Cephalometric Facial Soft Tissue Changes with the Twin Block Appliance in Class II division 1 Malocclusion Patients
|
|
|
- Collin Wesley Parsons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article Cephalometric Facial Soft Tissue Changes with the Twin Block Appliance in Class II division 1 Malocclusion Patients A Systematic Review Carlos Flores-Mir a ; Paul W. Major b ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate facial soft tissue changes after the use of the twin block appliance in Class II division 1 malocclusion patients. Materials and Methods: Several electronic databases (PubMed, MEDLINE, MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations, Cochrane databases, EMBASE, Web of Science, and LI- LACS) were searched with the help of a senior health-sciences librarian. Abstracts that appeared to fulfill the initial selection criteria were selected by consensus, and the original articles were retrieved. The article references were hand-searched for possible missing articles. Clinical trials that assessed facial soft tissue changes with the use of the twin block appliance without any surgical intervention or syndromic characteristics were considered. A comparable untreated control group was required to factor out normal growth changes. Results: Two articles fulfilled the selection criteria and quantified facial soft tissue changes. Although some statistically significant changes in the soft tissue profile were found, the magnitude of the changes may not be perceived as clinically significant. Changes produced in the upper lip seem to be controversial, although the study with sounder methodological quality did not report significant changes. No change in the anteroposterior position of the lower lip and the soft tissue menton or improvement of the facial convexity was found. Conclusions: Three-dimensional quantification of the soft tissue changes is required to overcome current limitations in our understanding of the soft tissue changes obtained after the use of the twin block appliance in Class II division 1 malocclusion patients. KEY WORDS: Functional appliances; Soft tissue; Profile; Facial changes; Twin block INTRODUCTION Different removable functional appliances have been used to treat patients with Class II division 1 malocclusions. Although one of the main reasons for lay persons to undergo orthodontic treatment is esthetic a Clinical Associate Professor, Orthodontic Graduate Program and Director, Craniofacial and Oral Health Evidence-based Practice Group, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. b Professor, Director of the Orthodontic Graduate Program and Member, Oral Health Evidence-based Practice Group, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. Corresponding author: Dr. Carlos Flores-Mir, Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry, Room 4051A, Dentistry/Pharmacy Centre, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, Canada T6G 2N8 ( carlosflores@ualberta.ca) Accepted: October Submitted: July by The EH Angle Education and Research Foundation, Inc. improvement, 1,2 of the multitude of reports evaluating the skeletal and dental changes produced by removable functional appliances, only a relatively small proportion have analyzed the soft tissue changes. The twin block appliance is the most popular functional appliance in the United Kingdom. 3 It was first introduced by Clark in and consists of two separate, upper and lower, removable plates with acrylic blocks trimmed to an angle of 70 degrees. These separate plates make the twin block appliance different in comparison with other removable functional appliances, which are basically monoblocks. Theoretically, this plus a less bulky appearance would increase patient acceptance of the appliance. Patients would also have more freedom in their mandibular movements. All these considerations could conceptually produce different treatment results compared with the removable functional monoblocks. Several studies have evaluated the soft tissue changes produced by the twin block Although 876 DOI: /
2 SOFT TISSUE CHANGES WITH TWIN BLOCK 877 TABLE 1. Search Results From Different Electronic Databases Database a Key Words Results Selected PubMed (1) functional appliance*; (2) twin block; (3) #1 OR #2, (4) soft tissue*; (5) facial change*; (6) profile change*; (7) #4 OR #5 OR #6; (8) #3 AND #7; (9) limit #8 to humans MEDLINE (1) functional appliance$.mp; (2) twin block.mp; (3) #1 OR #2; (4) soft tissue$.mp; (5) facial change$.mp; (6) profile change$.mp; (7) #4 OR #5 OR #6; (8) #3 AND #7; (9) limit #8 to humans MEDLINE In-Process & Other Nonindexed Citations (1) functional appliance$.mp; (2) twin block.mp; (3) #1 OR #2; (4) soft tissue$.mp; (5) facial change$.mp; (6) profile change$.mp; (7) #4 OR #5 OR #6; (8) #3 AND #7; EMBASE (1) functional appliance$.mp; (2) twin block.mp (3) #1 OR #2; (4) soft tissue$.mp; (5) facial change$.mp; (6) profile change$.mp; (7) #4 OR #5 OR #6; (8) #3 AND #7; All EBM reviews (Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, ACP Journal Club, DARE, and CCTR) Web of Science (1) functional appliance$.mp; (2) twin block.mp (3) #1 OR #2; (4) soft tissue$.mp; (5) facial change$.mp; (6) profile change$.mp; (7) #4 OR #5 OR #6; (8) #3 AND #7; (1) TS (functional appliance* OR twin block) AND (soft tissue* OR facial change* OR profile change*); DocType Article; Language All languages; Database(s) SCI- EXPANDED Total No. of Selected Abstracts (%) b LILACS twin block AND facial Hand search Reference list from selected articles 0 0 a EBM, Evidence-Based Medicine; ACP, American College of Physicians; DARE, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects; CCTR, Cochrane Database of Trial Registration. b Percentages do not add up to 100% because the same reference could be found in several databases. some literature reviews 3,15 25 and systematic reviews have focused on the effect of functional appliances on skeletal and dental structures, no systematic review has been specifically focused on the soft tissue changes produced by the twin block appliance. Such a review would permit the clinician to evaluate the quality of the available evidence and discuss the facial implications of this type of removable functional orthodontic treatment. Therefore, the objective of the present systematic review was to evaluate facial soft tissue changes by using lateral cephalograms after the use of the twin block appliance in Class II division 1 malocclusion cases. MATERIALS AND METHODS A computerized search was conducted of several electronic databases: MEDLINE (from 1966 to week 3 of October 2005), MEDLINE In-Process & Other Non- Indexed Citations (up to October 21, 2005), LILACS (from 1982 to October 2005), PubMed (from 1966 to week 3 of October 2005), EMBASE (from 1988 to week 43 of 2005), Web of Science (from 1945 to October 22, 2005), and all evidence-based medicine reviews (Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, American College of Physicians Journal Club, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects, and Cochrane Database of Trial Registration; to the fourth quarter of 2005). Terms used in this literature search were twin block, functional appliances, soft tissue, profile, and facial changes. The selection and specific use of each term inside each database search were made with the help of a senior librarian specialized in health sciences database searches (Table 1). The following inclusion criteria were chosen to initially select potential articles from the published abstract results: Human clinical trials; Facial soft tissue changes evaluated through lateral cephalograms; Use of the twin block appliance to correct Class II division 1 malocclusions; Nonsyndromic or medically compromised patients; No individual case reports or series of cases; and No surgical intervention. No attempts were made at this stage to identify studies that did not use adequate control groups to factor out growth changes. It was considered improbable that the abstracts would report enough information regarding control groups. This would potentially exclude some articles. Meeting abstracts were not selected but were used to trace articles when a full article was published from the data. All the article abstracts that appeared to meet the
3 878 FLORES-MIR, MAJOR initial inclusion criteria were selected, and the actual articles were collected. The selection process was independently made by the two researchers. Their results were compared and discrepancies were settled through discussion; except for the LILACS database, which was only evaluated by one of the researchers because of language limitation. When an article abstract did not provide enough information to make a decision, the actual article was obtained. The articles ultimately selected were chosen with the following additional inclusion criteria: A comparable control group to factor growth changes when required; and Only the twin block appliance was used. The actual articles from the selected abstracts were then independently evaluated by the two researchers. A consensus was reached regarding which articles fulfilled the final selection criteria. These articles were finally included in the systematic review. Articles that did not factor out growth changes when required (growing samples) were rejected at this stage. Craniofacial growth was considered important to factor out in order to accurately assess the true magnitude of the soft tissue changes. Failure to consider craniofacial growth changes would result in a potential overestimation of the magnitude of the changes attained. Simultaneous use of a fixed appliance was considered a confounder and a reason for exclusion. Although measurement error is needed for a correct interpretation of the clinical significance of the findings, it was not considered a reason to reject an article but was considered in the interpretation of the data. Knowing that more methodologically sound studies may provide more reliable conclusions, a methodological scoring process was developed to identify which selected studies would be most valuable (Table 2). No attempt was made to imply that this evaluation tool has been properly validated. Previous reports have shown that there is no sound evidence about the validity of the use of quality assessment of clinical trials, and these reports recommend that researchers examine the individual influence of key components on methodological quality. The reference lists of the retrieved articles were also hand-searched for additional relevant publications that may have been missed in the database searches. In cases where extra information was required for discussion or statistical analysis but was not specifically stated in the article, contact with the authors was sought to obtain the required information. RESULTS The search results and the final number of abstracts selected according to the initial selection criteria from TABLE 2. Methodological Score for the Clinical Trials I. Study Design (11 ) A. Objective objective clearly formulated () B. Population described () C. Selection criteria clearly described (); adequate () D. Sample size considered adequate (); estimated before collection of data () E. Baseline characteristics baseline characteristics (); similar between groups () F. Timing prospective (); long-term follow-up () G. Randomization stated () II. Study Measurements (4 ) H. Measurement method appropriate to the objective () I. Blind measurement blinding (examiner ; statistician ) J. Reliability described () III. Statistical Analysis (5 ) K. Dropouts included in data analysis () L. Statistical analysis appropriate for data () M. Confounders included in analysis () N. Statistical significance level P level stated (); confidence intervals () Maximum number of s 20 TABLE 3. Flow Diagram of the Literature Search Manual search 0 title Electronic search 42 abstracts excluded 35 Potentially appropriated to be included 0 paper Potentially appropriated to be included 7 papers 7 papers excluded 5 lack of control group 2 papers finally selected the various databases are provided in Table 1. Comparing the database results, PubMed showed all of the finally selected articles. MEDLINE did not find one article, but the article was identified from MEDLINE-In- Process. Abstracts selected in all evidence-based medicine reviews and the Web of Science were already found in PubMed. No selected abstract was found in LILACS, which included only Latin American publications. No article was missed in the electronic database searches that appeared during the hand search of the reference lists of the selected articles. From the seven studies 3,5,7,9,11,13,14 that based on the abstracts seemed to be potentially useful, after reading the complete article, only two 5,9 (29%) actually fulfilled the final selection criteria. The remaining five articles 3,7,11,13,14 were rejected due to the lack of an adequate control group to factor out expected normal growth changes. A flow diagram of the literature search appears in Table 3. The methodological quality checklist was applied to the selected articles (Table 4).
