treatment with apparently little added risk of implant failure or soft tissue complication. This approach is temporally equivalent to early placement procedures that involve tooth extraction followed by early implant placement concurrent with buccal bone augmentation utilizing demineralized bone xenograft and a collagen membrane without implant provisionalization. 4 Both approaches involve at least a 6-month period of partial edentulism that is followed by implant placement and restoration. Comparing the 5-year outcomes from the early placement protocol to the present approach, both provide high implant survival and buccal tissue stability. The increased interproximal soft tissue (papilla) dimensions recorded here were not observed for the early loading protocol. While both procedures require mucoperiosteal reflection involving the adjacent teeth, in the present investigation, both flapped (n = 7) and flapless (n = 16) procedures resulted in positive interproximal tissue changes. The interproximal tissue differences are minor and may not influence the reportedly high esthetic values recorded. 27 However, the time of provisionalization as a variable merits further investigation in terms of peri-implant mucosal architecture. The restorative protocol utilized a titanium abutment that was retained from provisionalization as the final abutment. This required the use of cement-retained provisional crowns. The perils of cementmediated inflammatory disease at implants, while identified nearly two decades ago by Walton and co-workers, 28 has become a recent prominent concern, although its impact remains debated. 29 The highest suspicion of cement retention must be adopted when cement-retained crowns are used for implant restorations. Every effort must be made to identify and remove excess cement. The present data set did not directly report on the occurrence of cement retention and removal, but the low incidence of inflammation (bleeding on probing) and absence of significant soft tissue complications suggest that efforts to control cement extrusion were carefully carried out. Although not adopted for this patient cohort, alveolar grafting can afford alternative implant orientation that favors screw retention, a therapeutic concept that offers several different advantages, including the elimination of cement from the protocol. Conclusions Alveolar bone augmentation required for implant placement within bound edentulous spaces can be performed using DBBM and a collagen membrane to create sufficient bone volume to permit subsequent implant placement and successful osseointegration. Alveolar ridge augmentation using DBBM and a collagen membrane supported the measured soft tissue architecture, including the buccal tissue levels, over a 5-year period. The immediate placement and provisionalization of implants into regenerated alveolar sites resulted in high implant survival and stability of both the interproximal papillae and buccal tissue architecture. Volume 34, Number 4, 2014
11 486 Acknowledgments The authors reported no conflicts of interest related to this study. References 1. den Hartog L, Slater JJ, Vissink A, Meijer HJ, Raghoebar GM. Treatment outcome of immediate, early and conventional singletooth implants in the aesthetic zone: A systematic review to survival, bone level, softtissue, aesthetics and patient satisfaction. Clin Periodontol 2008;35: Jung RE, Zembic A, Pjetursson BE, Zwahlen M, Thoma DS. Systematic review of the survival rate and the incidence of biological, technical and esthetic complications of single crowns on implants reported in longitudinal studies with a mean follow-up of 5 years. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012;23(suppl 6): Fürhauser R, Florescu D, Benesch T, Haas R, Mailath G, Watzek. Evaluation of soft tissue around single-tooth implant crowns: The pink esthetic score. Clin Oral Implants Res 2005;16: Belser UC, Grütter L, Vailati F, Bornstein MM, Weber HP, Buser D. Outcome evaluation of early placed maxillary anterior single-tooth implants using objective esthetic criteria: a cross-sectional, retrospective study in 45 patients with a 2- to 4-year follow-up using pink and white esthetic scores. J Periodontol 2009;80: Raes F, Cooper LF, Tarrida LG, Vandromme H, De Bruyn H. A case-control study assessing oral-health-related quality of life after immediately loaded single implants in healed alveolar ridges or extraction sockets. Clin Oral Implants Res 2012; 23: Cooper LF, Raes F, Reside GJ, et al. Comparison of radiographic and clinical outcomes following immediate provisionalization of single-tooth dental implants placed in healed alveolar ridges and extraction sockets. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2010;25: Cosyn J, Sabzevar MM, De Bruyn H. Predictors of inter-proximal and midfacial recession following single implant treatment in the anterior maxilla: A multivariate analysis. J Clin Periodontol 2012;39: Buser D, Chappuis V, Bornstein MM, Wittneben JG, Frei M, Belser UC. Longterm stability of contour augmentation with early implant placement following single tooth extraction in the esthetic zone: A prospective, cross-sectional study in 41 patients with a 5- to 9-year followup. J Periodontol 2013;84: Meijndert L, Raghoebar GM, Meijer HJ, Vissink A. Clinical and radiographic characteristics of single-tooth replacements preceded by local ridge augmentation: A prospective randomized clinical trial. Clin Oral Implants Res 2008;19: Esposito M, Grusovin MG, Felice P, Karatzopoulos G, Worthington HV, Coulthard P. The efficacy of horizontal and vertical bone augmentation procedures for dental implants A Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Oral Implantol 2009;2: Chiapasco M, Casentini P, Zaniboni M. Bone augmentation procedures in implant dentistry. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2009;24(suppl): Hämmerle CH, Araújo MG, Simion M; Osteology Consensus Group Evidencebased knowledge on the biology and treatment of extraction sockets. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23:(suppl 5): De Bruyn H, Raes F, Cooper LF, et al. Three-years clinical outcome of immediate provisionalization of single Osseospeed implants in extraction sockets and healed ridges. Clin Oral Implants Res 2013;24: Jensen SS, Terheyden H. Bone augmentation procedures in localized defects in the alveolar ridge: Clinical results with different bone grafts and bone-substitute materials. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2009; 24(suppl): Chen ST, Buser D. Clinical and esthetic outcomes of implants placed in postextraction sites. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 2009;24(suppl): Cosyn J, Hooghe N, De Bruyn H. A systematic review on the frequency of advanced recession following single immediate implant treatment. J Clin Periodontol 2012;39: Jung RE, Windisch SI, Eggenschwiler AM, Thoma DS, Weber FE, Hämmerle CH. A randomized-controlled clinical trial evaluating clinical and radiological outcomes after 3 and 5 years of dental implants placed in bone regenerated by means of GBR techniques with or without the addition of BMP-2. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009;20: Benić GI, Jung RE, Siegenthaler DW, Hämmerle CH. Clinical and radiographic comparison of implants in regenerated or native bone: 5-year results. Clin Oral Implants Res 2009;20: Berglundh T, Lindhe J. Healing around implants placed in bone defects treated with Bio-Oss. An experimental study in the dog. Clin Oral Implants Res 1997;8: Hämmerle CHF, Chiantella GC, Karring T, Lang NP. The effect of a deproteinized bovine bone mineral on bone regeneration around titanium dental implants. Clin Oral Implants Res 1998;9: De Santis E, Botticelli D, Pantani F, Pereira FP, Beolchini M, Lang NP. Bone regeneration at implants placed into extraction sockets of maxillary incisors in dogs. Clin Oral Implants Res 2011;22: Norton MR, Odell EW, Thompson ID, Cook RJ. Efficacy of bovine bone mineral for alveolar augmentation: A human histologic study. Clin Oral Implants Res 2003; 14: Carmagnola D, Berglundh T, Araújo M, Albrektsson T, Lindhe J. Bone healing around implants placed in a jaw defect augmented with Bio-Oss. An experimental study in dogs. J Clin Periodontol 2000;27: Browaeys H, Vandeweghe S, Johansson CB, Jimbo R, Deschepper E, De Bruyn H. The histological evaluation of osseointegration of surface enhanced microimplants immediately loaded in conjunction with sinuslifting in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res 2013;24: Spin-Neto R, Stavropoulos A, Coletti FL, Faeda RS, Pereira LA, Marcantonio E Jr. Graft incorporation and implant osseointegration following the use of autologous and fresh-frozen allogeneic block bone grafts for lateral ridge augmentation. Clin Oral Implants Res 2014;25: Rasmusson L, Thor A, Sennerby L. Stability evaluation of implants integrated in grafted and nongrafted maxillary bone: A clinical study from implant placement to abutment connection. Clin Implant Dent Relat Res 2012;14: Buser D, Halbritter S, Hart C, et al. Early implant placement with simultaneous guided bone regeneration following single-tooth extraction in the esthetic zone: 12-month results of a prospective study with 20 consecutive patients. J Periodontol 2009;80: Pauletto N, Lahiffe BJ, Walton JN. Complications associated with excess cement around crowns on osseointegrated implants: A clinical report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 1999;14: de Brandão ML, Vettore MV, Vidigal Júnior GM. Peri-implant bone loss in cement- and screw-retained prostheses: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Periodontol 2013;40: The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 06 MANAGEMENT OF ATROPHIC ANTERIOR MAXILLA USING RIDGE SPLIT TECHNIQUE, IMMEDIATE IMPLANTATION AND TEMPORIZATION Rakshith
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report
 C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
C A S E R E P O R T Replacement of a congenitally missing lateral incisor in the maxillary anterior aesthetic zone using a narrow diameter implant: A case report Rhoodie Garrana 1 and Govindrau Mohangi
Immediate Implant Placement Along With Guided Bone Regeneration In Mandibular Anterior Region A Case Report.
 IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
IMMEDIATE IMPLANT PLACEMENT ALONG WITH GUIDED BONE REGENERATION IN MANDIBULAR ANTERIOR REGION A CASE REPORT. Dr.C.P.Dhivakar 1, Dr.T.Saravanan 2, Dr.A.Aniz 3 1) Department of Periodontics, Karpaga Vinayaga
Submission to Clinical Oral Implants Research (adjusted version)
 Submission to Clinical Oral Implants Research (adjusted version) Title A prospective cohort study on the impact of smoking on soft tissue alterations around single implants Running title Soft tissue alterations
Submission to Clinical Oral Implants Research (adjusted version) Title A prospective cohort study on the impact of smoking on soft tissue alterations around single implants Running title Soft tissue alterations
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Immediate Implant Placement:
 Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Immediate Implant Placement: Parameters Influencing Tissue Remodeling Bernard Touati, DDS and Mario Groisman, DDS In esthetic implant therapy, the patient s objective is to obtain an imperceptible, natural-looking
Management of a complex case
 2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
2 Soft- and hard-tissue reconstruction of a severely deficient site prior to implant placement: a case report Management of a complex case Younes Khosroshahy, DDS, MFDS RCS (Eng), Dip Imp Dent RCSEd, Blue
Hyun-Jae Cho, Kun-Soo Jang, Ki-Hyun Jeong, Jae-Yun Jeon, Kyung-Gyun Hwang, Chang-Joo Park
 Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Vol. 33 No. 1, March 2014 Peri-implant gingival tissue changes following immediate placement of maxillary anterior single implant with a collagen-coated xenograft: A 1-year follow-up result Hyun-Jae Cho,
Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration
 Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
Indication Sheet PIR-1 Periimplant Regeneration Fenestration Treatment concept of Dr. Jean-Pierre Gardella (surgeon) and Dr. Christian Richelme (prosthodontist), Marseille, France > Filling of a peri-implant
The anatomic limitations of the. Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD*
 CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
CASE REPORT Implant Installation With Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation. Report of Three Cases Jun-Beom Park, DDS, MSD, PhD* The anatomic limitations of the residual alveolar bone may cause problems for
Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report
 Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Clinical Socket preservation in the daily practice: A clinical case report Rabih Abi Nader 1 and Carine Tabarani 2 Abstract Soft tissue contour depends on the underlying bone anatomy. Following tooth extraction,
Peri-implant Augmentation
 Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Indication Sheet PIR3 Peri-implant Augmentation Early implantation with simultaneous GBR for contour augmentation using the technique by Prof. Daniel Buser and Prof. Urs Belser, University of Berne, Switzerland
Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants
 Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Flapless Surgery Case Study 48 Flapless, Immediate Implantation & Immediate Loading with Socket Preservation in the Esthetic Area Using the Alpha-Bio Tec's NeO Implants Dr. Gadi Schneider DMD, Specialist
Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Rehabilitating a Compromised Site for Restoring Form, Function and Esthetics- A Case Report Priyanka Prakash* Division of Periodontology, Department of Dental
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1.
 Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
Patient s Presenting Complaint V.C. presented with discomfort and mobility from the crowned maxillary left central incisor tooth. Fig 1. A longitudinal root fracture was suspected and confirmed when the
BONE AUGMENTATION AND GRAFTING
 1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
1 A Computer-Guided Bone Block Harvesting Procedure: A Proof-of-Principle Case Report and Technical Notes Effectiveness of Lateral Bone Augmentation on the Alveolar Crest Dimension: A Systematic Review
Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A Case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 13, Issue 1 Ver. II (Jan. 2014), PP 97-101 Esthetic management of multiple missing anterior teeth A
Working together as a team, the periodontist
 The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
The Team Approach to Esthetic Immediate Implant Placement Bobby L. Butler, DDS; and Greggory Kinzer, DDS Working together as a team, the periodontist and restorative dentist can provide an increased level
Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area
 CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
CLINICAL SCIENCE IJOICR Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area Immediate Restorations on Implants in the Esthetic Area 1 Pedro Peña Martinez, 2 Ramón Palomero Langner, 3 Ramón Palomero
Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants
 Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Peer-Reviewed and Indexed Annual Implant Issue Masking Buccal Plate Remodeling in the Esthetic Zone with Connective Tissue Grafts: Concepts and Techniques with Immediate Implants of Continuing Education
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss. Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor
 Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
Dental Implants: A Predictable Solution for Tooth Loss Reena Talwar, DDS PhD FRCD(C) Oral & Maxillofacial Surgeon Associate Clinical Professor What are Dental Implants? Titanium posts used to replace missing
REGENERATIONTIME. A Case Report by. Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor
 A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
A Case Report by Dr. Daniele Cardaropoli Ridge Augmentation and Delayed Implant Placement on an Upper Lateral Incisor The Situation An adult female patient presented with an endodontic/prosthetic failure
Case Study. Case # 1 Author: Dr. Suheil Boutros (USA) 2013 Zimmer Dental, Inc. All rights reserved. 6557, Rev. 03/13.
 Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Placement of a Zimmer Trabecular Metal Dental Implant with Simultaneous Ridge Augmentation and Immediate Non-Functional Loading Following Tooth Extraction and Orthodontic Treatment for Implant Site Development
Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry. Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor
 Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Prosthetic Options in Dentistry Hakimeh Siadat, DDS, MSc Associate Professor Dental Research Center, Department of Prosthodontics & Dental s Faculty of Dentistry, Tehran University of Medical Sciences
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration. Ph.D. Thesis. Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban
 Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Vertical and Horizontal Augmentation Using Guided Bone Regeneration Ph.D. Thesis Dr. med. dent. et univ. Istvan Urban Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Katalin Nagy, DDS, PhD Faculty of Dentistry, University of Szeged
Case Report. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
 Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Case Report RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol. RapidSorb Rapid Resorbable Fixation System. Ridge augmentation in a one-step surgical protocol.
Early implant placement: 3D radiographic study on the fate of buccal wall
 Early implant placement: 3D radiographic study on the fate of buccal wall A. Lanza 1-2, F. Scognamiglio 1, G. De Marco 1, F. Di Francesco 1, F. Femiano 1-3, M. Lanza 4, A. Itro 5 1 DD-Multidisciplinary
Early implant placement: 3D radiographic study on the fate of buccal wall A. Lanza 1-2, F. Scognamiglio 1, G. De Marco 1, F. Di Francesco 1, F. Femiano 1-3, M. Lanza 4, A. Itro 5 1 DD-Multidisciplinary
Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases
 52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
52 STARGET 1 I 12 StraUMaNN CareS r ry vincenzo MiriSOLA Di TOrreSANTO AND LUCA COrDArO Guided surgery as a way to simplify surgical implant treatment in complex cases Background A 41-year-old woman with
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 715 Immediate Implant Placement and Loading of Single Implants in the Esthetic Zone: Clinical Outcome and Esthetic Evaluation in a Japanese
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques
 Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Alveolar ridge preservation techniques Semmelweis University, Department of Periodontology, Budapest Dr. Windisch Péter Head of Department of Periodontology Changes of the alveolar ridge dimensions after
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes
 Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Clinical Case Reports using Cytoplast GTR Barrier Membranes Barry K. Bartee, DDS, MD The Cytoplast Technique: Extraction Site Grafting Without Primary Closure 1. 1. Preoperative view. To maximize the result
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
 Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Neenu M Varghese et al Case Report 10.5005/jp-journals-10012-1148 A Novel Technique for the Management of a Maxillary Anterior Alveolar Defect with an Implant-retained Fixed Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 07 Page July 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 71.58 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i7.101 Immediate Implant Following
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 67 Efficacy Evaluation of a New Buccal Bone Plate Preservation Technique: A Pilot Study Federico Brugnami, DDS* Alfonso Caiazzo, DDS**
Initially, implant dentistry was focused on
 CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
CASE LETTER Correction of Esthetic Complications of a Malpositioned Implant: A Case Letter Sergio Alexandre Gehrke, PhD INTRODUCTION Initially, implant dentistry was focused on successful osseointegration
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols
 Group 3 Consensus Statements Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols Hans-Peter Weber, DMD, Dr Med Dent 1 /Dean Morton, BDS, MS 2 /German O. Gallucci, DMD,
Group 3 Consensus Statements Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Loading Protocols Hans-Peter Weber, DMD, Dr Med Dent 1 /Dean Morton, BDS, MS 2 /German O. Gallucci, DMD,
Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes BARRY P. LEVIN, DMD*, SERGIO RUBINSTEIN, DDS, LOUIS F. ROSE, DDS, MD ** ABSTRACT
CLINICAL ARTICLE Advanced Esthetic Management of Dental Implants: Surgical and Restorative Considerations to Improve Outcomes BARRY P. LEVIN, DMD*, SERGIO RUBINSTEIN, DDS, LOUIS F. ROSE, DDS, MD ** ABSTRACT
Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets
 Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
Jorge Ferrus Denis Cecchinato E. Bjarni Pjetursson Niklaus P. Lang Mariano Sanz Jan Lindhe Factors influencing ridge alterations following immediate implant placement into extraction sockets Authors affiliations:
The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges
 Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Case Study 48 The Use of Alpha-Bio Tec's Narrow NeO Implants with Cone Connection for Restoration of Limited Width Ridges Dr. Amir Gazmawe DMD, Specialist in Prosthodontics, Israel Dr. Amir Gazmawe graduated
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation. Sanju P. Jose
 Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
Evaluation of a Combination Allograft Material Compared to DFDBA in Alveolar Ridge Preservation by Sanju P. Jose B.S., University of Maryland Baltimore County, 2008 D.D.S., University of Maryland School
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits. Your combination for success
 Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Bringing you Geistlich biocompatibility with improved application and handling benefits Your combination for success Geistlich Combi-Kit Collagen: Combining ease and predictablility Geistlich Combi-Kit
Case study 61. Assisted Implant Rehabilitation in the Esthetic Zone Using TI-Base on Narrow Diameter Implants (NICE) Dr. Stuardo Valenzuela Manfredi
 Case study 61 Assisted Implant Rehabilitation in the Esthetic Zone Using TI-Base on Narrow Diameter Implants (NICE) Dr. Stuardo Valenzuela Manfredi Assisted implant rehabilitation in the esthetic zone
Case study 61 Assisted Implant Rehabilitation in the Esthetic Zone Using TI-Base on Narrow Diameter Implants (NICE) Dr. Stuardo Valenzuela Manfredi Assisted implant rehabilitation in the esthetic zone
Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations
 case report Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations Hugo A. ALBERA 1, Estela M. Ribotta de ALBERA 2 Several factors determine the success of functional
case report Planning: The key to obtaining aesthetic and functional results in implant-supported restorations Hugo A. ALBERA 1, Estela M. Ribotta de ALBERA 2 Several factors determine the success of functional
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior
 Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Extraction with Immediate Implant Placement and Ridge Preservation in the Posterior by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD The following case presentation illustrates the diagnosis, planning and treatment for
Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2011;41:60-66 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2011.41.2.60 Labial and lingual/palatal bone thickness of maxillary and mandibular anteriors in human cadavers in Koreans Ji Young
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 47 Provisional Restorations Used in Immediate Implant Placement Provide a Platform to Promote Peri-implant Soft Tissue Healing: A Pilot
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report
 Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
Surgery All at Once : Socket preservation and immediate placement of an implant in an infected site in the anterior region a Case Report W.P. van der Schoor*, A.R.M. van der Schoor Tooth extraction followed
In the esthetic zone, osseointegration
 CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
CASE REPORT A Method for Obtaining Peri-Implant Soft-Tissue Contours by Using Screw- Retained Provisional Restorations as Impression Copings: A Clinical Report Bi-Yuan Tsai, DDS, MS* In the esthetic zone,
 Wittneben JG, Kern M: Imitation der Rot-Weiß-Ästhetik im Frontzahnbereich Literatur: 1 Buser D, Sennerby L, De Bryn H: Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current
Wittneben JG, Kern M: Imitation der Rot-Weiß-Ästhetik im Frontzahnbereich Literatur: 1 Buser D, Sennerby L, De Bryn H: Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants. Agenda. Agenda. Smile line revitalization with implants Priest Prosthodontics, LLC 1
 Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
Smile Line Rehabilitation with Dental Implants Board Certified Prosthodontist Hilton Head Island, SC Agenda Implant placement and esthetic potential Single immediate implant placement Soft tissue preservation
From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement
 Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Dr. Giancarlo Romagnuolo Roma, Italy From planning to surgery: a totally digital working flow for Leone implants placement Keywords guided surgery, 3D implant planning, single missing tooth, delayed immediate
Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas
 2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
2 Long-term follow-up of 2.5mm NDIs supporting a fixed prosthesis Narrow-diameter implants in premolar and molar areas EDUARDO ANITUA, DDS, MD, PHD¹,² A narrow-diameter implant (NDI) is an implant with
The Original remains unique.
 The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
The Original remains unique. Geistlich leading regeneration 2A, 2B Geistlich is the world leader in regenerative dentistry. We transform natural biomaterials into safe and reliable treatment methods that
Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series NABIL KHZAM, BDS, MPhil, DClinDent*, NIKOS MATTHEOS, DDS, MASc, PhD, DAVID ROBERTS,
RESEARCH ARTICLE Immediate Placement and Restoration of Dental Implants in the Esthetic Region: Clinical Case Series NABIL KHZAM, BDS, MPhil, DClinDent*, NIKOS MATTHEOS, DDS, MASc, PhD, DAVID ROBERTS,
A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material
 74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
74 Bone grafting with simultaneous early implant placement A new approach with an in-situ self-hardening grafting material MINAS LEVENTIS 1,2, PHD; PETER FAIRBAIRN 1,3, BDS; ORESTIS VASILIADIS 2,4, DDS
Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space
 Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
Case Report Immediate Loading with Flapless Implant Surgery for Rehabilitation of Single Bound Edentulous Space Nidhi Bhatia 1, Shweta Bali 2, Meenu Taneja Bhasin 3, Priyanka Aggarwal 4, Vaibhav Joshi
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 2011 BY QUINTESSENCE PUBLISHING CO, INC. PRINTING OF THIS DOCUMENT IS RESTRICTED TO PERSONAL USE ONLY.. 215 Dental Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study
 Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Evaluation of immediate loading of single dental implants in the maxillary esthetic zone: Clinical and radiographical comparative study Received: 9/6/2013 Accepted: 30/7/2013 Serwan Saeb Al Naqshabandi
Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla
 Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla Franck Bonnet, DDS Private Practice, Cannes, Le Cannet, France Director
Esthetic evaluation of periimplant soft tissue of immediate single-implant placement and provisionalization in the anterior maxilla Franck Bonnet, DDS Private Practice, Cannes, Le Cannet, France Director
Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations
 C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
C L I N I C A L Planning for esthetics Part II: adjacent implant restorations William C Martin, 1 Emma Lewis, 2 Dean Morton 3 1 DMD, MS, Associate Professor & Clinical Director, Center for Implant Dentistry,
One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A Case Series
 Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2012 14/3:62-68 One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A