4 SOFT TISSUE CHANGES WITH TWIN BLOCK 879 TABLE 4. Methodological Score a of Selected Articles Articles A B C D E F G H I J K L M N Luo & Fang 5 Morris et al 9 Total No. of Checks a A N, methodological criteria in Table 2; satisfactorily fulfilled the methodological criteria (1 check point), partially fulfilled the methodological criteria (0.5 check point), did not fulfill the methodological criteria (0 check point) %of Total TABLE 5. Cephalometric Measurements Area Cephalometric point/distance Cephalometric Measurement Luo 5 Morris 9 Face Subnasale SnPgSnNBt NSnSnPg Sulcus inferious SiLLtSiMt NBPgSts Facial heights Gl-Sn Sn-M PgN Nose Subnasale horizontal Sn-SNpS Upper lip Sulcus superious horizontal Ss-SNpS Labrale superious horizontal Ls-PrnPg Ls-SNpS 1.9 Upper lip thickness Upper lip length Ss-A Sn-Sts Lower lip Labrale inferious horizontal Sulcus inferious horizontal Lower lip thickness Li-PrnPg Li-SNpS Si-SNpS Si-B Sti-M Menton ST pogonion horizontal Pg-OpS Pg-SNpS * Definition of cephalometric points in Athanassiou (Athanasiou AE. Orthodontic Cephalometry. Baltimore: Mosby-Wolfe; 1995.) angle between the mentioned lines; - distance (mm) between the mentioned points or lines. Morris et al 9 compared 16 adolescents (6 males/10 females with a mean age of 11 years 8 months) with 20 adolescents (13 males/7 females with a mean age of 11 years 2 months) during a 9-month evaluation period. All the patients had a Class II skeletal relationship with a mandibular retrognathia, Class II molar relationships, and an overjet greater than 7 mm. Luo and Fang 5 compared 12 adolescents (7 males/ 5 females with an age range of 10 to 12 years) against 11 adolescents (6 males/5 females with an age range of 10 to 12 years) in a 12-month evaluation period. Patients included in this study had a mandibular retrognathia, Class II molar relationships, and an overjet greater than 7 mm. No significant changes in the facial angles, nose, lower lip, and soft tissue menton were found. 5,9 For the upper lip, no significant changes were reported 9 except for the position of labrale superius relative to the esthetic line, which was in a more retruded position (1.9 mm). 5 Specific information about the measurements used and the magnitude of the changes are provided in Table 5. Landmarks used in the soft tissue profile analysis are provided in Figure 1. DISCUSSION The present review was performed to systematically analyze the soft tissue profile changes that were produced by the twin block appliance in patients with Class II division 1 malocclusions. Despite the extensive number of published studies regarding the skeletal and dental effects produced by the twin block appliance, only a few studies evaluated the soft tissue profile changes Only two of these studies 5,9 compared the changes produced by the twin block appliance with a comparable untreated control group. One 9 of these two studies was more methodologically sound and did not report any significant soft tissue profile changes. Lack of consensus exists regarding the impact of
5 880 FLORES-MIR, MAJOR Figure 1. Cephalometric points. functional appliances on the soft tissue profile. From a lay person s perspective changes in the anterior visible occlusion teeth-lip relationship are probably more important than changes in the posterior occlusion. 32 The level of evidence in the selected reports was low. Art students, dental students, and parents of orthodontic patients did not perceive any significant soft tissue changes in subjects treated with two types of removable functional appliances (Frankel s regulator or Harvold s activator). 33 The present results support those findings. Even in the case of the retruded upper lip position reported by one of the studies, 9 the second more methodologically sound study 5 did not find any significant change. Even though several studies have reported significant dentoalveolar changes and some skeletal changes with the twin block appliance, it seems that those changes do not produce significant soft tissue profile changes. A detailed esthetic judgment of the face should evaluate the patient s frontal face view during conversation, facial expressions, and smiling. 32 Current conventional orthodontic frontal and lateral cephalometric analysis are not capable of producing a real 3-dimensional image of the subject s face. Use of facial photos helps to complement conventional radiographic analysis, but the subjectivity in their analysis is still a limitation. Therefore, stereo photogrammetry or laser surface scanning seem to be the best available tools to overcome these limitations. A very limited number of studies evaluating 3-dimensional soft tissue changes after functional treatment have been published. 7,9,34 Only one clinical trial 9 and a report of two cases 35 have evaluated the 3-dimensional soft tissue changes that are produced with the twin block appliance. The main limitation of the clinical trial was that it presented the results as subjective visual changes rather than actual volumetric changes. Future studies using similar technology should also consider quantification of the volumetric changes. A recent article 36 evaluated the esthetic perception of different facial relationships in 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional formats. No consistency between the esthetic ratings from the 2-dimensional and 3-dimensional images was found. An increase in vertical dimensions may likely be perceived by lay persons. 37 Therefore, it is important not only to evaluate the horizontal soft tissue changes but also the vertical changes. Soft tissue vertical changes compared with a control group have been reported for the bionator 38 and Frankel. 39 Only one study 9 evaluated soft tissue facial height changes. No significant vertical changes were reported. Several different measurements have been used to evaluate the soft tissue changes after twin block treatment. Some of them have to be considered carefully because they used reference structures that could potentially change as a result of the treatment. For example, the esthetic plane is not a good reference plane to quantify changes in the lips because simultaneous changes in the soft tissue pogonion or pronasale could create the impression of lip changes that are really nonexistent. CONCLUSIO Evidence supporting the claim for an improvement of the facial convexity with twin block treatment of Class II division I malocclusion was not found. Changes produced by the twin block appliance in the upper lip seem to be controversial, although the study with sounder methodological quality did not report significant changes. No change in the anteroposterior position of the lower lip and soft tissue menton was found. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Special thanks to Linda Seale for her professional assistance in the database searches and to Dr. Guoping Xiong for his help translating the Chinese article. REFERENCES 1. Peck S, Peck L. Selected aspects of the art and science of facial esthetics. Semin Orthod. 1995;1: Vig KW, Weyant R, O Brien K, Bennett E. Developing outcome measures in orthodontics that reflect patient and provider values. Semin Orthod. 1999;5: Gill D, Sharma A, Naini F, Jones S. The twin block appli-
6 SOFT TISSUE CHANGES WITH TWIN BLOCK ance for the correction of Class II malocclusion. Dent Update. 2005;32: , , Clark WJ. The twin block technique. A functional orthopedic appliance system. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1988; 93: Luo Y, Fang G. Effect of Twin-block appliance in the treatment of Class II and division I malocclusion: a cephalometric study in 12 patients [in Chinese]. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2005;14: McDonagh S, Moss JP, Goodwin P, Lee R. Twin block and Bass appliances a prospective cephalometric and optical scanning evaluation. J Dent Res. 1997;76: McDonagh S, Moss JP, Goodwin P, Lee RT. A prospective optical surface scanning and cephalometric assessment of the effect of functional appliances on the soft tissues. Eur J Orthod. 2001;23: Morris DO. The effects of functional appliances on the softtissue facial form. J Dent Res. 1995;74: Morris DO, Illing HM, Lee RT. A prospective evaluation of Bass, bionator and twin block appliances, part II the soft tissues. Eur J Orthod. 1998;20: Sharma AA, Gill D, Lee RT. Soft tissue treatment changes produced by two types of twin block appliances. 2002;29: Sharma AA, Lee RT. Prospective clinical trial comparing the effects of conventional twin-block and mini-block appliances, part 2: soft tissue changes. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2005;127: Singh GD, Clark WJ. Soft tissue changes in patients treated using twin block appliances [abstract]. J Dent Res. 2000; 79: Singh GD. Morphospatial analysis of soft-tissue profile in patients with Class II division 1 malocclusion treated using twin block appliances: geometric morphometrics. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2002;5: Singh GD, Clark WJ. Soft tissue changes in patients with Class II division 1 malocclusions treated using twin block appliances: finite-element scaling analysis. Eur J Orthod. 2003;25: Bishara SE, Ziaja RR. Functional appliances: a review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1989;95: Crokaert JD, Marchal AM, Kleutghen J. Functional appliances: possibility of correction of a Class II malocclusion. [in French]. Rev Belge Med Dent. 1989;44: Mills JR. The effect of functional appliances on the skeletal pattern. Br J Orthod. 1991;18: Petrovic A, Stutzmann J, Lavergne J, Shaye R. Is it possible to modulate the growth of the human mandible with a functional appliance? Int J Orthod. 1991;29: Barton S, Cook PA. Predicting functional appliance treatment outcome in Class II malocclusions a review. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1997;112: Johnston LE Jr. Functional appliances: a mortgage on mandibular position. Aust Orthod J. 1996;14: Rudzki-Janson I, Noachtar R. Functional appliance therapy with the bionator. Semin Orthod. 1998;4: Macey-Dare LV, Nixon F. Functional appliances: mode of action and clinical use. South African Dental Journal. 1999; 54: Collett AR. Current concepts on functional appliances and mandibular growth stimulation. Aust Dent J. 2000;45: McSherry PF, Bradley H. Class II correction-reducing patient compliance: a review of the available techniques. J Orthod. 2000;27: Jacobs T, Sawaengkit P. National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research efficacy trials of bionator Class II treatment: a review. Angle Orthod. 2002;72: Aelbers CM, Dermaut LR. Orthopedics in orthodontics, part I: fiction or reality a review of the literature. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 1996;110: Chen JY, Will LA, Niederman R. Analysis of efficacy of functional appliances on mandibular growth. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2002;122: Shen G, Hägg U, Darendeliler M. Skeletal effects of bite jumping therapy on the mandible removable vs fixed functional appliances. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2005;8: Juni P, Witschi A, Bloch R, Egger M. The hazards of scoring the quality of clinical trials for meta-analysis. JAMA. 1999; 282: Juni P, Altman DG, Egger M. Systematic reviews in health care: assessing the quality of controlled clinical trials. BMJ. 2001;323: Verhagen AP, de Vet HC, de Bie RA, Boers M, van den Brandt PA. The art of quality assessment of RCTs included in systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 2001;54: Lombardi RE. The principles of visual perception and their clinical application to denture esthetics. J Prosthet Dent. 1973;29: O Neill K, Harkness M, Knight R. Ratings of profile attractiveness after functional appliance treatment. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop. 2000;118: ; discussion Illing HM, Morris DO, Lee RT. A prospective evaluation of Bass, bionator and twin block appliances, part I the hard tissues. Eur J Orthod. 1998;20: Bourne CO, Kerr WJ, Ayoub AF. Development of a threedimensional imaging system for analysis of facial change. Clin Orthod Res. 2001;4: Todd SA, Hammond P, Hutton T, Cochrane S, Cunningham S. Perceptions of facial aesthetics in two and three dimensions. Eur J Orthod. In press. 37. Johnson DJ, Hunt O, Johnston CD, Burden DJ, Stevenson MR, Hepper P. The influence of lower face vertical proportion on facial attractiveness. Eur J Orthod. In press. 38. Lange DW, Kalra V, Broadbent BH Jr, Powers M, Nelson S. Changes in soft tissue profile following treatment with the bionator. Angle Orthod. 1995;65: Falck F, Kobel EM. Changes in the soft tissue profile in treatment with function regulators. Fortschr Kieferorthop. 1985;46:
Soft and Hard Tissue Changes after Bimaxillary Surgery in Chinese Class III Patients
 Original Article Soft and Hard Tissue Changes after Bimaxillary Surgery in Chinese Class III Patients Ming Tak Chew a Abstract: Cephalometric studies have shown that the Chinese race tends to have a greater
Original Article Soft and Hard Tissue Changes after Bimaxillary Surgery in Chinese Class III Patients Ming Tak Chew a Abstract: Cephalometric studies have shown that the Chinese race tends to have a greater
SKELETAL AND DENTAL EFFECTS ON PATIENTS WITH SKELETAL CLASS II DUE TO MANDIBULAR CHIN RECEDING, TREATED WITH ORTHOPEDICAL APPLIANCE HERBST
 SKELETAL AND DENTAL EFFECTS ON PATIENTS WITH SKELETAL CLASS II DUE TO MANDIBULAR CHIN RECEDING, TREATED WITH ORTHOPEDICAL APPLIANCE HERBST Systematical Revision Bonilla, J., Carvajal W., Cuartas L., Espinosa
SKELETAL AND DENTAL EFFECTS ON PATIENTS WITH SKELETAL CLASS II DUE TO MANDIBULAR CHIN RECEDING, TREATED WITH ORTHOPEDICAL APPLIANCE HERBST Systematical Revision Bonilla, J., Carvajal W., Cuartas L., Espinosa
Skeletal And DentoalveolarChanges Seen In Class II Div 1 Mal- Occlusion Cases Treated With Twin Block Appliance- A Cephalometric Study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 1, Ver. VIII (Feb. 2014), PP 05-09 Skeletal And DentoalveolarChanges Seen In Class II Div 1
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 1, Ver. VIII (Feb. 2014), PP 05-09 Skeletal And DentoalveolarChanges Seen In Class II Div 1
Scientific Treatment Goals for Oral and Facial Harmony
 Scientific Treatment Goals for Oral and Facial Harmony AAO Lecture May 7, 2013 Philadelphia, PA Will A. Andrews, D.D.S. Optimal oral and facial harmony implies a state of maximum health, function and appearance
Scientific Treatment Goals for Oral and Facial Harmony AAO Lecture May 7, 2013 Philadelphia, PA Will A. Andrews, D.D.S. Optimal oral and facial harmony implies a state of maximum health, function and appearance
The Effect of Frankel II and Modified Twin Block Appliances on the C -axis: The Growth Vector of the Dentomaxillary Complex
 Original Article The Effect of Frankel II and Modified Twin Block Appliances on the C -axis: The Growth Vector of the Dentomaxillary Complex Stanley Braun, DDS, MME, PE a ; Nelson R. Diers, DDS b ; Gabriel
Original Article The Effect of Frankel II and Modified Twin Block Appliances on the C -axis: The Growth Vector of the Dentomaxillary Complex Stanley Braun, DDS, MME, PE a ; Nelson R. Diers, DDS b ; Gabriel
TWO PHASE FOR A BETTER FACE!! TWIN BLOCK AND HEADGEAR FOLLOWED BY FIXED THERAPY FOR CLASS II CORRECTION
 Case Report NUJHS Vol. 5, No.2, June 2015, ISSN 2249-7110 TWO PHASE FOR A BETTER FACE!! TWIN BLOCK AND HEADGEAR FOLLOWED BY FIXED THERAPY FOR CLASS II CORRECTION 1 2 3 4 U S Krishna Nayak, Ashutosh Shetty,
Case Report NUJHS Vol. 5, No.2, June 2015, ISSN 2249-7110 TWO PHASE FOR A BETTER FACE!! TWIN BLOCK AND HEADGEAR FOLLOWED BY FIXED THERAPY FOR CLASS II CORRECTION 1 2 3 4 U S Krishna Nayak, Ashutosh Shetty,
Correlation Between Naso Labial Angle and Effective Maxillary and Mandibular Lengths in Untreated Class II Patients
 9 International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies,2014,Vol 1,No.3,9-14. Available online at httt://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Correlation Between Naso Labial Angle and Effective
9 International Journal of Interdisciplinary and Multidisciplinary Studies,2014,Vol 1,No.3,9-14. Available online at httt://www.ijims.com ISSN: 2348 0343 Correlation Between Naso Labial Angle and Effective
A Cephalometric Comparison of Twin Block and Bionator Appliances in Treatment of Class II Malocclusion
 Journal section: Orthodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.53031 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53031 A Cephalometric Comparison of Twin Block and Bionator Appliances in Treatment of Class
Journal section: Orthodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.53031 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.53031 A Cephalometric Comparison of Twin Block and Bionator Appliances in Treatment of Class
Maxillary Growth Control with High Pull Headgear- A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. X January. (2018), PP 09-13 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Growth Control with High
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. X January. (2018), PP 09-13 www.iosrjournals.org Maxillary Growth Control with High
Comparison of Facial Heights Between Iraqi Arab and Kurdish
 ISSN: 1812 1217 Comparison of Facial Heights Between Iraqi Arab and Kurdish Hussain A Obaidi BDS, MSc (Prof) Alaa' D Al-Dawoody BDS, MSc (Lec) Dept of Pedod, Orthod and Prev Dentistry College of Dentistry,
ISSN: 1812 1217 Comparison of Facial Heights Between Iraqi Arab and Kurdish Hussain A Obaidi BDS, MSc (Prof) Alaa' D Al-Dawoody BDS, MSc (Lec) Dept of Pedod, Orthod and Prev Dentistry College of Dentistry,
The changes of soft tissue profile. skeletal class II patients with mandibular retrognathy treated with extraction of maxillary first premolars
 The changes of soft tissue profile in skeletal class II patients with mandibular retrognathy (Hendri et al) The changes of soft tissue profile in skeletal class II patients with mandibular retrognathy
The changes of soft tissue profile in skeletal class II patients with mandibular retrognathy (Hendri et al) The changes of soft tissue profile in skeletal class II patients with mandibular retrognathy
Dental Research Journal
 Dental Research Journal Original Article Comparative assessment of soft-tissue changes in Class II Division 1 patients following extraction and non-extraction treatment Sneh Lata Verma 1, Vijay Prakash
Dental Research Journal Original Article Comparative assessment of soft-tissue changes in Class II Division 1 patients following extraction and non-extraction treatment Sneh Lata Verma 1, Vijay Prakash
Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report
 Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report by Theodore R. Belfor, D.D.S.; and G. Dave Singh, D.D.Sc., Ph.D., B.D.S. Dr. Theodore Belfor graduated from New York University College
Developing Facial Symmetry Using an Intraoral Device: A Case Report by Theodore R. Belfor, D.D.S.; and G. Dave Singh, D.D.Sc., Ph.D., B.D.S. Dr. Theodore Belfor graduated from New York University College
The Modified Twin Block Appliance in the Treatment of Class II Division 2 Malocclusions
 Journal of Orthodontics/Vol. 28/2001/271 280 The Modified Twin Block Appliance in the Treatment of Class II Division 2 Malocclusions F. M. V. DYER H. F. MCKEOWN P. J. SANDLER Department of Orthodontics,
Journal of Orthodontics/Vol. 28/2001/271 280 The Modified Twin Block Appliance in the Treatment of Class II Division 2 Malocclusions F. M. V. DYER H. F. MCKEOWN P. J. SANDLER Department of Orthodontics,
Class II Correction using Combined Twin Block and Fixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Case Report
 Case Report Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/506 Class II Correction using Combined Twin Block and Fixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Case Report Ahmed Alassiry Assistant
Case Report Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/506 Class II Correction using Combined Twin Block and Fixed Orthodontic Appliances: A Case Report Ahmed Alassiry Assistant
IJCMR 553. ORIGINAL RESEARCH Different Population- Different Analysis A Cephalometric Study. Sachin Singh 1, Jayesh Rahalkar 2 ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 IJCMR 553 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Different Population- Different Analysis A Cephalometric Study Sachin Singh 1, Jayesh Rahalkar 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: Cephalometric norms derived for Caucasian population
IJCMR 553 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Different Population- Different Analysis A Cephalometric Study Sachin Singh 1, Jayesh Rahalkar 2 ABSTRACT Introduction: Cephalometric norms derived for Caucasian population
Correction of Class II Division 2 Malocclusion by Fixed Functional Class II Corrector Appliance: Case Report
 Case Report To cite: Kumar M, Sharma H, Bohara P. Correction of class II division 2 malocclusion by fixed functional class II corrector appliance: case report. Journal of contemporary orthodontics, February
Case Report To cite: Kumar M, Sharma H, Bohara P. Correction of class II division 2 malocclusion by fixed functional class II corrector appliance: case report. Journal of contemporary orthodontics, February
Smile Analyzer: A Software Package for Analyzing the Characteristics of the Speech and Smile
 Innovation Smile Analyzer: A Software Package for Analyzing the Characteristics of the Speech and Smile Roozbeh Rashed 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Leila Raziee 3 1 Dental Research Center, Department of Orthodontics,
Innovation Smile Analyzer: A Software Package for Analyzing the Characteristics of the Speech and Smile Roozbeh Rashed 1, Farzin Heravi 2, Leila Raziee 3 1 Dental Research Center, Department of Orthodontics,
Review Class II functional orthopaedic treatment: a systematic review of systematic reviews
 J o u r n a l o f Oral Rehabilitation Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2015 42; 624--642 Review Class II functional orthopaedic treatment: a systematic review of systematic reviews V. D ANT O* 1,R.BUCCI*
J o u r n a l o f Oral Rehabilitation Journal of Oral Rehabilitation 2015 42; 624--642 Review Class II functional orthopaedic treatment: a systematic review of systematic reviews V. D ANT O* 1,R.BUCCI*
Comparison of Skeletal Changes between Female Adolescents and Adults with Hyperdivergent Class II Division 1 Malocclusion after Orthodontic Treatment
 Comparison of Skeletal Changes between Female Adolescents and Adults with Hyperdivergent Class II Division 1 Malocclusion after Orthodontic Treatment Yun DING 1, Jian Hui ZHAO 2, Jin Rong DENG 1, Xiu Jing
Comparison of Skeletal Changes between Female Adolescents and Adults with Hyperdivergent Class II Division 1 Malocclusion after Orthodontic Treatment Yun DING 1, Jian Hui ZHAO 2, Jin Rong DENG 1, Xiu Jing
Comparison between the external gonial angle in panoramic radiographs and lateral cephalograms of adult patients with Class I malocclusion
 425 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 425-429, 2009 Original Comparison between the external gonial angle in panoramic radiographs and lateral cephalograms of adult patients with Class I malocclusion
425 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 51, No. 3, 425-429, 2009 Original Comparison between the external gonial angle in panoramic radiographs and lateral cephalograms of adult patients with Class I malocclusion
Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars
 Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
Received: 14 June. 2015 Accepted: 7 Dec. 2015 Arch dimensional changes following orthodontic treatment with extraction of four first premolars Abstract Asghar Ebadifar DDS, MSc 1, Mohammad Hossien Shafazand
Orthodontics-surgical combination therapy for Class III skeletal malocclusion
 [Downloaded free from http://www.contempclindent.org on Tuesday, July 16, 2013, IP: 164.100.31.82] Click here to download free Android application for this jou Orthodontics-surgical combination therapy
[Downloaded free from http://www.contempclindent.org on Tuesday, July 16, 2013, IP: 164.100.31.82] Click here to download free Android application for this jou Orthodontics-surgical combination therapy
Soft Tissue Changes after Upper Premolar Extraction in Class II Camouflage Therapy
 Original Article Soft Tissue Changes after Upper Premolar Extraction in Class II Camouflage Therapy R. Scott Conley a ; Christopher Jernigan b Abstract: The long-term effect on the facial profile has led
Original Article Soft Tissue Changes after Upper Premolar Extraction in Class II Camouflage Therapy R. Scott Conley a ; Christopher Jernigan b Abstract: The long-term effect on the facial profile has led
The removal of permanent teeth has been a
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cephalometric changes in overbite and vertical facial height after removal of 4 first molars or first premolars Mark G. Hans, a Gordon Groisser, b Clay Damon, c Douglas Amberman, d Suchitra
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cephalometric changes in overbite and vertical facial height after removal of 4 first molars or first premolars Mark G. Hans, a Gordon Groisser, b Clay Damon, c Douglas Amberman, d Suchitra
PREDICTING LOWER LIP AND CHIN RESPONSE TO MANDIBULAR ADVANCEMENT WITH GENIOPLASTY A CEPHALOMETRIC STUDY
 PREDICTING LOWER LIP AND CHIN RESPONSE TO MANDIBULAR ADVANCEMENT WITH GENIOPLASTY A CEPHALOMETRIC STUDY Dr. Deepthi T. Amanna Authors : Dr. Deepthi T. Amanna Assistant Professor Dr. E.T. Roy Professor
PREDICTING LOWER LIP AND CHIN RESPONSE TO MANDIBULAR ADVANCEMENT WITH GENIOPLASTY A CEPHALOMETRIC STUDY Dr. Deepthi T. Amanna Authors : Dr. Deepthi T. Amanna Assistant Professor Dr. E.T. Roy Professor
Facial planning for orthodontists and oral surgeons
 ADVANCES IN ORTHODONTICS & DENTOFACIAL SURGERY Facial planning for orthodontists and oral surgeons G. William Arnett, DDS, FACD, a and Michael J. Gunson, DDS, MD b Santa Barbara, Calif The bite indicates
ADVANCES IN ORTHODONTICS & DENTOFACIAL SURGERY Facial planning for orthodontists and oral surgeons G. William Arnett, DDS, FACD, a and Michael J. Gunson, DDS, MD b Santa Barbara, Calif The bite indicates
Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Angle Class II Division 1 Malocclusion between Nepalese and Chinese Students
 GENERAL SECTION Bishnu Prasad Sharma: Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Nepali and Chinese ORGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Angle Class II Division 1 Malocclusion between Nepalese
GENERAL SECTION Bishnu Prasad Sharma: Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Nepali and Chinese ORGINAL ARTICLE Comparative Study of Tweed Triangle in Angle Class II Division 1 Malocclusion between Nepalese
SURGICAL - ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT OF CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION IN AN ADULT PATIENT: A CASE REPORT
 Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 02 SURGICAL - ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT OF CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION IN AN ADULT PATIENT: A CASE REPORT Amit Dahiya 1,Minakshi
Case Report International Journal of Dental and Health Sciences Volume 02, Issue 02 SURGICAL - ORTHODONTIC TREATMENT OF CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION IN AN ADULT PATIENT: A CASE REPORT Amit Dahiya 1,Minakshi
Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction
 Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
Case Report Case Report: Long-Term Outcome of Class II Division 1 Malocclusion Treated with Rapid Palatal Expansion and Cervical Traction Roberto M. A. Lima, DDS a ; Anna Leticia Lima, DDS b Abstract:
The three-dimensional effects of orthodontic treatment on the facial soft tissues a preliminary study.