Journal of the International Academy of Periodontology 2012 14/3:62-68 One-year Re-entry Results of Guided Bone Regeneration around Immediately Placed Implants with Immediate or Conventional Loading: A
Surgical soft tissue improvement in the course of implant therapy
 C L I N I C A L Surgical soft tissue improvement in the course of implant therapy Daniel Bäumer 1, Otto Zuhr 2, Markus Hürzeler 3 Abstract Soft tissue management has become a crucial part of implant therapy
C L I N I C A L Surgical soft tissue improvement in the course of implant therapy Daniel Bäumer 1, Otto Zuhr 2, Markus Hürzeler 3 Abstract Soft tissue management has become a crucial part of implant therapy
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry
 Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
Controlling Tissue Contours with a Prosthetically Driven Approach to Implant Dentistry Go online for in-depth content by Timothy F. Kosinski, DDS, MAGD With continual improvements in the design and production
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 89 Pre-extractive Interradicular Implant Bed Preparation: Case Presentations of a Novel Approach to Immediate Implant Placement at Multirooted
Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS
 Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Page 1 of 5 Issue Date: March 2003, Posted On: 8/1/2005 Multi-Modality Anterior Extraction Site Grafting Increased Predictability for Aesthetics Michael Tischler, DDS The extraction of teeth creates a
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System
 Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Optimizing Lateral Incisor Function and Esthetics with the Hahn Tapered Implant System by Timothy Kosinski, DDS, MAGD Maxillary lateral incisor agenesis (MLIA) is a condition in which at least one of the
Vertical and horizontal alveolar ridge augmentation
 CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
CLINICAL SIMULTANEOUS VERTICAL GUIDED BONE REGENERATION AND GUIDED TISSUE REGENERATION IN THE POSTERIOR MAXILLA USING RECOMBINANT HUMAN PLATELET-DERIVED GROWTH FACTOR: A CASE REPORT Istvan Urban, DMD,
Dr. Jyoti Bansal, Dr. Abhishek Bansal, Dr. Suresh D.K., Dr. Anish Manocha
 Case Report 1 2 3 4 Dr. Jyoti Bansal, Dr. Abhishek Bansal, Dr. Suresh D.K., Dr. Anish Manocha Bansal J, Bansal A, DK Suresh, Manocha A. Immediate loading of single stage implants with minimally invasive
Case Report 1 2 3 4 Dr. Jyoti Bansal, Dr. Abhishek Bansal, Dr. Suresh D.K., Dr. Anish Manocha Bansal J, Bansal A, DK Suresh, Manocha A. Immediate loading of single stage implants with minimally invasive
Management of peri-implant recession associated with bone fenestration and dehiscence in the anterior region
 CLINICAL REPORT 269 George Nikou, Dimitris Nikolidakis, Peter Thoolen, Anton Sculean Management of peri-implant recession associated with bone fenestration and dehiscence in the anterior region KEY WORDS
CLINICAL REPORT 269 George Nikou, Dimitris Nikolidakis, Peter Thoolen, Anton Sculean Management of peri-implant recession associated with bone fenestration and dehiscence in the anterior region KEY WORDS
Vertical Augmentation
 Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Indication Sheet V Dr. Mauro Merli Vertical Augmentation Vertical alveolar ridge augmentation by means of the fence technique with Geistlich biomaterials > Original publication of the technique on PubMed;
Horizontal bone augmentation by means of guided bone regeneration
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 13 40 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Horizontal bone augmentation by means
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94
 ( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
( ) 2009;28(2):89-94 Osseointegration is important in the functional aspect, however, esthetics is also important, especially in the maxillary anterior region. An adequate surgical technique is necessary
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel
 PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
PALATAL POSITIONING OF IMPLANTS IN SEVERELY RESORBED POSTERIOR MAXILLAE F. Atamni, M.Atamni, M.Atamna, Private Practice Tel-aviv Israel Abstract: Objectives: To evaluate an alternative treatment for rehabilitation
Osseointegrated implant-supported
 CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
CLINICAL SCREWLESS FIXED DETACHABLE PARTIAL OVERDENTURE TREATMENT FOR ATROPHIC PARTIAL EDENTULISM OF THE ANTERIOR MAXILLA Dennis Flanagan, DDS This is a case report of the restoration of a partially edentulous
Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft
 The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
The Atrophic crest Deploying Alpha-Bio Tec s NeO Selftapping Implant in an Atrophic Crest: Vestibular-Cortical Stabilization with Bone Graft Dr. Paolo Borelli DDS, Italy Dr. Massimiliano Favetti DDS, Italy
Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived
 Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:227-231 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.227 Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived bone mineral Jang-Yeol Park, Ki-Tae Koo, Tae-Il Kim, Yang-Jo
Research Article J Periodontal Implant Sci 2010;40:227-231 doi: 10.5051/jpis.2010.40.5.227 Socket preservation using deproteinized horsederived bone mineral Jang-Yeol Park, Ki-Tae Koo, Tae-Il Kim, Yang-Jo
Several extraction socket classifications have been
 Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Case Report Type 3 ReceSSion DefeCTS Clinical Management of Type 3 Recession Defects With Immediate Implant and Provisional Restoration Therapy: A Case Report Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS; and Stephen J. Chu,
Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis
 CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
CASE REPORT Rehabilitation of atrophic partially edentulous mandible using ridge split technique and implant supported removable prosthesis Dr Ashish Yadav 1, Dr Aratee Gupta 2, Dr Archana Singh 3, 1,3-
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 15 No. 03 July 16
 Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
Bangladesh Journal of Medical Science Vol. 5 No. 03 July 6 Original article Dimensional changes of hard and soft tissue after immediate implantation in comparison with conventional tooth extraction Radvar
Alveolar Ridge Preservation:
 Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Alveolar Ridge Preservation: Preserving and Building up the Bony Structures after Extraction» By: Prof. Roland Hille Konigsallee 49c, 41747 Viersen, Germany E-mail: dr-hille@t-online.de» Prof. Rolf Vollmer
Immediate implants at fresh extraction sockets: from myth to reality
 Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 132 152 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Immediate implants at fresh extraction
Periodontology 2000, Vol. 66, 2014, 132 152 2014 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd Printed in Singapore. All rights reserved PERIODONTOLOGY 2000 Immediate implants at fresh extraction
Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report
 Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
Journal of Periodontology & Implant Dentistry Case Report Surgical reconstruction of lost papilla around implant with a modified technique: A case report Mahdi Faraji* Andre Van Zyl University of Pretoria,
TOPICS. T O P I C S Day 2. Introduction Surgical challenges to treat esthetic implant failures Treatment options & case reports Conclusions
 T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
T O P I C S Day 2 Implant placement post extraction with simultaneous contour augmentation using GBR: When immediate, when early, when late? CAD-CAM technology and zirconia: new opportunities for esthetic
International Journal of Applied Dental Sciences 2018; 4(1): Dr. Renu gupta, Dr. RP Luthra, Suhani Kukreja
 2018; 4(1): 213-218 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 213-218 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 06-11-2017 Accepted: 07-12-2017 Dr. Renu gupta Professor and head, Department
2018; 4(1): 213-218 ISSN Print: 2394-7489 ISSN Online: 2394-7497 IJADS 2018; 4(1): 213-218 2018 IJADS www.oraljournal.com Received: 06-11-2017 Accepted: 07-12-2017 Dr. Renu gupta Professor and head, Department
Immediate implant placement, with or without simultaneous implant provisionalization,
 Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
Saving Her Smile by Panos Papaspyridakos, DDS, MS, PhD and Michael Vizirakis, DDS, MS Immediate Implant Placement and Fixed Provisionalization with Extracted Tooth Introduction Following tooth extraction,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery
 Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Practical Advanced Periodontal Surgery Serge Dibart Blackwell Munksgaard Chapter 8 Papillary Construction After Dental Implant Therapy Peyman Shahidi, DOS, MScD, Serge Dibart, DMD, and Yun Po Zhang, PhD,
Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident
 Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
Case Report 13 2011 Oral Rehabilitation with CAMLOG implants after loss of dentition due to an accident Dr Hitoshi Minagawa Tokyo, Japan Prosthetics Dr Hitoshi Minagawa successfully completed his studies
major publications Geistlich Bio-Gide Geistlich Bio-Oss Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen Geistlich Mucograft
 Geistlich Bio-Gide Geistlich Bio-Oss Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen Geistlich Mucograft Geistlich Pharma AG Business Unit Biomaterials Bahnhofstrasse 40 CH-6110 Wolhusen/Switzerland phone +41/41/492 56 30
Geistlich Bio-Gide Geistlich Bio-Oss Geistlich Bio-Oss Collagen Geistlich Mucograft Geistlich Pharma AG Business Unit Biomaterials Bahnhofstrasse 40 CH-6110 Wolhusen/Switzerland phone +41/41/492 56 30