 IN BRIEF l Orthodontic treatment can effect the appearance of the face in all three dimensions of space. The extent of these effects can be accurately assessed using an imaging technique such as three-dimensional
IN BRIEF l Orthodontic treatment can effect the appearance of the face in all three dimensions of space. The extent of these effects can be accurately assessed using an imaging technique such as three-dimensional
Incisal and Soft Tissue Effects of Maxillary Premolar Extraction in Class II Treatment
 Original Article Incisal and Soft Tissue Effects of Maxillary Premolar Extraction in Class II Treatment Nevenka Tadic a ; Michael G. Woods b ABSTRACT Objective: This retrospective study was designed to
Original Article Incisal and Soft Tissue Effects of Maxillary Premolar Extraction in Class II Treatment Nevenka Tadic a ; Michael G. Woods b ABSTRACT Objective: This retrospective study was designed to
Anterior Face Height Values in a Nigerian Population
 Original Article Anterior Face Height Values in a Nigerian Population Folaranmi N, Isiekwe M 1 Departments of Child Dental Health, University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu, 1 Lagos University Teaching
Original Article Anterior Face Height Values in a Nigerian Population Folaranmi N, Isiekwe M 1 Departments of Child Dental Health, University of Nigeria Teaching Hospital, Enugu, 1 Lagos University Teaching
How predictable is orthognathic surgery?
 European Journal of Orthodontics 26 (2004) 303 309 European Journal of Orthodontics vol. 26 no. 3 European Orthodontic Society 2004; all rights reserved. How predictable is orthognathic surgery? Charlotte
European Journal of Orthodontics 26 (2004) 303 309 European Journal of Orthodontics vol. 26 no. 3 European Orthodontic Society 2004; all rights reserved. How predictable is orthognathic surgery? Charlotte
Ortho-surgical Management of Severe Vertical Dysplasia: A Case Report
 Case Report Ortho-surgical Management of Severe Vertical Dysplasia: A Case Report 1 Vinni Arora, 2 Rekha Sharma, 3 Sachin Parashar 1 Senior Resident, 2 Professor and Head of Department, 3 Former Resident
Case Report Ortho-surgical Management of Severe Vertical Dysplasia: A Case Report 1 Vinni Arora, 2 Rekha Sharma, 3 Sachin Parashar 1 Senior Resident, 2 Professor and Head of Department, 3 Former Resident
Most patients who visit orthodontic clinics
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between orthodontic expertise and perception of treatment needs for maxillary protrusion: Comparison of dental students, residents, and orthodontists Shingo Kuroda, a Akihito
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Relationship between orthodontic expertise and perception of treatment needs for maxillary protrusion: Comparison of dental students, residents, and orthodontists Shingo Kuroda, a Akihito
A correlation between a new angle (S-Gn-Go angle) with the facial height
 A correlation between a new angle (S-Gn-Go angle) with the facial height Esraa S. Jassim B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Marwan S. Al-Daggistany B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Jinan E. Saloom B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background:
A correlation between a new angle (S-Gn-Go angle) with the facial height Esraa S. Jassim B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Marwan S. Al-Daggistany B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) Jinan E. Saloom B.D.S., M.Sc. (1) ABSTRACT Background:
Different Non Surgical Treatment Modalities for Class III Malocclusion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 6 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 48-52 Different Non Surgical Treatment Modalities for Class III Malocclusion
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 9, Issue 6 (Sep.- Oct. 2013), PP 48-52 Different Non Surgical Treatment Modalities for Class III Malocclusion
2008 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. Correction of Asymmetry with a Mandibular Propulsion Appliance
 2008 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CASE REPORT Correction of Asymmetry with a Mandibular Propulsion Appliance JOSÉ AUGUSTO MENDES MIGUEL, DDS, MSC, PHD GUSTAVO
2008 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CASE REPORT Correction of Asymmetry with a Mandibular Propulsion Appliance JOSÉ AUGUSTO MENDES MIGUEL, DDS, MSC, PHD GUSTAVO
Evaluation of Correlation between Wits Appraisal and a New Method for Assessment of Sagittal Relationship of Jaws
 Original Article Evaluation of Correlation between Wits Appraisal and a New Method for Assessment of Sagittal Relationship of Jaws Z. Hedayati 1, S. Heidari 2, F. Khaje 3 1 Orthodontic Research Center,
Original Article Evaluation of Correlation between Wits Appraisal and a New Method for Assessment of Sagittal Relationship of Jaws Z. Hedayati 1, S. Heidari 2, F. Khaje 3 1 Orthodontic Research Center,
Evaluation of maxillary protrusion malocclusion treatment effects with prosth-orthodontic method in old adults
 Evaluation of maxillary protrusion malocclusion treatment effects with prosth-orthodontic method in old adults Peicheng Xu, DDS, MSD, a and Honghu Liu, DDS, PhD b a Shanghai Xuhui Dental Hospital and b
Evaluation of maxillary protrusion malocclusion treatment effects with prosth-orthodontic method in old adults Peicheng Xu, DDS, MSD, a and Honghu Liu, DDS, PhD b a Shanghai Xuhui Dental Hospital and b
The impact of extraction vs nonextraction treatment on soft tissue changes in Class I borderline malocclusions
 Original Article The impact of extraction vs nonextraction treatment on soft tissue changes in Class I borderline malocclusions Dimitrios Konstantonis a ABSTRACT Objective: To obtain through the use of
Original Article The impact of extraction vs nonextraction treatment on soft tissue changes in Class I borderline malocclusions Dimitrios Konstantonis a ABSTRACT Objective: To obtain through the use of
Nonsurgical Treatment of Adult Open Bite Using Edgewise Appliance Combined with High-Pull Headgear and Class III Elastics
 Case Report Nonsurgical Treatment of Adult Open Bite Using Edgewise Appliance Combined with High-Pull Headgear and Class III Elastics Isao Saito, DDS, PhD a ; Masaki Yamaki, DDS, PhD b ; Kooji Hanada,
Case Report Nonsurgical Treatment of Adult Open Bite Using Edgewise Appliance Combined with High-Pull Headgear and Class III Elastics Isao Saito, DDS, PhD a ; Masaki Yamaki, DDS, PhD b ; Kooji Hanada,
Racial Variations in Cephalometric Analysis between Whites and Kuwaitis
 Original Article Racial Variations in Cephalometric Analysis between Whites and Kuwaitis Faraj Behbehani a ; E. Preston Hicks b ; Cynthia Beeman c ; G. Thomas Kluemper d ; Mary K. Rayens e Abstract: The
Original Article Racial Variations in Cephalometric Analysis between Whites and Kuwaitis Faraj Behbehani a ; E. Preston Hicks b ; Cynthia Beeman c ; G. Thomas Kluemper d ; Mary K. Rayens e Abstract: The
Self-Perception of Dentofacial Attractiveness among Patients Requiring Orthognathic Surgery
 Original Article Self-Perception of Dentofacial Attractiveness among Patients Requiring Orthognathic Surgery Chris Johnston a ; Orlagh Hunt b ; DonaldBurden c ; Mike Stevenson d ; Peter Hepper e ABSTRACT
Original Article Self-Perception of Dentofacial Attractiveness among Patients Requiring Orthognathic Surgery Chris Johnston a ; Orlagh Hunt b ; DonaldBurden c ; Mike Stevenson d ; Peter Hepper e ABSTRACT
Prediction of Mandibular Growth Potential Using Cervical Vertebral Bone Age in Saudi Subjects
 J. King Saud Univ., Vol. 22, Dental Sci. (1), pp. 1-7, Riyadh (2010/1431H.) Prediction of Mandibular Growth Potential Using Cervical Vertebral Bone Age in Saudi Subjects Adel M. Alhadlaq Assistant Professor
J. King Saud Univ., Vol. 22, Dental Sci. (1), pp. 1-7, Riyadh (2010/1431H.) Prediction of Mandibular Growth Potential Using Cervical Vertebral Bone Age in Saudi Subjects Adel M. Alhadlaq Assistant Professor
Xbow Blended Two Phase The Other Way To Use Class II Springs
 Xbow Blended Two Phase The Other Way To Use Class II Springs Conflict of Interest Declaration I receive royalties from orthodontic labs that are licensed to fabricate the appliance discussed in this presentation.
Xbow Blended Two Phase The Other Way To Use Class II Springs Conflict of Interest Declaration I receive royalties from orthodontic labs that are licensed to fabricate the appliance discussed in this presentation.
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS
 EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER:44 CASE NUMBER: 2 Year: 2010 ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 5 CASE CATEGORY: CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION A MALOCCLUSION WITH SIGNIFICANT MANDIBULAR
EUROPEAN SOCIETY OF LINGUAL ORTHODONTISTS CANDIDATE NUMBER:44 CASE NUMBER: 2 Year: 2010 ESLO 01 RÉSUMÉ OF CASE 5 CASE CATEGORY: CLASS II DIVISION 1 MALOCCLUSION A MALOCCLUSION WITH SIGNIFICANT MANDIBULAR
Maxillary Expansion and Protraction in Correction of Midface Retrusion in a Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patient
 Case Report Maxillary Expansion and Protraction in Correction of Midface Retrusion in a Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patient Masayoshi Kawakami, DDS, PhD a ; Takakazu Yagi, DDS, PhD b ; Kenji
Case Report Maxillary Expansion and Protraction in Correction of Midface Retrusion in a Complete Unilateral Cleft Lip and Palate Patient Masayoshi Kawakami, DDS, PhD a ; Takakazu Yagi, DDS, PhD b ; Kenji
Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite
 BBO Case Report Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite Arno Locks 1 Angle Class II, division 2, malocclusion is characterized by a Class II molar relation associated with retroclined
BBO Case Report Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with deep overbite Arno Locks 1 Angle Class II, division 2, malocclusion is characterized by a Class II molar relation associated with retroclined
Non Extraction philosophy: Distalization using Jone s Jig appliance- a case report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. IV (Sep. 2014), PP 36-41 Non Extraction philosophy: Distalization using Jone s Jig appliance-
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. IV (Sep. 2014), PP 36-41 Non Extraction philosophy: Distalization using Jone s Jig appliance-
The Dynamax System: A New Orthopedic Appliance
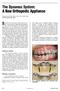 The Dynamax System: A New Orthopedic Appliance NEVILLE M. BASS, BDS, LDS, FDS, DOrth RCS ANTON BASS, BS, BDS Skeletal Class II treatment requires harmonization of the structures supporting the dentition,
The Dynamax System: A New Orthopedic Appliance NEVILLE M. BASS, BDS, LDS, FDS, DOrth RCS ANTON BASS, BS, BDS Skeletal Class II treatment requires harmonization of the structures supporting the dentition,
The effect of tooth agenesis on dentofacial structures
 European Journal of Orthodontics 19 (1997) 71 78 9 1997 European Orthodontic Society The effect of on dentofacial structures Sema Yª and Tuba Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Gazi University,
European Journal of Orthodontics 19 (1997) 71 78 9 1997 European Orthodontic Society The effect of on dentofacial structures Sema Yª and Tuba Department of Orthodontics, Faculty of Dentistry, Gazi University,
The most common maxillary characteristics of
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of the bionator and high-pull facebow combination followed by fixed appliances in patients with increased vertical dimensions Christopher S. Freeman, a James A. McNamara,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of the bionator and high-pull facebow combination followed by fixed appliances in patients with increased vertical dimensions Christopher S. Freeman, a James A. McNamara,
Removable appliances
 Removable appliances Melinda Madléna DMD, PhD associate professor Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Faculty of Dentistry Semmelweis University Budapest Classification of the orthodontic anomalies
Removable appliances Melinda Madléna DMD, PhD associate professor Department of Pedodontics and Orthodontics Faculty of Dentistry Semmelweis University Budapest Classification of the orthodontic anomalies
Predictors of favorable soft tissue profile outcomes following Class II Twin-block treatment
 Original Article THE KOREAN JOURNAL of ORTHODONTICS pissn 2234-7518 eissn 2005-372X Predictors of favorable soft tissue profile outcomes following Class II Twin-block treatment Ji-Eun Kim a Su-Jung Mah
Original Article THE KOREAN JOURNAL of ORTHODONTICS pissn 2234-7518 eissn 2005-372X Predictors of favorable soft tissue profile outcomes following Class II Twin-block treatment Ji-Eun Kim a Su-Jung Mah
Influence of Orthodontic Treatment on Smile Attractiveness as perceived by Common People, General Dentists and Orthodontists
 Prasanna Kumar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1357 Influence of Orthodontic Treatment on Smile Attractiveness as perceived by Common People, General Dentists and Orthodontists 1 Prasanna
Prasanna Kumar et al ORIGINAL RESEARCH 10.5005/jp-journals-10015-1357 Influence of Orthodontic Treatment on Smile Attractiveness as perceived by Common People, General Dentists and Orthodontists 1 Prasanna
Orthodontic Outcomes Assessment Using the Peer Assessment Rating Index
 Original Article Orthodontic Outcomes Assessment Using the Peer Assessment Rating Index Renee Allen Dyken, DMD a ; P. Lionel Sadowsky, DMD, BDS, MDent, Dip Orth b ; David Hurst, PhD c Abstract: The purpose
Original Article Orthodontic Outcomes Assessment Using the Peer Assessment Rating Index Renee Allen Dyken, DMD a ; P. Lionel Sadowsky, DMD, BDS, MDent, Dip Orth b ; David Hurst, PhD c Abstract: The purpose
Longitudinal study of cephalometric soft tissue profile traits between the ages of 6 and 18 years
 Original Article Longitudinal study of cephalometric soft tissue profile traits between the ages of 6 and 18 years Robert T. Bergman a ; John Waschak b ; Ali Borzabadi-Farahani c ; Neal C. Murphy d ABSTRACT
Original Article Longitudinal study of cephalometric soft tissue profile traits between the ages of 6 and 18 years Robert T. Bergman a ; John Waschak b ; Ali Borzabadi-Farahani c ; Neal C. Murphy d ABSTRACT
Gentle-Jumper- Non-compliance Class II corrector
 15 CASE REPORT Gentle-Jumper- Non-compliance Class II corrector Amit Prakash 1,O.P.Mehta 2, Kshitij Gupta 3 Swapnil Pandey 4 Deep Kumar Suryawanshi 4 1 Senior lecturer Bhopal - INDIA 2 Professor Bhopal
15 CASE REPORT Gentle-Jumper- Non-compliance Class II corrector Amit Prakash 1,O.P.Mehta 2, Kshitij Gupta 3 Swapnil Pandey 4 Deep Kumar Suryawanshi 4 1 Senior lecturer Bhopal - INDIA 2 Professor Bhopal
Several studies have shown that a Twin-block appliance
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of 2 modifications of the Twinblock appliance in matched Class II samples Nicola Ann Parkin, BDS, MMedSci, FDS RCS(Eng), M Orth RCS(Eng), a Helen Fiona McKeown, BDS, MMedSci,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of 2 modifications of the Twinblock appliance in matched Class II samples Nicola Ann Parkin, BDS, MMedSci, FDS RCS(Eng), M Orth RCS(Eng), a Helen Fiona McKeown, BDS, MMedSci,
Management of Severe Class II Division 1 Malocclusion with Hybrid Functional Appliance by Double Advancement A Case Report
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 2 Ver. IV (February. 2017), PP 83-88 www.iosrjournals.org Management of Severe Class II Division
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 2 Ver. IV (February. 2017), PP 83-88 www.iosrjournals.org Management of Severe Class II Division
Treatment effects of the twin block appliance: A cephalometric study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of the twin block appliance: A cephalometric study Christine M. Mills, DOS, MS, a and Kara J. McCulloch, DMD, b Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, and Seattle, Washington
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects of the twin block appliance: A cephalometric study Christine M. Mills, DOS, MS, a and Kara J. McCulloch, DMD, b Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, and Seattle, Washington
Correlation of Incisors Inclination and Position with Facial Profile
 ISSN: 1812 1217 Correlation of Incisors Inclination and Position with Facial Profile Ne'am F Agha 1 BDS, MSc (Asst Prof) Zeina M Ahmad 2 BDS, MSc (Lec) 1 Dept of Pedod, Orthod and Prev Dentistry College
ISSN: 1812 1217 Correlation of Incisors Inclination and Position with Facial Profile Ne'am F Agha 1 BDS, MSc (Asst Prof) Zeina M Ahmad 2 BDS, MSc (Lec) 1 Dept of Pedod, Orthod and Prev Dentistry College
Frenkel 2 and Bionator: dental and skeletal effects. A systematic review.
 Article ID: WMC005350 ISSN 2046-1690 Frenkel 2 and Bionator: dental and skeletal effects. A systematic review. Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, attender, Department of Oral
Article ID: WMC005350 ISSN 2046-1690 Frenkel 2 and Bionator: dental and skeletal effects. A systematic review. Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, attender, Department of Oral
ISW for the Treatment of Bilateral Posterior Buccal Crossbite
 Journal of Dentistry and Oral Health Case report ISW for the Treatment of Bilateral Posterior Buccal Crossbite Chun-Shuo HUANG 1,2, Chien-Chih YU 3,*, Jian-Hong YU 1,2, and Yuan-Hou CHEN 1 1 Department
Journal of Dentistry and Oral Health Case report ISW for the Treatment of Bilateral Posterior Buccal Crossbite Chun-Shuo HUANG 1,2, Chien-Chih YU 3,*, Jian-Hong YU 1,2, and Yuan-Hou CHEN 1 1 Department
Orthognathic treatment of facial asymmetry due to temporomandibular joint ankylosis
 Orthognathic treatment of facial asymmetry due to temporomandibular joint ankylosis Ayse Gulsen 1, Serhat Sibar 2, Selahattin Ozmen 3 1 Department of Plastic, Reconstructive, and Aesthetic Surgery, Gazi
Orthognathic treatment of facial asymmetry due to temporomandibular joint ankylosis Ayse Gulsen 1, Serhat Sibar 2, Selahattin Ozmen 3 1 Department of Plastic, Reconstructive, and Aesthetic Surgery, Gazi
UNLV School of Dental Medicine Advanced Education in Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics Course Descriptions, updated Dec.
 UNLV School of Dental Medicine Advanced Education in and Dentofacial Orthopedics Course Descriptions, updated Dec. 2012 Year 1 Summer Courses Intro to 8001 8011 8201 Cephlometrics Year 1 Fall Courses 1.
UNLV School of Dental Medicine Advanced Education in and Dentofacial Orthopedics Course Descriptions, updated Dec. 2012 Year 1 Summer Courses Intro to 8001 8011 8201 Cephlometrics Year 1 Fall Courses 1.
Angle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with severe overbite and pronounced discrepancy*
 O C a s e R e p o r t ngle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with severe overbite and pronounced discrepancy* Daniela Kimaid Schroeder** bstract This article reports the treatment of a young patient at
O C a s e R e p o r t ngle Class II, division 2 malocclusion with severe overbite and pronounced discrepancy* Daniela Kimaid Schroeder** bstract This article reports the treatment of a young patient at
Clarifying the mechanism of effect of the Bionator for treatment of maxillary protrusion: A percentile growth study
 H. Oda*, M. Sandou**, C-M Lin***, M. Kamata****, T. Kawata***** *Professor, Division of Orthodontics, Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Yokohama Clinical Education Center, Kanagawa Dental University,
H. Oda*, M. Sandou**, C-M Lin***, M. Kamata****, T. Kawata***** *Professor, Division of Orthodontics, Department of Comprehensive Dentistry, Yokohama Clinical Education Center, Kanagawa Dental University,
Treatment effects produced by the Twin-block appliance and the FR-2 appliance of Fränkel compared with an untreated Class II sample
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects produced by the Twin-block appliance and the FR-2 appliance of Fränkel compared with an untreated Class II sample Linda Ratner Toth, DDS, MS, a and James A. McNamara,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment effects produced by the Twin-block appliance and the FR-2 appliance of Fränkel compared with an untreated Class II sample Linda Ratner Toth, DDS, MS, a and James A. McNamara,
Comparison between conventional Twin block and a modified Essix twin block in adolescents with Class II malocclusion
 International Journal of Dentistry Research 2016; 1(1): 1-5 Research Article IJDR 2016; 1(1): 1-5 December 2017, All rights reserved www.dentistryscience.com Comparison between conventional Twin block
International Journal of Dentistry Research 2016; 1(1): 1-5 Research Article IJDR 2016; 1(1): 1-5 December 2017, All rights reserved www.dentistryscience.com Comparison between conventional Twin block
Facial analysis using a new clinical device: The Kattan Facio-meter
 Journal section: Orthodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.55394 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.55394 : The Kattan Facio-meter Ehab S. El Kattan 1, Omnia A. Elhiny 2, Mohamed E. El Kattan
Journal section: Orthodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.55394 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.55394 : The Kattan Facio-meter Ehab S. El Kattan 1, Omnia A. Elhiny 2, Mohamed E. El Kattan
How much incisor decompensation is achieved prior to orthognathic surgery?
 Journal section: Orthodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51310 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51310 How much incisor decompensation is achieved prior to orthognathic surgery? Calum McNeil
Journal section: Orthodontics Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/jced.51310 http://dx.doi.org/10.4317/jced.51310 How much incisor decompensation is achieved prior to orthognathic surgery? Calum McNeil
The Long Term Outcome of Mandibular Orthognathic Surgery
 The Long Term Outcome of Mandibular Orthognathic Surgery Mohammed Ibrahim Al-Ajmi B.D.S (Ireland), MFDS RCPS (Glasgow) Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctorate of Clinical Dentistry (Oral and Maxillofacial
The Long Term Outcome of Mandibular Orthognathic Surgery Mohammed Ibrahim Al-Ajmi B.D.S (Ireland), MFDS RCPS (Glasgow) Thesis submitted for the degree of Doctorate of Clinical Dentistry (Oral and Maxillofacial
Reliability and accuracy of Centrographic analysis in comparisonwith other superimposition techniques A Cephalometric study
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. III (Oct. 2017), PP 81-86 www.iosrjournals.org Reliability and accuracy of Centrographic
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 10 Ver. III (Oct. 2017), PP 81-86 www.iosrjournals.org Reliability and accuracy of Centrographic
UNILATERAL UPPER MOLAR DISTALIZATION IN A SEVERE CASE OF CLASS II MALOCCLUSION. CASE PRESENTATION. 1*
 UNILATERAL UPPER MOLAR DISTALIZATION IN A SEVERE CASE OF CLASS II MALOCCLUSION. CASE PRESENTATION. 1* Department of Orthodontics and Pedodontics 1 Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and
UNILATERAL UPPER MOLAR DISTALIZATION IN A SEVERE CASE OF CLASS II MALOCCLUSION. CASE PRESENTATION. 1* Department of Orthodontics and Pedodontics 1 Faculty of Dental Medicine, University of Medicine and
Original Article. Sayeh Ehsani a ; Brian Nebbe b ; David Normando c ; Manuel O. Lagravere d ; Carlos Flores-Mir e
 Original Article Dental and skeletal changes in mild to moderate Class II malocclusions treated by either a Twin-block or Xbow appliance followed by full fixed orthodontic treatment Sayeh Ehsani a ; Brian
Original Article Dental and skeletal changes in mild to moderate Class II malocclusions treated by either a Twin-block or Xbow appliance followed by full fixed orthodontic treatment Sayeh Ehsani a ; Brian
Impact of Bimaxillary Position on Esthetic Preferences among Health Professionals and Lay Persons
 Received: 10 Sep 2013 Revised: 21 Nov 2013 Accepted:03 Dec 2013 Impact of Bimaxillary Position on Esthetic Preferences among Health Professionals and Lay Persons Abstract Shabnam Ajami 1, Morteza Oshagh
Received: 10 Sep 2013 Revised: 21 Nov 2013 Accepted:03 Dec 2013 Impact of Bimaxillary Position on Esthetic Preferences among Health Professionals and Lay Persons Abstract Shabnam Ajami 1, Morteza Oshagh
Effects of Extraction and Nonextraction Treatment on Class I and Class II Subjects
 Original Article Effects of and Treatment on Class I and Class II Subjects Faruk Ayhan Basciftci, DDS, MS a ; Serdar Usumez, DDS, PhD a Abstract: This study aims to examine the profile as well as the dentoalveolar
Original Article Effects of and Treatment on Class I and Class II Subjects Faruk Ayhan Basciftci, DDS, MS a ; Serdar Usumez, DDS, PhD a Abstract: This study aims to examine the profile as well as the dentoalveolar
Reliability of an Objective Method of Evaluating Skeletal Maturity based on Cervical Vertebral Bone Age as Compared with the TW2 Method
 10.5005/jp-journals-10021-1158 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vasu Murthy et al Reliability of an Objective Method of Evaluating Skeletal Maturity based on Cervical Vertebral Bone Age as Compared with the TW2 Method
10.5005/jp-journals-10021-1158 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vasu Murthy et al Reliability of an Objective Method of Evaluating Skeletal Maturity based on Cervical Vertebral Bone Age as Compared with the TW2 Method
Treatment Effects of Twin-Block and Mandibular Protraction Appliance-IV in the Correction of Class II Malocclusion
 Original Article Treatment Effects of Twin-Block and Mandibular Protraction Appliance-IV in the Correction of Class II Malocclusion Ashok Kumar Jena a ;Ritu Duggal b ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the
Original Article Treatment Effects of Twin-Block and Mandibular Protraction Appliance-IV in the Correction of Class II Malocclusion Ashok Kumar Jena a ;Ritu Duggal b ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the
Changes of the Transverse Dental Arch Dimension, Overjet and Overbite after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME)
 Dental Journal Changes of the Transverse Dental Arch Dimension, Overjet and Overbite after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME) Department of Advanced General Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University.
Dental Journal Changes of the Transverse Dental Arch Dimension, Overjet and Overbite after Rapid Maxillary Expansion (RME) Department of Advanced General Dentistry Faculty of Dentistry, Mahidol University.
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences
 Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Orthodontic Camouflage of Skeletal Class I, Class II and Class III Malocclusion in Borderline Cases Report of Three Cases Dr. Seema Kapil Lahoti 1 *, Dr.
Research & Reviews: Journal of Dental Sciences Orthodontic Camouflage of Skeletal Class I, Class II and Class III Malocclusion in Borderline Cases Report of Three Cases Dr. Seema Kapil Lahoti 1 *, Dr.
1. Muhammad Moazzam 2. Waheed-ul-Hameed 3. Rana Modassir Shamsher Khan 4. Abdul Samad Khan 5. Imran Rahber 6. Muhammad Osman Masood
 Single Arch Treatment in Class II Div 1 Malocclusion {Original Article (Dentistry)} 1. Muhammad Moazzam 2. Waheed-ul-Hameed 3. Rana Modassir Shamsher Khan 4. Abdul Samad Khan 5. Imran Rahber 6. Muhammad
Single Arch Treatment in Class II Div 1 Malocclusion {Original Article (Dentistry)} 1. Muhammad Moazzam 2. Waheed-ul-Hameed 3. Rana Modassir Shamsher Khan 4. Abdul Samad Khan 5. Imran Rahber 6. Muhammad
Twin Block appliance. A Systematic Review.
 Article ID: WMC005372 ISSN 2046-1690 Twin Block appliance. A Systematic Review. Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, Submitting Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, Other Authors: Dr.
Article ID: WMC005372 ISSN 2046-1690 Twin Block appliance. A Systematic Review. Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, Submitting Author: Dr. Martina Mezio, Other Authors: Dr.
Original Research. Journal of International Oral Health 2014; 6(5): Contributors: 1
 Received: 12 th March 2014 Accepted: 13 th June 2014 Conflict of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Soft Tissue Cephalometric Norms for Central India (Malwa) Female Population Shweta
Received: 12 th March 2014 Accepted: 13 th June 2014 Conflict of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Soft Tissue Cephalometric Norms for Central India (Malwa) Female Population Shweta
2007 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission.
 2007 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CSE REPORT Correction of an symmetrical Class II Malocclusion Using Predictable Force Systems PIERO PLCIOS, DDS, MDS FLVIO URIBE,
2007 JCO, Inc. May not be distributed without permission. www.jco-online.com CSE REPORT Correction of an symmetrical Class II Malocclusion Using Predictable Force Systems PIERO PLCIOS, DDS, MDS FLVIO URIBE,
Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach
 Case Report Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach Dr Tapan Shah, 1 Dr Tarulatha Shyagali, 2 Dr Kalyani Trivedi 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, Darshan
Case Report Correction of Crowding using Conservative Treatment Approach Dr Tapan Shah, 1 Dr Tarulatha Shyagali, 2 Dr Kalyani Trivedi 3 1 Senior Lecturer, 2 Professor, Department of Orthodontics, Darshan
The Class II relationship is the most prevalent. Extraction of maxillary first permanent molars in patients with Class II Division 1 malocclusion
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extraction of maxillary first permanent molars in patients with Class II Division 1 malocclusion Mattijs J. P. Stalpers, a Johan W. Booij, b Ewald M. Bronkhorst, c Anne Marie Kuijpers-Jagtman,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extraction of maxillary first permanent molars in patients with Class II Division 1 malocclusion Mattijs J. P. Stalpers, a Johan W. Booij, b Ewald M. Bronkhorst, c Anne Marie Kuijpers-Jagtman,
KJLO. A Sequential Approach for an Asymmetric Extraction Case in. Lingual Orthodontics. Case Report INTRODUCTION DIAGNOSIS
 KJLO Korean Journal of Lingual Orthodontics Case Report A Sequential Approach for an Asymmetric Extraction Case in Lingual Orthodontics Ji-Sung Jang 1, Kee-Joon Lee 2 1 Dream Orthodontic Clinic, Gimhae,
KJLO Korean Journal of Lingual Orthodontics Case Report A Sequential Approach for an Asymmetric Extraction Case in Lingual Orthodontics Ji-Sung Jang 1, Kee-Joon Lee 2 1 Dream Orthodontic Clinic, Gimhae,
Dentoalveolar Heights in Vertical and Sagittal Facial Patterns
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentoalveolar Heights in Vertical and Sagittal Facial Patterns Zafar Ul Islam 1, Attiya Jawaid Shaikh 2 and Mubassar Fida 2 ABSTRACT Objective: To determine and compare the mean dentoalveolar
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dentoalveolar Heights in Vertical and Sagittal Facial Patterns Zafar Ul Islam 1, Attiya Jawaid Shaikh 2 and Mubassar Fida 2 ABSTRACT Objective: To determine and compare the mean dentoalveolar
Non-surgical management of skeletal malocclusions: An assessment of 100 cases
 Non-surgical management of skeletal malocclusions: An assessment of 100 cases In early 1970 s reduced risks associated with surgical procedures allowed the treatment planning process for skeletal malocclusions
Non-surgical management of skeletal malocclusions: An assessment of 100 cases In early 1970 s reduced risks associated with surgical procedures allowed the treatment planning process for skeletal malocclusions
Early Mixed Dentition Period
 REVIEW ARTIC CLE AODMR The Effects of a Prefabricated Functional Appliance in Early Mixed Dentition Period Toshio Iwata 1, Takashi Usui 2, Nobukazu Shirakawa 2, Toshitsugu Kawata 3 1 Doctor of Philosophy
REVIEW ARTIC CLE AODMR The Effects of a Prefabricated Functional Appliance in Early Mixed Dentition Period Toshio Iwata 1, Takashi Usui 2, Nobukazu Shirakawa 2, Toshitsugu Kawata 3 1 Doctor of Philosophy
Dental-arch form consists of both size and shape.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparison of dental arch forms between Class II Division 1 and normal occlusion assessed by euclidean distance matrix analysis Qiong Nie a and Jiuxiang Lin b Beijing, China Introduction:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A comparison of dental arch forms between Class II Division 1 and normal occlusion assessed by euclidean distance matrix analysis Qiong Nie a and Jiuxiang Lin b Beijing, China Introduction:
Combined Orthodontic And Surgical Correction Of An Adolescent Patient With Thin Palatal Cortex And Vertical Maxillary Excess
 Combined Orthodontic And Surgical Correction Of An Adolescent Patient With Thin Palatal Cortex And Vertical Maxillary Excess Hegde M, 1 Hegde C, 2 Parajuli U, 3 Kamath P, 4 MR D 1 Department of orthodontics
Combined Orthodontic And Surgical Correction Of An Adolescent Patient With Thin Palatal Cortex And Vertical Maxillary Excess Hegde M, 1 Hegde C, 2 Parajuli U, 3 Kamath P, 4 MR D 1 Department of orthodontics
Original Research. This appraisal is based on a system of cephalometric analysis that was developed at Indiana University by Burstone and Legan.
 Received: 08 th June 2015 Accepted: 13 th September 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Hard Tissue Cephalometric Norms for Orthognathic Surgery in Karnataka Population
Received: 08 th June 2015 Accepted: 13 th September 2015 Conflicts of Interest: None Source of Support: Nil Original Research Hard Tissue Cephalometric Norms for Orthognathic Surgery in Karnataka Population
Cephalometric Comparison of Treatment with Twin Block Appliance in Skeletal Class II Div 1 Patients with Normal and Vertical Growth Pattern
 Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Sciences 2018, Volume 6, Issue 2, Page No: 506-513 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Cephalometric
Journal of Research in Medical and Dental Sciences 2018, Volume 6, Issue 2, Page No: 506-513 Copyright CC BY-NC-ND 4.0 Available Online at: www.jrmds.in eissn No. 2347-2367: pissn No. 2347-2545 Cephalometric
CASE: HISPANIC SAMPLE Dr. TRAINING F (LA) Latin AGE: 10.5 VISUAL NORMS RMO X: 06/23/ R: 02/21/2003 MISSING PERMANENT TEETH RMO 2003
 O C RMO CASE: HISPANIC SAMPLE Dr. TRAINING F (LA) Latin AGE:. X: // - R: // MISSING PERMANENT TEETH VISUAL NORMS RMO R L RMO Diagnostic Services RMO, Inc. ()- Post Office Box 7 ()7- Canoga Park, CA -7
O C RMO CASE: HISPANIC SAMPLE Dr. TRAINING F (LA) Latin AGE:. X: // - R: // MISSING PERMANENT TEETH VISUAL NORMS RMO R L RMO Diagnostic Services RMO, Inc. ()- Post Office Box 7 ()7- Canoga Park, CA -7
LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS
 POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
POLSKI PRZEGLĄD CHIRURGICZNY 2009, 81, 1, 23 27 10.2478/v10035-009-0004-2 LATERAL CEPHALOMETRIC EVALUATION IN CLEFT PALATE PATIENTS PRADEEP JAIN, ANAND AGARWAL, ARVIND SRIVASTAVA Department of Plastic
